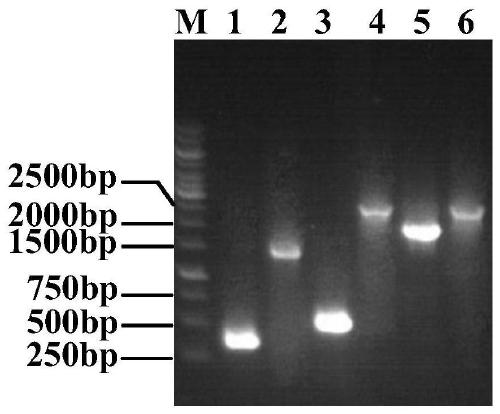
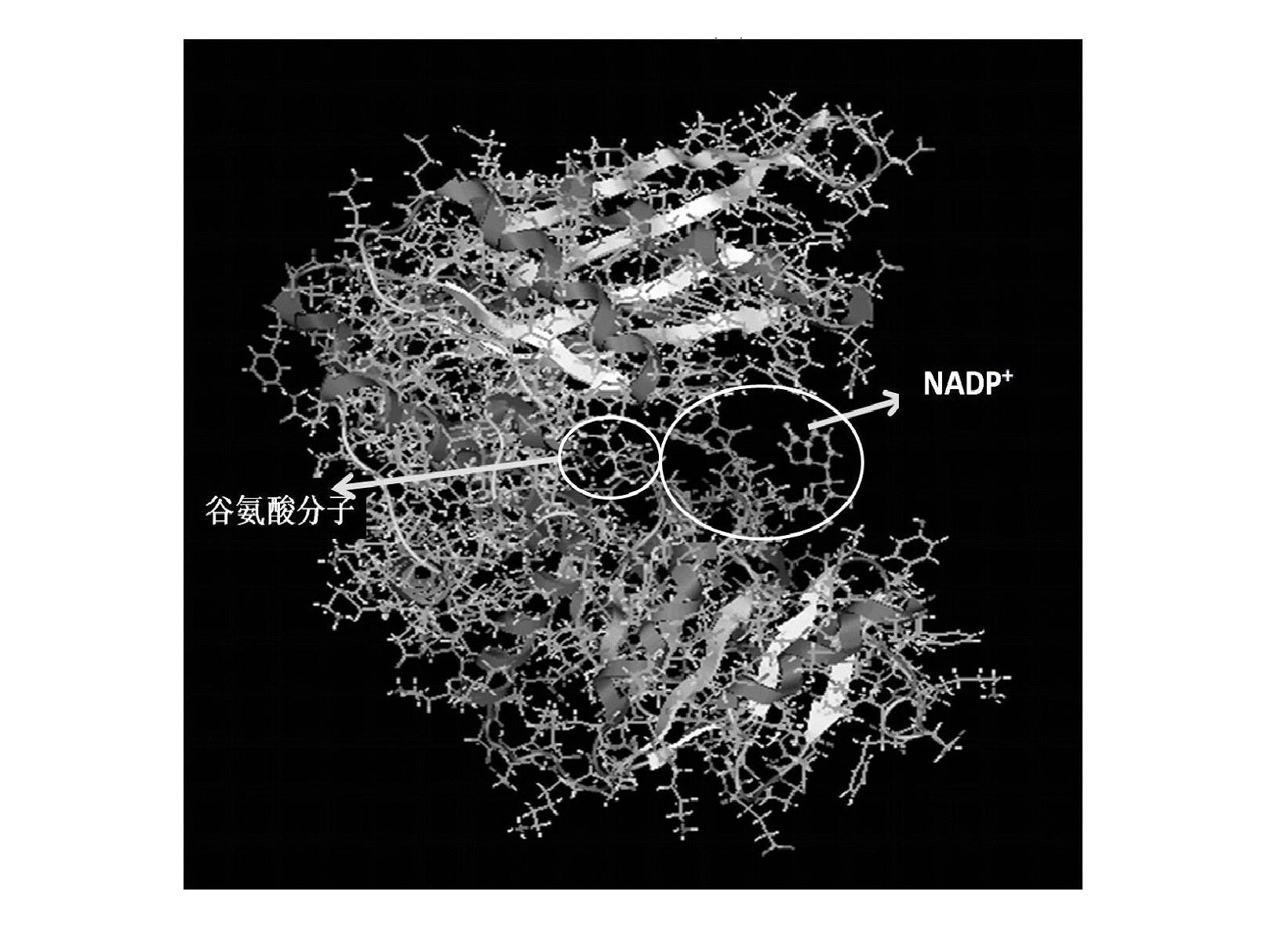
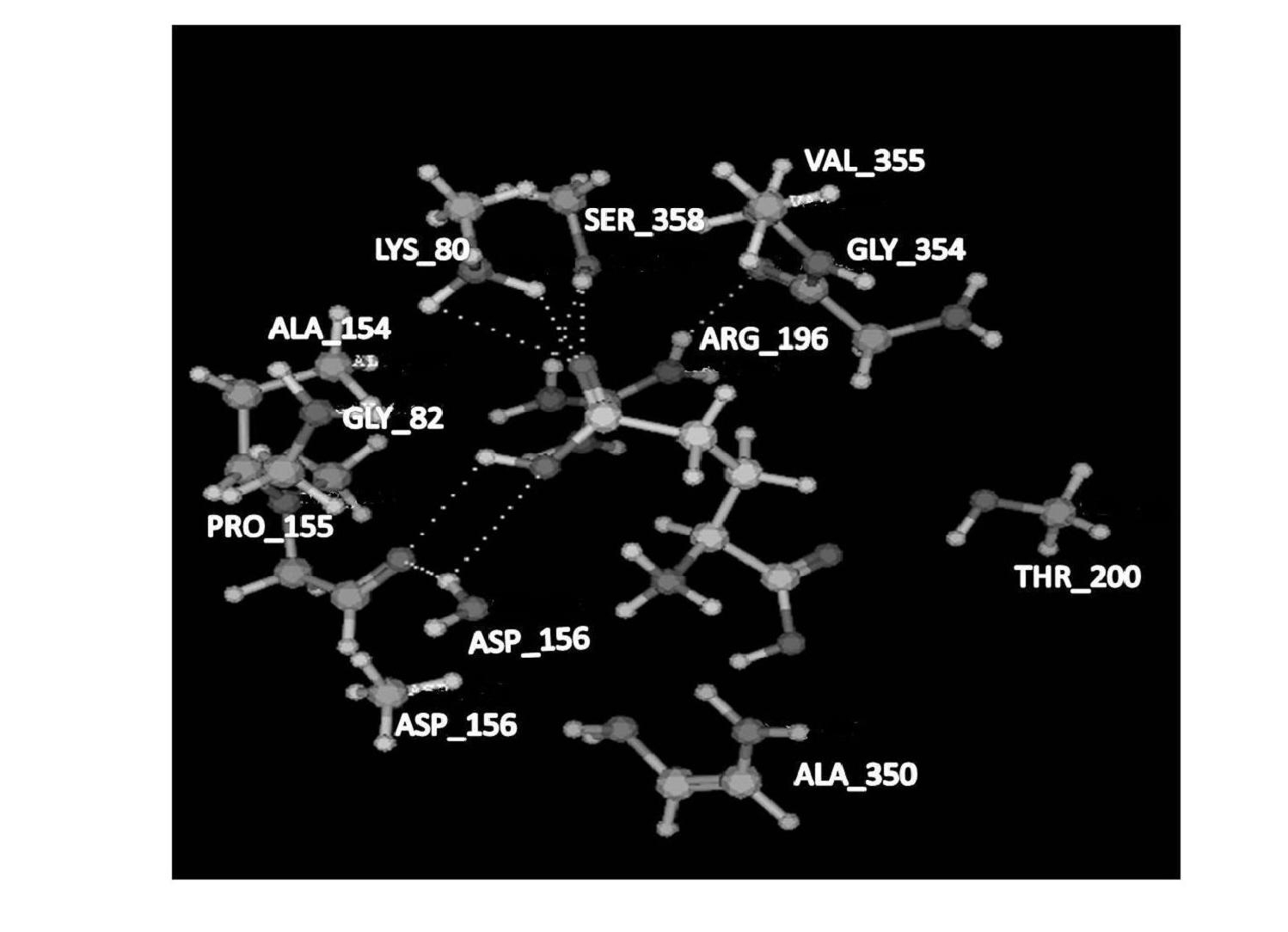
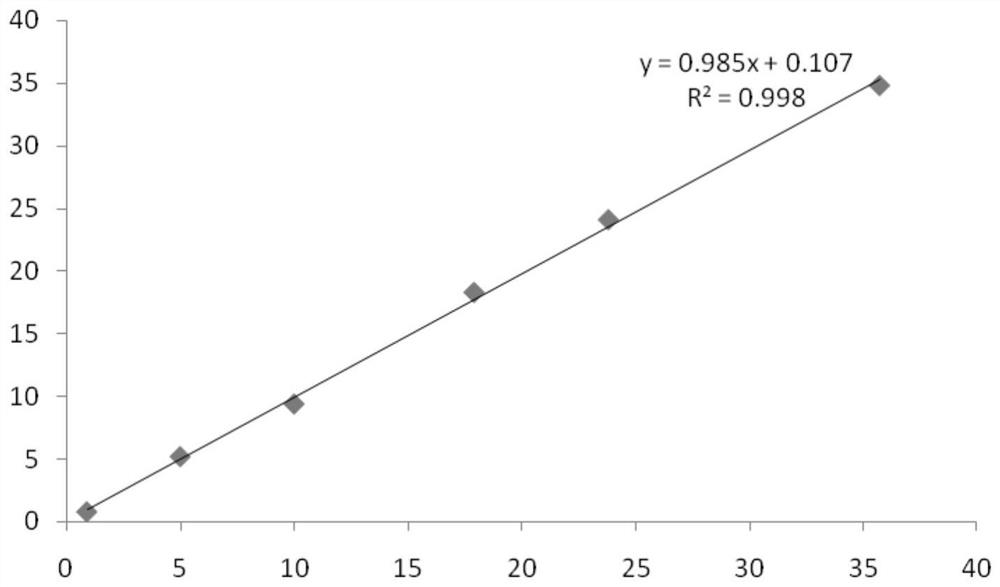
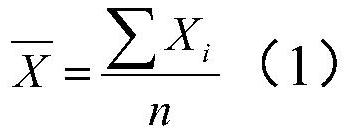Patents
Literature
100 results about "Glutamate Dehydrogenase (NADP+)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
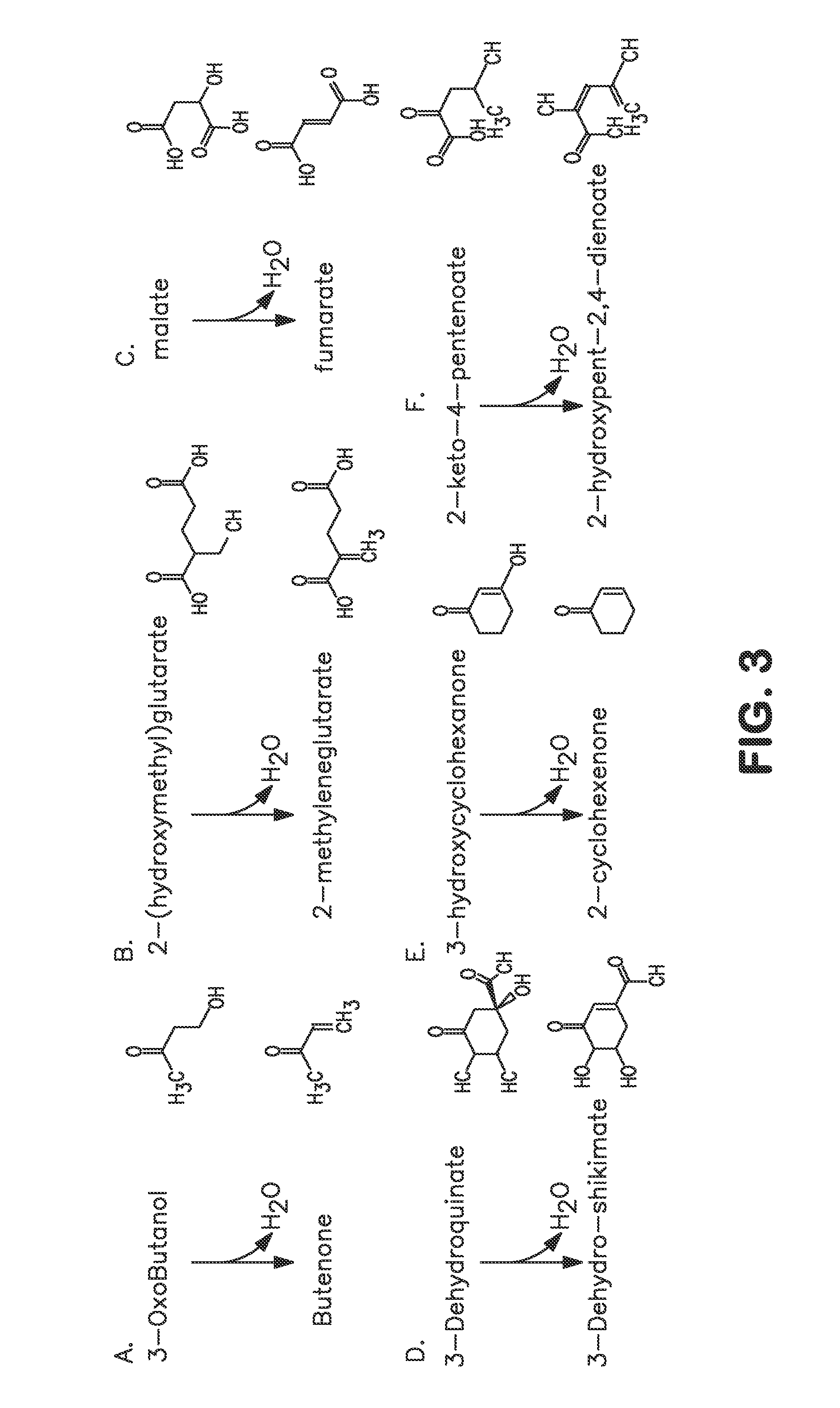
An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of L-glutamate, H2O, and NADP+ to 2-oxoglutarate, NH3, and NADPH. (From Enzyme Nomenclature, 1992) EC 1.4.1.4.
