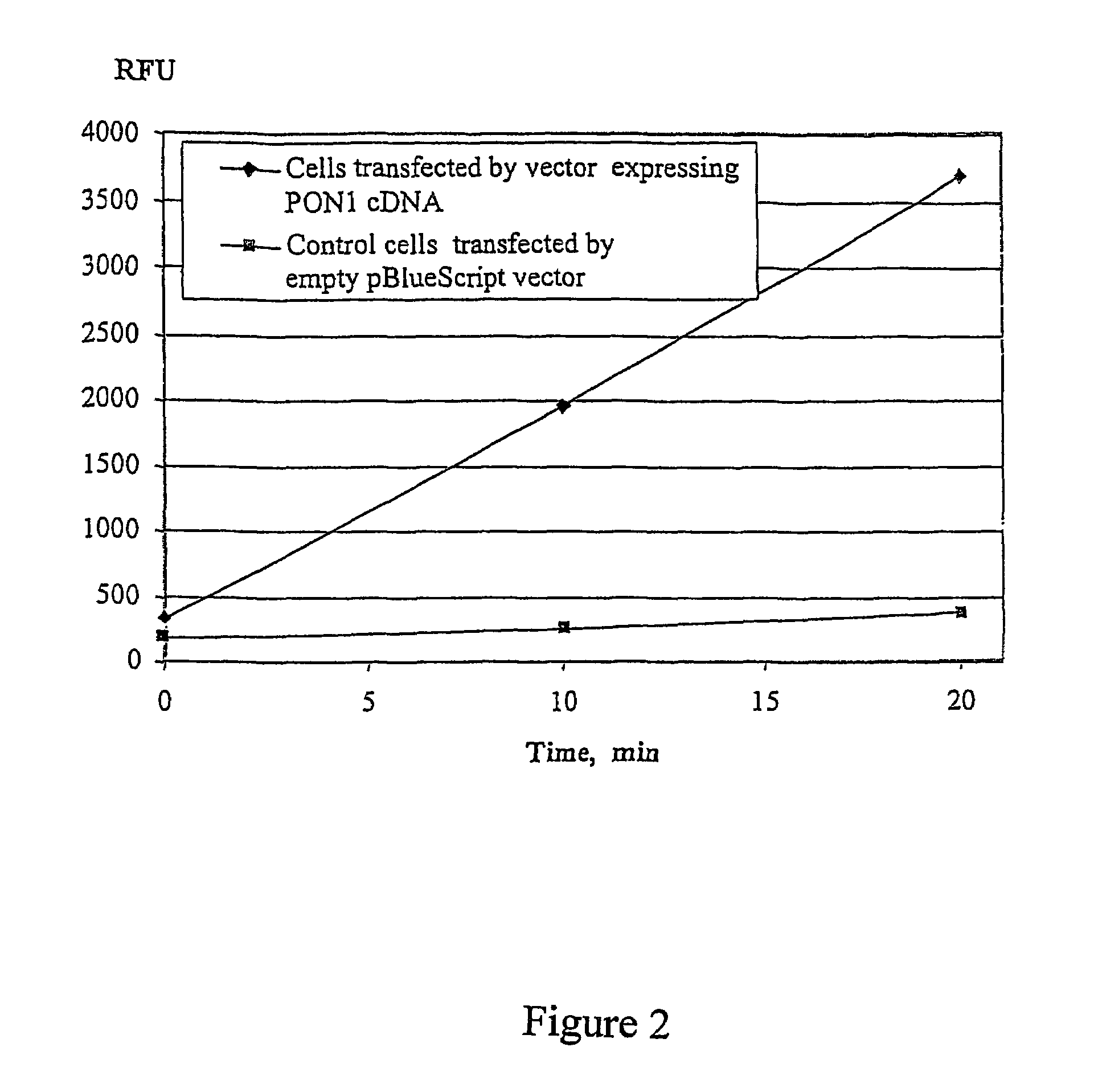
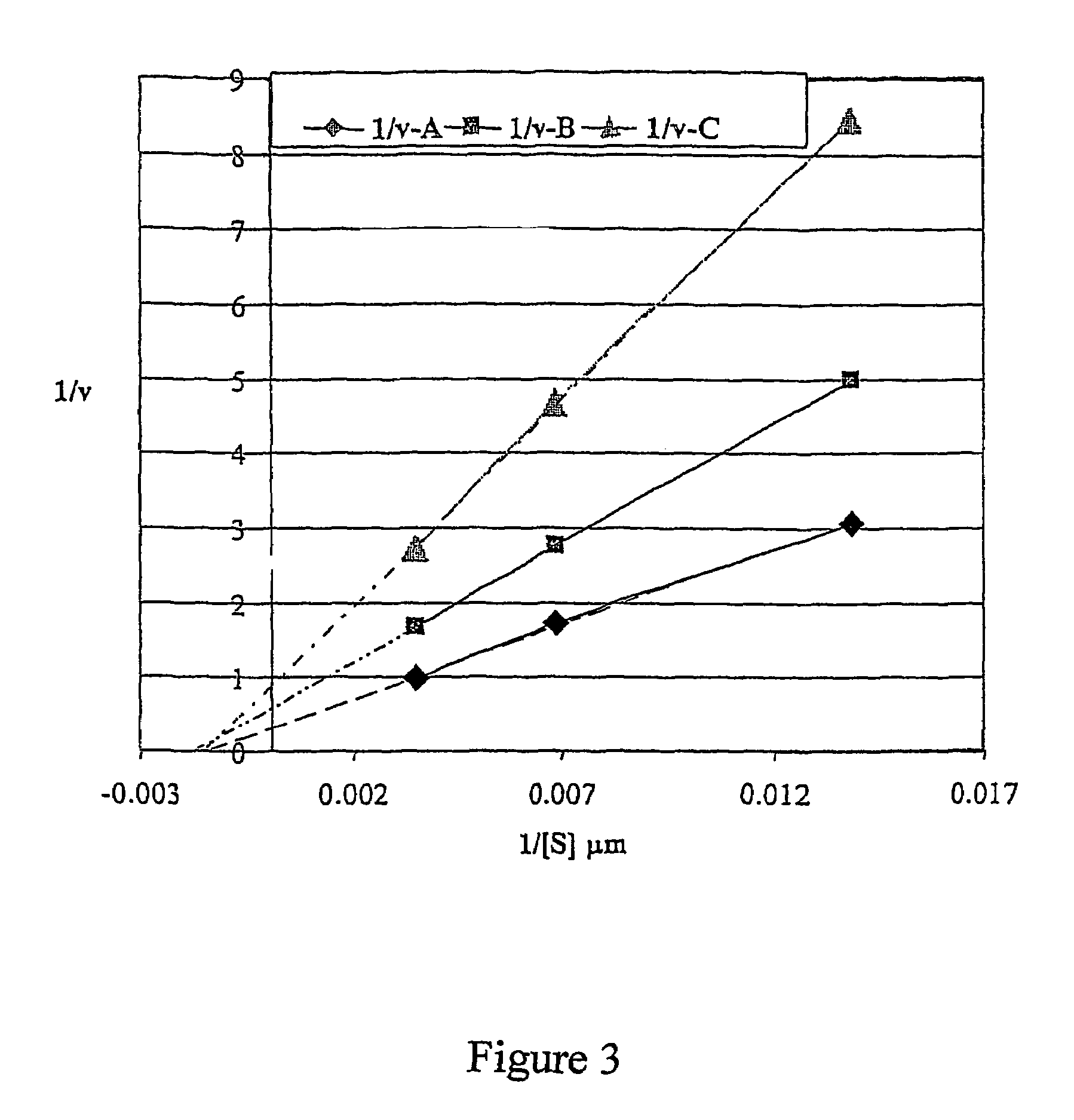
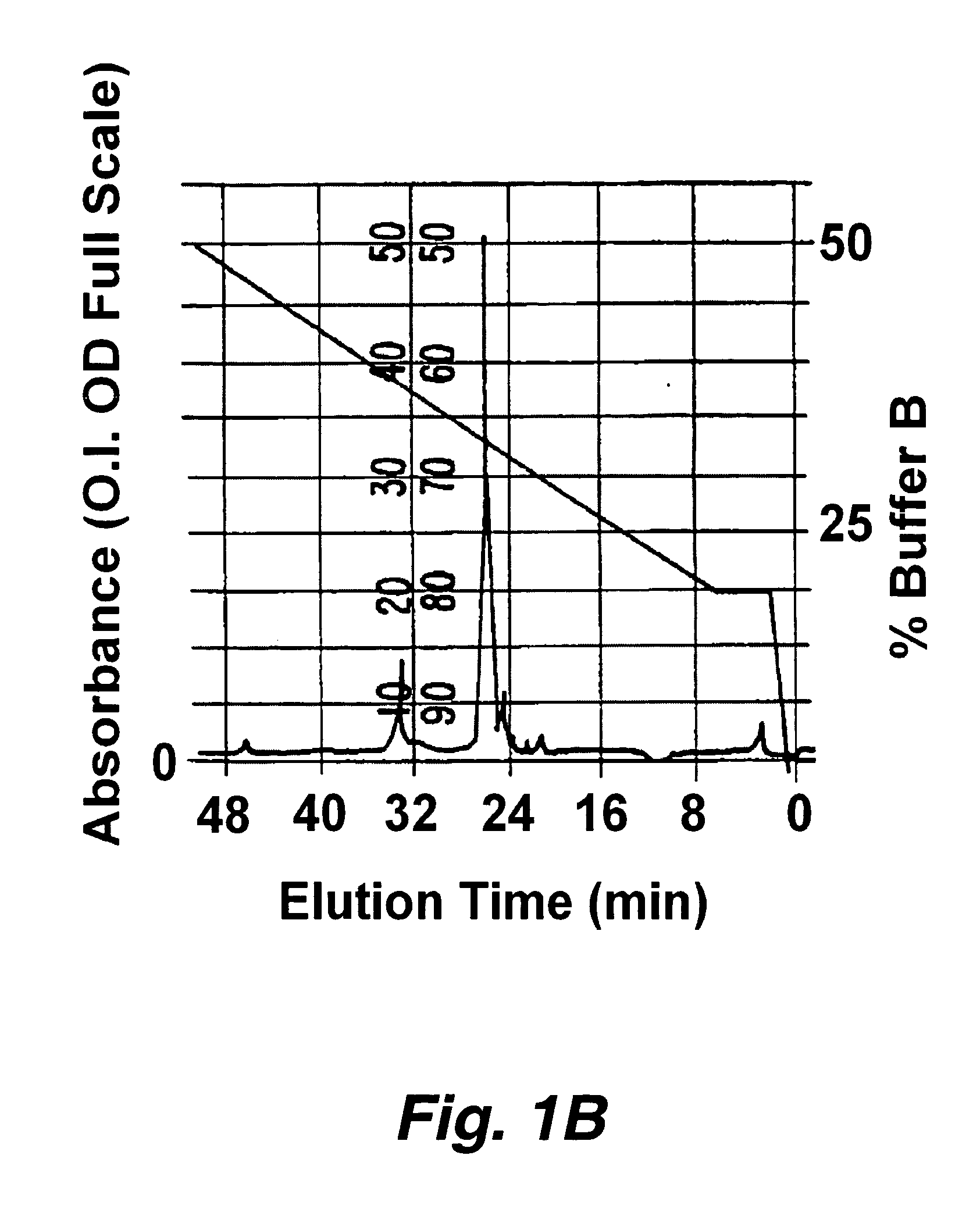
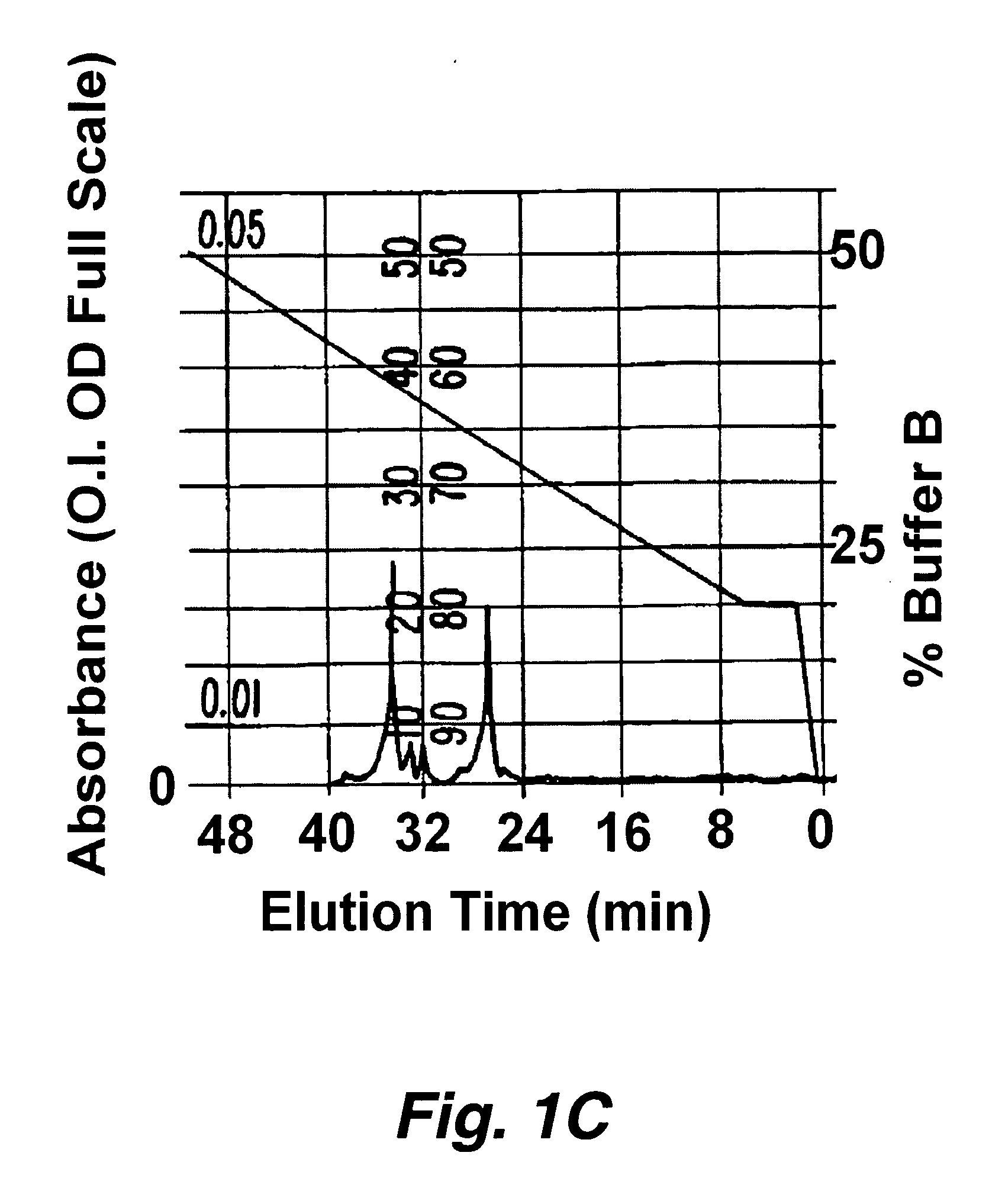
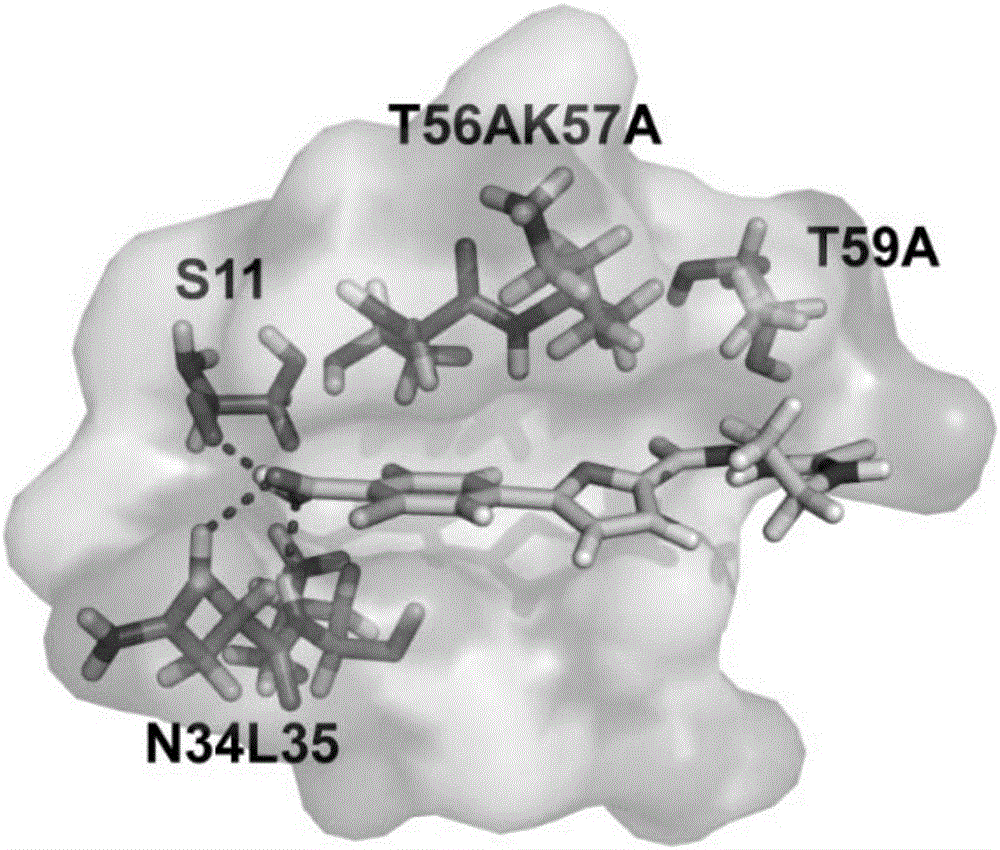
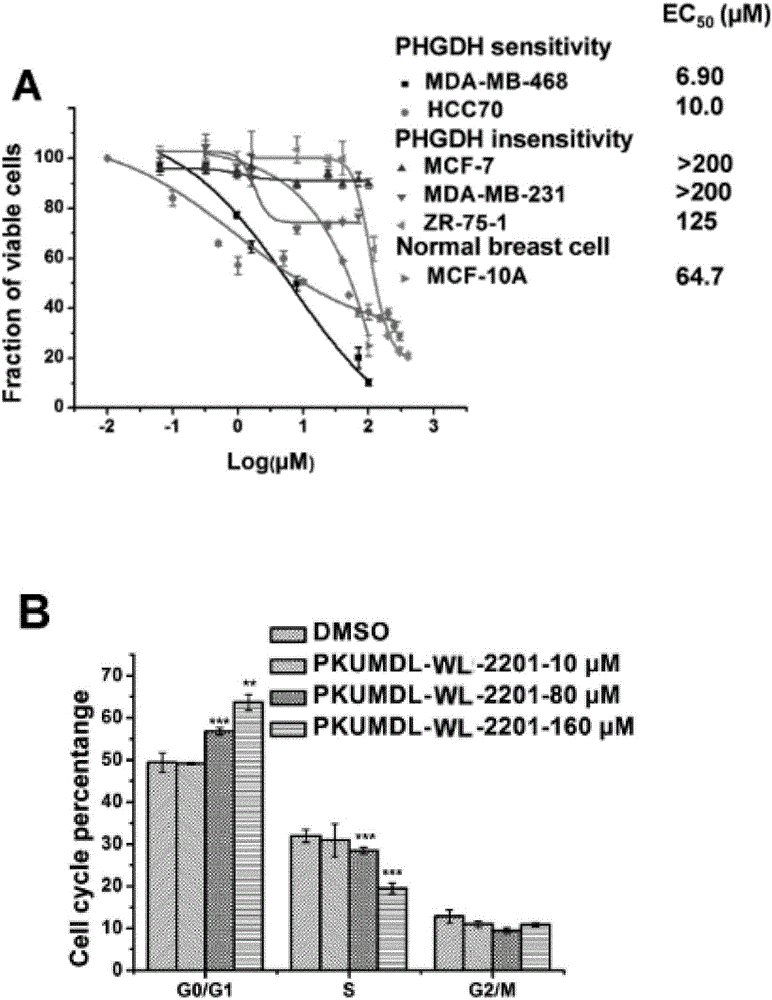
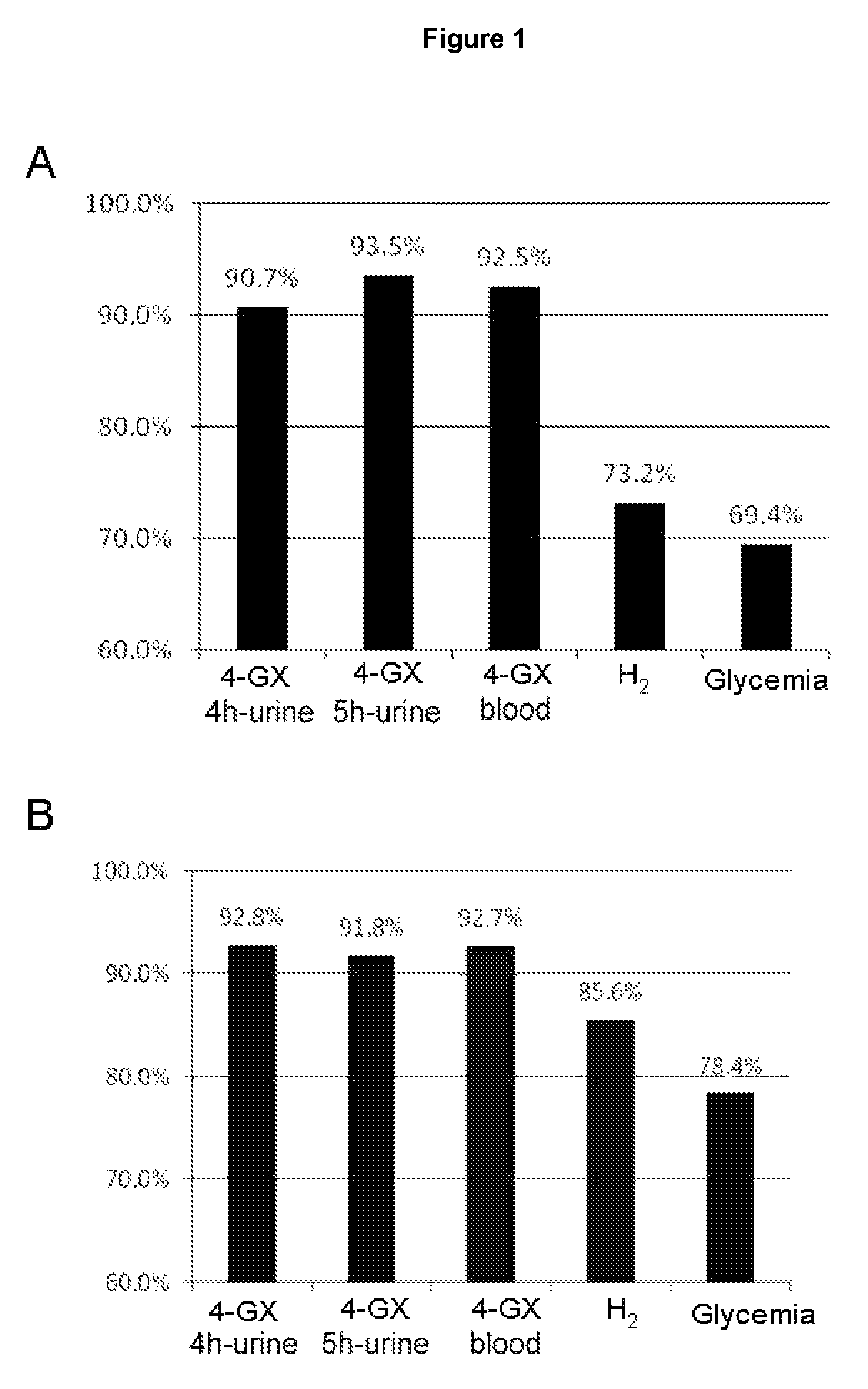
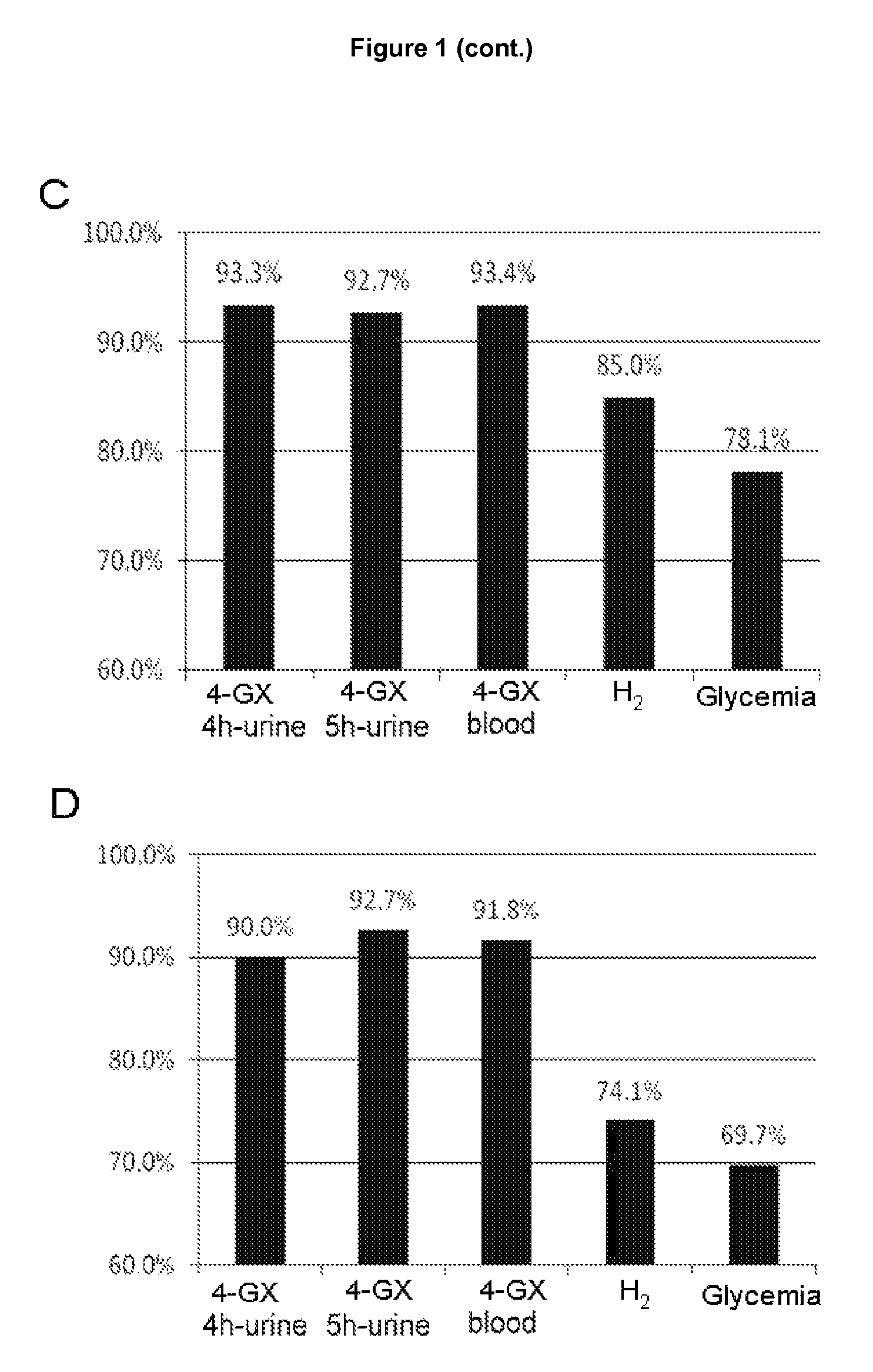
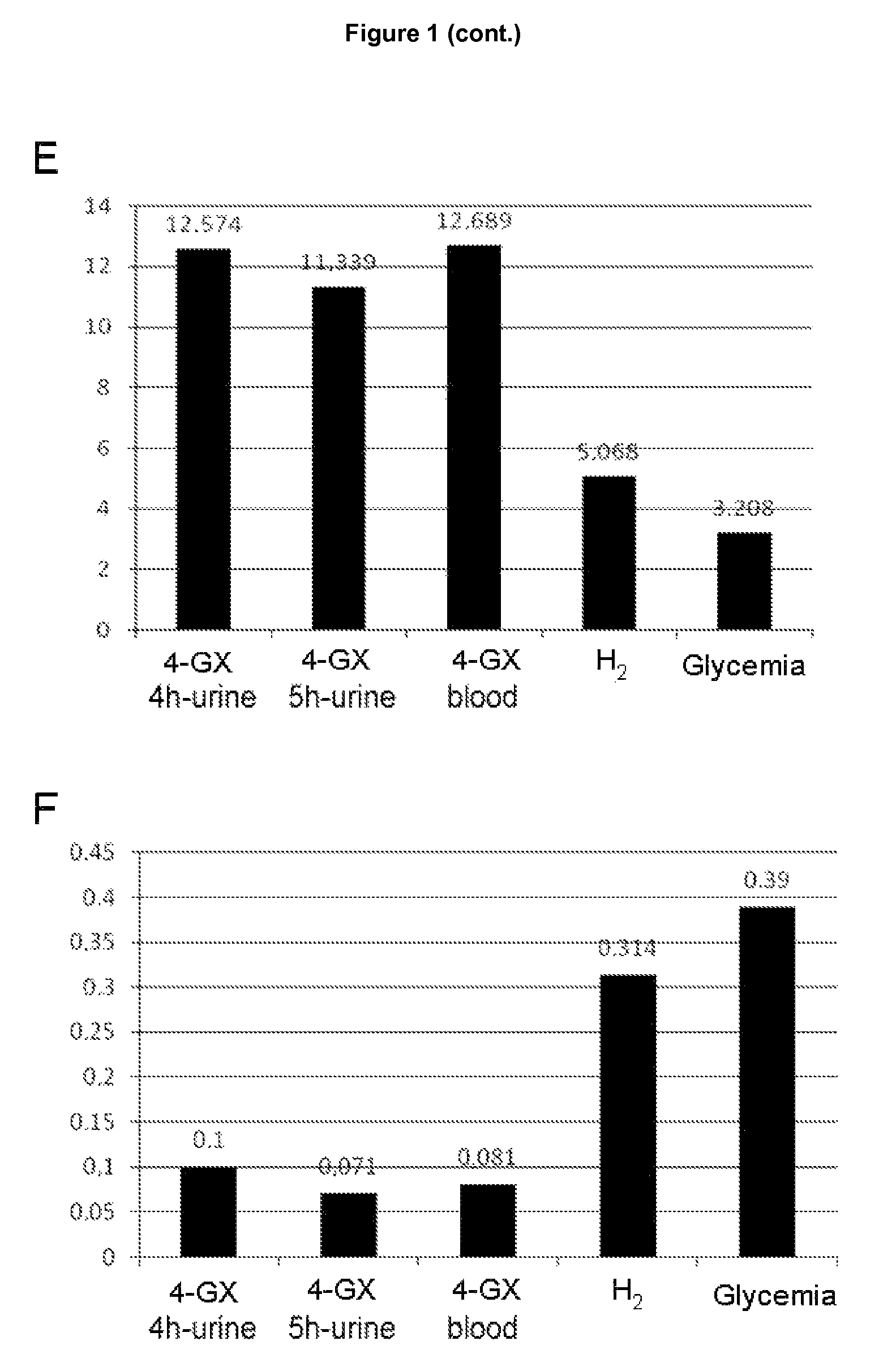
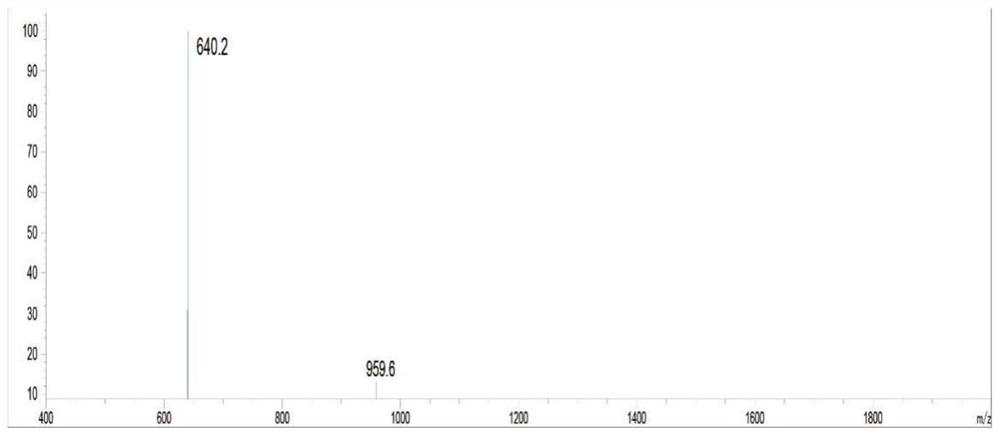
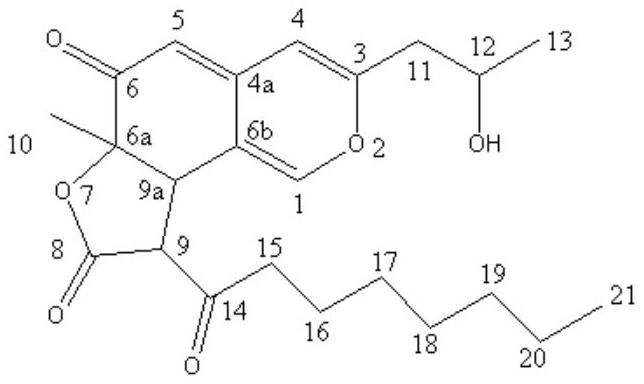
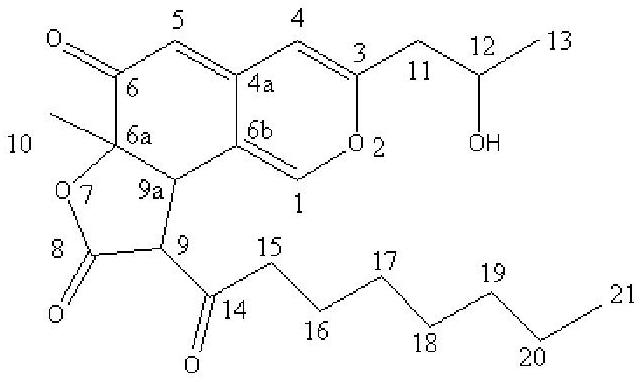
