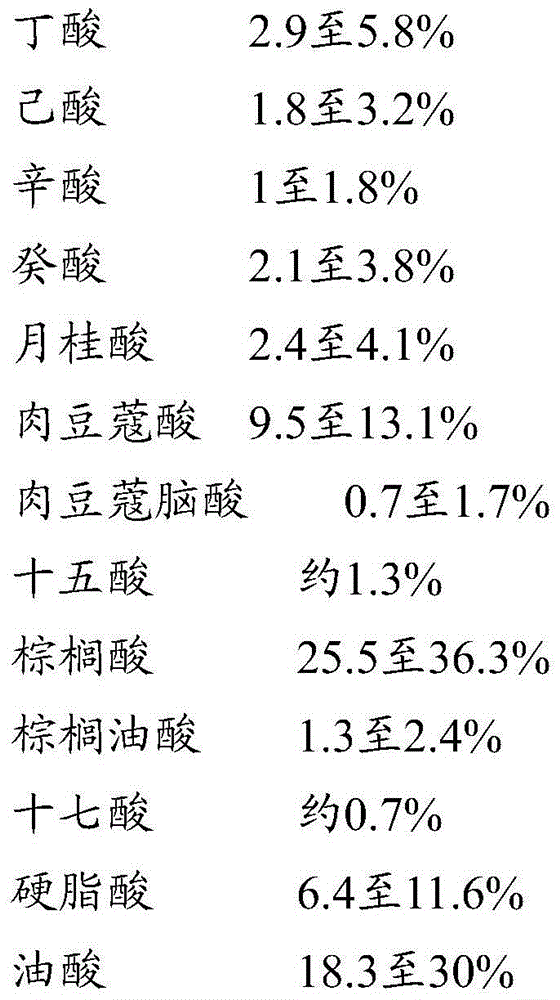
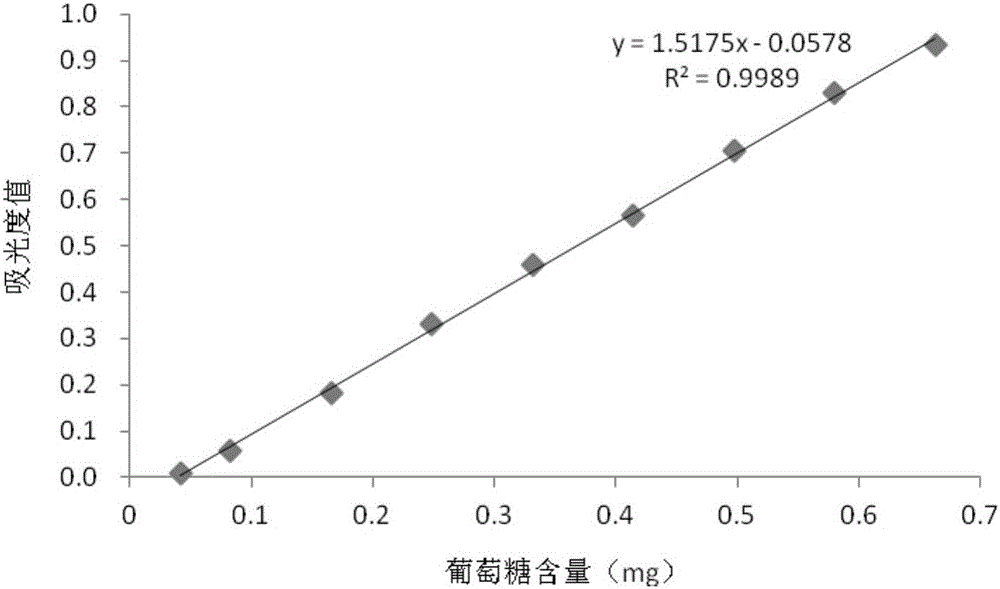
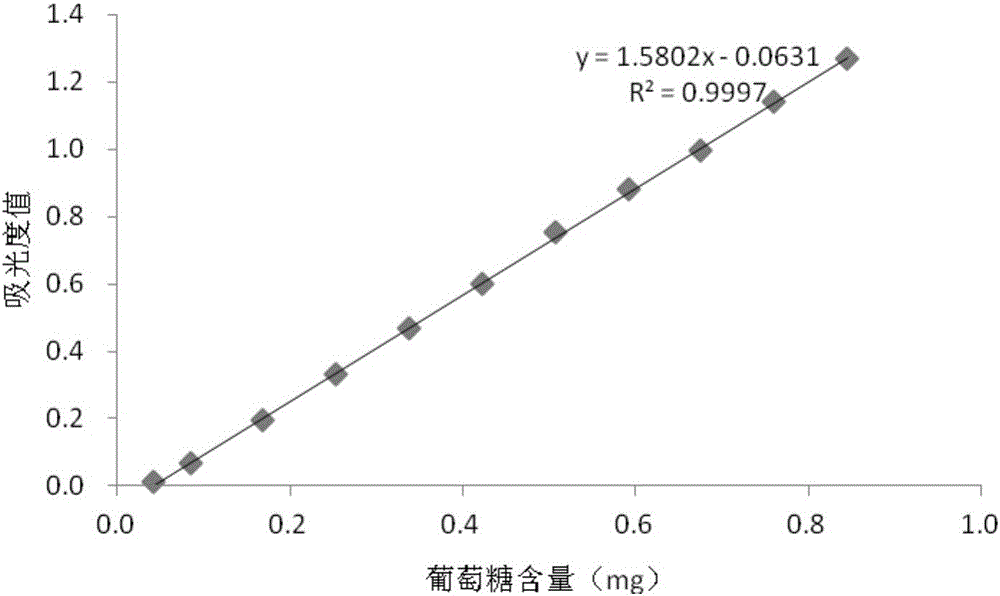
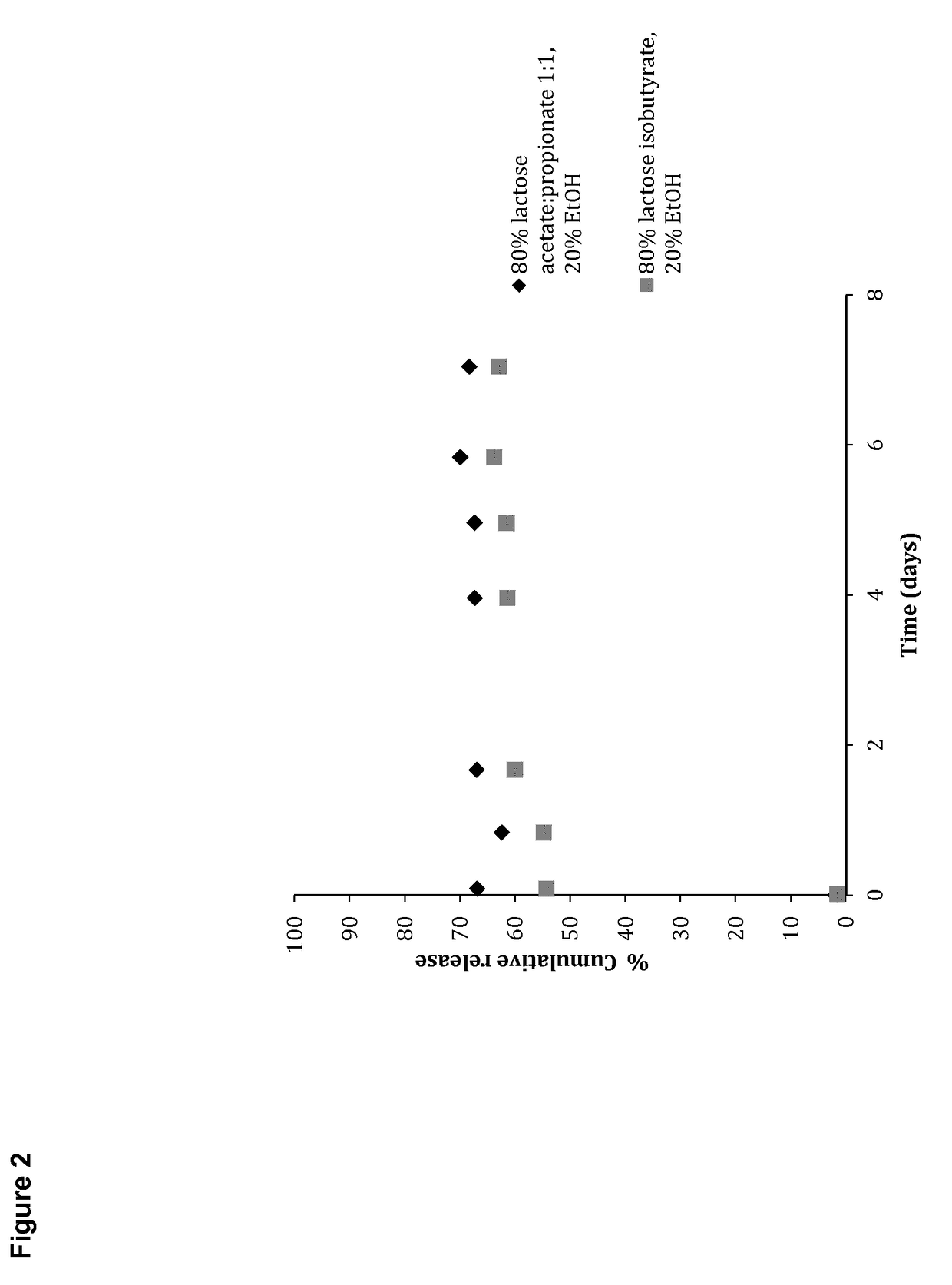
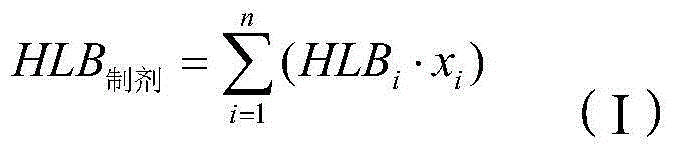Patents
Literature
68 results about "Water soluble carbohydrate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
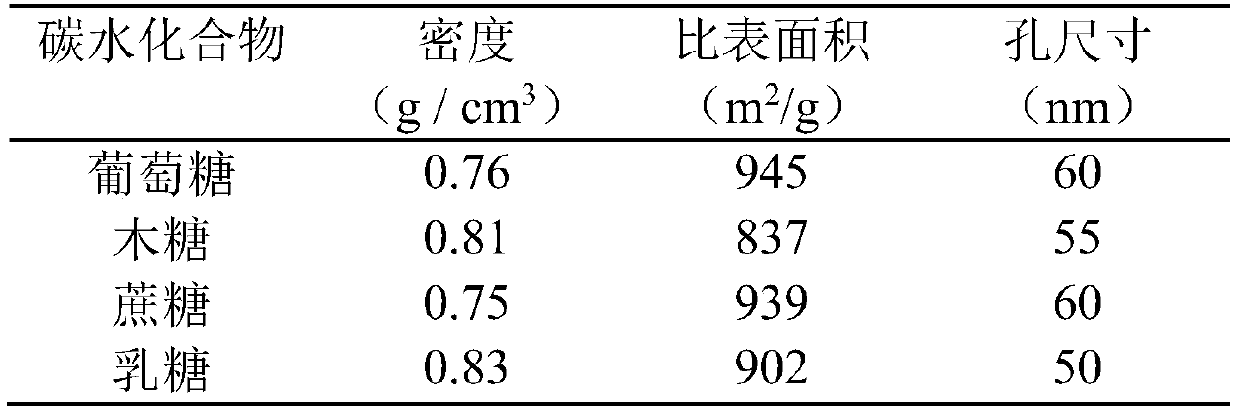
Water soluble carbohydrates (WSC) are sugars such. as fructans, sucrose, glucose and fructose which are. accumulated in the stem as reserves.
