Patents
Literature
35results about How to "Does not cause inflammation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
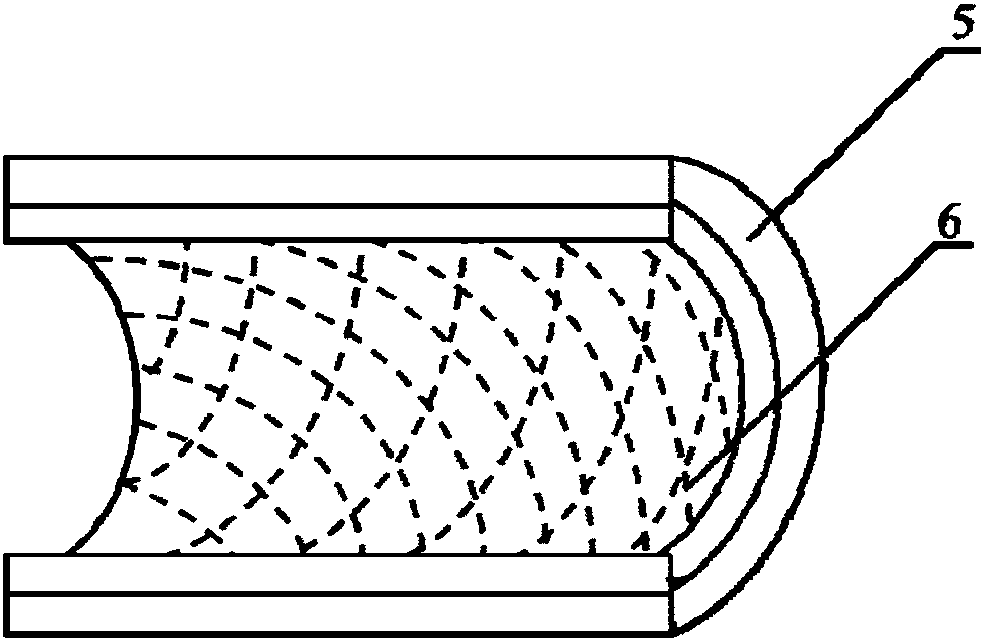
Novel biodegradable zinc-based metal material and ureteral expandable stent obtained through material
ActiveCN105925847AGood biocompatibilityPromote degradationStentsSurgeryMetallic materialsBiocompatibility Testing
The invention belongs to the field of medical implant materials and particularly relates to a novel biodegradable zinc-based metal material and a ureteral expandable stent obtained through the material. The zinc-based metal material is composed of zinc and / or zinc alloy. The zinc alloy is composed of Zn and one or more elements of Mg, Al, Ti, Cu, Ag, Si, Ca, Sr, Y, Zr, Sc, Gd, Nd, Dy, Er, Li, Mn, La, Ce, Pr, Sm, Tb, Ho, Tm, Yb and Lu. The biodegradable zinc-based metal material has good biocompatibility, degradability and mechanical properties, and has wide market application prospects.
Owner:管仁国
Injectable temperature sensitive gel used for filling and repairing damaged tissues
The invention relates to an injectable temperature sensitive gel used for filling and repairing damaged tissues. The gel is characterized in that: medical-grade hyaluronic acid and chitosan are used as gel raw materials; the gel swelling ratio is 2-500; and a temperature sensitive temperature is 32-37 DEG C. The gel provided by the invention has the advantages that the injection temperature sensitive gel has physical and chemical properties of a general gel, also has injectable and temperature sensitive properties and a good fluidity at a room temperature and is easy for injection; the formability in organisms is good and the degradation is slow so that the general gel can not be compared; a cross-linking agent is not used for the gel so that harms of the cross-linking agent to a human body are avoided; a gel system can prolong a persistence time of the gel in a body, and also can continuously stimulate the body to produce reactions so that the tissue in-situ regeneration and repair is promoted and the filling quality is increased; and the gel simultaneously has the advantages of reducing bacterial invansion, anticoagulation and low allergic reaction and the like.
