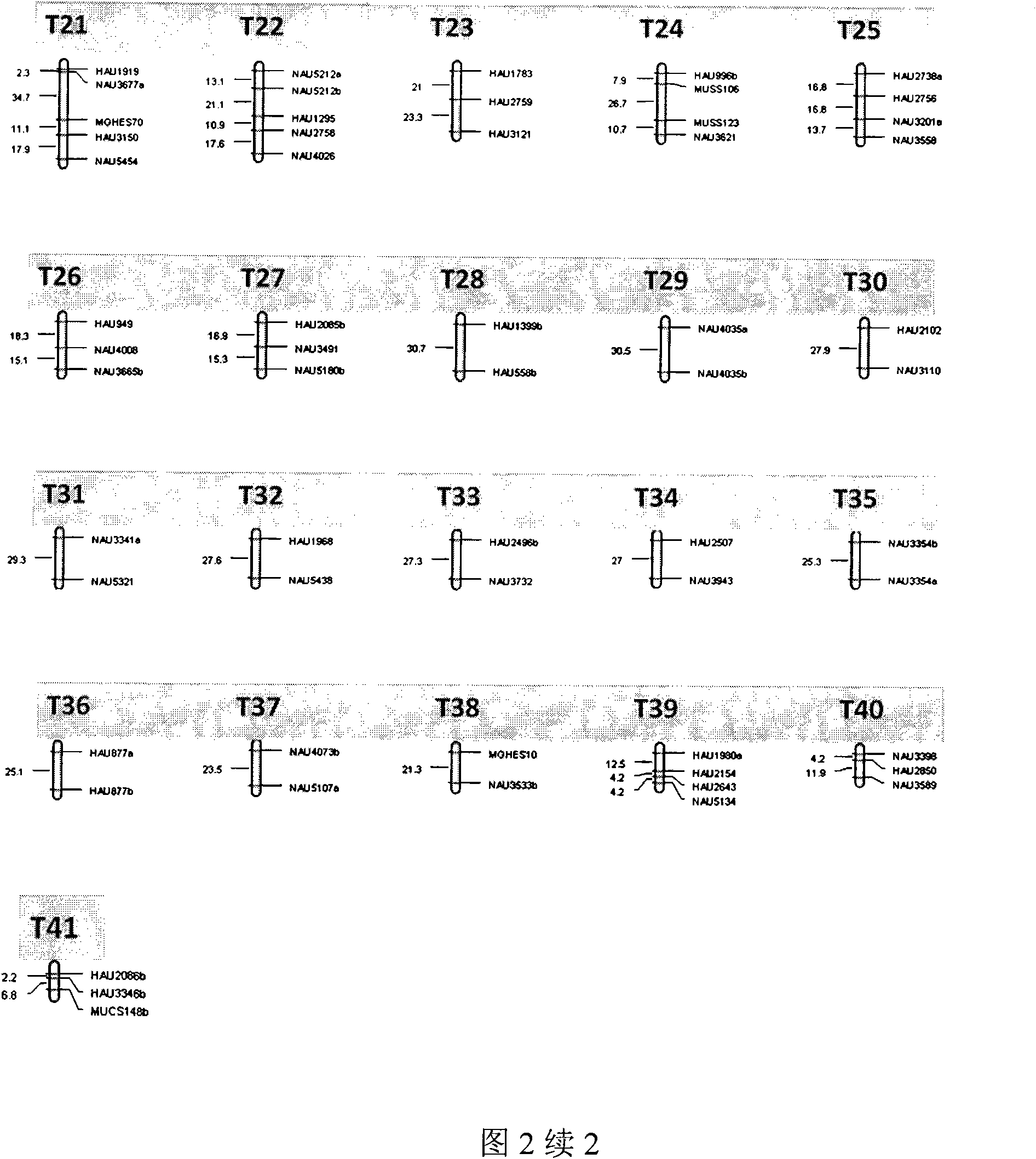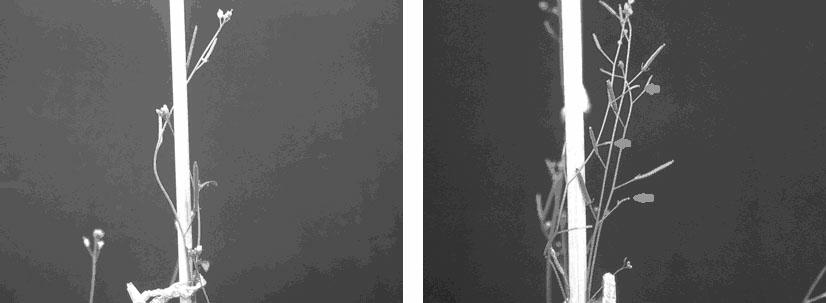Patents
Literature
144 results about "Cloning genes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Process for producing freeze dried competent cells and use thereof in cloning
InactiveUS20020081565A1Improve efficiencyAvoid utilizationBacteriaUnicellular algaeCompetent cellFreeze-drying
A process for producing lyophilized competent cells wherein competent cells are that can be stored or shipped as freeze-dried cells at temperatures between 0° C. and 8° C. and remain suitable for cloning genes or DNA fragments. The process includes culturing cells, rending the cells competent, and lyophilizing the cells. Once lyophilized, the cells can be stored or shipped as freeze-dried cells. The lyophilized cells are prepared for transformation protocols by being re-hydrated in a solution of dimethyl sulfoxide. Once re-hydrated, the transformation efficiency of the competent cells is at least 5x105 transformations per microgram of DNA.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
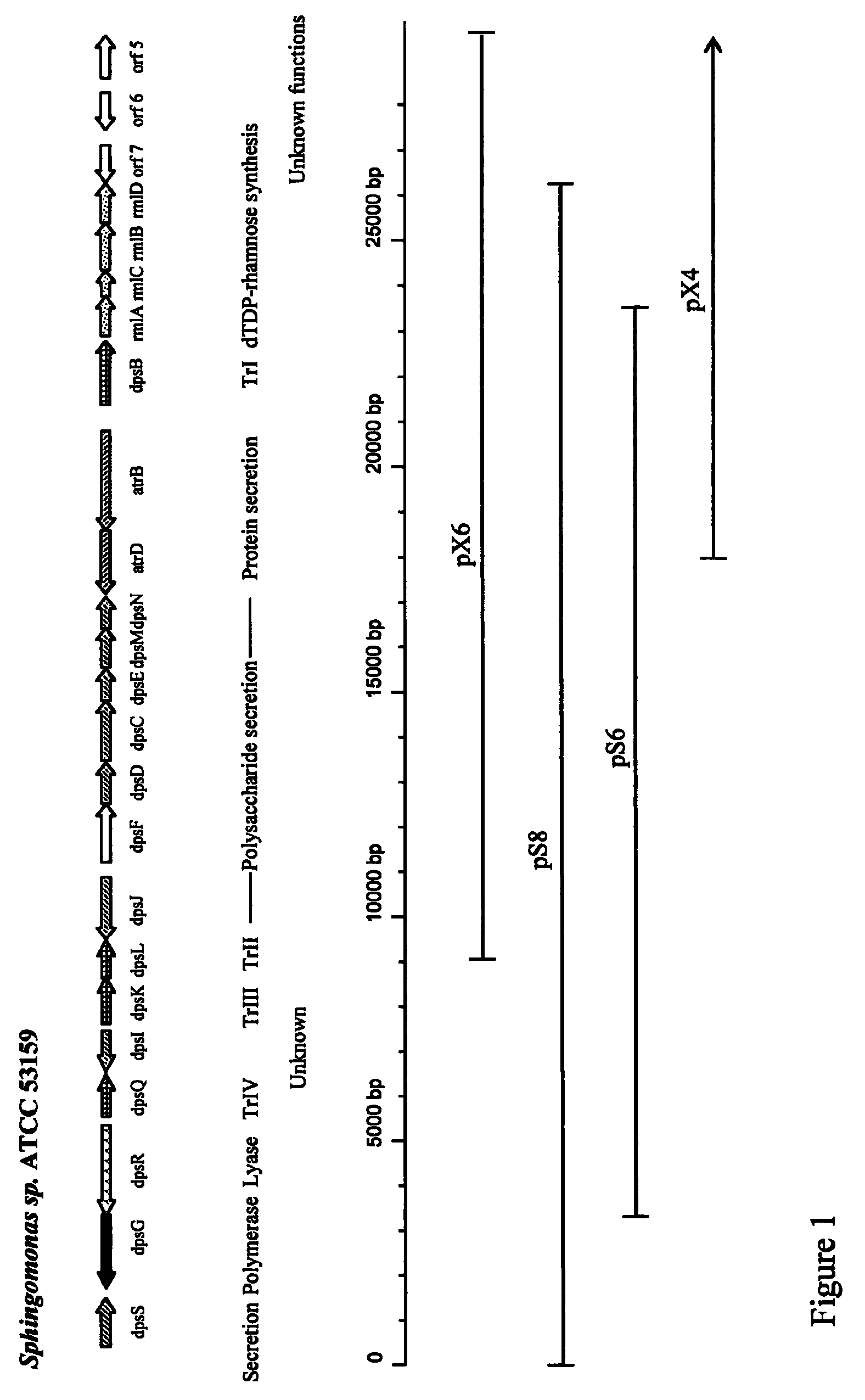
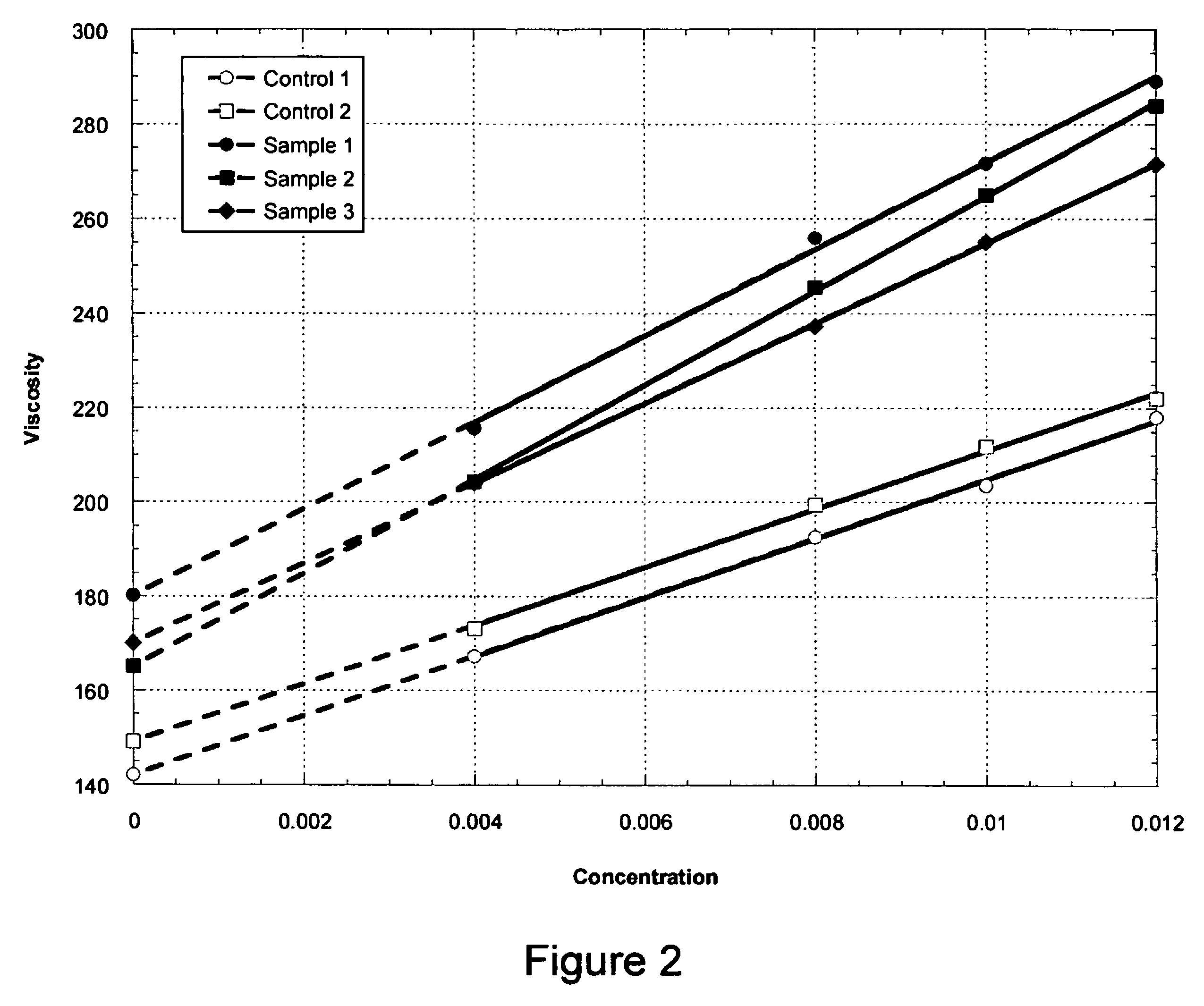
High viscosity diutan gums
ActiveUS7868167B2Increase productionImproved viscosity propertiesBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyPhysical property
The production of a diutan polysaccharide exhibiting increased viscosity properties as compared with previously produced polysaccharide of the same type of repeating units. Such an improved diutan polysaccharide is produced through the generation of a derivative of Sphingomonas sp. ATCC 53159 that harbors a multicopy broad-host-range plasmid into which genes for biosynthesis of diutan polysaccharide have been cloned. The plasmid provides the capability within the host Sphingomonas strain to produce multiple copies of genes for such polysaccharide synthesis. In such a manner, a method of not just increased production of the target diutan polysaccharide, but also production of a diutan polysaccharide of improved physical properties (of the aforementioned higher viscosity) thereof is provided. Such a diutan polysaccharide has proven particularly useful as a possible viscosifier in oilfield applications and within cement materials. The inventive methods of production of such an improved diutan polysaccharide, as well as the novel cloned genes required to produce the improved diutan within such a method, are also encompassed within this invention. Additionally, the novel engineered Sphingomonas strain including the needed DNA sequence is encompassed within this invention.