Rapidly disintegrable tablets
InactiveUS7282217B1Reduce brittlenessHigh porosityDispersion deliveryPill deliveryAdditive ingredientWater insoluble
The invention provides a rapidly disintegrating tablet comprising an active ingredient, a water soluble, directly compressible carbohydrate, and a water soluble, directly compressible filler. Also provided is a method of producing a rapidly disintegrating tablet, which method comprises wet granulating a mixture comprising a directly compressible, water soluble carbohydrate, a directly compressible, water insoluble filler, a beneficial ingredient, and a solvent, and compressing the granulate to produce the tablet.
Owner:AMAG PHARMA USA INC
Method for preparing aluminum oxide/carbon aerogel composite material
The invention discloses a method for preparing an aluminum oxide / carbon aerogel composite material. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving a water-soluble carbohydrate and a water-soluble high polymer in water in a closed container; adding an aluminum salt or aluminum hydroxide reacting at the temperature of 140-300 DEG C, drying, and calcining in an inert atmosphere of 300-1500 DEG C, thereby obtaining the aluminum oxide / carbon aerogel composite material. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the aluminum oxide / carbon aerogel composite material with low density and high porosity is prepared by adopting a one-pot process, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the raw materials are readily available, the preparation process is simple, the cost is low and the like, and the prepared aluminum oxide / carbon aerogel composite material is light in weight and high in porosity and can be used for catalyst carriers, gas sensitive elements, solid electrolytic films and molten steel oxygen-measuring probe materials.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
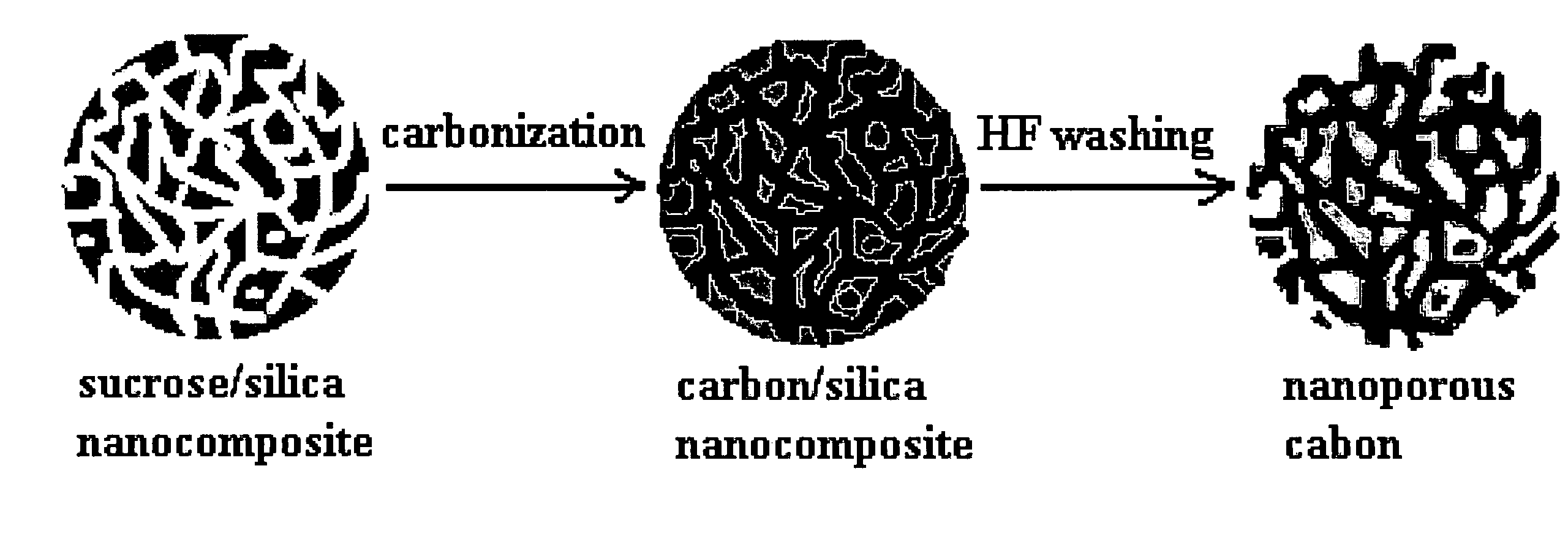
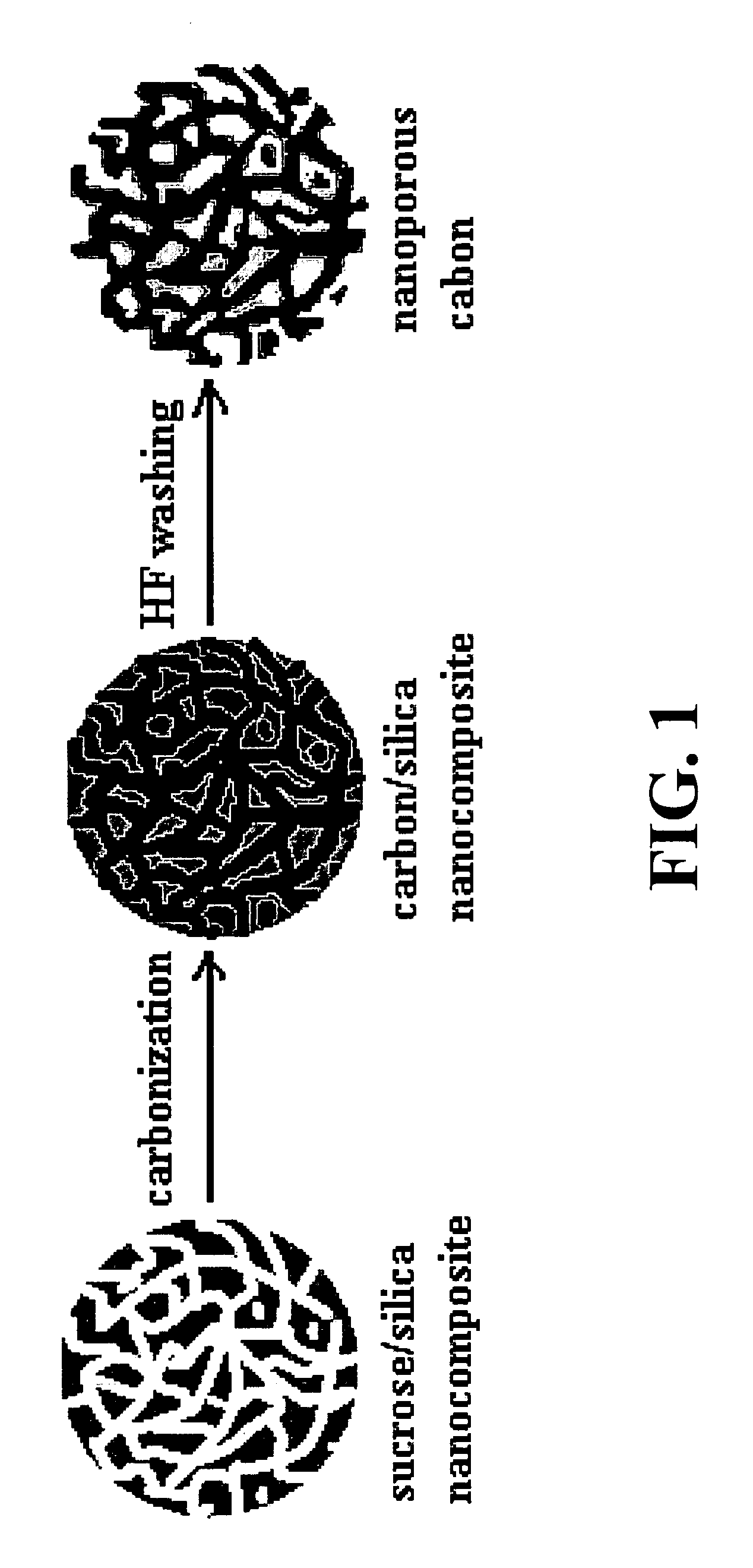
Mesoporous carbon films and methods of preparation thereof
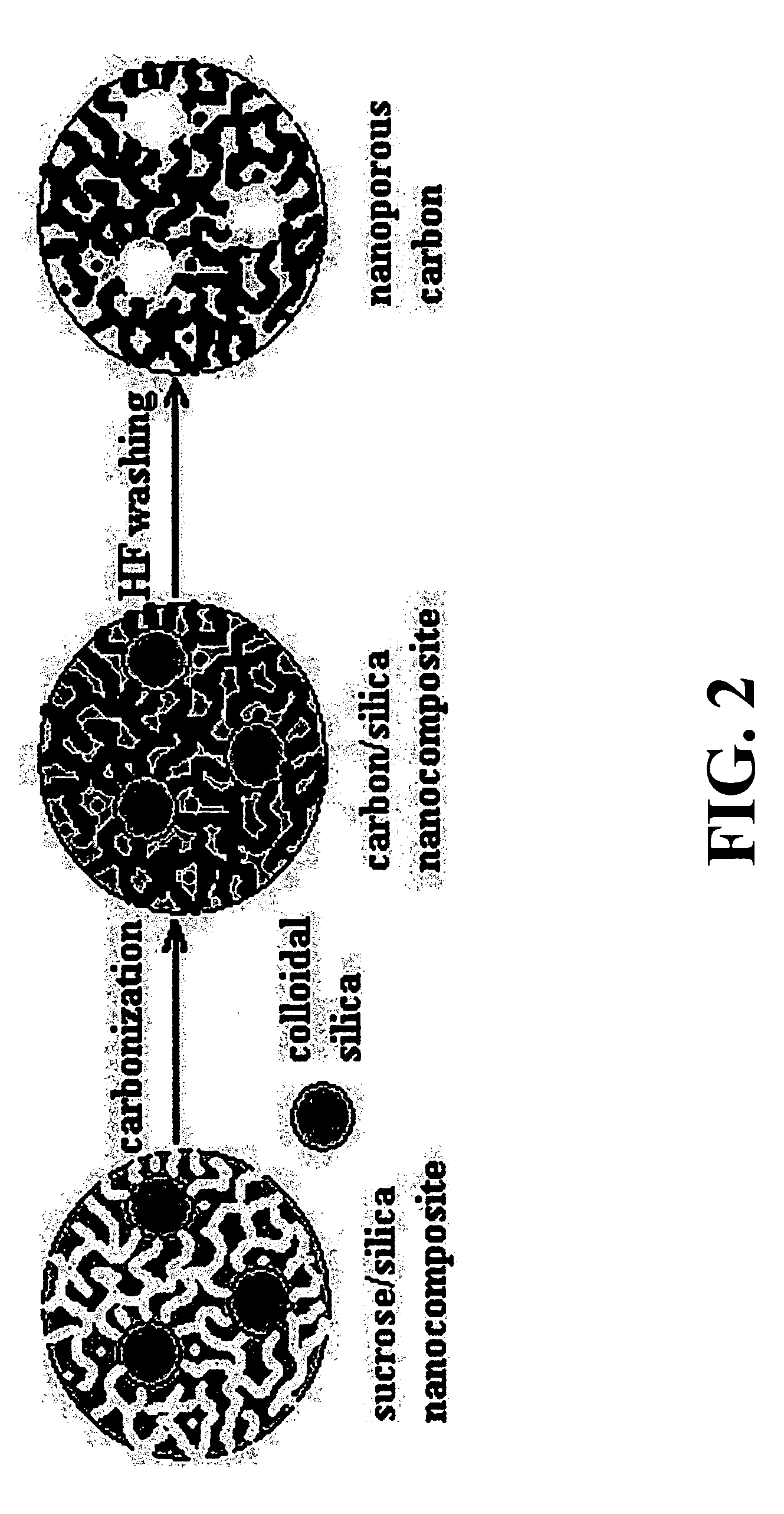
A mesoporous carbon film having a unimodal pore structure comprises a film of carbon defining an open network of interconnected primary pores arrayed in a uniform, random manner throughout the film. The pores in the film have an average pore diameter in the range of about 2 to about 3 nm, and the diameters of the pores have a substantially unimodal pore diameter distribution. Not more than about 20% of the pores in the film have a diameter of less than about 1 nm. The mesoporous carbon films can be prepared by depositing a thin film of an aqueous sol-gel composition comprising a polysiloxane gel precursor, and a water soluble carbohydrate onto a substrate, heating the thin film to carbonize the carbohydrate and form a carbon / silica nanocomposite film, and removing the silica from the carbon / silica nanocomposite film to provide a continuous mesoporous carbon film. Suspending colloidal silica in the aqueous sol-gel composition prior to depositing the thin film on the substrate affords a mesoporous carbon film having a hierarchical, bimodal pore structure, which includes spherical secondary pores randomly distributed throughout the film and interconnecting with the network of primary pores.
