Patents
Literature
336 results about "Plasma activation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Plasma activation (or plasma functionalization) is a method of surface modification employing plasma processing, which improves surface adhesion properties of many materials including metals, glass, ceramics, a broad range of polymers and textiles and even natural materials such as wood and seeds. Plasma functionalization also refers to the introduction of functional groups on the surface of exposed materials. It is widely used in industrial processes to prepare surfaces for bonding, gluing, coating and painting. Plasma processing achieves this effect through a combination of reduction of metal oxides, ultra-fine surface cleaning from organic contaminants, modification of the surface topography and deposition of functional chemical groups. Importantly, the plasma activation can be performed at the atmospheric pressure using air or typical industrial gases including hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen. Thus, the surface functionalization is achieved without expensive vacuum equipment or wet chemistry, which positively affects its costs, safety and environmental impact. Fast processing speeds further facilitate numerous industrial applications.
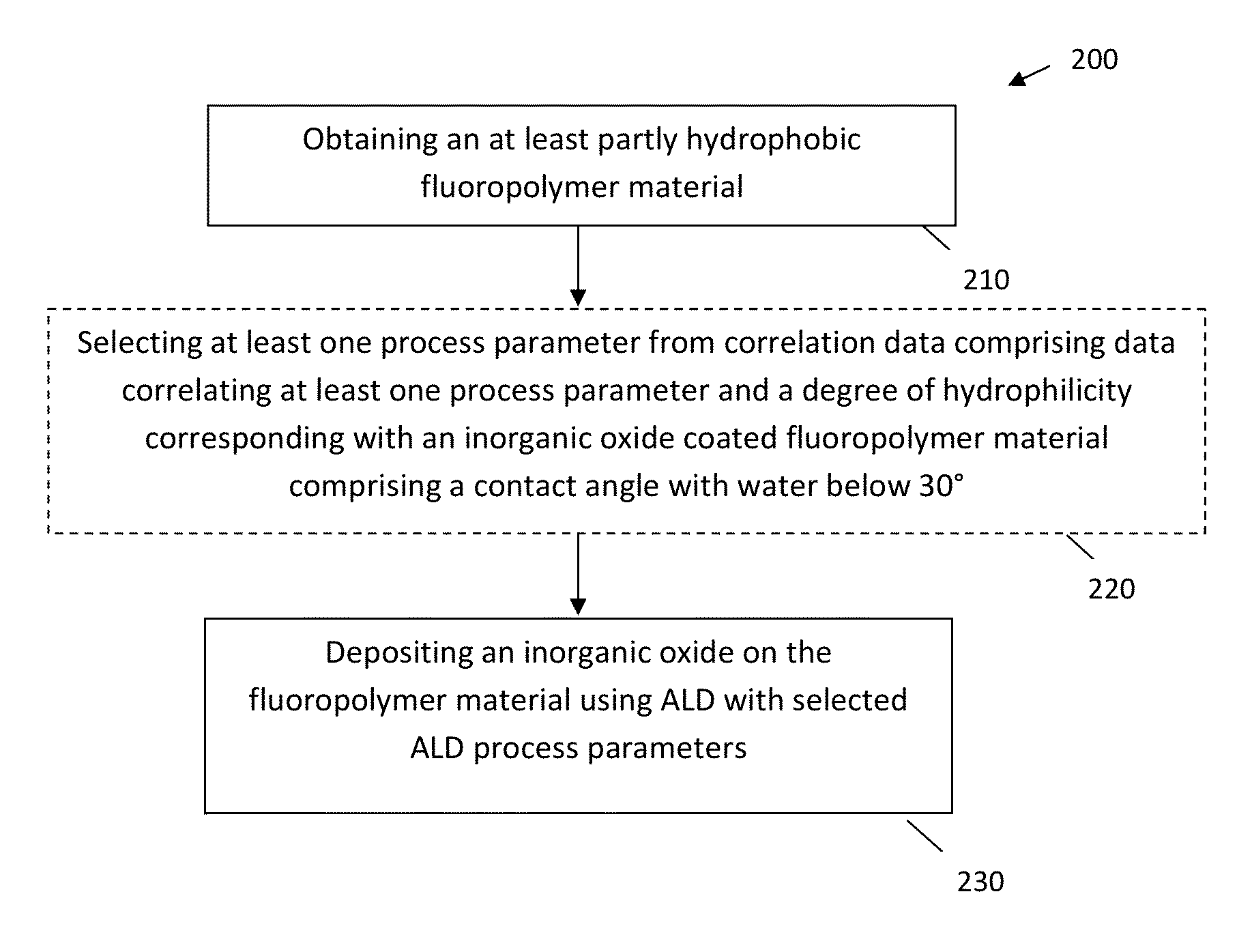
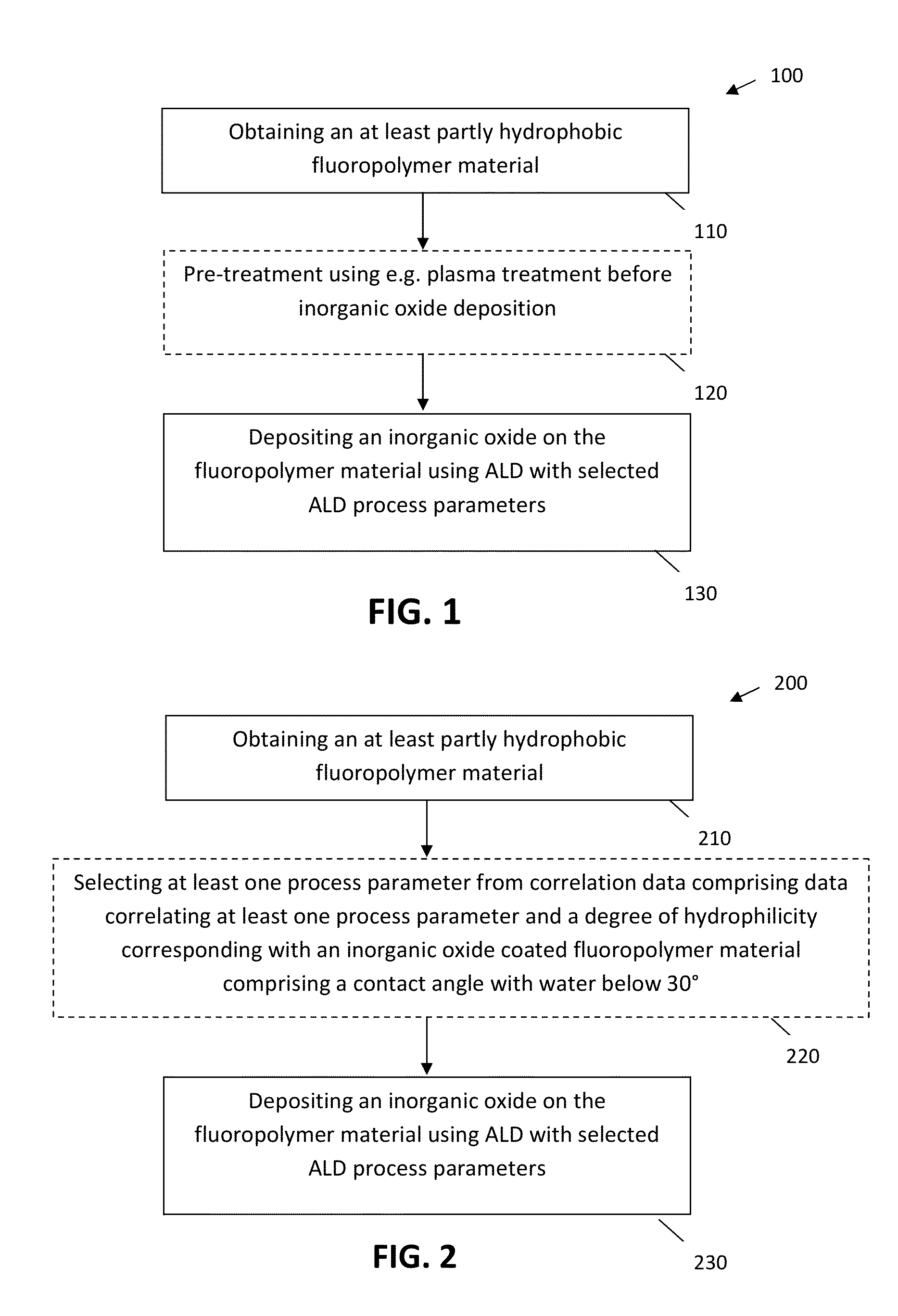
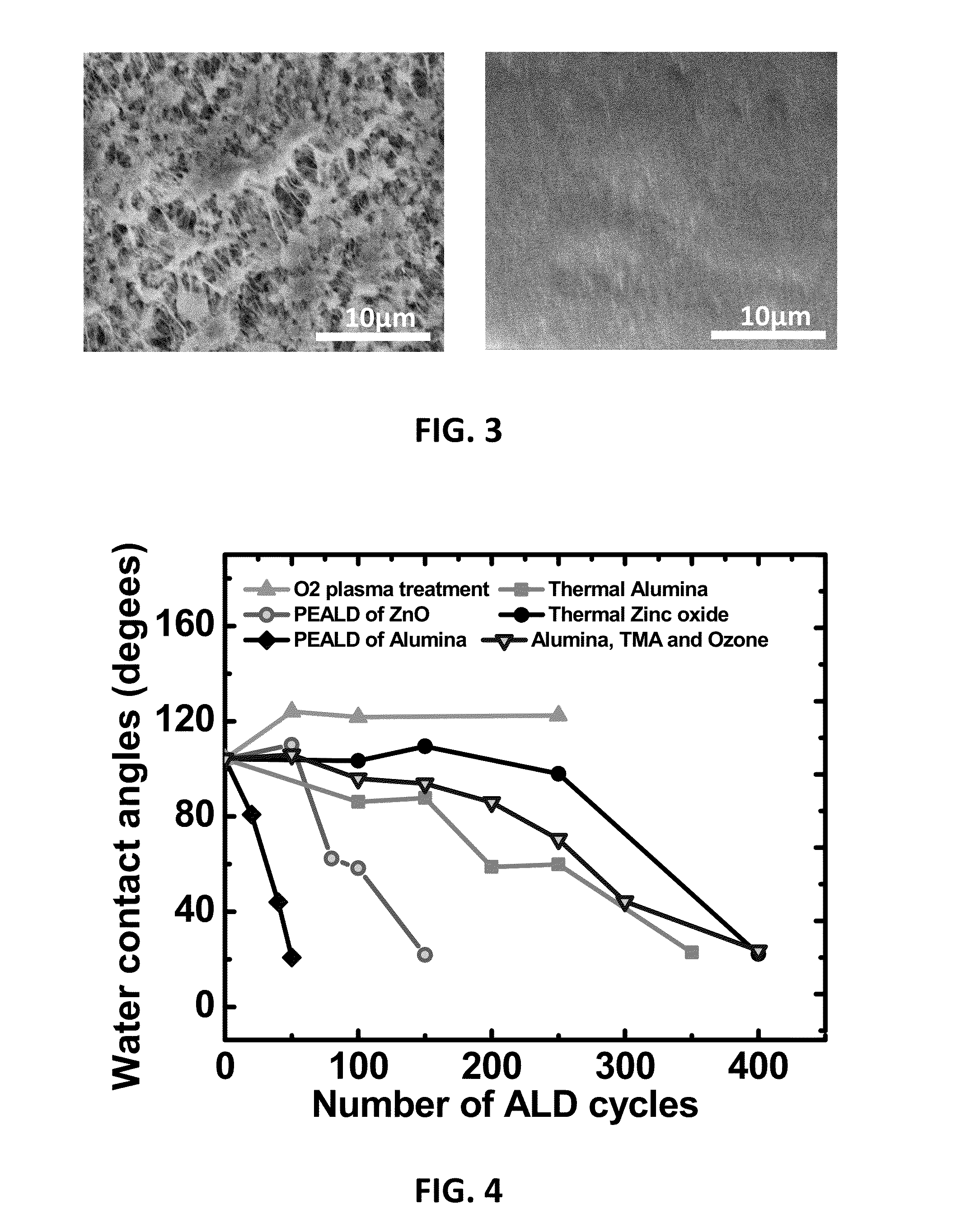
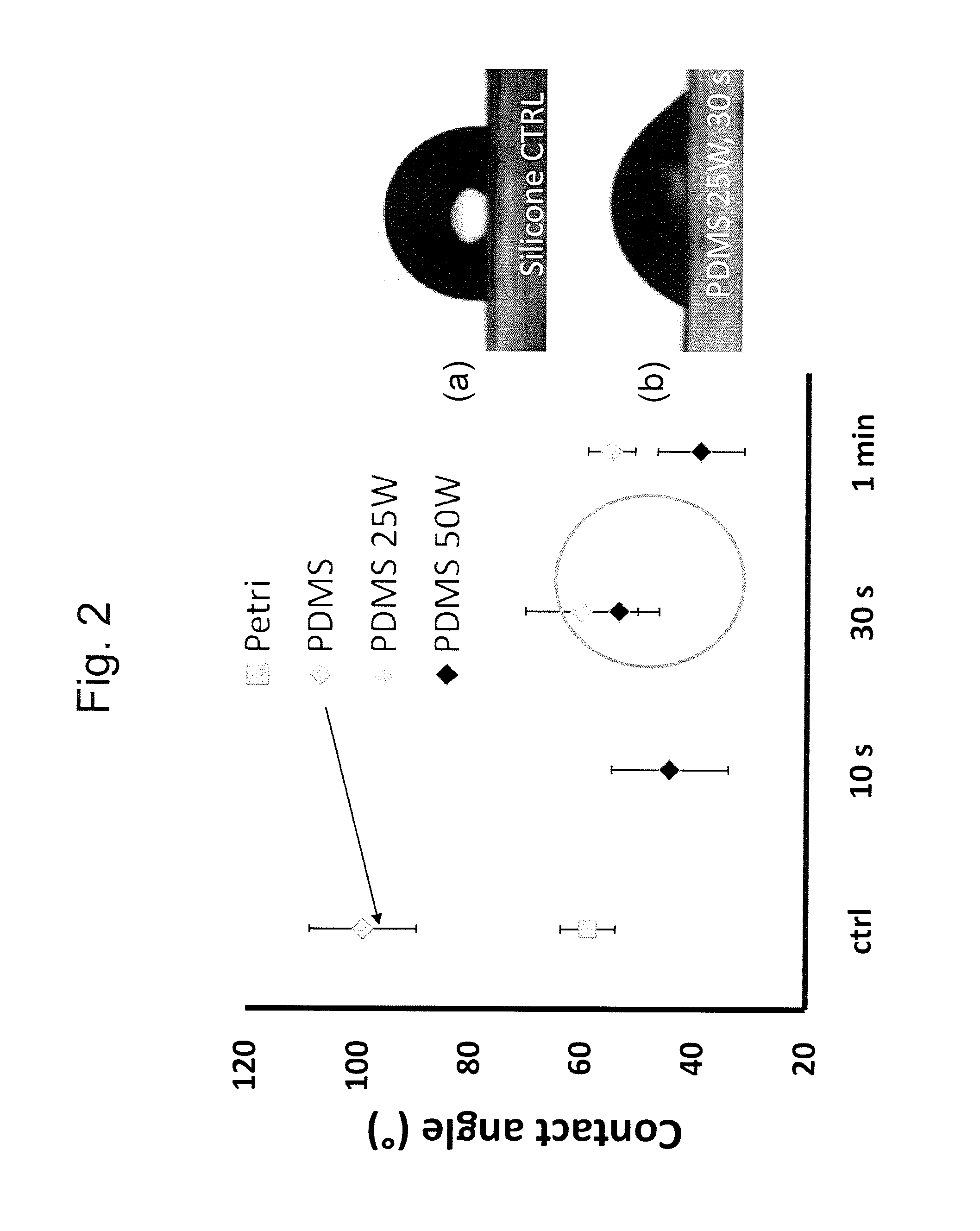
Methods for Obtaining Hydrophilic Fluoropolymers
InactiveUS20150345018A1Rendering fluoropolymers hydrophilicSimple methodSynthetic resin layered productsChemical vapor deposition coatingFluoropolymerPlasma activation
A method is described for providing a hydrophilic effect to a fluoropolymer, e.g. polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) material. The method comprises obtaining an at least partly hydrophobic fluoropolymer material, applying a plasma and / or ozone activation step and depositing an inorganic coating using an atomic layer deposition process. Plasma activation step and / or said atomic layer deposition process thereby comprises using process parameters determining a high interaction probability between one or more precursors for the atomic layer deposition process and the fluoropolymer material so as to obtain a coated fluoropolymer material having a contact angle with water below 30°.
