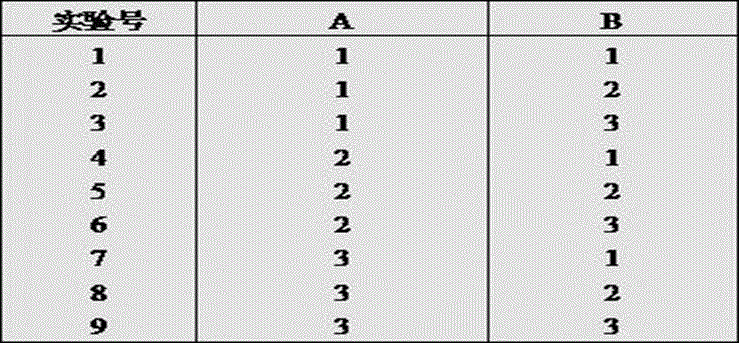
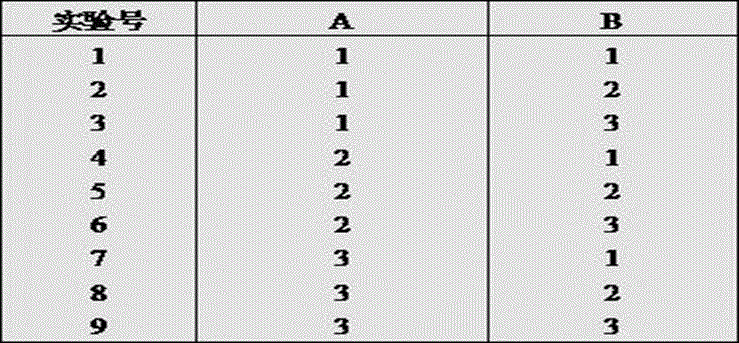
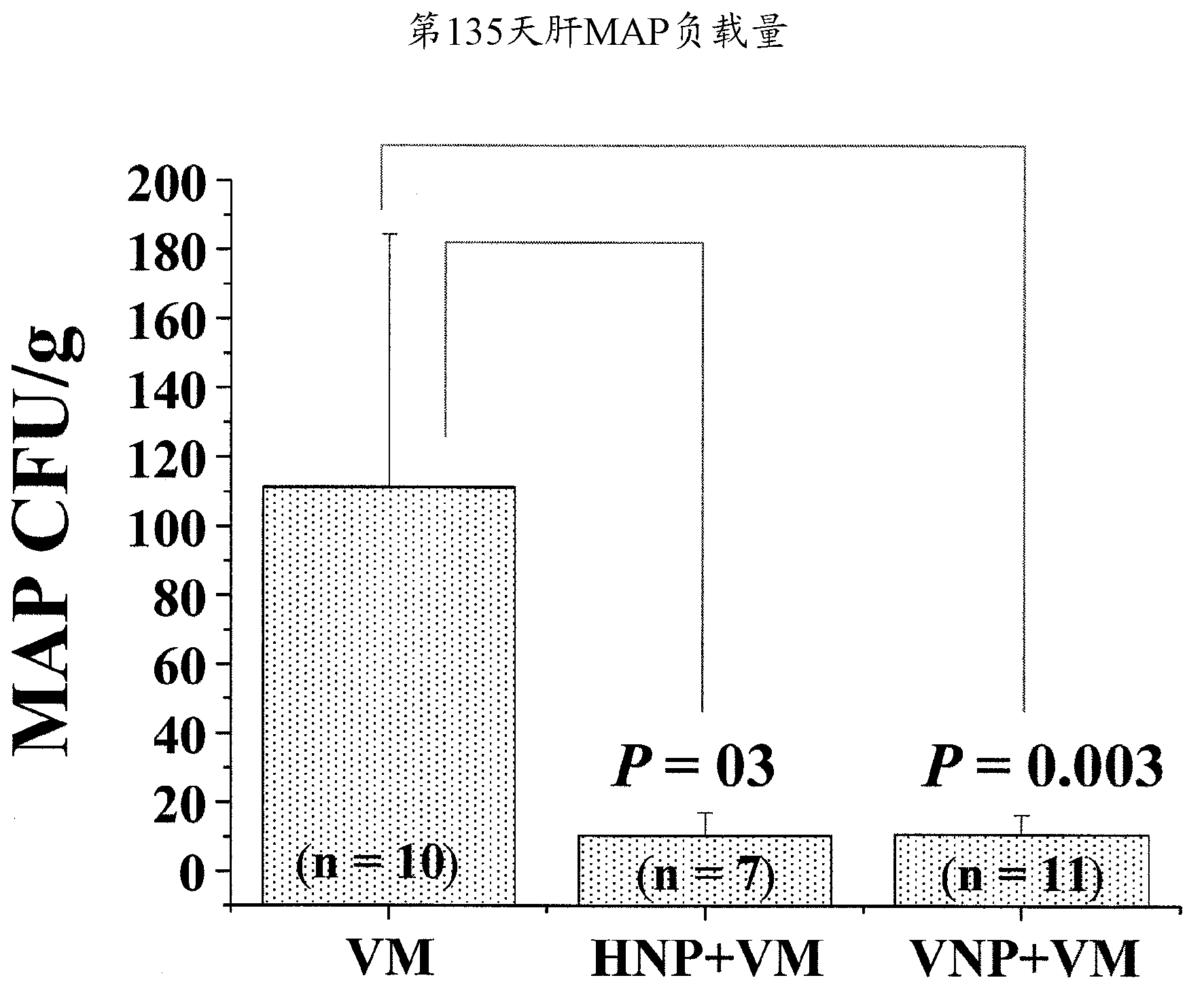
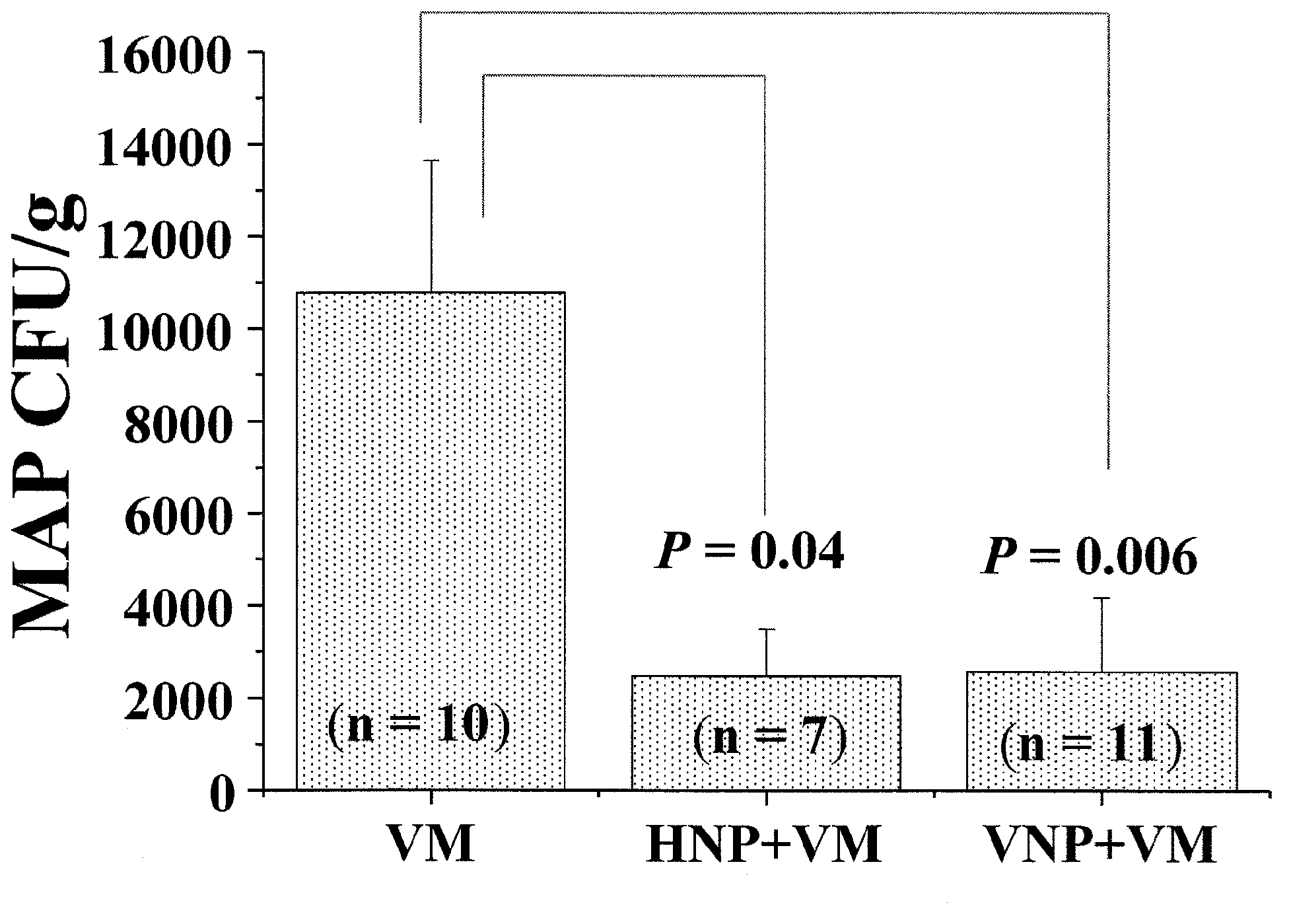
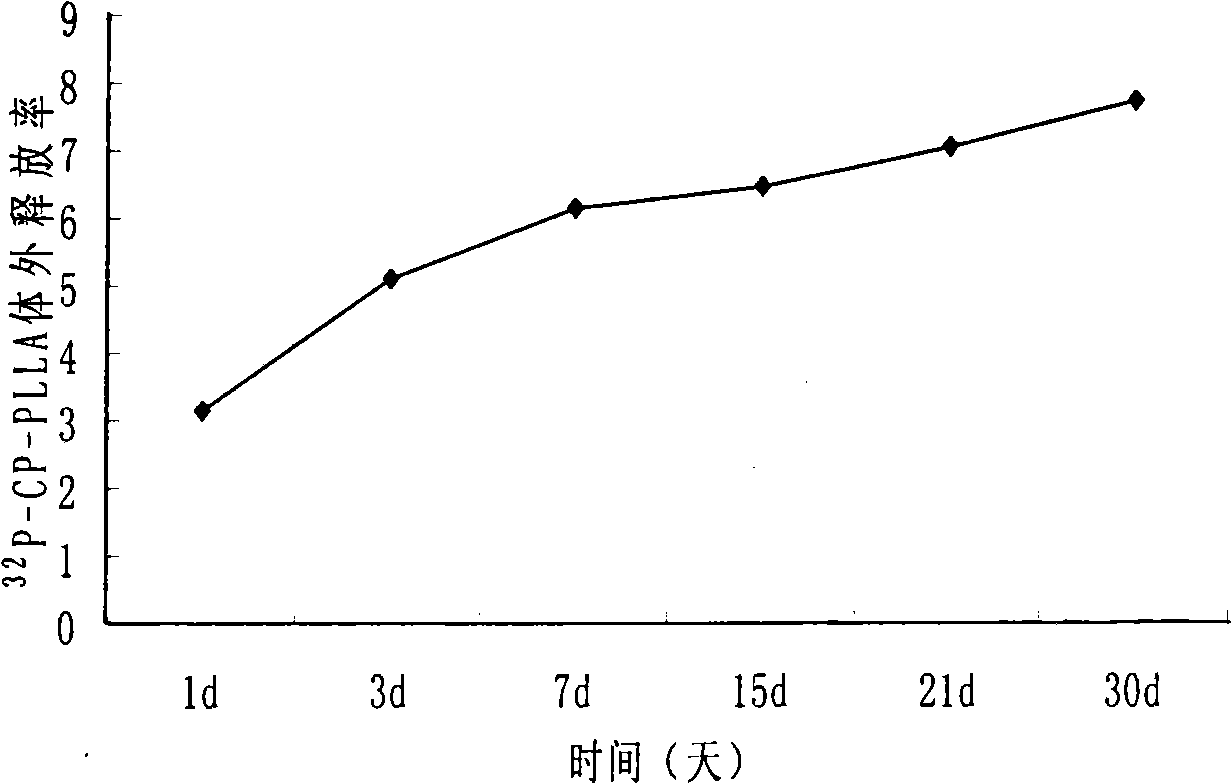
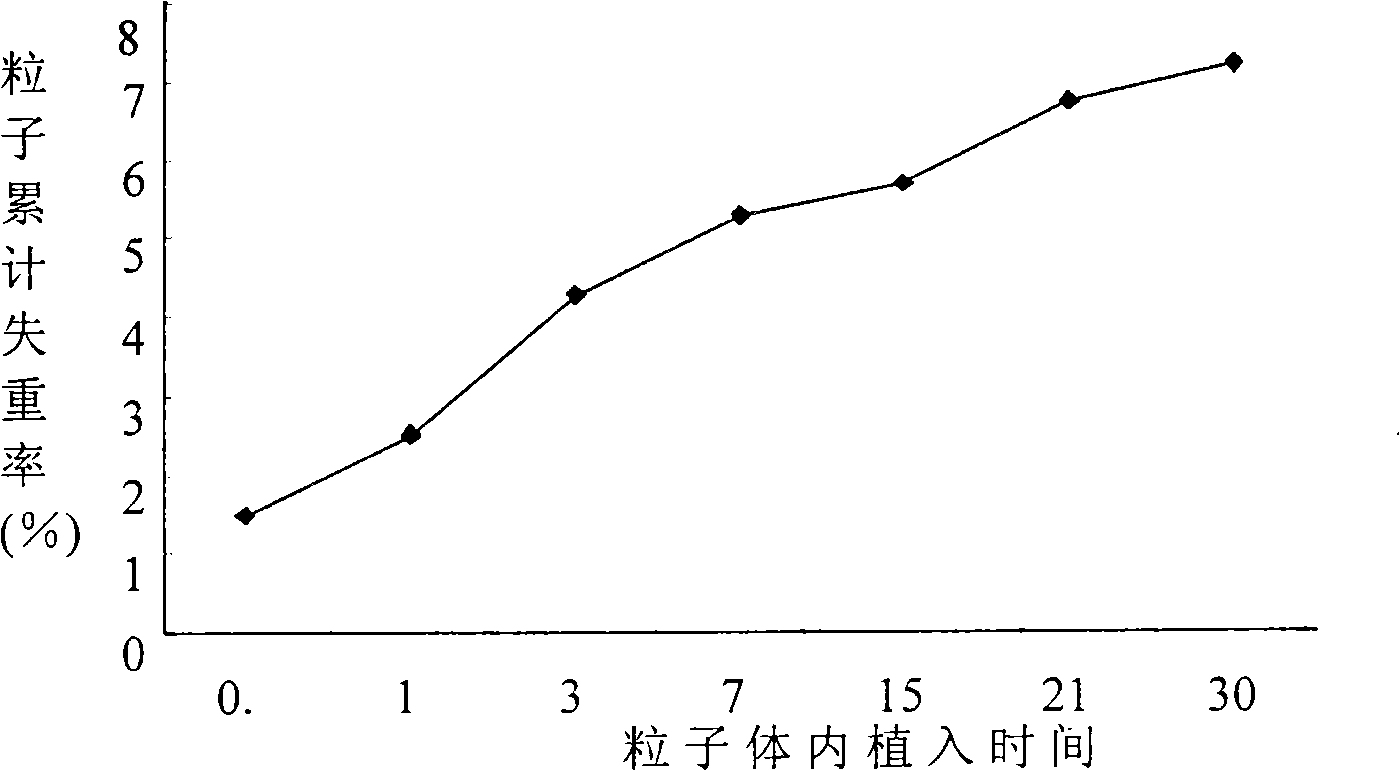
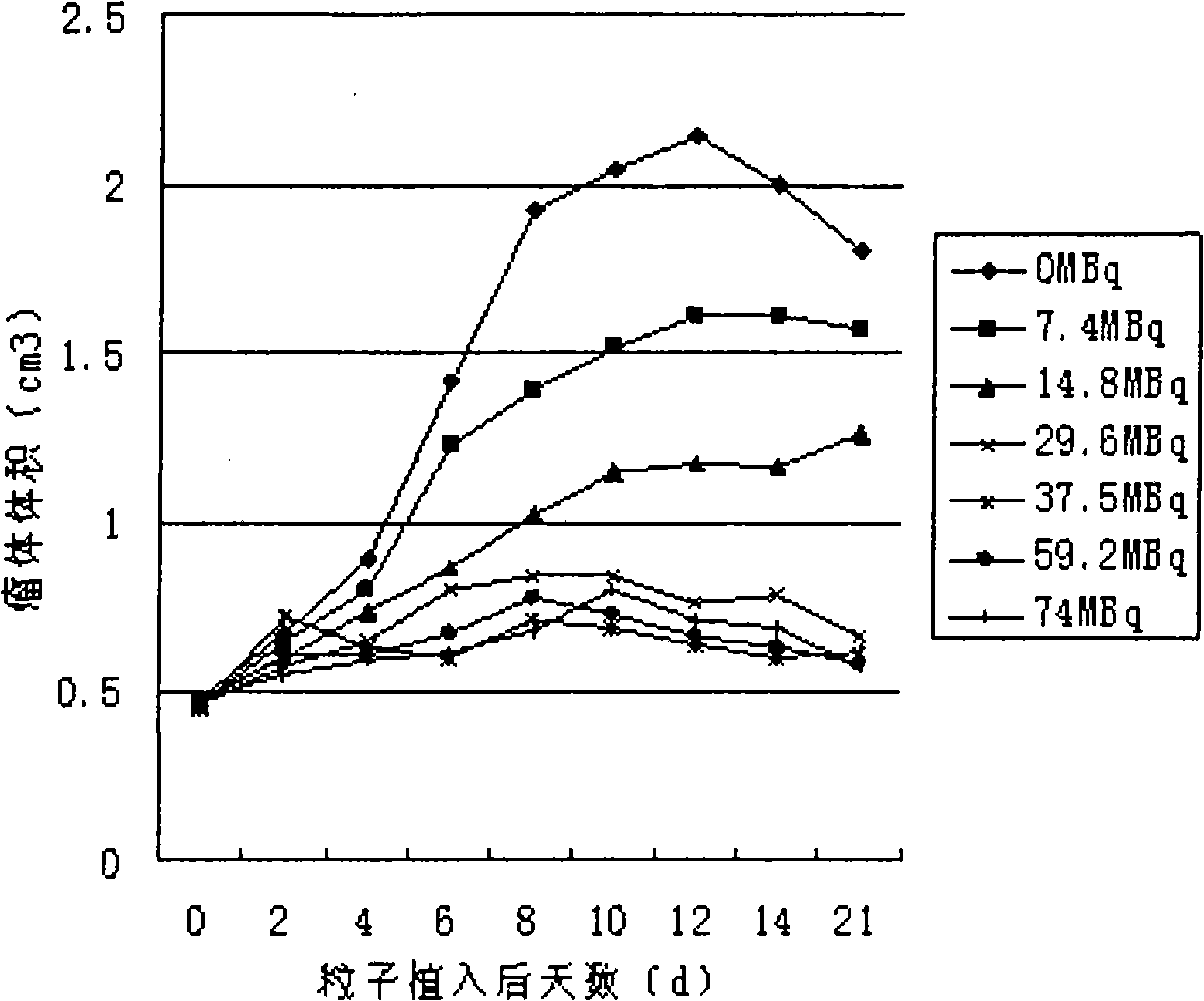
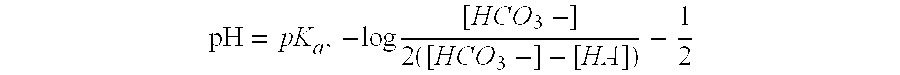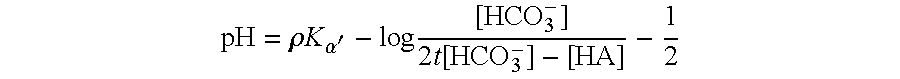Patents
Literature
42 results about "D lactate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
D-lactate is produced by bacteria residing in the colon when carbohydrates are not completely absorbed in the small intestine. When large amounts of D-lactate are present, individuals can experience metabolic acidosis, altered mental status (from drowsiness to coma), and a variety of other neurologic symptoms, particularly dysarthria and ataxia.
