Patents
Literature
94results about How to "Realize miniaturization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
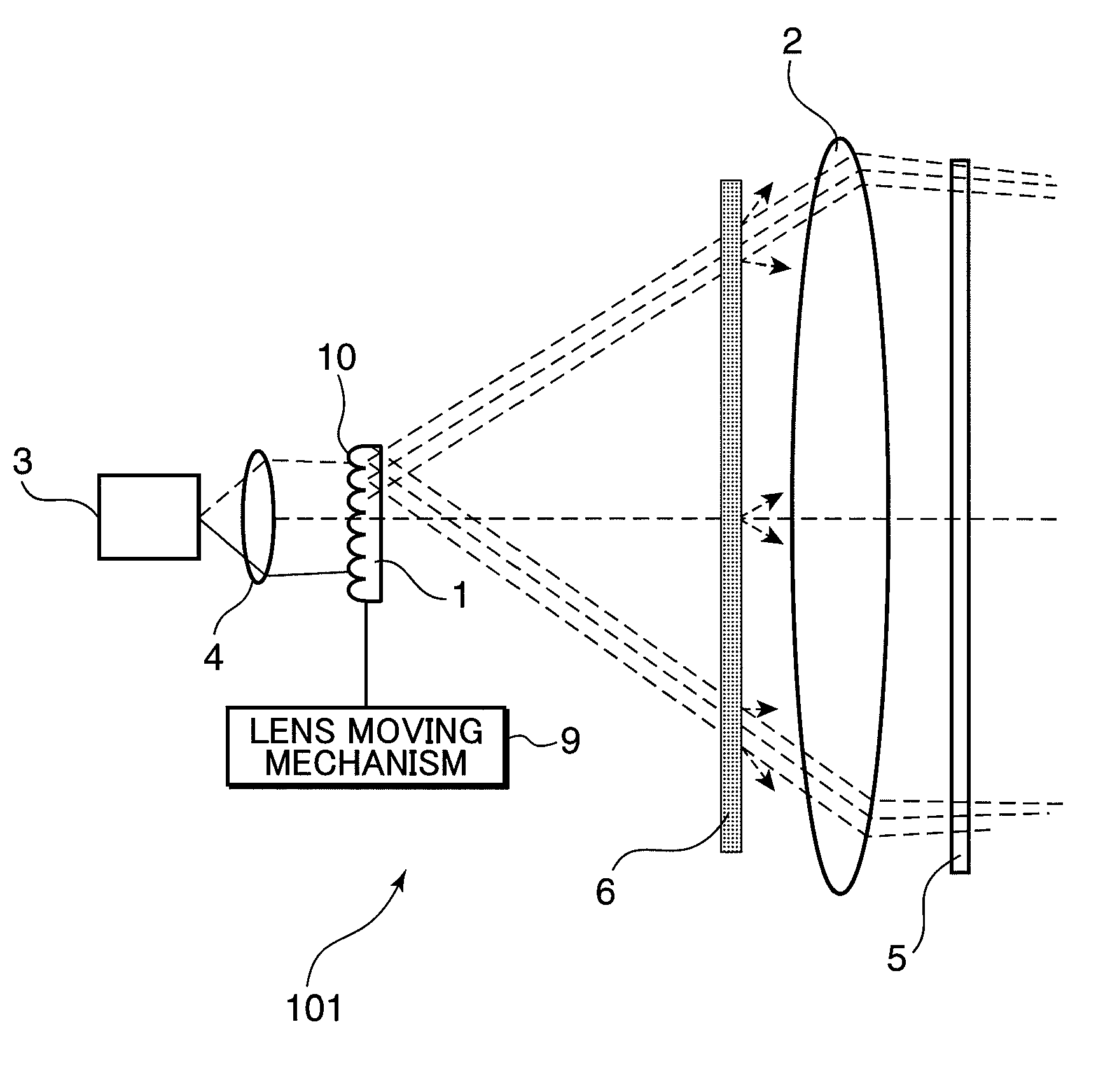
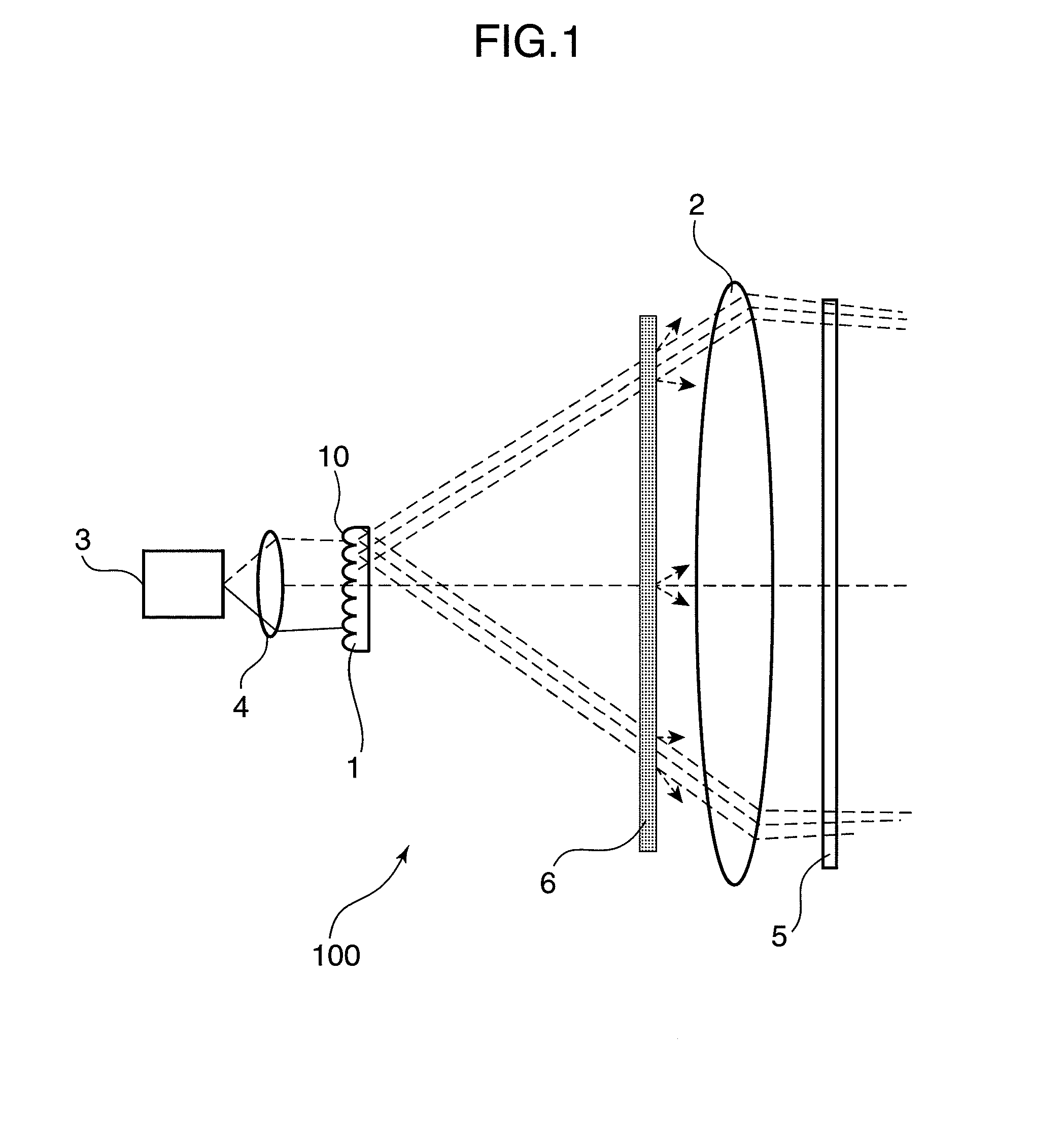
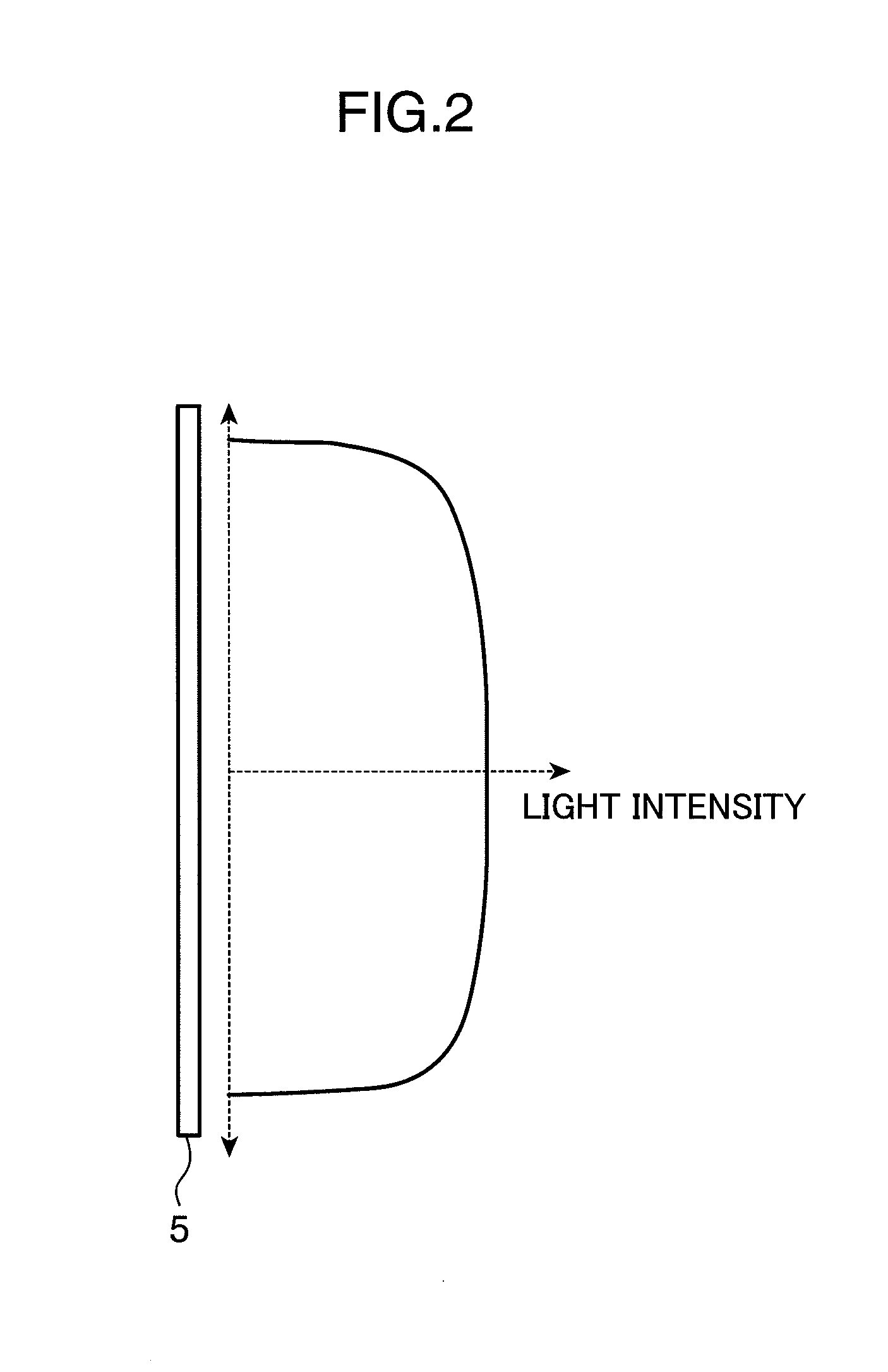
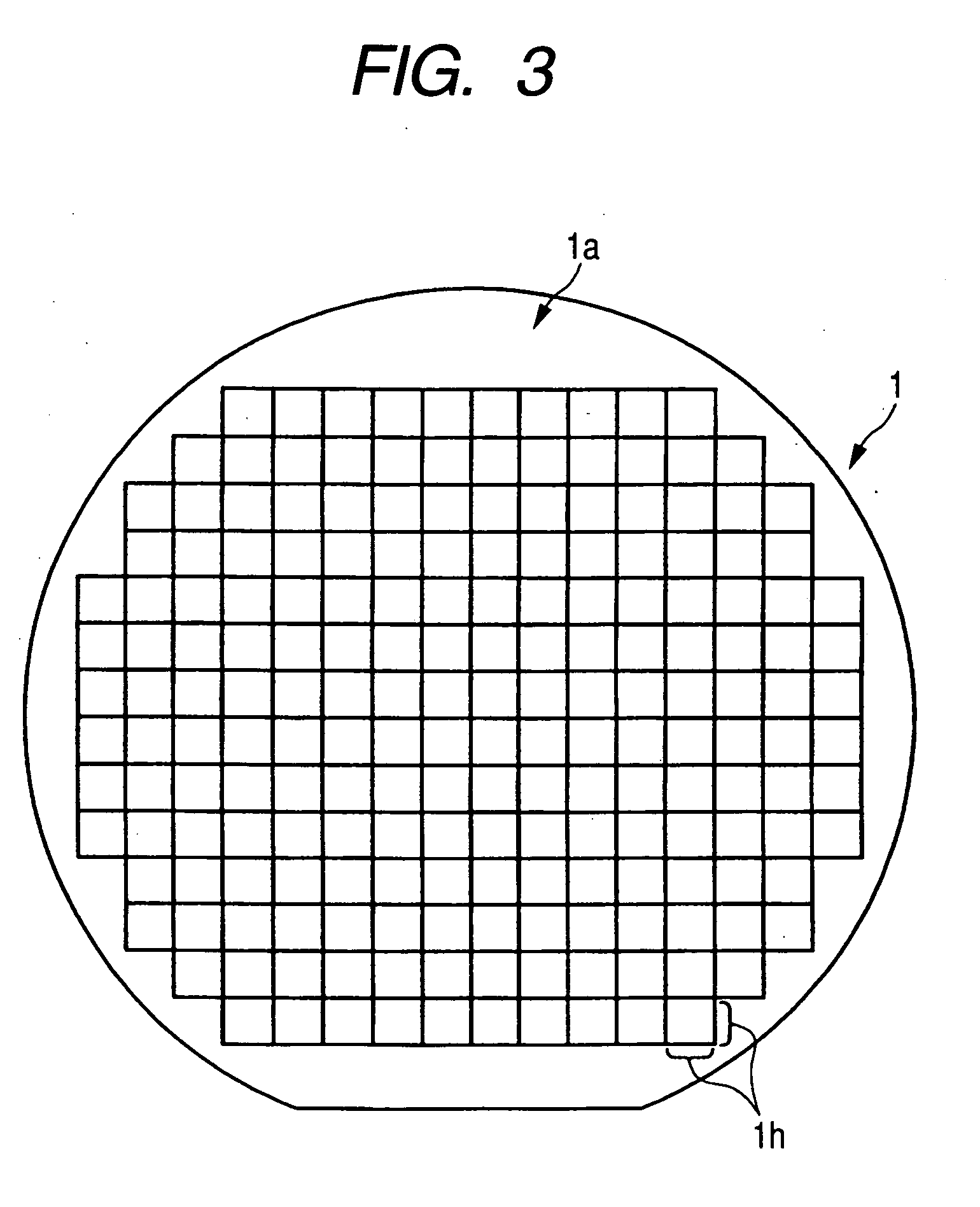
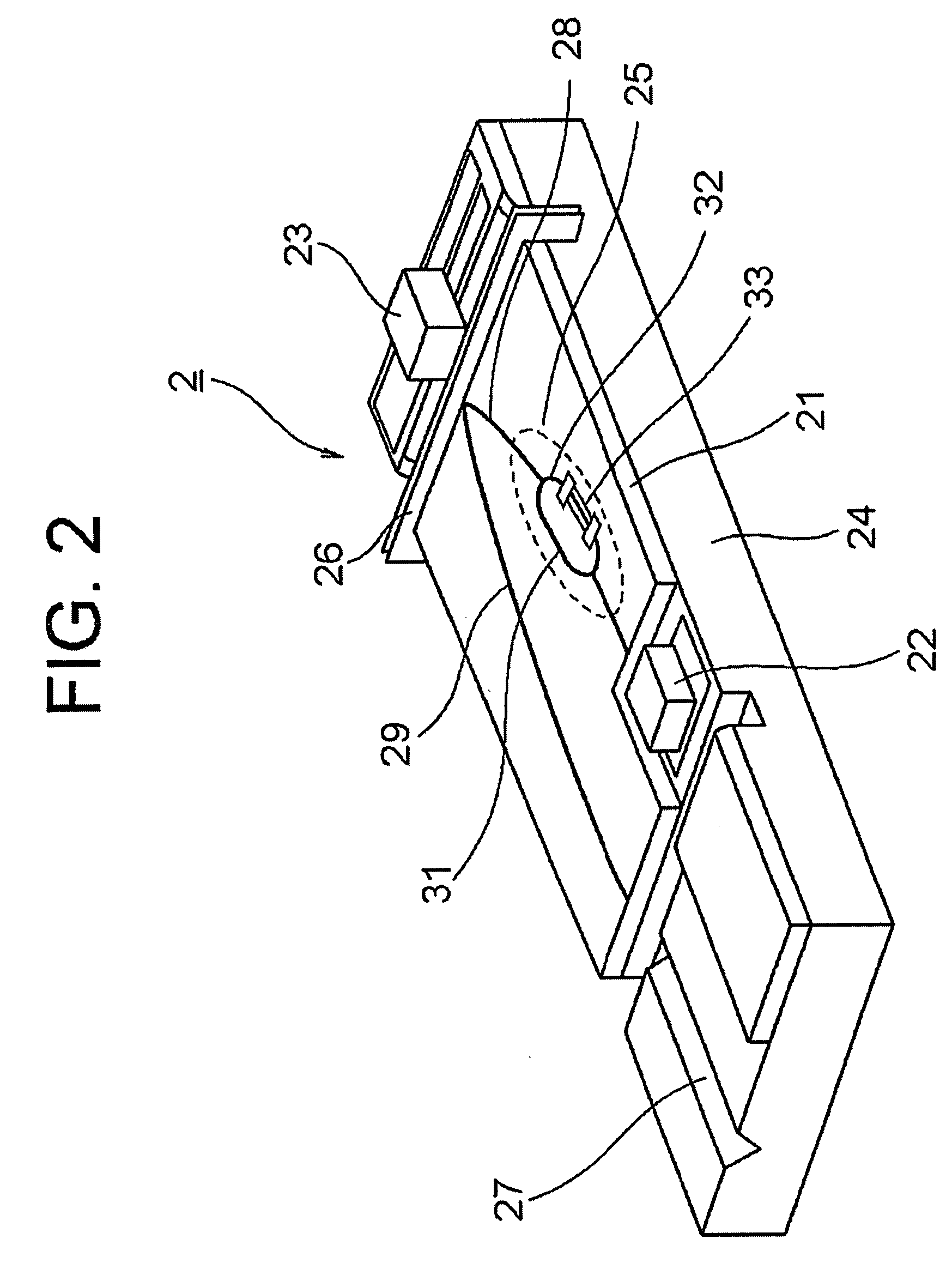
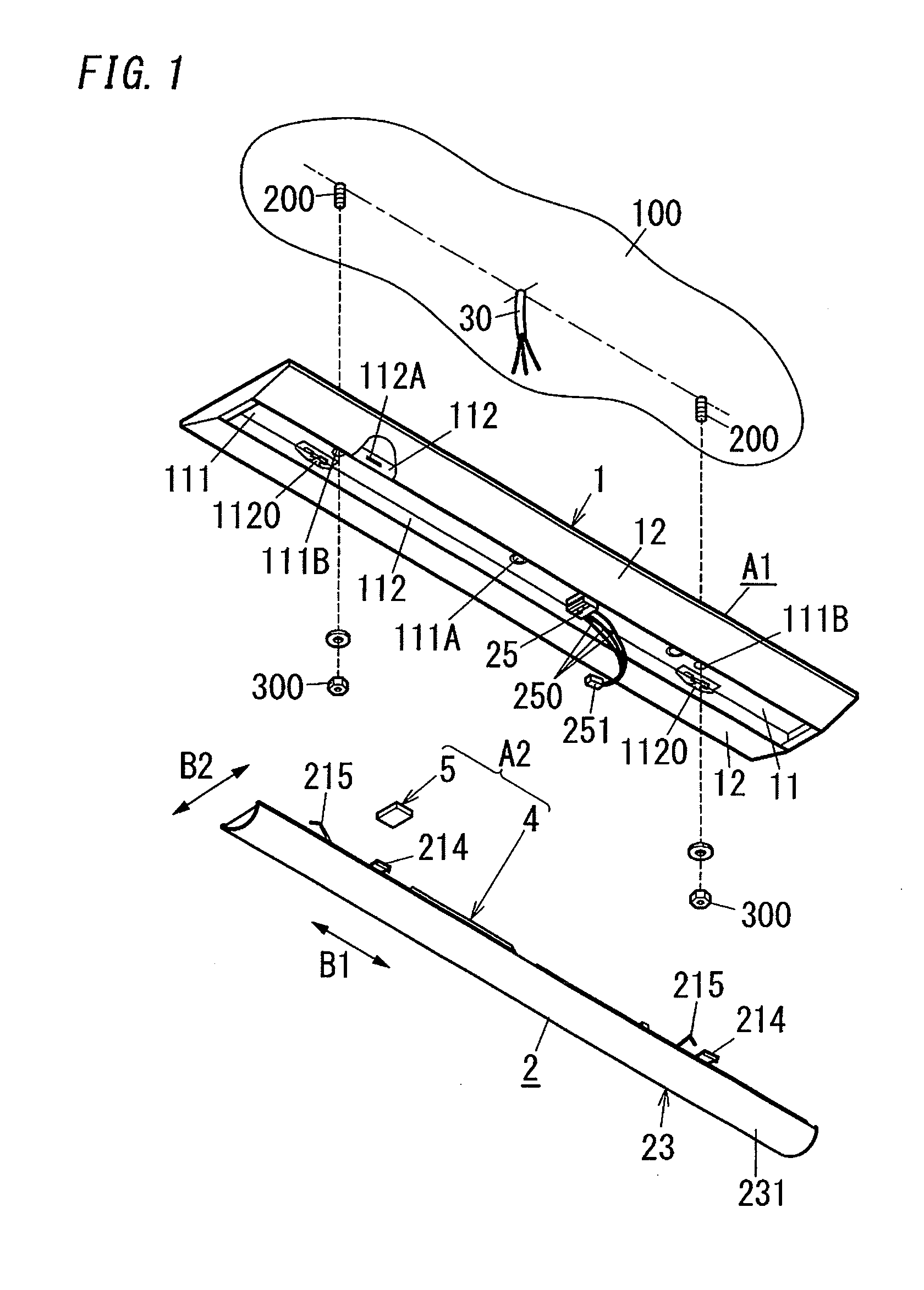
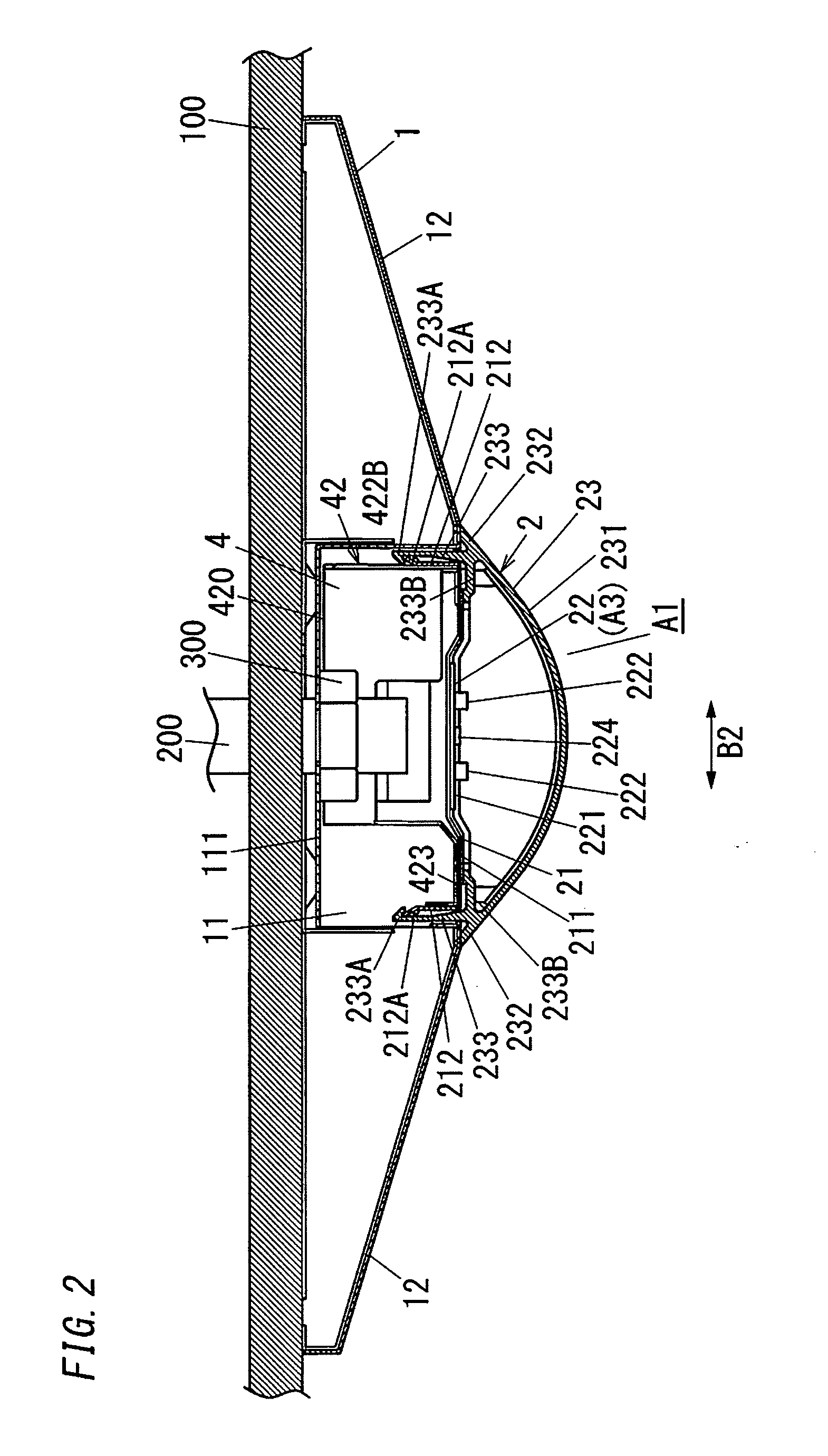
Laser illuminating device and image display device
InactiveUS20100053565A1Remove speckle noiseUniform lightDiffusing elementsProjectorsDivergence angleLaser light
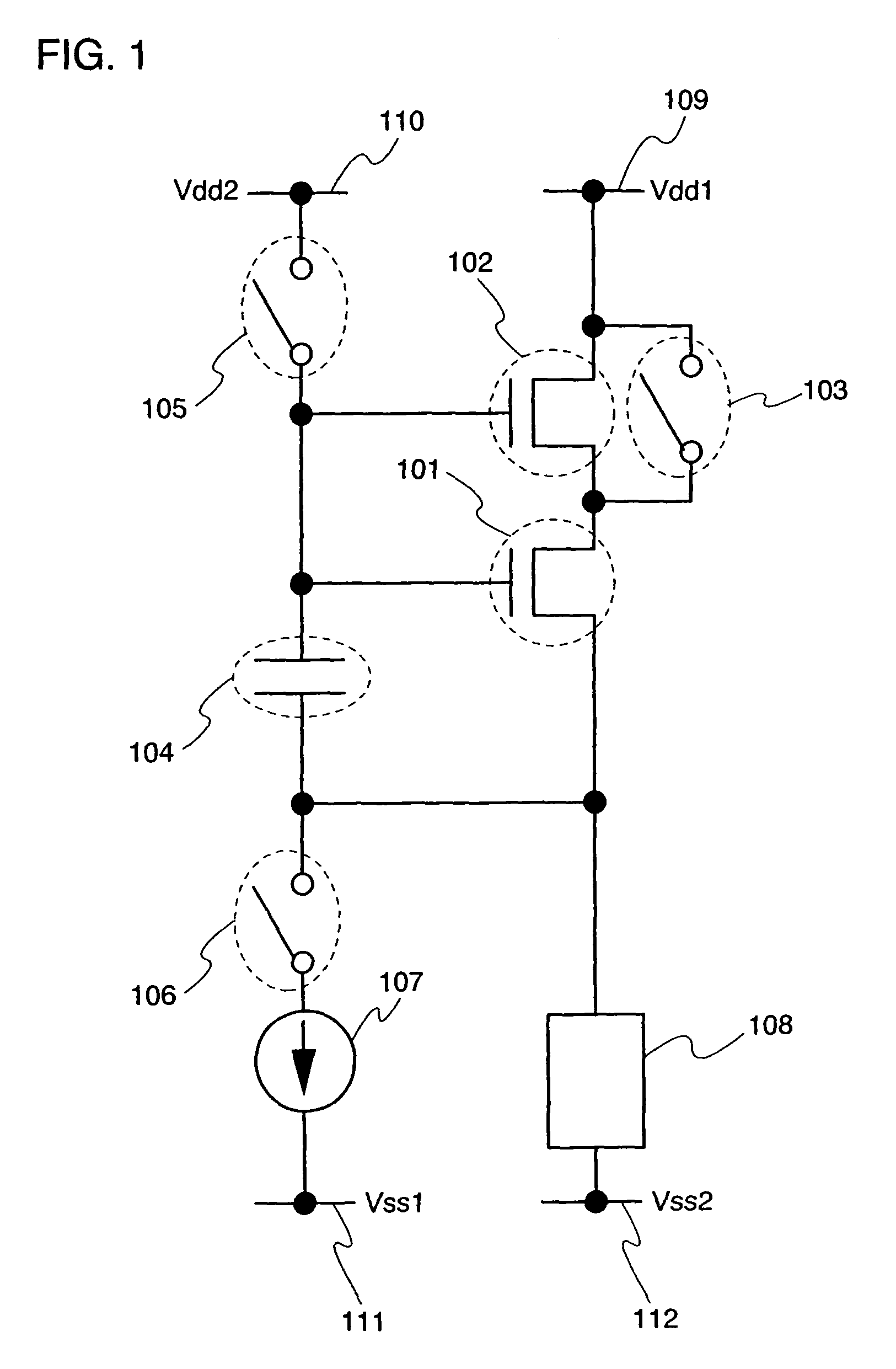
An object of the invention is to provide a laser illuminating device and an image display device that enable to remove speckle noises in a diffraction field and an image field, uniformly illuminate an illumination plane, and realize miniaturization. A laser illuminating device 100 includes a laser light source 3, a first lens 1 including a plurality of microlenses 10 each having a predetermined numerical aperture in an in-plane direction, each of the microlenses 10 being adapted to expand laser light emitted from the laser light source 3 to thereby superimpose the laser light transmitted through each of the microlenses 10; and a second lens 2 having an effective diameter larger than an effective diameter of the first lens 1, and for compensating for a divergence angle of the laser light expanded by each of the plurality of the microlenses 10.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
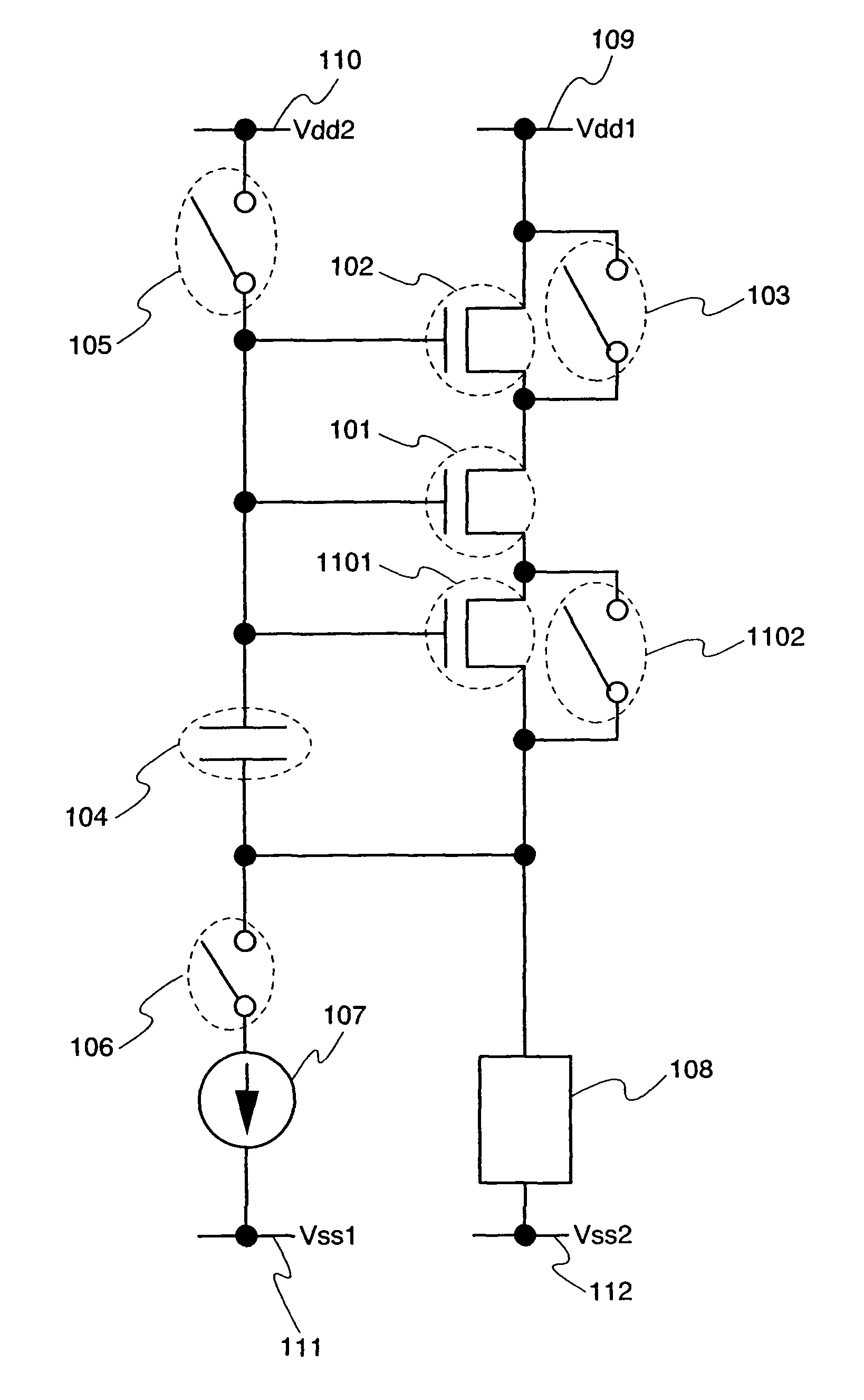
Semiconductor device, display device and electronic device equipped with the semiconductor device
InactiveUS20070035340A1Reduce power consumptionAvoid flowImpedence convertorsElectroluminescent light sourcesCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
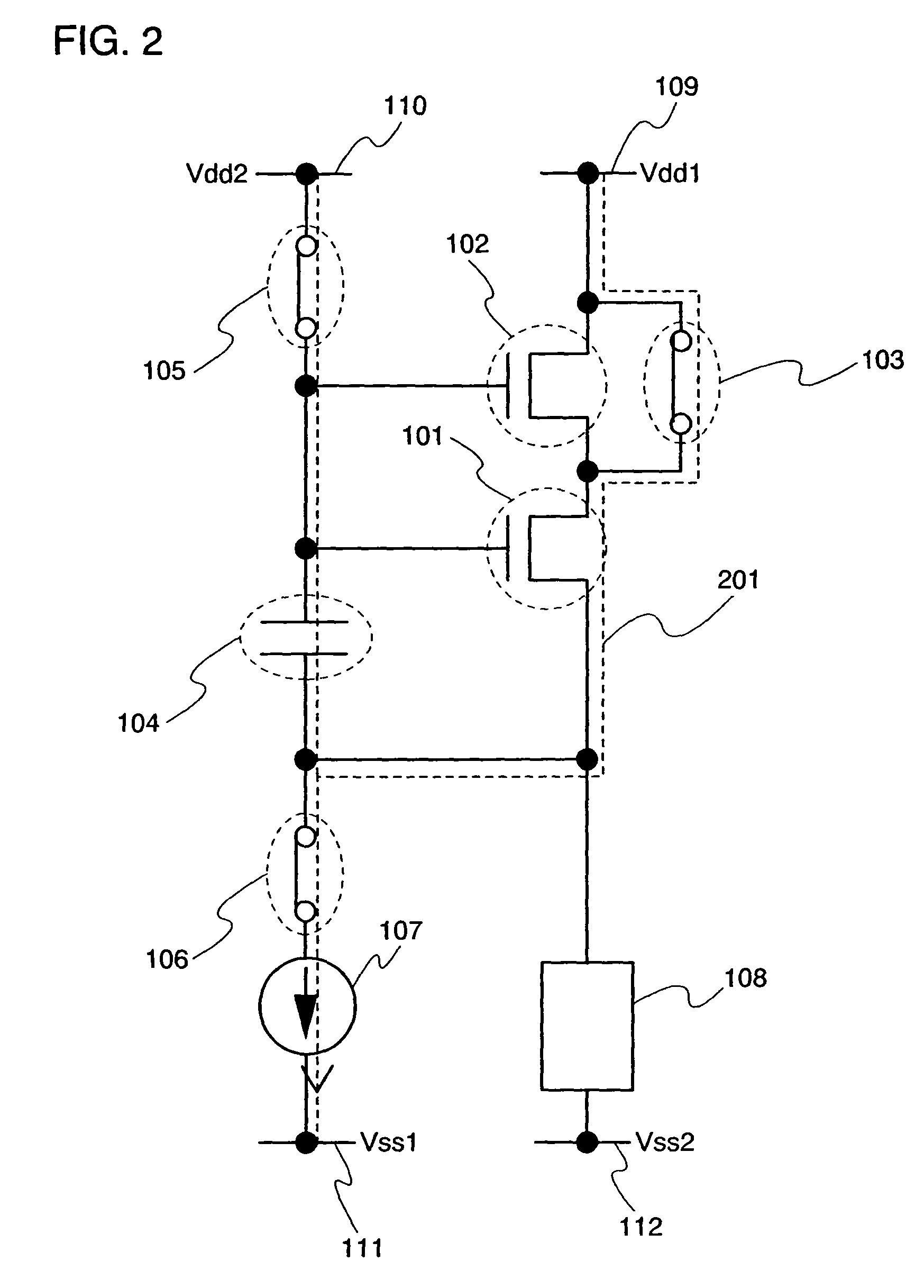
The present invention provides a semiconductor device which can prevent a current from flowing into a display element at a signal writing operation, without increasing power consumption and without changing a potential of a power supply for supplying a current to a load in each row. When a predetermined current is supplied to a transistor to set a gate-source voltage of the transistor, a