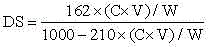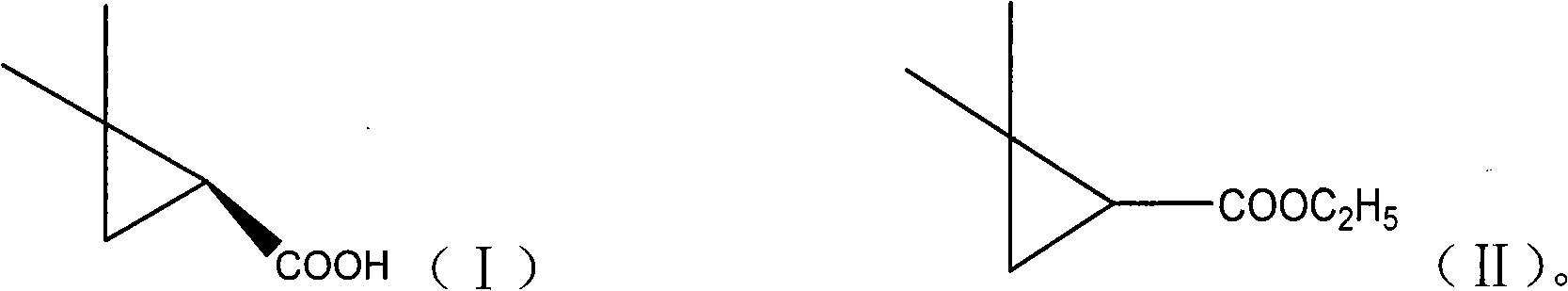Patents
Literature
36 results about "Novozym 435" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for preparing biological diesel oil with methyl acetate act acyl acceptor
InactiveCN101343551ANon-toxicEffect on catalytic activityBiofuelsFatty-oils/fats refiningVegetable oilBiodiesel
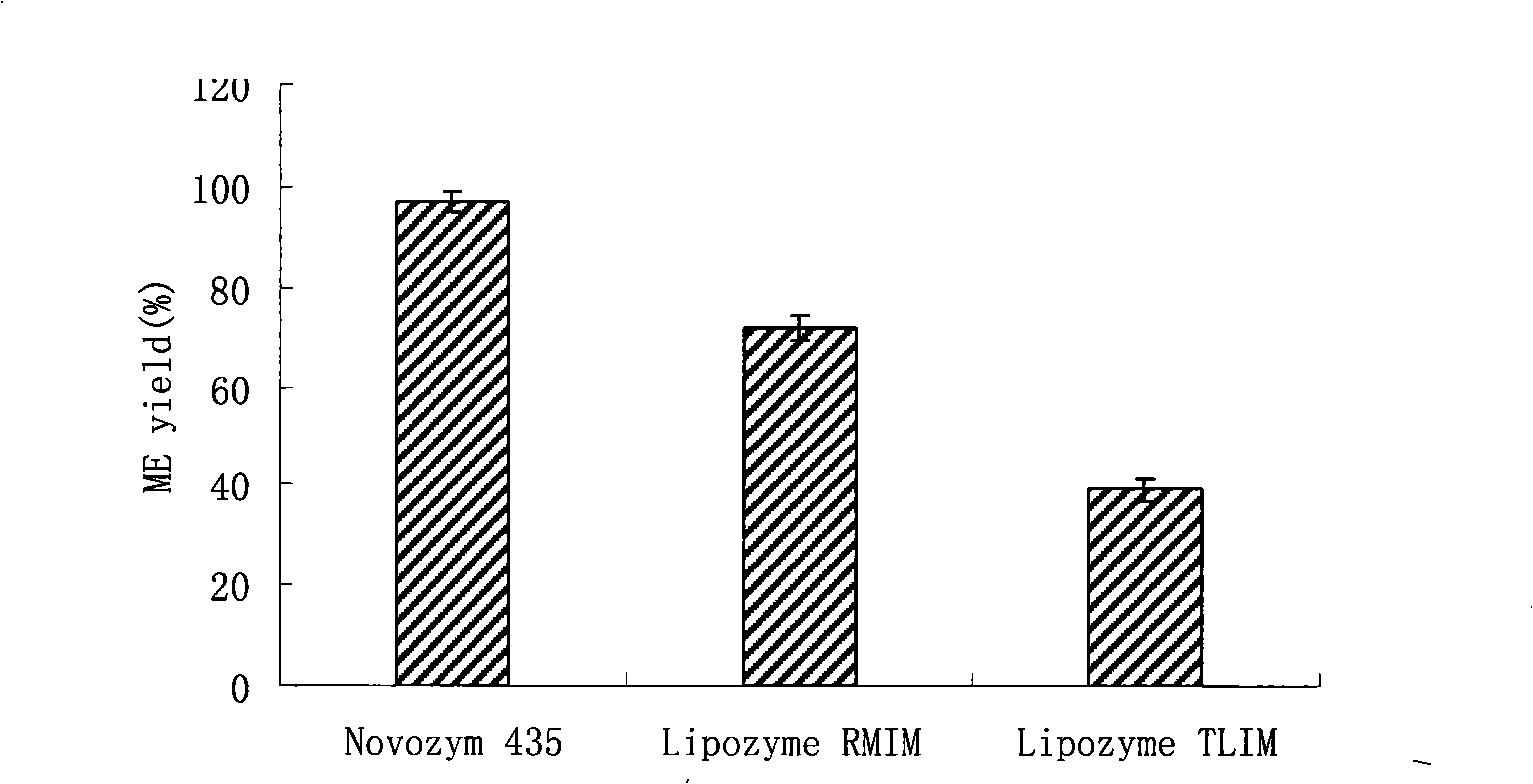
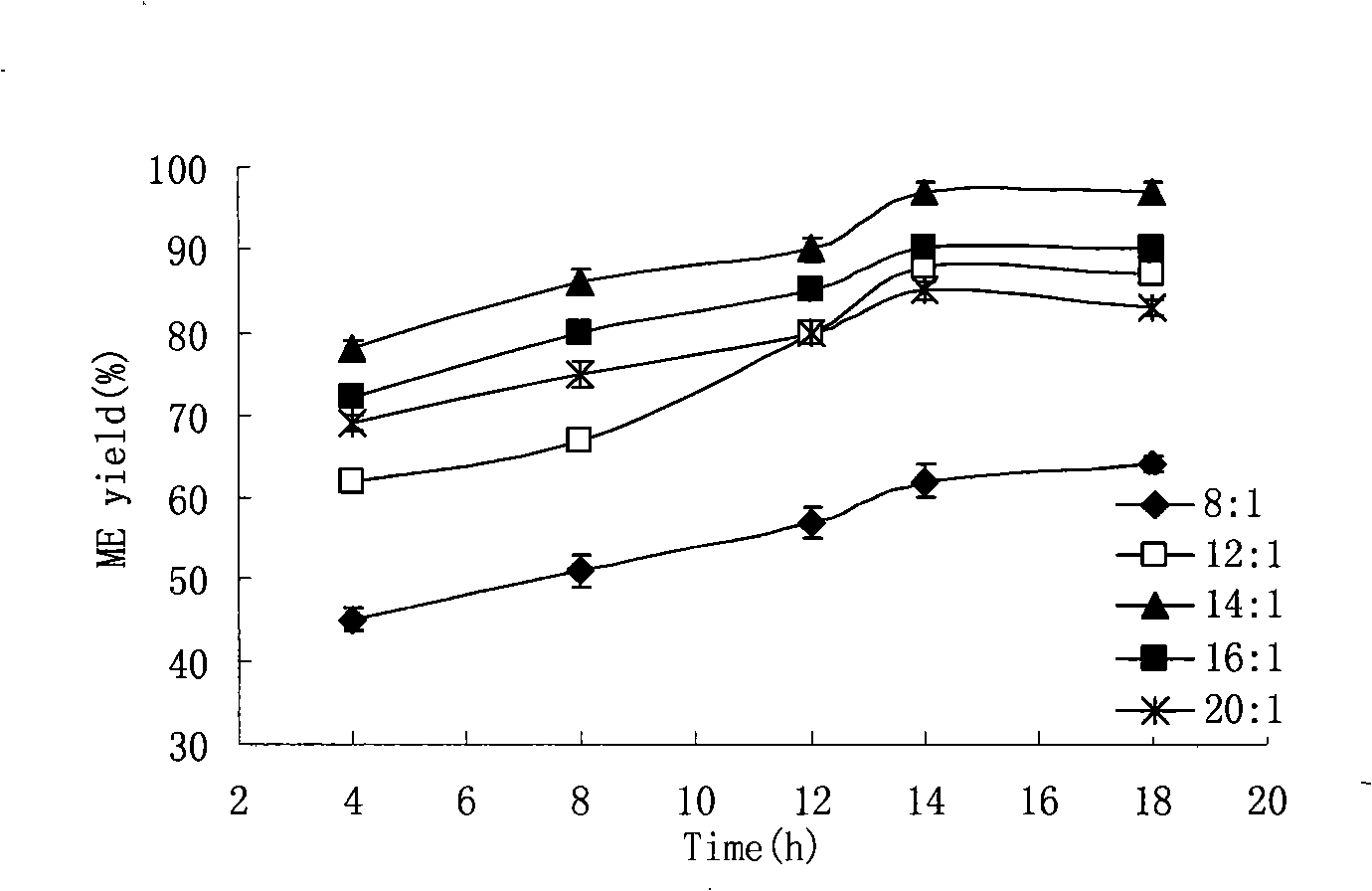
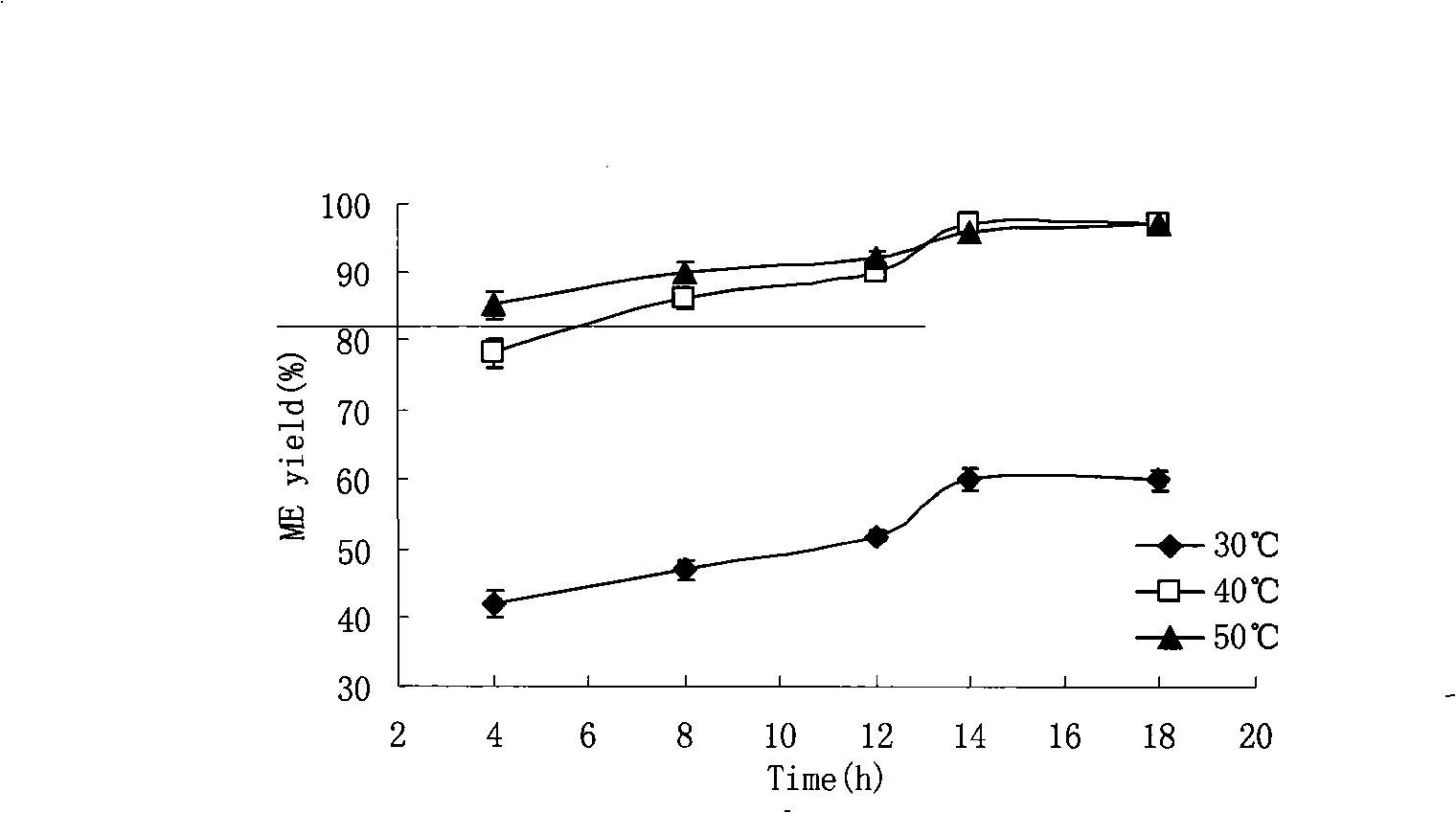
The invention relates to a preparation method of biodiesel which takes methyl acetate as acyl receptor. The preparation method is characterized in that methyl acetate is taken as acyl receptor, immobilized lipase Novozym 435 is used to catalyze various types of vegetable oil, the reactions are performed under the conditions that the mole ratio between the methyl acetate and the vegetable oil is (12 to 16):1, the addition level of the Novozym 435 enzyme is 30 percent of the vegetable oil, the reaction temperature is 40 DEG C and the reaction time lasts for 10 to 14 hours, however, the methyl acetate is adopted to synthesize the biodiesel, the by-product of the reaction is glyceryl triacetate, which has no obvious negative impact on the catalytic activity of lipase, therefore, the lipase can be directly reclaimed without any treatment. The methyl ester yield of the biodiesel prepared through catalyzing refined soybean oil is 91 percent. According to the actual condition of China, cottonseed oil, colza oil and tea oil which are more appropriate for the national conditions of China are selected to study, and the methyl ester yield all reaches more than 90 percent, wherein, the methyl ester yield of the biodiesel prepared through catalyzing refined cottonseed oil reaches 97 percent.