Owner:UNIV GENT
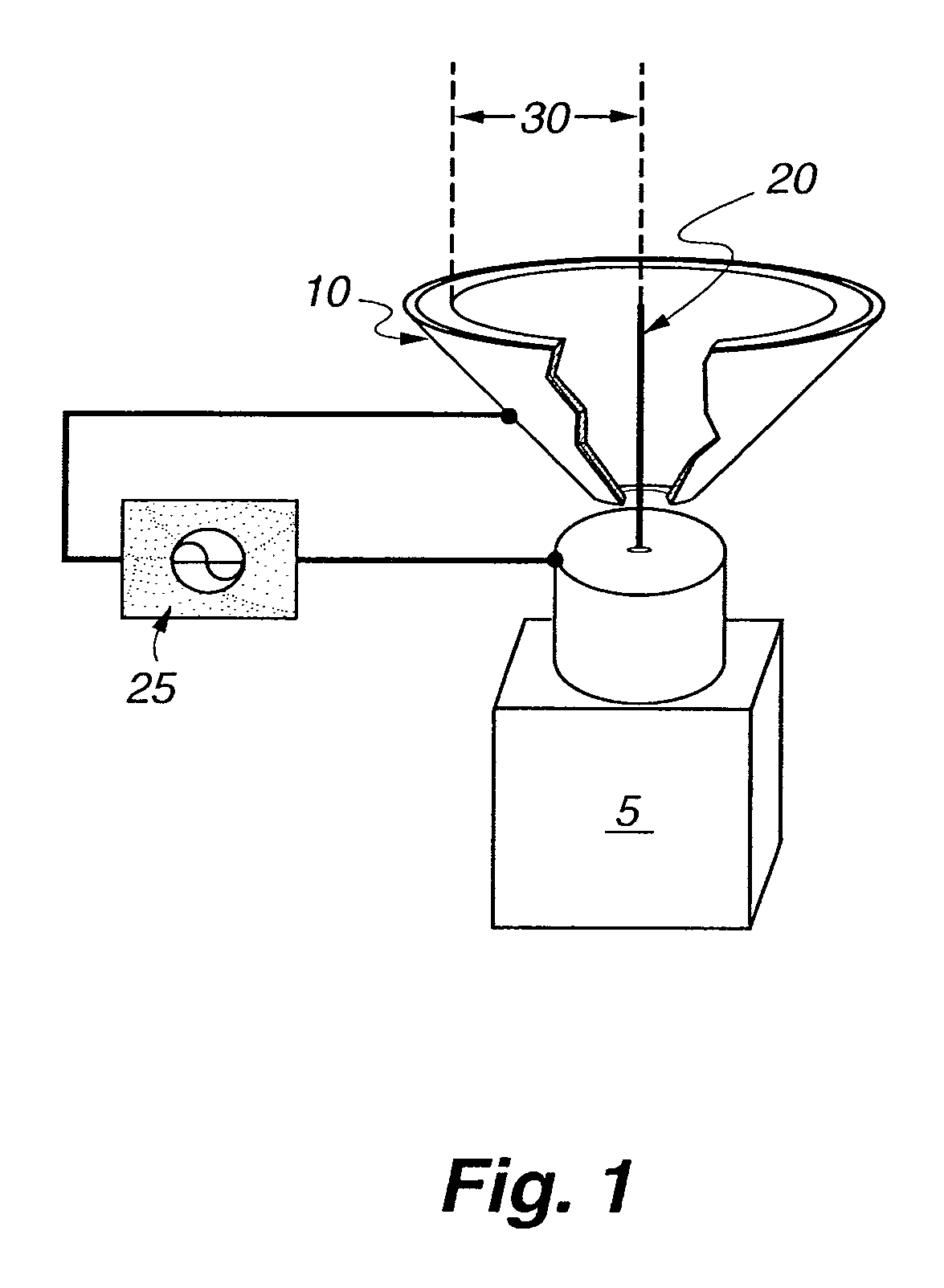
Fuel injector utilizing non-thermal plasma activation
A non-thermal plasma assisted combustion fuel injector that uses an inner and outer electrode to create an electric field from a high voltage power supply. A dielectric material is operatively disposed between the two electrodes to prevent arcing and to promote the formation of a non-thermal plasma. A fuel injector, which converts a liquid fuel into a dispersed mist, vapor, or aerosolized fuel, injects into the non-thermal plasma generating energetic electrons and other highly reactive chemical species.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
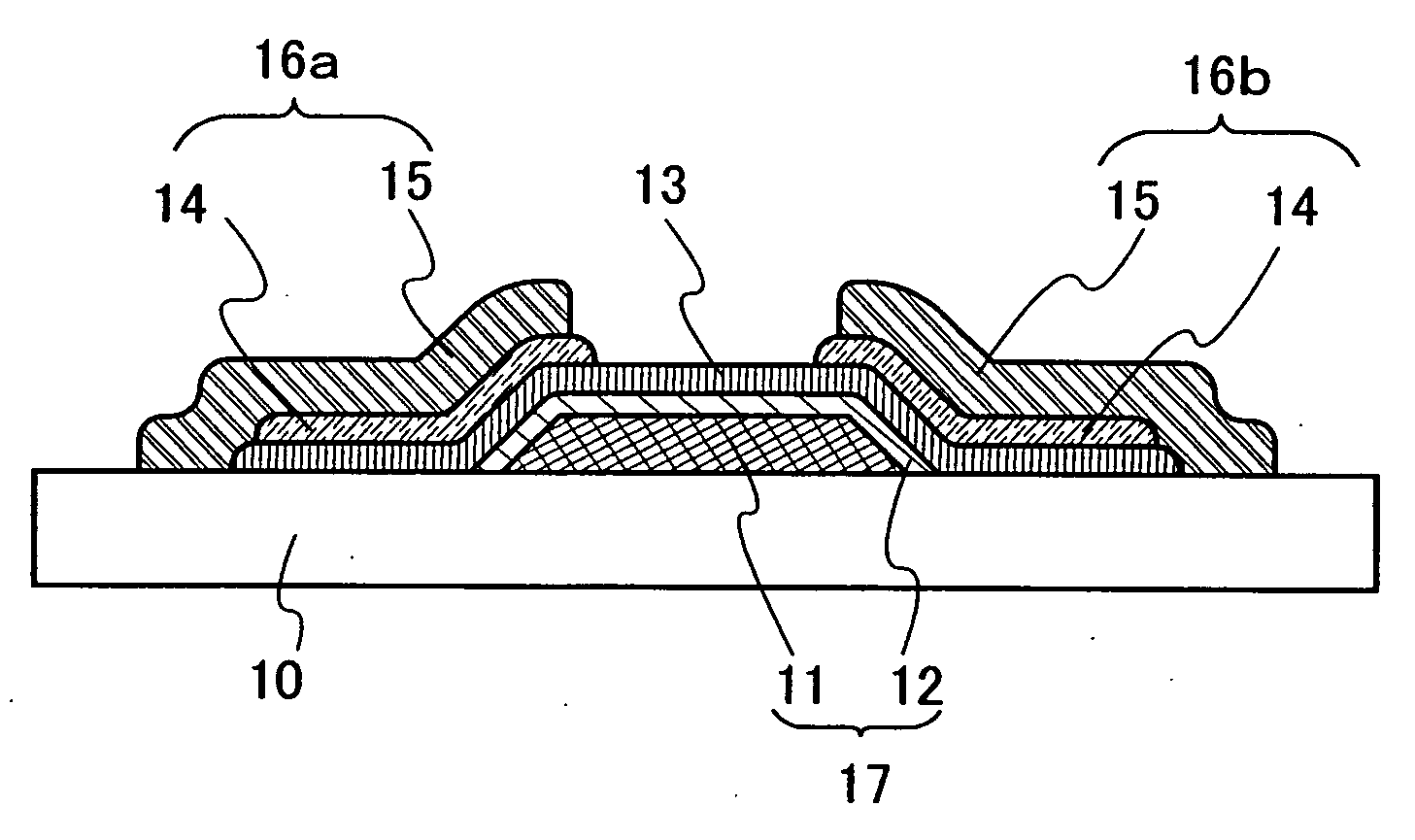
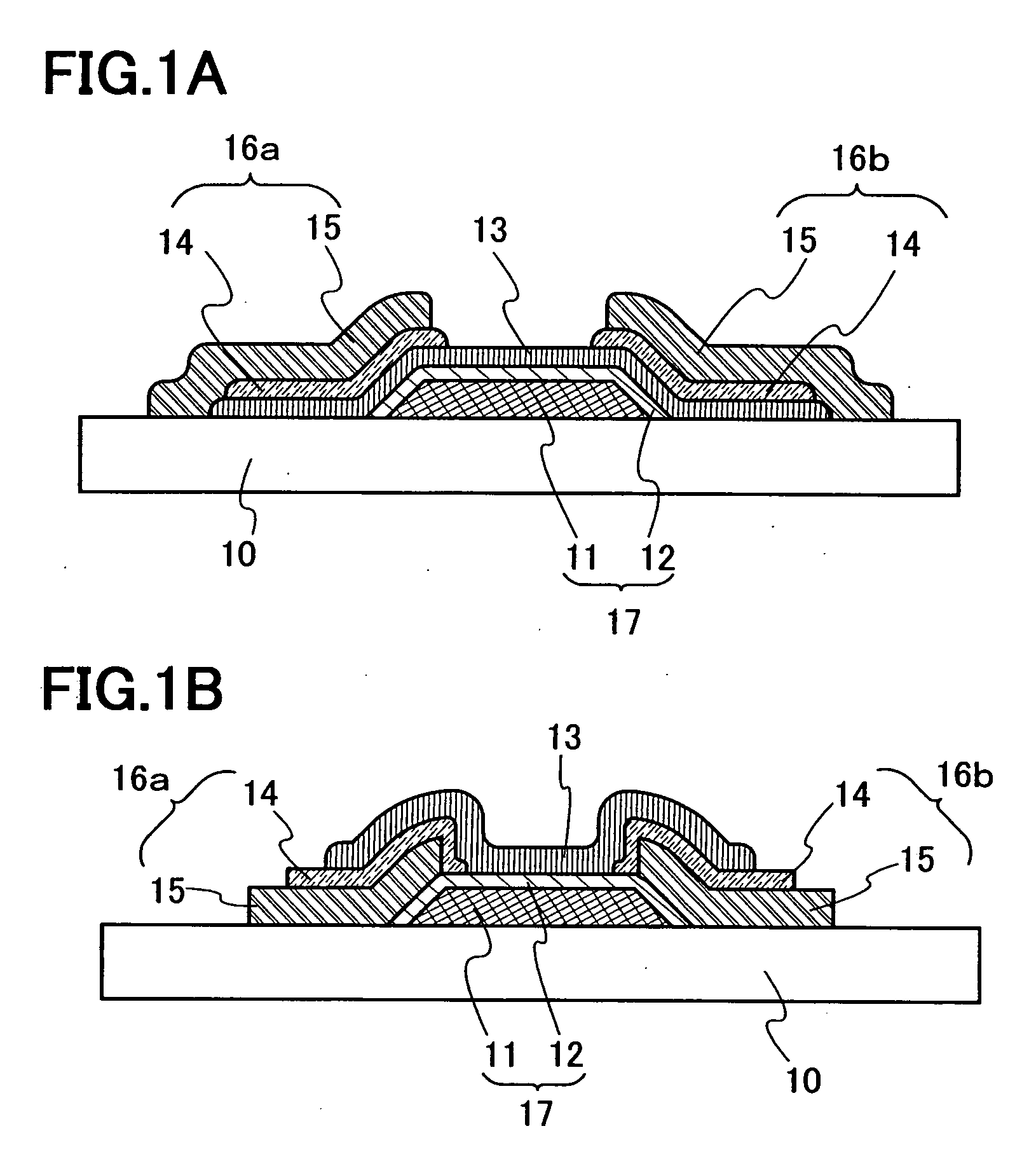
Organic transistor, manufacturing method of semiconductor device and organic transistor
InactiveUS20060270066A1Reduce leakage currentReduce tunnel leakage currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConductive polymerPlasma activation
It is an object to form a high quality gate insulating film which is dense and has a strong insulation resistance property, and to propose a high reliable organic transistor in which a tunnel leakage current is little. One mode of the organic transistor of the present invention has a step of forming the gate insulating film by forming the conductive layer which becomes the gate electrode activating oxygen (or gas including oxygen) or nitrogen (or gas including nitrogen) or the like using dense plasma in which density of electron is 1011 cm−3 or more, and electron temperature is a range of 0.2 eV to 2.0 eV with plasma activation, and reacting directly with a portion of the conductive layer which becomes the gate electrode to be insulated.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method for manufacturing circuit board layer-adding structure
ActiveCN103491732AMeet processing needsAchieve preparationInsulating layers/substrates workingMultilayer circuit manufactureCopper platingEtching
Owner:NAT CENT FOR ADVANCED PACKAGING CO LTD
Method of fabricating a composite substrate with improved electrical properties
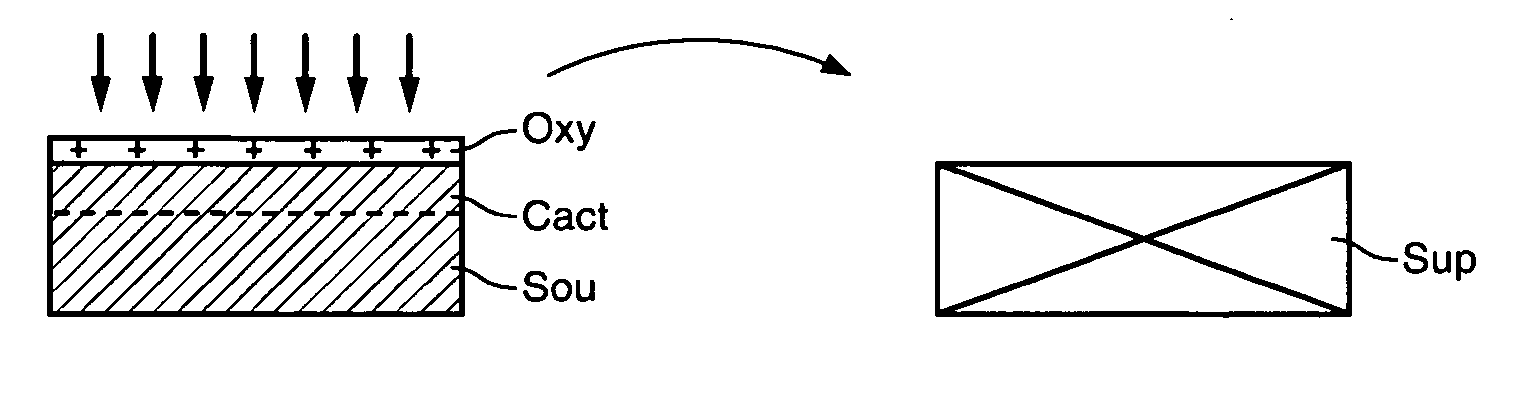
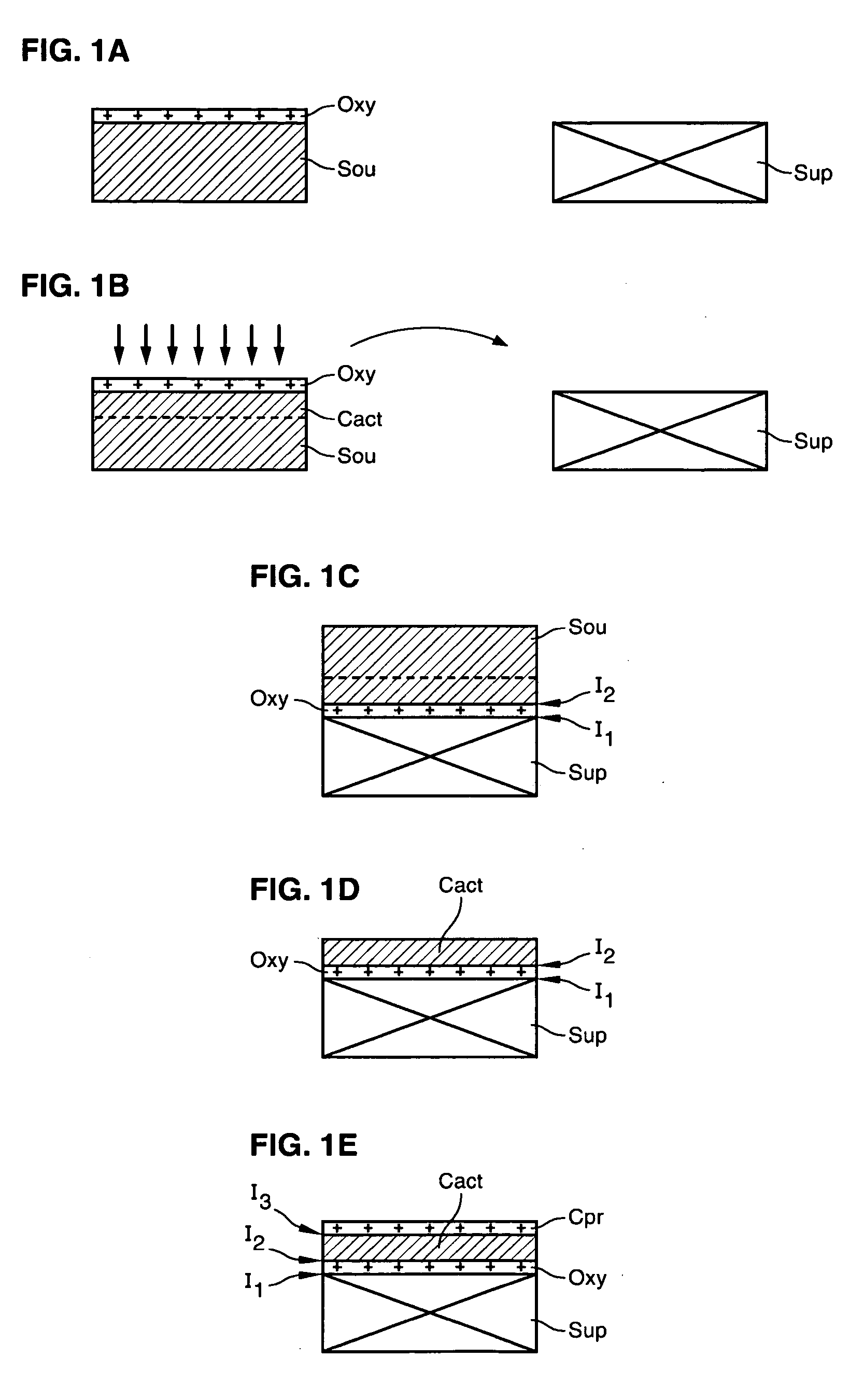
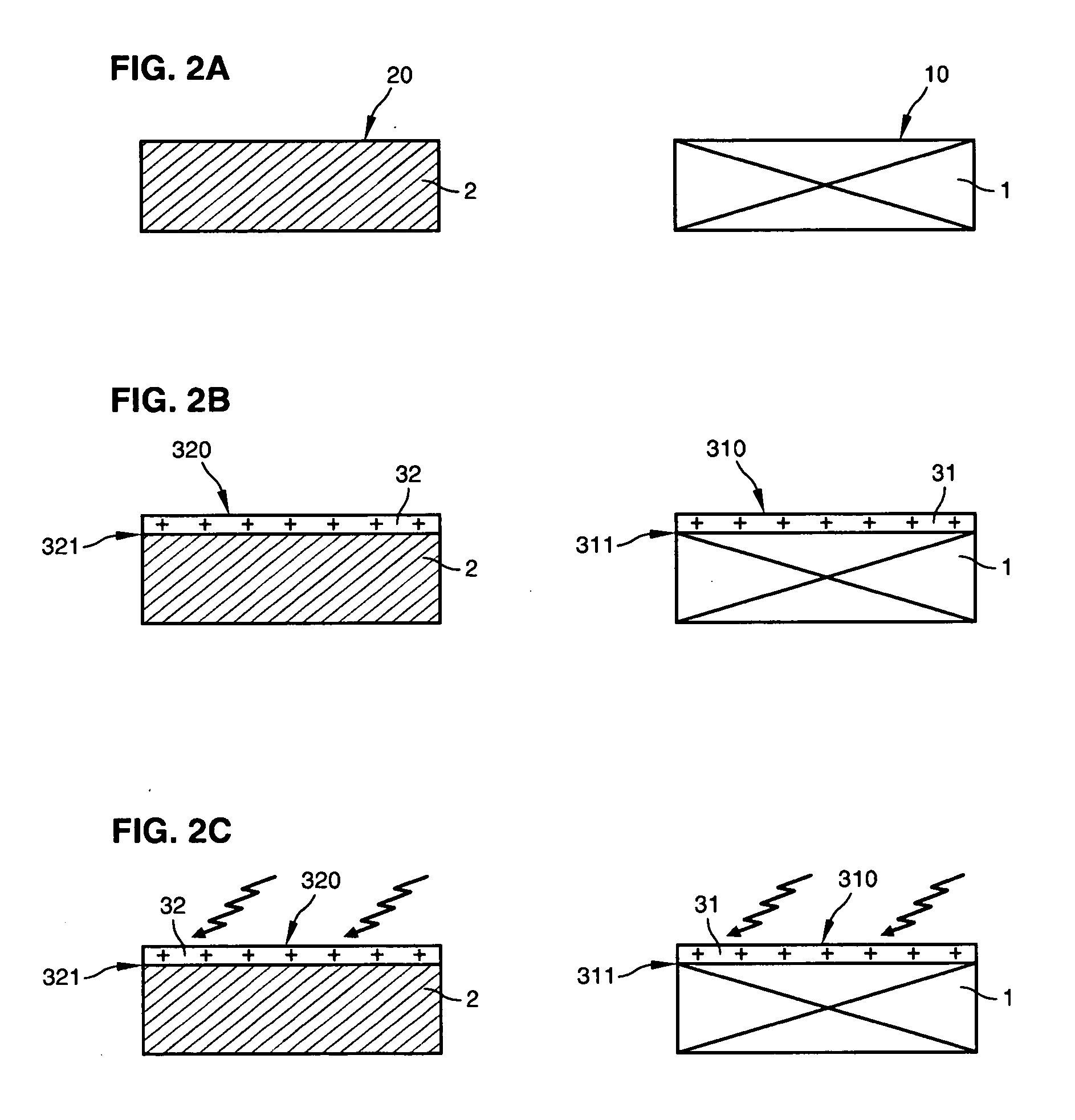
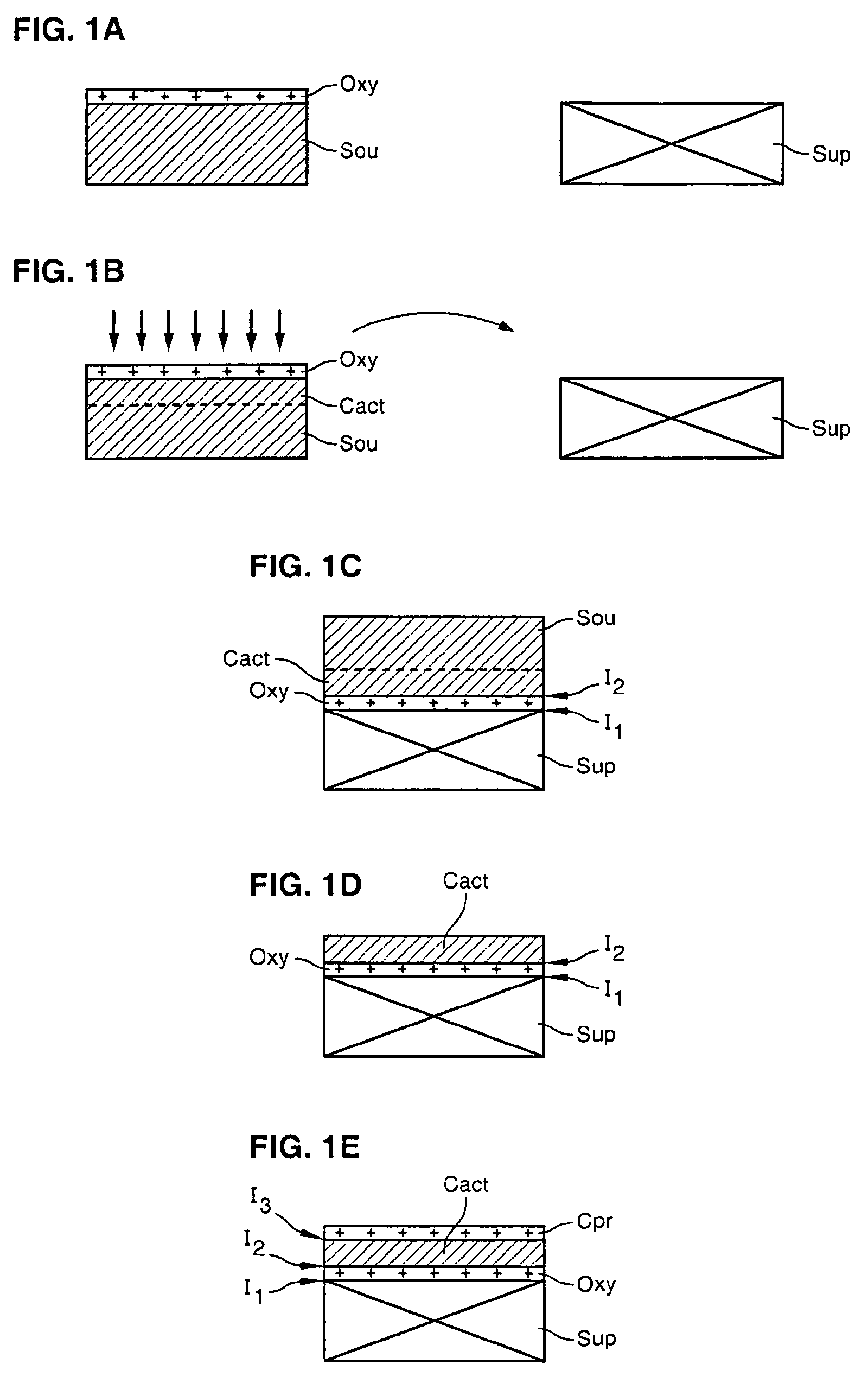
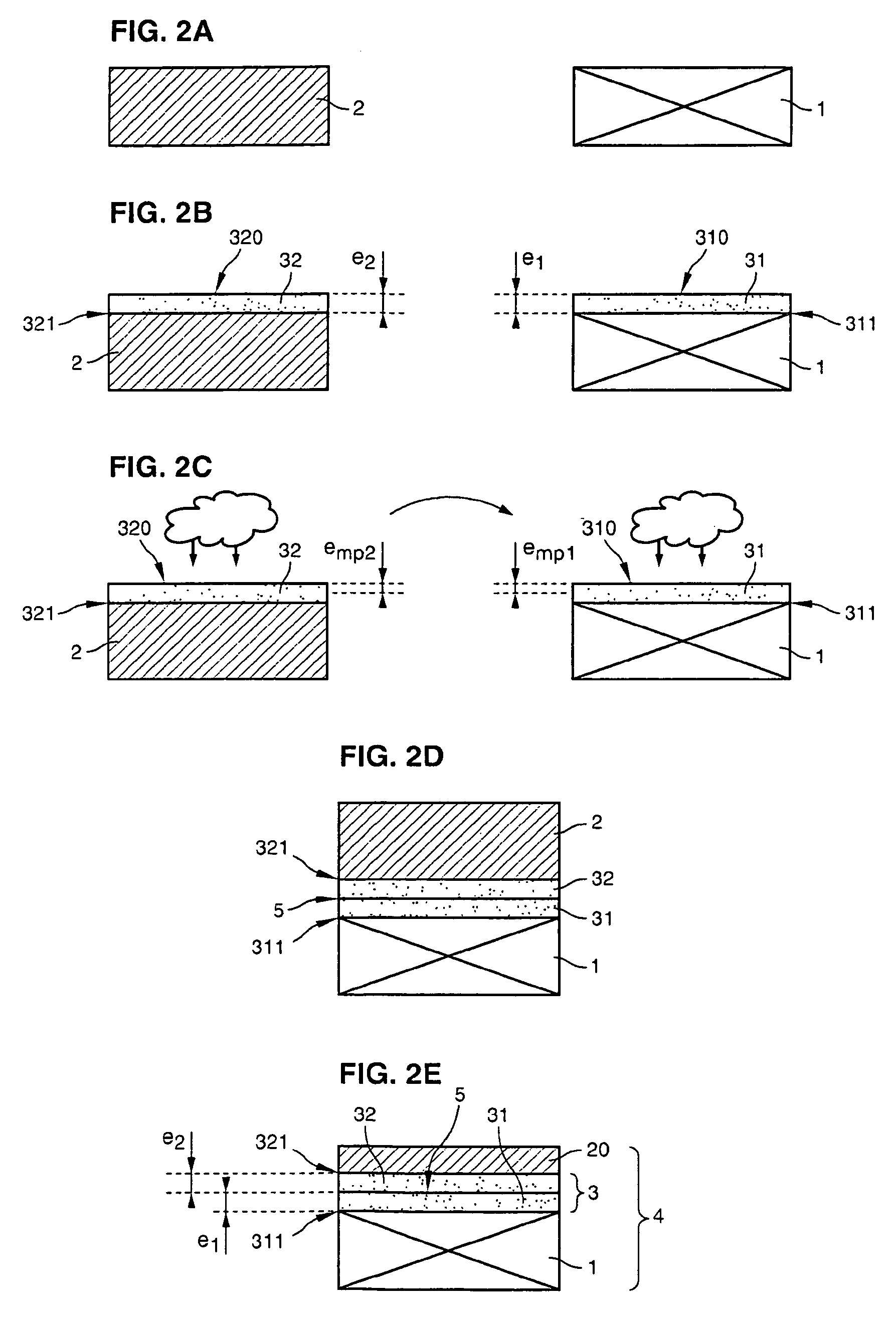
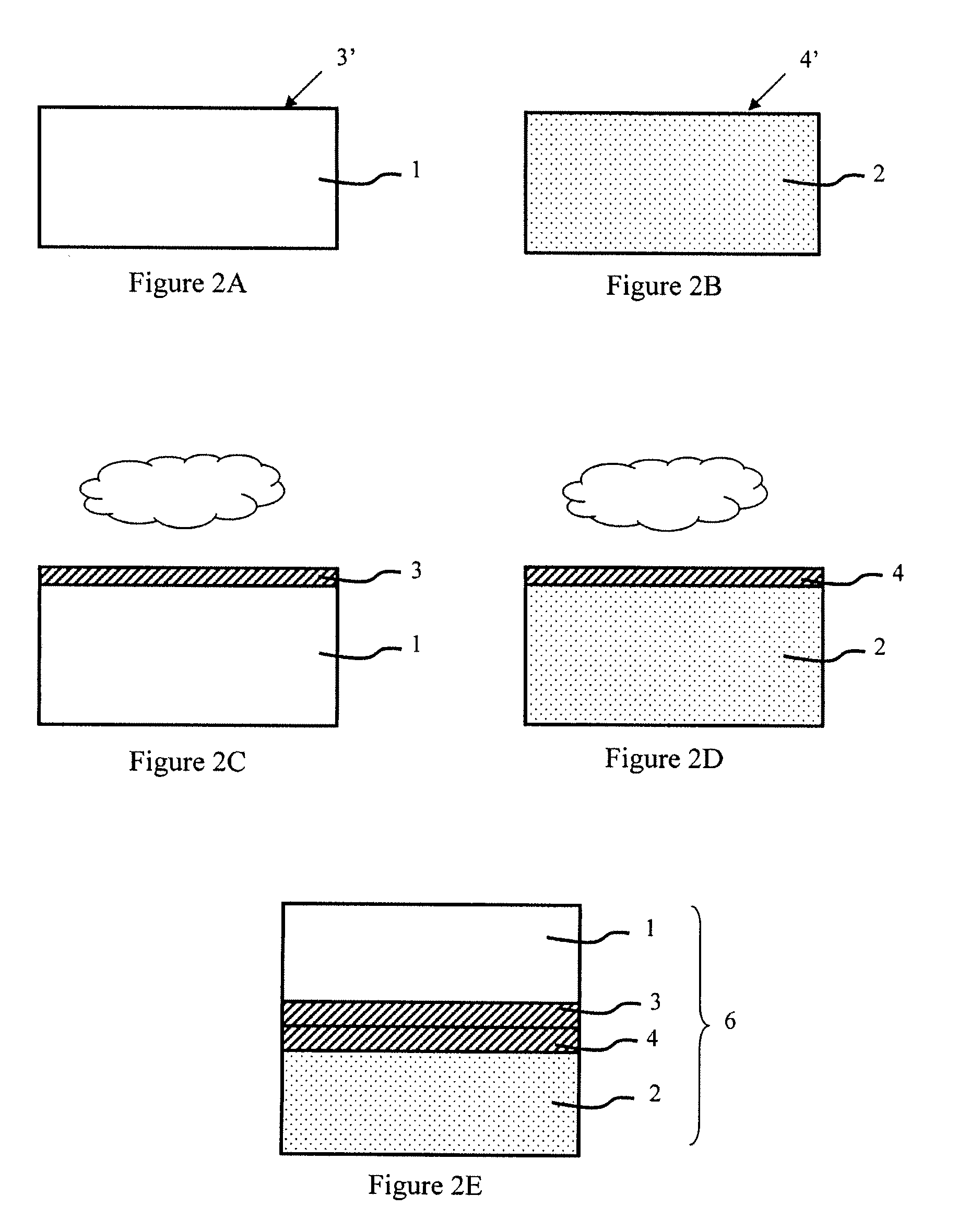
ActiveUS20070173033A1Improve electrical performanceOvercome disadvantagesFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlasma activationIon
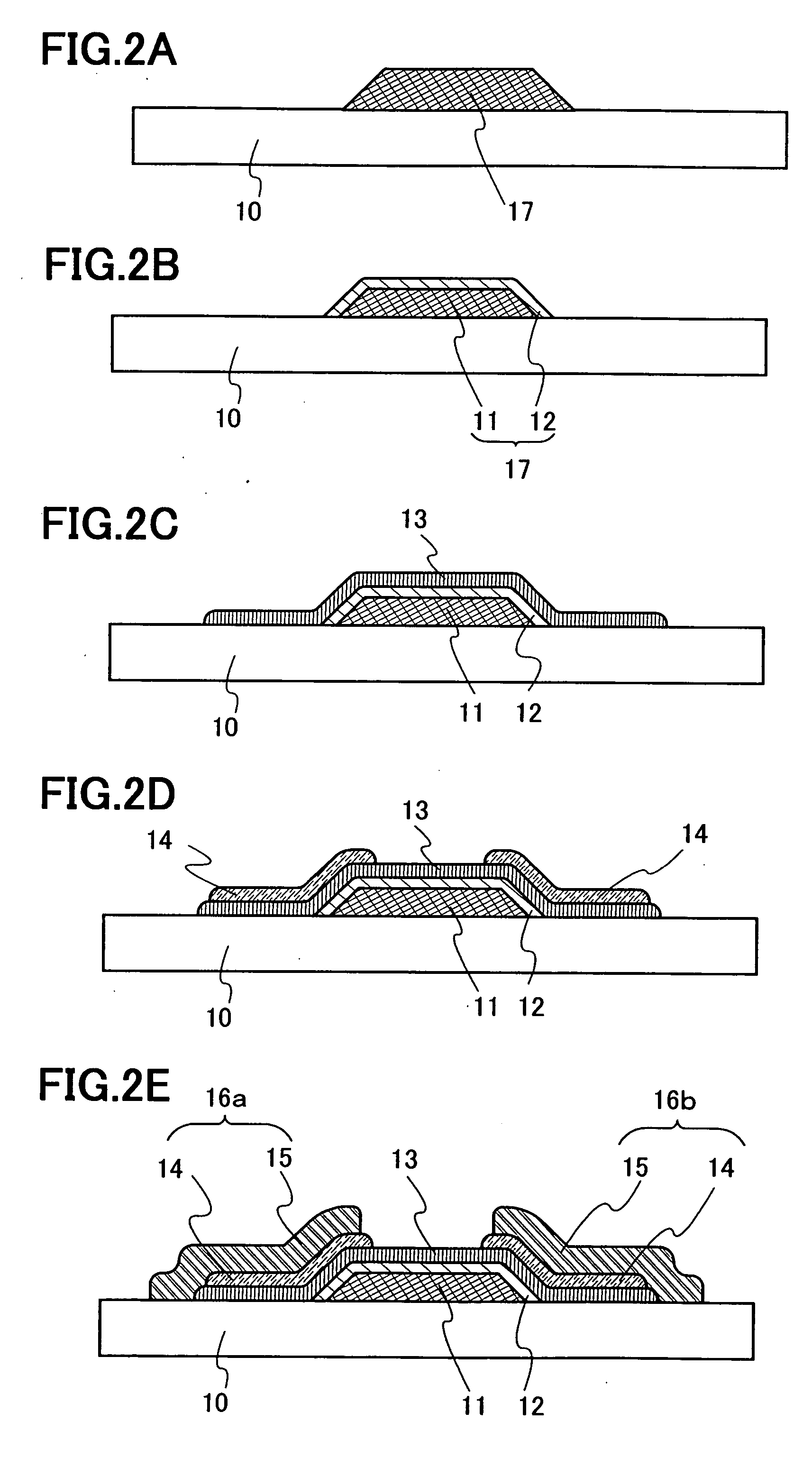
The invention concerns a method of fabricating a composite substrate comprising at least one thin insulating layer interposed between a support substrate and an active layer of semiconductor material. The method comprises: providing a source substrate that comprises a semiconductor material and a support substrate; forming or depositing an insulating layer on the source substrate; providing recovery heat treatment of the insulating layer; providing plasma activation of a front face of the recovery heat treated insulating layer or a front face of the support substrate; molecular bonding, after the plasma activation, the front face of the insulating layer with the front face of the support substrate to form a bonded substrate; and lifting off a back portion of the source substrate from the bonded substrate to retain an active layer that comprises a remaining portion of the source substrate.
Owner:S O I TEC SILICON ON INSULATOR THECHNOLOGIES
The method for preparing high-entropy oxide ceramic material is simple and low in consumption