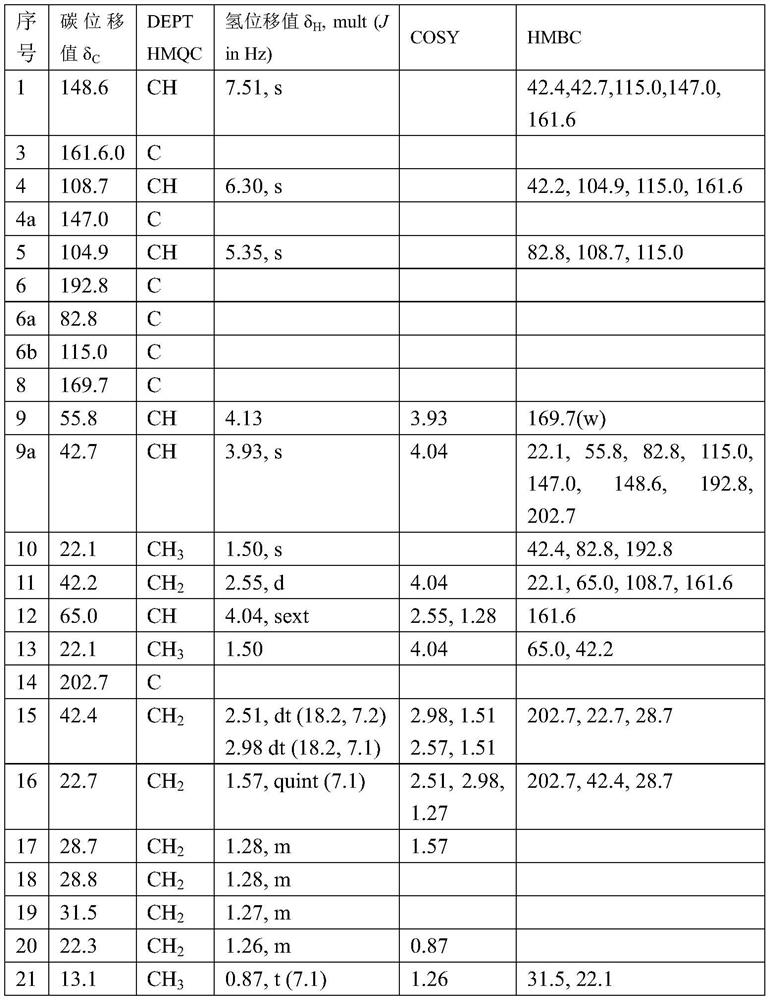
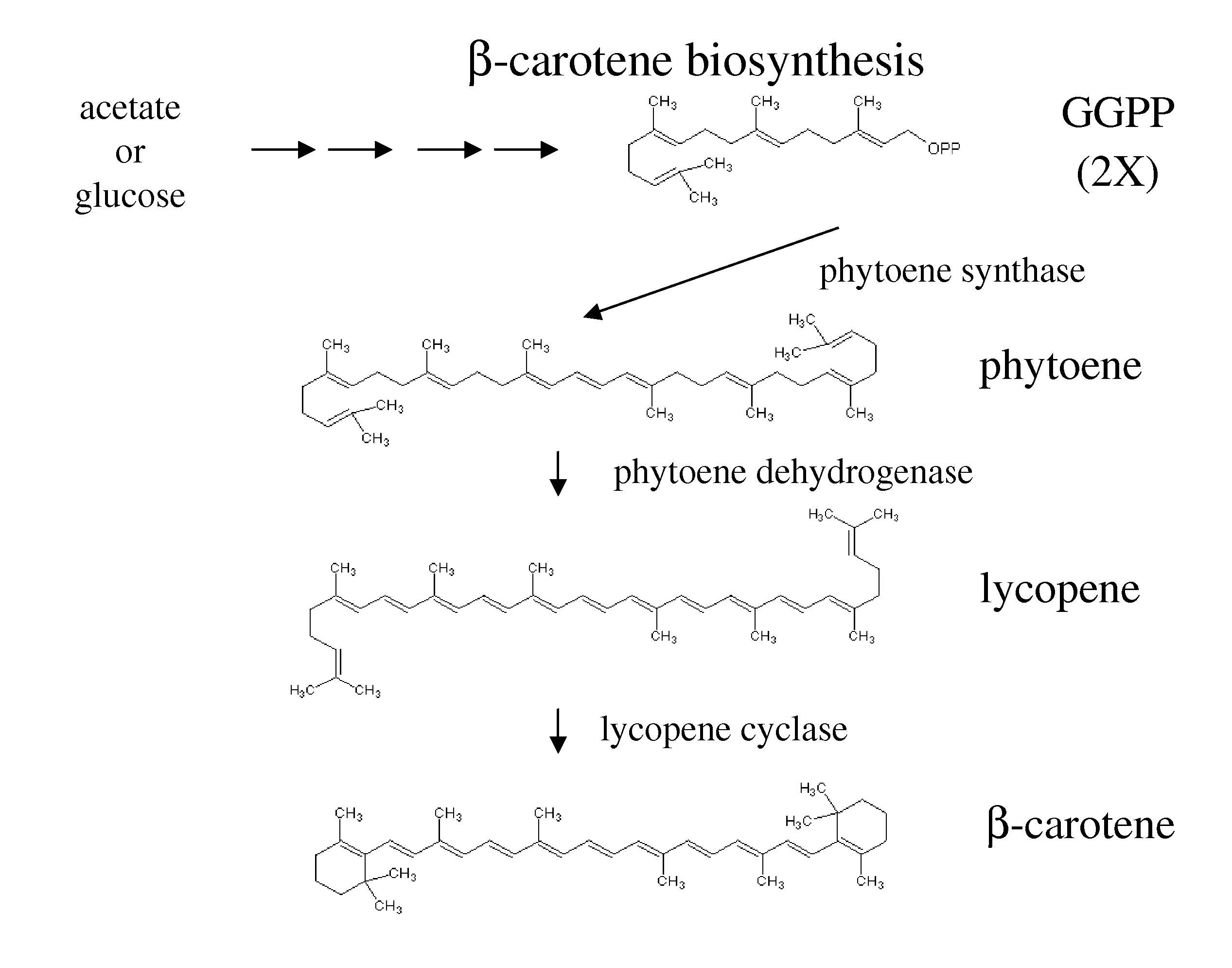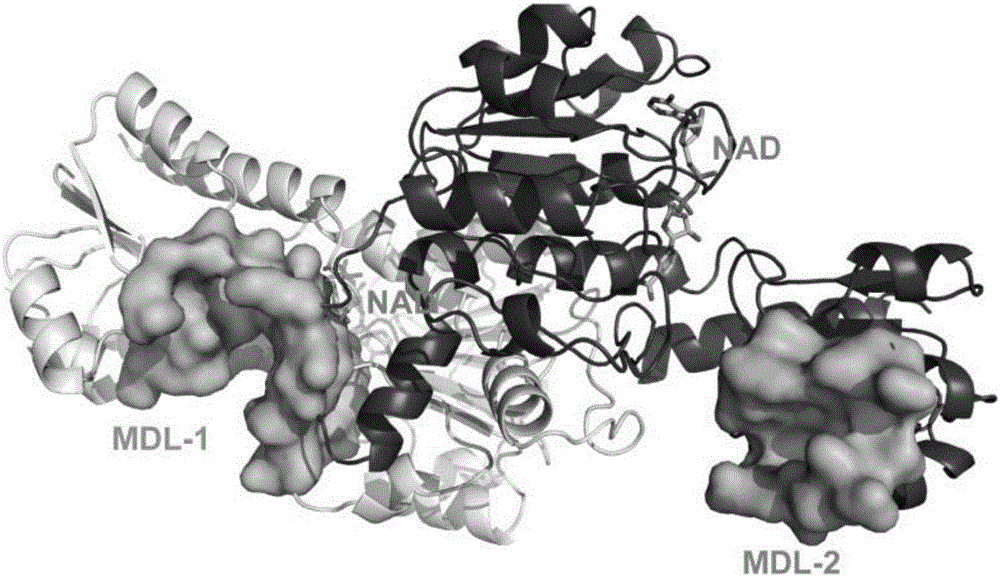Patents
Literature
50 results about "TNase activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polypeptide having cellobiohydrolase activity
Polypeptides having the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1 or derived therefrom by at least one of deletion, addition, insertion or substitution of one or more amino acids in the above sequence and showing a cellobiohydrolase activity.
