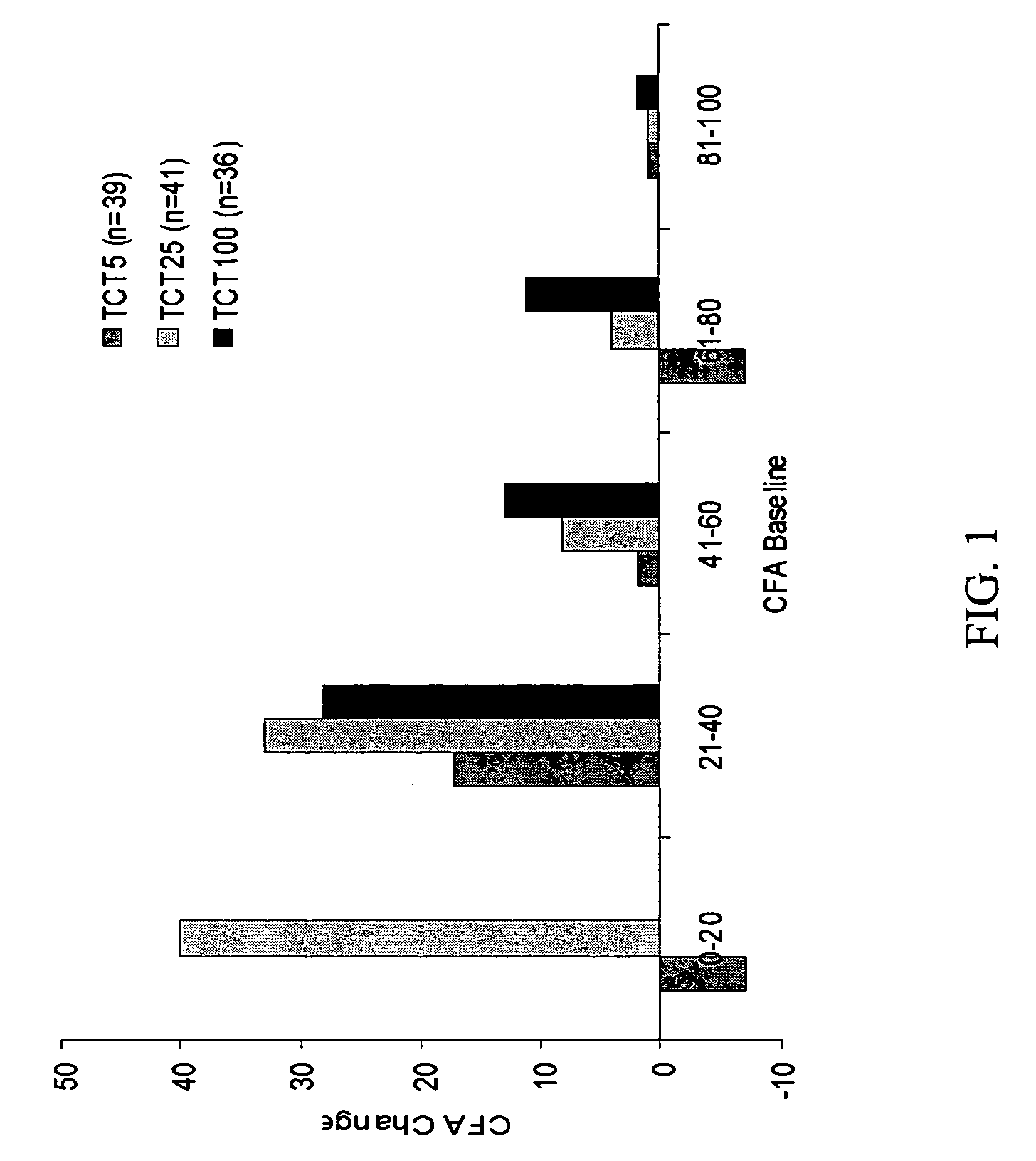
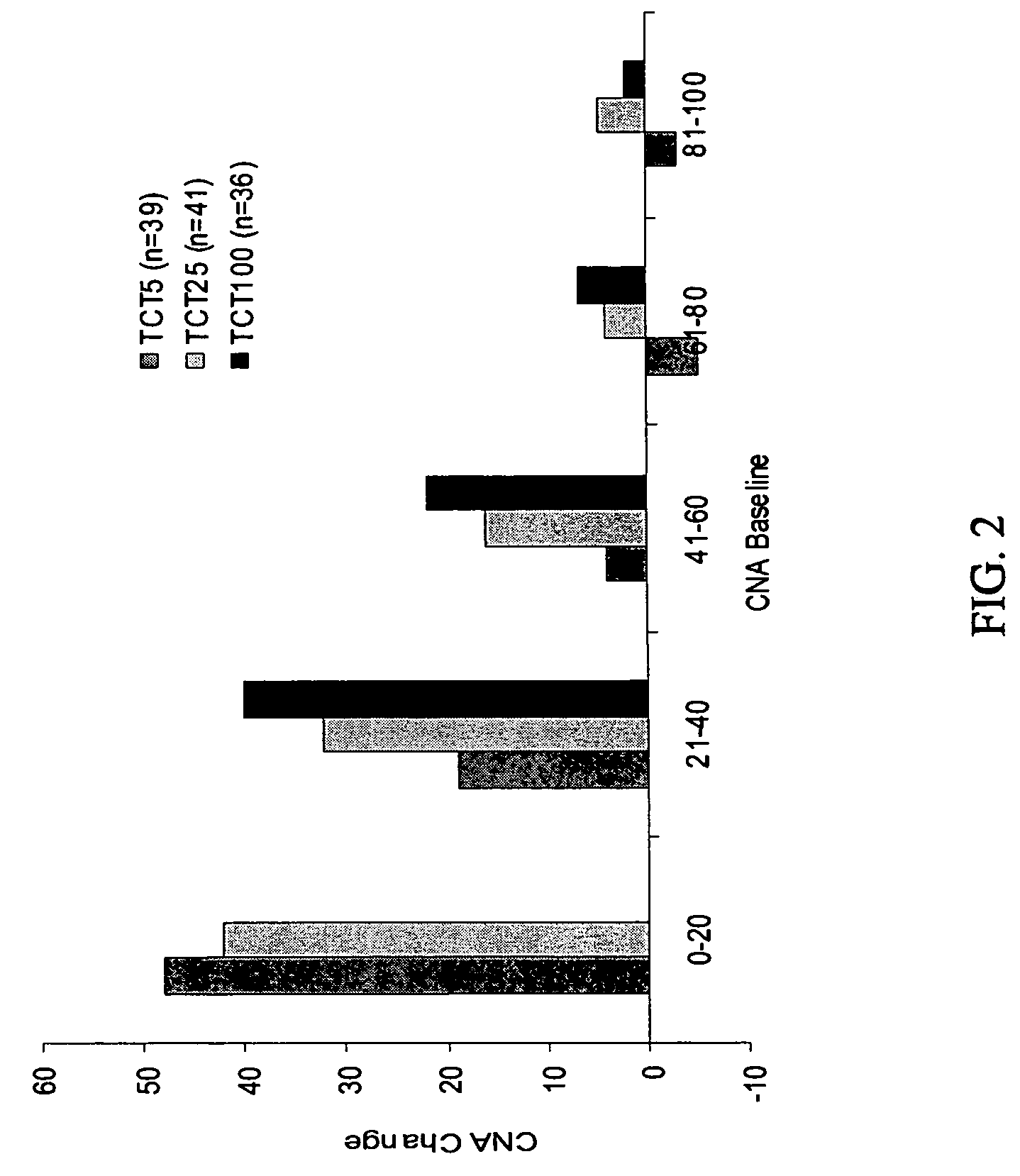
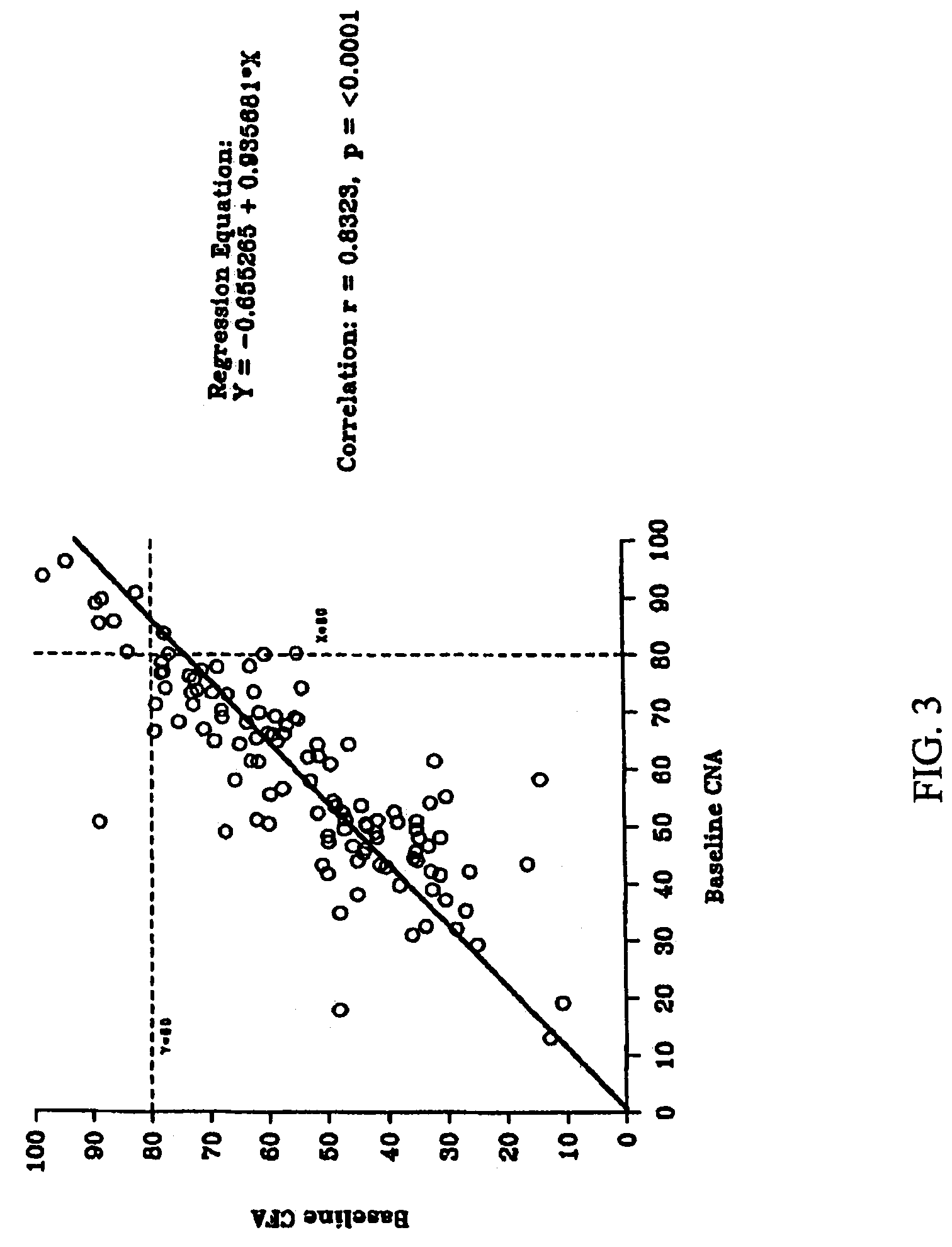
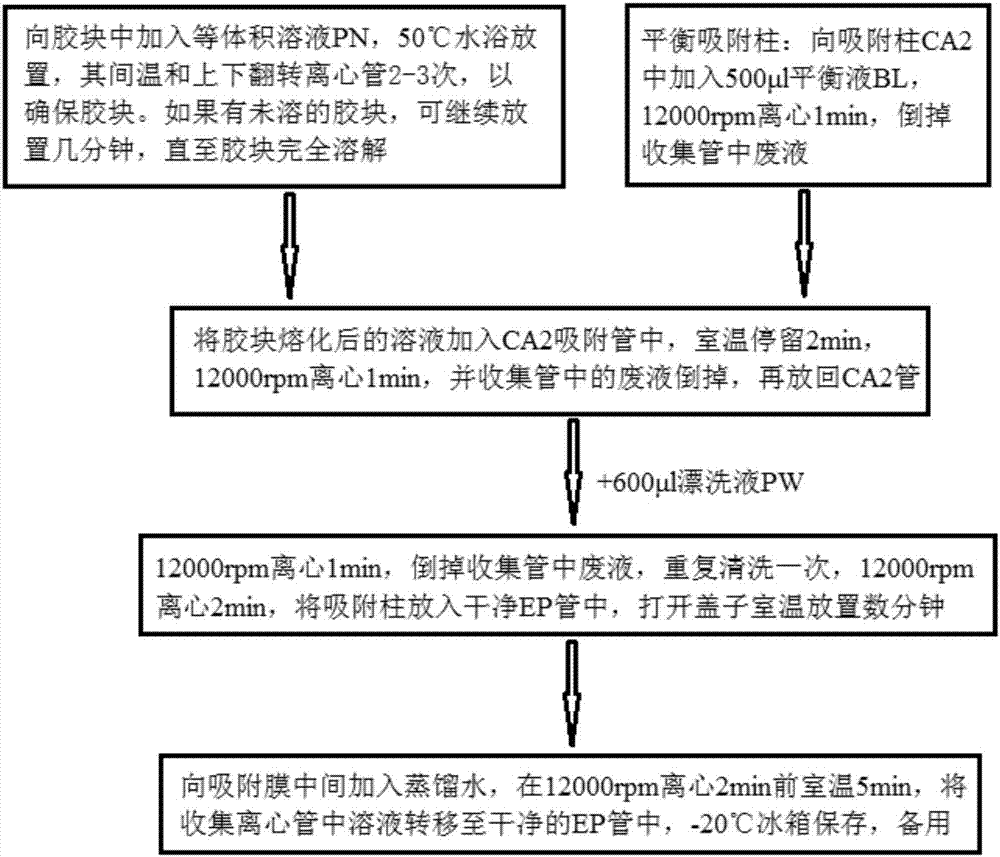
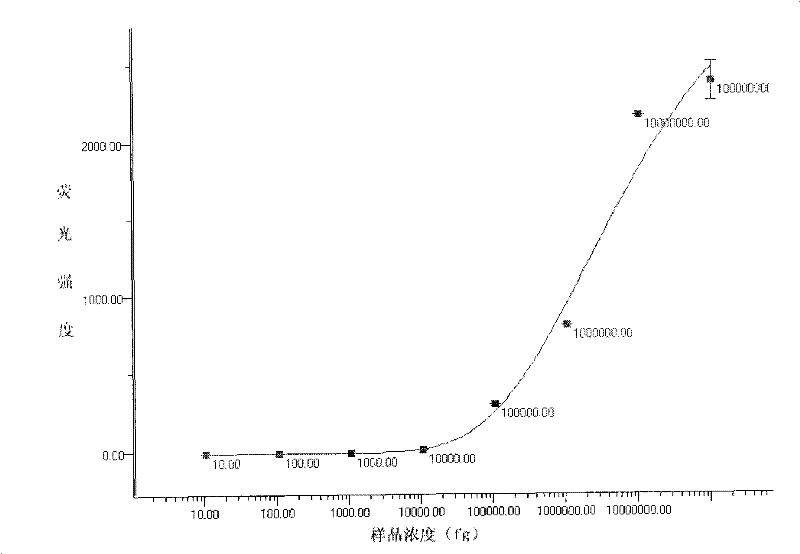
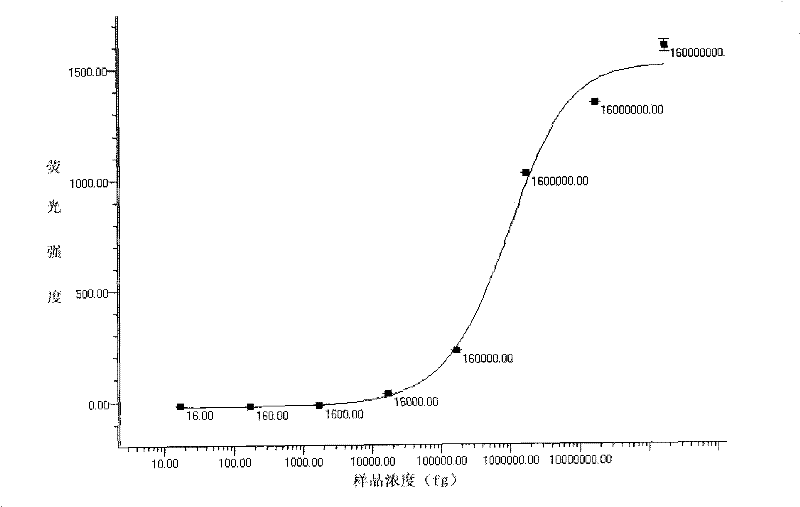
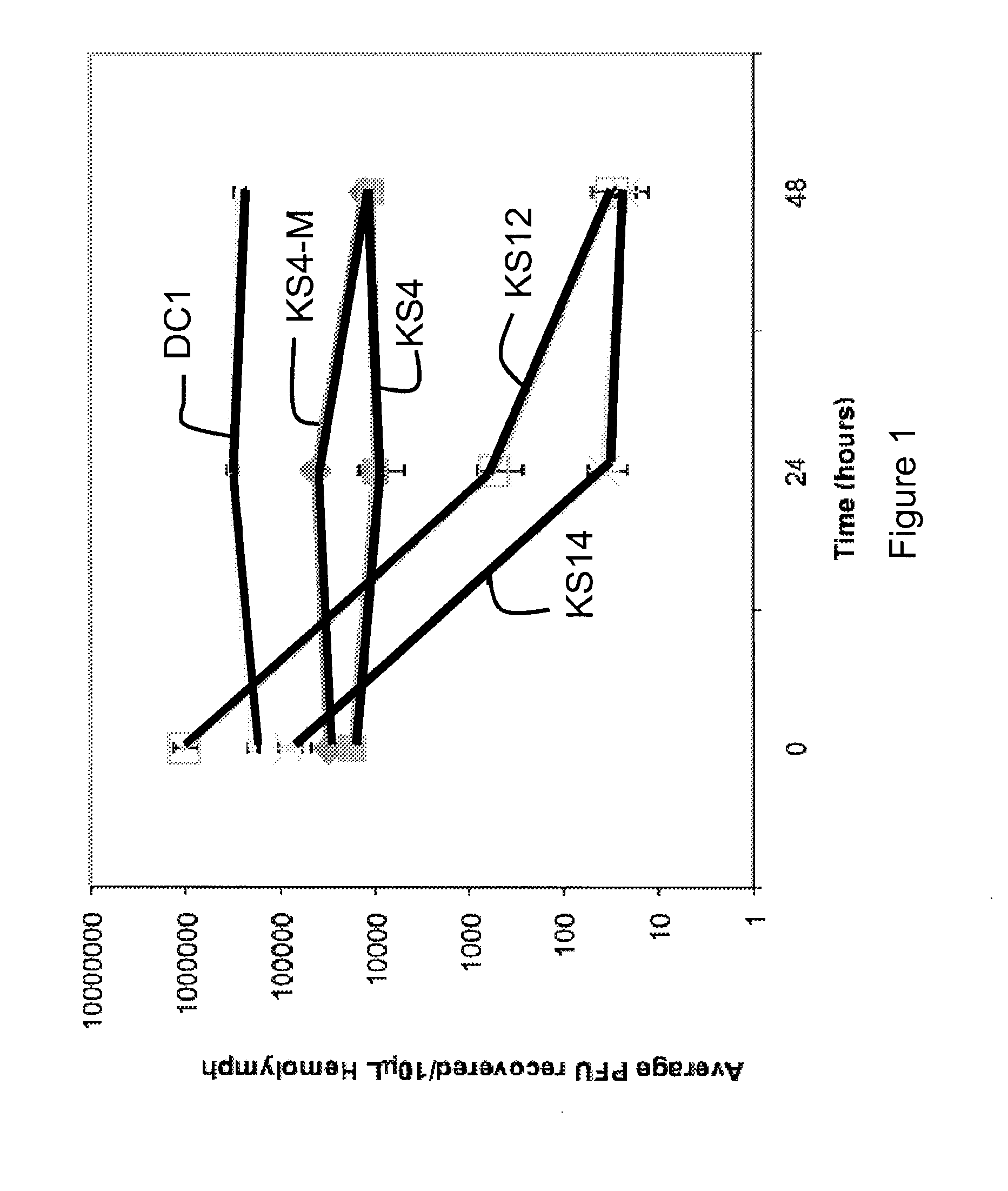
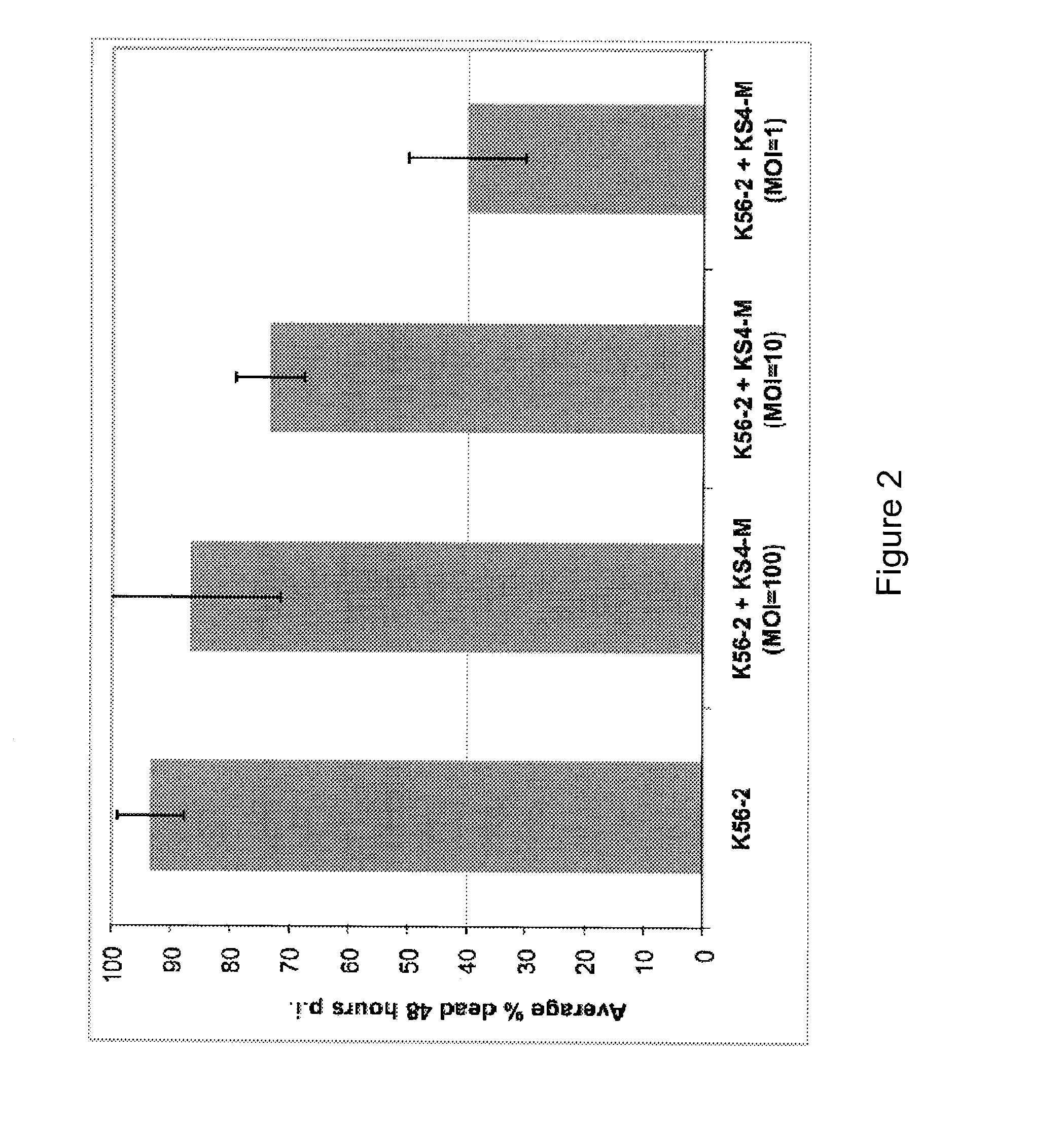
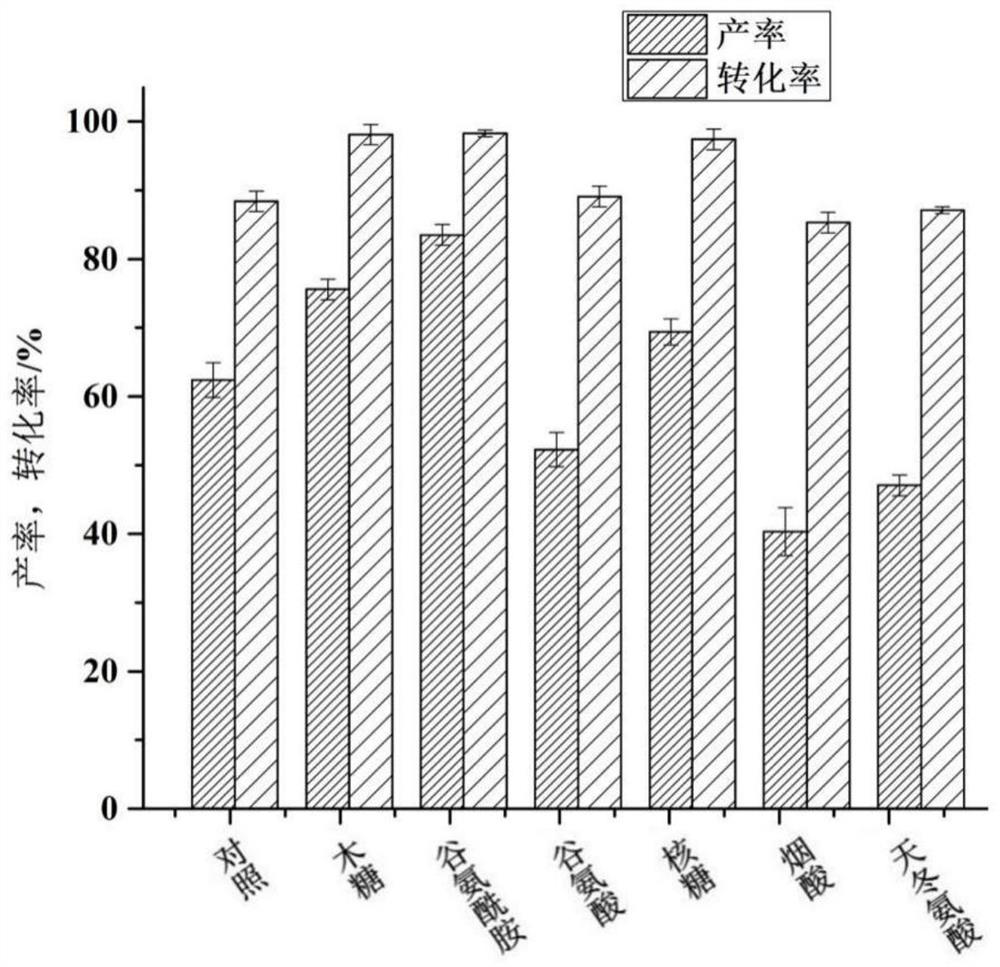
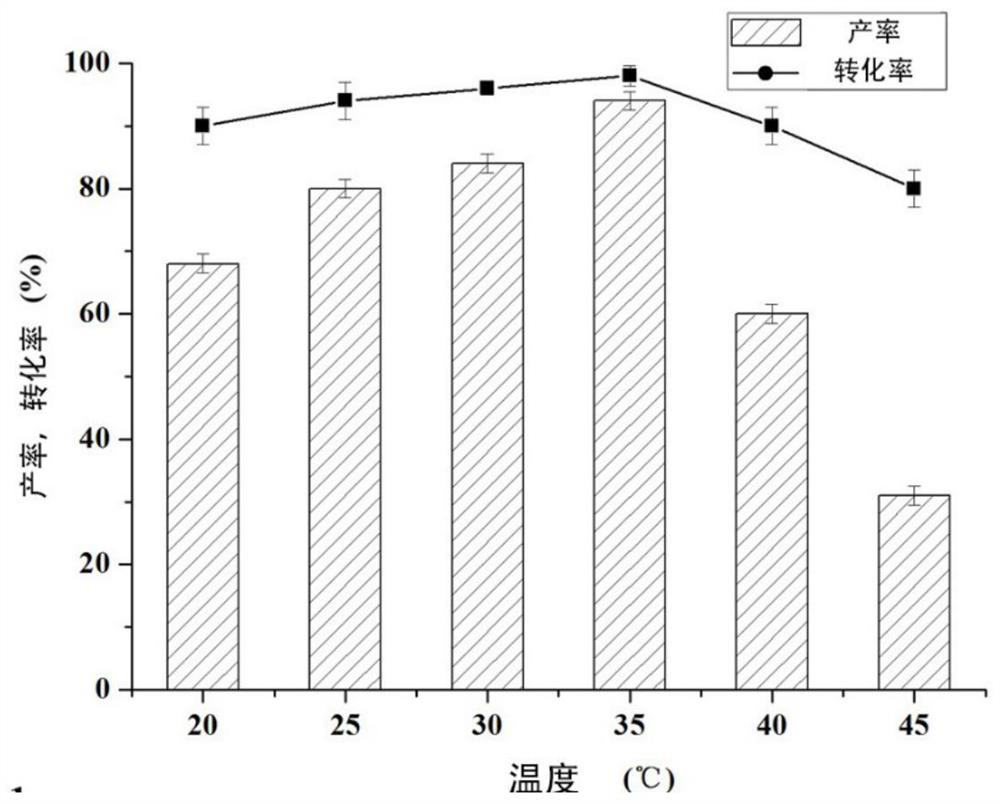
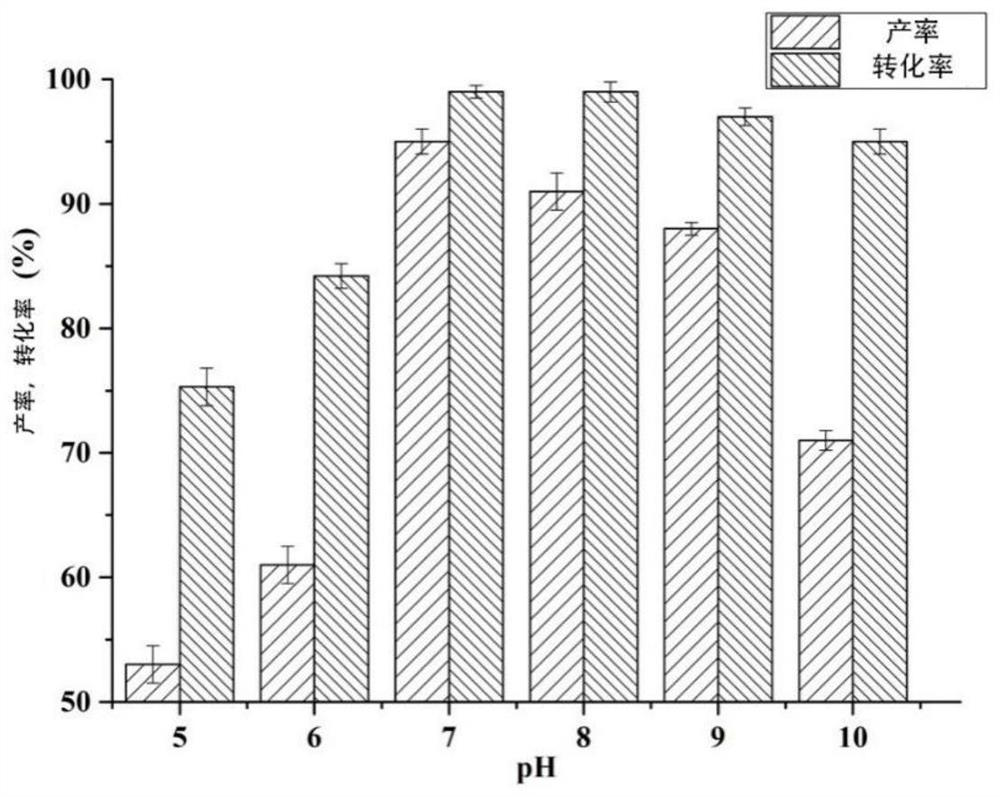
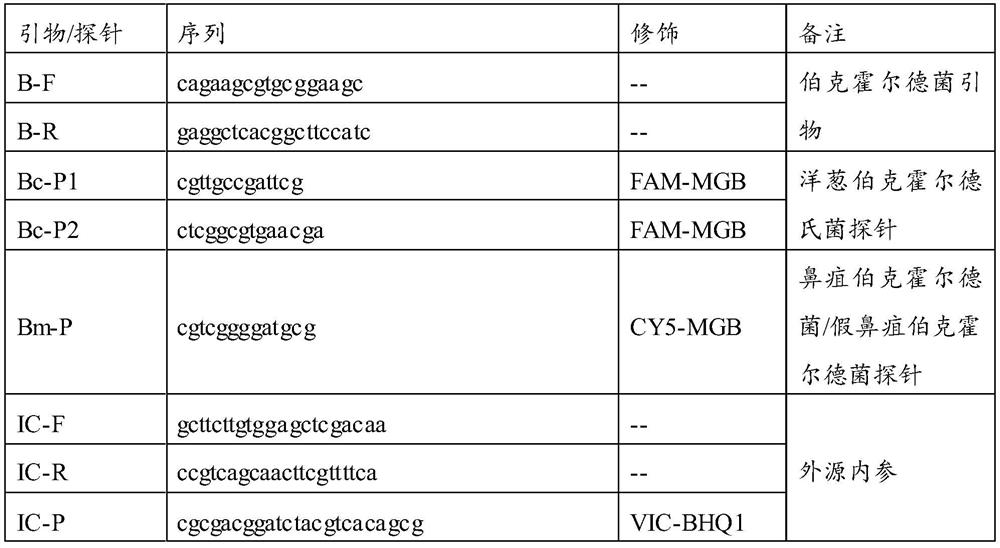
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
39 results about "Burkholderia lata" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Burkholderia lata is a bacterium from the genus of Burkholderia and the family of Burkholderiaceae which belongs to the Burkholderia cepacia complex.
Compositions and methods for treating pancreatic insufficiency
InactiveUS7718169B2Stable enzyme componentEffective low dose treatment regimensPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemProteinase activityExocrine pancreatic insufficiency
The present invention relates to compositions for the treatment of conditions, including pancreatic insufficiency. The compositions of the present invention comprise lipase, protease and amylase in a particular ratio that provides beneficial results in patients, such as those afflicted with pancreatic insufficiency. This invention also relates to methods using such compositions for the treatment of pancreatic insufficiency. The compositions specifically comprise crosslinked Burkholderia cepacia lipase crystals, Aspergillus melleus protease crystals and amorphous Aspergillus oryzae amylase in a ratio of about 1:1:0.15 USP units.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Kit for quickly detecting 15 pneumonia pathogenic bacteria
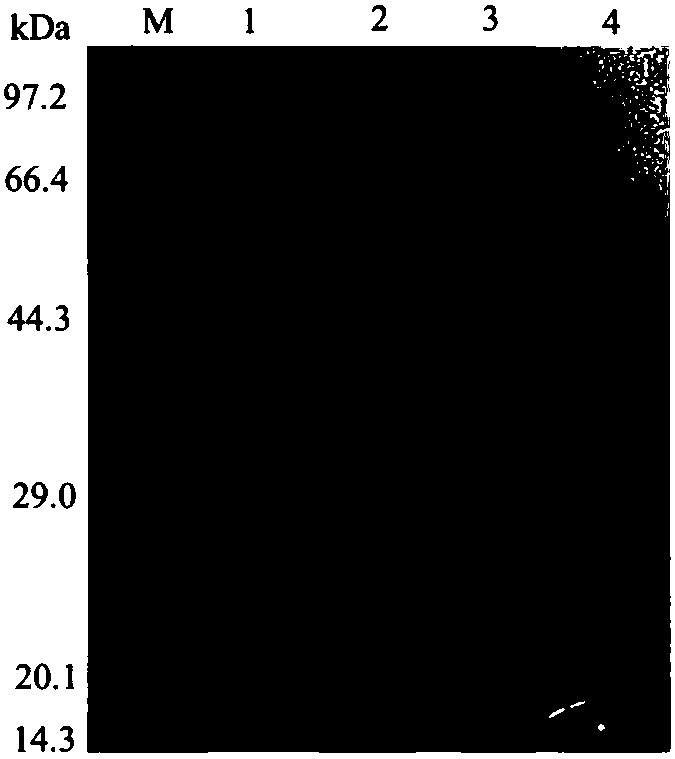
ActiveCN107338315AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesStaphylococcus aureus