potential of a gate terminal of the transistor is adjusted so as to prevent a current from flowing into a load which is connected to a source terminal of the transistor. Thus, a potential of a wire connected to the gate terminal of the transistor is made different from that of a wire connected to a drain terminal of the transistor. At that time, an operation of a transistor is shifted so as to allow a large amount of current to flow, and influences by intersection capacitance parasitic to a wire or the like or wire resistance are hardly caused, and a set operation is conducted quickly.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Cooling device and cooling method
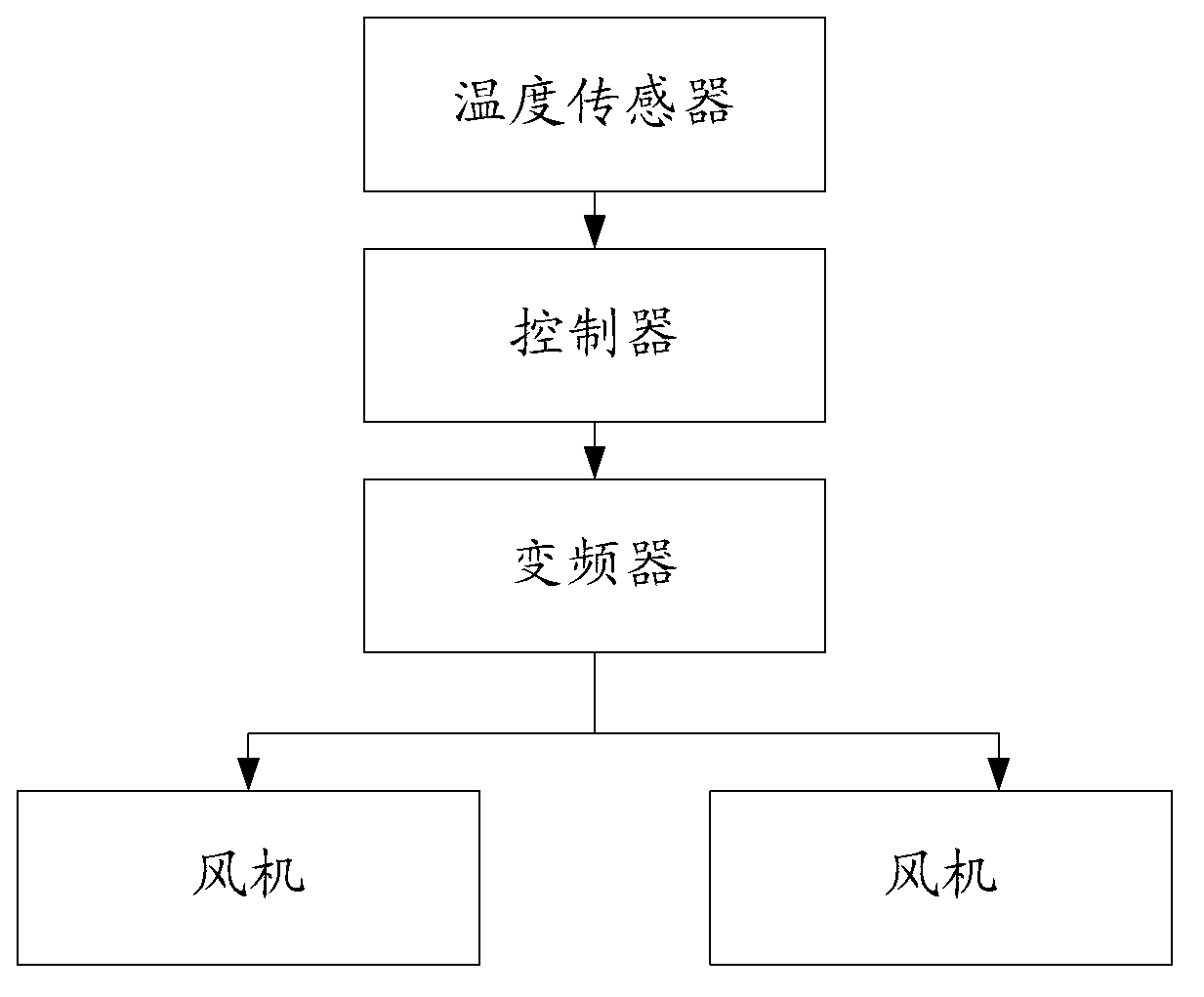
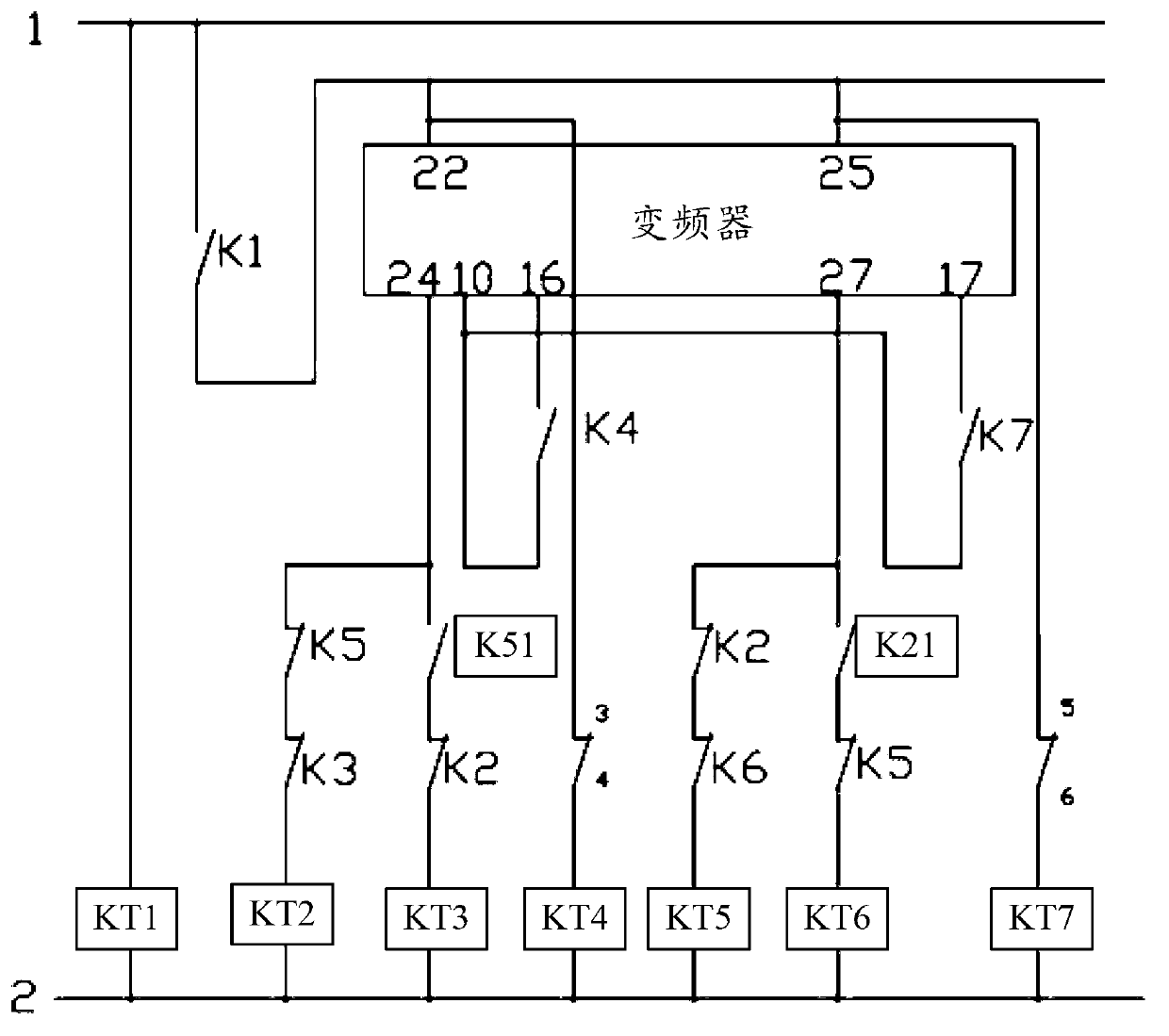
ActiveCN102996481AIncrease powerRealize miniaturizationPositive displacement pump componentsPump controlFrequency changerAir volume
The invention discloses a cooling device used for cooling an air compressor. The cooling device comprises at least one fan, a temperature sensor, a controller and a frequency converter, wherein the temperature sensor is used for detecting exhaust temperature of the air compressor; the controller is connected with the temperature sensor and is used for comparing the exhaust temperature with preset exhaust temperature and outputting a signal after comparison; and the frequency converter is respectively connected with the at least one fan and the controller and is used for controlling the at least one fan to output cooling air volume corresponding to the signal after comparison according to the signal after comparison. When the cooling device is in use, a cooing temperature is firstly set, the exhaust temperature of the air compressor is detected by the temperature sensor, when the controller determines that the temperature is lower than the cooling temperature, the power supply frequency of the fan is reduced by the frequency converter, the power of the corresponding fan can be reduced, and the cooling air volume is reduced, therefore, the energy consumption is reduced, the energy sources are saved, and the service life of lubricating oil in the air compressor is effectively prolonged simultaneously. The invention also discloses a cooling method.
