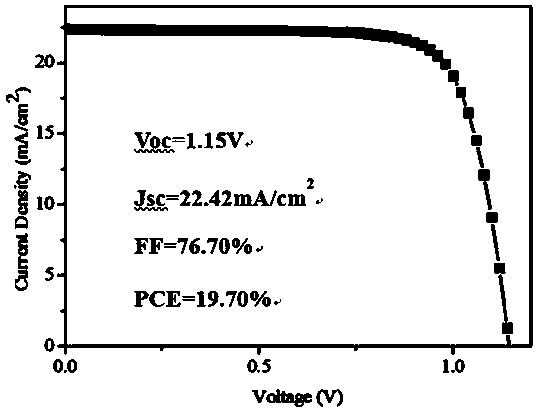
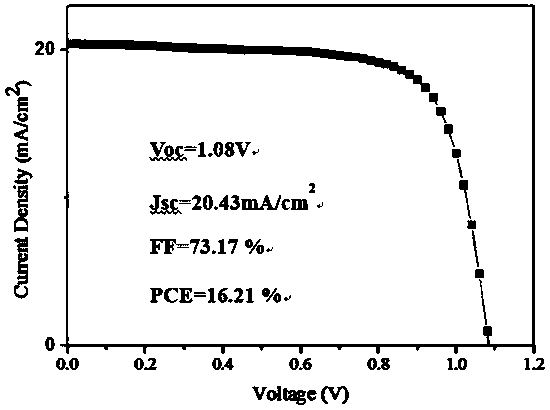
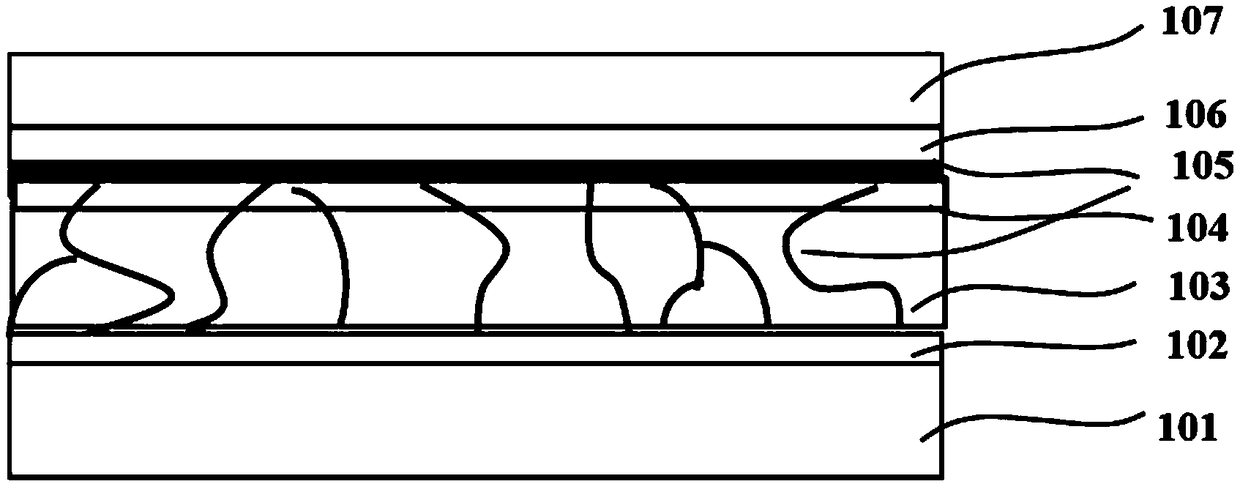
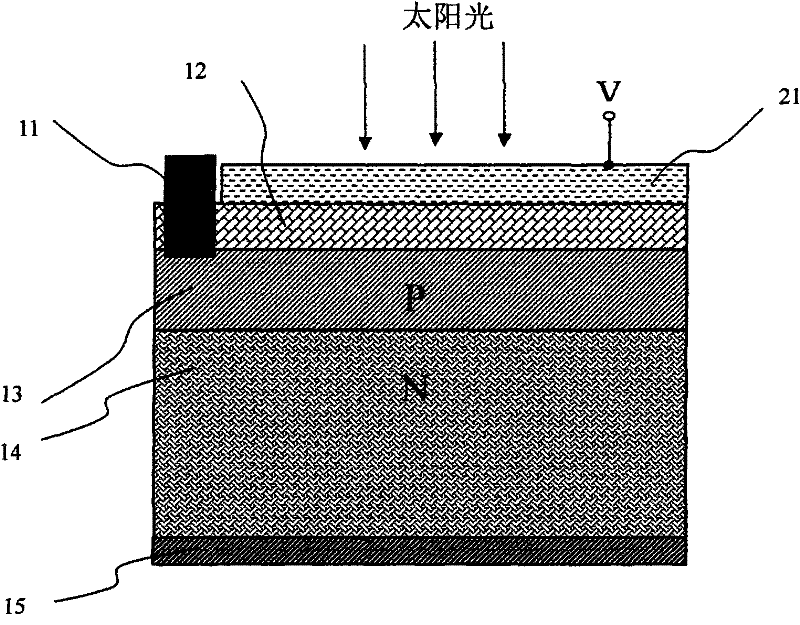
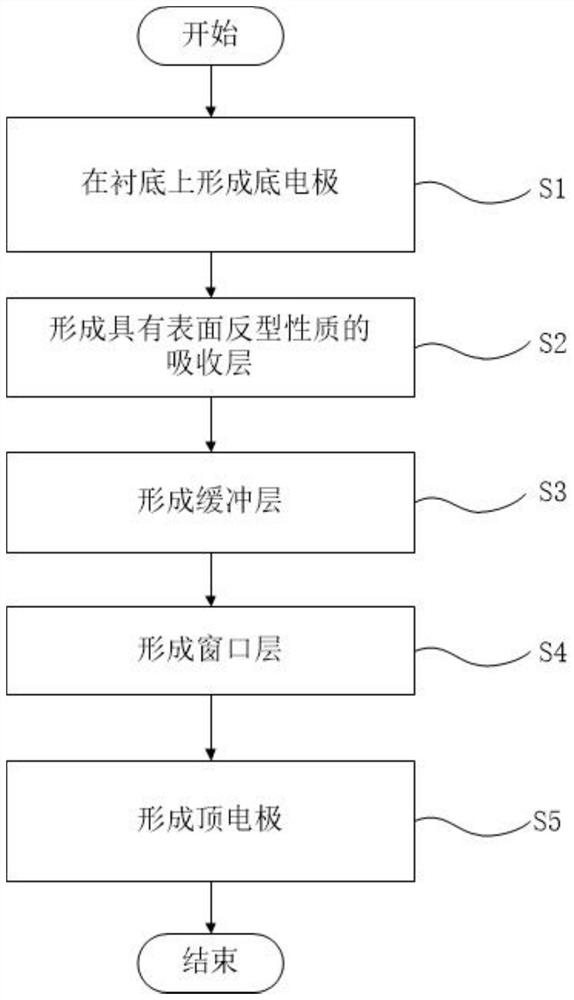
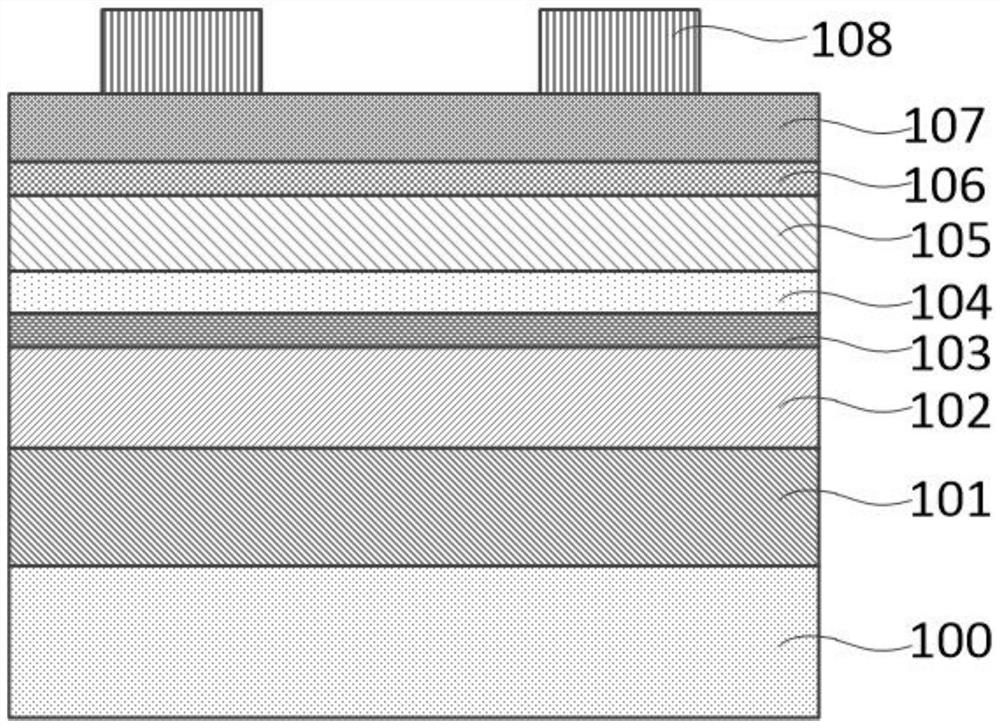
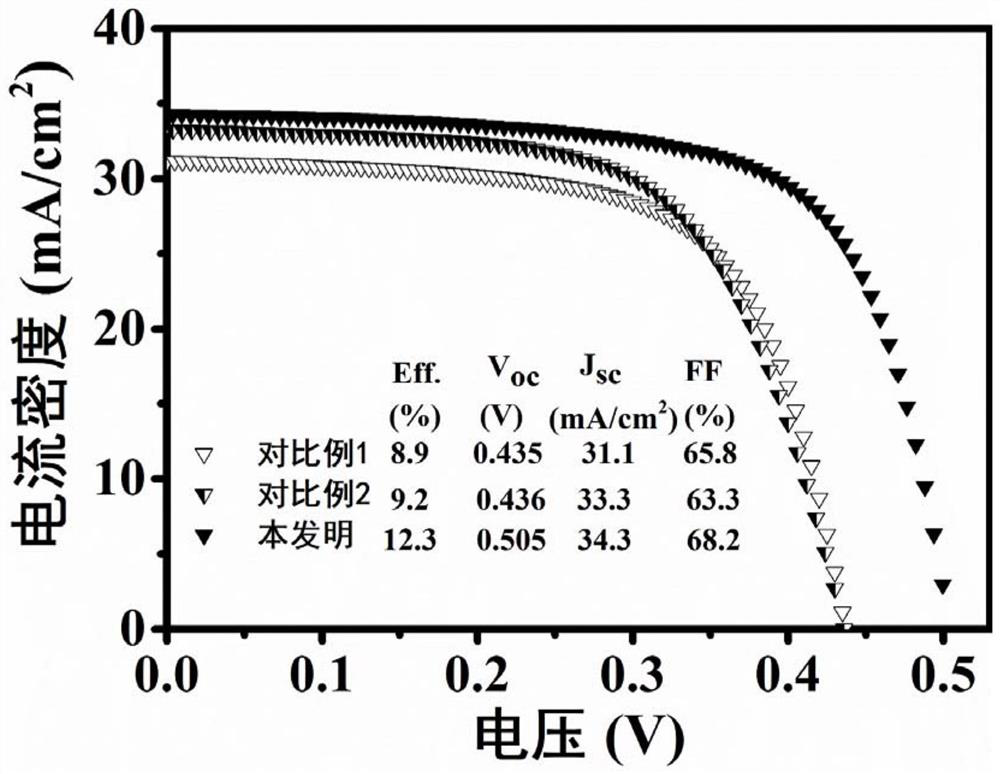
Patents
Literature
56results about How to "Reduce interfacial recombination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Heterojunction thin film composed of same metals and oxygen family elements as well as preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN108479806ALow costAdjustable thicknessPhysical/chemical process catalystsCell electrodesHeterojunctionSulfur
The invention relates to a preparation method of a heterojunction thin film composed of same metals and oxygen family elements. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing metal salt,acid and water to obtain a metal precursor solution; depositing the metal precursor solution on the surface of a base under the conditions that the pH is 2-11, and the temperature is 30-90 DEG C to form metal oxide; performing heat treatment on the metal oxide and at least one of sulfur source and selenium source for 2-120 minutes at a temperature of 100-600 DEG C and an air pressure of minus 0.05-1 MPa to obtain the heterojunction thin film; the heterojunction thin film is a metal oxide-sulfide heterojunction thin film, a metal oxides-selenide heterojunction thin film or a metal oxide-sulfide-selenide heterojunction thin film. The invention further discloses the heterojunction thin film prepared by the preparation method provided by the invention and application thereof. The preparationmethod has the advantages of being simple in equipment, low in cost, easy for large-area continuous production and the like; the prepared thin film is controllable in thickness component, dense and uniform in appearance and good in crystallization and optoelectronic properties.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Heterojunction solar cell with buried grid structure
InactiveCN102709347AReduce shading areaImprove performancePhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionBroadband
The invention relates to a heterojunction solar cell with a buried grid structure, which comprises an N-type monocrystalline silicon substrate, anodes, cathodes, two layers of transparent conductive thin films and a plurality of film layers prepared and formed on the front and the back surfaces of the N type monocrystalline silicon substrate; each of the film layers prepared and formed on the front surface of the N type monocrystalline silicon substrate comprises a P type hydrogenated nanometer silicon film layer and a P type heavily-doped hydrogenated nanometer silicon carbide film layer and forms a p+ / p high-low junction; the two layers of transparent conductive thin films are respectively prepared and formed on the outermost layers of the front surface and the back surface of the N type monocrystalline silicon substrate; grooves are formed on the front surface of the N type monocrystalline silicon substrate; the anodes of the cell are arranged in the grooves; and the cathodes of the cell are arranged on the back surface of the N type monocrystalline silicon substrate. The heterojunction solar cell has the beneficial effects that the P type heavily-doped hydrogenated nanometer silicon carbide film layer is used as a broadband gap window layer, the adsorption of visible light is increased, and a higher built-in electric field is formed in heavy doping; the shading area of a gate line is reduced by utilizing a grooving technology; and the performance of the solar cell is improved by hydrogenated nanometer silicon with high electrical property and photoconduction, so that the purposes of high efficiency and low cost are realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JINKO SOLAR CO LTD