Owner:TULANE EDUCATIONAL FUND
Preparation method of titanium dioxide and doped body of titanium dioxide
InactiveCN104741137AHigh crystallinityUniform sizePhysical/chemical process catalystsCrystallinityRaw material
The invention discloses a preparation method of a titanium dioxide photocatalyst. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving water-soluble carbohydrate and water-soluble macromolecules into water in a closed container, adding with organic acid or alkali, and then adding with a soluble titanium salt, and reacting at 140-300 DEG C, dewatering and calcining, so as to obtain the titanium dioxide photocatalyst. The titanium dioxide photocatalyst is cheap and easily available in raw material, and simple in preparation method; with three-dimensional net carbon aerogel as a template, a silver halide-doped titanium dioxide photocatalyst is hotly synthesized by a one-pot method; and the obtained titanium dioxide photocatalyst is good in crystallization degree, uniform in size and high in catalytic efficiency in a visible light region, and can be applied to degradation of organic pollutants.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Rapidly disintegrable tablets
InactiveUS7425341B1Reduce brittlenessHigh porosityDispersion deliveryPill deliveryAdditive ingredientWater insoluble
The invention provides a rapidly disintegrating tablet comprising an active ingredient, a water soluble, directly compressible carbohydrate, and a water soluble, directly compressible filler. Also provided is a method of producing a rapidly disintegrating tablet, which method comprises wet granulating a mixture comprising a directly compressible, water soluble carbohydrate, a directly compressible, water insoluble filler, a beneficial ingredient, and a solvent, and compressing the granulate to produce the tablet.
Owner:LUMARA HEALTH IP
Creamy, milk-free o/w emulsion, process for its preparation and its use
InactiveUS20050031764A1Improved microbiologicalGood freezing resistanceFood shapingCream substitutesColloidWater soluble
A creamy, milk-free oil-in-water emulsion (o / w emulsion) having an aqueous phase (a) which contains water, water-soluble carbohydrate, hydrocolloid and optionally further hydrophilic constituents, and an oil phase (b), which contains edible oil and / or edible fat, emulsifier and optionally further lipophilic constituents. The weight ratio of the aqueous phase to the oil phase (a:b) is in the range of 9:1 to 6:4. The creamy, milk-free o / w emulsion is used as a cream substitute in cake and pastry and dessert products.