Owner:FUSHENG IND SHANGHAI
Linear frequency-modulated signal generator with predistortion function
ActiveCN104267385AWith pre-distortion functionCompensate for nonlinear effectsWave based measurement systemsAngle demodulation by oscillations conversionSignal generatorPredistortion
The invention provides a linear frequency-modulated signal generator with a predistortion function. The linear frequency-modulated signal generator comprises an FPGA unit, a digital-analog conversion unit and a filtering unit, wherein the FPGA unit is used for generating a phase position predistortion digital linear frequency-modulated signal and conducting amplitude predistortion processing on the phase position predistortion digital linear frequency-modulated signal to generate two orthogonal amplitude-phase predistortion digital linear frequency-modulated signals; the digital-analog conversion unit is connected with the output end of the FPGA unit and used for converting the two orthogonal digital linear frequency-modulated signals subjected to amplitude-phase predistortion into two orthogonal discrete analog linear frequency-modulated signals; the filtering unit is connected with the digital-analog conversion unit and used for filtering out frequency components beyond a preset frequency range of the two orthogonal discrete analog linear frequency-modulated signals to obtain two continuous orthogonal analog linear frequency-modulated signals. The linear frequency-modulated signal generator can compensate for non-linear influences of an analog circuit on the linear frequency-modulated signals by means of amplitude-phase predistortion processing, and guarantee that the high-quality linear frequency-modulated signals can be obtained finally.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
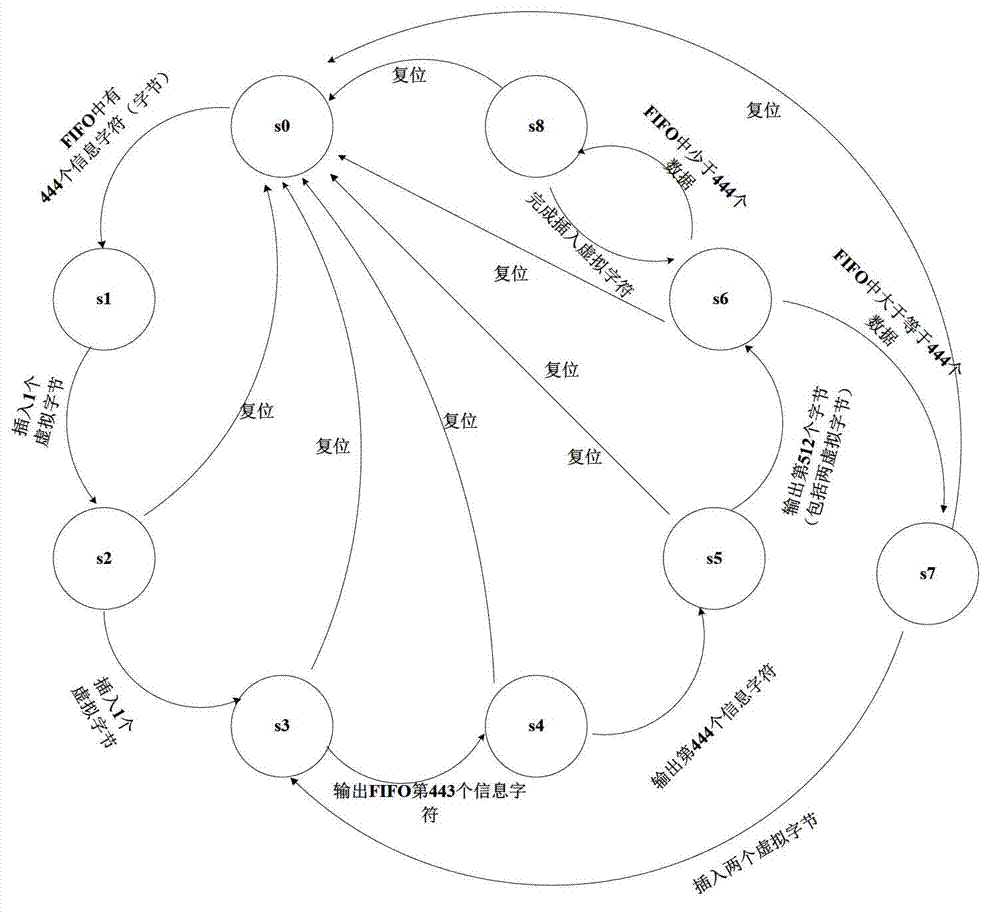
Data communication protocol controller suitable for satellite mounted equipment
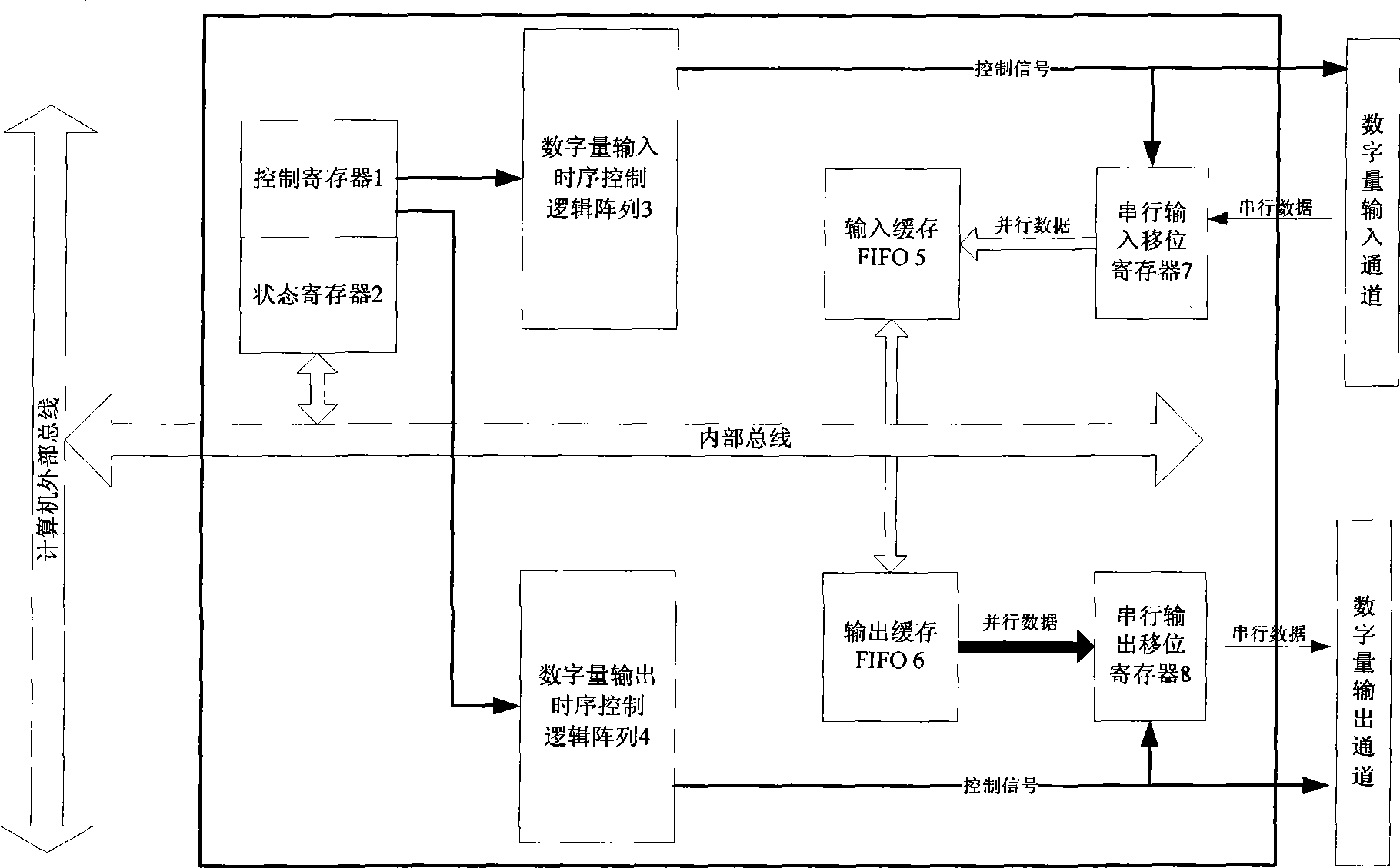
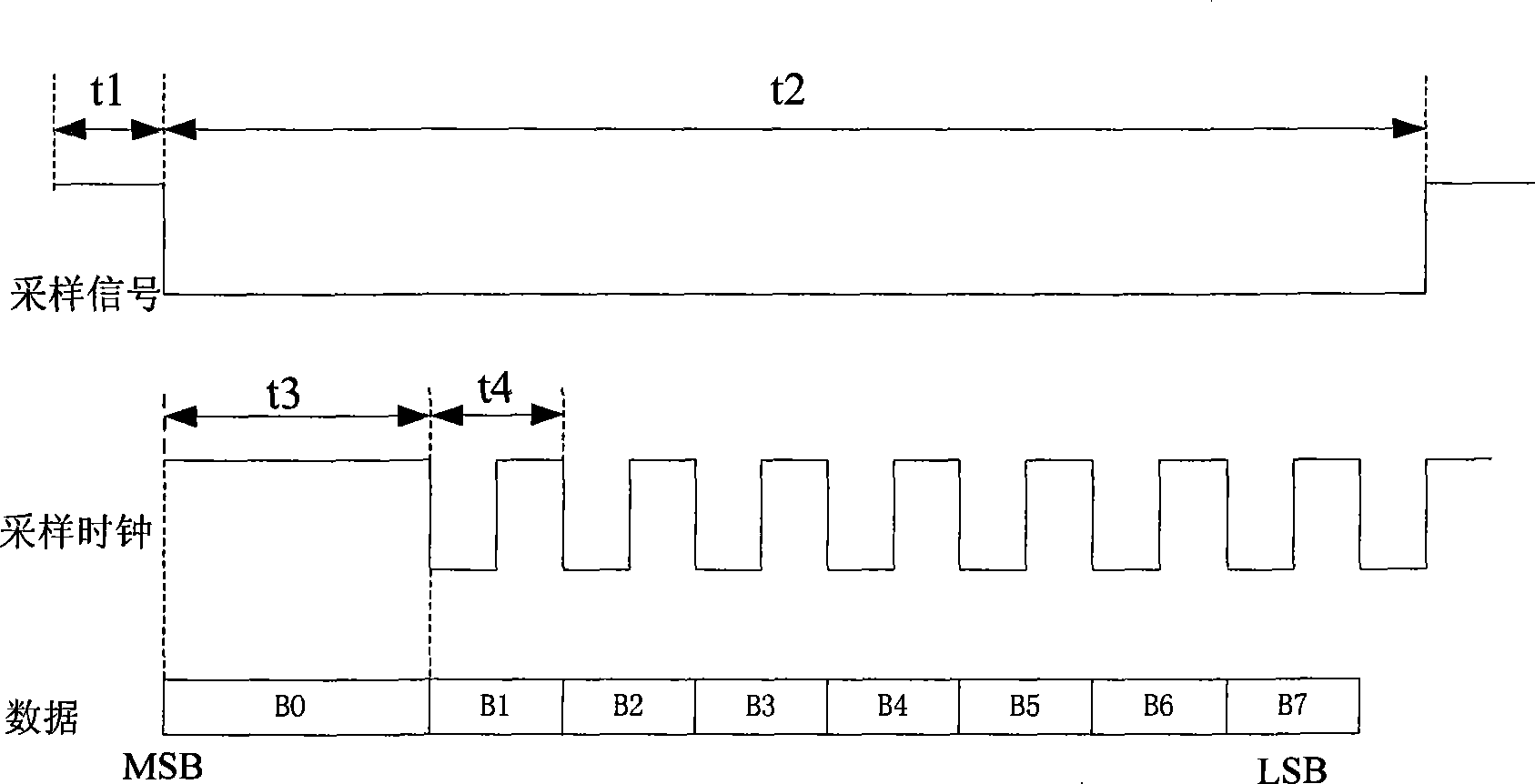
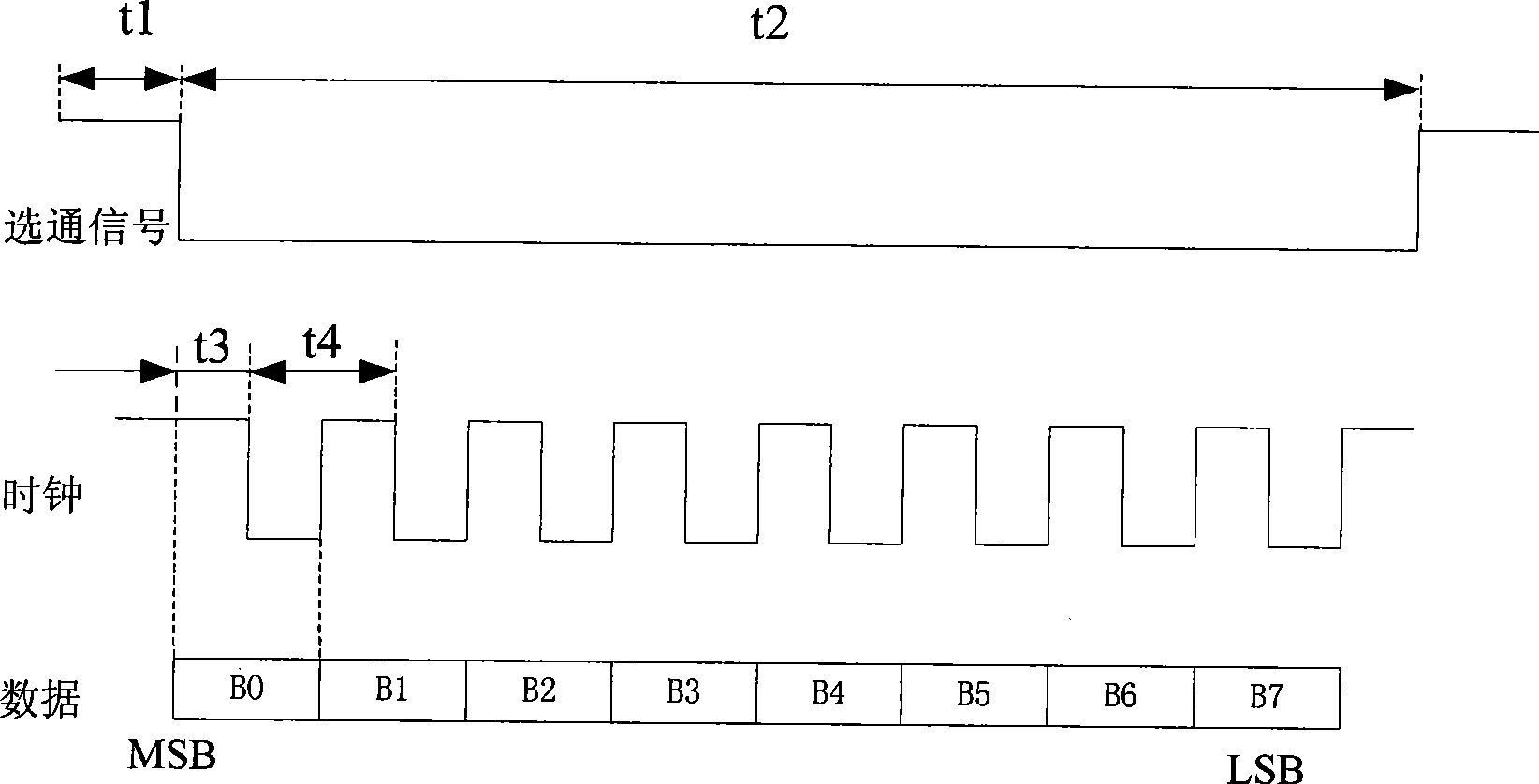
InactiveCN101453468AImprove communication efficiencyImprove reliabilityData switching by path configurationSequence controlShift register
The invention relates to a data communication protocol controller applicable to satellite borne equipment. The controller comprises a control register, a status register, an input cache and an output cache which are all electrically connected with an internal bus, wherein the control register 1 is in electrical connection with a digital quantity input time-sequence control logic array and a digital quantity output time-sequence control logic array through signal wires; a control signal of the digital quantity input time-sequence control logic array is in electrical connection with a serial-in shift register and an external digital quantity input channel; the serial-in shift register is in electrical connection with the input cache through an input parallel data wire; a control signal of the digital quantity output time-sequence control logic array is in electrical connection with a serial-out shift register and an external digital quantity output channel; and the serial-out shift register is in electrical connection with the output cache through a parallel output data wire. The data communication protocol controller solves the problem of automatic control on multiple communication protocols and multipath communication channels, realizes light-minimization of a data acquisition unit, and is established based on a digital logic hardware circuit, so that reliability and stability of the controller can be sufficiently guaranteed.
Owner:CENT FOR SPACE SCI & APPLIED RES
Base band digital signal encoding modulation integrated system
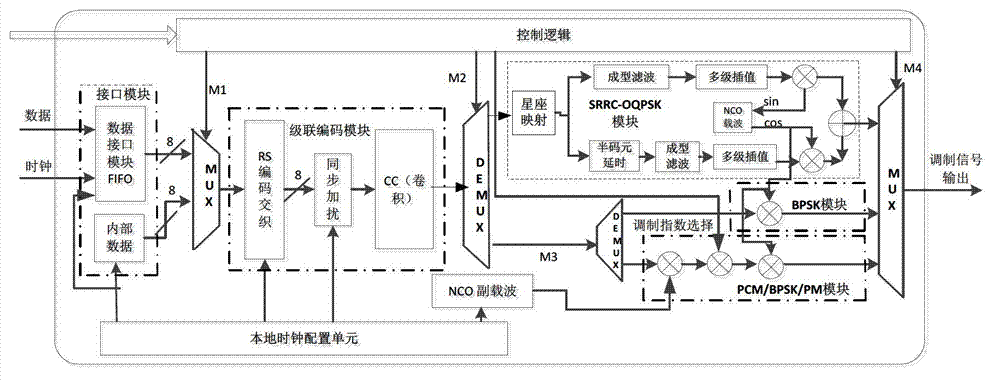
InactiveCN103166743AMeet functional application requirementsOvercome functionError preventionPhase-modulated carrier systemsSignal encodingDigital signal
The invention provides a base band digital signal encoding modulation integrated system comprising a cascade encoding module, a PCM / PSK / PM modulation module and a BPSK / NRZ modulation module. The system is characterized by further comprising a control subsystem used for controlling encoding modulation modes of the cascade encoding module, the PCM / PSK / PM modulation module and the BPSK / NRZ modulation module, wherein the subsystem further comprises an interface module, a first multiplexer, an SRRC-OQPSK modulation module, a data distributor, a multiplexer and a control logic module. The first multiplexer is used for selecting data in one path from two path data output from the interface module and outputting the data to a post-stage circuit which is the cascade coding module. The system is used for completing reed-solomon (RS) coding interface data selection of base band data and coding framing, and can correspondingly select different modulation mode functions according to different transmission code rates including a low transmission code rate, a medium transmission code rate and a high transmission code rate. The system correspondingly selects PCM / PSK / PM.BPSK / NRZ and RC-OQPSK modulation modes according to a downlink low data code rate, a downlink medium data code rate and a downlink high data code rate after achieving base band signal encoding.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Lean-type selenium-enriched pig feed for reducing cholesterol
InactiveCN104664161AIncrease appetiteIncrease profitAnimal feeding stuffWeight gainingAnimal science
The invention relates to a lean-type selenium-enriched pig feed for reducing cholesterol. The lean-type selenium-enriched pig feed for reducing the cholesterol is characterized in that 0.3-0.5% of a feed additive is added, so that the content of selenium is more than or equal to 0.1mg / kg in the feed; and the content of selenium in the feed additive is more than or equal to 20.4mg / kg. The lean-type selenium-enriched pig feed for reducing the cholesterol accords with compatibility principles of traditional Chinese veterinary and has the effects of reducing the cholesterol, and improving the lean rate so that selenium-enriched nutrient meet can be produced; the lean-type selenium-enriched pig feed has the unexpected effects on weight gaining, fat lowering, selenium supplying and lean rate increasing.
Owner:石爱华
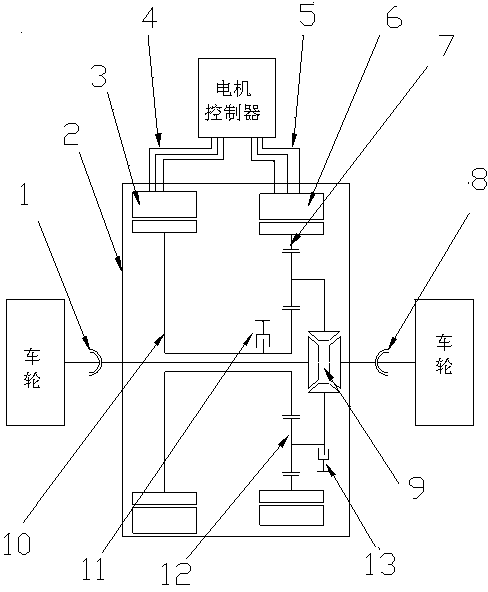
Power assembly of full electric vehicle electric drive system
The invention provides a power assembly of a full electric vehicle electric drive system. The invention has a core that the power assembly is provided with an integral integration power assembly design consisting of one set of planetary gear train mechanism and two sets of drive motors; the motors and the transmission shaft of the power assembly adopt a coaxial design; two sets of motors are respectively connected with a planetary gear sun gear and a gear ring; two motors are in coordination control to realize stepless speed regulation; for an electric vehicle which requires high performance, an original single big motor is changed into two small motors for input, and the optimal matching of the revolving speed, the torque and the high efficiency area of the motors can be realized so as to realize the low cost and the high reliability of motor miniaturization, realize the high efficiency of the electric drive system and improve an endurance mileage to the maximum limit. Meanwhile, a speed change mechanism formed by a planetary mechanism has the advantages of compact structure and the like and is favorable for arrangement.
Owner:奇瑞新能源汽车股份有限公司
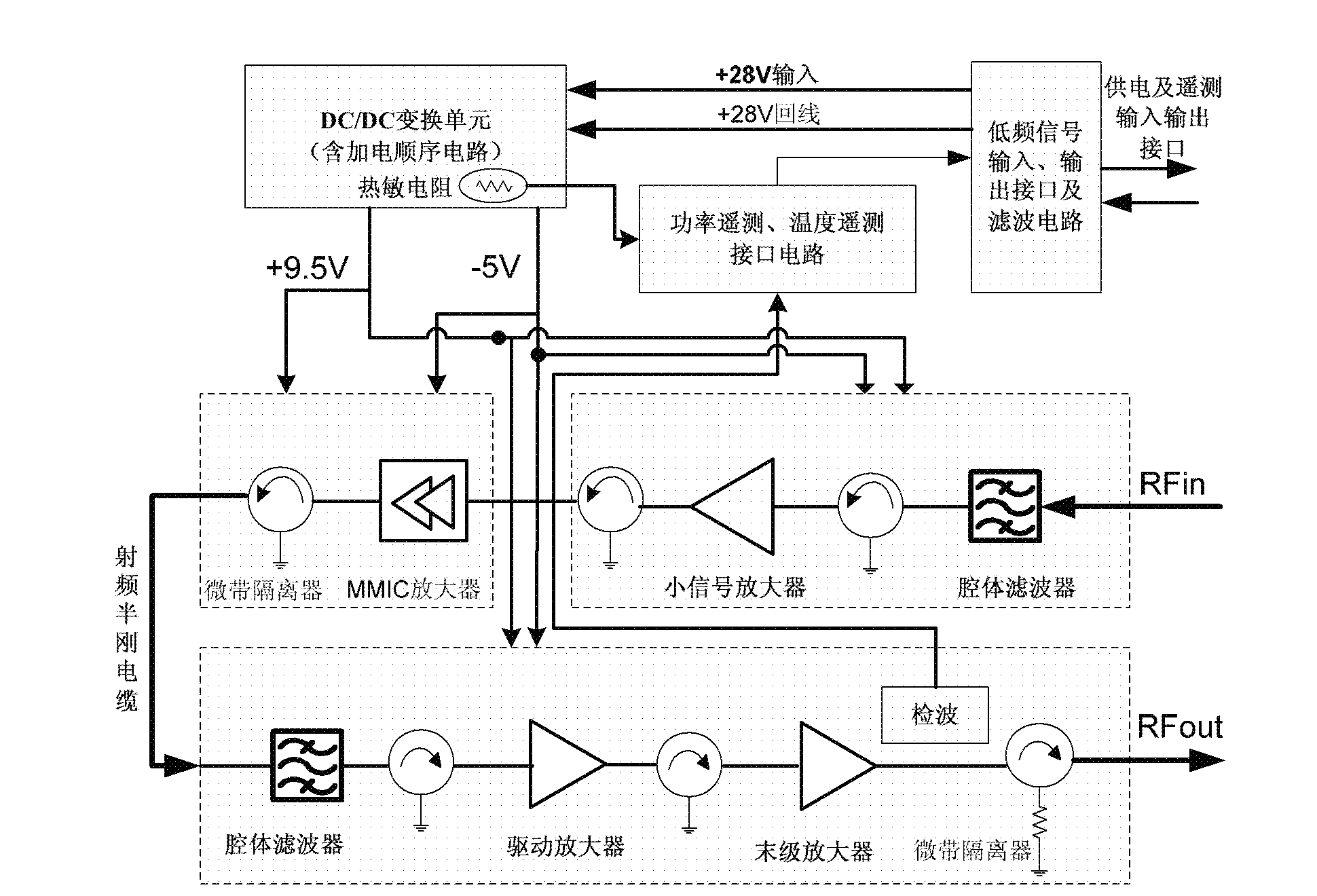
Microwave solid-state power amplifier
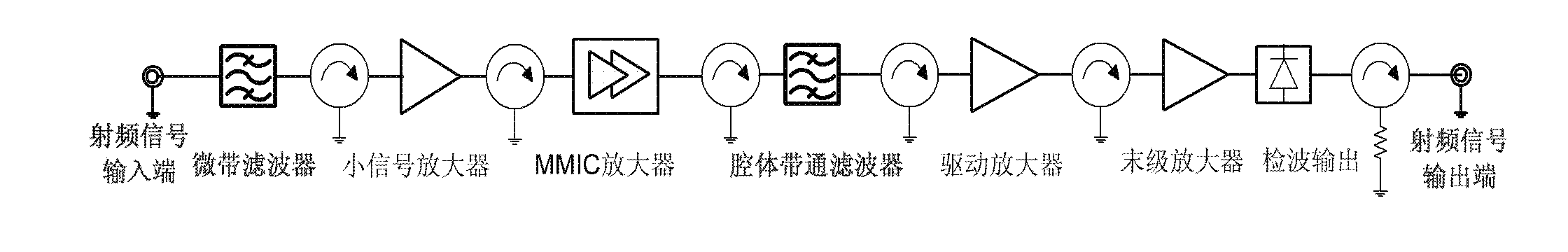
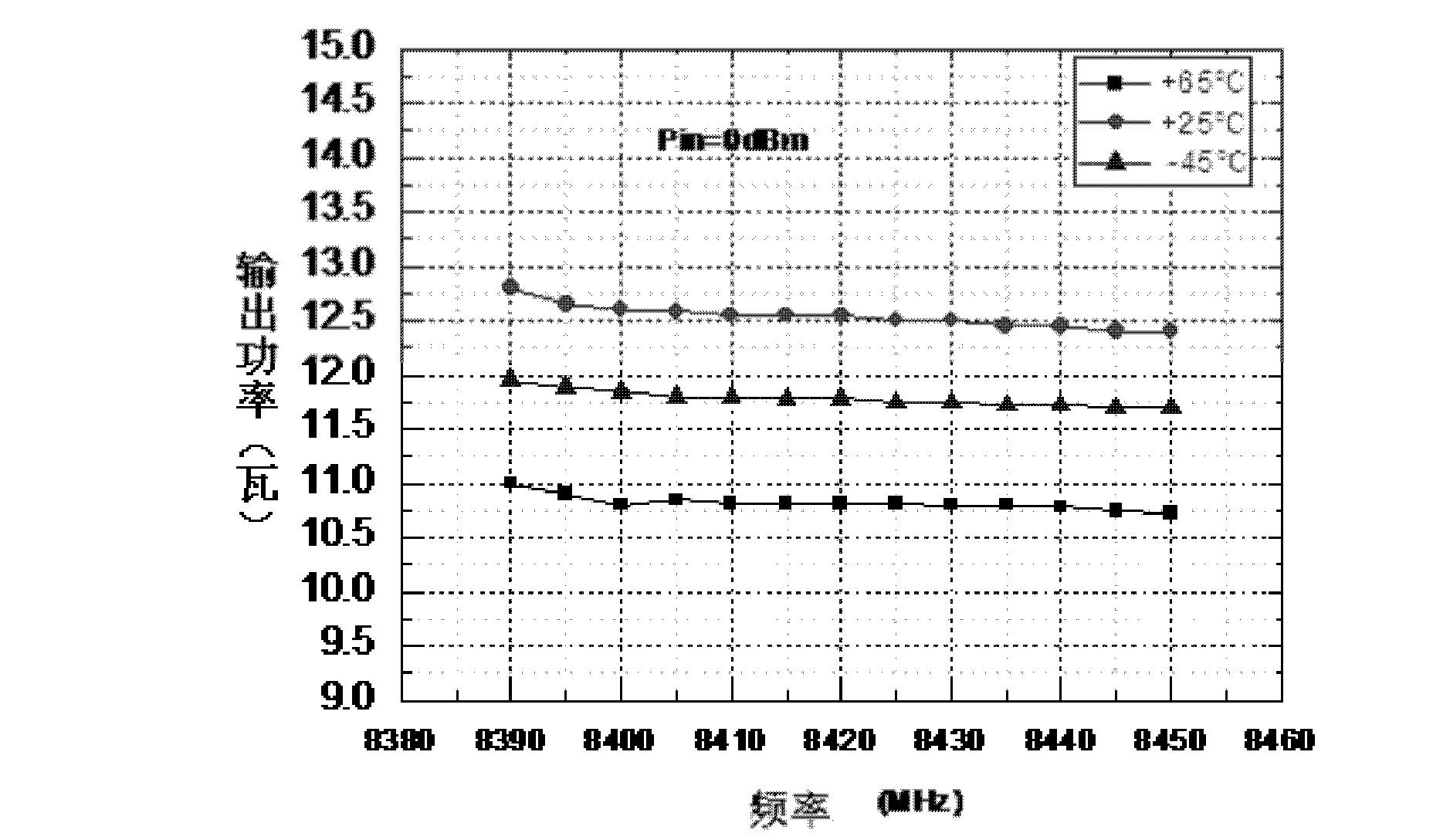
InactiveCN102611396AReduce the number of seriesAvoid concentrationPower amplifiersBand-pass filterEngineering
The invention relates to a microwave solid-state power amplifier. The power amplifier works at the environmental temperature ranging from -45 DEG C to +65 DEG C and is used for amplifying a beacon signal and a remote signal between the star and the ground in the communication task, and the solid-state power amplifier adopts multi-stage amplifier cascading, the power amplifier comprises a preamplifier, a driving power amplifier and a final power amplifier connected in series orderly; a microwave signal input end is connected with an input end of the preamplifier, an radio frequency input and output end of each amplifier circuit is connected with a micro-strip isolator; two X-waveband cavity band-pass filters are respectively connected between the microwave signal input end and the preamplifier input end and between an output end of the preamplifier and an input end of the driving power amplifier. The preamplifier also comprises a small signal amplifier and a high-gain microwave integrated power amplifier which are connected in series orderly.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Fin-tube type heat exchanger
ActiveCN104884889APrevent localized overheatingIncreased turbulenceRecuperative heat exchangersHeat exhanger finsInterior spaceTubing types
The present invention relates to a pin-tube type heat exchanger, comprising: tubes through the inside of which a heat medium flows and which are arranged in parallel with a uniform distance therebetween, so that a combustion product can pass through space between the tubes; and heat transfer fins which are separately coupled to the outer surface of the tubes along the lengthwise direction thereof, so as to be parallel to the direction of flow of the combustion product, wherein inside the tubes a first turbulent flow-generating member is installed for creating turbulence in the flow of the heat medium, wherein the first turbulent flow-generating member comprises a flat plate portion, arranged in the lengthwise direction of the tubes, for dividing the inner space of the tubes into two sides, and first guide pieces and second guide pieces which are protrudingly provided at a tilted angle and are separately and alternately provided along the lengthwise direction of both sides of the flat plate portion.
