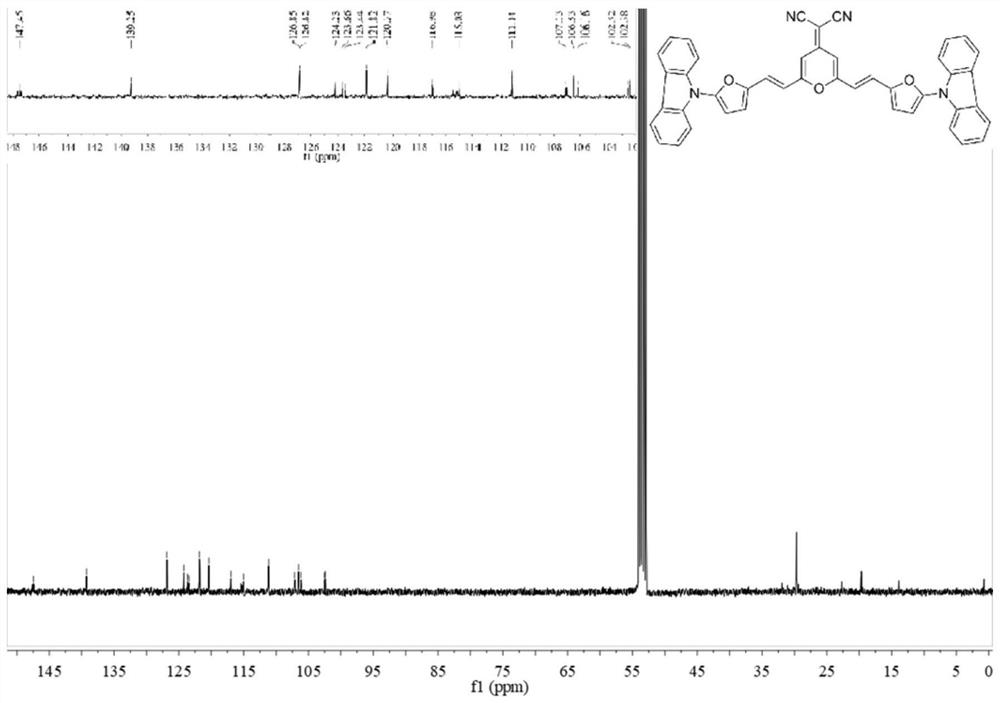
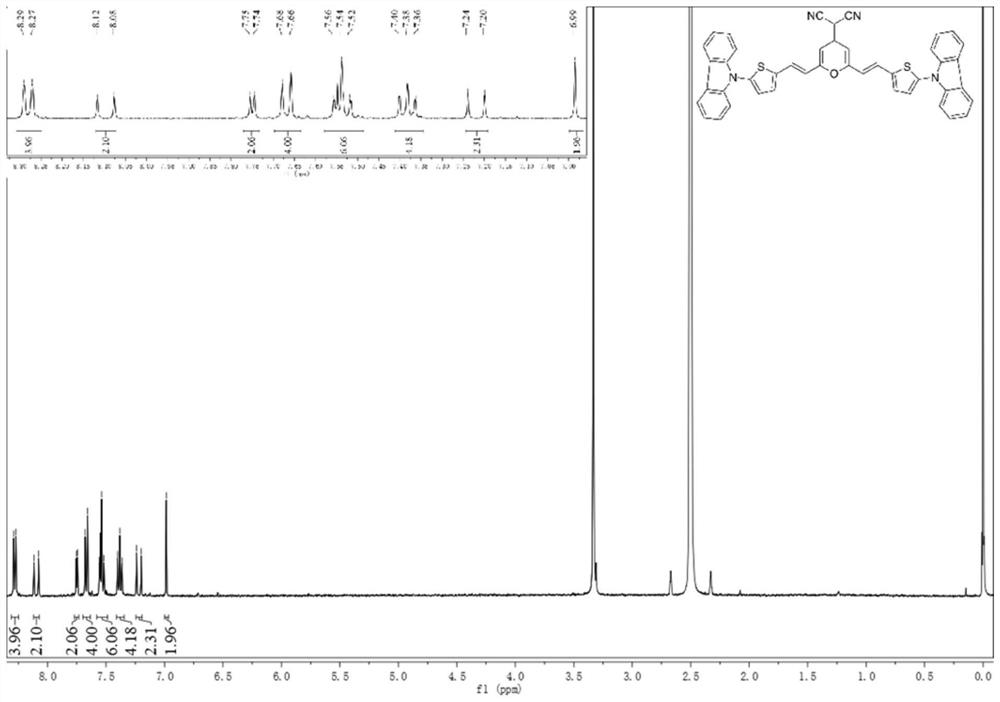
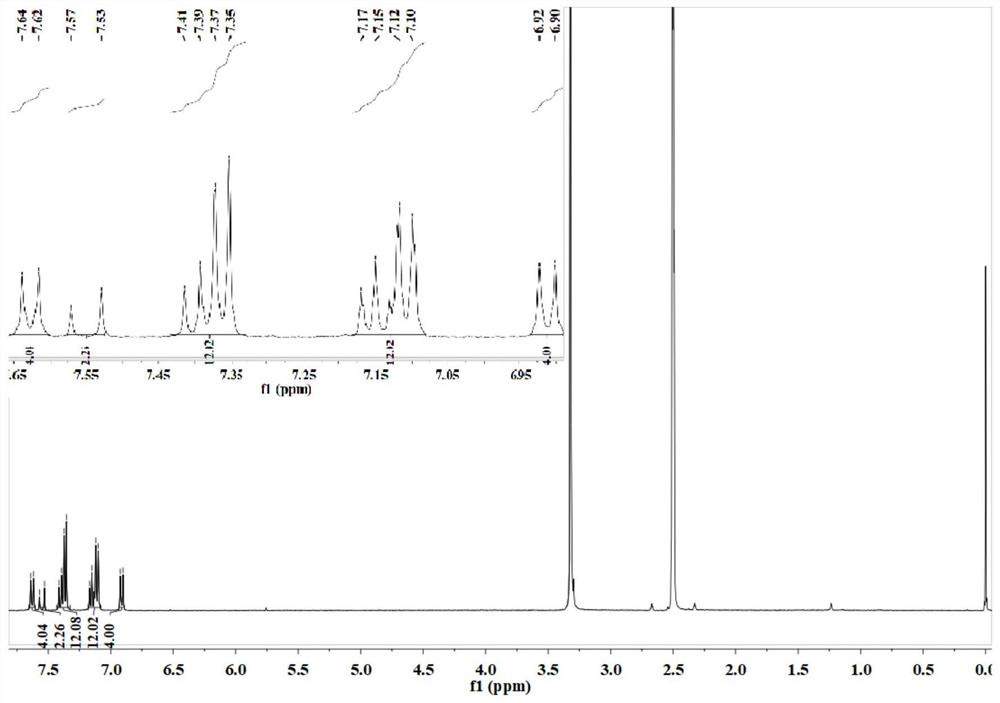
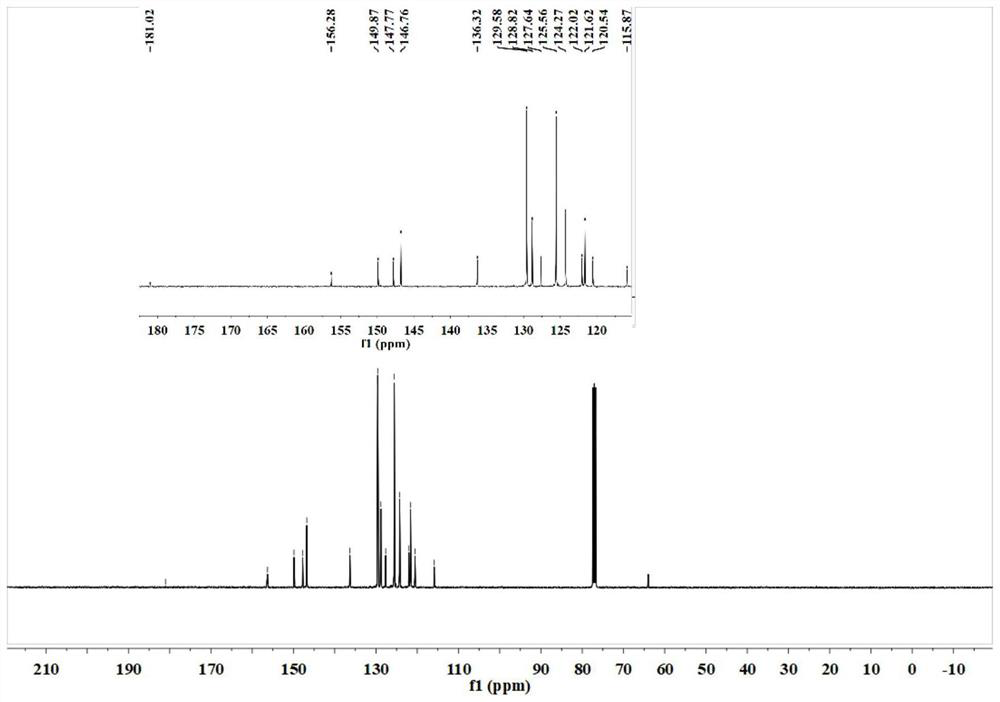
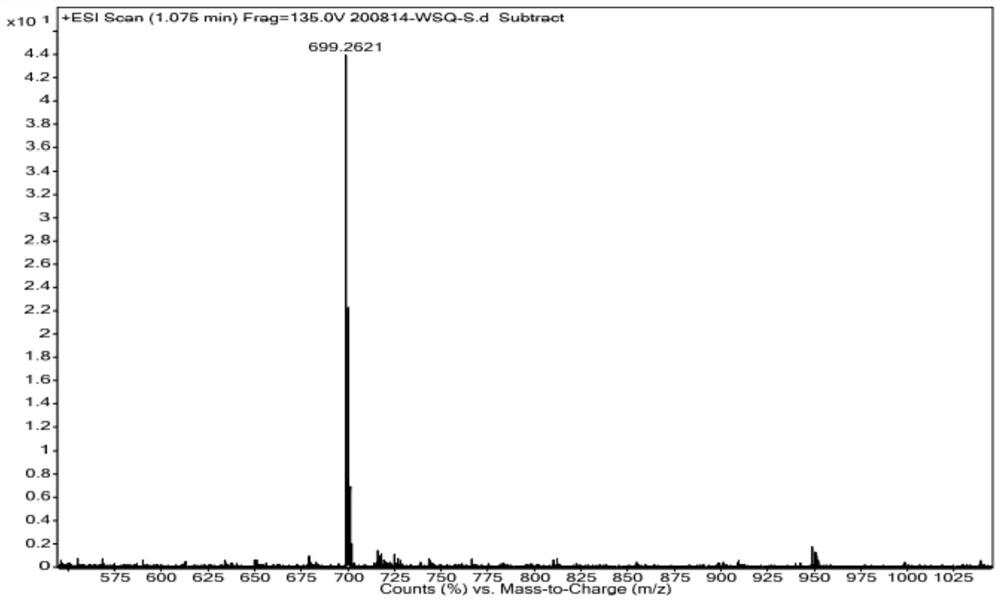
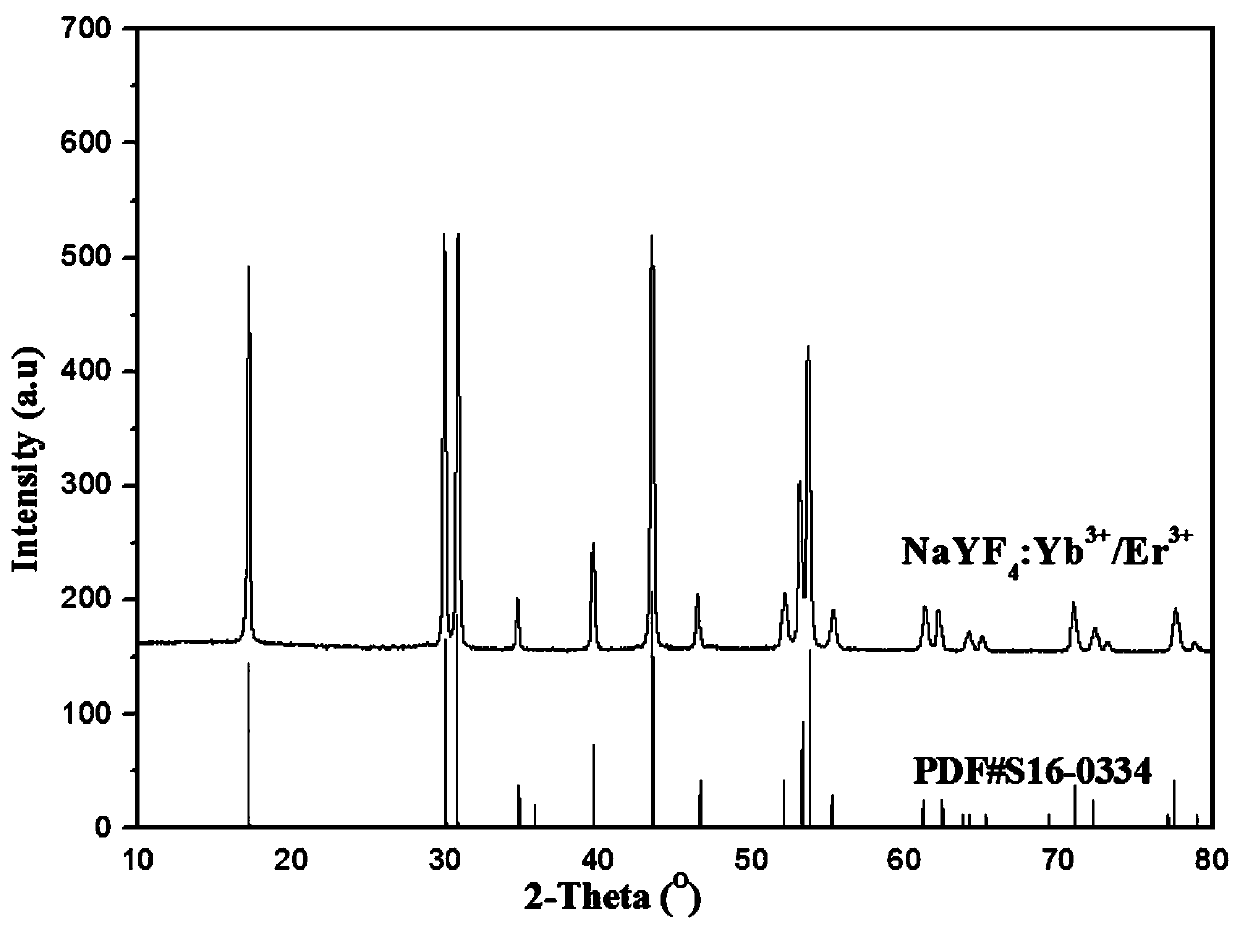
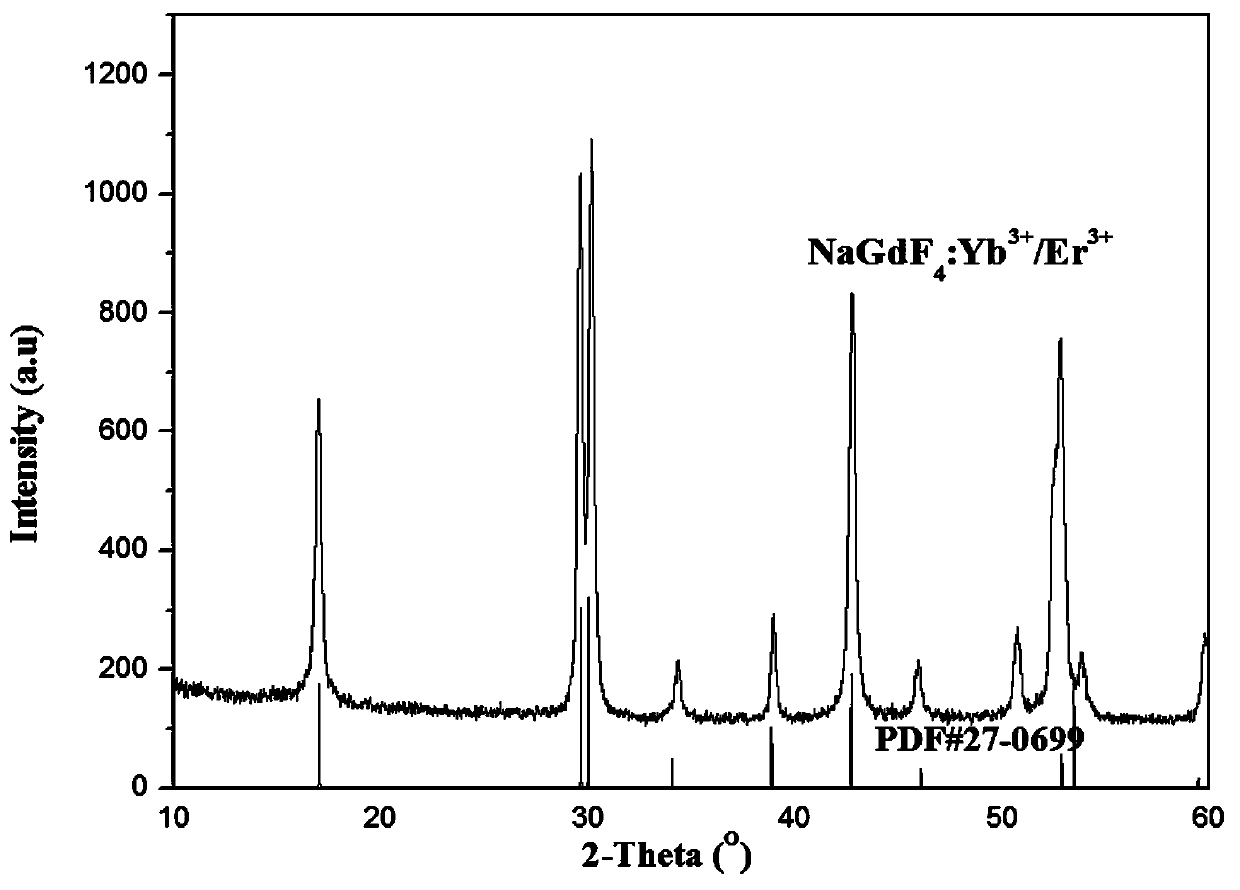
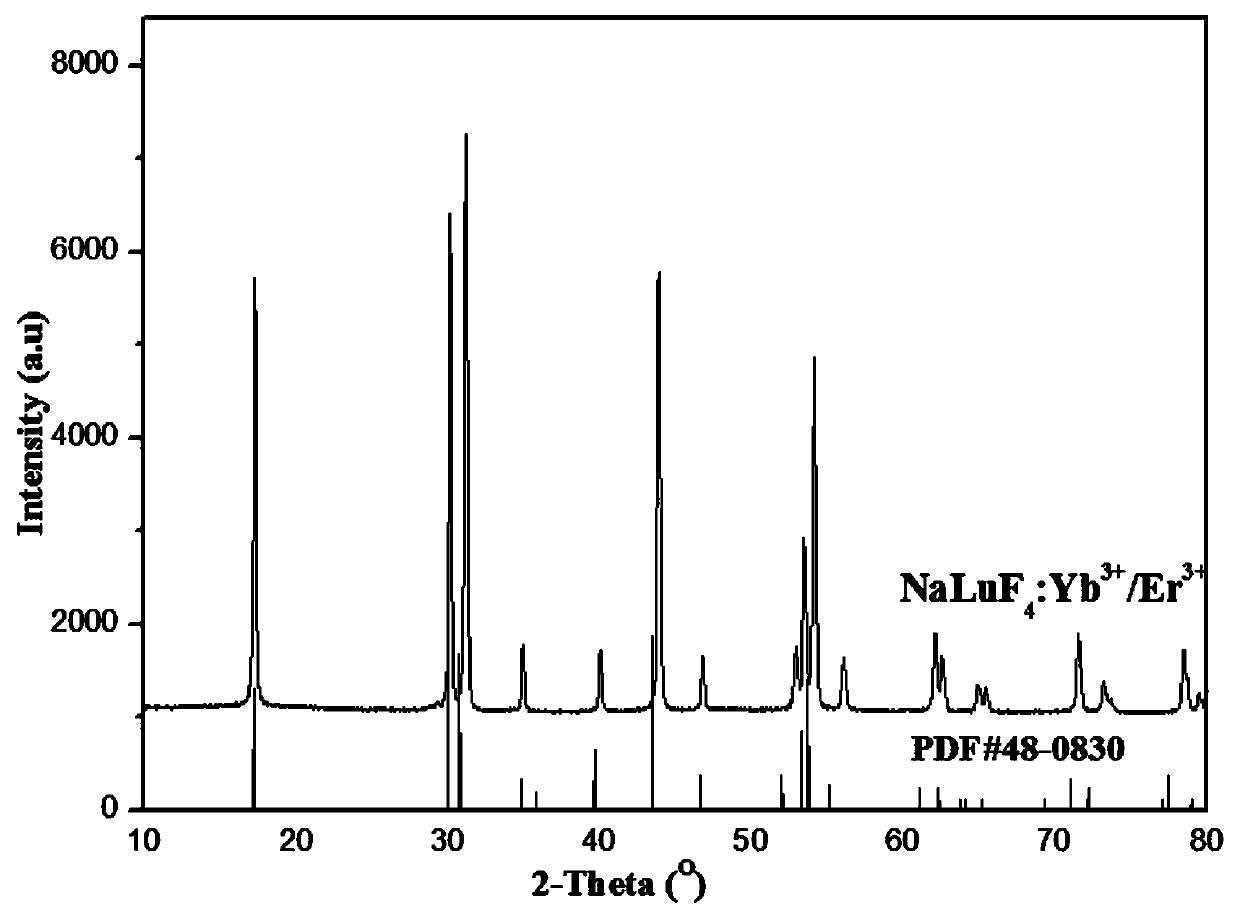
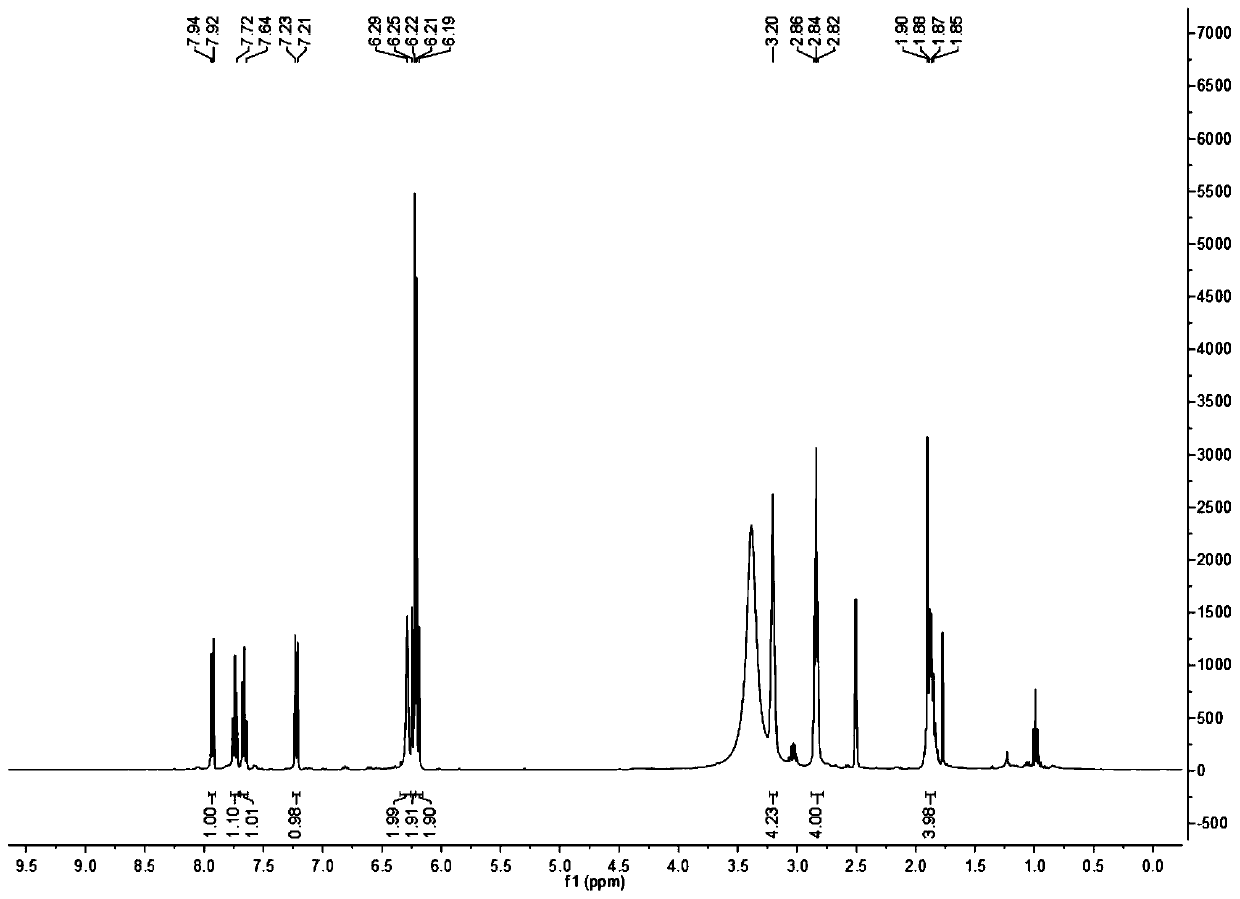
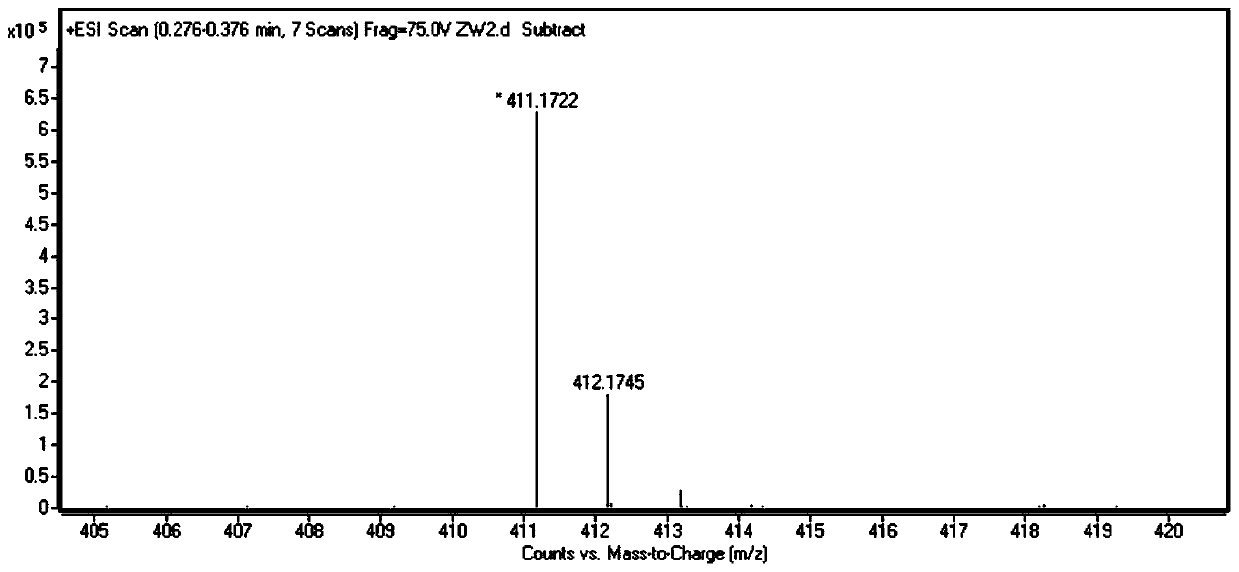
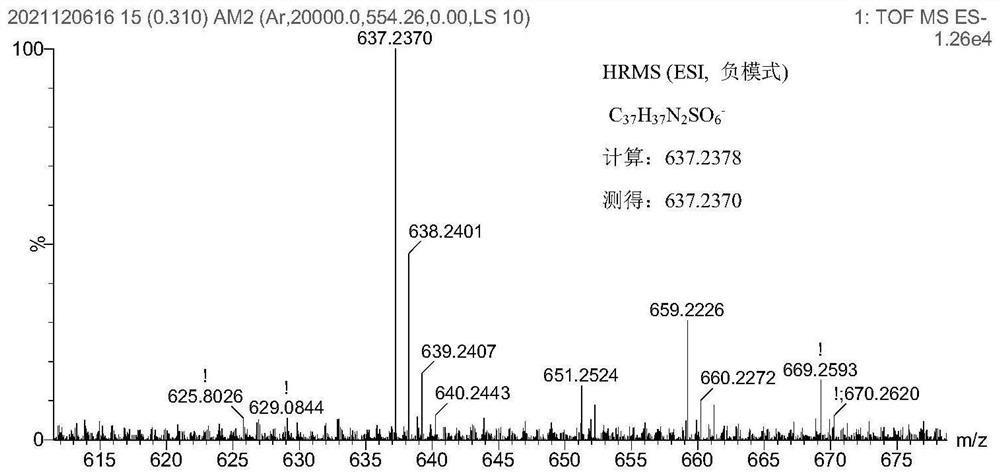
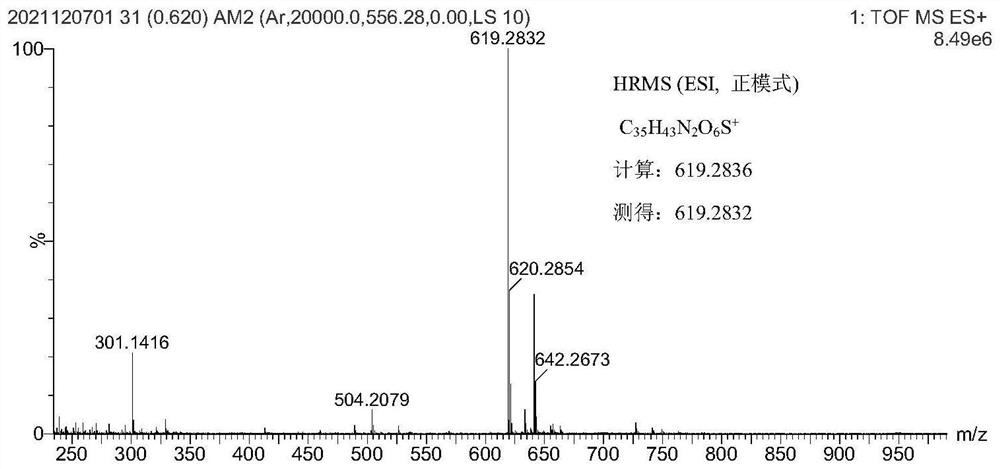
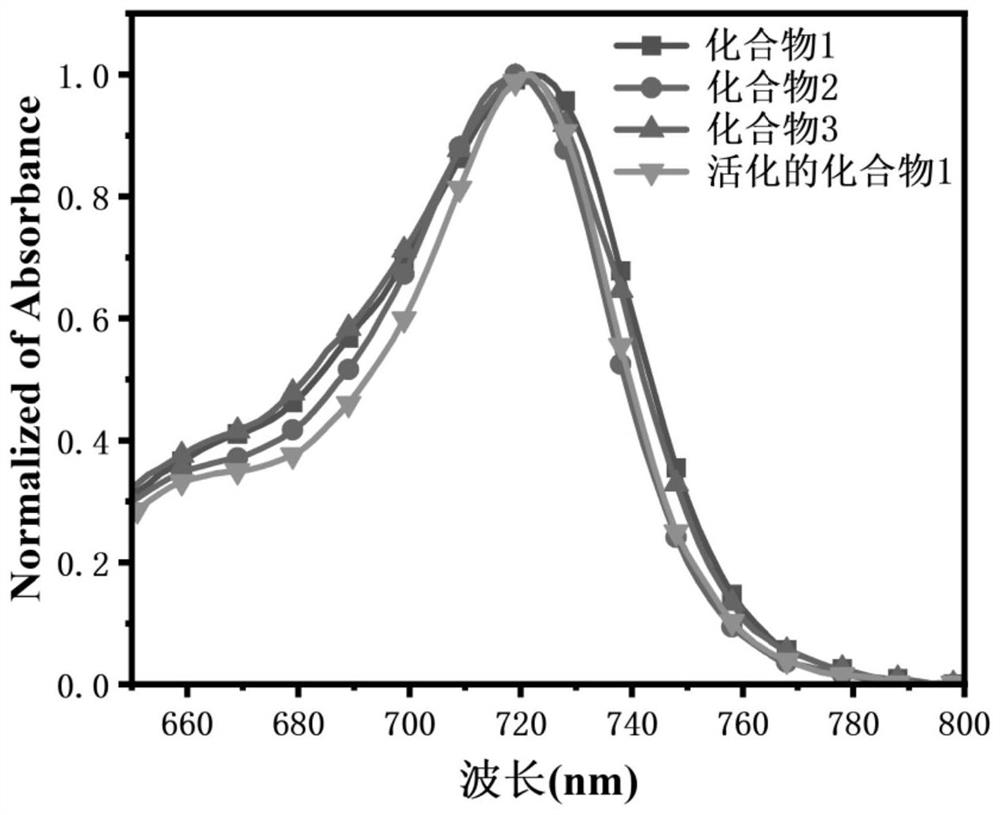
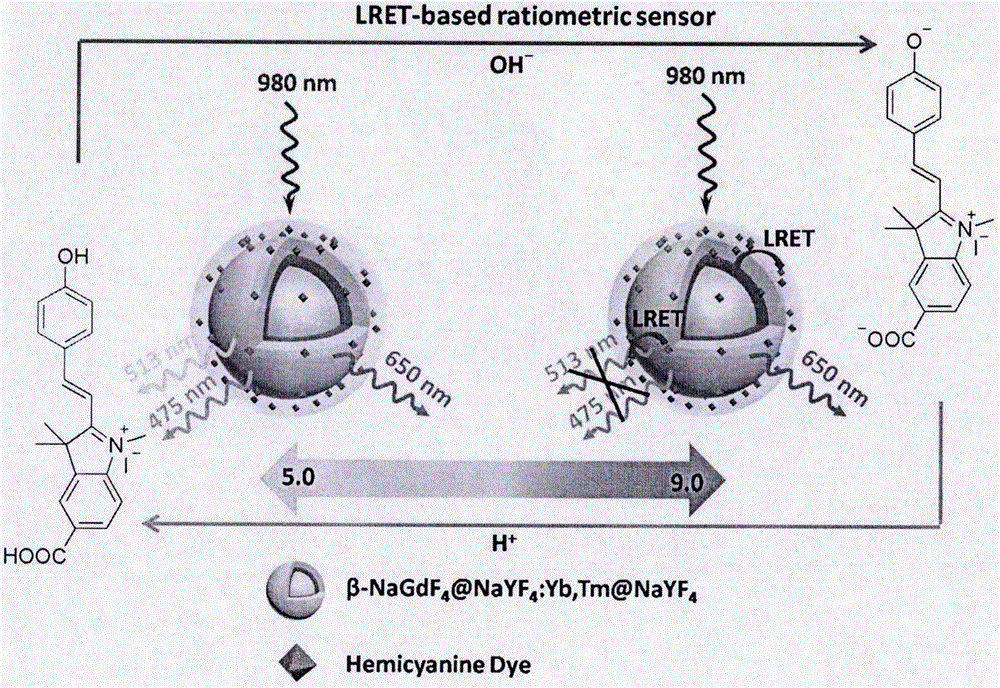
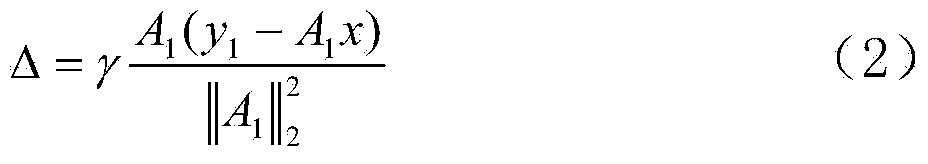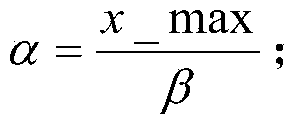Patents
Literature
61 results about "Bioluminescence imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bioluminescence imaging (BLI) is a technology developed over the past decade that allows for the noninvasive study of ongoing biological processes in small laboratory animals. Recently, bioluminescence tomography (BLT) has become possible and several systems have become commercially available. In 2011, PerkinElmer acquired one of the most popular lines of optical imaging systems with bioluminescence from Caliper Life Sciences.
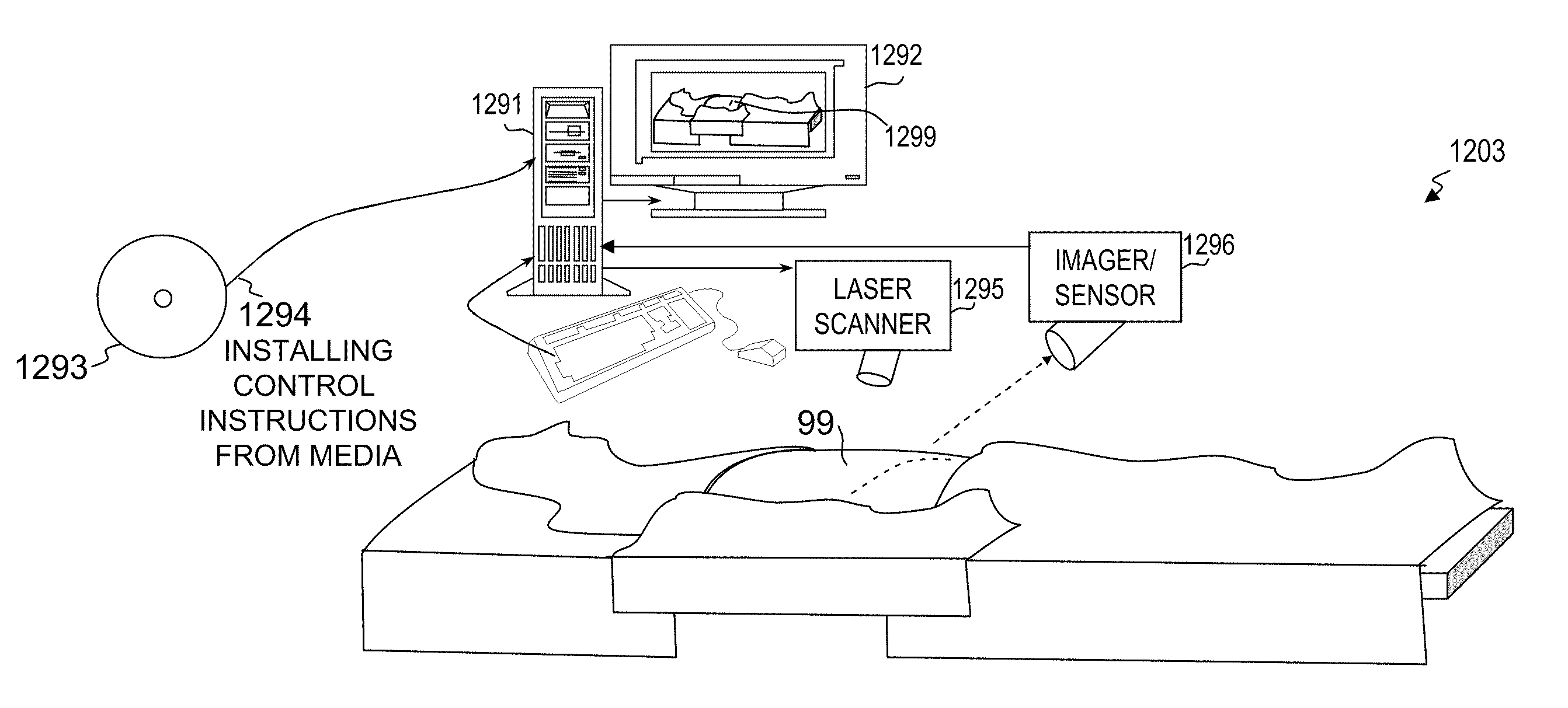
System and method for conditioning animal tissue using laser light
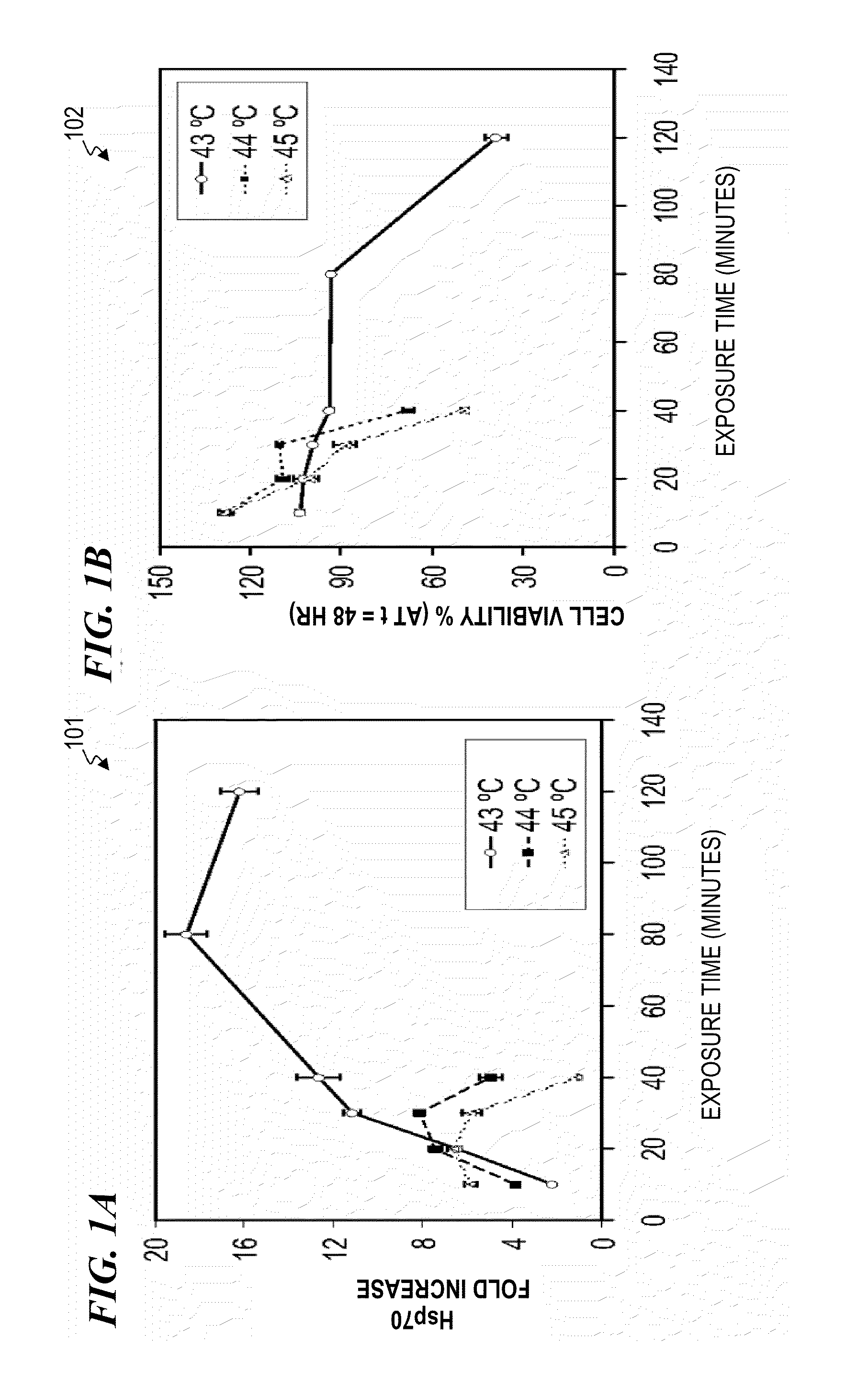
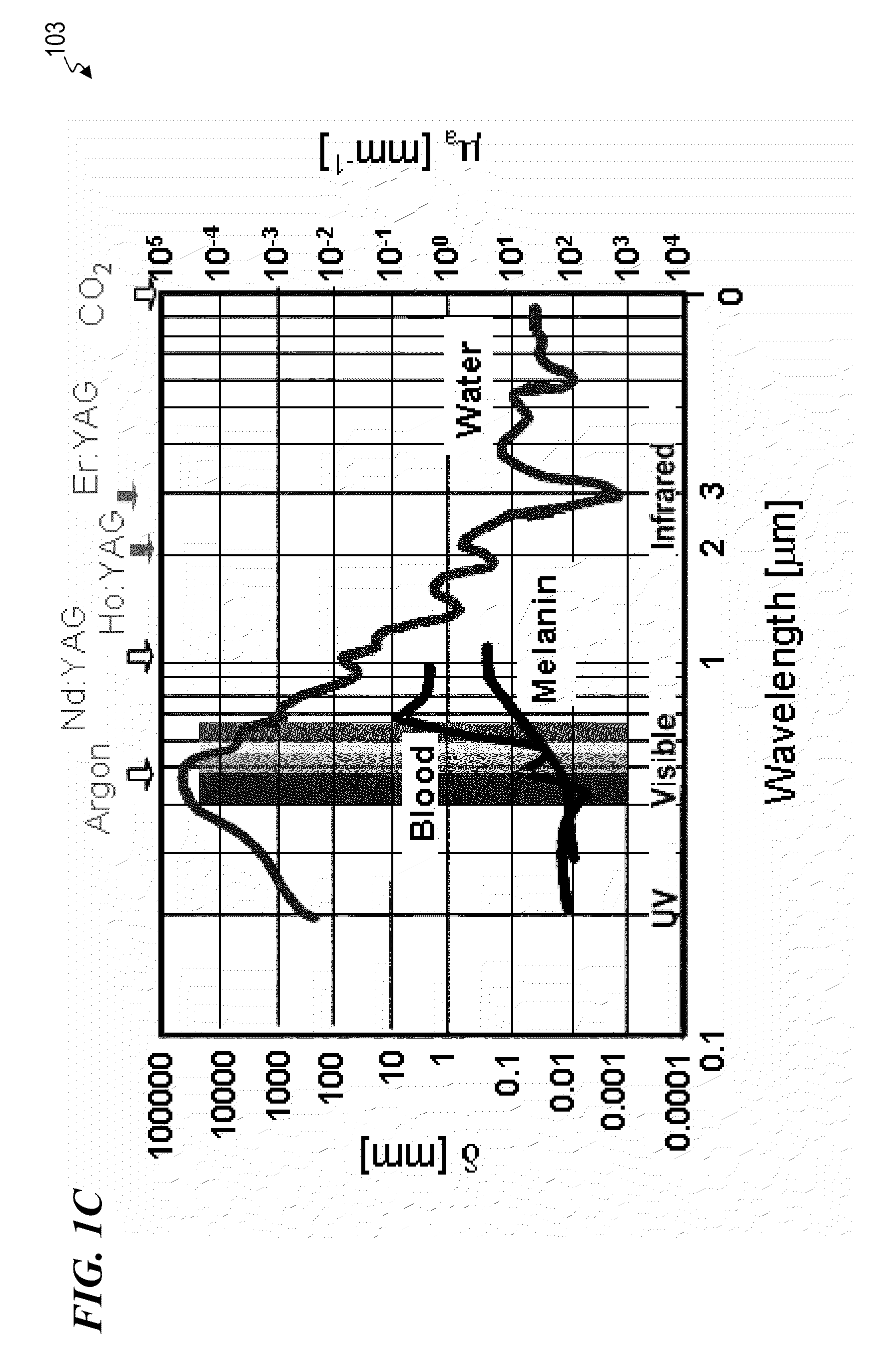
InactiveUS20100049180A1Promote wound repairEnhances surgical wound healingSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyLaser lightHsp70 expression
Systems and methods for prophylactic measures aimed at improving wound repair. In some embodiments, laser-mediated preconditioning would enhance surgical wound healing that was correlated with hsp70 expression. Using a pulsed laser (λ=1850 nm, Tp=2 ms, 50 Hz, H=7.64 mJ / cm2) the skin of transgenic mice that contain an hsp70 promoter-driven luciferase were preconditioned 12 hours before surgical incisions were made. Laser protocols were optimized using