The invention discloses a kit for quickly detecting 15 pneumonia pathogenic bacteria. The kit can detect streptococcus pneumoniae, staphylococcus aureus, haemophilus influenzae, mycoplasma pneumoniae, pseudomonas aeruginosa, baumanii, enterococcus faecalis, enterococcus faecium, klebsiella pneumoniae, escherichia coli, enterobacter cloacae, stenotrophomonas maltophilia, burkholderia cepacia, legionella pneumophila and chlamydia pneumoniae which cover clinically common pneumonia pathogenic bacteria difficult to culture. 16S rDNA and specific gene sequences corresponding to the pneumonia pathogenic bacteria are detected by combining gene chips with multiple asymmetric PCR reactions, and the categories of the bacteria in a to-be-detected sample are identified in genus and species. The kit makes up for the defect that current clinical detection of pneumonia pathogenic bacteria is not in time or comprehensive and a novel detection means for early diagnosis and early treatment of patients suffering from pneumonia is provided.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA +1
Burkholderia kururiensis strain and application thereof
ActiveCN104911122AImprove effectivenessIncrease nitrogenase activityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMicroorganismNicotiana tabacum
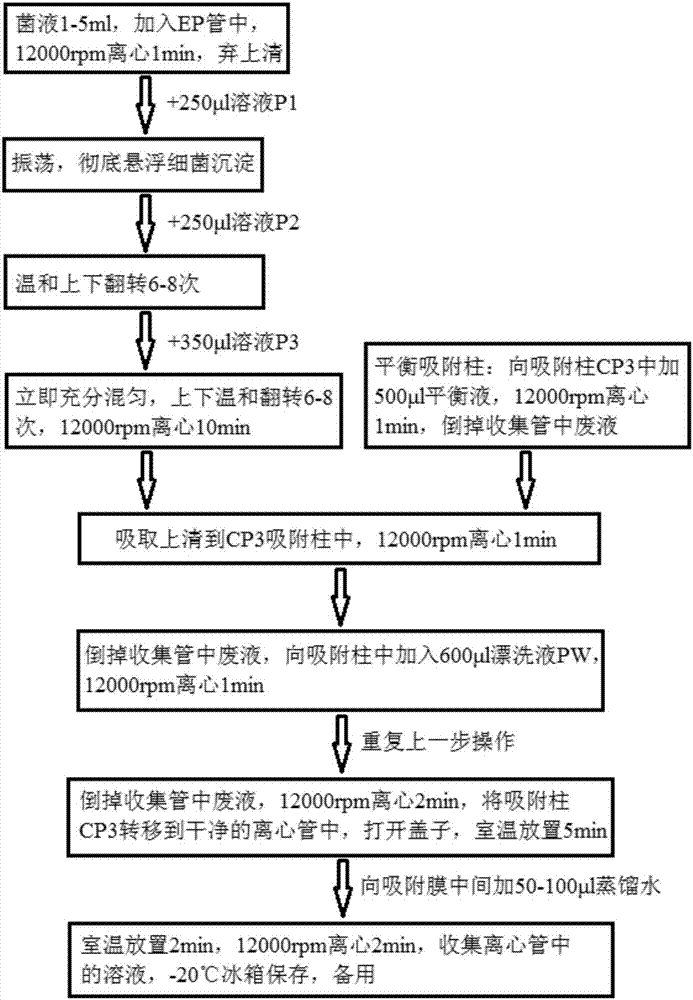
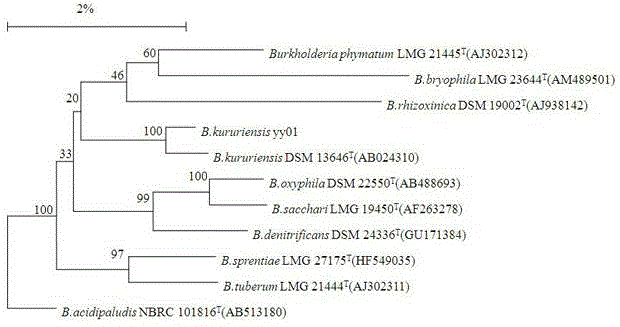
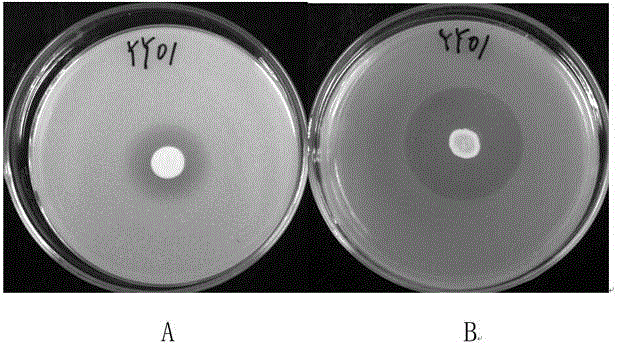
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms, and specifically discloses a Burkholderia kururiensis strain and application thereof. The strain is Burkholderia kururiensis yy01, and is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on March 17, 2015, and has preservation No. CGMCC No. 10631. The strain yy01 has both efficient releasing of phosphorus and potassium and high nitrogenase activity, increases the effectiveness of insoluble phosphorous and potassium in soil and convert free nitrogen in the air into ammonia for absorption and utilization by crops, and has significant growth-promoting effect on rice, tobacco and other crops.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Antimicrobial agent and method for the production thereof
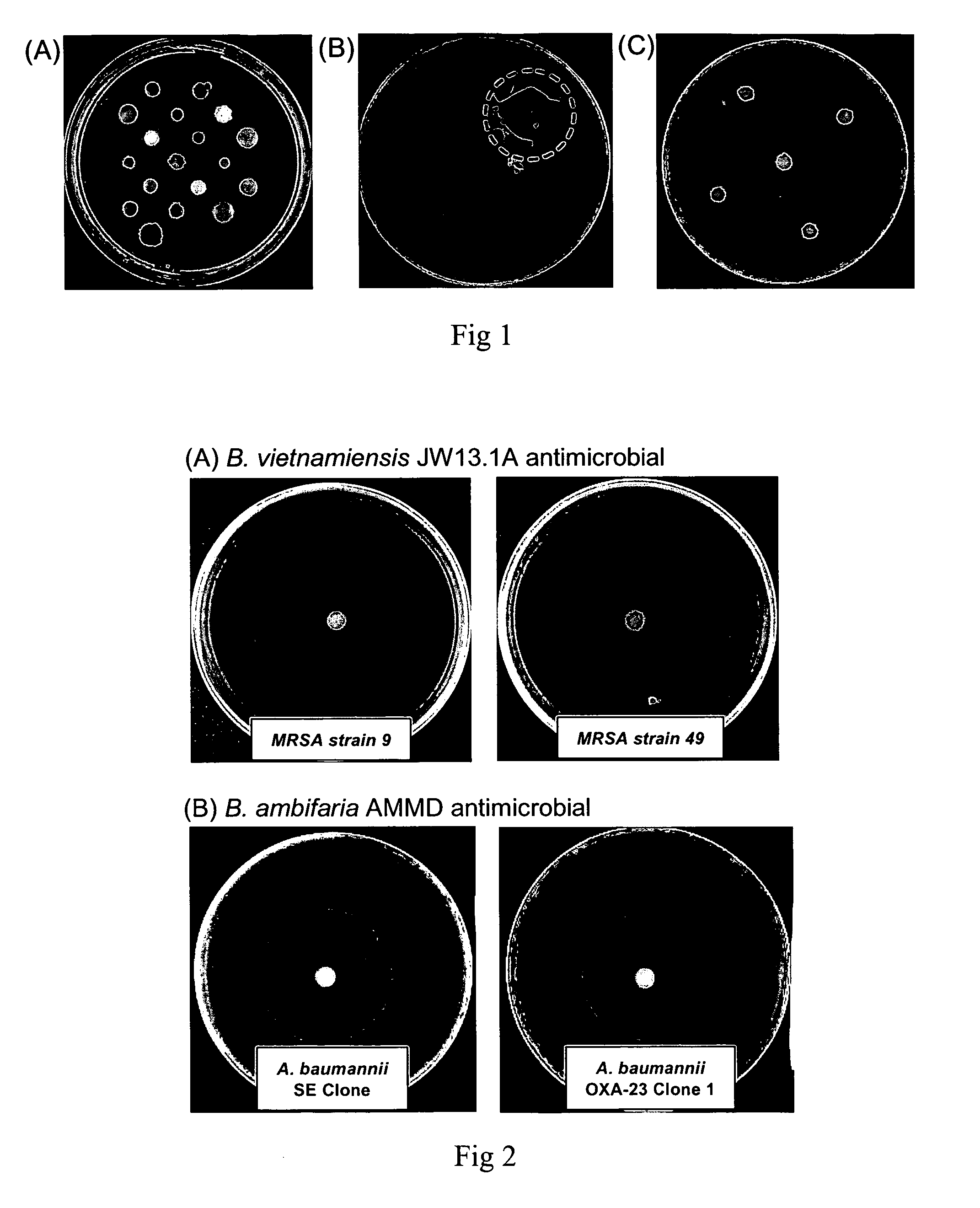