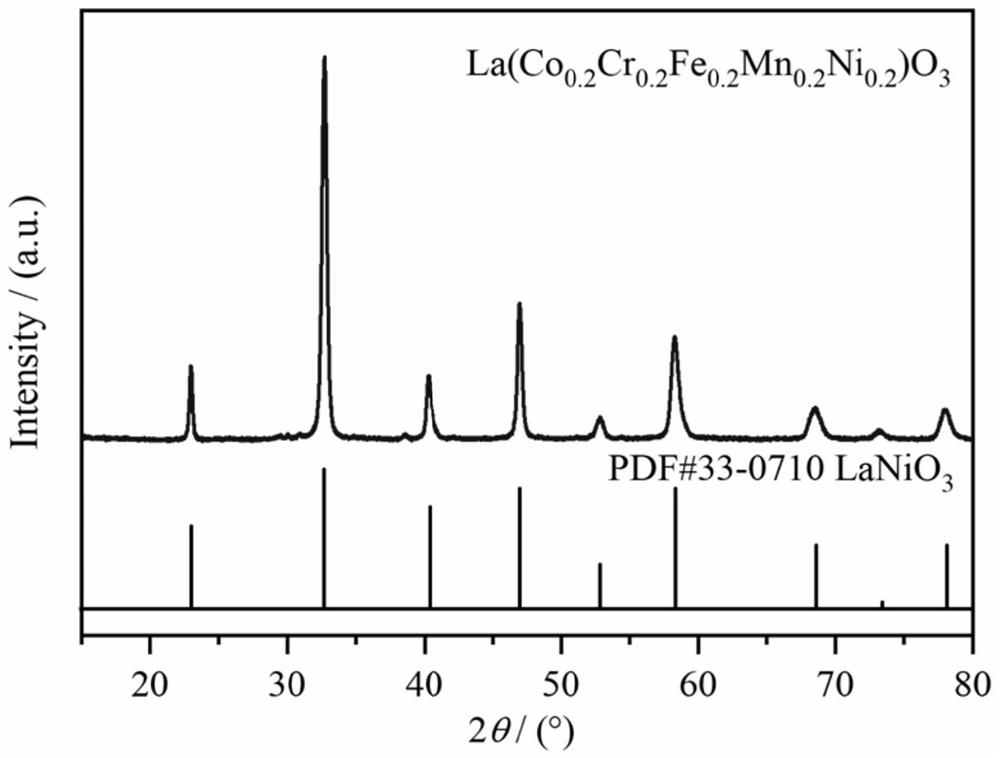
ActiveCN112723862AThe primary particle size is fine and uniformHigh activityOxide ceramicPlasma activation
The invention relates to the technical field of high-entropy ceramic preparation, and discloses a simple and low-consumption method for preparing a high-entropy oxide ceramic material, which comprises the following steps: S1, weighing raw materials: weighing the raw materials required for preparation according to a set ratio; s2, performing particle refinement: adding the raw materials weighed in the step S1 and a dispersing agent into a ball milling tank of a planetary ball mill together for particle refinement grinding to prepare uniformly mixed slurry, then drying the slurry, and grinding again to obtain refined powder; s3, performing spark plasma treatment: performing spark plasma activation on the refined powder obtained in the step S2 to obtain a ceramic raw material; and S4, performing microwave sintering: carrying out microwave sintering on the ceramic raw material obtained in the step S3 to obtain the high-entropy oxide ceramic material.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
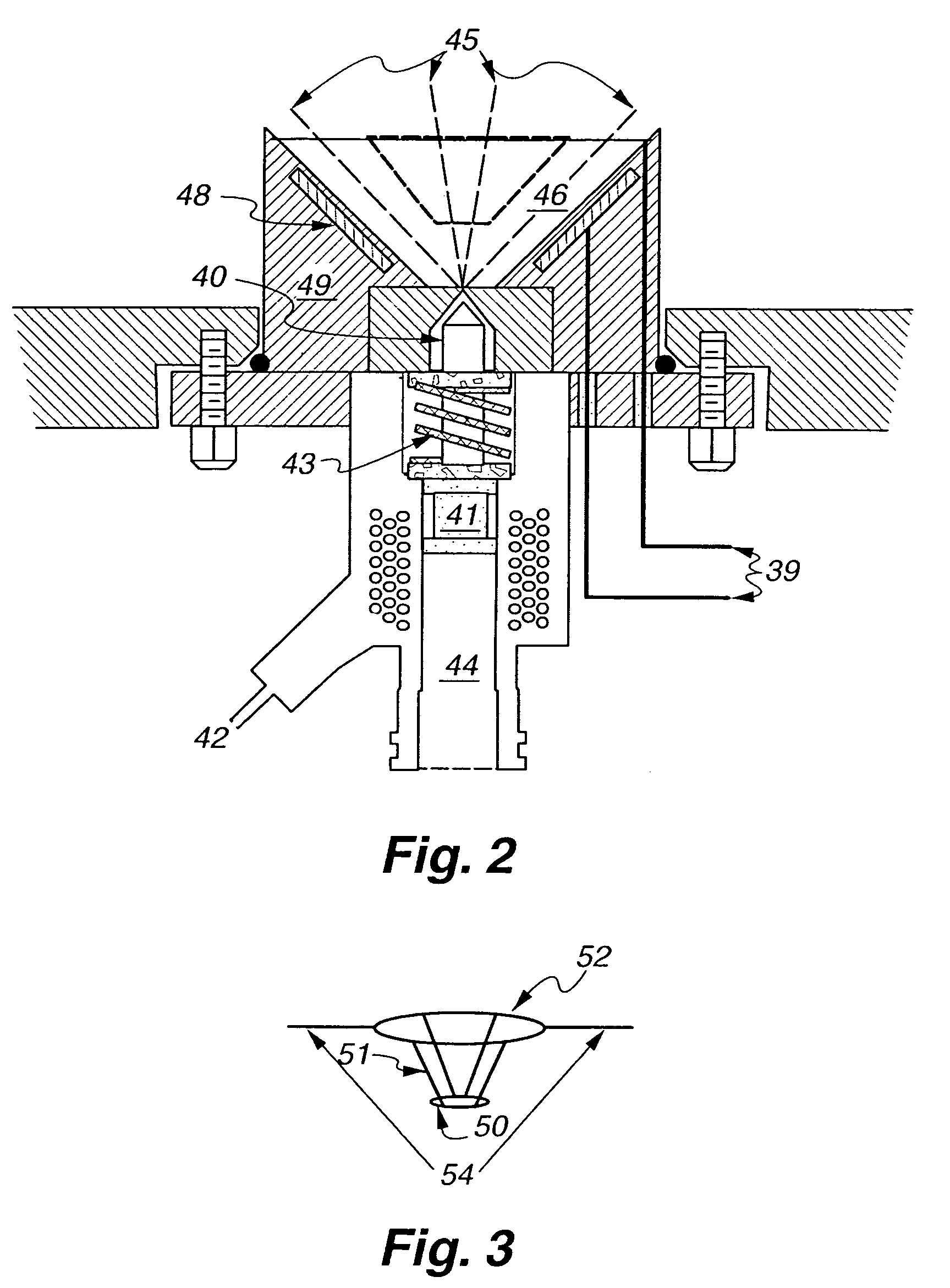
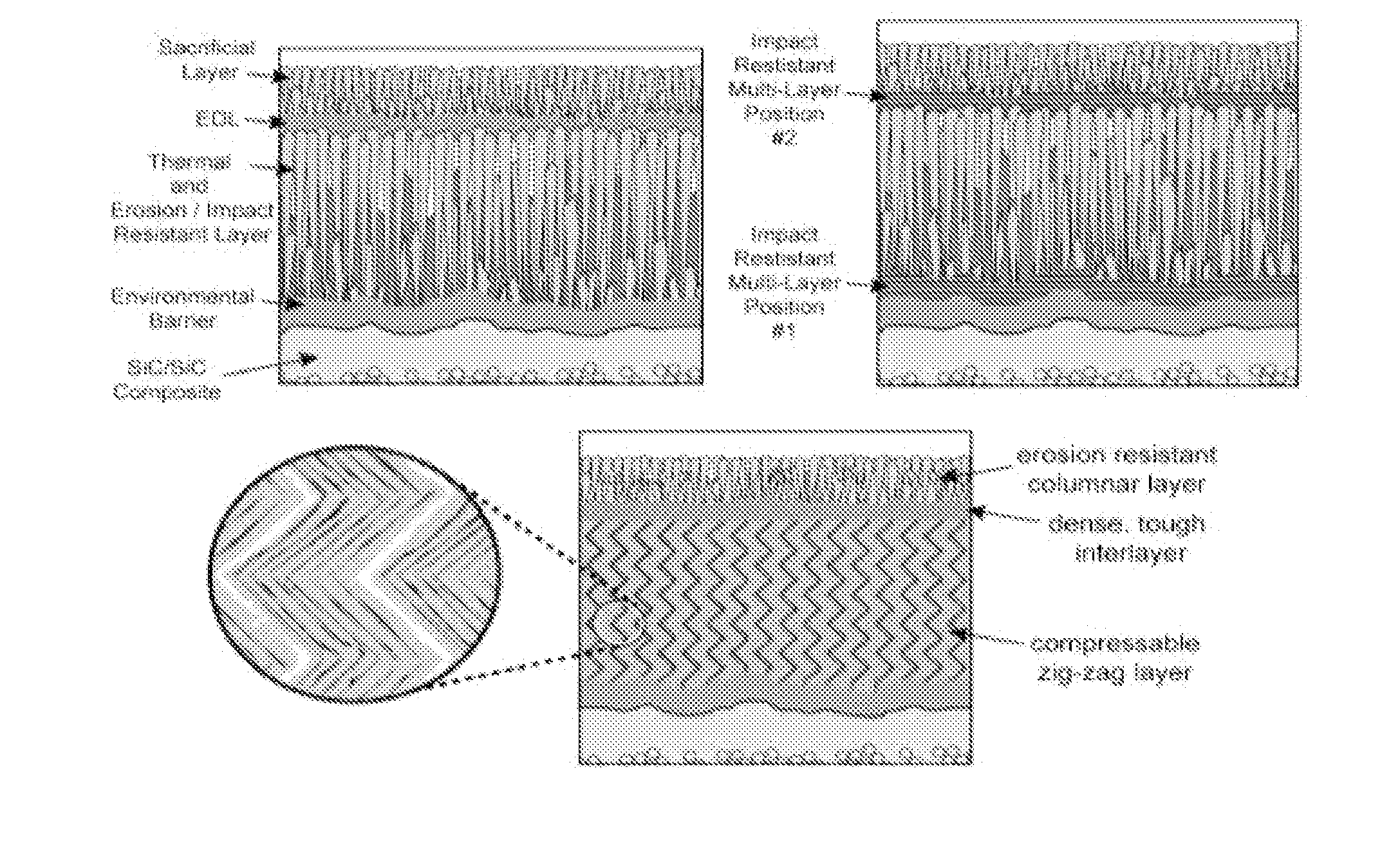
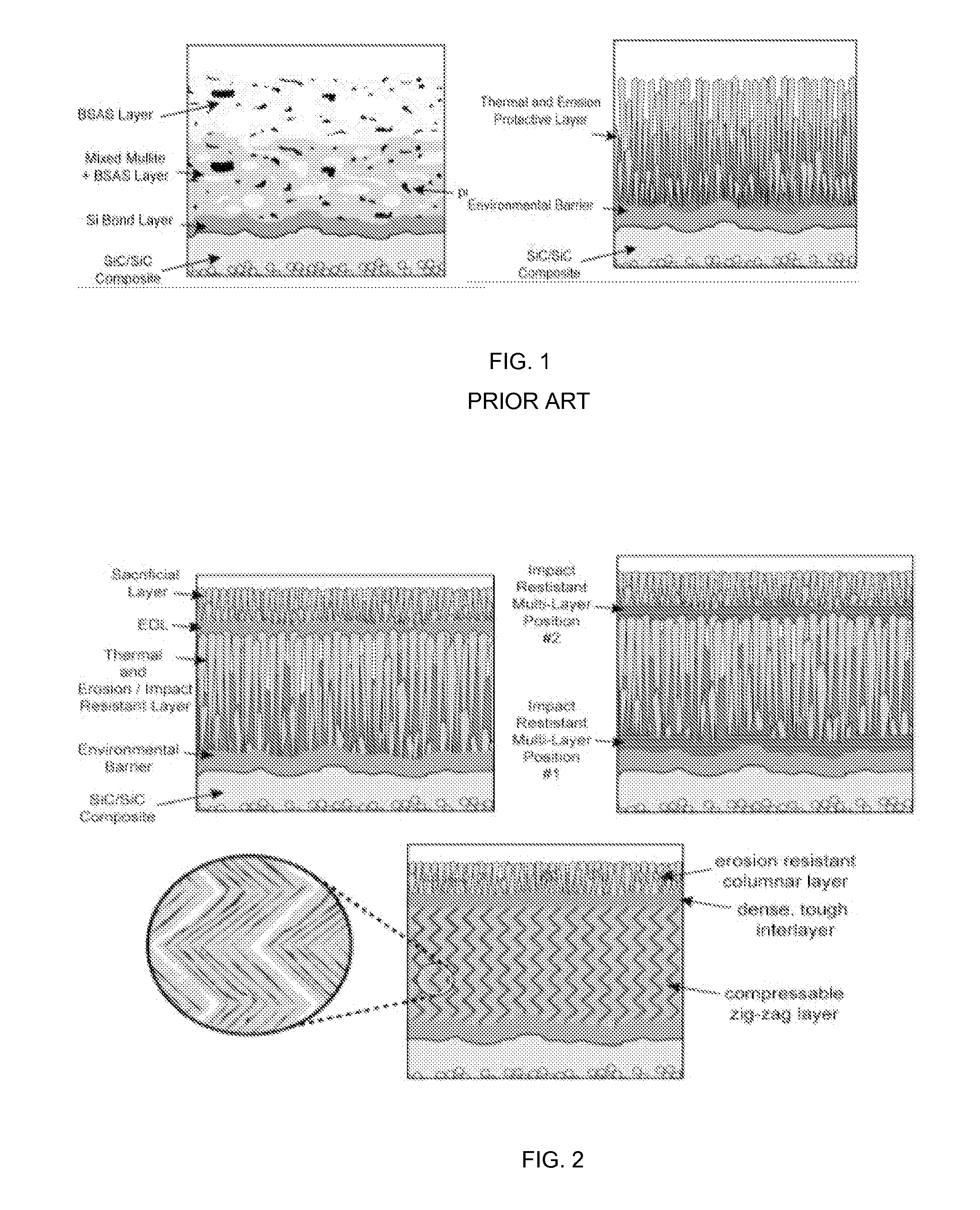
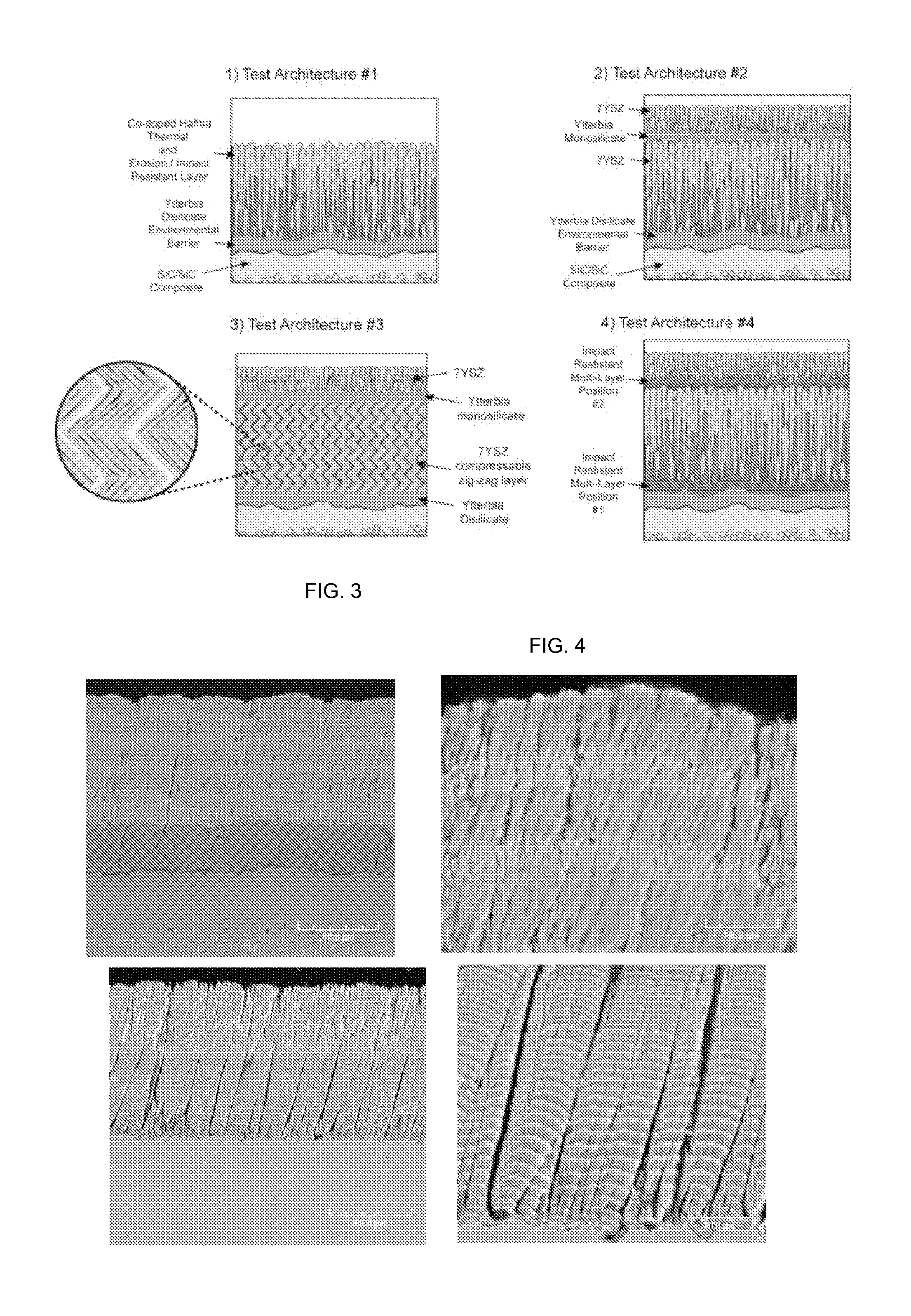
Impact and erosion resistant thermal and environmental barrier coatings
InactiveUS20130095256A1Resistant to erosion damageResistant to impact damageElectric discharge heatingBlade accessoriesCoating systemPlasma activation
The present invention provides a process for the application of high temperature coating that provide enhanced impact resistance and erosion damage for the coatings. For high temperature coating systems that provide environmental protection to silicon based ceramics, the process provides the deposition of a silicon-based bond coat on the substrate using the directed vapor deposition with plasma activation and at least one supersonic gas jet nozzle. The process provides the deposition of an EBC layer using the directed vapor deposition with the gas jet nozzle. In one embodiment, the thermal barrier layer may also contain one or more dense embedded layers which further promote impact resistance. Within the process, the particular layers, silicon bond coat, EBC layer and / or TBC layer may be deposited together or specific novel layers applied in combination with other layers deposited using prior known deposition techniques.
Owner:DIRECTED VAPOR TECH INT
Method for preparing composite interlayer coating film on surface of engineering plastics
ActiveCN102152541AReduce consumptionAnti-corrosionVacuum evaporation coatingPretreated surfacesWater savingMetallurgy
The invention discloses a method for preparing a composite interlayer coating film on the surface of engineering plastics, relates to a method for obtaining a metal composite layer on the surface of the engineering plastics and provides a method for preparing a composite interlayer coating film on the surface of engineering plastics, which can improve the function and the quality of metal-coated plastic products, reduce the production cost and is water-saving and environment-friendly because any aqueous solution is not needed in the whole processing flow. The method comprises the following steps of cleaning plastic blanks in a dry method, activating the plastic blanks, putting the activated plastic blanks into a PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) furnace, plating a metal base film layer on the activated plastic blanks, spraying and plating an organic coating to the plastic blanks after plasma activation is carried out on the plastic blanks plated with metal base film layer, and finally putting the plastic blanks into PVD furnace to be plated with a metal facial film layer in order to obtain metalized engineering plastic products. The method is suitable for industries, such as bathroom accessories, electron, appliances, automobiles, and the like.