Microorganisms and methods for carbon-efficient biosynthesis of MEK and 2-butanol
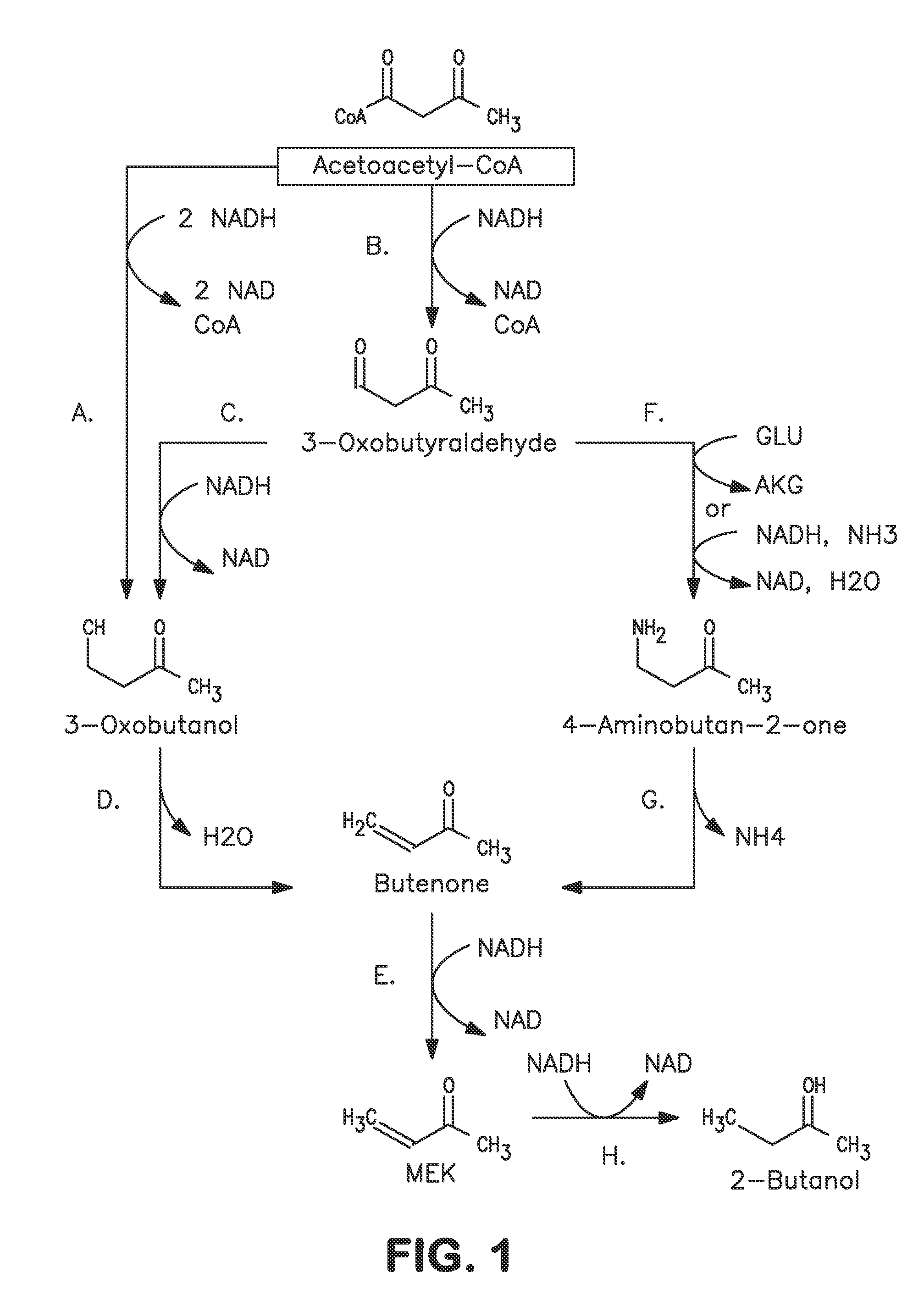
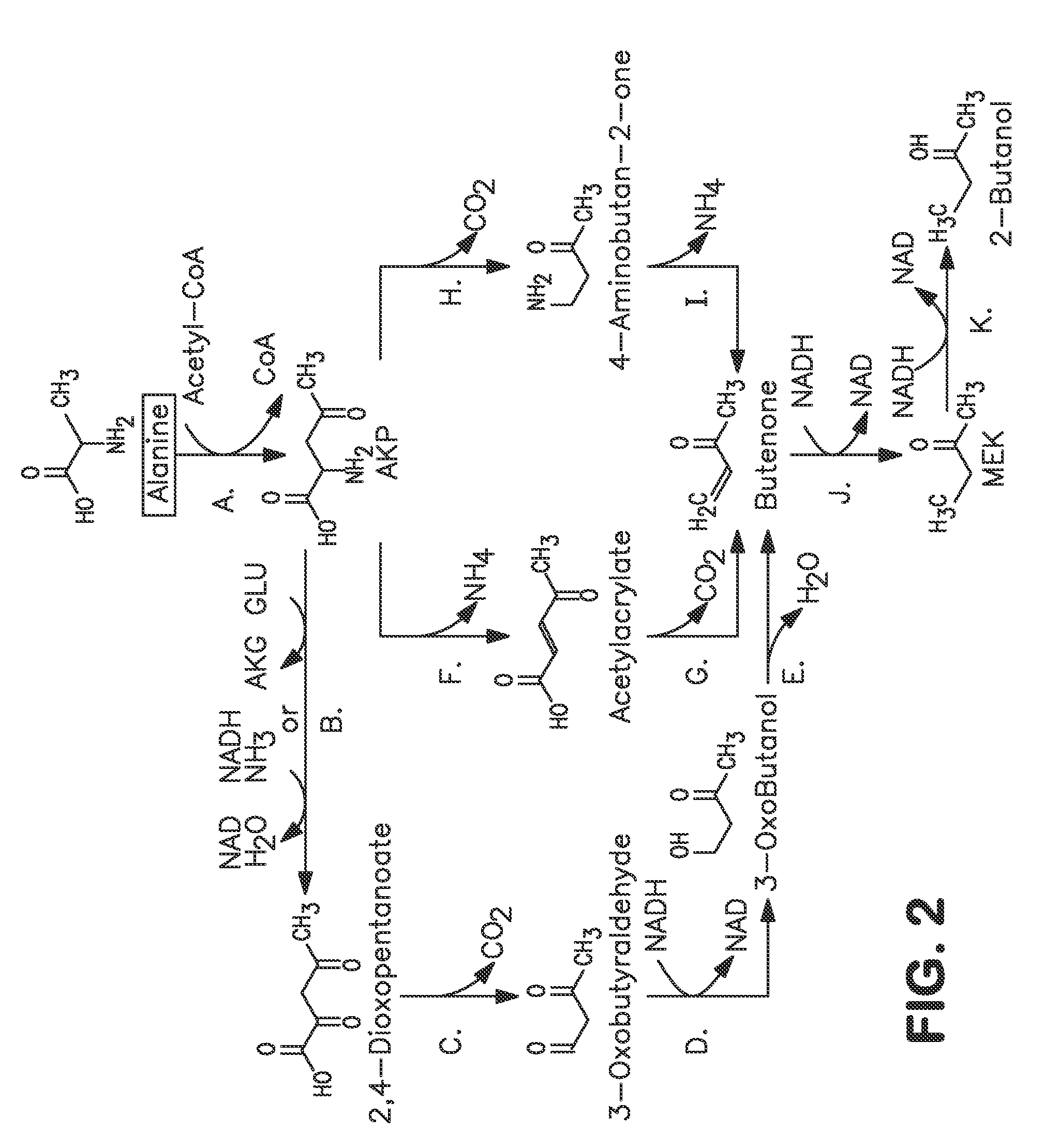
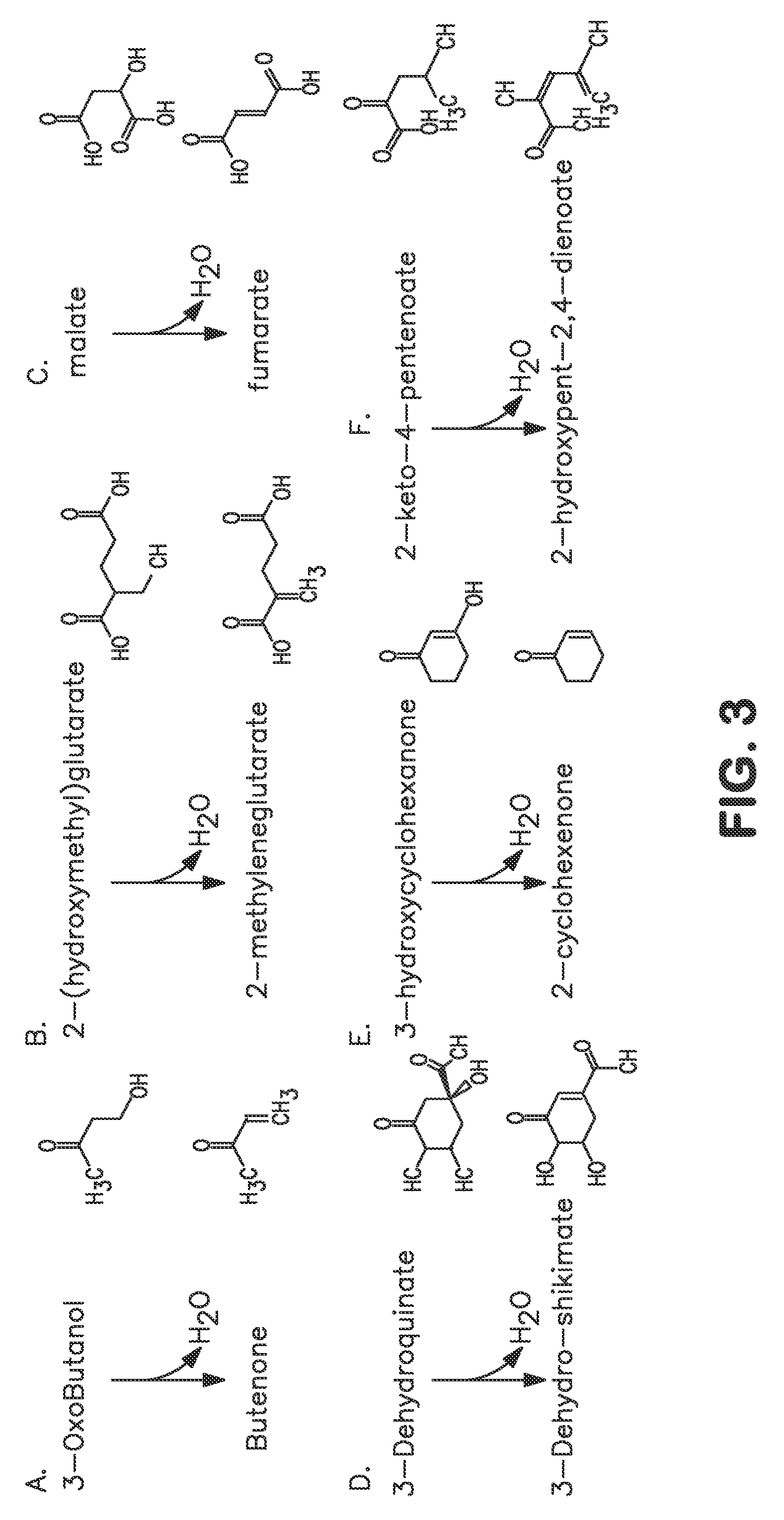
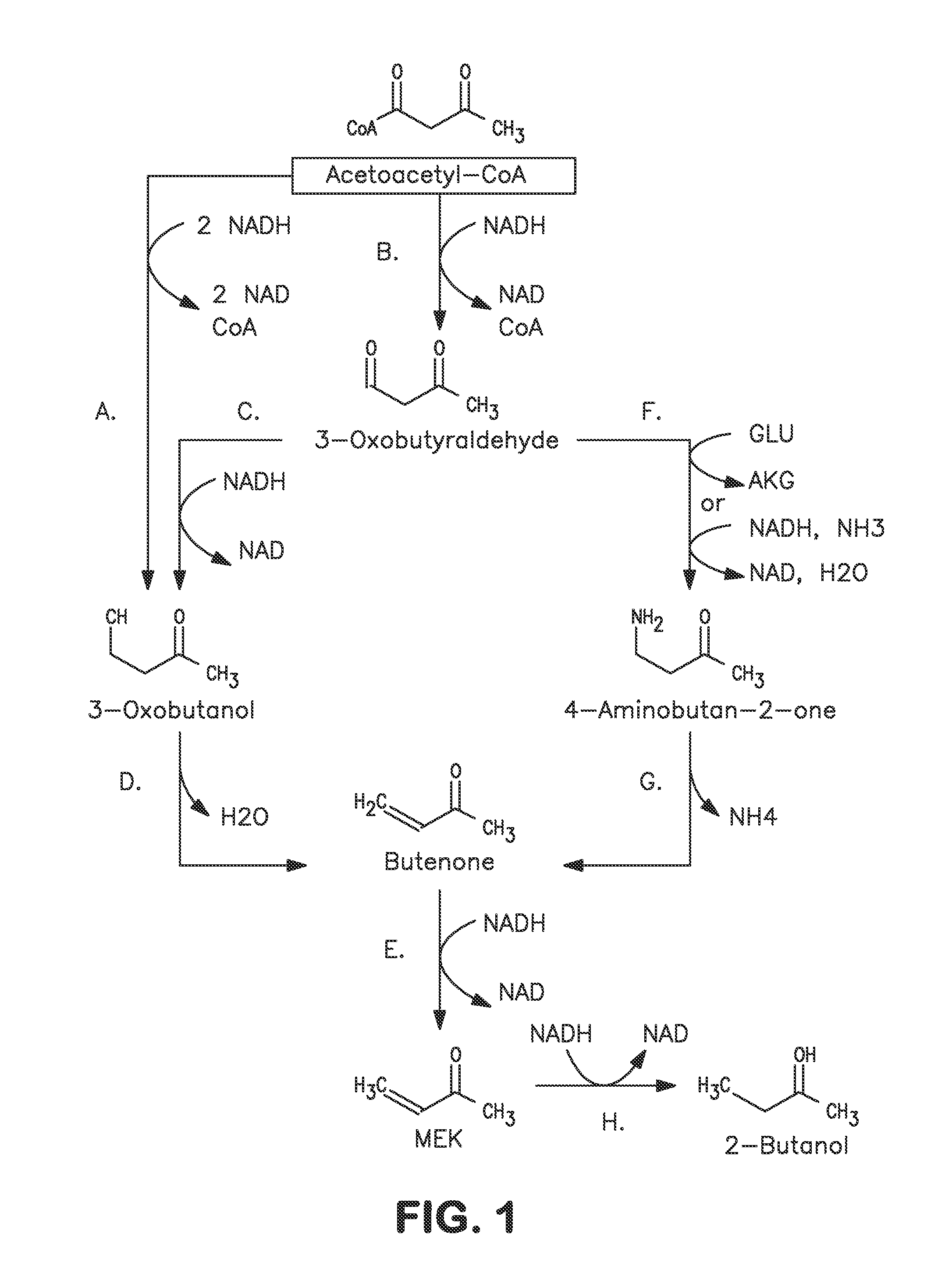
A non-naturally occurring microbial organism has at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a MEK pathway enzyme expressed in a sufficient amount to produce MEK. The MEK pathway includes an enzyme selected from an acetoacetyl-CoA dehydrogenase (bifunctional), an acetoacetyl-CoA aldehyde dehydrogenase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde reductase, a 3-oxobutanol dehydratase, an MEK oxidoreductase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde aminotransferase, a 4-aminobutan-2-one deaminase, a 2-amino-4-ketopentanoate (AKP) thiolase, an AKP aminotransferase, a 2,4-dioxopentanoate decarboxylase, an AKP deaminase, an acetylacrylate decarboxylase, an AKP decarboxylase, a glutamate dehydrogenase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde oxidoreductase (aminating) and an AKP oxidoreductase (aminating). A 2-butanol pathway further includes an MEK reductase. A method for producing MEK or 2-butanol includes culturing these organisms under conditions and for a sufficient period of time to produce MEK or 2-butanol.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Determination of blood ammonia content and blood ammonia diagnostic reagent kit
InactiveCN1778963AStrong specificityImprove test accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementBlood ammoniaChemistry
The invention is about a method of measuring the content of blood ammonia, and it also concerns the reagent box of blood ammonia diagnosis. This invention belongs to the field of medical testing and measuring technology. The reagent box is consisted of buffer solution, 2ú¡ketoglutarate, reduced coenzyme, adenosine triphosphate, phosphoenolpyruvate, glutamate dehydrogenase, glutamate kinase, pyruvate kinase, lactate dehydrogenase and stabilizer. Firstly, we cause an enzyme-coupled reaction through mixing the sample and the reagent according to a certain proportion of volume; secondly, put the final reactant under the biochemical analyzer and test the absorbance variational situation (speed) of dominant wavelength; then we can get the content of blood ammonia. By using this invention, we can get the necessary measuring result with high sensitiveness and fine precision through biochemical analyzer, and the result would not be contaminated by material of internal and exogenous sources. Thus, this method can be conveniently promoted and applied.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
A genetically engineered bacterium producing 2-phenylethanol and an applying method thereof
ActiveCN106566794AImprove cycle efficiencyDisinhibitionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhenethyl alcoholPhenylpyruvate decarboxylase
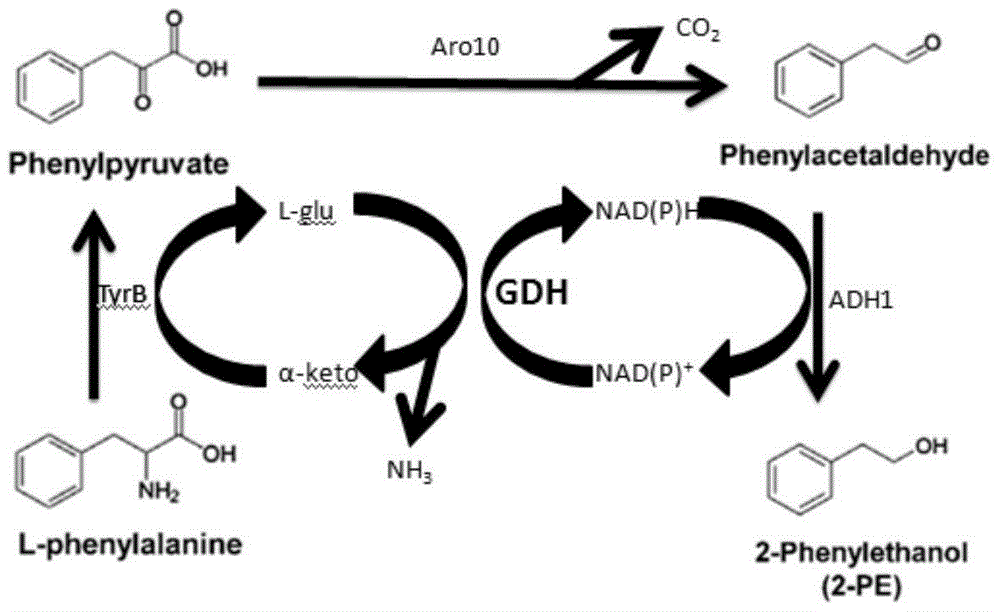
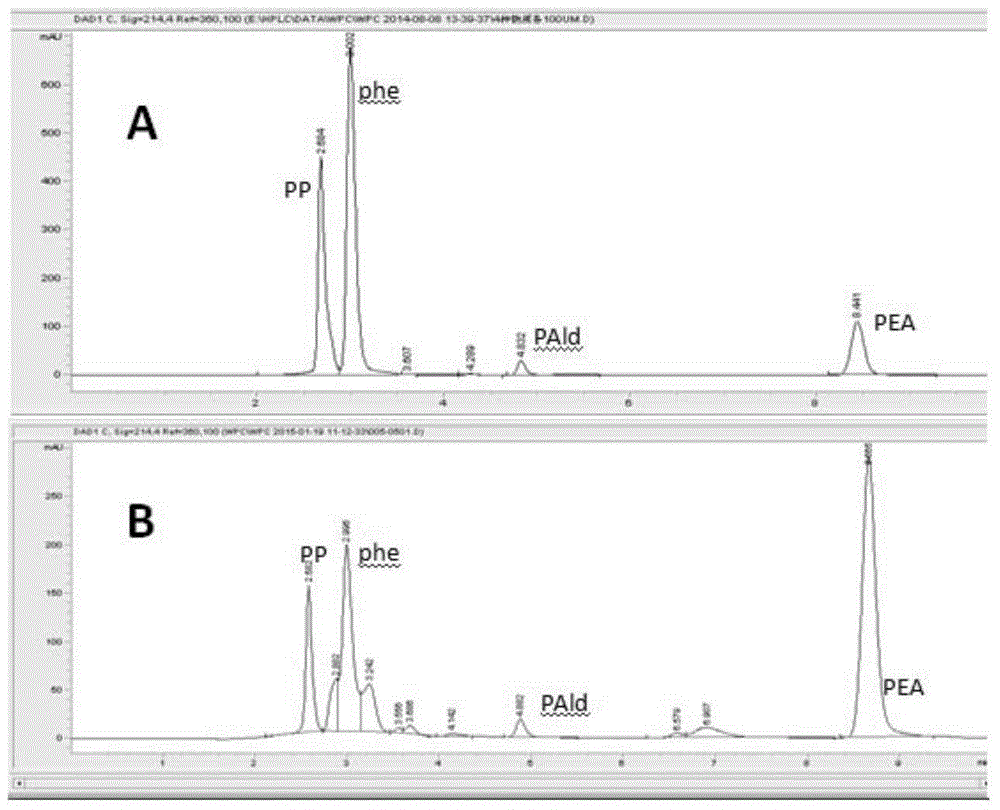
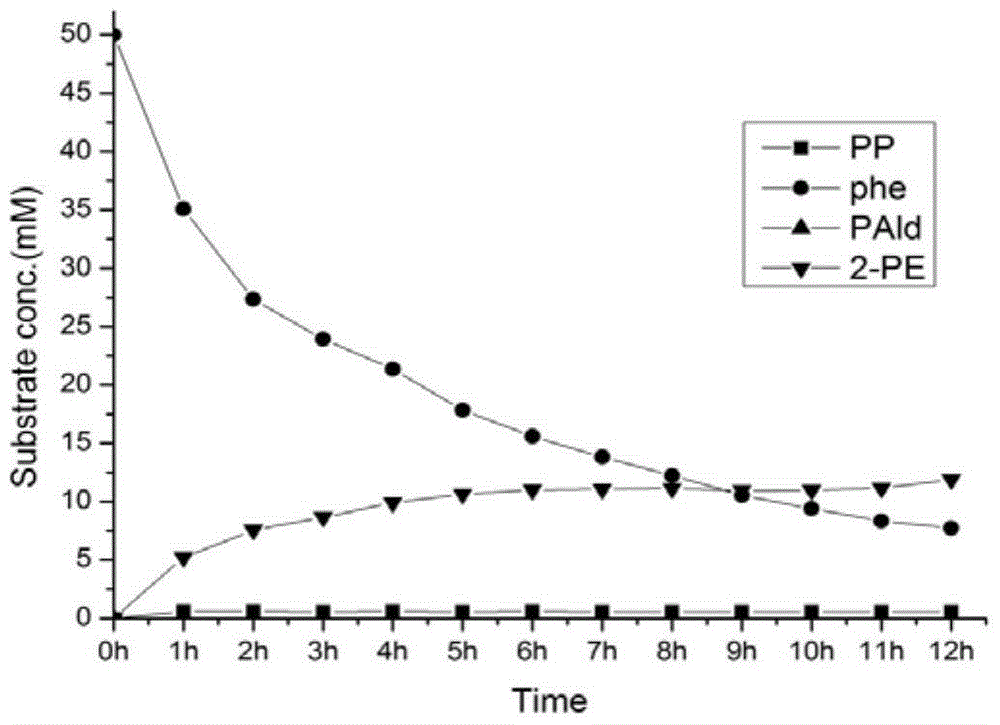