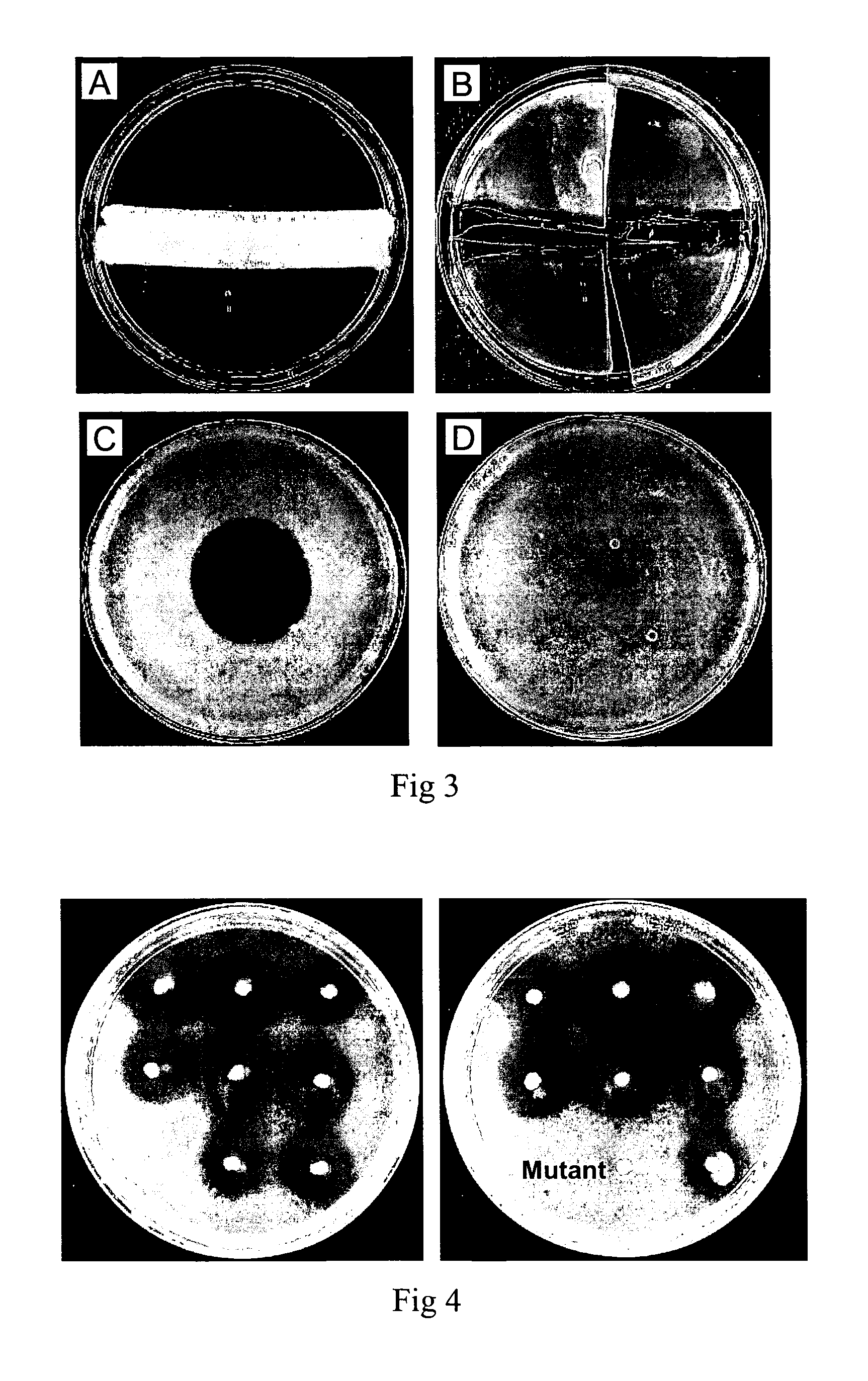
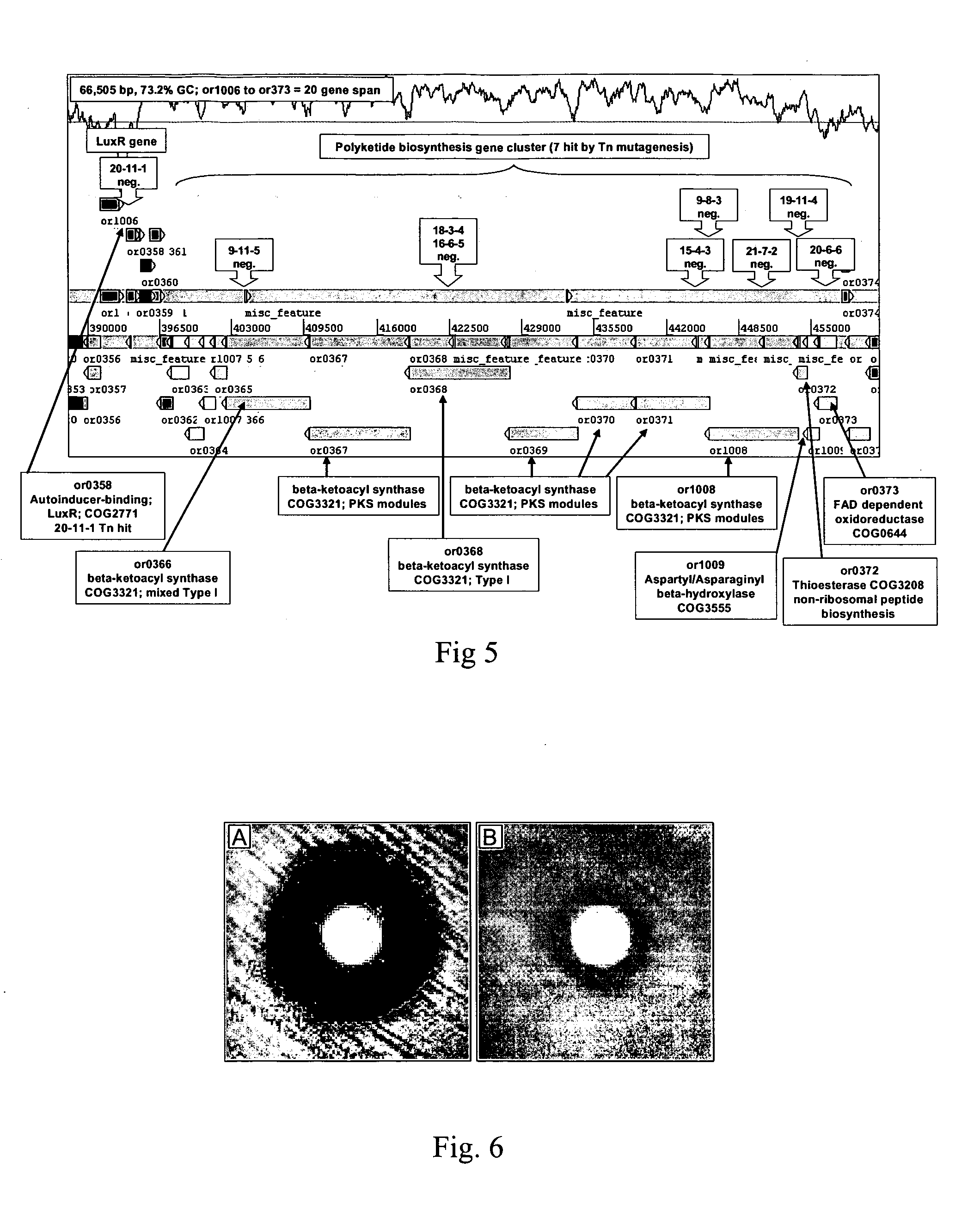
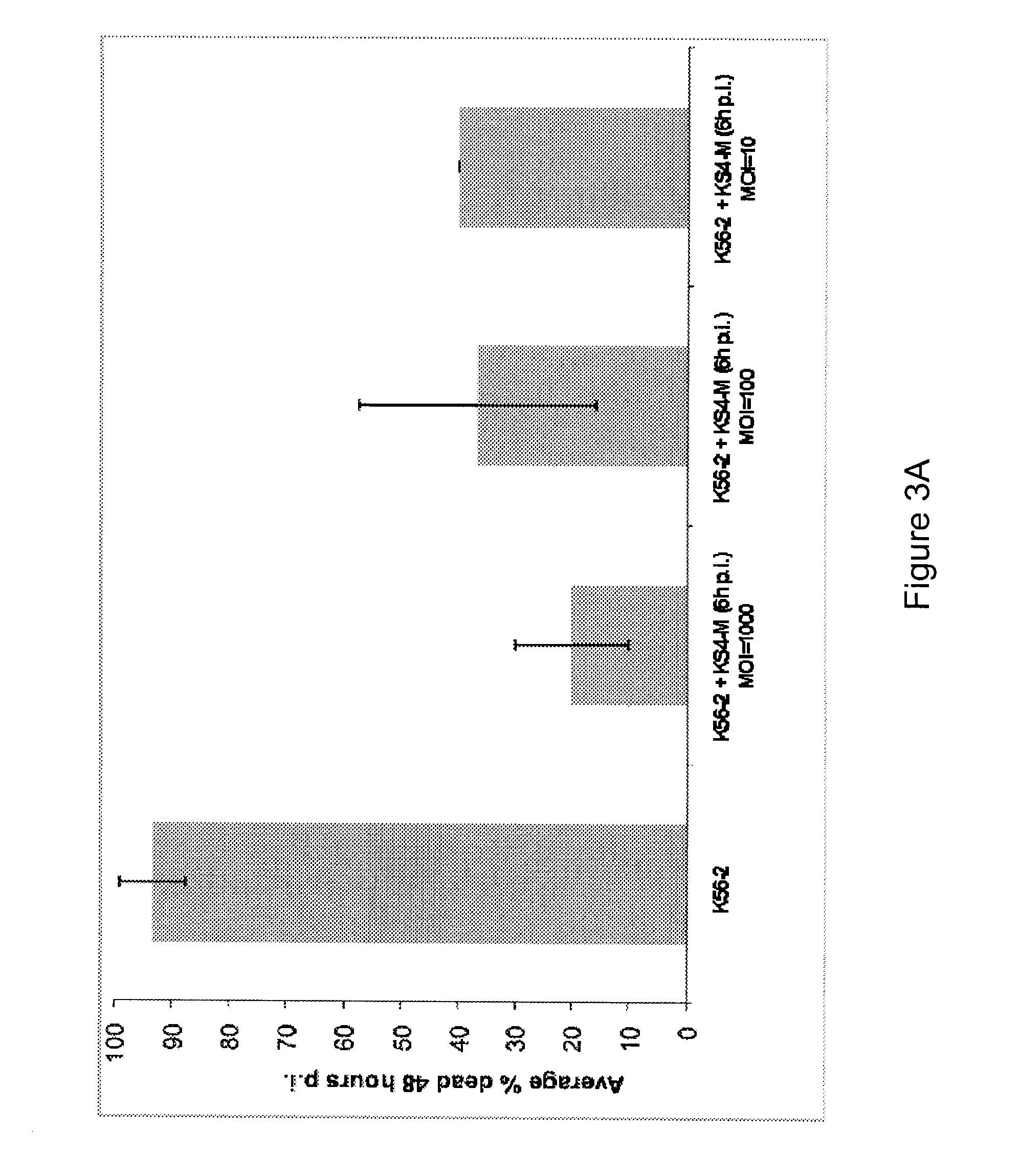
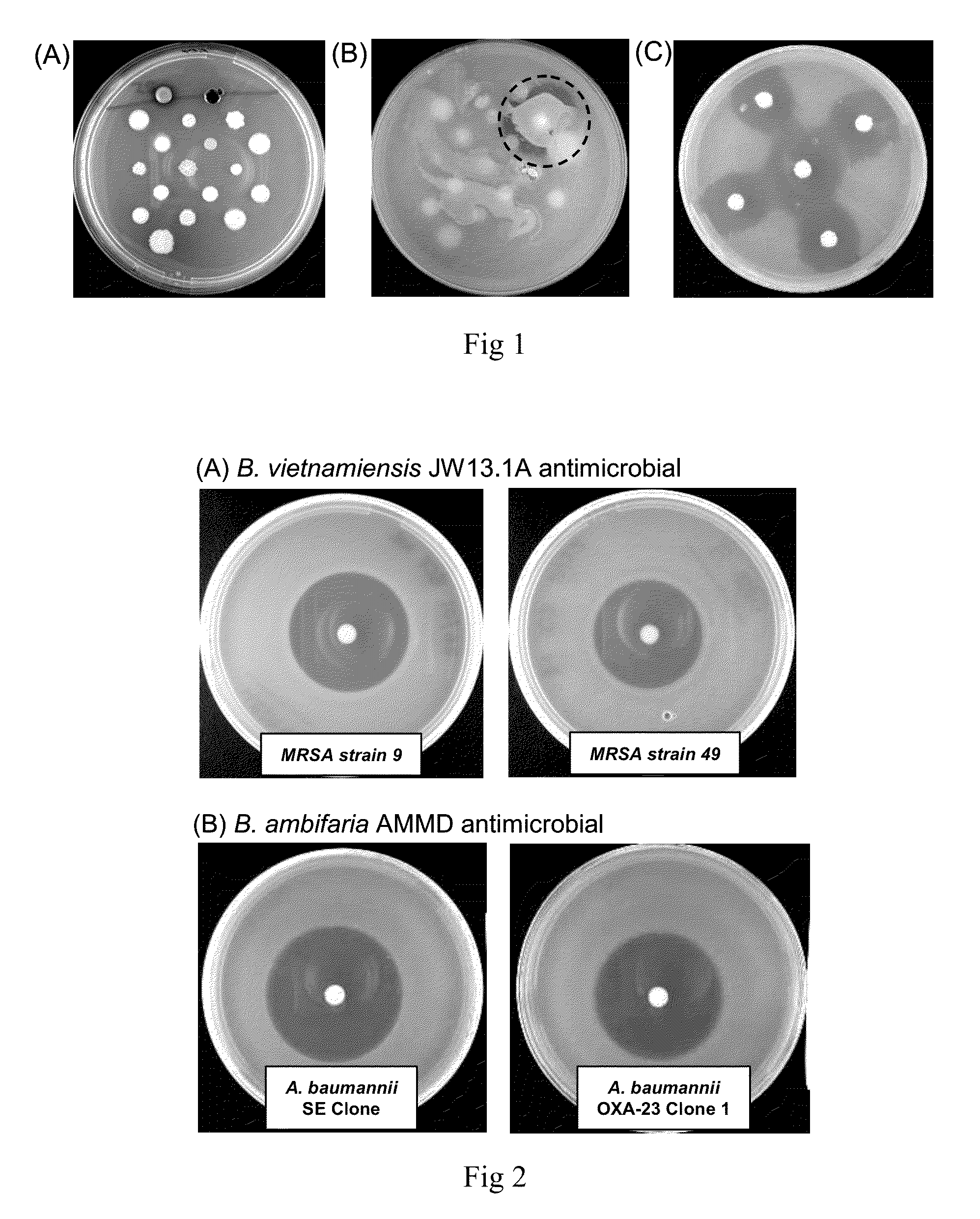
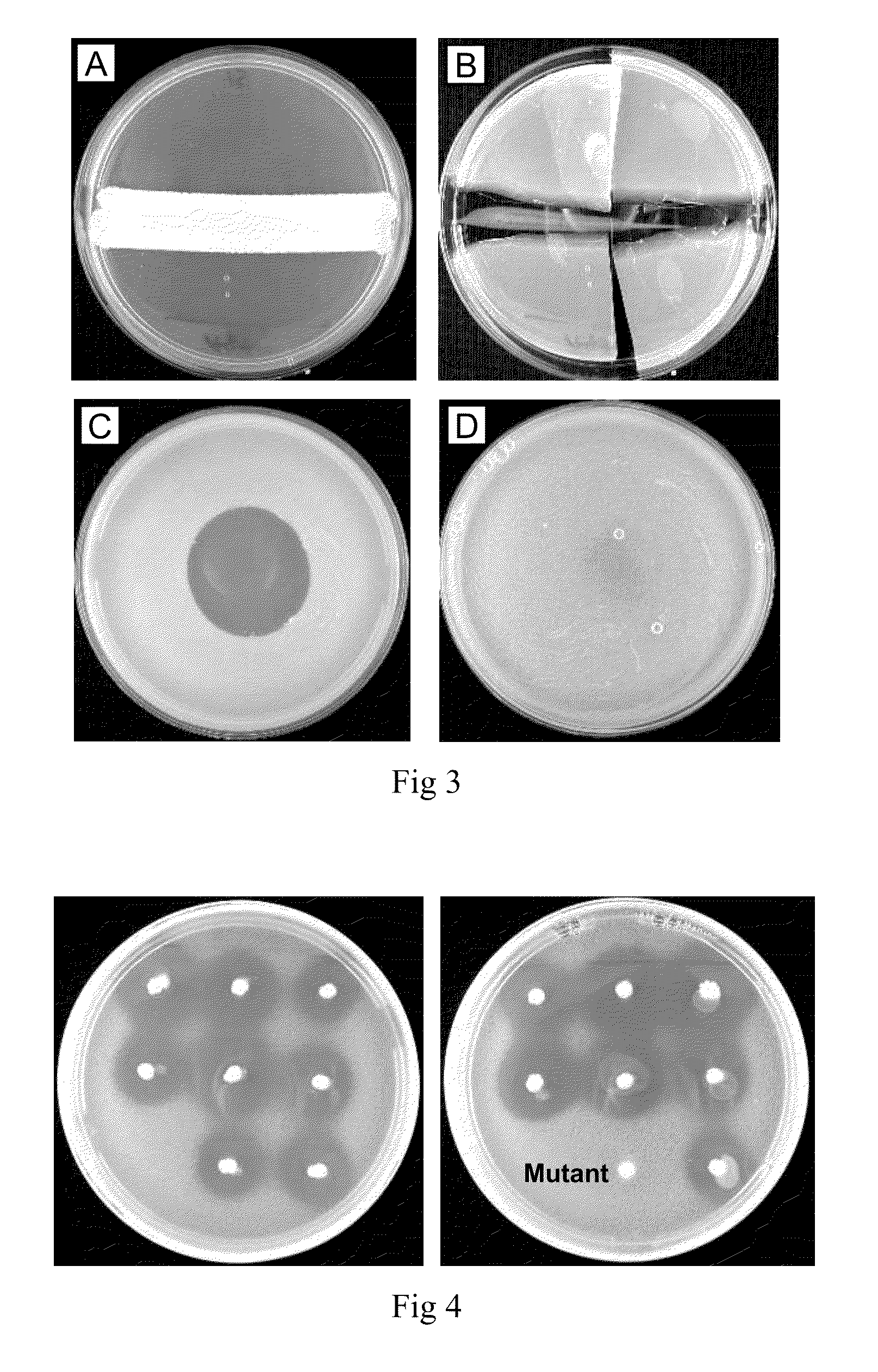
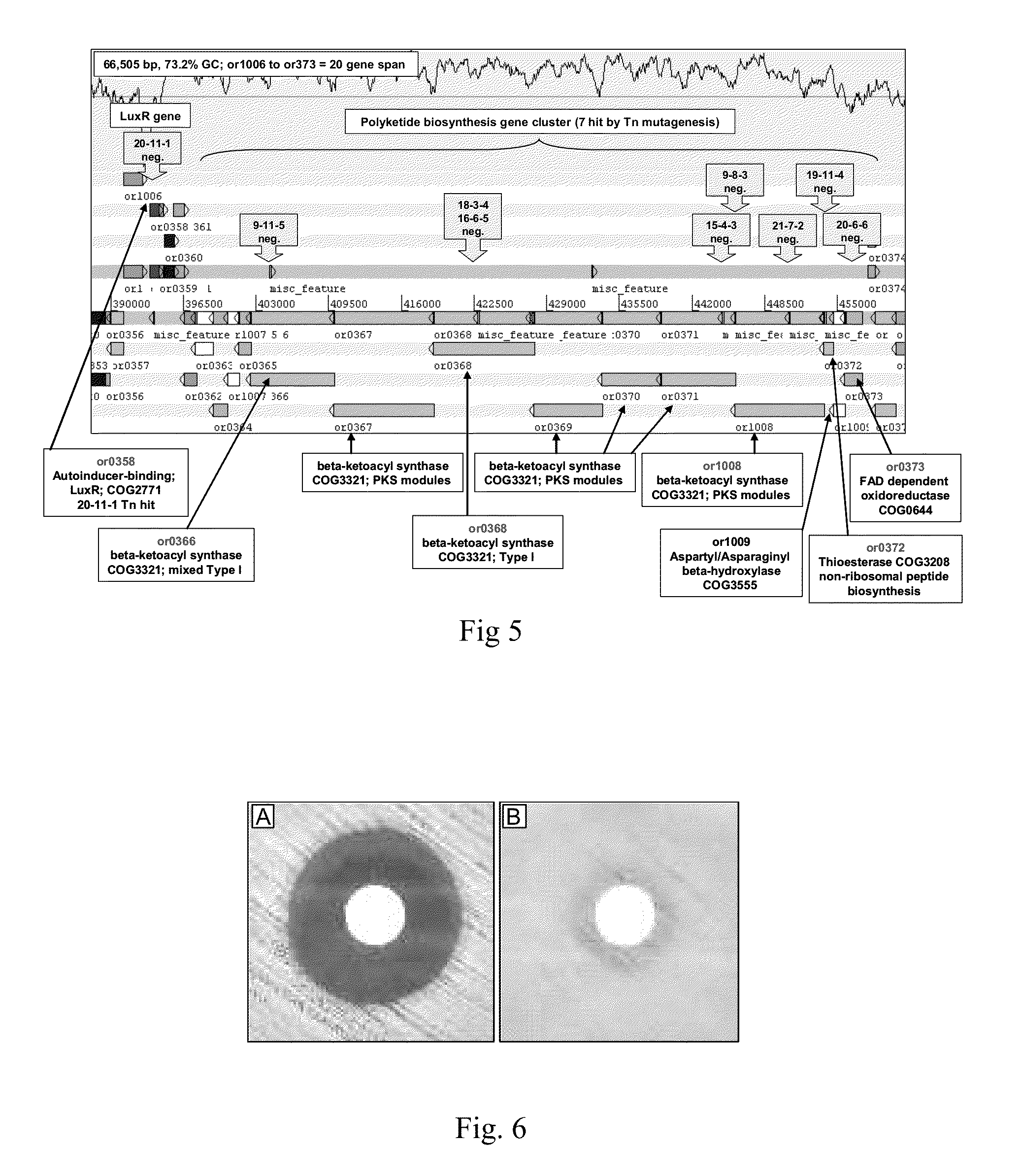
Provided are antimicrobial agents produced from Burkholderia cepacia complex (Bcc) bacteria, in particular from bacteria which comprise a cluster of polyketide synthesis genes. Also provided is use of the antimicrobial agents in the treatment of disease. Further provided are methods for producing antimicrobials, methods for detecting antimicrobial producing bacterial strains and kits for use in the methods.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE CARDIFF CONSULTANTS LTD
Application of enzyme FadD1 in pseudomonas aeruginosa for degrading DSF family signal molecules
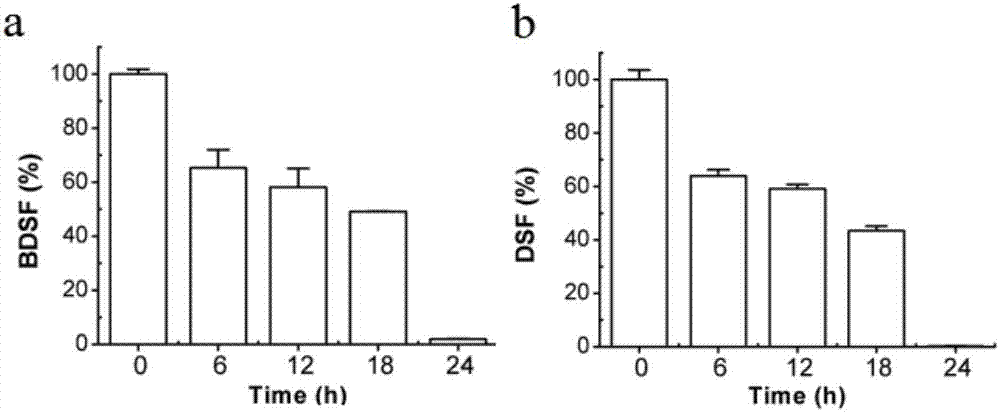
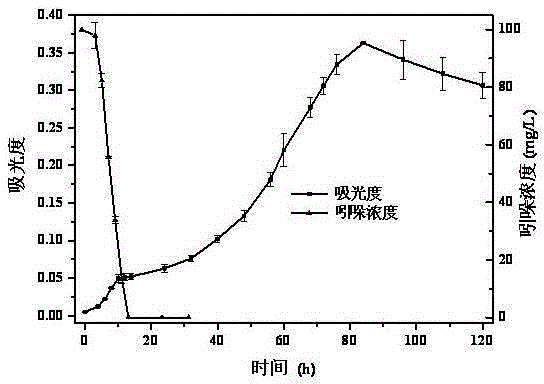
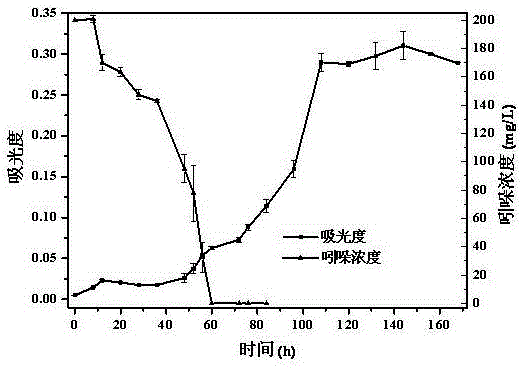
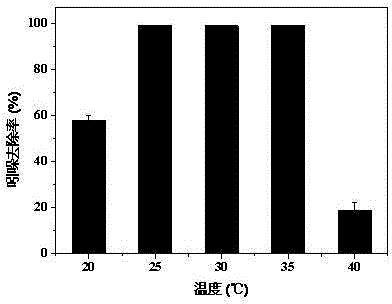
The invention discloses application of an enzyme FadD1 in pseudomonas aeruginosa for degrading DSF family signal molecules. The enzyme FadD1 capable of degrading DSF family signal molecules produced by thalli in vitro is obtained from the pseudomonas aeruginosa, and has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 2. The enzyme FadD1 disclosed by the invention is capable of degrading the DSF familysignal molecules outside the thalli, including signal molecules DSF of xanthomonas campestris and quorum sensing signaling BDSF in burkholderia cepacia. Therefore, the enzyme FadD1 can be used for preparing a preparation capable of degrading the DSF family signal molecules in vitro, so as to be applied to controlling plant or animal diseases caused by pathogenic bacteria taking the DSF or BDSF asthe quorum sensing signaling, particularly plant black rot caused by xanthomonas campestris and diseases caused by burkholderia cepacia.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Burkholderia sp. for aerobic degradation of benzpyrole, and application of burkholderia sp.