Owner:TAKARA HOLDINGS
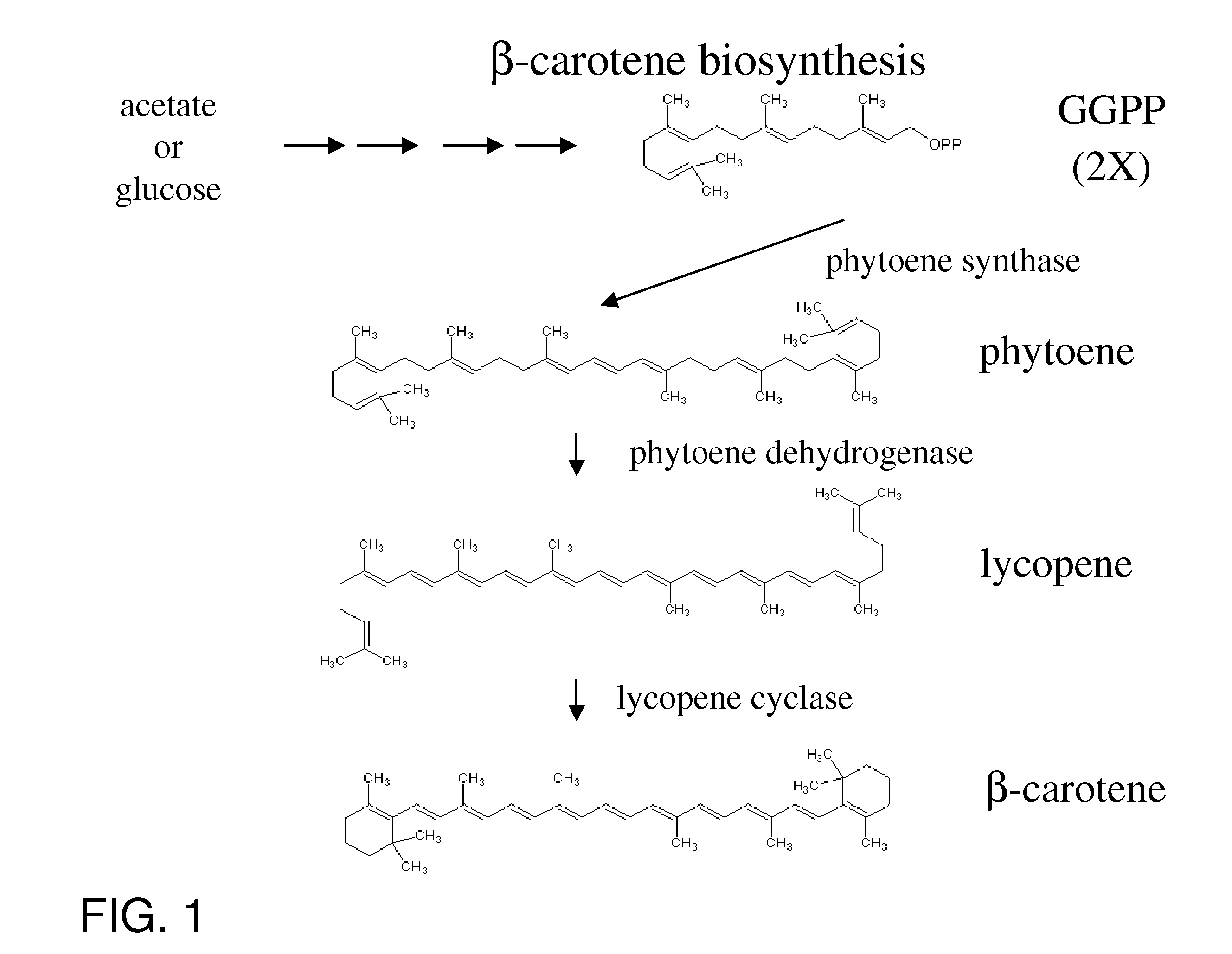
Manipulation of genes of the mevalonate and isoprenoid pathways to create novel traits in transgenic organisms
InactiveUS20050241017A1Other foreign material introduction processesIsomerasesOpen reading frameNucleotide
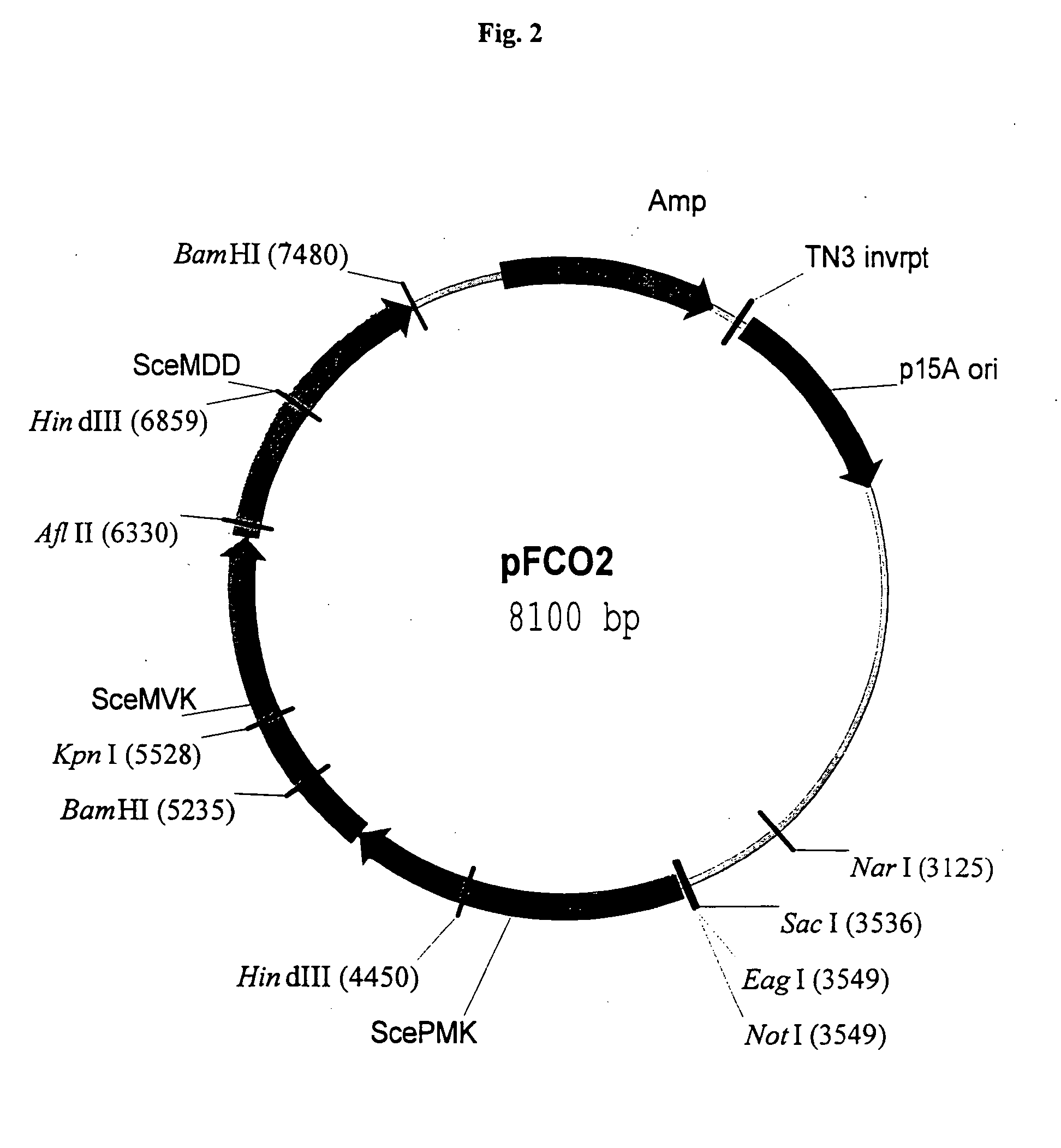
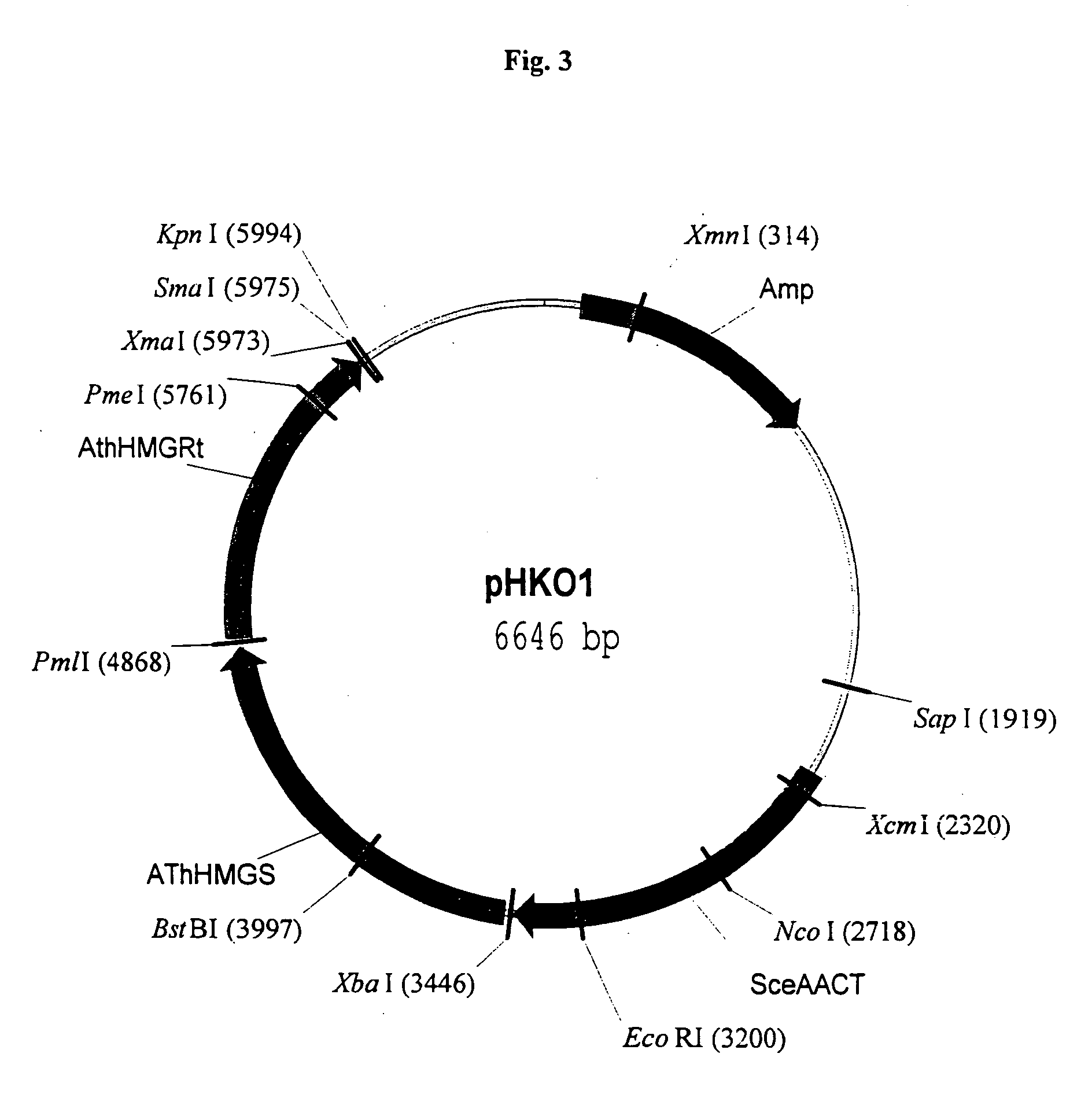
Disclosed are the uses of specific genes of the mevalonate and isoprenoid biosynthetic pathways, and of inactive gene sites (the pseudogene) to (1) enhance biosynthesis of isopentenyl diphosphate, dimethylallyl diphosphate and isoprenoid pathway derived products in the plastids of transgenic plants and microalgae, (2) create novel antibiotic resistant transgenic plants and microalgae, and (3) create a novel selection system and / or targeting sites for mediating the insertion of genetic material into plant and microalgae plastids. The specific polynucleotides to be used, solely or in any combination thereof, are publicly available from GeneBank and contain open reading frames having sequences that upon expression will produce active proteins with the following enzyme activities: (a) acetoacetyl CoA thiolase (EC 2.3.1.9), (b) 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) synthase (EC 4.1.3.5), (c) HMG-CoA reductase (EC 1.1.1.34), (d) mevalonate kinase (EC 2.7.1.36), (e) phosphomevalonate kinase (EC 2.7.4.2), (f) mevalonate diphosphate decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.33), (g) isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) isomerase (EC 5.3.3.2), and (h) phytoene synthase (EC 2.5.1.32).
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII +1
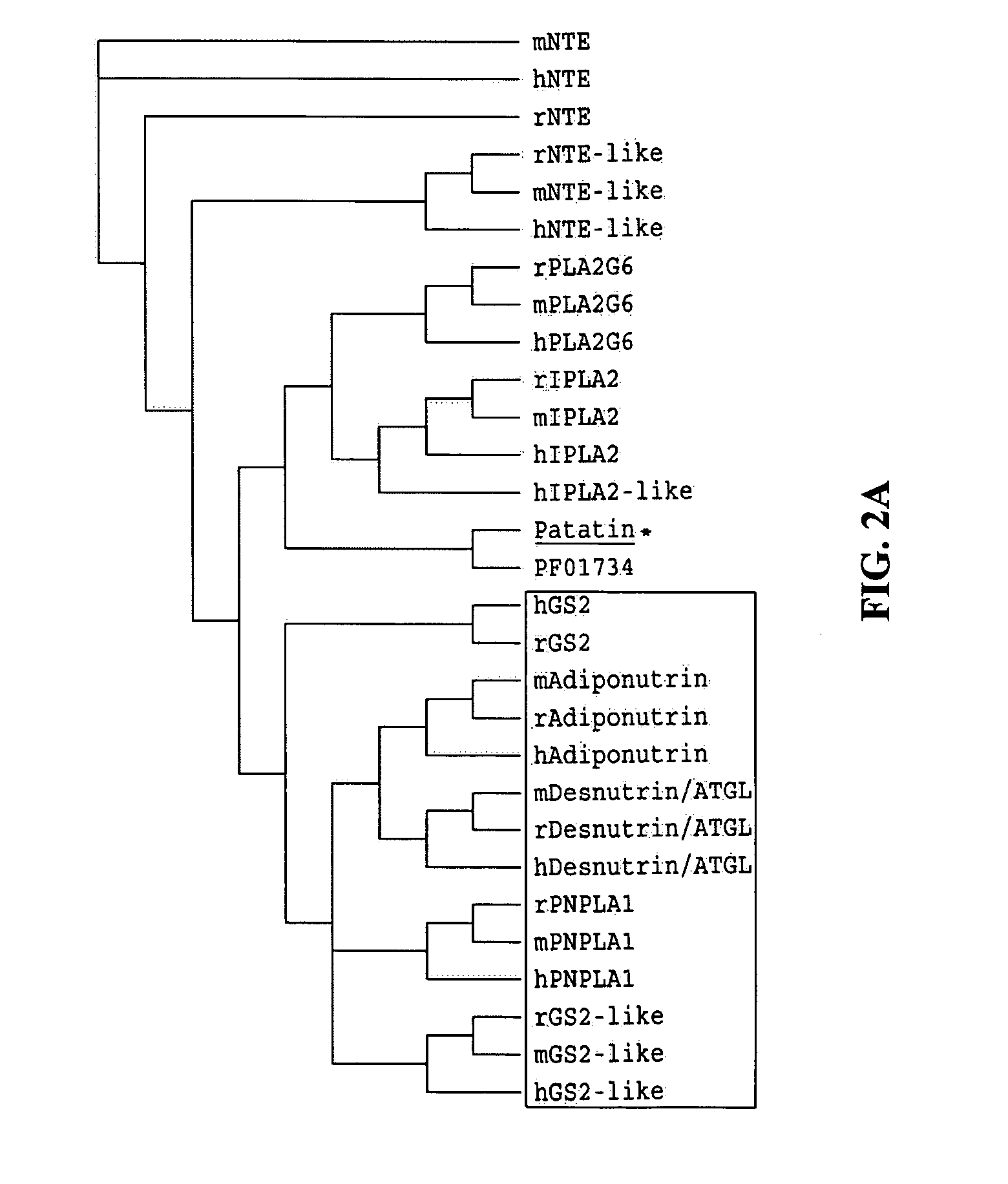
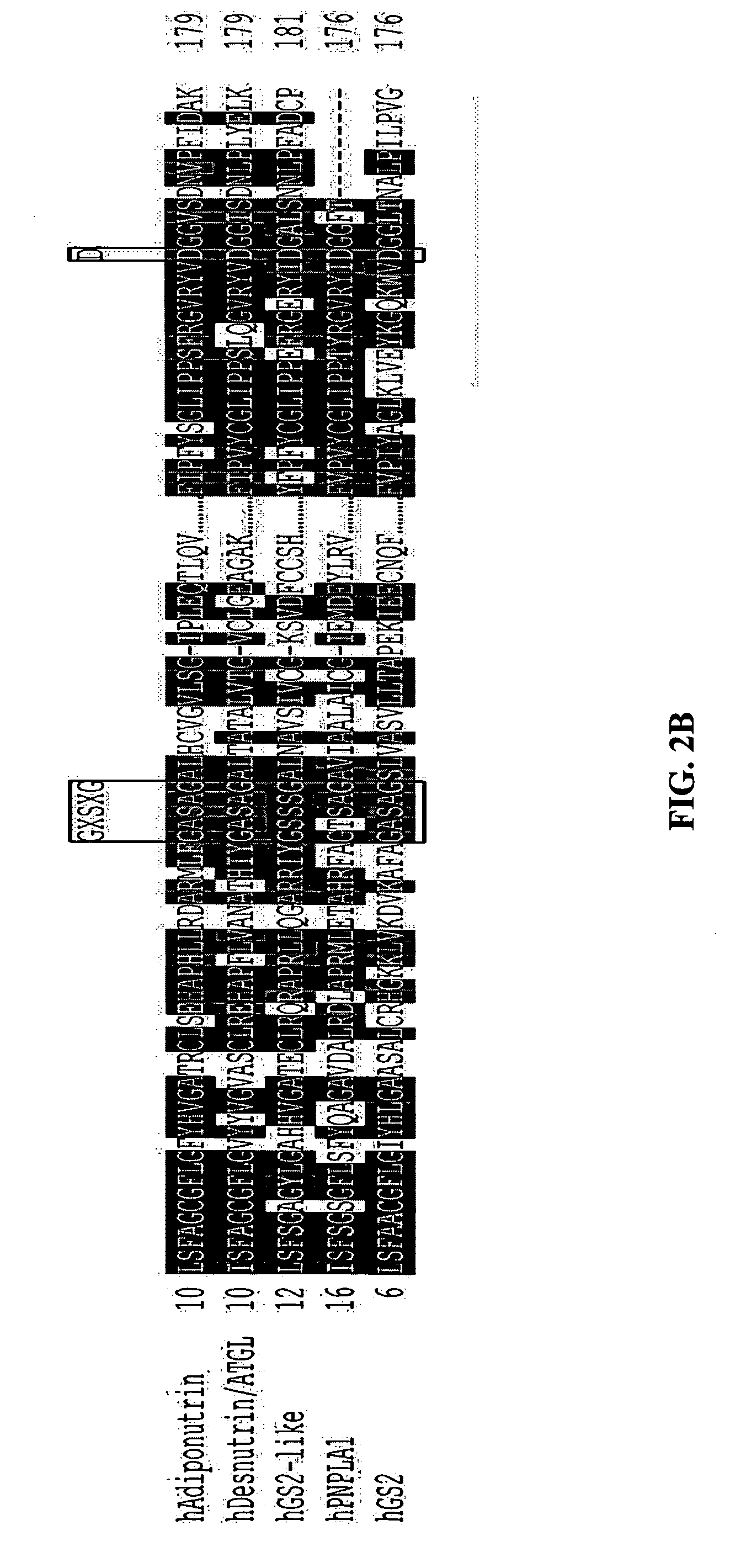
Identification of adiponutrin-related proteins as esterases and methods of use for the same
InactiveUS20070014776A1Modulate its functionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionDyslipidemiaNucleotide
The present invention provides methods of identifying polypeptides that have enzymatic activity associated with nutrient and / or energy homeostasis, and thus, are involved in the development of one or more cardiovascular and metabolic disorders, e.g., cardiovascular disease, obesity, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and metabolic syndrome. One such method comprises identifying a polypeptide as a member of the adiponutrin family of proteins. As such, the invention is related to the polynucleotides and polypeptides belonging to the adiponutrin family, and provides novel isolated and purified polynucleotides and polypeptides of a novel member of the adiponutrin family, patatin-like phospholipase domain 1 (PNPLA1). Also provided are methods of using the polynucleotides and polypeptides related to or provided by the invention for screening a test compound, e.g., a small molecule, antibody, etc., for the ability of the test compound to detect and / or modulate the activity of one or more members of the adiponutrin family of proteins. The present invention also is directed to novel methods for diagnosing, prognosing, and monitoring the progress of at least one cardiovascular and metabolic disorder using polynucleotides or polypeptides belonging to the adiponutrin family, and / or modulators of one or more members of the adiponutrin family. The present invention is further directed to novel therapeutics and therapeutic targets for the intervention (treatment) and prevention of cardiovascular and metabolic disorders arising from dysregulated energy homeostasis, as related to one or more members of the adiponutrin family of proteins.
Owner:WYETH
Method for screening restriction endonucleases
InactiveUS6905837B2Facilitate characterizationPromote productionSugar derivativesHydrolasesOpen reading frameCytotoxicity
A method is provided for identifying a restriction endonuclease, which includes the steps of (a) screening a target DNA sequence for the presence of known methylase sequence motifs, (b) identifying any open reading frames which lie close to the methylase sequence motifs screened in step (a), and (c) assaying the protein products of these open reading frames for restriction endonuclease activity.Methods for identifying isoschizomers of known restriction endonucleases, which isoschizomers possess a desired physical property, such as thermostability, are also provided by the present invention, as are several novel restriction endonucleases isolated from M. jannaschii, MjaIII and MjaIV. Additionally, a gene was identified that encoded a previously observed endonuclease activity, designated MjaII.Also provided by the present invention are vectors suitable for cloning a DNA sequence encoding a cytotoxic protein, via independent transcription promotors which may be selectively controlled by several conditions. A method for producing these cytotoxic proteins using such vectors is also provided, as are stable clones of PacI and NlaIII.