Owner:XIAMEN RUNNER IND CORP
Chemical fibers grafted with quaternary ammonium group by plasma method and grafting method thereof
The present invention is one kind of chemical fiber with plasma process grafted quaternary ammonium group and its grafting process. The process includes treating chemical fiber in a corona discharge electric field of 3000-12000 V voltage and 10-500 W power for the surface of the fiber to produce free radical or ion group, soaking the fiber in water solution of double bond-containing quaternary ammonium monomer for grafting polymerization reaction to graft cationic group, eliminating un-reacted monomer, washing, oiling and drying to obtain modified chemical fiber containing cationic quaternary ammonium group.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Composite substrate and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20070170503A1Improve electrical performanceOvercome disadvantagesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComposite substratePlasma activation
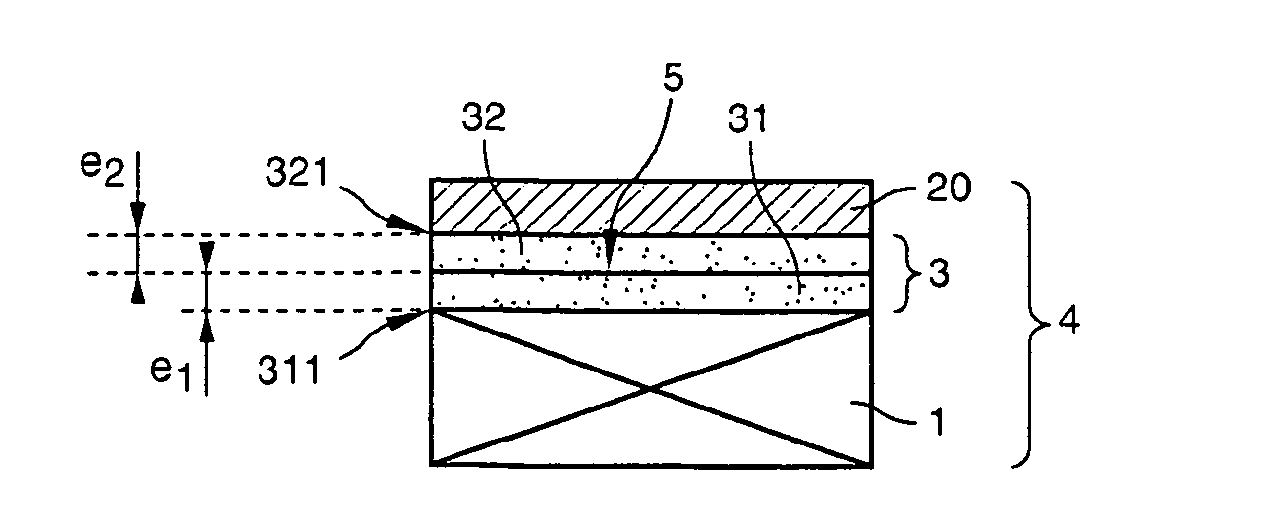
The invention specifically relates to methods of fabricating a composite substrate by providing a first insulating layer on a support substrate at a thickness of e1 and providing a second insulating layer on a source substrate at a thickness of e2, with each layer having an exposed face for bonding; providing plasma activation energy in an amount sufficient to activate a portion of the thickness of the face of the first insulating layer emp1 and a portion of the thickness of the face of the second insulating layer emp1; providing a final insulating layer by molecular bonding the activated face of the first insulating layer with the activated face of the second insulating layer; and removing a back portion of the source substrate while retaining an active layer comprising a remaining portion of the source substrate bonded to the support substrate with the final insulating layer interposed therein to form the composite substrate. The thicknesses e1, e2 of the first and second insulating layers are sufficient to provide the final insulating layer with a thickness of 50 nanometers or less, and the plasma activation energy and respective thicknesses e1, e2 of the first and second insulating layers are selected such that only respective thicknesses emp1 and emp2 of the faces of the first insulating layer and the second insulating layer are activated.
Owner:S O I TEC SILICON ON INSULATOR THECHNOLOGIES
Soi substrates with a fine buried insulating layer
ActiveUS20090111243A1Thin layerQuality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor structurePlasma activation
A method of producing a semiconductor structure having a buried insulating layer having a thickness between 2 and 25 nm, by: forming at least one insulating layer on a surface of a first or second substrate, or both, wherein the surfaces are free from an insulator or presenting a native oxide layer resulting from exposure of the substrates to ambient conditions; assembling the first and second substrates; and thinning down the first substrate, in order to obtain the semiconductor structure. In this method, the insulating layer forming stage is a plasma activation based on an oxidizing or nitriding gas.