temperature, blood flow, and hsp70-mediated bioluminescence measurements as benchmarks. Bioluminescent imaging studies in vivo indicated that an optimized laser protocol increased hsp70 expression by 15-fold. Under these conditions, healed areas from incisions that were laser-preconditioned were two times stronger than those from control wounds. Our data suggest that these methods can provide effective and improved tissue-preconditioning protocols and that mild laser-induced heat shock that correlated with an expression of Hsp70 may be a useful therapeutic intervention prior to or after surgery.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP +2
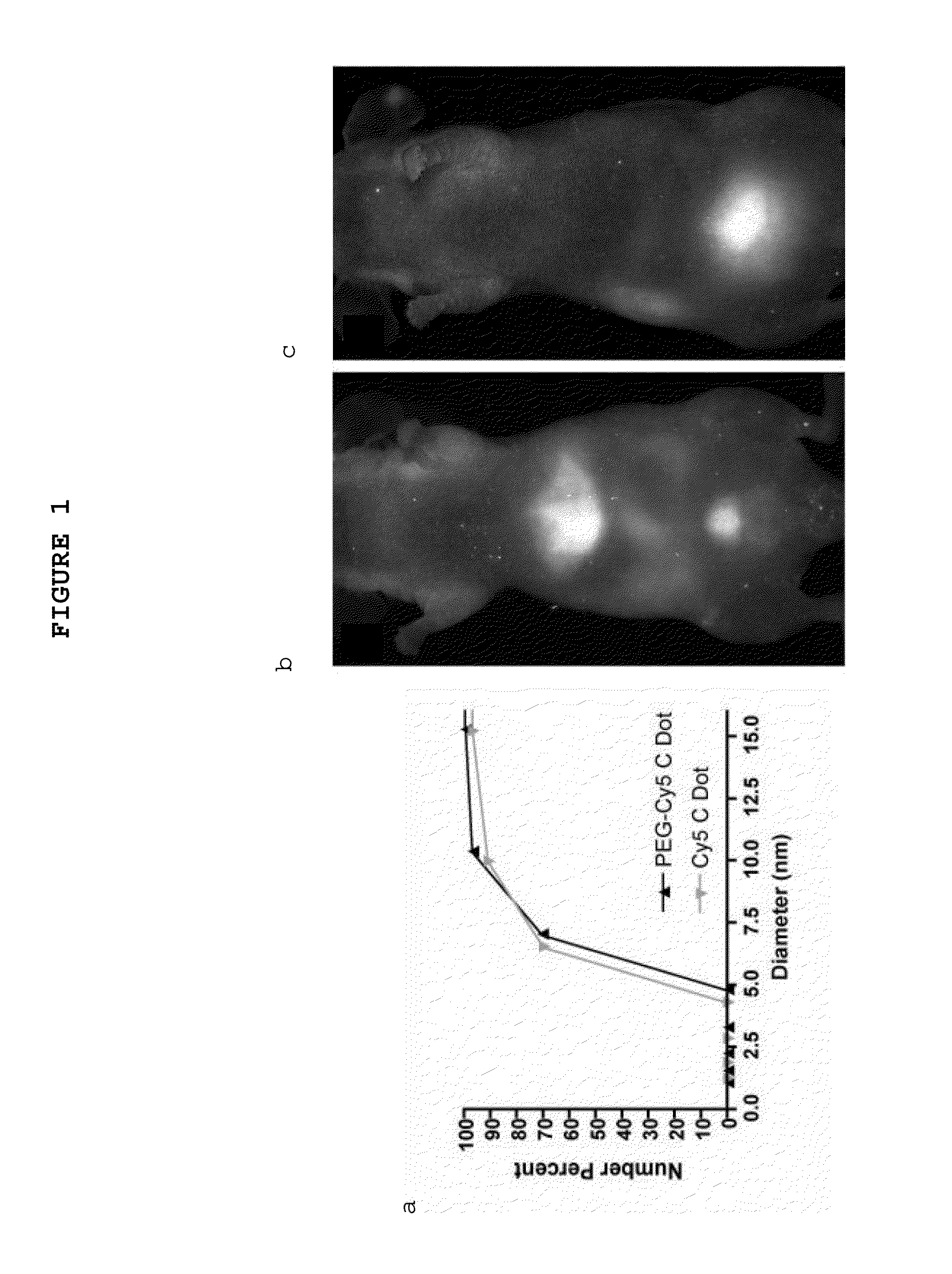
Multimodal silica-based nanoparticles
ActiveUS20140248210A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryCellular componentDisease
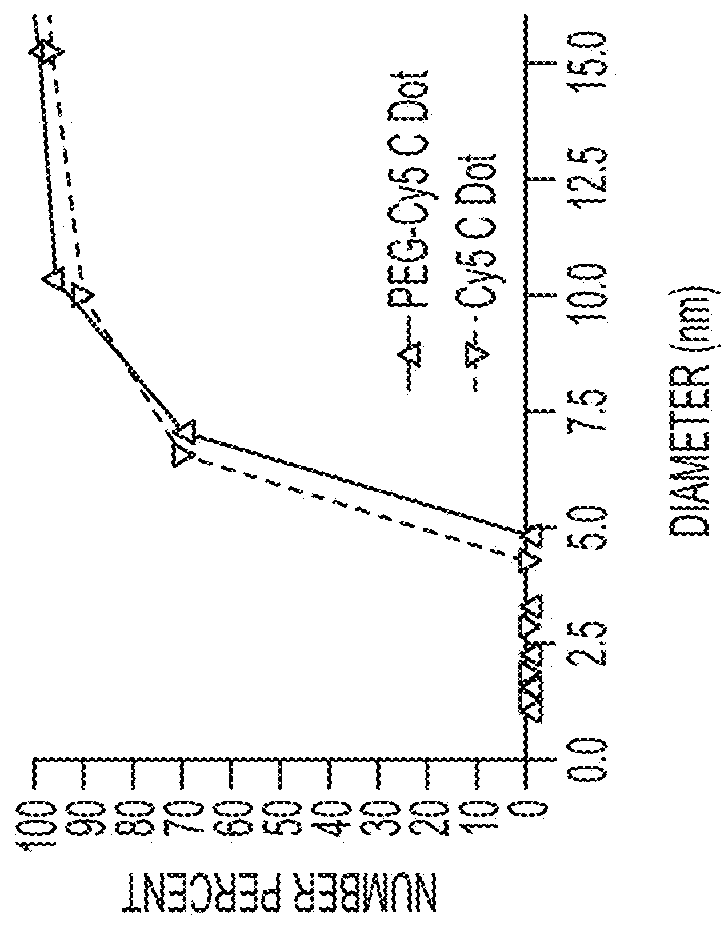
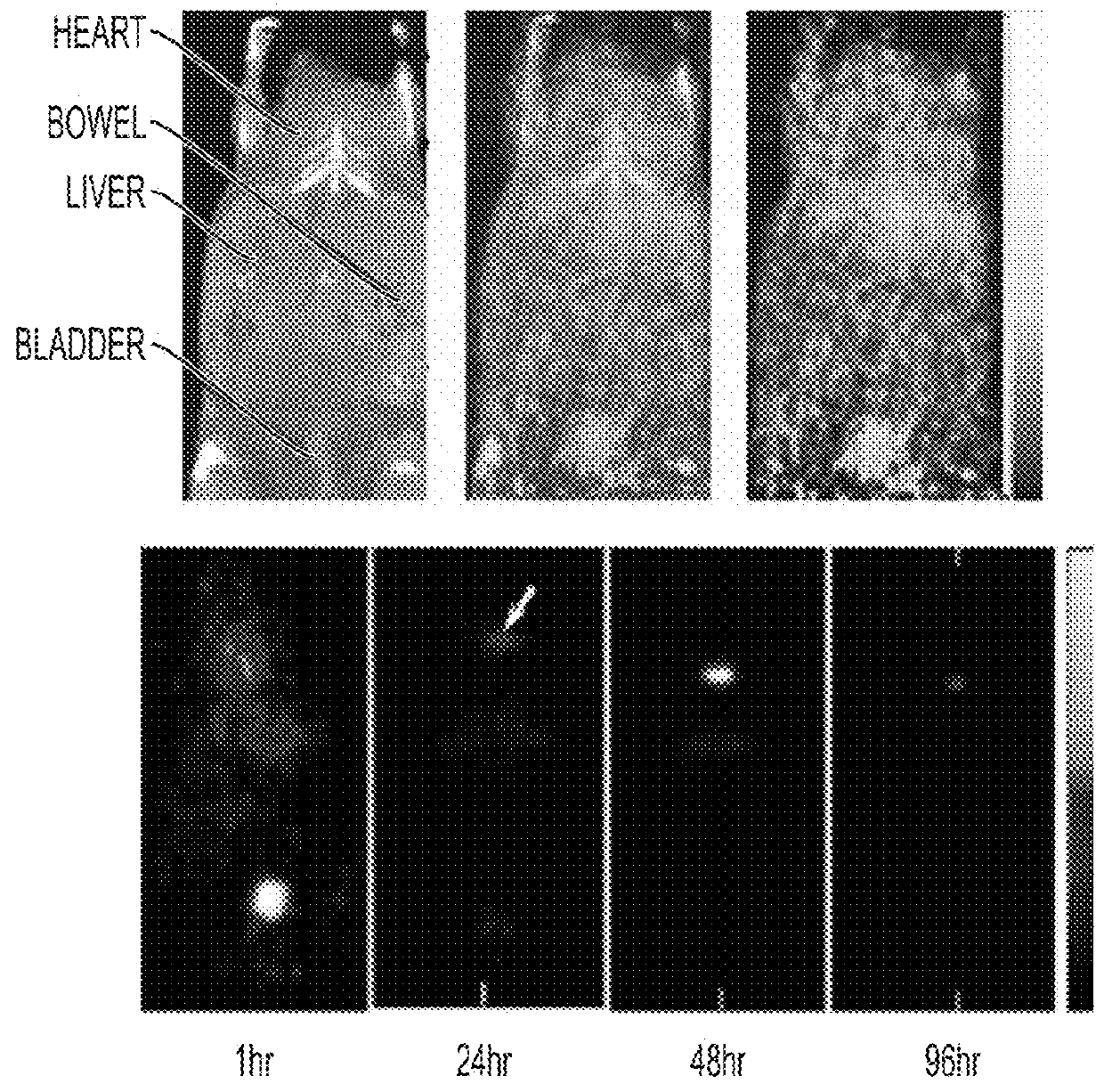
The present invention provides a fluorescent silica-based nanoparticle that allows for precise detection, characterization, monitoring and treatment of a disease such as cancer. The nanoparticle has a range of diameters including between about 0.1 nm and about 100 nm, between about 0.5 nm and about 50 nm, between about 1 nm and about 25 nm, between about 1 nm and about 15 nm, or between about 1 nm and about 8 nm. The nanoparticle has a fluorescent compound positioned within the nanoparticle, and has greater brightness and fluorescent quantum yield than the free fluorescent compound. The nanoparticle also exhibits high biostability and biocompatibility. To facilitate efficient urinary excretion of the nanoparticle, it may be coated with an organic polymer, such as poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG). The small size of the nanoparticle, the silica base and the organic polymer coating minimizes the toxicity of the nanoparticle when administered in vivo. In order to target a specific cell type, the nanoparticle may further be conjugated to a