InactiveCN104946563AHigh similarityPromote degradationWaste water treatment from quariesBacteriaBiotechnologyActivated sludge
Burkholderia sp. for aerobic degradation of benzpyrole and the application of burkholderia sp. belong to the technical field of microorganism. The strain separated from activated sludge of a reactor is preserved in the Center for General Microorganisms of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms (CCCCM) on January 28, 2015, with the preservation number of CGMCC No.,10457. 16S Rrna gene sequence determination shows that strain IDO3 and Burkholderia have high similarity, therefore, the strain is classified and named as Burkholderia sp. IDO3, and the accession number of the gen bank of the gene sequence of the strain 16S rRNA is KP895480. The strain has a relatively stronger degradation capacity to benzpyrole, also has excellent Ph and temperature tolerances, and shows the application prospect in treating waste water with high concentration benzpyrole.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
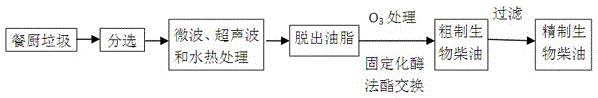
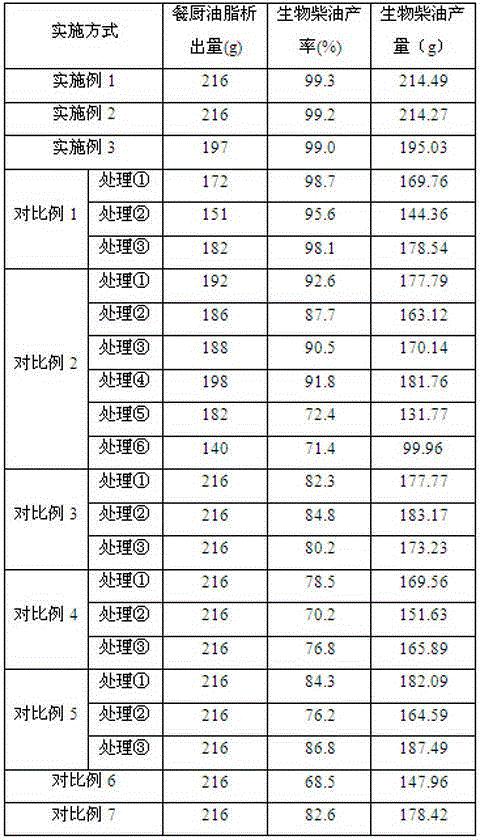
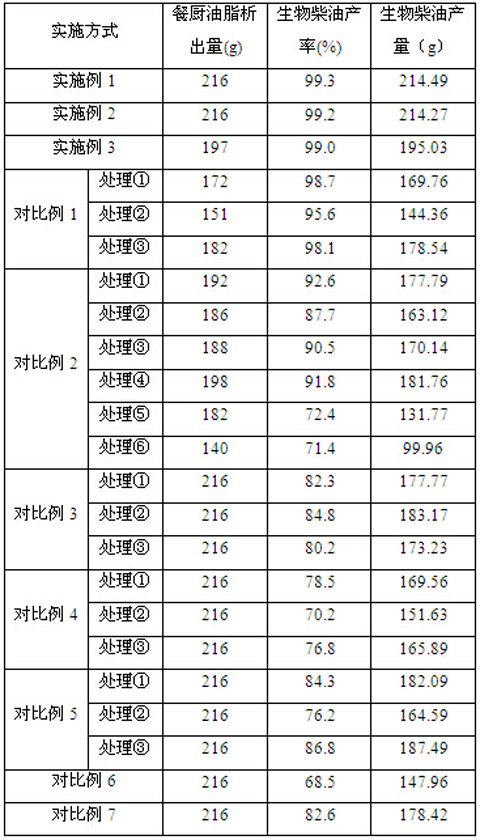
Method for improving yield of biodiesel prepared through kitchen grease enzymic method through pretreatment
ActiveCN105062697AAccelerated precipitationHigh yieldFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationTrans esterificationTransesterification
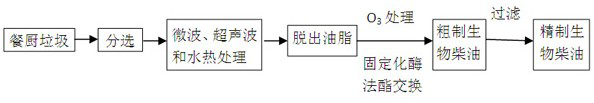
The invention belongs to the technical field of kitchen waste treatment and particularly discloses a method for improving the yield of biodiesel prepared through a kitchen grease enzymic method through pretreatment. The method includes the following steps that firstly, impurities in kitchen waste are removed, and microwave treatment, ultrasonic wave treatment and hydro-thermal treatment is conducted on the kitchen waste in sequence; secondly, three-phase separation is conducted, and upper-layer grease is obtained; thirdly, oxidation is conducted by leading ozone in; fourthly, immobilized composite lipase is added into grease obtained in the third step, and short chain alcohol is added for conducting a transesterification reaction to prepare the biodiesel, wherein the immobilized composite lipase in the forth step comprises geotrichum candidum lipase, candida lipase and burkholderia cepacia lipase. According to the method, microwave treatment, ultrasonic wave treatment and hydro-thermal treatment are combined for treating kitchen waste, the kitchen grease precipitated amount is increased by 10-50 % than that before treatment and is increased by 2-30% than that obtained by adopting single pretreatment, the kitchen grease precipitated amount is effectively increased, and the productivity and the yield of the biodiesel prepared through the enzymic method are obviously improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Glucose dehydrogenase β-subunit and DNA encoding the same
A DNA fragment encoding a β subunit is obtained by inverse PCR using primers designed based on the nucleotide sequence of a N-terminal signal sequence region of a GDH β subunit derived from Burkholderia cepacia KS1 strain.
Owner:SODE
Production and purification method of glucose dehydrogenase by taking FAD (Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide) as prothetic group
InactiveCN108486027AGood substrate specificityImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliFlavin adenine dinucleotide
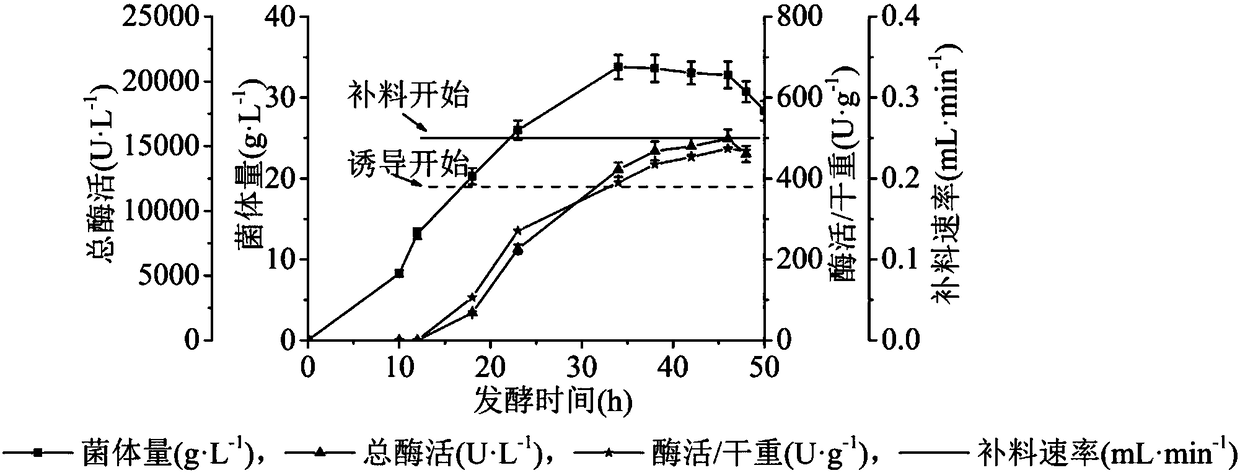
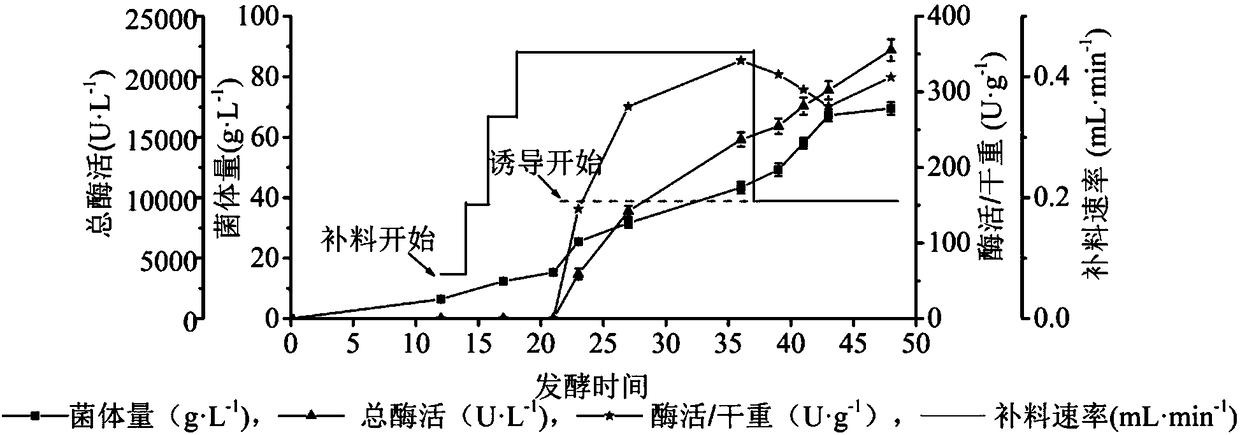
The invention discloses a production and purification method of glucose dehydrogenase by taking FAD (Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide) as a prothetic group, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. Theproduction and purification method is characterized by expressing the glucose dehydrogenase sourced from burkholderia cepacia by taking Escherichia coli as a host, carrying out batch feeding, controlling the temperature in stages, and expressing the glucose dehydrogenase. According to the production and purification method disclosed by the invention, the activity of the glucose dehydrogenase is upto 22200.0U / L, and the mycelia content is up to 69.8g / L; a crude enzyme solution is separated and purified through three-step chromatography, so that recombinase of which the specific enzyme activityis 10<9>U / mg, the property problem of enzyme is solved, and the recombinase is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Nucleic acid reagent, kit and system for detecting lower respiratory tract infection bacteria
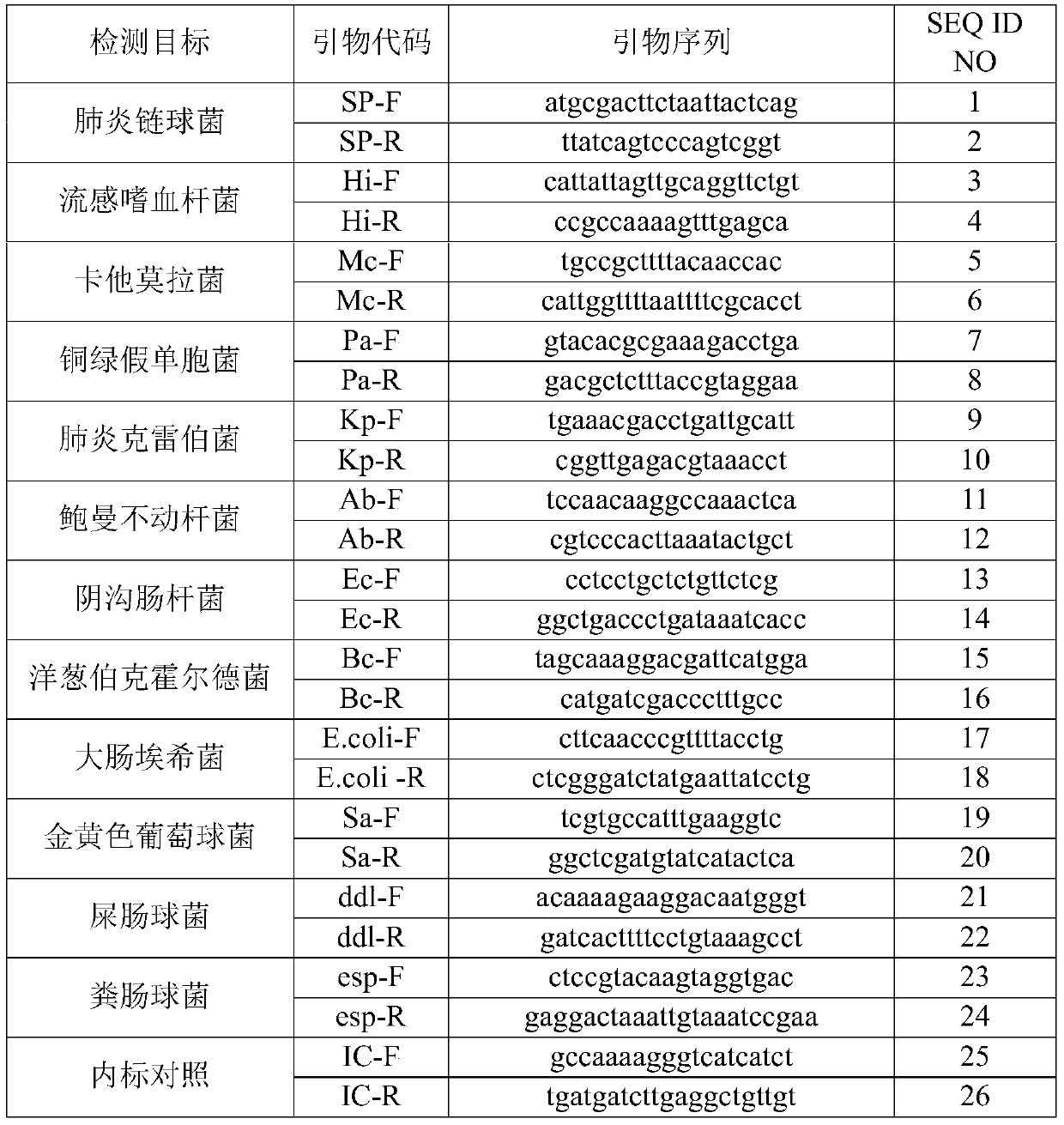
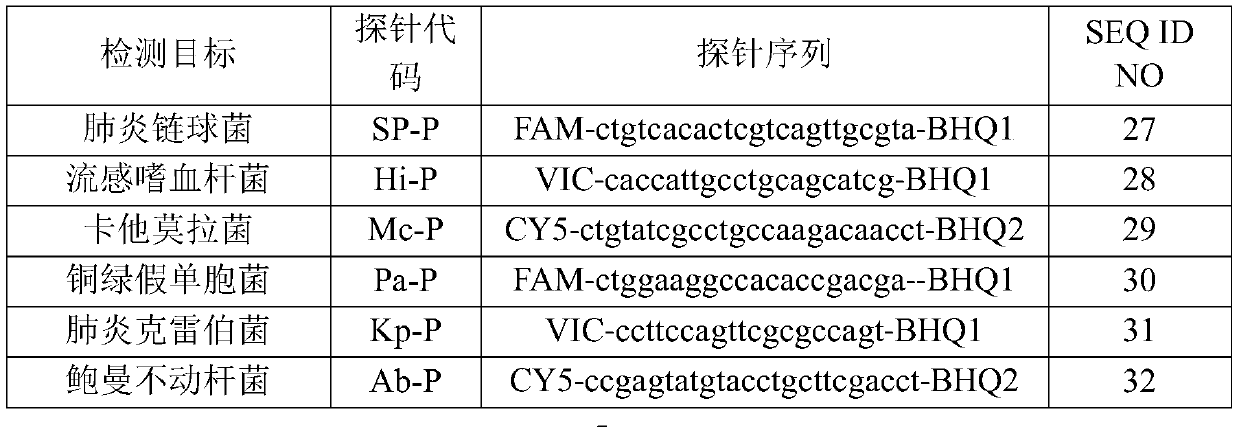
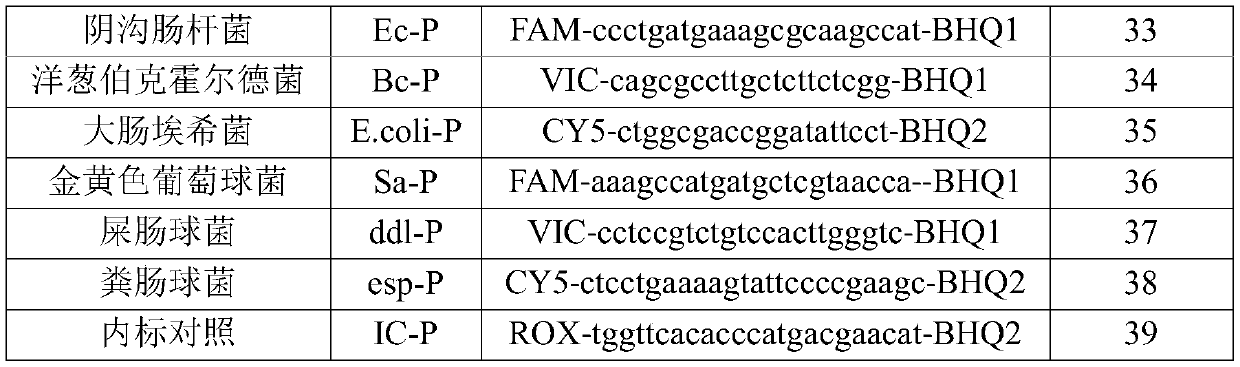
ActiveCN110894533AEasy to operateTo achieve the detection effectMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesChemistryBurkholderia lata
The disclosure relates to a nucleic acid reagent for detecting lower respiratory tract infection bacteria. The nucleic acid reagent comprises primers shown in SEQ ID NO.1-24 and probes shown in SEQ IDNO.27-38 which are stored in a respective and independent manner or in a mutual and arbitrary mixing manner. Through the primers and probes described above, the nucleic acid reagent, a kit, a systemand a method for detecting 12 types of lower respiratory tract infection bacteria such as streptococcus pneumoniae, haemophilus influenzae, moraxella catarrhalis, pseudomonas aeruginosa, klebsiella pneumonia, acinetobacter baumannii, enterobacter cloacae, burkholderia cepacia, escherichia coli, staphylococcus aureus, enterococcus faecium, and enterococcus faecalis are established, at the same time, internal reference genes are added as controls, the above 12 types of bacteria can be quantitatively detected through a double standard curve method, the uniform quantification treatment of samplescan be performed, the fast, comprehensive, sensitive, specific and automatic detection result determination is realized, and sensitivity, specificity, and simplicity of simultaneously detecting the above detection target genomes are significantly improved.