Probiotic lactic acid bacterium to treat bacterial infections associated with SIDS
Compositions including a non-pathogenic lactic acid-producing bacteria, such as a Bacillus species, spores or an extracellular product of B. coagulans, formulated for oral administration to the intestinal tract for inhibiting bacterial gastrointestinal infections are described. Methods and systems using the compositions for treating gastrointestinal infections, particularly sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) are also disclosed.
Owner:GANEDEN BIOTECH
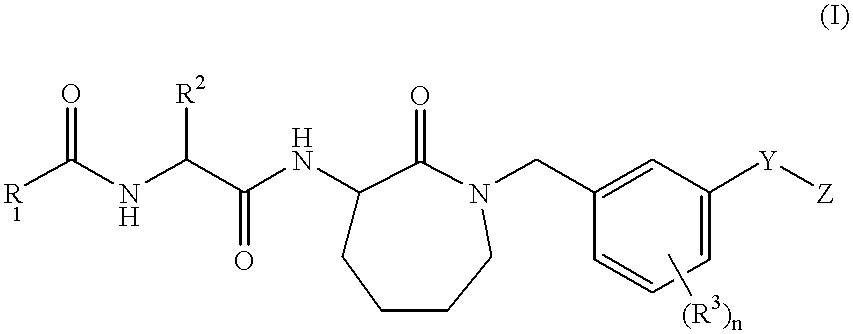
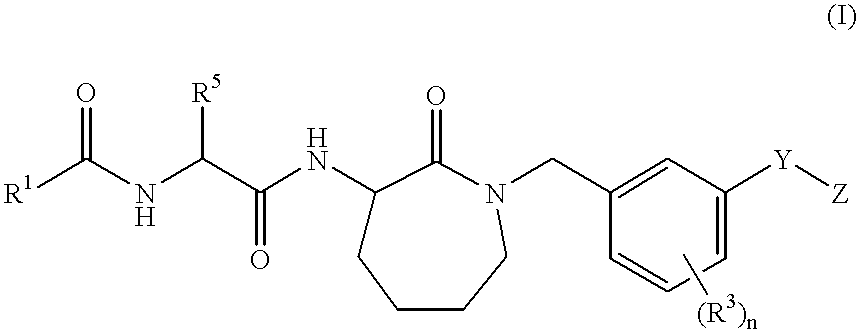
Lactams as inhibitors of A-beta protein production
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB PHARMA CO
Composition with disintoxicating and liver-protecting effects and application thereof in food and health-care food
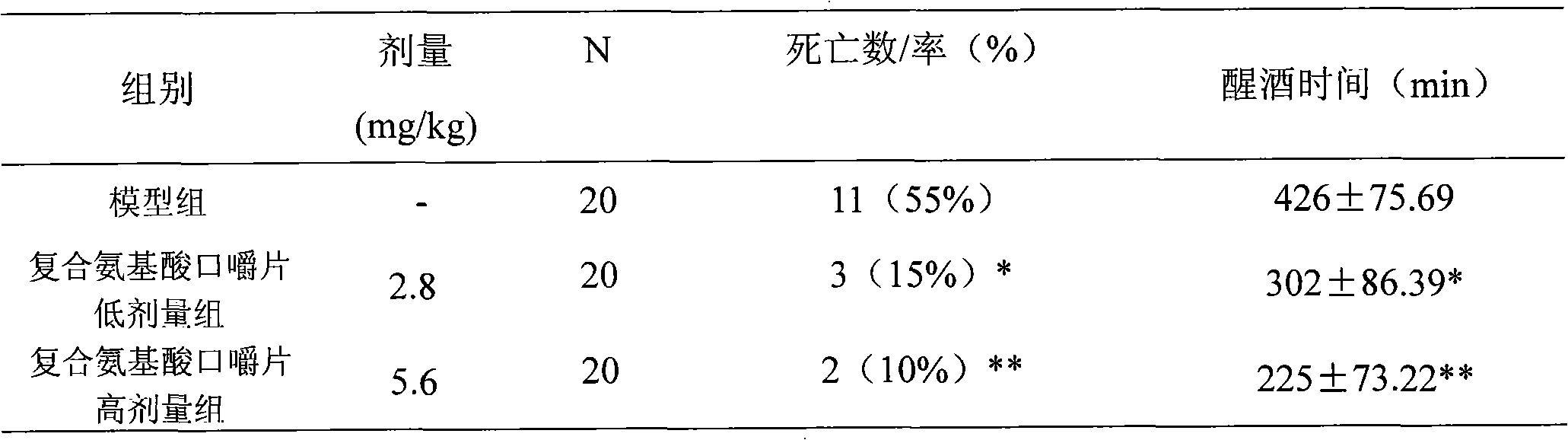
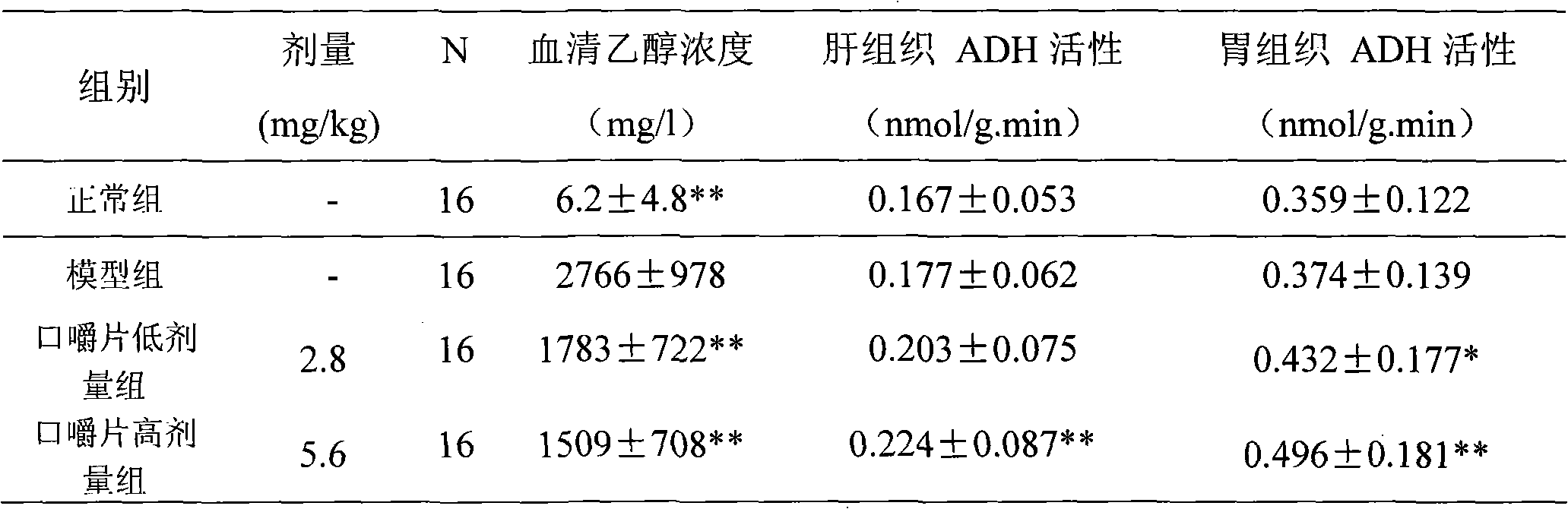
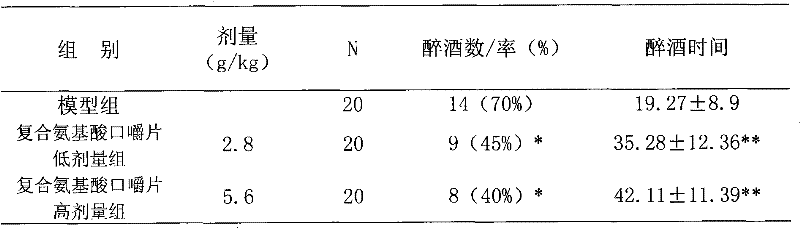
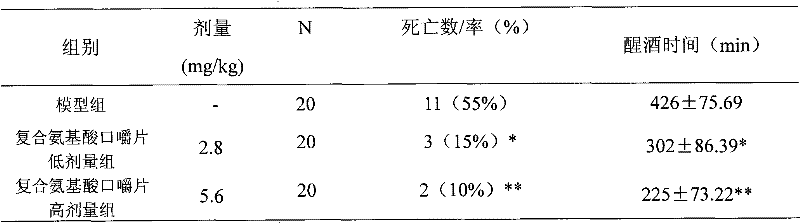
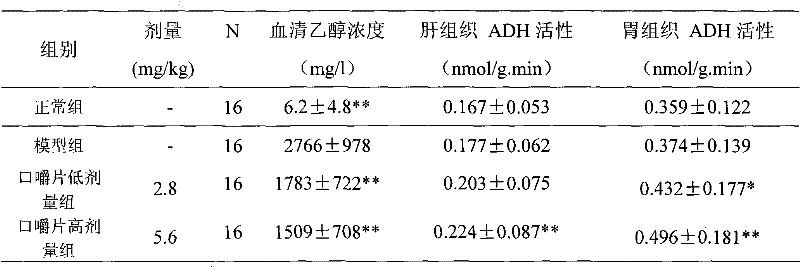
ActiveCN101889679AIncrease contentImprove toleranceDigestive systemKetone active ingredientsEthanol dehydrogenaseNon toxicity
Owner:SHANDONG MINGREN FURUIDA PHARMA
Neratinib sustained-release implant for treating solid tumor
InactiveCN101185633AOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismProstate cancerTherapeutic effect
A sustained release implant includes 0.1%-50% (w / w) nilotinib, 50-99% sustained release excipients and 0-15% sustained release moderator. Sustained release excipients are mainly one or combination of poly (L-lactide-co-ethyl phosphate), poly (L-lactide-co- phosphoric acid propyl), polylactic acid, the copolymer of polylactic acid and hydroxyacetic acid and polifeprosan; sustained release moderator is one or combination of mannitol, sorbic alcohol and chondroitin; sustained release implant applied in local tumor can slowly release nilotinib onto local tumor, thus maintaining effective drug concentration of local tumor as well as significantly reducing overall toxic reaction; the invention not only reduces overall toxic reaction of nilotinib, but also selectively improves drug concentration in local tumor, enhancing the therapeutic effects of non-operative therapy such as chemotherapy drugs and radiotherapy. The implant can be used for treating solid tumors including lung cancer, esophageal carcinoma, gastric cancer, liver cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, prostatic carcinoma, pancreatic cancer, bladder carcinoma, cerebroma, and colorectal cancer.
Owner:SHANDONG LANJIN PHARMA +1
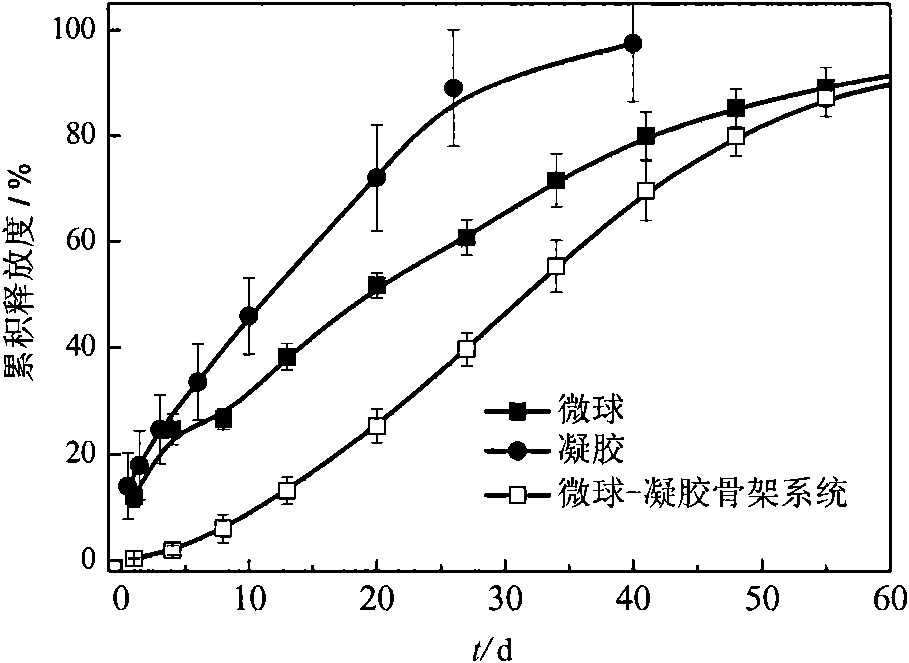
In-situ implantation drug delivery system of naltrexone microsphere-hydrogel matrix
InactiveCN101612437AStable release rateReduce high speed releaseSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMicrosphereDetoxification Process
The invention discloses an in-situ implantation drug delivery system of microsphere-hydrogel matrix of detoxification drug naltrexone, belonging to the field of medicinal preparation. The drug naltrexone is embedded in microspheres of biodegradable materials polylactic acid / glycolic acid polymer; the microspheres disperse in reverse temperature sensitive hydrosol of methylcellulose; the hydrosol is solidified into a hydrogel matrix at body temperature during hypodermic injection to form a composite system of microsphere-hydrogel matrix and to control the release of naltrexone. The invention integrates the advantages of medicine carrying controlled release particles and temperature sensitive gel matrix in-situ implantation system, realizes injected implantation, realizes release at a constant speed for 60 days after implantation, and can adjust drug release speed by adjusting the content of naltrexone microspheres in hydrogel, thus having great significance in improving clinical application effect of naltrexone and in solving the problem of relapse in the detoxification process.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Chinese medicinal composition for preventing and treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and resisting fatigue
ActiveCN102178734ADilated blood vesselsInhibition formationMetabolism disorderAntinoxious agentsSalvia miltiorrhizaDisease
The invention provides a Chinese medicinal composition for preventing and treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and resisting fatigue, which comprises the following components in part by weight: 30 to 90 parts of glossy ganoderma extract, 40 to 120 percent of notoginseng root extract, 40 to 120 parts of root of red-rooted salvia extract and 40 to 120 parts of ginkgo leaf extract. The Chinese medicinal composition has the effects of regulating blood fat, improving hemorheology and resisting atherosclerosis, anoxia and fatigue, can reduce the level of lactic acid and serum urea and can relieve the discomfort feeling of limb weakness, oscitancy, muscular soreness, anorexia and the like which are caused by sports effectively. The invention also provides a Chinese medicinal preparation containing the Chinese medicinal composition and a preparation method thereof.
Owner:庞会心
Mediucm for detecting Van A and Van B vancomycin-resistant entercocci and method of using the same
InactiveUS7364874B2Reduce detectionEasy to useBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementSodium lactateMicroorganism
Owner:TOKYO WOMENS MEDICAL UNIV
Fluid therapy with l-lactate and/or pyruvate anions
Electrolyte solutions are provided which are useful in electrolyte and fluid therapy, parenteral nutrition and dialysis. The Na:Cl ratio is normalized, plasma and cellular pH are normalized and cellular cofactor ratios are normalized in a manner which decreases toxicity over prior art solutions.