Owner:冯淑芹
Biodegradable stent composite
InactiveCN105169496ADoes not lower pHDoes not cause inflammationSurgeryCoatingsAcetic acidTrimethylene carbonate
The invention discloses a biodegradable stent composite. The biodegradable stent composite is prepared from biodegradable medical polyurethane and a biodegradable metal material. The weight ratio between the biodegradable medical polyurethane and the biodegradable metal material is 0.1-99%:1-99.9%, preferably 5-90%:10-95%. To regulate the hardness of the material, other high molecular materials, such as polylactic acid, polycaprolactone, poly-p-dioxanone and copolymers thereof (PPDO and P(LA-PDA)), poly trimethylene carbonate, polylactic acid-trimethylene carbonate copolymer, polycaprolactone-trimethylene carbonate copolymer, polyglycolic acid and polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer, can be added, so that clinical usage is facilitated.
Owner:COMSCAFFOLDS NANJING MEDICAL DEVICE CO LTD
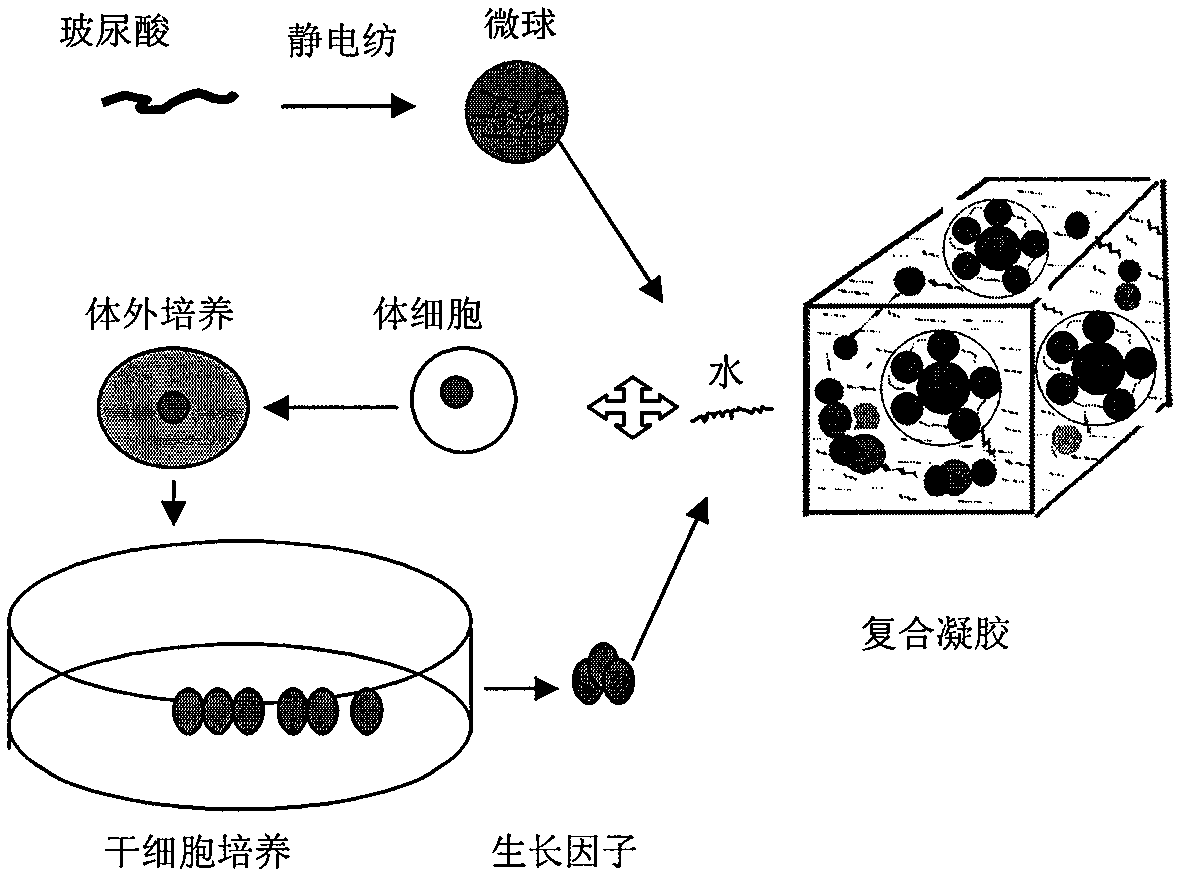
Injection gel containing submicron hyaluronic acid microspheres and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an injection gel containing submicron hyaluronic acid microspheres and a preparation method thereof. The diameter of each microsphere is 100 nanometers to 50 micrometers. Swelling ratio of the injection gel is 2-2000. The preparation method includes: dissolving biodegradable hyaluronic acid into organic solvent to obtain spinning solution; electrospinning the spinning solution using electrostatic spinning, and crosslinking through coagulating bath to obtain nano / submicron microspheres; dialyzing to purify the microspheres, preparing into injection with phosphate buffer or normal saline, and homogenizing with suspension of a stem cell growth factor system according to a certain volume ratio to obtain the injection gel. The injection gel containing submicron hyaluronic acid microspheres prepared by the method is fine in shaping performance, long in shape preservation, and fine in cell compatibility, and is applicable as therapeutic for ophthalmology and orthopedics, also applicable as tissue-engineered repair materials such as bone tissues, cartilage tissues, blood vessel tissues, heart tissues and nerve tissues or as filling material for plastic surgery.