Owner:CP KELCO U S INC
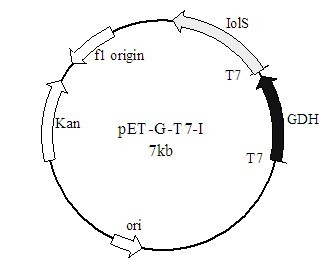
Method for preparing (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate by catalyzing with recombinant carbonyl reductase
InactiveCN102618590AAvoid inhibitionImprove conversion abilityMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliEthyl butyrate
The invention discloses a method for preparing (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate by catalyzing recombinant carbonyl reductase, which belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The method comprises the following steps of: cloning gene segments of carbonyl reductase (IolS) and glucose dehydrogenase (GDH) from bacillus subtilis CGMCC NO.1.1508, expressing an IolS gene and a GDH gene in series by adopting a dual-starter method to construct a recombinant plasmid pET24a-G-T7-I, and introducing the plasmid into escherichia coli BL21(DE3); and under the condition of not adding or adding a small amount of NADP+cofactors, performing biotransformation by taking a cell-free extract of the escherichia coli recombinant plasmid as a catalyst, 2-oxo-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate as a substrate and glucose as a substrate to obtain (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate, wherein the enantiomeric excess value of the product is higher than 99.5 percent. In the method, IolS and GDH are co-expressed, so that efficient regeneration of an intra-cellular cofactor NADP(H) is realized, production cost is lowered, and a good industrial application prospect is achieved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Identification of sortase gene
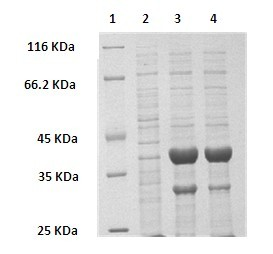
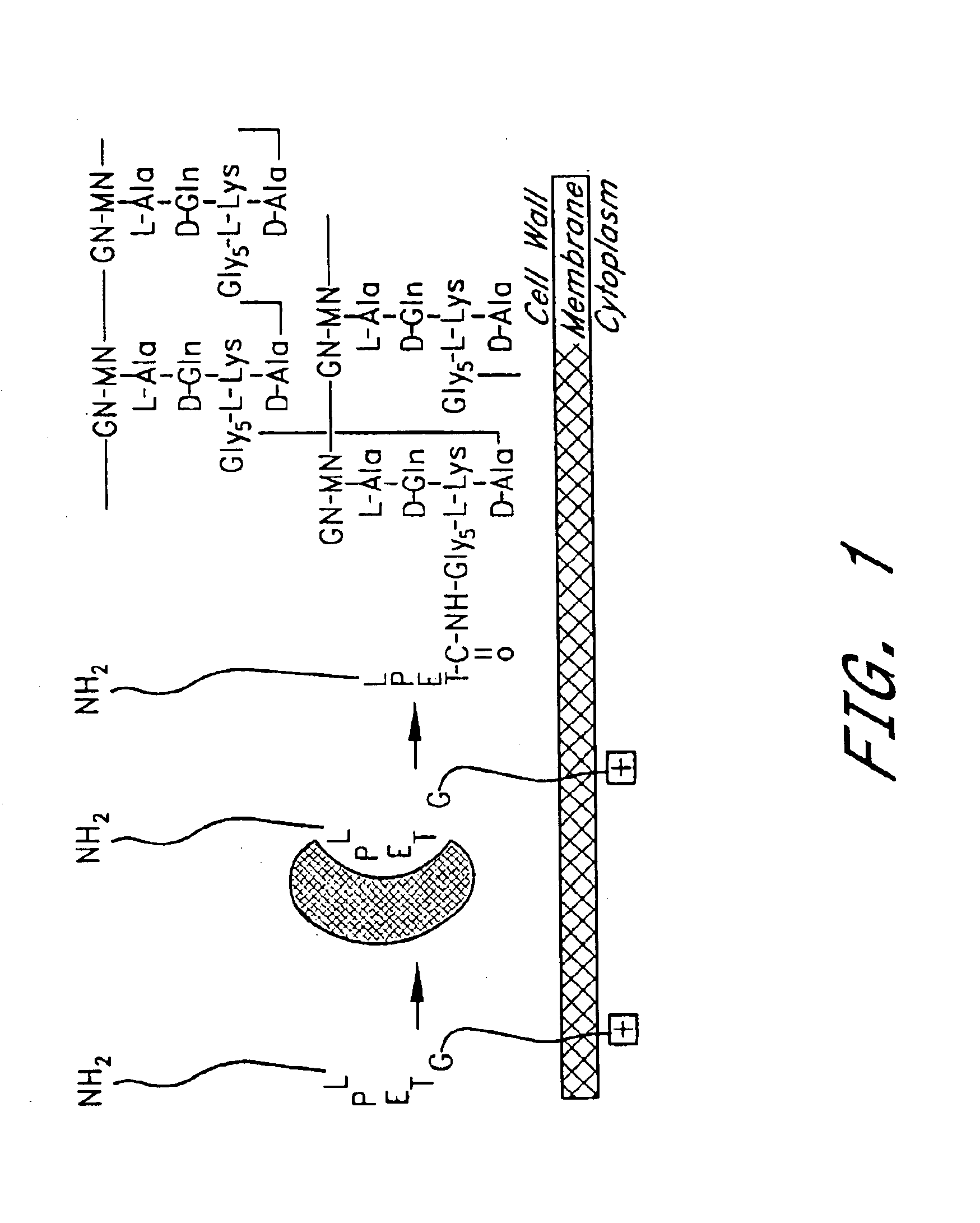
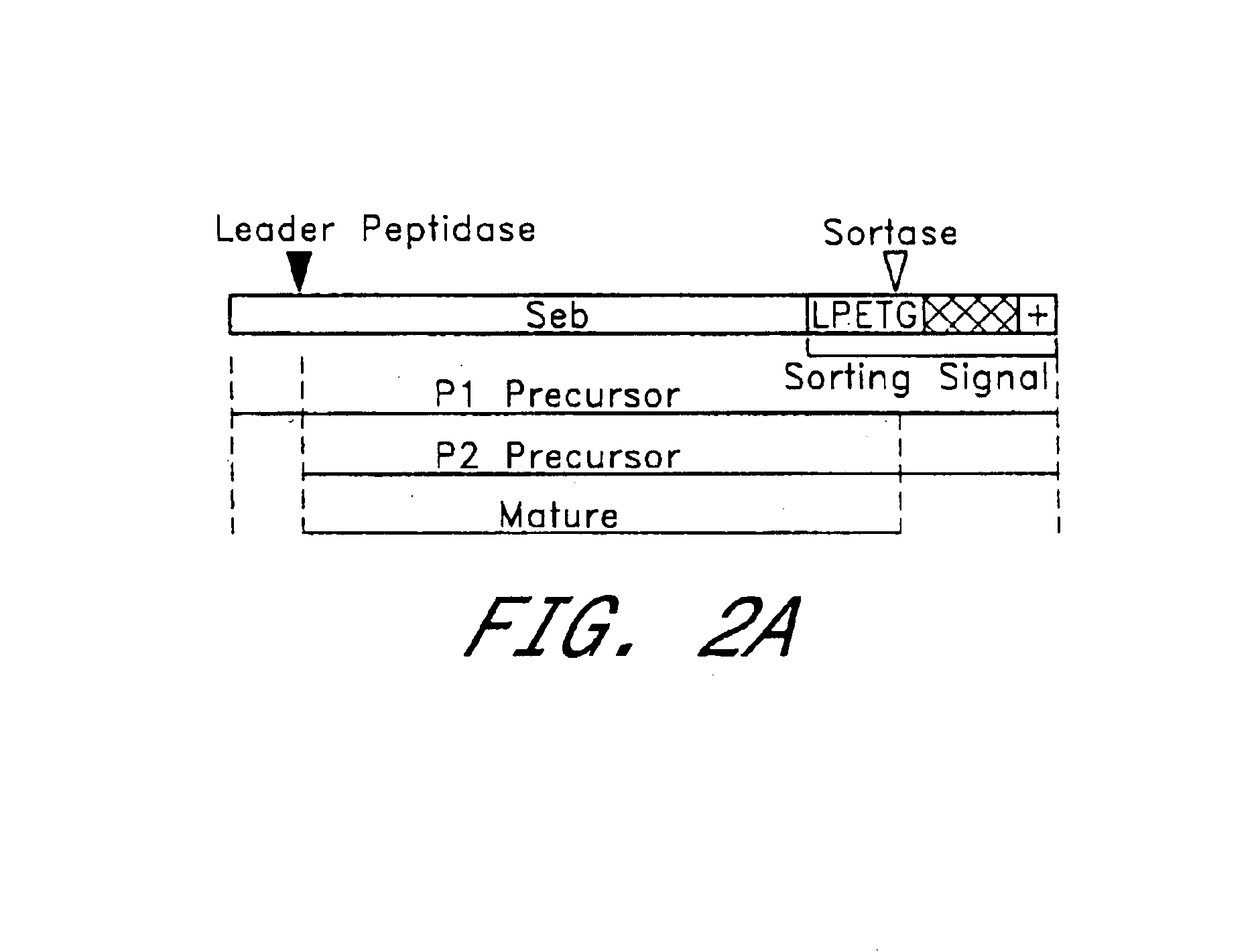
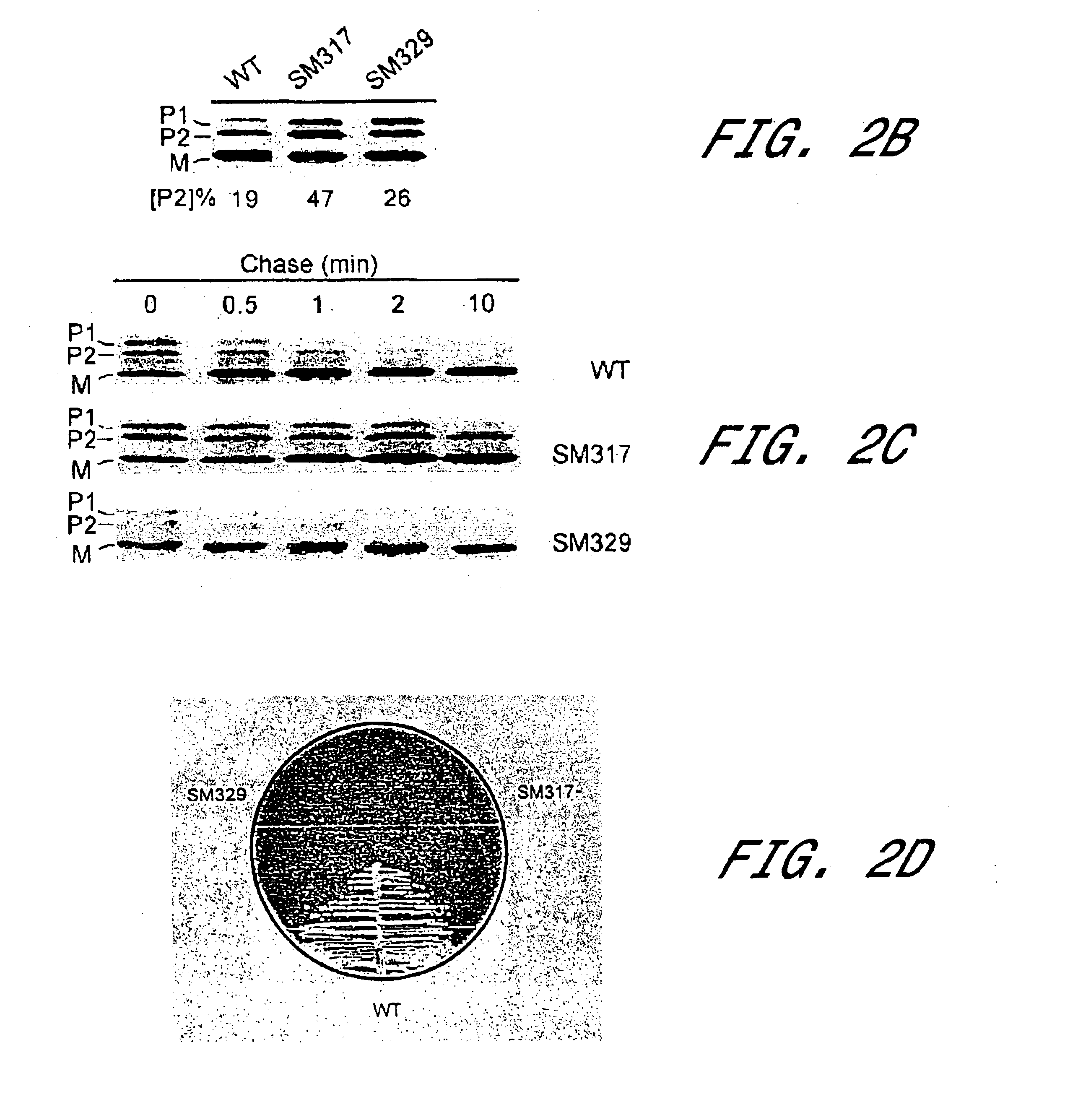
The present invention is a substantially purified sortase-transamidase enzyme from Gram-positive bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus. The enzyme having a molecular weight of about 23,539 or about 29,076 daltons and catalyzing a reaction that covalently cross-links the carboxyl terminus of a protein having a sorting signal to the peptidoglycan of a Gram-positive bacterium, the sorting signal having: (1) a motif of LPX3X4G therein; (2) a substantially hydrophobic domain of at least 31 amino acids carboxyl to the motif; and (3) a charged tail region with at least two positively charged residues carboxyl to the substantially hydrophobic domain, at least one of the two positively charged residues being arginine, the two positively charged residues being located at residues 31-33 from the motif, wherein X3 is any of the twenty naturally-occurring L-amino acids and X4 is selected from the group consisting of alanine, serine, and threonine, and wherein sorting occurs by cleavage between the fourth and fifth residues of the LPX3X4G motif. Variants of the enzyme, methods for cloning the gene encoding the enzyme and expressing the cloned gene, and methods of use of the enzyme, including for screening for antibiotics and for display of proteins or peptides on the surfaces of Gram-positive bacteria, are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
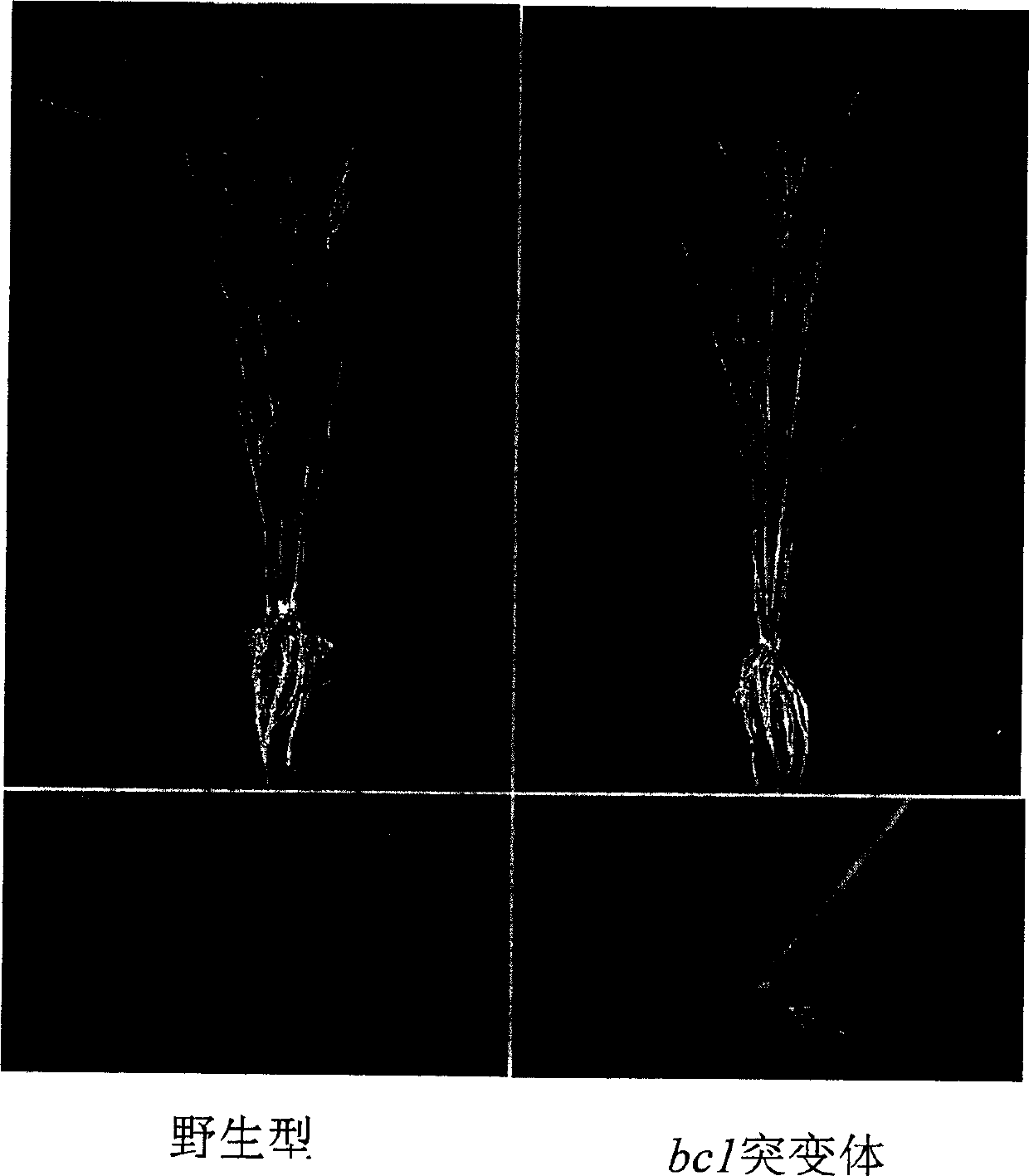
Paddy rice fragile straw controlling gene BC1 and use thereof
InactiveCN1488643AReduce pollutionImprove lodging resistanceClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesPlant cellFragility
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
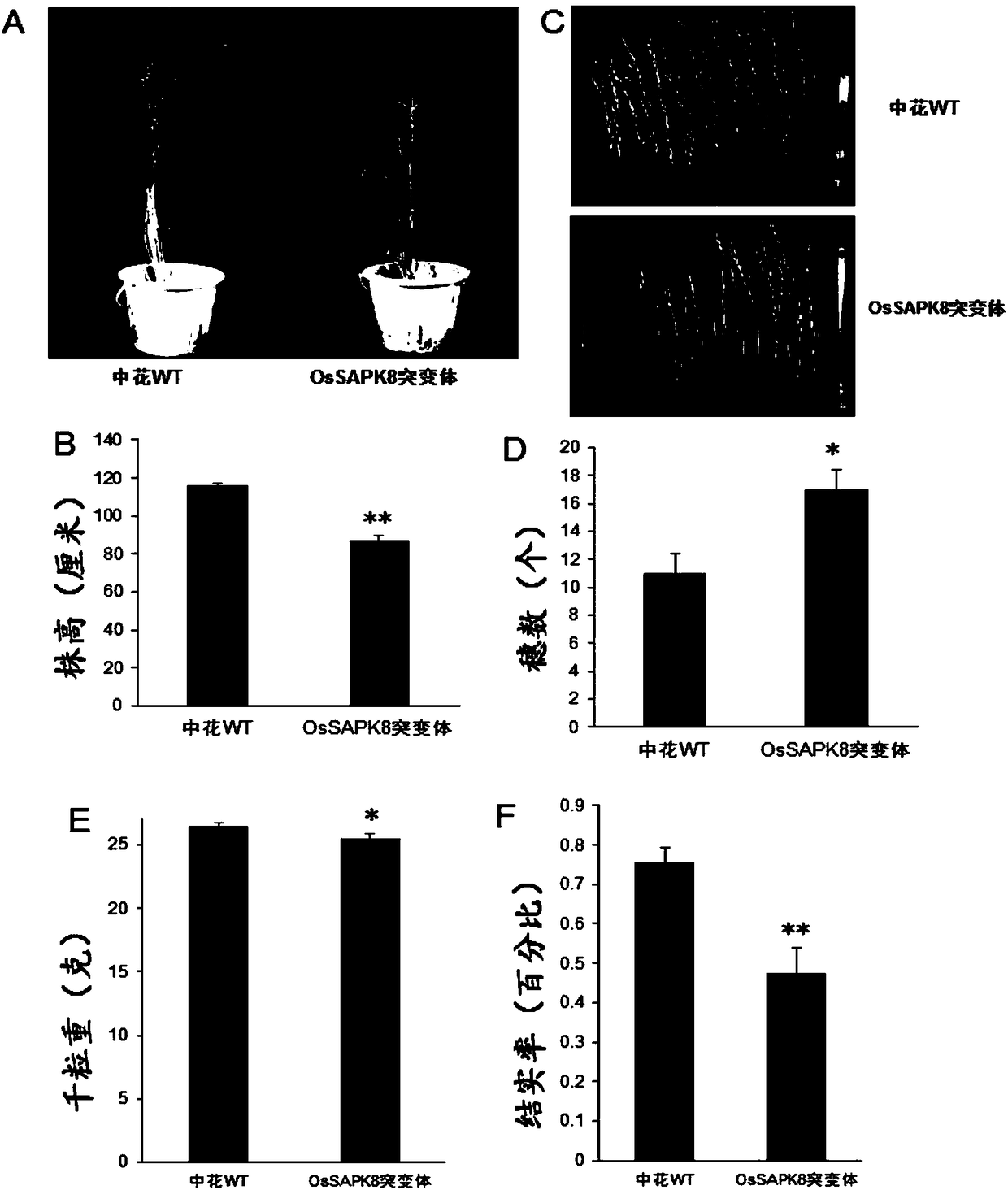