Owner:BTG INT LTD
Lactate sensor
ActiveCN103018291AEfficient determinationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisLactate oxidaseD lactate
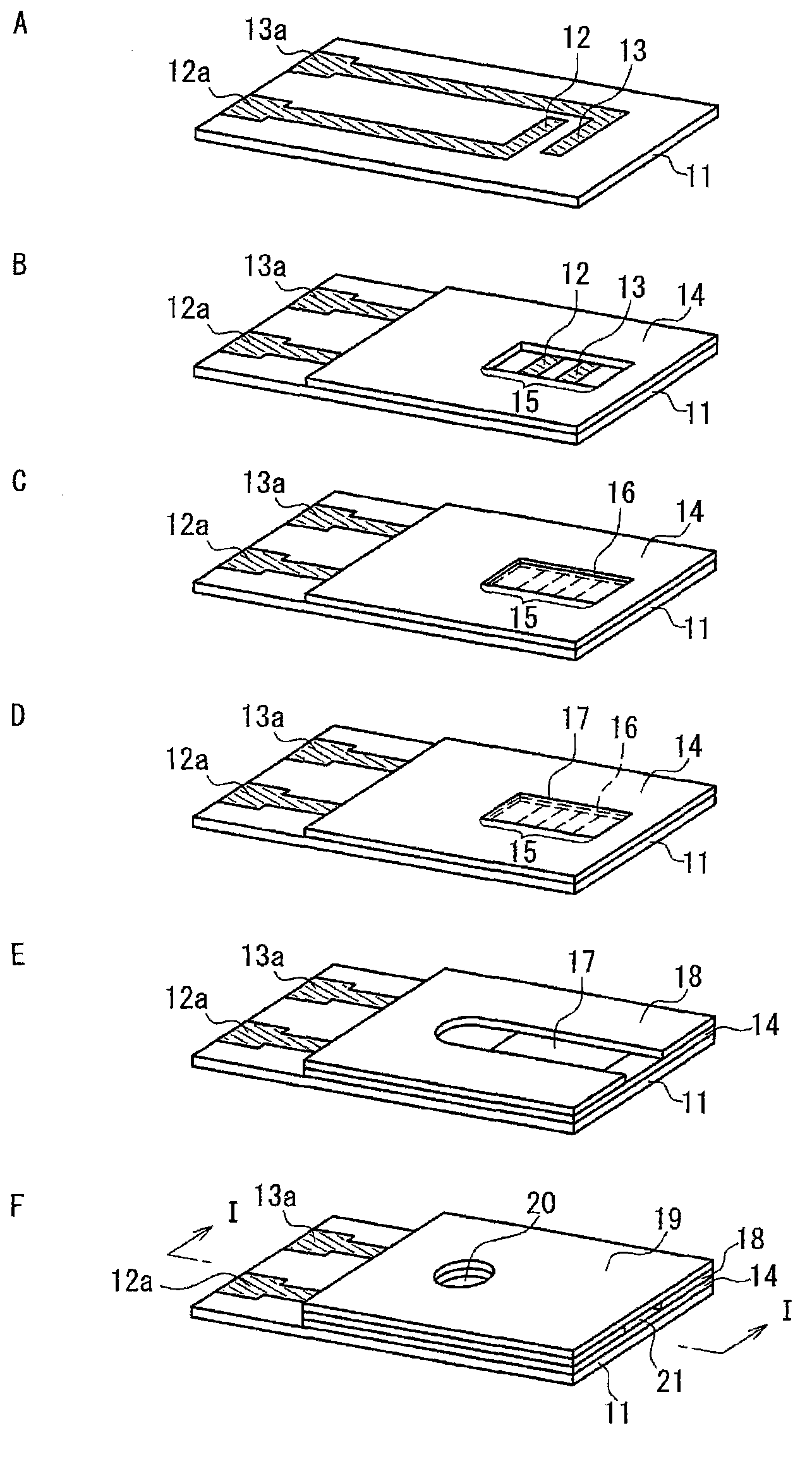
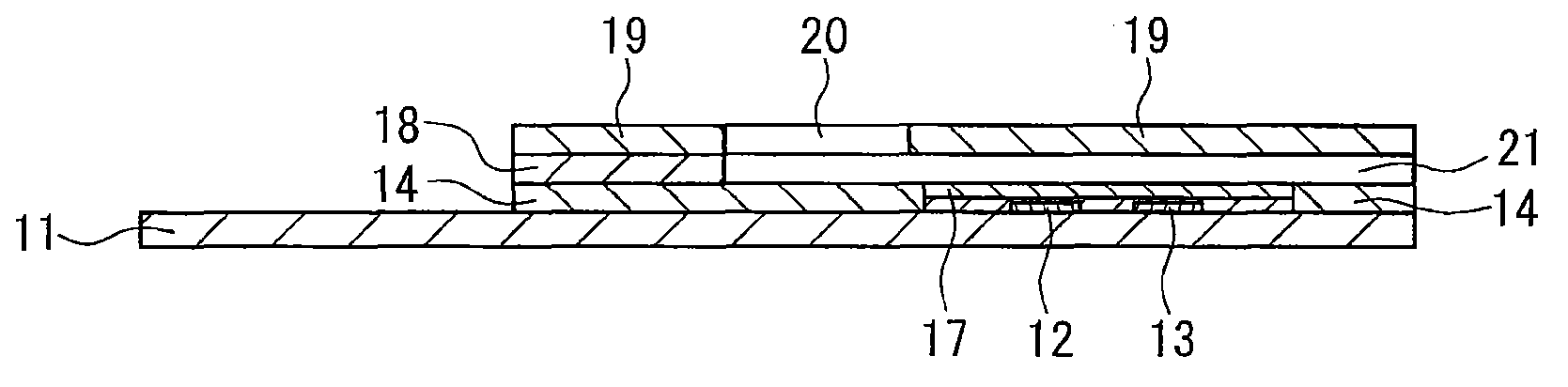
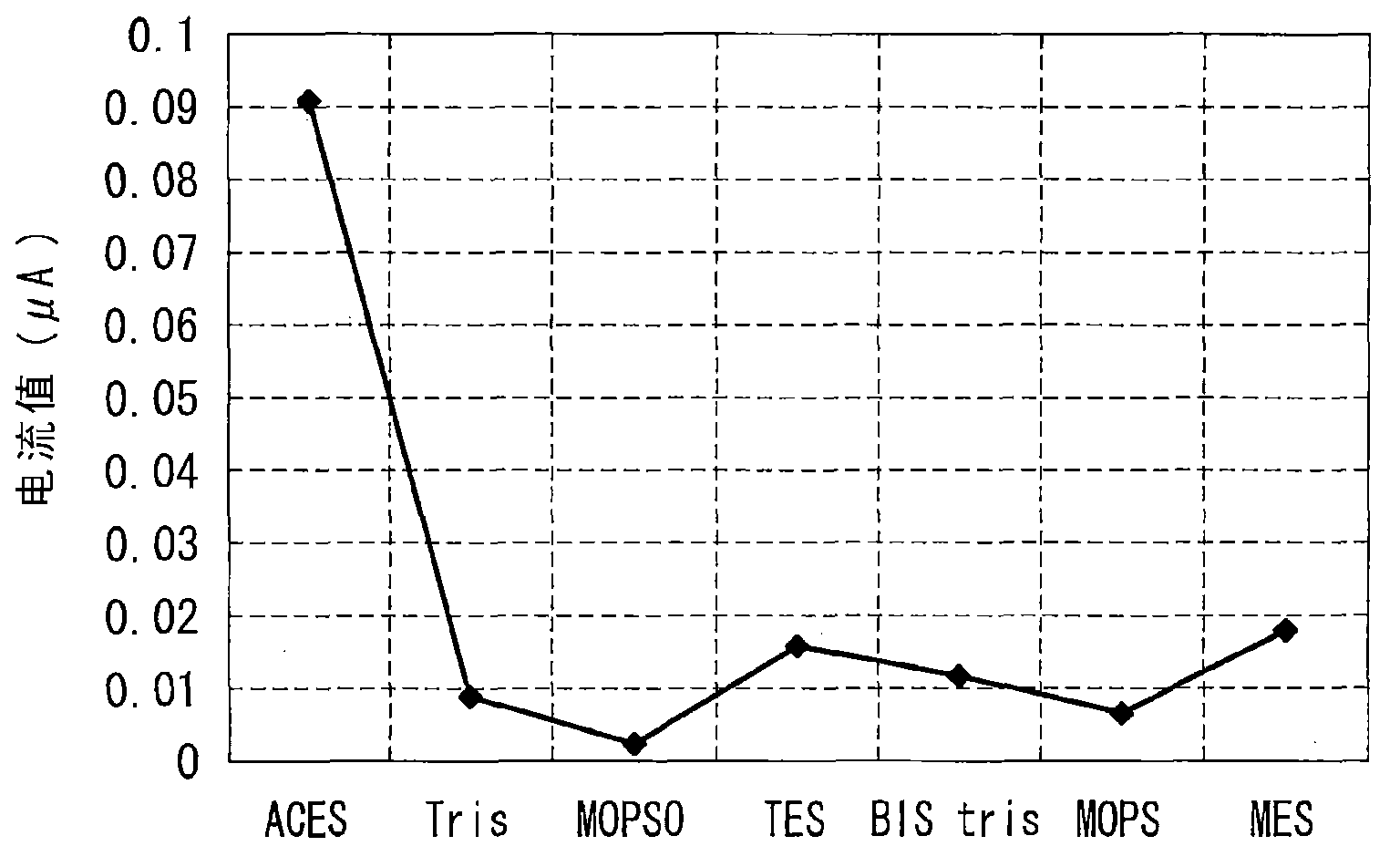
The invention relates to a lactate sensor, and specifically a lactate sensor capable of accurately measuring a lactate concentration in a short period of time. The lactate sensor includes an insulating substrate, an electrode system including at least a working electrode and a counter electrode provided on the substrate, and a reagent layer provided on the electrode system. The reagent layer contains lactate oxidase, a mediator, and N-(2-acetamide)-2-aminoethanesulfonic acid.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Xylitol compound for curing or preventing female colpitis and cervical erosion
InactiveCN101530403ADoes not cause allergiesNo local irritationHydroxy compound active ingredientsInorganic non-active ingredientsCervixSecretion
The invention provides a method for preparing compound of xylitol and lactic acid; the solution of the compound can directly wash vagina and cervix. The compound can cure or prevent colpitis and cervical erosion, can rapidly improve the congestion of vagina and cervix, can remove white or yellow purulent secretion, and can remove the inflammation of the vagina and cervix, thus recovering the health of the patient.
Owner:郭进军 +2
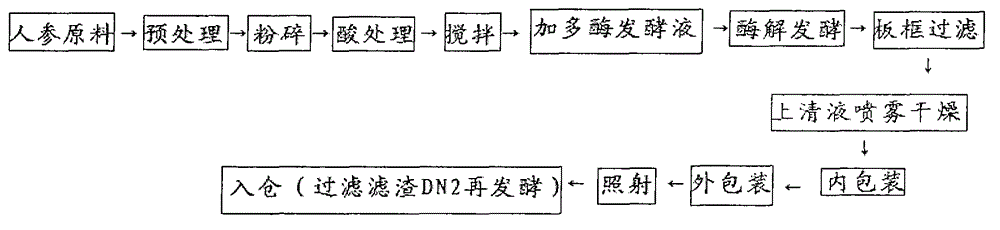
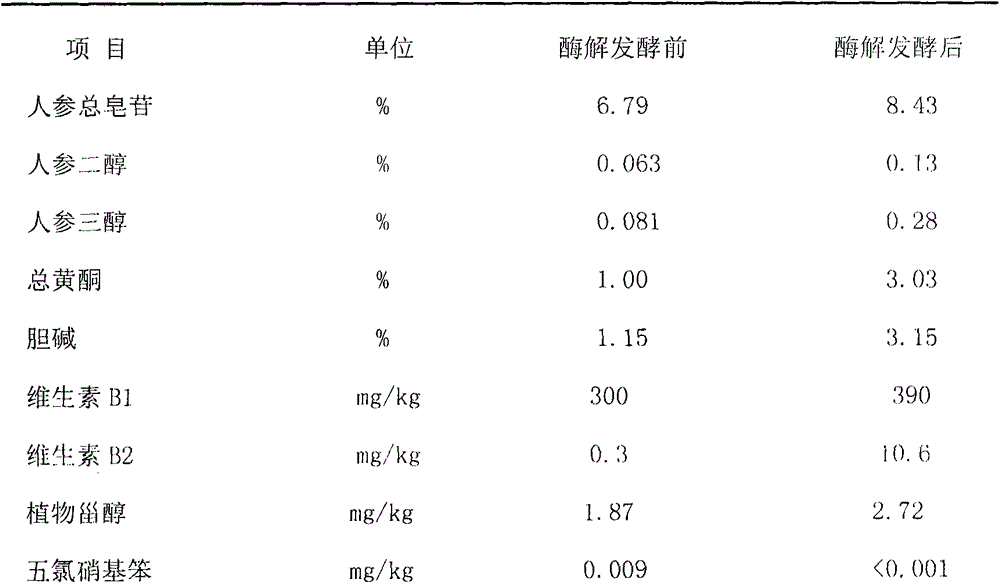
Method for preparing panaxoside and panaxynol through enzymatic zymotechnics
InactiveCN104784233AChange molecular structureIncrease contentGlycosidesGlycosideD lactateIrradiation
The invention discloses a method for preparing panaxoside and panaxynol through enzymatic zymotechnics. The method comprises the following steps: cleaning Changbai mountain ginseng, drying the ginseng at 50 to 60 DEG C, and crushing the ginseng to be 40 meshes; clustering raw material powder in hands, releasing namely dispersing the raw material power, adding mineral water to the raw material power, soaking the raw material power for 18 hours, and adjusting the PH value to be 4.5 to 6.5; putting mixed liquor into an enzymatic zymotechnics tank, adding enzymatic zymotechnics liquid to perform enzymatic zymotechnics, setting the enzymatic zymotechnics temperature to be 35 DEG C and the enzymatic zymotechnics time to be 72 hours, stirring and oxygenating once every 4 hours, and controlling the PH value to be 3.5 to 6.2; performing frame filtering, performing spray drying on supernate, ensuring that the drying temperature does not exceed 65 DEG C, and controlling the moisture to be lower than 7 percent to obtain powder; crushing the powder to be 120-mesh powder, then performing Co60 irradiation sterilization, and packing and warehousing finished products. The method is convenient in technology, easy to operate, low in energy consumption, clean and environment-friendly.
Owner:珲春绿源参业生物科技有限公司
Mediucm for detecting vana and vanb vancomycin-resistant enterocci and method of using the same
Van A and Van B vancomycin resistant enterococci detection media as well as a method of selectively detecting Van A and Van B vancomycin resistant enterococci clinically important in vancomycin resistant enterococci from testing microorganisms or specimens using the media. The media for selectively detecting Van A and Van B VRE from testing microorganisms and specimens are media where enterococci can grow where vancomycin, D-cycloserine and D-lactate are added. Preferably 32-256 mug / ml of vancomycin, 1-64 mug / ml of D-cycloserine, and 0.025-0.8 mol / l of sodium lactate are added to culture medium where enterococci can grow.