QLED (quantum dot light-emitting diode) device and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106784191AImprove efficiencyImprove stabilitySemiconductor devicesQuantum dotHole transport layer
The invention provides a QLED (quantum dot light-emitting diode) device. The QLED device comprises an anode, a hole transport layer, a quantum dot light emitting layer, an electron transfer layer and a cathode which are stacked sequentially, wherein the quantum dot light emitting layer adopts core-shell quantum dots with ZnS as the shell layer; the hole transport layer and the electron transfer layer are made of a compound the same as the shell layer material of the core-shell quantum dots; the electron transport layer is made of N-type ZnS; the hole transfer layer is made of P-type ZnS which is Sb doped ZnS.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
Perovskite film preparation method based on anti-solution bath, and solar cell
ActiveCN109904318AAchieve crystallization controlRealize shape controlFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesPerovskite solar cellAnti solvent
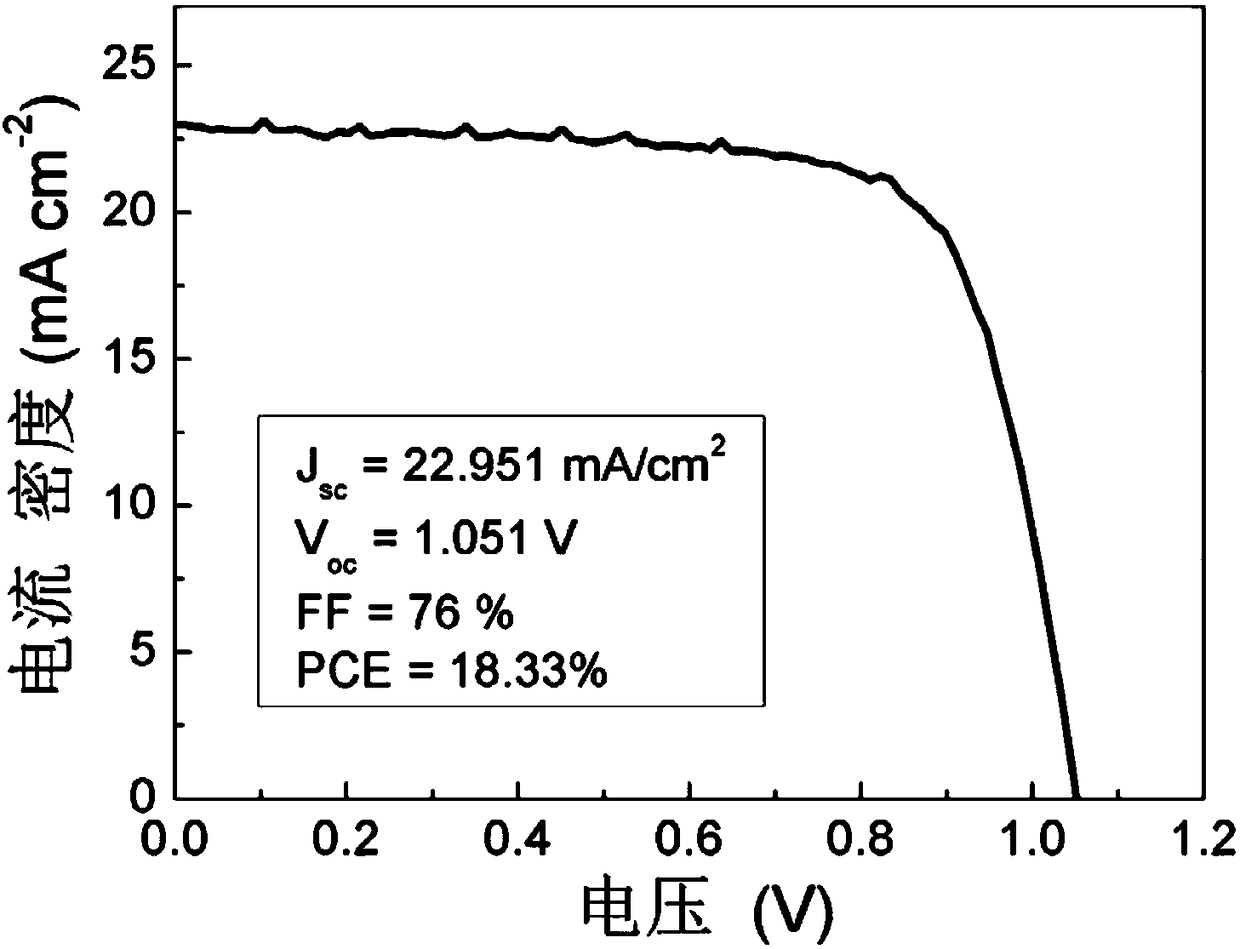
The invention discloses a perovskite film preparation method based on an anti-solution bath, and a solar cell. A proper solute is added into an anti-solvent to prepare anti-solutions with different functions; crystallization control and morphology regulation of a perovskite film are realized; and meanwhile, an interface between the perovskite film and a carrier transmission layer is passivated, sothat the surface defect state and the interface recombination are reduced, the carrier concentration and the extraction efficiency at the interface are improved, and the carrier transmission is better facilitated. The perovskite solar cell prepared with the anti-solution bath method has relatively high photoelectric conversion efficiency and high stability. The preparation method is simple and convenient, relatively short in production period and high in controllability and repeatability, and has a wide application prospect in the production and preparation of large-area and large-scale perovskite solar cells.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Flip-chip solar cell and manufacture method thereof
ActiveCN102832274AAvoid damageInhibited DiffusionFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationHeterojunctionEngineering
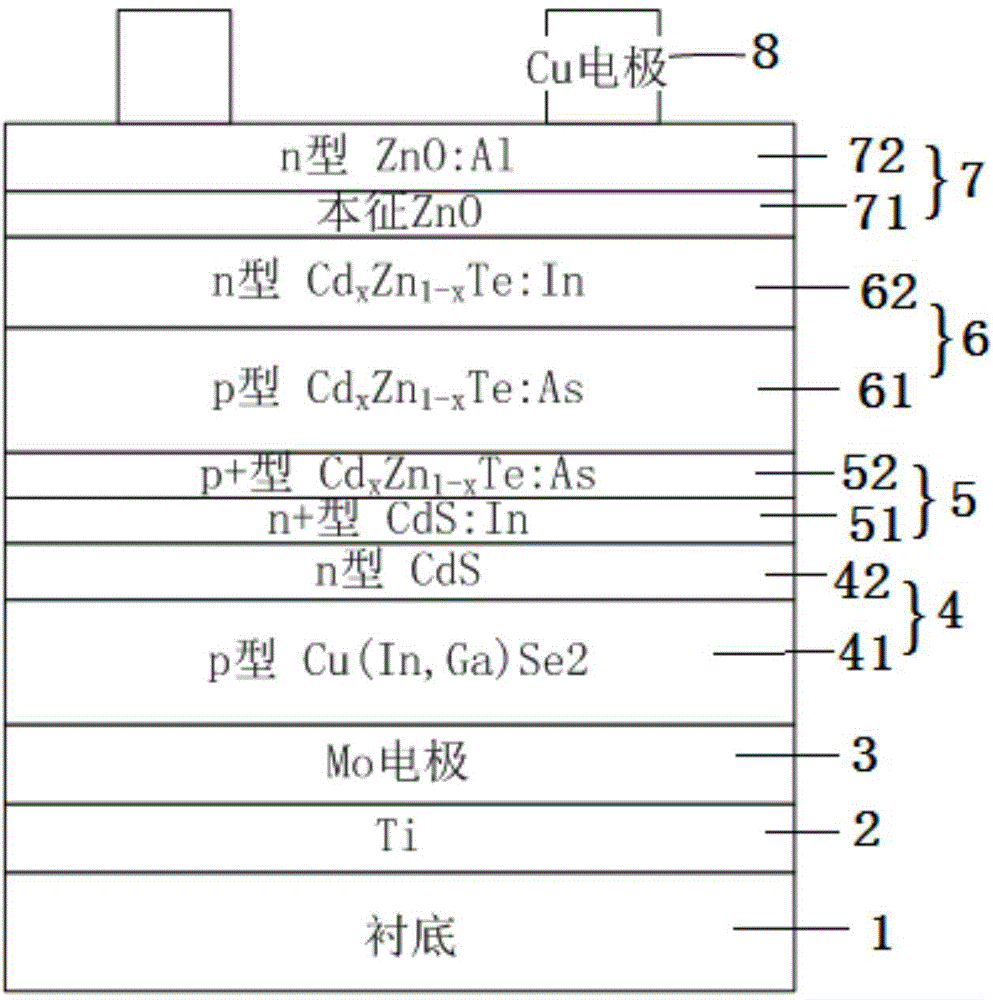
The invention discloses a flip-chip solar cell and a manufacture method thereof. In a flip growing procedure of the flip-chip solar cell, a heterojunction window layer is imported in a top cell structure so as to prevent the window layer from being damaged by over etching which probably occurs in a manufacturing process, so that a serious consequence that the performance of the cell is influenced after a single-material window layer is damaged is avoided.