ligand, which is capable of binding to a cellular component associated with the specific cell type, such as a tumor marker. In one embodiment, a therapeutic agent may be attached to the nanoparticle. To permit the nanoparticle to be detectable by not only optical fluorescence imaging, but also other imaging techniques, such as positron emission tomography (PET), single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), computerized tomography (CT), bioluminescence imaging, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), radionuclides / radiometals or paramagnetic ions may be conjugated to the nanoparticle.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES +1
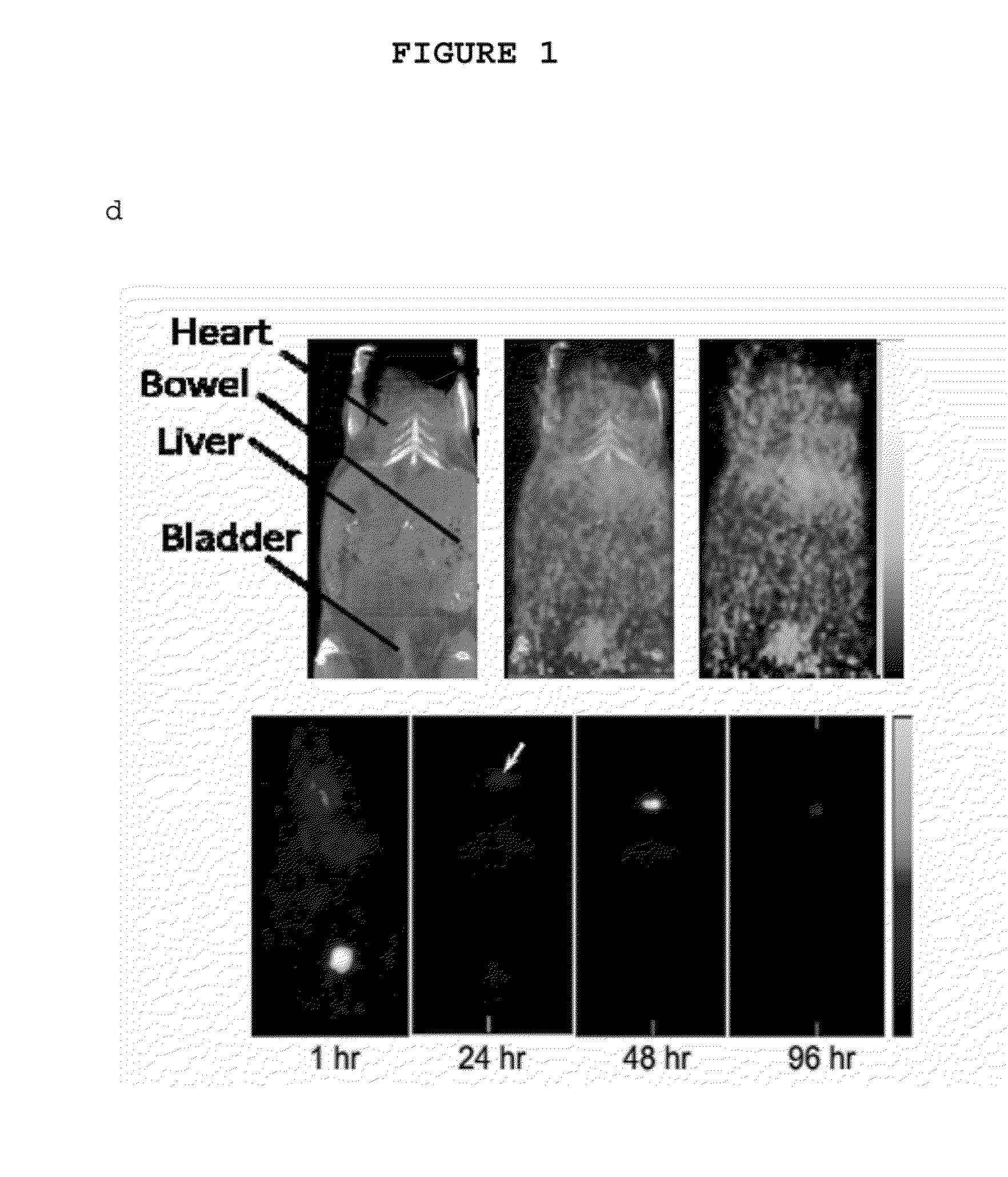
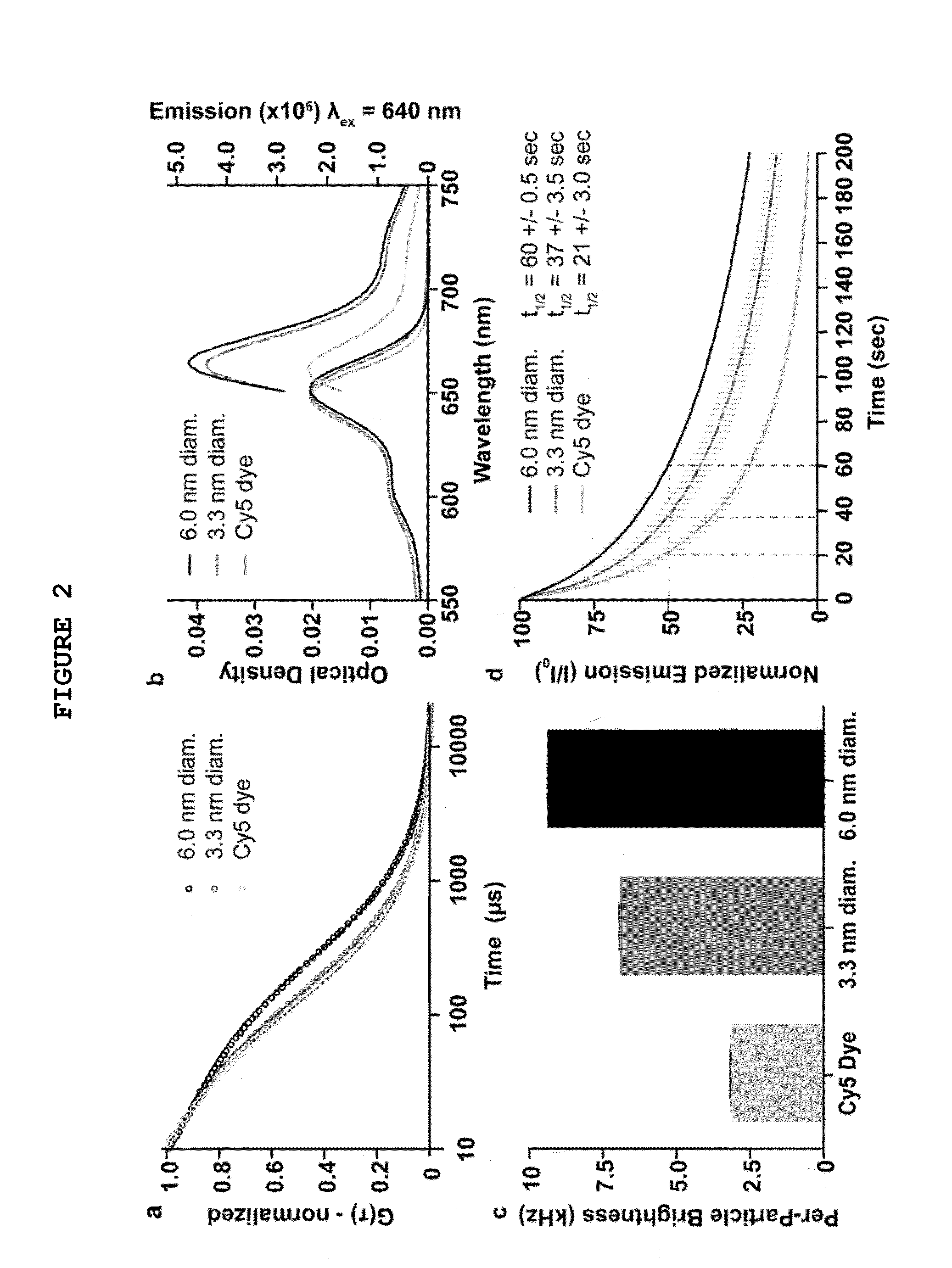
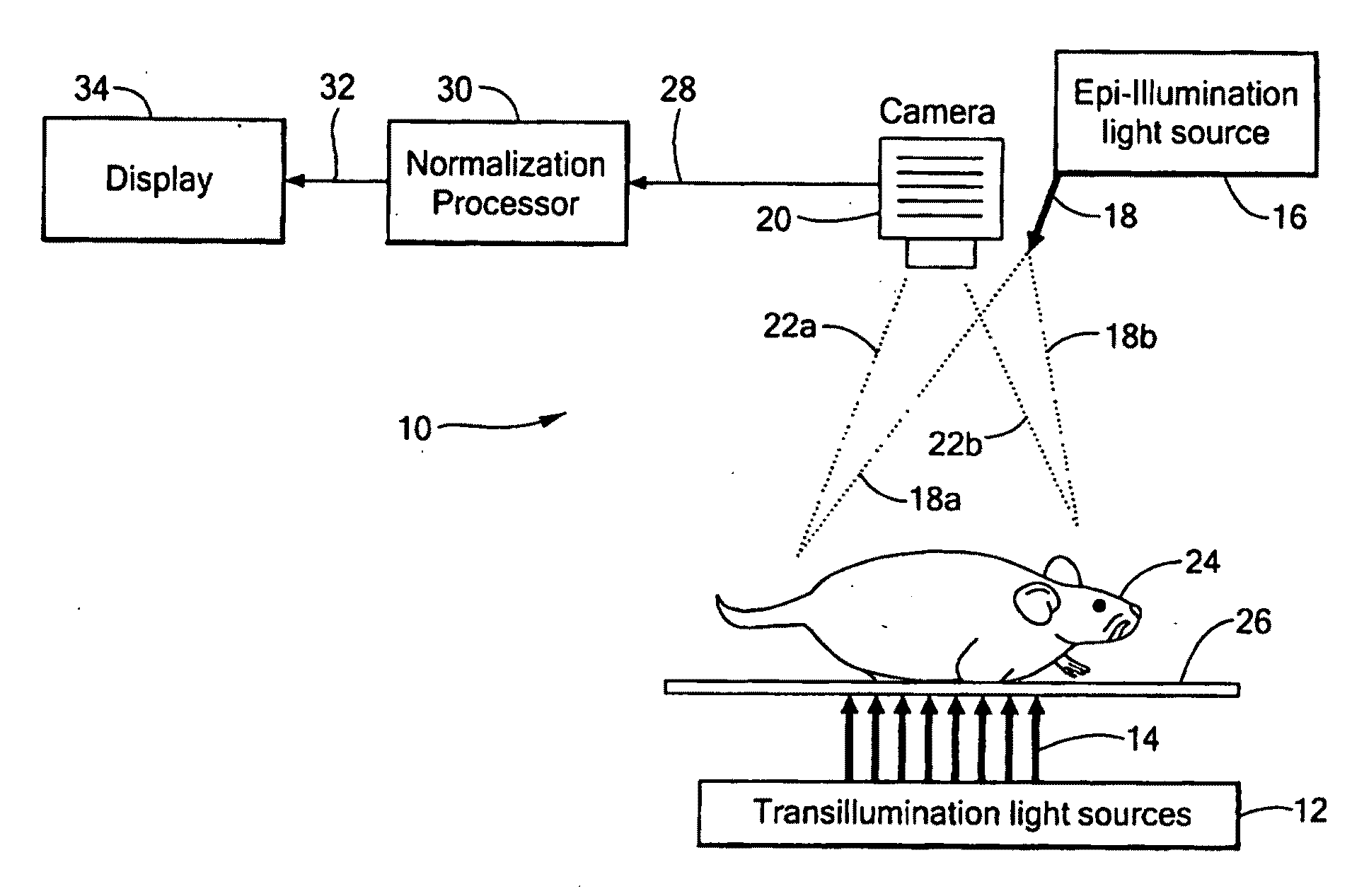
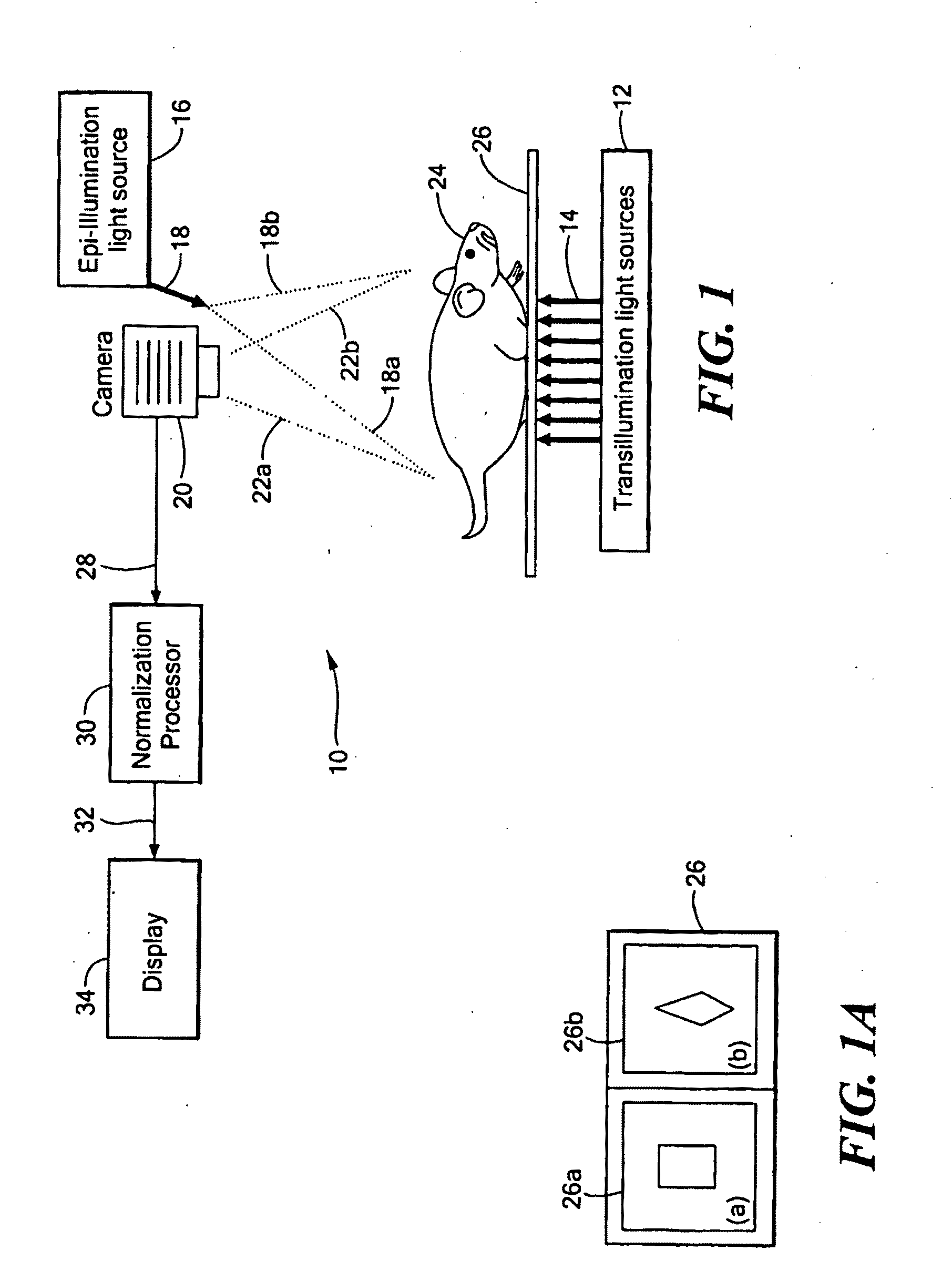
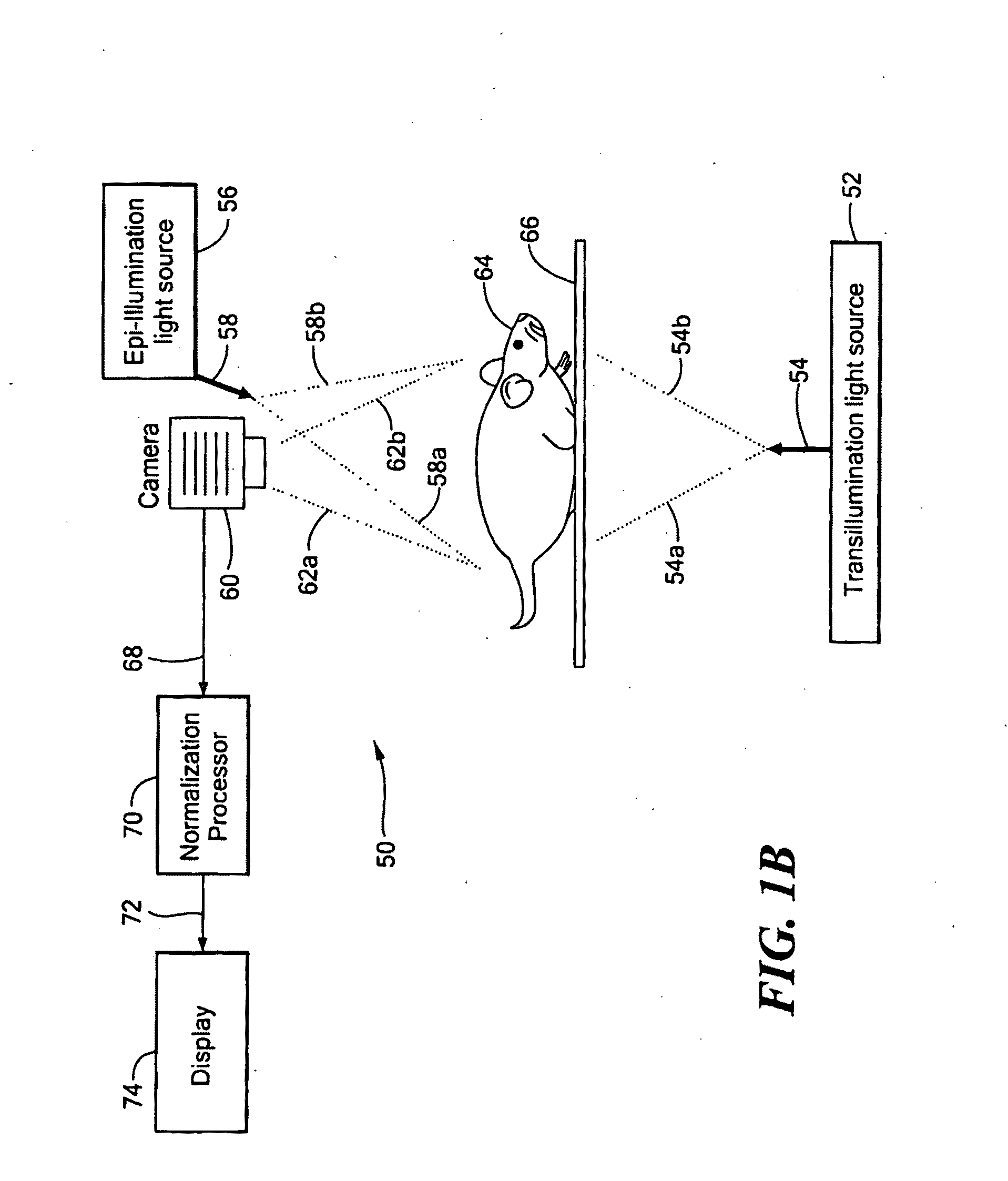
System and Method for Normalized Flourescence or Bioluminescence Imaging
A system and method provide normalized fluorescence epi-illumination images and normalized fluorescence transillumination images. The normalization can be used to improve two-dimensional (planar) fluorescence epi-illumination images and two-dimensional (planar) fluorescence transillumination images. The system and method can also provide normalized bioluminescence epi-illumination images and normalized bioluminescence transillumination images. In some arrangements, the system and method can provide imagine of small animals, into-operative imaging, endoscopic imaging, and / or imaging of hollow organs.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Preparation and application of metal ion directly induced fluorescent supramolecular gel
ActiveCN103374132AShort gel timeStrong fluorescent emissionLuminescent compositionsFluorescenceBiopolymer