Owner:TOKYO WOMENS MEDICAL UNIV
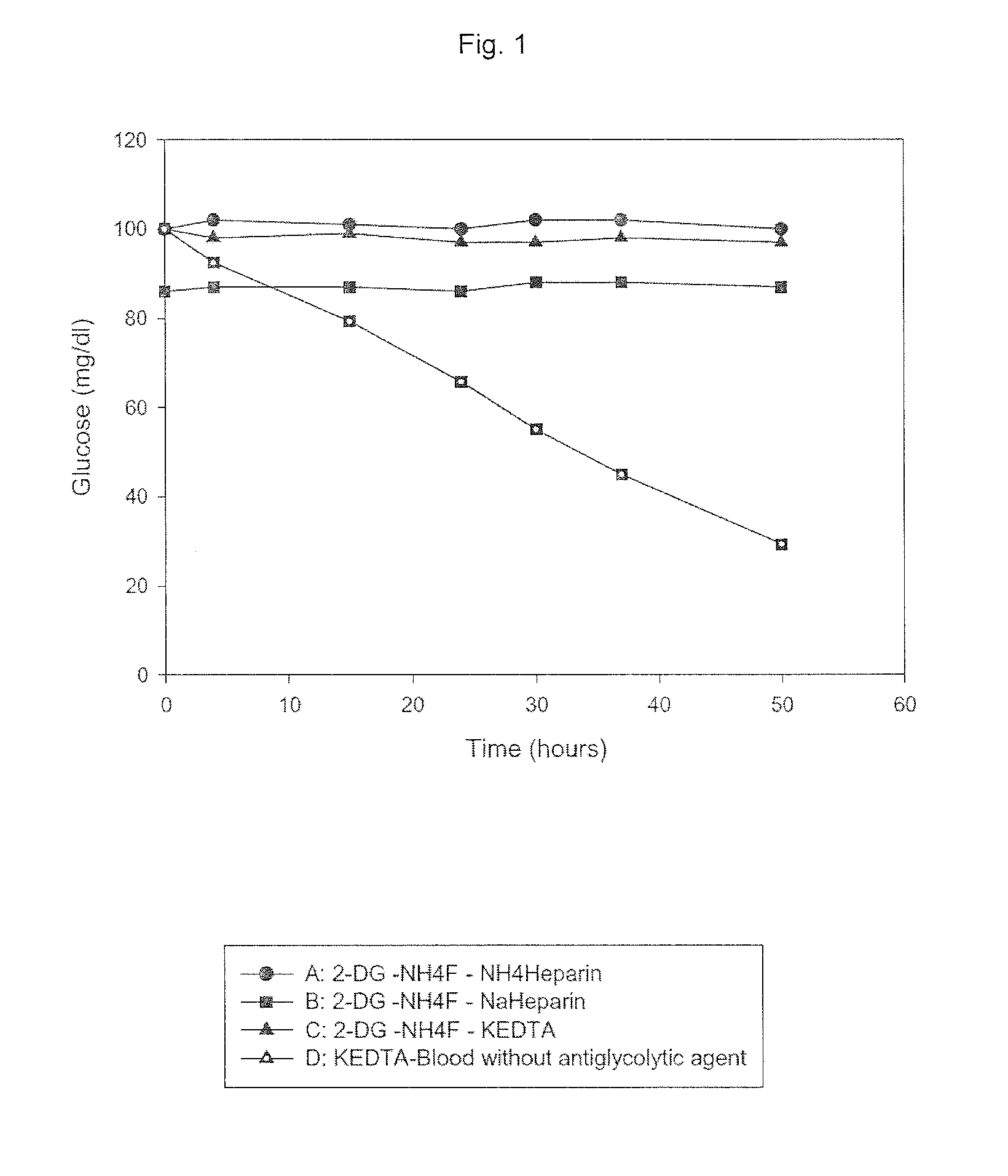
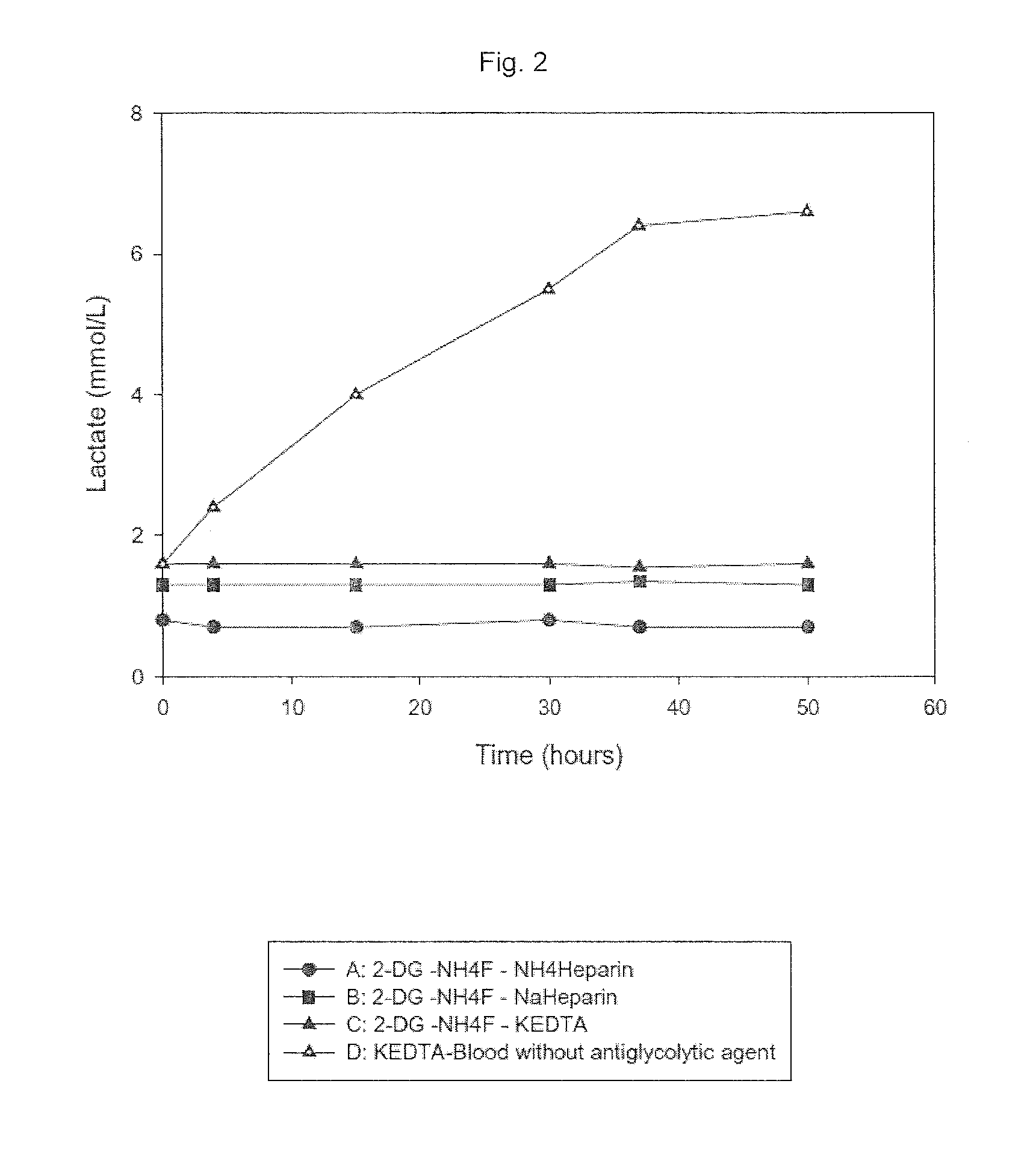
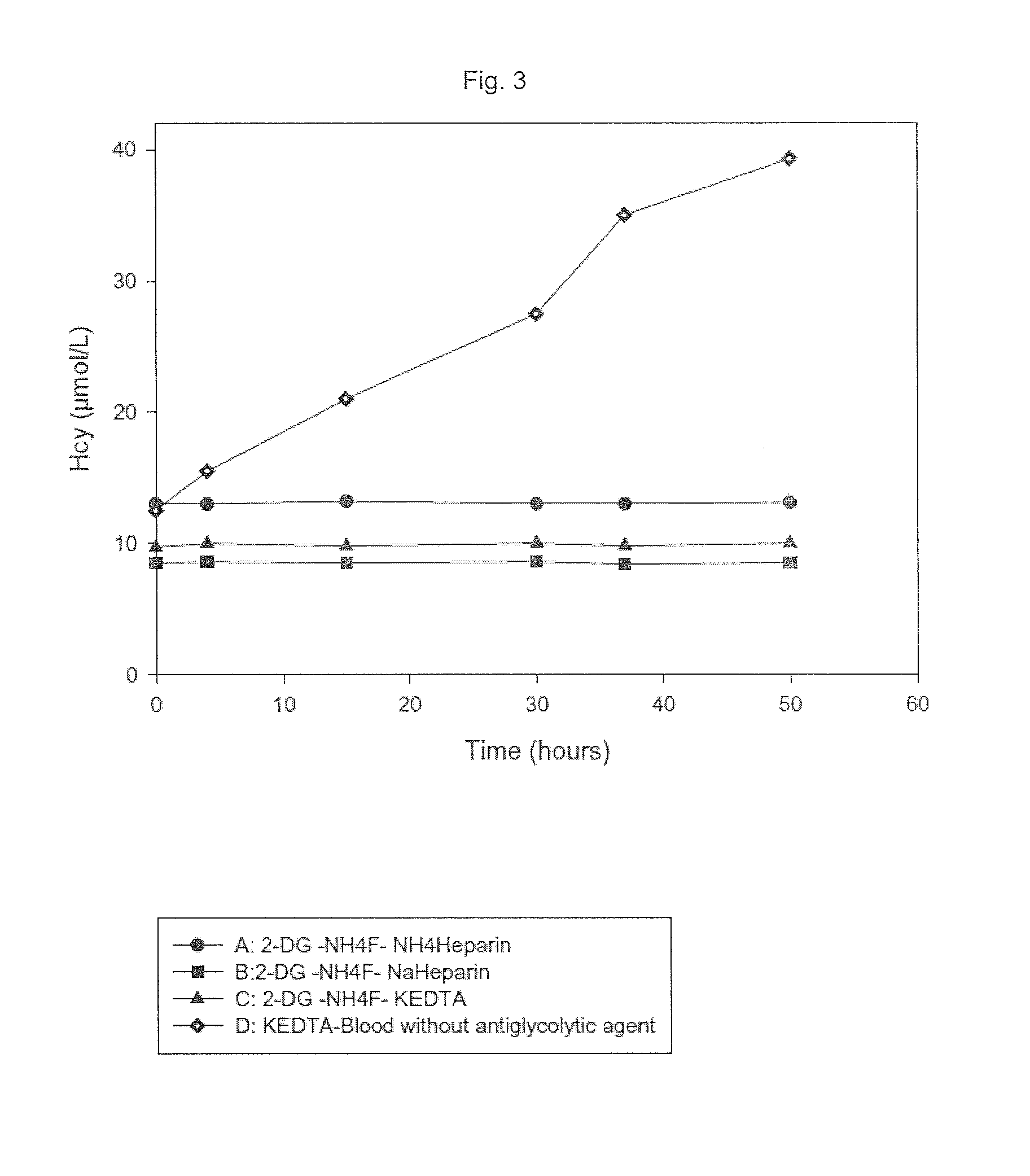
Composition and use of substances for the in vitro stabilization of glucose, lactate and homocysteine in blood
ActiveUS20150208644A1Microbiological testing/measurementDead animal preservationBlood collectionMedicine
Owner:WESER BISSE PETRA
Treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with lactate
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a devastating disease that leads initially to death of motor nerves with some progression to death of sensory and autonomic nerves. Experimental work shows that more electrical energy is required to successfully stimulate motor vs. sensory nerve components of a nerve and longer vs. shorter components of a nerve. This discovery explains sparing of the nerves of ocular motion and nerves of rectal and urethral sphincters in patients suffering from ALS and supports the energy hypothesis of ALS. Neurons and peripheral nerves are dependent upon glial cells and oligodendrocytes respectively to support their high energy demands. These supporting cells shuttle lactate to neurons and nerves. Lactate is required to sustain contraction of skeletal muscle. Administration of racemic or L-lactate in an amount greater than the capacity of the liver to oxidize will increase the available lactate to nerves and neurons and improve the symptoms of ALS.
Owner:GOLDBERG JOEL STEVEN
Probiotic lactic acid bacterium to treat bacterial infections associated with sids
Compositions including a non-pathogenic lactic acid-producing bacteria, such as a Bacillus species, spores or an extracellular product of B. coagulans, formulated for oral administration to the intestinal tract for inhibiting bacterial gastrointestinal infections are described. Methods and systems using the compositions for treating gastrointestinal infections, particularly sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) are also disclosed.
Owner:GANEDEN BIOTECH
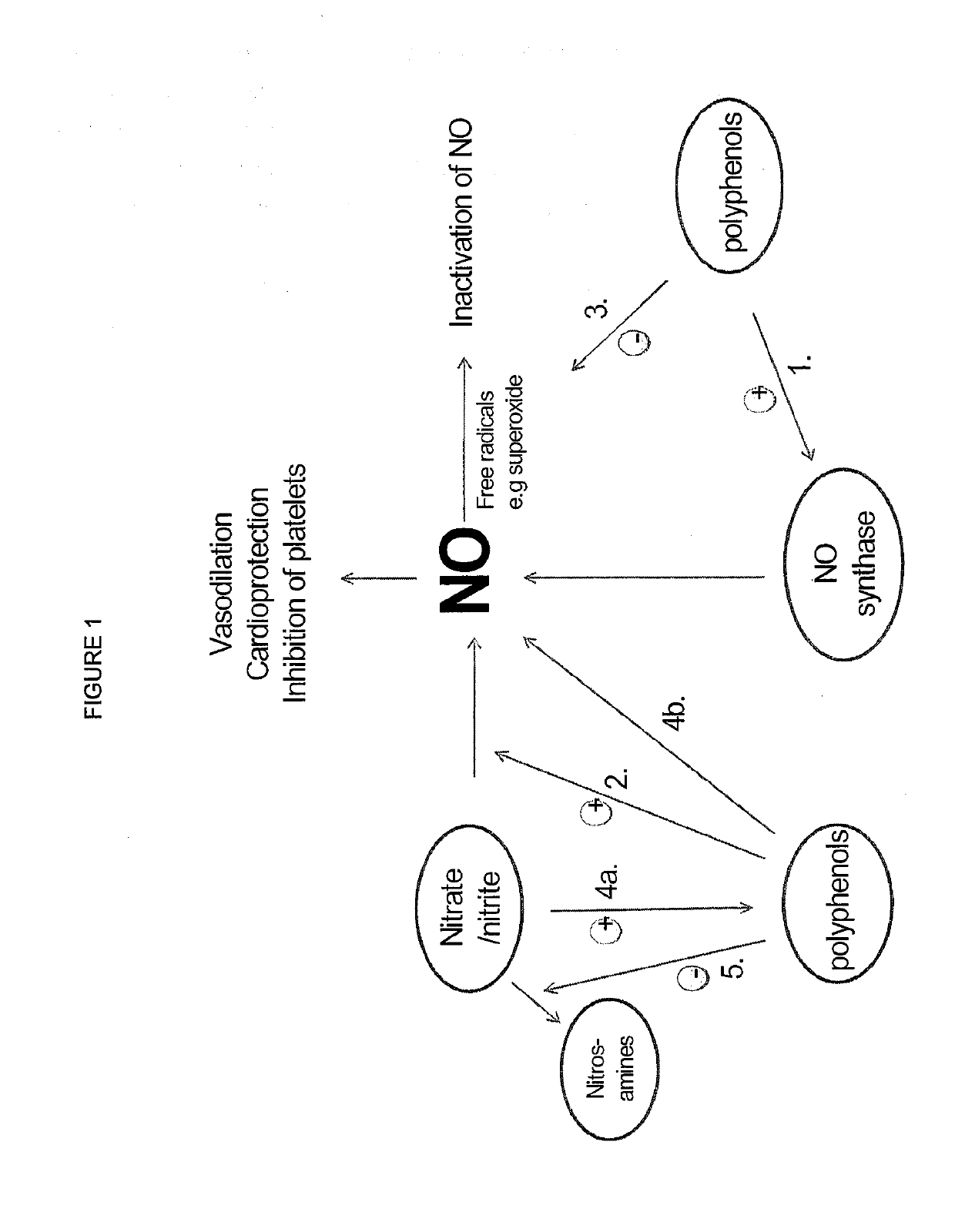
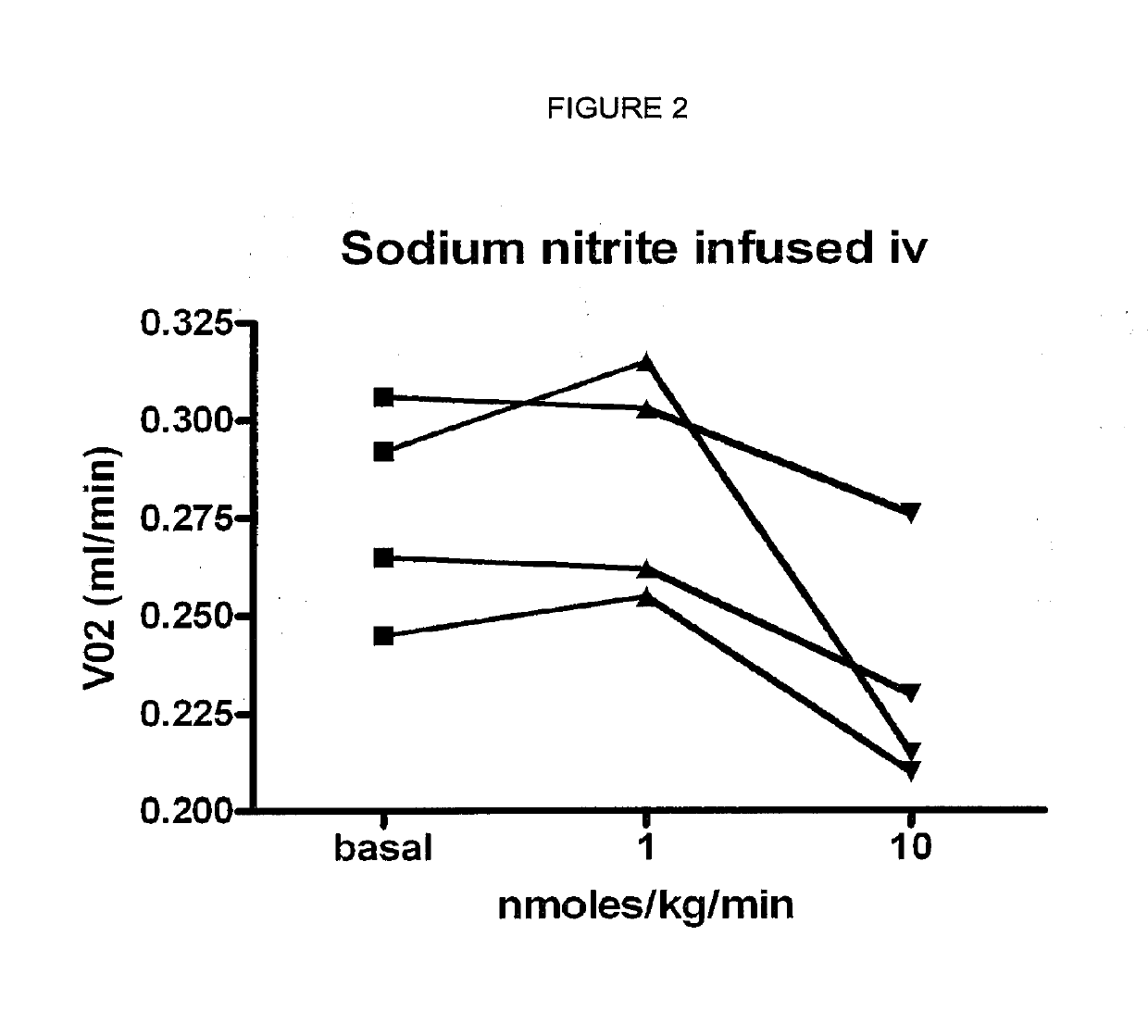
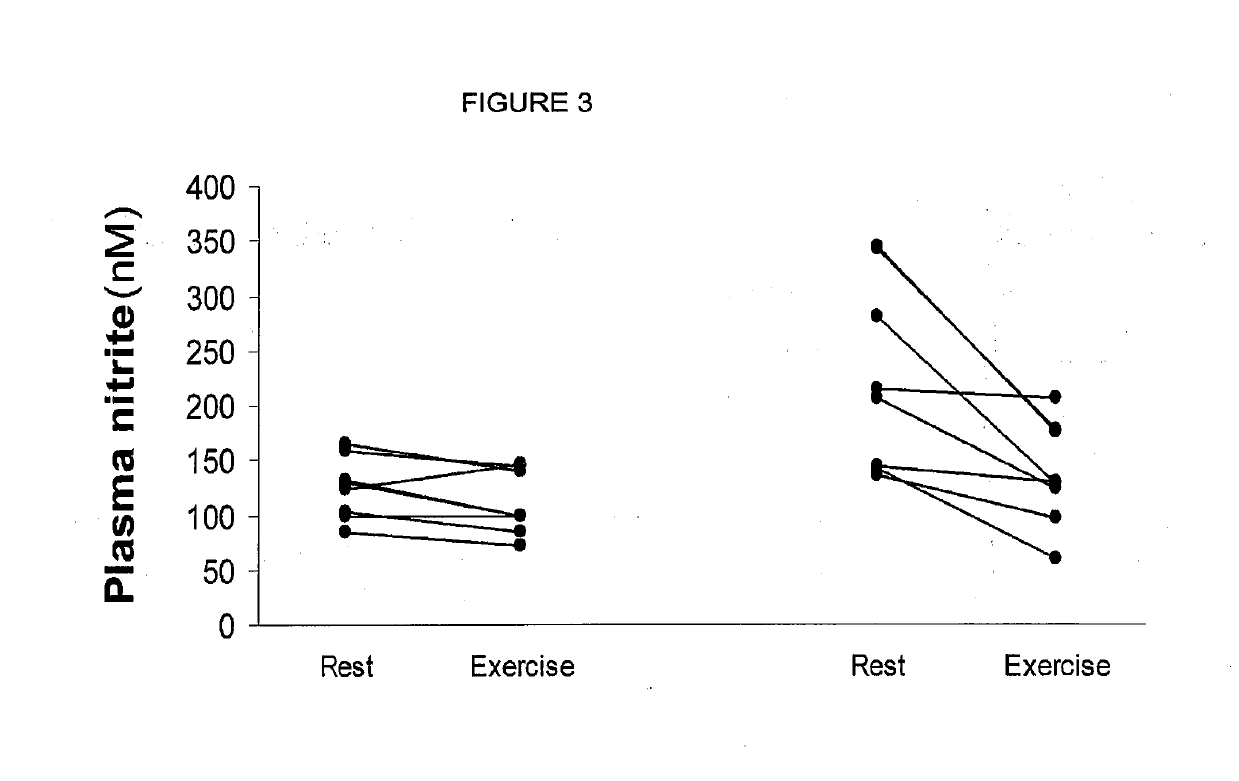
Compositions of nitrates and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20190125784A1Lower systolic blood pressureDispersion deliveryHydroxy compound active ingredientsResting energy expenditureHomeostasis
Inorganic anions nitrate and nitrite influence metabolic rate and glucose homeostasis. Infusion of nitrite iv caused an acute drop in resting energy expenditure (oxygen consumption) and nitrate, when given perorally, caused a reduction in oxygen consumption during exercise and a depression of the increase in blood glucose observed after an oral glucose tolerance test. The doses of nitrate and nitrite did not cause any detectable change in methemoglobin levels of blood. Also, nitrate and nitrite did not alter lactate levels in blood. This discovery provides useful treatments to regulate the energy expenditure and glucose homeostasis of a mammal by administration of inorganic nitrite and / or nitrate.