Owner:TIANJIN SANAN OPTOELECTRONICS
Graphene/palladium diselenide/silicon heterojunction self-driven photoelectric detector
ActiveCN111341875ASelf-driving performanceImprove responsivenessFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionIndium
The invention discloses a graphene / palladium diselenide / silicon heterojunction self-driven photoelectric detector, which is applied to the technical field of photoelectric detection. In view of the problem that the existing photoelectric detector is limited by weak light absorption performance of graphene and low in responsivity, a technical scheme as follows is adopted: firstly, an n-type siliconwindow is exposed on an n-type silicon dioxide / silicon substrate through dry etching; a gold / indium electrode is plated near the silicon window, a palladium diselenide microchip is prepared by adopting mechanical stripping, and palladium diselenide is transferred to the silicon window by utilizing a positioning dry method; and finally, graphene is transferred in a wet transfer mode and covers thesurfaces of palladium diselenide and the electrode, palladium diselenide serves as an interface modification layer between graphene and silicon, and a graphene / palladium diselenide / silicon heterojunction is formed by the graphene layer, the palladium diselenide layer and the n-type silicon substrate corresponding to the single silicon window. The device provided by the invention is simple in preparation process, has self-driving performance, and has excellent performances such as relatively high responsivity in a visible-near-infrared light band.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Organic solar cell based on polyfluorene cathode interface self-assembly anode plasma resonance effect and preparation method of organic solar cell
InactiveCN105470396AImprove performanceIncrease profitFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesOrganic solar cellPlasma effect
The invention belongs to the technical field of polymer solar cells, and particularly relates to an organic solar cell based on the polyfluorene cathode interface self-assembly anode plasma resonance effect and a preparation method of the organic solar cell. According to the method, an amphipathic polyfluorene material with high conductivity serves a cathode transmission layer, interface contact with ITO is increased through self-assembly of the cathode transmission layer, the cathode transmission layer replaces a traditional TiO2 or ZnO inorganic transmission layer, interface combination is reduced, and the performance of the organic solar cell is improved; meanwhile, a vacuum evaporation method is adopted for directly arranging a layer of gold nanoparticles on an active layer in an evaporation mode, light scattering is increased by utilizing the surface plasma effect of the layer of gold nanoparticles, the light path is increased, then the light utilization rate is increased, and thus the performance of a device is improved. The efficiency of the organic solar cell is effectively improved through the method, and the method is of great reference significance for nanoimprint lithography and development of organic solar cells in the future.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Large-area efficient stable passivated tunneled organic-inorganic hybrid perovskite solar cell and laminated cell
PendingCN109326717ASolve the leakAvoid the problem of severe loss of efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionHole transport layer
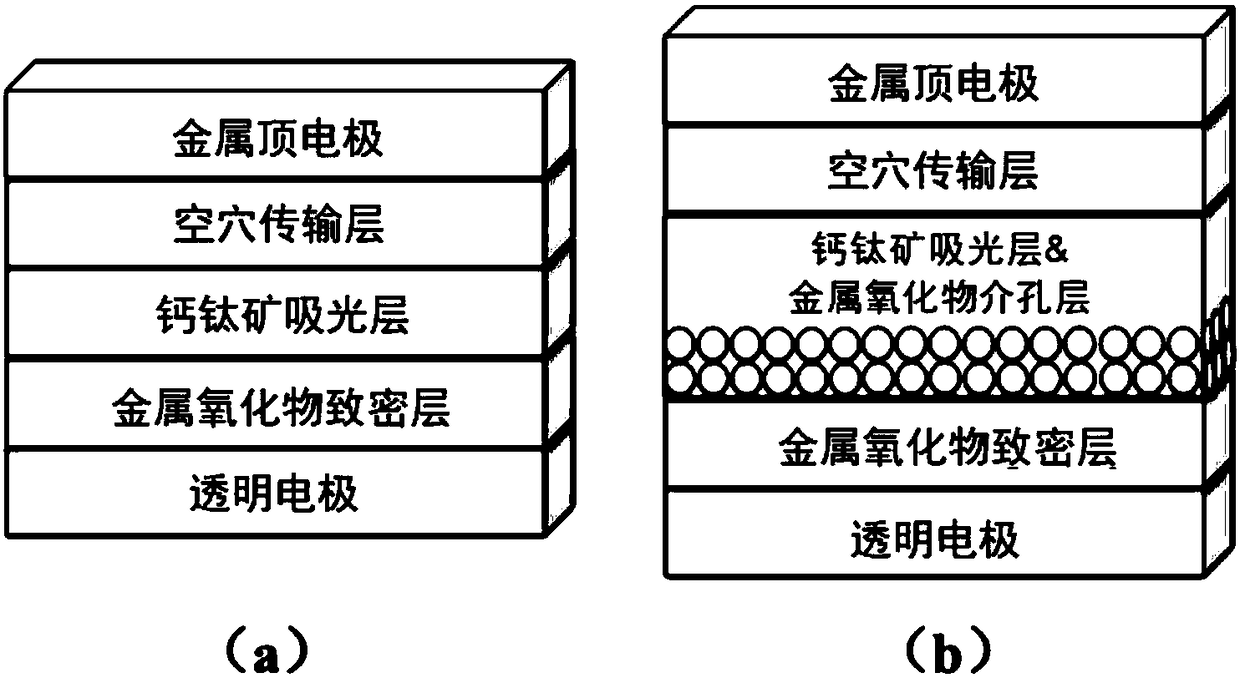
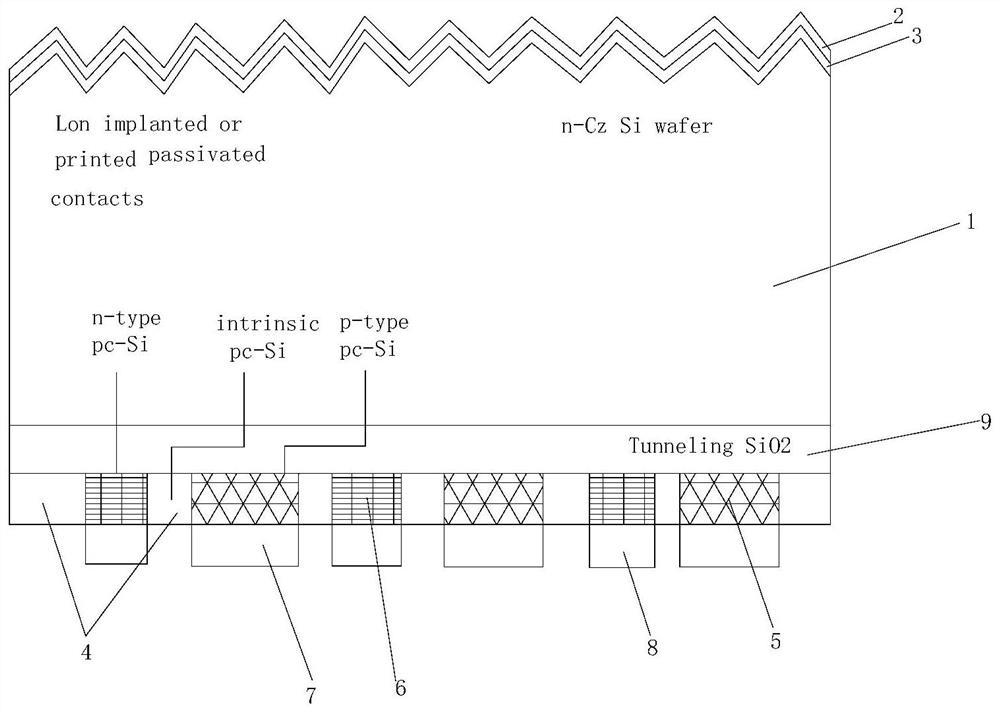
The invention belongs to the technical field of solar cells and particularly relates to a large-area efficient stable passivated tunneled organic-inorganic hybrid perovskite solar cell and a laminatedcell. The large-area efficient stable passivated tunneled organic-inorganic hybrid perovskite solar cell comprises, when of upright structure, conductive glass, an electron transport layer, an organic-inorganic hybrid perovskite light absorbing layer, a hole transport layer, an ALD (atomic layer deposition) nitride, a heavily-doped hole transport layer and a metal electrode, or comprises, when ofinverted structure, conducive glass, a hole transport layer, an organic-inorganic hybrid perovskite light absorbing layer, an electron transport layer, ALD nitride, a heavily-doped electron transportlayer and a metal electrode. In addition, the passivated electron transport layer or hole transport layer has surface effects, such that carrier interfacial recombination is decreased. The heavily-doped layer helps improve the ability of transporting carriers to an outer circuit. The upright or inverted solar cell may be stacked to a HIT (heterojunction with intrinsic thin-layer) cell to form a large-area laminated cell.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV +1
A technology to improve the conversion efficiency of solar photovoltaic cells
InactiveCN102263156AImprove current efficiencyImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringSolar battery
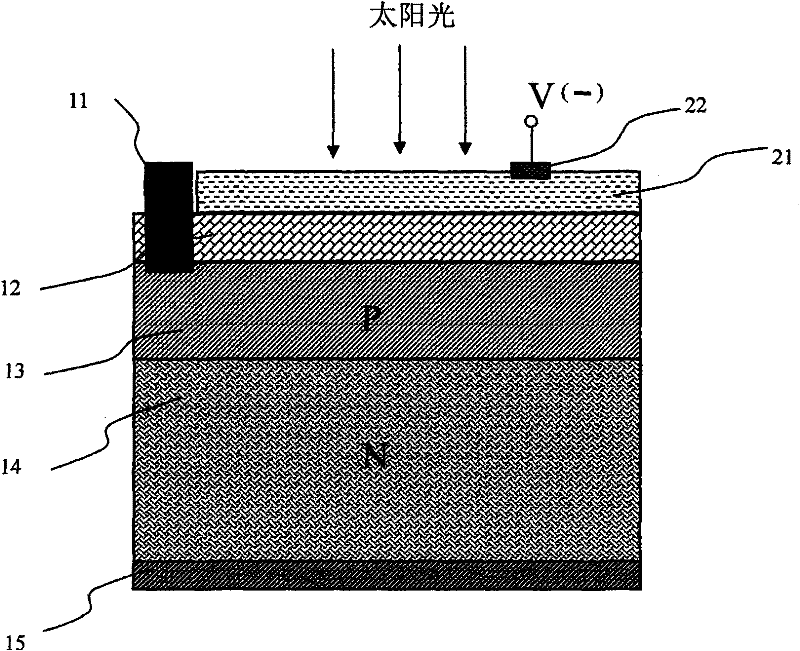
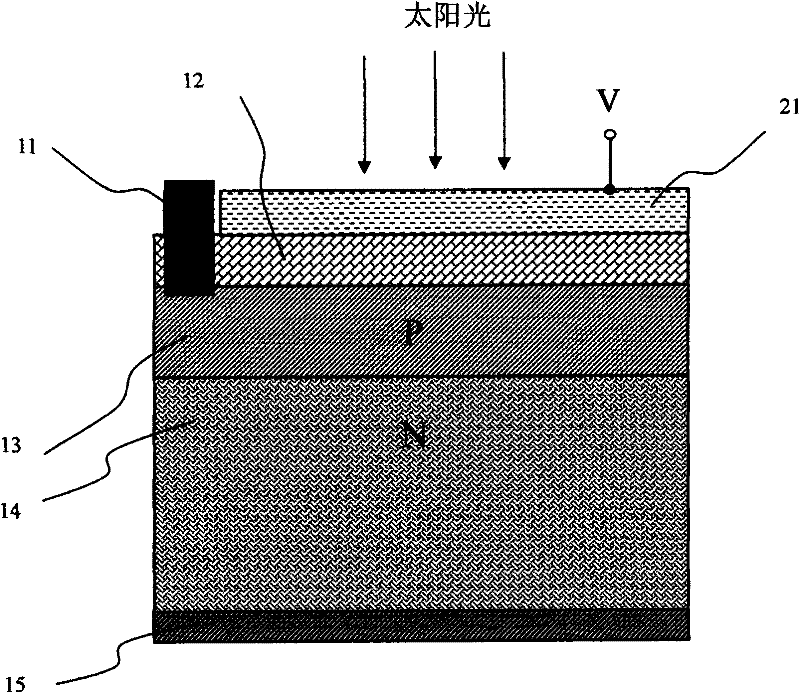
The invention belongs to the technical field of solar photovoltaic cells, and relates to a technology for improving the conversion efficiency of solar photovoltaic cells. A transparent conductive film layer is added to the front surface of the solar photovoltaic cell, and a voltage is applied to the transparent conductive film layer to work as a solar photovoltaic cell. The auxiliary voltage can eliminate the existence of the "dead layer" region and reduce the interfacial recombination of photogenerated carriers, increase the photocurrent output by the solar photovoltaic cell, and improve the conversion efficiency of the solar photovoltaic cell. In particular, this technology can effectively improve the photoelectric conversion efficiency of solar photovoltaic cells based on N-type silicon series substrates.