Rice serine/threonine protein kinase gene OsSAPK8 coding sequence and applications thereof
InactiveCN108359674AIncreased ability to respond to abiotic stressesIncrease productionMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesGenetic engineeringMutant
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and specifically relates to a rice serine / threonine protein kinase gene OsSAPK8 coding sequence and applications thereof. The applications comprise cloning of gene OsSAPK8 gene OsSAPK8, the organ expression pattern of the OsSAPK8 gene, and the change of the expression level of the OsSAPK8 after treatment using different hormonesand different stresses. The invention also discloses sequencing identification of the Tilling mutant of the gene OsSAPK8. A result of phenotype identification of the mutant shows that the OsSAPK8 plays a great role in the resistance of the plant to cold stress. The gene OsSAPK8 can be used for improving the plant variety, for example, improving the resistance of rice to cold, drought and salt stress, improving the ability of rice to cope with abiotic stress and increasing the rice yield.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Production of polyketides and other natural products
ActiveUS20050272132A1Rapid and parallel generationEasy to assembleBiocideAntimycoticsNatural productPolyketide
The present invention relates to production of polyketides and other natural products and to libraries of compounds and individual novel compounds. One important area is the isolation and potential use of novel FKBP-ligand analogues and host cells that produce these compounds. The invention is particularly concerned with methods for the efficient transformation of strains that produce FKBP analogues and recombinant cells in which cloned genes or gene cassettes are expressed to generate novel compounds such as polyketide (especially rapamycin) FKBP-ligand analogues, and to processes for their,preparation, and to means employed therein (e.g. nucleic acids, vectors, gene cassettes and genetically modified strains).
Owner:BIOTICA TECH
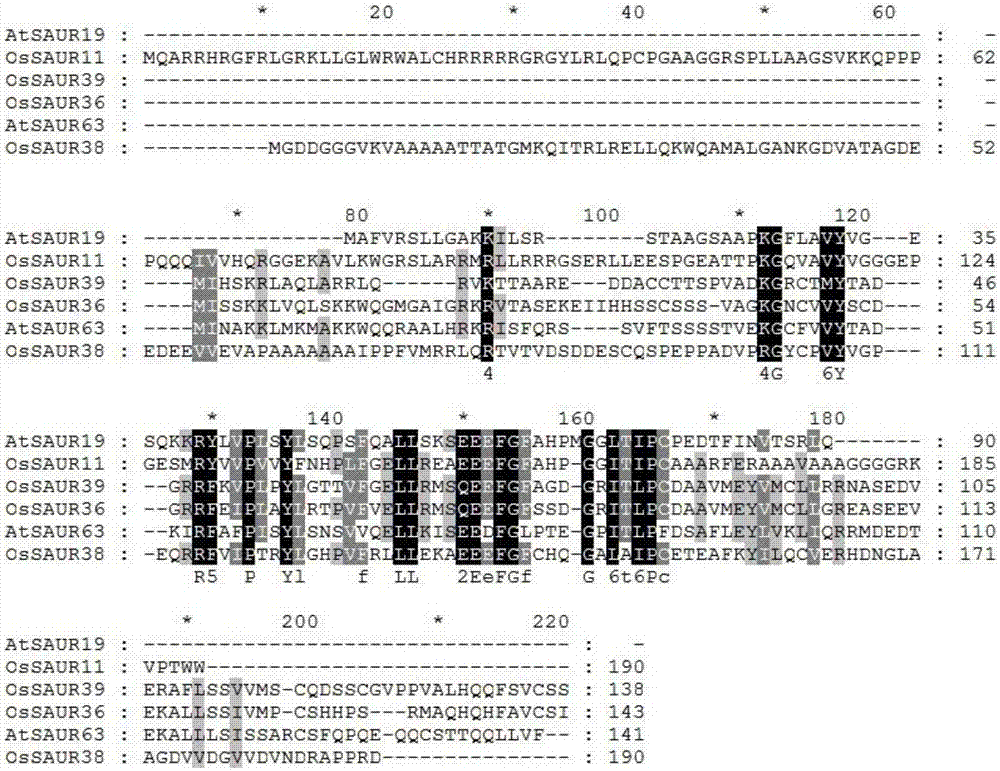
Rice root development and stress resistance related OsSAUR11 genes and encoding protein and application
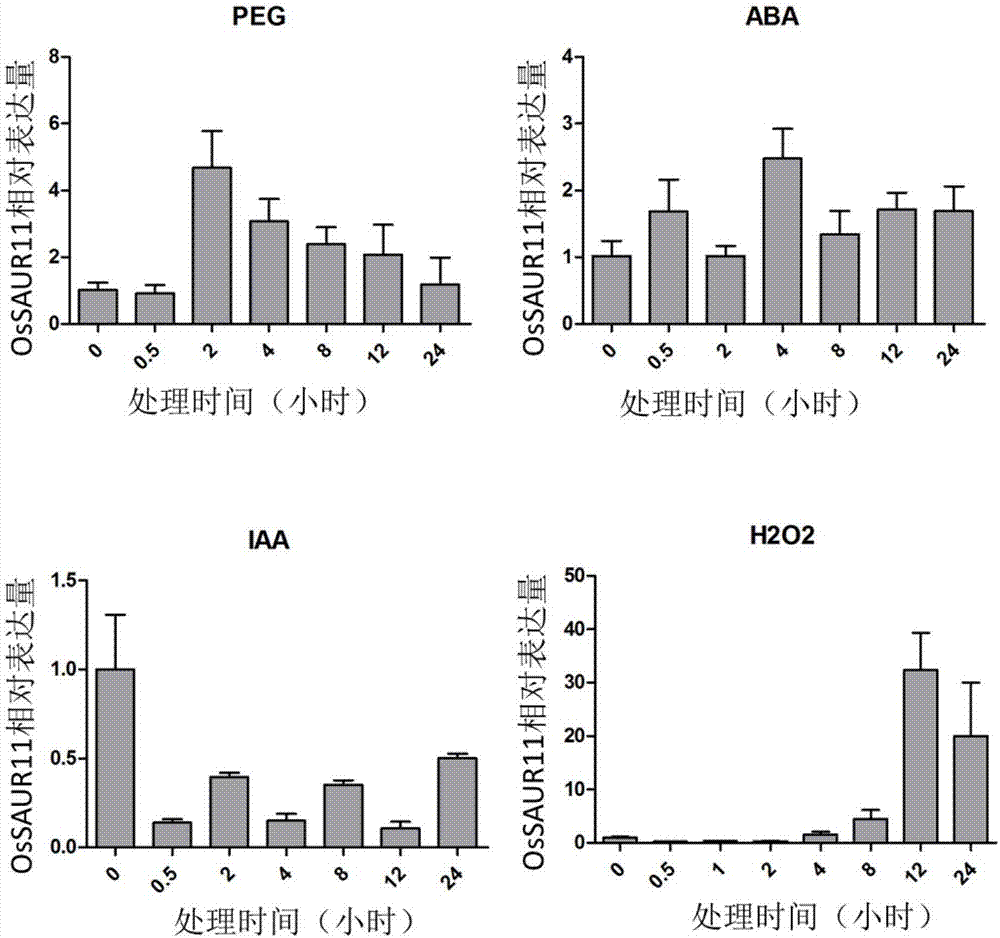
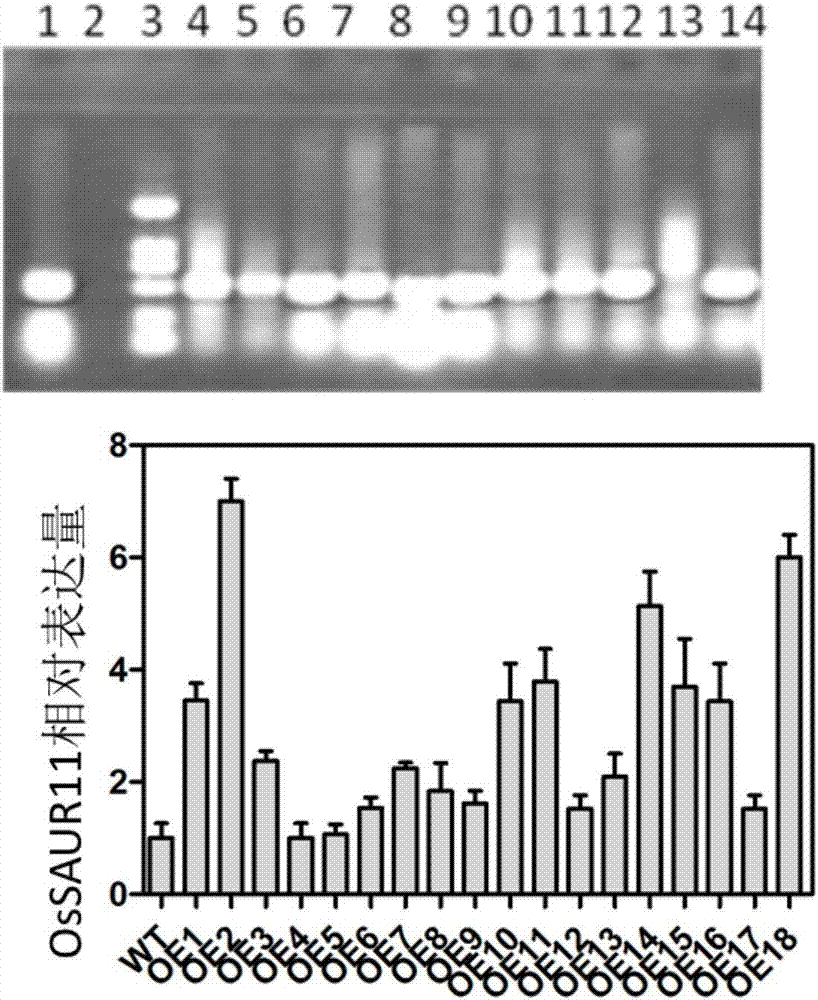
The invention discloses rice root development and stress resistance related OsSAUR11 genes which are isolated and cloned from rice DNA fragments. Protein encoded by the genes contains SAUR family conserved structural domains. The rice root development and stress resistance related OsSAUR11 genes belong to the field of rice cloning genes. The sequence of the OsSAUR11 genes is as shown in followingsequences: a DNA sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, a DNA sequence at least 90% homologous to SEQ ID NO: 1 and a subfragment functionally equivalent to the sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1; the expression of the OsSAUR11 genes is the root development and stress resistance. The rice root development and stress resistance related OsSAUR11 genes disclosed by the invention have the beneficial effectsthat the OsSAUR11 genes are in inducible expression of osmotic stress, abscisic acid and auxins, and overexpression of OsSAUR11 can enhance the deep root ratio of rice and enhance drought resistanceof the rice, is related to rice stress resistance, and has obvious response to adverse environments, thereby being applied to plant drought-resistance breeding, improving the root configuration and enhancing plant stress resistance.