Owner:GOSS INT AMERICAS
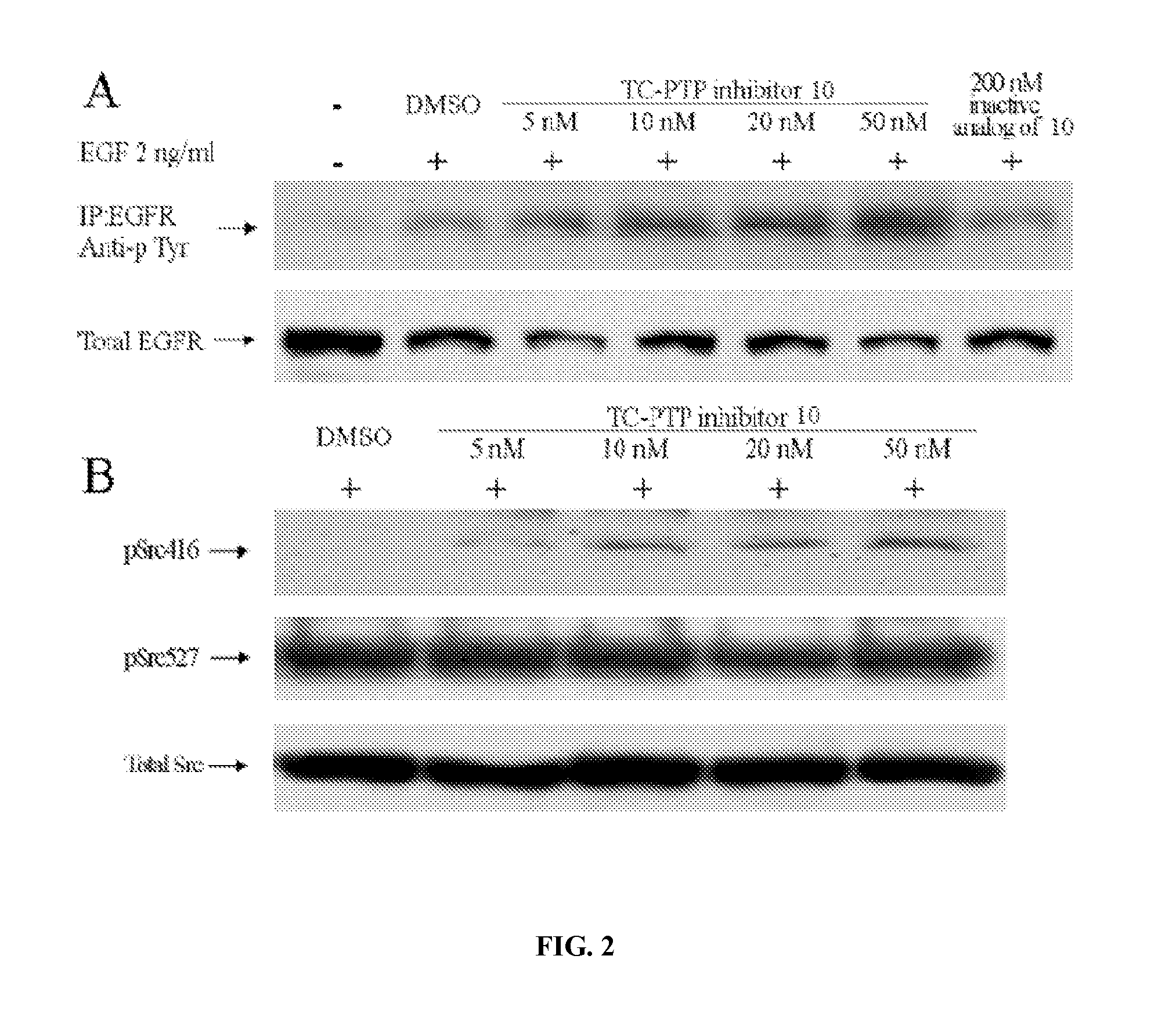
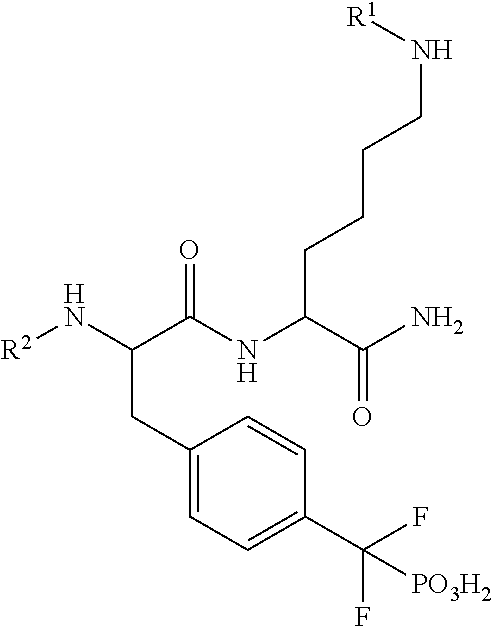
Inhibitors of protein tyrosine phosphatases
Disclosed herein are compounds that selectively inhibit members of the PTP family of enzymes. Synthesized compounds demonstrated selective inhibition of TC-PTP. Also provided are methods of using the compounds and formulations containing the compounds. Also described is a fluorescence-tagged combinatorial library synthesis and screening method. And methods of using these compounds to effect enzyme activity both in cells and in vitro as well as method of using these compounds to treat diseases in human and animals.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Carotene Synthase Gene and Uses Therefor
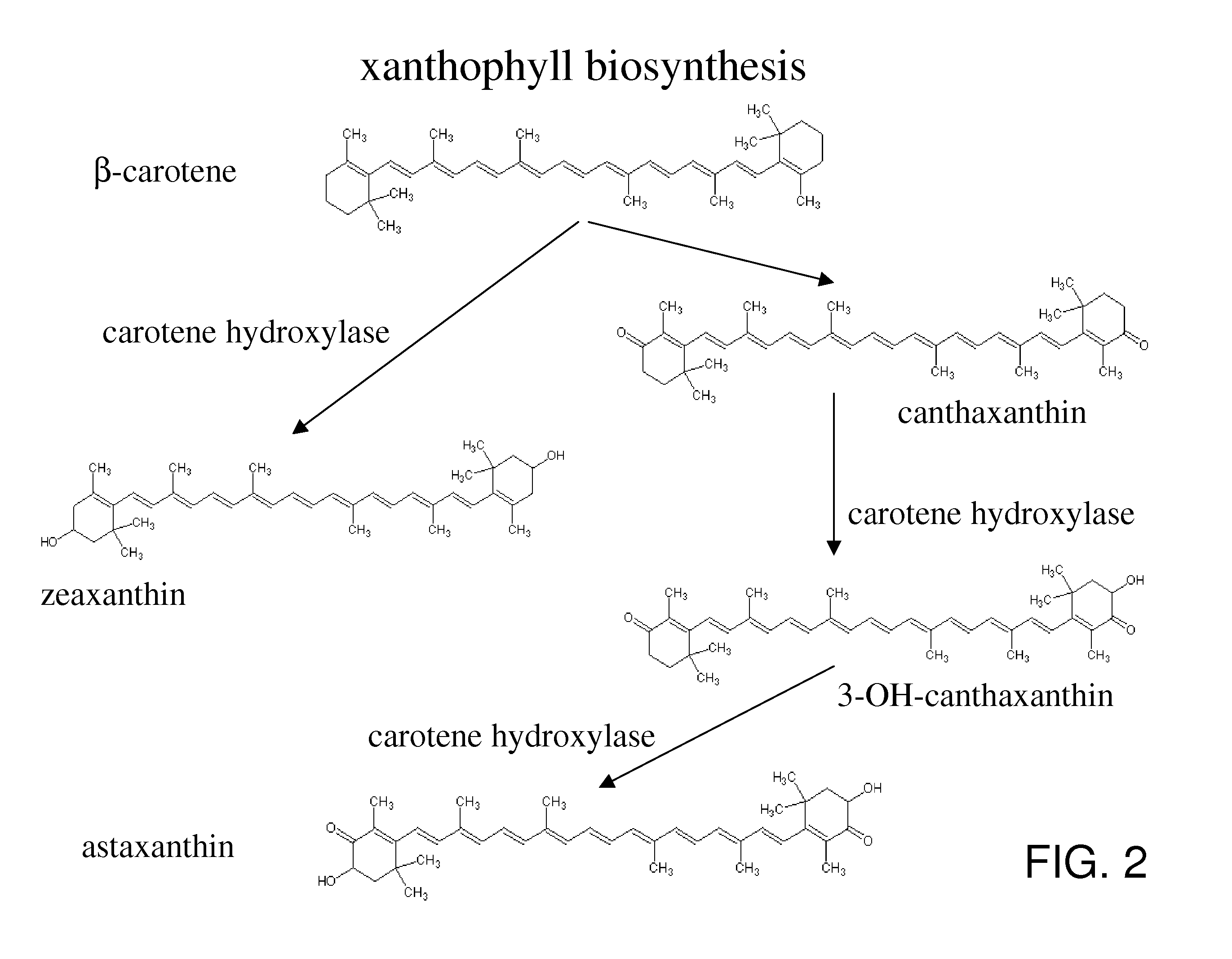
Described herein is a novel three domain gene from Schizochytrium, denoted carotene synthase, that encodes a protein with three different enzymatic activities: phytoene dehydrogenase (PD), phytoene synthase (PS), and lycopene cyclase (LC). Also described is the isolated gene encoding the carotene synthase, homologues thereof, the enzyme encoded by such gene, biologically active portions and homologues thereof, recombinant nucleic acid molecules, microorganisms and plants that have been genetically modified to increase or decrease the action of such gene, and methods of producing carotenoids and derivatives thereof or methods of producing microorganisms and lipid products lacking pigmentation using the knowledge of the carotene synthase described herein.
Owner:MARTEK BIOSCIENCES CORP
Method for obtaining natural variant of enzyme and super thermostable cellobiohydrolase
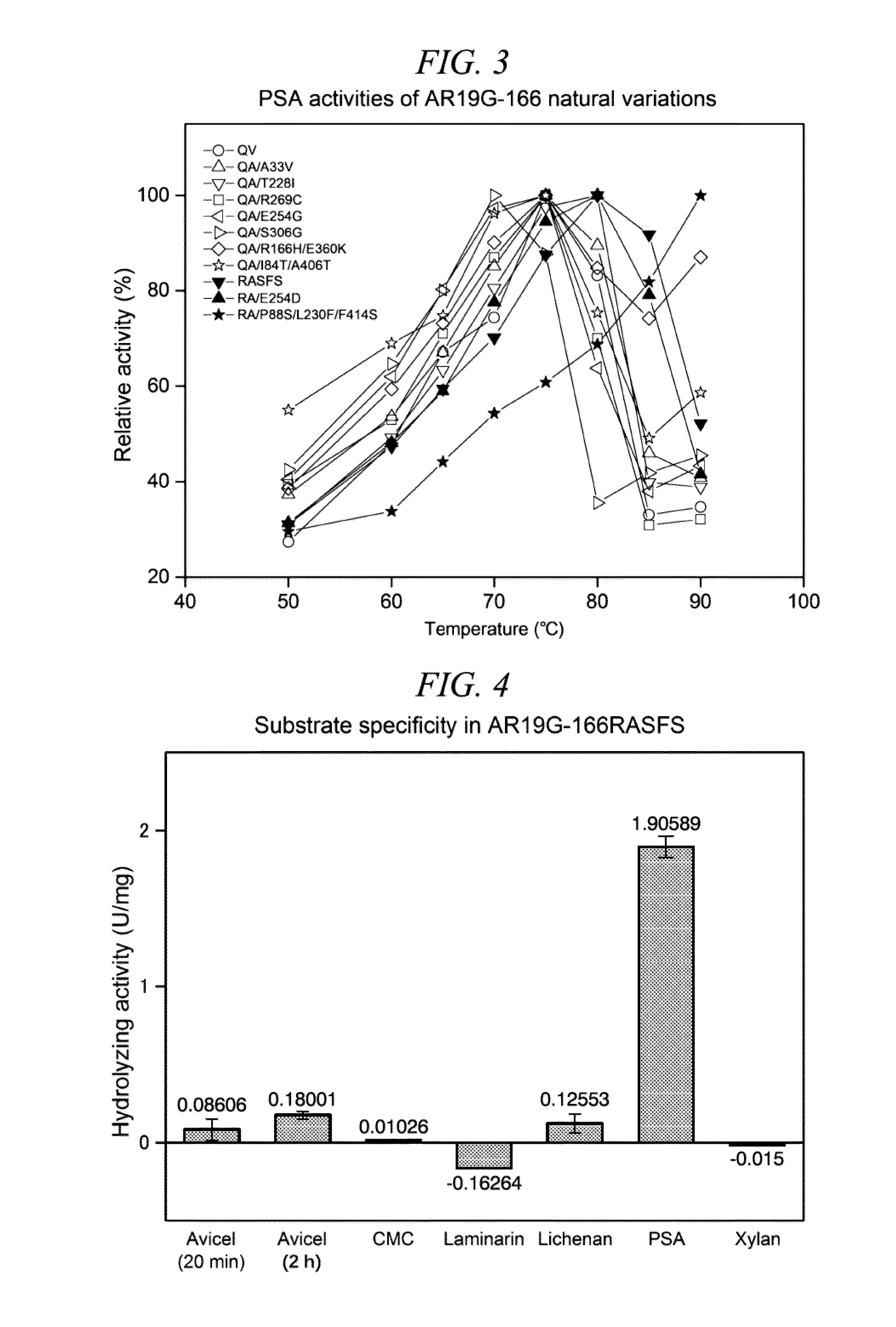
InactiveUS20150259659A1Efficiently obtainedIncrease enzyme activityMicroorganismsLibrary screeningGenome databaseEnzyme
A method for selectively obtaining a natural variant of an enzyme having activity includes (1) a step of detecting an ORF sequence of a protein having enzyme activity from a genome database including base sequences of metagenomic DNA of environmental microbiota; (2) a step of obtaining at least one PCR clone including the ORF sequence having a full length, a partial sequence of the ORF sequence, or a base sequence encoding an amino acid sequence which is formed by deletion, substitution, or addition of at least one amino acid residue in an amino acid sequence encoded by the ORF sequence, by performing PCR cloning on at least one metagenomic DNA of the environmental microbiota by using a primer designed based on the ORF sequence; (3) a step of determining a base sequence and an amino acid sequence which is encoded by the base sequence for each PCR clone obtained in the step (2); and (4) a step of selecting a natural variant of an enzyme having activity by measuring enzyme activity of proteins encoded by each PCR clone obtained in the step (2).
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Enzyme composition for use as a clinical diagnostic reagent
Disclosed is a stabilized enzyme composition for use in clinical examination, comprising: (a) an enzyme component comprising at least two enzymes selected from the group consisting of alkaline phosphatase, creatine kinase and alanine aminotransferase; (b) a stabilizer component comprising effective stabilizing amounts of an albumin, and at least one saccharide selected from the group consisting of trehalose and sorbitol; and (c) an aqueous medium having dissolved therein the components (a) and (b). The enzyme composition of the present invention is stable for a prolonged period of time not only under non-freeze refrigeration conditions, but also under freezing conditions or under conditions for non-freeze refrigeration after thawing of the frozen composition, as compared to the conventional enzymatic compositions. The enzyme composition of the present invention can be advantageously used for the purpose of checking the precision in measurement, correcting measured values and calibrating the amount and activity of an enzyme, in a clinical examination for measuring the enzymatic activity in a sample, such as serum or the like.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI KK
Fluorescent substrates for detecting organophosphatase enzyme activity
InactiveUS7374900B2Facilitate large through put methodsHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphorus organic compoundsHydrogenFluorescence
Disclosed are compounds of the formula (I): wherein R3, R4, R5, R9, and R10 are selected from the group consisting of H and groups or atoms other than H, and R6 and R8 are halo or hydrogen; X1, X2, and X3 are independently O or S; provided that R9 and R10 are not simultaneously H, when all of X1, X2, and X3 are O; and of the formula (II) wherein R11-R14 are selected from the group consisting of H and groups or atoms other than H; X4-X9 are independently O or S; n and m are 0 or 1 but m and n cannot be 0 simultaneously; R15-R24 can be H or any substituent so long as the compound of formula II upon hydrolysis provides a fluorescent compound. These compounds are useful as substrates with high specificity for organophosphatase particularly human paraoxonase and bacterial organophosphorus hydrolase. Also disclosed is a method for detecting and / or measuring the paraoxonase activity in a fluid comprising contacting the fluid with a fluorescent substrate and measuring the fluorescence of the fluorescent product formed.