Owner:S O I TEC SILICON ON INSULATOR THECHNOLOGIES
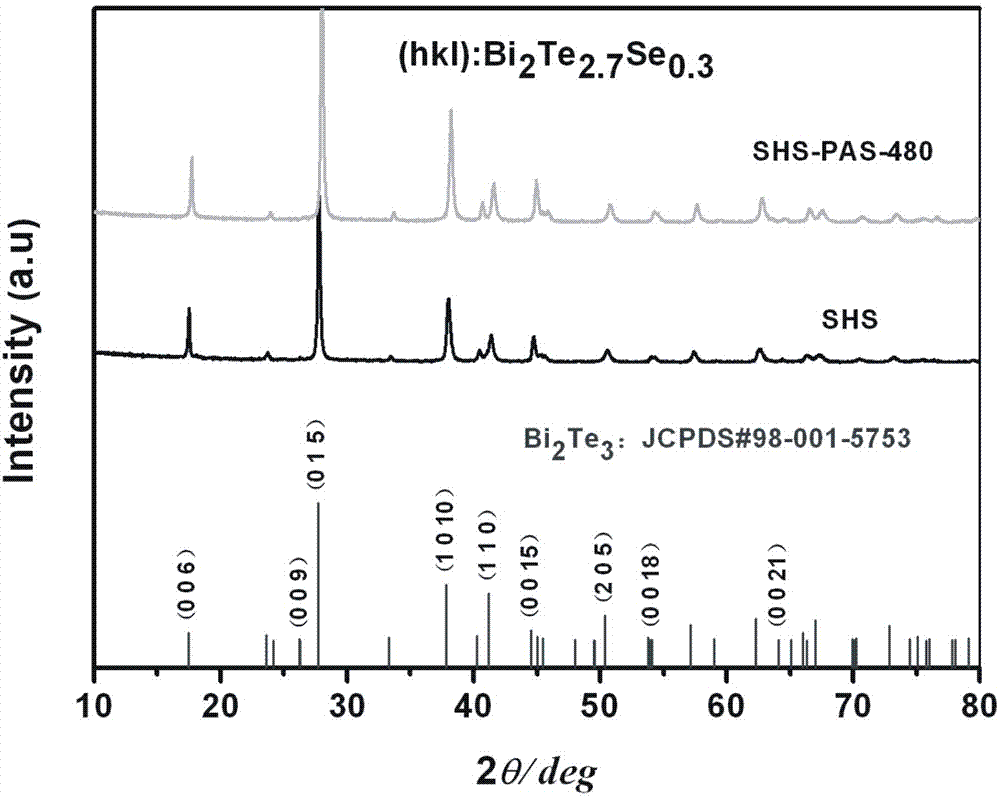
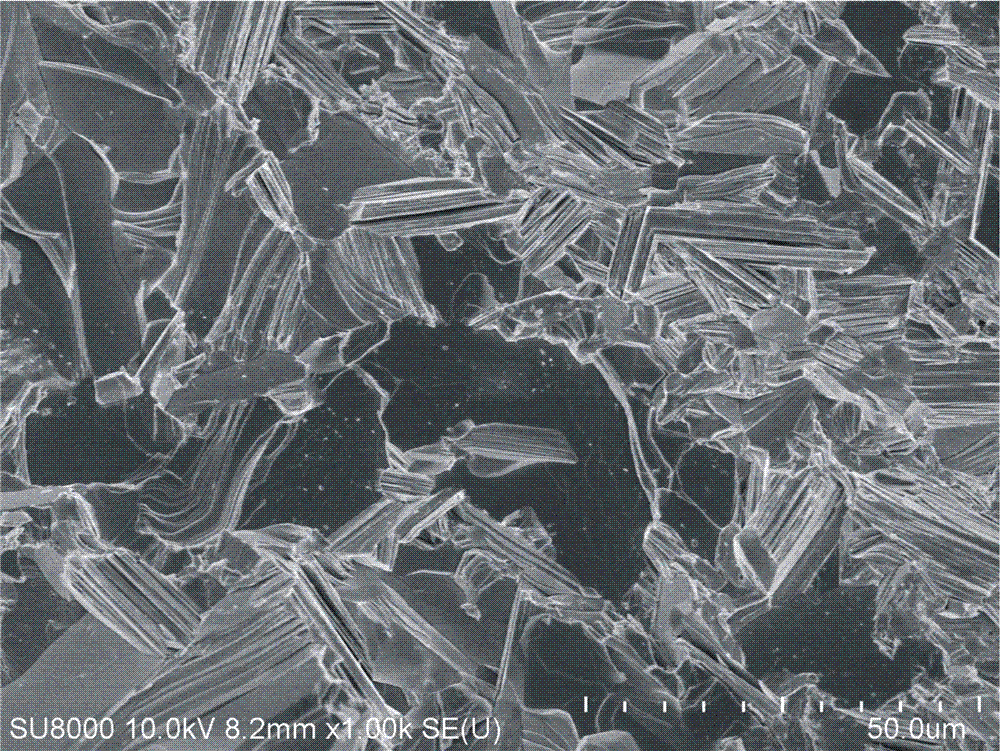
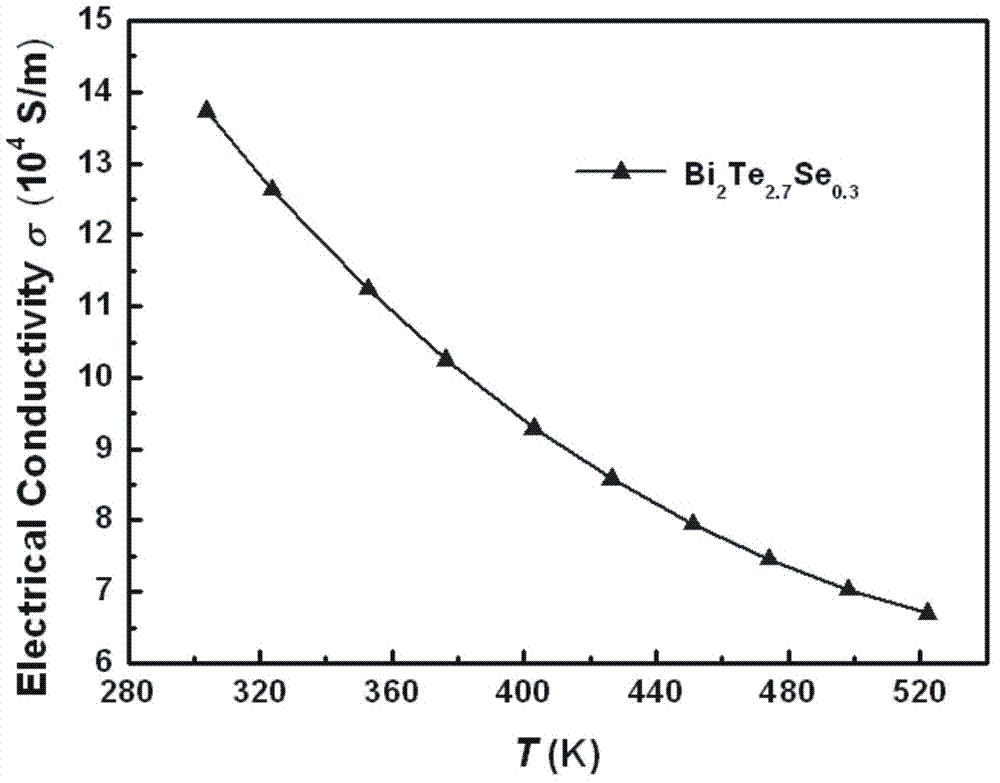
Method for fast manufacturing n-type bismuth telluride based high-performance thermoelectric materials
ActiveCN103928604AShort preparation timeSimple processThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device junction materialsMetallurgyBismuth telluride
The invention provides a method for fast manufacturing n-type bismuth telluride based high-performance thermoelectric materials. The method specifically comprises the steps that 1), Bi powder, Te powder and Se powder are weighed according to the stoichiometric ratio of all elements in Bi2Te3-xSex, 0=<x<=3, and the Bi powder, the Te powder and the Se powder are evenly mixed and pressed to be blocks; 2), a self-propagating reaction is generated on the blocks in the step 1), cooling is carried out after the reaction is completed, and a single-phase Bi2Te3-xSex compound is obtained; 3), the single-phase Bi2Te3-xSex compound obtained in the step 2) is ground to be powder, then plasma activation sintering is carried out, and the high-performance Bi2Te3-xSex thermoelectric materials are obtained. The technology with self-propagating combustion synthesis combined with plasma activation sintering is adopted, the n-type bismuth telluride block thermoelectric materials with the thermoelectric optimal value zT reaching 0.95 within 426 K are manufactured within 20 min, and the advantages of being short in manufacturing time, simple in technology, high in thermoelectric performance of the materials and the like are achieved.
Owner:武汉新赛尔科技有限公司
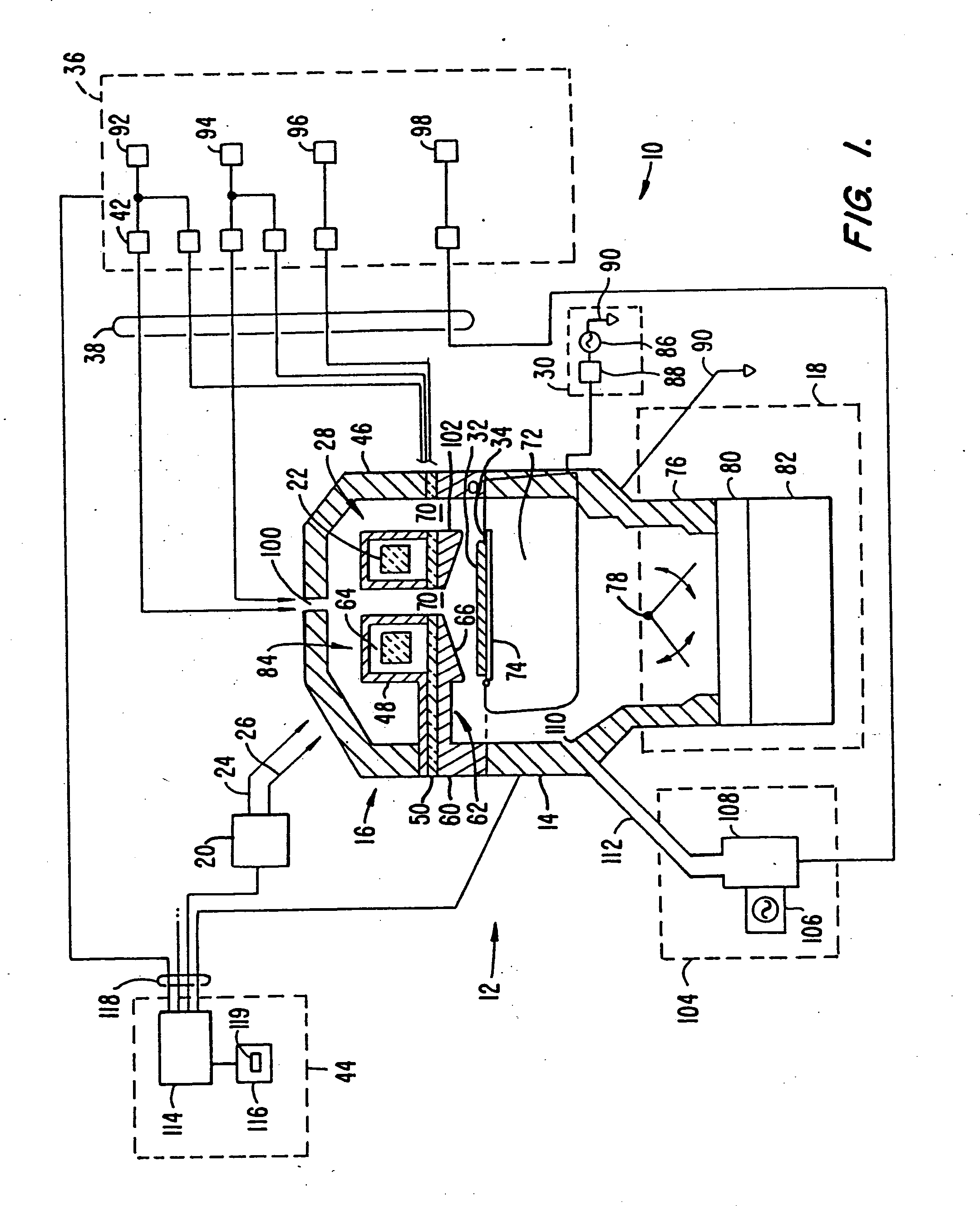
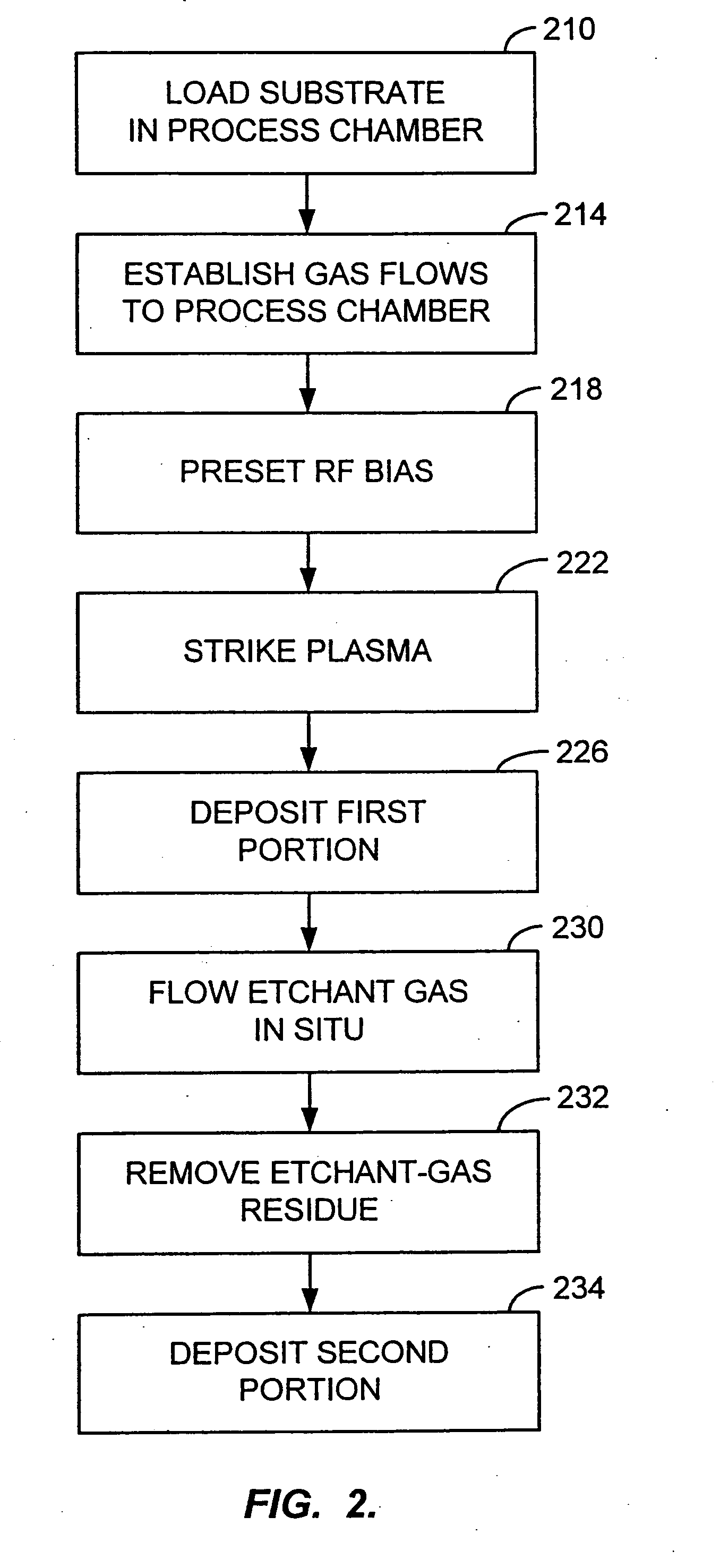
In situ application of etch back for improved deposition into high-aspect-ratio features
InactiveUS20050124166A1Easy to controlIncreased level of controlElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringPlasma activation
A continuous in situ process of deposition, etching, and deposition is provided for forming a film on a substrate using a plasma process. The etch-back may be performed without separate plasma activation of the etchant gas. The sequence of deposition, etching, and deposition permits features with high aspect ratios to be filled, while the continuity of the process results in improved uniformity.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
High temperature capacitive static/dynamic pressure sensors and methods of making the same
ActiveUS20120024073A1Low temperature requirementWave amplification devicesFluid pressure measurement using elastically-deformable gaugesCapacitive pressure sensorPlasma activation
Disclosed are capacitive pressure probes or sensors for high temperature applications. The capacitive pressure sensors of the present invention include, inter alia, a sapphire diaphragm which is disposed within an interior sensing chamber of the probe housing and has a first electrode formed on a central portion thereof. The central portion of the diaphragm and the first electrode are adapted and configured to deflect in response to pressure variations encountered within an interior sensing chamber and by the pressure sensor. A sapphire substrate which has a second electrode formed thereon is fused to the sapphire diaphragm about its periphery to form a sapphire stack and to define a reference chamber therebetween. Prior to fusing the sapphire diaphragm to the sapphire substrate, all contact surfaces are chemically treated and prepared using plasma activation, so as to create a bonding layer and to reduce the temperature required for the fusion.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT AEROSPACE
Method of fabricating a composite substrate with improved electrical properties
ActiveUS7449395B2Improve electrical performanceOvercome disadvantagesFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsComposite substrate
The invention concerns a method of fabricating a composite substrate comprising at least one thin insulating layer interposed between a support substrate and an active layer of semiconductor material. The method comprises: providing a source substrate that comprises a semiconductor material and a support substrate; forming or depositing an insulating layer on the source substrate; providing recovery heat treatment of the insulating layer; providing plasma activation of a front face of the recovery heat treated insulating layer or a front face of the support substrate; molecular bonding, after the plasma activation, the front face of the insulating layer with the front face of the support substrate to form a bonded substrate; and lifting off a back portion of the source substrate from the bonded substrate to retain an active layer that comprises a remaining portion of the source substrate.
Owner:SOITEC SA
Method for removing film
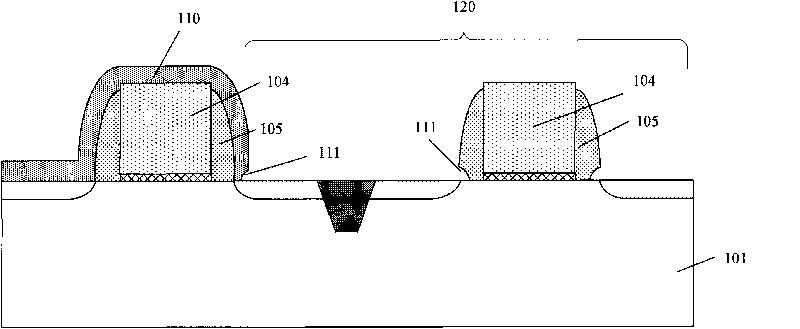
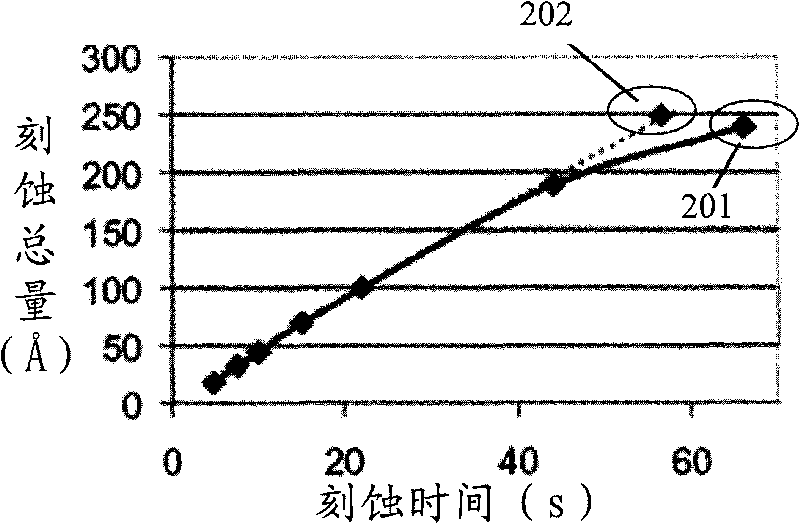
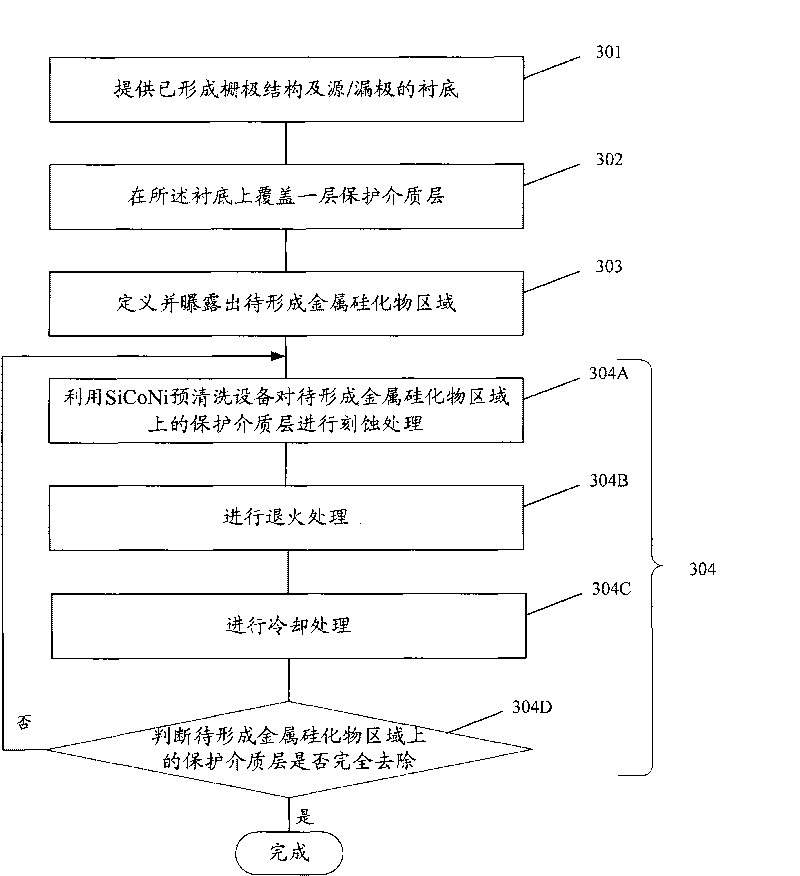
InactiveCN101740338AAvoid damageAchieve removalSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal silicidePlasma activation
The invention discloses a method for removing a film. The method comprises the following steps of: providing a substrate the surface of which is provided with a film; transmitting the substrate to a treating room; carrying out the plasma activation on reactant gas outside the treating room by using a low-powered radio-frequency power supply; introducing the reactant gas after being subjected to the plasma activation to the treating room; and carrying out etching treatment by using the reactant gas after being subjected the plasma activation to remove the film, and removing resultants produced in the etching treatment process by using the annealing treatment. The invention also discloses specific implementation steps for forming a local metal silicide and forming the opening of a contact hole by using the method correspondingly. By using the method for removing a film, the damage to the understructure by a traditional dry etching method can be avoided, and the damage to the side-wall structure by an isotropic wet corrosion method can be also avoided.