Owner:冯淑芹
Method of producing artificial prosthesis of disci intervertebrales nucleus pulposus
The invention discloses a preparing method of artificial intervertebral disc nucleus pulposus prosthesis in the macromolecular technical domain, which comprises the following steps: preparing polyurethane bag material; blending the polymer dihydroxy alcohol and diisocyanate; stirring the composition protected by nitrogen to make the prepolymer; heating to add chain-expanding cross linker; stirring to react; maturing; moulding the polyurethane bag; preparing the silicon rubber filler through blending base gel, cross linker, filler and catalyst to stir evenly; injecting the silicon rubber filler into the polyurethane bag through injector. The invention doesn't harm human body with good biological compatibility and dynamic property, which has chemical inert to possess long-term mechanic strength.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Long-acting subcutaneous implant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106063948ADoes not lower pHDoes not cause inflammationPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationLong actingDrug
The invention discloses a long-acting subcutaneous implant that contains degradable polyurethane coated collagen and is used for subcutaneous soft tissue filling and a preparation method thereof. The implant has the advantages of good elasticity, excellent degradation resistance, and long duration after injection, is very suitable for subcutaneous filling, wrinkle removing, breast prosthesis filling and use as a drug carrier, etc.
Owner:YUANRONG BIOLOGICAL PHARMA WUXI CO LTD
Method for preparing developing polyurethane
InactiveCN101392048ALong lasting developing effectExcellent developabilitySurgeryCatheterPolymer scienceBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to a preparation method of developing polyurethane, which pertains to the technical field of high polymer material. The preparation method comprises the steps that: firstly, polymers, diatomic alcohol and diisocyanate are mixed; the mixture of the diatomic alcohol and the diisocyanate is stirred and reacts under the protection of nitrogen gas to obtain a prepolymer; after the temperature thereof is