Owner:KYUNGDONG NAVIEN
Optical pickup and optical disk device
InactiveUS20060181970A1Reduce power consumptionReduce part costRecord information storageMountingsOptical pickupOptical axis
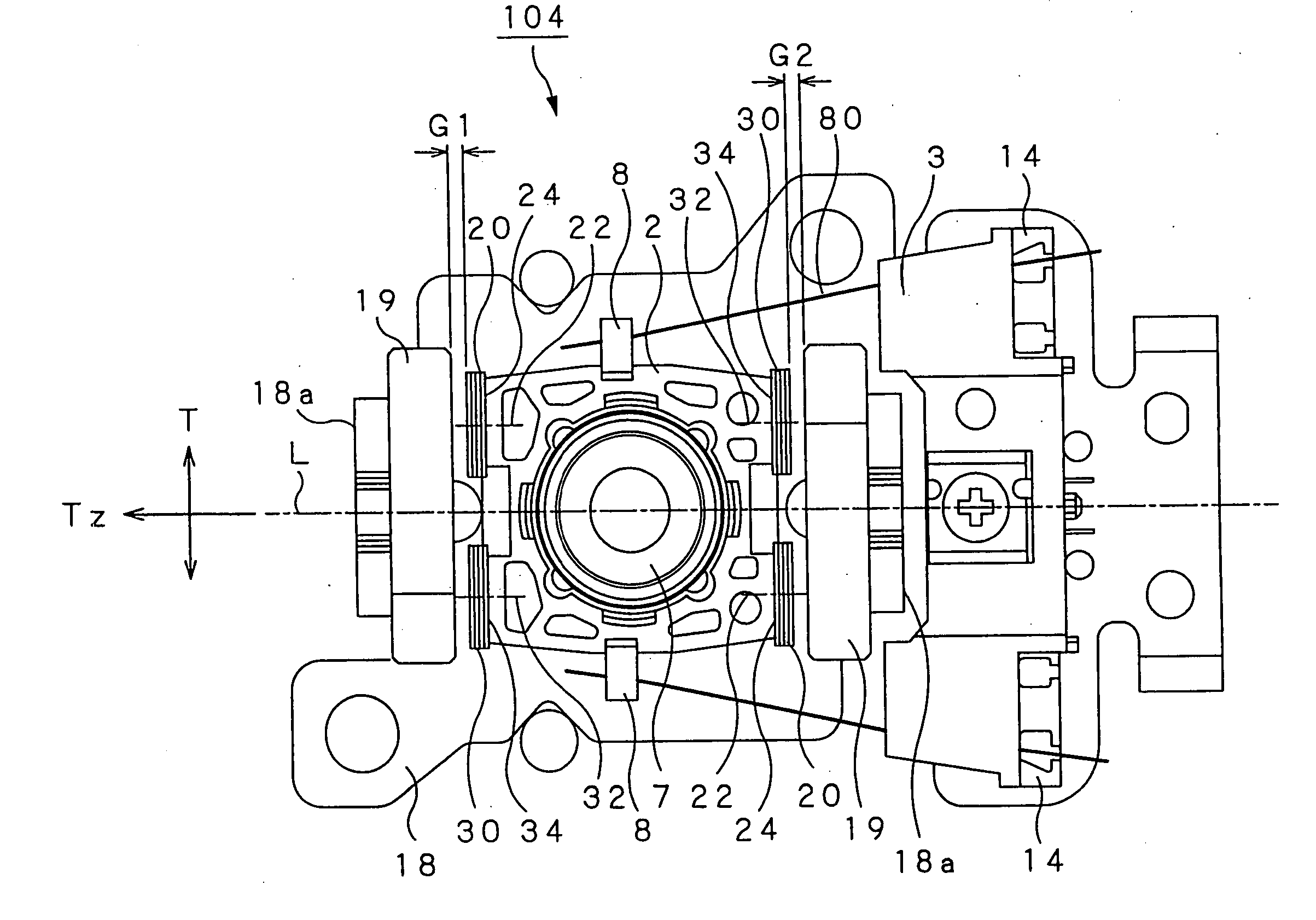
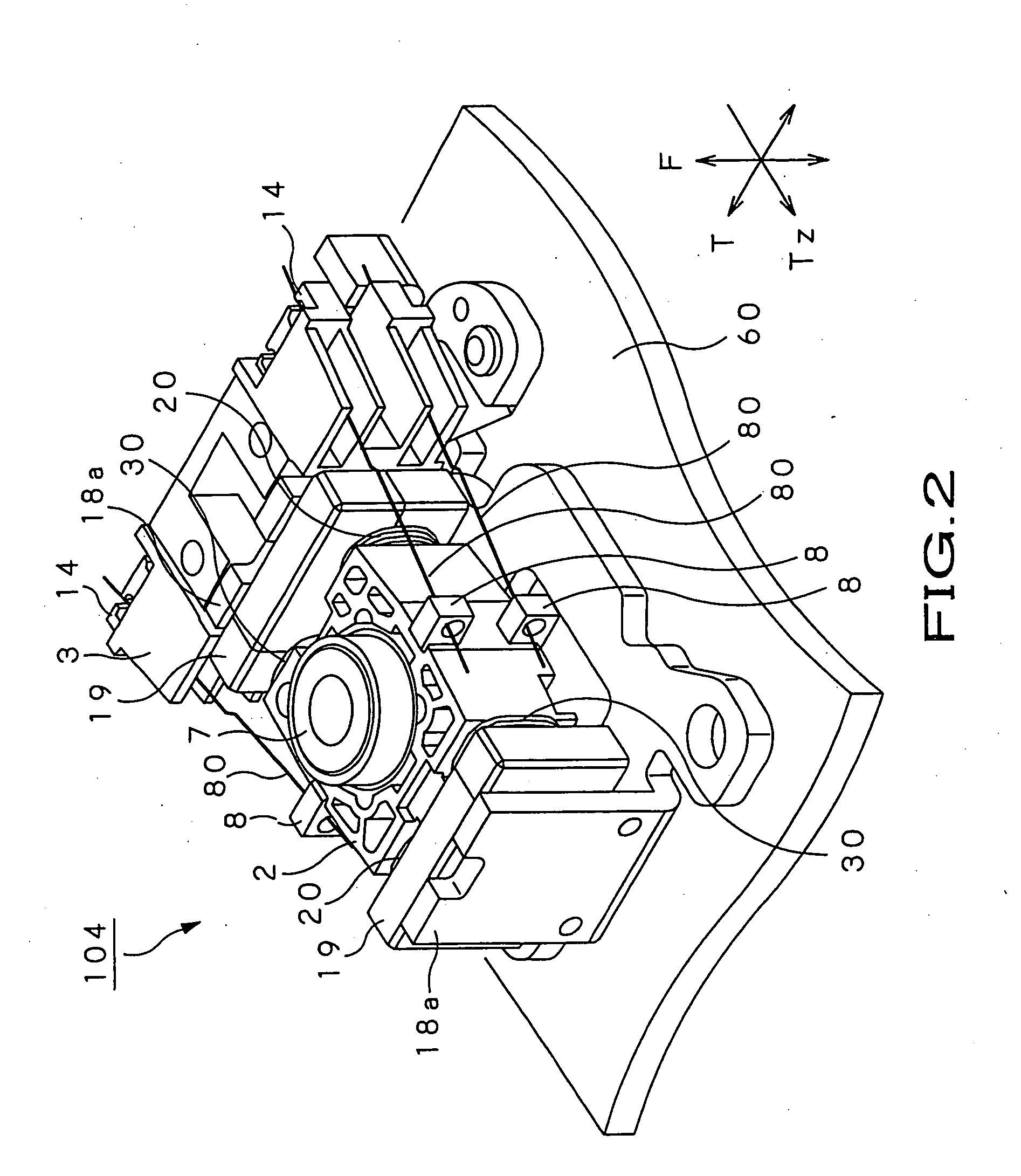
The present invention is directed to an optical pick-up adapted for moving an object lens (7) supported by a lens holder (2) in a focus direction in parallel to the optical axis direction thereof and in a tracking direction perpendicular to the focus direction, and for performing control of tilt angle serving to tilt the optical axis of the object lens following inclination of an optical disc. At the lens holder, there are provided a pair of focus coils (20) and a pair of tracking coils (30). The pair of focus coils have coil surfaces which are perpendicular to winding axes of coil portions constituting the respective focus coils and face magnets, and are so attached to the lens holder as to face the tangential direction with the object lens put therebetween, the pair of focus coils being shifted in left and right directions respectively away from a virtual axis which is perpendicular to the tracking direction and passes along the optical axis of the object lens, the coil surfaces being directed toward the tangential direction. By changing a drive force produced at the pair of focus coil portions, tilt angle of the object lens is controlled.
Owner:SONY CORP
Semiconductor Device
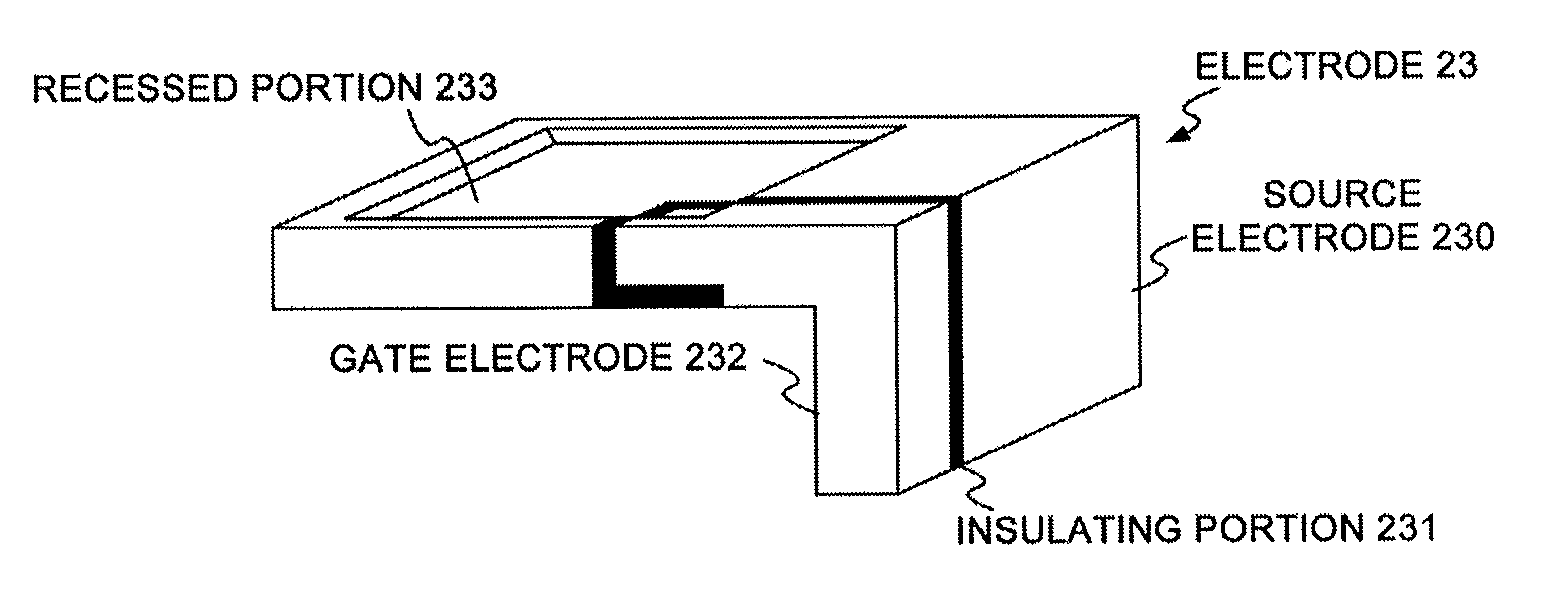
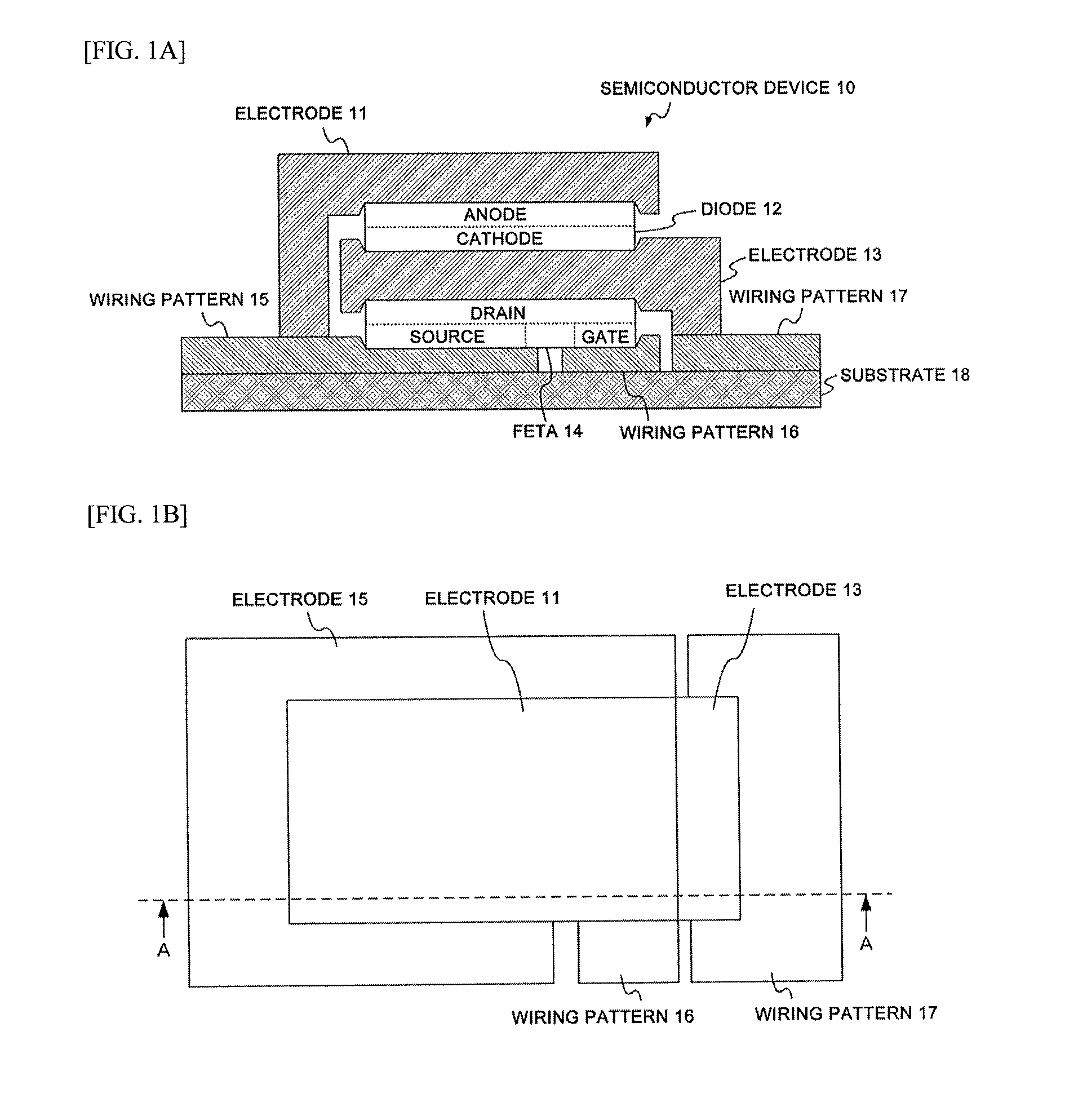
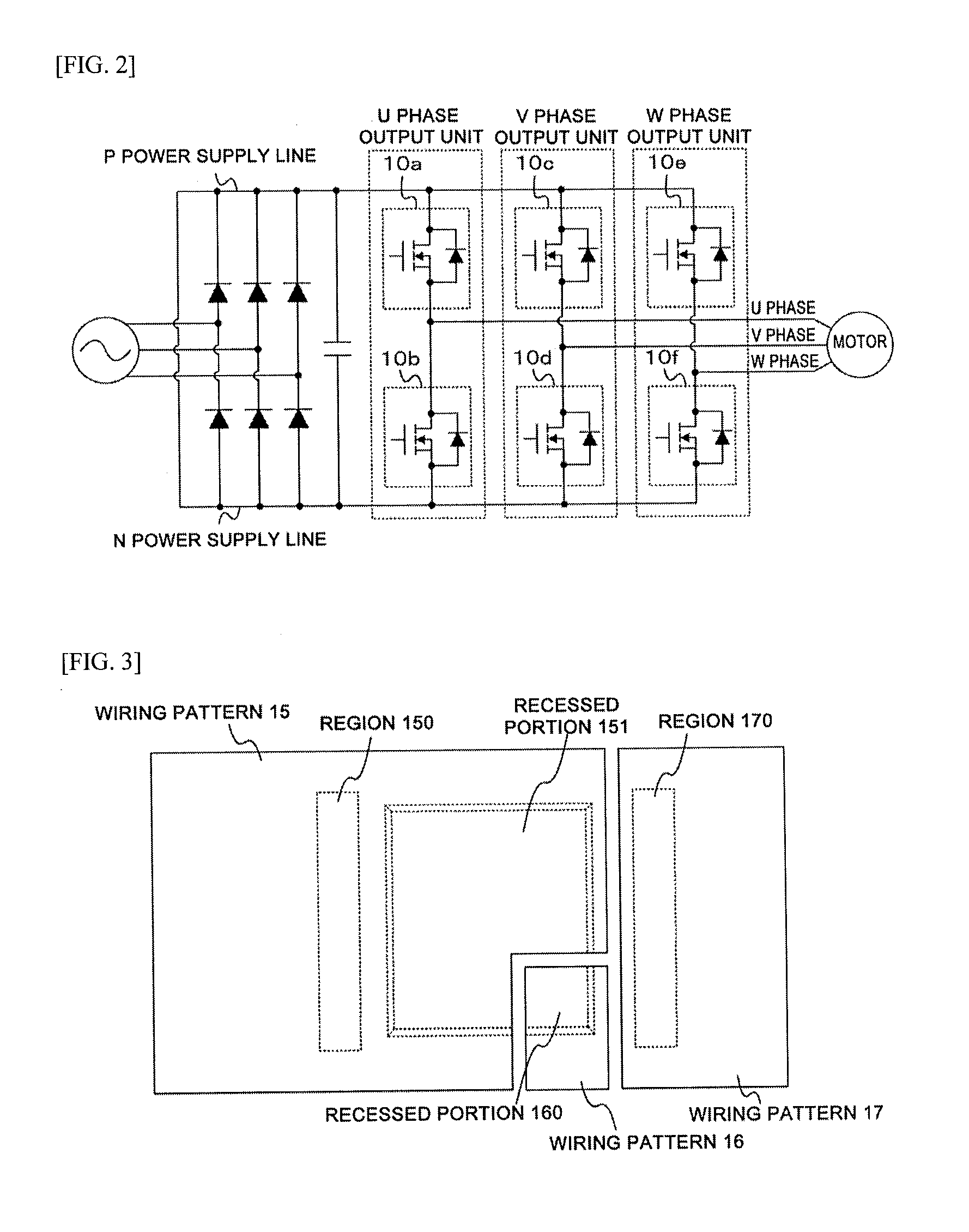
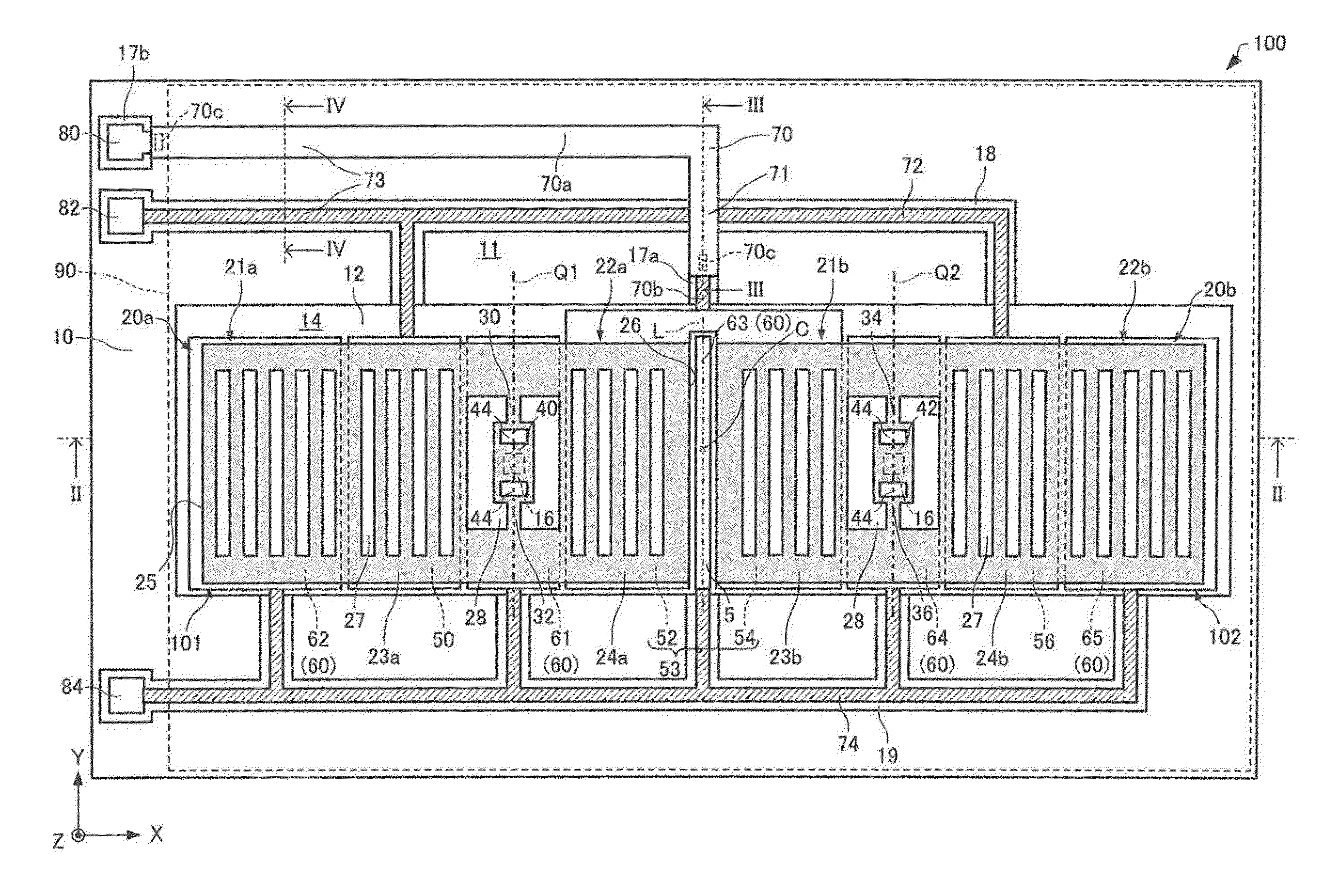
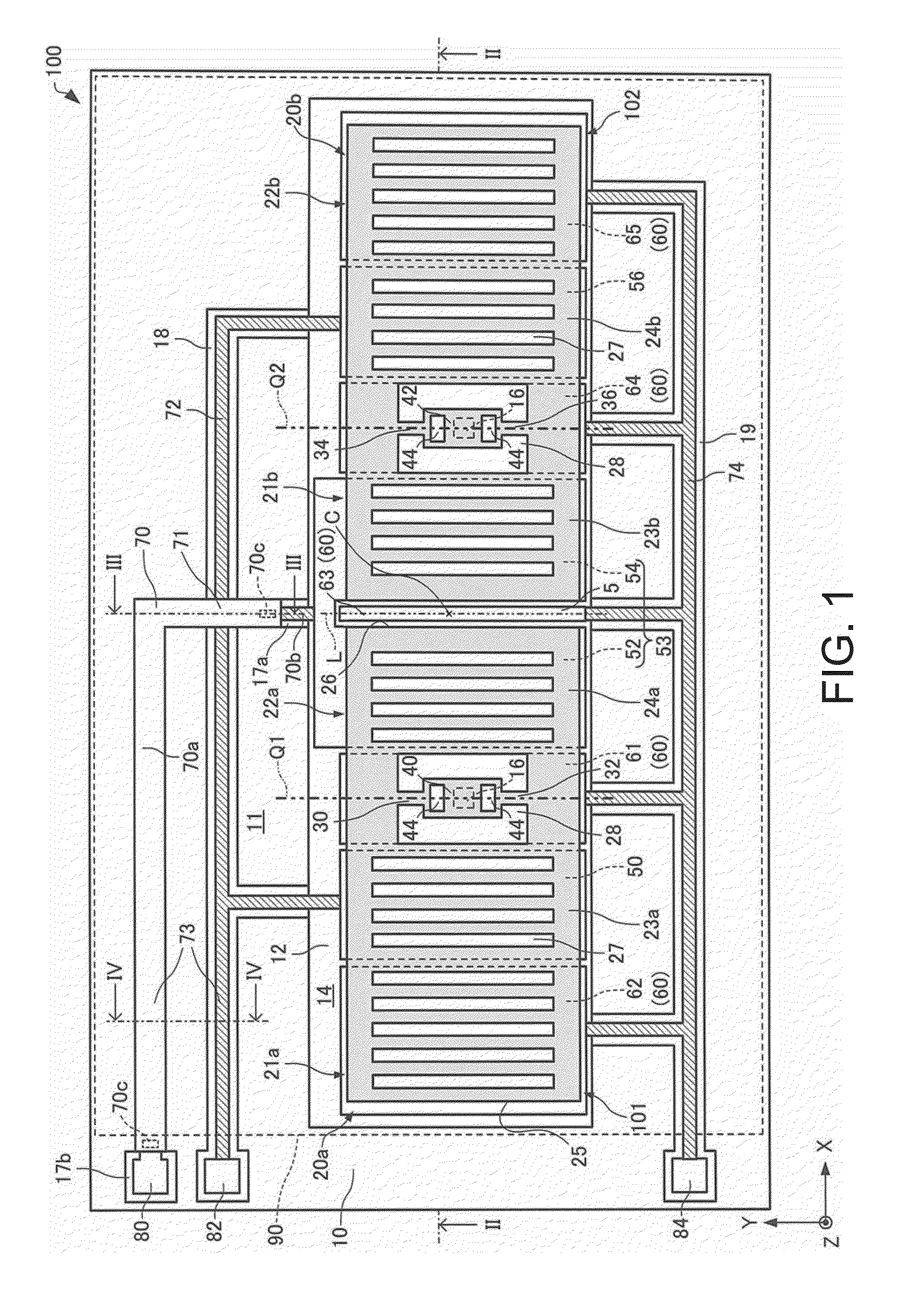
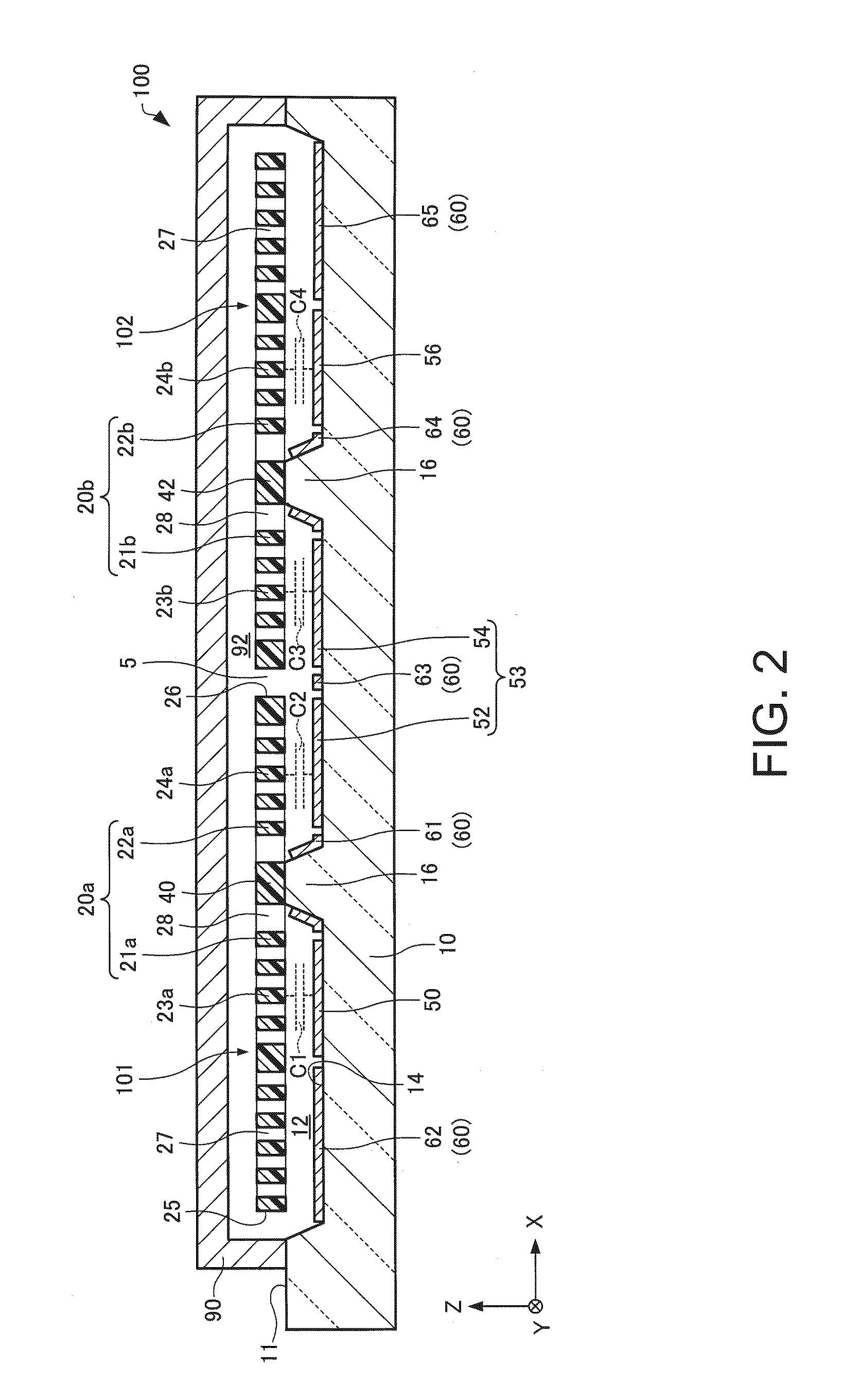
ActiveUS20150206864A1Realize miniaturizationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceMiniaturization
To realize further miniaturization of a semiconductor device.The semiconductor device 10 is provided with a switching element (FET 14) provided on a substrate 18, a first electrode (electrode 13) provided on an opposite side of the substrate 18 interposing the switching element, a diode 12 provided on an opposite side of the switching element interposing the first electrode, and a second electrode (electrode 11) provided on an opposite side of the first electrode interposing the diode 12.
Owner:MICRO MODULE TECH
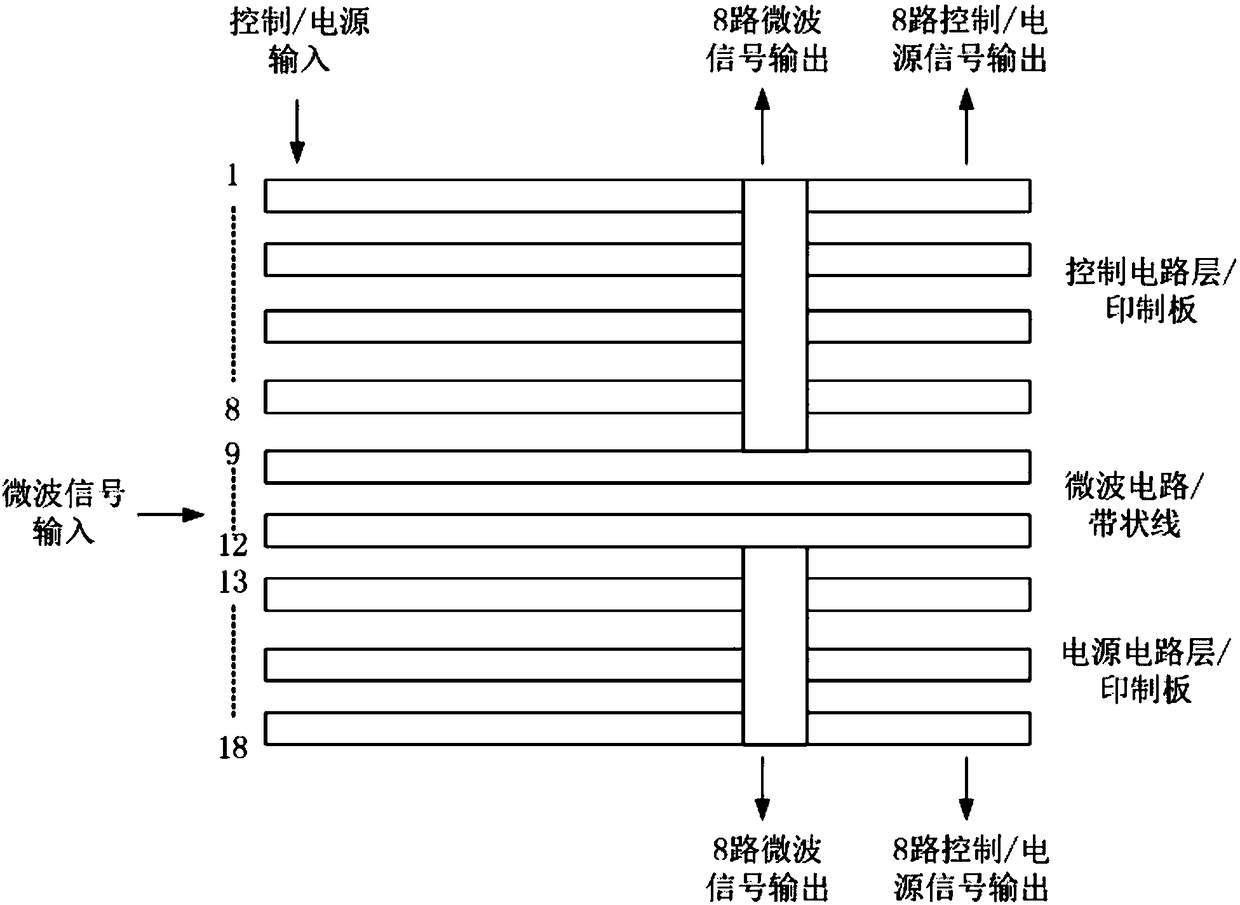
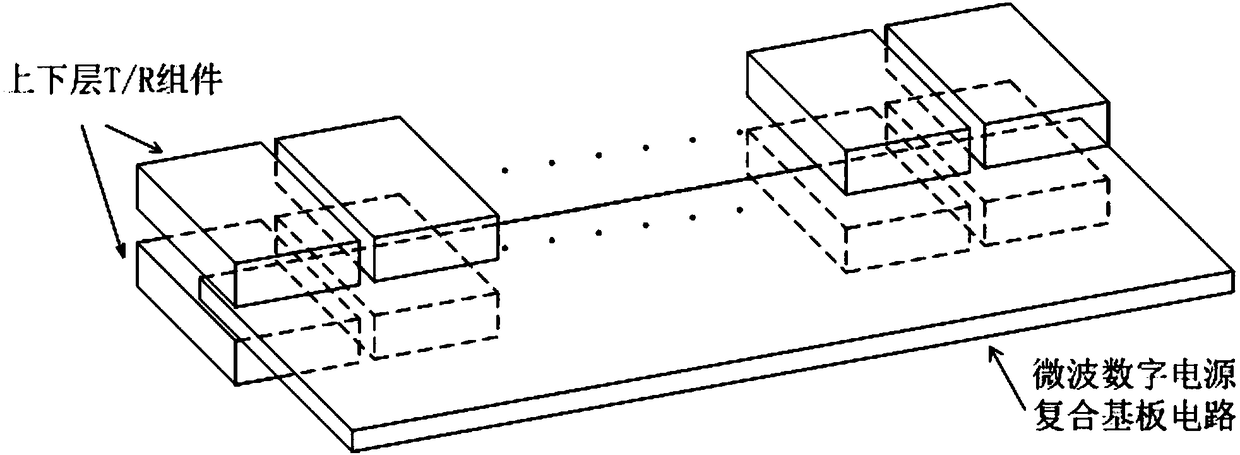
Microwave digital power supply composite substrate circuit based on sandwich structure and feeder device
InactiveCN108226870AReduce excess spaceReduce demandWave based measurement systemsControl signalComposite substrate
The invention provides a microwave digital power supply composite substrate circuit based on a sandwich structure and a feeder device. The microwave digital power supply composite substrate circuit ischaracterized in that the sandwich structure adopts a three-layer structure, namely a control circuit printing board, a microwave strip line and a power supply circuit printing board; the input end of a final-stage wave control circuit is connected with a photoelectric conversion module for input through optical fibers, and an access control signal