Owner:黎洁
Method for synthetizing starch octenylsuccinate with enzymic method in ionic liquids
ActiveCN104480159AMild reaction conditionsIncrease reaction rateFermentationBulk chemical productionSolubilityNovozym 435
The invention discloses a method for synthetizing starch octenylsuccinate with an enzymic method in ionic liquids and belongs to the technical field of starch processing. The principle of the method is based on the fact that the acetic acid typeionic liquids with high cation concentration are used as efficient solvent environments for synthetizing the starch octenylsuccinate with the enzymic method, so that starch solubility is enhanced, lipase activity is kept, and the synthetizing efficiency of the starch octenylsuccinate with the enzymic method is significantly improved. According to the method, the two ionic liquids, namely, an ionic liquid 1 (Me(OEt)2-Al-Im)Ac and an ionic liquid 2 (Me(OEt)3-Al-Im)Ac, are designed and synthetized, then one of the two ionic liquids is used as a reaction solvent, 10% of common corn starch is added, subjected to pregelatinization treatment at the temperature of 100 DEG C for 10 minand cooled to the subsequent enzymic reaction temperature of 50 DEG C, octenyl succinic anhydrides accounting for 3% of the dry-basis mass of the starch and a lipase Novozym 435 accounting for 10% of the dry-basis mass of the starch are added for an esterification reaction for 30 min, a product is deposited and washed by 95% ethyl alcohol until the concentration of theanhydrides in a washing liquid is lower than 0.3%, the product is dried at the temperature of 40 DEG C and crushed, and a starch octenylsuccinate product with the substitution degree ranging from 0.014 to 0.019 is obtained.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
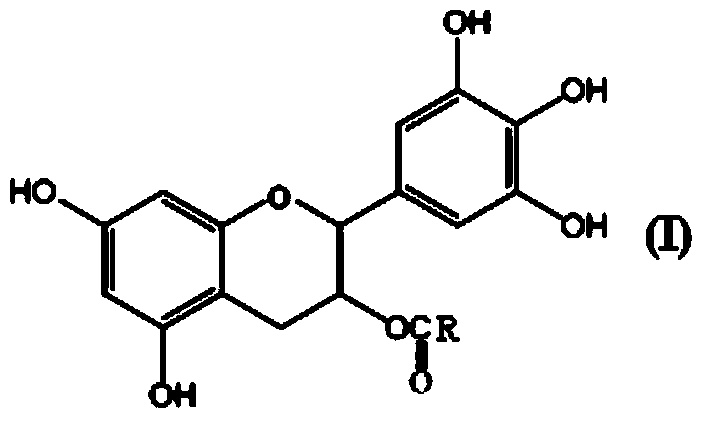
3-O-catechin higher fatty acid ester and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103524474AGood reaction selectivityIncrease fat solubilityOrganic chemistryFatty substance preservation using additivesSolubilityMolecular sieve
The invention discloses 3-O-catechin higher fatty acid ester represented by a formula (I) and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the steps as follows: lipase Novozym 435 is adopted as a catalyst; higher fatty acid is adopted as an acyl donator; a 4A molecular sieve is adopted as a water absorbing agent in an esterification reaction; and catechin long-chain fatty acid is prepared. A product has good lipid solubility and oxidation resistance, and the 3-O-catechin higher fatty acid ester has an important significance on structural modification of flavonoid compounds.
Owner:BIOCHEM ENG COLLEGE OF BEIJING UNION UNIV
Ester zymoid method production process of azeotropy water elimination coupling simulated moving bed
ActiveCN101429529AImprove conversion rateHigh yieldChemical recyclingFermentationChromatographic separationBiotechnology
The invention belongs to the biotechnology field of non-aqueous phase enzymatic organic synthesis application, and particularly relates to an ester enzyme method production process for an azeotropic dewatering coupling simulated moving bed. The process is applied to the synthesis of various ester bonds by catalysis of a biological catalyst (such as Novozym 435). The invention provides a commonly used ester enzyme method synthesis novel process; in the premise of not affecting the catalytic activity of the biological catalyst, the process can continuously remove water by decompression azeotropy and make the reaction balance move towards the ester synthesis, thereby greatly improving the conversion rate of the enzymatic organic synthesis, ensuring the complete reaction and thoroughly solving the continuous dewatering problem in the non-aqueous phase enzymatic organic synthesis; by the coupling of the enzymatic reaction system and the simulated moving bed chromatographic separation system, the process can ensure the complete separation of reaction products and excessive reaction materials, solve the problem of recycling the excessive reaction materials, improve the conversion rate of raw materials, the product yield and the product purity to be nearly 100 percent, greatly lower production cost, realize the zero emission of waste water and waste residue during the production of ester chemical products and has wide application prospect in fields such as medicine, food, material, fine chemical industry.
Owner:南京宏瑞药业有限公司
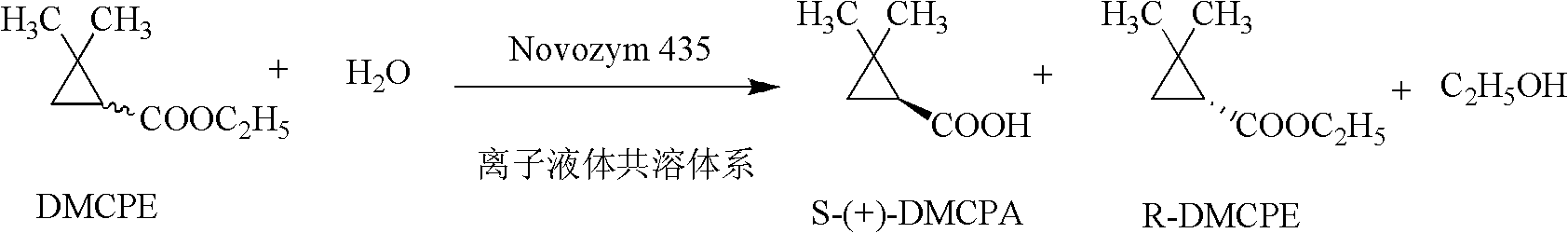
Preparation method of (S)-(+)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylic acid by biocatalysis
The invention discloses a novel preparation method of (S)-(+)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylic acid by biocatalysis. The method uses ethyl 2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate as substrate and Novozym 435 lipase as biological catalyst, then biological catalyst asymmetric hydrolysis reaction is carried out on the mixture at a temperature of 25-45 DEG C and at pH ranging from 6.0-8.0 in a water phase reaction system, after the reaction is completed, the reaction solution is isolated to obtain (S)-(+)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylic acid. The asymmetric hydrolysis reaction utilizes Novozym 435 lipase to catalyze ethyl 2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate, therefore, the enzyme specificity is strong, the catalytic efficiency is high, no side product is generated, and the optical purity and yield of the product are both higher than those of the product obtained by chemical methods.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Ester exchange method synthesizing process of aryl acetic acid (propionic acid) L-ascorbic acid ester