Owner:HEARTBEET LTD
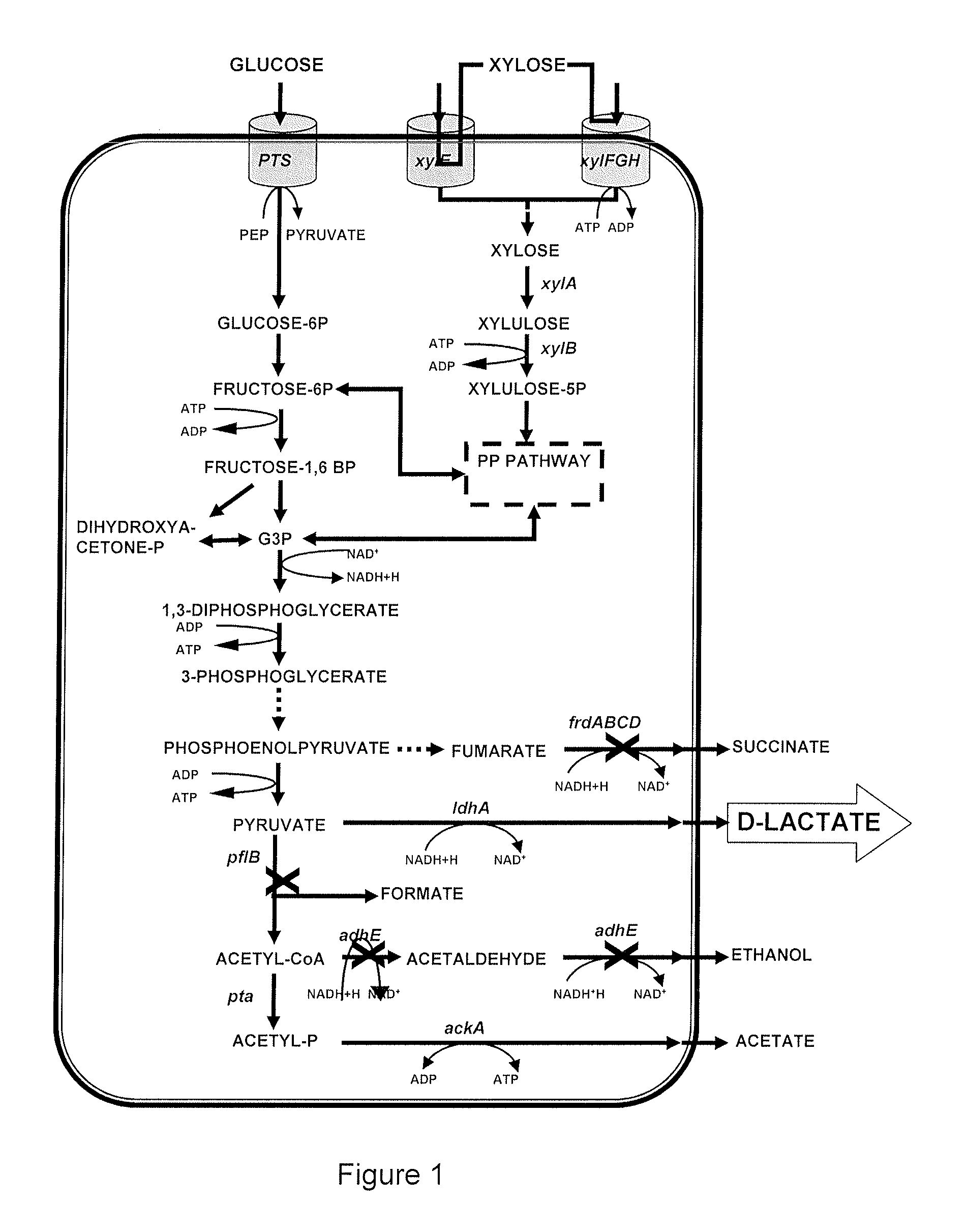
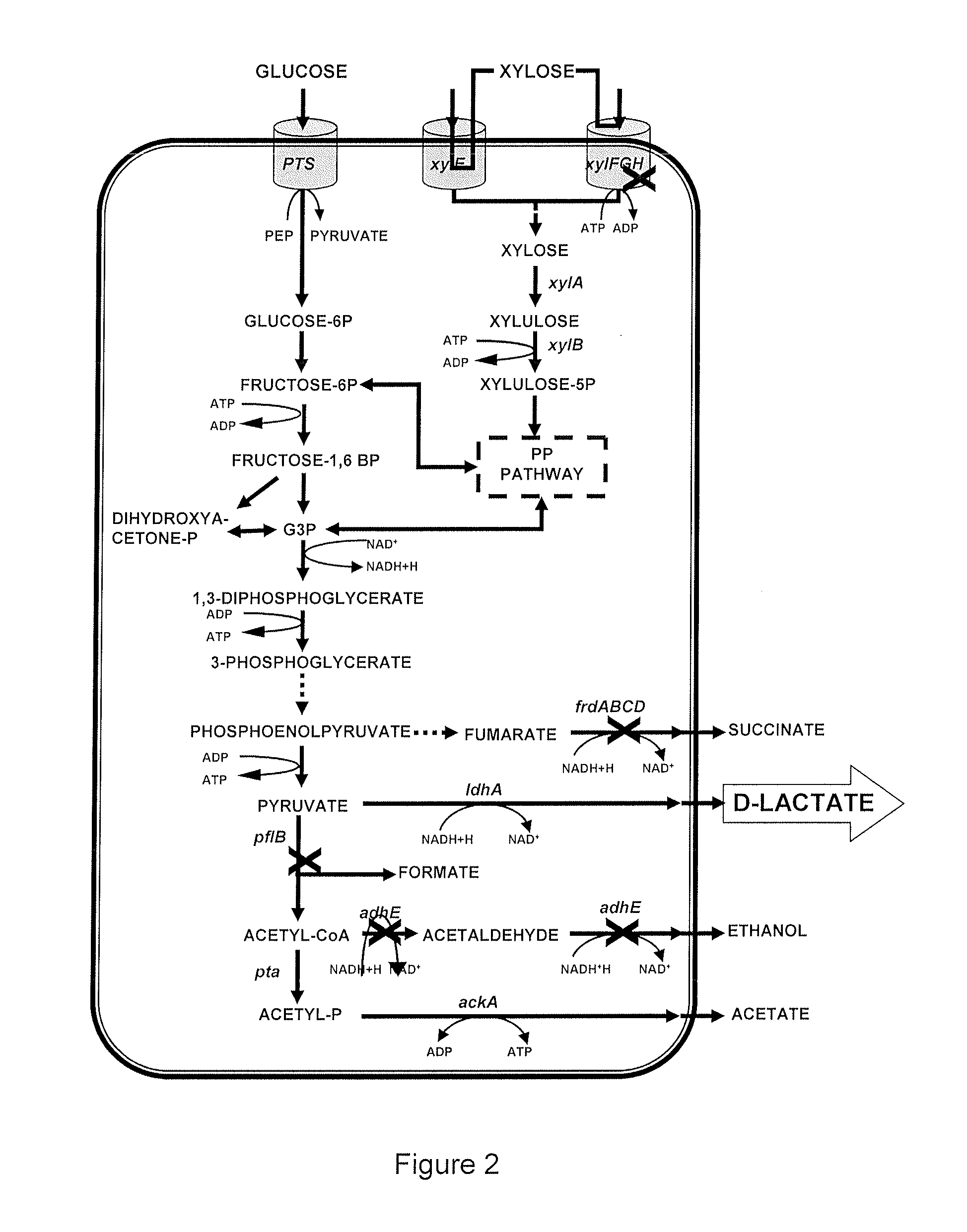
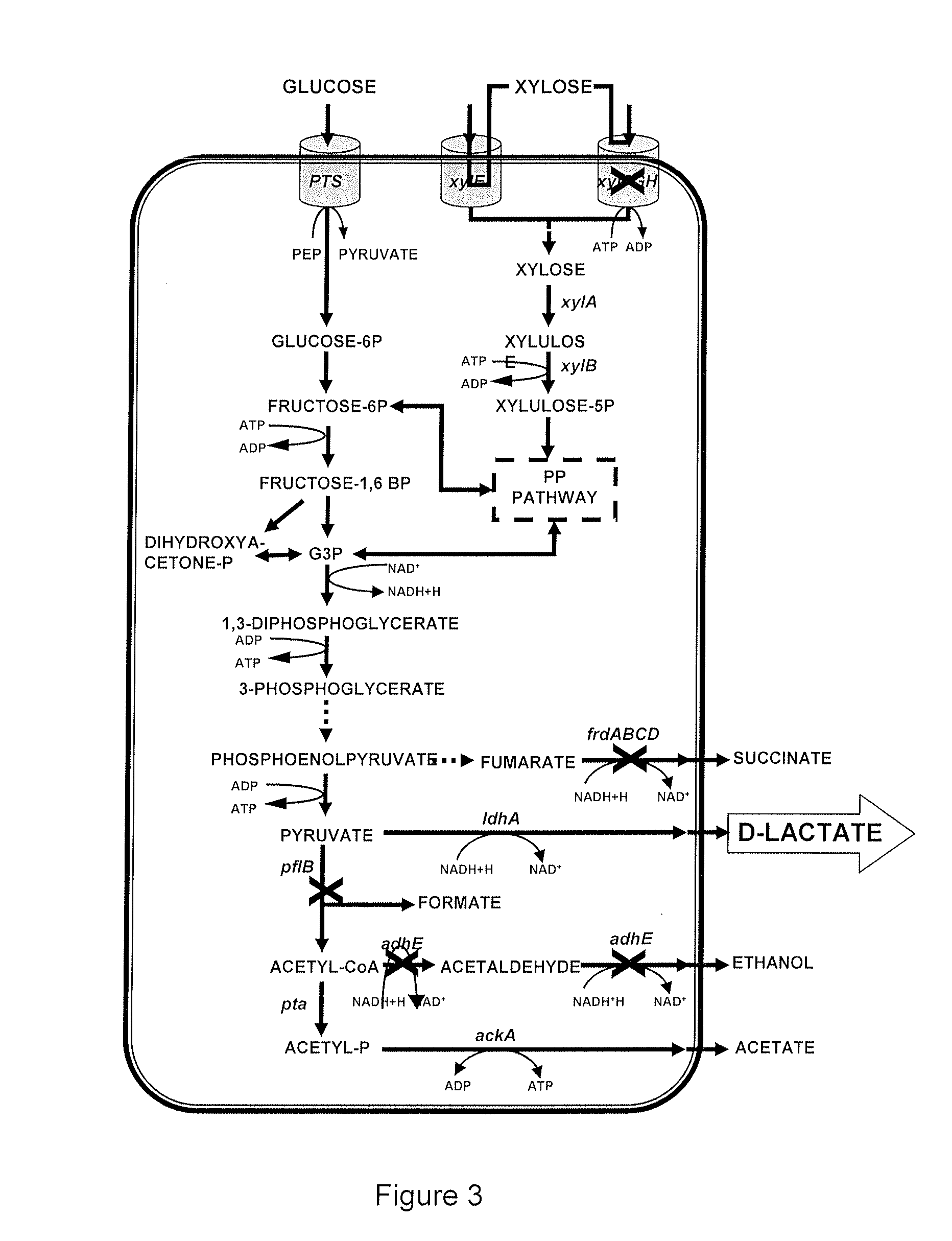
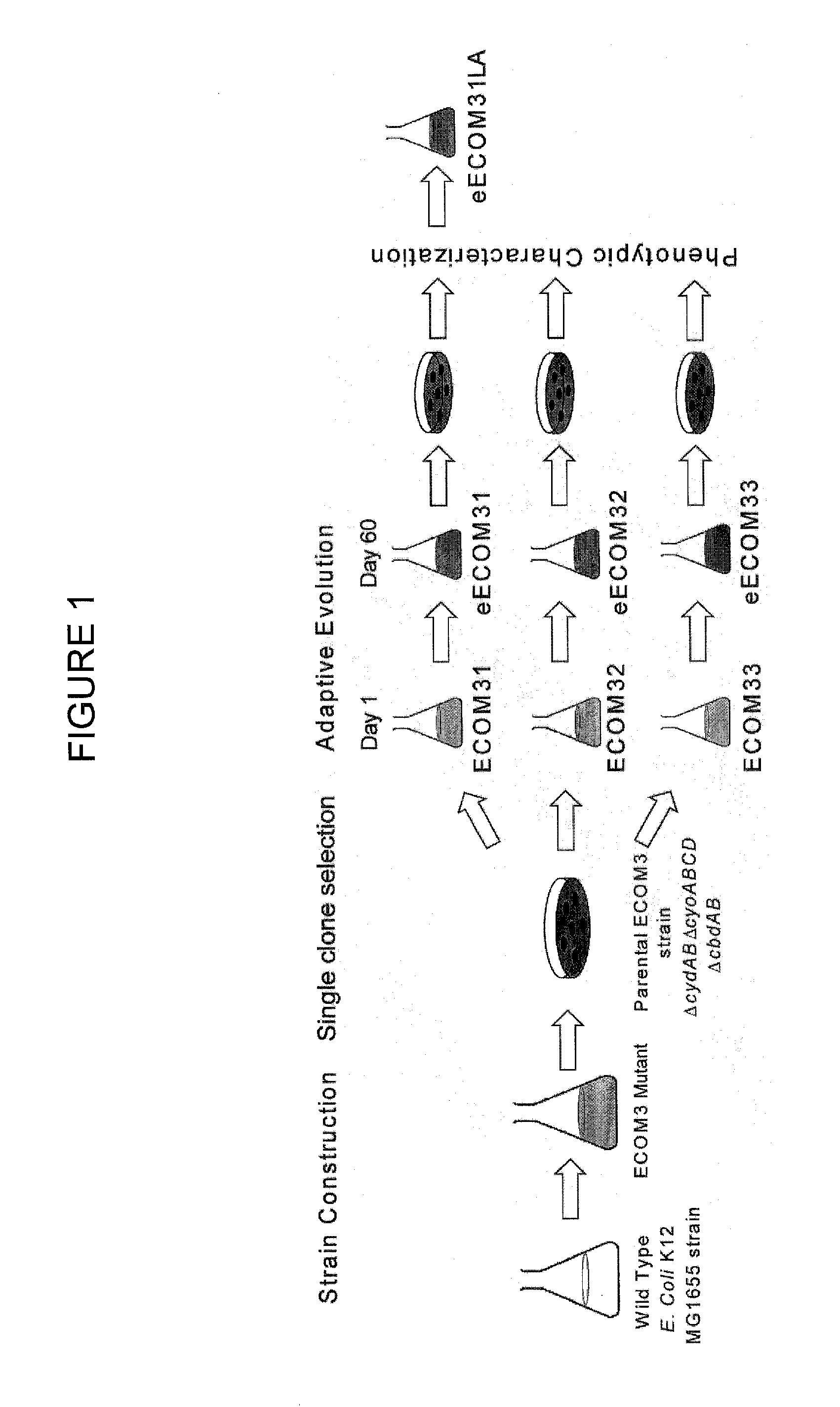
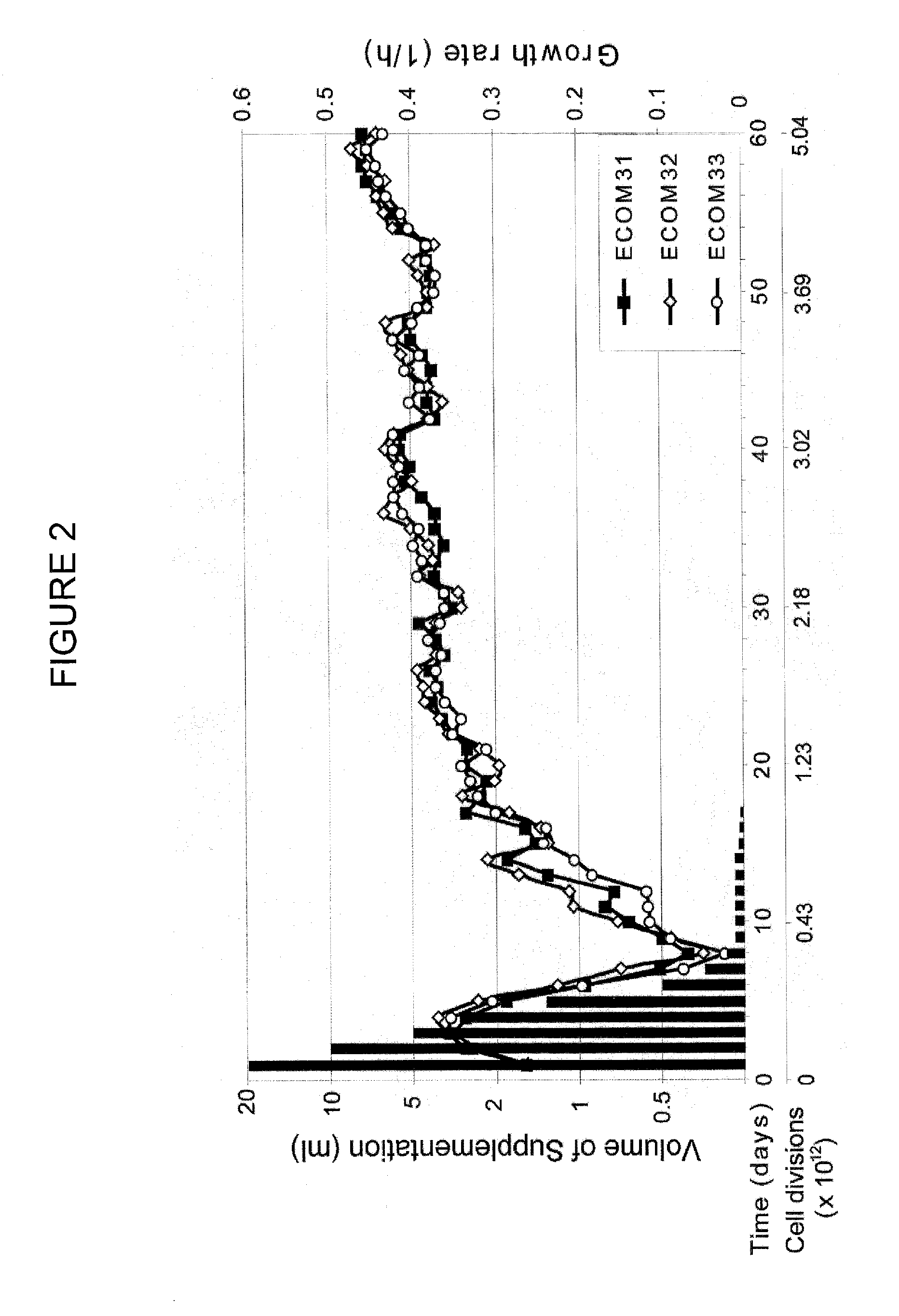
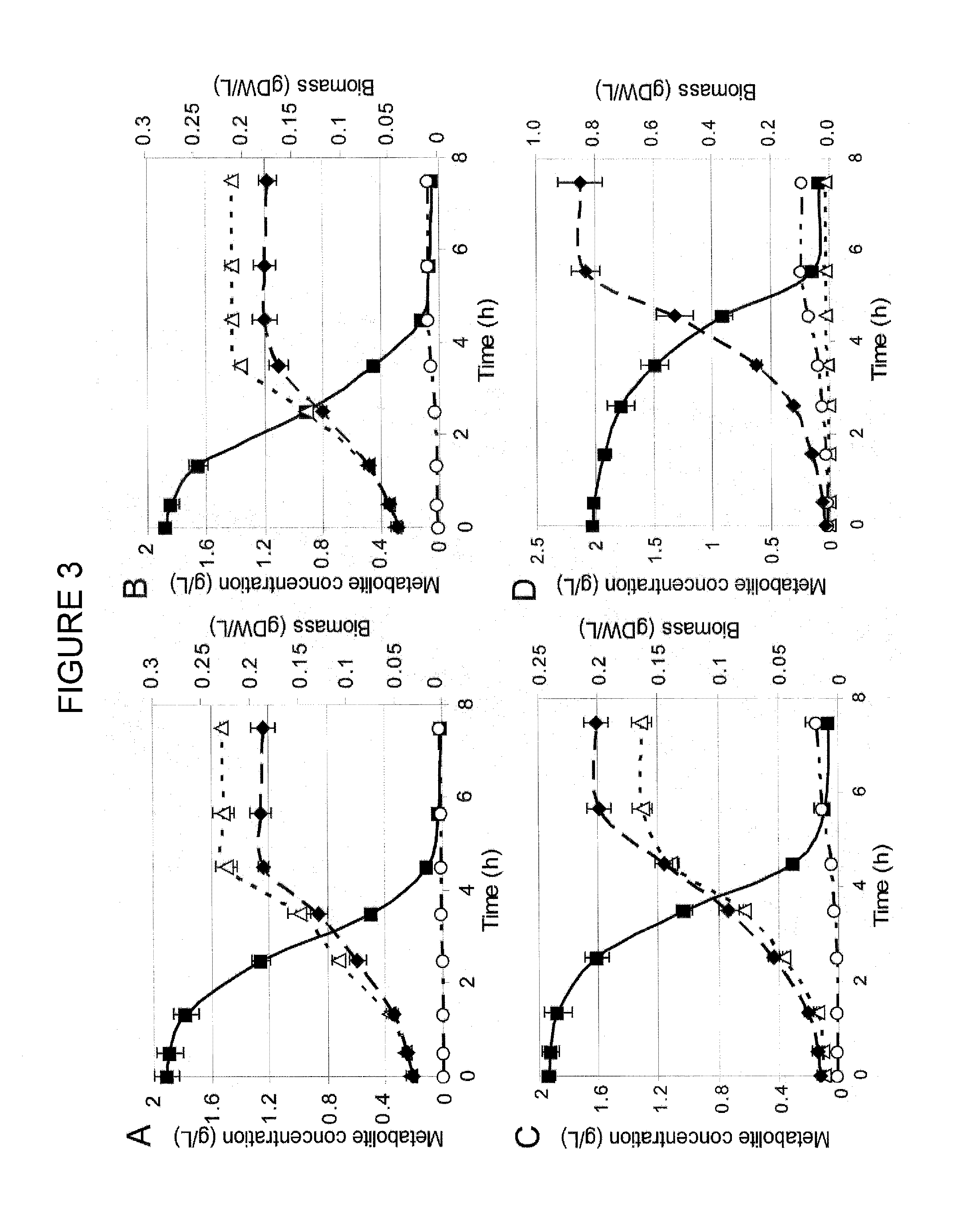
Strains of escherichia coli modified by metabolic engineering to produce chemical compounds from hydrolyzed lignocellulose, pentoses, hexoses and other carbon sources
The present invention refers to the new Escherichia coli strains denominated JU15, JU15A, LL26 and MS04 and their derivatives that produce metabolites, particularly D-lactate, L-lactate or ethanol, with high yield and selectivity from a wide variety of carbon sources, such as culture media with a high xylose content (as the main carbon source) and, in particular, media formulated with hydrolyzed vegetables, such as sugarcane bagasse, agave bagasse and fast-growing grasses, and a wide variety of agricultural and industrial wastes, such as whey or forestry wastes, celluloses, grasses, agave bagasse, paper wastes, shavings and sawdust, shrubs and generally any material derived from lignocellulose. These strains use the production of the metabolite of interest (especially D-lactate, L-lactate or ethanol) as the only way of regenerating the reducing power. The invention also refers to fermentation methods to produce these metabolites from media with a diversity of carbon sources, including glucose, lactose or xylose.
Owner:UNIV NAT AUTONOMA DE MEXICO
Fluid therapy with L-lactate and/or pyruvate anions
InactiveUSRE38604E1Simple methodAvoid complicationsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsL lactateBlood plasma
Electrolyte solutions are provided which are useful in electrolyte and fluid therapy, parenteral nutrition and dialysis. The Na:Cl ratio is normalized, plasma and cellular pH are normalized and cellular cofactor ratios are normalized in a manner which decreases toxicity over prior art solutions.
Owner:BTG INT LTD
Composition with disintoxicating and liver-protecting effects and application thereof in food and health-care food
ActiveCN101889679BAct quicklyReasonable formulaDigestive systemKetone active ingredientsHeadachesAdjuvant therapy
The invention relates to a composition with disintoxicating and liver-protecting effects, which comprises the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 0.15 to 5 percent of crucumin, 0.04 to 1.0 percent of zinc lactate, 10 to 50 percent of glutamine, 10 to 50 percent of alanine and 10 to 50 percent of xylooligosaccharide. It is proved that, by an animal experiment and a human tasting experiment, the composition increases the alcohol dehydrogenase and acetaldehyde dehydrogenase content of a body and rapidly decomposes alcohol, so that the composition has the effects of promoting alcohol metabolism in a liver and reducing the alcohol concentration and active oxygen concentration in a blood; and the composition increases an endurance capacity of a human body to the alcohol, reduces the discomforts such as headache, nausea, vomiting and the like due to the alcohol, and reduces the damages of the alcohol to the liver. The composition can be prepared into food and health-care food withthe disintoxicating and liver-protecting effects, can be used as a disintoxicating product for preventing and improving excessive drinking, and can be used as an adjuvant therapy product for an alcoholic liver, a fatty liver due to the alcohol or non-alcohol and protecting the liver; and the composition has the advantages of safety, non-toxicity and a reliable curative effect.
Owner:SHANDONG MINGREN FURUIDA PHARMA
Degradable material for disposable uterine probe
Owner:台州市中心医院
Flushing fluid containing sorbitol and mannitol and suitable for urologic surgeries
ActiveCN107349189AReduced risk of hemolysisTo promote metabolismHydroxy compound active ingredientsSurgical drugsUrologic surgeryMetabolite
The invention relates to the field of medical reagents and discloses a flushing fluid containing sorbitol and mannitol and suitable for urologic surgeries. The flushing fluid is prepared from components as follows: 2.5wt%-2.9wt% of sorbitol, 0.5wt%-0.6wt% of mannitol and the balance of water for injection. The flushing fluid is mainly prepared from sorbitol and mannitol serving as main ingredients, adopts perfusion therapy through a proper urinary system instrument via the urethra and is applicable to flushing in the transurethral resection of the prostate and other urologic surgeries. The flushing fluid has the advantages as follows: 1) the flushing fluid is non-hemolytic; 2) the flushing fluid can also be used for diabetics; 3) the flushing fluid has a good diuretic function; 4) the flushing fluid can prevent blood coagulation in the surgeries, and a good intra-operative view can be kept; 5) the flushing fluid serving as a washing fluid used after the surgeries has a good blood coagulation prevention function; 6) the flushing fluid facilitates rapid excretion of sorbitol due to higher content of mannitol, and the potential risks of the sorbitol liver metabolite, namely, lactic acid are reduced.