Owner:HAHNTECH INT
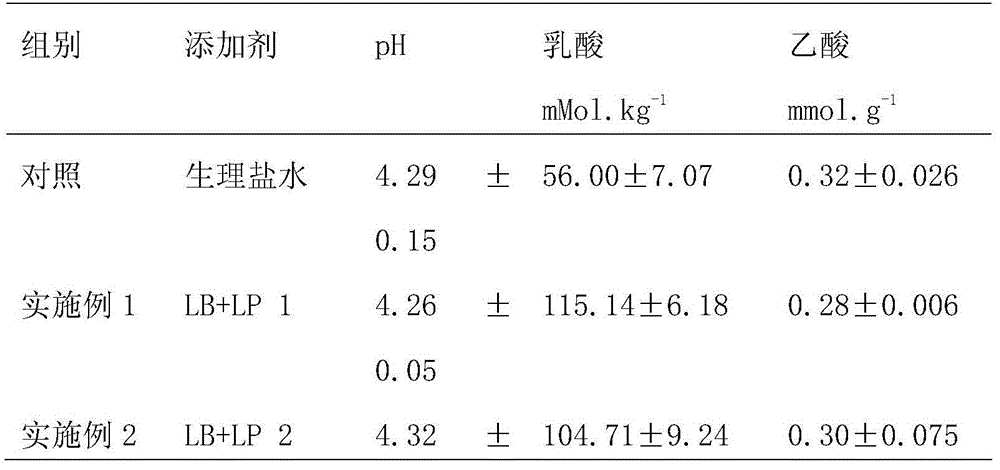
Method for preparing sugarcane tail silage by lactobacillus buchneri and lactobacillus plantarum
InactiveCN104351588AEasy to prepareSimple operating conditionsAnimal fodder preservationAcetic acidGenetics
The invention discloses a method for preparing sugarcane tail silage by lactobacillus buchneri and lactobacillus plantarum. The method comprises the steps of cutting mowed sugarcane tails into short pieces with the lengths of 1-4cm; evenly spraying the mixed preparation of the lactobacillus plantarum and the lactobacillus buchneri onto the fresh sugarcane tail raw material to enable the viable count of the lactobacillus plantarum and the lactobacillus buchneri in the fresh sugarcane tails to reach 1*106cfu / g-2*106cfu / g, evenly mixing, filling, compacting and sealing, wherein the density of the mixture is 0.4kg / L; storing the product for 40 days at the normal temperature to obtain the sugarcane tail silage. After the method is adopted, the problem of poor palatability caused when a ruminant is directly fed with the sugarcane tails can be solved; the lactobacillus buchneri is combined with the lactobacillus plantarum for application, so that the content of lactic acid is improved, the content of acetic acid is reduced, and the utilization efficiency of water soluble carbohydrate (WSC) of the silage is improved.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION BUFFALO INST
Carbohydrate-enriched plant pulp composition
InactiveUS20120183646A1Attractive propertyGrowth inhibitionDough treatmentTea extractionBiotechnologyPolydextrose
The invention pertains to a plant or vegetable pulp composition comprising: a) plant or vegetable pulp comprising 5-30 wt % cell wall materials comprising or consisting of cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin and / or pectin, and / or fragments and / or hydrolysates thereof, wherein said pulp is obtained by disrupting plant or vegetable cell membranes and removing at least part of the intracellular content; b) 45-85 wt % of one or more water-soluble carbohydrate(s) selected from the group consisting of inulin, oligofructose, fructo-oligosaccharide, galacto-oligosaccharide, glucose, maltose, maltodextrins, polydextrose, sucrose, fructose, lactose, isomaltulose and polyols, and / or combinations thereof; and c) 5-25 wt % water, all numbers based on total weight of said composition. The invention also pertains to the method of preparing such a composition, and the use in (human) food applications.
Owner:KONINK COOPERATIE COSUN U A
Aqueous curable binder composition
InactiveUS20130005870A1Binder viscosityGreat flexingOrganic detergent compounding agentsDextran coatingsEmulsionWater soluble carbohydrate
This invention is an aqueous curable binder composition useful as a thermosetting binder for a variety of applications, particularly for substrates that need to retain at least some flexibility. More particularly, the present invention relates to curable aqueous binder compositions comprising at least one water-soluble carbohydrate binder; at least one polyacid crosslinking agent; and one or more high acid polycarboxy emulsion copolymers, as latex modifiers.
Owner:KELLY MICHAEL D +1
Preparation method of mesoporous carbon-based solid acid and mesoporous carbon-based solid acid prepared through method and application
InactiveCN105597789ALow costEasy to operatePhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic chemistrySolid acidCarbonization
A preparation method of mesoporous carbon-based solid acid includes the steps of dissolving water-soluble carbohydrate in water to obtain a precursor solution, dissolving nonionic surface active agent in the solution to obtain a mixed solution of a precursor and a template, adding inorganic acid to transfer the solution into a culture dish, evaporating the culture dish at a temperature of 40-60 DEG C for 6 hours, conducting thermal setting at a temperature of 100-150 DEG C for 6-24 hours to obtain a mixture of the precursor and the template, and directly calcinating the obtained mixture under the inert atmosphere to remove the template to obtain the mesoporous carbon-based solid acid. Carbohydrate low in price is adopted as the precursor, inorganic acid serves as carburizer, the acid is prepared through an evaporation, induction, self-assembly and carbonization method, the method is easy to operate and beneficial to large-scale production, and the mesoporous carbon-based solid acid synthesized through the method has a large specific surface and abundant surface acid groups and can be widely applied to heterogeneous acid catalysis and biomass conversion.
Owner:HUANGGANG NORMAL UNIV +1
Detection method of Cd2+
ActiveCN102944551AQuick checkRapid Colorimetric DetectionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationPolymer modifiedWater quality
The invention provides a detection method of Cd2+. The method comprises: reacting a water-soluble carbohydrate polymer aqueous solution having reducibility with a gold or silver salt solution to get an aqueous solution containing carbohydrate polymer-modified gold or silver nanoparticles, adsorbing Cd2+ on surfaces of the gold or silver nanoparticles through electrostatic adsorption, then adding a sulfhydryl compound to interact with Cd2+, and forming a layer of cadmium complexes on the surface of gold or silver nanoparticles to result in that the surface plasmon resonance absorption intensity and peak position of the gold or silver nanoparticles change, and the color and UV-visible absorption intensity of the gold or silver nanoparticle solution change. Therefore, naked eyes or a UV-visible spectrophotometer can be directly used for quick detection whether a solution contains Cd2+, fast and simple colorimetric detection for Cd2+ in a solution is realized, and the method is applicable to water quality survey of lakes and rivers, sewage testing, and detection of Cd2+ in food, blood and urine.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Application of carbon aerogel in regulating plant growth as nano-carbon fertilizer synergist
InactiveCN105000952AImprove the situationImprove adsorption capacityFertilizer mixturesGrowth plantWater soluble carbohydrate
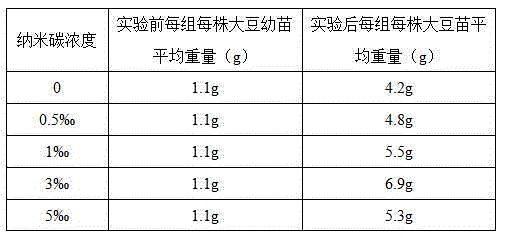
The invention discloses application of carbon aerogel in promoting plant growth, and particularly relates to application of carbon aerogel in regulating plant growth as a nano-carbon fertilizer synergist. In a closed container, a water-soluble carbohydrate and a water-soluble polymer are dissolved in water, react at the temperature of 140 DEG C-300 DEG C and then are dried to obtain the carbon aerogel. Serving as the nano-carbon fertilizer synergist, the carbon aerogel can prompt plant growth and absorb heavy metal and organic pollutants in soil, so that the purposes of improving soil quality and purifying the soil are achieved.
Owner:XIAN BONA MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Preparation method of anticlotting materials
InactiveCN102698323AReduce incidenceConducive to adhesion and proliferationPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingMorpholineDevice material
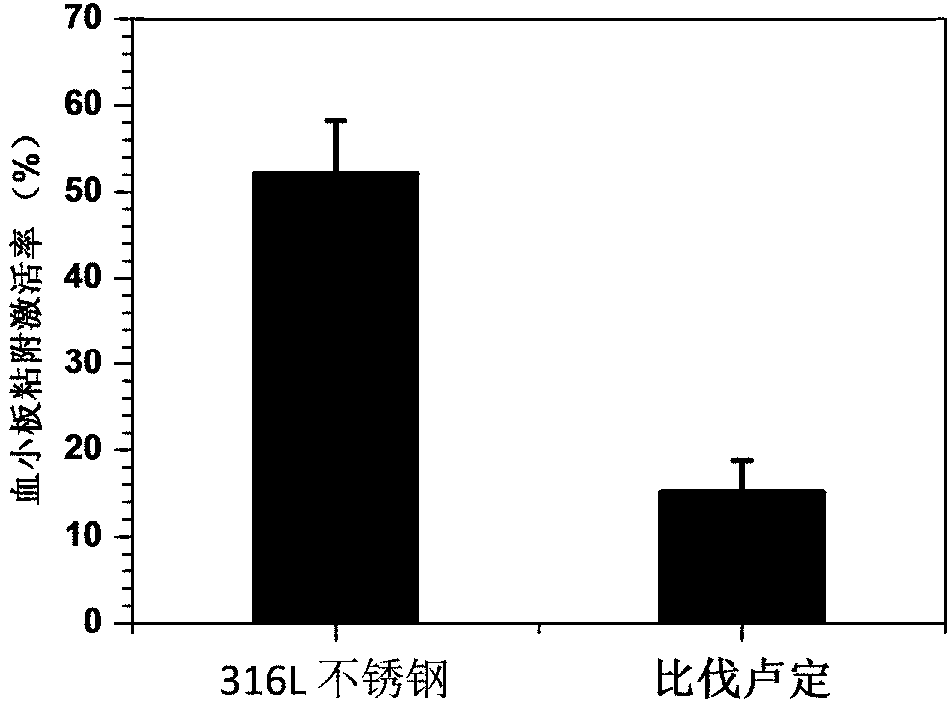
The invention discloses a preparation method of anticlotting materials, which is used for performing the anticlotting modification on the surface of an implanting device material so as to improve the anticoagulant activity of an intravascular stent. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving 0.1mug / ml-10mg / ml of bivalirudin in a water soluble carbohydrate (WSC) solution, wherein the WSC solution is composed of 9.76mg / ml of 2-(N-morpholine) ethanesulfonic acid buffer solution, 1mg / ml of 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylamino propyl) carbodiimide and 0.24mg / ml of N-hydroxy-succinamide; obtaining bivalirudin-WSC solution; immersing the biomedical materials containing amido on surface in the bivalirudin-WSC solution to react for 1-48 hours, and then fully rinsing the biomedical materials by phosphate buffer solution (PBS) with pH value of 7.4 and distilled water respectively, and drying to obtain the objective matter. The anticlotting materials or an apparatus obtained by the invention can play the role of anticlotting by directly or specially imhibiting the activity of thrombin. The preparation method of the anticlotting materials is definite in the anticlotting effect, safe in use and simple in operation of the method, and free from the limit of the physical structure of materials or apparatus.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Alfalfa silage for dairy cows and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107912605AImprove silage qualityHigh protein contentFood processingClimate change adaptationRumenSweet sorghum
The invention relates to the technical field of dairy cow feed processing, in particular to alfalfa silage for dairy cows and a preparation method thereof. The alfalfa silage comprises, by weight, 20-40 parts of alfalfa, 60-200 parts of lolium perenne, 5-10 parts of sweet sorghum straw, 5-20 parts of fructus crataegi, 2-4 parts of astragalus polysaccharide and 4.0-7.0mg / kg of lactobacillus preparation. Rumen swelling of dairy cows caused by frequent eating of the alfalfa silage is prevented by adding hawthorn powder, and palatability of the alfalfa silage is improved by adding the sweet sorghum straw and astragalus polysaccharide. The preparation method is simple in preparation process, pH value of the silage is lowered, content of lactic acid and water-soluble carbohydrate is increased, ensiling quality of alfalfa is improved obviously, and the preparation method is an effective way to solve the problem that fresh forage grass lacks in winter during livestock production and is of important significance in reasonably utilizing alfalfa.