Owner:石郧熙
Chelated perovskite material, film, device, and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN111403607AEffective passivationReduce the density of defect statesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPerovskite solar cellPhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a chelated perovskite material, a film, a device, and a preparation method and application thereof. The catalyst is prepared by adding a chelating agent into a perovskite solution, wherein the chelating agent comprises a complexing agent or chelating agent capable of generating coordination with metal ions by coordination atoms, or a chelate or complex formed by coordination reaction of the complexing agent or chelating agent and the corresponding metal ions; according to the material, body defects and surface defects of the perovskite thin film are effectively passivated, and non-radiative recombination of carriers is reduced, so that the efficiency and long-term operation stability of the perovskite solar cell are effectively improved.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Solar cell and preparation method thereof
PendingCN112820793AImprove conversion efficiencyEasy to manufactureFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringSolar cell
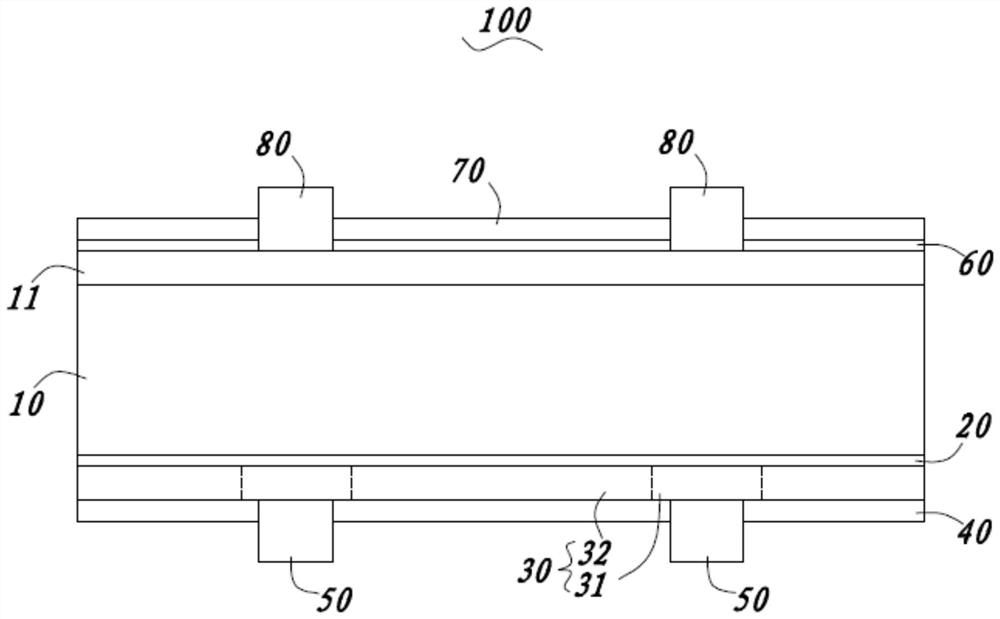
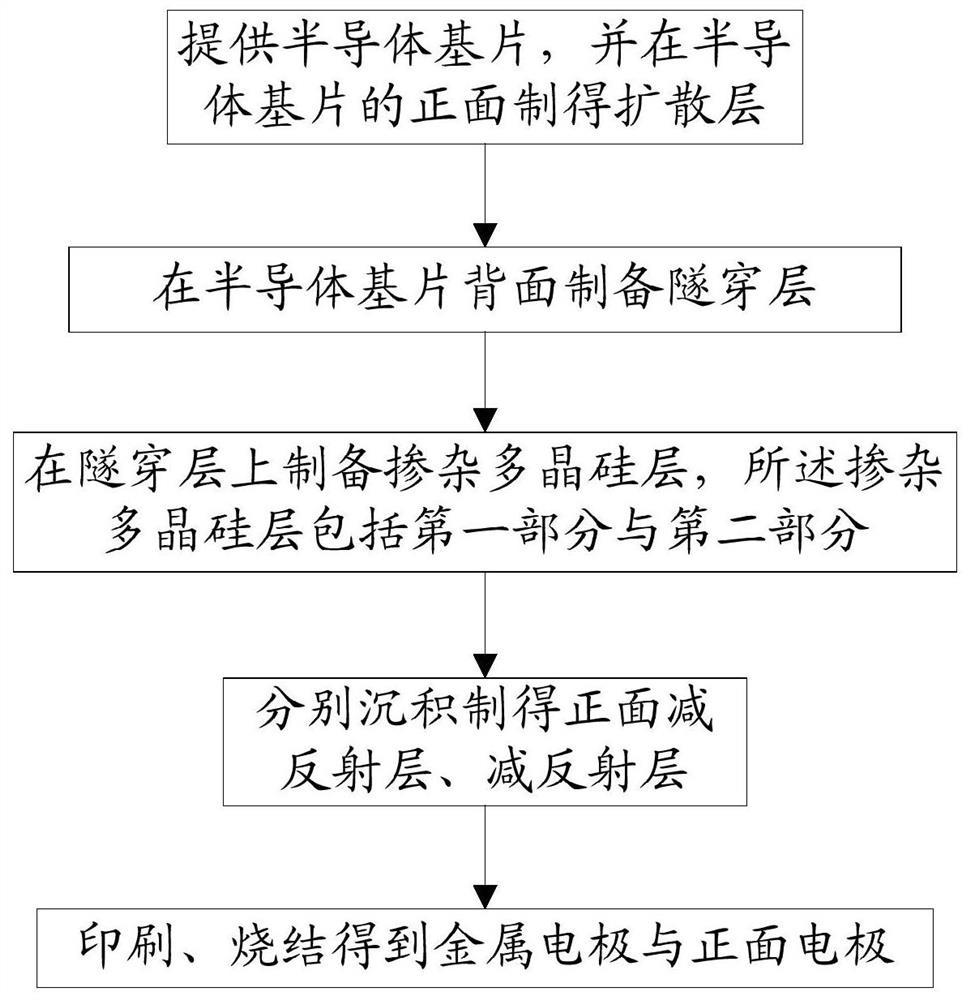
The invention provides a solar cell and a preparation method thereof, the solar cell comprises a semiconductor substrate, a metal electrode, and a tunneling layer, a doped polycrystalline silicon layer and an antireflection layer which are sequentially stacked on the surface of one side of the semiconductor substrate, the doped polycrystalline silicon layer is provided with a first part and a second part, the doping concentration of the first part is greater than that of the second part, and the metal electrode penetrates through the antireflection layer and is in contact with the first part. The preparation of the doped polycrystalline silicon layer is simpler, the first part with higher doping concentration is obtained through local doping, and the interface recombination and contact resistance at the position of a metal electrode are effectively reduced; and due to the fact that the doping concentration of the second part is low, the non-electrode area is passivated, and meanwhile light absorption is reduced.
Owner:CSI CELLS CO LTD +1
Solar cell modified polymer electrolyte and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102543451AReduce interfacial recombinationIncrease the open circuit voltageLight-sensitive devicesSolid-state devicesChemistryPolytetrafluoroethylene
The invention discloses solar cell modified polymer electrolyte, which is characterized by comprising the following components: a polyoxyethylene and polytetrafluoroethene hexafluoropropene mixture, silica nano particles, an I2 / KI redox couple in a molar ratio of 1:10, amide and an organic solvent A. The invention also discloses a preparation method and application of the electrolyte. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages that: a composite interface can be effectively reduced; and therefore, open-circuit voltage of the cell is improved, and the efficiency of a dye-sensitized nanocrystalline solar cell employing the polymer electrolyte is improved.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
United boron compound modification-based perovskite type solar cell and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108539023AIncrease concentrationEasy transferSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPerovskite solar cellCharge carrier
The invention discloses a united boron compound modification-based perovskite type solar cell and a preparation method thereof. The solar cell comprises a planar type structure and a mesoporous type structure, wherein a metal oxide compact layer or mesoporous layer used as an electron transmission layer is modified by a united boron compound, so that the valence state of metal ions on the surfaceof a metal oxide is changed, surface N-type doping is implemented, and the carrier concentration is increased; meanwhile, a passivation effect is achieved, and the shape of a metal oxide thin film isfurther improved. The perovskite type solar cell with the united boron-modified electron transmission layer is relatively high in photoelectric conversion efficiency and high light stability.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Laminated thin film solar battery and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105742390AImprove reliabilityImprove efficiencyFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationElectrical batteryOptical transmittance
The invention relates to a laminated thin film solar battery. The laminated thin film solar battery includes a substrate as well as a back electrode, a bottom cell, a top cell and a window layer which are arranged on the substrate sequentially; a tunnel junction is arranged between the bottom cell and the top cell; the tunnel junction includes an n+ type semiconductor layer and a p+ type semiconductor layer; the n+ type semiconductor layer contacts with an n type semiconductor layer of the bottom cell; and the p+ type semiconductor layer contacts with a p type semiconductor layer of the top cell. The invention also provides the preparation method of the above structure. According to the laminated thin film solar battery and the preparation method thereof of the invention, the bottom cell and the top cell are connected with each other through the tunnel junction, so that electric conduction connection between the two cells can be realized, and the adjustment of optical transmittance and electrical resistivity can be facilitated compared with a mechanical lamination mode; the appropriate tunnel junction is adopted to achieve continuous growth of the laminated layers, and therefore, compared with the mechanical lamination method, process steps can be reduced, the reliability of the battery can be improved, the overall efficiency of the battery can be improved, and carrier interface recombination can be weakened.