Owner:SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING INTERNATIONAL (BEIJING) CORP
Method for preparing aluminum nitride ceramic substrate by adopting composite powder grain shape
The invention discloses a method for preparing an aluminum nitride ceramic substrate by adopting a composite powder grain shape. The method is innovatively characterized by comprising the following steps: calcining aluminum nitride and aluminum oxide composite powder through plasma activation, adding a sintering aid, an organic mixed solvent and other auxiliary solvents for performing ball-milling, performing vacuum defoaming, performing casting molding, performing pre-sintering and sintering on the casting green bodies to obtain the aluminum nitride ceramic substrate. The composite powder of aluminum oxide and aluminum nitride serves as a raw material, the surface state of the powder is changed through plasma calcining, the activity and diffusing capacity of atoms on the surface of the powder are improved, the sintering process is increased, and the sintering temperature is reduced. The powder is sintered in a reducing atmosphere in the sintering process, and novel ecological atoms are formed through a reduction reaction, so that the sintering process is improved, the production cost is saved, and the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:莱鼎电子材料科技有限公司
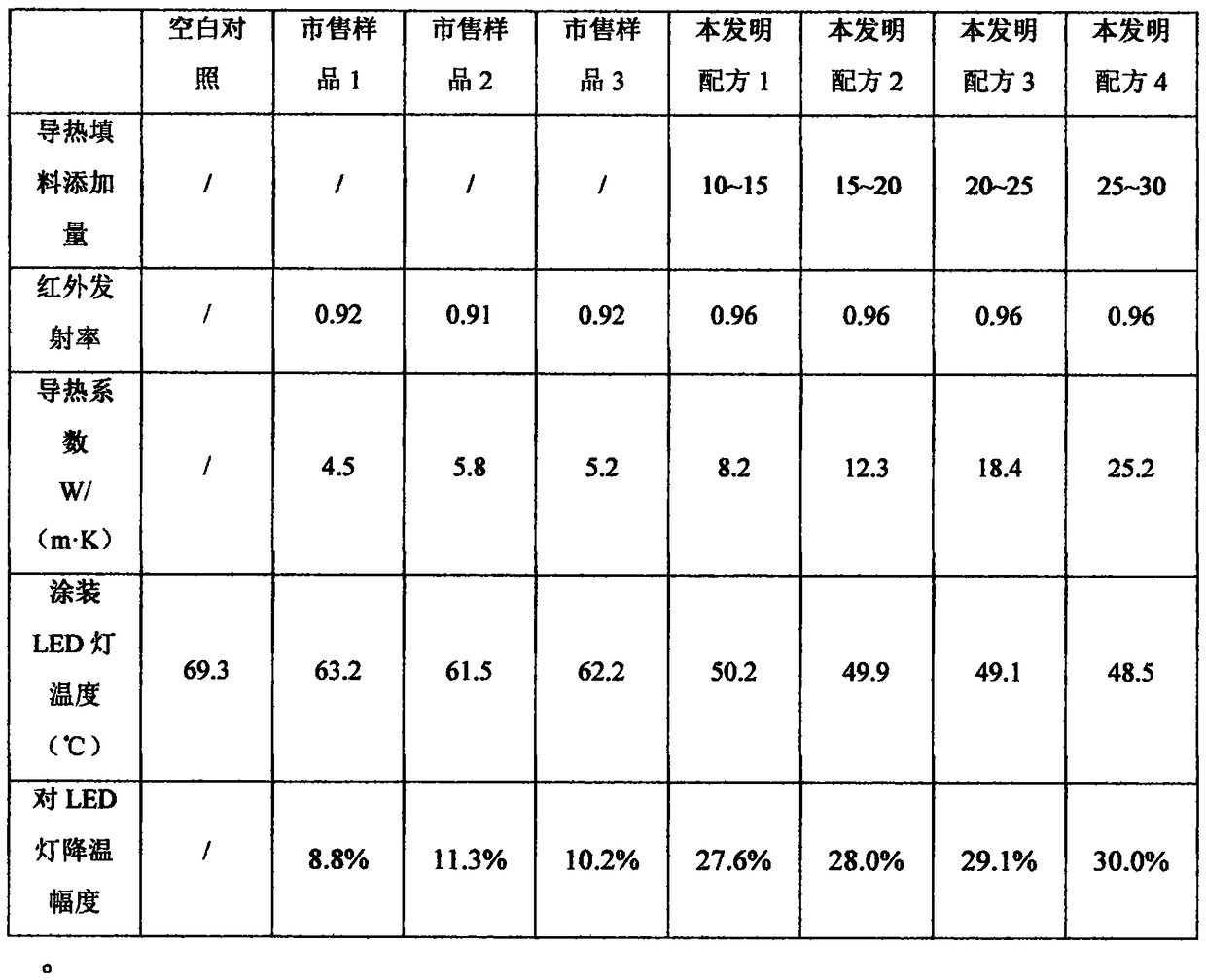
Isocyanate modified graphene containing heat-dissipating coating material and preparation method
ActiveCN109266187AEvenly dispersedCompact formAnti-corrosive paintsPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsCross-linkPolymer science
The invention belongs to the technical field of heat dissipating materials and discloses an isocyanate modified graphene containing heat-dissipating coating material and a preparation method. The heat-dissipating coating material is prepared from a main agent and a curing agent, wherein the mole ratio of hydroxyl radicals of the main agent to isocyanate radicals of the curing agent is 1: (1 to 1.1); the main agent is prepared from a film forming matter, a solvent, adjuvants and heat conducting fillers according to a mass ratio; the curing agent is an isocyanate trimer modified low-temperatureoxygen plasma activated graphene solution. The invention simultaneously discloses the preparation method. The heat-dissipating coating material disclosed by the invention has excellent heat-conductingproperty and high infrared radiance, and heat can be rapidly conducted to a whole coating and is dissipated in an infrared radiating manner; graphene is activated by plasma, the hydroxyl radicals areintroduced to the surface of the graphene under the condition of not carrying in a large number of defects, and can be subjected to a cross-linking reaction with isocyanate, and after isocyanate is grafted, the graphene still reserve original heat-conducting property.
Owner:四川恒力盛泰石墨烯科技有限公司
Antimicrobial material, and a method for the production of an antimicrobial material
InactiveUS20100040659A1Overcome disadvantagesAvoid mergingBiocideInorganic active ingredientsSputteringHydrogen
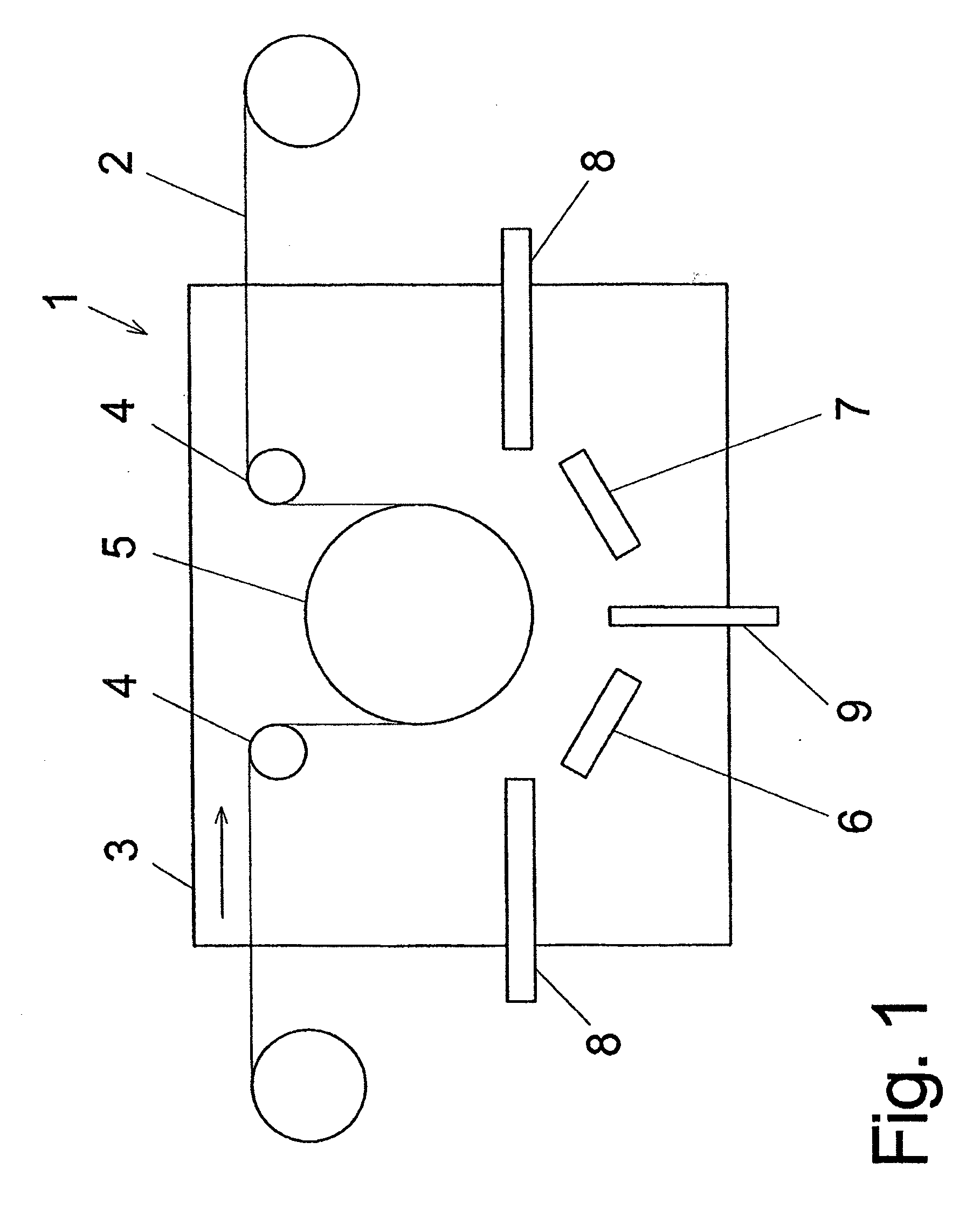
The invention relates to an antimicrobial material and a method for producing an antimicrobial material, which is deposited on a substrate (2), comprising the steps: Providing the substrate (2) in a vacuum working chamber (3); atomizing a biocidal metal by means of a sputtering device inside the vacuum working chamber (3) in the presence of an inert gas; simultaneous introduction of a precursor, which contains silicon, carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, into the vacuum working chamber (3) so that the sputtered metal particles and the precursor are exposed to a plasma action; deposition of a material on the substrate (2) such that a matrix is formed through the plasma activation of the precursor, in which matrix clusters of sputtered metal particles are incorporated.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Surgical Implant
A surgical implant comprising: a substrate having an exterior surface and a plurality of layers disposed over the substrate exterior surface. The substrate comprises a polymeric material, and the plurality of layers comprises: an activated substrate surface layer; a valve metal layer; and a porous valve metal oxide layer, wherein the valve metal layer is disposed between the activated substrate layer and the porous valve metal oxide layer. The disclosure provides for a method for producing a polymeric surgical implant. The exterior substrate surface is treated by one or more processes comprising: plasma activation; electron beam irradiation; ultraviolet light; and low energy Ar+ ion beam irradiation; producing an activated substrate surface layer. A plurality of layers is applied over the activated substrate surface layer. The surface is converted by a spark-anodization process in an alkaline bath containing Ca and P ions into a layer of porous valve metal oxide.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Preparation method of silver composite antibacterial material of carbon nano tube
InactiveCN103843822AEliminate agglomerationSolve the problem of mutual reunion inactivationBiocideDisinfectantsActivated carbonAlcohol
The invention discloses a preparation method of a silver composite antibacterial material of a carbon nano tube. The method comprises the following steps: 1, plasma activating of a carbon nano tube, namely soaking the carbon nano tube in absolute ethyl alcohol, cleaning and drying, and performing plasma activating in a plasma activating instrument; 2, sensitization of the carbon nano tube, namely preparing sensitizing liquid, sensitizing the carbon nano tube subjected to plasma activating in the sensitizing liquid, and drying the carbon nano tube after reaction; and 3, silver plating of the carbon nano tube, namely performing silver plating on the surface of the sensitized carbon nano tube under the protection of inert gases by adopting a vacuum plating machine to obtain the silver composite antibacterial material. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the carbon nano tube is adopted as a supporting carrier, and the carbon nano tube is subjected to plasma activating and sensitizing in sequence, so that the activity of surface functional groups of the activated carbon nano tube is improved, and the silver plating is finally performed, so that agglomeration of silver nanoparticles can be eliminated, the problem of inactivation caused by mutual agglomeration of the silver nanoparticles can be solved, and the antimicrobial activity of the silver nanoparticles can be improved.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
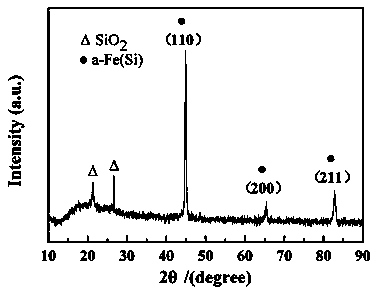
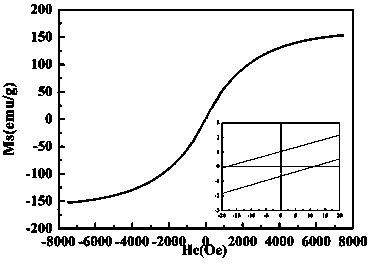