Owner:湖南德人牧业科技有限公司
Application of carbon aerogel to heavy metal contaminated soil restoration
InactiveCN105013809ASimple processLow costContaminated soil reclamationWater solubleWater soluble carbohydrate
The invention discloses application of carbon aerogel to heavy metal contaminated soil restoration. According to the application of the carbon aerogel to the heavy metal contaminated soil restoration, in a sealed container, water-soluble carbohydrates and water-soluble polymers are dissolved in water, and after the reaction at 140-300 DEG C, the carbon aerogel is obtained through drying. According to theapplication of the carbon aerogel to the heavy metal contaminated soil restoration, the prepared carbon aerogel has a prominent adsorbing effect on heavy metal cadmium and chromium in soil, and therefore the purpose of restoring the soil is achieved. The application of the carbon aerogel to the heavy metal contaminated soil restoration has the technical effects of being simple in technology, low in cost and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:XIAN BONA MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Preparation method of barium sulfate-carbon aerogel composite support supported palladium catalyst
ActiveCN104741135AHigh strengthGood dispersionHydrocarbonsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsBarium saltPalladium catalyst
The invention discloses a preparation method of a barium sulfate-carbon aerogel composite support supported palladium catalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: in a closed container, dissolving water-soluble carbohydrate compounds and water-soluble polymers as well as barium hydroxide or soluble barium salt in water; adding sulfuric acid or soluble sulfate to react at 140-300 DEG C; washing and drying to obtain a barium sulfate-carbon aerogel support; and supporting palladium on the barium sulfate-carbon aerogel support to obtain the barium sulfate-carbon aerogel composite support supported palladium catalyst. The barium sulfate-carbon aerogel composite support supported palladium catalyst prepared by the preparation method is good in dispersibility, difficult to condensate, high in stability, strong in catalytic performance and long in service life.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Aqueous curable binder composition