Owner:CHINA JAPAN FRIENDSHIP HOSPITAL +1
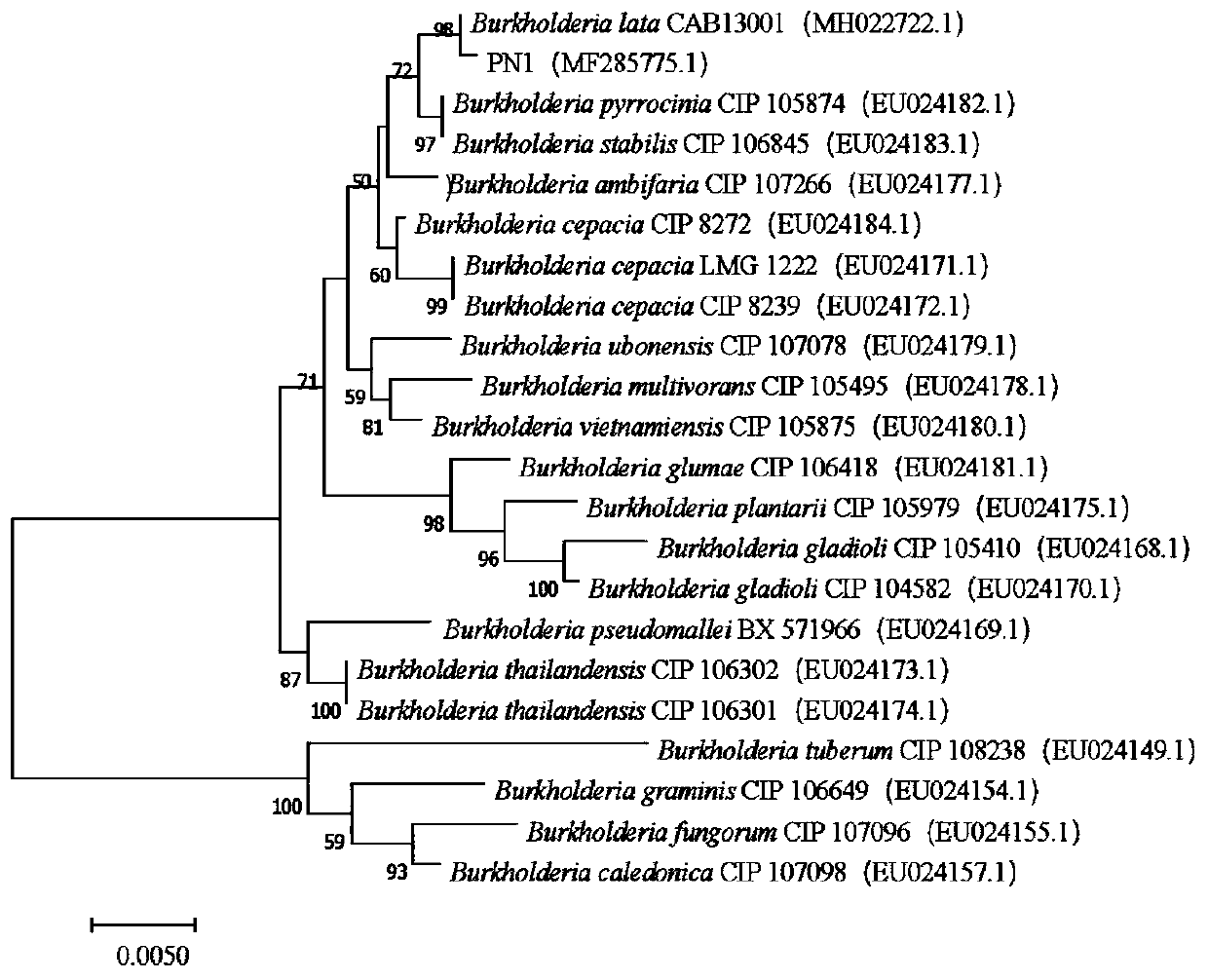
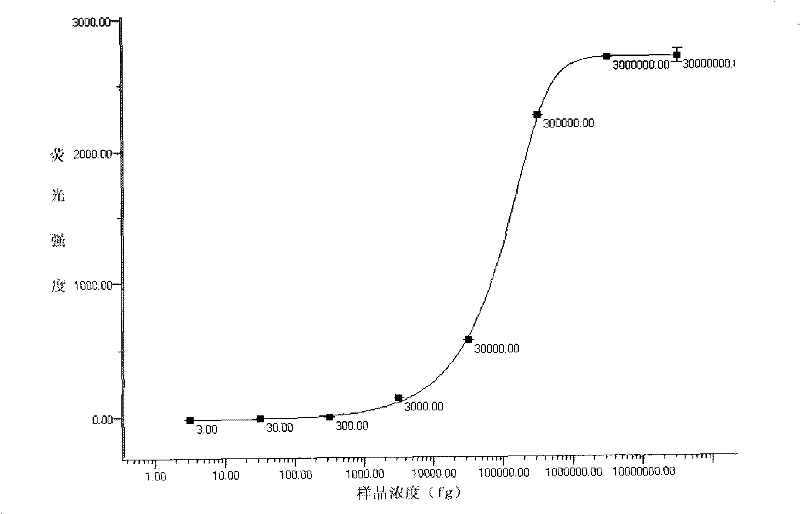
Burkholderia lata strain PN1 and application thereof
ActiveCN111100812APromote growthHigh antibacterial activityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyBlight
The invention discloses a burkholderia lata strain PN1 and application thereof. The classification name of the strain is Burkholderia lata, the strain number is PN1, the strain is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M 2019880. The strain PN1 screened out from phyllostachys edulis root systems has a significant inhibiting effect on phyllostachys edulis shoot blight pathogens ceratosphaeria phyllostachydis, a bacteriostasis rate of fermentation broth of the strain PN1 screened out from the phyllostachys edulis root systems can reach58.82%, and the strain PN1 screened out from the phyllostachys edulis root systems has efficient capability of phosphate solubilizing and IAA secretion; and the phyllostachys edulis endophytic bacteria PN1 can significantly promote growth of phyllostachys edulis seedlings, and test data shows that a liquid bacterial agent produced from the strain PN1 significantly increases growth indexes of the ground diameter, the seedling height, chlorophyll and the like of phyllostachys edulis. Therefore, excellent strain resources are provided for development of an environment-friendly bio-fertilizer special for the phyllostachys edulis.
Owner:JIANGXI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Genetic liquid phase chip for joint detection of five drastic pathogenic bacteria and detection method thereof
InactiveCN101560557BMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesYersinia pestisBrucella
The invention discloses a genetic liquid phase chip for rapid detection of five drastic pathogenic bacteria of bacillus anthracis, yersinia pestis, brucella bacteria, francisella tularensis and burkholderia pseudomallei. The liquid phase chip for detecting the five drastic pathogenic bacteria has the advantages of large flux, less required sample capacity, strong specificity, high sensitivity, accuracy, high efficiency, and the like.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
Bacteriophage compositions for treatment of bacterial infections
A respirable composition for treatment of a bacterial infection includes one or more active bacteriophages in combination with a pharmaceutically acceptable respirable carrier. The composition includes a carbohydrate carrier, and is prepared as fine powder. In another aspect, bacteriophages are provided in a liquid carrier for administration by nebulization. In one aspect, the bacteriophages have anti-bacterial activity against one or more species or strains of Burkholderia cepacia complex (BCC) bacteria. The invention further relates to the use of a BCC bacteriophage to treat a BCC infection, in particular in an individual suffering from cystic fibrosis.
Owner:FINLAY WARREN H +4
Antimicrobial agent and method for the production thereof
Provided are antimicrobial agents produced from Burkholderia cepacia complex (Bcc) bacteria, in particular from bacteria which comprise a cluster of polyketide synthesis genes. Also provided is use of the antimicrobial agents in the treatment of disease. Further provided are methods for producing antimicrobials, methods for detecting antimicrobial producing bacterial strains and kits for use in the methods.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE CARDIFF CONSULTANTS LTD
Strain for producing 2, 5-furandimethanol and application of the strain
The invention provides a strain for producing 2, 5-furandimethanol and application of the strain, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The invention relates to a strain for producing 2, 5-furandimethanol, which is classified and named as a Burkholderia cepacia NJPI15 strain, and the preservation number of the strain is CCTCC NO: M 2020636. A method for converting 5-hydroxymethylfurfural into 2, 5-furandimethanol is characterized in that the strain is used as a biocatalyst to convert 5-hydroxymethylfurfural into 2, 5-furandimethanol. The strain Burkholderia contaminans NJPI15 with high tolerance to 5hydroxymethylfurfural is separated from chemically polluted soil, and the yield of 2, 5-furandimethanol can be high. The strain Burkholderia contaminans NJPI15 disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the yield is high;.
Owner:NANJING POLYTECHNIC INSITUTE
Kit for digital PCR detection of Burkholderia
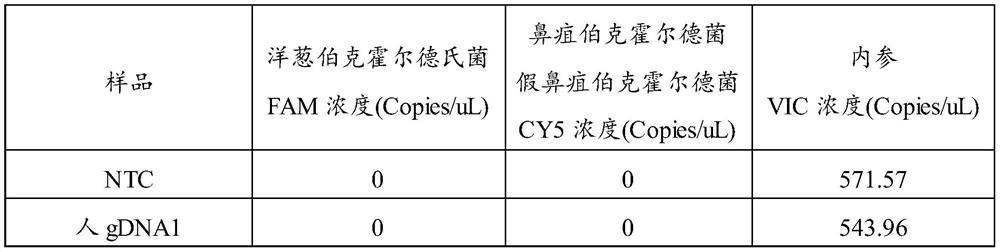
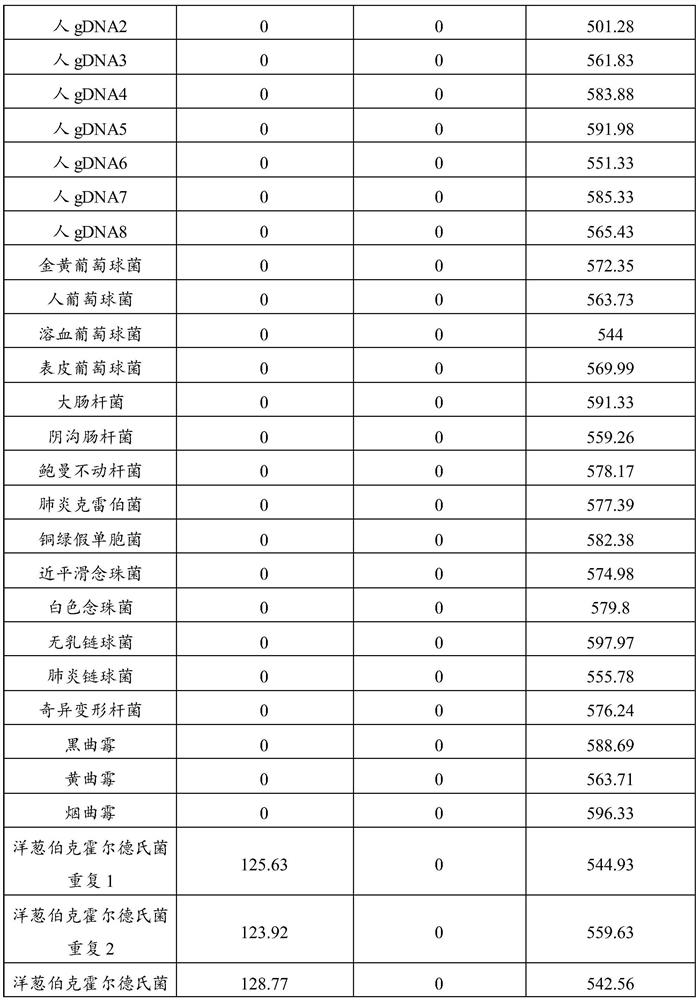
PendingCN113755619AIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBurkholderia lataB cepacia
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to a kit for digital PCR detection of Burkholderia. The invention provides a primer probe group for digital PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection of Burkholderia, and provides a kit for digital PCR detection of Burkholderia. The primer and the probe group can be used for accurately identifying whether a sample contains DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) of burkholderia cepacia, burkholderia pseudomallei and burkholderia pseudomallei or not, and the primer and the probe group have good sensitivity in detection of the three kinds of the burkholderia cepacia, the burkholderia pseudomallei and the burkholderia pseudomallei.