and serial control data are allocated to each ofbranches of the microwave digital power supply composite substrate circuit for output; a double-sided vertical interconnection power division network adopts the design of integration of a linear power distribution network with a resistive film and double-sided vertical interconnection transformation; a final-stage power supply conversion circuit converts input voltage into multiple DC voltages for output, and instantaneous power output is provided for a final-stage active circuit. According to the sandwich structure, the complete composite substrate circuit is mixed and integrated, so that the space and weight requirements of an active phased array sub-array module can be greatly reduced, and the array surface light miniaturization is realized.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 38 RES INST
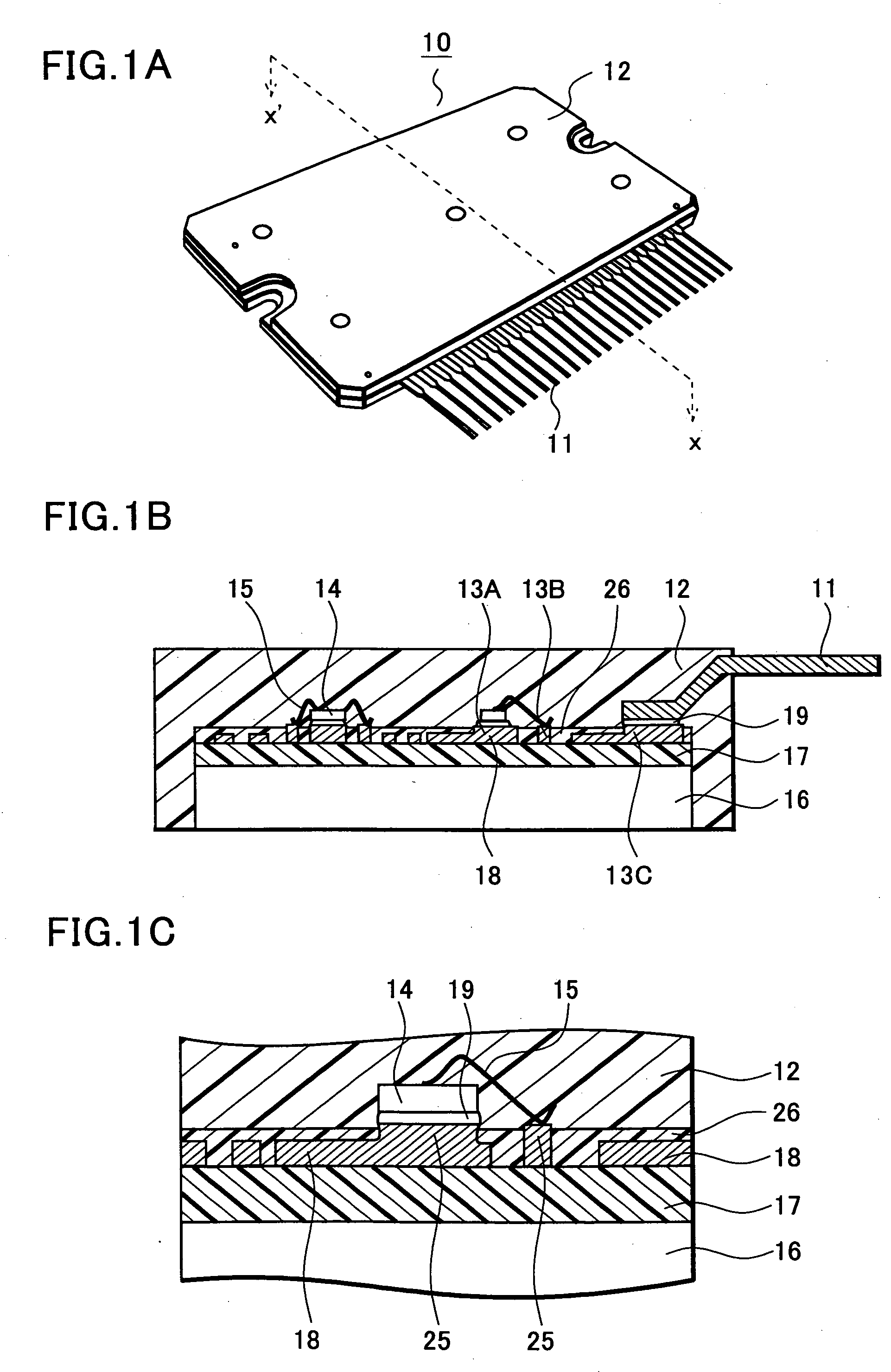
Method of manufacturing circuit device
InactiveUS20050263482A1Improve accuracyReduce manufacturing costPrinted circuit assemblingDecorative surface effectsElectrical connectionEngineering
In a method of manufacturing a circuit device of the present invention, protruding portions protruding upward are formed in part of a conductive pattern formed on the front surface of a circuit substrate. Next, the front surface of the circuit substrate including the protruding portions is coated with coating resin. Subsequently, the coating resin is etched so that the top surfaces of the protruding portions are exposed. Then, the fixation and electrical connection of circuit elements are performed. Finally, an electric circuit formed on the front surface is sealed, whereby a hybrid integrated circuit device is completed.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Separator for aluminium electrolytic capacitor, and aluminium electrolytic capacitor
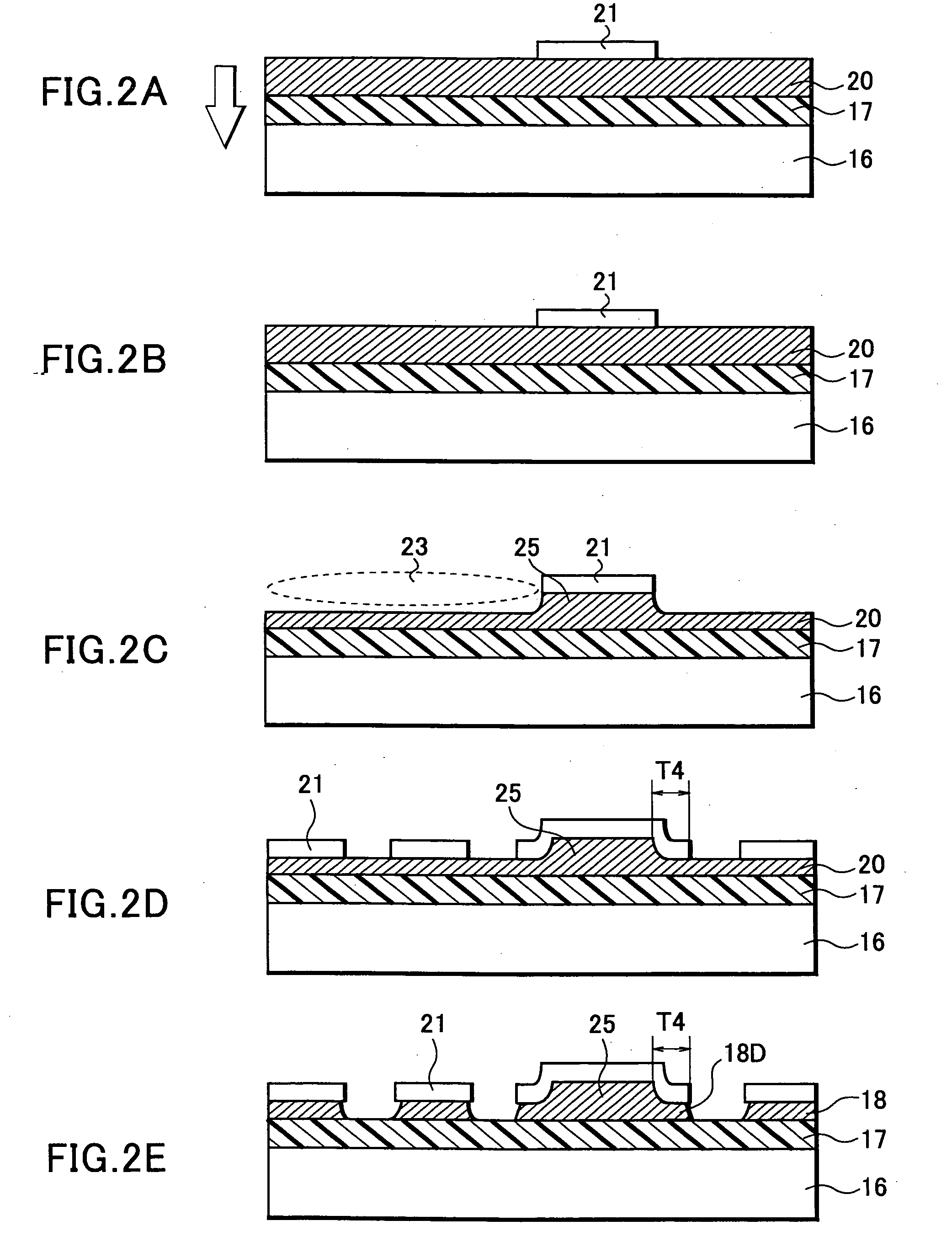
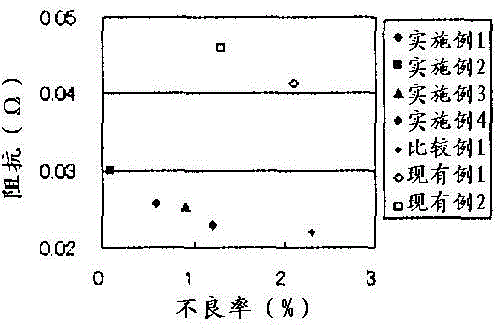
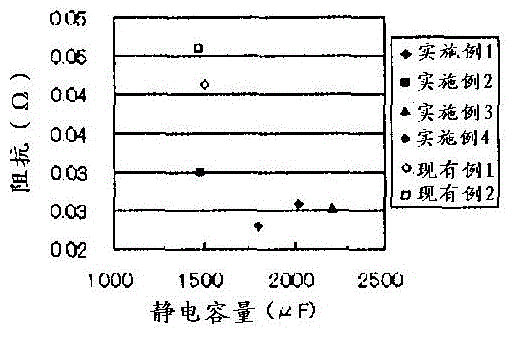
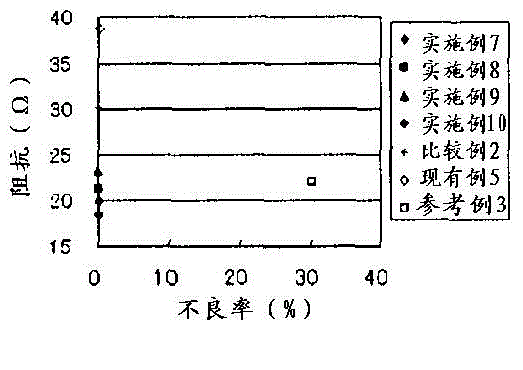
InactiveCN104919554ARealize miniaturizationIncrease capacityElectrolytic capacitorsAluminium electrolysisPhysical chemistry
[Problem] To provide a separator for an aluminium electrolytic capacitor and an aluminium electrolytic capacitor, the separator exhibiting excellent impedance characteristics and short-circuiting resistance, and comprising a cellulose porous membrane manufactured using an amine oxide cellulose solution. [Solution] A separator for an aluminium electrolytic capacitor and an aluminium electrolytic capacitor that is characterised by using the separator, the separator being formed from a cellulose porous membrane that comprises regenerated cellulose that has been dissolved and regenerated without forming a cellulose derivative, the cellulose porous membrane comprising regenerated cellulose that is obtained by forming a cellulose solution, which is cellulose dissolved in an amine oxide solvent or the like, into a membrane, solidifying and regenerating cellulose by immersing the membrane in water or a poor solvent of an amine oxide solvent, and, after having removed the amine oxide solvent from the regenerated cellulose, drying the result.