Owner:SHANGHAI AGROBIOLOGICAL GENE CENT
Method for building cotton fiber transcription genetic linkage map by EST-SSR sign
InactiveCN101880714AThe method is simple and fastMicrobiological testing/measurementFiberAgricultural science
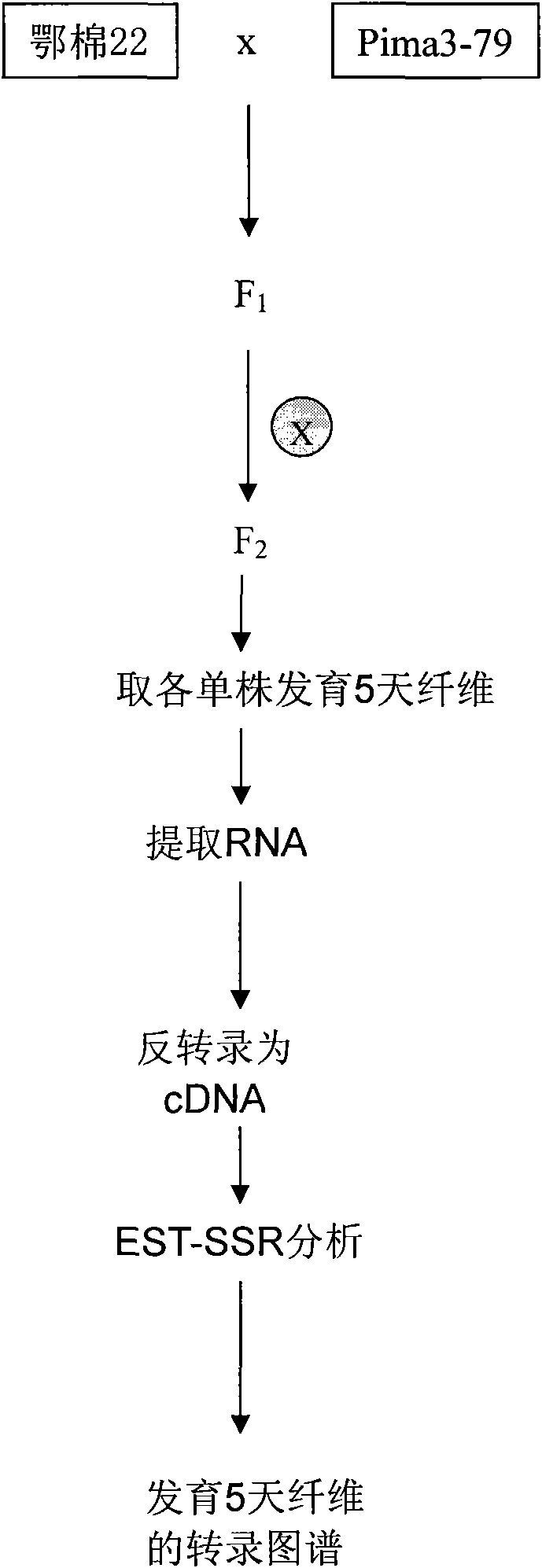
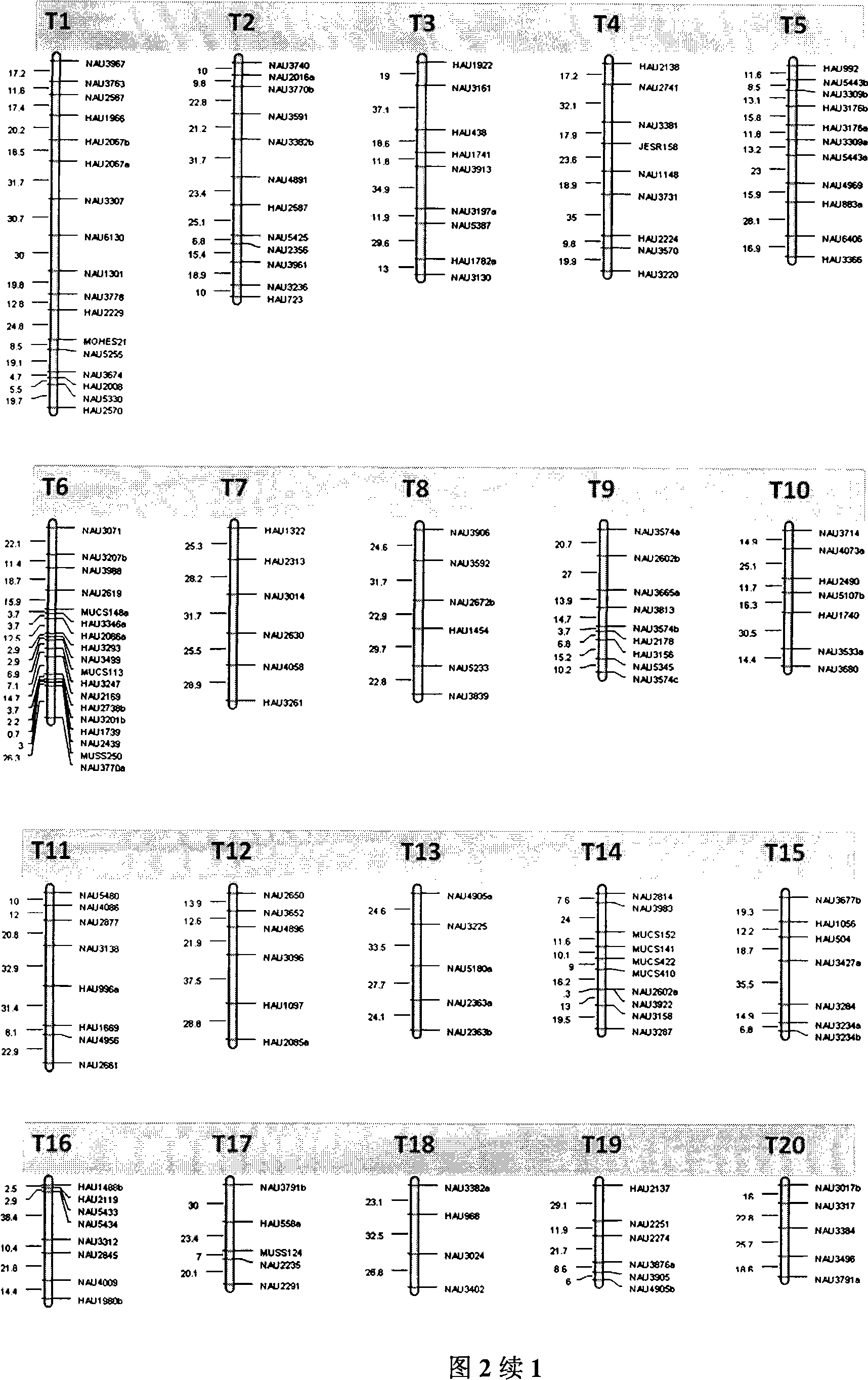
The invention belongs to the technical field of cotton molecule breeding, particularly relating to a method for building a cotton fiber transcription genetic linkage map by EST-SSR signs. The method comprises the following steps: taking gossypium barbadense Pima 3-79 as a male parent and Gossypium hirsutum Emian 22 as a female parent, and hybridizing to obtain F1; planting F1, and causing F1 to be inbreeded to obtain F2; taking the F2 single plant as a starting material for the fiber transcription map to be plotted; extracting the RNA of the fiber of the field F2 single plant in 5 days after the single plant blooms, and carrying out reverse transcription of the RNA into cDNA to be served as a plotting group of the transcription map; utilizing the reported EST-SSR primer and the primer shown by a self-designed sequence table SEQ ID NO:1-90 to carry out the plotting group analysis to the F2 single plant by a denatured polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic analysis; and finally, analyzing data by MAPMAKER / EXP.3.0 mapping software, and manufacturing and obtaining the transcription map. Compared with the existing method, the method of the invention is simple and practical, has accurate QTL positioning and is convenient for cloning genes relevant to cotton fiber development.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
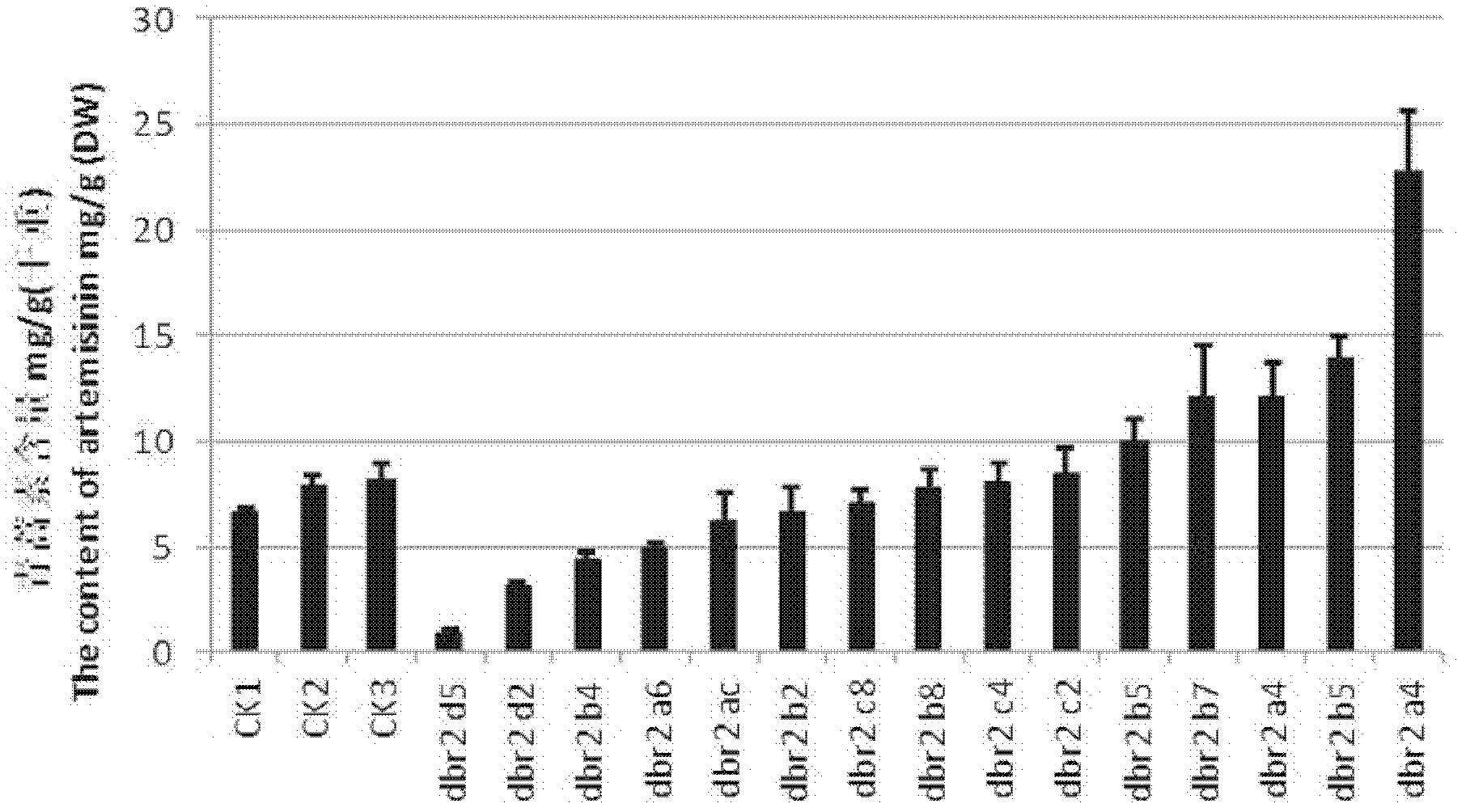
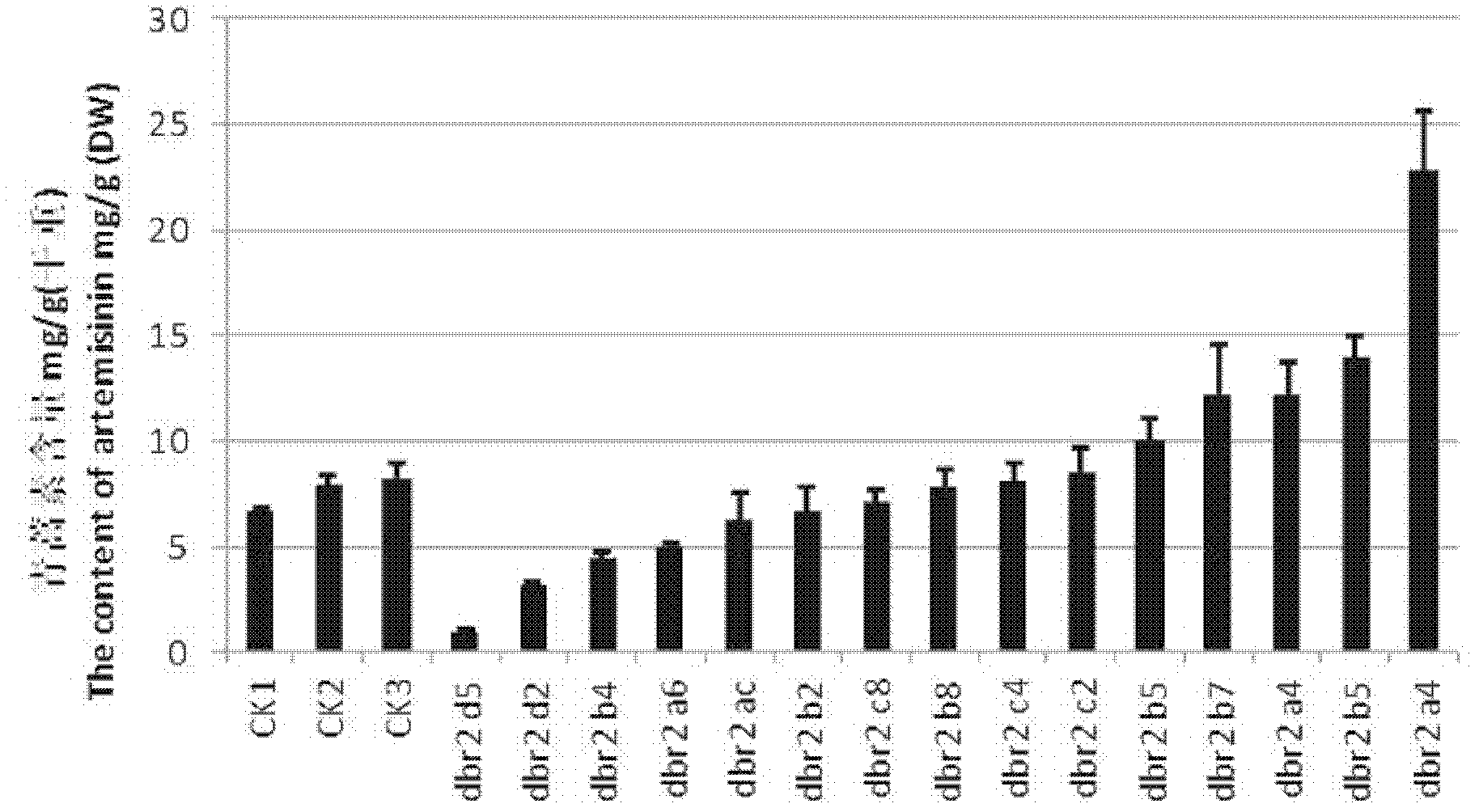
Method for increasing artemisinin content in sweet wormwood by DBR2 (double bond reductase 2) gene transfer
The invention provides a method for increasing artemisinin content in sweet wormwood by DBR2 (double bond reductase 2) gene transfer in the field of biotechnology. The method includes the steps: cloning genes of artemisinic aldehyde delta 11(13) DBR2 from the sweet wormwood, constructing a plant expression vector containing the DBR2 genes, using agrobacterium tumefaciens for mediation to transfer the DBR2 genes into the sweet wormwood so that plants regenerate, using PCR (polymerase chain reaction) to detect integration conditions of the exogenous targeted DBR2 genes, determining the artemisinin content in the transgenic sweet wormwood by means of HPLC-ELSD (high performance liquid chromatography-evaporative light scattering detector), and screening the transgenic sweet wormwood plants with the improved artemisinin content. The artemisinin content in the obtained transgenic sweet wormwood can be remarkably increased and is 2.83 times maximally of that of a non-transgenic control plant, and accordingly the method for increasing the artemisinin content in the sweet wormwood lays a foundation for large-scale artemisinin production by the aid of the transgenic sweet wormwood.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SUBEI RES INST
Common mussel C type lysozyme and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102643787AStrong inhibitory activityMicroorganism based processesEnzymesComplementary deoxyribonucleic acidFeed additive
The invention discloses a common mussel C type lysozyme and a preparation method thereof. The amino acid sequence of the common mussel C type lysozyme is shown by a sequence table SEQ ID No.1. The preparation method of the common mussel C type lysozyme comprises the following steps of: extracting common mussel gross RNA (ribonucleic acid), purifying mRNA (Messenger ribonucleic acid), preparing a cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) template solution, cloning gene, building recombinant plasmid, expressing expression plasmid and purifying protein to obtain the C type lysozyme. The common mussel C type lysozyme is a new C type lysozyme which has strong inhibitory activity on various gram positive and negative microorganisms, and has application value in the aspects of developing food preservatives, feed additive, etc.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Analysis and application of salvia miltiorrhiza bunge isopentenylpyrophosphate isomerase (SmIPPI) gene
InactiveCN101654678AImprove qualityRelieve severe plaque deficiencyBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologySalvia miltiorrhiza
The invention discloses a salvia miltiorrhiza bunge isopentenylpyrophosphate isomerase (IPPI) gene, a protease coded by the IPPI genes and an application thereof. The gene is obtained by cloning fromsalvia miltiorrhiza bunge through utilizing a cDNA chip technology for the first time, thus the invention fills the blank of separating and cloning the SmIPPI gene from the salvia miltiorrhiza bunge which is a conventional famous and precious Chinese medicinal plant. The SmIPPI gene has a nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO.1 or adds, substitutes, inserts or deletes one or more nucleotidehomologous sequences or an allele thereof and a nucleotide sequence derived from the nucleotide homologous sequence. A protein coded by the SmIPPI genes has an amino acid sequence represented by SEQID NO.2 or adds, substitutes, inserts or deletes one or more amino acid homologous sequences. The SmIPPI gene can be applied to researches and industrialization for improving the content of diterpeneactive constituents in the salvia miltiorrhiza bunge by a biotechnology method and improving the content of tanshinone substances by utilizing a transgenic technology, is helpful to the quality improvement, the selective breeding, and the like of medicinal materials of the salvia miltiorrhiza bunge and has good application prospect.