raised, the prepolymer is added with a chain extender and stirred for reaction; and the polymers are cured. As the chain extender contains developing atoms and developing groups are connected with the polyurethane by the effect of chemical bonds, the developing polyurethane prepared by the preparation method has long lasting development effect, good stability, biocompatibility and anticoagulant performance, arouses no inflammation in human bodies, is biological aging resistant and animalcule resistant, has good physical properties, can be sterilized by usual methods, is easy to be processed and takes advantages over non-developing polyurethane when being applied to heart valves, conduits and vascular stents. The preparation method is flexible, effective, simple and easy to be realized.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Porous degradable blood vessel and preparation method thereof
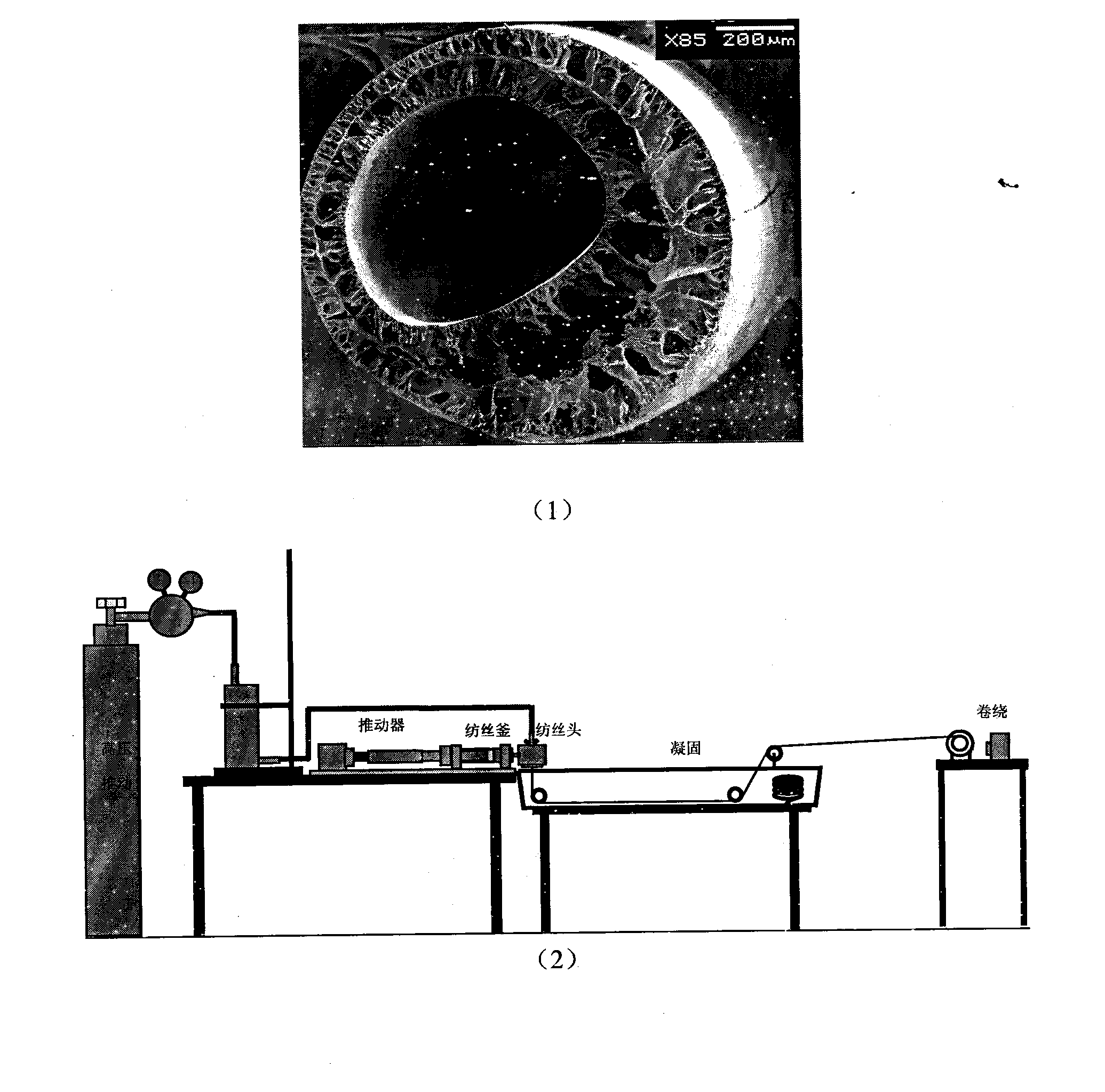
InactiveCN102871772ARelieve painNon-toxicHollow filament manufactureWet spinning methodsHollow fibreFiber
The invention aims to provide a porous degradable blood vessel prepared by a wet method spinning process and a preparation method thereof. The blood vessel is prepared from hollow fiber, has rough and porous surface, contributes to adhesion and growth of vascular cells, and has an effect of regenerating vascular tissues. The preparation method is simple, economic and suitable for industrialized production. The blood vessel has the inner diameter of 0.01 mm to 1 cm, the outer diameter of 0.02 mm to 2 m and the thickness of 0.01 mm to 5 mm. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving a PLC raw material and additives into an organic solvent to prepare a uniform and transparent spinning solution at a certain temperature; standing and defoaming the spinning solution for half an hour, injecting the spinning solution into spinning equipment, injecting core liquid and performing wet method spinning; continuously immersing the hollow fiber into washing liquid for 0.5 minute to 48 hours to remove the residual core liquid and additives; repeatedly washing with deionized water, soaking for 0.5 minute to 48 hours, performing vacuum drying, and intercepting to prepare a vascular stent.