This invention is an aqueous curable binder composition useful as a thermosetting binder for a variety of applications, particularly for substrates that need to retain at least some flexibility. More particularly, the present invention relates to curable aqueous binder compositions comprising at least one water-soluble carbohydrates binder; at least one polyacid crosslinking agent; and one or more high acid polycarboxy emulsion copolymers, as a latex modifier.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
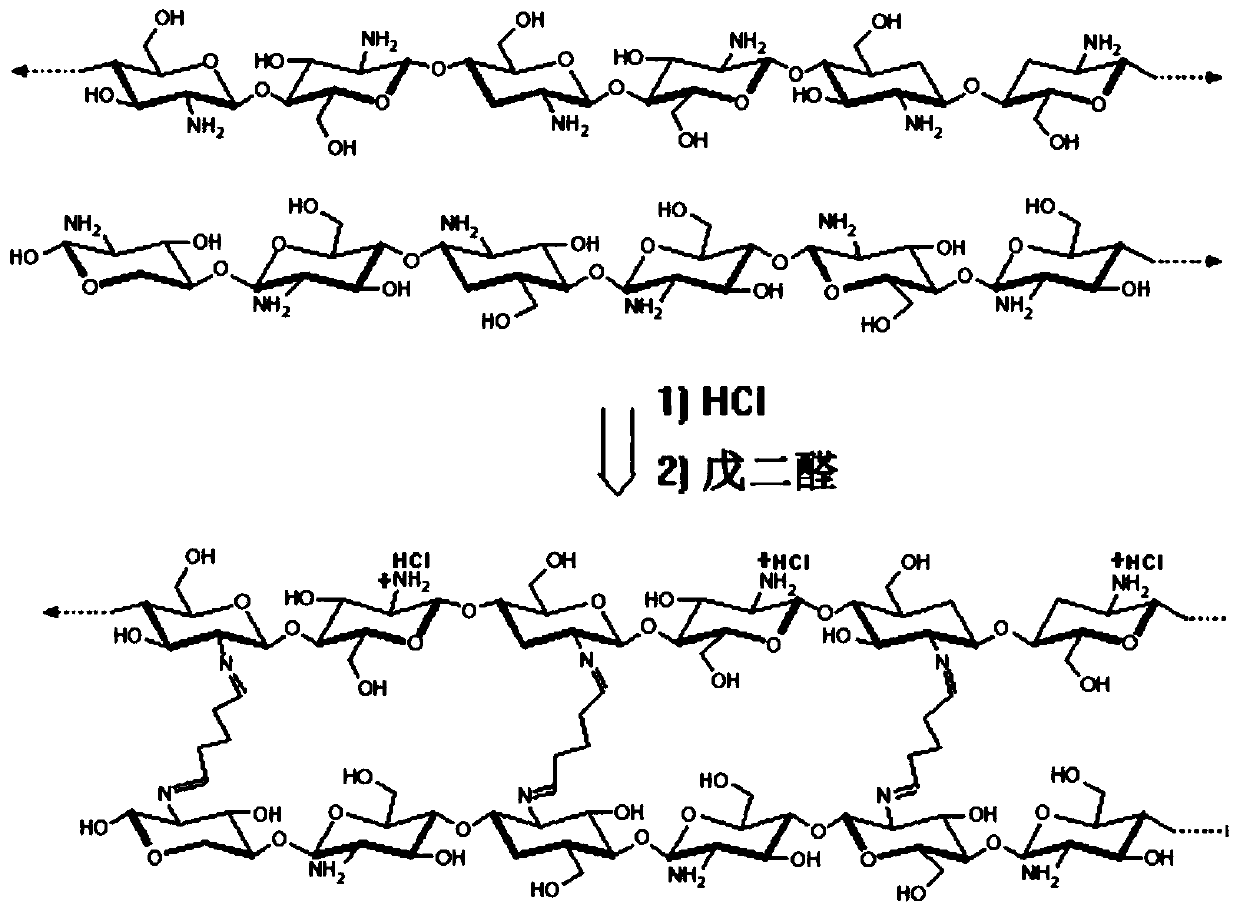
Aminated hemicellulose molecule and method for production thereof
Owner:SWETREE TECHOLOGIES AB
Green feed storing method
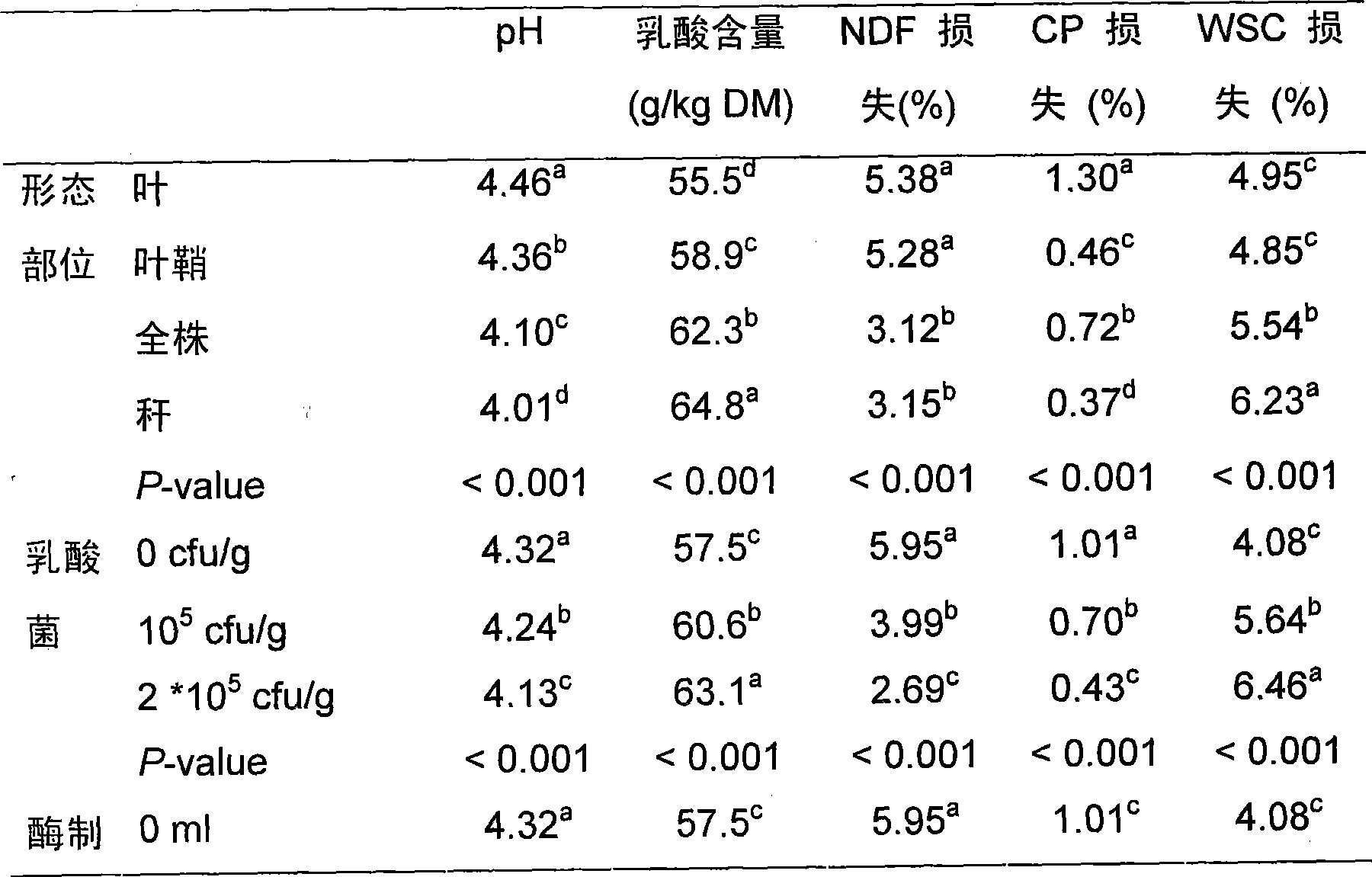
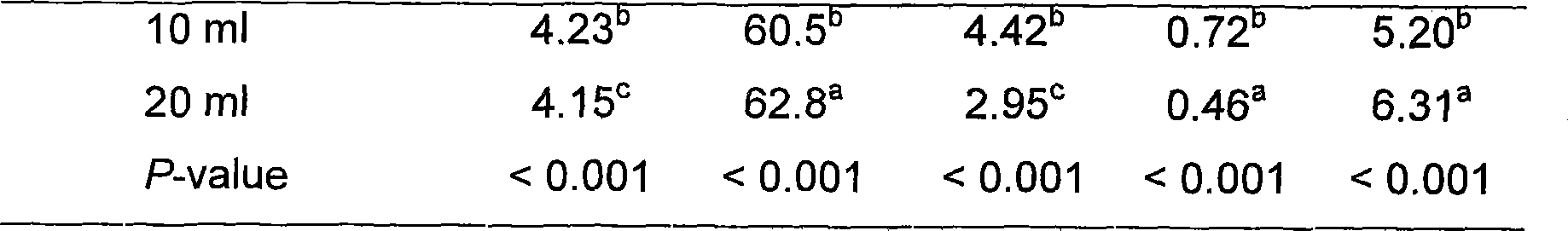
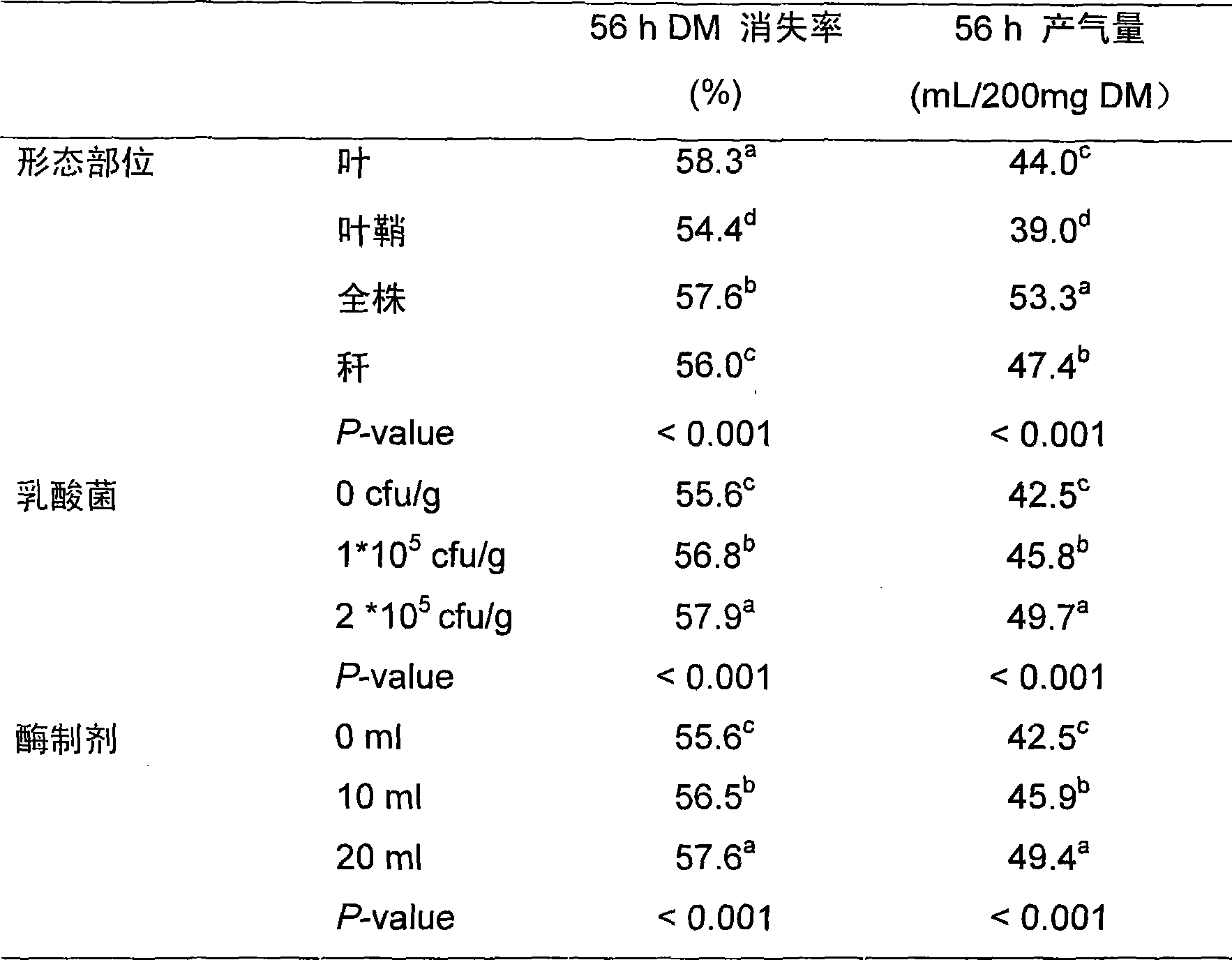
The invention discloses a method for storing green feed, which comprises (1) classifying corns in the wax ripeness stage into leaves, leaf sheaths, stems and corns, and measuring chemical compositions of various parts, with measurement indices of crude protein (CP), neutral detergent fiber (NDF) and water soluble carbohydrate (WSC); (2) preparing enzyme preparation solutions with four concentration gradients and lactobacillus solutions with four concentration gradients, adding enzyme preparation solutions and lactobacillus solutions with different concentration gradients into leaves, leaf sheaths, stems and corns, respectively, and ensiling; (3) analyzing the chemical composition of silage, including pH value, lactic acid, NDF, CP and WSC; (4) mixing silages subjected to the same treatment, and drying at 60-70 DEG C; and (5) determining the type and amount of additives with different chemical composition characteristics, which are added into the green feed in accordance with silage fermentation characteristics and in vitro fermentation characteristics. The inventive method has simple process and easy operation, and can effectively reduce loss of nutrients such as proteins in the green feed and improve the utilization ratio of nutritional ingredients in the green feed.
Owner:INST OF SUBTROPICAL AGRI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Whippable topping with high freeze-thaw stability
A whippable topping composition comprising: (a) water-soluble carbohydrates, (b1) hydrogenated vegetable fat, (b2) optionally milk fat, (c) an emulsifier formulation having an HLBFormulation value of less than 9, (d1) a first hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, (d2) a second hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, (e) protein, (f) optionally a non-protein hydrocolloid stabilizer, and (g) water, wherein the weight ratio of first hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (d1) to second hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (d2) is within the range of from 3:1 to 13:1.