InactiveCN102827893AMultiple conversion rate increasesHigh yieldOrganic chemistryChemical recyclingPhenyl acetic acidPropanoic acid
The invention belongs to the field of nonaqueous phase enzymatic organic synthesis, in particular to an ester exchange method synthesizing process of aryl acetic acid (propionic acid) L-ascorbic acid ester. The process is applicable to synthesis of the aryl acetic acid (propionic acid) L-ascorbic acid ester under catalysis of a biocatalyst (such as Novozym 435). The synthesizing process provides a commonly-used synthesizing process of the aryl acetic acid (propionic acid) L-ascorbic acid ester, can move to a ester synthesizing direction in balance through decompression and continuous alcohol removal on premises of influencing no catalytic activity of the biocatalyst, accordingly improves conversion rate of the enzymatic organic synthesis and guarantees reaction to trend to completion. Through simulated moving bed chromatography separation, through separation of reaction products and excess reaction raw materials are guaranteed, circulation and reuse problems of the excess reaction raw materials are solved, the conversion rate, product yield and product purity of the raw materials are all improved to be close to 100%, cost of production is substantially lowered, zero discharge of waste water and waste residues of product production is achieved, and the synthesizing process has wide application prospects in fields such as medicines and fine chemical engineering.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
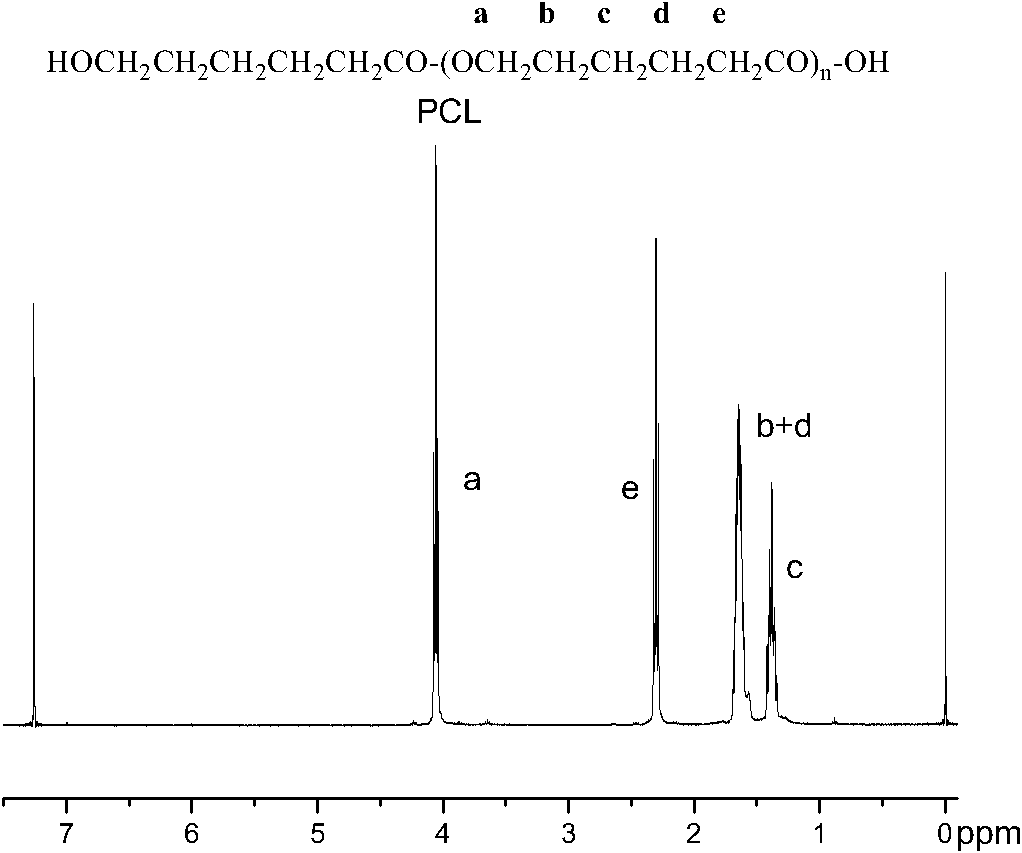
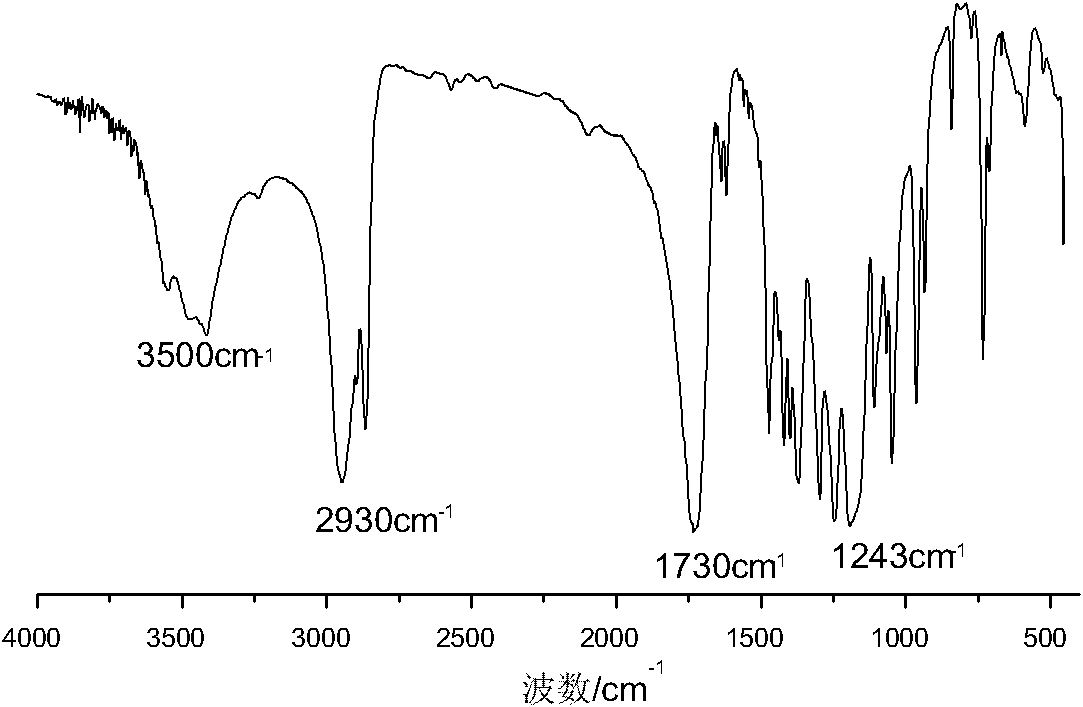
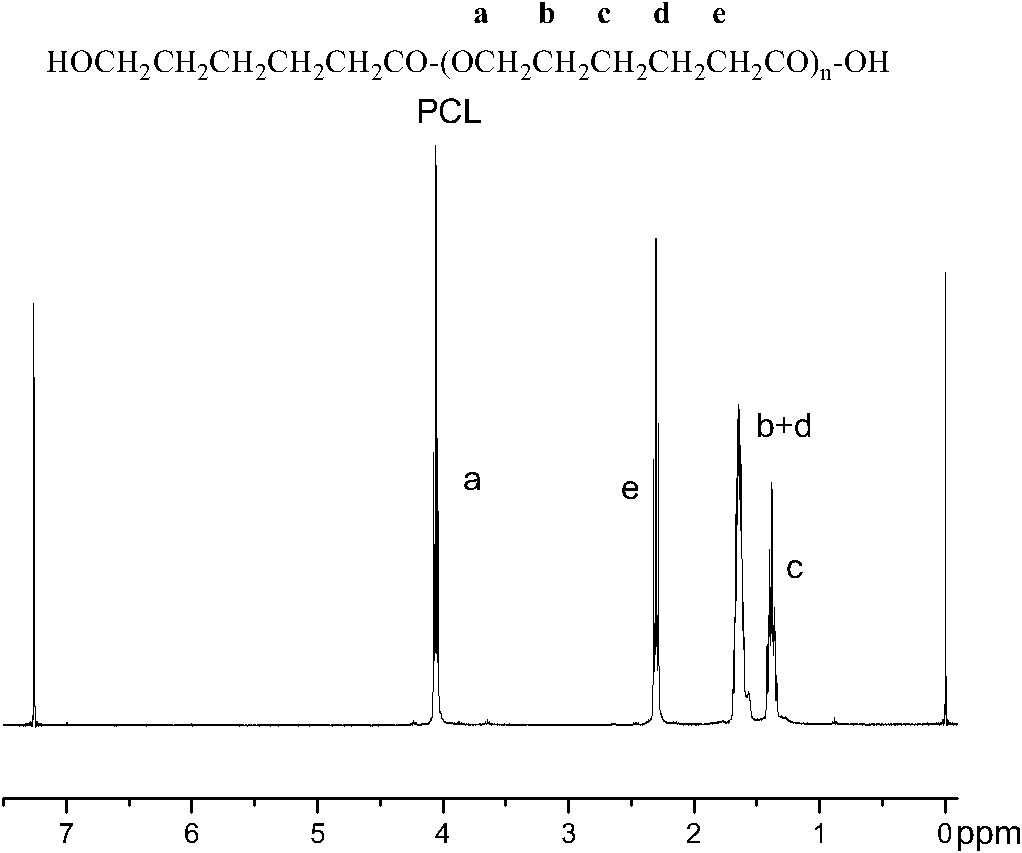
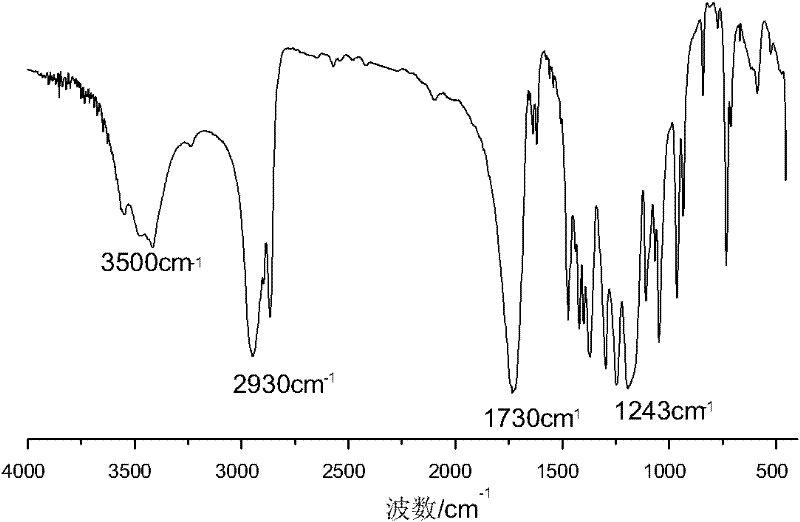
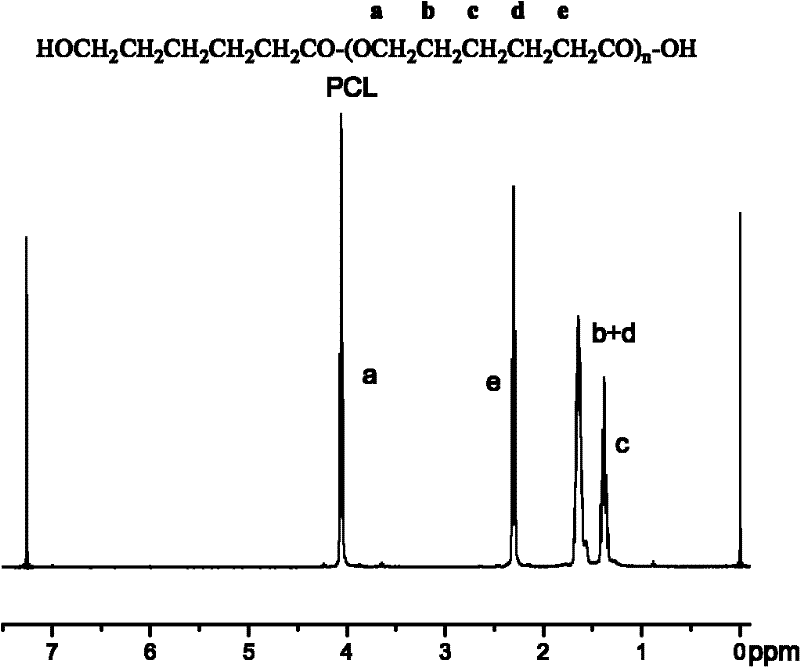
Synthesis of medicinal biodegradable poly(epsilon-caprolactone) and application method thereof
InactiveCN101831468ASimple processThe process is gentle and controllableSurgeryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsNovozym 435Solution polymerization
The invention relates to synthesis of medicinal biodegradable poly(epsilon-caprolactone) and an application method thereof in the field of high polymer chemistry technique. The medicinal biodegradable poly (epsilon-caprolactone) can be obtained by separating and purifying the reactant after epsilon-caprolactone and immobilized lipase Novozym 435 are mixed and reacted at the temperature of between 60 and 80 DEG C for 2 to 48 hours by using a mass polymerization method or a solution polymerization method in a closed reaction system. Due to the adoption of the immobilized lipase Novozym 435 which serves as a catalyst, the biodegradable poly (epsilon-caprolactone) can be prepared by the method which has the advantages of no catalyst residue and easy control of conditions.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
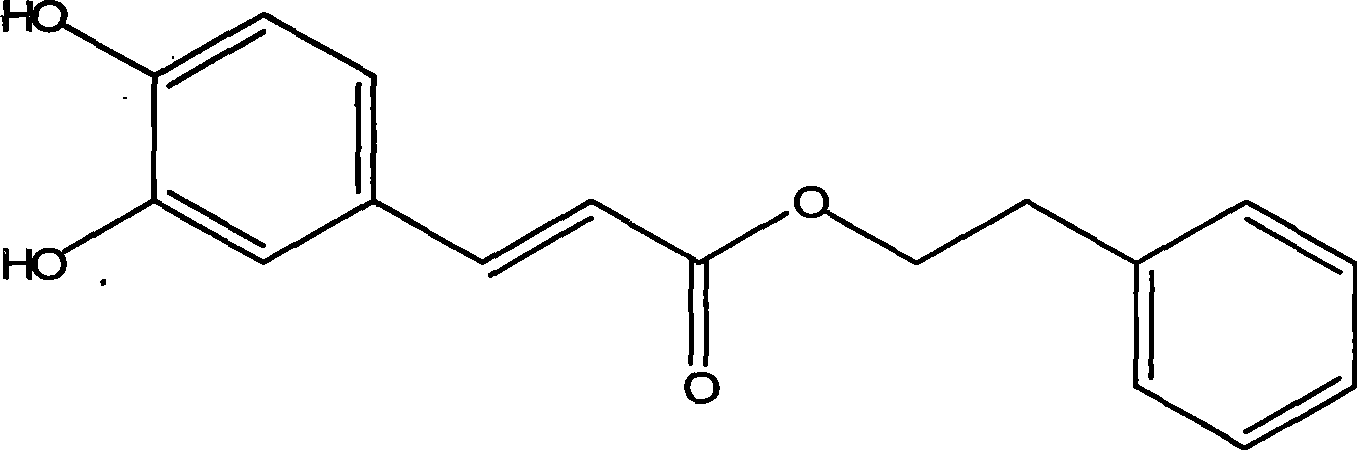
Method for enzymatic synthesis of caffeic acid phenethyl ester by solvent-free system
InactiveCN101392272AIncrease concentrationHigh selectivityFermentationEnzymatic synthesisAcrylic resin
The invention relates to a method for producing caffeic acid phenethyl ester by carrying out the enzymatic synthesis of a solvent-free system, which comprises the steps: (1) a 4-type molecular sieve and phenethyl alcohol are placed in a triangular flask according to a mass ratio of 1 to 5 and protected form light; and after shaking on a shaker for 48h, the molecular sieve is removed, thus obtaining anhydrous phenethyl alcohol; (2) caffeic acid reacts with the phenethyl alcohol for 32h to 60h under the catalytic reaction of Novozym 435(lipase from C.antarctica on macroporous acrylic resin) lipase; the mole ratio of the caffeic acid and the phenethyl alcohol is 1: 86 to 1: 96, and reaction temperature is controlled to be 60 DEG C to 70 DEG C; and (3) after reaction, a biological catalyst is removed by filtering; the residual phenethyl alcohol is removed by rotary evaporation, thus obtaining caffeic acid phenethyl ester after the isolation and purification of column chromatography. The synthesizing method of the invention promotes the concentration of substrates and products and reaction selectivity; the yield rate of the caffeic acid phenethyl ester is up to 90 percent approximately; the reaction condition of the method is safe and mild and purification process is easy and has few steps, thus being convenient to industrialized production.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
A synthesis technology of decompressed azeotropic continuous dewatering esterase enzyme method
The invention belongs to the technical field of biotechnology of non-water phase enzymatic organic synthesis application, and particularly relates to a synthesis technology of decompressed azeotropic continuous dewatering esterase enzyme method. The technology is suitable for the synthesis of each ester bond under the catalysis of biocatalyst (such as Novozym 435). The invention provides a universally applicable novel synthesis technology using esterase enzyme method, and can carry out continuous dewatering through decompressed azeotropy under the condition that the catalytic activity of the biocatalyst is not influenced, so as to lead the balanced reaction to move towards the synthetic direction of ester, thereby greatly increasing the conversion rate of enzymatic organic synthesis, ensuring the completion of the reaction; completely solving the problem of non-water phrase enzymatic organic synthesis, increasing purity and yield of the product and reducing manufacturing cost. The invention has wide application prospect in the fields of medicine, food, material, fine chemistry industry, etc.