Owner:INST OF CHINESE MATERIA MEDICA CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI
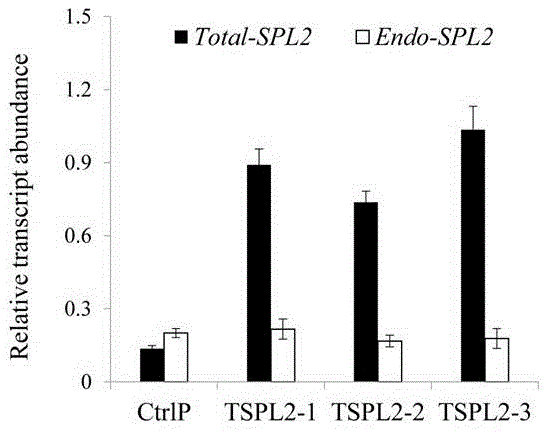
Application of SBP-box type transcription factors of switchgrass in aspect of increasing plant biomass and fermentable sugar yields
ActiveCN105602962AIncrease biomassIncrease productionVectorsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGermplasmPlant genetic engineering
The invention discloses application of SBP-box type transcription factors of switchgrass in the aspect of increasing plant biomass and fermentable sugar yields, and belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. The application mainly includes cloning genes of the SBP-box type transcription factors PvSPL1 and 2 of the switchgrass and determining sequences of the SBP-box type transcription factors of the switchgrass; inhibiting the transcription activity of integral subfamilies of the transcription factors PvSPL1 and 2 on the basis of the genes and the sequences by the aid of chimeric repressor silencing technologies (CRES-T) so as to generate transgenic switchgrass plants with increased tiller quantities. The application has the advantages that dry matter biomass of the obtained transgenic switchgrass plants can be increased by 2.0-2.3 times, and the total fermentable sugar yields can be increased by 2.0-2.2 times; the generated transgenic switchgrass energy plants can be integrated in conventional breeding projects, and accordingly precious germplasm resources can be provided for creating novel varieties of high-yield and efficiently degradable energy plants; novel targets for molecular breeding in future can be provided by the authenticated SBP-box type transcription factors PvSPL1 and 2 of the switchgrass, and the SBP-box type transcription factors PvSPL1 and 2 of the switchgrass can be used for designing oriented molecules of commercialized energy plant products.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
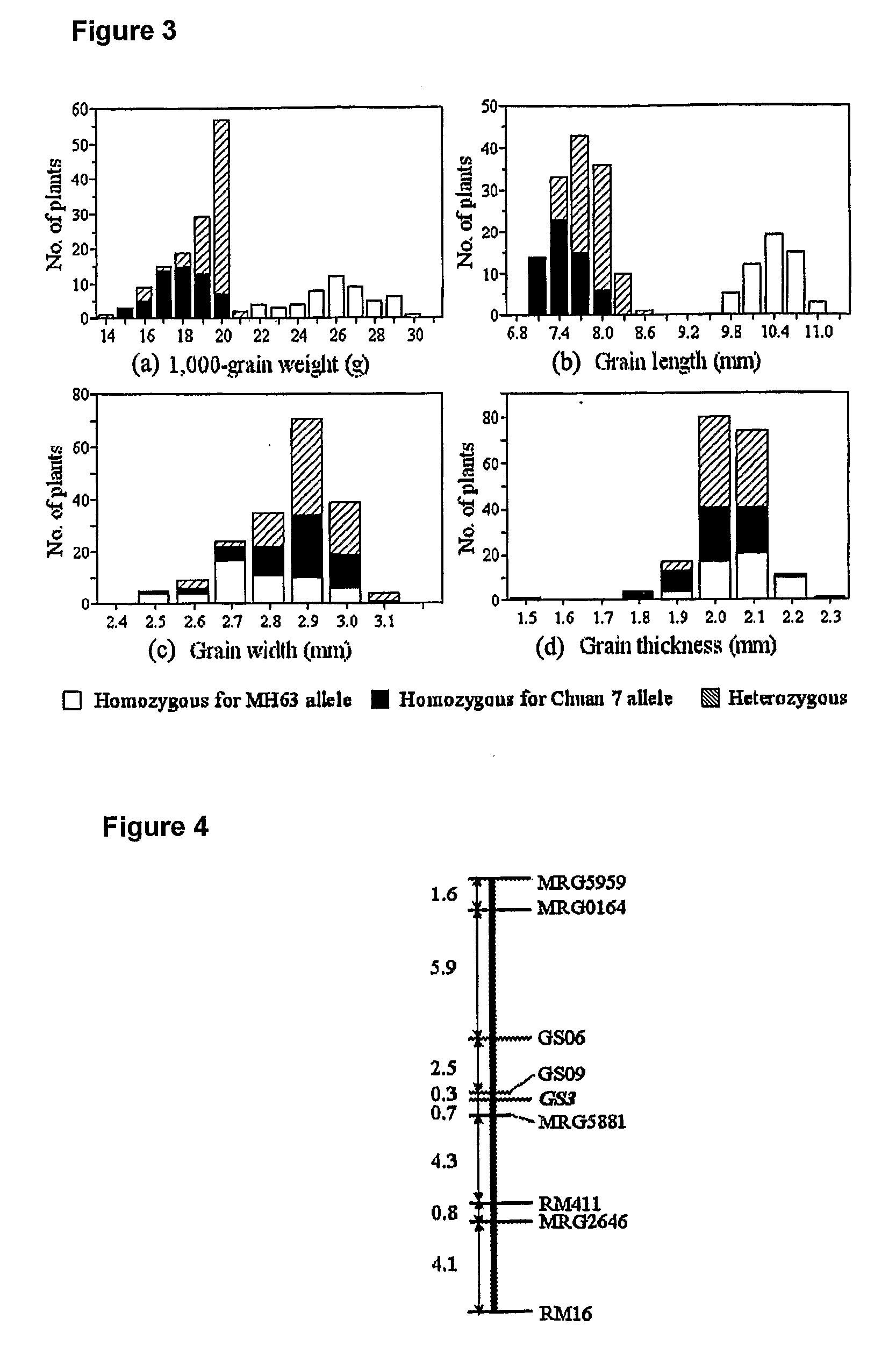
Rice Gene, GS3, Exerting Primary Control Over Grain Length and Grain Weight
InactiveUS20100017919A1High yieldQuality improvementFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyNucleotide
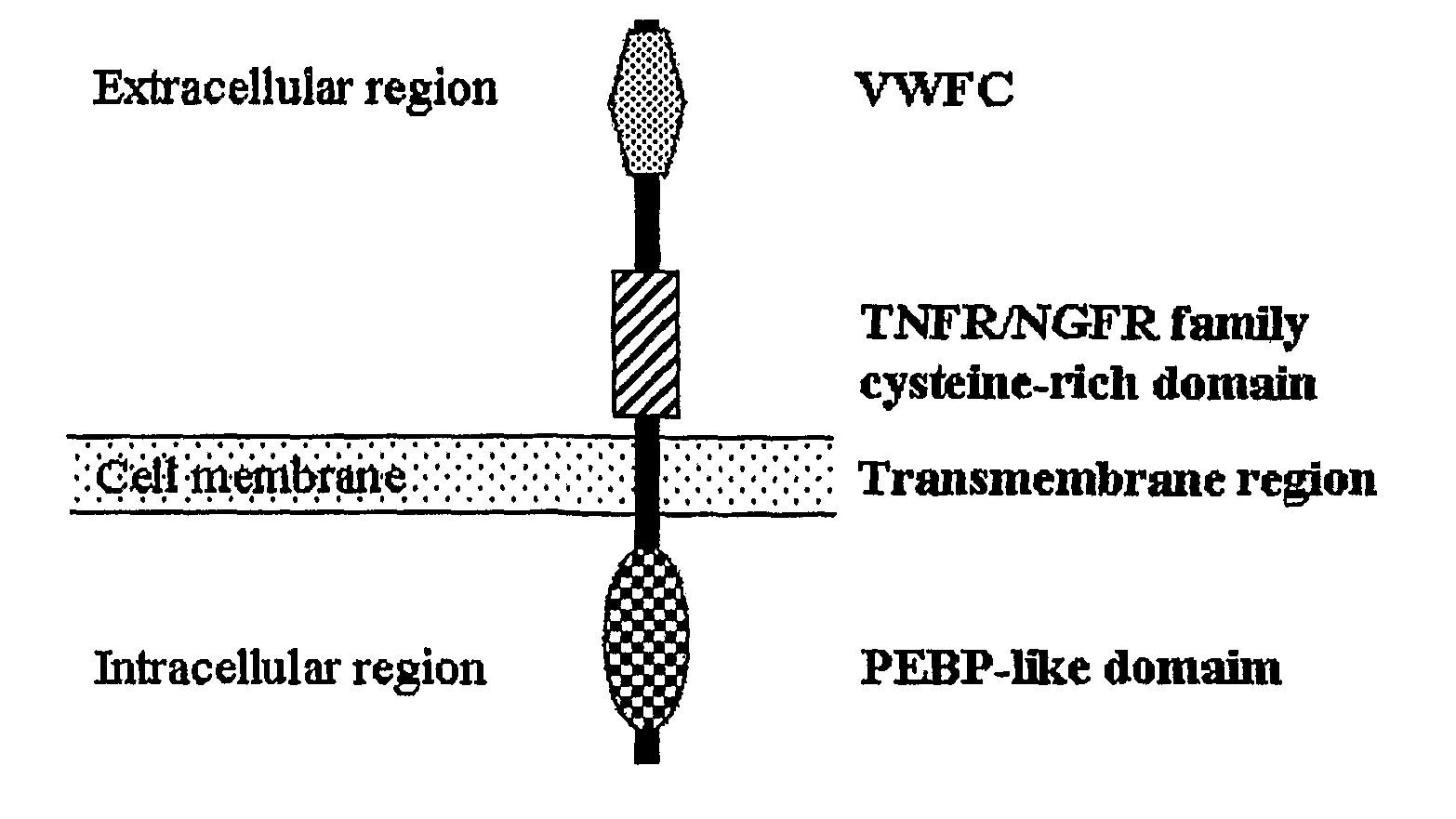
The present invention relates to an isolated major gene GS3 which regulates grain weight and grain length in the rice and the cloning of said gene. The DNA sequence of GS3 gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 and is 7883 bp in length. GS3 gene comprises 5 exons and encodes 232 amino acids. It is predicted based on bioinformatics analysis that said protein contains conserved domains including a PEBP-like domain, a transmembrane domain, a cysteine-rich domain of TNFR / NGFR and a VWFC domain. cDNA sequence of said gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. By sequence alignment between three large grain species and 3 small grain species of rice, it is revealed there is only one common single nucleotide mutation in a 7.9-kb region between the two different grain-length groups. Said nucleotide mutation is located at the second exon of the GS3 gene, in which a cysteine codon (TGC) in the small-grain group is mutated to a termination codon (TGA) in the large-grain group. This mutation causes a premature termination in the large-grain group, which leads to a 178-amino acids truncation (including part of the PEBP-like domain and all the other three conserved domains). The present invention also provides methods of producing transgenic plants comprising sequences disclosed herein.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
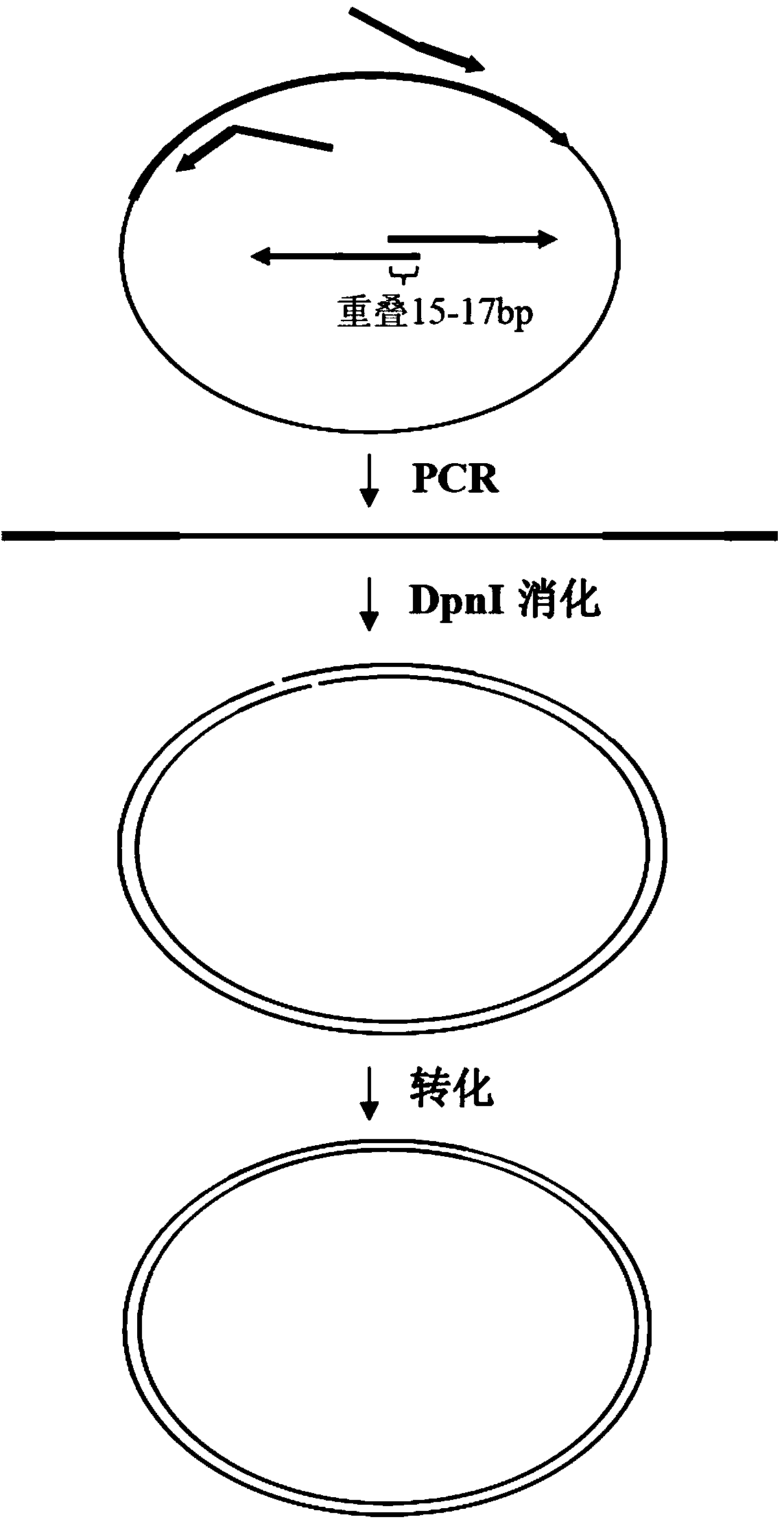
Biomedical molecule cloning method
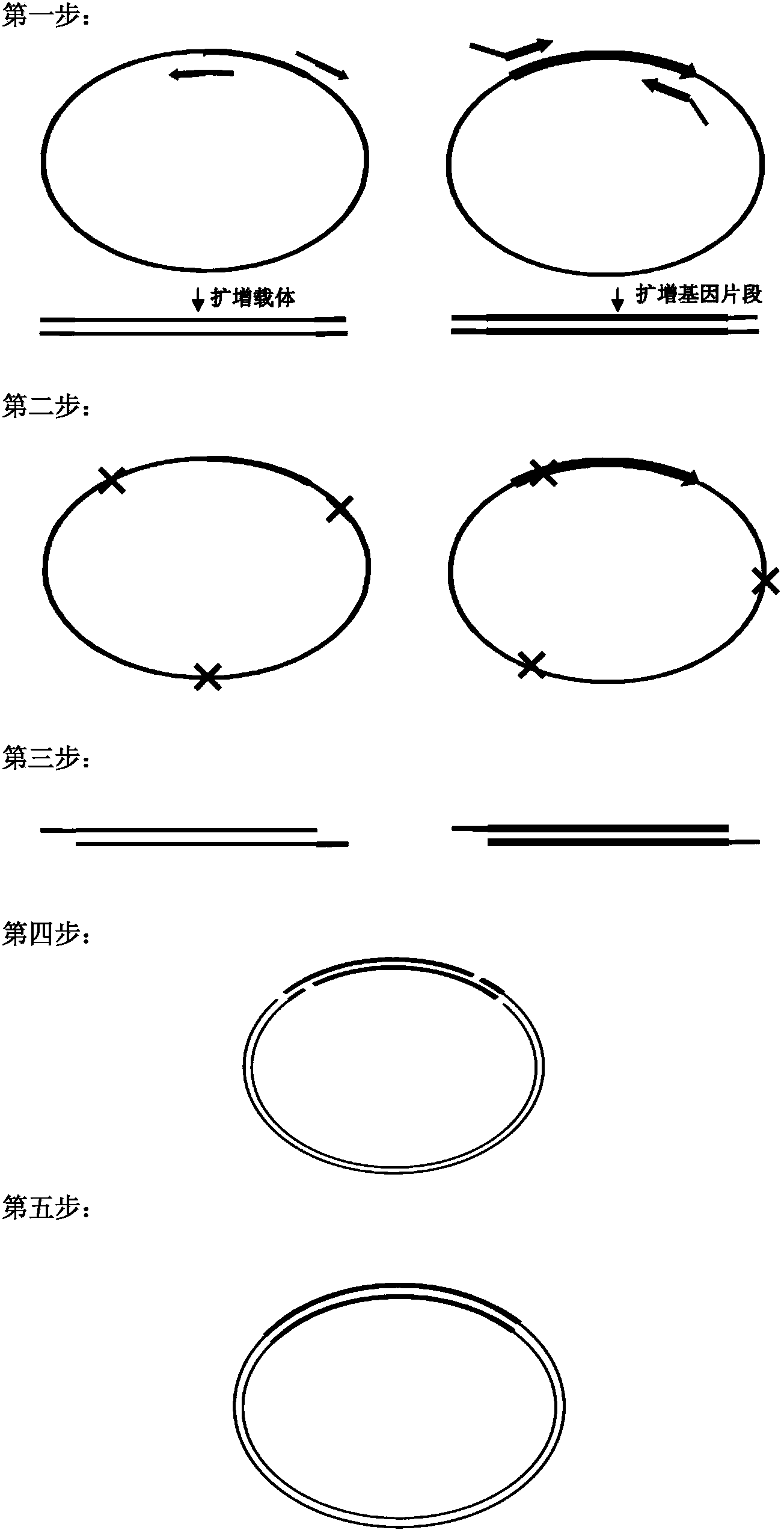
The invention discloses a molecule cloning method. The molecule cloning method comprises the following steps: amplifying a vector and a target gene to be inserted by DNA polymerase with 3'-5' exonuclease activity, destroying a mehylated DNA template by restrictive endonuclease DpnI, and directly transforming a DpnI digestion product to competent cells in order to obtain a cloned gene. Experiments prove that the molecule cloning method has the advantages of simplicity, reliability, high efficiency, no DNA fragment purification and recovery, no consideration to the enzyme site of the vector, no linkage reaction, and realization of the insertion of any DNA fragment into a plasmid vector only through a PCR-based cloning technology.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Mammalian expression vector pUHAB
The present invention relates to the construction and utilization of a new mammalian expression vector that contains a unique multiple cloning site (MCS), designated pUHAB. The pUHAB vector comprises a high copy replication origin (ColE1), a drug resistance gene (TK-Hygromycin), and a human cytomegalovirus promoter operably associated with a unique intron (hCMV / intron). Further, pUHAB comprises a selectable marker conferring resistance to kanamycin in bacterial cells, and a phage f1(+) region. pUHAB can be used to transiently or stably express cloned genes when transfected into mammalian cells. The invention also encompasses kits and host cells and cell lines comprising pUHAB, and methods of producing a recombinant protein using pUHAB.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Clone and application of molecule mark used as swine mark auxiliary selection and correlated with immunity
InactiveCN101215565AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMarker-assisted selectionAgricultural science