The invention discloses preparation and application of a metal ion directly induced fluorescent supramolecular gel, which belongs to the field of functional materials. According to the invention, combined action of coordination bonds formed between metal ions and terpyridyl units in a polymer, and intermolecular hydrogen bonds formed by amide bonds in N-isopropylacrylamide units in the polymer are utilized for induction preparation of the fluorescence supramolecular gel. The preparation method is simple and easy for mass production; meanwhile, because coordination bonded hydrogen bonds are employed to assemble the supramolecular gel, the prepared supramolecular gel overcomes the defects of a general supramolecular gel, such as long preparation time, industrial complex and instability; besides, the supramolecular gel with fluorescence characteristics expands its application to fields of diffusion process tracking, control of transition of biological polymer phase, environmental stimuli induction and bioluminescence imaging.
Owner:GUANGZHOU CHEM CO LTD CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
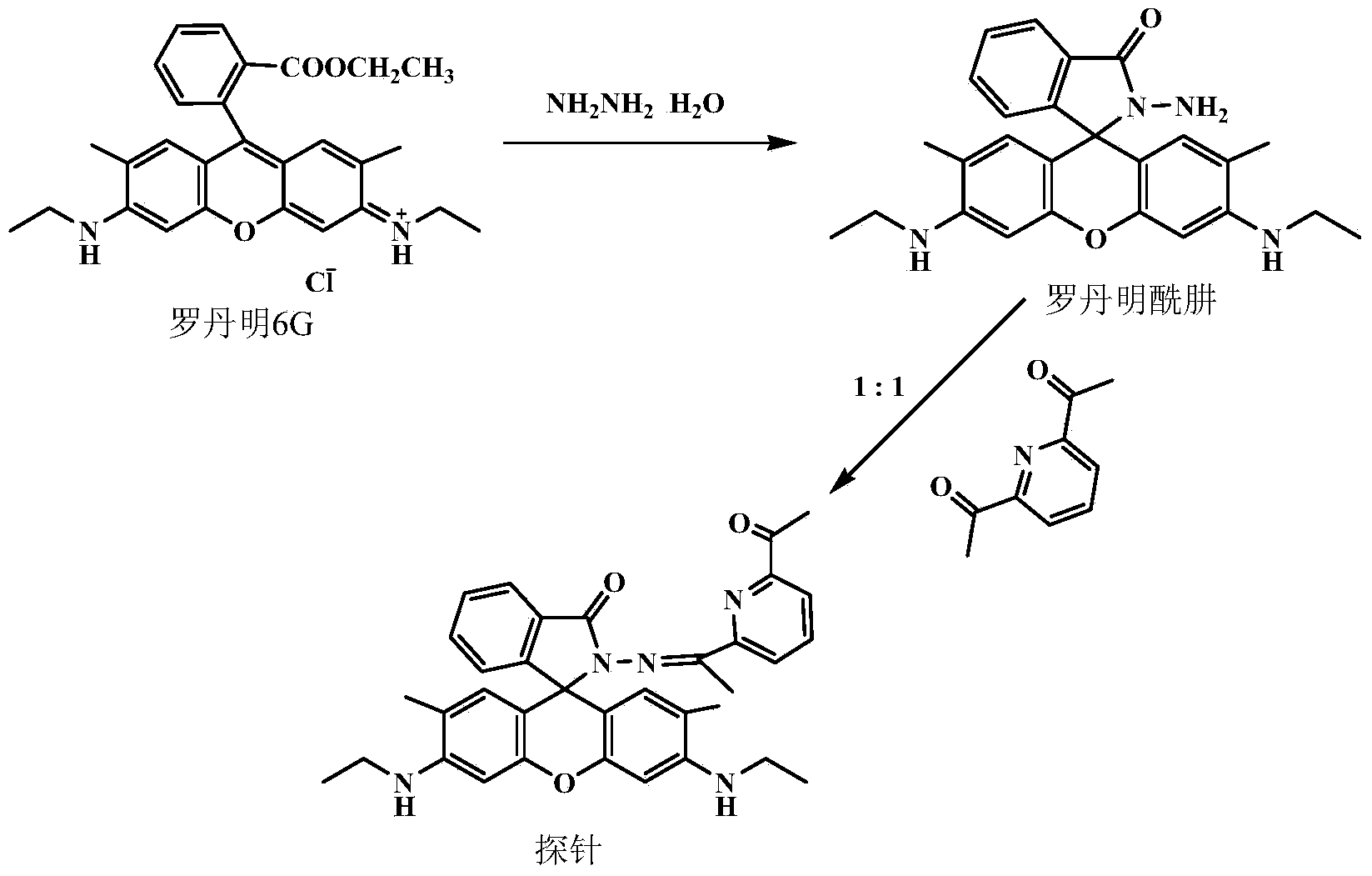
Rhodamine fluorescent probe for detecting ferrous ion, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103436253AHigh synthetic yieldShort reaction timeOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceHydrazine compoundPhotochemistry
The invention relates to a rhodamine fluorescent probe for detecting Fe <2+>, and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: enabling rhodamine 6G and hydrazine hydrate to perform reflux reaction in alcohol to generate rhodamine hydrazide, then enabling rhodamine hydrazide and 2,6-diacetylpyridine to perform reflux reaction in alcohol, and through neutral aluminium trioxide column chromatography purification, obtaining the rhodamine acylhydrazone and acetyl pyridine fluorescent probe. The fluorescent probe is high in synthesis productivity, quick in reaction and high in selectivity, has high specificity to Fe <2+>, can work under the physiological environmental condition with the pH value of 7.4, and has a prospect of being applied to bioluminescence imaging.