Owner:紫石能源有限公司
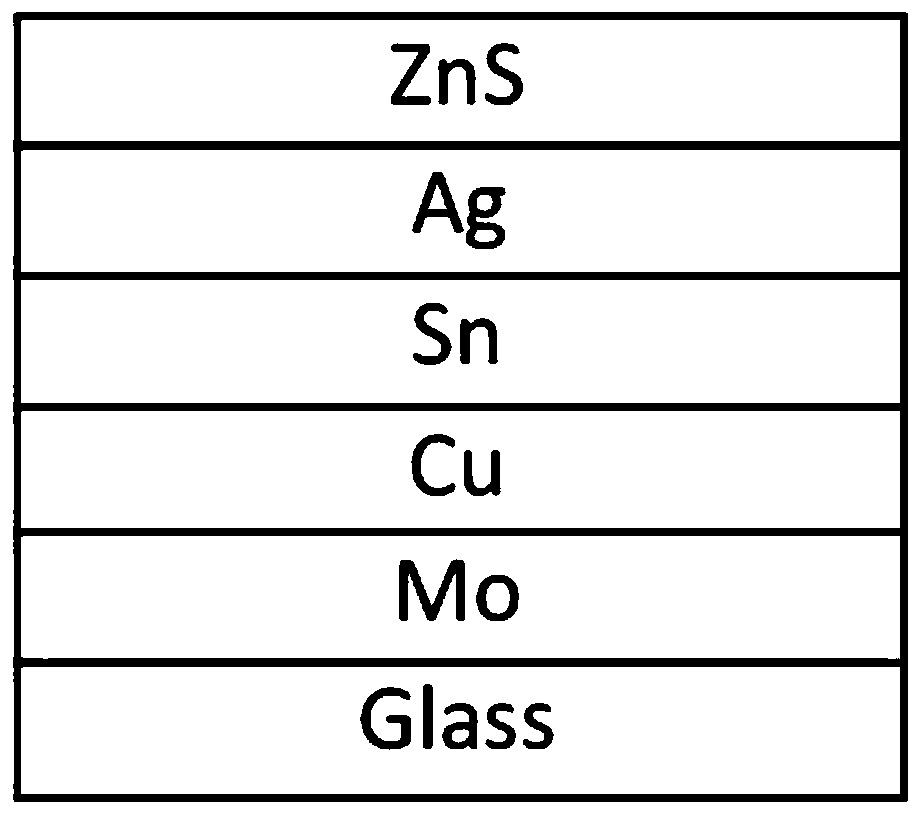
Structure-optimized silver-doped Cu-Zn-Sn sulfur thin film solar cell and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110176517AInhibition lossTightly boundFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingSulfurCopper
The invention discloses a structure-optimized silver-doped Cu-Zn-Sn sulfur thin film solar cell and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of solar cells. The solar cell comprises a glass substrate, an absorption layer, a buffer layer, a transparent conductive window layer and an upper electrode which are sequentially connected, wherein a pre-fabrication layer structure of the absorption layer is Cu / Sn / Ag / ZnS. The pre-fabrication layer structure of the absorption layer employs a Cu / Sn / Ag / ZnS structure, the loss of a Sn element is prevented by depositing Ag on a Sn layer, and holes among boundaries are reduced; meanwhile, the defect of a CuZn reverse structure is effectively reduced by employing Ag to Cu, and the collection efficiency of photoproduction carrier is improved;and moreover, silver doping has benefits to expansion of the grain size of the Cu-Zn-Sn sulfur thin film and improvement of attachment of a Mo back electrode.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
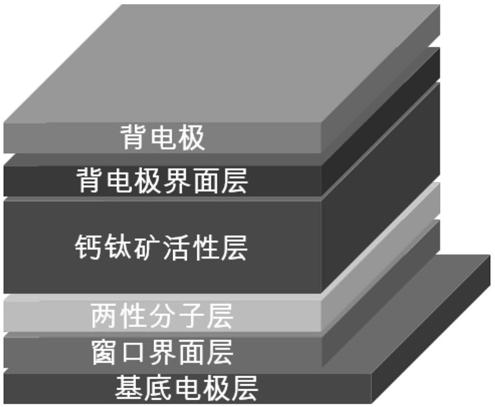
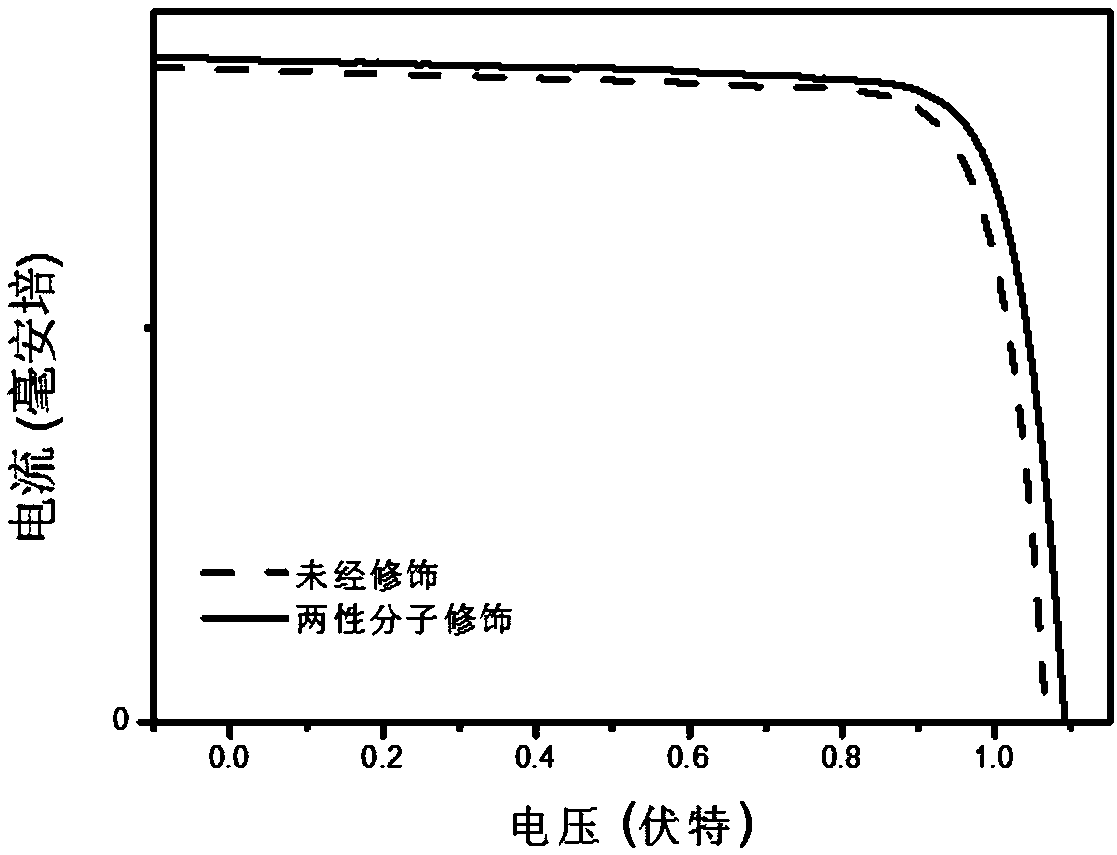
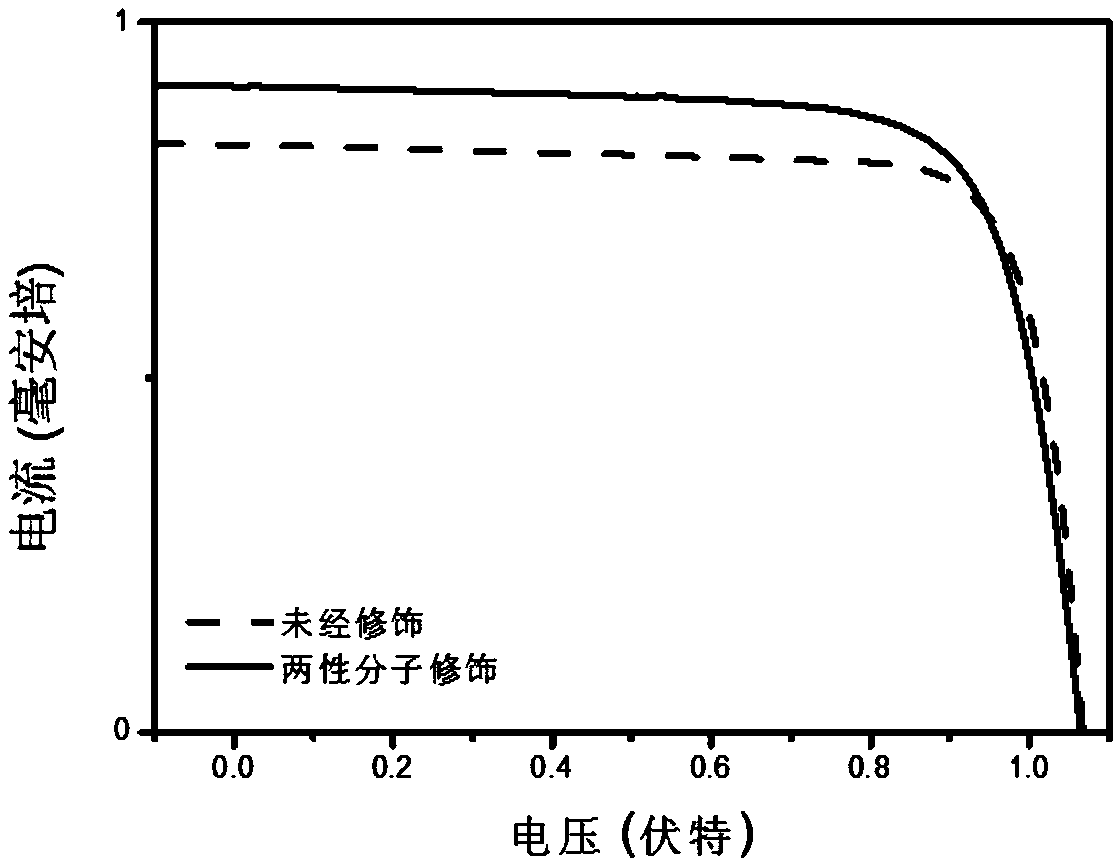
Amphoteric molecule modified perovskite photovoltaic device and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111223989AEasy to prepareLow costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInterface layerEnergy consumption
The invention discloses an amphoteric molecule modified perovskite photovoltaic device and a preparation method and application thereof. The invention relates to amphoteric molecules, an amphoteric molecule interface modification layer is introduced into a perovskite photovoltaic device interface layer; the perovskite photoactive layer in the perovskite photovoltaic device is modified to passivatethe surface defects of the perovskite photoactive layer and improve the transmission efficiency of electrons and holes at the interface of the device, so that the perovskite photovoltaic device withhigh photoelectric conversion efficiency and high stability is realized. The interface defects in the perovskite photovoltaic device are passivated. The amphoteric molecule modified perovskite photovoltaic device prepared by adopting the method is environment-friendly and low in energy consumption.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
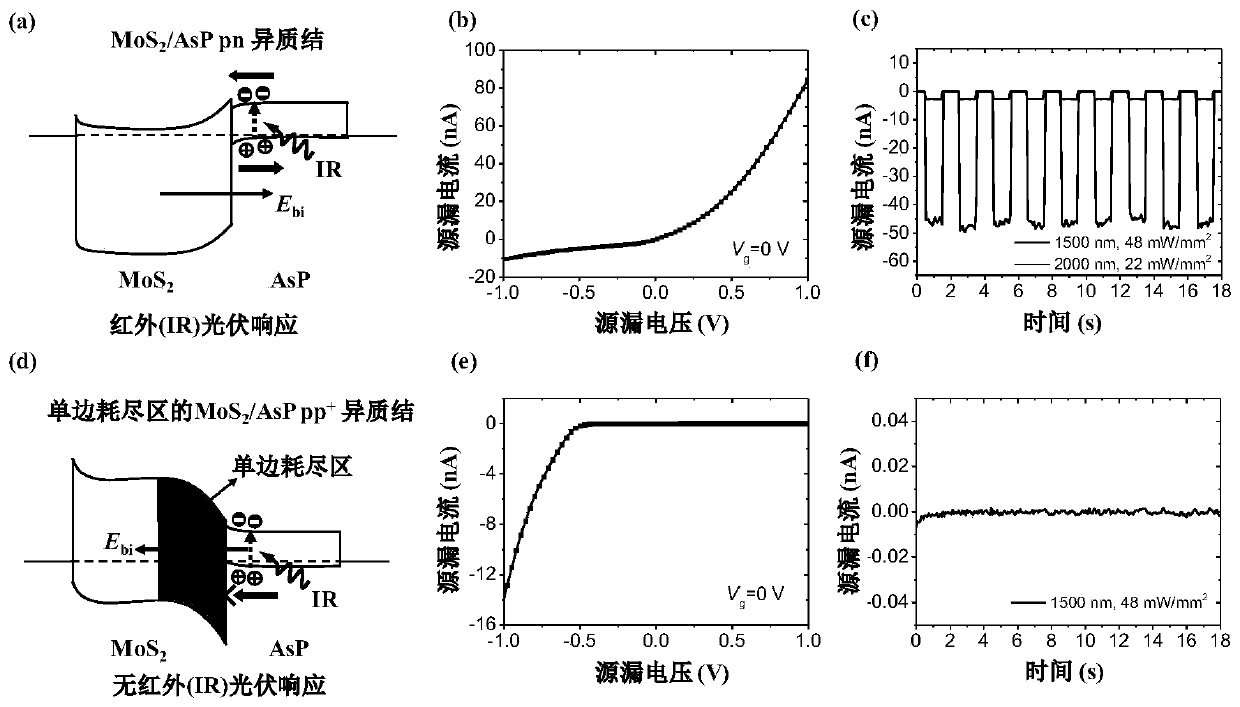
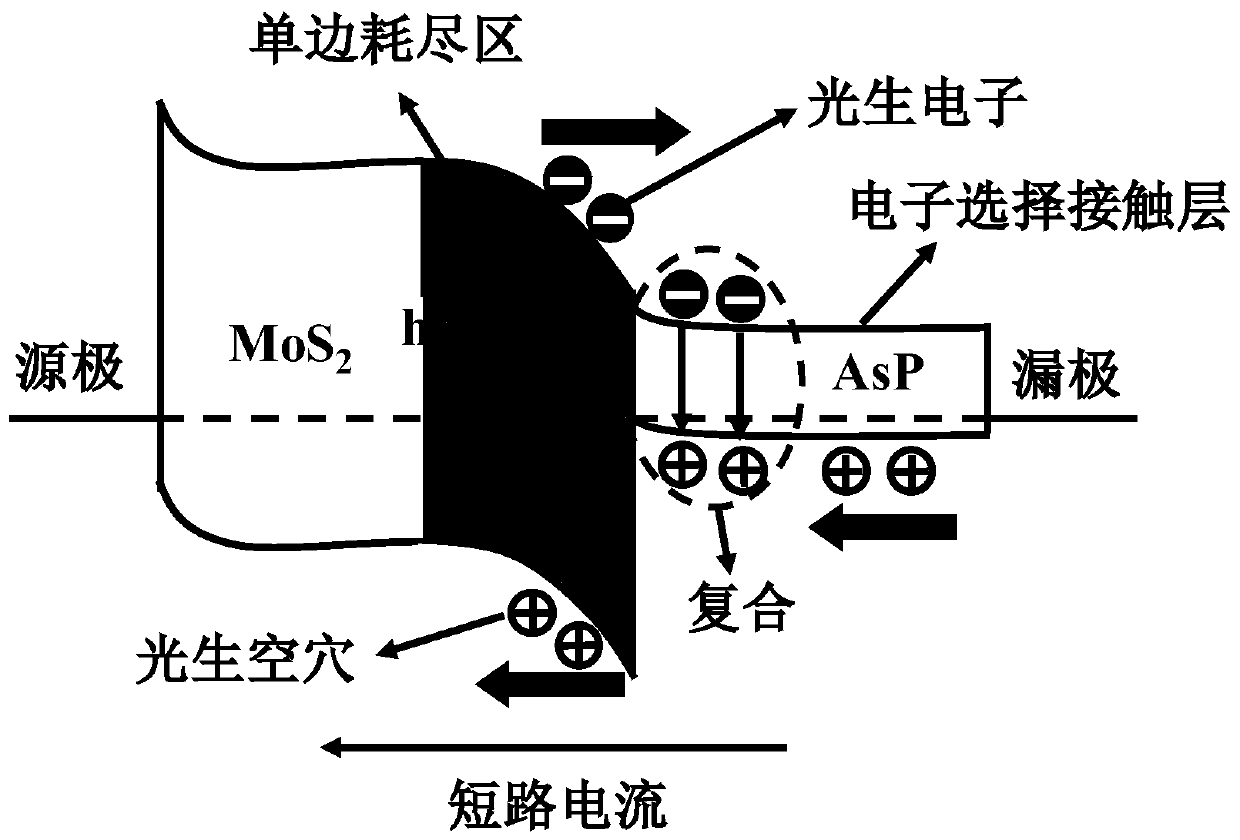
Efficient and rapid Van der Waals heterojunction detector with unilateral depletion region and preparation method
PendingCN110729375AReduce interfacial recombinationImprove quantum efficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionField effect
The invention discloses an efficient and rapid Van der Waals heterojunction detector with a unilateral depletion region and a preparation method. The detector structurally comprises a substrate, a Vander Waals heterojunction, a metal source electrode and a metal drain electrode which are sequentially distributed from bottom to top. According to the preparation method of the detector, a mechanically stripped black arsenic phosphide (AsP) sheet and molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) sheet are sequentially transferred to a silicon substrate through fixed-point transfer, so that the Van der Waals heterojunction is formed; and the metal source electrode and the metal drain electrode are prepared on the basis of electron beam lithography and a lift-off process, so that a heterojunction field effect transistor structure can be formed. The detector is characterized in that the heterojunction of the detector is a unilateral depletion pp junction which is different from a bilateral depletion pn junction. With the unilateral depletion heterojunction adopted, tunneling-assisted interface recombination and interface defect capture effects can be effectively inhibited, and therefore, high quantum efficiency, high photoelectric conversion efficiency and high response speed can be realized. The detector provided by the invention has the advantages of high signal-to-noise ratio, high quantum efficiency, photoelectric conversion efficiency and fast response, and can be applied to the field of solar cells.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Solar cell modified polymer electrolyte and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102543451BIncrease the open circuit voltageImprove efficiencyLight-sensitive devicesSolid-state devicesHexafluoropropyleneElectrical battery