The invention belongs to the technical field of the livestock genetic engineering and in particular is a molecular marker which is used as the application to pig marker-assisted selection and relative with immune traits and the application. The molecular marker is obtained by cloning gene BCL10, the nucleotide sequence of the molecular marker is displayed as the sequence table SEQ ID NO: 2, and the number 144 basic group position of the sequence which is displayed in the sequence table SEQ ID NO: 2 has a gene mutation of C144-T144, which leads to the polymorphism of the RFLP-HinP1I. The invention also discloses a process for preparing the molecular marker and the application of a polymorphism testing method and provides a new molecular marker for the pig marker-assisted selection.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for rapidly screening Cucurbitaceae new RIP gene
The fast cucurbitaceae RIP gene screening method includes designing degenerate primer pair LY1 / LY2 based on highly conservative amino acid sequence and its codon bias in the upstream and downstream of known cucurbitaceae RIP, Touchdown-PCR amplification with total DNA as template, direct PCR product clonal sequencing of cucurbitaceae plant with un-reported RIP gene to obtain new RIP gene; and fast distinguishing known and unknown RIP genes of cucurbitaceae plant with reported RIP gene according to the length polymorphism of limiting segment in RIP gene LY1 / LY2 segments. Compared with available method of first separating RIP and then cloning gene, the method of the present invention has the features of being fast and accurate, and may be used widely in RIP gene screening.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV +1
Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) type I receptor gene of chlamys farreri and single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) locus of TGF-beta type I receptor gene
InactiveCN102899330AImprove seed selection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationComplementary deoxyribonucleic acidMolecular genetics
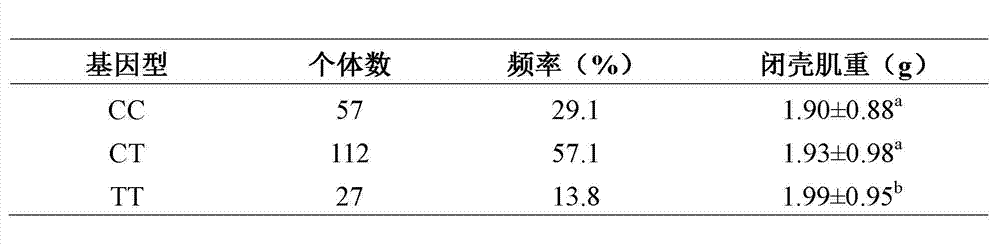
The invention relates to the cloning of a transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) superfamily type I receptor gene Tgfbrl1 of chlamys farreri in a molecular genetic marker technology, a screening and typing technology of a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) locus which is relevant with the weight of adductor muscles in the gene and a method for the application of the gene to the breeding of the high-yield chlamys farreri. A total-length complementary deoxyribonucleic acid (cDNA) sequence of the Tgfbr1 gene of the chlamys farreri is obtained by utilizing a homology-based cloning strategy; an SNP lotus is discovered by blastn comparison, and primers and a probe are designed for the locus; and SNP typing is performed in a natural population of the chlamys farreri by using a high-resolution melting curve technology, and the weight of the adductor muscle of an individual is measured. Statistic analysis displays that the loci c.1815C>T are obviously relevant with the weight of the adductor muscles of the chlamys farreri, and the weight of the adductor muscles of individuals with TT genetypes is obviously higher than that of the adductor muscles of individuals with CC and CT genetypes. In the selective breeding process of the high-yield chlamys farreri, the breeding candidate colonies of the chlamys farreri can be subjected to c.1815C>T typing, and the individuals of which the loci c.1815C>T are TT genetypes are used as a breeding parent preferably by combining typing information of other loci which are relevant with growth properties.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Rice OsNAC coding sequence and application thereof
InactiveCN102120763AStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyGenetic engineering
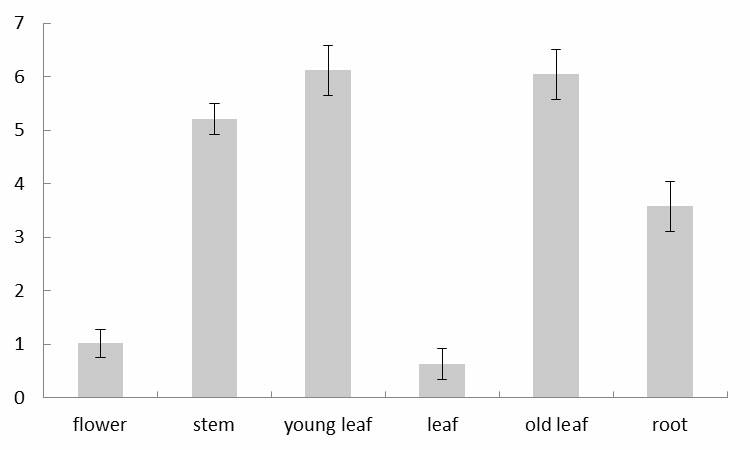
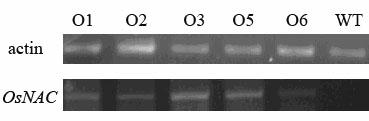
The invention discloses a coding sequence of an NAC family transcription factor expressed in rice and application thereof in pollen growth, belonging to the technical fields of molecular biology and genetic engineering. In the invention, the following processes of cloning of the NAC family transcription factor, analysis of a gene expression pattern, establishment of a transgenic carrier, phytotransformation, obtainment of a transgenic plant, and identification of a corresponding phenotype and a cellular level are comprised. The gene presented in the invention is expressed in Arabidopsis, and the obtained transgenic plant is abnormal in pollen growth and has a decreased ripening rate.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Higher plant cytosolic er-based glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase genes
InactiveUS20060206960A1Modifying lipid metabolismChange outputSugar derivativesTransferasesBiotechnologyHeterologous
Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase is the initial enzyme of the glycerolipid biosynthetic pathway. Biochemical analyses indicated that the reaction mediated by glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase represents a potential rate-limiting step for the synthesis of phospholipids and storage neutralipid, triacylglycerol. The present invention relates to the cloning of genes encoding extraplastidic membrane-bound glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferases. Heterologous expression of the genes, GPAT1, GPAT2, and GPAT3 in a yeast glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase mutant demonstrated that the encoded products could efficiently utilize glycerol-3-phosphate to mediate sn-1 stereo-specific fatty acid acylation. The invention encompasses the glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase peptides disclosed and fragments and homologues thereof, the corresponding gene sequences and fragments and homologues thereof, as well as the use of the peptide and gene sequences of the present invention for use in generating recombinant proteins, and transgenic plants with altered lipid metabolism. In this way, the present invention also encompasses the use of such recombinant peptides and transgenic plants for the production of lipid products for use, for example, in pharmaceutical and nutritional applications.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