Owner:AMERICAN NAT RED CROSS
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecule for expressing hairpin type RNA (ribonucleic acid) for suppressing sitobion avenae carboxylesterase and application of DNA molecule
InactiveCN103589728AReduce expressionReduce enzyme activityBiocideAnimal repellantsBiotechnologyA-DNA
The invention discloses a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecule for expressing a hairpin type RNA (ribonucleic acid) for suppressing sitobion avenae carboxylesterase and application of the DNA molecule. The structure of the DNA molecule disclosed by the invention is SEQ (forward)-X-SEQ (reverse); the sequence of the SEQ (forward) is from a locus 1 to a locus 345 of a sequence 1; the sequence of the SEQ (reverse) is reversely complementary to that of the SEQ (forward); the X is an interval sequence between the SEQ (forward) and the SEQ (reverse); according to the sequence, the X is not complementary to the SEQ (forward) and the SEQ (reverse). An experiment shows that the DNA molecule is converted into an immature embryo callus of wheat to obtain a transgenic line; the transgenic line is subjected to an aphid feeding test; after sitobion avenae is fed on transgenic leaves, the carboxylesterase gene expression quantity and the enzymatic activity are obviously alleviated, and the rate of reproduction is reduced; furthermore, the tolerance of the sitobion avenae to a phoxim solvent is reduced by 20-30 percent. Therefore, the DNA molecule has a great significance for prevention and treatment of insects of agricultural production.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
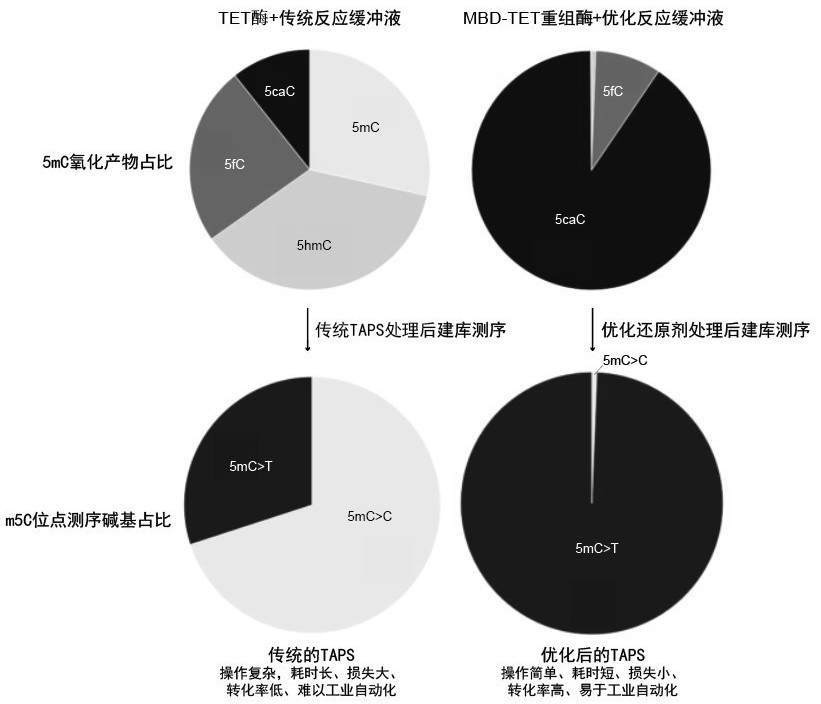
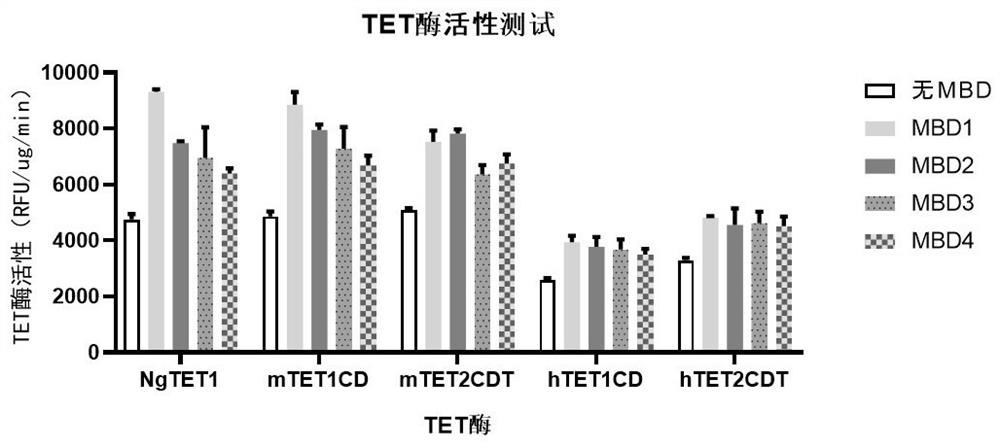
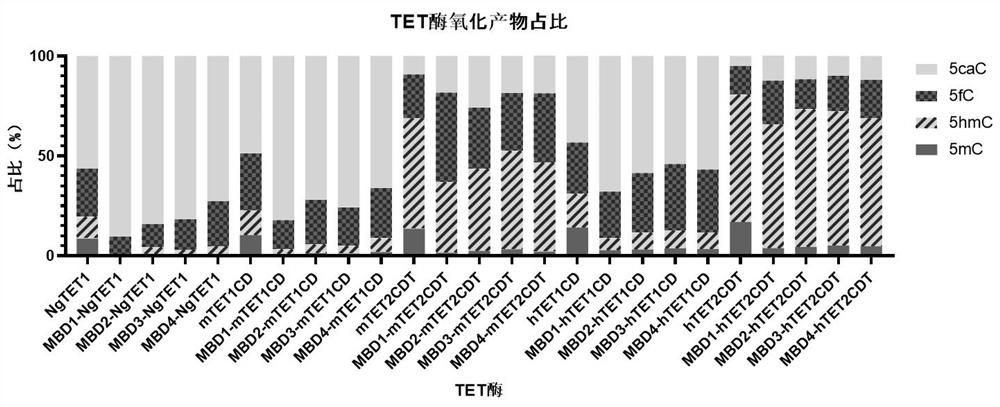
Recombinant protein structural domain and coding DNA thereof, enhanced TET enzyme and whole genome DNA methylation detection method
ActiveCN113637053AImprove oxidation activityHigh sensitivityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationA-DNA
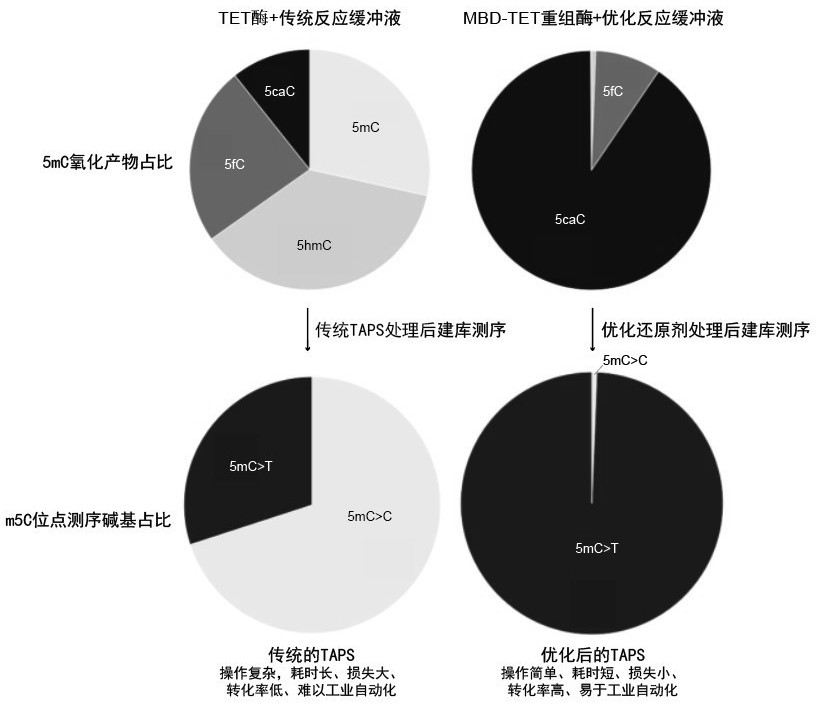
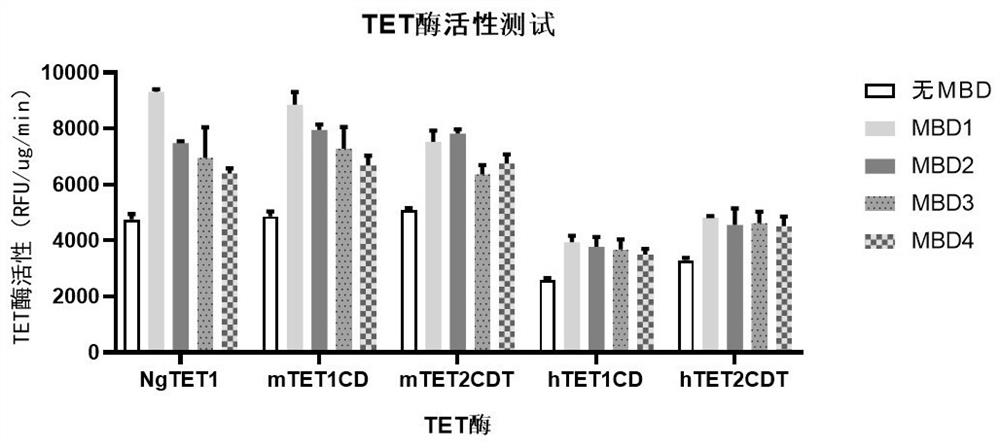
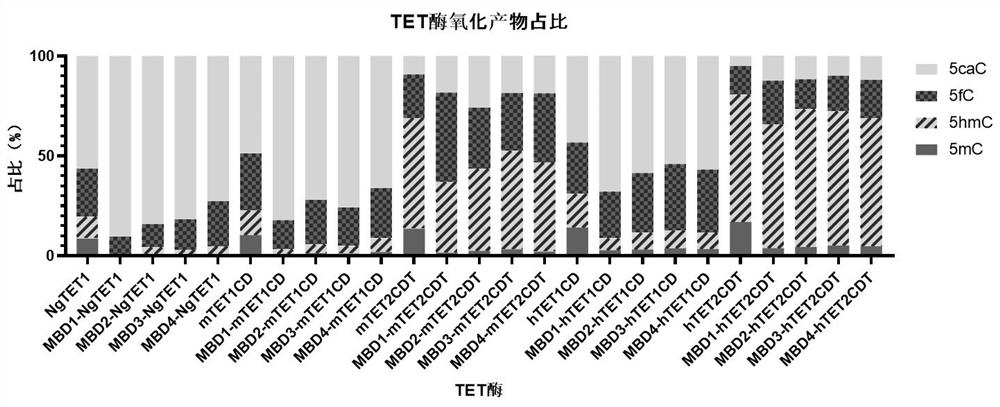
The invention provides a recombinant protein structural domain for enhancing TET enzyme activity. The recombinant protein structural domain is a DNA methylation binding structural domain (MBD), and the amino acid sequence of MBD1-4 is as shown in SEQ ID 1-4. The recombinant protein MBD-TET formed by fusing the MBD and the TET enzyme can be used for remarkably enhancing the oxidation activity of the TET enzymes, including NgTET1, mTET1CD, mTET2CDT, hTET1CD and hTET2CDT, on 5mC. In addition, the invention further provides a simple, convenient and rapid high-throughput DNA methylation detection process, and the sensitivity and accuracy of a TET enzymatic oxidation reaction-based DNA methylation detection technology are improved.
Owner:YEASEN BIOTECHNOLOGY (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Mutant of epimerase and application of mutant
ActiveCN111793616AIncrease productionIncrease productivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHeterologousIsomerization
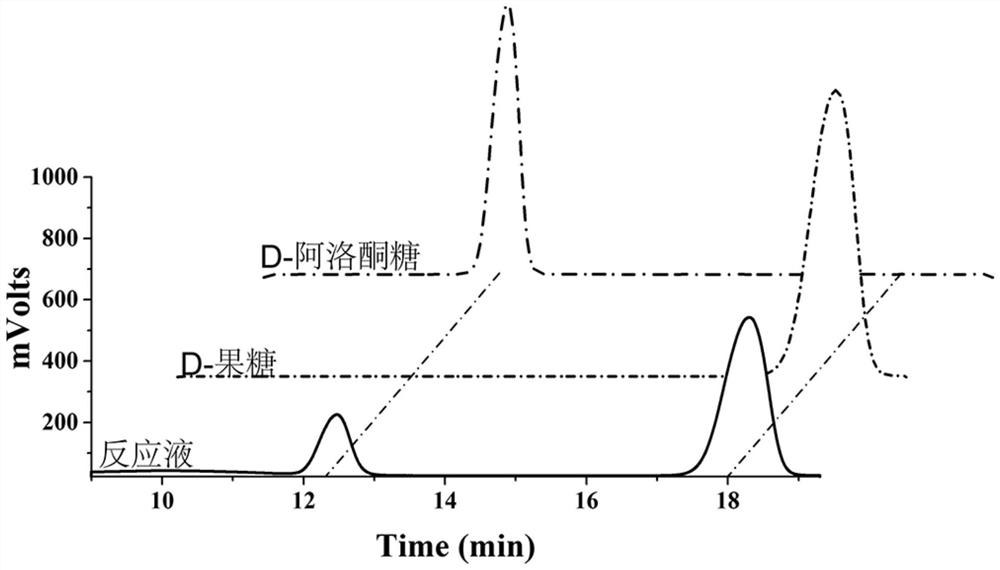
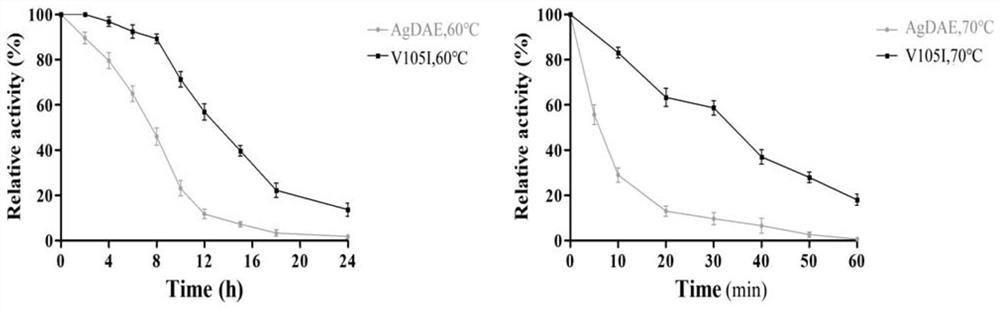
The invention provides a method for constructing and applying a mutant of a D-allulose-3-epimerase (DAE). The method for constructing the mutant of the enzyme comprises the steps as follows: a DAE gene from Arthrobacter globiformis is used as a parent, valine (105th amino acid residue) in an activity catalytic center of the enzyme is changed into isoleucine with homology comparison and site-directed mutagenesis technologies; and then, an expression vector is constructed, and the mutant of the enzyme is obtained with an E. Coli BL21 (DE3) as a heterologous expression host. The activity determination shows that the temperature stability of the obtained mutant enzyme is significantly increased. The t1 / 2 values at 60 DEG C and 70 DEG C reach 12.5 h and 0.5 h respectively, and the half-life at70 DEG C is 6 times longer than that of a wild type. The activity of the mutant enzyme is also improved. The mutant enzyme obtained by screening can more efficiently catalyze the isomerization of D-fructose into D-allulose at high temperature, provides broad prospects for the industrial production of the D-allulose and has important industrial applications value.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
7 beta-HSDH enzyme and DPS fusion protein
ActiveCN110776572AImprove thermal stabilityIncrease enzyme activityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsOxidoreductasesGlycineThermoanaerobacter pseudethanolicus
The invention relates to a 7 beta-HSDH enzyme and DPS fusion protein. The 159th glycine of the 7 beta-HSDH enzyme of which an amino acid sequence is as shown in SEQUENCE NO.1 is mutated to form histidine, the 165th lysine is mutated to form histidine, a 7 beta-HSDH enzyme mutant of which an amino acid sequence is as shown in SEQUENCE NO.2 is obtained, the 7 beta-HSDH enzyme mutant and DPS proteinwhich is derived from thermoanaerobacter pseudethanolicus are subjected to fusion expression so as to obtain the 7 beta-HSDH enzyme and DPS fusion protein. Compared with a wild 7 beta-HSDH enzyme, the7 beta-HSDH enzyme and DPS fusion protein obtained by the invention has the advantages that the heat stability is significantly improved, and the enzymic activity is improved by 70%.
Owner:BIORTUS BIOSCI
Construction of recombinant bacterium capable of efficiently expressing chitinase and screening of mutant with high enzyme activity
ActiveCN112831510AImprove hydrolysis efficiencySavings for screening signal peptidesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChitinaseMutant
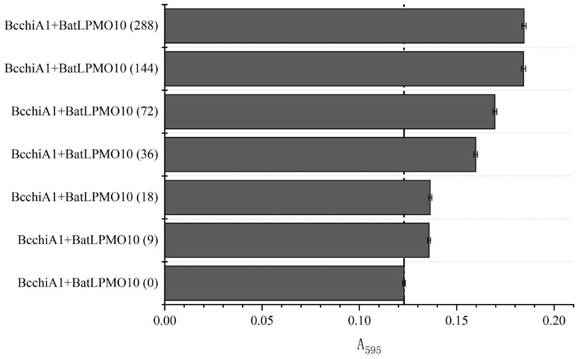
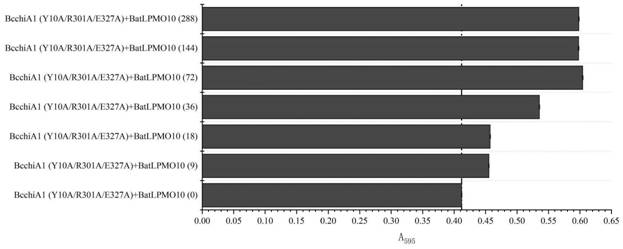
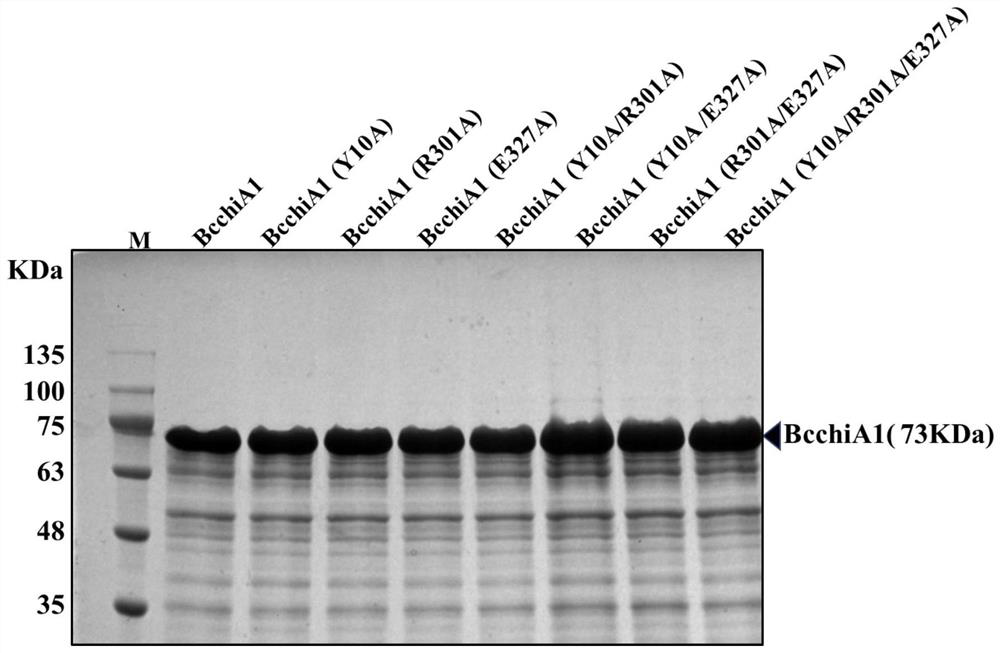
The invention relates to construction of a recombinant bacterium for efficiently expressing chitinase and screening of a mutant with high enzyme activity. According to the invention, efficient secretory expression of BcchiA1 in bacillus subtilis is realized by means of a recombinant protein technology, and the problem of insufficient chitinase secretion amount of most microorganisms is solved. Meanwhile, a novel chitinase high-throughput screening method is created, and the screening throughput and efficiency are greatly improved. In addition, the invention relates to several strains of chitinase mutants with high enzyme activity, the enzyme activities of BcchiA1 (Y10A), BcchiA1 (R301A), BcchiA1 (E327A), BcchiA1 (Y10A / R301A), BcchiA1 (Y10A / E327A), BcchiA1 (R301A / E327A) and BcchiA1 (Y10A / R301A / E327A) are respectively improved by 2.49 times, 0.67 times, 3.61 times, 2.39 times, 3.46 times, 4.75 times and 16.89 times compared with the enzyme activities of the wild type BcchiA1, and the enzyme activity of BcchiA1 (Y10A / R301A / E327A) is optimal. Finally, after the chitinase BcchiA1 and the optimal mutant BcchiA1 (Y10A / R301A / E327A) of the chitinase BcchiA1 and the monooxygenase BatLPMO10 from bacillus atrophaeus are subjected to a synergistic effect respectively, the hydrolysis efficiency of the chitinase BcchiA1 can be improved by 50.00%, and the hydrolysis efficiency of the chitinase BcchiA1 (Y10A / R301A / E327A) can be improved by 46.71%.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
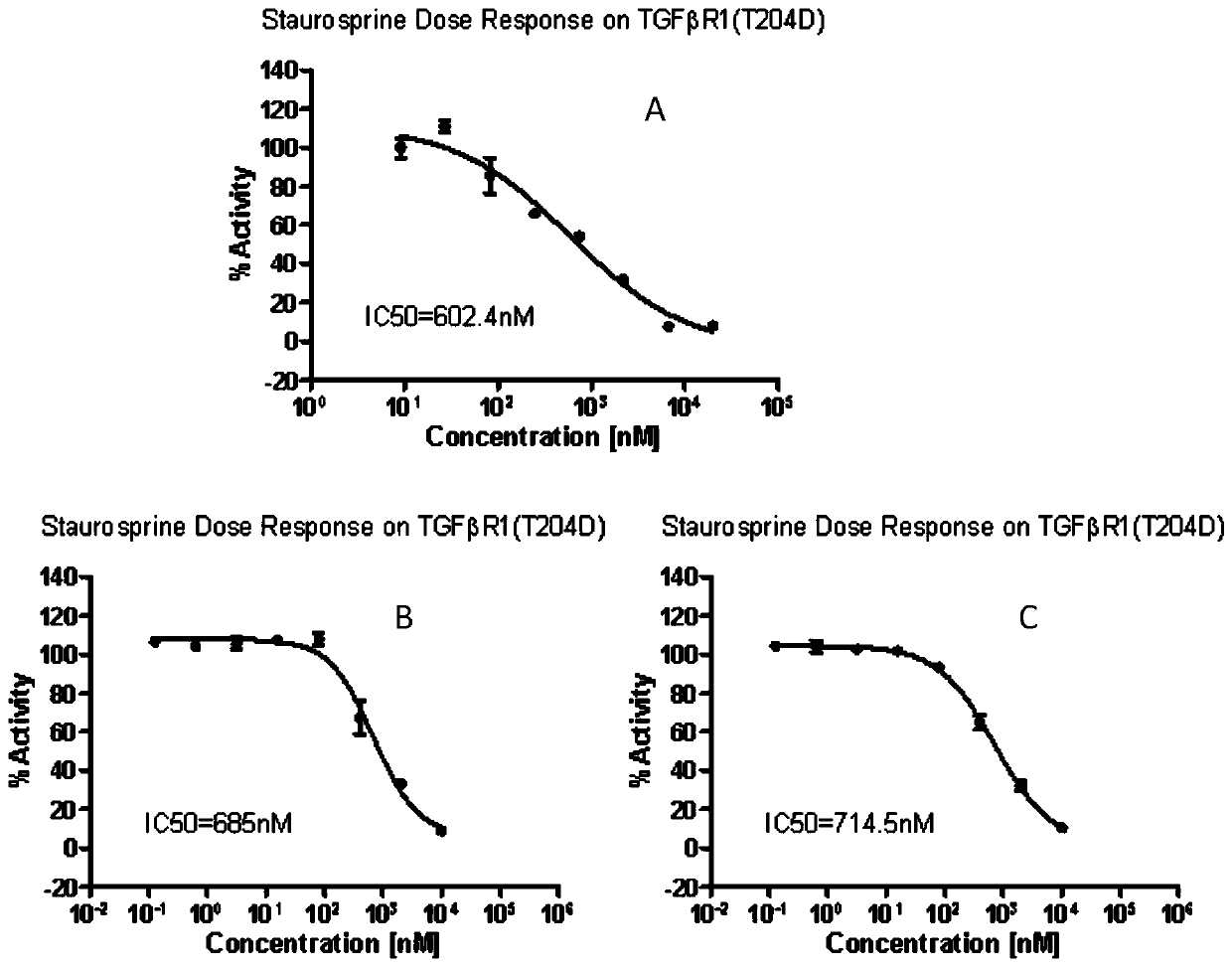
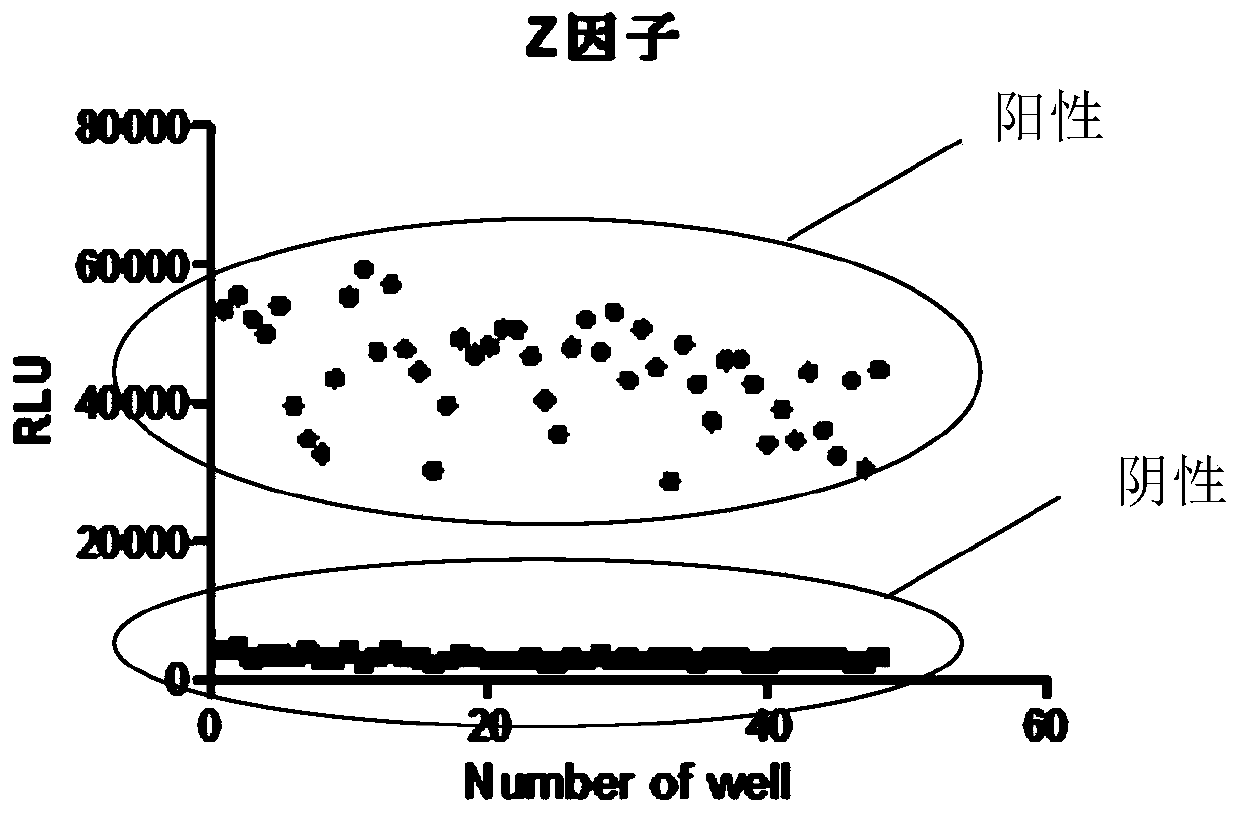
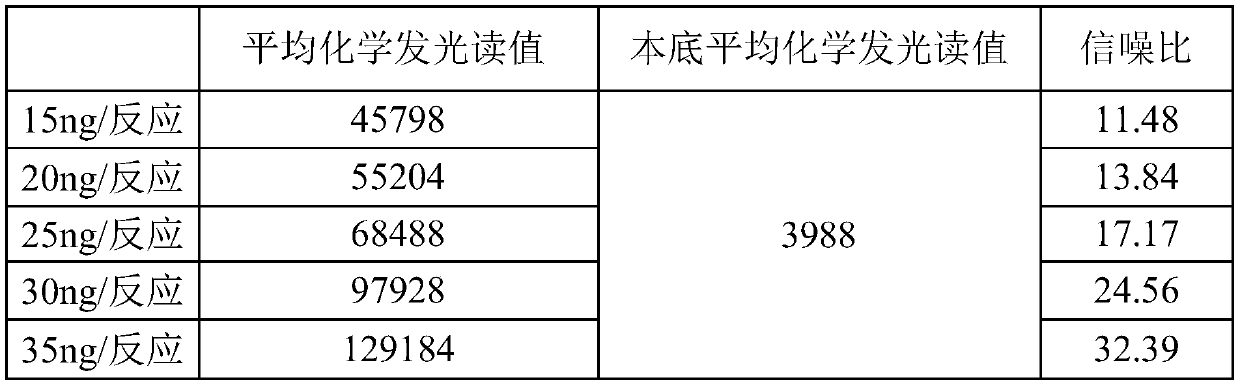
Quick detection method of TGFbetaR1(T204D) enzyme activity, and application thereof
PendingCN110196326AShorten detection timeReduce dosageBiological material analysisPharmaceutical drugReceptor Inhibition
The invention belongs to the technical field of the biochemistry, and specifically relates to a quick detection method of TGFbetaR1(T204D) enzyme activity, and an application thereof. The detection method comprises the following steps: (1) taking each of a to-be-detected sample, a blank reference substance and a positive reference substance to co-incubate with the TGFbetaR1 (T204D) enzyme, TGFbetaR1 primer / ATP mixed solution, performing kinase reaction to produce ADP; (2) adding ADP-GloTM reaction reagent in each of three groups of kinase reaction systems in the step (1) to perform co-incubation; (3) adding the kinase detection reagent in each of three groups of reaction systems in the step (2) to perform co-incubation, transforming the ADP into ATP, and reading a light unit RLU of the newly synthesized ATP; and (4) computing TGFbetaR1(T204D) enzyme activity according to a condition that the enzyme activity is equal to (RLU(Sample)-RLU(Blank)) / (RLU(Pos.Ctrl)-RLU(Blank))*100%. The method is based on the ADP-GloTM kinase experiment, and the reaction progress is quantified by directly determining the ATP consumed in the reaction; all experiments can be accomplished only in one day, and the detection time is greatly shortened. The method can be applied to the screening of TGFbetaR1(T204D) receptor antagonist and the anti-tumor medicine related to the target spot.