Owner:河北兴润生物科技股份有限公司
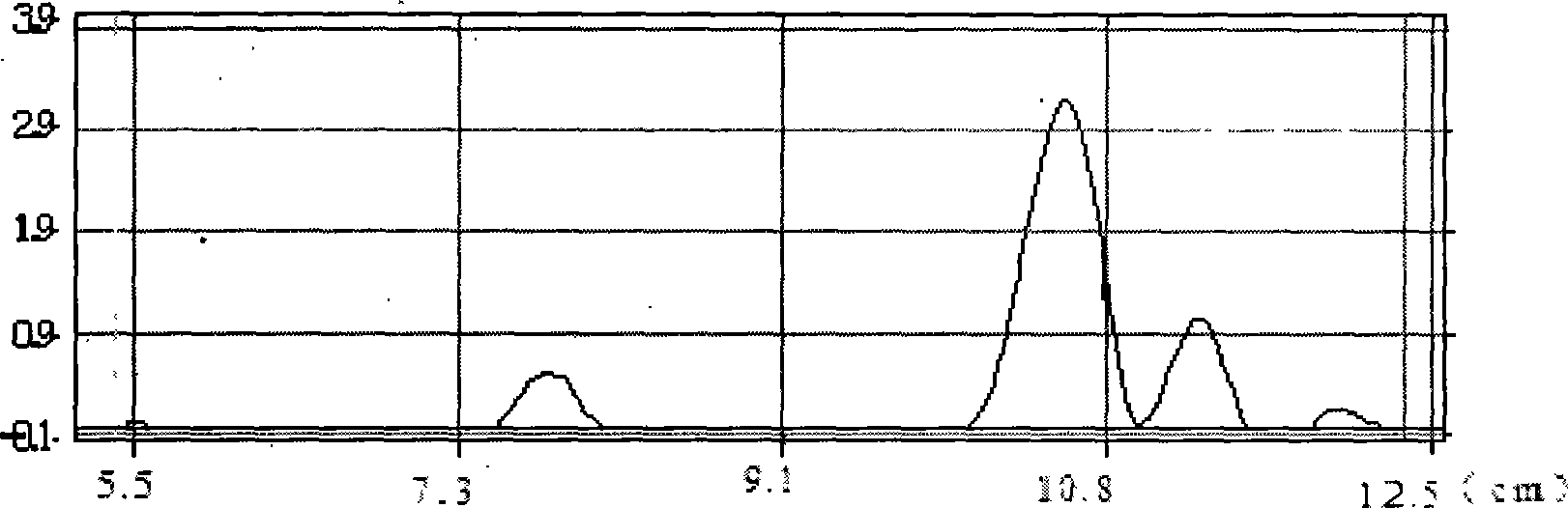
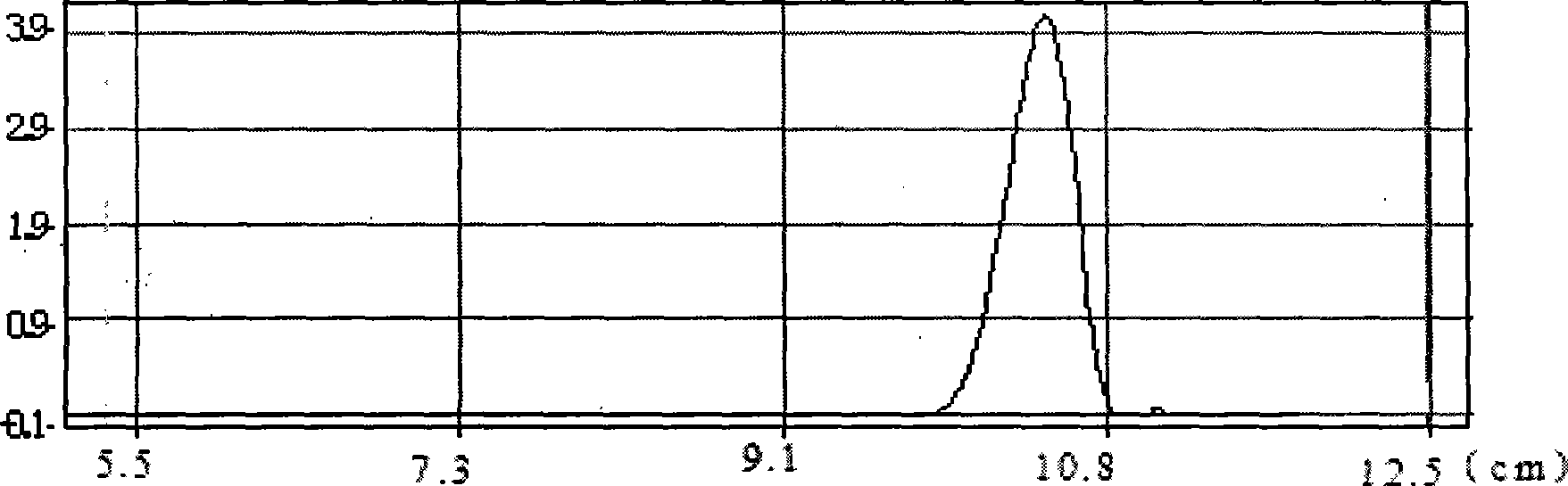
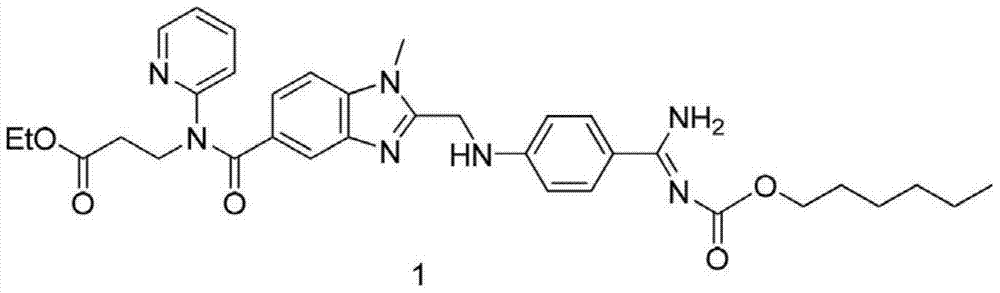
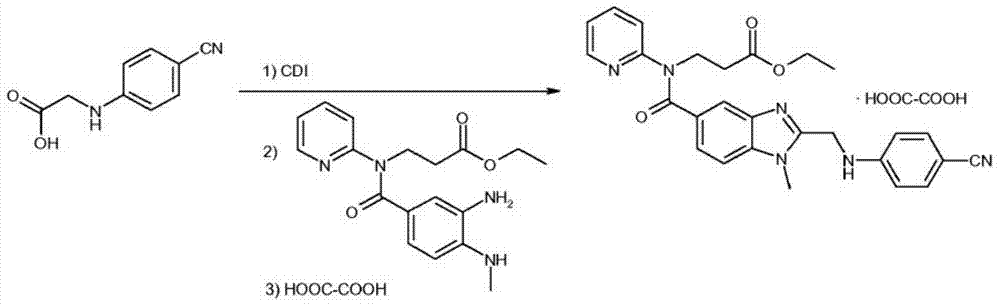
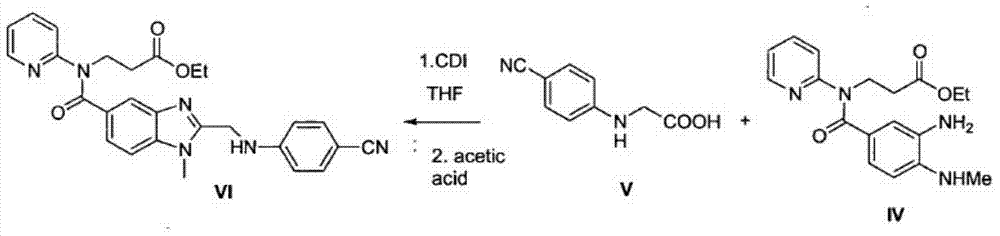
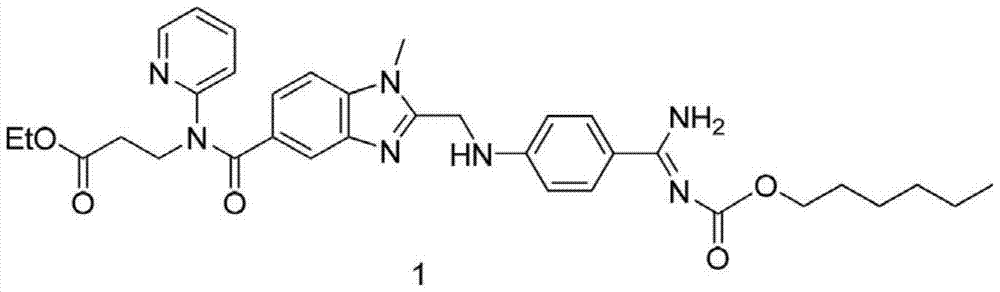
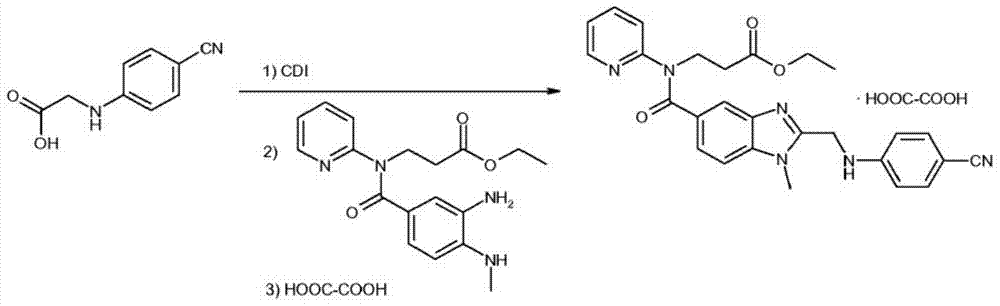
Method for preparing main intermediate of dabigatran etexilate through enzymatic reaction
ActiveCN103710406AHigh activityHigh activity and high selectivityFermentationBulk chemical productionPropanoic acidNovozym 435
The invention discloses a method for preparing a main intermediate of dabigatran etexilate through enzymatic reaction. The main steps are as follows: first, 3-[4-methylamino-3-amino-N-(2-pyridyl)-benzamido]-ethyl acrylate and 2-(4-cyano aniline) acetic acid are added in a reaction solvent, mixed and dissolved; immobilized enzyme Novozym 435 is added and reaction is carried out; second, after the reaction is finished, the immobilized enzyme Novozym 435 is removed through filtration, an organic phase layer and a filtrate are obtained; third, the obtained organic layer is subjected to solvent evaporation, and an oil-like substances are obtained, acetic acid is added and a reflux reaction is carried out; fourth, after the reaction is finished, acetic acid is evaporated, ethyl acetate and an alkaline solution are added, washing and extraction are carried out, the obtained organic layer is subjected to drying by distillation, and 3-[[[2-[[(4-cyano phenyl)amino] methyl]-1-methyl-1H-benzimidazole-5-group] carbonyl] pyridine-2-group amino] ethyl propionate ethyl ester. The method has simple operations and mild reaction conditions, the product with high purity is easy to obtain, the yield is high and the method is suitable for industrial amplification production.