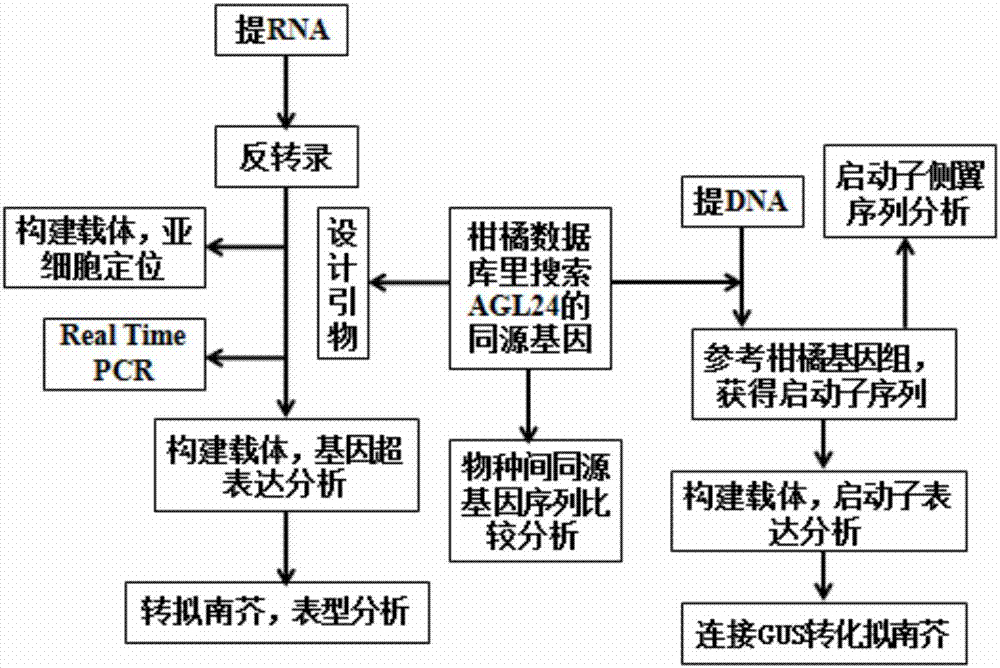
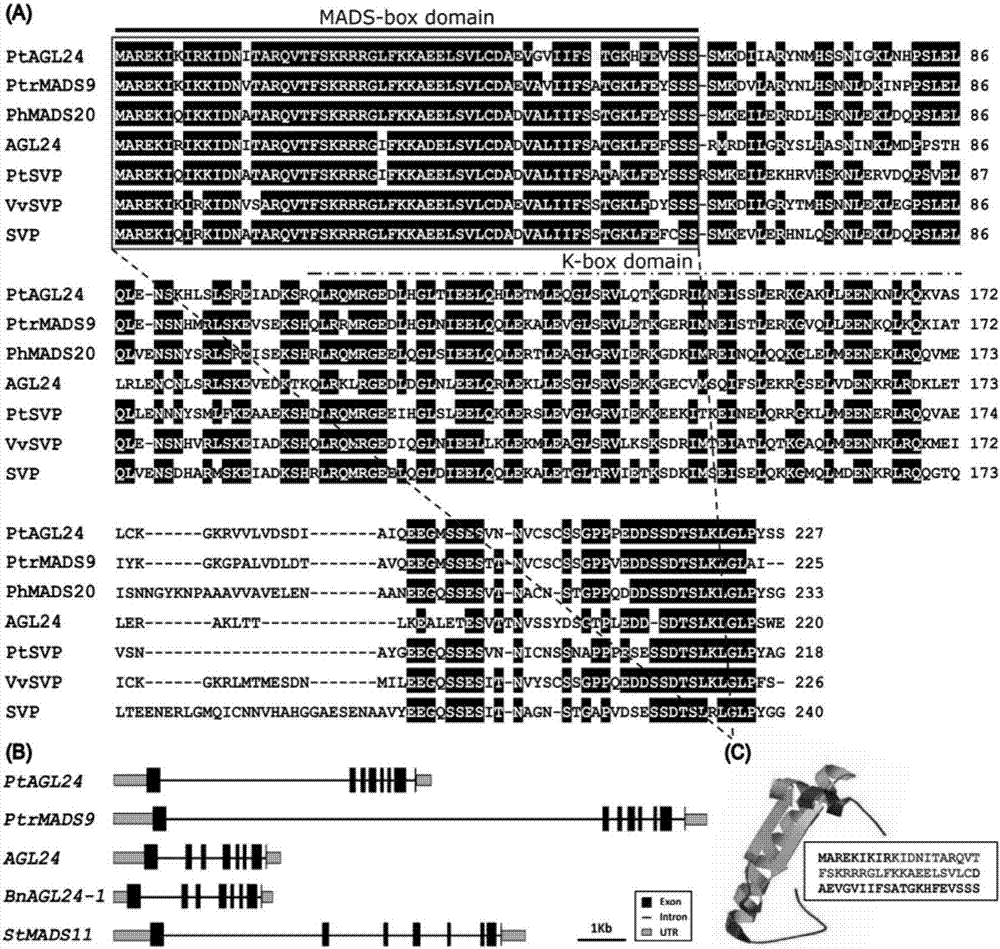
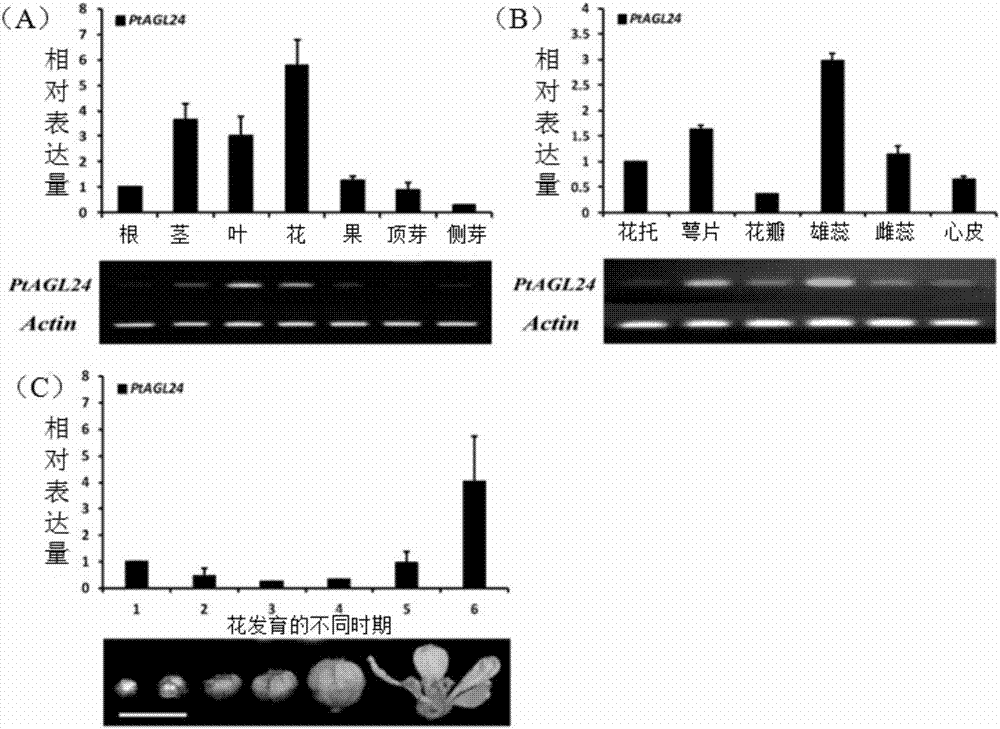
Precocious trifoliate orange PtAGL24 gene separation and application with effect of regulating and controlling plant early blossoming
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. Specifically, it relates to the separation and application of the PtAGL24 gene that can regulate the early flowering of plants. The nucleotide sequence of the PtAGL24 gene is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, the sequence of the protein encoded by the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO: 2; the nucleotide sequence of the promoter PtAGL24P is shown in SEQ ID NO: 3. The ectopic overexpression of the gene can significantly shorten the childhood period of the plant and promote the early flowering of the plant. The gene and promoter of the invention provide biological resources for the breeding of perennial woody fruit trees and the shortening of flowering process. The role of PtAGL24 in the whole development process of the plant is further revealed through the spatial expression of the promoter, which shows that the cloned gene of the present invention is also induced by the low temperature of the environment, and has a certain response to the external environmental stress. The gene and promoter of the present invention can be used in regulating plant flowering period and low temperature stress.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for improving content of verbascoside in rehmannia by virtue of transformation of RgPAL1 gene
ActiveCN104357480AIncrease contentMature methodFermentationGenetic engineeringRehmannia glutinosaAgronomy
The invention discloses a method for improving the content of verbascoside in rehmannia by virtue of transformation of RgPAL1 gene, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The method comprises the following steps: cloning gene RgPAL1 from rehmannia, constructing a plant expression vector containing the RgPAL1, transforming the RgPAL1 into the rehmannia by virtue of mediation of agrobacterium tumefaciens and promoting regeneration of a plant, detecting integration of an exogenous target gene RgPAL1 through polymerase chain reaction (PCR), quantitatively analyzing the content of verbascoside in the transgenic rehmannia by virtue of HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatoraphy)-PDA, and screening to obtain a transgenic rehmannia plant having improved verbascoside content. By virtue of the method disclosed by the invention, the content of verbascoside in the transgenic rehmannia is significantly improved, and the content of verbascoside in the RgPAL1 transgenic rehmannia is 2.57 times as much as that in non-transgenic rehmannia, so that a feasible method is provided for scaled production of verbascoside from the transgenic rehmannia. The method disclosed by the invention provides an innovative and practical related method and technology for improving the verbascoside content.
Owner:MAANSHAN SHENLUKERUI PHARMA
Method for applying miRNA clusters in changing cell fates
InactiveCN102199622AImprove efficiencyQuality improvementVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsOncogeneGenome
The objective of the invention is to provide a method for applying miRNAs or miRNA clusters in changing cell fates by promoting the formation of induced pluripotent stem cells. The method comprises a first step of cloning genes of miRNAs or miRNA clusters in a donor genome and obtaining a donorcell, a second step of changing the cell fate of the donorcell in step 1 by using the miRNAs or miRNA clusters in step 1, and a third step of identifying the cell obtained in step 2. Compared to the prior art, stem cells are induced by miRNAs or miRNA clusters in the invention instead of by oncogenes c-Myc, thereby reducing potential carcinogenicity, accelerating the change of cell fates and enabling a high induction efficiency and high-quality induced pluripotent stem cells with ability of germ line transmission to be obtained.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Turtle collagen gene functional fragment as well as recombinant protein and application thereof
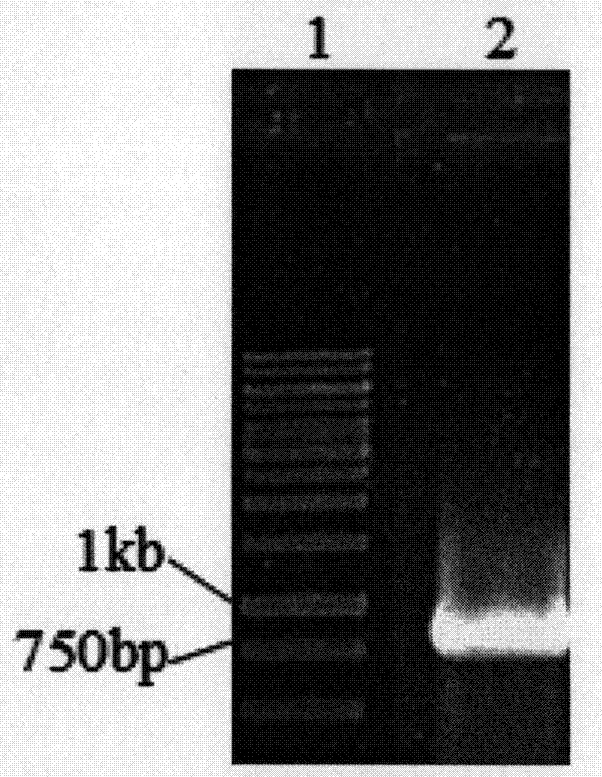
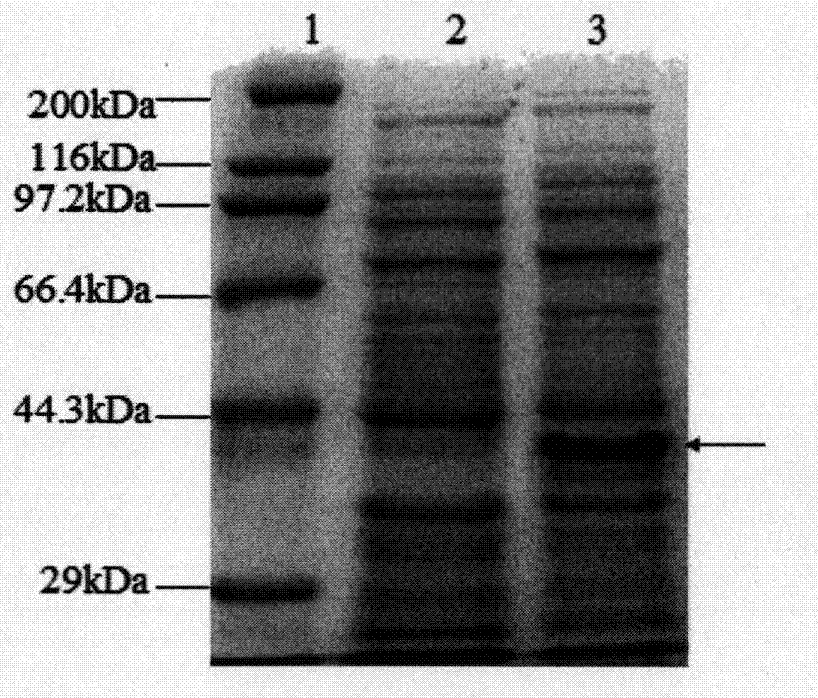
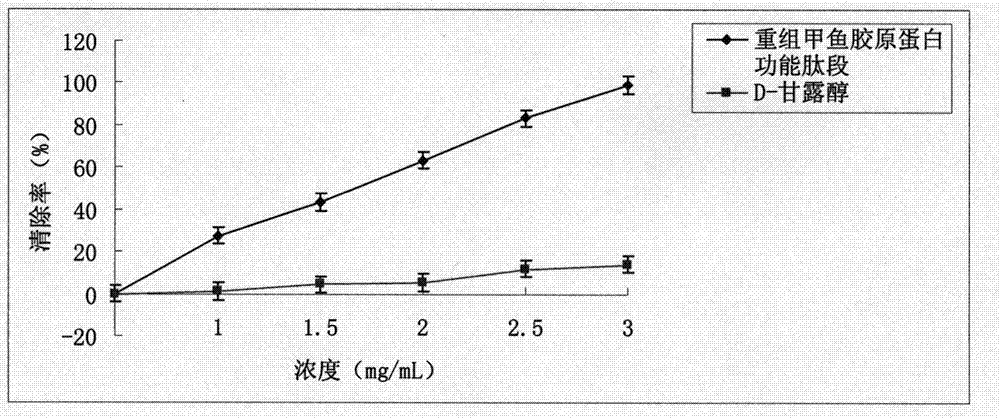
ActiveCN104726461AStrong antioxidant activityIncrease productionConnective tissue peptidesFermentationEscherichia coliAntioxidant
The invention discloses a collagen gene functional fragment cloned from a turtle and shown in sequence SEQ ID NO.1 in a sequence table and a recombinant protein obtained by the expression of the clone gene functional fragment and shown in sequence SEQ ID NO.2 in the sequence table, wherein the recombinant protein is a recombinant turtle collagen gene functional peptide fragment. The whole length of the recombinant turtle collagen gene functional peptide fragment includes 252 amino acids, 27 specific Gly-X-Y repeating fields of collagen are contained and the molecular weight is 38kDa. The preparation method comprises the steps of constructing a colibacillus genetic engineering bacterium for expressing the recombinant turtle collagen gene functional peptide fragment; culturing the colibacillus genetic engineering bacterium; inducing and expressing the recombinant turtle collagen gene functional peptide fragment; performing purification renaturation on the recombinant turtle collagen gene functional peptide fragment. The experiment shows that the recombinant turtle collagen gene functional peptide fragment prepared by the method provided by the invention has a high antioxidant activity and also has a value of application as an antioxidant.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