Owner:武汉合研生物医药科技有限公司
Polynucleotide Sequencing Using a Helicase
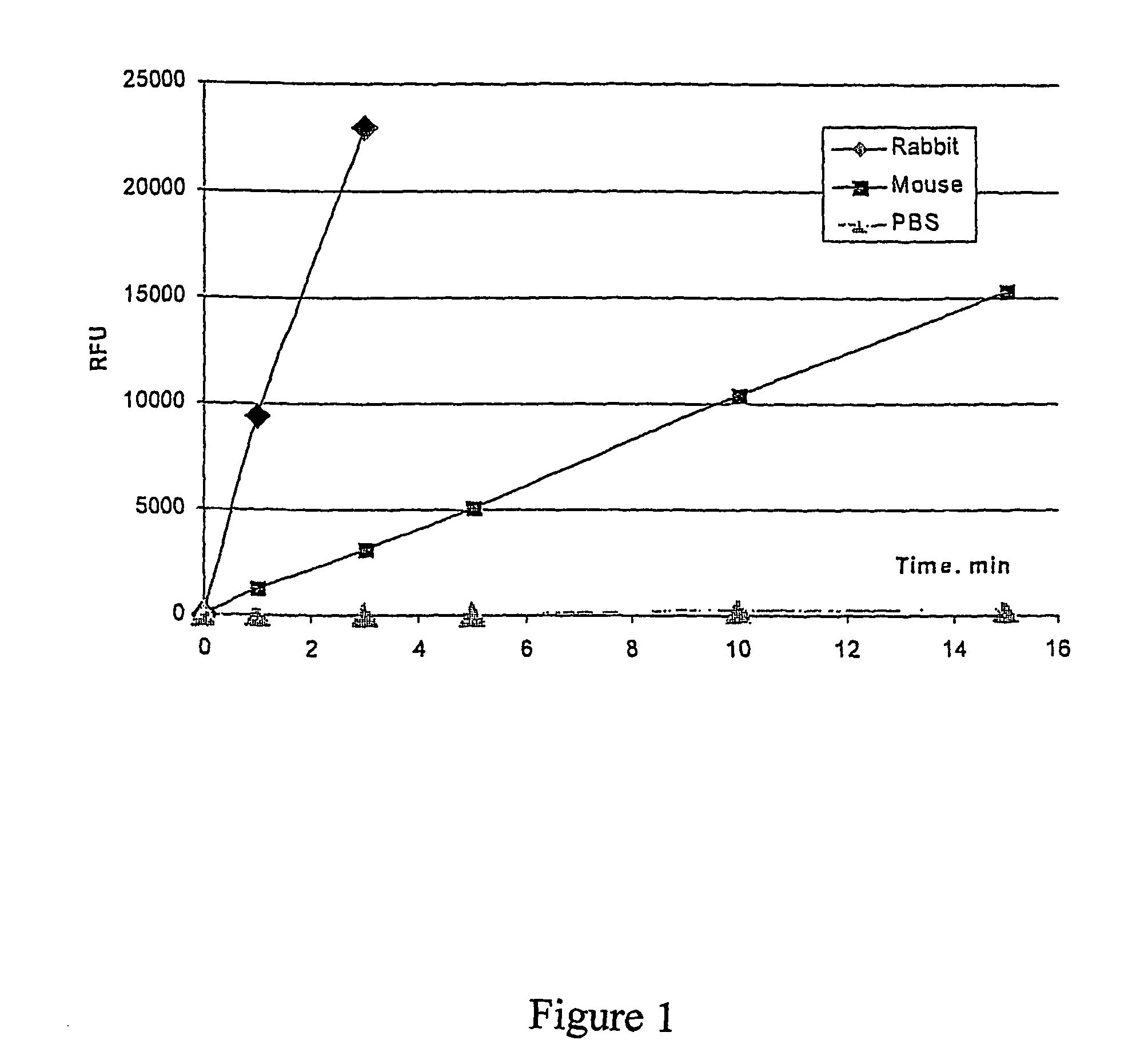
InactiveUS20080096206A1Reduce decreaseEasy to operateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDNA unwinding enzymeHelicase
The present invention pertains to a method for sequencing a polynucleotide, comprising the steps of: (i) reacting a target polynucleotide with a helicase / primase enzyme (which may be immobilised), under conditions suitable for enzyme activity; and (ii) detecting the interaction between the enzyme and a nucleotide on the target, by measuring radiation.
Owner:DENSHAM DANIEL HENRY
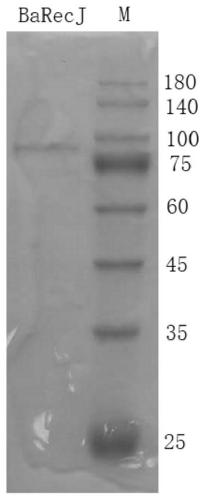
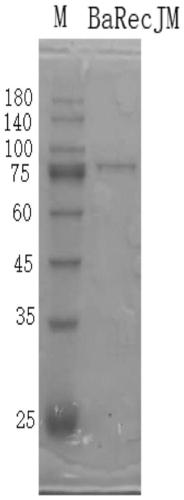
RecJ protein guided with DNA guide and having nucleic acid incision enzyme activity and application of RecJ protein to gene editing
ActiveCN110093390AConvenient genetic engineering operationHydrolasesFermentationPhosphorylationMutant
The invention provides RecJ protein guided with DNA guide and having nucleic acid incision enzyme activity and an application of the RecJ protein to gene editing. The RecJ nuclease from bacteria, provided by the invention, can be combined with small DNA after phosphorylation, exerts nucleic acid incision enzyme effects on complementary target DNA specific sites, and perform gene editing. The aminoacid sequence of the BaRecJ nuclease is shown as SEQID NO:1. On the other hand, the invention provides a mutant of the BaRecJ nuclease, so that the excision enzyme activity can be effectively weakened, and the capacity for shearing fixedpoints of target DNA by the DNA guide, can be improved. The amino acid sequence of the mutant BaRecJM of the RecJ nuclease is shown as SEQID NO:3. Current reportsshow that Ago protein sheared by the DNA fragment lead is from thermophilic bacteria, and the effect can be exerted at the temperature of being high 65 DEG C. The BaRecJ and the mutant BaRecJM thereof can be used for shearing DNA dual chains at the mild condition of 37 DEG C, so that genetic engineering can be convenient to operate.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV +3
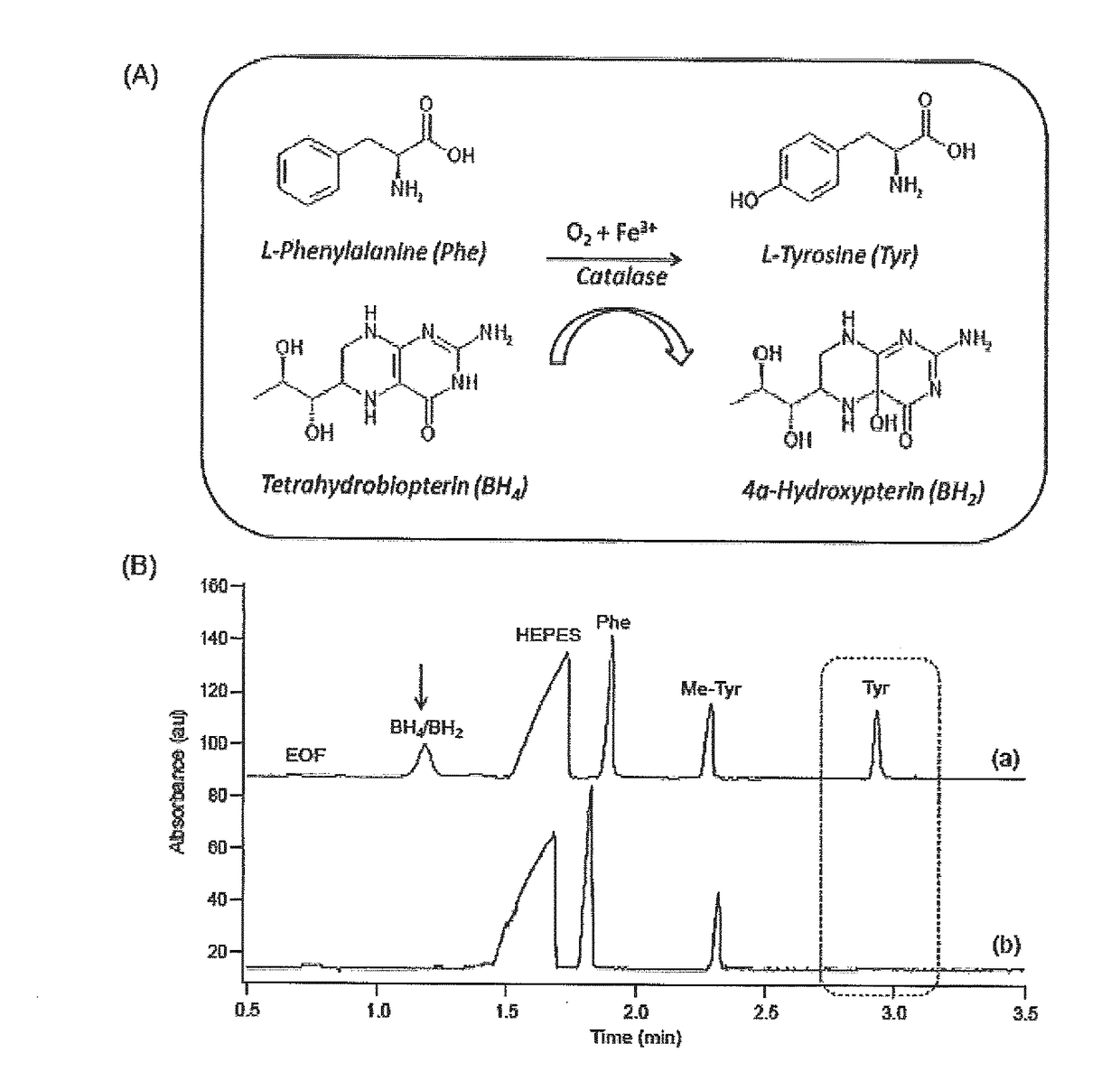
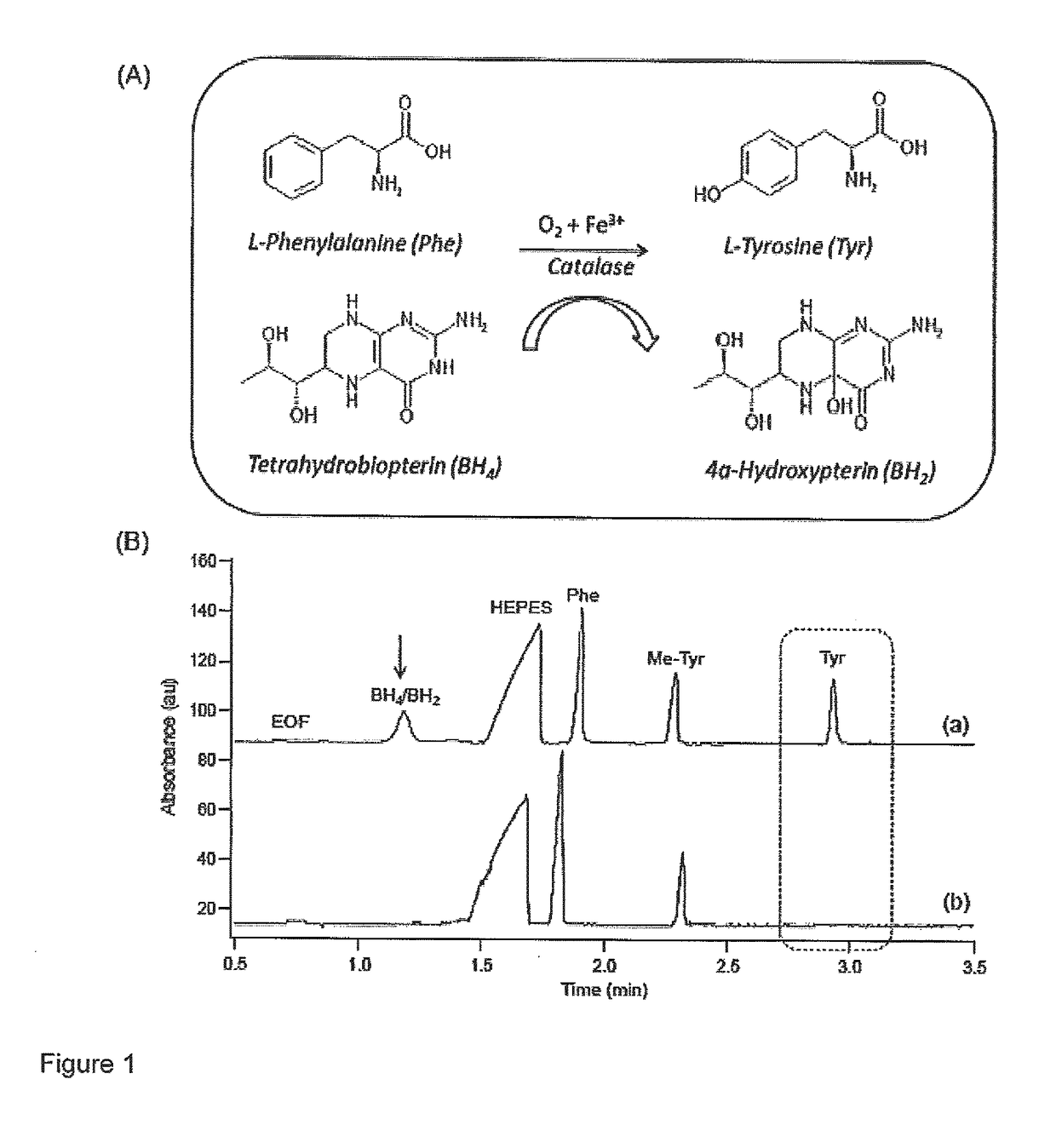
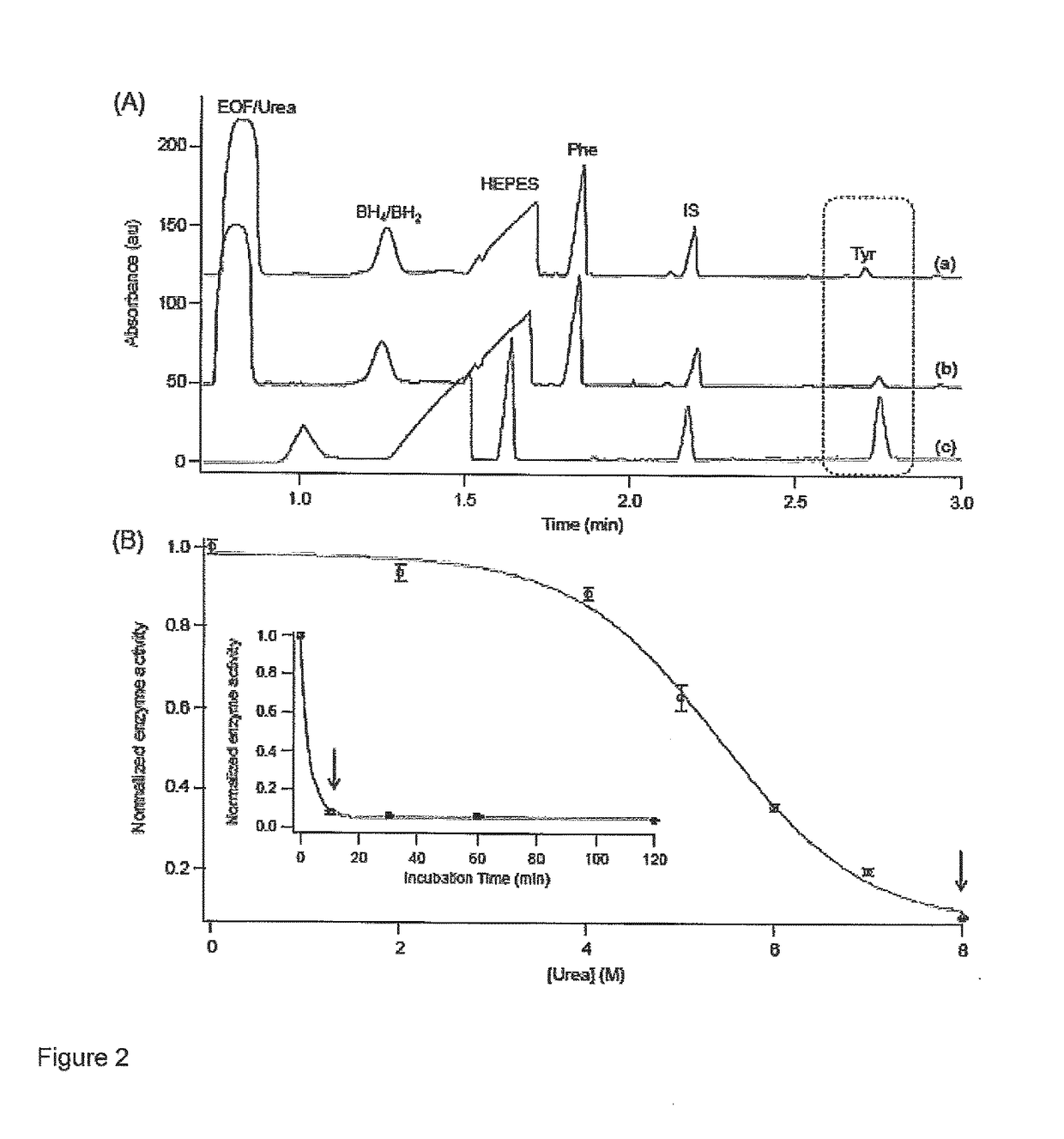
Allosteric activators for treatment of phenylketonuria
A method of restoring activity in phenylalanine hydroxylase is provided. The method comprises exposing the phenylalanine hydroxylase to shikimic acid, a functionally equivalent analogue thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of shikimic acid or analogue thereof, or combinations thereof. A method of screening for allosteric activators for a target enzyme is also provided comprising the steps of: denaturing the target enzyme with a first chaotropic agent to yield denatured enzyme, incubating the denatured enzyme with a candidate compound under denaturing conditions to allow enzyme refolding, and assaying enzyme activity in the presence of enzyme substrate and a candidate compound; and if enzyme activity of the denatured enzyme was restored in step i) by at least about 10% of residual enzyme activity, denaturing the target enzyme with a second chaotropic agent to yield denatured enzyme, incubating the denatured enzyme with the candidate compound under non-denaturing conditions to allow enzyme refolding, and assaying enzyme activity in the presence of enzyme substrate and the candidate compound, wherein an increase in enzyme activity of at least about 10% of residual enzyme activity indicates that the candidate compound is an allosteric activator of the target enzyme.