Owner:冯淑芹
Medical mesh for hernia repair patch
The invention relates to a medical mesh for a hernia repair patch. The mesh is characterized by adopting medical grade polycaprolactone monofils as weaving material and having a breaking strength of 500 to 700 CN, a breaking elongation of 30 to 100 percent, a knot breaking strength of 400 to 600 CN and a knot breaking elongation of 10 to 50 percent. Besides the basic physical and chemical properties of common polycaprolactone, the medical grade polycaprolactone surpasses the common polycaprolactone regarding the purity, biological stability and biological solubility because the components of parent material and low molecular additives are strictly controlled in the processing process. The polycaprolactone monofils has a higher rigidity and is more suitable for being used to weave the hernia repair patch which has certain strength and bending rigidity and is capable of resisting human body abdominal pressure and defected body pressure.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Biosoluble antibacterial ultrafine glass wool and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108658468AThin diameterLow thermal conductivityGlass making apparatusThermal insulationMaterials science
The invention discloses biosoluble antibacterial ultrafine glass wool and a preparation method thereof. The biosoluble antibacterial ultrafine glass wool comprises the following chemical components bymass: 60-68 parts of SiO2, 0 to 3 parts of Al2O3, 6 to 12 parts of CaO and MgO, 15 to 20 parts of Na2O and