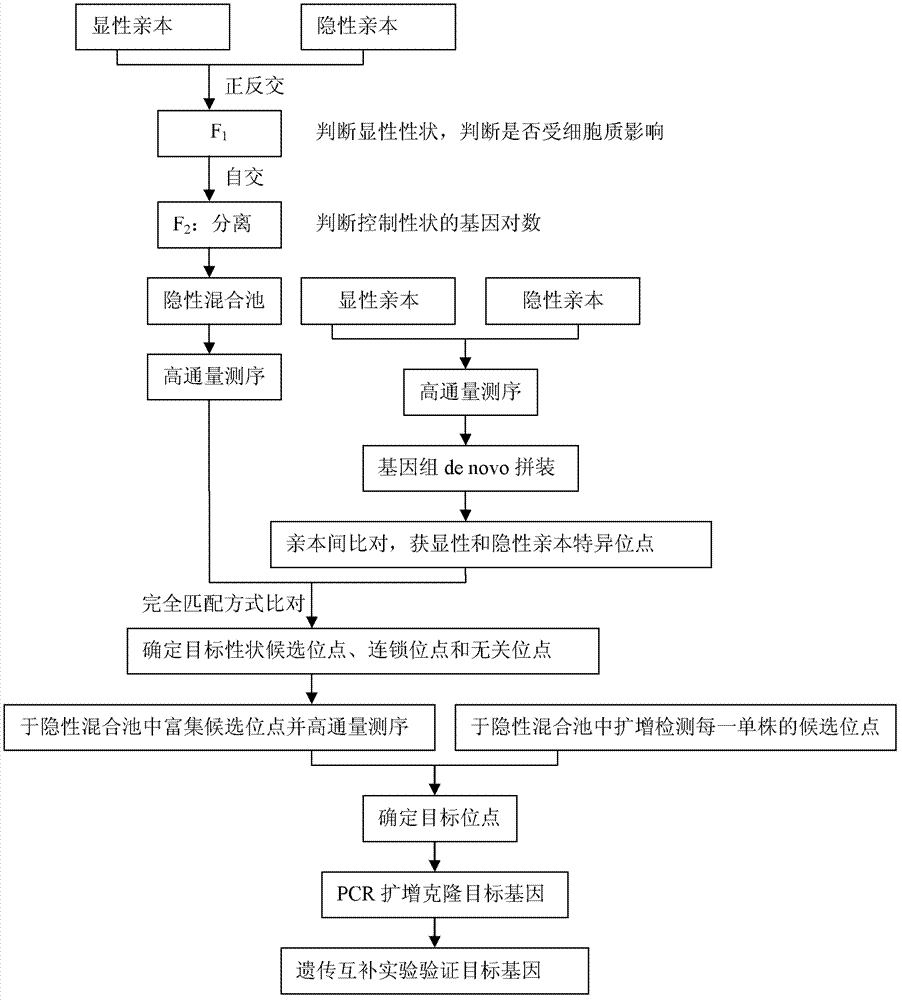
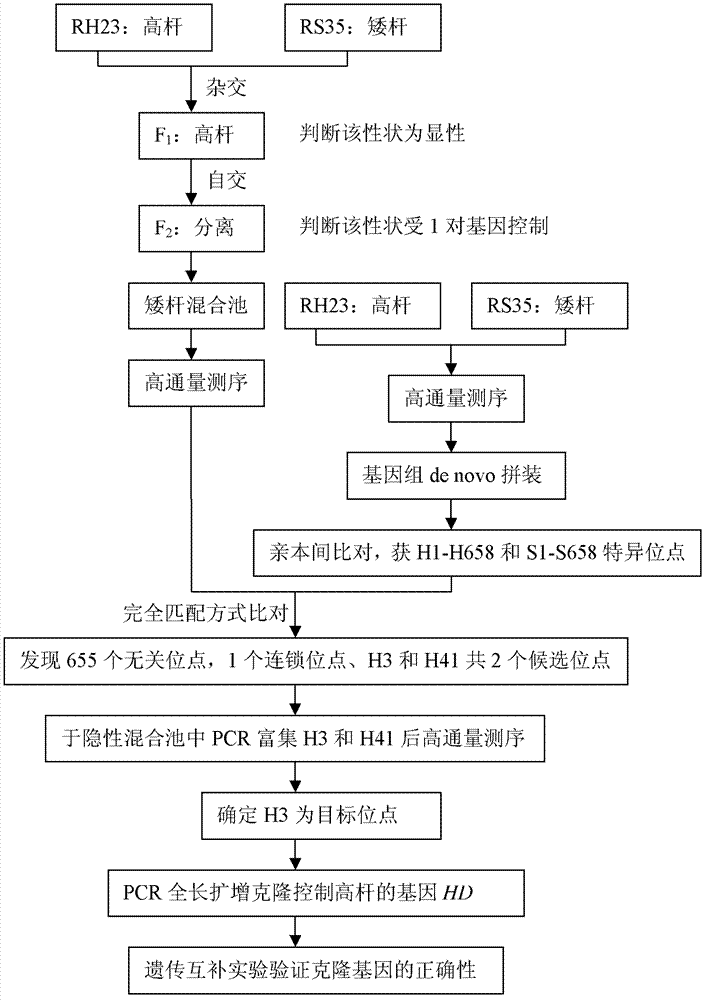
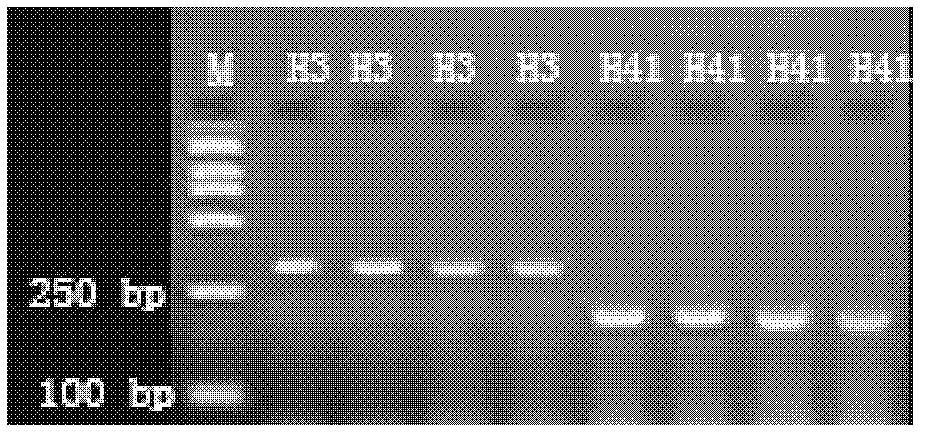
Method for sequencing clone genes with recessive mixed pools
InactiveCN102899315AExpand the scope of useReduce workloadMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationRe sequencingCandidate Gene Association Study
The invention discloses a method for sequencing clone genes with recessive mixed pools. The method comprises the following steps of constructing segregation populations by hybridizing parents; allocating pools for the segregation populations according to individual target properties; obtaining dominant and the recessive specific loci of the parents through high-throughput sequencing; comparing with the sequencing results of the recessive mixed pools to obtain candidate genes; gathering the candidate genes in the recessive mixed pools and re-sequencing clone target genes; The method is on the basis of sequencing, can be used for any species, and directly clones genes themselves. With the method, workload is decreased greatly, speed is substantially accelerated; and risks are reduced.
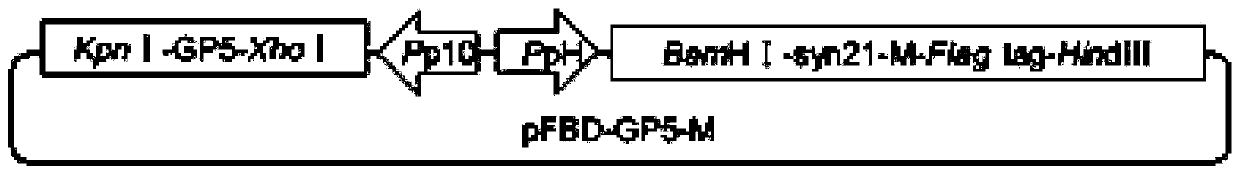
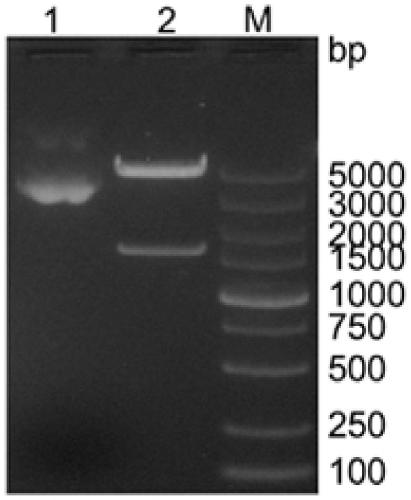
PRRSV-1 virus-like particles and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109721643AEasy to operateEasy to scale up productionViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesCompetent cellShuttle vector
The embodiment of the invention discloses PRRSV-1 virus-like particles. The particles comprise PRRSV LV strain structural protein GP5, PRRSV LV strain matrix protein M, expressed PRRSV LV matrix protein M and co-expressed PRRSV LV structural protein GP5 of the virus-like particles. The embodiment further provides a method for preparing the PRRSV-1 virus-like particles. The method comprises the following steps: respectively cloning genes expressing GP5 protein and matrix protein M in a PRRSV LV strain; cloning the gene expressing the GP5 protein and matrix protein M to a baculovirus shuttle vector to acquire a recombinant baculovirus shuttle vector; and transforming the recombinant baculovirus shuttle vector to a DH10Bac competent cell to acquire a recombinant baculovirus genome. The methodis suitable for large-scale amplified preparation of anti-European porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome vaccines, and has high safety and excellent development and application prospect.
Owner:ACAD OF MILITARY SCI PLA CHINA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI INST OF MILITARY VETERINARY MEDICINE
Coding gene of haemaphysalis qinghaiensis aquaporin (AQP) and application of coding gene
The invention discloses a coding gene of haemaphysalis qinghaiensis aquaporins (AQPs) and an application of the coding gene. The coding gene of the AQPs can be used for preparing novel anti-tick medicines and anti-tick vaccines. A sequence of the coding gene of the AQPs is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. The invention also provides specific primers cloned by the coding gene of the AQPs, wherein sequences ofthe specific primers are shown as SEQ ID NO:2 and SEQ ID NO:3; the invention also provides a method for cloning the coding gene of the AQPs, and the cloned gene product can be also applied to in-vitro recombinant protein expression and antibody preparation; and an obtained antibody can be used for preparing the novel anti-tick medicines and the anti-tick vaccines. The invention has important theoretical significance an potential application value on prevention and control of ticks. The coding gene of the haemaphysalis qinghaiensis aquaporins (AQPs) and the cloning method of the coding gene provided by the invention are applicable to systematic researches of subtype, varieties, expression distributin, protein structures, biological functions and the like of the AQPs.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Process for clone gene of virus host factor
A method for cloning the virus host factor gene by use of dual-chain RNA low-poison virus (chesnut blight bacterium system) includes such steps as light irradiating to induce the generation of conidia of chestnut phytophthora disease bacteria, inducing to obtain mutant, purifying, discriminating the virus carried by said mutant, testing the activity of its mRNA precursor, transforming and complementing of said mutant, discriminating, sequentially the exogenous DN'A fragment of the transformed plasmid with complem entary power, and configuring gene map.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
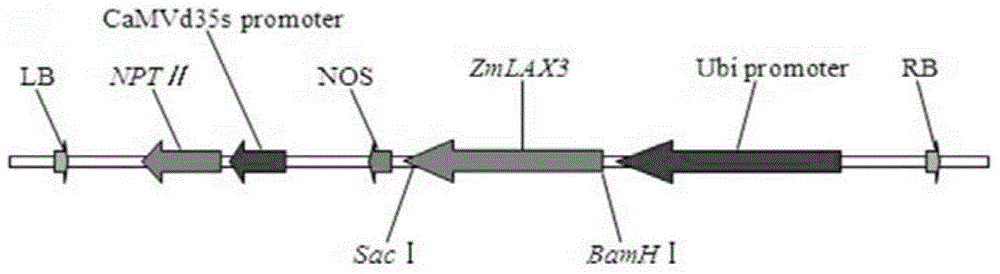
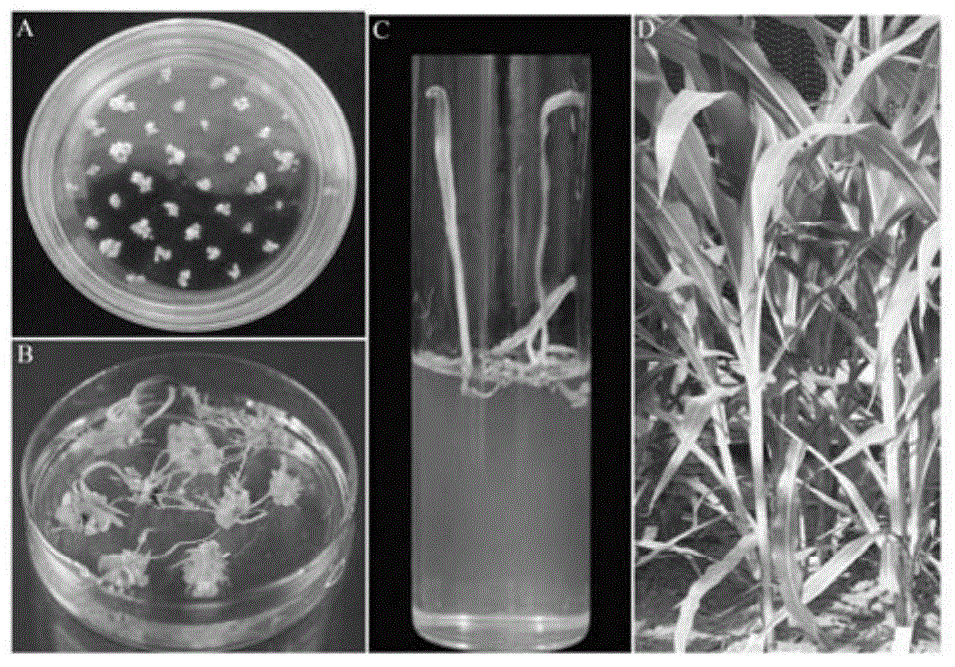
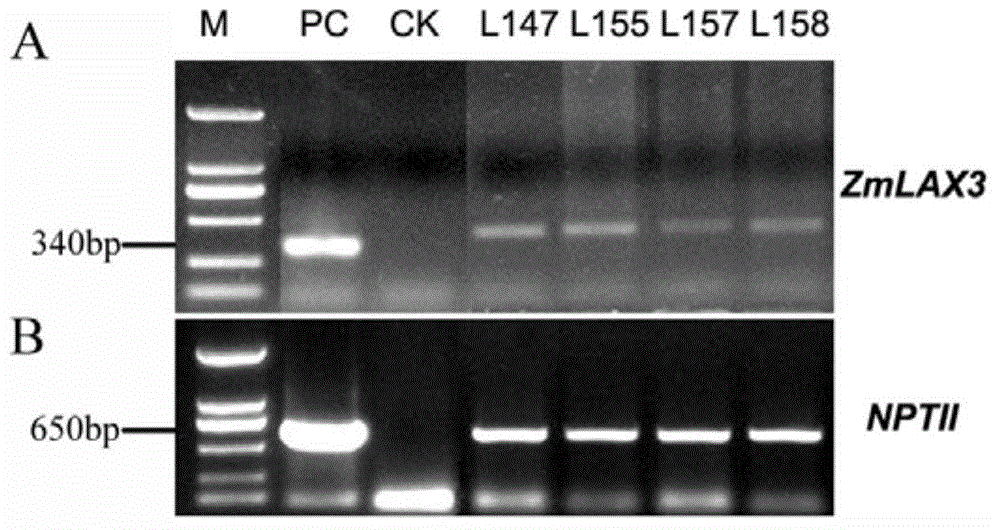
ZmLAX3 protein, and coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN104628841AIncrease productionImprove qualityPlant peptidesFermentationCharacter changeAgricultural science
The invention discloses a ZmLAX3 protein, and a coding gene and application thereof. The invention provides a protein disclosed as 1) or 2): protein disclosed as Sequence 2 in the sequence table; and 2) Sequence-2-derived protein subjected to substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more nucleotide residues with the same functions as the nucleotide sequence disclosed as Sequence 2 in the sequence table. The experiment proves that the cloning of the ZmLAX3 gene detects that the transgenic crop obtained from the gene has plant types, fringe character change and other phenotypes. The transgenic positive plant can improve the plant types, fringe characters and other important agronomic characters when being used for production, is used for enhancing the yield and quality of the crops, and has important economic value and social benefits.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com