Owner:JIMIN HEALTH MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Veterinary levamisole gel implant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106361685ASmall doseProlong the action timeOrganic active ingredientsAerosol deliverySide effectIrritation
The invention relates to a veterinary levamisole gel implant which is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 2-5 parts of levamisole hydrochloride, 8-12 parts of polylactic acid, 70-90 parts of benzyl benzoate, 0.01-5 parts of poloxamer 188, 0.01-2 parts of monoethanolamine and 5-20 parts of potassium sorbate. The veterinary levamisole gel implant can simultaneously expel and kill many different kinds of parasites. The veterinary levamisole gel implant has the physicochemical characteristics applicable to group administration, and does not have local stimulation for people subjected to injection administration. The veterinary levamisole gel implant is low in price, and can be subjected to large-scale popularization and application in animal production. After the veterinary levamisole gel implant is applied to food animals, the drugs do no reside in the meat, eggs, milk and products thereof. The veterinary levamisole gel implant is simple in preparation technique and convenient for administration, is capable of prolonging the drug action time, reducing the drug dosage and lowering the side effects of drugs, and can improve the compliance and comfort of patients / applied animals.
Owner:河南中盛生物工程有限公司
Prevention and treatment of gastrointestinal infection in mammals
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
Radioactive sustained-release particle and preparation and use thereof
InactiveCN101322849AEasy to killSolve the problem of targeted drug deliveryRadioactive preparation carriersRadioactive preparation formsSide effectMedicine
The invention discloses a radioactive slow-release particle and a preparation method and the application thereof, pertaining to the field of radiation medicine. The particle mainly consists of <32> P-chromium phosphate and poly-L-lactic acid and can better solve the problem of targeted delivery of drugs in the treatment of tumors. The transplant of the particles in a tumor body or around a tumor can increase the local concentration of the drug, prolong the time of drug action and reduce systemic toxic and side effects.
Owner:王自正 +7
Escherichia coli metabolic engineering oxygen independent platform strains and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20120064581A1Easy maintenanceReduction in energy investmentBacteriaEnzymesEscherichia coli2,3-Butanediol
The invention provides transgenic Escherichia coli cells comprising a mutation in cydAB gene, and / or cyoABCD gene, and / or cbdAB gene, and / or ygiN gene, wherein the mutation reduces (preferably, but not necessarily, by 100%) the cytochrome oxydase activity of a protein encoded by cydAB gene, and / or cyoABCD gene, and / or cbdAB gene, and / or ygiN gene. In a preferred embodiment, the mutation is a deletion of the cydAB gene, cyoABCD gene, and cbdAB gene. In another embodiment, the mutation is a deletion of the cydAB gene, cyoABCD gene, cbdAB gene, and ygiN gene. In another embodiment, the transgenic Escherichia coli cell, which comprises a deletion of cydAB gene, and / or cyoABCD gene, and / or cbdAB gene, and / or ygiN gene a) has substantially the same level of growth in oxic conditions as the level of growth in anoxic conditions of Escherichia coli that lacks said deletion of cydAB gene, and / or cyoABCD gene, and / or cbdAB gene, and / or ygiN gene, and b) is capable of converting glucose to D-lactate and / or amino acid and / or 2,3-butanediol (2,3-BDO) under one or both of oxic conditions and anoxic conditions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
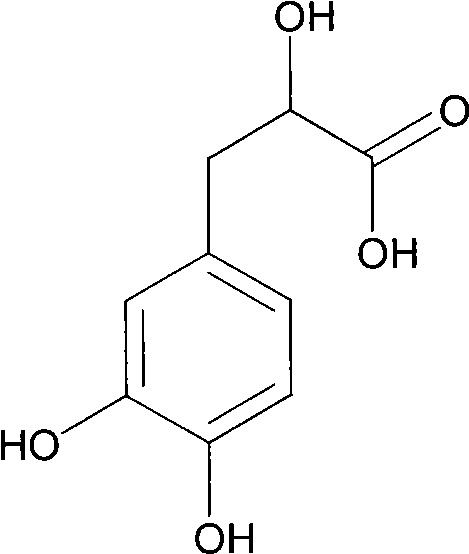
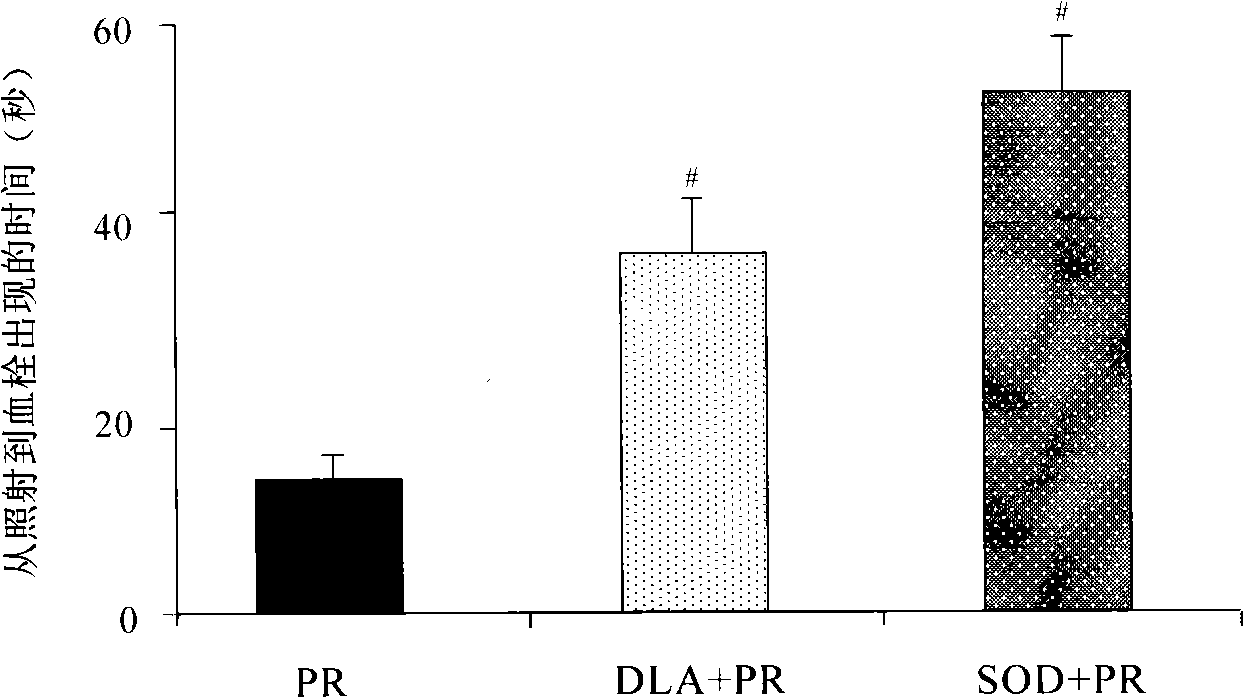
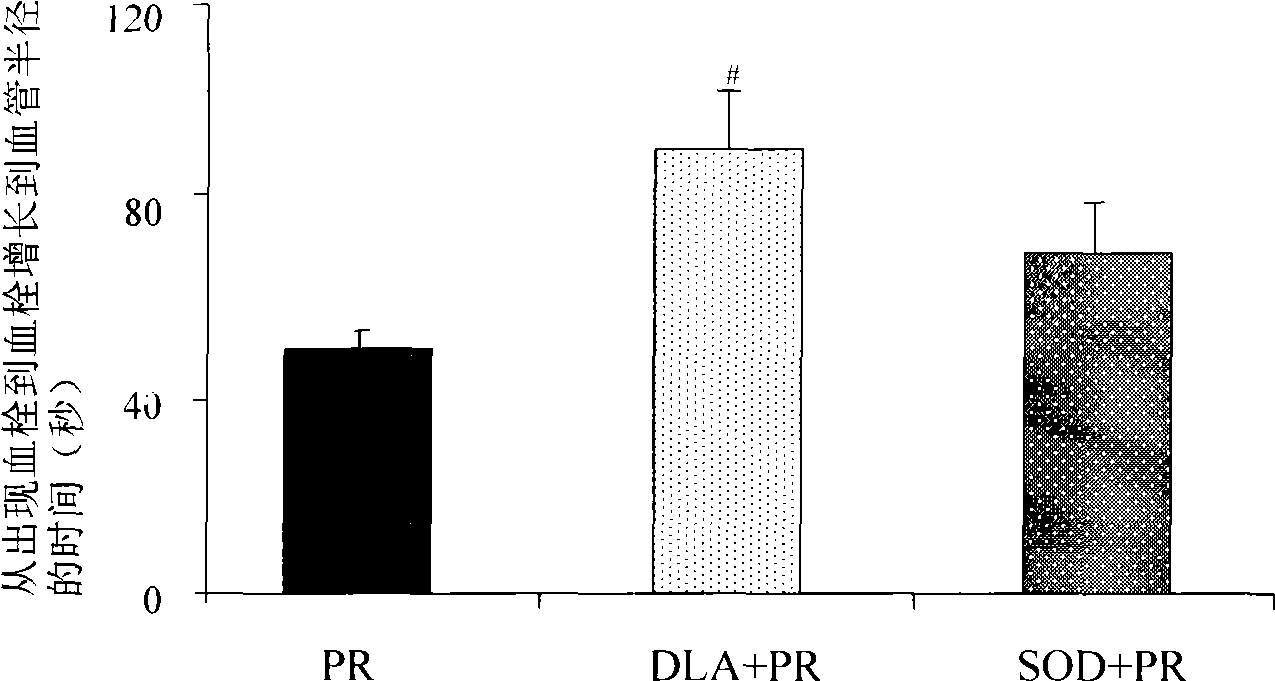
Thrombi-resistant application of dihydroxyphenyl lactate
InactiveCN101530404AOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMedicineSalvia extract
The invention relates to the new application of the Chinese traditional medicine, in particular to the application of salvia extract, namely dihydroxyphenyl lactate in the treatment and prevention of thrombi. The test data indicate that the dihydroxyphenyl lactate can delay the time from the stimulation to the formation of thrombi and can prolong the half-volume time of the thrombi.