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI +1
Method for producing (1s,2r)-2-chloro-2-fluorocyclopropanecarboxylic acid
ActiveCN102089439AHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsBurkholderia lataCarboxylic acid
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD +1
Antibacterial compounds
ActiveUS20200199118A1Good effectGood chemical stabilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryClostridium difficileBurkholderia lata
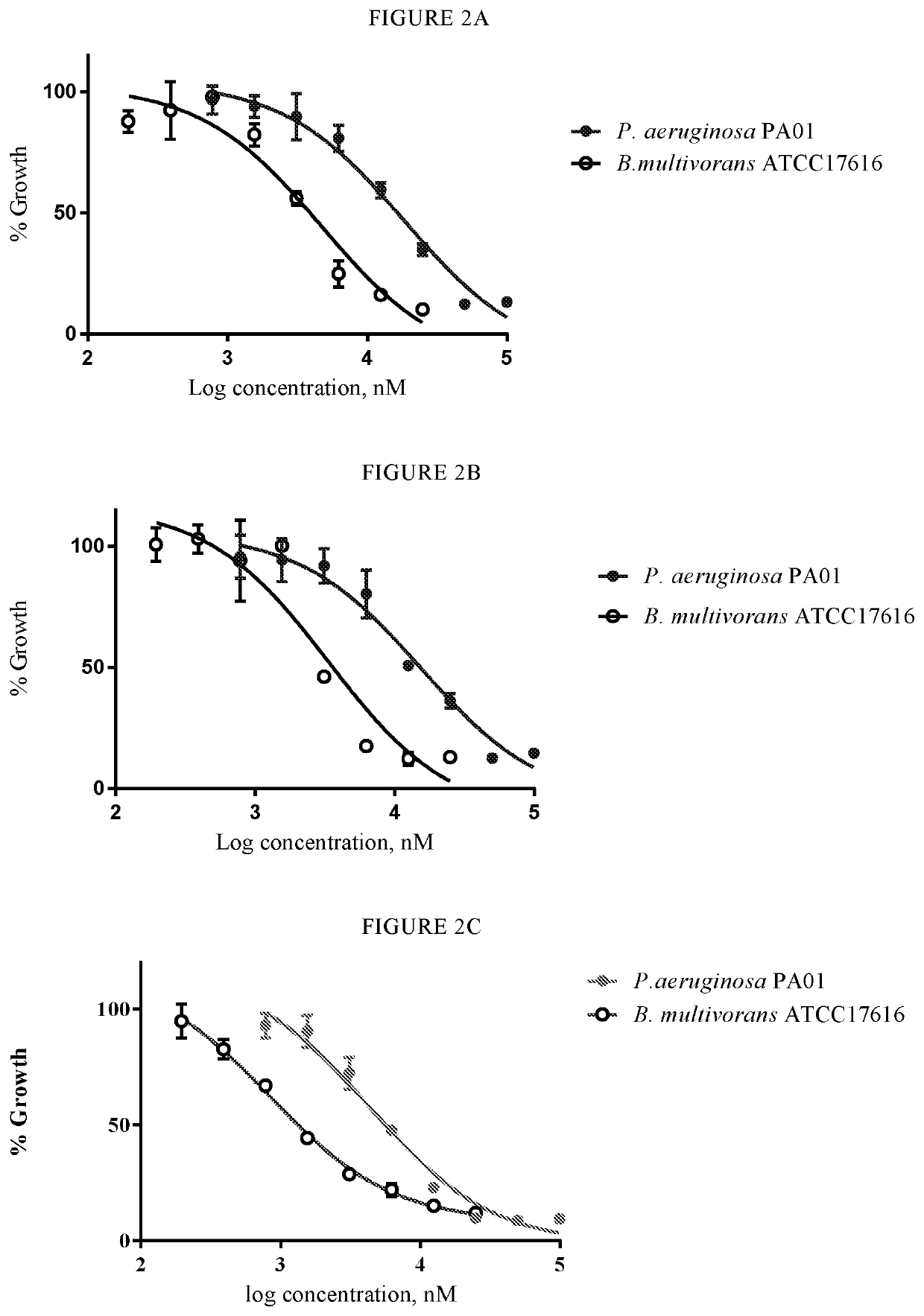
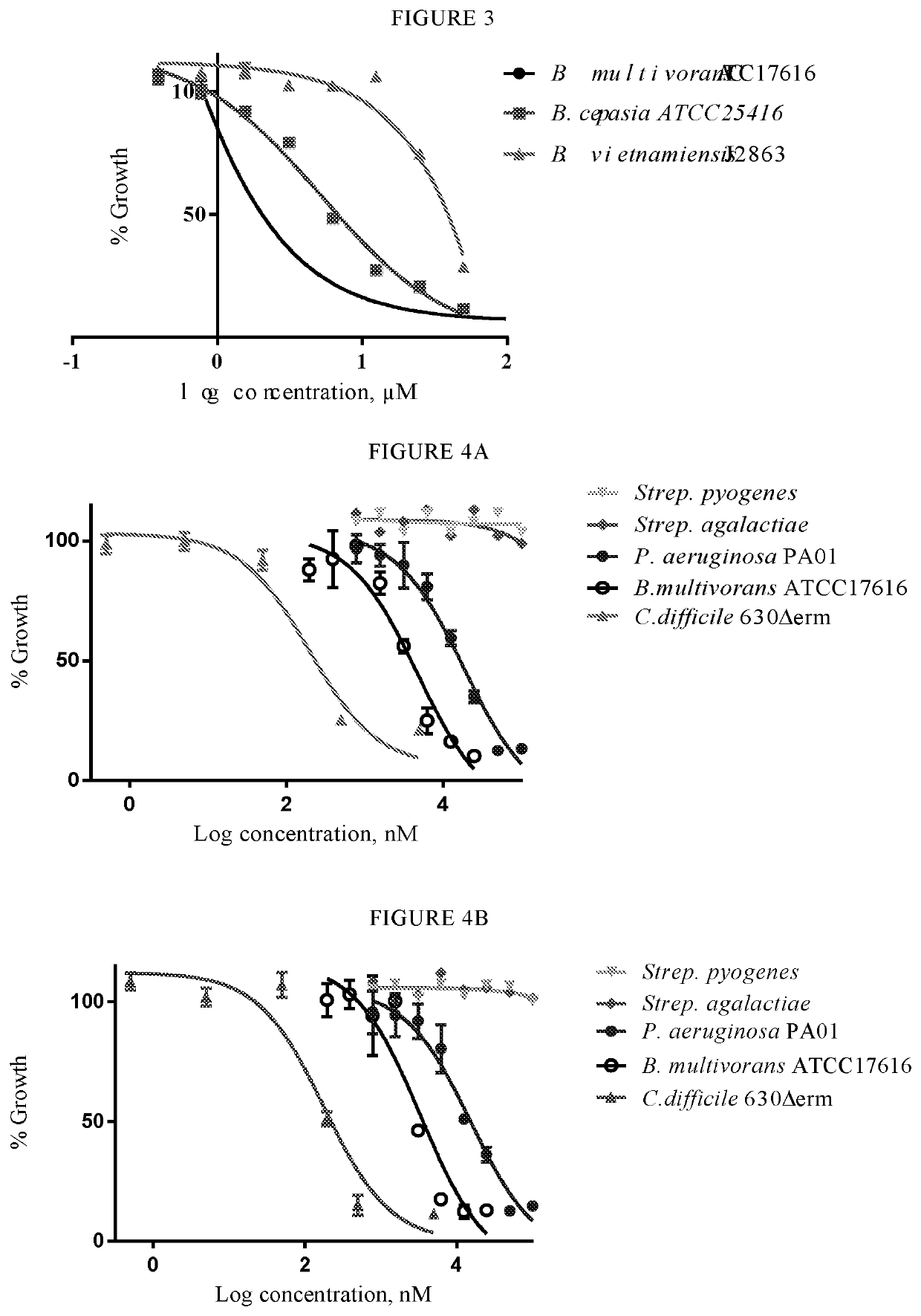
Novel compounds having antimicrobial activity, in particular against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Burkholderia cepacia and / or Clostridium difficile, and a pharmaceutical composition containing the novel compound.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NOTTINGHAM
A kit for identifying bacteria using molecular beacon-melting curve technology and its application
ActiveCN106834520BAvoid contamination riskNot easy to misjudgeMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesListeria monocytogenesAerobacter cloacae
The invention discloses a molecular beacon and a kit for quickly identifying various clinically common bacteria and belongs to the technical field of microbiological detection. The sequences SEQ ID of the molecular beacon are as shown in v6p1, v6p2, v1p1 and v1r. Through comparison between various clinically common bacteria 16s ribosome RNA sequences in an NCBI gene sequence database and design of the molecular beacon at a tag sequence, clinically common 18 bacteria, including baumanii, A.hydrophila, burkholderia cepacia, citrobacter freundii, enterobacter cloacae, enterococcus faecium, enterococcus faecalis, enterobacter aerogenes, escherichia coli, klebsiella pneumoniae, listeria monocytogenes, proteus mirabilis, pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococcus epidermidis, staphylococcus aureus, salmonella, serratia marcescens and stenotrophomonas maltophilia, can be quickly identified. The invention further discloses the kit containing the molecular beacon and used for detecting various bacteria, and the kit can quickly and accurately identify various clinically common bacteria.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIAN BIOTECH CO LTD
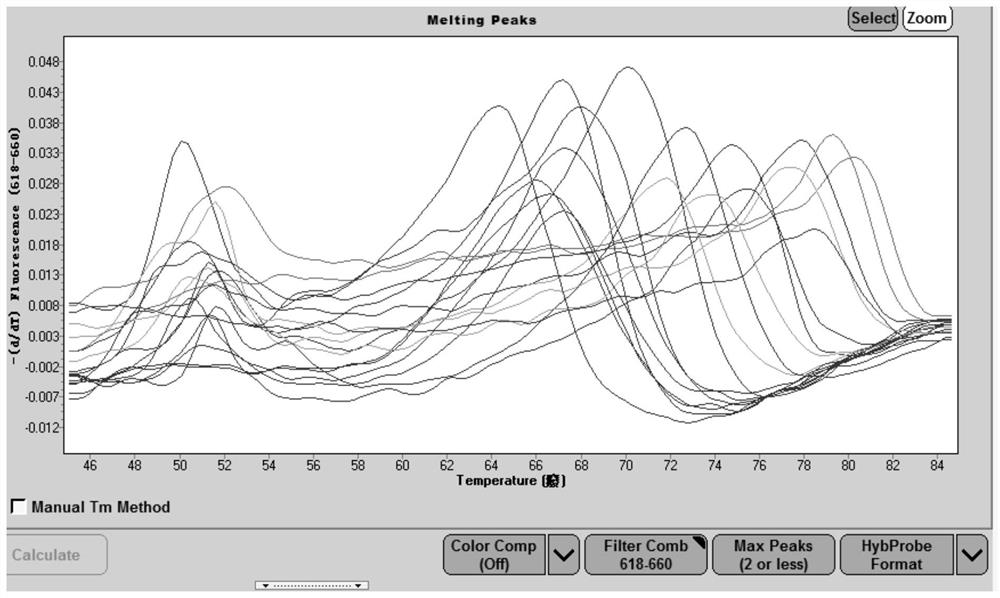
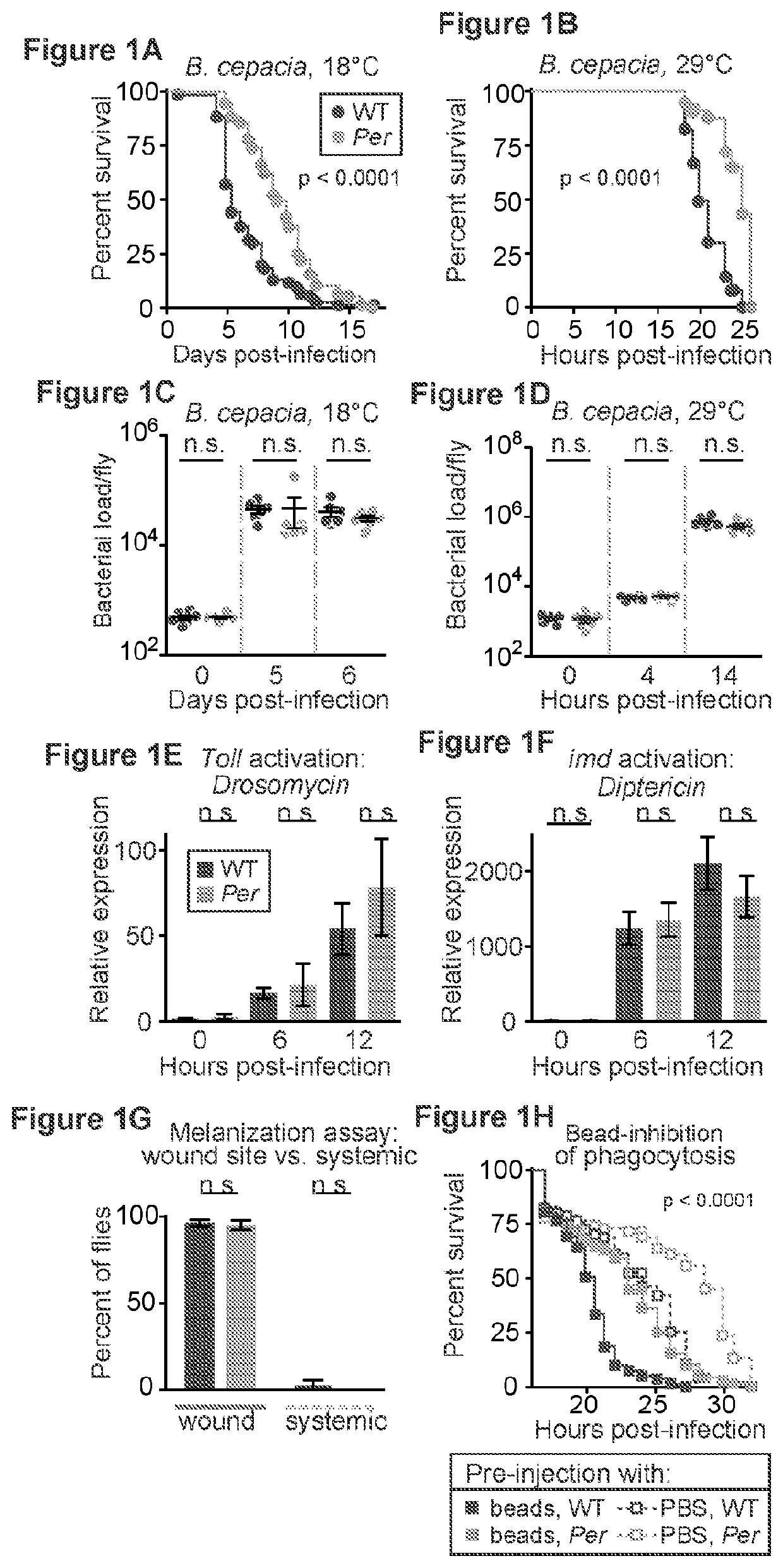
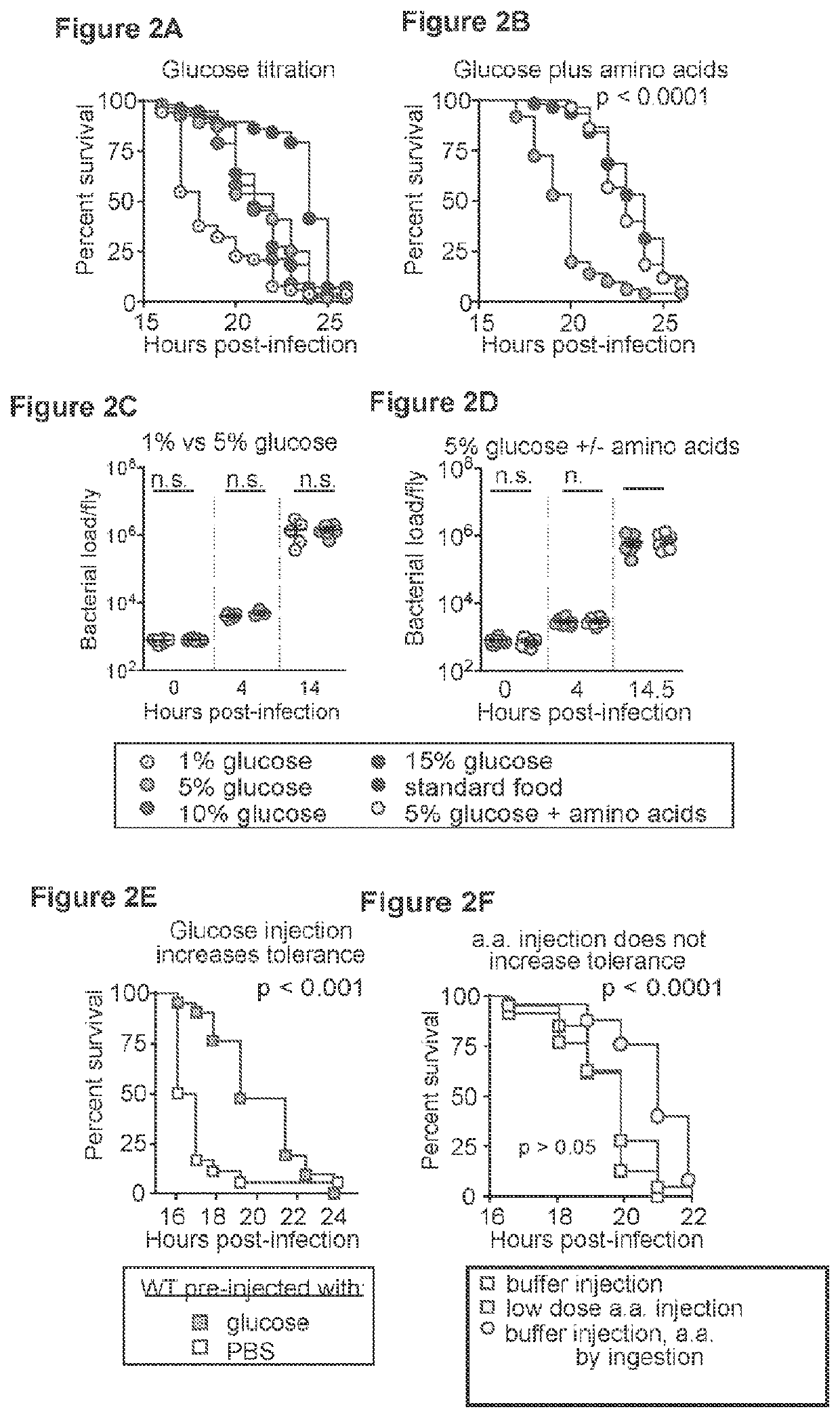
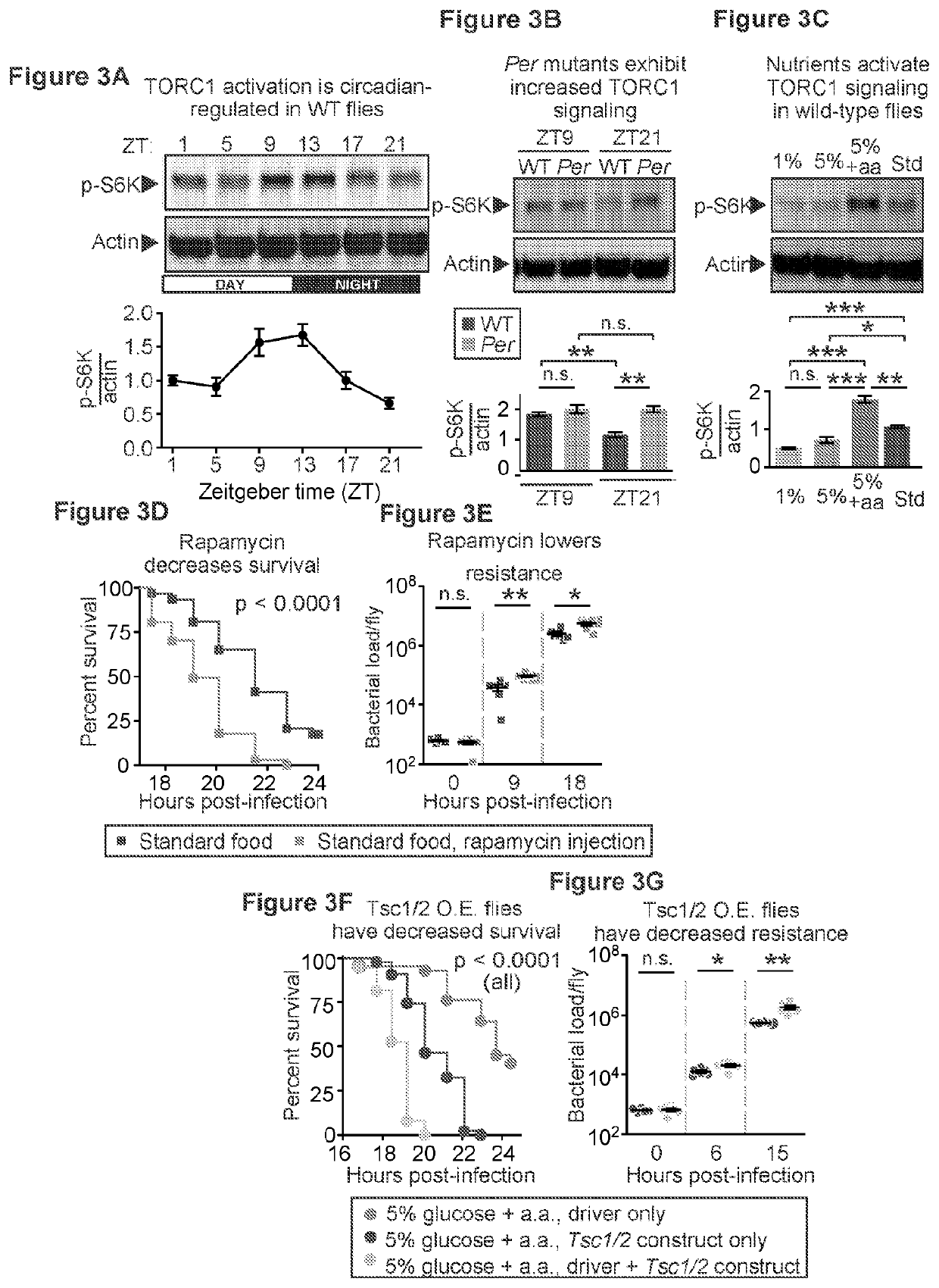
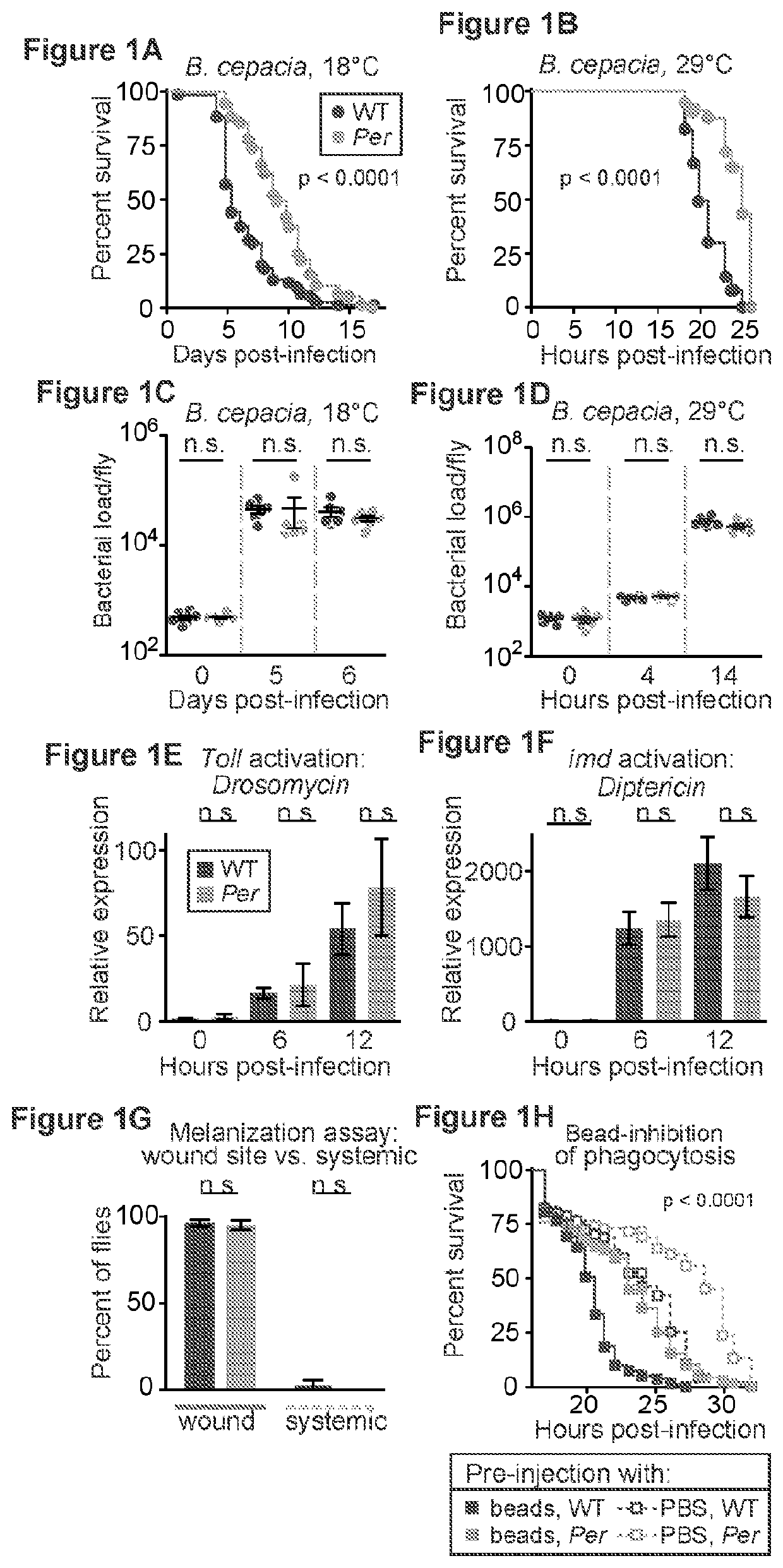
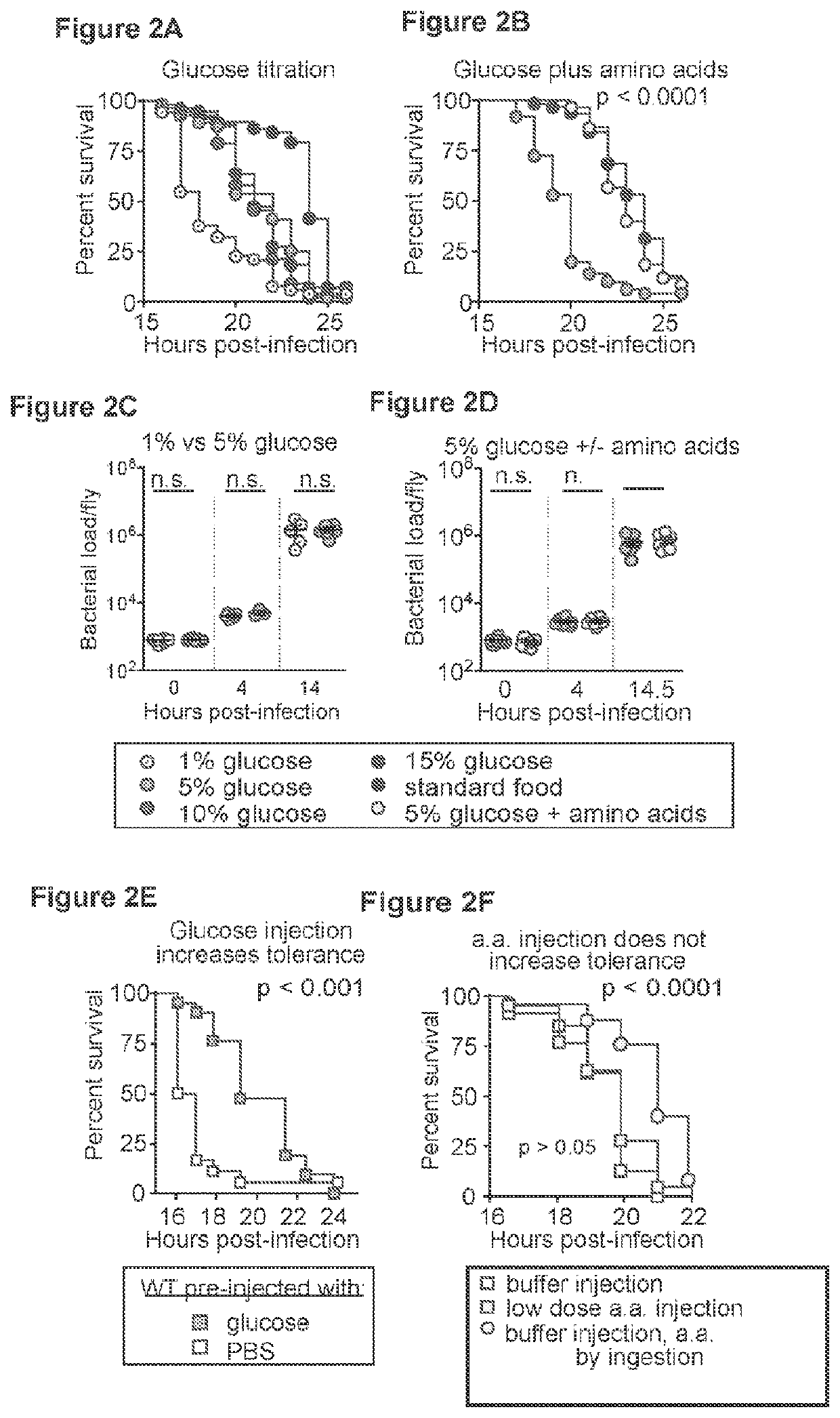
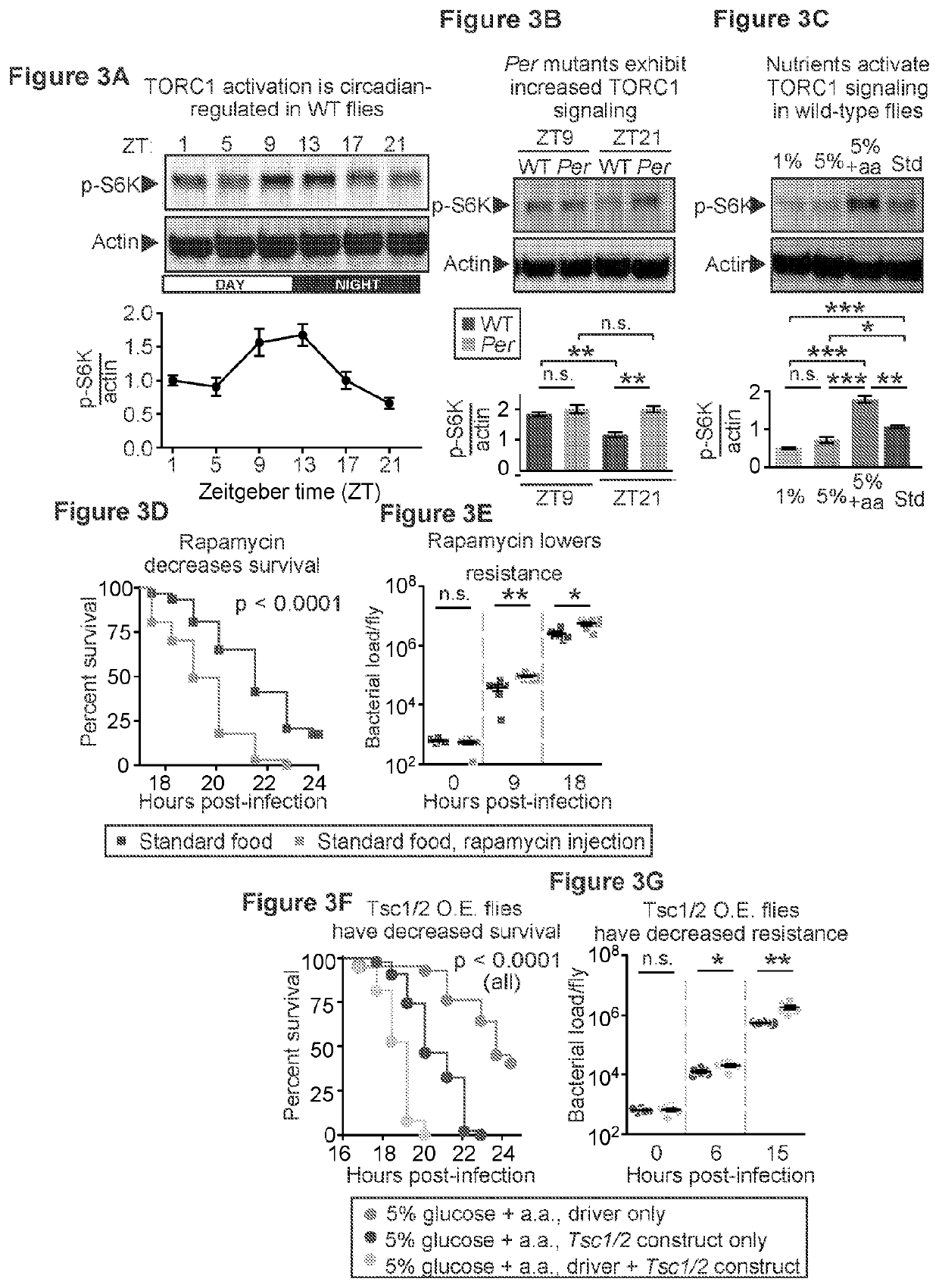
Inhibition of tor complex 2 increases immunity against bacterial infection
ActiveUS20200281902A1Improve survivalImprove immunityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsImmunopotencyBurkholderia lata
This invention relates to methods and compositions for increasing immunity against, and survival of, a bacterial infection by inhibiting Target of Rapamycin (TOR) complex 2 or TORC 2. In particular, the current invention is useful in increasing immunity and survival after infection by Burkholderia cepacia as well as other bacteria since the agents that target TORC2 increase host tolerance of infection rather than target the clearance or containment of specific types of bacteria. This invention also relates to methods and compositions for increasing immunity against, survival of, and host tolerance to a bacterial infection by inhibiting the circadian regulator, Period protein.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Method for preparing sterol derivative through Burkholderia conversion and application
InactiveCN111471737AIncrease conversion rateMicroorganism based processesFermentationOrganic solventBurkholderia lata
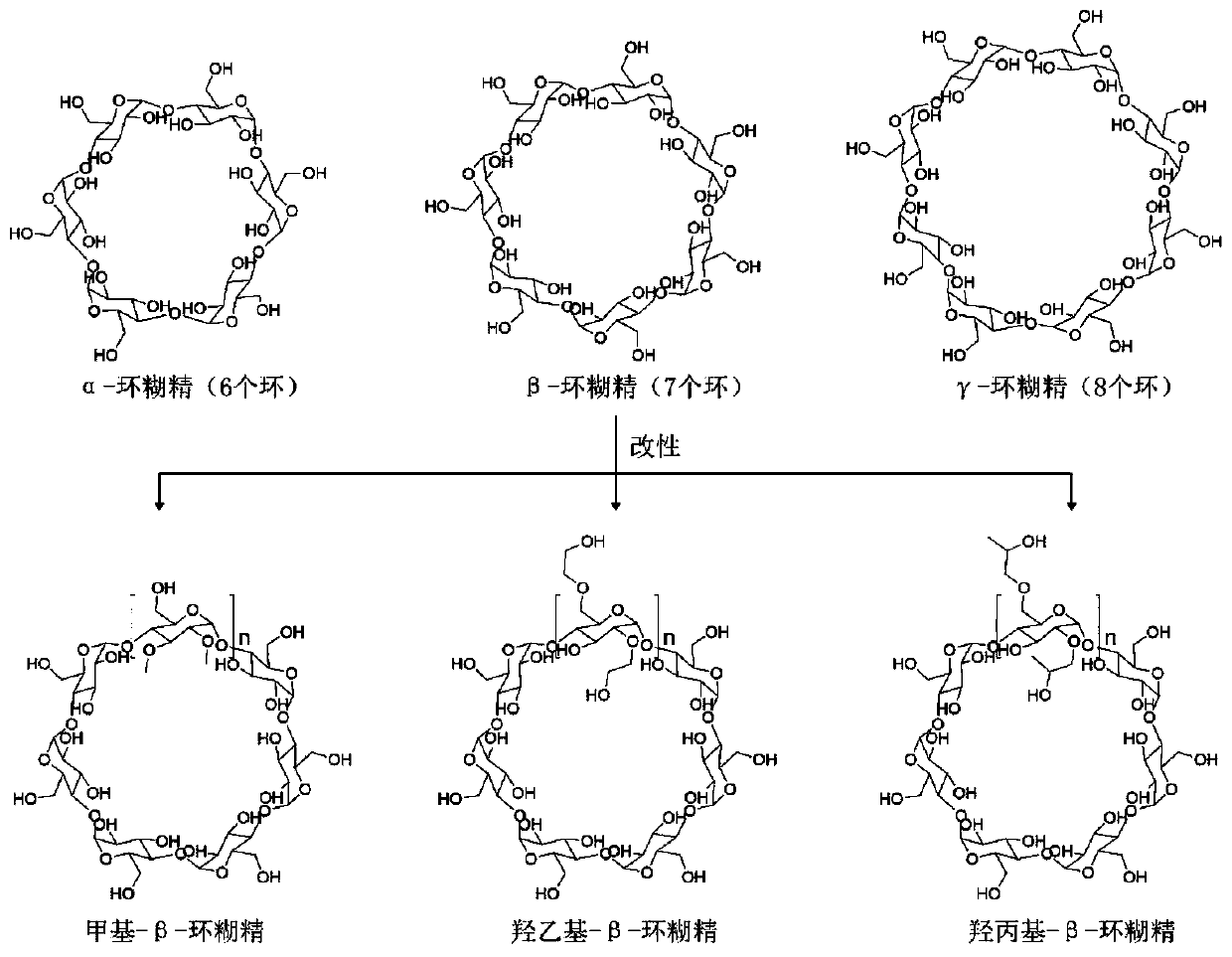
The invention discloses a method for preparing a sterol derivative through Burkholderia conversion and application, and belongs to the technical field of sterol microbial conversion. Burkholderia is added into a reaction system containing cyclodextrin or a derivative thereof, so that the product conversion yield can be increased to 12-15% from 0.1-0.3% of a control group; and in addition, an organic solvent does not need to be added in the preparation process of the method, so that the method is more environment-friendly, economical and safe.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A method for improving the yield of biodiesel produced by enzymatic method of cooking oil by using pretreatment
ActiveCN105062697BAccelerated precipitationHigh yieldFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationOil and greaseWaste treatment
The invention belongs to the technical field of kitchen waste treatment, and specifically discloses a method for improving the yield of biodiesel produced by enzymatically preparing kitchen grease by utilizing pretreatment. The method comprises the following steps: S1. removing sundries in the kitchen waste, and sequentially subjecting the kitchen waste to microwave, ultrasonic and hydrothermal treatment; S2. separating the three phases to obtain the upper layer of grease; S3. passing in ozone for oxidation; S4 .Add immobilized compound lipase to the oil obtained in S3, and add short-chain alcohol to carry out transesterification to prepare biodiesel; wherein, the immobilized compound lipase described in S4 includes Geotrichum candidum lipase, Candida lipase and onion lipase Burkholderia lipase. The invention adopts microwave, ultrasonic and hydrothermal treatment to jointly treat kitchen waste, and the amount of kitchen grease precipitation increases by 10-50% compared with that before treatment, and increases by 2-30% compared with single pretreatment, effectively increasing the amount of kitchen grease precipitation, and significantly Improve the yield and yield of biodiesel produced by enzymatic method.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