Owner:NUTRITION & BIOSCIENCES USA 1 LLC
Simple and effective mulberry leaf polysaccharide detection method
InactiveCN105806793AEasy extractionUndisturbedColor/spectral properties measurementsWater solubleGlucose polymers
The invention discloses a simple and effective mulberry leaf polysaccharide detection method. The method specifically comprises steps as follows: mulberry leaf water-soluble carbohydrates and mulberry leaf total carbohydrates are extracted, hydrolyzed and converted into reducing sugar, the light absorption values of a mulberry leaf water-soluble carbohydrate extracting solution and a mulberry leaf total carbohydrate extracting solution in the position of 540 nm are measured with a 3,5-DNS acid (dinitrosalicylic acid) colorimetric method, the mass of the mulberry leaf water-soluble carbohydrate extracting solution and the mulberry leaf total carbohydrate extracting solution in a measurement liquid are calculated on the basis of glucose according to the glucose standard curve, the content of mulberry leaf water-soluble carbohydrates and the content of mulberry leaf total carbohydrates (on the basis of reducing sugar) are calculated, and the content of mulberry leaf polysaccharides is calculated according to the formula that the quantity of the mulberry leaf polysaccharides (%) is equal to the product obtained by multiplying the difference between the quantity of mulberry leaf total carbohydrates (%) and mulberry leaf water-soluble carbohydrates (%) by 0.9. By means of the method, the problem that the color developing condition is difficult to control due to the fact that sulfuric acid releases much heat when meeting water is solved, besides, the measurement process is not affected by monosaccharide components, the operation is simple and safe, the result is stable and reliable, and the method is suitable for detecting the content of the polysaccharides in massive mulberry leaf samples.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Gel formulations for local drug release
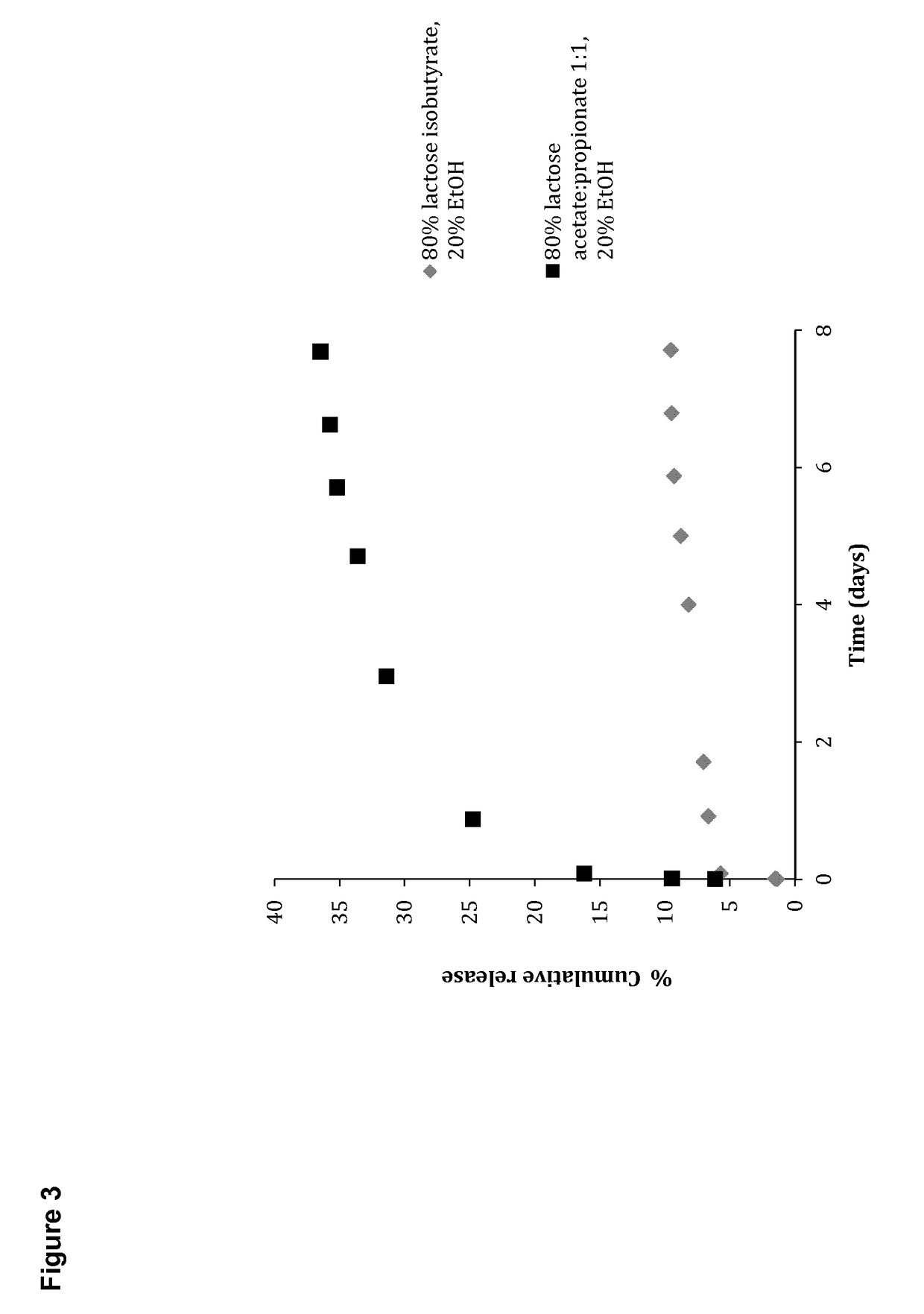
The present invention relates to a composition comprising non-water soluble carbohydrates, wherein at least 50% of the non-water soluble carbohydrates are carbohydrates selected from derivatives of lactose, maltose, trehalose, raffinose, glucosamine, galactosamine, lactosamine, or derivatives of disaccharides with at least two pyranose saccharide units, trisaccharides, tetrasaccharides, or mixtures thereof, and wherein the composition is a liquid before administration into the human or animal body and increases in viscosity by more than 1,000 centipoise (cP) after administration, for use as a medicament.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
Extraction and purification process for total phenolic acid in chaenomeles speciosa
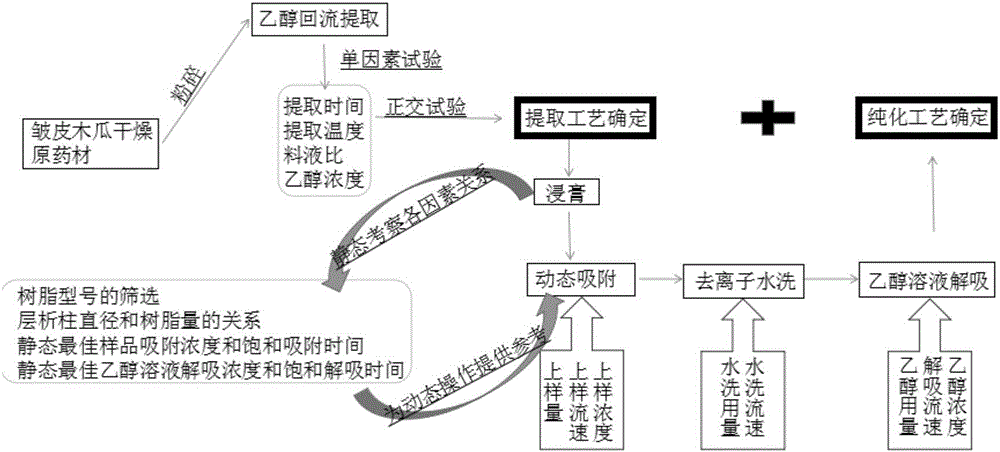
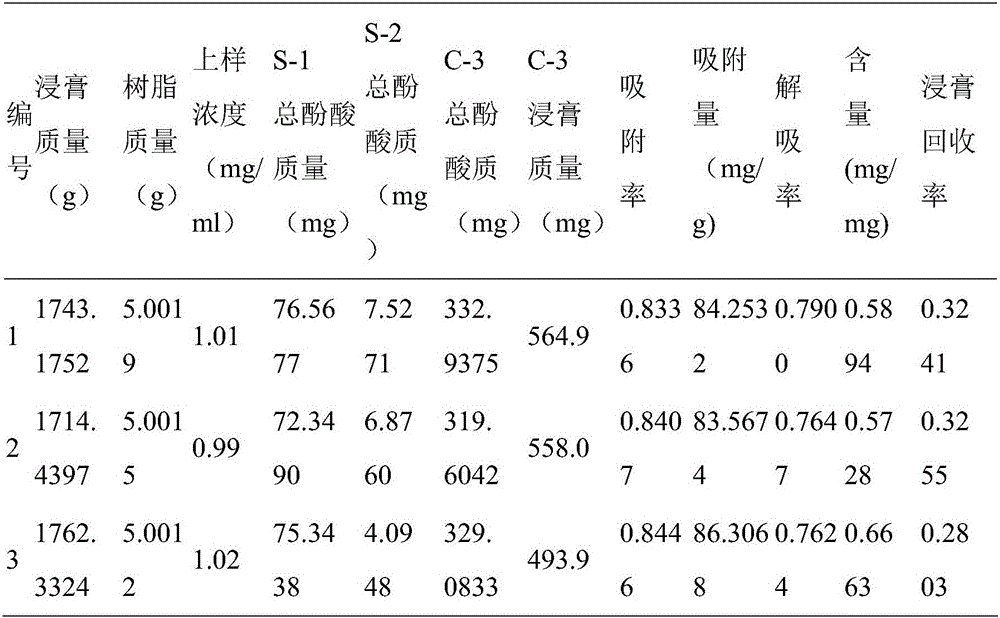
ActiveCN106177020AHigh extraction rateThe extraction and purification process steps are simplePlant ingredientsRefluxPurification methods
The invention provides an extraction and purification process for total phenolic acid in chaenomeles speciosa. The extraction and purification process includes the following steps that the chaenomeles speciosa raw medicinal material is smashed, powder obtained after smashing is subjected to heating reflux for 3-5 h with an ethanol solution, and after filtering, filter liquor is collected; the filter liquor is concentrated to a constant weight, extract is obtained, and the content of total phenolic acid in the extract is measured through the foline-phenol method; the extract is dissolved with deionized water and then prepared into a phenolic acid solution for use; the model of macroporous resin in use is selected, the selected macroporous resin is packed into a column, and after the resin is pretreated, the phenolic acid solution is subjected to dynamic sample loading adsorption; substances on the surface of the resin and part of water-soluble carbohydrates are washed off with deionized water; finally, the resin is eluted with ethyl alcohol, phenolic acid adsorbed in the resin is desorbed, and collected eluate is total phenolic acid in chaenomeles speciosa. According to the extraction and purification method, the process of performing ethanol extraction and then resin purification is adopted, the extraction rate is high, and the extraction and purification method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Method for modifying the flavor profile of a plant protein preparation
ActiveUS20100092654A1Process economyStrong flavorProtein composition from vegetable seedsVegetable proteins working-upFlavorWater soluble
A method for modifying the flavor profile of a plant protein preparation, especially a protein preparation from a leguminous plant. The protein preparation is brought into contact with water-soluble carbohydrates in an aqueous solution before being added to a food product, the contact advantageously influencing the flavor profile of protein preparations from leguminous plant, so that the preparations can be used in foodstuffs without essentially changing the flavor thereof.