Owner:BINZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
Symmetrical double-rhodamine B fluorescent probe for detecting mercury ion and preparation method of fluorescent probe
InactiveCN103254893AEnables visualization of fluorescence imagingFluorescent signal enhancementOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceAcyl group
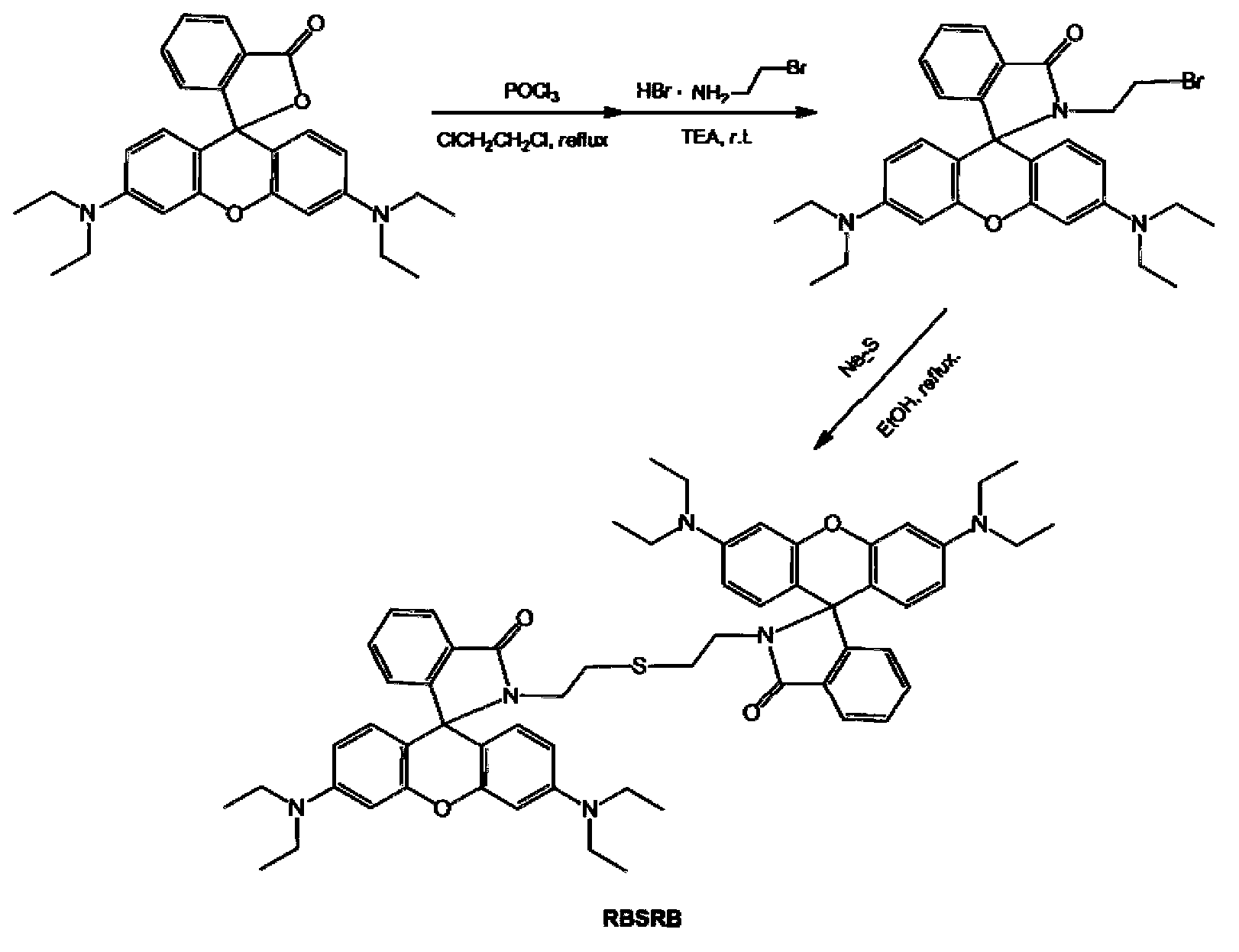
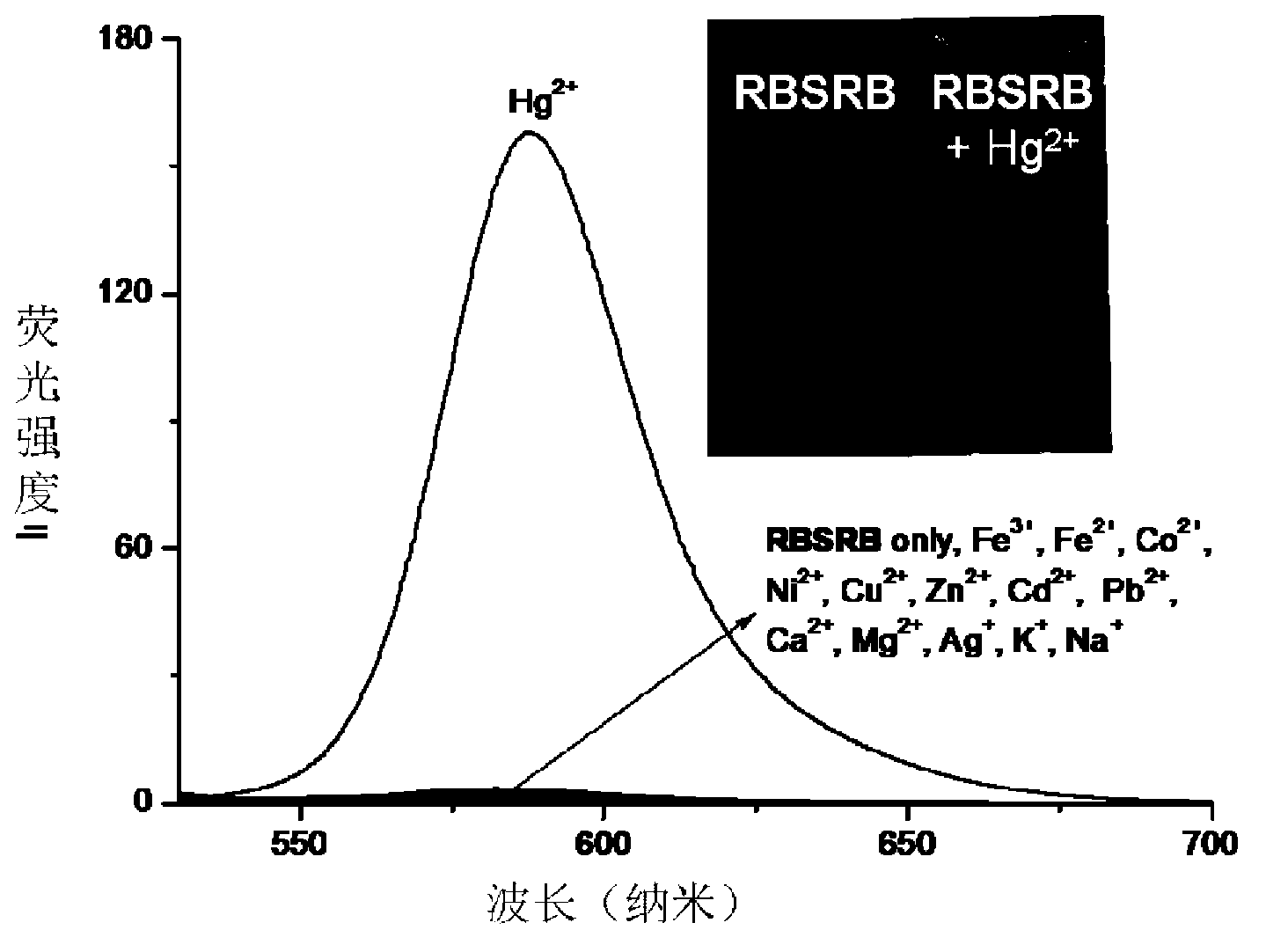
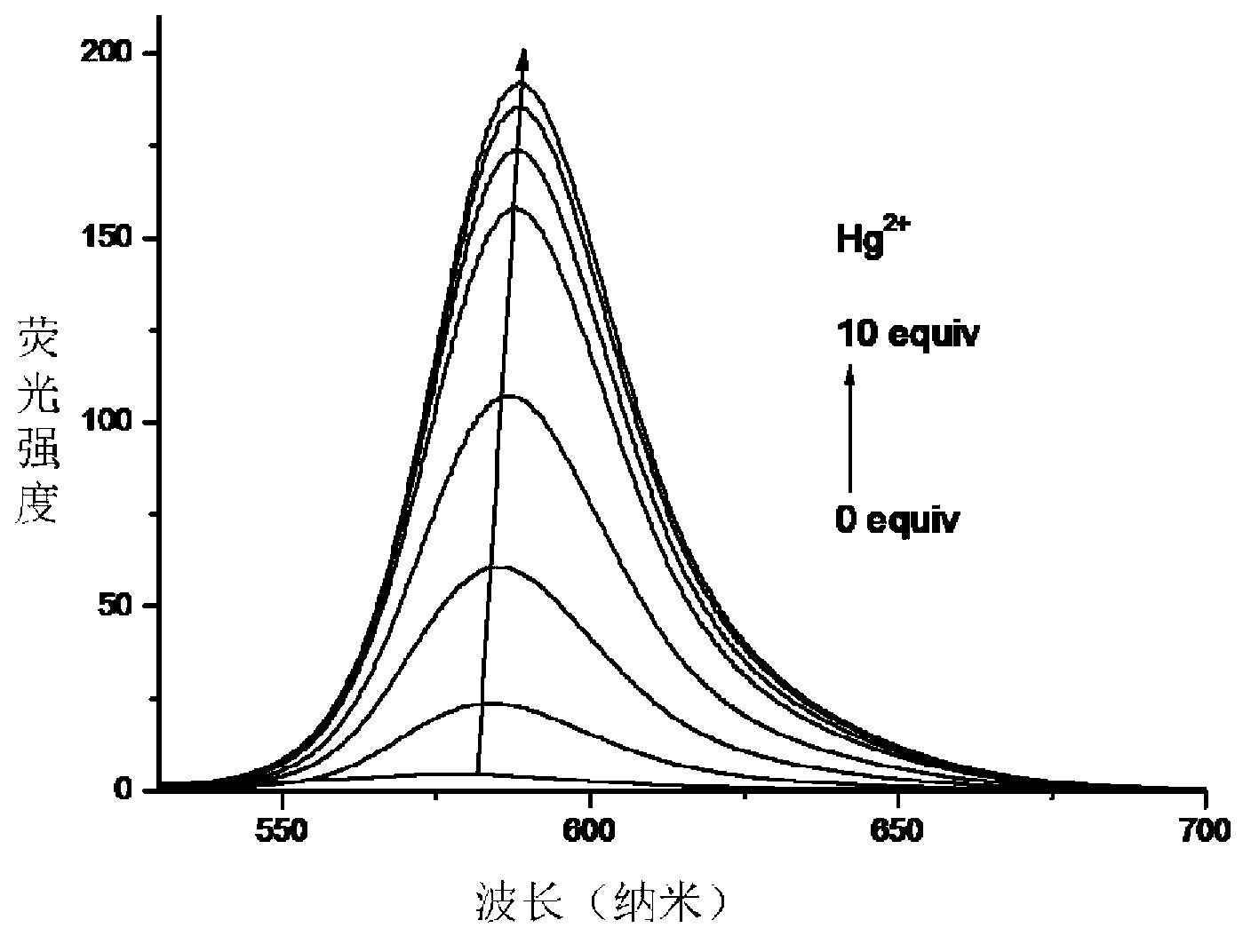
The invention relates to a symmetrical double-rhodamine B fluorescent probe for detecting a mercury ion and a preparation method of the fluorescent probe. The structural formula of the symmetrical double-rhodamine B fluorescent probe RBSRB (rhodamine B-symmetrical-rhodamine B) is as shown in the specification. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding rhodamine B and phosphorus oxychloride into a solvent for reflux reaction for 20-24h at 85-90 DEG C, obtaining rhodamine B acyl chloride, dissolving rhodamine B acyl chloride and 2-bromine ethylamine in the solvent, stirring for reaction for one night at room temperature, purifying to obtain rhodamine B acyl-2-bromine ethylamine, adding rhodamine B acyl-2-bromine ethylamine and sodium sulfide into the solvent for reflux reaction for 5-8h at 80-85 DEG C, and purifying to obtain the fluorescent probe. The fluorescent probe is symmetrical double-rhodamine B amide connected by a sulphur atom; only alcohol under 1% is introduced as a cosolvent during an experiment; the fluorescent probe is high in selectivity, and has high selectivity to the mercury ion; other common ions do not interfere with the fluorescent probe obviously; and the fluorescent probe has an application prospect in bioluminescence imaging.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
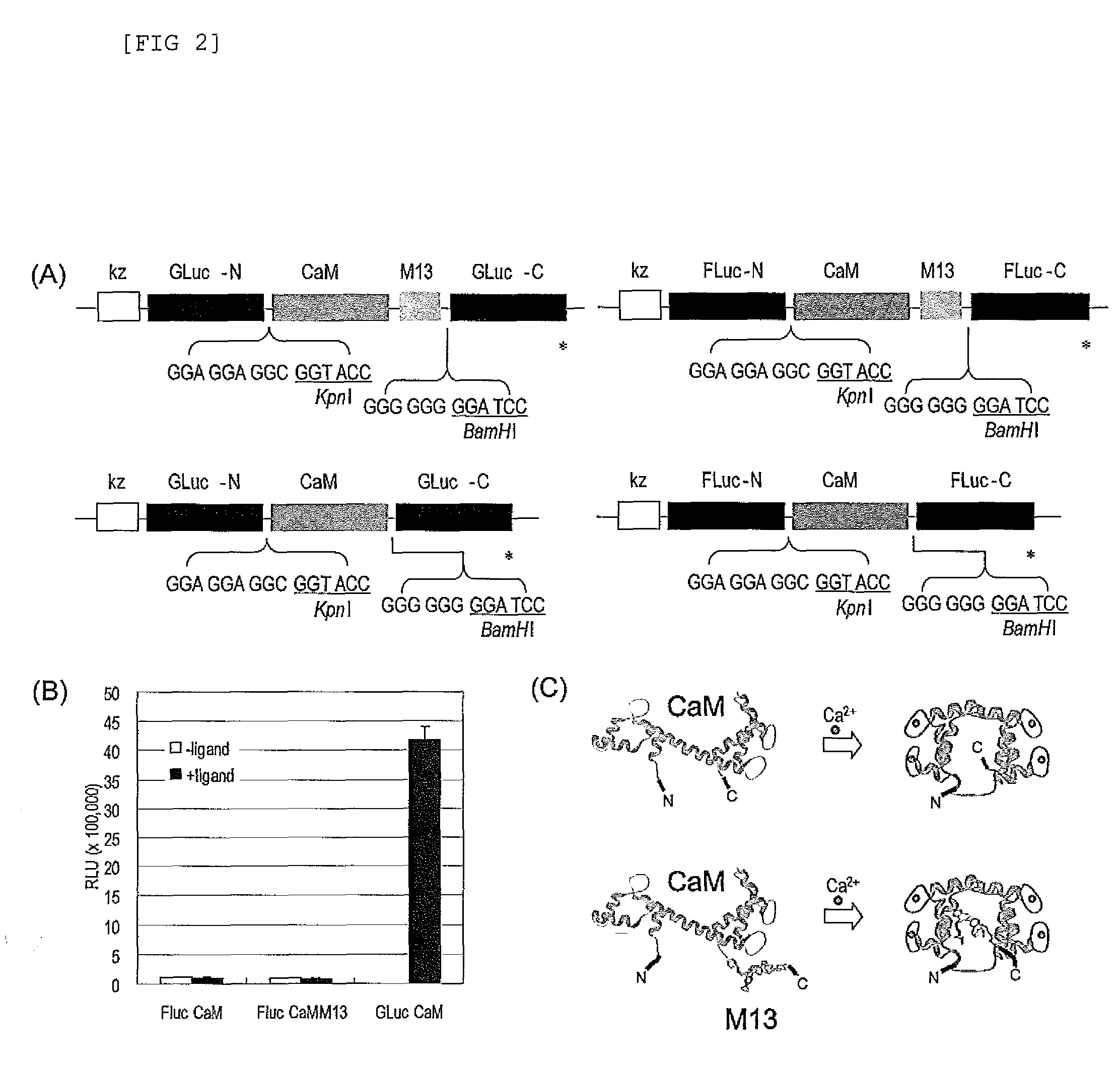
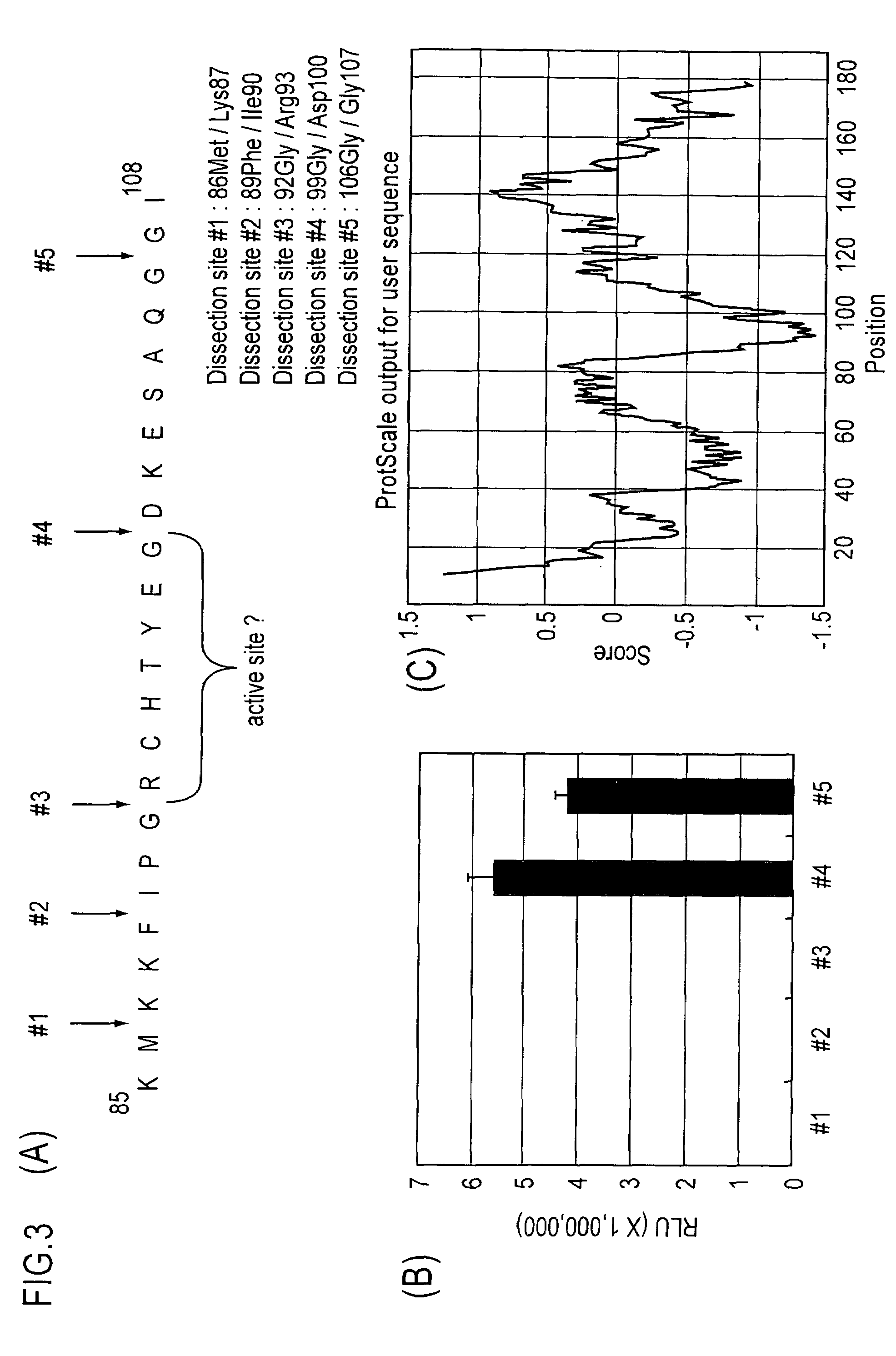
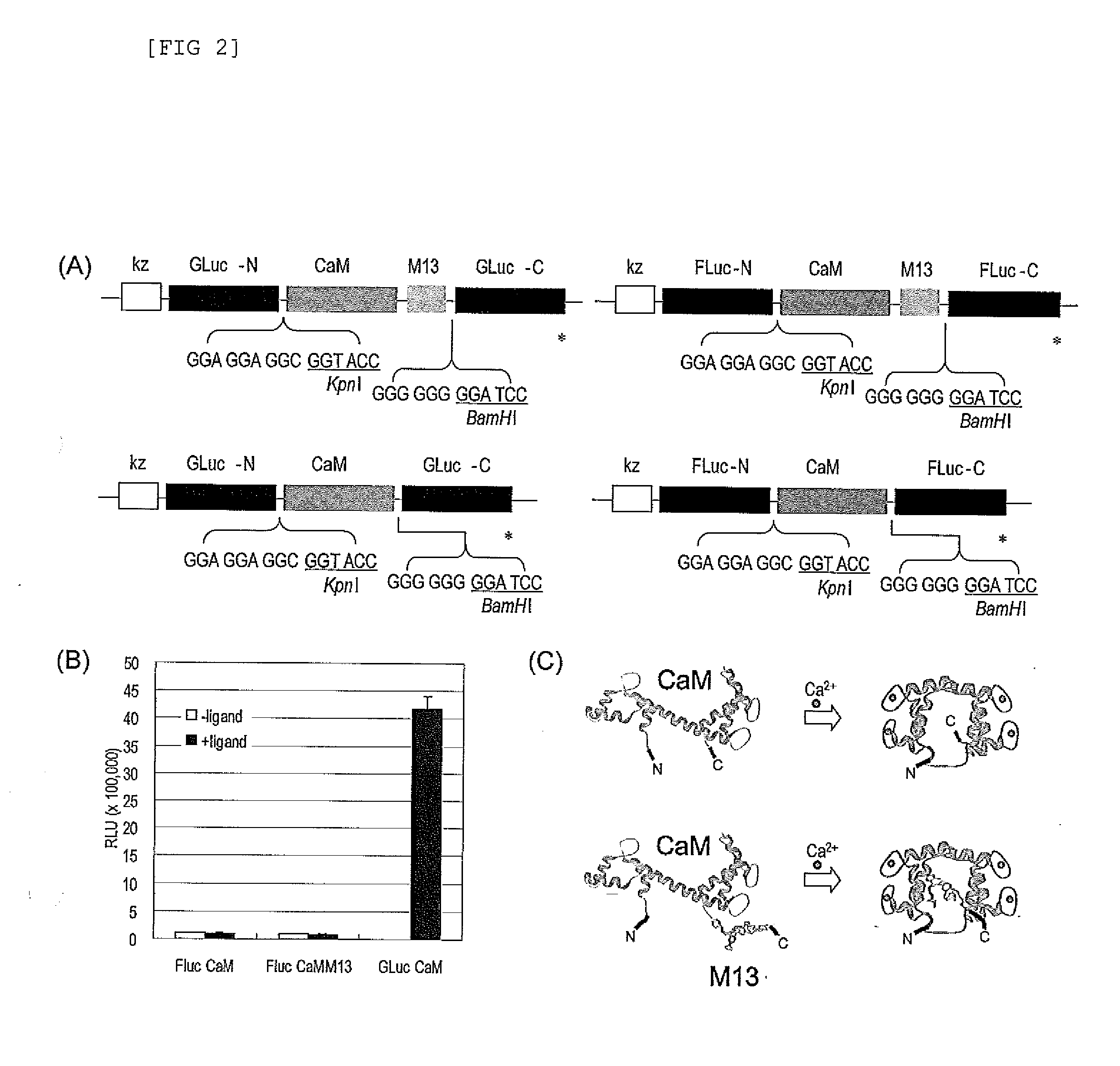
Single molecule-format real-time bioluminescence imaging probe
InactiveUS8043827B2Analysis method is simpleMeasure sensitivelyAnimal cellsSugar derivativesExtinctionIn vivo
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
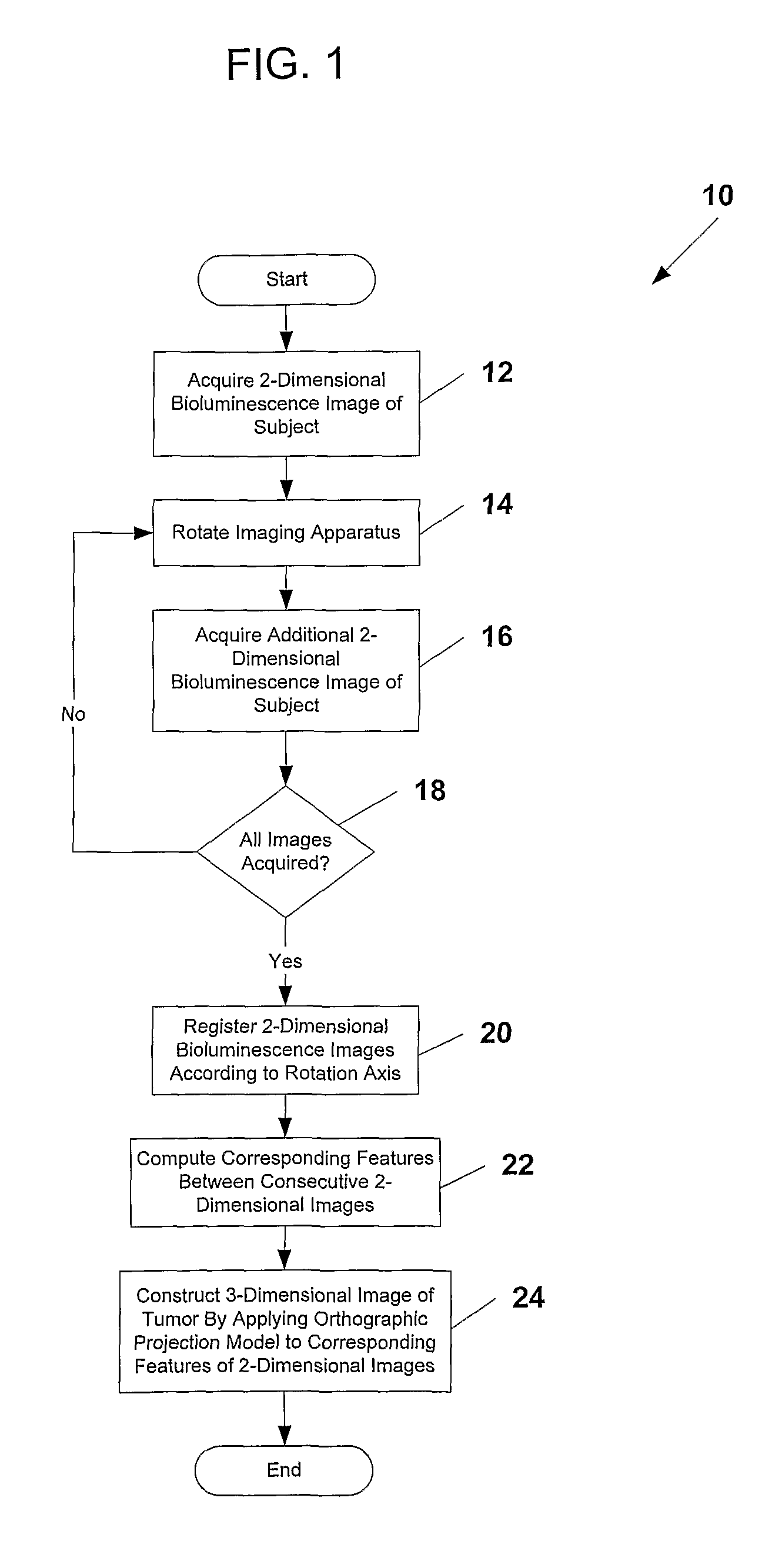
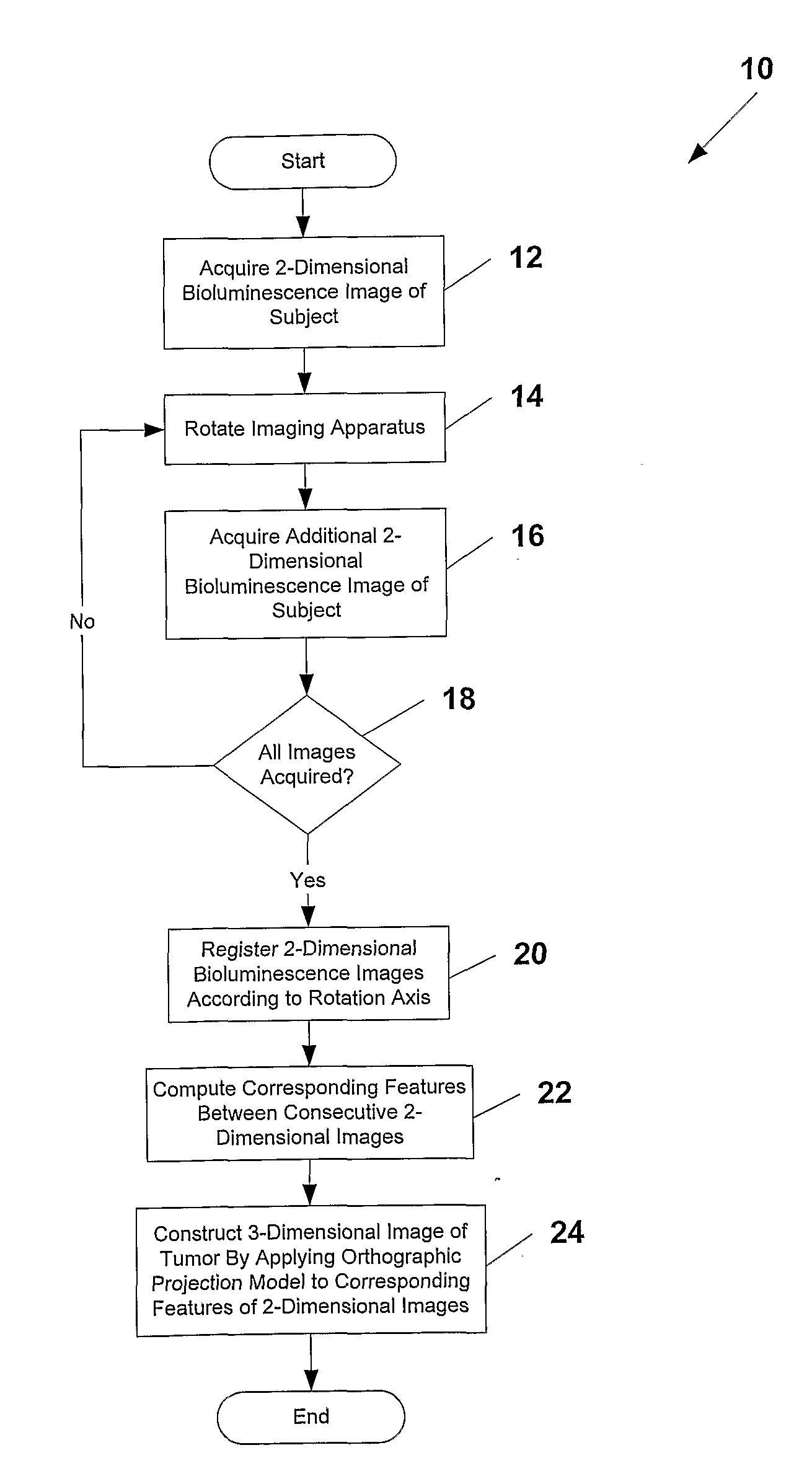
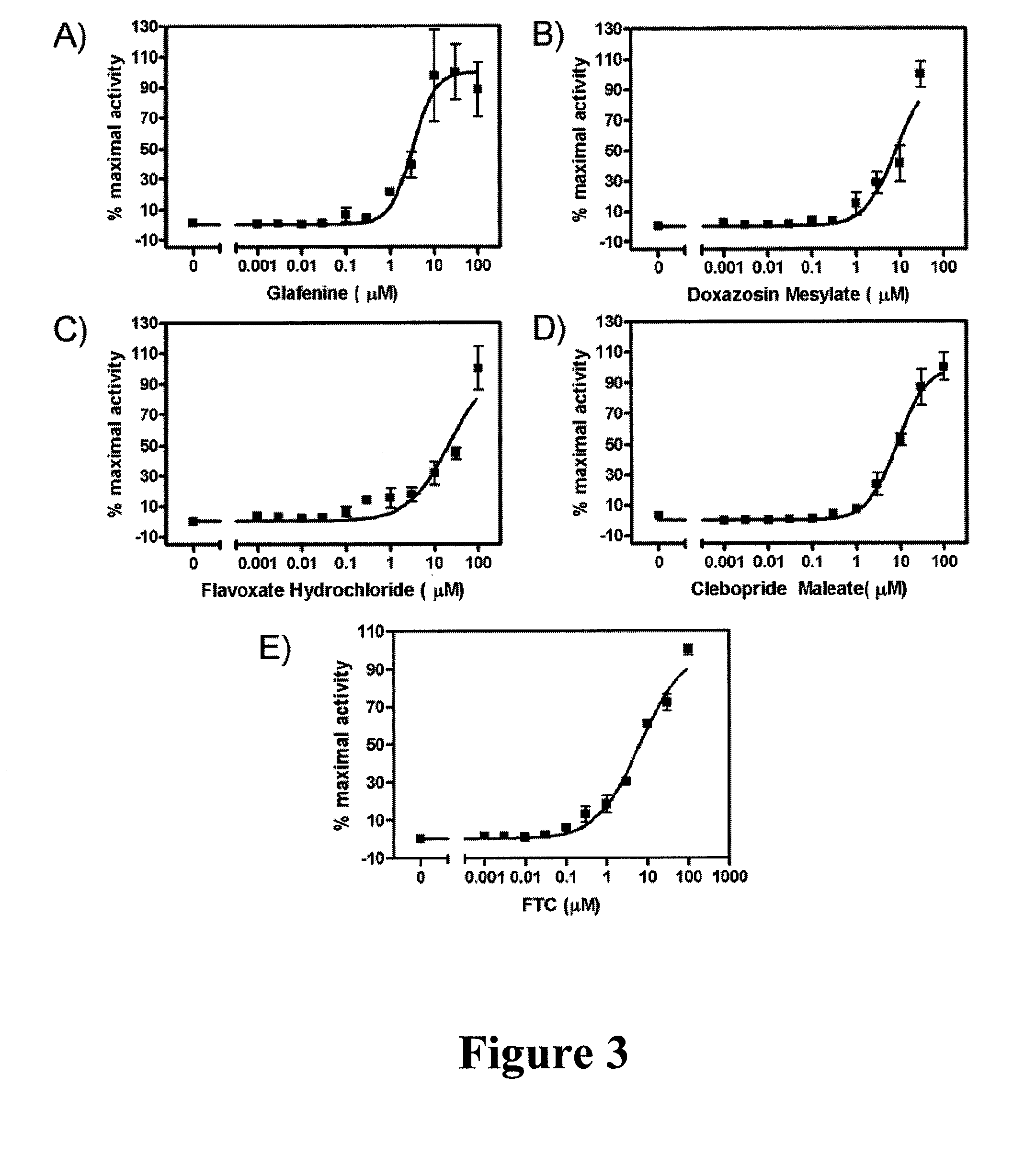
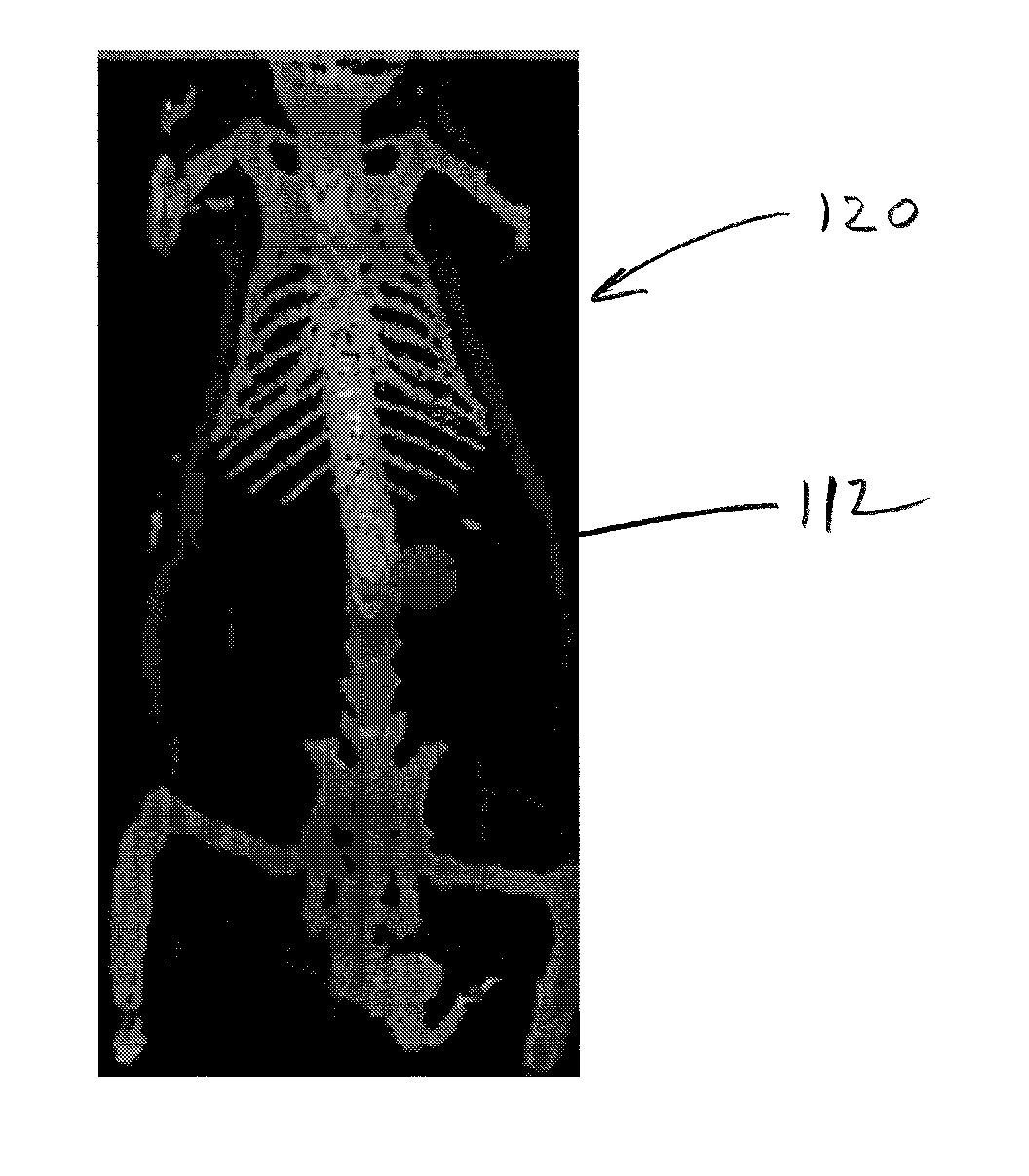
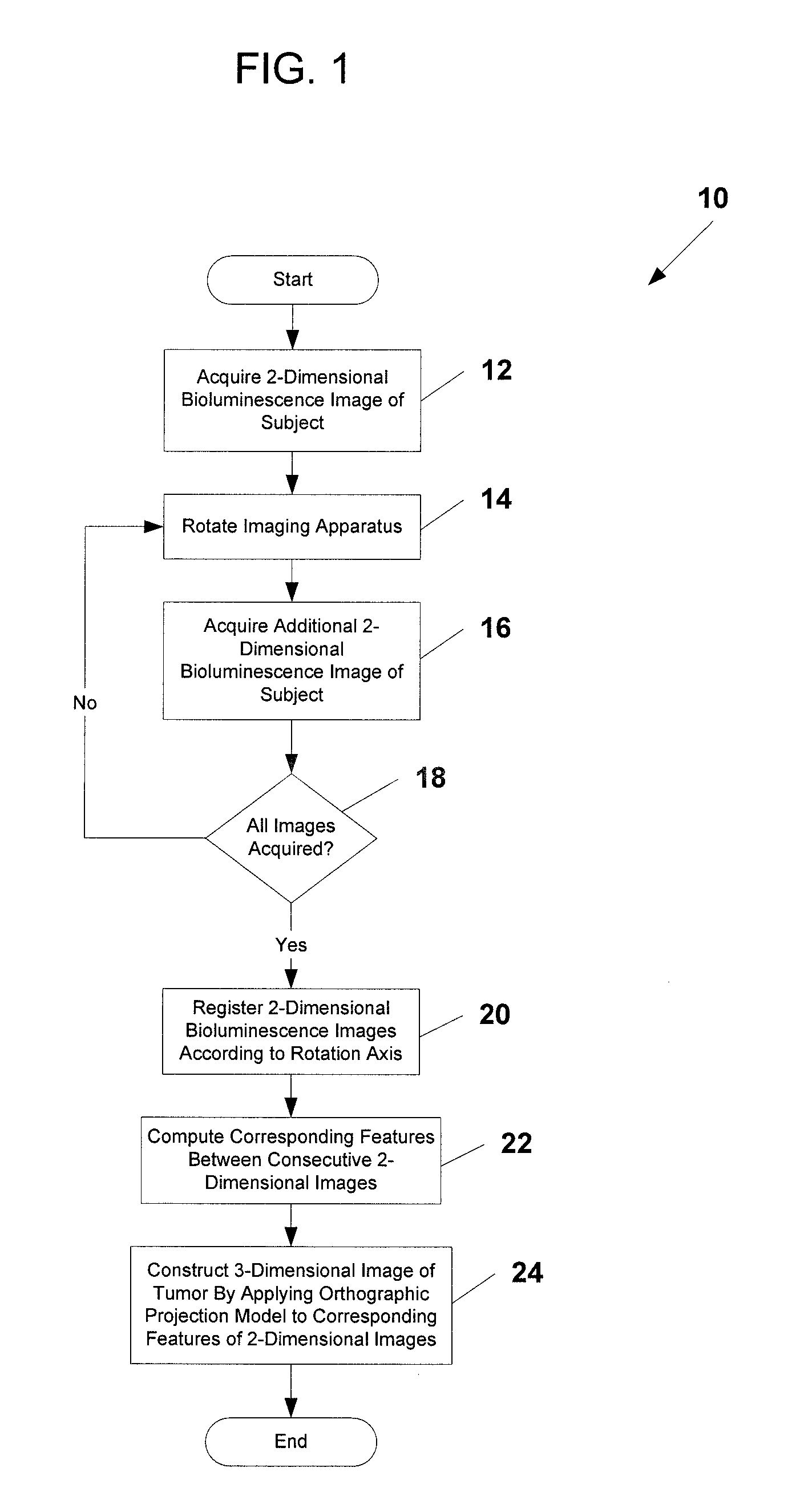
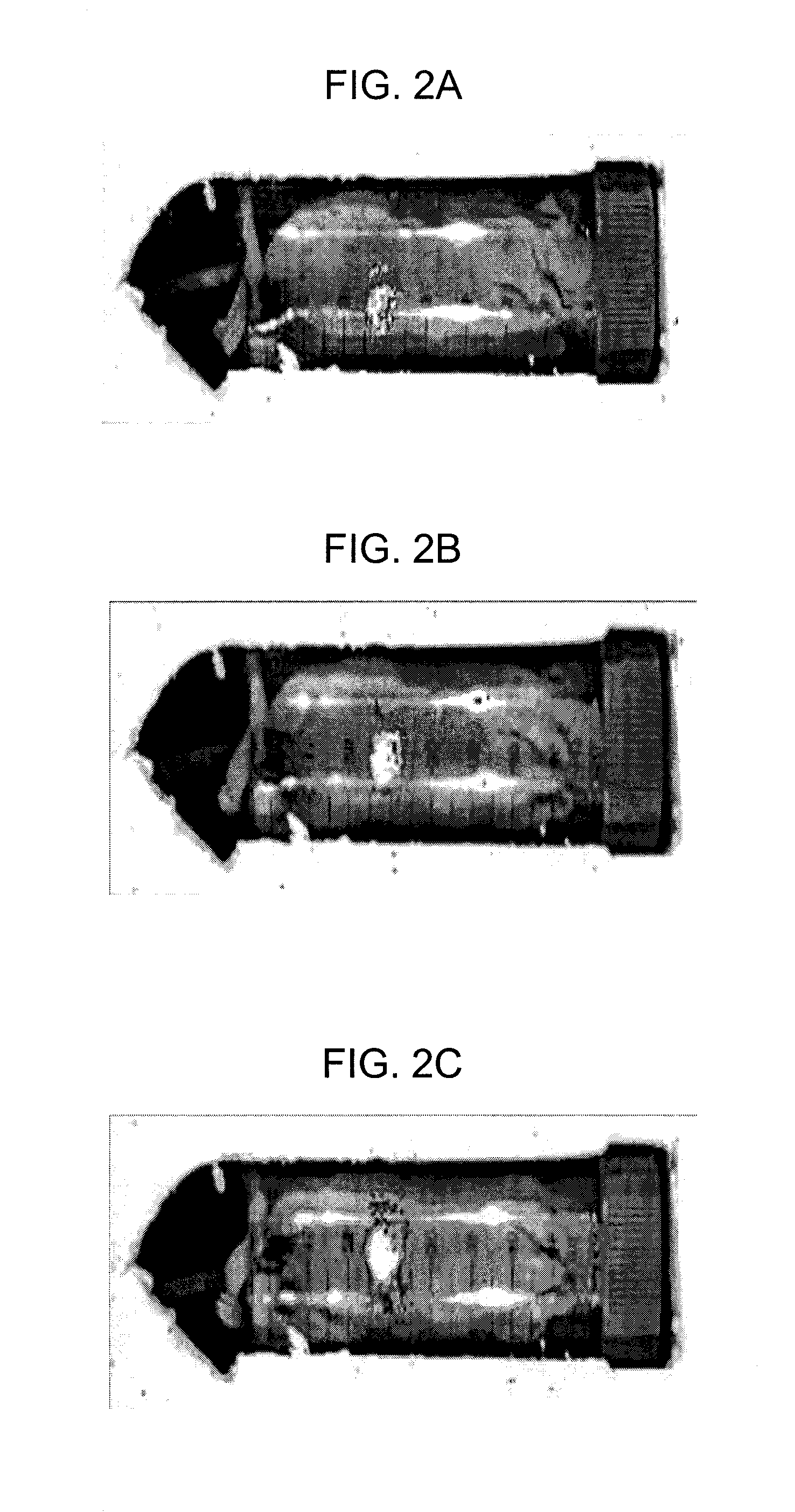
System and methods for generating three-dimensional images from two-dimensional bioluminescence images and visualizing tumor shapes and locations
A system and methods for generating 3D images (24) from 2D bioluminescent images (22) and visualizing tumor locations are provided. A plurality of 2D bioluminescent images of a subject are acquired during a complete revolution of an imaging system about a subject, using any suitable bioluminescent imaging system. After imaging, the 2D images are registered (20) according to the rotation axis to align each image and to compensate for differences between adjacent images. After registration (20), corresponding features are identified between consecutive sets of 2D image (22). For each corresponding feature identified in each set of 2D images an orthographic projection model (24) is applied, such that rays are projected through each point in the feature. The intersection point of the rays are plotted in a 3D image of a tumor is generated. The 3D image can be registered with a reference image of the subject, so that the shape and location of the tumor can be precisely visualized with respect to the subject.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Novel rhodafluor fluorescent dye with characteristics of large stokes shift and near-infrared fluorescence emitting, and synthesis method thereof
ActiveCN104710815ALarge Stokes shiftHigh fluorescence quantum yieldAzo dyesLuminescent compositionsQuantum yieldSynthesis methods
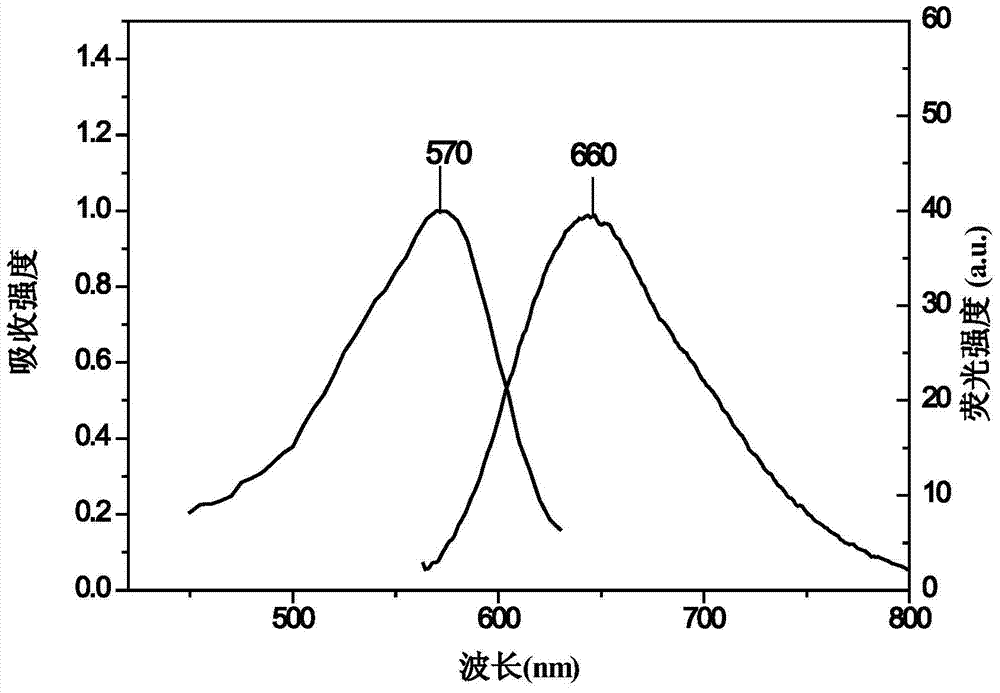
The invention relates to a novel rhodafluor fluorescent dye with characteristics of large stokes shift and near-infrared fluorescence emitting, and a synthesis method thereof, wherein catalytic hydrogenation reduction, glyoxal condensation, sodium borohydride reduction, Vilsmeier formulation, acid-catalyzed demethylation and other reactions are performed to obtain the intermediate, and the intermediate and diphenyl keto acid react to obtain the target product rhodafluor fluorescent dye. According to the present invention, compared with the conventional fluorescent dye, the obtained novel rhodafluor compound of the present invention has characteristics of high photostability, fluorescence emission wavelength in the near-infrared region (-660 nm), large stokes shift (-90 nm) and high fluorescence quantum yield (0.62), and can be used for the fields of light emitting materials / biological fluorescent probes, bioluminescence imaging and the like.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
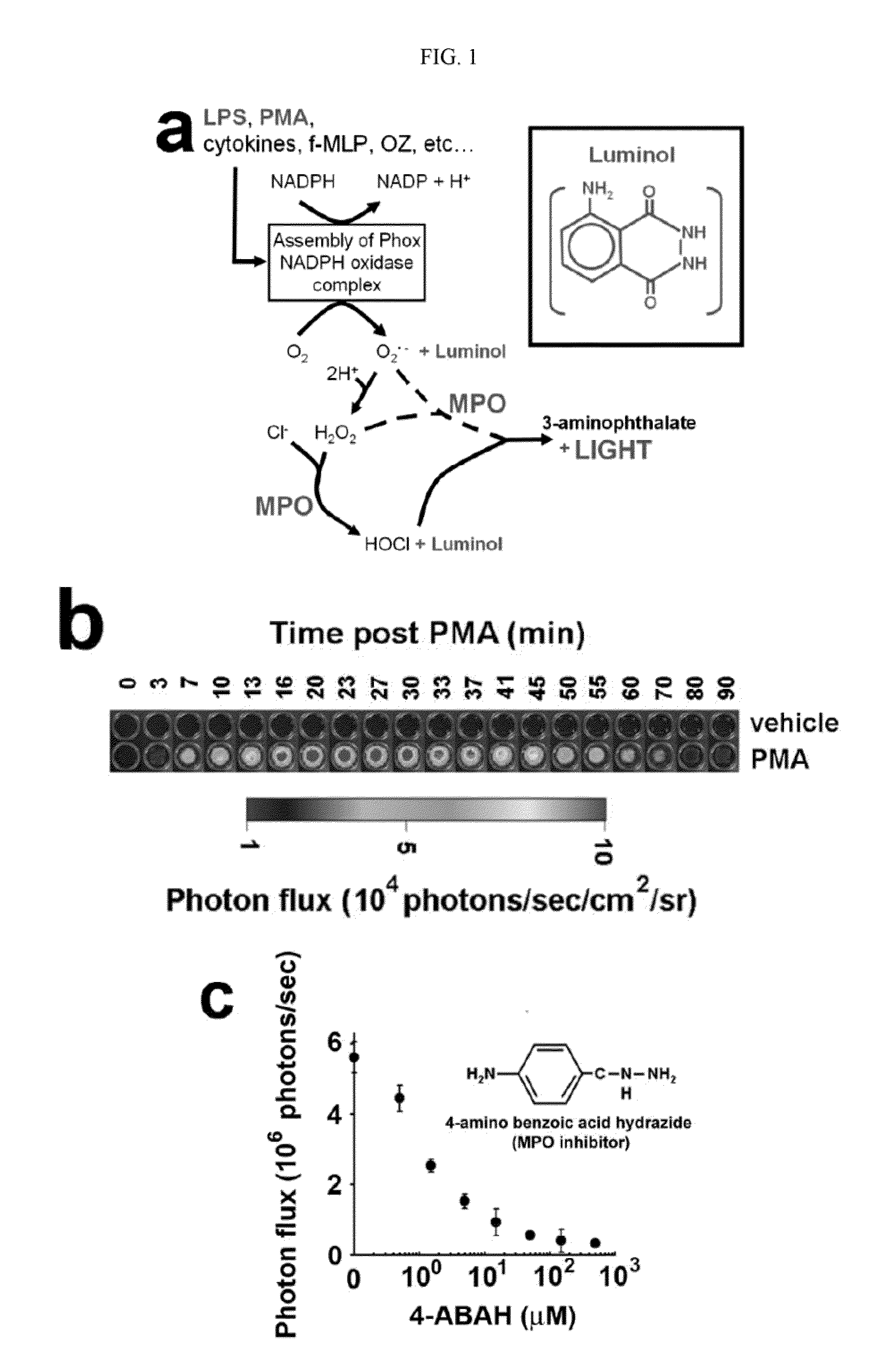
Bioluminescence imaging of myeloperoxidase activity in vivo, methods, compositions and apparatuses therefor
InactiveUS20110250145A1Improve stabilityLow costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic chemistryLuminolMyeloperoxidase activity
Methods of imaging distribution of myeloperoxidase activity in a subject are disclosed. These methods include the use of bioluminescent substrates, including luminol and wavelength-shifted analogues of luminol. Bioluminescent myeloperoxidase substrates that emit light at longer wavelengths compared to luminol are shown to be useful for imaging myeloperoxidase activity in vivo. The disclosed methods can be used for imaging sites of inflammation and other pathological conditions associated with abnormal levels of MPO activity in vivo. Methods of synthesis of luminol analogues are also disclosed.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Single-molecule-format real-time bioluminescence imaging probe
InactiveUS20090176239A1Convenient bioluminescence analysis methodBroad spectrumAnimal cellsSugar derivativesExtinctionIn vivo
The present invention provides an “in vivo and in vitro real-time bioluminescence imaging means,” which can transmit a detection signal promptly in response to an external signal, while taking advantage of a single-molecule-format luminescent probe as a bioluminescent means.The present invention is characterized by using, as a single-molecule-format luminescent probe utilizing the increase and decrease of a second messenger level as an index, a fusion protein including a single-chain protein containing a second messenger recognition protein and optionally a peptide which is capable of binding with the protein, and linked respectively to the N-terminus and the C-terminus thereto, an N-terminal fragment (N-LE) and a C-terminal fragment (C-LE) generated by dissecting a luminescent enzyme (LE). A single-molecule-format luminescent probe could be provided, which makes it possible to observe light emission (extinction) in vivo as well as in vitro, as a result of a conformational change of the second messenger recognition protein induced by the binding (unbinding) with a second messenger, and the subsequent association or dissociation between the N-LE and the C-LE flanked at both termini of the recognition protein.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Microplastic labeled by long-persistence luminescent nano particles, preparation method and application