K2O, 0 to 3 parts of ZnO, 0 to 6 parts of Ag2O, 4 to 8 parts of B2O3, and no more than 3 parts of Fe2O3, SO3, ZrO2 and CeO2, wherein the content of CeO2 is not less than 0.5 part. The biosoluble antibacterial ultrafine glass wool has good biosolubility, bacteriostatic effect and thermal insulation properties.
Owner:CHONGQING MAGU FIBER NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
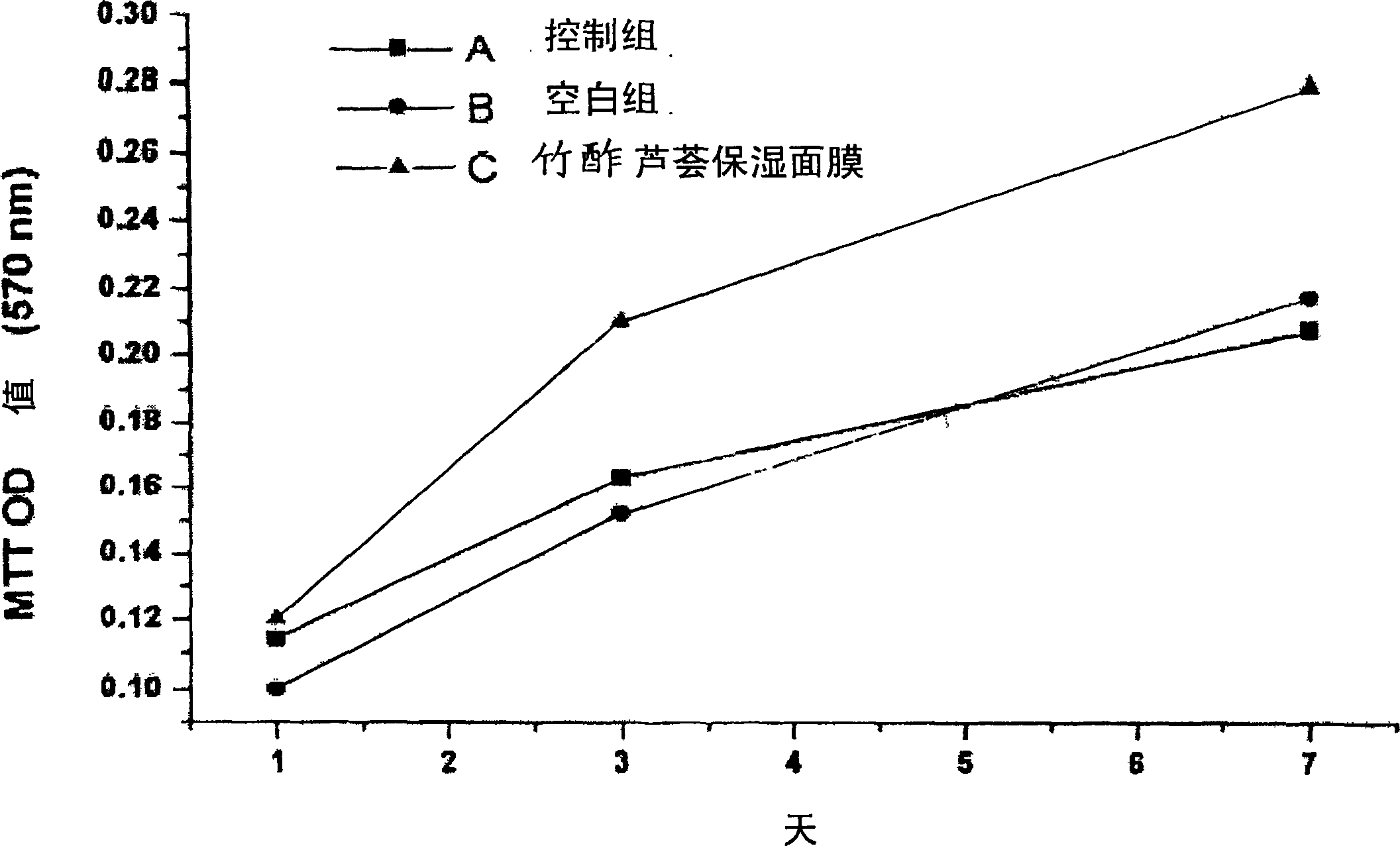
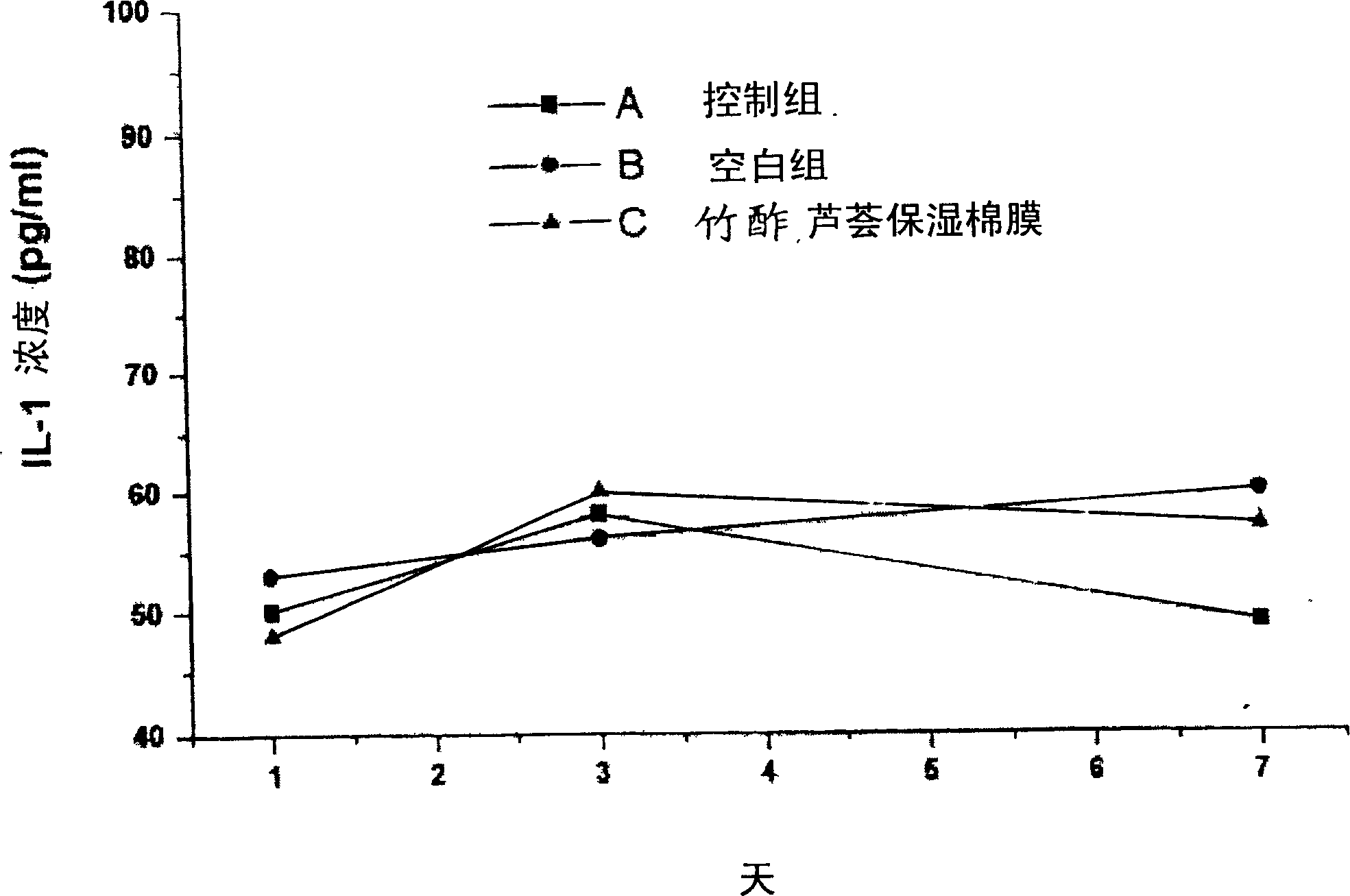
Moisture-keeping bamboo vinegar and aloe facial mask and its manufacturing method
InactiveCN1768730APromote spot removalDoes not cause inflammationCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsWater bathsEngineering
The invention provides a moisture-protection face pack with bamboo vinegar and aloe and its making process, which comprises, (1) provided a bamboo vinegar liquid, an aloe juice and a face pack paper, (2) mixing bamboo vinegar liquid with aloe juice in water-bath, (3) immersing the face pack paper, the concentration of the used bamboo vinegar is 1-5%, the concentration of the used aloe is 10-50%.
Owner:林峰辉
Double-layer drainage tube
PendingCN108236751AAvoid cloggingIncrease inner diameterWound drainsMedical devicesEngineeringDrainage tubes
The invention provides a double-layer drainage tube. The double-layer drainage tube is composed of an inner layer and an outer layer which fit tightly, wherein the inner layer is made from a hydrophobic material, and the outer layer is made from a human body biocompatible material. Liquid can not be retained on the