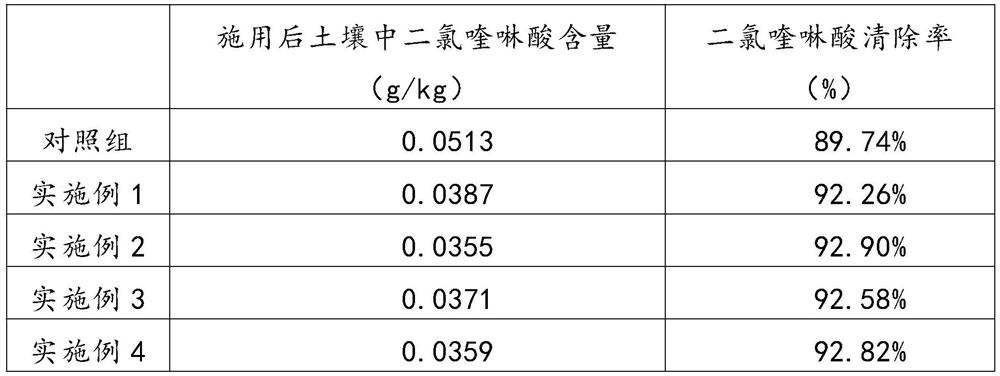
Microbial agent used for degrading quinclorac herbicides
The invention discloses a microbial agent used for degrading quinclorac herbicides. The microbial agent takes several strains of bordetella, arthrobacterium, bacillus megatherium, burkholderia cepacia, ochrobactrum anthropi, pseudomonas, alcaligenes faecalis, aspergillus niger and neurospora and cellulase, amylase, protease, lipase and a biological accelerating agent as raw materials, and fermented solutions obtained after the several strains of the bordetella, the arthrobacterium, the bacillus megatherium, the burkholderia cepacia, the ochrobactrum anthropi, the pseudomonas, the alcaligenes faecalis, the aspergillus niger and the neurospora undergo fermentation culture are mixed to form a mixed fermented solution, after thalli are collected by centrifugation from the mixed fermented solution, skimmed milk and sucrose are added, freeze drying is performed, and then, the thalli are compounded with the cellulase, the amylase, the protease, the lipase and the biological accelerating agentto obtain the microbial agent.
Owner:SHANDONG SUNWAY LANDSCAPE TECH
A kind of microbial quorum sensing signal quenching bacteria and its application as bio-control bacteria
ActiveCN108739860BPromote degradationGreat application potentialBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyXanthomonas campestris
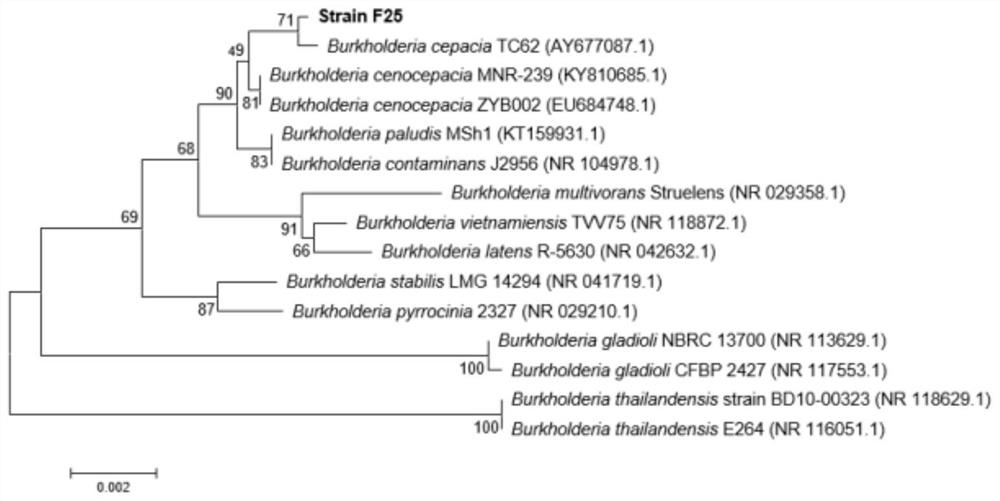
The invention discloses microbial population sensing signal quenching bacteria and application thereof as biocontrol bacteria. Through study, the invention finds that Burkholderia cepacia has an obvious degradation effect on a population sensing signal molecule DSF; meanwhile, the Burkholderia cepacia F25 for efficiently degrading the DSF signal molecule is obtained by screening. The strain was preserved in the Guangdong Province Microbiological Culture Center on April 3, 2018, with a preservation number of GDMCC No:60346. The bacteria can quickly and efficiently degrade the DSF, and has population sensing and quenching functions and remarkable biocontrol effects on DSF pathogenic diseases such as black rot caused by xanthomonas campestris XC1. The microbial population sensing signal quenching bacteria disclosed by the invention can replace a chemical control method and eliminate potential safety hazards of antibiotic use, is environmentally-friendly and has important application valuefor preventing and treating plant diseases caused by pathogens relying on the DSF.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Inhibition of TOR complex 2 increases immunity against bacterial infection
ActiveUS11116754B2Improve survivalImprove toleranceAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiotechnologyImmunopotency
This invention relates to methods and compositions for increasing immunity against, and survival of, a bacterial infection by inhibiting Target of Rapamycin (TOR) complex 2 or TORC 2. In particular, the current invention is useful in increasing immunity and survival after infection by Burkholderia cepacia as well as other bacteria since the agents that target TORC2 increase host tolerance of infection rather than target the clearance or containment of specific types of bacteria. This invention also relates to methods and compositions for increasing immunity against, survival of, and host tolerance to a bacterial infection by inhibiting the circadian regulator, Period protein.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
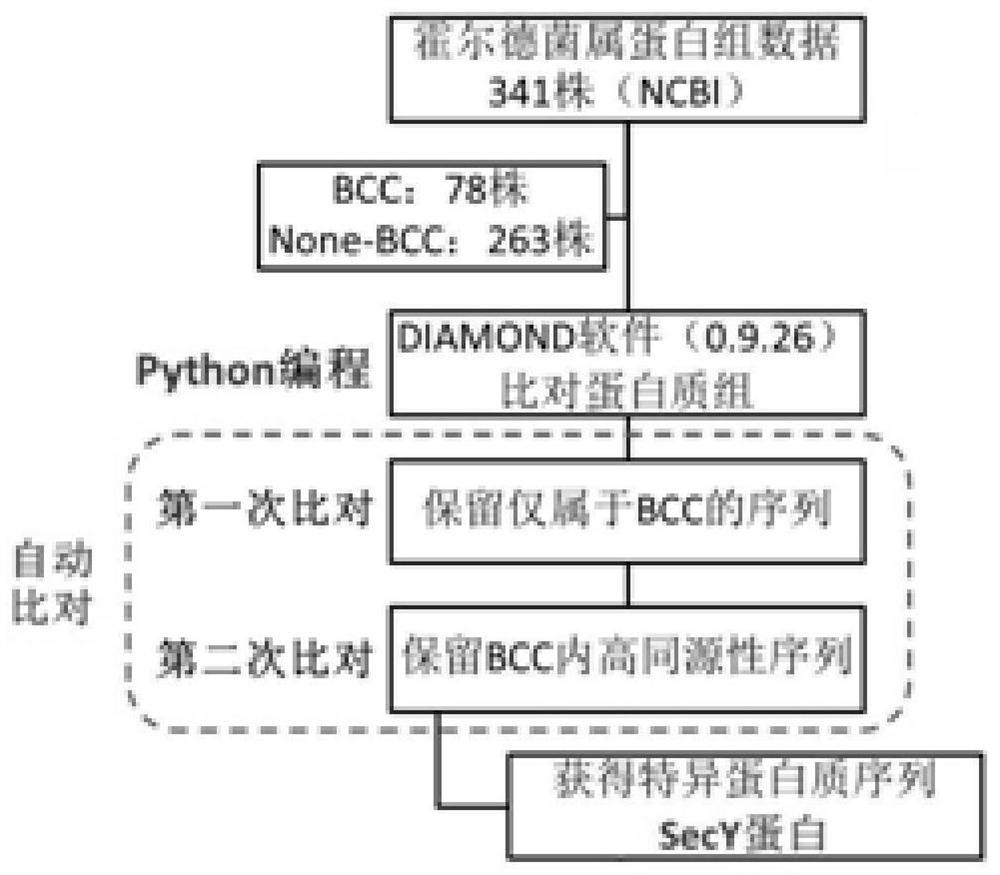
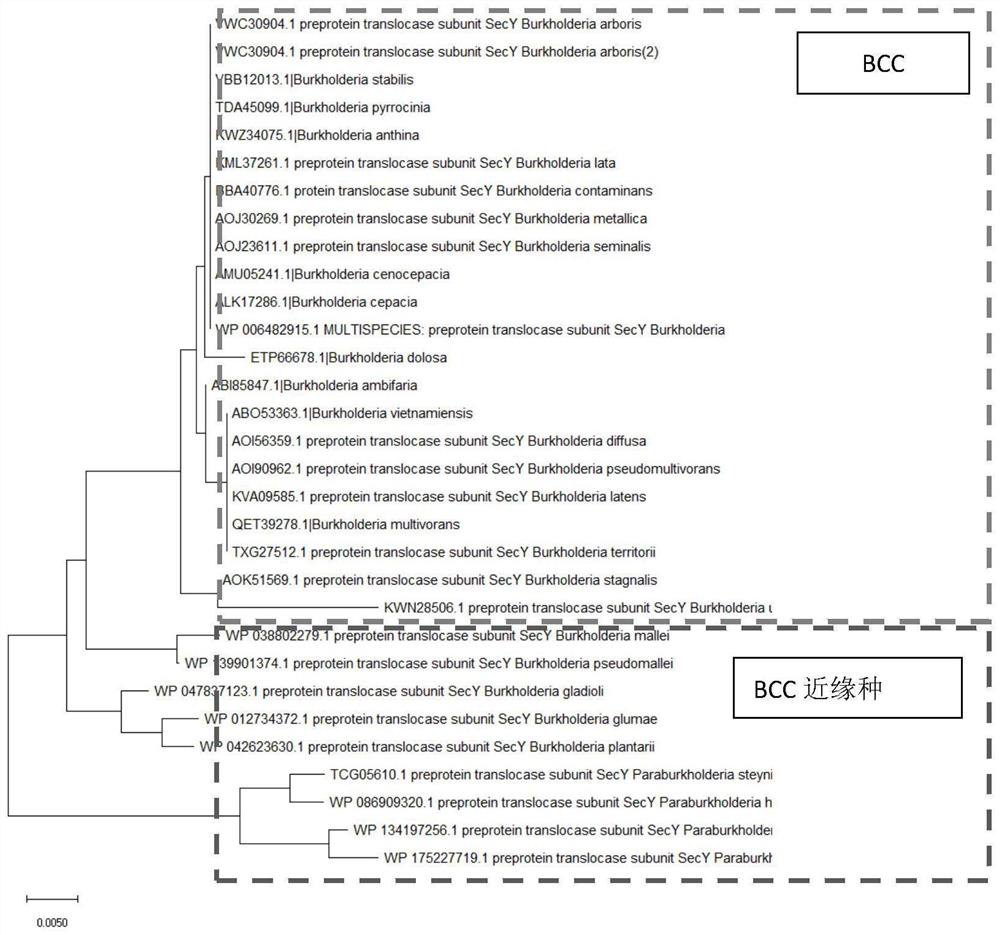
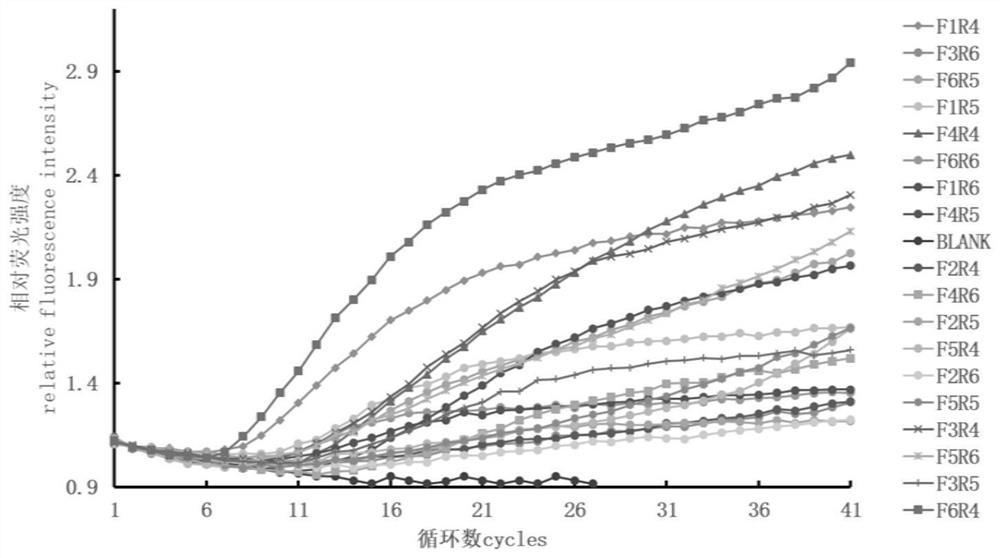
Specific detection target of BCC (Burkholderia cepacia complex) and constant-temperature rapid detection method
PendingCN113699257AStrong specificityConfirmation of specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteria peptidesMedical equipmentSpecific detection
The invention provides a specific detection target of a BCC (Burkholderia cepacia complex) and a constant-temperature rapid detection method. The specific detection target is a sec Y gene, an RPA primer composition is designed according to the gene, the RPA primer composition comprises an upstream primer with a sequence selected from one of SEQ ID No.1 to SEQ ID No.6, a downstream primer with a sequence selected from one of SEQ ID No.7 to SEQ ID No.9, and a probe with a sequence as follows: CAGGGCAACGGAAGATCACGCAGTACACGCGG[FAM-dT]A[THF][BHQ1-dT]TCACCGTGGTGCTCG[C3Spacer]. On the basis, the invention develops a high-throughput and rapid screening and detection method for the specific BCC; and the method is high in accuracy, strong in specificity and high in sensitivity, and is suitable for daily screening work of medical institutions, medicine and medical equipment production enterprises, cosmetic production enterprises and related detection institutions.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST FOR FOOD & DRUG CONTROL
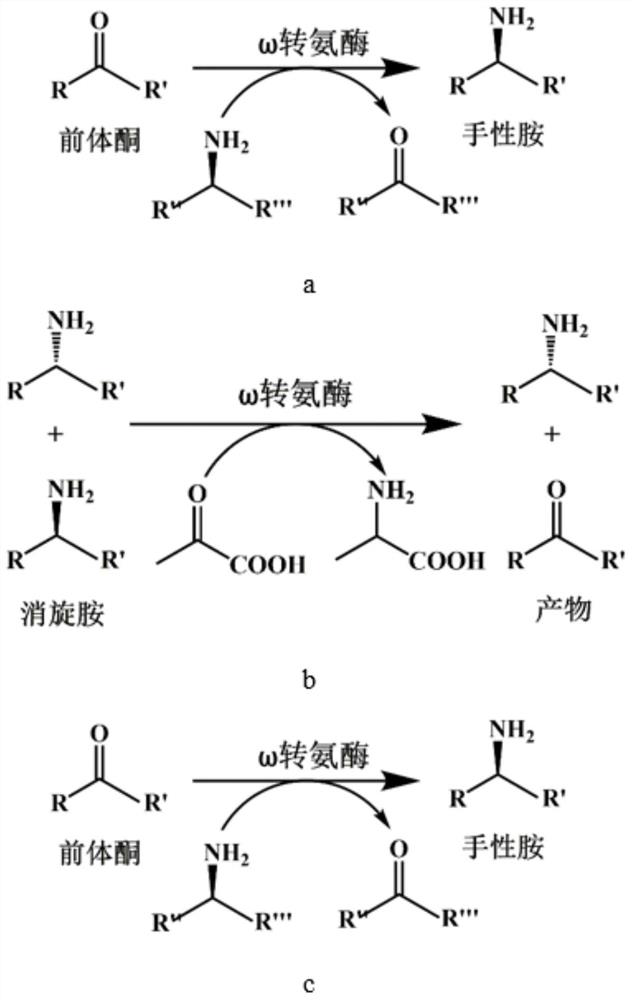
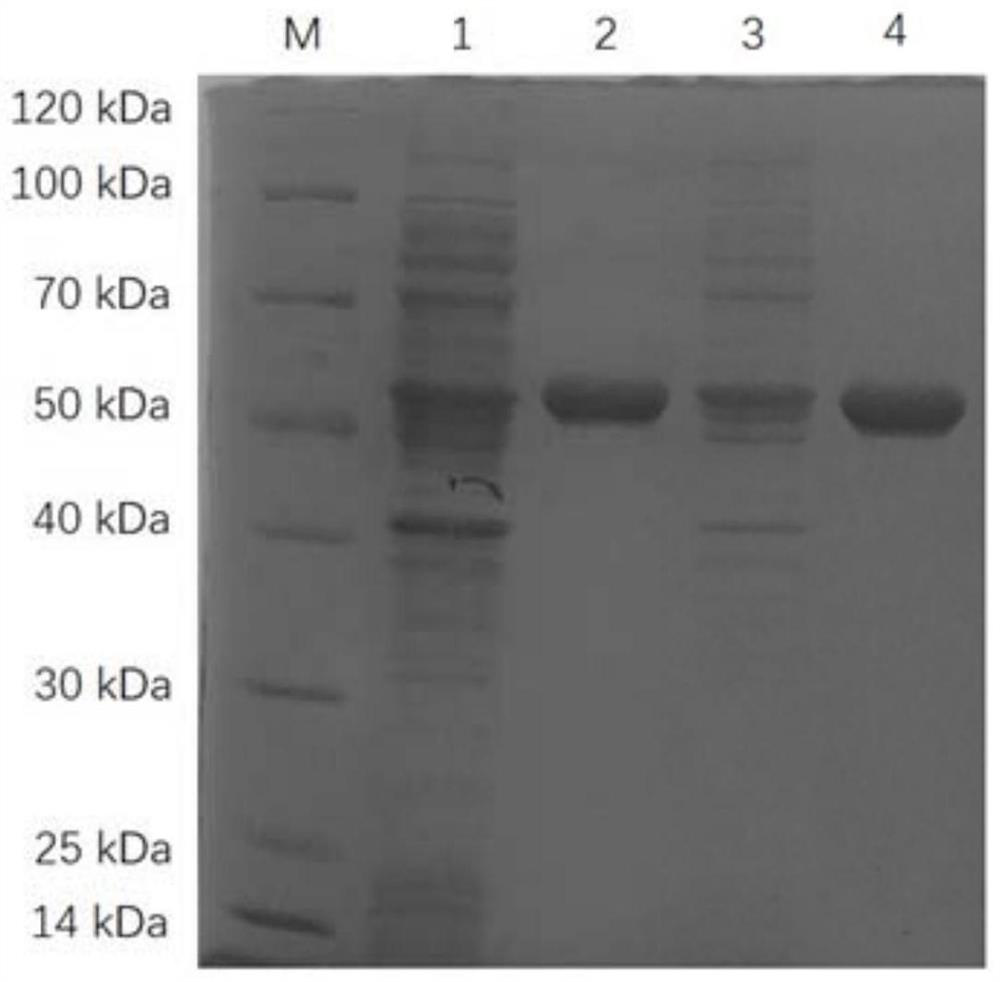