The invention discloses solar cell modified polymer electrolyte, which is characterized by comprising the following components: a polyoxyethylene and polytetrafluoroethene hexafluoropropene mixture, silica nano particles, an I2 / KI redox couple in a molar ratio of 1:10, amide and an organic solvent A. The invention also discloses a preparation method and application of the electrolyte. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages that: a composite interface can be effectively reduced; and therefore, open-circuit voltage of the cell is improved, and the efficiency of a dye-sensitized nanocrystalline solar cell employing the polymer electrolyte is improved.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Method for filling surface molecular layer defects of wide bandgap semiconductor adopting nano structure
ActiveCN103390504ABlock approachExtended tunneling distanceLight-sensitive devicesCapacitor electrodesSemiconductor electrodeSolubility
The invention provides a method for filling surface molecular layer defects of a wide bandgap semiconductor adopting a nano structure, and effectively solves the problems that the interface charge composition is fast and the charge collecting efficiency is reduced during short-circuit due to the use of a cobalt-based single electron mediator with characteristics of low charge transfer reorganization energy and the like. The method comprises the steps as follows: an electrode of the wide bandgap semiconductor adopting the nano structure is soaked in a dye solution for dyeing; then a dyed semiconductor film is soaked in a solution containing a filling agent for filling the dye molecular layer defects; and the solubility of the dye in the solution containing the filling agent is smaller than 10 micromoles per litre. The invention further provides an application of the semiconductor electrode obtained with the method for filling the molecular layer defects of the wide bandgap semiconductor in dye-sensitized solar cells. According to the method for filling the surface molecular layer defects of the wide bandgap semiconductor adopting the nano structure, an electron tunneling distance of an interface composite reaction can be effectively controlled, so that the interface charge composition of the dye-sensitized solar cells is slowed down, and photovoltage, photocurrent and power conversion efficiency of a device can be improved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
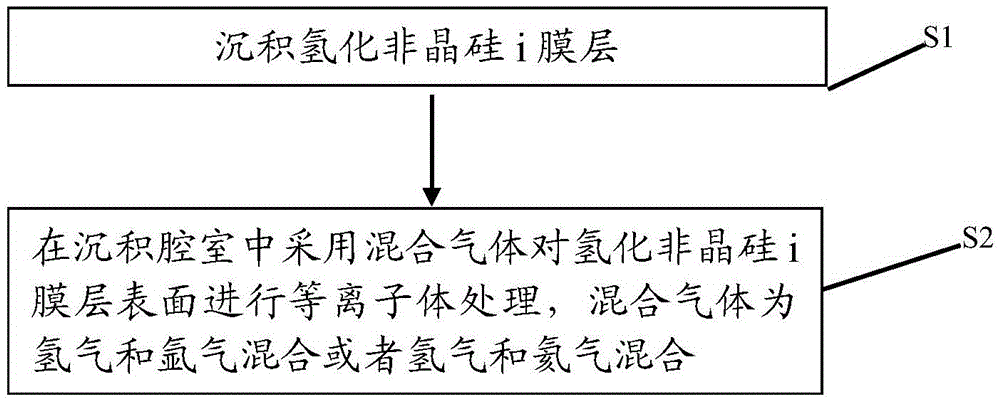
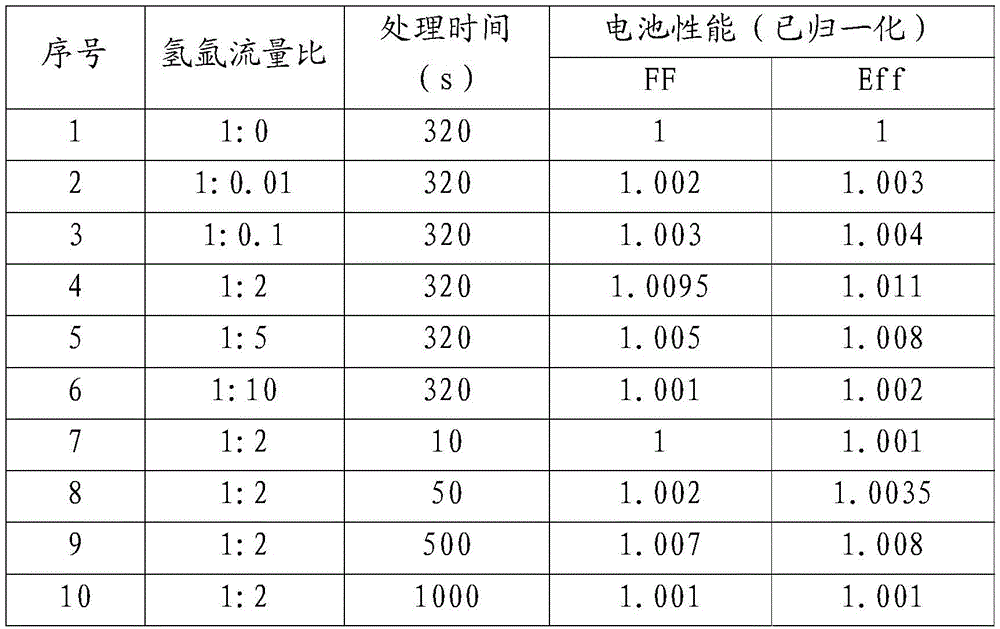
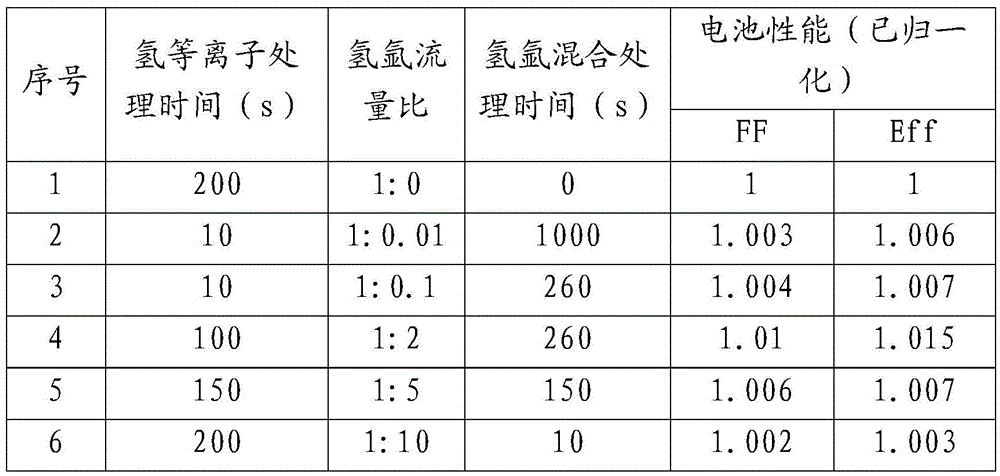
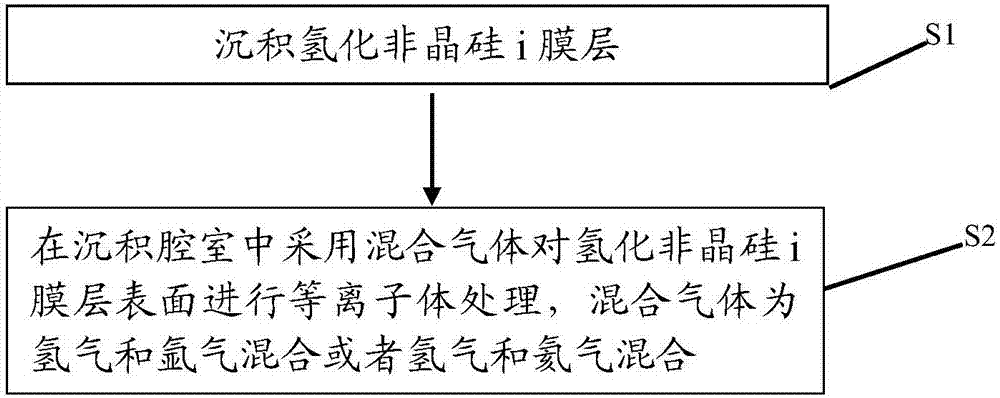
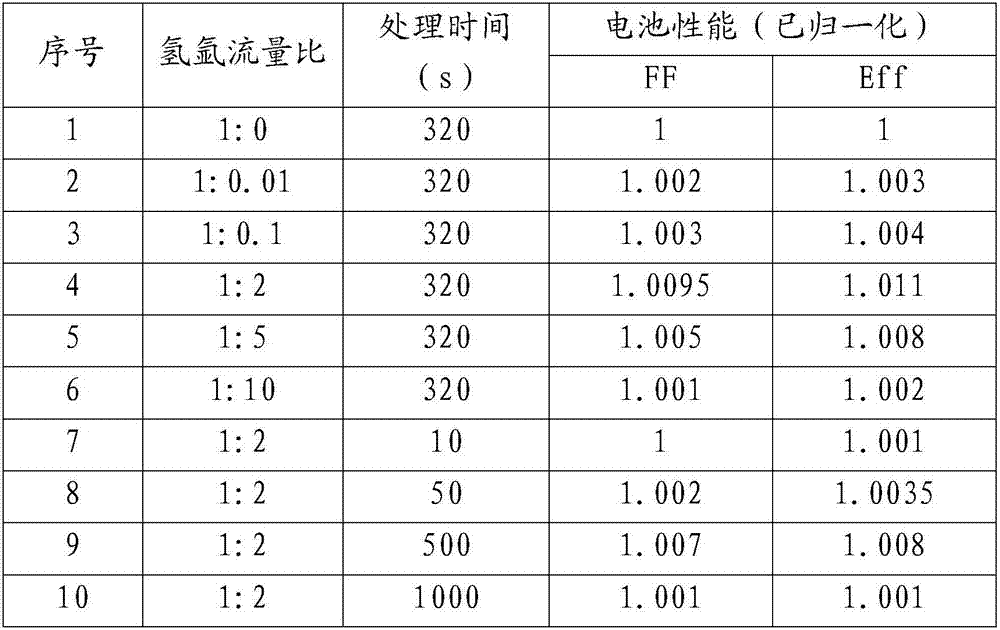
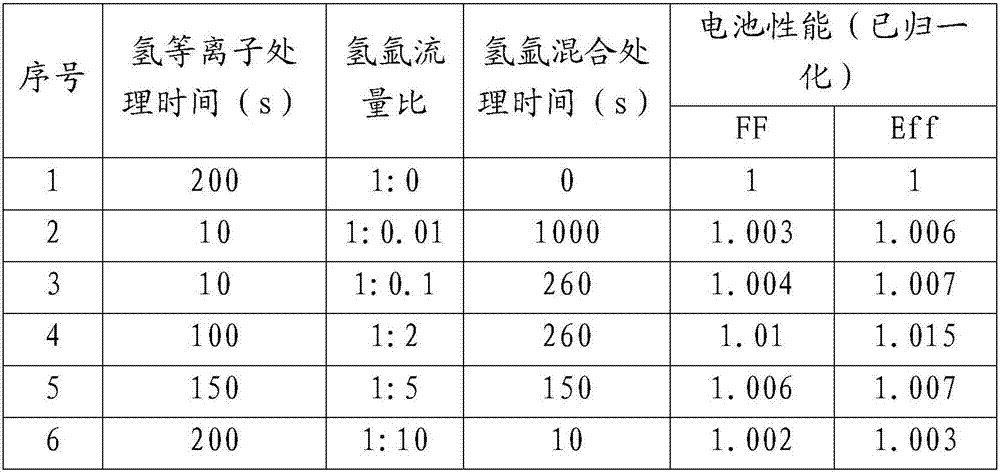
Solar cell and surface treatment method of hydrogenated amorphous silicon i film layer thereof
ActiveCN105489668AImprove performanceEasy to cleanFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationHydrogenSolar cell
The invention discloses a silicon heterojunction solar cell and a surface treatment method of a hydrogenated amorphous silicon i film layer thereof. Plasma treatment is carried out on the surface of the hydrogenated amorphous silicon i film layer by adopting a gas mixture of hydrogen and argon or hydrogen and helium, the hydrogenated amorphous silicon i film layer can be preferably cleaned in a physical manner through argon or helium plasmas, and the increase of the amount of the helium plasmas is further promoted, so that the passivating and cleaning effects for the surface of the hydrogenated amorphous silicon i film layer are strengthened; and moreover, slight damage to the surface of the hydrogenated amorphous silicon i film layer can be generated in the physical bombarding process of the argon or helium plasmas, and the hydrogen plasmas can play a passivating role on the surface of the hydrogenated amorphous silicon i film layer and can also repair the slight damage. Through the synergistic effect of the gas mixture of hydrogen and argon or hydrogen and helium, better passivating and cleaning effects can be achieved for the surface of the hydrogenated amorphous silicon i film layer, so that the battery performance is promoted.