A genetically engineered bacterium producing 2-phenylethanol and an applying method thereof are disclosed. The recombinant bacterium is constructed by coexpressing aromatic amino acid aminotransferase and exogenous phenylpyruvate decarboxylase (Aro10) (or indole-3-pyruvic acid decarboxylase), phenylethanol dehydrogenase or phenylacetaldehyde reductase in escherichia coli to obtain the recombinant bacterium producing the 2-phenylethanol. Glutamate dehydrogenase is coexpressed on this basis to achieve self-balancing cofactor circulation, thus increasing the yield of the 2-phenylethanol. The conversion ratio of the 2-phenylethanol prepared through the recombinant bacterium is high. The bacterium and the method have important application value in production of the 2-phenylethanol in the future.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microorganisms and methods for carbon-efficient biosynthesis of mek and 2-butanol
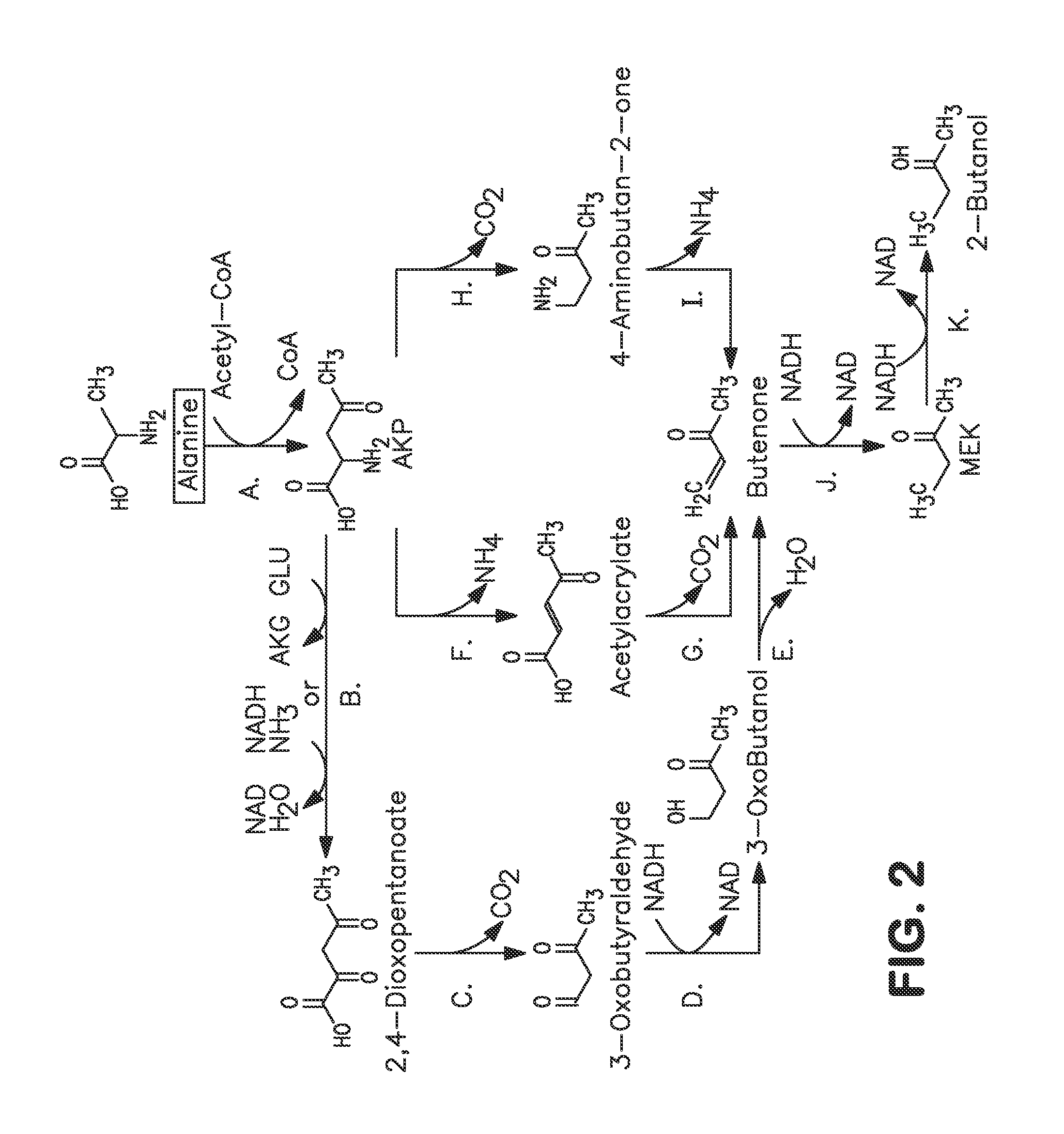
A non-naturally occurring microbial organism has at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a MEK pathway enzyme expressed in a sufficient amount to produce MEK. The MEK pathway includes an enzyme selected from an acetoacetyl-CoA dehydrogenase (bifunctional), an acetoacetyl-CoA aldehyde dehydrogenase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde reductase, a 3-oxobutanol dehydratase, an MEK oxidoreductase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde aminotransferase, a 4-aminobutan-2-one deaminase, a 2-amino-4-ketopentanoate (AKP) thiolase, an AKP aminotransferase, a 2,4-dioxopentanoate decarboxylase, an AKP deaminase, an acetylacrylate decarboxylase, an AKP decarboxylase, a glutamate dehydrogenase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde oxidoreductase (aminating) and an AKP oxidoreductase (aminating). A 2-butanol pathway further includes an MEK reductase. A method for producing MEK or 2-butanol includes culturing these organisms under conditions and for a sufficient period of time to produce MEK or 2-butanol.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Nano antibody of clostridium difficile glutamate dehydrogenase, and encoding sequence, screening method and application thereof
ActiveCN109336979ASimple and fast operationReduced operating requirementsFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionScreening methodCoat protein
The invention provides a nano antibody of clostridium difficile glutamate dehydrogenase, and an encoding sequence, a screening method and the application thereof and belongs to the technical field ofimmunology. The invention provides an amino sequence of the nano antibody of clostridium difficile glutamate dehydrogenase. By using a phage display technology, a sequence with a constant region specific gene is inserted into a vector of a phage encoding coat protein, after recombination expression, an exogenous gene expression product is fused with the phage encoding coat protein and demonstratedon the surface of phage to form a phage demonstration library, phage monocloning of the nano antibody is expressed through screening, and the nano antibody is prepared through sequencing. Phage-ELLSAidentification shows that the phage that the nano antibody is expressed on the surface can be specifically combined with clostridium difficile glutamate dehydrogenase antigen and has a good developing property, the result shows that the nano antibody has a good combination property with glutamate dehydrogenase, therefore, the nano antibody can be adopted to replace a common antibody applied to aclostridium difficile immunodetection kit.