Owner:NIPPON KODOSHI
Solid-state image pickup device and driving method thereof
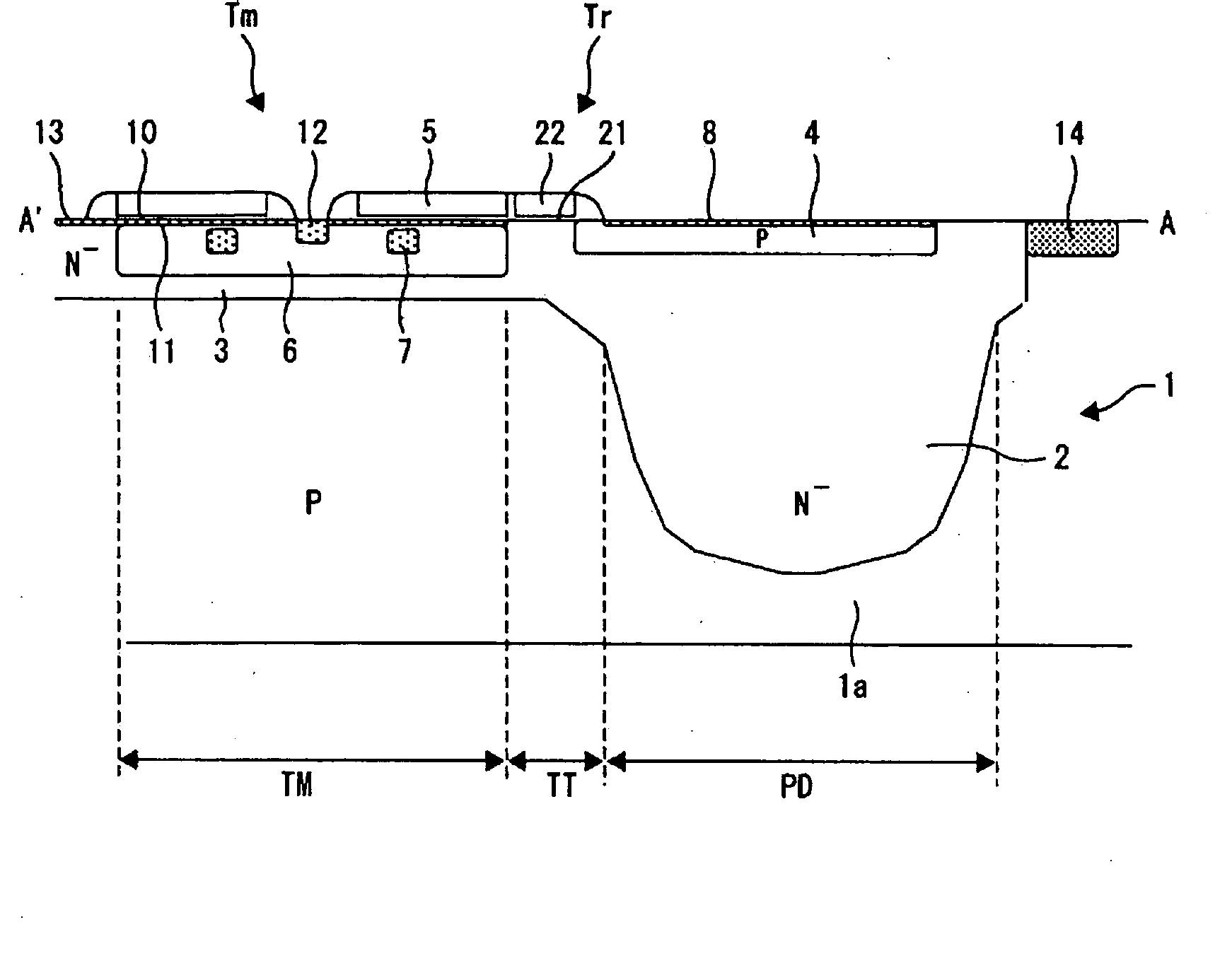
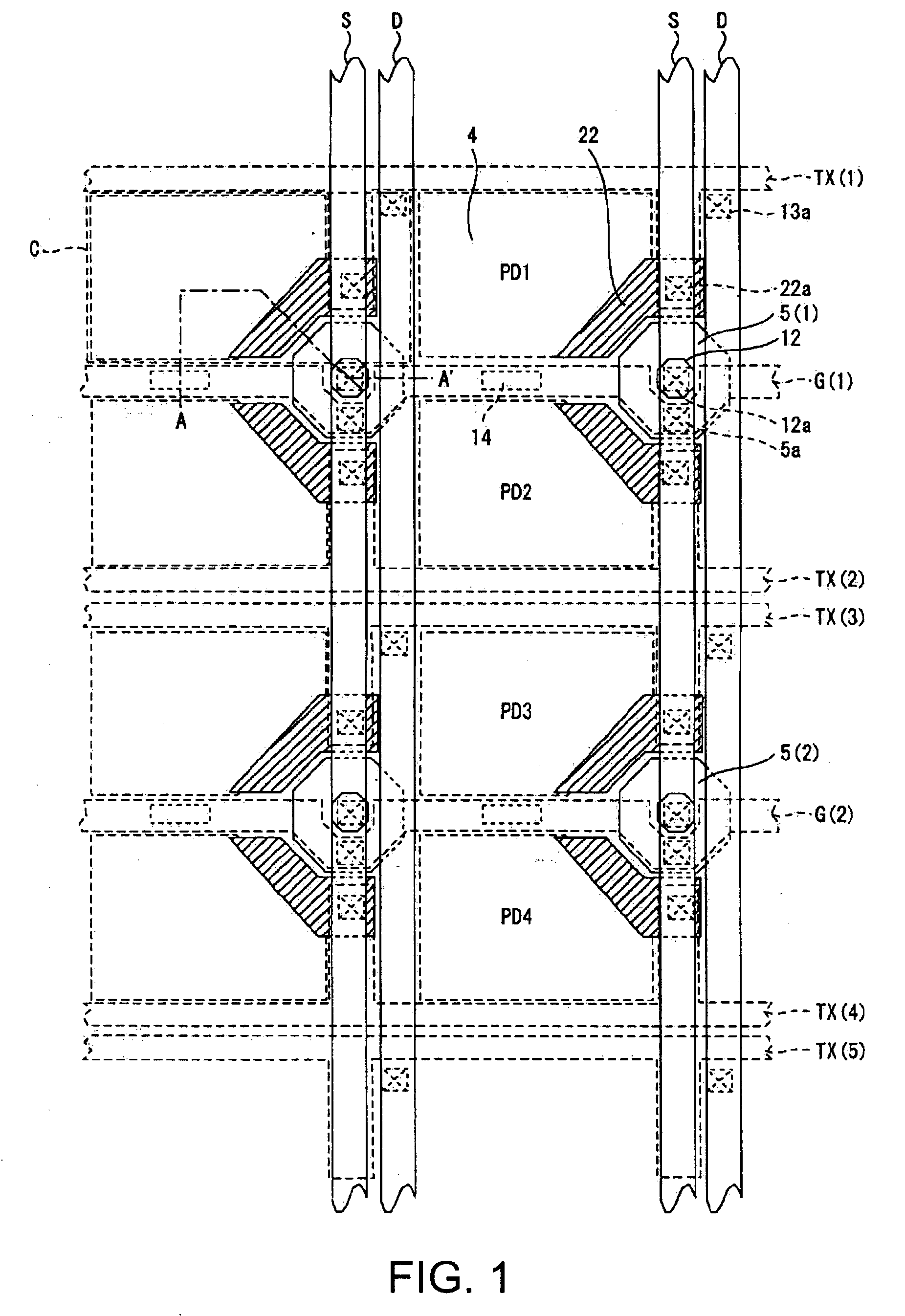
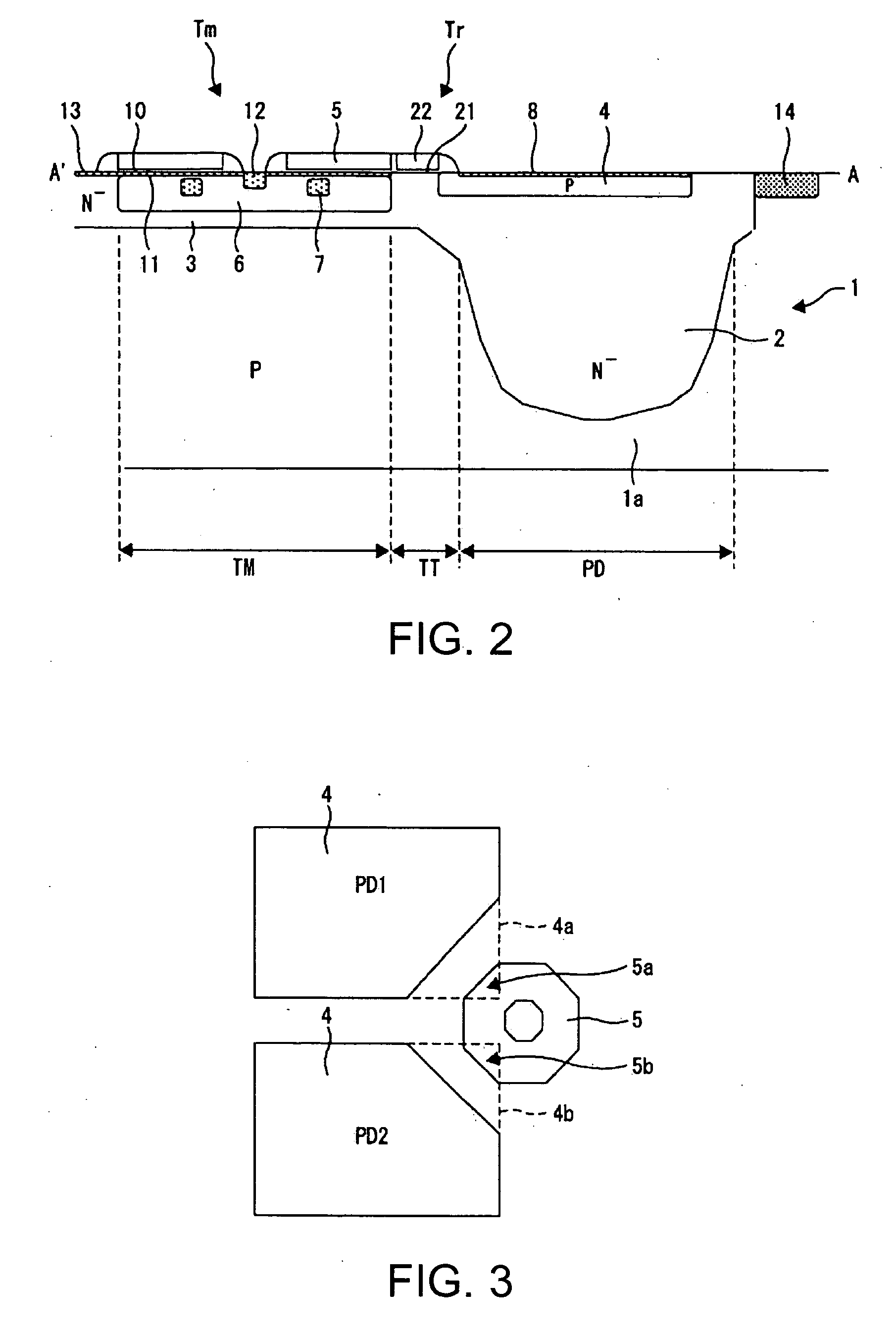
InactiveUS20060063295A1Realize miniaturizationTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesPhotoelectric conversionThreshold voltage
A solid-state image pickup device having inside a substrate a plurality of accumulation wells that accumulate light-producing electric charge produced in a photoelectric conversion region corresponding to light applied thereto, the plurality of photoelectric conversion regions being arranged in a two-dimensional matrix on the substrate, including: a plurality of modulation transistors, each of which is provided in every pair of the photoelectric conversion regions adjoined in one direction of the two-dimensional matrix, which control a threshold voltage of a channel using the light-producing electric charge held in a modulation well, and which output a pixel signal corresponding to the light-producing electric charge; a plurality of transfer control elements, each pair of which is provided in every pair of the adjoining photoelectric conversion regions, which shift a potential barrier of a path for transferring the light-producing electric charge between each accumulation well and the corresponding modulation well in the pair of photoelectric conversion regions, and which control the transfer of the light-producing electric charge; and a plurality of transfer gate lines coupled to each of the transfer control elements in the plurality of photoelectric conversion regions arranged in the other direction of the two-dimensional matrix; in that each gate of the plurality of modulation transistors is in a ring-like shape, each gate being provided in a manner that at least a portion of the gate is interposed between partially cut-off portions of every pair of the approximately rectangular photoelectric conversion regions adjoined in one direction of the two-dimensional.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Torque transmission device
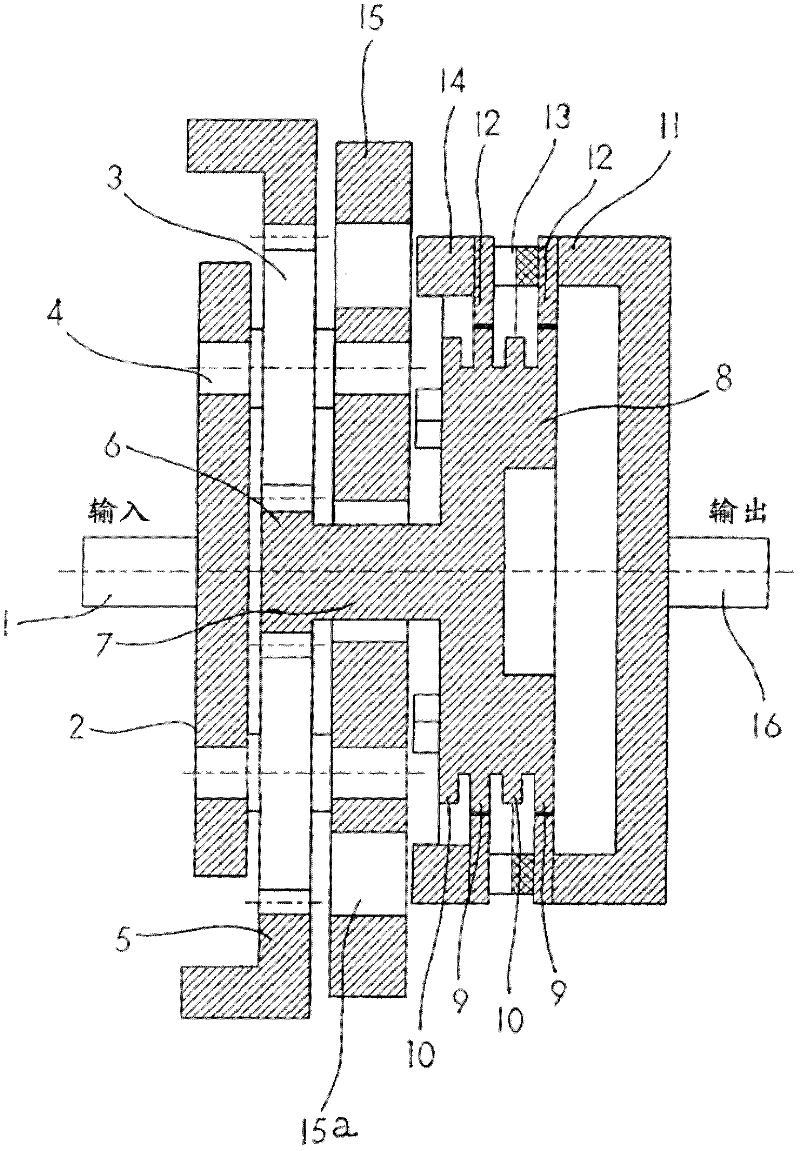
ActiveCN102575756AAuto switchReduce the numberToothed gearingsMagnetically actuated clutchesMagnetic tension forceLow load
A torque transmission device which is provided with a low torque input means (8), an output rotating means (11) which is magnetic-coupled to the low torque input means so as to generate thrust force by sensing a load, and a high torque input means (15) which is engaged with the output rotating means (11) to transmit the torque during the rotation of a high load, wherein the low torque input means (8) has pole teeth (9) which face magnetic poles (12) of the output rotating means so as to be magnetic-coupled during the rotation of a low load, and side section magnetic substances (10) which face the magnetic poles (12) slid by the thrust force generated by the relative rotation of the magnetic poles (12) and pole teeth (9) so as to be magnetic-coupled during the rotation of the high load, and wherein the output rotating means has the magnetic poles (12), a magnet (13); sandwiched between the magnetic poles (12), and a claw clutch section (14) which is engaged with the high torque input means (15) during the rotation of the high load. Conventional torque transmission devices have a problem of causing cases in which power transmission cannot be always sufficiently achieved, and the clutch capacity does not sufficiently function during a high load. Furthermore, the conventional torque transmission devices have a problem that a rotation-thrust conversion mechanism for operating a speed switching member has a hollow disk in which a permanent magnet is provided, and an output disk in which a magnet for moving the hollow disk, magnetic force for a magnetic cushion which gives return force to the hollow disk, or the like is provided, and, because the conversion mechanism, the configuration of which is complicated and the number of components of which is high in number is provided aside from a transmission body, the complicated and upsized configuration of a transmission and an increase in the number of components cause an increase in cost.
Owner:KITO CORP
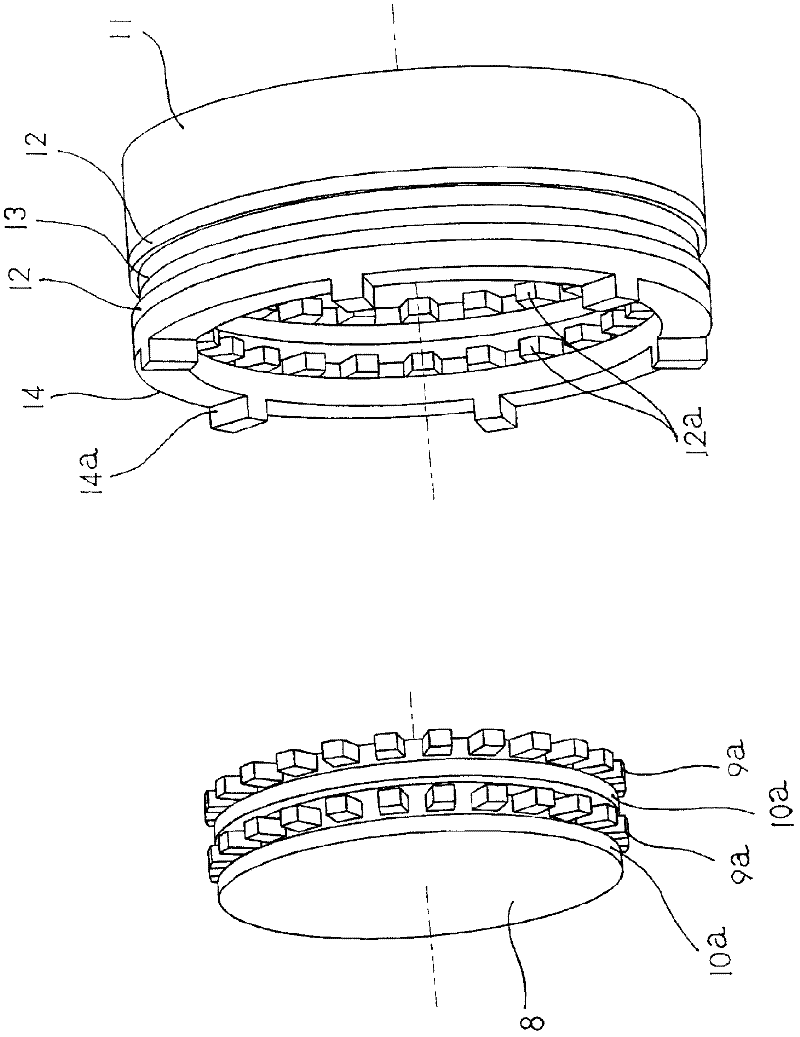
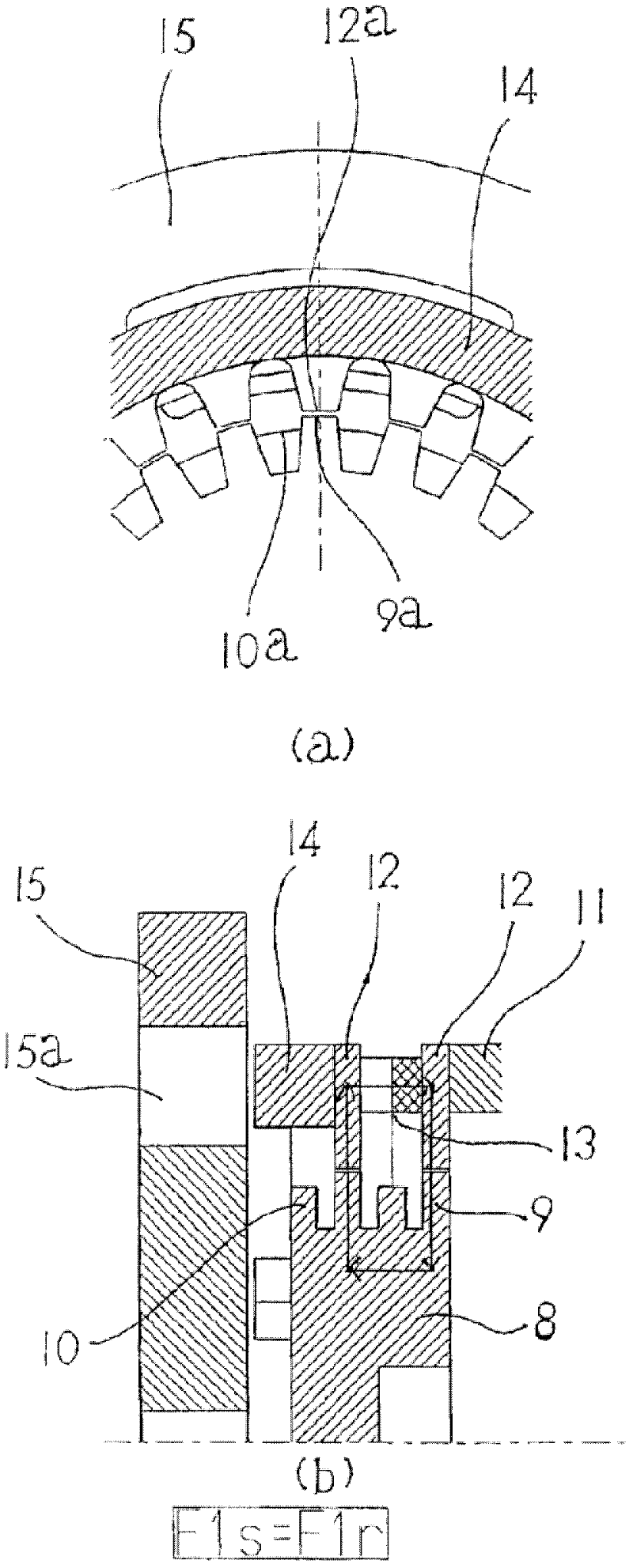
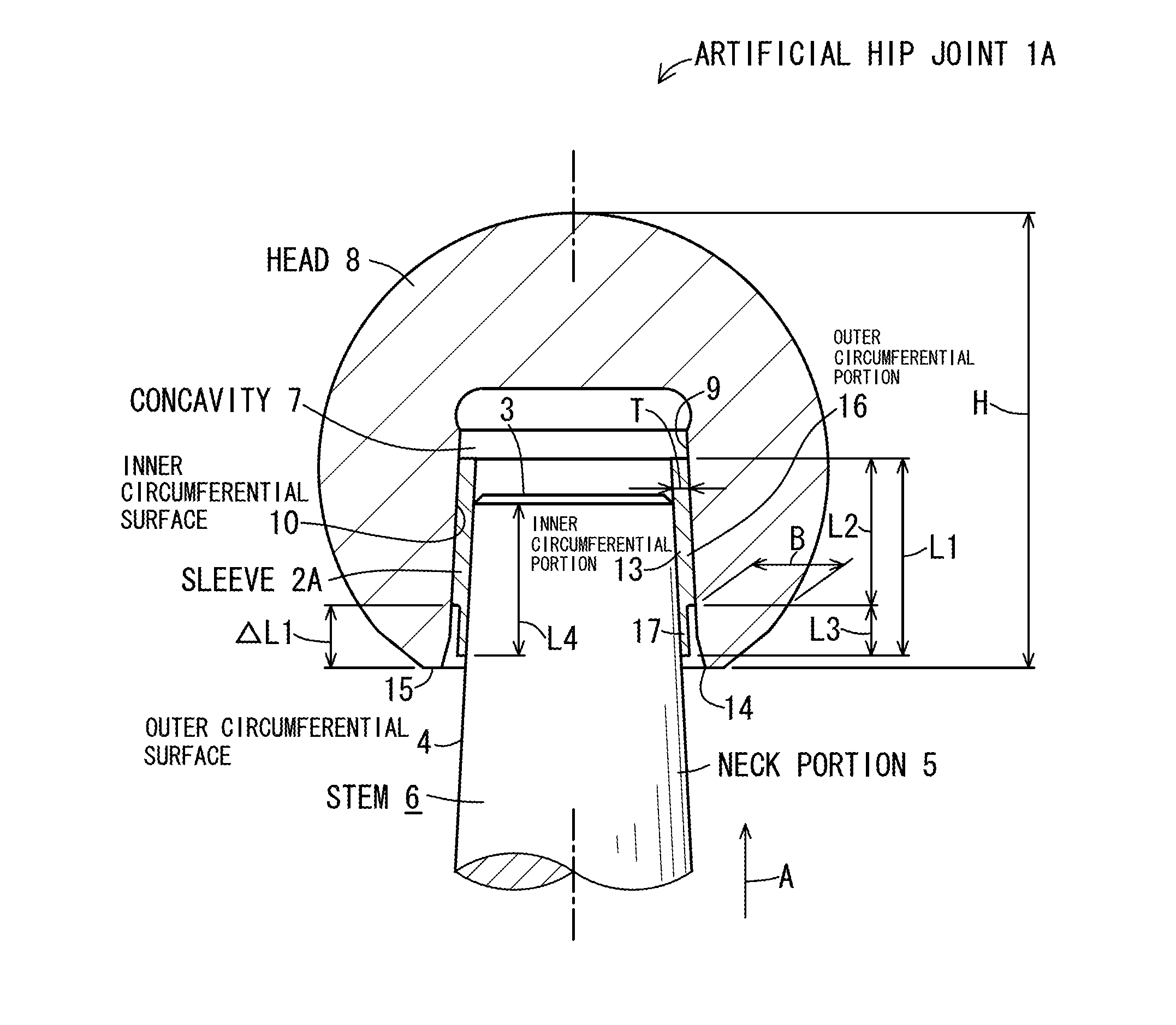
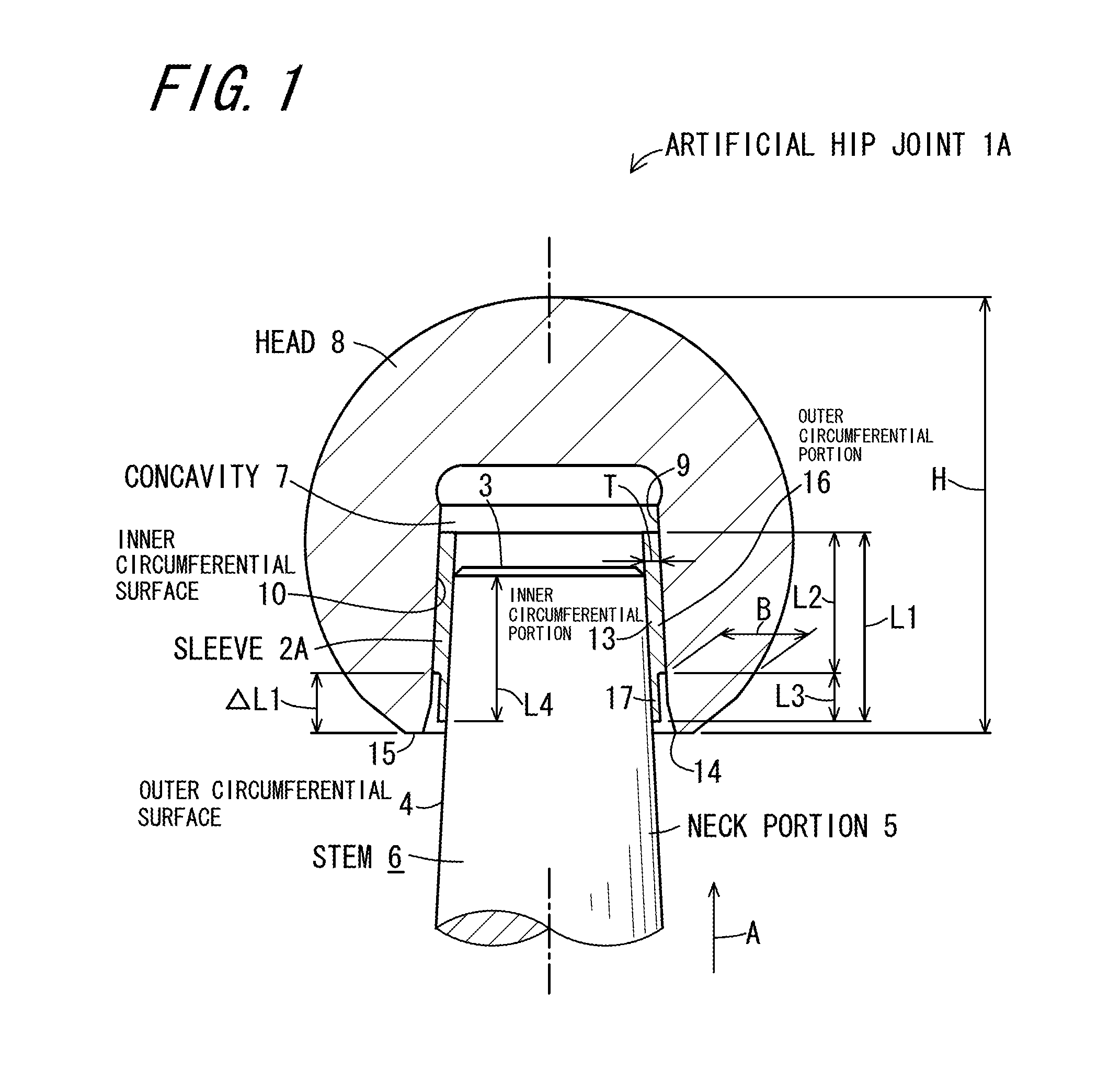
Artificial hip joint
InactiveUS20150272740A1Avoid insufficient lengthEnsure fixing strengthJoint implantsFemoral headsArtificial hip jointsBiomedical engineering
An artificial hip joint includes a stem having a neck portion which has a truncated conical outer circumferential surface decreased in diameter toward a tip thereof; a head provided with a concavity in which the neck portion is inserted, an inner surface of the concavity including a truncated conical inner circumferential surface decreased in diameter toward an insertion direction of inserting the neck portion; and a sleeve inserted between the outer circumferential surface of the neck portion and the inner circumferential surface of the head. The sleeve has an inner circumferential portion which makes contact with the outer circumferential surface of the neck portion, and an outer circumferential portion which makes contact with the inner circumferential surface of the head, a starting end of the outer circumferential portion being located at a position retracting from an opening portion of the concavity in the insertion direction.