Owner:BENGBU BBCA MEDICINE SCI DEV
Process for biotransformation of fat into ascorbic acid fatty acid ester
InactiveCN101319240ARealize environment-friendly productionImprove conversion rateFermentationAlcoholNovozym 435
The invention discloses a process for synthesizing ascorbyl fatty acid ester, which starts from natural raw materials, is carried out by a biocatalytic mode, is relatively cheap, has high yield, and is environment-friendly. The process, under the catalysis of a biocatalyst (such as Novozym 435), takes alcohol as a medium and combines a fat alcoholysis reaction between fat and the alcohol with an ester exchange reaction between ascorbic acid and fatty acid ethyl ester together to realize the transformation of the fat to the ascorbyl fatty acid ester, which completely roots out the pollution threat of the prior chemical production technology to the environment, remarkably improves the yield and the purity of a product, and has a byproduct, namely pure glycerol. The process consists of the following methods: the fat and the alcohol react at a temperature of between 55 and 60 DEG C under the catalysis of enzyme, and the produced glycerol is recovered and removed; then the ascorbic acid is added, the fatty acid ethyl ester and the ascorbic acid react at a temperature of between 55 and 60 DEG C under the catalysis of the enzyme, and the produced alcohol is recovered and removed to produce the ascorbyl fatty acid ester.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for preparing functional grease by ester exchange between frozen and separated heavy-phase rice bran oil and conjugated linoleic acid
The invention provides a method for preparing functional grease by ester exchange between frozen and separated heavy-phase rice bran oil and conjugated linoleic acid. The method comprises the following steps of taking white clay as a crystallizing agent; carrying out gradient freezing centrifugation to enable saturated fatty acid of the rice bran oil to be enriched; and carrying out ester exchangeon the conjugated linoleic acid under the catalysis of Novozym 435 lipase to prepare the functional grease. The recycling problem of an organic solvent is solved, and the high value of rice bran is improved. With the improvement of the unsaturation degree, the thermal stability of an unsaturated fatty acid complex is gradually reduced, and due to the influence of factors such as crystallization temperature and conditions, different structural components in mixed fatty acid can be separated and enriched. The technological conditions of gradient freezing centrifugation separation of the rice bran oil are selected; and a result shows that the optimal conditions for preparing the functional grease are that the adding amount of the lipase is 9%, the reaction temperature is 60 DEG C, the reaction time is 24 hours, the obtained grease is rich in phytosterol, oryzanol and tocopherol, and the CLA esterification rate is 38%.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
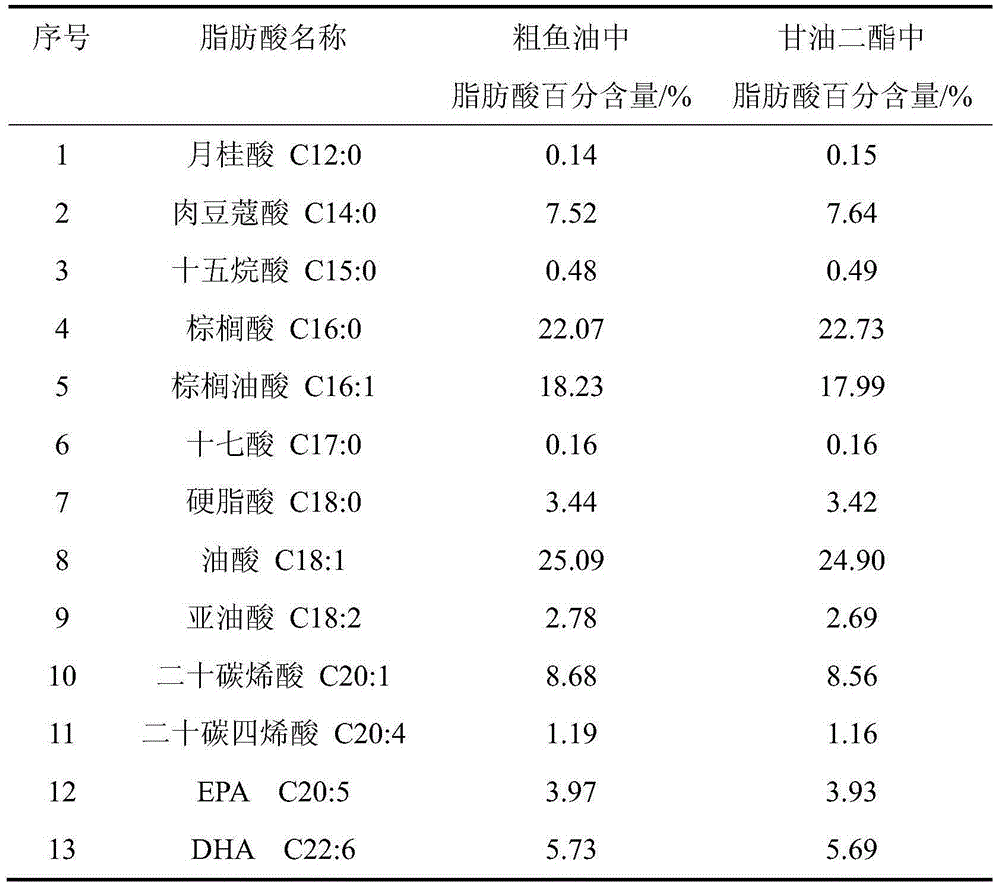
Method for preparing diglyceride from crude fish oil of marine aquatic fishes
The invention discloses a method for preparing diglyceride from crude fish oil of marine aquatic fishes, wherein the method comprises the following steps: (1) uniformly mixing a crude fish oil raw material from marine aquatic fishes with glycerol; (2) adding 0.1-1.0% of immobilized lipase Lipozyme TMIM, Lipozyme TLIM or Novozym 435 to the materials of the step (1), stirring at rate of 150-170r / min and reacting at 40-80 DEG C for 6-10h; (3) after the reaction, filtering or centrifuging the materials of the step (2), and removing the immobilized lipase so as to obtain a mixture containing diglyceride; and (4) obtaining a finished diglyceride product from the mixture obtained from the step (3) through molecular distillation or silica gel chromatography. The method disclosed by the invention can achieve synthesis researches of the diglyceride by taking the crude fish oil prepared from leftovers of marine aquatic fishes as a raw material; and the method is capable of effectively improving the use value of aquatic leftovers, increasing the additional value of low-value fishes and reducing environmental pollution, and the method is conducive to the creation of economic and social benefits.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY +1
Method for preparing (S)-(+)-2,2-dimethyl cyclopropane methanoic acid by biological resolution in ionic liquid cosolvent
ActiveCN102559833BImprove solubilityImprove stabilityFermentationBulk chemical productionNovozym 435Solvent
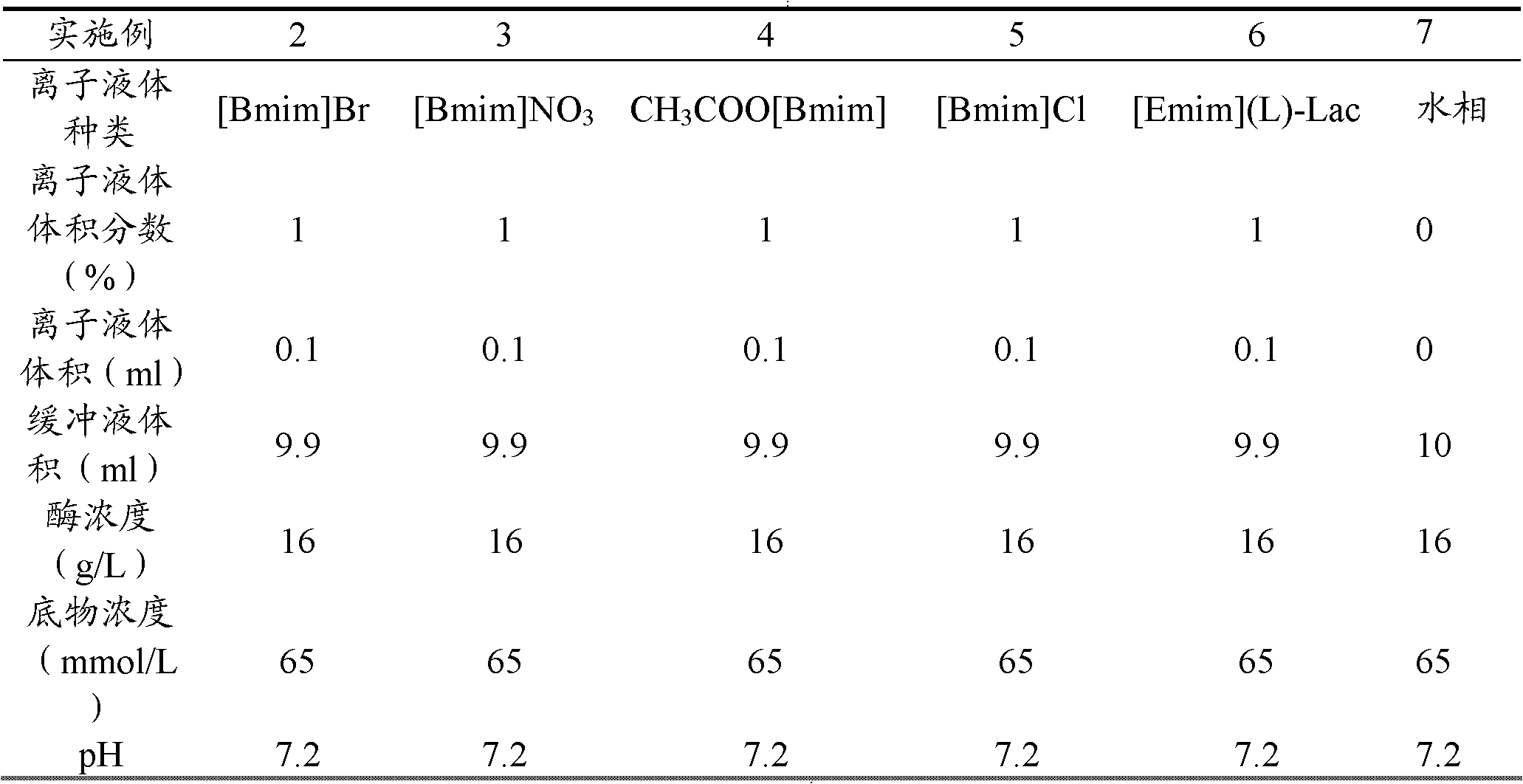
The invention provides a method for preparing (S)-(+)-2,2-dimethyl cyclopropane methanoic acid by biological resolution in a water-ionic liquid cosolvent system. The method comprises the following steps of: performing biological catalytic asymmetric hydrolysis reaction by taking racemic 2,2-dimethyl cyclopropane ethyl formate as a substrate and lipase Novozym 435 as a biocatalyst at the temperature of 30 DEG C at a speed of 200 revolutions / minute in the water-ionic liquid cosolvent system which is formed by mixing a phosphate buffer solution of which the pH value is between 6.0 and 7.8 and a hydrophilic ionic liquid for 24 to 56 hours, and after reacting, separating and purifying a reaction solution to obtain the (S)-(+)-2,2-dimethyl cyclopropane methanoic acid. According to the method, a biological resolution effect of catalyzing the 2,2-dimethyl cyclopropane ethyl formate by the lipase Novozym 435 can be improved effectively by a reaction system containing the hydrophilic ionic liquid cosolvent; and by solubilizing the substrate, the concentration of the reacted substrate is improved from 65 mmol / L during water-phase conversion to 100 mmol / L, the yield is up to 47.1 percent, and the reaction time is shortened to 52 hours from 64 hours during the water-phase conversion.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing cigarette spice with plum flavor and milk flavor
ActiveCN101747993AEasy to transform and decomposeReduce rateTobacco treatmentEssential-oils/perfumesLiquid glucoseNovozym 435
The invention relates to a method for preparing cigarette spice with plum flavor and milk flavor, comprising the following steps: mixing 20-40 portions by weight of Alpha-linoleic acid, 40-60 portions by weight of glutamic acid and 10-30 portions by weight of Chinese medicinal herb extract H-005 according to proportion so as to obtain the mixture used as substrate; adding liquid glucose, propylene glycol and water to a reactor, controlling the temperature of the reactor at 35-45 DEG C and stirring the liquid glucose, the propylene glycol and the water without stop; adding and stirring evenly lipase Novozym 435 to the substrate, and adding the mixture of the lipase Novozym 435 and the substrate to the reactor to make the mixture react for 6-10h to obtain the cigarette spice. The ratio of the weight portions of the substrate, the liquid glucose, the propylene glycol and the water is 1:2-4:4-6:1-3, and the addition amount of the lipase Novozym 435 is 1-2 per mill of the total addition amount of the substrate, the liquid glucose, the propylene glycol and the water. The method for preparing the cigarette spice has low cost, and the cigarette spice prepared with the method has strong plum flavor and the milk flavor and little mixed gases and is suitable for producing high-quality cigarette.
Owner:YINGTAN HUABAO FLAVORS & FRAGRANCES
Method for preparing biodiesel by utilizing Chinese tallow kernel oil
The invention relates to a method for preparing biodiesel by utilizing Chinese tallow kernel oil. The method comprises the following steps of: adding 4.0 grams of the Chinese tallow kernel oil to a 50mL glass conical flask with a stopper, adding methanol according to the methanol-oil ratio of 3-5, adding 5%-6% by weight of molecular sieves, adding 2%-3% by weight of enzymes Novozym 435 and 1%-2% by weight of enzymes Lipozyme TLIM by taking a proper amount of tert-butyl alcohol as a solvent, and placing into a temperature-controlled shaking table at 35-40 DEG C for reaction; centrifugalizing and sampling after 6-10 hours, and calculating transformation ratio. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for preparing the biodiesel through a biological enzyme method by adopting the Chinese tallow kernel oil, is moderate in reaction condition and environmental-friendly, sufficiently utilizes the Chinese tallow kernel oil and provides an advisable method for relieving energy shortage.
Owner:QINGDAO JIENENG ENERGY SAVING ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Method for splitting 2-phenylpropionic acid enantiomer by catalyzing esterification of Novozym 435 lipase
The invention relates to a novel chiral splitting method for obtaining an enantiomer of (R)-2-phenylpropionic acid, which belongs to the technical field of biochemical splitting of chiral compounds. By using the stereoselectivity of Novozym 435, the catalytic esterification of a 2-phenylpropionic acid enantiomer in (S)-2-phenylpropionic acid is carried out with high catalytic efficiency to synthesize (S)-2-n-hexyl phenylpropionate, the remaining unreacted substrate is high optical purity (R)-2-phenylpropionic acid, the substrate conversion rate is 97.23%, the enantiomeric excess value is 89.20%, and the target enantiomer yield is 5.24 %. Compared with other methods, the method has the advantages of simple reaction system, high reaction concentration, fast reaction rate, high optical purityof target products, environmental protection, and simple post-treatment.
Owner:HUNAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Stable black rice anthocyanin monomer and molecular modification preparation method
ActiveCN109706205AImprove stabilityImprove purification efficiencySugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationNovozym 435Freeze-drying
The invention relates to a molecular modification method for improving the stability of a black rice anthocyanin monomer (cyaniding-3-glucoside, C3G). The specific steps are as follows: (1) cleaning and impurity removing; (2) pulverization and extraction; (3) centrifugation; (4) resin purification; (5) nanofiltration concentration; (6) vacuum freeze-drying; (7) C3G extraction purification; (8) vacuum freeze-drying; (9) enzymatic modification of C3G; (10) separation of C3G modified product; and (11) vacuum freeze-drying. The method firstly uses the mild conditions to separate and purify the black rice anthocyanin monomer C3G from the black rice to ensure the integrity of a reaction substrate; and then performs the enzymatic modification of the C3G, the whole process is safe, efficient, thereaction condition is mild and easy to control, the selected Novozym 435 lipase has strong specificity and the modified product is single, s preparative liquid chromatography can be used for efficientseparating and purifying, and the modified product is dried by a vacuum freeze-drying technology to maximize the stability of the anthocyanin structure.