Owner:NINGXIA MEDICAL UNIV
Methylovorus sp. MP688 and application thereof
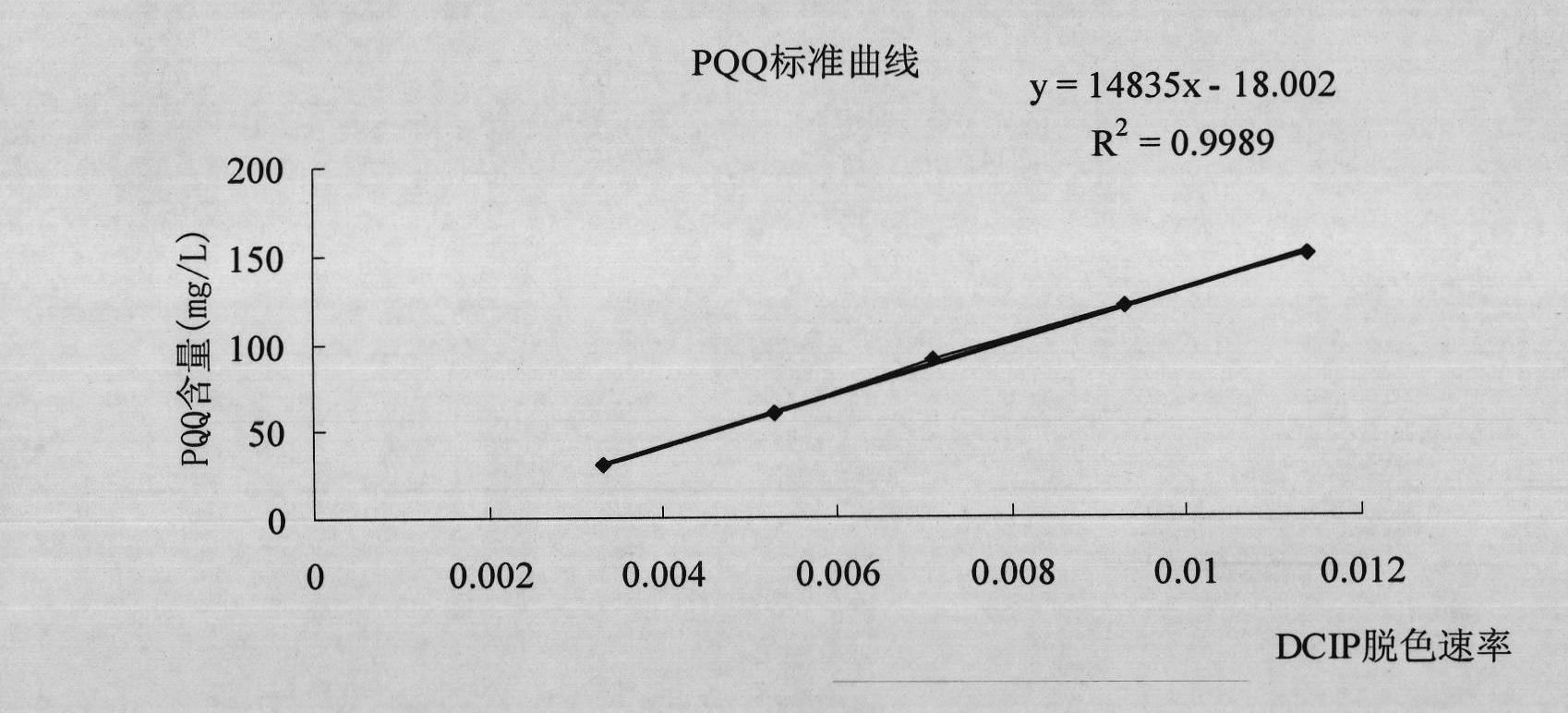
The invention discloses a new strain MP688 of Methylovorus sp., of which the preservation number is CGMCC No.4096, the preservation date is August 20th, 2010, and the preservation unit is China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center. The strain MP688 is separated from soil by using a GDH (glutamate dehydrogenase) recombinase method of PQQ (pyrroloquinoline quinone). By using the Methylovorus sp. strain disclosed by the invention, the yield of PQQ can reach 125 mg / L in a conventional culture medium under conventional culture conditions; and the Methylovorus sp. strain can be used for industrial production of PQQ, and has important meaning for promoting the industrialization of PQQ.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
Plants having enhanced yield-related traits and a method for making the same
The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for improving various plant growth characteristics by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a GDH (Glutamate DeHydrogenase) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a GDH polypeptide, which plants have improved growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants or other control plants. The invention also provides constructs useful in the methods of the invention. The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for enhancing various economically important yield-related traits in plants. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for enhancing yield-related traits in plants by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a FLA-like (Fasciclin-like) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a FLA-like polypeptide, which plants have enhanced yield-related traits relative to control plants. The invention also provides constructs comprising FLA-like- encoding nucleic acids, useful in performing the methods of the invention. The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for enhancing yield-related traits in plants by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a SAUR polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a SAUR polypeptide, which plants have enhanced yield-related traits relative to corresponding wild type plants or other control plants. The invention also provides constructs useful in the methods of the invention. Furthermore, the present invention also relates to a SAUR-based protein complex. It further relates to the use of the complex to enhance yield-related traits, and to a method for stimulating the complex formation, by overexpressing at least two members of the complex. The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for enhancing yield traits in plants by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a dehydroascorbate reductase (DHAR) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a DHAR polypeptide, which plants have enhancing yield traits relative to corresponding wild type plants or other control plants. The invention also provides constructs useful in the methods of the invention.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Enzyme combination for producing L-phosphinothricin, and production method of L-phosphinothricin
InactiveCN111139270AReduce manufacturing costTake full advantage of catalytic activityOxidoreductasesFermentationPhosphorous acidPhosphite dehydrogenase
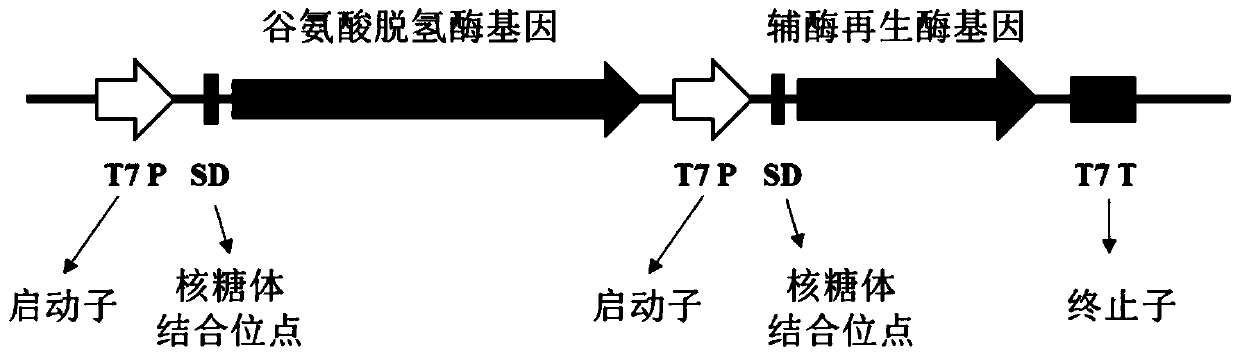
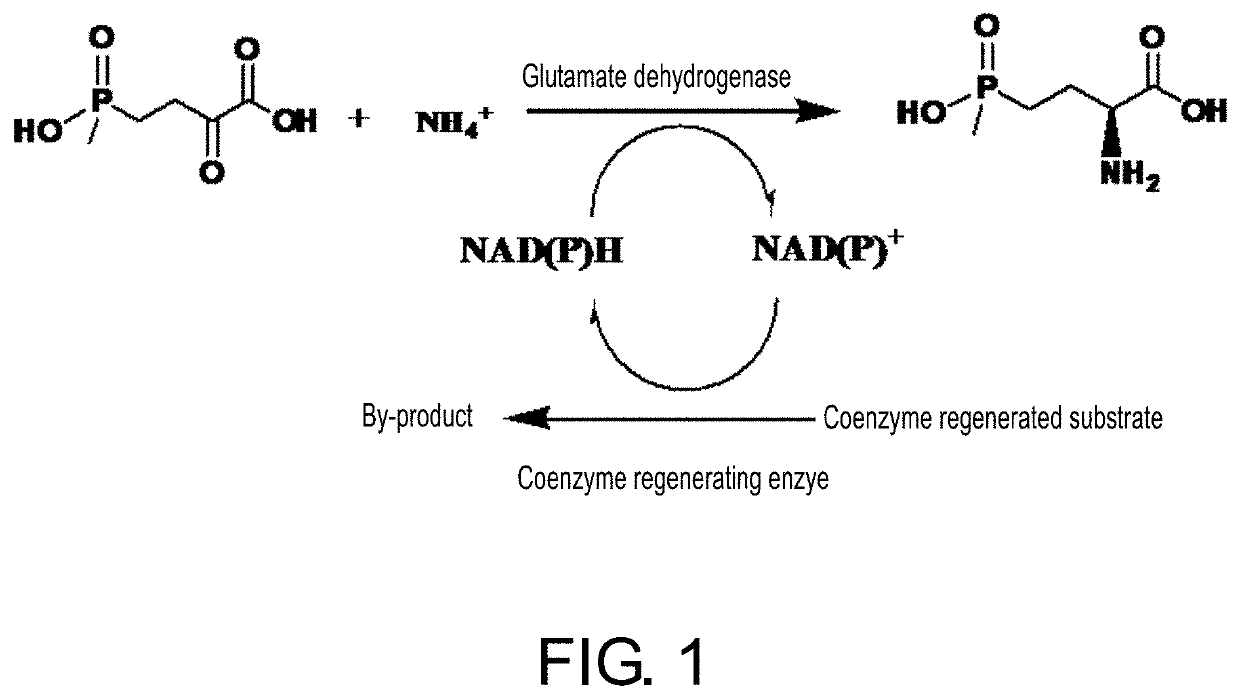
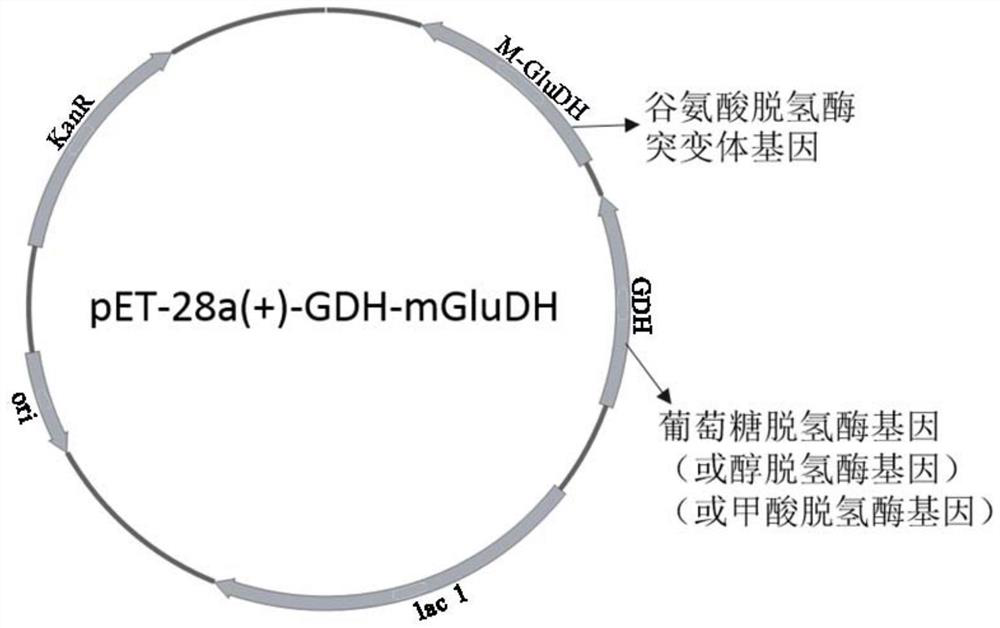
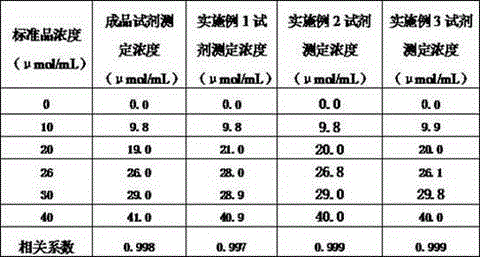
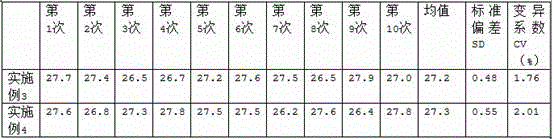
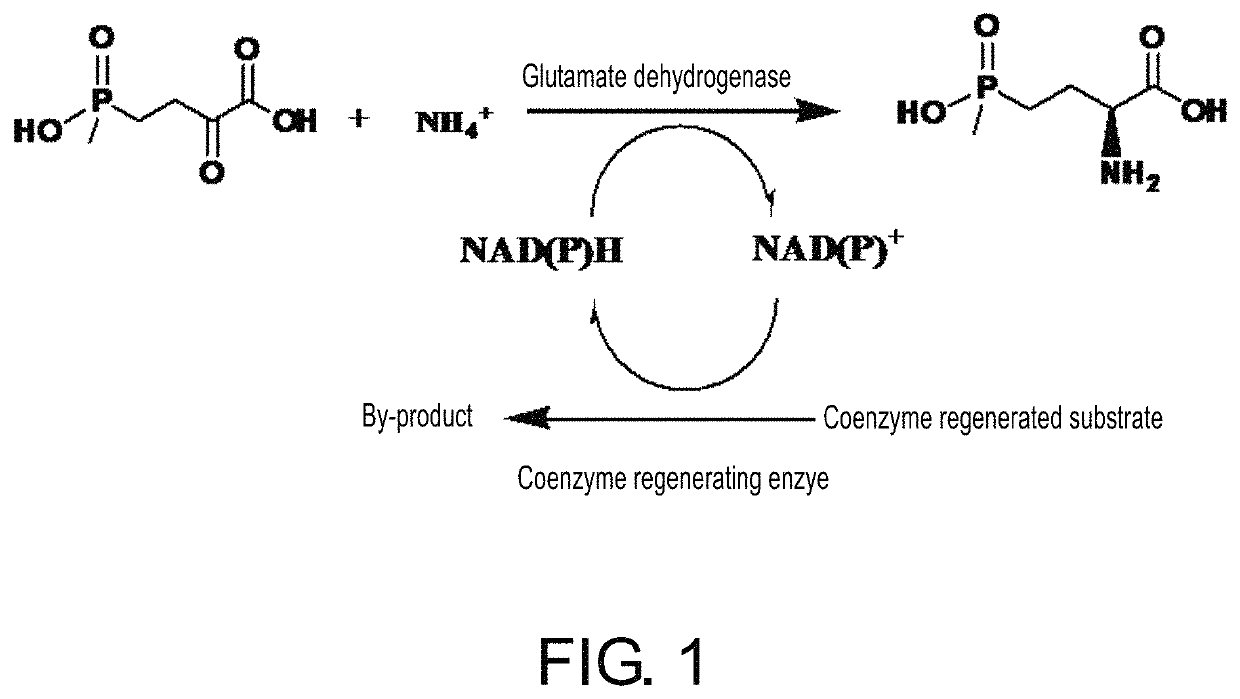
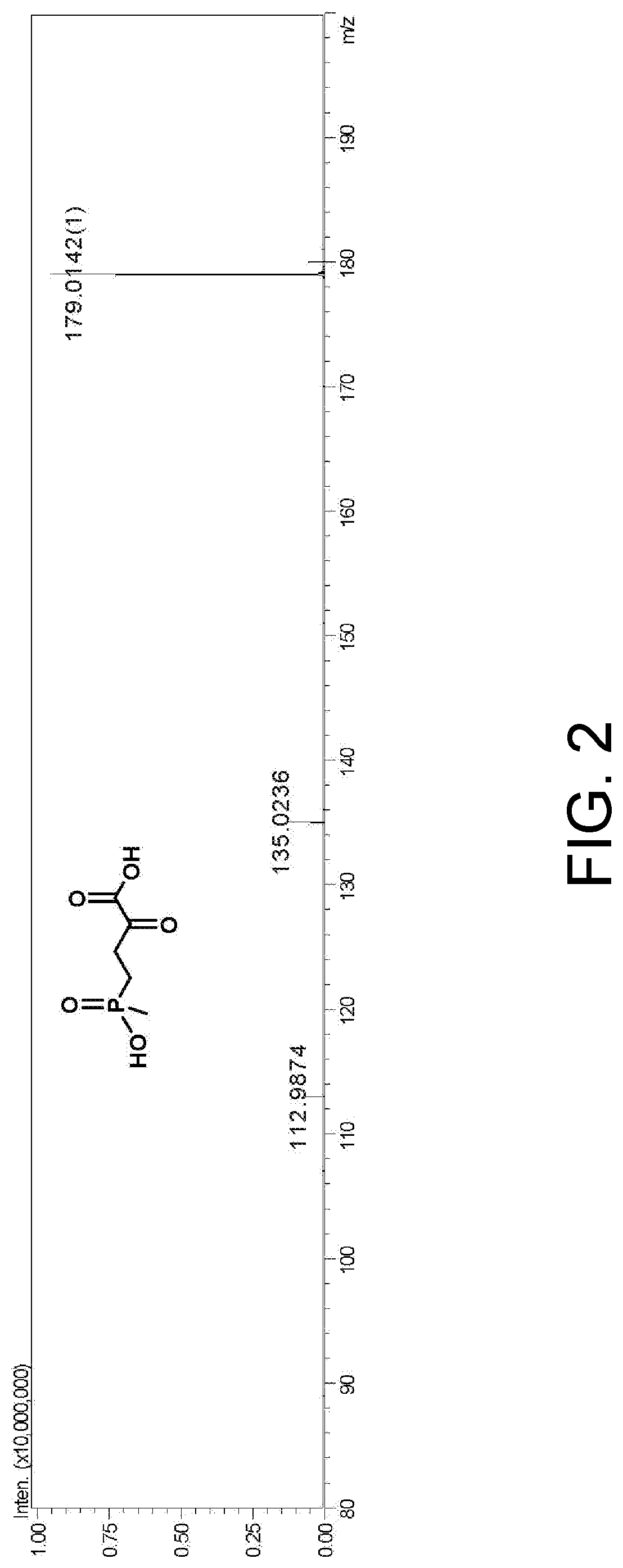
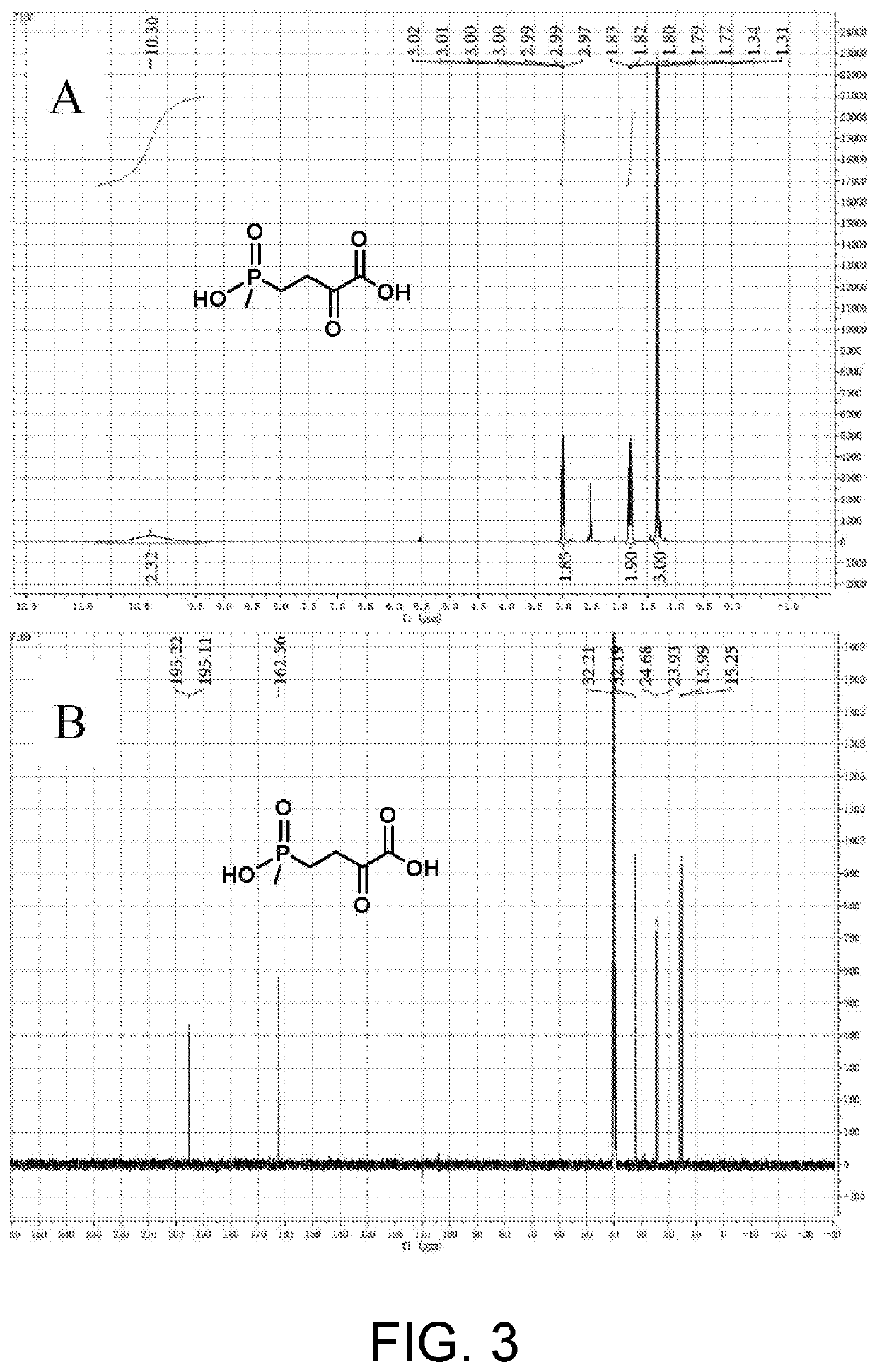
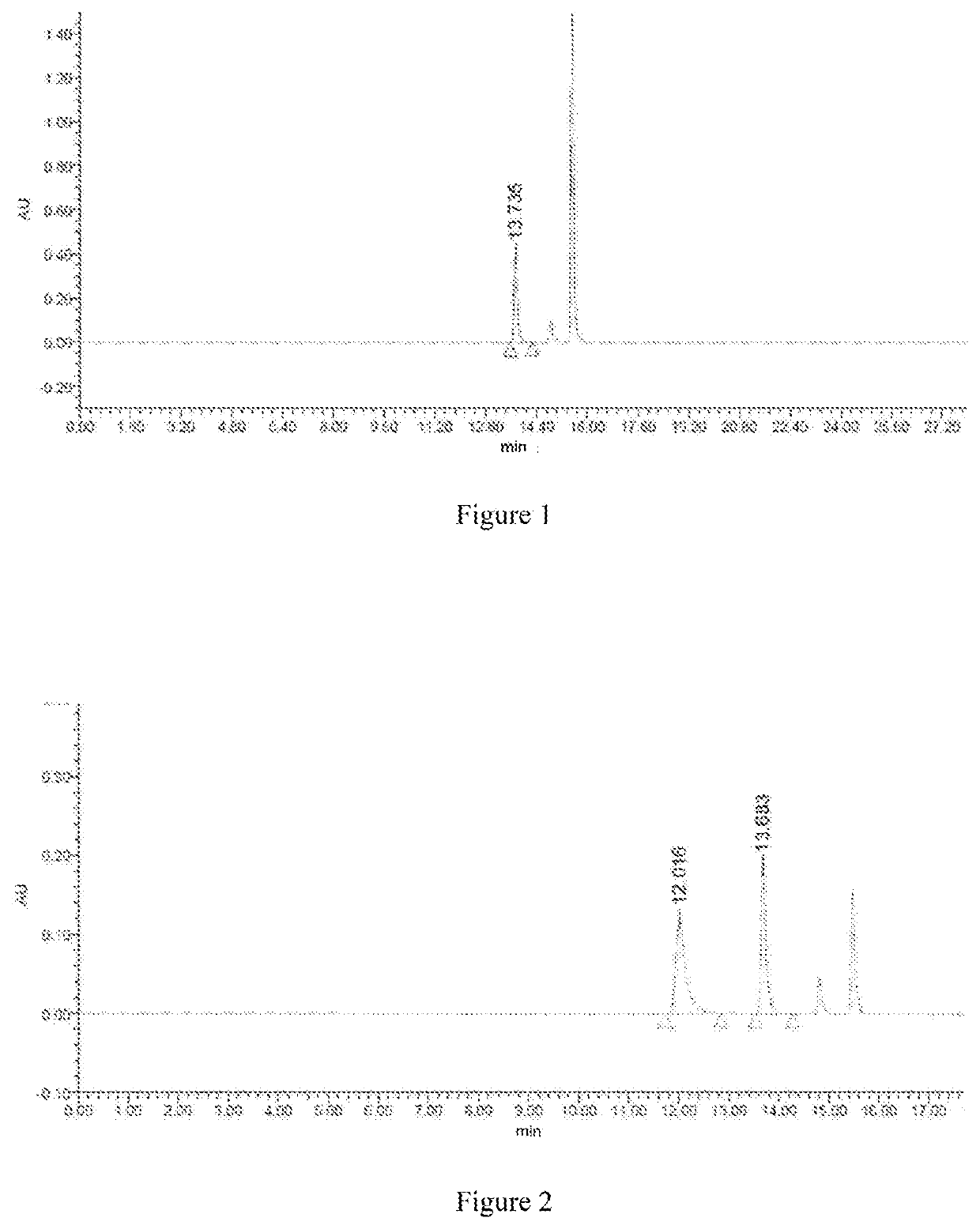