Owner:KYOCERA MEDICAL CORP
Physical quantity sensor, electronic device, and moving object
InactiveUS20160041198A1Realize miniaturizationOptimize layoutAcceleration measurementForming microstructural systemsEngineeringPhysical quantity
A physical quantity sensor according to the embodiment includes: a substrate; a first movable body which is disposed on the substrate, can be displaced around a first support shaft, and includes a first movable electrode portion; a second movable body which is disposed on the substrate, can be displaced around a second support shaft, and includes a second movable electrode portion; and a fixed electrode portion which is overlapped on the first movable electrode portion and the second movable electrode portion and is disposed on the substrate in a plan view.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
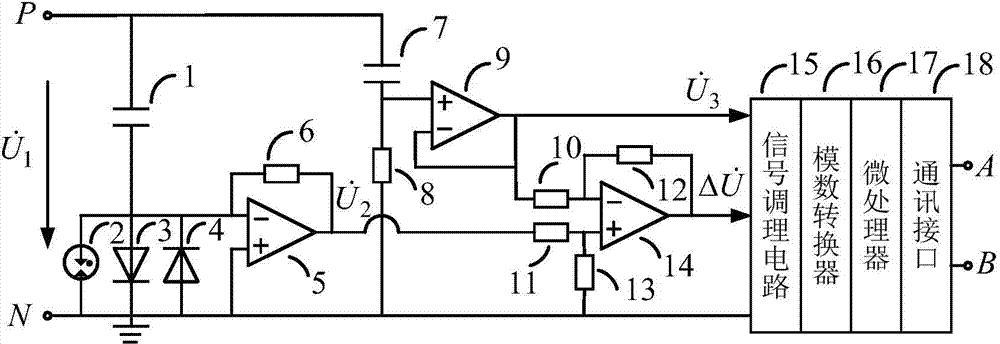
Electronic type voltage transformer based on capacitor and resistance-capacitance voltage divider parallel connection
ActiveCN104764915AAvoid serious impactRealize miniaturizationVoltage dividersMeasurement using digital techniquesTransformerHigh voltage capacitors
The invention discloses an electronic type voltage transformer based on capacitor and resistance-capacitance voltage divider parallel connection. The electronic type voltage transformer comprises a first capacitor, a second capacitor, a diode gas discharge tube, a first power diode, a second power diode, a first operational amplifier, a second operational amplifier, a third operational amplifier, a first resistor, a second resistor, a third resistor, a fourth resistor, a fifth resistor, a sixth resistor, a signal conditioning circuit, an analog-digital converter, a microprocessor and a communication interface. A primary sensor is formed by connecting the capacitors with a resistance-capacitance voltage divider in parallel, two routes of signals output by the primary sensor are calculated, fundamental components and harmonic components of primary voltage are measured, the accuracy error problems caused by element nominal error, temperature drift and the like of primary sensors of resistance voltage dividers, capacitance voltage dividers, the resistance-capacitance voltage dividers and the like are solved, the high voltage capacitors can be monitored online, and guarantees are provided for long-time safe running of the transformer.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Method of manufacturing a semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060131365A1Well formedMiniaturizationSolid-state devicesWelding apparatusEngineeringPolyimide membrane
Realization of the projection electrode formation with a narrow pad pitch is planned. In preparing a semiconductor wafer, by forming a polyimide film, which does not cover each of a plurality of lands, between the respective lands which adjoin each other among the plurality of lands on the main surface of the semiconductor wafer, applying a soldering paste material with the printing method via the mask for printing on each of a plurality of lands after polyimide film formation, and forming a solder bump by performing heat curing of the soldering paste material after removing the mask for printing, a solder bump can be formed without generating a electric short circuit between bumps even in the case of a narrow pad pitch.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Single-side touch liquid type quartz crystal microbalance detector
InactiveCN104792649AReasonable designSimple structureMaterial weighingQuartz crystal microbalanceEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of sensing detection, and particularly relates to a single-side touch liquid type quartz crystal microbalance detector. The single-side touch liquid type quartz crystal microbalance detector comprises a detection tank and a quartz crystal wafer sensor, wherein the detection tank comprises a seal cover, a liquid filling tank, an annular washer I and an annular washer II, wherein the center of the seal cover is provided with a cylindrical groove; a first seal cover through hole and a second seal cover through hole are respectively formed in two sides of the cylindrical groove; the liquid filling tank is of an L shaped structure, and is provided with a sample charge hole and a sensing contact hole which are perpendicular to each other and are communicated with the cylindrical through hole; a left threaded hole and a right threaded hole are respectively formed in two sides of the sensing contact hole of the liquid filling tank. According to the single-side touch liquid type quartz crystal microbalance detector, the design is reasonable, the structure is simple, the size is small, the liquid consumption amount is small, and the sensor can be detached and can be used repeatedly, and the stability is relatively high.
Owner:谭亮 +2
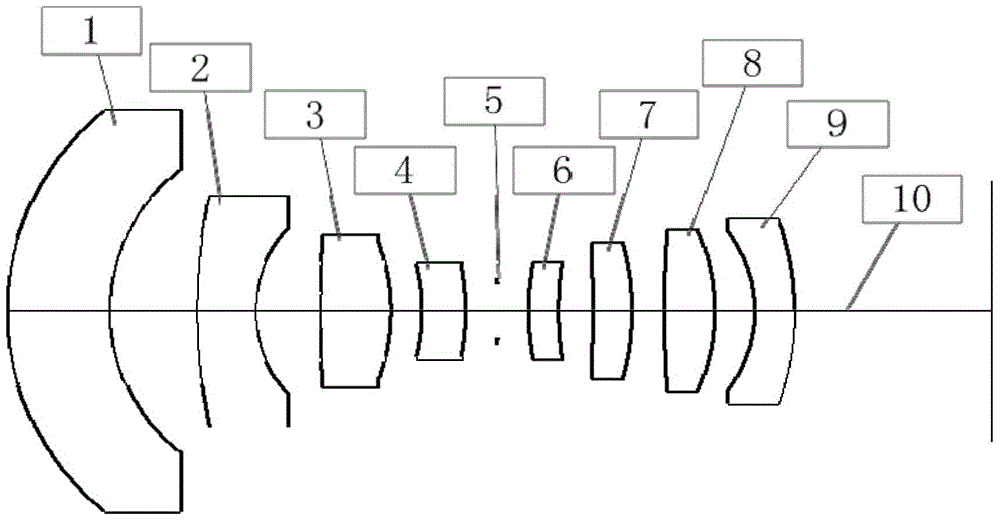
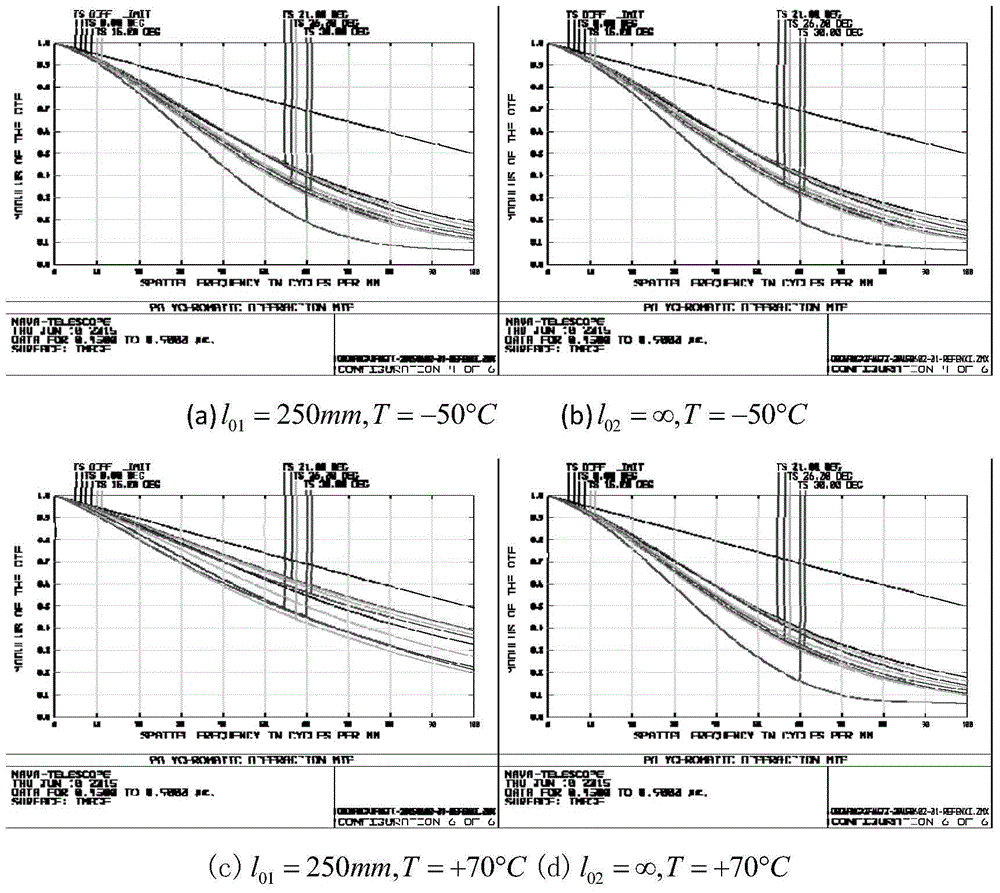
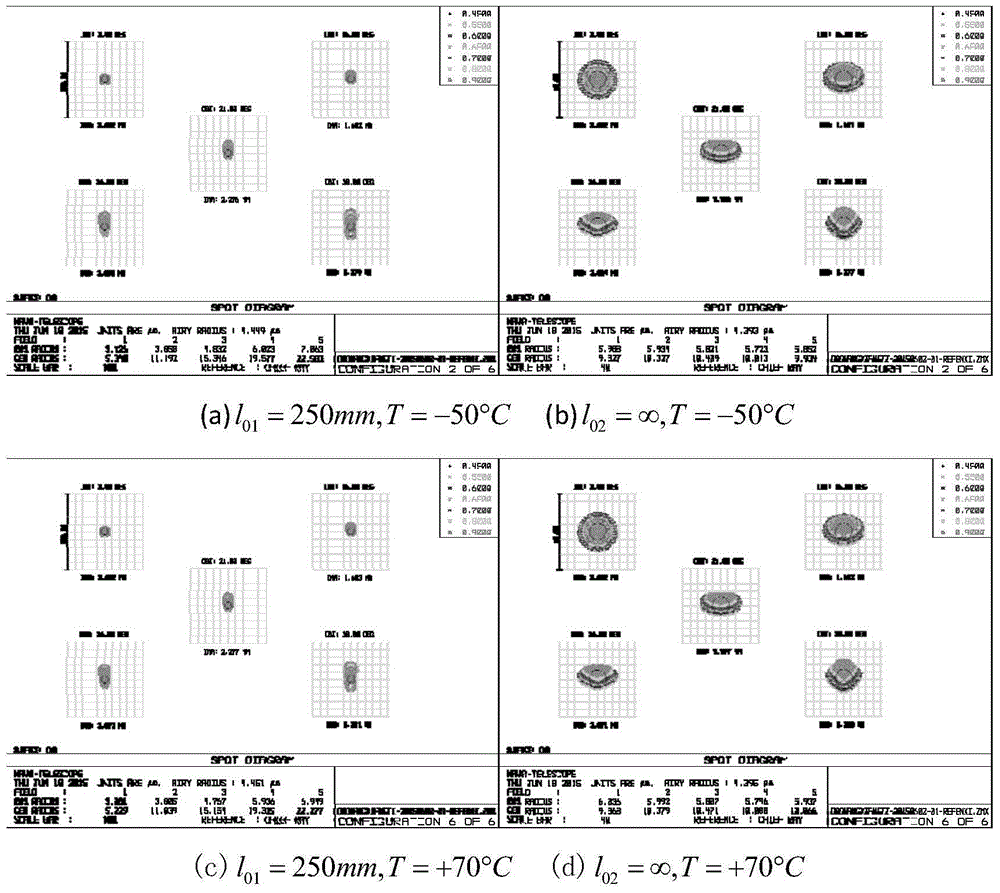
Large-field-depth large-view-field wide-temperature-variance high-image-quality optical system
ActiveCN105759394AEasy to correctImprove radiation resistanceOptical elementsSpace environmentImaging quality
The invention relates to a large-field-depth large-view-field wide-temperature-variance high-image-quality optical system. A first negative lens, a second negative lens, a first positive lens, a third negative lens, a diaphragm, a second positive lens, a third positive lens, a fourth positive lens and a fourth negative lens which are successively arranged on an optical path. The large-field-depth large-view-field wide-temperature-variance high-image-quality optical system provided by the invention facilitates correction of field curvature, effectively resists complex particle irradiation in space, prevents degumming in a complex space environment and is applied to space environment.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
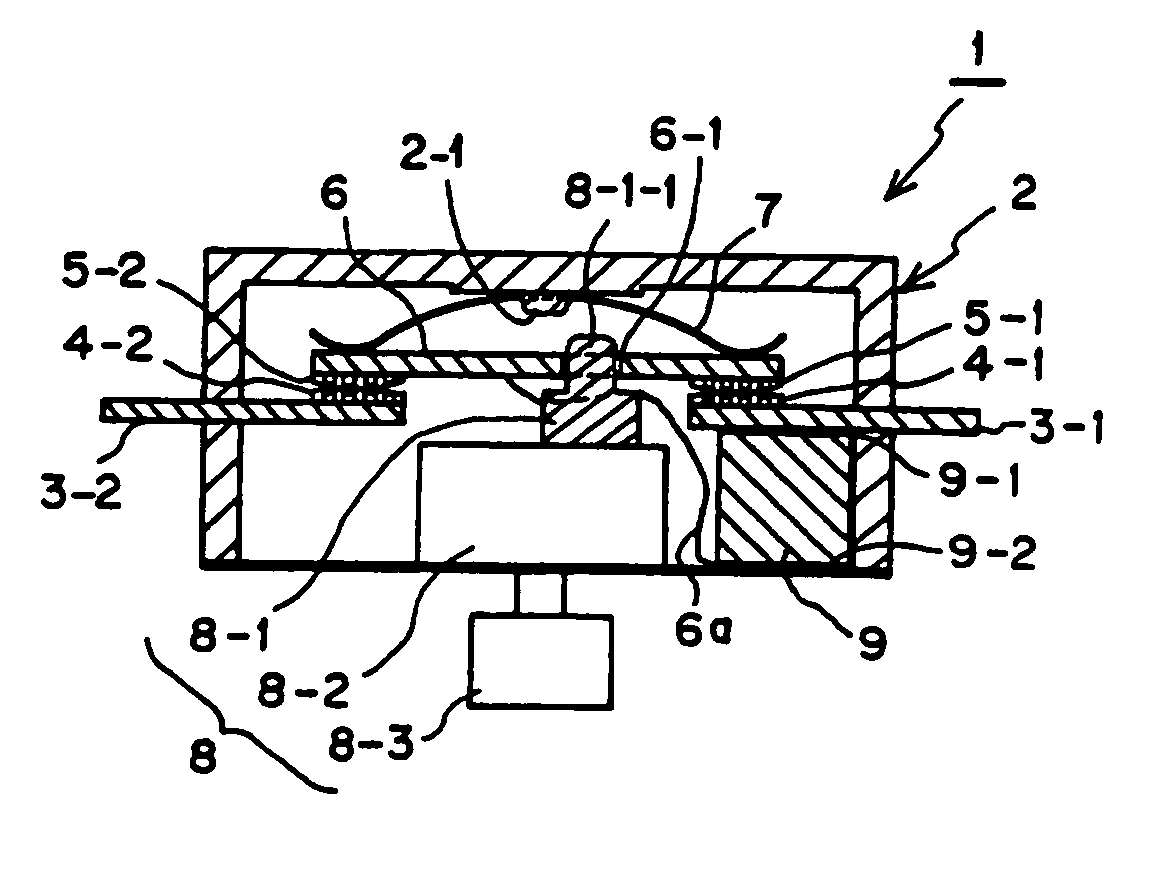
Direct current cutoff switch
InactiveUS20050189206A1Easy to useDirect currentSnap-action arrangementsThermal switch detailsNonlinear resistorEngineering
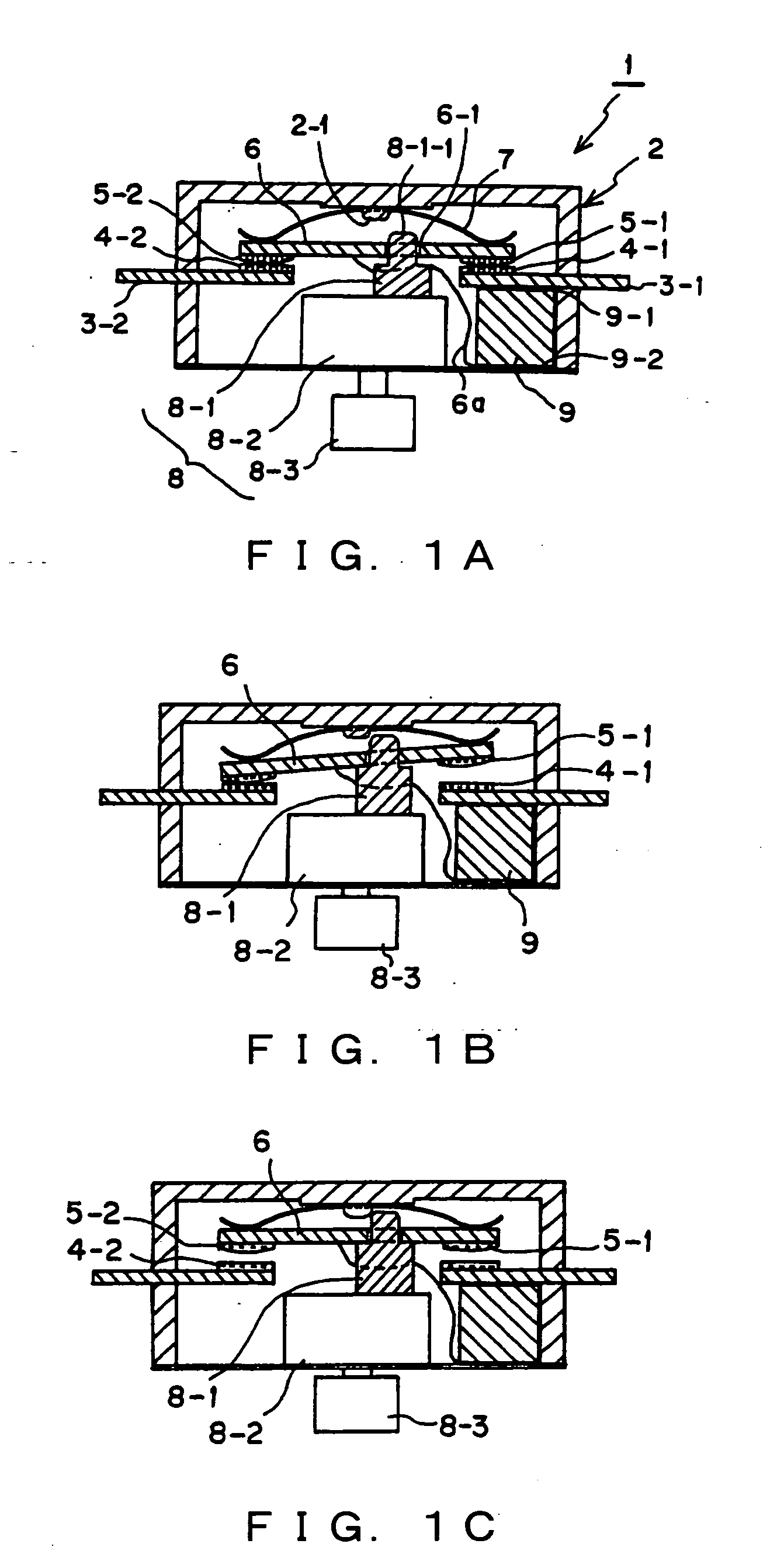
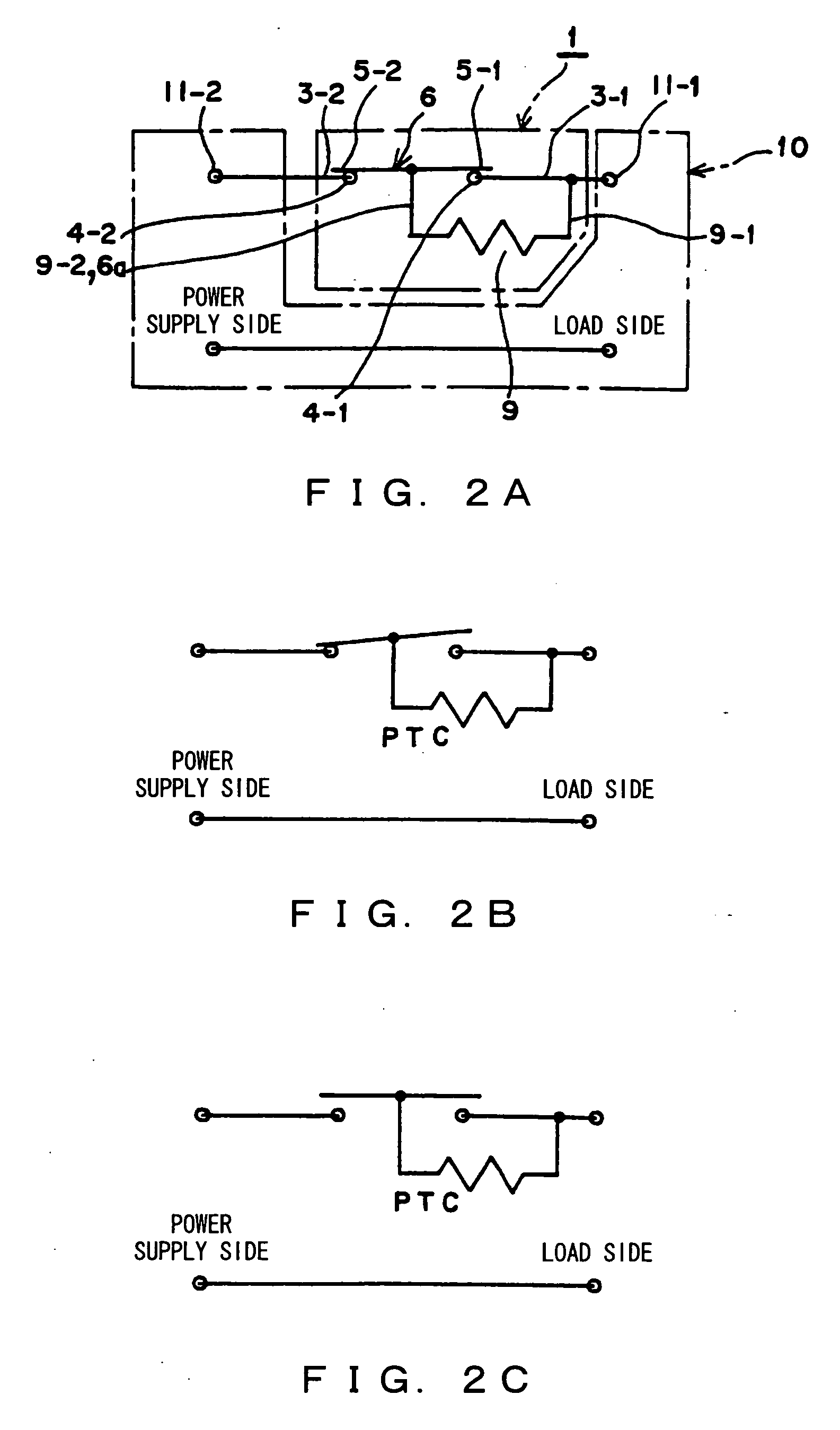
In a manually operated switch for cutting off direct current, a PTC 9 as a non-linear resistor is parallel connected to a contact circuit composed of a first fixed contact 5-1 and a first movable contact 4-1, via a connecting unit 3-1, a top electrode 9-1, a bottom electrode 9-2, a connecting wire 6a and a movable unit 6. Firstly, the first fixed contact 5-1 and the first movable contact 4-1 are opened. However, since the PTC 9 is parallel connected and the contact circuit forms a closed circuit, surge voltage is difficult to occur, and cutoff current flows in the PTC 9. After peak current passes by the decrease of a resistance value due to the instantaneous heating of the PTC 9, voltage returns to power supply voltage by the increase of the resistance value of the PTC 9, and then the fixed contact 5-2 and the second movable contact 4-2 are opened. Accordingly, current is completely cut off.