InactiveCN108485097AAvoid interferenceAccurate and reliable scientific experiment dataLuminescent compositionsOrganic solventEnvironmental effect
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental science, and discloses a microplastic labeled by long-persistence luminescent nano particles, a preparation method and application. The method includes the steps that 1, the long-persistence luminescent nano particles are dispersed in organic solvent to obtain long-persistence luminescent nano particles dispersion liquid; 2, plastic macromolecules are dissolved in organic solvent to obtain a plastic macromolecule solution; 3, the long-persistence luminescent nano particles dispersion liquid and the plastic macromolecules solution are evenly mixed to obtain mixed dispersion liquid; 4, under stirring conditions, the mixed dispersion liquid is added into a dispersion medium aqueous solution dropwisely, and after dropwise adding, stirring is continued to obtain dispersion liquid of microplastic particles labeled by the long-persistence luminescent nano particles, or the microplastic particles labeled by the long-persistence luminescent nano particles are separated from the dispersion liquid. The method is simple, the product is stable in structure and good in luminescence performance, no background fluorescence disturbance exists, and the sensitivity is high; the microplastic labeled by the long-persistence luminescent nano particles, the preparation method and the application have potential application values in the fields of environmental effects of microplastics and bioluminescence imaging.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
System and Methods for Generating Three-Dimensional Images From Two-Dimensional Bioluminescence Images and Visualizing Tumor Shapes and Locations
A system and methods for generating 3D images (24) from 2D bioluminescent images (22) and visualizing tumor locations are provided. A plurality of 2D bioluminescent images of a subject are acquired during a complete revolution of an imaging system about a subject, using any suitable bioluminescent imaging system. After imaging, the 2D images are registered (20) according to the rotation axis to align each image and to compensate for differences between adjacent images. After registration (20), corresponding features are identified between consecutive sets of 2D image (22). For each corresponding feature identified in each set of 2D images an orthographic projection model (24) is applied, such that rays are projected through each point in the feature. The intersection point of the rays are plotted in a 3D image of a tumor is generated. The 3D image can be registered with a reference image of the subject, so that the shape and location of the tumor can be precisely visualized with respect to the subject.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Carbazolyl-based organic double-heterocyclic near-infrared fluorescent probe as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111961040ALarge Stokes shiftLarge displacementOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceQuantum yieldCarbazole
The invention relates to a carbazolyl-based organic double-heterocyclic near-infrared fluorescent probe, which has a structural formula I shown in the specification. The near-infrared fluorescent probe has strong emission in a near-infrared wavelength region, and has high photo-thermal property and chemical stability. The near-infrared fluorescent probe is simple in preparation method, high in fluorescence quantum yield and large in Stokes shift, and has important application prospects in development of near-infrared fluorescent probes and bioluminescence imaging, wherein X is O or S.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Bioluminescence imaging-based screening assay and inhibitors of abcg2
A bioluminescence imaging-based high-throughput assay for inhibitors of ABCG2 is described. Compositions of inhibitors of ABCG2 and methods of using ABCG2 inhibitors are also described.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
System and Method for Generating Three-Dimensional Images From Two-Dimensional Bioluminescence Images and Visualizing Tumor Shapes and Locations
A system and methods for generating 3D images from 2D bioluminescent images and visualizing tumor locations are provided. A plurality of 2D bioluminescent images of a subject are acquired using any suitable bioluminescent imaging system. The 2D images are registered to align each image and to compensate for differences between adjacent images. After registration, corresponding features are identified between consecutive sets of 2D images. For each corresponding feature identified in each set of 2D images, an orthographic projection model is applied, such that rays are projected through each point in the feature. The intersection points of the rays are plotted in a 3D image space. All of the 2D images are processed in the same manner, such that a resulting 3D image of a tumor is generated.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Preparation method and application of tetraphenyl ethylene derivative containing imidazole ring structure
ActiveCN111995579AThe synthesis method is simpleMild reaction conditionsOrganic chemistryAzo dyesBenzaldehydePhenyl group
The invention discloses a fluorescent dye with AIE properties and a preparation method thereof. The invention provides a synthesis method of a tetraphenyl ethylene (TPE) derivative fluorescent dye with a structure shown as a formula (I), wherein the substituent R is an aryl conjugated system. 4-(1, 2, 2-triphenylvinyl) benzaldehyde is used as a starting raw material and reacts with aryl diketone derivatives respectively to synthesize a series of imidazole ring-containing compounds, and the compounds have typical aggregation-induced emission (AIE) properties. The preparation method of the fluorescent dye is simple, the operation is simple and convenient, the cost is low, and the series of fluorescent dyes show strong solid fluorescence. The fluorescent dye can be applied to the fields of bioluminescence imaging and the like.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Multimodal silica-based nanoparticles
ActiveUS20180093000A1Powder deliveryGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsDiseaseCellular component
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY +2
Preparation method of rare earth complex grafted luminescent titanium dioxide mesoporous microsphere