The invention discloses an enzyme combination for producing L-phosphinothricin. The enzyme combination comprises glutamate dehydrogenase and a coenzyme regenerating enzyme, wherein the coenzyme regenerating enzyme is alcohol dehydrogenase, formate dehydrogenase and phosphite dehydrogenase. The invention also discloses a production method of L-phosphinothricin, 4-(methylhydroxyphosphinyl)-2-oxobutyric acid is used as a raw material, NH<4><+>, a coenzyme NADP<+> / NADP, and a coenzyme regeneration substrate are added, and then the enzyme combination is used for catalysis, wherein the glutamate dehydrogenase is used to catalyze a reaction of 4-(methylhydroxyphosphinyl)-2-oxobutyric acid to obtain L-phosphinothricin, and the coenzyme regenerating enzyme is used to reduce NADP<+> to NADP. According to the enzyme combination and the production method of L-phosphinothricin provided by the invention, by-products produced are very easy to remove, a post-treatment process of the product is simplified, the total yield of the product is greater than 95%, and the production cost of L-phosphinothricin is reduced, so that the method is a green, environment-friendly, and low-carbon process route, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production applications.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Glycine diagnosis/measuring reagent kit and glycine concentration determination method
InactiveCN101464280AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurements2-ketoglutaric acidEnzymatic Colorimetry
The invention relates to a kit for diagnosing / measuring glycine by utilizing the technologies of the enzymatic doubling amplification method, the enzymic colorimetry and the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. The invention further relates to a method, a principle and the composition and the components of a reagent for measuring the concentration of the glycine, and belongs to the technical field of medical / food inspection and measurement. The main components of the kit include a buffer solution, coenzyme, a 2-ketoglutaric acid, guanosine monophosphate, glycine aminotransferase, glutamate dehydrogenase, guanosine monophosphate reduced enzyme and a stabilizer. Through mixing a sample and the reagent by a certain volume ratio, a series of enzymatic reactions occur, then the reactant is placed under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer, and the degree / velocity of the increase in absorbance at 340 nm of the dominant wavelength is detected, thereby measuring the active concentration of the glycine.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
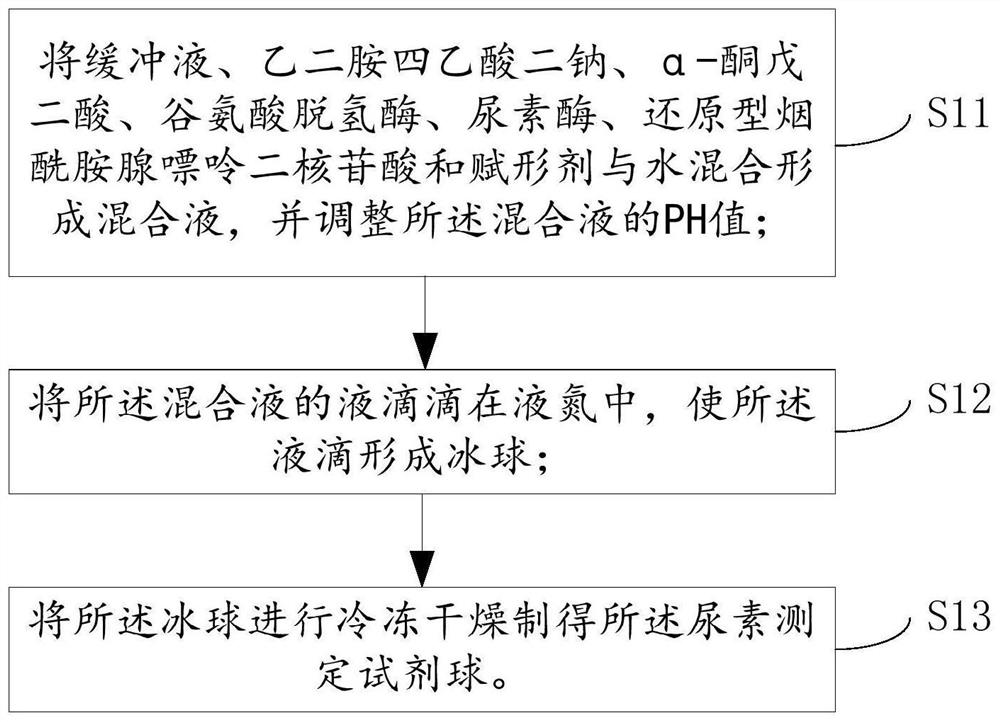
Preparation method of urea determination reagent ball, reagent ball and detection chip
PendingCN111707631AWide effective test rangeHigh maximum concentrationPreparing sample for investigationLaboratory glasswaresGlutaric acidFreeze-drying
The invention relates to the technical field of urea detection, in particular to a preparation method of a urea determination reagent ball, the reagent ball and a detection chip. The embodiment of theinvention provides a preparation method of a urea determination reagent ball. The method comprises the following steps of mixing a certain dosage of buffer solution, disodium ethylene diamine tetraacetate, alpha-ketoglutarate, glutamate dehydrogenase, urease, reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and excipient with water to form a mixed solution, dropwise adding the mixed solution into liquidnitrogen to enable liquid drops of the mixed solution to form ice balls, and freeze-drying the ice balls to obtain spherical urea determination reagent balls. The urea determination reagent ball prepared by the method has good thermal stability, can be stored for 8 days at a high temperature of 37 DEG C, is not easy to deteriorate in the storage process, has a wide effective test range on urea inblood, and can test the highest concentration of blood urea as high as 35mmol / L.