Owner:ENN SOLAR ENERGY
Solar cell and hydrogenated amorphous silicon i membrane surface processing method thereof
ActiveCN107425087AImprove performanceEasy to cleanFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationHydrogenPhysical chemistry
Owner:ENN SOLAR ENERGY
Equipment and method for preparing perovskite material based on atomization gas-liquid-solid thermal deposition method
ActiveCN112239409AIncrease profitUniform thicknessOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationPhysical chemistryHeat deposition
The invention provides equipment for preparing a perovskite material based on an atomization gas-liquid-solid thermal deposition method, wherein the equipment comprises an atomization part, a deposition part and a heating part; the atomization part is used for continuously atomizing a perovskite material precursor solution obtained through dissolving a perovskite material precursor in a solvent, so as to generate a perovskite precursor atomization flow; the deposition part is used for allowing the perovskite material precursor atomized flow to continuously deposit thereon to form a solvent-containing perovskite material precursor deposit; and the heating part is used for continuously heating the deposition part and volatilizing the solvent to grow the perovskite material while the perovskite material precursor deposit containing the solvent is formed. The invention further provides a method for preparing the perovskite material by adopting the equipment. The equipment and the method disclosed by the invention are carried out in real time by adopting atomization, deposition and heating curing, belong to a gas-liquid-solid method, have high utilization rate on the perovskite materialprecursor solution, and can be used for preparing the perovskite material with adjustable and uniform thickness and large grain size.
Owner:深圳市惠能材料科技研发中心(有限合伙)
Application of compound in solar cell
PendingCN114335346AImprove efficiencyImprove stabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSimple aromatic ringSolar battery
The invention discloses an application of a compound in a solar cell, the structural formula of the compound is (G1) n-R-(G2) m, G1 is selected from at least one of a Si-containing group, a phosphate group, a phosphate group, a carboxyl group, a carboxylic ester group, a sulfonic group or an aldehyde group; r is selected from at least one of aromatic rings or aromatic heterocyclic rings; g2 is selected from at least one of halogen, an N-containing group, an S-containing group, an O-containing group or a P-containing group; n > = 1, m > = 1. The invention also provides a solar cell and a preparation method thereof. The invention also provides a laminated solar cell. According to the invention, the compound is applied to the solar cell, the defects of the lower interface of the perovskite absorption layer can be passivated, the interface recombination is reduced, the surface work function of the first carrier transmission layer can be adjusted, the energy level of the first carrier transmission layer is enabled to be better matched with the energy level of the perovskite absorption layer, and the transmission and collection of carriers at the interface are improved.
Owner:LONGI SOLAR TECH (XIAN) CO LTD
Electroluminescent device, preparation method thereof and display device
ActiveCN112349853AFlat surfaceReduce gapMaterial nanotechnologySolid-state devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
The invention discloses an electroluminescent device, which comprises a cathode layer, an electronic function layer, a luminescent layer and an anode layer, and is characterized in that the cathode layer and the anode layer are oppositely arranged, the electronic function layer is arranged between the cathode layer and the anode layer, and the luminescent layer is arranged between the electronic function layer and the anode layer. The electronic function layer comprises a functional material for transmitting and / or injecting electrons and a hydroxyl-modified two-dimensional layered nano material doped in the functional material, and the work function of the hydroxyl-modified two-dimensional layered nano material is smaller than that of the functional material. The invention also disclosesa preparation method of the electroluminescent device. The invention further discloses a display device.
Owner:GUANGDONG JUHUA PRINTING DISPLAY TECH CO LTD
Solar cell and preparation method thereof
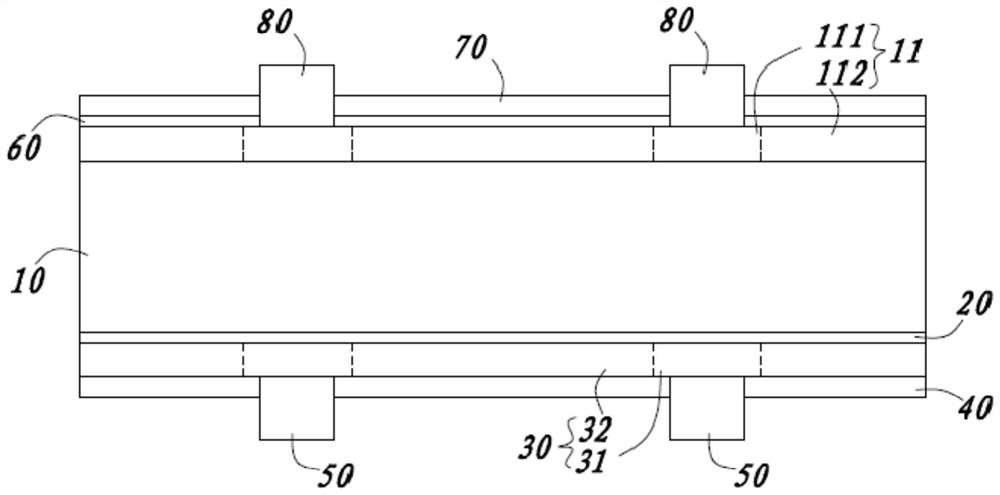
PendingCN112542519AImprove thermal stabilityGood optical performanceFinal product manufactureNanotechnologyCarbide siliconEngineering
The invention provides a solar cell and a preparation method thereof. The solar cell comprises a silicon wafer, and a front electrode and a back electrode which are respectively arranged at two sidesof the silicon wafer; a diffusion layer is formed at the front surface of the silicon wafer; the silicon wafer is provided with a first area and a second area; the solar cell further comprises a tunneling layer, a doped silicon carbide layer and an antireflection layer, wherein the tunneling layer and the doped silicon carbide layer are sequentially arranged on the front face of the first area, the antireflection layer is arranged on the doped silicon carbide layer and the diffusion layer of the second area; and the front electrode penetrates through the antireflection layer and makes contactwith the doped silicon carbide layer. The composite loss and contact resistance of the front electrode position of the solar cell are reduced, the light absorption of the surface of the solar cell isensured, and the conversion efficiency is improved.
Owner:CSI CELLS CO LTD +1
Selenium antimony sulfide thin film solar cell with 3D structure and preparation method thereof
PendingCN114050189AReduce thicknessIncrease the open circuit voltageFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationHeterojunctionElectrical battery
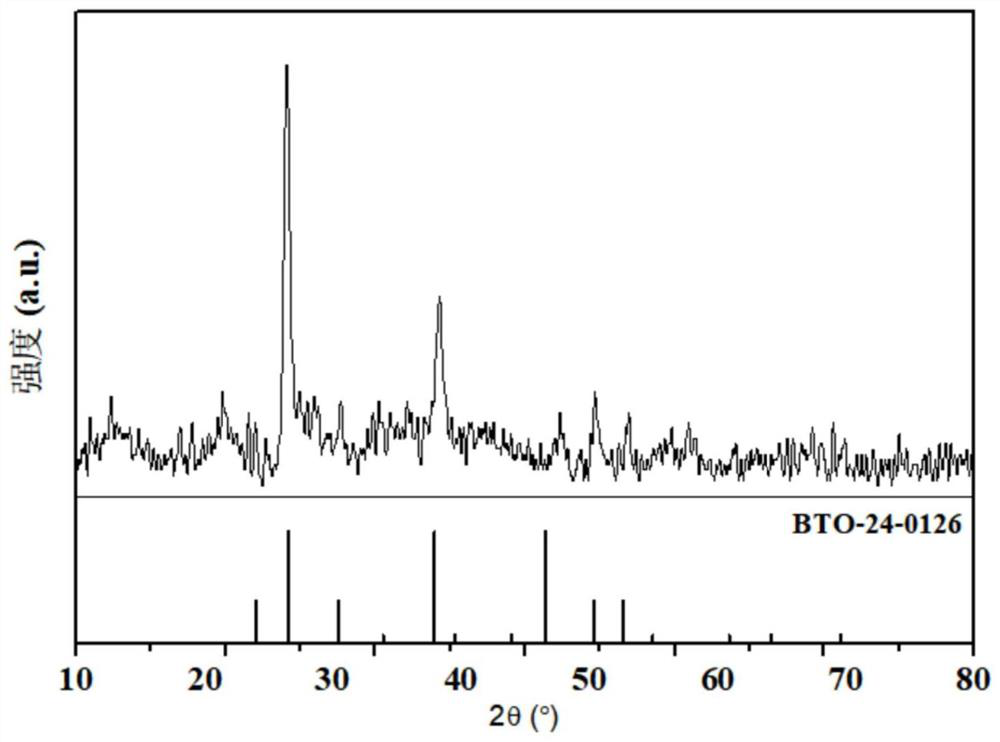
The invention relates to a selenium antimony sulfide thin film solar cell with a 3D structure and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of cell preparation. The thin film solar cell comprises substrate glass, a TiO2 layer, a BaTiO3 thin film layer, a Sb2 (S, Se) 3 thin film layer, a hole transport layer and an electrode layer which are sequentially stacked from bottom to top. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the Sb2 (S, Se) 3 thin film solar cell, the TiO2 layer of the prepared Sb2 (S, Se) 3 thin film solar cell is of a 3D-TiO2 array structure, pn junctions are formed by the TiO2 layer and the Sb2 (S, Se) 3 thin film layer, the BaTiO3 thin film serves as a passivation layer to be inserted between the pn junctions, and recombination of heterojunctions at an interface is reduced. The BaTiO3 thin film layer and the TiO2 layer form a double-buffer-layer structure, the width of a depletion layer is increased, and the open-circuit voltage of the cell can be effectively improved. And the ferroelectricity of BaTiO3 is utilized, so that the separation capacity of current carriers and the open-circuit voltage of the battery are improved. And the thickness of the BaTiO3 film is relatively small, so that the problem of high internal resistance of the battery caused by poor conductivity of BaTiO3 is solved based on the quantum tunneling effect.