Owner:MCMASTER UNIV
Recombinant protein structural domain enhanced TET enzyme and whole genome DNA methylation detection method
ActiveCN114195902AImprove oxidation activityHigh sensitivityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationGenetics
The invention provides a recombinant protein structural domain for enhancing TET enzyme activity, the recombinant protein structural domain is a DNA methylation binding structural domain (MBD), and the amino acid sequence of MBD1-4 is as shown in SEQ ID 1-4. The recombinant protein MBD-TET formed by fusing the MBD and the TET enzyme can be used for remarkably enhancing the oxidation activity of the TET enzyme, including NgTET1, mTET1CD, mTET2CDT, hTET1CD and hTET2CDT, on the 5mC. In addition, the invention further provides a simple, convenient and rapid high-throughput DNA methylation detection process, and the sensitivity and accuracy of a TET enzymatic oxidation reaction-based DNA methylation detection technology are improved.
Owner:YEASEN BIOTECHNOLOGY (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Homo-doubly labeled compositions for the detection of enzyme activity in biological samples
InactiveUS20050158766A1Fluorescent signal enhancementFluorescence enhancementBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsEnergy transferResonance
The present invention provides for novel reagents whose fluorescence changes upon cleavage or a change in conformation of a backbone. The reagents comprise a backbone (e.g. nucleic acid, polypeptide, etc.) joining two fluorophores of the same species whereby the fluorophores form an H-dimer resulting in quenching of the fluorescence of the fluorophores. When the backbone is cleaved or changes conformation, the fluorophores are separated, no longer forming an H-type dimer, and are de-quenched thereby providing a detectable signal. The use of a single fluorophore rather than an “acceptor-donor” fluoresecence resonance energy transfer system offers synthesis and performance advantages.
Owner:ONCOIMMUNIN
Furan D-3-phosophoglycerate dehydrogenase allosteric inhibitor and application thereof
The invention discloses a furan D-3-phosophoglycerate dehydrogenase allosteric inhibitor and an application thereof. The structure of the furan D-3-phosophoglycerate dehydrogenase allosteric inhibitor is shown in a formula I defined in the specification, wherein R1, R2 and R3 are same or different, and each of R1, R2 and R3 independently represents hydrogen, halogen, nitryl, hydroxyl, amino, carboxyl, alkyl, alkoxy, halogen substituted alkyl, carboxylic acid ester, sulphonylamino, acylamino or N-alkyl substituted acylamino, or two adjacent substituent groups are cyclized; R4 represents alkyl, halogen substituted alkyl, amino, cycloalkyl, aryl or substituted aryl; and X is O, N or S. Through an in-vitro enzyme activity test, a cell activity test and a mouse xenograft transplantation model experiment, it is proved that a compound can specifically inhibit the activity of a D-3-phosophoglycerate dehydrogenase, and cancer cell growth is delayed by reducing over-expression of the D-3-phosophoglycerate dehydrogenase in cancer cells. The compound is applied separately or is combined with other anti-cancer drugs to be applied, and can treat, prevent or inhibit tumor diseases such as breast cancers, colon cancers, melanin tumors, non-small cell lung cancers and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Non-invasive diagnostic method for the evaluation of intestinal lactase deficiency (hypolactasia)
InactiveUS9128100B2Absence of adverseFunction increaseMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDiagnostic testDirect evaluation
The test of the invention comprises the measuring the total amount of xylose in urine and / or its concentration in blood following oral administration of 4-O-β-D-galactopyranosyl-D-xylose (4-GX) to the patient. It is a non-invasive test that is based on the direct evaluation of the global enzyme activity in the whole individual, not on measuring the metabolic consequences derived from its deficiency. It does not require specialized equipment, does not cause apparent discomfort in patients with lactase deficiency and is very reliable, thus overcoming the drawbacks of the diagnostic tests currently in use and is a statistically significantly better test in terms of its reliability; consequently it should become the reference or gold standard test for the indication of hypolactasia.
Owner:VENTER PHARMA
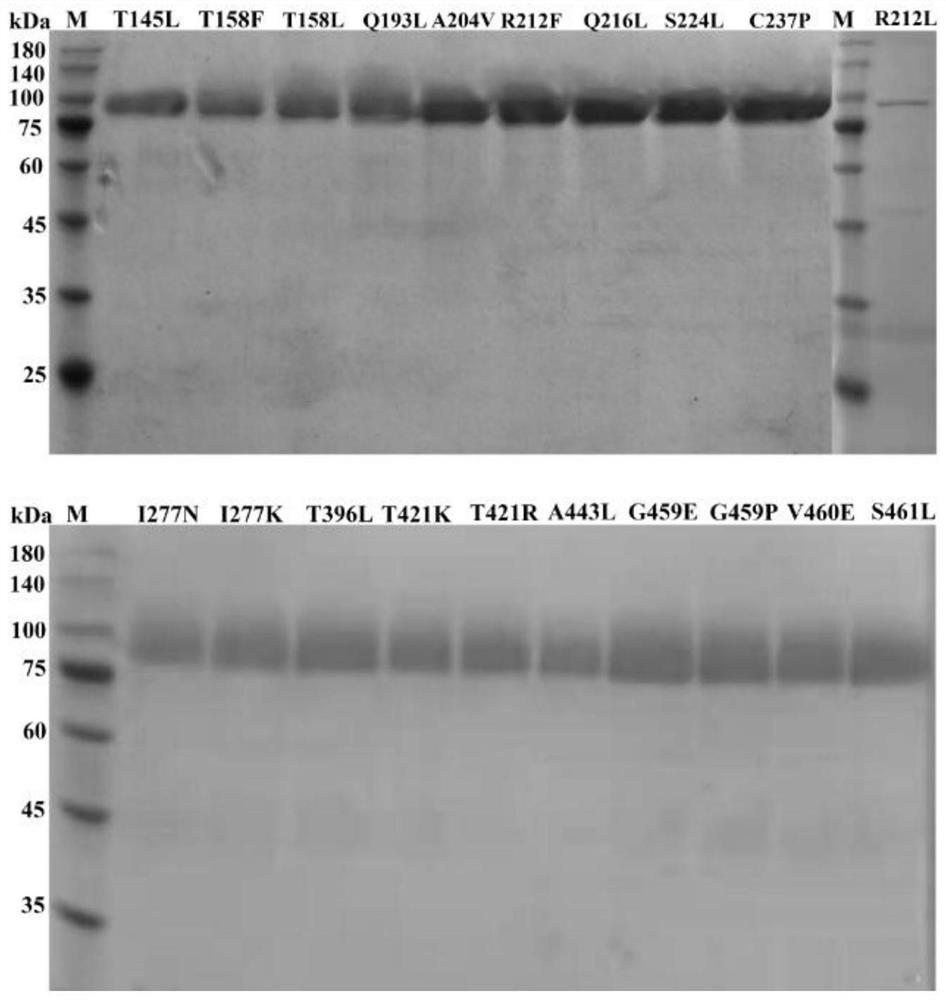
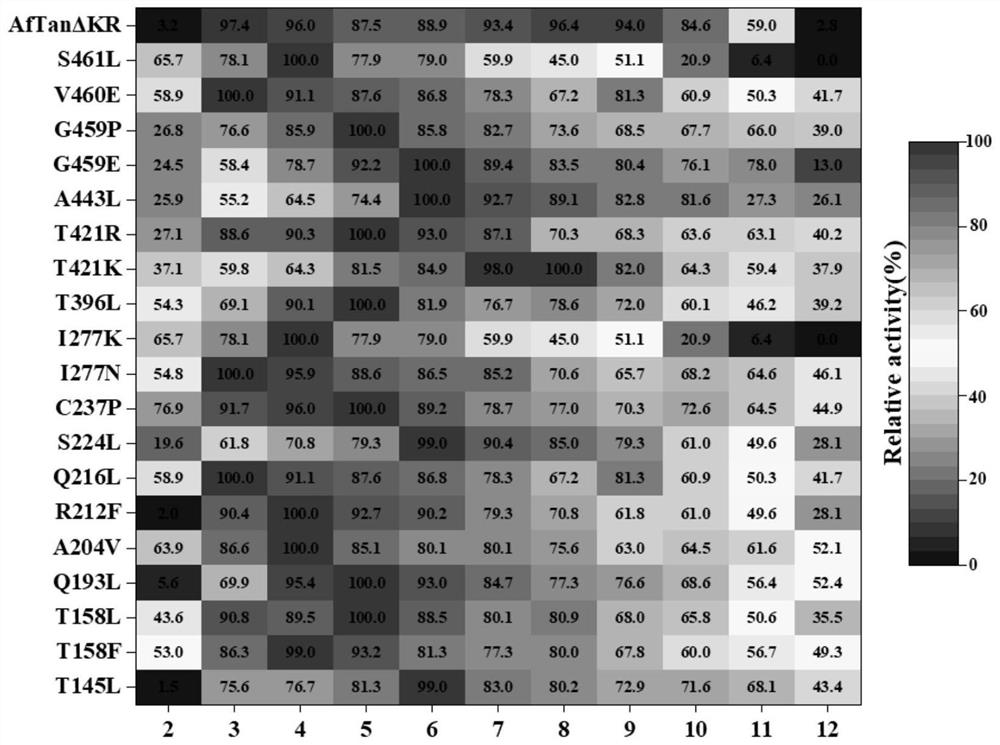
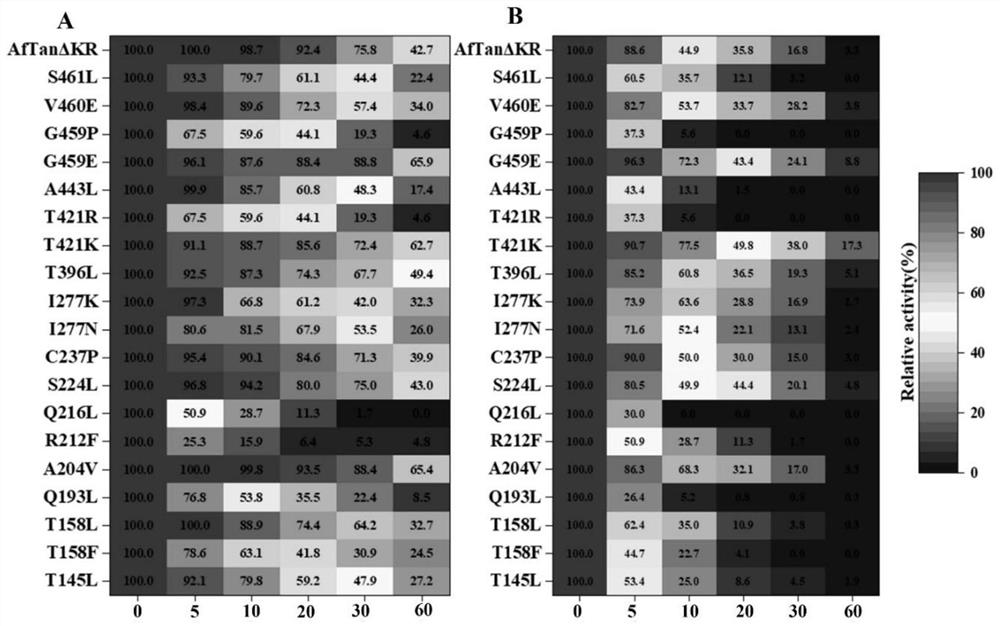
Tannase AfTan2.0 mutant and application thereof
The invention discloses a tannase AfTan2.0 gene mutant and application thereof. The mutants are G475E, T437K and A222V. According to the invention, 20 single-point mutants are designed on the basis of molecular dynamics simulation by applying a calculation program FoldX; activity identification shows that the mutant R212L loses the tannase activity; and the mutants G475E, T437K and A222V which have an obvious improvement effect on the thermal stability of tannase are screened out by measuring the residual enzyme activity of the residual 19 mutants under the treatment conditions of 50 DEG C and 60 DEG C.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
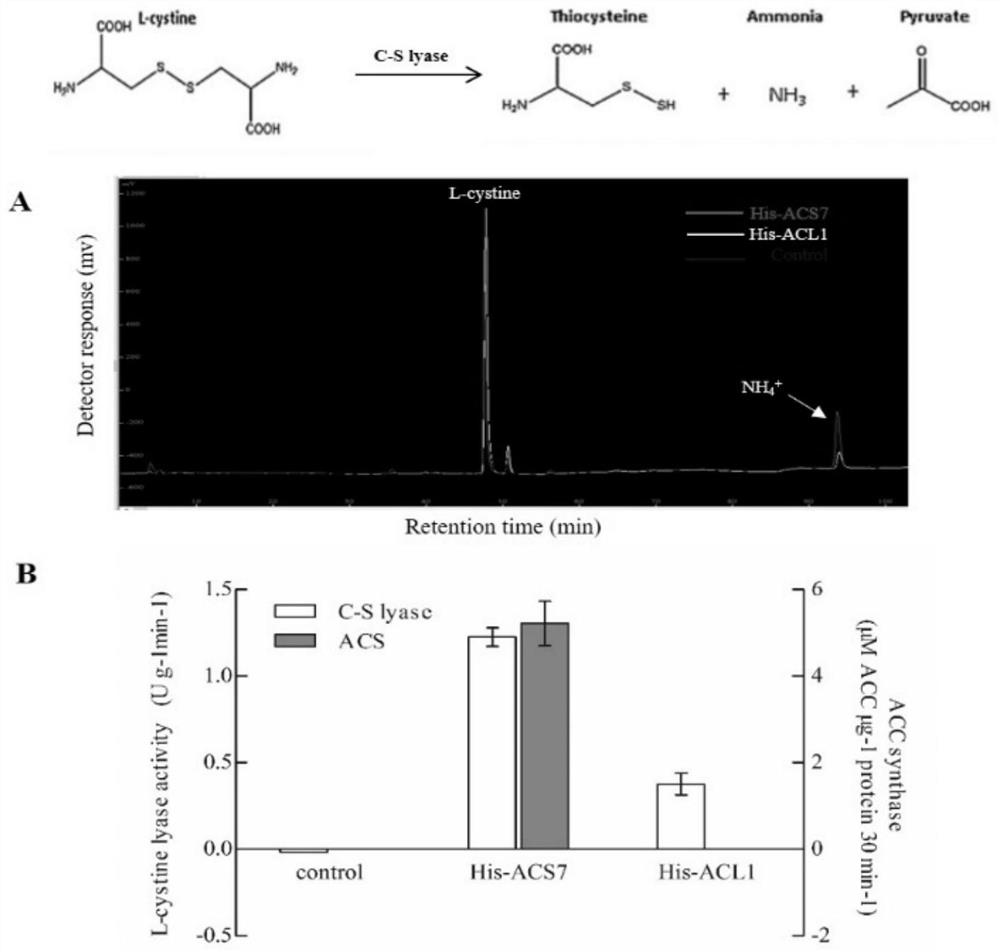
Monoenzyme mutant prepared through replacement of higher plant ACS double-enzyme activity key structural domain and application of monoenzyme mutant
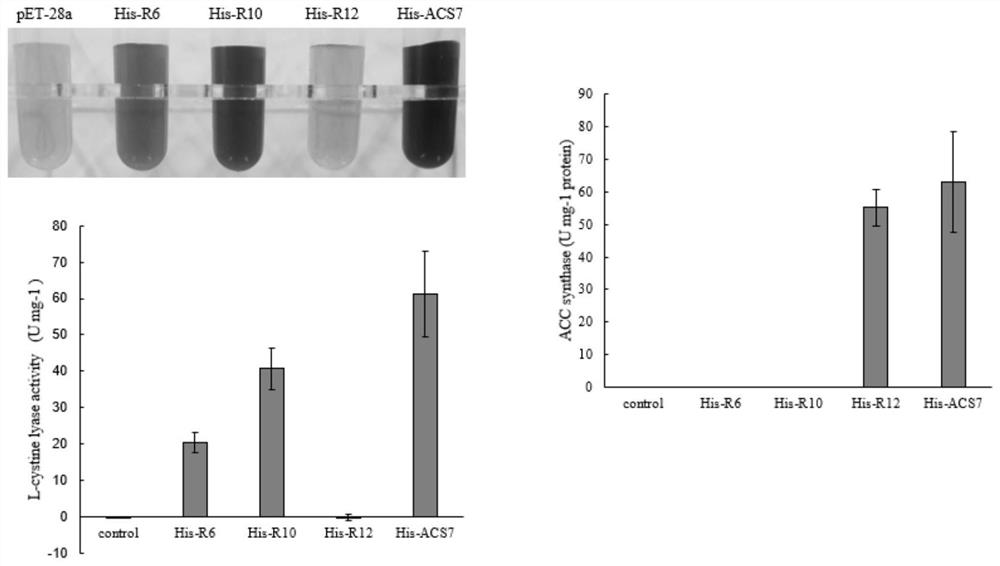
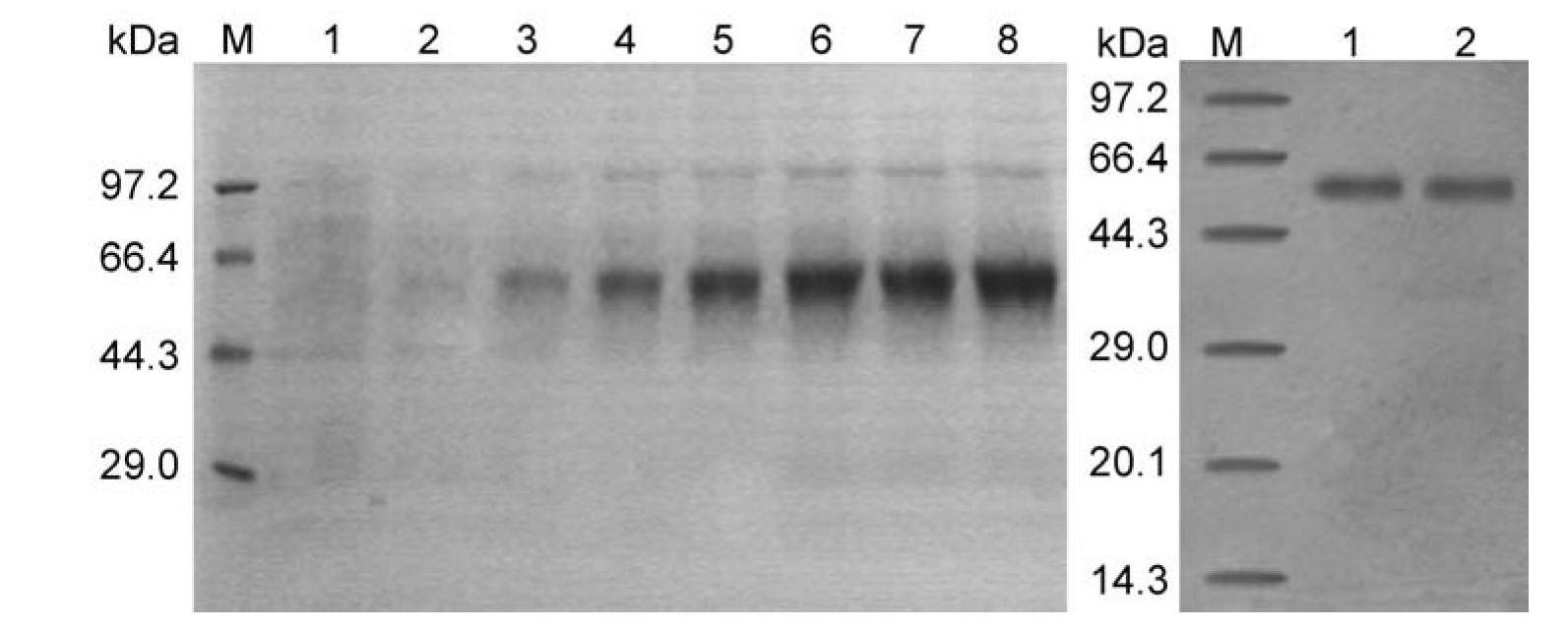
The invention is applicable to the technical field of gene engineering, and provides a single enzyme mutant prepared by replacing a higher plant ACS double enzyme activity key structural domain, which comprises a BOX2 conserved domain with a conserved sequence of F-Q-D-Y-H-G-[LM]-[PSKL], a BOX6 conserved domain with a conserved sequence of M-S-S-F-[GT]-L-[VI]-S-S-Q-T-Q, and a BOX4 conserved domain with a conserved sequence of T-N-P-S-N-P-L-G-[TA]-[TAMVIF]. After the conserved domain sequences are subjected to recombination replacement, the ACS recombinant protein only has ACS or C-S lyase single enzyme activity. The key structural domain influencing the ACS and C-S lyase activity of higher plant ACS protein is identified, a key target spot is provided for controlling multiple life processes in which ethylene participates by utilizing a genetic engineering method, and wide application prospects and important economic values are achieved.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Polygalacturonase PCIPG21 from phytophora capsic, and coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses polygalacturonase PCIPG21 from phytophora capsic, and a coding gene and application thereof. The polygalacturonase PCIPG21 is the following protein shown in a), b) or c): a) the protein comprises the amino acid sequence shown as the 20th to the 390th site of the sequence 2 in the sequence table; b) the protein comprises the amino acid sequence shown as the sequence 2 in the sequence table; and c) the protein is derived from a) and formed by substituting and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amino acid residues in the amino sequence shown as the sequence 2 in the sequence table or the 20th to the 390th site of the sequence 2 in the sequence table, and has the polygalacturonase activity. The polygalacturonase PCIPG21 has high enzyme activity, wherein the specificactivity of the polygalacturonase is 63 + / - 0.2 U / mg protein; and the specific activity of pectinase is 43 + / - 0.2 U / mg.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
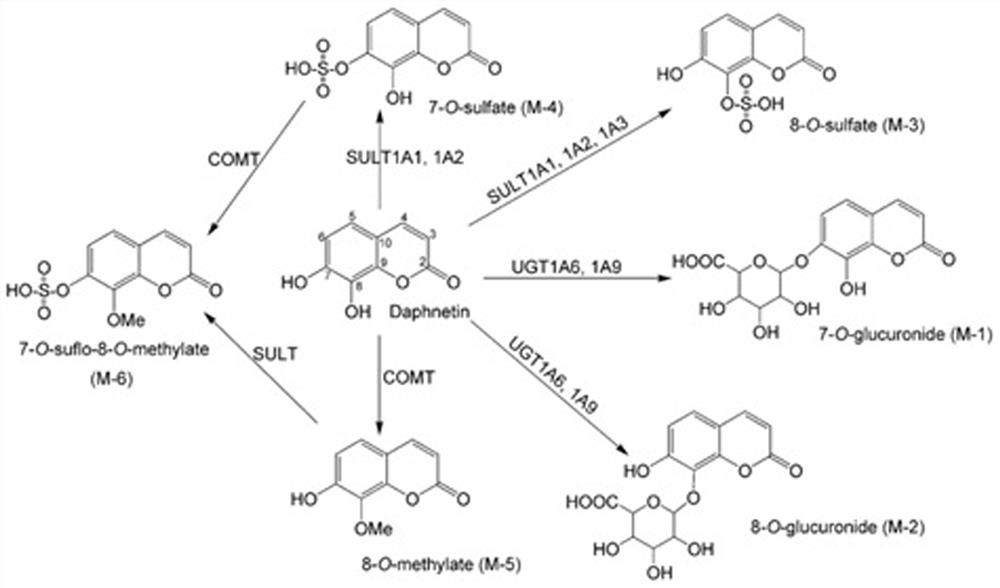
Overall level characterization method of COMT enzyme activity and application thereof
ActiveCN113801913AStrong specificityImprove detection accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMetaboliteMethyl palmoxirate
The invention discloses an overall level characterization method of COMT enzyme activity. The overall level characterization method is characterized in that daphnetin or a derivative thereof is used as a substrate, the substrate is subjected to a C-8-site methyl substitution reaction under the action of COMT enzyme and is treated by sulfotransferase and glucuronic acid hydrolase to generate an 8-O-methylated product, and the activity of the COMT enzyme in each biological sample is determined by quantitatively detecting the contents of the substrate and 8-O-methyl metabolite thereof in unit time. According to the method provided by the invention, the activity level of COMT enzyme in a living body can be represented from the overall level, daphnetin or the derivative thereof can only be converted into 8-methyl metabolite thereof, the specificity is good, and the detection accuracy is high; the detection sensitivity is good, and the safety is relatively high; and when the method is applied to a kit, the activity of the COMT enzyme can be accurately detected, the activity of the COMT enzyme in a biological sample is determined according to the ratio of the content of the substrate to the content of the 8-O-methylated product, and a definite evaluation standard for the activity of the COMT enzyme is given.