Iron-based alloy magnetic powder core adopting core-shell heterostructure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104078181AEasy to operateReduce manufacturing costInorganic material magnetismHeat stabilityAlloy composite
The invention relates to an iron-based alloy magnetic powder core adopting a core-shell heterostructure and a preparation method thereof. The technical scheme is as follows: 80-95wt% of iron-based alloy powder and 5-20wt% of inorganic oxide powder are evenly mixed and subjected to ball milling for 1-5 h under the shielding of an inert gas, the ball-milled iron-based alloy composite powder is contained in a graphite die, then the graphite die is placed in a plasma activation sintering furnace to be heated to 900-1250 DEG C, the pressure is exerted on the graphite die to 20-50 MPa, and the temperature is kept for 5-30 min under the shielding of the inert gas; the temperature is reduced to 400-500 DEG C at the temperature reduction rate of 30-50 DEG C / min, and the graphite die is cooled along with the furnace; the pressure exerted on the graphite die is unchanged when the temperature is kept and reduced to 400-500 DEG C, and the pressure is reduced to 0 at a constant speed during cooling; the graphite die is taken out of the furnace, and demolding is performed to obtain the iron-based alloy magnetic powder core adopting the core-shell heterostructure. The preparation method is simple in process, high in preparation efficiency and low in preparation cost; the iron-based alloy magnetic powder core is high in saturation flux density, high in density, good in insulating property, low in eddy-current loss and good in thermal stability.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
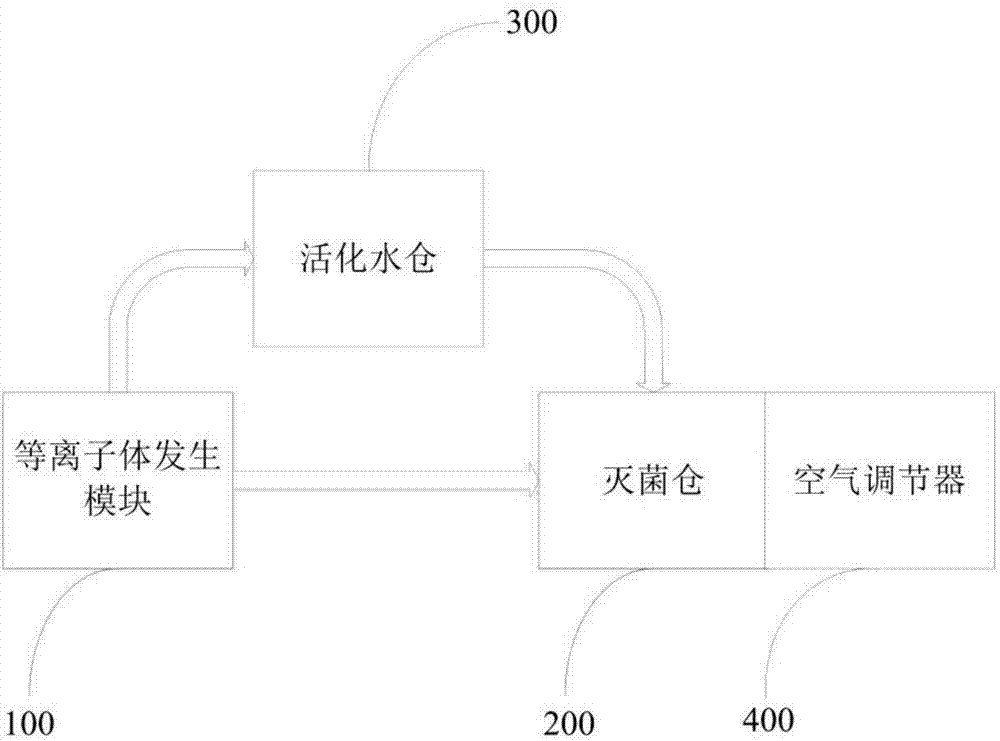
Dry-wet plasma sterilization device and method
ActiveCN104707154AEfficient killingHigh densityLavatory sanitoryChemicalsHigh concentrationPlasma sterilization
The invention discloses a dry-wet plasma sterilization device and method. The device is characterized by comprising a plasma generation module, a sterilization chamber, an activation water chamber and an air conditioner. The device works in the manner of generating plasmas for sterilization under low temperature and normal pressure, and under a dry-wet condition, activated particles generated by the plasmas are different, and the endurance of bacteria is different, so that sterilization effects better than those achieved by the independent use of a dry method or a wet method are achieved. Wet sterilization refers to atomizing and spraying the activated particles in the plasma activation water chamber into the sterilization chamber and condensing the activated particles on the surface and in a sterilized object to realize set sterilization without any dead angle. Dry sterilization refers to generating high-concentration activated particles directly acting on the object in the sterilization chamber for sterilization by virtue of the plasma generation module and removing surface residues left by sterilization treatment by virtue of dry hot airflow. Dry sterilization and wet sterilization are alternately carried out, and sterilization condition selectivity, low temperature, high efficiency and no residues are achieved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
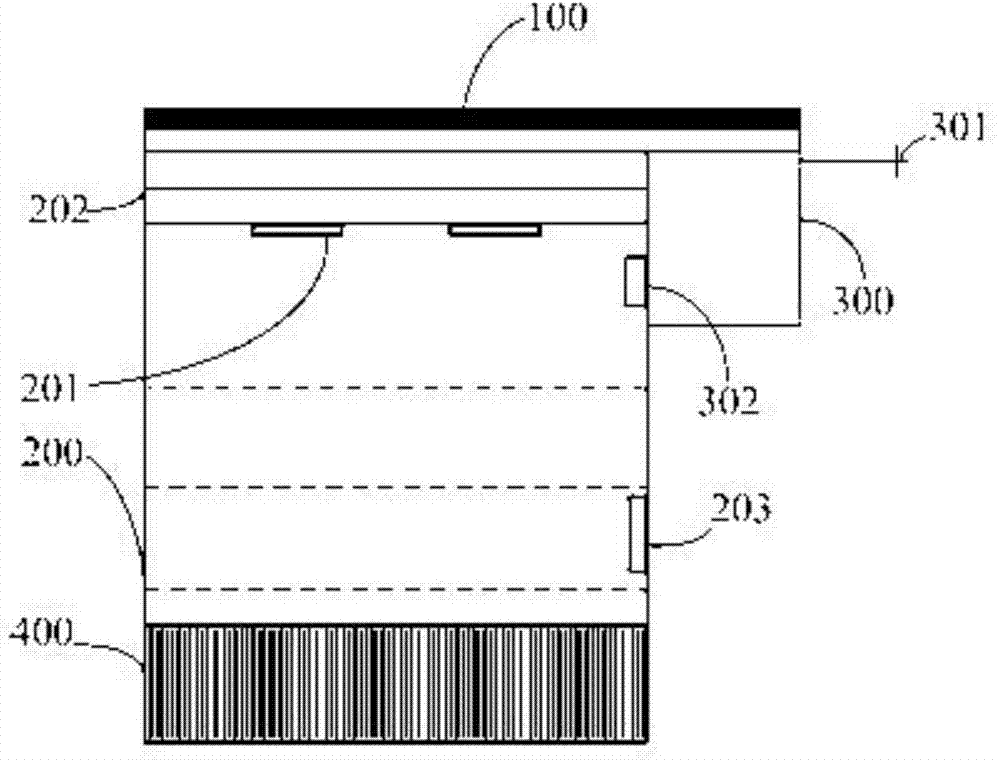
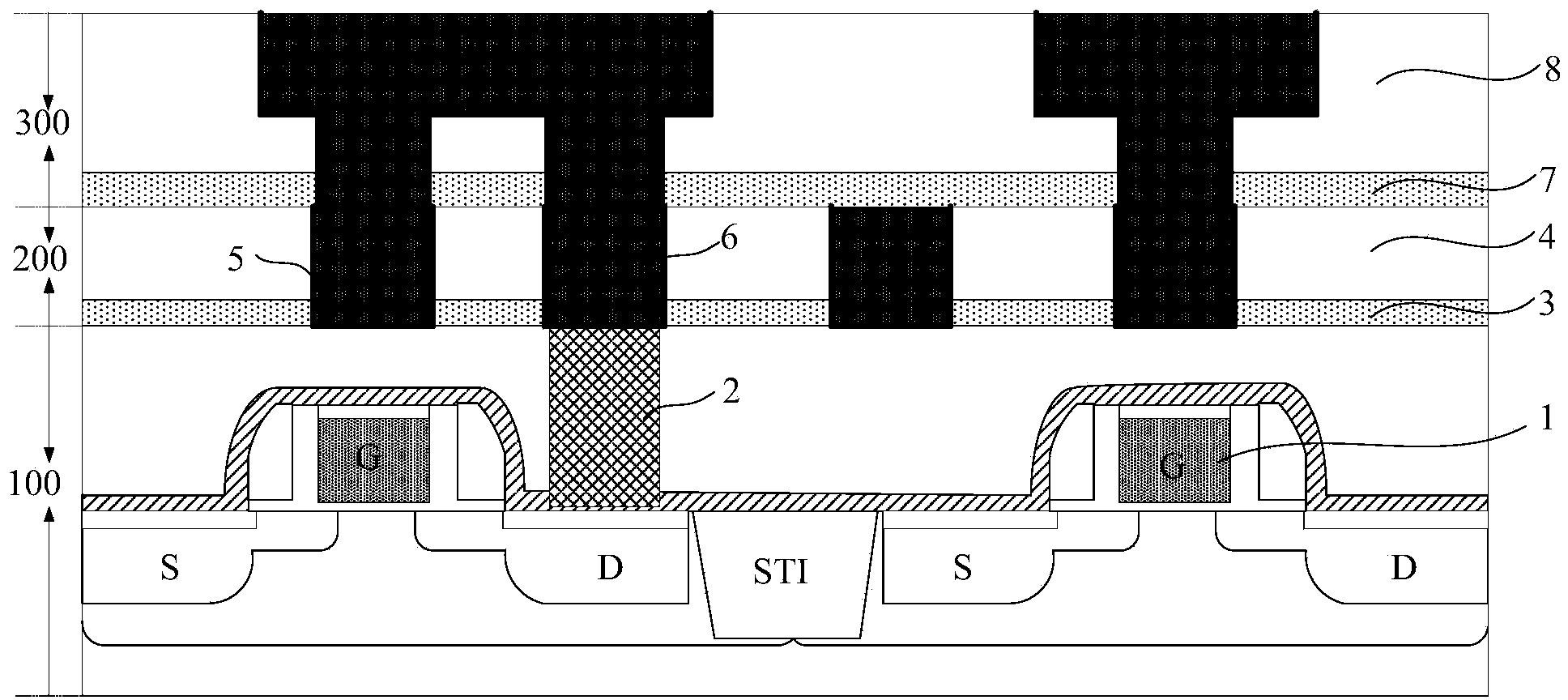
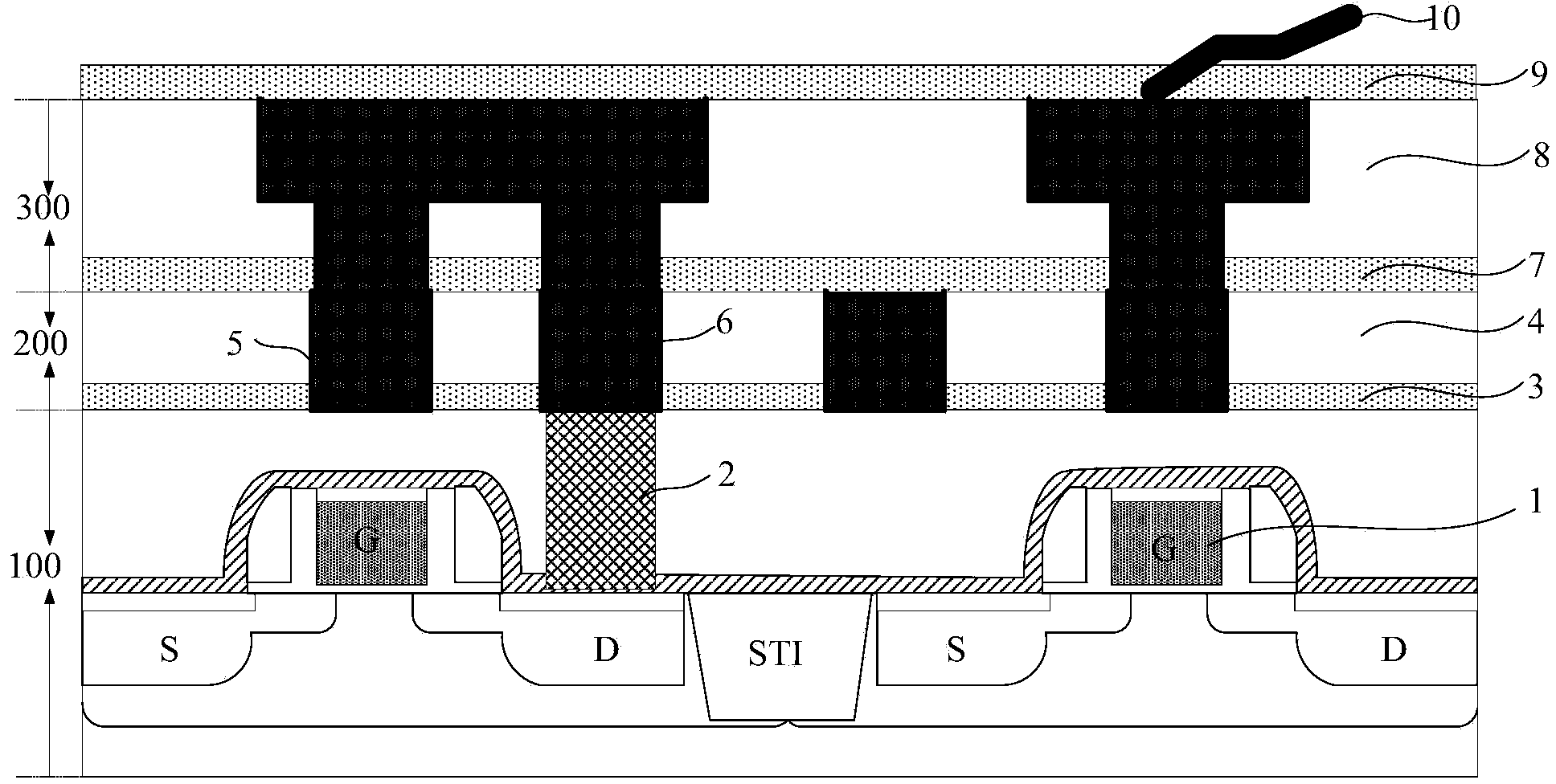
Method for lowering influence on copper interconnection reliability from online WAT testing
ActiveCN103972160AConvenient thermal protectionEfficient removalSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingReduction treatmentSurface plasmon
The invention provides a method for lowering the influence on the copper interconnection reliability from the online WAT testing. The method comprises the steps that at least one layer of to-be-tested copper interconnection structure comprising a testing component is formed on a semiconductor substrate; a dielectric barrier layer is deposited on the surface of the to-be-tested copper interconnection structure in advance, and a wafer to be tested is obtained; a testing probe penetrates through the dielectric barrier layer and keeps contact with the copper surface of the testing component, and online WAT testing is carried out on the wafer to be tested; surface activation and reduction treatment are carried out on the tested dielectric barrier layer and a small part of copper exposed after making contact with the testing probe through reducing plasma gas; the dielectric barrier layer continues to be deposited to be at the preset thickness. Through the method for combining the pre-deposited dielectric barrier layer serving as an isolation protection layer before the testing with the surface plasma activation and reduction treatment after the testing, defects in copper and dielectric materials are effectively restrained from being generated in the online WAT testing process, and the influence on the copper interconnection reliability from the online WAT testing is lowered significantly.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Manufacturing method for novel shadow mask for producing OLED display panel
ActiveCN103866230AThe production process is easy to etchShorten etch cycleVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingEvaporationPlasma activation
The invention discloses a manufacturing method for a novel shadow mask for producing an OLED display panel. The manufacturing method comprises the steps of preparing a substrate or a framework workpiece, processing an alignment marker, embedding a filler, coating a photosensitive layer, performing exposure, development and plasma activation treatment, protecting a non-electric depositional surface, electrically depositing a fine mask, removing the photosensitive layer, removing the filler and the like. The filler is very convenient to remove and etch; in an etching process, a protection layer does not need to be added, and the filler etching work can be finished within 2-3 hours, so that the etching period is greatly shortened, and the production cost of a product is lowered. According to the shadow mask manufactured by the method disclosed by the invention, the fine mask and the substrate or the framework are tightly combined to form an integrated structure; on one hand, the process for welding the fine mask on a border is canceled, and the manufacturing process is simplified; on the other hand, an inner separation frame on the substrate or the framework can achieve a certain supporting and protecting effect in a corresponding operation process for cleaning and OLED evaporation, so that drop-down of the fine mask is alleviated, and the service life of the shadow mask is greatly prolonged.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN AISCENT TECH
Composite diamond coating hard alloy cutter mold and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109930129AAvoid it happening againImprove stress distributionChemical vapor deposition coatingMicro nanoEtching