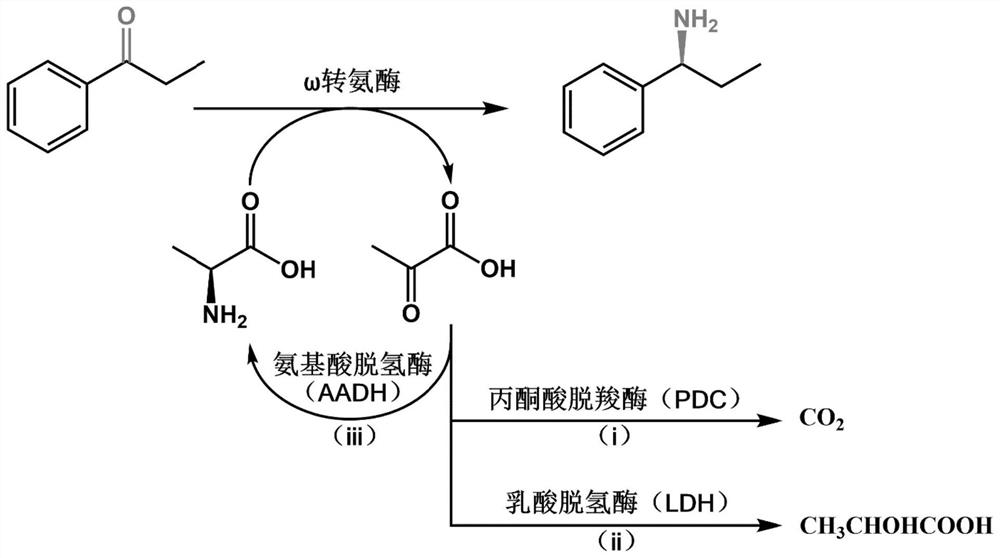
Omega transaminase as well as mutant, recombinant plasmid, genetically engineered bacterium and application thereof
ActiveCN112481229AHigh stereoselectivityMild reaction conditionsBacteriaTransferasesHeterologousChiral selectivity
The invention provides omega transaminase as well as a mutant, a recombinant plasmid, a genetically engineered bacterium and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the omega transaminase is shown as SEQ ID No: 2, wherein the omega transaminase mutant is obtained by mutation of the amino acid sequence of the omega transaminase and has at least 90% of homology with the SEQ ID No: 2. According to the invention, the omega transaminase gene is extracted from Burkholderia phymatum, the heterologous expression of the omega transaminase gene is realized, and the generated omega transaminase strain shows excellent catalytic activity on a series of aryl alkyl substrates. The omega transaminase is mutated to obtain a series of omega transaminase mutants, and the omega transaminase mutants are coupled with different enzymes to be applied to the production of asymmetric synthesis of (S)-1-amphetamine and other chiral amine products by a biological enzyme method, so that the method has thecharacteristics of economy, environmental protection and high chiral selectivity; thus, the invention provides a potential choice for industrial application of transaminase.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
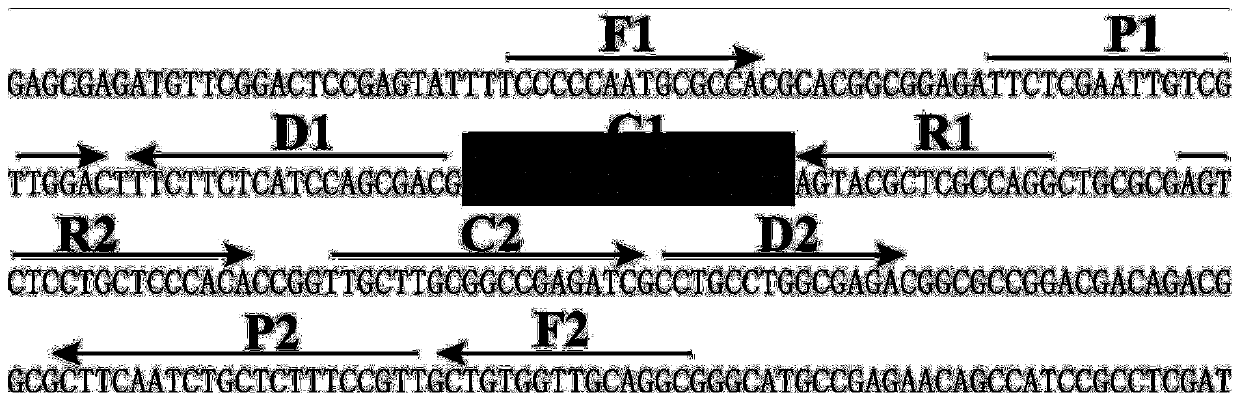
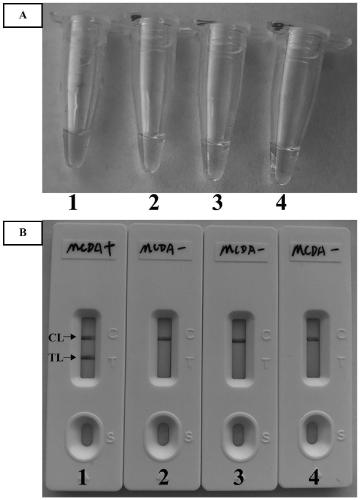
Method for detecting Burkholderia pseudomallei by multi-cross isothermal amplification in combination with gold nano-biosensing
PendingCN111518930AImprove featuresImprove good performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNano biosensorBurkholderia lata
The invention discloses a method for detecting Burkholderia pseudomallei by multi-cross isothermal amplification in combination with gold nano-biosensing. Corresponding specific primers is designed based on Burkholderia pseudomallei TTS1 genes, and meanwhile fluorescein is marked at the 5'end of an amplification primer C1 and biotin is marked at the 5'end of an amplification primer D2 to obtain C1* and D1 * newly labeled amplification primers. The method can realize visual detection of the Burkholderia pseudomallei via the gold nano-biosensor, and the method is convenient, rapid, high in sensitivity and good in specificity.
Owner:三亚市人民医院
A special compound microbial agent for eliminating the obstacle of Pseudostellaria heterophylla and its preparation method
ActiveCN105779305BGood rhizosphere colonization abilityNo pathogenic infection abilityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyContinuous cropping
The invention discloses a special compound microorganism bacterium agent capable of eliminating continuous cropping obstacles of radix pseudostellariae. The special compound microorganism bacterium agent is prepared from common probiotics and aboriginal probiotics at the volume ratio of 4 to 6, wherein the common probiotics are prepared by mixing lactic acid bacteria, photosynthetic bacteria, saccharomycetes and actinomyces at the volume ratio of 1 to 1 to 1 to 1; the aboriginal probiotics are prepared by mixing burkholderia, pseudomonas and bacillus at the volume ratio of 4 to 1 to 1. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the special compound microorganism bacterium agent capable of eliminating the continuous cropping obstacles of the radix pseudostellariae. The preparation method comprises the following steps: step 1, screening aboriginal antagonistic bacteria; step 2, preparing common compound bacterium liquid; step 3, activating and carrying out expanding culture on the aboriginal probiotics; step 4, preparing the compound microorganism bacterium agent. The special compound microorganism bacterium agent prepared by the method has a good root fixed planting capability and is safe and reliable, has obvious prevention and control effects on the continuous cropping obstacles of the radix pseudostellariae and soil-borne diseases, and has no pathogenic infection capacity on other succession crops.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
A strain of Burkholderia cepacia and its application
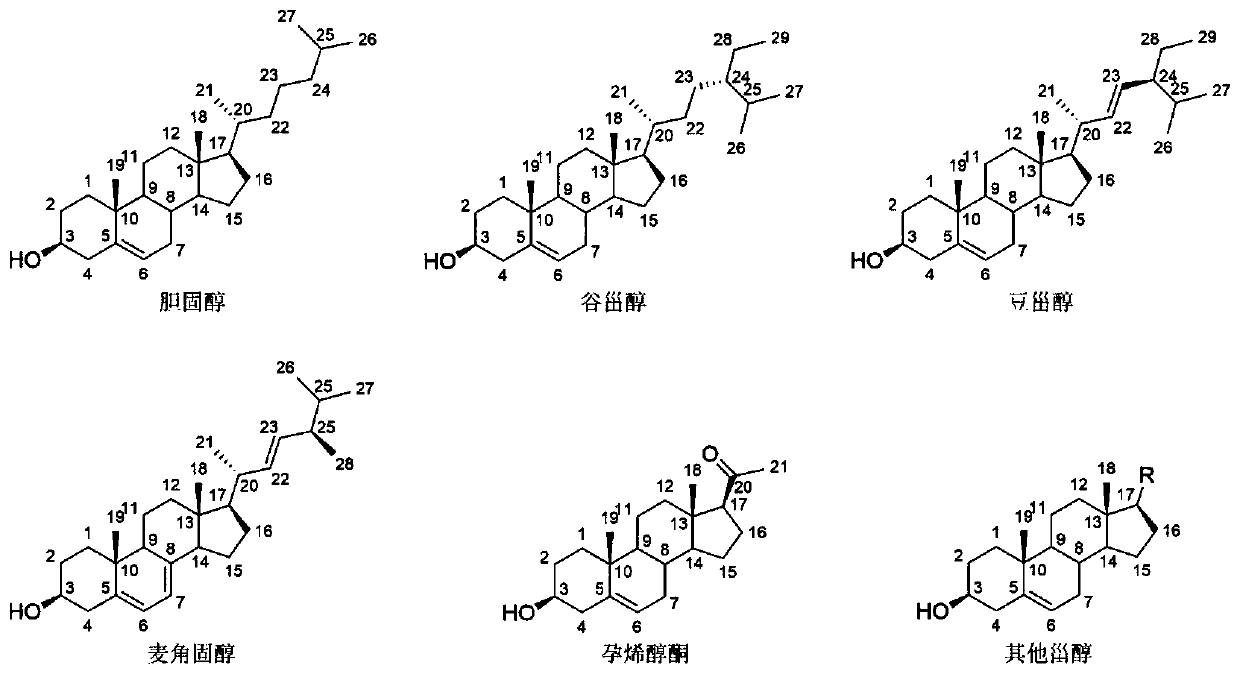
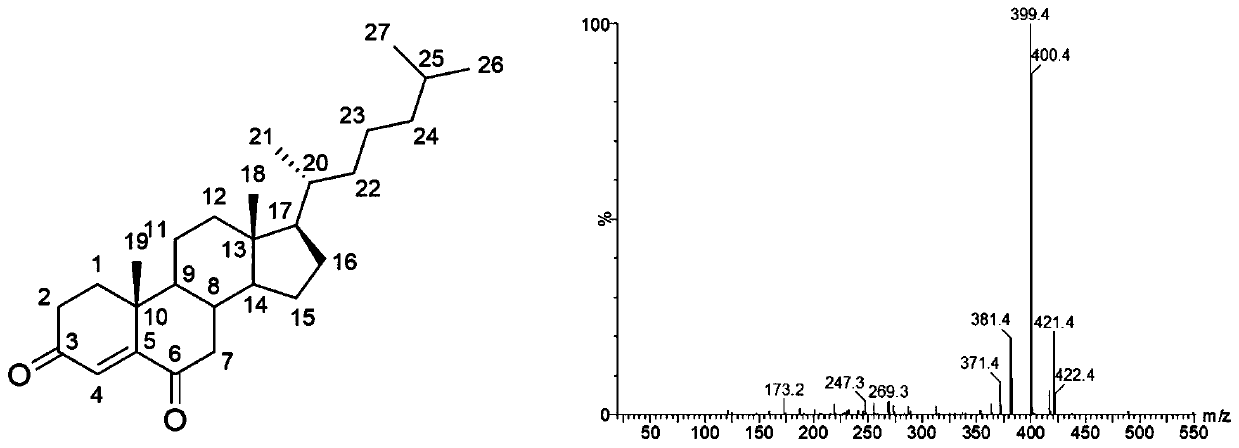
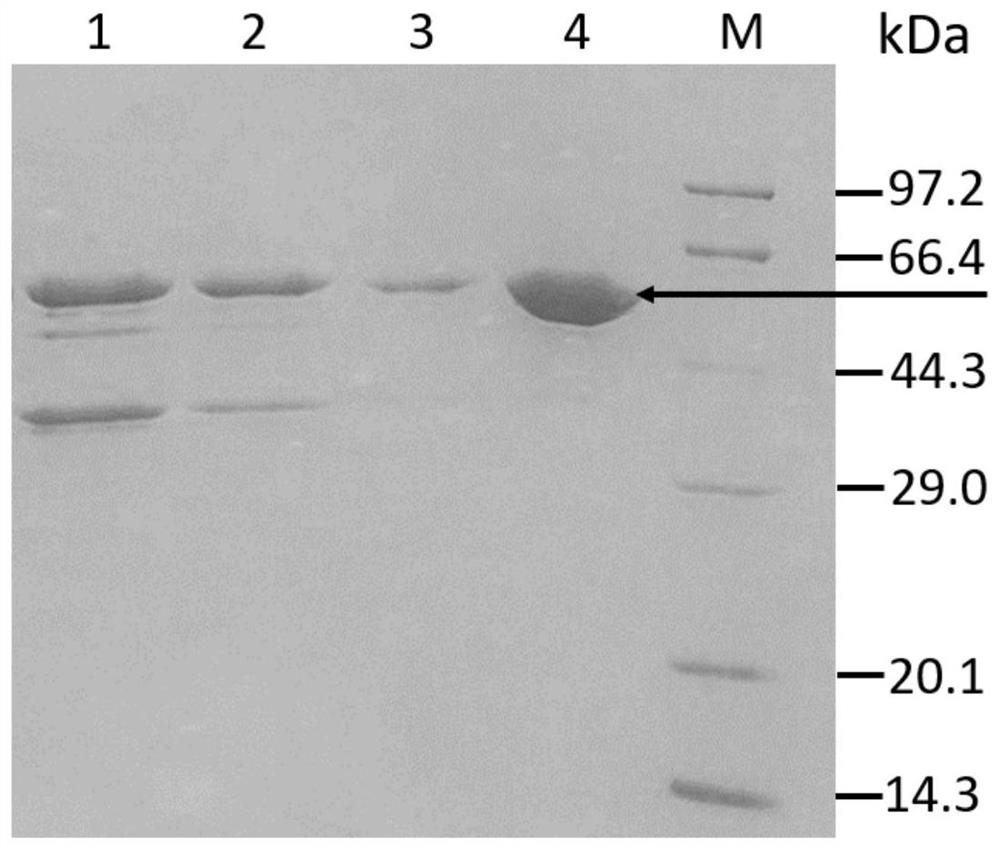
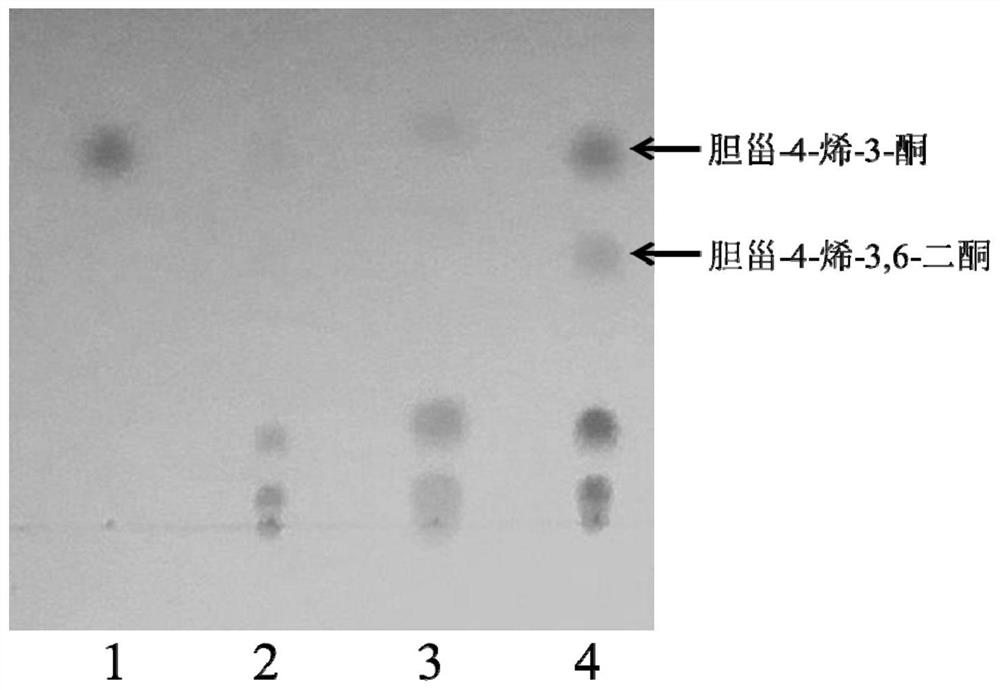
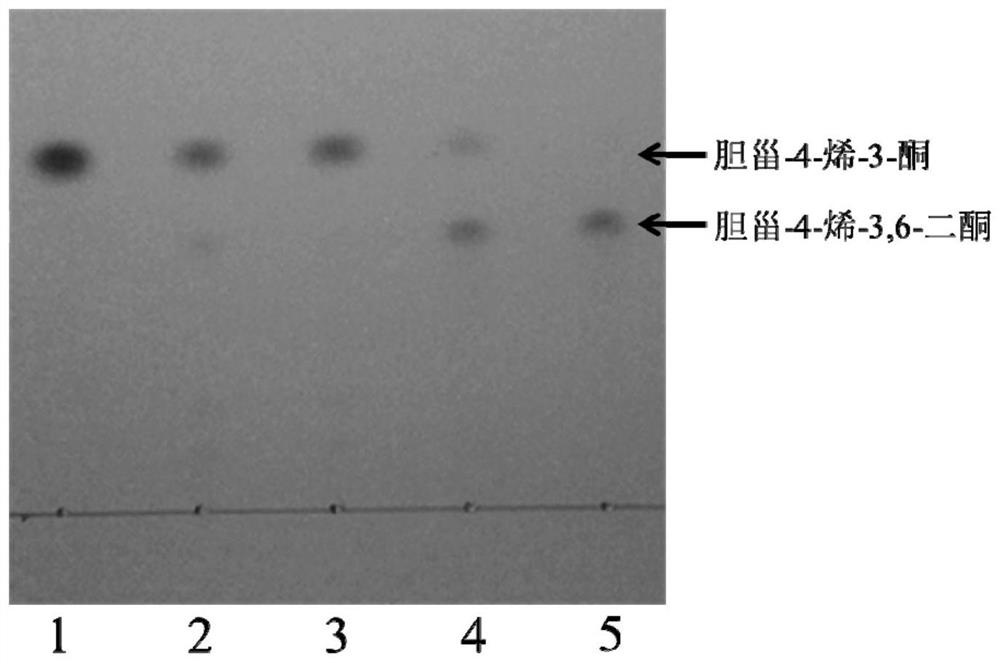
The invention discloses a strain of Burkholderia cepacia and its application, belonging to the field of microorganisms. The Burkholderia cepacia ZWS15 was deposited in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on November 6, 2017, with the preservation number CCTCC NO: M2017661, and the preservation address is Wuhan University, Wuhan, China. The bacterium can use cholesterol as the sole carbon source, can grow at 50°C, tolerates 10% organic solvents, and the enzyme activity of cholesterol oxidase in the crude enzyme liquid obtained by its fermentation is as high as 200U / L. Using Burkholderia cepacia ZWS15 fermented crude enzyme solution to catalyze cholesterol in a two-phase system in the presence of organic solvents, the amount of cholest-4-en-3-one collected was about 5-11% of the added amount of substrate %, the amount of cholest-4-ene-3,6-dione is about 10-15% of the amount of substrate added.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com