Owner:THE AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SOUTHWEST MEDICAL UNIV
A method for enzymatically synthesizing kaempferol
ActiveCN107880134BHas flavanone 3-hydroxylase activitySimple methodOxidoreductasesFusions for enhanced expression stability/foldingGlycerolFerrous sulphate
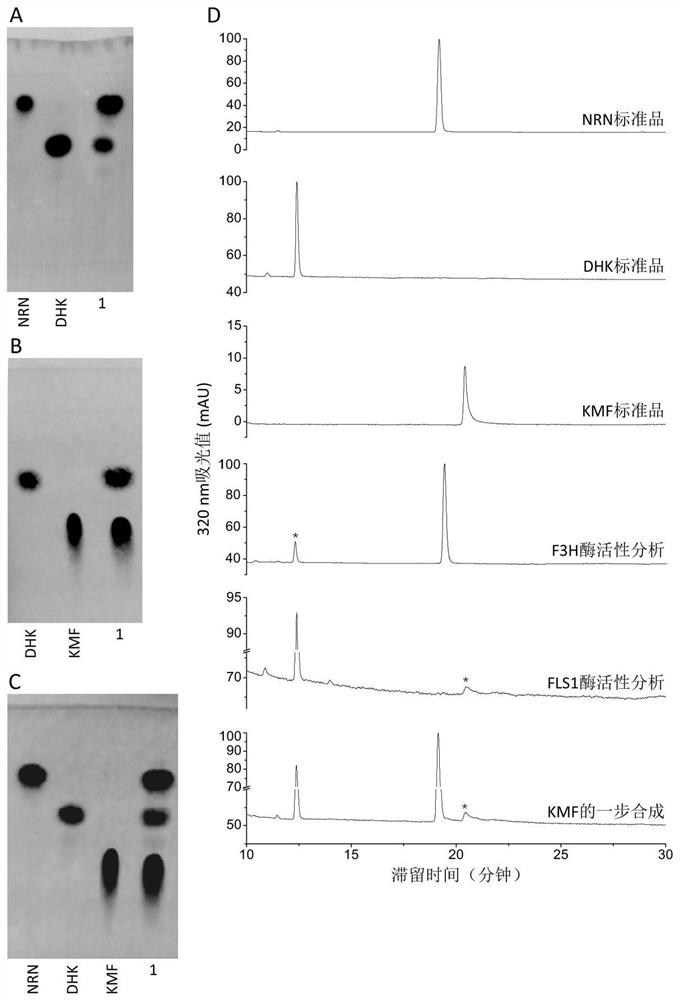
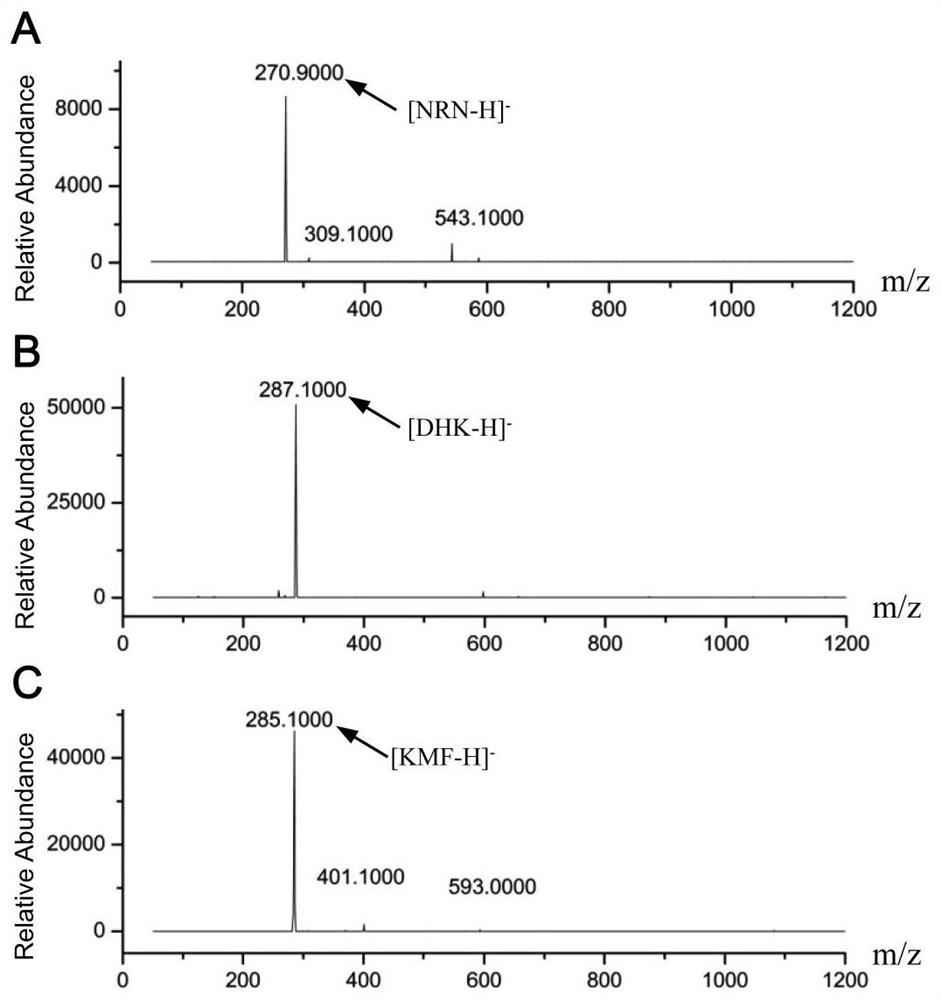
The invention discloses a method for enzymic synthesis of kaempferol. Preparation and detection of enzyme activity of two kinds of fusion protein, TrxA-His-F3H and TrxA-His-FLS1 are involved, and a buffer solution system is designed, wherein the reaction buffer solution is 0.1 M of Tris-HCl with a pH value of 7.2, and every 100 muL of a reaction system contains 0.4% of ascorbic acid, 10% of glycerol, 8.2 mM of alpha-ketoglutaric acid, 0.01 mM of ferrous sulfate, 0.5 mM of naringenin, 3.3 umg of TrxA-His-F3H and 1.8 umg of TrxA-His-FLS1. The method for efficient one-step synthesis of kaempferolis established in vitro by optimizing the pH value, reaction time and temperature of the reaction system, and a CCK-8 method is applied to the detection of the inhibiting effect of the synthesized kaempferol on the growth of tumor cells.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Method for detecting OGT enzyme activity in vitro
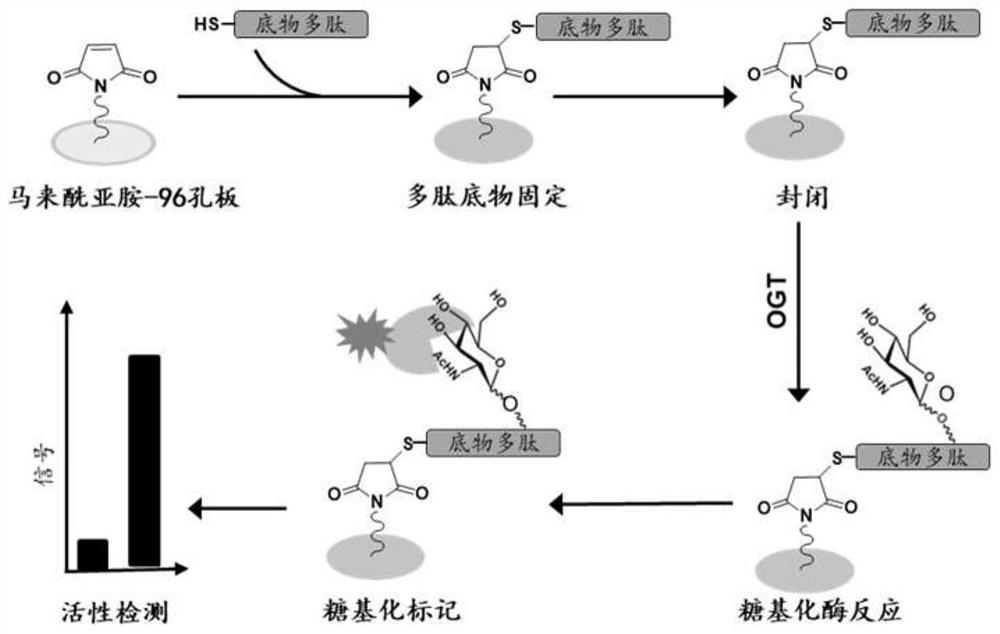
PendingCN114137213ANo emissionsIncrease detection signal strengthCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsBiological material analysisPharmaceutical drugAcetylglucosamine
The invention discloses a method for detecting the enzyme activity of O-linked-N-acetylglucosamine transferase OGT in vitro, namely a method for detecting the enzyme activity of O-linked-N-acetylglucosamine transferase OGT in vitro, and the method is low in construction cost, simple to operate and high in detection sensitivity. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: (1) synthesizing and purifying an OGT high-activity substrate polypeptide ZO3-S371A; (2) carrying out coupling immobilization on the OGT substrate polypeptide ZO3-S371A, and closing a non-specific site of the OGT substrate polypeptide ZO3-S371A; (3) carrying out glycosylation modification on the substrate polypeptide by using the OGT; and (4) detecting the substrate polypeptide subjected to OGT glycosylation through WGA-FITC or WGA-HRP. According to the method, the activity of the substrate polypeptide is high, the preparation cost is low, the detection operation is simple, the sensitivity is high, and the method can be used for measuring the enzyme activity of OGT expressed and purified and OGT in pathological tissue source samples in vitro and can also be used for evaluating the activity of OGT inhibitor drugs.
Owner:无锡麦迪科思生物科技有限公司
Monascus B with glycosidase inhibition activity and immunomodulatory activity and preparation method of monascus B
PendingCN114292280AInhibit inflammationGreat application potentialOrganic chemistryAntipyreticBiotechnologyMonascus anka
The invention relates to monascus B with glycosidase inhibition activity and immunomodulatory activity and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of extraction and preparation of biological products. The monascus B is red powder, and the molecular formula of the monascus B is C23H30O6; the compound has the advantages that the compound has the activity of inhibiting glycosidase, the median inhibitory concentration (IC50) on alpha-glycosidase is 174 mu g / mL, and the transcriptional level of IL-1beta, TNF-alpha and TGF-beta of in-vitro cultured mouse macrophages RAW264.7 is obviously reduced: the change of the IL-1beta (0.01 + / -0.01), the change of the TNF-alpha (0.02 + / -0.01) and the change of the TGF-beta (0.03 + / -0.01) relative to a DMSO (dimethylsulfoxide) control group are obvious (P is less than 0.05). The monascus purpureus B is obtained by culturing monascus purpureus and then extracting and separating the monascus purpureus. The monascus used in the invention is an edible fungus and is safe and reliable, and the preparation method adopts microbial fermentation production, is environment-friendly, is not influenced by natural environment and resources, and is easy to realize industrial, automatic and continuous production.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
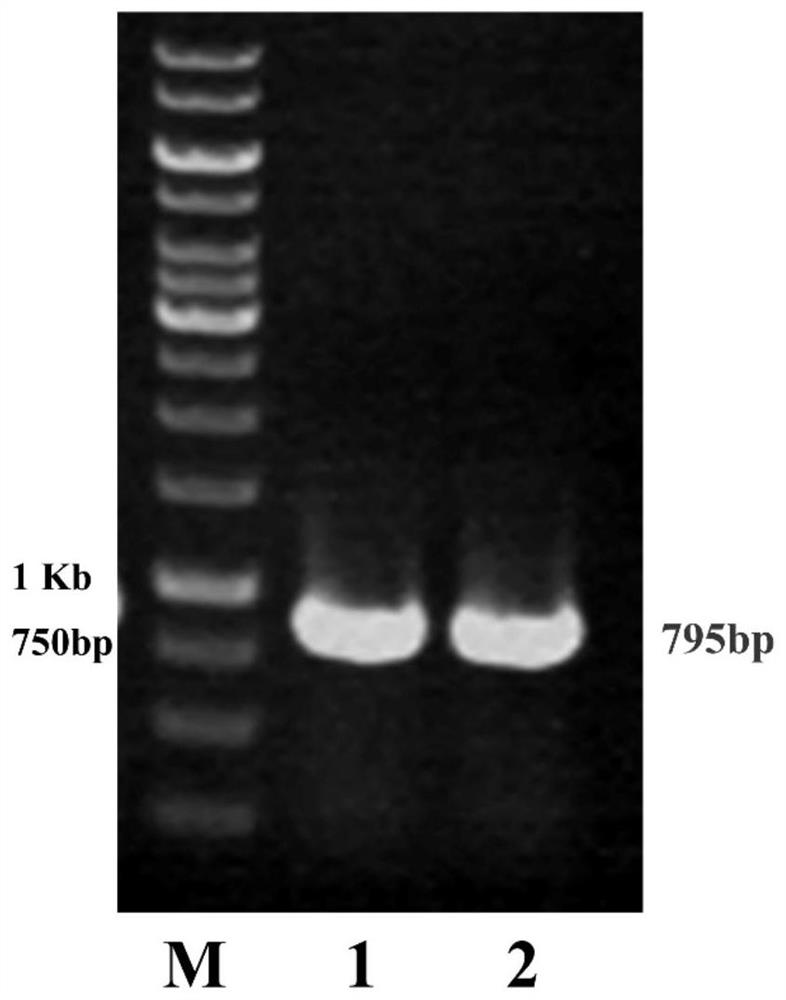
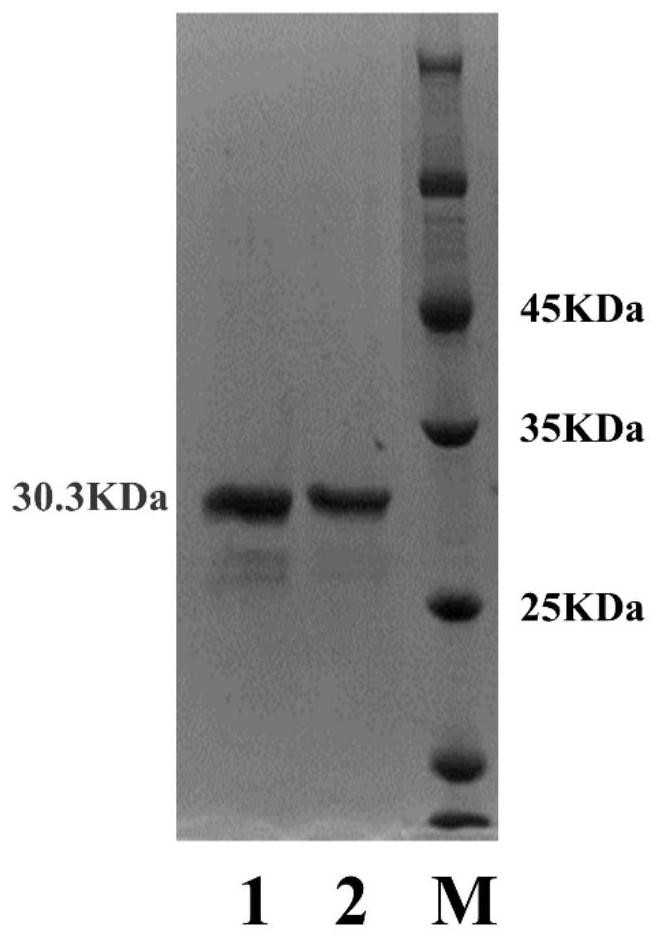
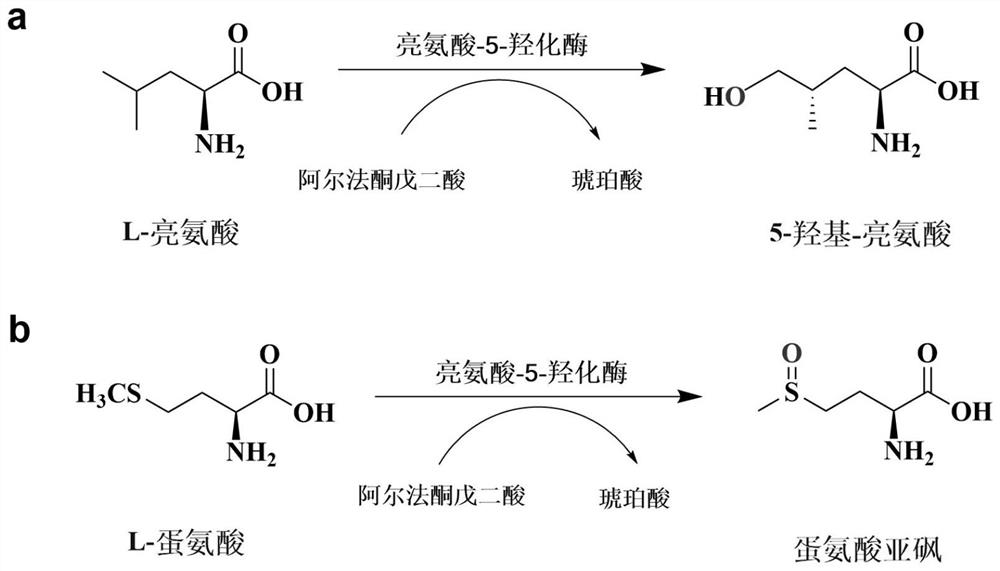
A kind of leucine-5-hydroxylase mutant and its application
ActiveCN109576234BHigh activityIncreased specific enzyme activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHeterologousMutant
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering, and in particular relates to a leucine-5-hydroxylase mutant with improved activity and an application thereof. The present invention obtains the leucine-5-hydroxylase encoding gene derived from Nostoc punctiforme NIES-2108 by means of molecular biology, adopts inverse PCR to carry out site-directed mutation to obtain the gene encoding the mutant, and then uses the encoding mutant The leucine-5-hydroxylase mutant V77A was obtained by heterologous expression of the gene. When the mutant used leucine and methionine as substrates, its relative enzyme activity was increased by 69.53% and 23.26%, respectively, compared with the wild type. The variant with improved activity screened out by the present invention can more efficiently realize the hydroxylation of the 5th carbon position at the far end of leucine, and can catalyze the generation of methionine sulfoxide from methionine, which is the enzymatic catalytic production of industrial pharmaceutical intermediates Provide broad prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com