Owner:安徽一雄生物科技有限公司
Method for biosynthesizing sterol ester through esterification and ester interchange in vacuum solvent-free system
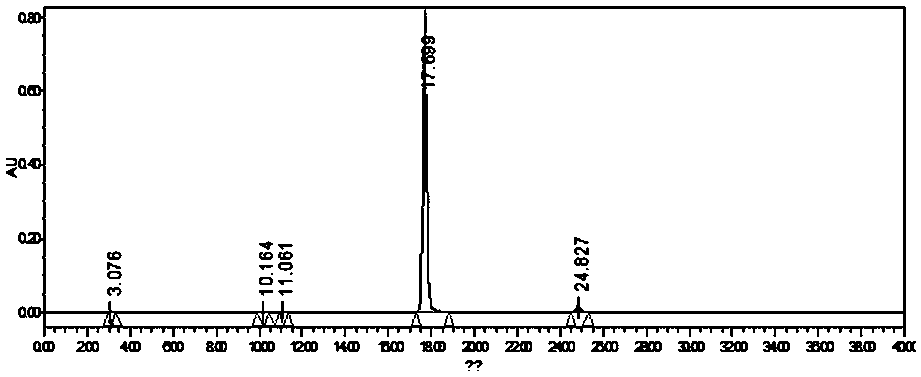
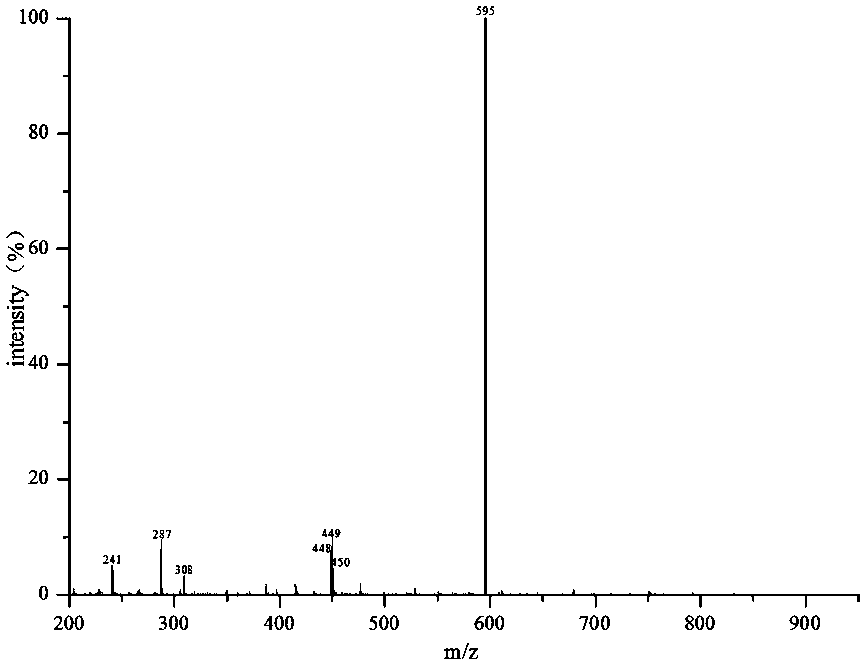
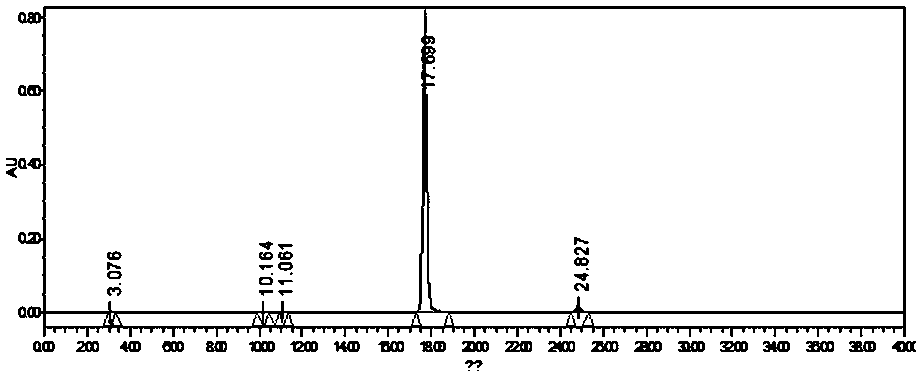
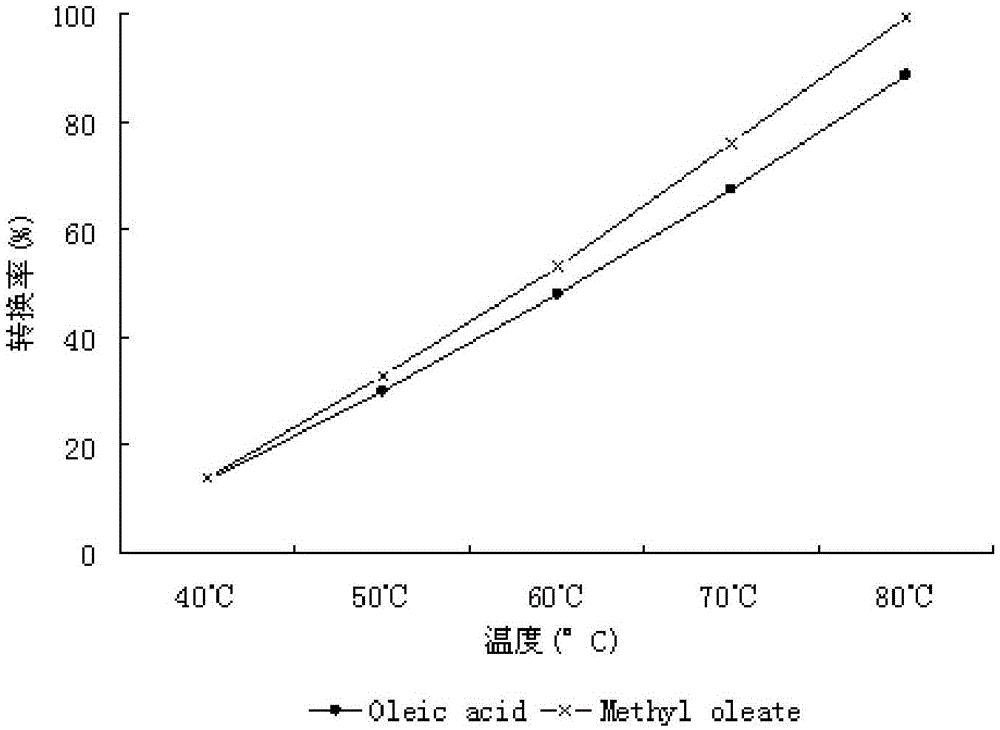
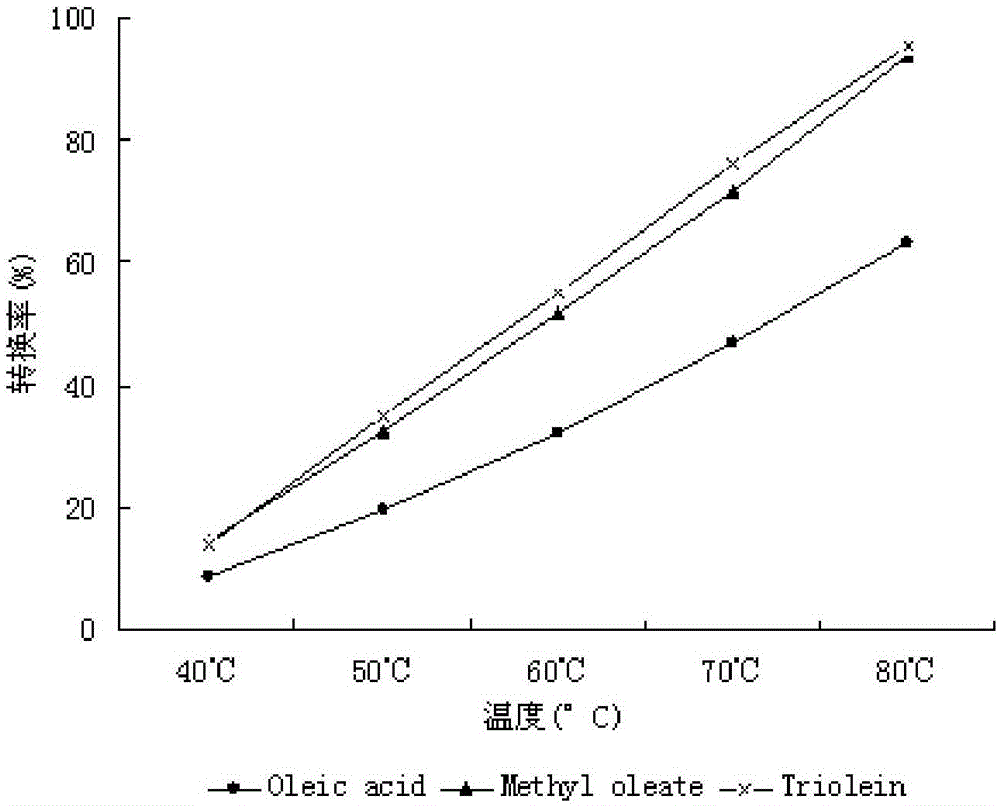
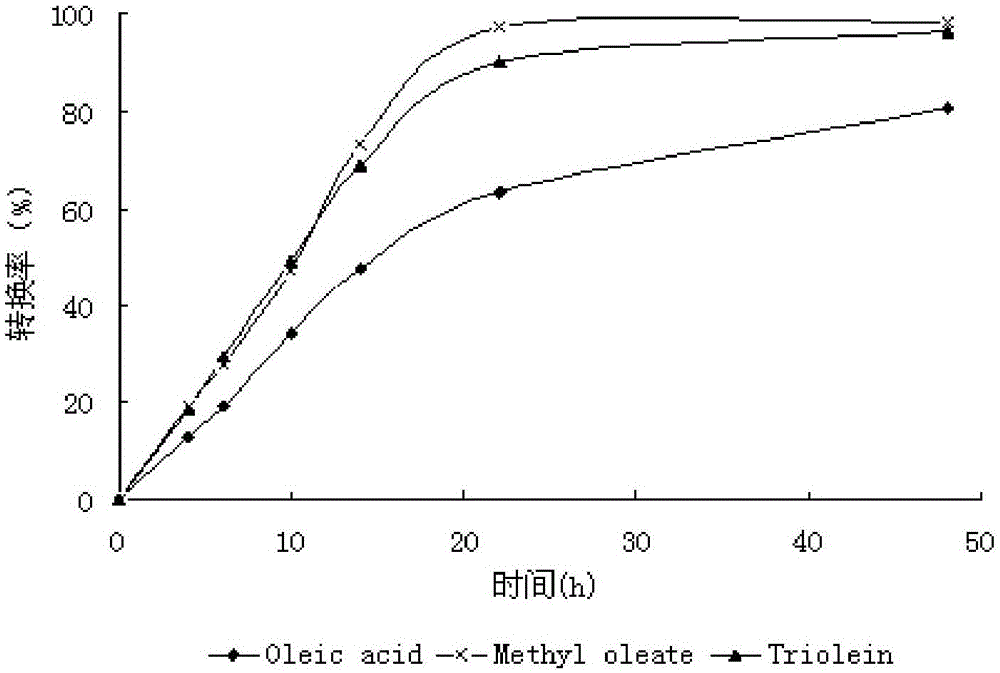
A method for biosynthesizing sterol ester through esterification and ester interchange in a vacuum solvent-free system is characterized in that corresponding long-chain acyl ester is generated through esterification of sterol and oleic acid and ester interchange of methyl oleate and triglyceride at a high conversion rate under vacuum solvent-free added water-free reaction conditions with immobilized lipase Lipozyme IM and Novozym 435 as a catalyst. Ester interchange of sterol and methyl oleate is carried out under optimum reaction conditions, and the immobilized lipase Lipozyme IM still has a conversion rate being greater than 90% even after the immobilized lipase Lipozyme IM is repeatedly used 10 times, and the lipase Novozym 435 still has a conversion rate being greater than 40% after the lipase Novozym 435 is repeated used 10 times.