Owner:GENRUI BIOTECH INC
Sirt4 and uses thereof
Provided herein are SIRT4 compositions and methods of use thereof. The invention provides functional information for use in the identification and design of compounds that modulate SIRT4 enzyme activity (e.g., inhibition of fatty acid oxidation, ADP ribosylation, and / or downregulation of glutamate dehydrogenase), and to the compounds identified by such methods and the research, diagnostic and therapeutic uses of such compounds.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
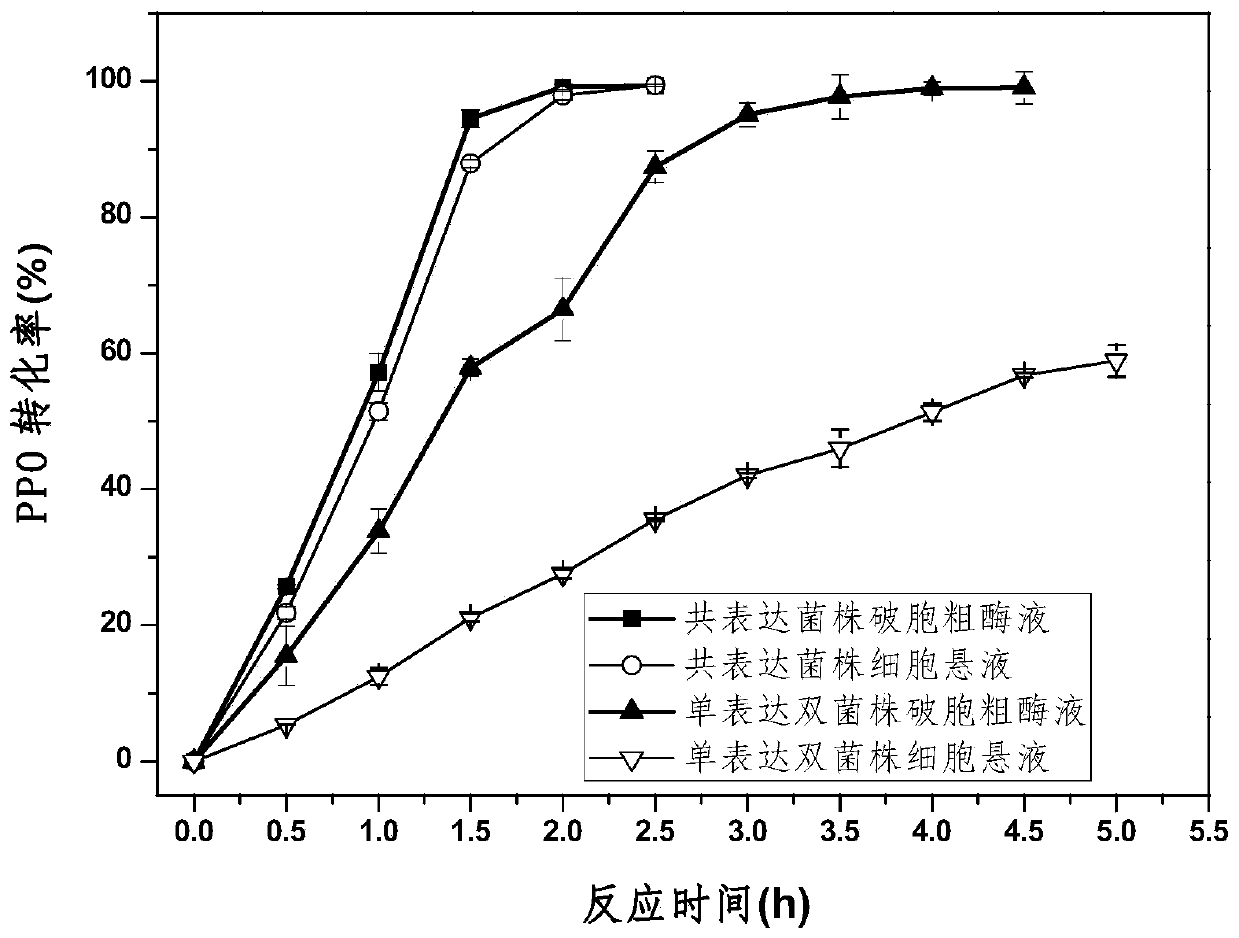
Glutamate dehydrogenase mutants and their application in preparation of l-phosphinothricin
ActiveUS20200102546A1High catalytic activityLow glutamateOxidoreductasesFermentationValineAcyl CoA dehydrogenase
The present invention relates to glutamate dehydrogenase mutants and their application in preparation of L-phosphinothricin. The amino acid sequences of the glutamate dehydrogenase mutants are as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1˜9, 11, 13, 15, 17˜19 and 22. By means of molecular engineering, mutating the specific alanine in glutamate dehydrogenase substrate-binding pocket into glycine and / or mutating the specific valine in glutamate dehydrogenase substrate-binding pocket into alanine, the present invention has obtained NADPH-specific glutamate dehydrogenase mutants with high enzyme activity in catalyzing the substrate 2-oxo-4-[(hydroxy)(methyl)phosphinoyl]butyric acid or its salt for L-phosphinothricin preparation or NADH-specific glutamate dehydrogenase mutants with catalytic activity toward PPO; this has significantly improved substrate conversion, and increased the product concentration of the L-phosphinothricin preparation process.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
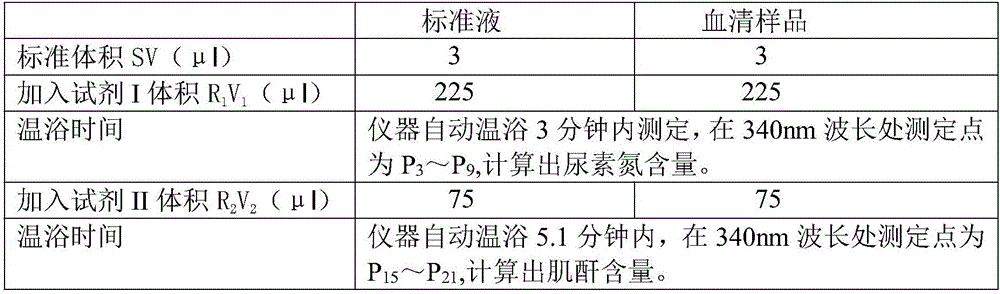
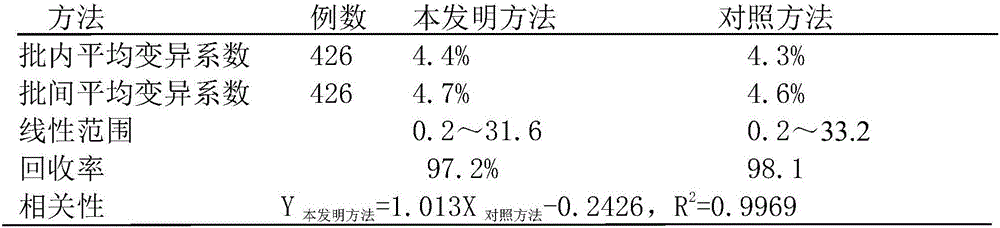
Method for simultaneous determination of double items of urea nitrogen and creatinine in serum
The invention discloses a method for simultaneous determination of double items of urea nitrogen and creatinine in serum, and belongs to the method for testing a material through testing color changes of reaction results by using visible light; the technical scheme comprises that a reagent II only comprises effective components of creatinine amidohydrolase and creatine amidinohydrolase; a reagent I contains effective components of urease, glutamate dehydrogenase, alpha-ketoglutarate and NADH. The determination method comprises the steps: firstly, carrying out 37 DEG C warm bath of serum with the reagent I for 3-5 minutes; carrying out a reaction of urea in the serum with the reagent I to generate NAD+; adding the reagent II, carrying out 37 DEG C warm bath for 4-7 minutes, hydrolyzing creatinine with the creatinine amidohydrolase to generate creatine; making the creatine generate urea under the action of the creatine amidinohydrolase, and making the urea and the reagent I generate NAD+ under the action of urease; at the wavelength of 340 nm, comparing the reaction speed with that of a standard treated by the same way, determining the change of the first-step reaction NADH, namely the content of urea nitrogen in the serum, and determining the change of the second-step reaction NADH, namely the content of the creatinine in the serum.
Owner:TIANJIN BAODI HOSPITAL
A genetically engineered bacterium for the production of l-theanine and its construction and application
ActiveCN109777763BIncrease enzyme activityGene expression is stableBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to novel high-efficiency gamma-glutamyl methylamine synthetase and a plasmid-free genetic engineering bacterium for L-theanine production and construction and application thereof. The plasmid-free genetic engineering bacterium which performs denovo synthesis on L-theanine efficiently by taking cheap carbon sources such as glucose as a substrate is provided, escherichia coli serves as a host, and gamma-glutamyl methylamine synthase genes gmas-Mu copied three times are integrated on a genome of the escherichia coli; a glutamate dehydrogenase gene Cgl2079 is copied once; a pyruvate carboxylase gene Cgl0689 is copied once; a citrate synthase gene gltA is copied once, and the genetic engineering bacterium is obtained. After metabolic transformation of a system, the engineering bacterium can perform denovo synthesis on the L-theanine by taking the glucose as the raw material, the fermentation yieldand sugar-acid conversion rate are the highest values reported so far, in fermentation of a 5 L fermentor, the maximum production of the L-theanine can reach 60 g / L, and the sugar-acid conversion ratecan reach 40%.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Mutant gene and coding protein of glutamate dehydrogenase of Bacillus natto
The invention relates to a mutant gene and coding protein of glutamate dehydrogenase of Bacillus natto, belonging to the field of biotechnology. The base sequence of the mutant gene of the coding gene of glutamate dehydrogenase of Bacillus natto is shown as follows: SEQ ID NO: 3, SEQ ID NO: 5, SEQ ID NO: 7, SEQ ID NO: 9, SEQ ID NO: 11, SEQ ID NO: 13 or SEQ ID NO: 15; the protein amino acid sequence of the mutant gene of the coding gene of glutamate dehydrogenase of Bacillus natto is shown as follows: SEQ ID NO: 4, SEQ ID NO: 6, SEQ ID NO: 8, SEQ ID NO: 10, SEQ ID NO: 12, SEQ ID NO: 14 or SEQ ID NO: 16. The invention also relates to a recombinant vector containing the mutant gene. When the mutation of the invention is introduced to wild strains by homologous recombination, gene engineering bacteria with low ammonia yield and unchanged growth speed is obtained, thus producing natto without ammonia odor.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Fungus PcGDH protein for improving efficient utilization of nitrogen, and application thereof
InactiveCN103820408AIncrease productionIncrease profitOxidoreductasesFermentationBiotechnologyGenetically modified rice
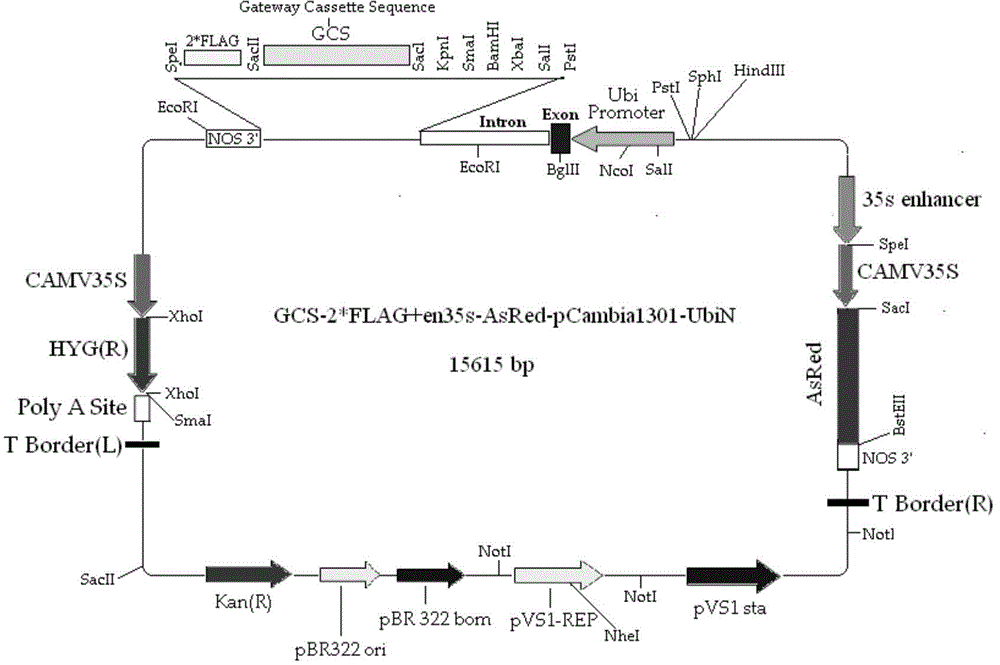
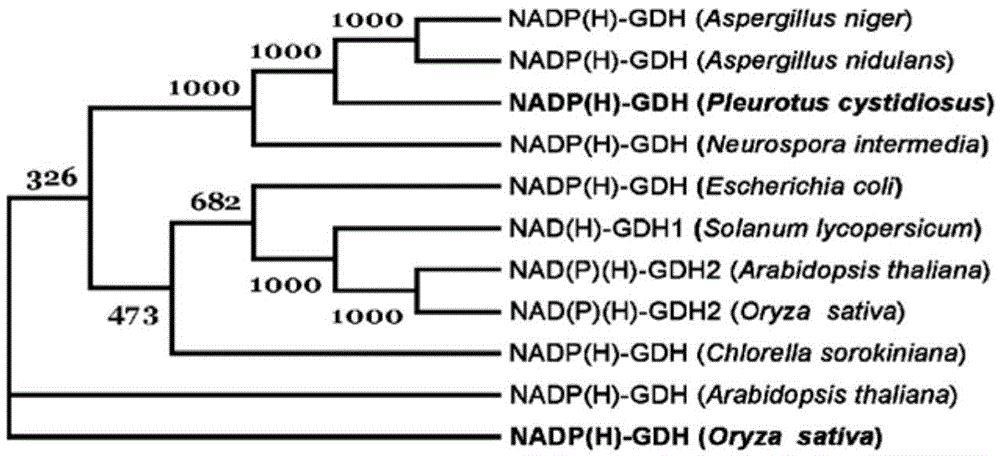
The invention belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering, and discloses clone and application of a fungus PcGDH (Pleurotuscystidiosus Glutamate Dehydrogenase) gene for improving efficient utilization of nitrogen. The NADP (H) (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate) enzymatic activity of a PcGDH in-vitro positive reaction is larger than that of a reverse reaction, that is the PcGDH protein is inclined to utilize NH4+ to translate alpha-oxoglutarate into glutamic acid. In addition, the affinity of the PcGDH to NH4+ is larger than glutamic acid. By virtue of a genetic engineering technology, the PcGDH gene is over-expressed in rice in a heterogeneous manner to improve utilization of nitrogen by transgenic rice, improve growth of the transgenic rice and increase absolute plant and thousand seed weight of the transgenic rice. Therefore, the PcGDH gene for improving the rice nitrogen can be utilized to culture novel rice products with good agronomic characters.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV +1
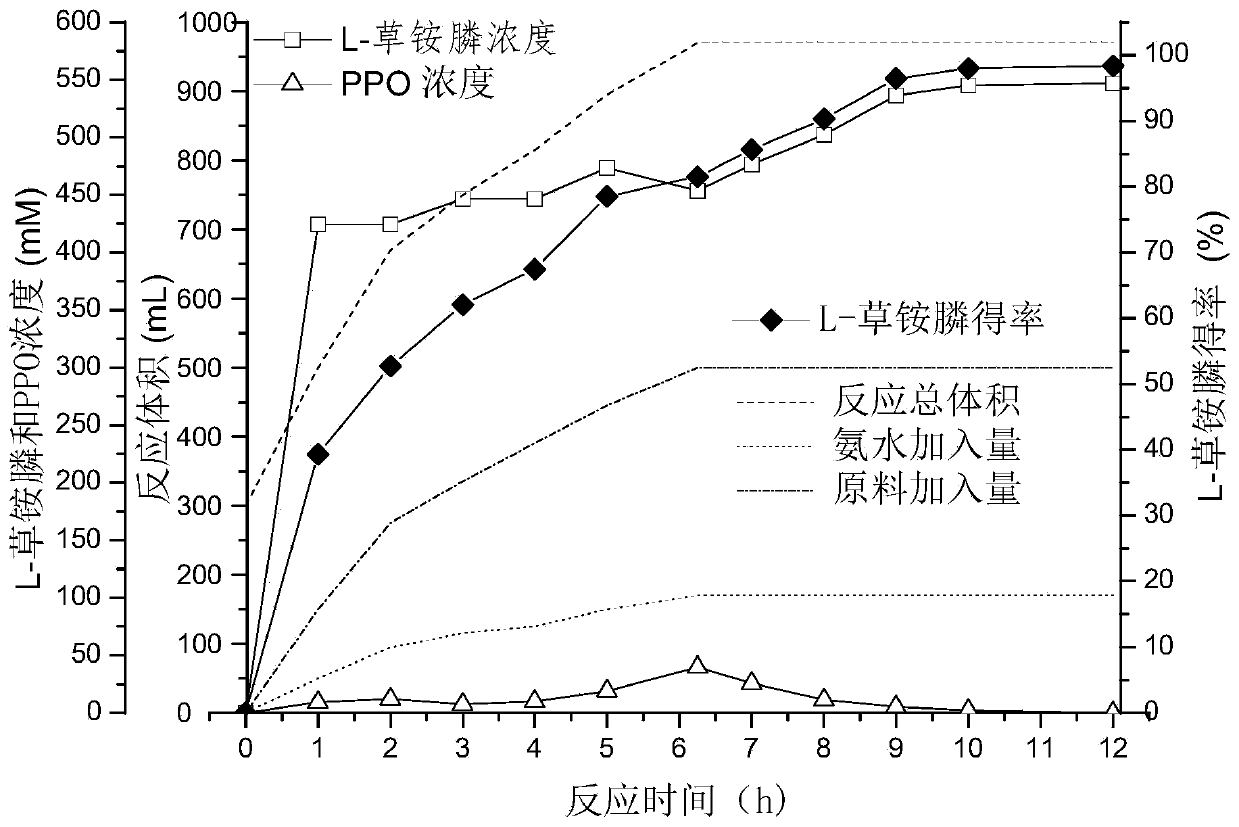
Glutamate dehydrogenase mutant for producing L-glufosinate-ammonium and L-glufosinate-ammonium production method
ActiveCN113088501AMild reaction conditionsGreen Process RouteBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNiacinamideNucleotide
The invention discloses a glutamate dehydrogenase mutant for producing L-glufosinate-ammonium, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and the amino acid sequence after mutation is shown as SEQ ID NO.1-SEQ ID NO.11. The invention also discloses a production method of L-glufosinate-ammonium, which comprises the following steps: by taking 2-carbonyl-4-[hydroxyl (methyl) phosphonyl]-butyric acid as a raw material, adding NH4<+> and coenzyme NADH / NAD<+>, then catalyzing by using the glutamate dehydrogenase mutant, and reducing and aminating the 2-carbonyl-4-[hydroxyl (methyl) phosphonyl]-butyric acid into L-glufosinate-ammonium by using glutamate dehydrogenase. A large number of glutamate dehydrogenase mutant genes are developed through the method, L-glufosinate-ammonium can be prepared from glutamate dehydrogenase mutants by using nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH or NAD<+>) which is low in price as coenzyme, the substrate conversion rate is larger than or equal to 99%, the optical purity of the product exceeds 99%, reaction conditions are mild, and the method is a green, environment-friendly and low-carbon process route, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production and application.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Gene mining method combining functional sequence and structural simulation, NADH preference type glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutant and application
PendingCN112908417AHigh catalytic efficiencyImprove conversion rateProteomicsGenomicsEnzyme structureProtein structure
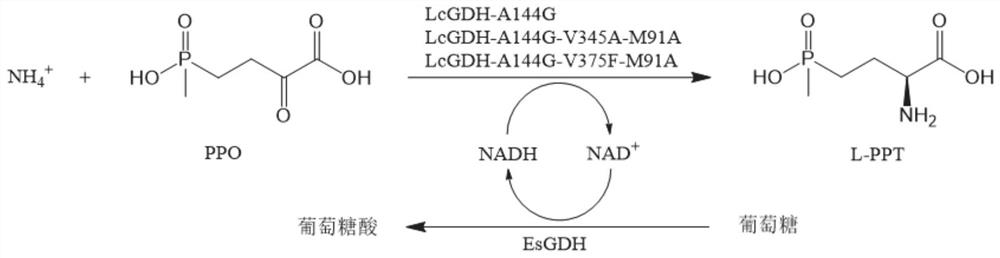
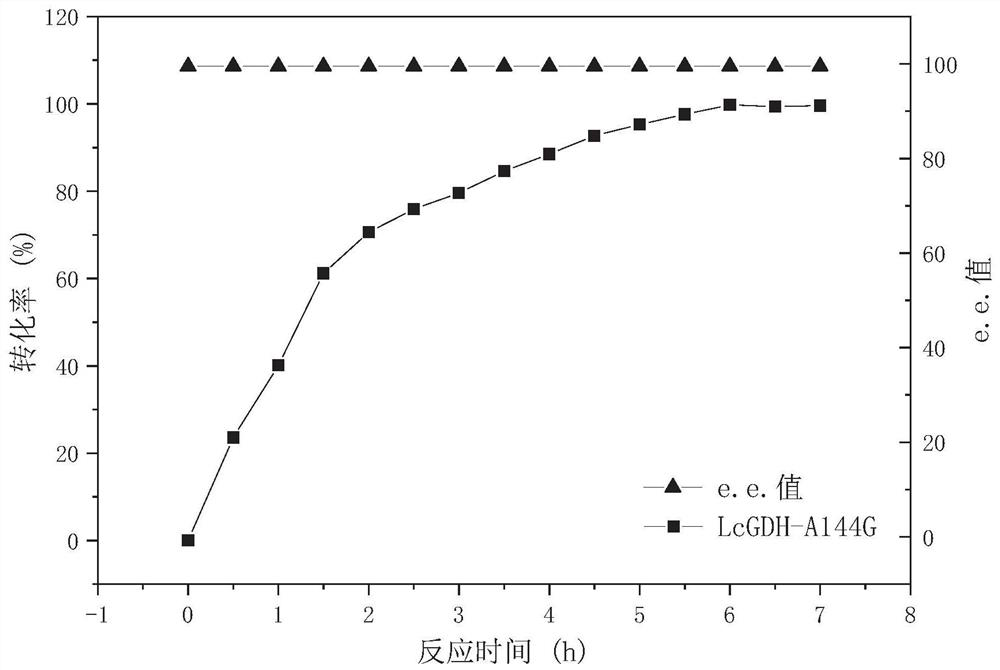
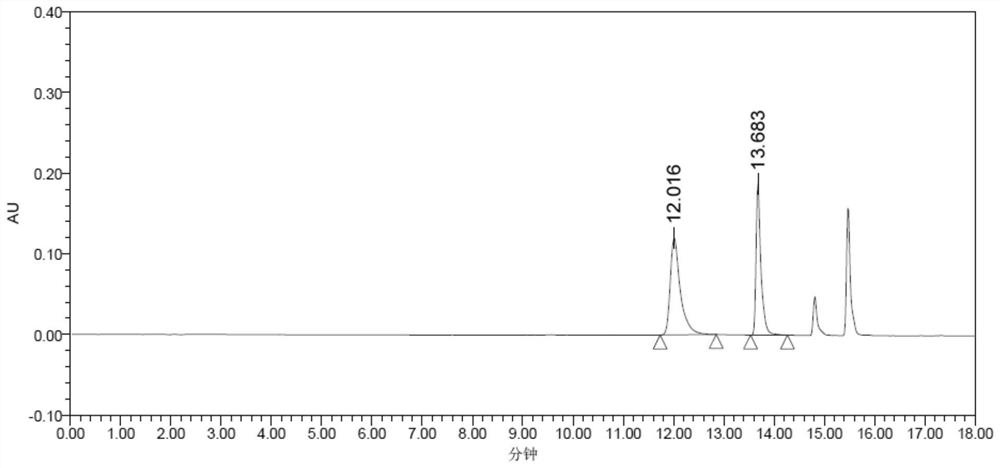
The invention discloses a gene mining method combining a functional sequence and structural simulation, an NADH preference type glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutant and an application. The gene mining method comprises the following steps: (1) analyzing a characteristic sequence of NADH type glutamate dehydrogenase; (2) searching a gene pool according to the characteristic sequence; (3) performing clustering analysis and protein structure simulation on the searched genes; and (4) selecting a gene with high gene polymerization degree and a protein structure similar to that of known glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase as a candidate gene. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out gene mining to obtain wild glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase which is derived from Lysinibacillus composti and has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No.2, carrying out mutation screening to obtain an NADH preference type glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutant, and selecting a mutation site from one of the following: (1) A144G-V375F-M91A; (2) A144G-V345A-M91A; and (3) A144G. The mutant enzyme can be subjected to catalytic reaction by using cheap coenzyme NAD.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
L-glutamate dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN111979208AImprove efficiencyImprove conversion rateMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesAcyl CoA dehydrogenaseGlutamate Dehydrogenase (NADP+)
The invention discloses an L-glutamate dehydrogenase mutant. The sequence of the L-glutamate dehydrogenase mutant is obtained by mutating a 175 amino acid residue A of the sequence shown in SEQ IDNO. 1 into G and mutating a 386 amino acid residue V into an amino acid residue with smaller steric hindrance. The invention also discloses application of the L-glutamate dehydrogenase mutant inpreparation of L glufosinate-ammonium or salts thereof. When the L-glutamate dehydrogenase mutant is used for preparing the L-glufosinate-ammonium or salts thereof, compared with the L-glutamate dehydrogenase mutant which is only mutated at the 175 site or 386 site, the L-glutamate dehydrogenase mutant has higher enzyme activity, thereby improving the action efficiency of the enzyme, decreasing the reaction cost and being beneficial to industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI QIZHOU ZIYUE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
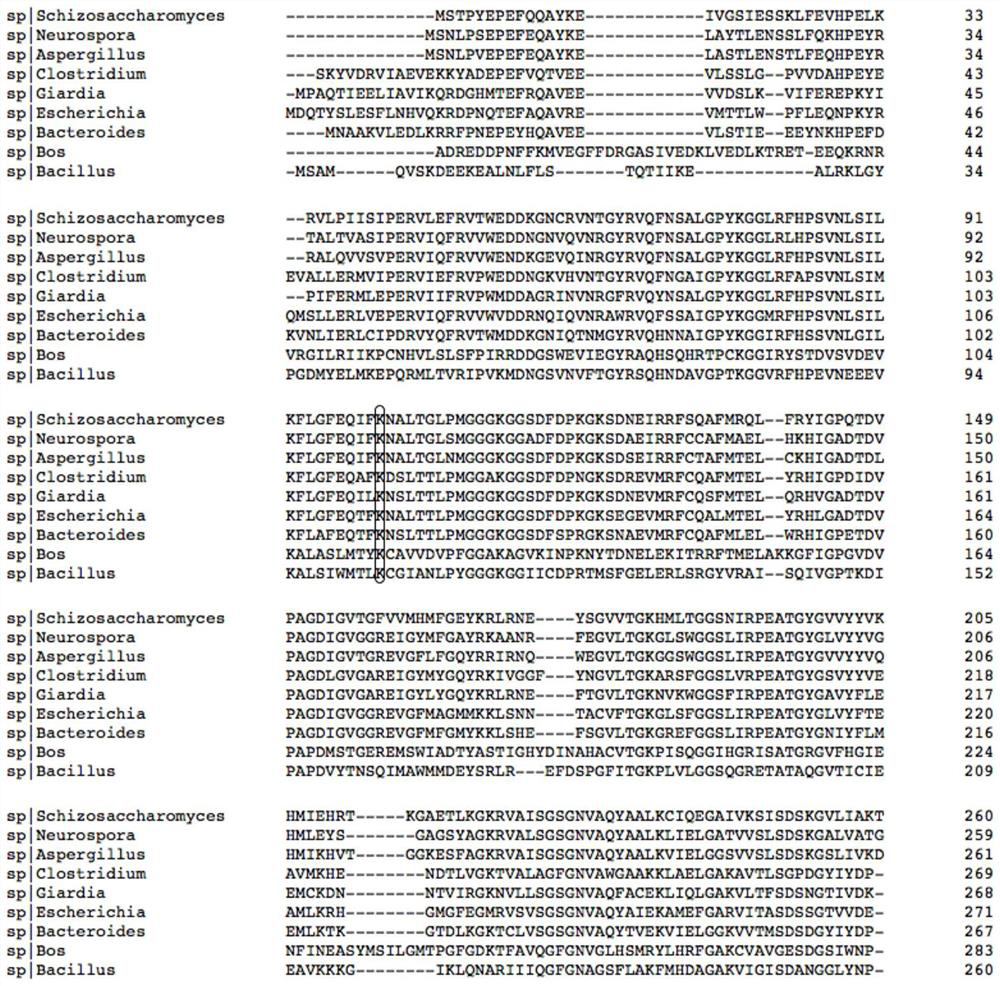
Mutant of glutamate dehydrogenase gene promoter and application thereof
ActiveCN113201535AHigh promoter activityImprove expression strengthBacteriaNucleotide librariesPromoter activityWild type
The invention discloses a mutant of a corynebacterium glutamicum glutamate dehydrogenase gene promoter and application of the mutant. The mutant has improved promoter activity compared with a wild type promoter. Therefore, the mutant can be used for enhancing the expression of a target gene, for example, the expression intensity of glutamate dehydrogenase can be enhanced by operably connecting the mutant with a glutamate dehydrogenase gene, so that the amino acid production efficiency of the recombinant strain is improved, and the application value is relatively higher.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Stable serum-potassium detection reagent with high anti-interference capability and detection method
InactiveCN105420344AImprove stabilityImprove anti-interference abilityMicrobiological testing/measurementPolyethylene glycolNon ionic
The invention relates to the technical field of serum potassium detection, in particular to a serum-potassium detection reagent. A reagent R1 is prepared from a buffer solution, a cryptate agent, PEP, ADP, formic acid, formate dehydrogenase, alpha-ketoglutaric acid, NADH, GLDH (glutamate dehydrogenase), polyethylene glycol 6000, ethylene glycol, mannitol, trehalose, BSA, PK (pyruvate kinase), alkyl polyglucoside (APG) and preservative; a reagent R2 is prepared from a buffer solution, polyethylene glycol 6000, ethylene glycol, mannitol, trehalose, BSA, LDH (lactic dehydrogenase), alkyl polyglucoside (APG) and preservative. The Tris buffer solutions are adopted, multiple stabilizers are added, an NADH cyclic regeneration system is introduced, and therefore the stability of the reagent is remarkably improved; as the novel nonionic surfactant alkyl polyglucoside (APG) is added, turbidity of the reaction system can be effectively prevented, and the sensitivity and the stability of the reagent are remarkably improved.
Owner:BIOBASE BIODUSTRY (SHANDONG) CO LTD
Serum ammonia detection reagent
ActiveCN104374906AHigh activityEliminate distractionsColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingAdenosineBovine serum albumin
Owner:BIOBASE BIODUSTRY (SHANDONG) CO LTD
Kit for determining homocysteine and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106053830AImprove enzyme stabilityEasy to operateBiological testingS-Adenosyl-l-methioninePhosphate
The invention discloses a kit for determining homocysteine and a preparation method thereof. The kit is composed of dual-liquid components of a reagent R1and a reagent R2 which are independent from each other. The reagent R1 is prepared from a phosphate buffer, sodium chloride, S-adenosylmethionine, a reduced coenzyme II, tri(2-carboxyl) phosphine hydrogen chloride and sodium azide; the reagent R2 is prepared from phosphate buffer, HCY transmethylase, glutamate dehydrogenase, S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase, bovine serum albumin and sodium azide. The preparation method comprises the steps that the reagents are prepared according to the component content; a to-be-tested sample is mixed with the reagent R1 and the reagent R2 to perform a sufficient reaction; a fully automatic biochemical analyzer is used for determining the reacted absorptivity difference; according to the absorptivity change value, the concentration of homocysteine in the sample is worked out. The kit has the advantages of being convenient to operate, high in accuracy and the like.