Owner:SUZHOU TALESUN SOLAR TECH CO LTD +1
A new composite structure full back heterojunction solar cell and its preparation method
ActiveCN108963005BGuaranteed lifeIncrease short circuit current densityPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSolar cell
The invention discloses a novel composite structure full-back heterojunction solar cell and a preparation method thereof. The solar cell includes: an N-type silicon substrate, a silicon nitride film, an aluminum oxide film, intrinsic polysilicon, P-type polysilicon, N-type polysilicon; the front surface of the N-type silicon substrate is covered with an aluminum oxide film, and the aluminum oxide film is covered with a silicon nitride film; the back surface of the N-type silicon substrate is deposited with intrinsic polysilicon P-type polysilicon and N-type polysilicon. In the present invention, the polysilicon layer is deposited by the LPCVD of the horizontal slice mode or the PECVD of the horizontal slice type, and the homogeneous junction layer can effectively reduce the interface defect state and reduce the interface recombination; the laser doping technology is used to realize the doping of the P-type polysilicon layer, and the maximum Maximize the minority carrier life of the silicon substrate and reduce the recombination current density of the metal-silicon contact; at the same time, the battery with the IBC structure allows the battery to make full use of the solar spectrum and maximize the short-circuit current density of the battery.
Owner:LAPLACE RENEWABLE ENERGY TECH CO LTD
Silicon-germanium heterojunction solar cell and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105047748AIncrease the open circuit voltageIncrease short circuit currentFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationHeterojunctionAluminum doped zinc oxide
The invention discloses a silicon-germanium heterojunction solar cell. The structure of the silicon-germanium heterojunction solar cell sequentially comprises a silver electrode, an aluminum-doped zinc oxide (AZO) conductive layer, n-type monocrystalline silicon, an i-type SiGe alloy buffer layer film, a p-type Ge film and a gold electrode from top to bottom. The silicon-germanium heterojunction solar cell has a broad spectrum response value of 300-1800nm. According to the cell disclosed by the invention, a SiGe alloy buffer layer is deposited between silicon and germanium, thereby being capable of effectively reducing the interface state, reducing interface recombination, and increasing open-circuit voltage of the cell. In addition, a band gap of the buffer layer changes gradually, so that sunlight can be absorbed better, and short-circuit current of the cell is increased. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the silicon-germanium heterojunction solar cell. The preparation method is safe in raw material, capable of directly applying existing equipment and relatively low in cost.
Owner:江苏润阳悦达光伏科技有限公司
Thin film solar cell absorption layer forming method, thin film solar cell and preparation method
ActiveCN112201702AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyEasy transferFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationPhysical chemistryMaterials science
The invention discloses a thin film solar cell absorption layer forming method, a thin film solar cell and a preparation method. The thin film solar cell absorption layer forming method comprises thefollowing steps of: sequentially forming a first precursor film, an Al2O3 layer and a second precursor film on a bottom electrode to form a precursor film laminatation layer; and carrying out high-temperature selenylation or vulcanization treatment on the precursor film lamination layer to form an absorption layer, wherein the surface of the absorption layer has the characteristic of a semiconductor type opposite to that in the body of the absorption layer, the first precursor film and the second precursor film are I-II-IV-VI group compound semiconductors, the first precursor film at least comprises a Cu element, and the second precursor film at least contains Ag element. According to the invention, an open-circuit voltage (VOC) is increased, so that the corresponding open-circuit voltagedeficit (VOC,def) is as low as 0.327 V, the carrier transmission is optimized, the carrier collection efficiency is improved, the interface recombination of the absorption layer / buffer layer is reduced, and the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the thin film solar cell is remarkably improved.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
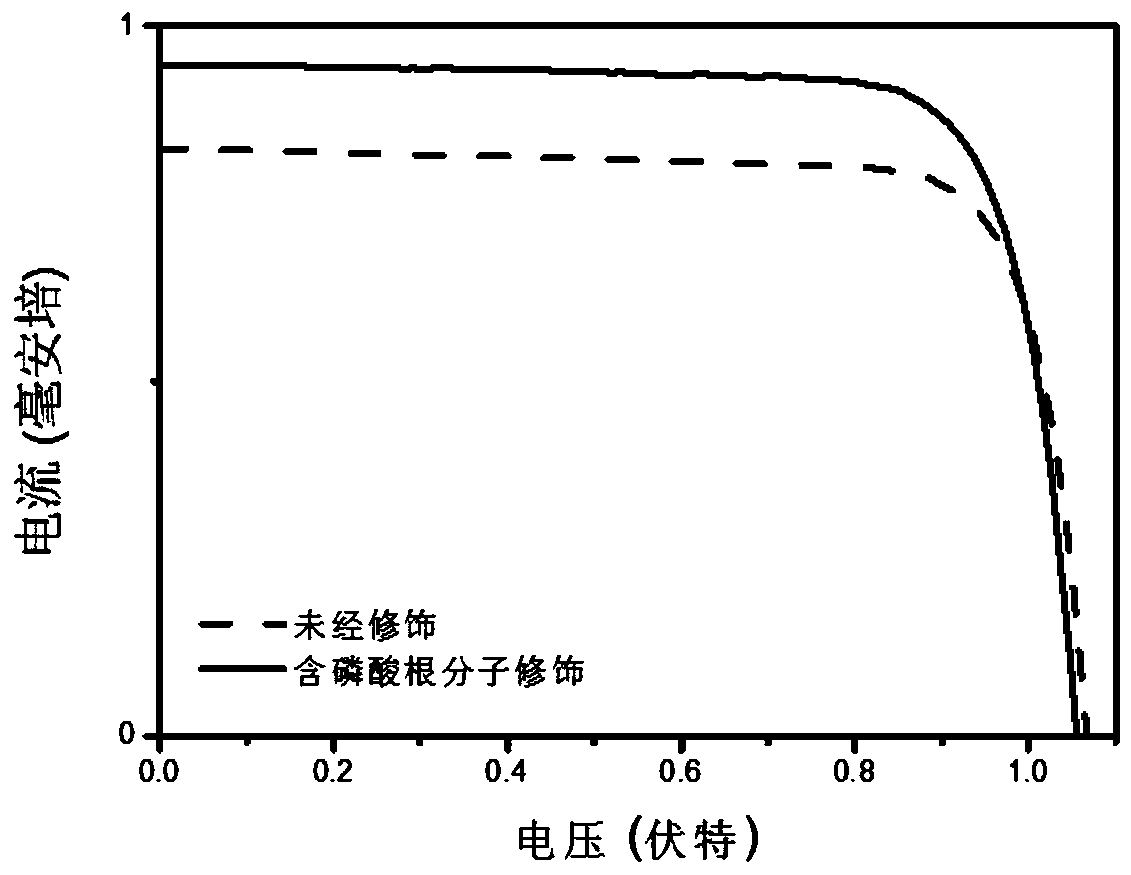
Phosphate molecule modified perovskite photovoltaic device and preparation method and application thereof
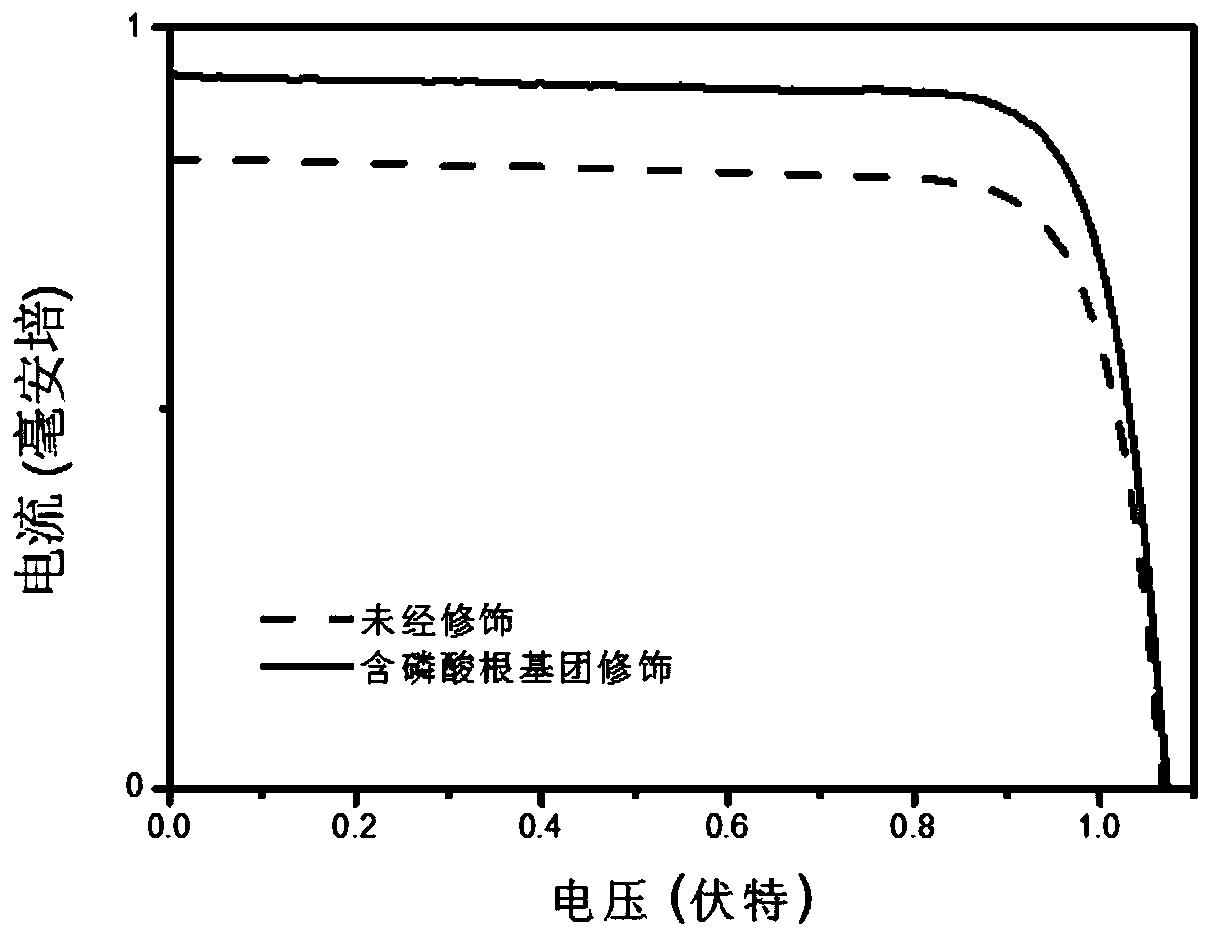
ActiveCN111223988AEasy to prepareLow costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingO-Phosphoric AcidPhosphate
The invention discloses a phosphate molecule modified perovskite photovoltaic device and a preparation method and application thereof. Phosphoric acid organic molecules are used, an interface modification layer containing phosphate molecules is introduced into an interface layer of a perovskite photovoltaic device; the perovskite photoactive layer in the perovskite photovoltaic device is modifiedto passivate the surface defects of the perovskite photoactive layer and improve the transmission efficiency of electrons and holes at the interface of the device, so that the perovskite photovoltaicdevice with high photoelectric conversion efficiency and high stability is realized. The interface defects in the perovskite photovoltaic device are passivated. The phosphate radical-containing molecular modified perovskite photovoltaic device prepared by adopting the method is environment-friendly and low in energy consumption.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com