Owner:SOYBEAN TECH DEV RES CENT HEILONGJIANG PROV
A method for resolution and preparation of optically pure r-2-naphthylethylamine
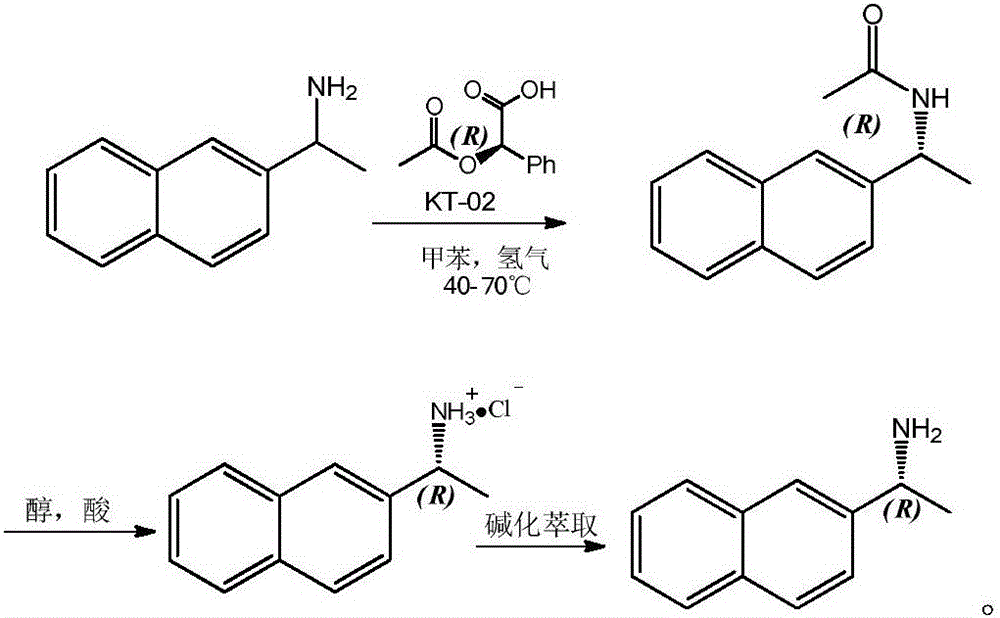
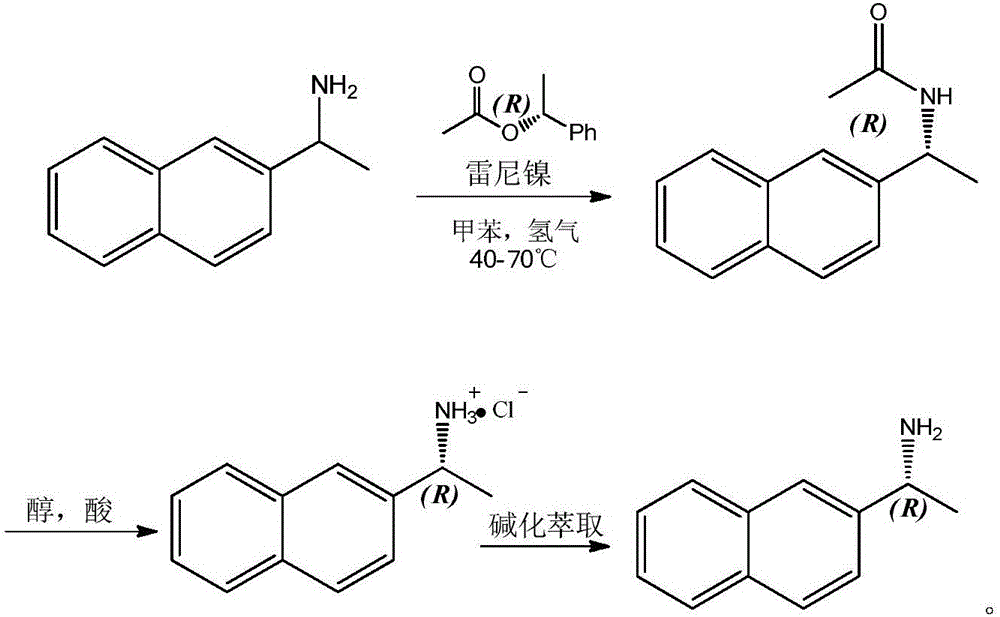
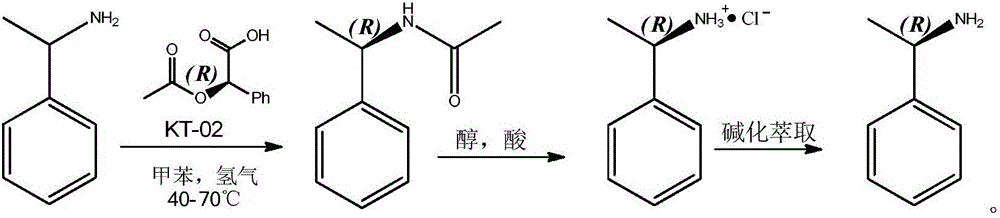
ActiveCN104152528BHigh yieldHigh optical purityOrganic compound preparationFermentationHydrogenNovozym 435
The invention relates to a method for preparing R-2-naphthylethylamine by dynamic kinetic resolution. Using 2‑naphthylethylamine as raw material, Novozym 435 as resolution catalyst, D‑(‑)‑O‑acetylmandelic acid as acyl donor, KT‑02 (nickel catalyst) as racemization catalyst, in autoclave 2-Naphthylethylamine is completely converted to obtain (R)-(1-(2-naphthyl)ethyl)acetamide (ee value 99%); acidolysis is carried out after amide purification to obtain R-2 ‑Naphthylethylamine salt, the salt is then basified, extracted, dried, concentrated, etc. to obtain R‑2‑naphthylethylamine. The product yield of each step can reach more than 90%, and the ee value is greater than 99%. The invention has the characteristics of cheap and easy to obtain racemic catalyst, complete utilization of raw materials, good product yield, high optical purity and the like. In the production and preparation of R-2-naphthylethylamine, it has great guidance and application value.
Owner:陈永军
A method for resolution and preparation of optically pure r-2-naphthylethylamine
ActiveCN104152527BHigh yieldHigh optical purityOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationHydrogenNovozym 435
Owner:六安佳诺生化科技有限公司
Method for preparing low-energy SLS (sodium lauryl sulfate) type structure lipid by utilizing secondary enzymolysis
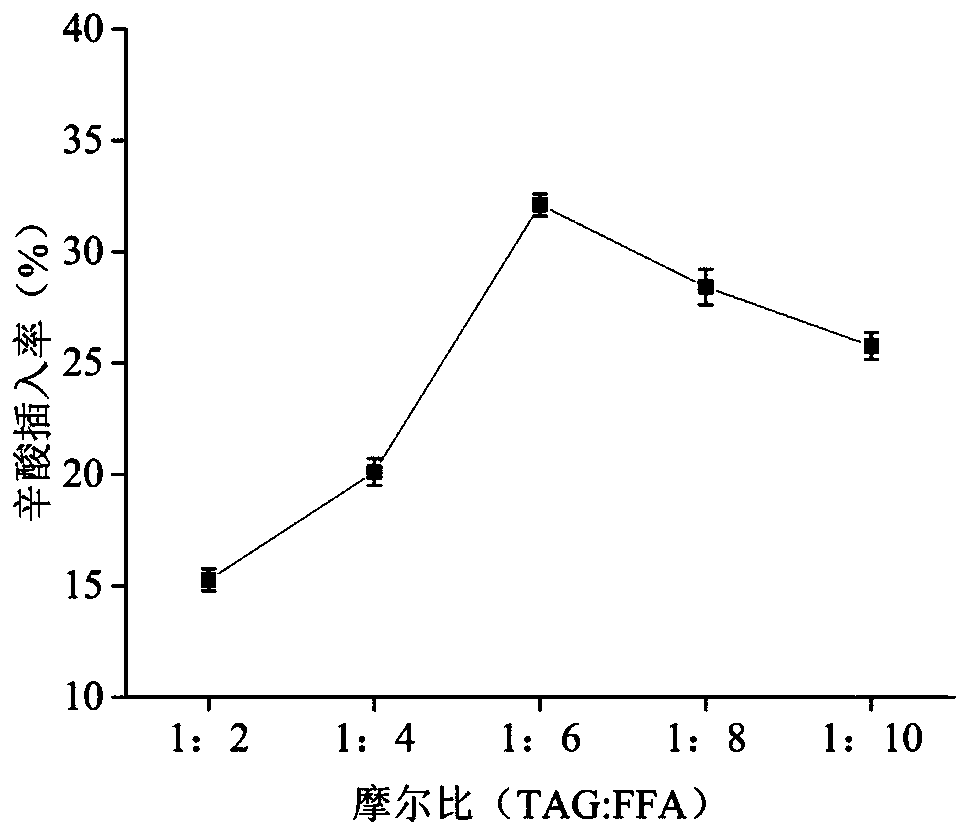
The invention provides a method for preparing low-energy SLS (sodium lauryl sulfate) type structure lipid by utilizing secondary enzymolysis. According to the method, first grade bean oil, ethyl alcohol and acetic acid are used as raw materials; lipase Novozym 435 is utilized; then, a secondary enzyme method combing alcoholysis and esterification is adopted for preparing the low-energy SLS type structure lipid; through the method, the yield of the low-energy SLS type structure lipid can be effectively improved, and the reaction time is shortened. Compared with the structure lipid synthesized by a one-step method, fatty acid obtained by a two-step method has higher insertion rate and higher product yield. The method has the advantages that esterification process parameters such as reaction time, enzyme adding quantity, substrate mole ratio, reaction temperature and the like are optimized; the reaction is carried out in the optimum state, the acetic acid insertion rate is 64.5 percent, and the purity of low-energy grease after molecular distillation purification is 94.3 percent; the basis is provided for a subsequent industrial production low-energy grease process.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
A synthesis technology of decompressed azeotropic continuous dewatering esterase enzyme method
The invention belongs to the technical field of biotechnology of non-water phase enzymatic organic synthesis application, and particularly relates to a synthesis technology of decompressed azeotropic continuous dewatering esterase enzyme method. The technology is suitable for the synthesis of each ester bond under the catalysis of biocatalyst (such as Novozym 435). The invention provides a universally applicable novel synthesis technology using esterase enzyme method, and can carry out continuous dewatering through decompressed azeotropy under the condition that the catalytic activity of the biocatalyst is not influenced, so as to lead the balanced reaction to move towards the synthetic direction of ester, thereby greatly increasing the conversion rate of enzymatic organic synthesis, ensuring the completion of the reaction; completely solving the problem of non-water phrase enzymatic organic synthesis, increasing purity and yield of the product and reducing manufacturing cost. The invention has wide application prospect in the fields of medicine, food, material, fine chemistry industry, etc.
Owner:河北兴润生物科技股份有限公司
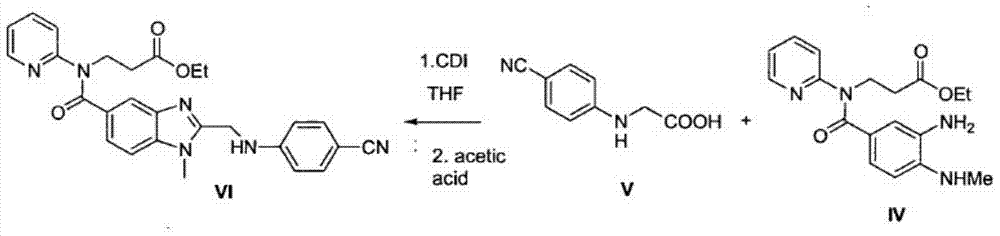
A kind of method that enzymatic reaction prepares main intermediate of dabigatran etexilate
ActiveCN103710406BHigh activityHigh activity and high selectivityFermentationBulk chemical productionPropanoic acidNovozym 435
The invention discloses a method for preparing a main intermediate of dabigatran etexilate through enzymatic reaction. The main steps are as follows: first, 3-[4-methylamino-3-amino-N-(2-pyridyl)-benzamido]-ethyl acrylate and 2-(4-cyano aniline) acetic acid are added in a reaction solvent, mixed and dissolved; immobilized enzyme Novozym 435 is added and reaction is carried out; second, after the reaction is finished, the immobilized enzyme Novozym 435 is removed through filtration, an organic phase layer and a filtrate are obtained; third, the obtained organic layer is subjected to solvent evaporation, and an oil-like substances are obtained, acetic acid is added and a reflux reaction is carried out; fourth, after the reaction is finished, acetic acid is evaporated, ethyl acetate and an alkaline solution are added, washing and extraction are carried out, the obtained organic layer is subjected to drying by distillation, and 3-[[[2-[[(4-cyano phenyl)amino] methyl]-1-methyl-1H-benzimidazole-5-group] carbonyl] pyridine-2-group amino] ethyl propionate ethyl ester. The method has simple operations and mild reaction conditions, the product with high purity is easy to obtain, the yield is high and the method is suitable for industrial amplification production.