Owner:TIANJIN TASLY PHARMA CO LTD
Drinking water containing microelement for infant<
InactiveCN1504126AMake up for malnutritionMake up for nutritional deficienciesMetabolism disorderWater/sewage treatment by substance additionSodium fluorideD lactate
The invention discloses a trace element containing infant drinking water, characterized by that, each liter of RO pure water contains sodium fluoride 0.5-0.7mg, calcium powder 200-300mg, phosphatidy lcholine 150-200ug, ferric lactate 8-10mg, and glucose 100-250mg. The glutacid-containing nutritious drinking water according to the invention can be supplied to infants for direct drinking or as modulation food.
Owner:上海金创投资管理有限公司
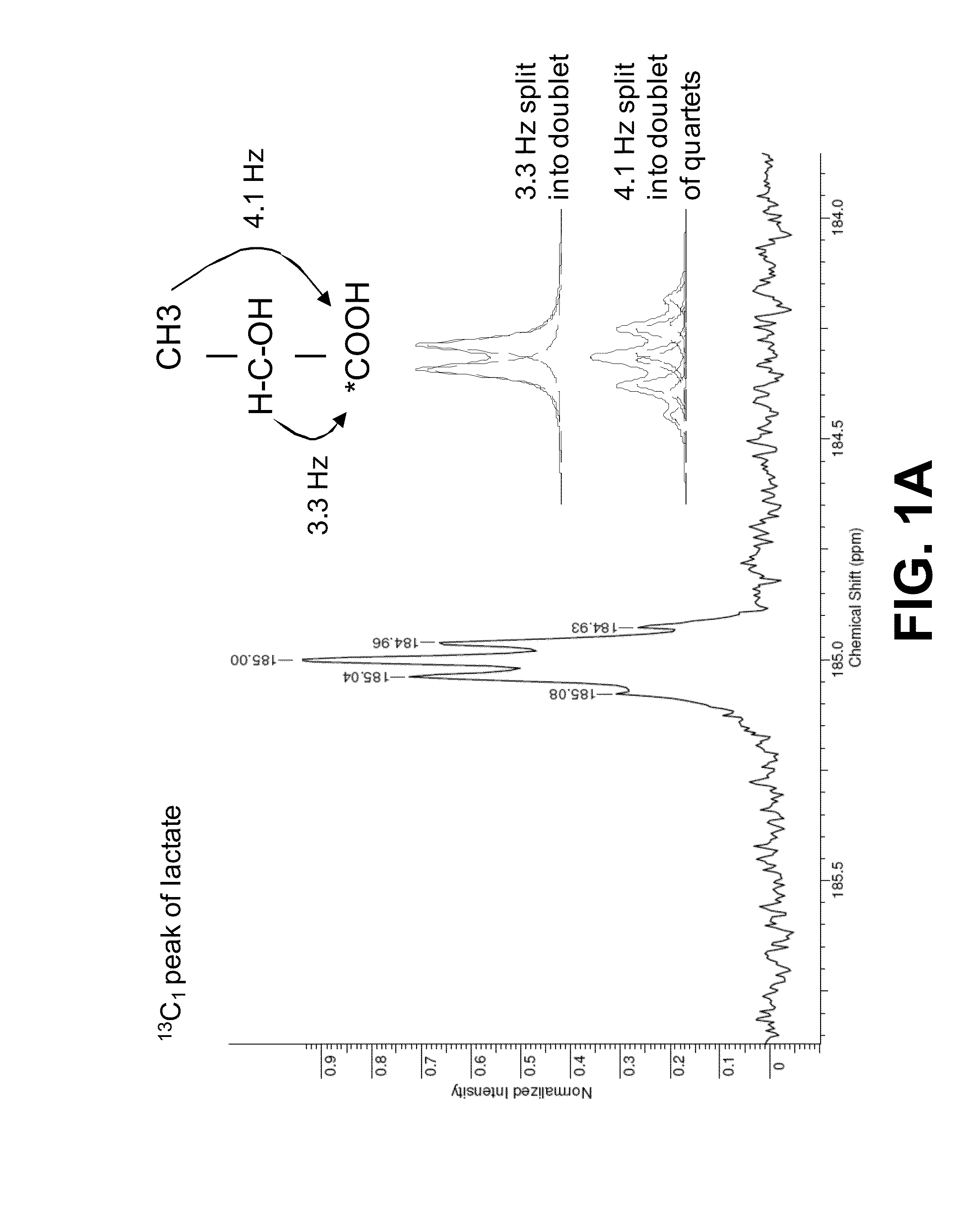
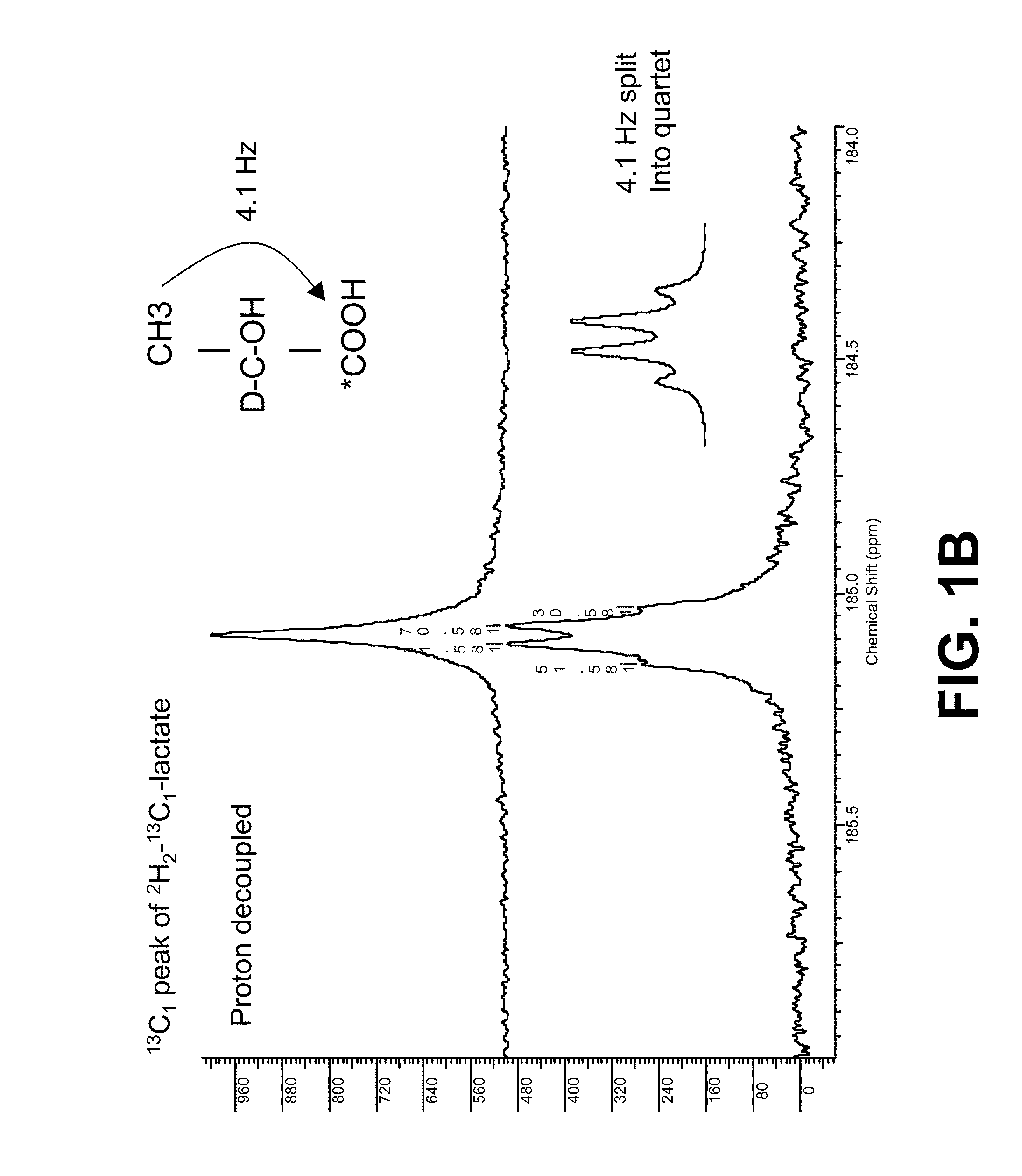
Hyperpolarized lactate contrast agent for determination of LDH activity
ActiveUS20160184462A1Microbiological testing/measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringMedicineD lactate
A hyperpolarized MR imaging medium and a method of 13C-MR detection using a hyperpolarized MR imaging medium for the determination of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity. The contrast media comprises hyperpolarised [13C, 2H] lactate.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Compositions And Methods For Increasing Athletic Performance
ActiveUS20180296544A1Improve athletic performanceDecreased heart rateOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderBetaineRed blood cell
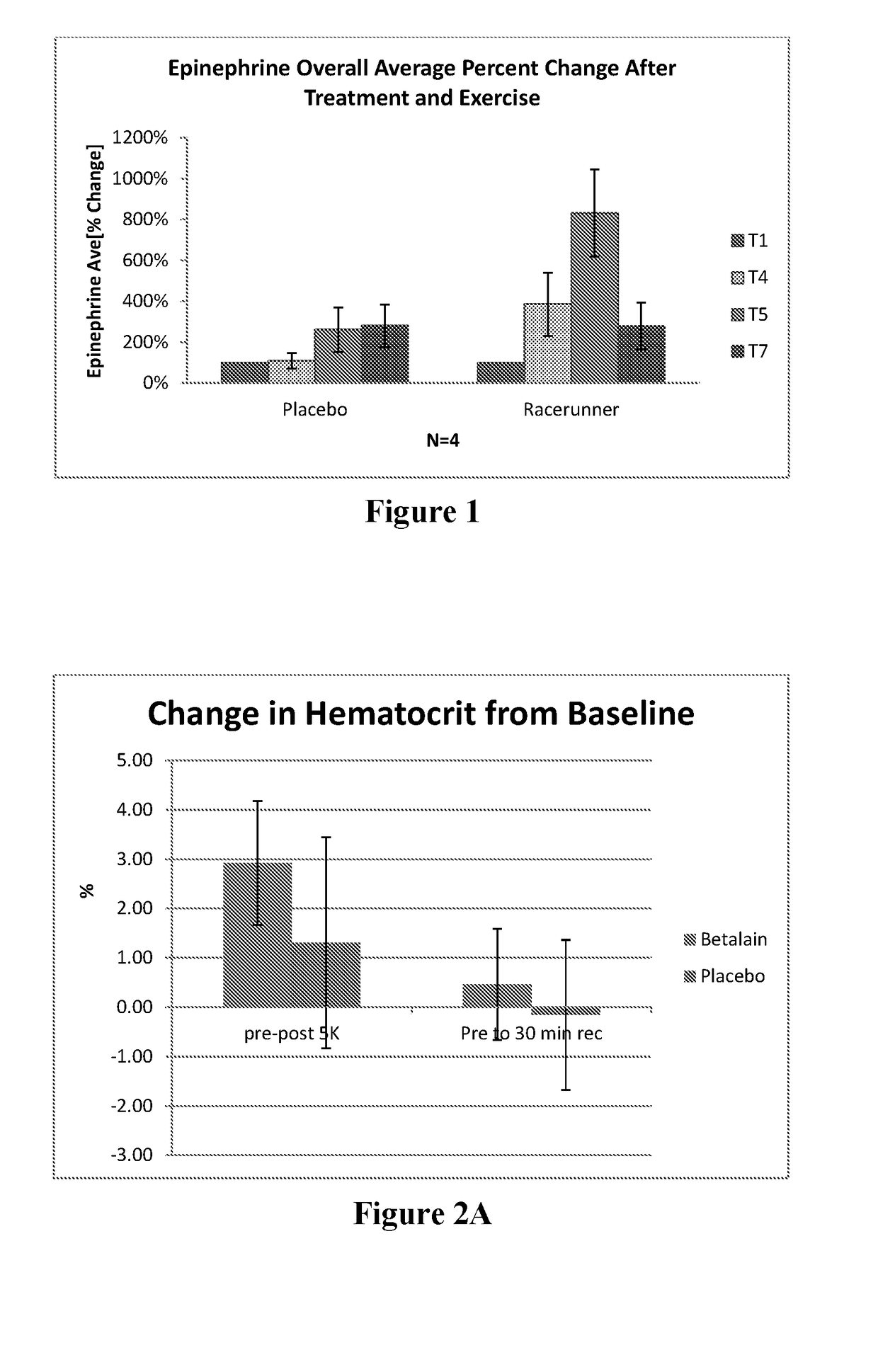