The invention discloses a composite diamond coating hard alloy cutter mold and a preparation method thereof. The surface layer of the hard alloy cutter mold is provided with composite coatings composed of boron-doped or non-boron-doped micron-crystal diamonds and nanocrystalline diamonds which are alternately arranged, and a layer of diamond-like coating DLC is deposited on the surface of each composite diamond coating. The preparation method comprises the steps of oil removal and degreasing, chemical micro-etching, plasma activation, plasma enhanced gaseous boronizing, plasma cleaning, diamond slurry ultrasonic grinding, nano-scale and micron-diamond seed crystal planting, and vapor-phase deposition of the diamond composite coatings. According to the method, boron atoms enter diamond crystal lattices by doping boron in the diamond deposition process, the internal stress of the diamond coatings is adjusted, and the generation of a stress sudden change region is avoided, so that the situation that the stress of each layer is not matched is avoided fundamentally, the stress distribution inside the composite coatings is effectively improved, the integrity of the micro-nano composite coatings is further improved, the substrate-film binding force is improved, and the comprehensive mechanical property of the composite coatings is improved.
Owner:HU-NAN NEW FRONTIER SCI & TECH LTD
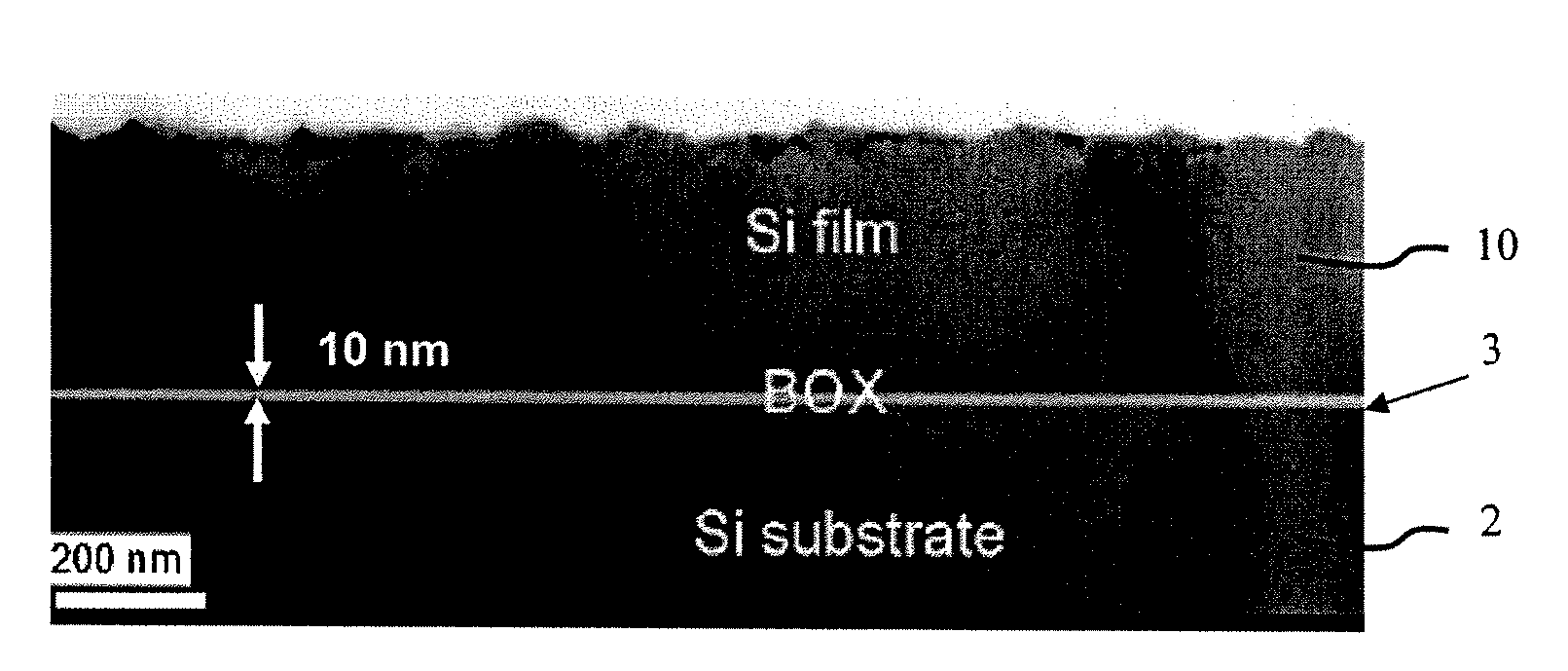
Method for manufacturing SOI wafer
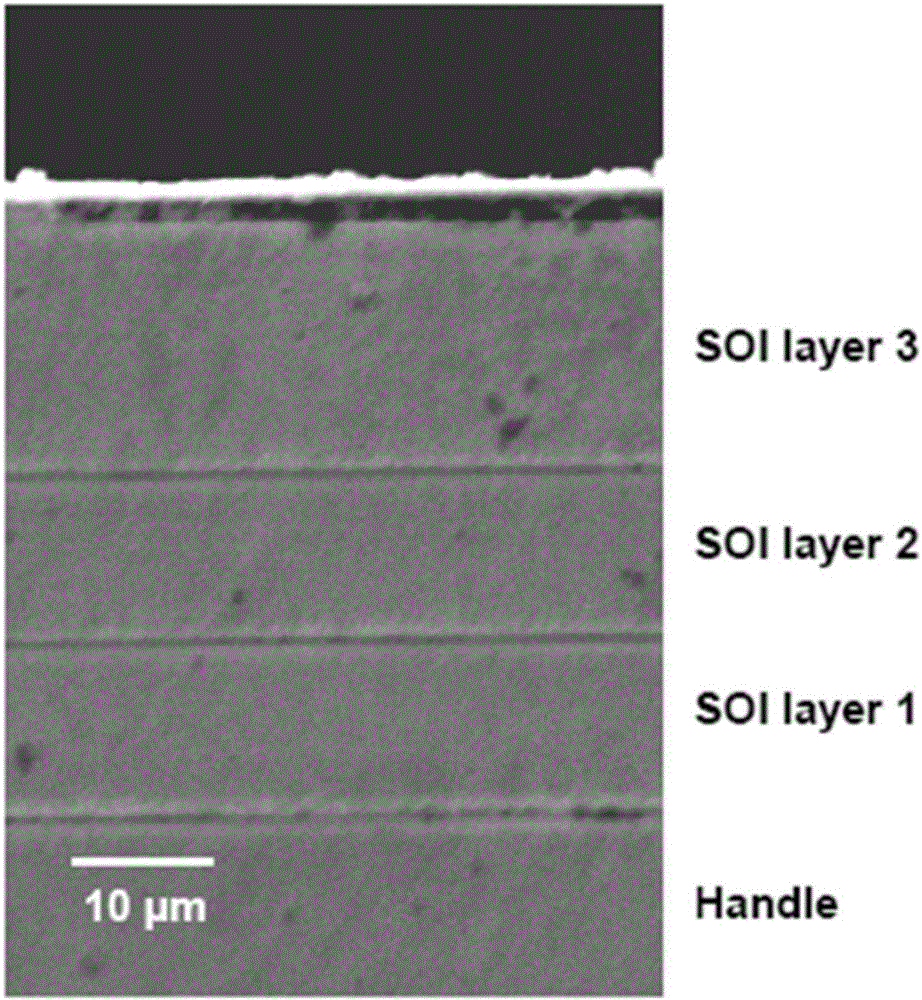
ActiveUS20090023270A1Improve film thickness uniformityIncrease production capacitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProduction rateWafering
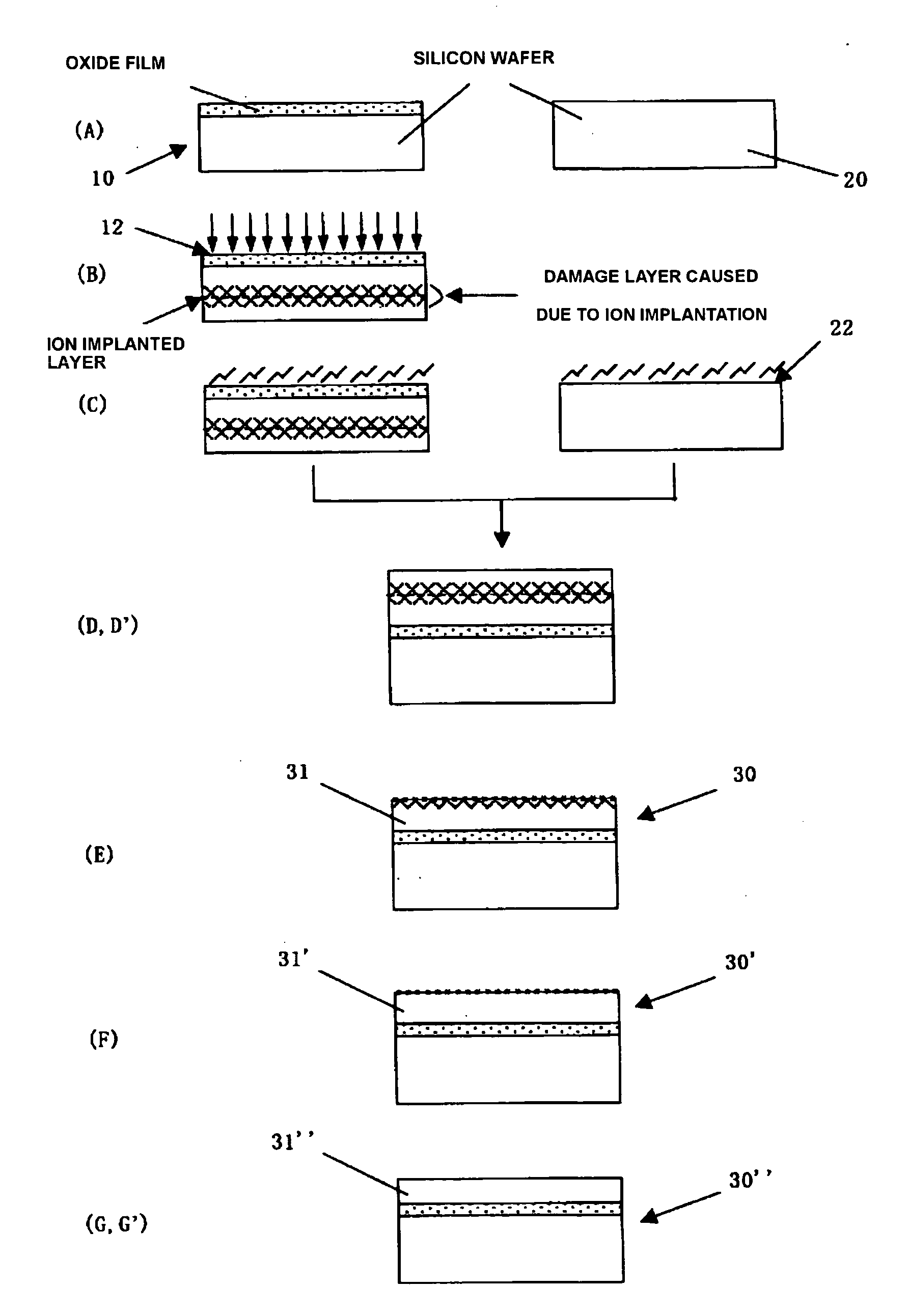
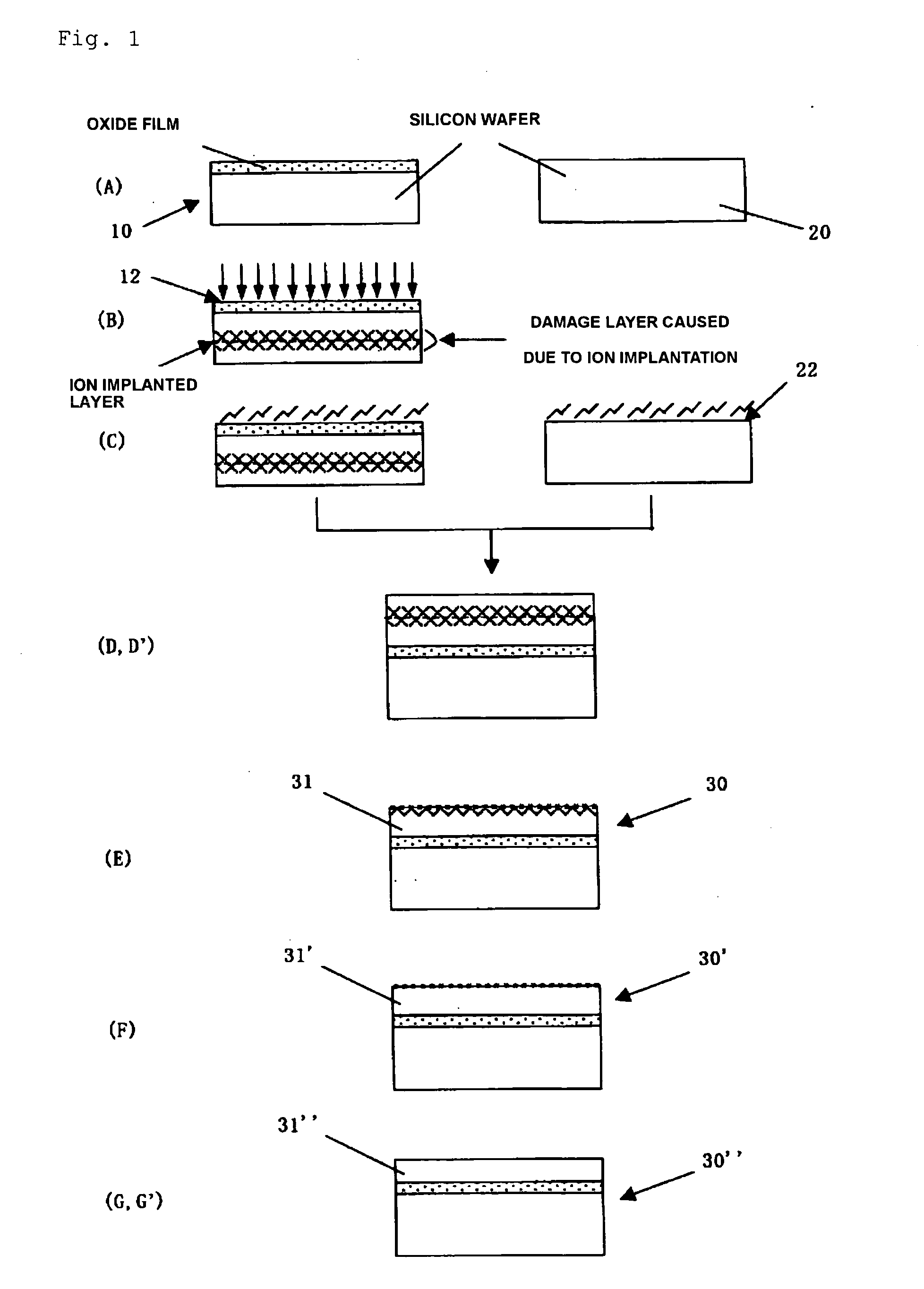
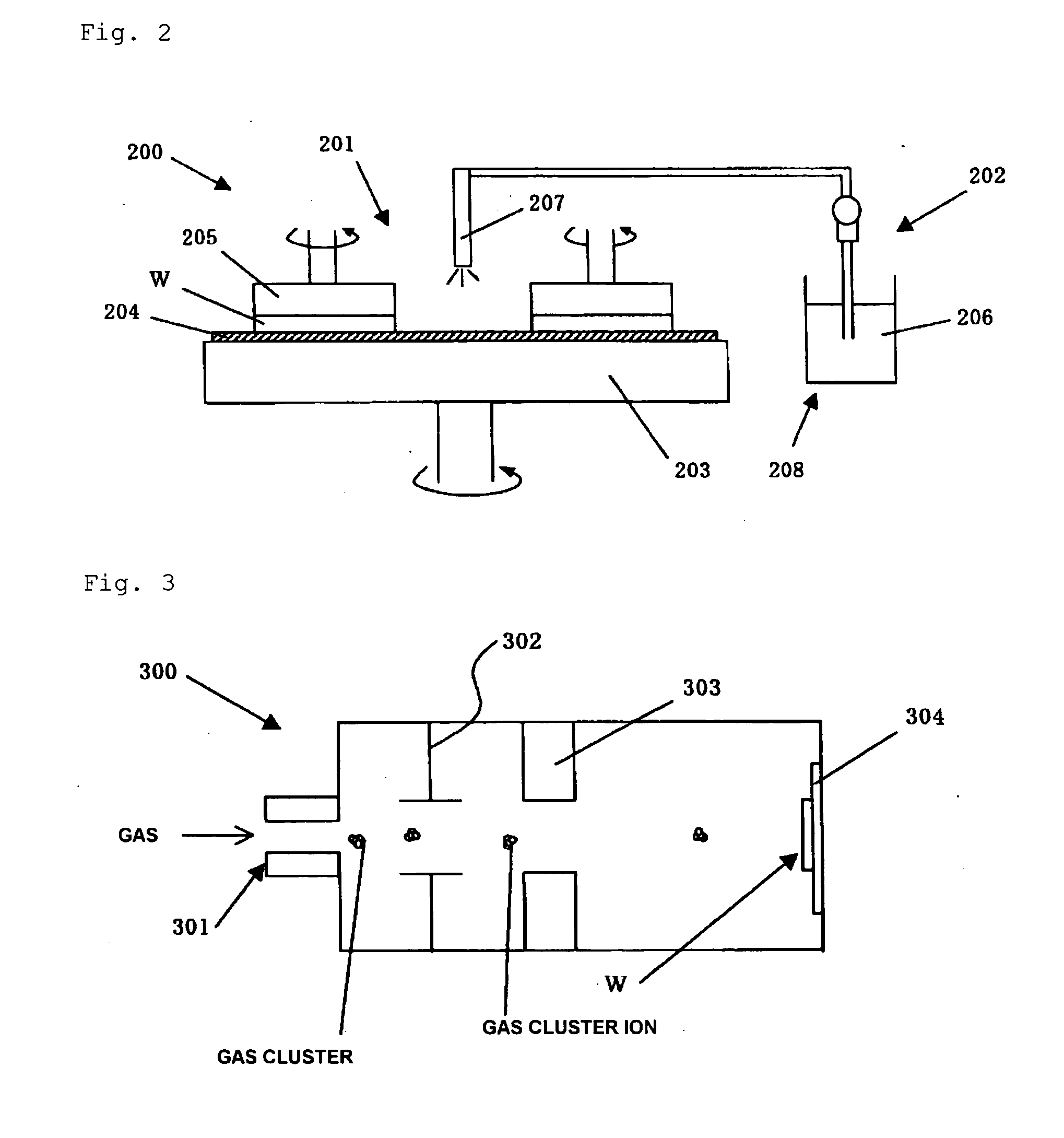
There is disclosed a method for manufacturing an SOI wafer comprising at least: implanting a hydrogen ion, a rare gas ion, or both the ions into a donor wafer formed of a silicon wafer or a silicon wafer having an oxide film formed on a surface thereof from a surface of the donor wafer, thereby forming an ion implanted layer; performing a plasma activation treatment with respect to at least one of an ion implanted surface of the donor wafer and a surface of a handle wafer, the surface of the handle wafer is to be bonded to the ion implanted surface; closely bonding these surfaces to each other; mechanically delaminating the donor wafer at the ion implanted layer as a boundary and thereby reducing a film thickness thereof to provide an SOI layer, and performing a heat treatment at 600 to 1000° C.; and polishing a surface of the SOI layer for 10 to 50 nm based on chemical mechanical polishing.A method for manufacturing with excellent productivity an SOI wafer having an SOI layer with a mirror-finished surface and high film thickness uniformity can be provided.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
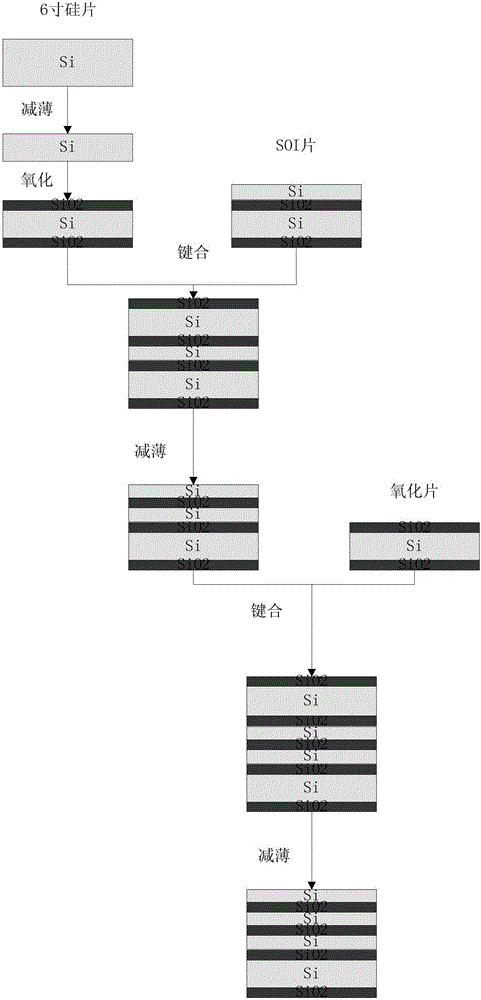
Multilayer SOI material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106409649ANo defectSmall edge lossSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsMetallurgy
The invention discloses a multilayer SOI material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of semiconductor material preparation. The material is a multilayer SOI stacked structure, the top surface and the bottom surface of the stacked structure are silicon chips, and the middle portion is formed by alternative arrangement of silicon chips and BOX layers. In a preparation process, the stress of an oxidation sheet is removed through a CMP method, and bonding of the multilayer SOI can be stacked on the oxidation sheet. Surface treatment of the silicon chip with the surface of the oxidation sheet is performed for 1-5 minutes by employing HF, and plasma activation treatment is also performed; and surface treatment of the silicon chip with the surface of the silicon chip is performed for 1-5 minutes by employing concentrated H2SO4. After the treatment, normal-temperature bonding is then performed, low-temperature annealing can be performed at the temperature of lower than 500 DEG C, extremely good bonding quality is obtained, and the edge loss is less than 0.5 mm in the subsequent thinning process. The whole bonding process is accomplished at a low temperature, and the multi-layer SOI device layer is prevented from high temperature so that defects can be avoided.
Owner:SHENYANG SILICON TECH
Method for adopting spark plasma for sintering high-performance copper tungsten electrical contact materials
ActiveCN104014792AFacilitate the control of fine structureHigh densityElectric switchesFine structureElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses a method for adopting spark plasma for sintering high-performance copper tungsten electrical contact materials. According to the method, tungsten powder and copper powder are prepared into copper tungsten composite powder and placed into a graphite mould; the graphite mould is placed into a spark plasma sintering furnace, the pressure of 20 MPa to 60 MPa is applied on the copper tungsten composite powder, inert gas is introduced into the sintering furnace, or the sintering furnace is vacuumized, the sintering temperature ranges from 900 DEG C to 1200 DEG C, heat is preserved for 5 minutes to 25 minutes, finally the copper tungsten composite powder is cooled to the room temperature along with the furnace to manufacture the copper tungsten electrical contact materials. In comparison with a traditional sintering process, the spark plasma sintering method is the integrated sintering technology integrating hot pressing, plasma activating and resistance heating and has the advantages that the temperature rises fast, sintering time is short and crystal grains are uniform, the fine structure of a sintered body can be controlled easily, and therefore the obtained materials are high in compactness and good in performance.
Owner:福建国福天合电气科技有限公司
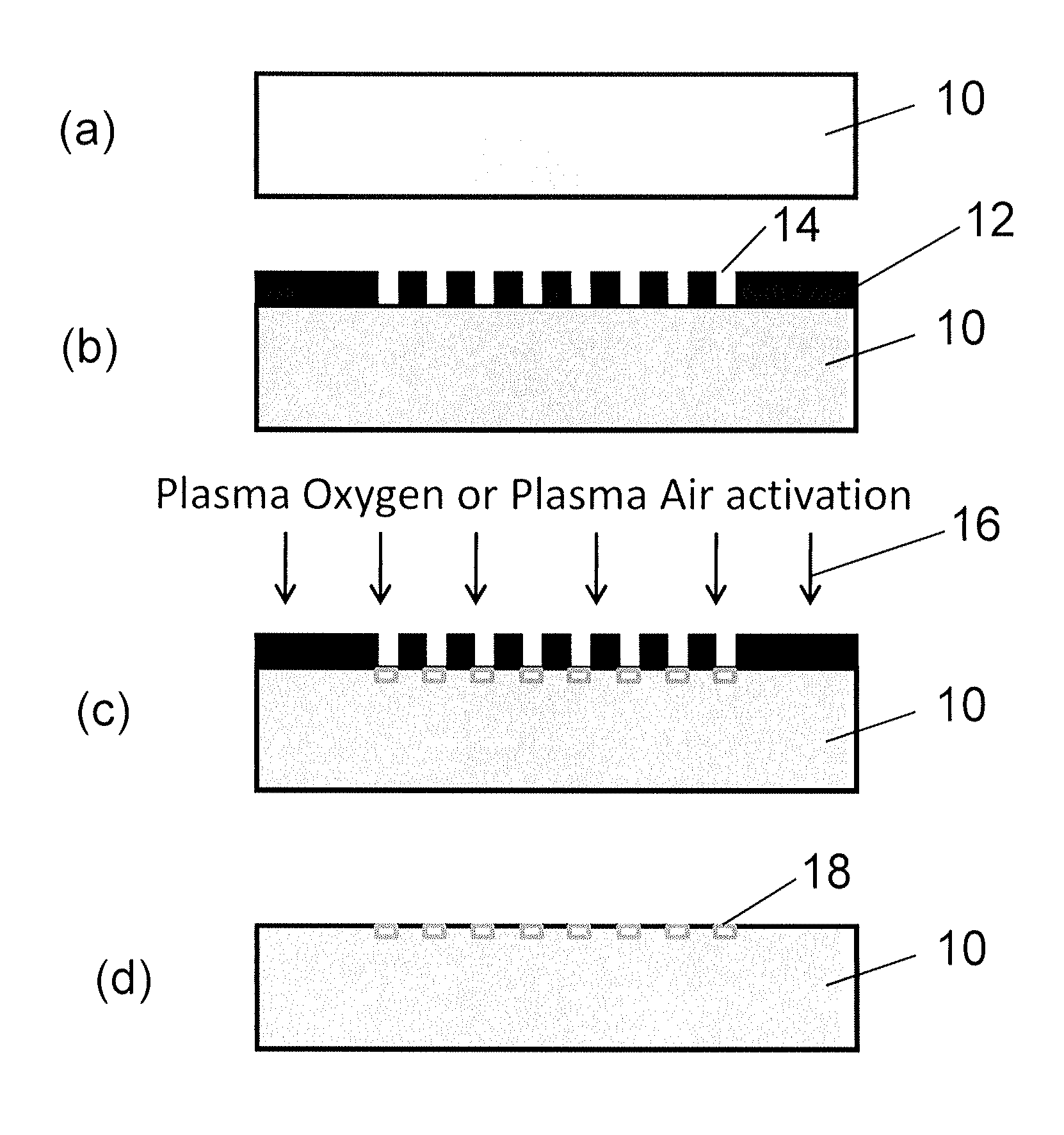
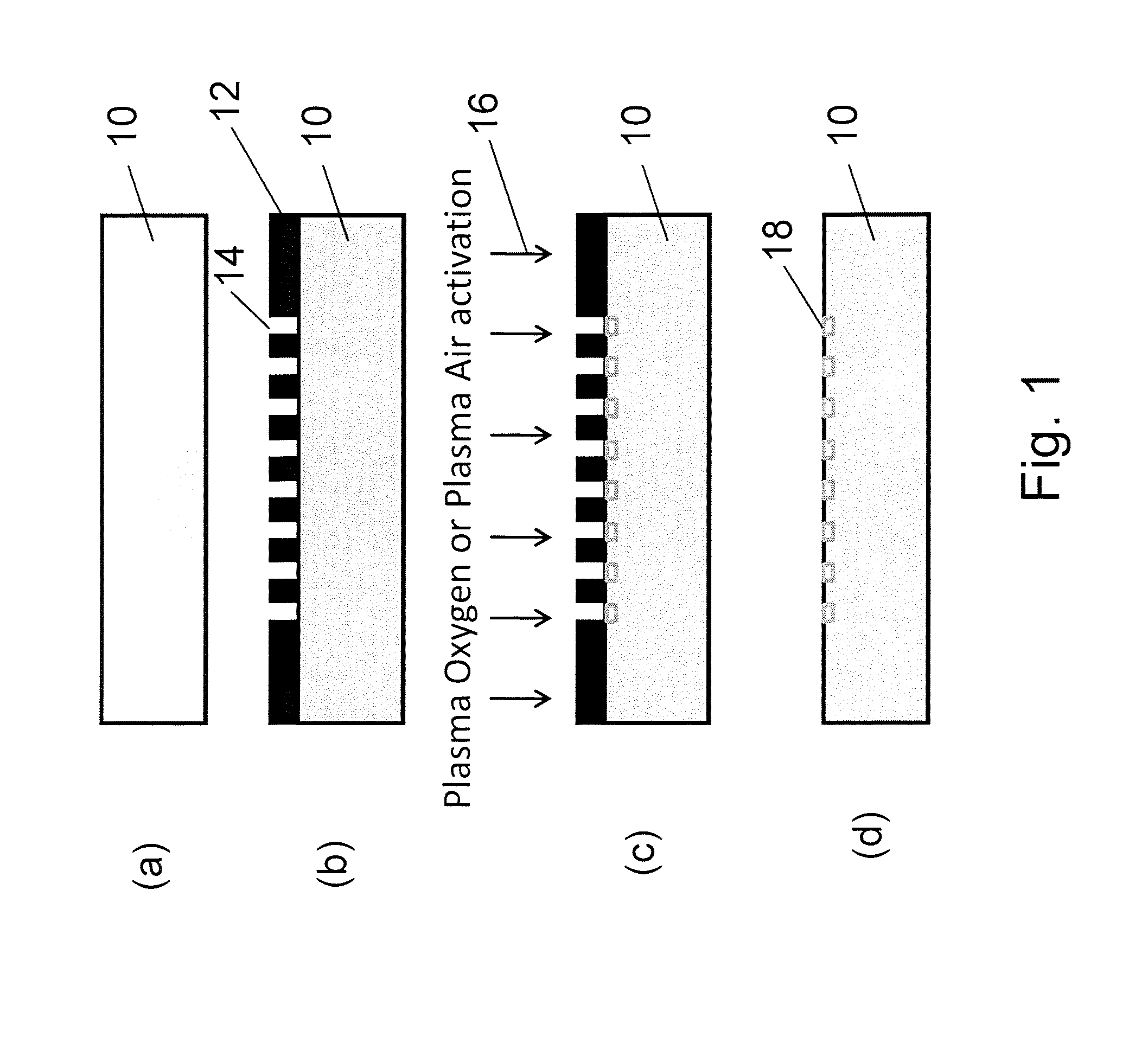
Selective Plasma Activation for Medical Implants and Wound Healing Devices
InactiveUS20140377320A1Small sizeRetard and inhibit and prevent fibrotic growthBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsFiberWound healing
A treated surface of a device (10) for implantation or for application as a wound dressing, comprises an array of plasma-activated hydrophilic cell-adhesive areas (18) having the ability to reduce fibrous reaction, is in the form of an array of islets of activation. Each islet of activation (18) has a length which is less than 6 μm, a width which is less than 2 μm and the distance between islets is preferably from 4 μm to 6 μm. The islets of activation (18) are surrounded by non-activated, non-adhesive, hydrophobic areas.
Owner:CENT HOSPITALIER UNIV VAUDOIS C H U V
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com