Owner:BENGBU BBCA MEDICINE SCI DEV
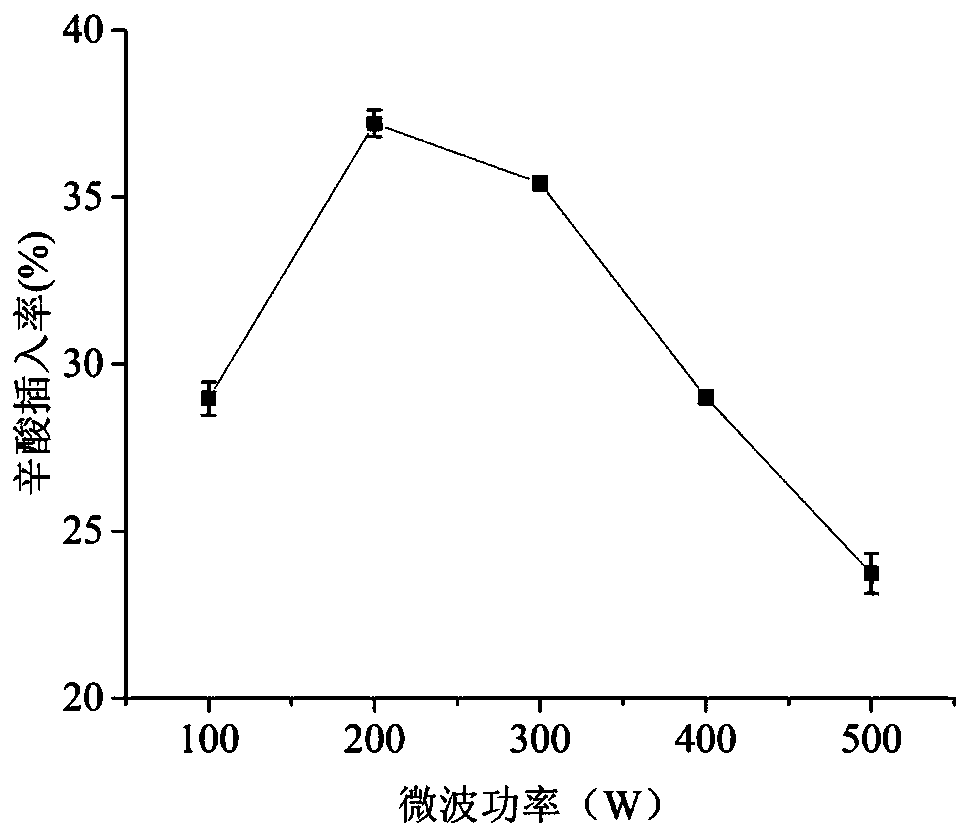
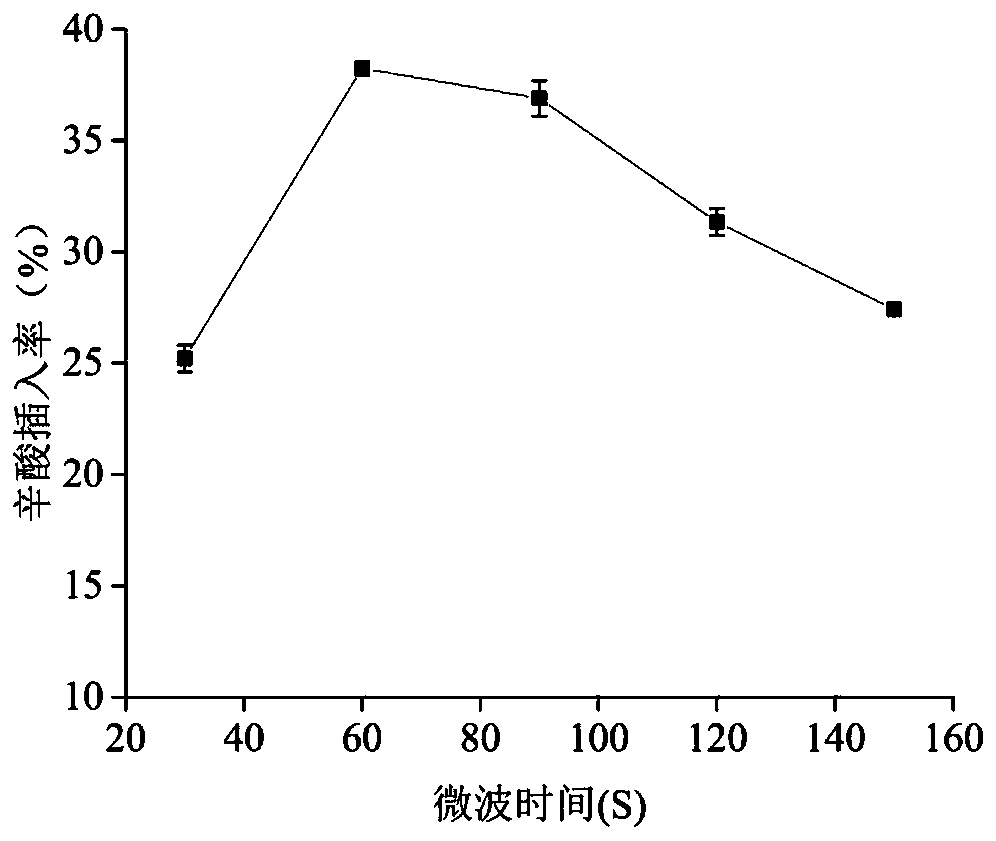
Method for synthesizing low-calorie structure lipid by using microwave treatment with assistance of enzymolysis
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a low-calorie structure lipid by using microwave treatment with the assistance of enzymolysis, and belongs to the field of preparation of structure lipids. The preparation method comprises the specific steps that 1, caprylic acid and rapeseed oil are weighed in a certain molar ratio and put into 50 mL conical flasks with covers, and a certain amount (based on the total substrate mass) of immobilized Novozym 435 lipase is added; 2, the conical flasks are placed in a microwave instrument and pretreated for a certain time at different microwave powers; 3, the conical flasks are placed in a constant temperature water bath oscillator at 200 r / min to carry out a reaction for different time at different reaction temperatures; 4, rotary evaporationis conducted at the temperature of 40 DEG C to remove an organic solvent, and a product is obtained. Through single factor experiments, the optimal material proportion, enzyme adding amount, microwave pretreatment time, microwave power, reaction temperature and reaction time are determined. The method solves the problem that a traditional method for synthesizing the low-calorie structure lipid through transesterification is low in synthesizing efficiency. In the method, microwave treatment is combined with enzymolysis, the method is simple in process and saves energy sources, and the reactionefficiency can be well improved.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Ester zymoid method production process of azeotropy water elimination coupling simulated moving bed
ActiveCN101429529BImprove conversion rateHigh yieldChemical recyclingFermentationChromatographic separationBiotechnology
The invention belongs to the biotechnology field of non-aqueous phase enzymatic organic synthesis application, and particularly relates to an ester enzyme method production process for an azeotropic dewatering coupling simulated moving bed. The process is applied to the synthesis of various ester bonds by catalysis of a biological catalyst (such as Novozym 435). The invention provides a commonly used ester enzyme method synthesis novel process; in the premise of not affecting the catalytic activity of the biological catalyst, the process can continuously remove water by decompression azeotropy and make the reaction balance move towards the ester synthesis, thereby greatly improving the conversion rate of the enzymatic organic synthesis, ensuring the complete reaction and thoroughly solving the continuous dewatering problem in the non-aqueous phase enzymatic organic synthesis; by the coupling of the enzymatic reaction system and the simulated moving bed chromatographic separation system, the process can ensure the complete separation of reaction products and excessive reaction materials, solve the problem of recycling the excessive reaction materials, improve the conversion rate ofraw materials, the product yield and the product purity to be nearly 100 percent, greatly lower production cost, realize the zero emission of waste water and waste residue during the production of ester chemical products and has wide application prospect in fields such as medicine, food, material, fine chemical industry.
Owner:南京宏瑞药业有限公司
Enzymatical method for synthesizing water-soluble ferulic acyl glyceride
InactiveCN101200738ASolve processing problemsShort reaction timeFermentationNovozym 435Synthesis methods
An enzymic synthesis method of an oil-soluble feruloyl glyceride belongs to the technical field of the comprehensive utilization of the agricultural byproduct ferulic acid. The present invention synthesizes the oil-soluble feruloyl glyceride which has the functions of antioxidation and ultraviolet absorption by the reaction of ferulic acid ethyl ester and glycerin under the effect of Novozym 435 lipase by a pressure-reduction rotary biological reaction vessel. The present invention realizes that the transformation rate of the ferulic acid ethyl ester is 100 percent, and the yield of the feruloyl glyceride is 96 percent; the reaction time is shortened by more than 60 hours than an ordinary method, which is shorted to be less than 10 hours from 70 to 144 hours; the yield is improved by 1.5 times; the present invention successfully solves the problem that the enzymic catalysis synthesizes the oil-soluble feruloyl glyceride hardly. The pressure-reduction rotary biological reaction vessel can eliminate the influence of an external mass transfer on the reaction velocity; by-product ethanol can be removed well under the pressure reduction; the stir during the reaction is from the self rotation of the reaction vessel, which avoids the damage effect to immobilized enzyme caused by directly contacting and prolongs the service life of the enzyme.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
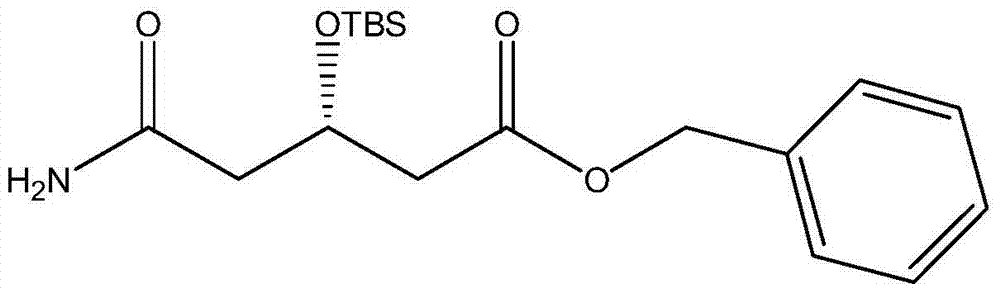
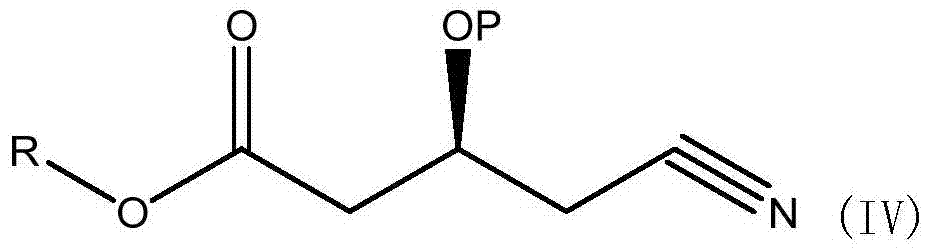
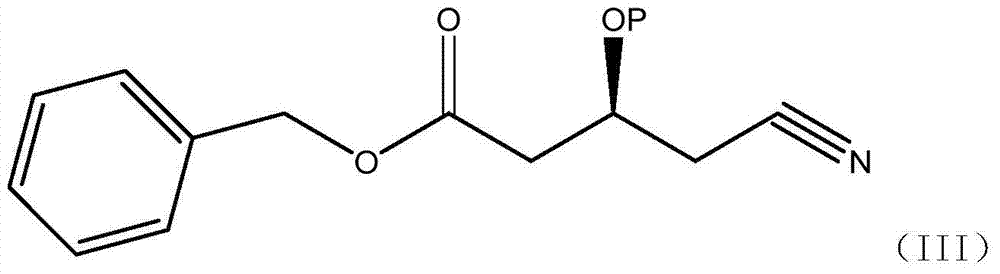
A kind of preparation method of (s)-tert-butyldimethylsiloxy-glutaric acid monobenzyl ester monoamide
ActiveCN104829644BHigher yield than the original processHigh process yieldGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsGlutaric acidNovozym 435
The invention discloses a preparation method of (S)-tert-butyldimethylsiloxy-glutaric acid monobenzyl monoamide, which belongs to the field of medicine. The method uses the compound (S)-4-cyano-3-hydroxybutyrate as a raw material, catalyzed by Novozymes lipase 435, and benzyl alcohol is transesterified to obtain (S)-4-cyano-3-hydroxybutyrate Benzyl ester, combined with TBSCl again, obtains TBS protection (S)-4-cyano-3-tert-butyldimethylsiloxane monobenzyl butyrate, and then oxidizes to obtain S)-3-tert-butyldimethyl Siloxyglutarate monobenzyl monoamide. Using NOVO‑435 to carry out transesterification to obtain benzyl ester has a higher yield than the original process, less waste, and avoids the pollution of titanium tetrachloride. Use hydrogen peroxide and alkali or catalytic oxidation of amides, less waste, and avoid the high-pollution oxidation method of manganese dioxide, and avoid the high-cost method of catalytic oxidation with Wilkinson precious metals. The process cost is lower and industrialization is easier.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LEPU PHARMA CO LTD
A kind of method for splitting and preparing optically pure r-1-phenethylamine
ActiveCN104152526BHigh optical purityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationFermentationHydrogenNovozym 435
The invention relates to a method for preparing R-1-phenethylamine through dynamic kinetic resolution. Using 1‑phenethylamine as raw material, Novozym 435 as resolution catalyst, D‑(‑)‑O‑acetylmandelic acid as acyl donor, KT‑02 (nickel catalyst) as racemization catalyst, in autoclave 1-Phenylethylamine is completely converted to obtain (R)-(1-Phenylethyl)acetamide (ee value 99%); acidolysis is carried out after purification of the amide to obtain R-1-Phenylethylamine Salt, the salt is then subjected to operations such as alkalization, extraction, drying, and concentration to obtain R-1-phenylethylamine, and the product yield and ee value of the whole step can reach more than 90%. The invention has the characteristics of cheap and easy-to-obtain racemization catalyst, complete utilization of raw materials, good product yield, high purity and the like. In the production and preparation of R-1-phenethylamine, it has great guidance and application value.
Owner:六安佳诺生化科技有限公司
Synthesis of medicinal biodegradable poly(epsilon-caprolactone) and application method thereof
InactiveCN101831468BSimple processThe process is gentle and controllableSurgeryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsNovozym 435Solution polymerization
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com