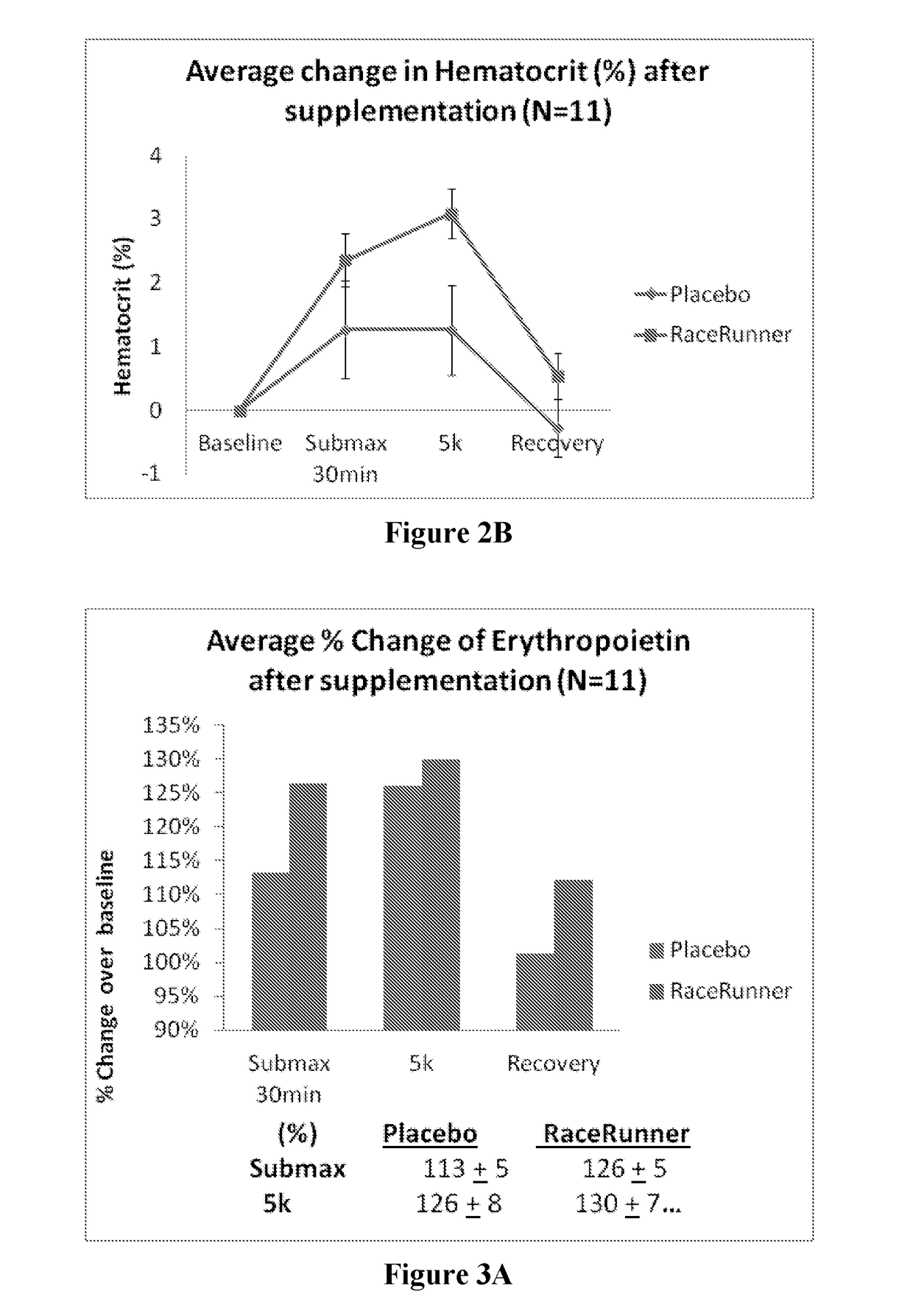
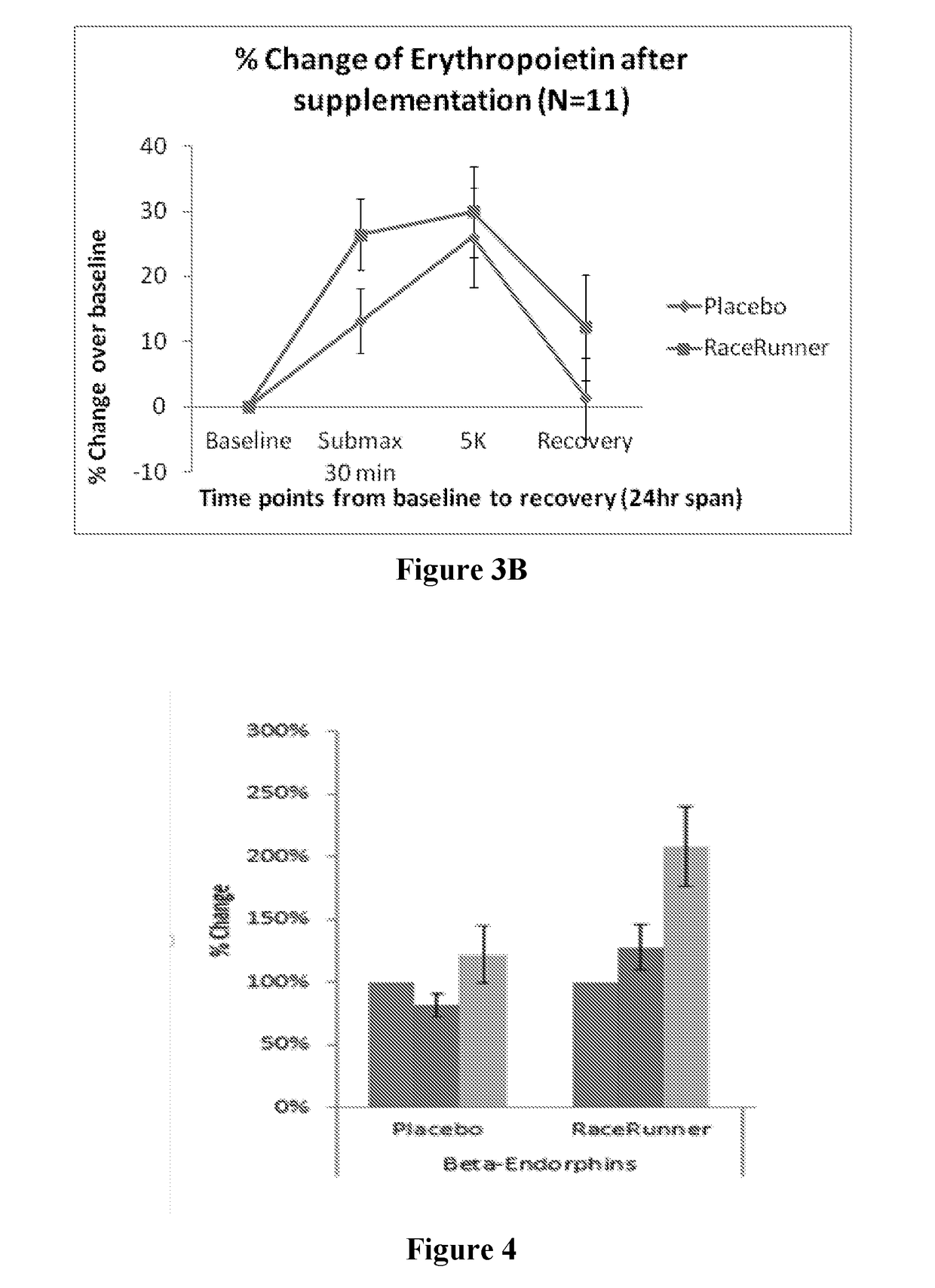
Compositions, methods, and uses are contemplated in which a betalain-containing preparation is administered to a mammal to enhance athletic performance. Most preferably, the preparations are substantially nitrate free and acutely and transiently increase hematocrit, erythropoietin, adrenalin, and beta endorphin, while reducing serum lactate, serum lactate dehydrogenase, heart rate and a rate of perceived exertion.
Owner:VDF FUTURECEUTICALS
Therapeutic method
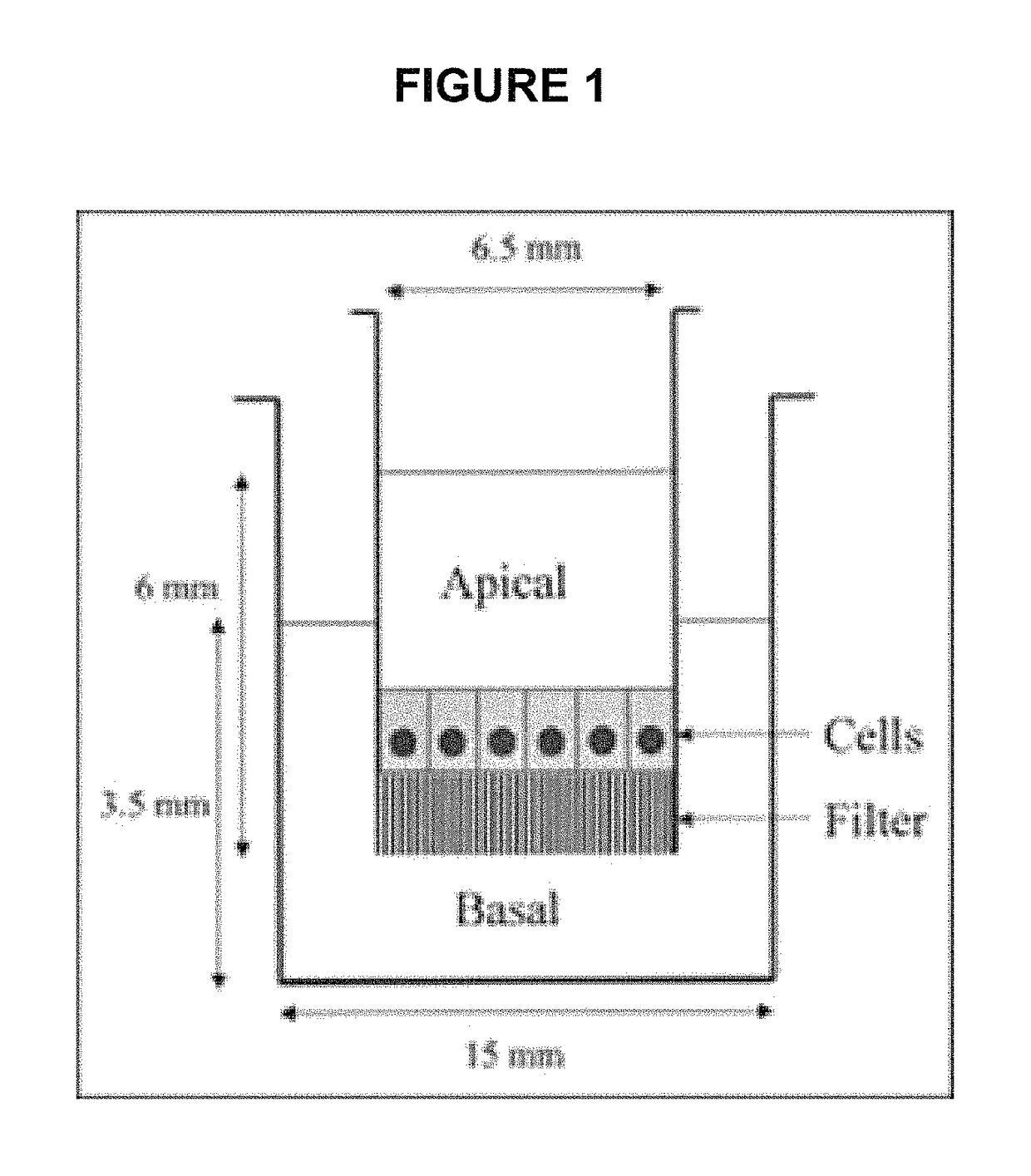
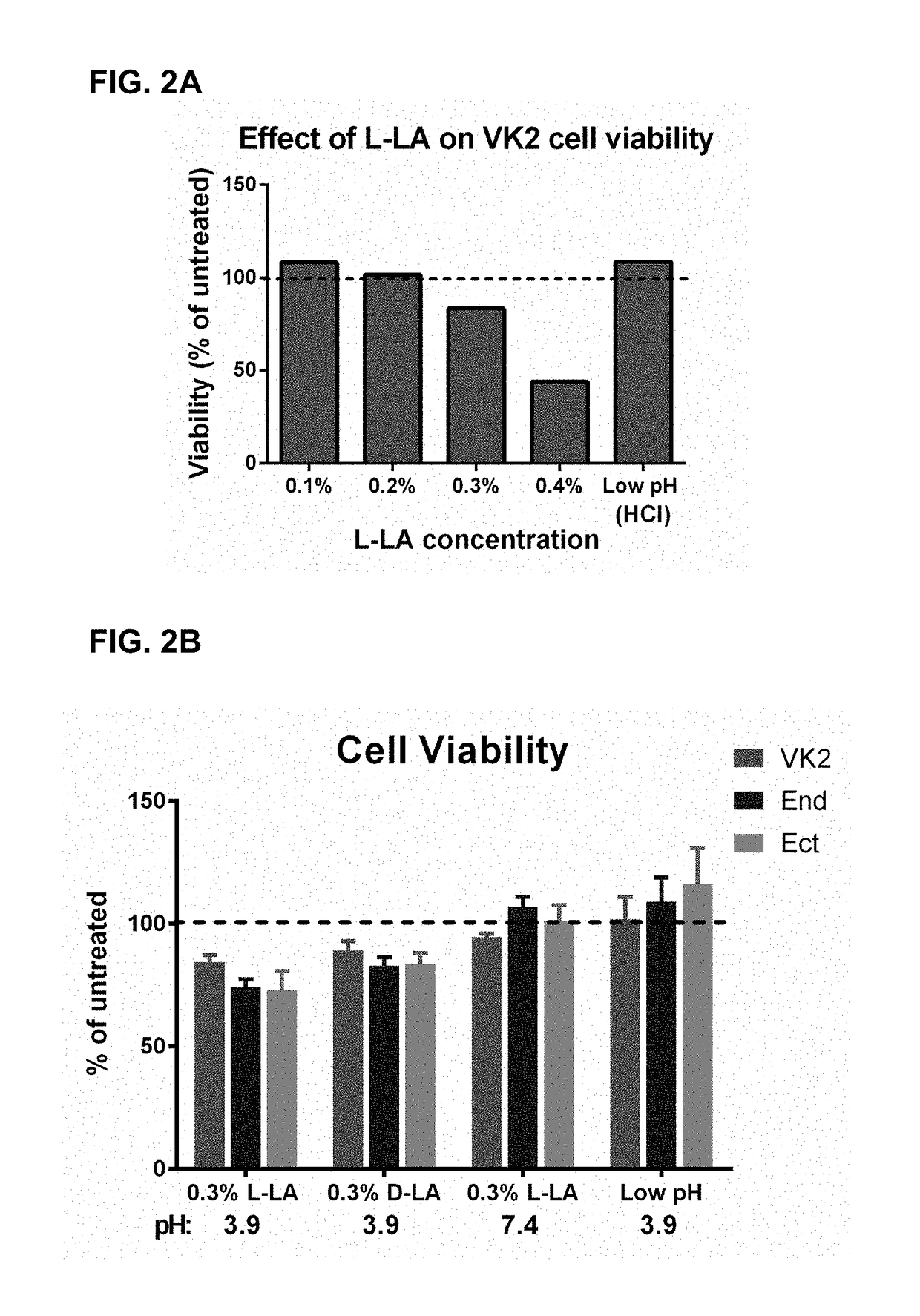
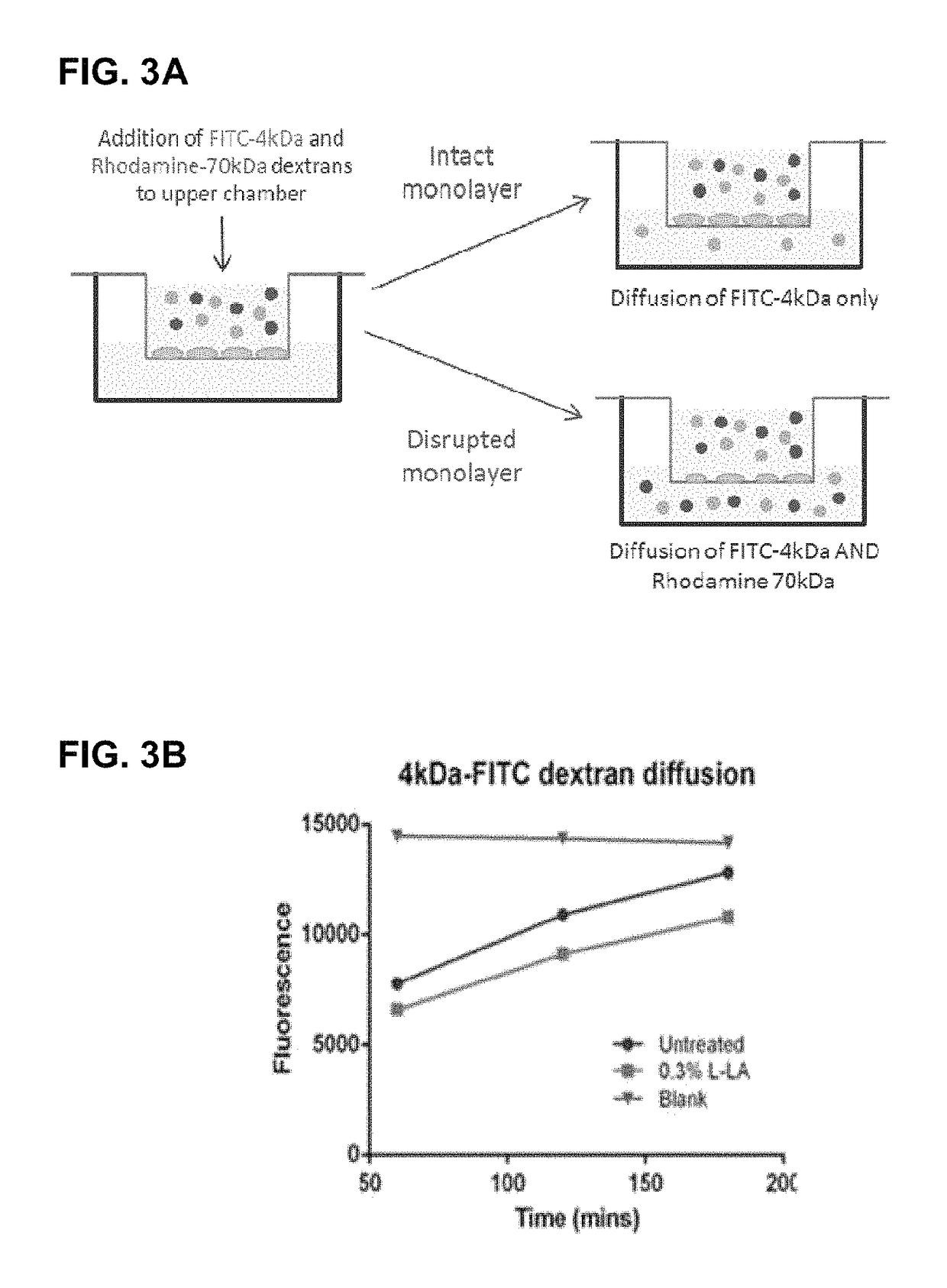
The present invention relates generally to a method of down-regulating an inflammatory response in a mammal and to agents useful for same. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method of down-regulating an inflammatory response in the reproductive tract or external genital tissue of a female mammal by contacting the mucosal tissue of the reproductive tract and / or genitalia with lactic acid and to agents useful for same. The method of the present invention is useful, inter alia, in the treatment and / or prophylaxis of conditions characterised by an aberrant, unwanted or otherwise inappropriate inflammatory response including, for example, atrophic vaginitis, irritant vaginitis or infectious vaginitis.
Owner:THE MACFARLANE BURNET INST FOR MEDICAL RES & PUBLIC HEALTH LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com