Owner:UCHIYA THERMOSTAT
Illuminating system
InactiveCN102361526ARealize miniaturizationLow calorific valuePoint-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsManufacturing cost reductionManagement unit
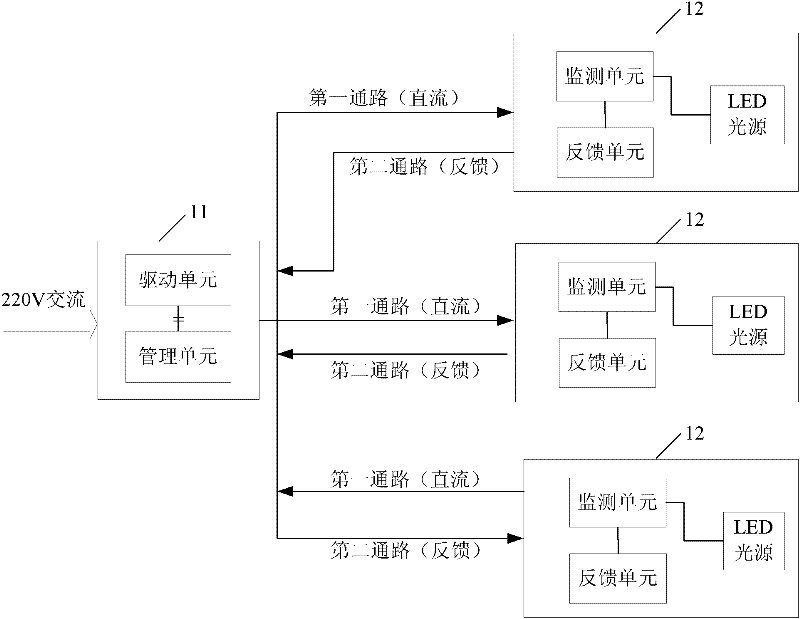
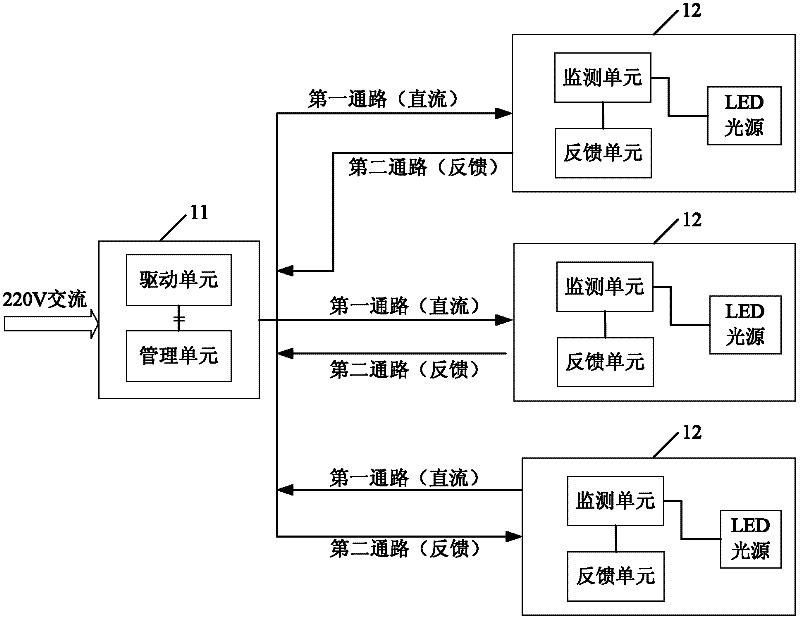
The invention provides an illuminating system comprising a control end and a far end which are mutually separated, wherein the control end comprises a driving unit and a management unit; the far end comprises an LED (Light-Emitting Diode) light source, a monitoring unit and a feedback unit; the driving unit is used for supplying a direct-current power supply to the LED light source; the monitoring unit is used for obtaining a working state parameter of the LED light source; the feedback unit is used for sending the working state parameter obtained by the monitoring unit to the management unit; and the management unit is used for receiving the working state parameter sent by the feedback unit and controlling the output of the driving unit according to the working state parameter so as to adjust the working state of the LED light source. According to the illuminating system, the miniaturized manufacture of an LED lamp can be realized, the manufacturing cost can be reduced, the service life and luminous efficiency of the LED lamp can be improved, and simultaneously the adjustment of the working state of the far-end illumination also can be realized.
Owner:瑞峰(张家港)光伏科技有限公司
Mine conveyer belt carrier roller fire wireless monitoring device
PendingCN107424376ARealize real-time monitoringAchieving ForecastingBatteries circuit arrangementsMining devicesComputer moduleEngineering
The present invention relates to a mine conveyer belt carrier roller fire wireless monitoring device. The problems are solved that a current conveyer belt fire monitoring device cannot perform trend prediction of fire, the monitoring accuracy is low and the monitoring cannot be continuously performed. The device comprises a housing, a control unit, a temperature detection unit, a self power unit and a wireless communication module. The output end of the control unit is connected with the wireless communication module; the temperature detection unit comprises a digital temperature sensor and a temperature semiconductor switch, the output end of the digital temperature sensor is connected with the control unit, a probe inserts the end face of the conveyer belt carrier roller, and the temperature semiconductor switch is connected with the IO interface of the control unit; and the self power unit comprises a standby battery and an energy collection unit, the energy collection unit is configured to store electric energy to the standby battery, and the standby battery supplies electric energy for the whole monitoring device. The mine conveyer belt carrier roller fire wireless monitoring device can realize prediction forecast of the conveyer belt fire in zero-distance contact and effective continuous mode so as to avoid generation of fire.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Optical transmitter-receiver module
InactiveUS20080193141A1Realize miniaturizationImprove the inconvenienceLaser detailsCoupling light guidesComputer moduleLaser light
A small optical transmitter-receiver module capable of regulating the light output level, without changing the mounting position of a laser diode or modifying the laser diode itself, is provided. In the module, a waveguide substrate which forms a planar lightwave circuit, a semiconductor laser element serving as a laser oscillation element which oscillates laser light to be output to the outside transmission path through the planar lightwave circuit, and a photodiode element serving as a light receiving element which receives laser light from the outside transmission path through the planar lightwave circuit, are integrated on a silicon substrate. On an optical waveguide of the planar lightwave circuit, a variable optical attenuator for laser light propagating the optical waveguide is arranged.
Owner:NEC CORP
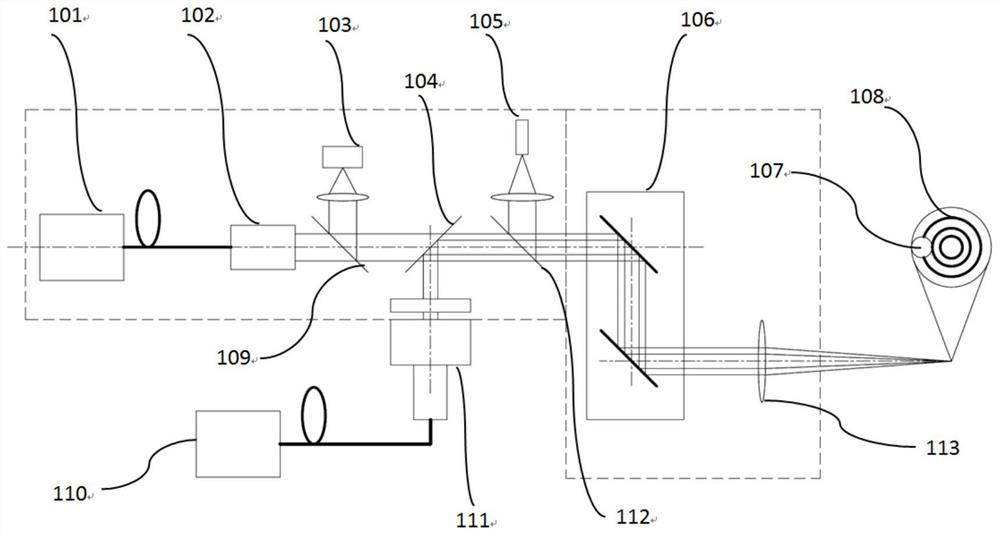
Method and equipment for precise micro-welding of nonferrous metals through composite dual wavelengths
ActiveCN112676702AReduce sizeMeet the requirements of precision micro-weldingLaser beam welding apparatusNonferrous metalGalvanometer
The invention discloses a method and equipment for precise micro-welding of nonferrous metals through composite dual wavelengths. After being collimated, a first laser beam produced by a first laser device is collimated with a second laser beam which is formed by outputting a laser beam produced by a second laser device through a second laser galvanometer, then combined laser is output through a first laser galvanometer, and the combined laser acts on a welded body through focusing; and a focused second laser spot moves in a first laser spot. According to the method, in a welding process, a high-power long-wavelength focused laser spot is fused into a low-power short-wavelength focused laser spot, and moves in the low-power focused laser spot, so that when a welding point of the welded body absorbs low-power laser energy, high-power laser energy is absorbed by the absorption power of the welding point, therefore, the size of the welding point is determined through the high-power laser spot, so that the size of the welding point is further reduced to the maximum extent, the size of the welding point can be made to be very small, and the requirement for the precise micro-welding of difficult-to-weld metal and anisotropic metal is met.
Owner:WUHAN LINGYUN PHOTOELECTRONICS SYST
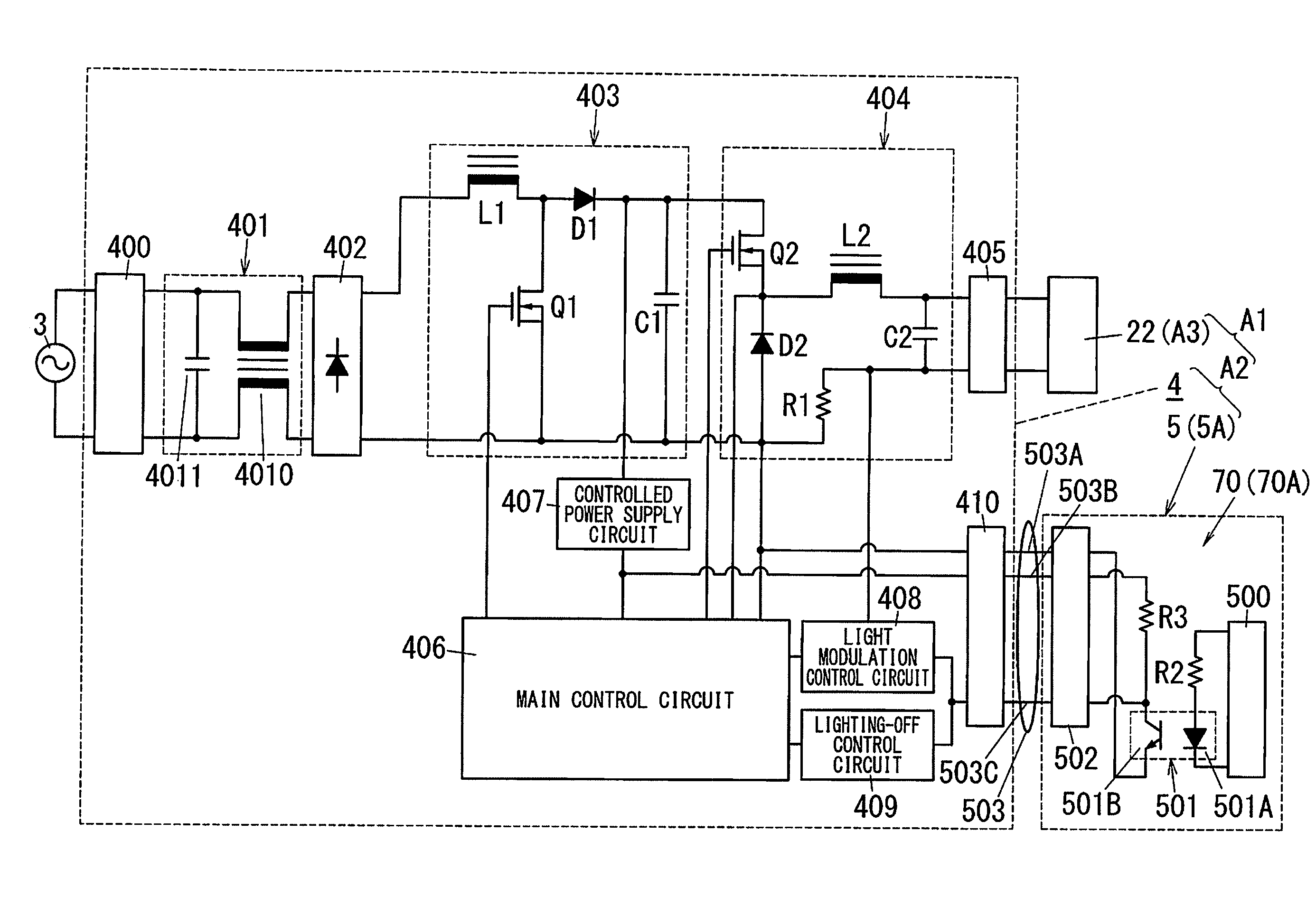
Power supply device and illumination device
InactiveUS20160065085A1Realize miniaturizationAc-dc conversion without reversalElectric circuit arrangementsEngineeringElectric power
A power supply device includes a power supply input portion, a rectification portion, a smoothing portion, a power conversion portion, a power supply output portion, a signal input portion, a control portion, a circuit substrate, and a case. The circuit substrate is formed in an elongated rectangular plate-like shape. The power supply input portion is mounted on a first end portion of the circuit substrate in a longitudinal direction. The rectification portion, the smoothing portion, the power conversion portion, the control portion, and the power supply output portion are mounted on the circuit substrate in the stated order from the first end portion toward a second end portion in the longitudinal direction. The signal input portion is mounted at a position closer to the second end portion than the rectification portion in the circuit substrate.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
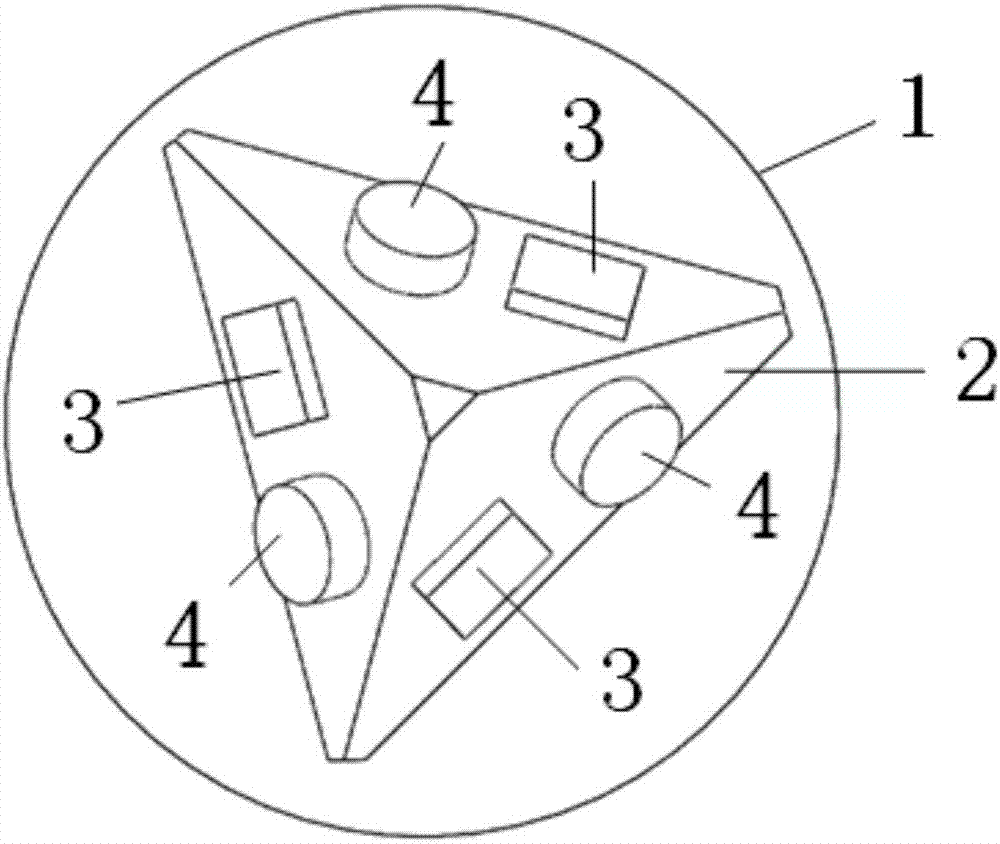
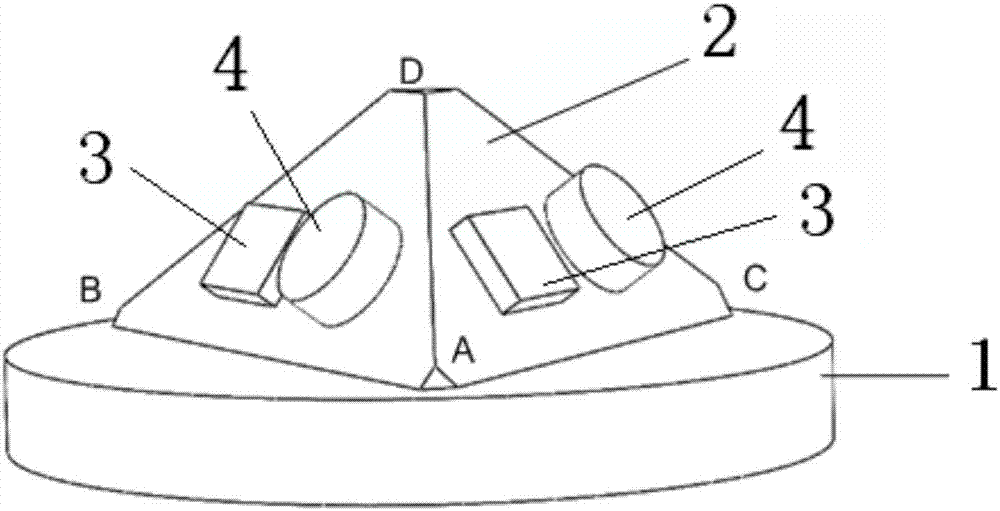
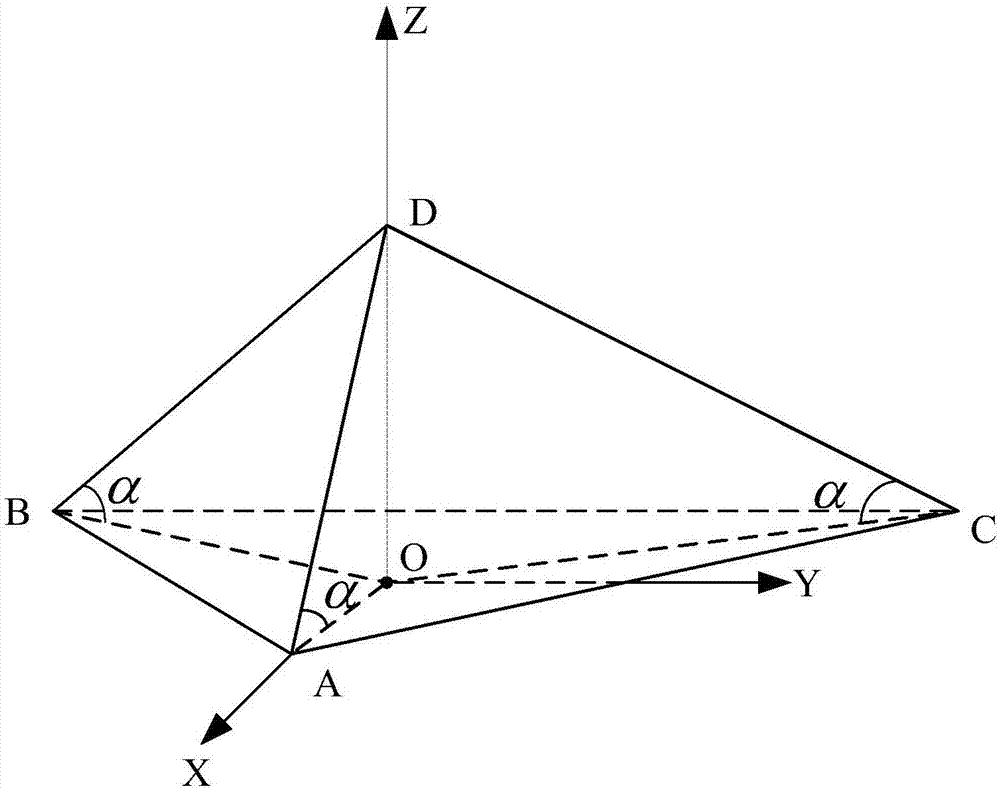
Pyramid inertial measurement unit and three-axis gyroscope scale factor self-calibration method
The invention relates to a pyramid inertial measurement unit and a three-axis gyroscope scale factor self-calibration method; the pyramid inertial measurement unit is disposed on a turntable and comprises a pyramid mounting tool, uniaxial gyroscopes, and uniaxial accelerometers; a pyramid is of tetrahedral structure; the bottom of the turntable is fixedly connected with an existing motor rotor; the turntable is driven by a motor to rotate; the bottom of the pyramid mounting tool is fixed to the top of the turntable; each side of the pyramid mounting tool is provided with the corresponding uniaxial gyroscope and uniaxial accelerometer which are staggered. The pyramid inertial measurement unit and the three-axis gyroscope scale factor self-calibration method have the advantages that scale factors can be calibrated in situ and navigation precision is improved accordingly.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com