Owner:PROLUPIN GMBH
Method for producing carbon aerogel from hydrogel precursor material by means of hydrothermal process
ActiveCN111285345AAtmospheric pressure dryingSimple structure controlCarbon preparation/purificationAerogel preparationSupercritical dryingActive agent
The invention relates to a method for preparing carbon aerogel from a hydrogel precursor material through a hydrothermal process, belongs to the field of new materials, and solves the problems of complex carbon preparation process and high cost due to adoption of supercritical drying in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, acidifying chitosan with diluted hydrochloric acid, and forming a mixed solution with water-soluble carbohydrates; step 2, adding a polysorbate nonionic surfactant and liquid paraffin, and then adding glutaraldehyde to form hydrogel; step 3, placing the hydrogel in a reaction kettle, and carrying out a hydrothermal reaction, to obtain a primary carbonization product; step 4, cleaning the primary carbonization product and replacing the primarycarbonization product with a two-stage solvent; and step 5, carrying out further heat treatment on the primary carbonization product, characterizing the microstructure of the primary carbonization product by using a scanning electron microscope, and determining the pore property of the sample by nitrogen adsorption. The carbon aerogel structure is generated in one step by utilizing low-cost raw materials; normal-pressure drying of the carbon aerogel structure is achieved through two-stage solvent replacement.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Additivated coal dust with water soluble carbohydrates for use in the green sand composition for casting molding
Coal dust additivated with water soluble carbohydrates for use in the green sand composition for molding of castings refers to a process for obtaining coal additivated with carbohydrates to be used in the green molding sand composition, commonly used for making casting molds, having as a scope to inhibit the sand sintering on the castings and so to improve their finish.
Owner:COQUE DO SUL DO BRASIL
Preparation method of graphene/activated carbon composite adsorption package
The invention relates to the field of graphene materials, in particular to a preparation method of a graphene / activated carbon composite adsorption package. The graphene / activated carbon composite adsorption package is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 90 to 130 parts of water-soluble carbohydrate, 2 to 6 parts of sodium hydroxide, 1 to 5 parts of styrene, 2 to 6 partsof octadecyl acrylate, 120 to 130 parts of attapulgite and 1 to 6 parts of oxidized graphene. The graphene / activated carbon composite adsorption package prepared by the preparation method of the graphene / activated carbon composite adsorption package disclosed by the invention has the function of adsorbing harmful gases, such as formaldehyde.
Owner:SHANDONG XINGHUO SCI TECH INSTITYTE
Application of corn flour in improving quality of mulberry twig and leaf silage
PendingCN110810638AImprove WSCImprove silage environmentAnimal fodder preservationBiotechnologyCorn flour
The invention provides application of corn flour in improving quality of mulberry twig and leaf silage and in particular relates to the technical field of mulberry twig and leaf silage fermentation. According to the application, the corn flour is added to a silage raw material of mulberry twigs and leaves, the silage is fermented, samples are taken and analyzed, and results show that (1) WSC (water soluble carbohydrate) and LA (lactic acid) in a mulberry twig and leaf silage product can be effectively increased by the corn flour; (2) the pH value of the mulberry twig and leaf silage product can be reduced to 4.5-5.0 by the corn flour; and (3) the mixed silage of the corn flour and the mulberry twigs and leaves can be subjected to lactic acid type fermentation, and in addition, no BA (butylacrylate) is generated, so that the silage environment of the mulberry twigs and leaves can be effectively improved, and the obtained silage product has good effects in smell, texture and color.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
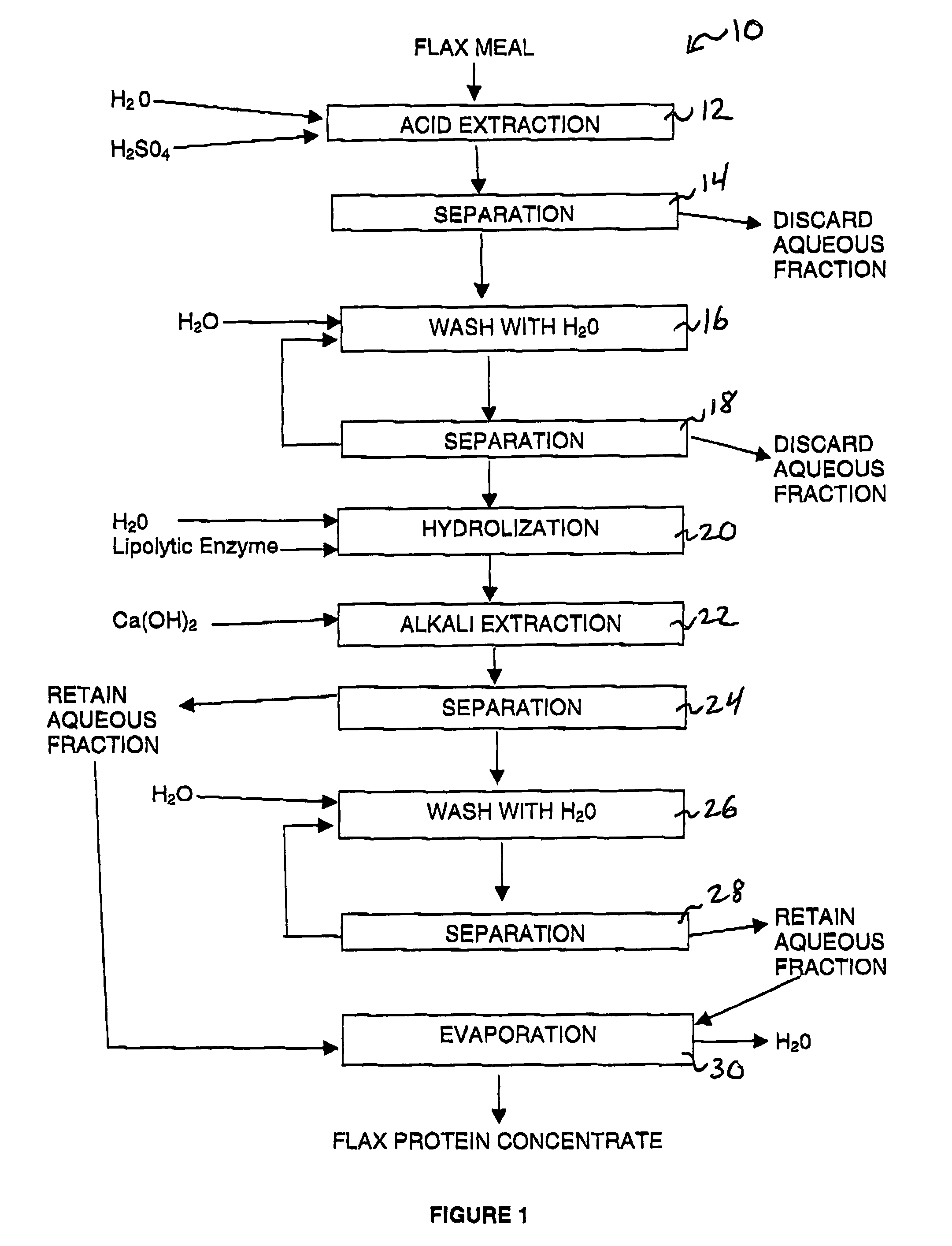
Process for extracting flax protein concentrate from flax meal
InactiveUS6998466B2High yieldAvoid pollutionPeptide/protein ingredientsProtein composition from vegetable seedsWater solubleWater soluble carbohydrate
A process for extracting flax protein concentrate from flax meal is disclosed wherein flax meal is added to an aqueous acidic solution to form a first mixture having a solid fraction and an aqueous fraction containing water soluble-carbohydrates. The mixture is separated and the solid fraction is then hydrolyzed using a lipolytic enzyme. An aqueous alkali solution is then added to the hydrolyzed solution to form a second mixture having a second aqueous fraction containing said flax protein, and a second solid fraction. The second mixture is then separated into the aqueous fraction and the solid fraction, such that the second aqueous fraction may be evaporated to recover the flax protein.
Owner:NUTREX WELLNESS
Water-Soluble Carbohydrate Polyethers
ActiveUS20120046435A1Easy to controlLarge degree of structural variationSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationWater solubleWater soluble carbohydrate
The present invention relates to novel carbohydrate polyether compositions that are soluble in aqueous media and particularly to carbohydrate polyether compositions exhibiting reverse thermogelation properties in aqueous media. Also, since the carbohydrate polyethers of the present invention can be conveniently controlled with respect to functionality, molecular weight, polydispersity index, microstructure and tertiary structure, they can be customized for use in a variety of applications.
Owner:TRGEL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com