The invention discloses a preparation method of a rare earth complex grafted luminescent titanium dioxide mesoporous microsphere. The preparation method mainly comprises the following steps: firstly, synthesizing a mesoporous titanium dioxide microsphere, modifying the mesoporous titanium dioxide microsphere with 2-2'-bipyridyl-4,4'-dicarboxylic acid to obtain a functionalized mesoporous titanium dioxide microsphere precursor, and then, carrying out reflux reaction on the precursor obtained in the former step and a synthesized binary rare earth complex in ethanol for hours to obtain a solid product, washing and drying the solid product to prepare a mesoporous composite material of the rare earth complex covalent grafted luminescent mesoporous titanium dioxide microsphere. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, a ternary rare earth complex is grafted into the mesoporous titanium dioxide microsphere through a covalent bond, and the obtained rare earth functionalized mesoporous titanium dioxide microsphere composite material can emit visible light and near-infrared light under visible light excitation, so that the composite material has a potential application prospect on the aspects of bioluminescence imaging, dye-sensitized solar cells, photocatalysis, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method for positioning bioluminescence imaging light sources in small animal
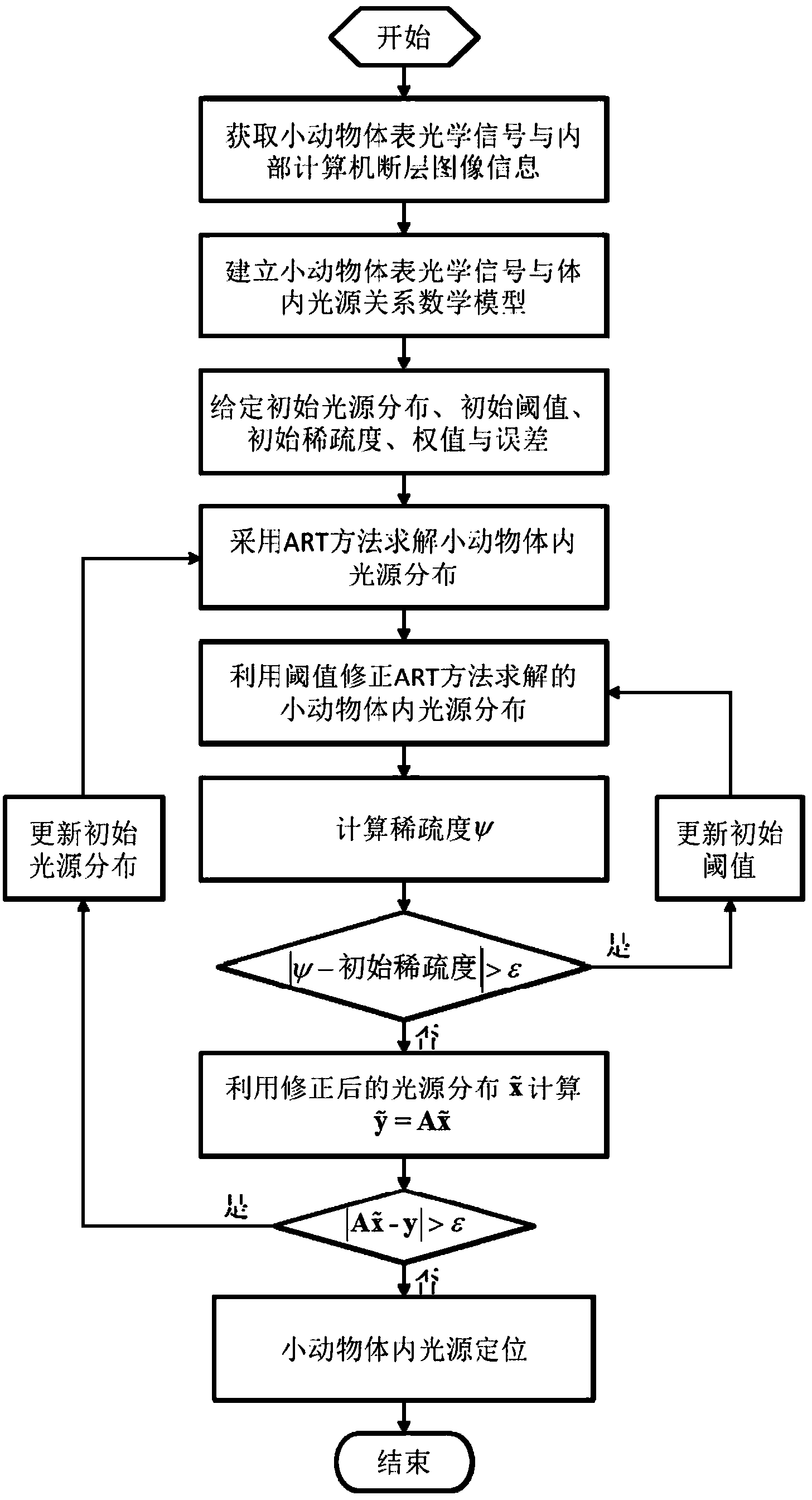
InactiveCN103767686AAchieve positioningImprove light source positioning accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSmall animalMathematical model
The invention discloses a method for positioning bioluminescence imaging light sources in small animal. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: building a relation between body surface measured data vectors and in-vivo unknown light source distribution of the small animal by utilizing a quantitative optical molecular tomography device and a finite element method; computing the in-vivo light source distribution of the small animal by adopting an algebraic iterative reconstruction method; determining a threshold value according to sparseness, and performing correction on the light source distribution, obtained by adopting the algebraic iterative reconstruction method, by utilizing the threshold value; circulating for multiple times to finally obtain the in-vivo light source distribution of the small animal to realize the positioning of the bioluminescence imaging light sources. The method disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the L0 normalization item does not need to be added to a mathematic model of the reconstruction problem, and approximation analysis does not even to be performed on the L0 norm by adopting the L1 norm and the Lp (0&1t; p≪ 1) norm, but the correction is performed on the light source distribution, obtained by adopting the algebraic iterative reconstruction method, directly by utilizing the sparseness. As norm approximation in the prior art is not adopted, the in-vivo light source positioning precision of the small animal is improved by the method provided by the invention.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Water-soluble rhodamine-based fluorescent/colorimetric dual-mode probe as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112159522AGood water solubilityGood biocompatibilityOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBenzoic acidBenzaldehyde
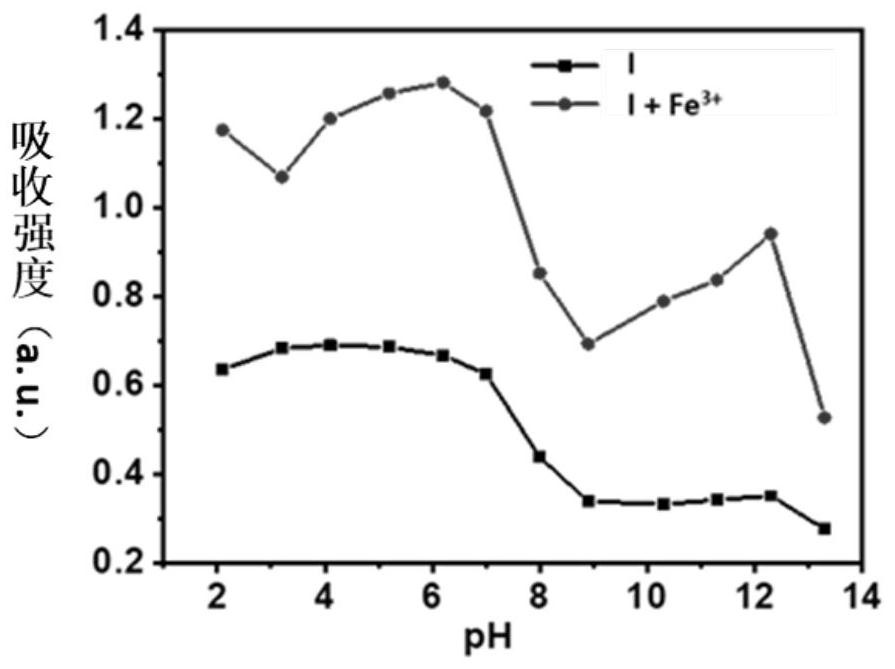
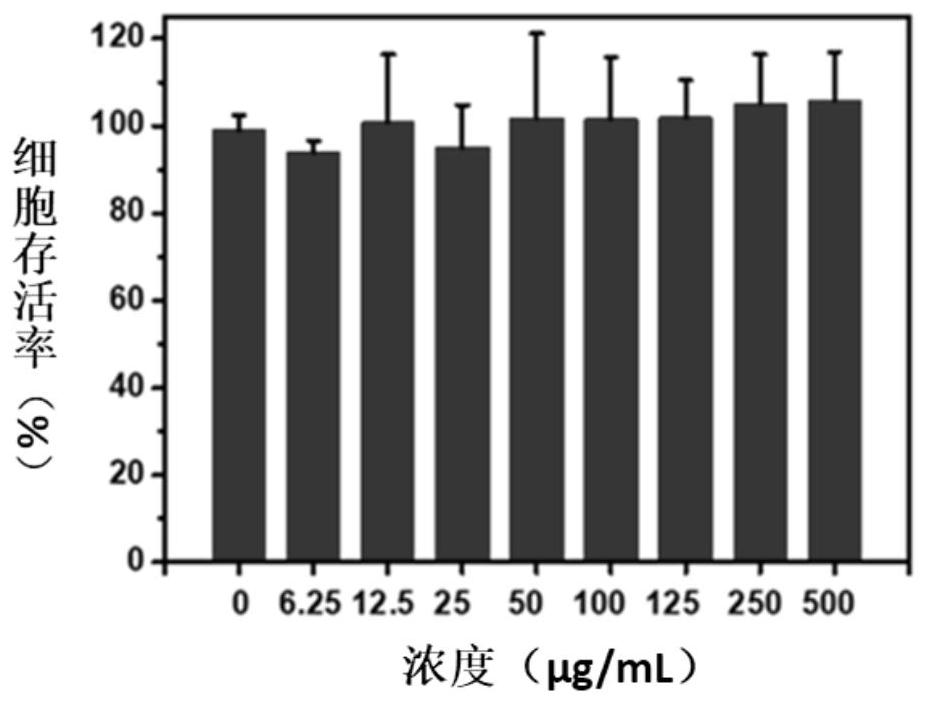
The invention provides a water-soluble rhodamine-based fluorescence / colorimetric dual-mode probe, and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the probe comprises the following steps: reacting rhodamine 6G with hydrazine hydrate to prepare rhodamine 6G hydrazide; reacting polyethylene glycol with 4-aldehyde benzoic acid to prepare benzaldehyde terminated polyethyleneglycol; and reacting the rhodamine 6G hydrazide with the benzaldehyde terminated polyethylene glycol to prepare the water-soluble rhodamine-based fluorescent / colorimetric dual-mode probe. The obtained dual-mode probe has good water solubility, biocompatibility and safety, and can be used in the field of bioluminescence imaging or disease diagnosis; and the probe is used for detecting ferric ions,is simple in sample preparation, can be observed through fluorescence emission and naked eyes, shows high selectivity, sensitivity and anti-interference capability, and is wide in pH application range.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Porous rare earth doped Li4ZrF8 up-conversion nano crystal and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108359458AStrong up-conversion luminescence abilityDrug loading capacityLuminescent compositionsLithium hydroxideRare earth
The invention discloses a porous rare earth doped Li4ZrF8 up-conversion nano crystal and a preparation method thereof. The up-conversion nano crystal is the monoclinic phase Li4ZrF8 nano crystal, thesize of the Li4ZrF8 nano crystal is 20-60 nanometers, and the nano crystal has a lot of micropores. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) dissolving lithium hydroxide, rare earth acetate and zirconium acetate in a solvent; 2) adding an alcoholic solution dissolved with ammonium fluoride in the solution obtained in the step 1), and heating the material to remove alcohol; and 3) heating the solution after alcohol is removed, cooling the material to room temperature, and preparing the rare earth doped Li4ZrF8 up-conversion nano crystal. The preparation method has the advantagesof simple process and good repeatability, and a prepared nano luminescent material has the advantages of dispersibility and good homogeneity. The prepared Li4ZrF8 nano crystal has strong up-conversion luminescence capability, has medicine slow-release capability, and has large application prospect on the fields of bioluminescence imaging and tumour drug treatment.
Owner:HUZHOU TEACHERS COLLEGE
Transgenic rosa26-luciferase mice for bioluminescent imaging
The invention relates to non-human transgenic animals expressing bioluminescent markersThe invention provides a transgenic mouse whose genome comprises a nucleotide sequence encoding lucif erase, operably linked to murine control sequences whereby the lucif erase is expressed in all cells. Administration of a luciferin substrate to the mouse results in bioluminescence. The control sequence is the Rosa 26 promoter. This mouse is useful to monitor in situ cell growth, differentiation or proliferation
Owner:GENENTECH INC
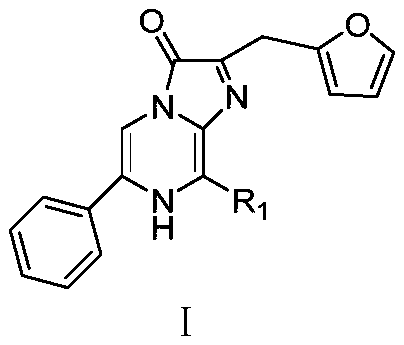
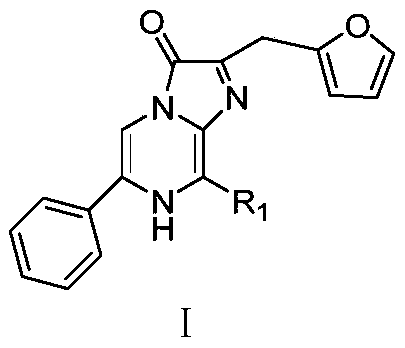
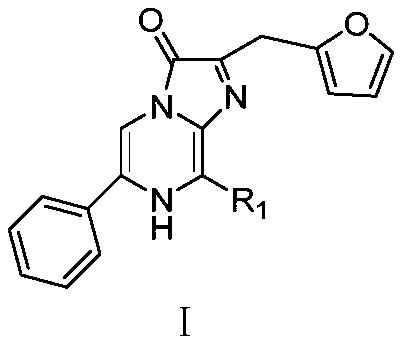
Phenyl imidazopyrazinone compound as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111072669AWith wavelength red shiftImprove stabilityOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementFuranChemical structure