Owner:ANHUI IPROCOM BIOTECH CO LTD
Glutamate dehydrogenase mutants and their application in preparation of L-phosphinothricin
ActiveUS10865391B2High catalytic activityIncrease concentrationOxidoreductasesFermentationValineAcyl CoA dehydrogenase
The present invention relates to glutamate dehydrogenase mutants and their application in preparation of L-phosphinothricin. The amino acid sequences of the glutamate dehydrogenase mutants are as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1-9, 11, 13, 15, 17-19 and 22. By means of molecular engineering, mutating the specific alanine in glutamate dehydrogenase substrate-binding pocket into glycine and / or mutating the specific valine in glutamate dehydrogenase substrate-binding pocket into alanine, the present invention has obtained NADPH-specific glutamate dehydrogenase mutants with high enzyme activity in catalyzing the substrate 2-oxo-4-[(hydroxy)(methyl)phosphinoyl]butyric acid or its salt for L-phosphinothricin preparation or NADH-specific glutamate dehydrogenase mutants with catalytic activity toward PPO; this has significantly improved substrate conversion, and increased the product concentration of the L-phosphinothricin preparation process.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Application of glutamate dehydrogenase as target spot in pest control
ActiveCN114058618AIndividual smallNo drug resistanceHydrolasesNucleic acid vectorBiotechnologyAcyl CoA dehydrogenase
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and discloses application of glutamate dehydrogenase as a target spot in pest control. The invention discloses the application of glutamate dehydrogenase as a target spot in pest control for the first time, GDH is knocked out through target gene screening in combination with a CRISPR / Cas9 technology, and the importance of glutamate dehydrogenase to growth and development of pests is proved. GDH gene mutants are successfully obtained in pests by utilizing a transgenic CRISPR / Cas9 technology, GDH gene mutation seriously affects normal growth and development of the pests, individuals become small, and the pests are prone to being infected with viruses in a larval stage and die, and massive death caused by GDH gene mutation in the larval stage can be used for pest control.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
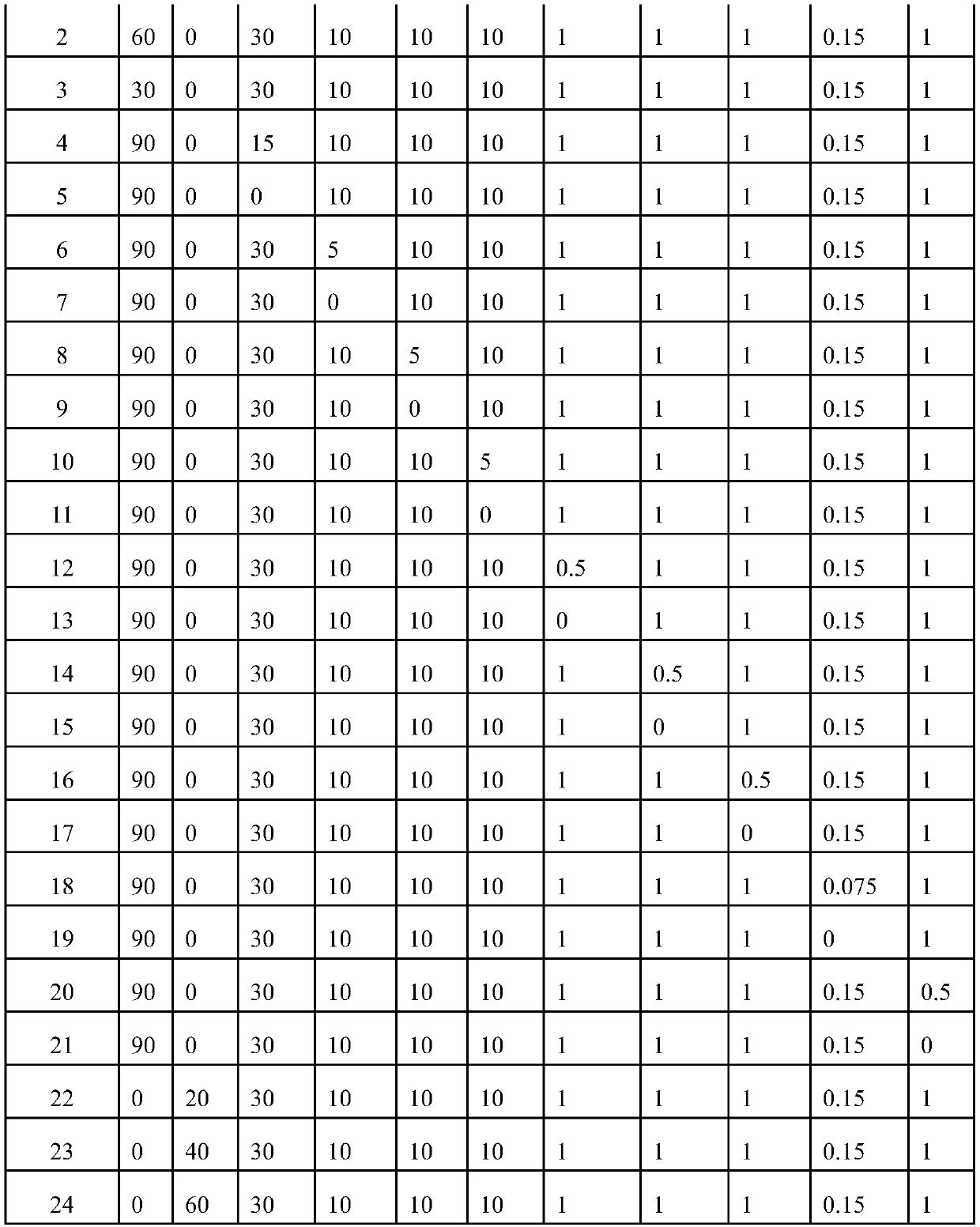
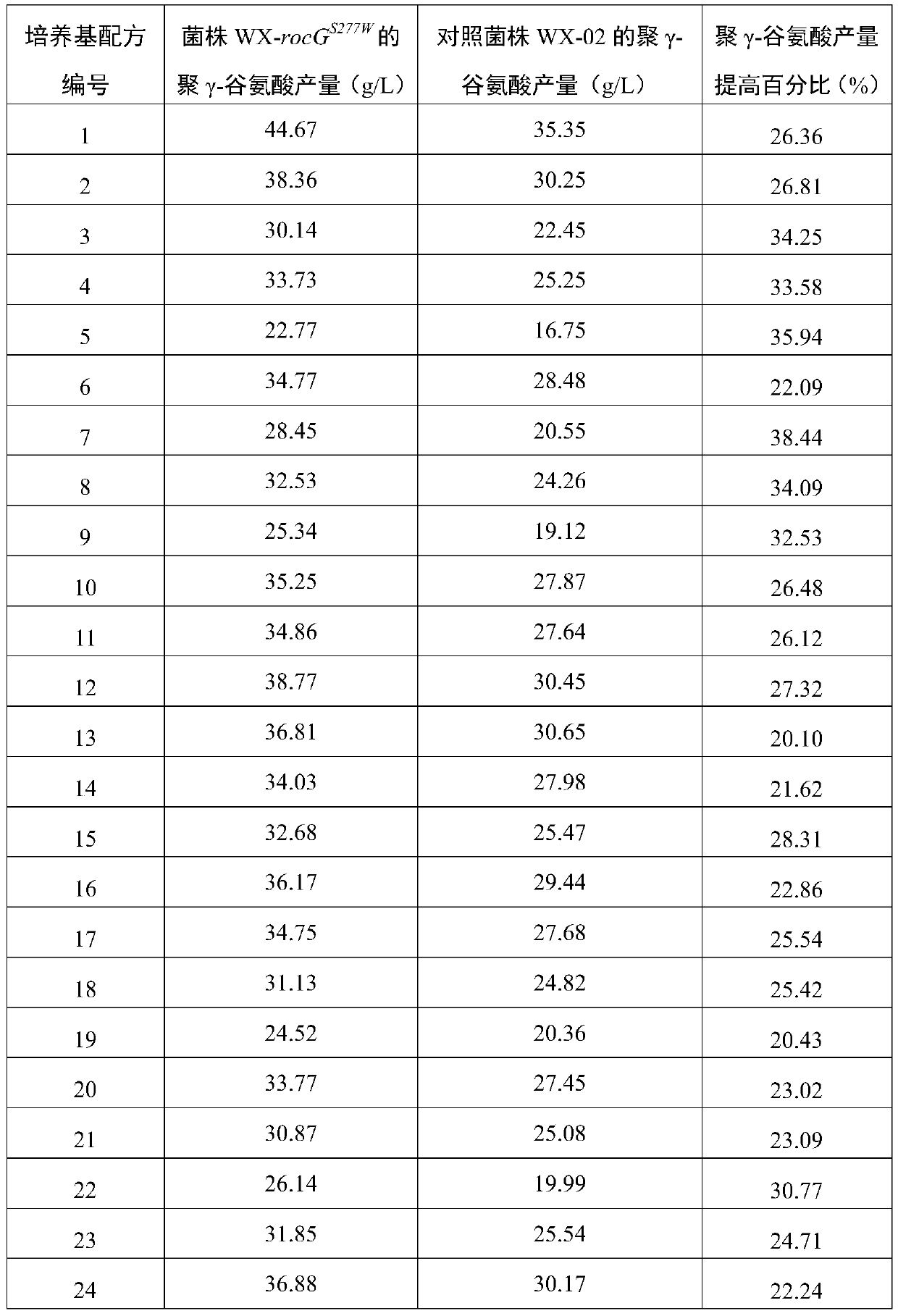
Application of Peptostreptococcus asaccharoly glutamate dehydrogenase (GdhA) in increasing yield of Bacillus licheniformis poly-gamma-glutamic acid
ActiveCN110951797ASolve the shortage of supplyIncrease synthesis levelBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPeptostreptococcusBacillus licheniformis
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering and enzyme engineering, and discloses application of Peptostreptococcus asaccharoly glutamate dehydrogenase (GdhA) in increasing the yield of Bacillus licheniformis poly-gamma-glutamic acid. According to the invention, with a homologous recombination mode, glutamate dehydrogenase (GdhA) derived from Peptostreptococcus asaccharoly replaces glutamate dehydrogenase of Bacillus licheniformis (WX-02), the synthesis level of the Bacillus licheniformis poly-gamma-glutamic acid is remarkably improved, and the yield of the obtained strainpoly-gamma-glutamic acid is at least increased by 20% or above compared with that of a control strain. The invention provides a new strategy for efficient production of poly gamma-glutamic acid.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Glutamate dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN112280760ACatalytic activity achievedHigh catalytic activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGlutamate dehydrogenase.NADAcyl CoA dehydrogenase
The invention discloses a glutamate dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering and microbial engineering. By adopting the method provided bythe invention, a brand-new method for synthesizing (R) -4-aminovaleric acid by a biological method is provided; wild glutamate dehydrogenase has no measurable catalytic activity, but the glutamate dehydrogenase mutant has catalytic activity, and the catalytic activity of the mutants K116S / N348L, K116E / N348M and K116Q / N348M can reach 1.87 U / mg, 3.16 U / mg and 4.55 U / mg respectively, so that the catalytic activity of the 4-oxovaleric acid is improved from zero. The biological method for synthesizing (R) -4-aminovaleric acid provided by the invention is green, environment-friendly and efficient,and has a wide industrial application prospect.
Owner:宿迁市江南大学产业技术研究院
Glutamate dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof
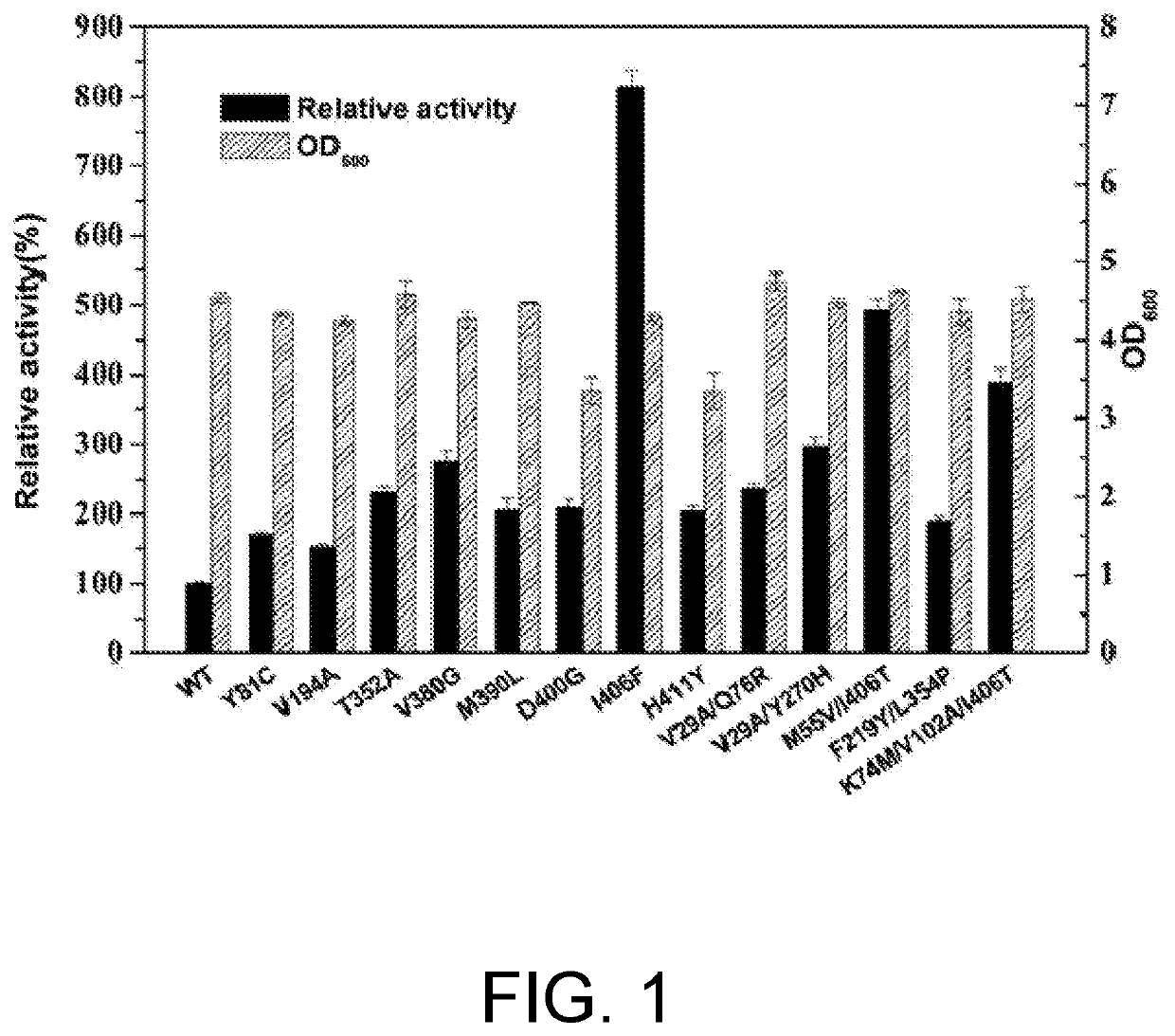
ActiveUS11339380B2Improve stabilityReduced activityOxidoreductasesFermentationPseudomonas putidaThreonine
The invention discloses a glutamate dehydrogenase mutant and an application thereof. The mutant is one of the following: a mutant of the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO. 1 which has a mutation at lysine at position 402 to phenylalanine or aspartic acid; a mutant which has a mutation at isoleucine at position 406 to phenylalanine or threonine; a mutant which has a mutation at threonine at position 121 and leucine at position 123; a mutant which has a mutation at alanine at position 379 and leucine at position 383. In the invention, the catalytic activity of glutamate dehydrogenase derived from Pseudomonas putida to 2-carbonyl-4-(hydroxymethylphosphonoyl)butanoic acid (PPO) is significantly improved by a molecular transformation method combining directed evolution and a semi-rational design; and the issue of low glutamate dehydrogenase activity in the process of preparing L-glufosinate by reductive amination is solved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
L-glutamate dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof
ActiveUS20210024902A1High substrate concentrationLower reaction costOxidoreductasesFermentationButyrateAcyl CoA dehydrogenase
Provided are an L-glutamate dehydrogenase mutant and an application thereof, the mutant mutating the amino acid residue A at position 166 and / or the amino acid residue V at position 376 shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 into a hydrophilic or small sterically hindered amino acid residue, the application performing an amination reaction of 2-oxo-4-(hydroxymethylphosphinyl)butyrate in the presence of an L-amino acid dehydrogenase mutant, an inorganic amino donor, and a reduced coenzyme NADPH, and performing an acidification reaction on the obtained L-glufosinate salt to obtain L-glufosinate. Compared to wild L-glutamate dehydrogenase, the present L-glutamate dehydrogenase mutant has a higher concentration of substrates that can be catalysed when preparing L-glufosinate, thereby increasing the efficiency of the action of the enzyme and reducing reaction costs.
Owner:SHANGHAI QIZHOU ZIYUE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Urea detection kit as well as preparation method and use method thereof
PendingCN112126674ASimple ingredientsHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisAdenosineAdenosine diphosphate
The invention provides a urea detection kit as well as a preparation method and a use method thereof. The kit comprises a reagent R1 and a reagent R2, wherein the reagent R1 comprises a Tris buffer solution, adenosine diphosphate, urease and glutamate dehydrogenase, and the reagent R2 comprises a Tris buffer solution, reduced coenzyme I and alpha-ketoglutaric acid. The kit provided by the invention is simple in component, maintains the advantages of higher sensitivity, wide linear range, low cost, strong anti-interference capability and high accuracy by adopting an enzyme coupling rate methodin an enzyme method, and can be universally applied to full-automatic and semi-automatic analyzers.
Owner:LANZHOU BAIYUAN GENE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com