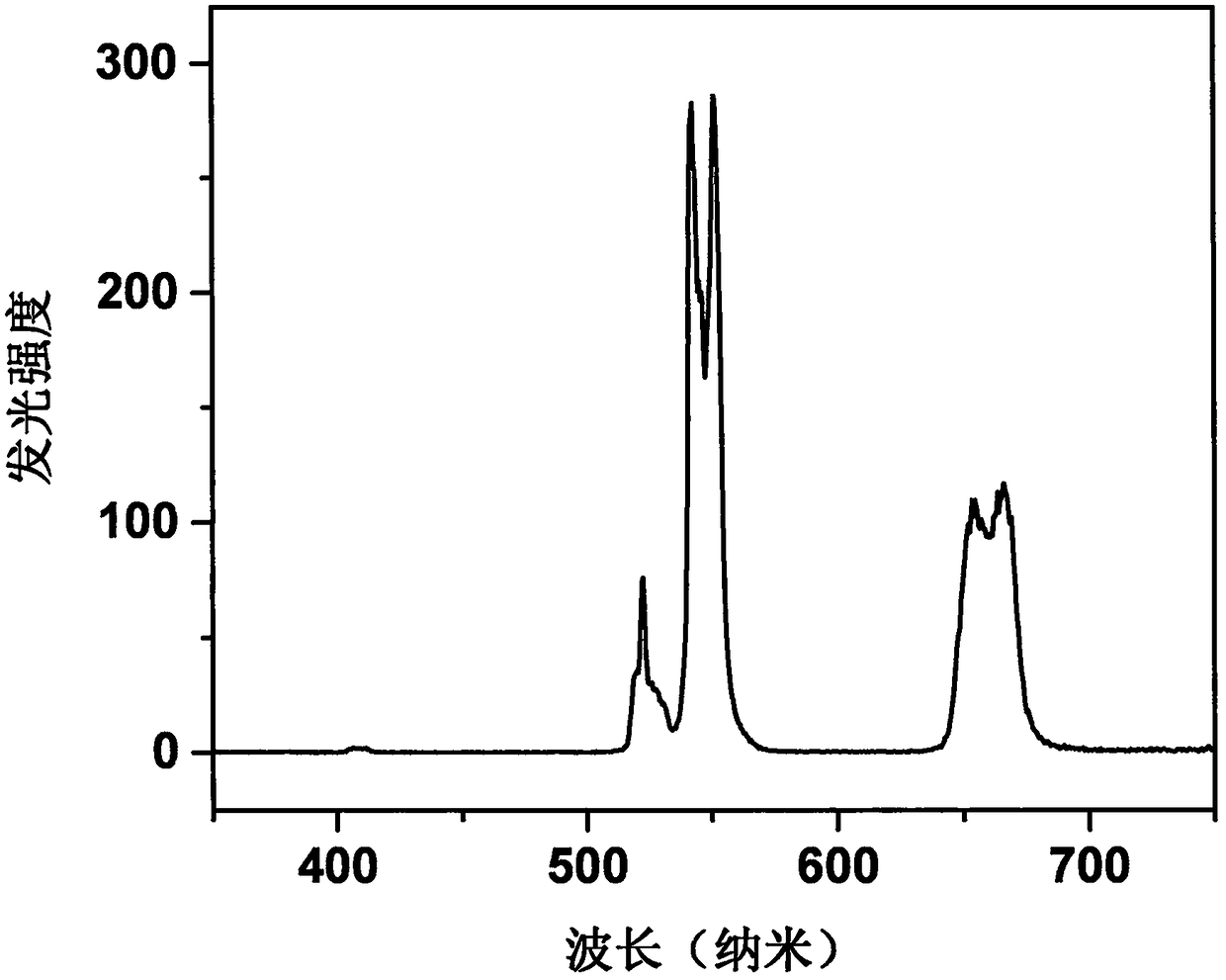
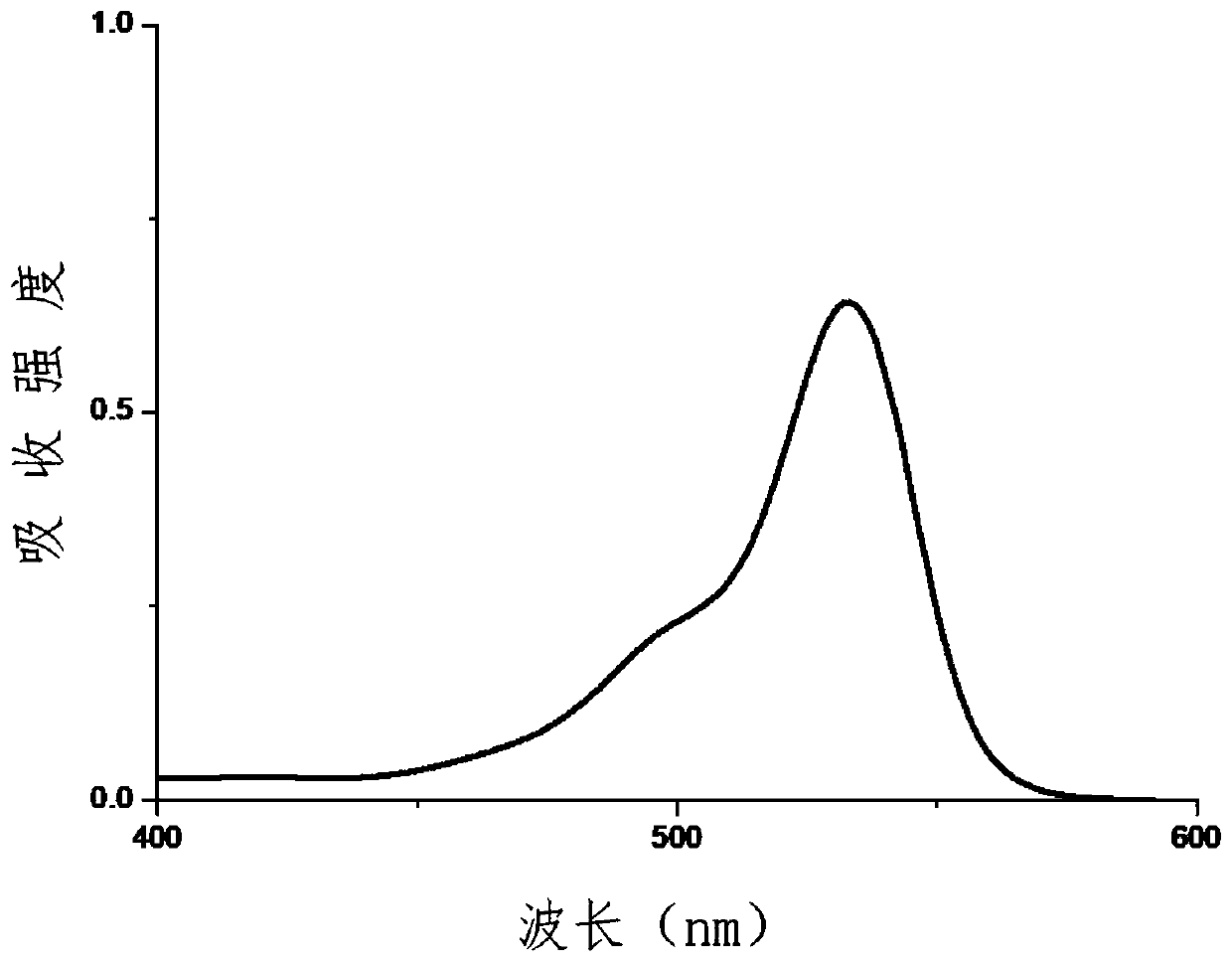
The invention provides a phenyl imidazopyrazinone compound as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The chemical structure is shown as a formula (I), wherein R1 is selected from phenoxy, thiophenyl, 5-methylfuryl, 4-methoxyphenyl, 4-fluorophenyl, 4-chlorphenyl, 4-bromophenyl, 3-fluoro-4-aminophenyl, 3-furyl, 4-methylfuryl, naphthalene-2-yl, 4-methylphenyl, 3, 5-dimethylphenyl, 4-hydroxymethylphenyl, 4-hydroxymethylphenyl and 4-hydroxyphenyl. The C8 site of a Furimazine substrate is modified, so that the imaging wavelength of the Furimazine substrate can generate red shift, theluminous intensity of the Furimazine substrate is enhanced, and particularly, bioluminescence imaging at an animal level is enhanced.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Triphenylamine-based organic near-infrared fluorescent probe as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN112279832ALarge Stokes shiftLong emission wavelengthOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceStructural formulaChemical stability
The invention relates to a triphenylamine-based organic near-infrared fluorescent probe, and the structural formula of the organic near-infrared fluorescent probe is shown as the following formula I.The near-infrared fluorescent probe provided by the invention has strong emission in a near-infrared wavelength region, and has high photo-thermal property and chemical stability. The near-infrared fluorescent probe provided by the invention is simple in preparation method, large in Stokes shift, relatively long in emission wavelength and good in chemical stability, and has important application prospects in development of near-infrared fluorescent probes and bioluminescence imaging.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for preparing hexagonal rare earth tetrafluoride sodium salt material through low-temperature molten salt fluorination
InactiveCN110804439AGood dispersionHigh crystallinityNanoopticsRare earth metal compoundsFluorescenceSodium salt
The invention discloses a method for preparing a rare earth tetrafluoride sodium salt material through low-temperature molten salt fluorination, and belongs to the field of inorganic material preparation. The method is simple and convenient to operate, common cheap substances are used as raw materials, sodium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate are used as sodium sources, and ammonium hydrogen fluoride is used as a fluorinating agent and a fluxing agent. According to the method, the hexagonal rare earth tetrafluoride sodium salt material with uniform size and regular morphology can be prepared. The prepared rare earth doped luminescent fluoride material has strong upconversion fluorescence performance and pure photochromaticity, and has potential application value in the fields of bioluminescence imaging, 3D display and photocatalysis. The preparation method has low requirements on environmental equipment, can be used for large-scale production and is expected to be used for industrial production.
Owner:黄新阳
532nm excited rhodamine fluorescent dye and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111334070ARaw materials are cheap and easy to getThe synthesis steps are simpleAzo dyesFluorescence/phosphorescenceQuantum yieldOrganic chemistry
The invention provides 532nm excited rhodamine fluorescent dye and a preparation method thereof. The structure of the 532nm excited rhodamine fluorescent dye is shown as (1), and the fluorescence quantum yield is higher and reaches 0.85 or above in ethanol through modification with different six-membered ring positions at the nitrogen end. Meanwhile, the raw materials used in the invention are cheap and easily available, the synthesis operation is simple, the requirements on experimental conditions are low, and the dye can be widely applied to the field of bioluminescence imaging.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Mammal dedicated cell line from human hepatocellular carcinoma cell
InactiveUS20120295349A1Improve filtering effectArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsHepg2 cellsLuminescence
A mammal dedicated cell line is provided, which is a HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cell line (HepG2 / NF-kB / Luc / sr39tk)1_18 obtained by co-transformation with NF-kB / Luc and NF-kB / sr39tk. Firstly, a successfully transformed pNF-kB / Luc HepG2 cell is obtained. Then, a dedicated cell line sensitive to TPA and MTX is generated by experimental screening Next, a plasmid construct carrying pNF-kB / sr39tk genome is introduced into the dedicated cell line by means of Superfect protocol. Finally, a HepG2 cell line co-expressing NF-kB / Luc and NF-kB / sr39tk is screened with G418 and ZEOCIN, and transformation result is confirmed by luminescence and radio activity. The (HepG2 / NF-kB / Luc / sr39tk)1_18 obtained is suitable to screen drug for treating liver cancer and examine these cells by bioluminescence imaging and nuclear medicine imaging.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
Xanthene-hemicyanine near-infrared fluorescent dye as well as synthesis method and application thereof
ActiveCN114591633APromote absorptionIncreased emission wavelengthMethine/polymethine dyesPhotodynamic therapyProtein labelingBiological macromolecule
The invention discloses a xanthene-hemicyanine near-infrared fluorescent dye as well as a synthesis method and application thereof. The dye has longer absorption and emission wavelengths, the water solubility of the dye is improved, and the change of spectral properties after the dye interacts with biomacromolecules is avoided by reasonably introducing active groups. Experiments prove that the dye has good photophysical properties and bioluminescence imaging potential, and can be applied to the aspects of biological recognition imaging, cell imaging, protein labeling, specific recognition of antibodies, nucleic acid labeling, DNA sequencing, tumor photodynamic therapy and the like.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Compound for preparing near-infrared rate light-emitting upconversion nanomaterial as well as preparation method and application of compound
InactiveCN106674078AGood reversibilityGood light and heat stabilityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceInterference resistanceRate change
The invention provides a compound for preparing a near-infrared rate light-emitting upconversion nanomaterial as well as a preparation method and an application of the compound. The light emission of the upconversion nanomaterial presents rate change in a pH range of 6.8-8.8, and the upconversion nanomaterial has pH-sensing reversibility, very good light stability, thermal stability and interference resistance and is suitable for bioluminescence imaging in a pH near-infrared rate.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com