inner wall, bile is avoided from being adhered to block the drainage tube, the outer wall is soft and elastic, the surface is smooth, compatibility with organism tissues is good, and inflammation can not be caused; meanwhile, diameter and cost of an outer tube are reduced under thecondition that a stainless steel wire intermediate layer does not exist, insertion difficulty is reduced, and meanwhile, inner diameter of the drainage tube is increased, and effective drainage crosssectional area of the drainage tube is effectively increased.
Owner:INNOVEX MEDICAL CO LTD
Method for constructing engineering arterial blood vessel in vivo by taking melt-spinning fiber as skeleton
InactiveCN106730030AGood biocompatibilityHigh mechanical strengthMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentAv graftAutologous tissue
The invention provides a method for constructing engineering arterial blood vessel in vivo by taking melt-spinning fiber as a skeleton. The method comprises the following steps: firstly preparing a melt spinning and medical silica gel tube composite mandrel, and then preparing the in-vivo engineering arterial blood vessel taking melt-spinning fiber as a skeleton by taking subcutaneous part of an animal as a bioreactor; the specific steps are as follows: 1) preparing the melt spinning and medical silica gel tube composite mandrel; 2) preparing the in-vivo engineering arterial blood vessel taking melt-spinning fiber as a skeleton by taking subcutaneous part of an animal as a bioreactor; and 3) performing in-situ transplanting of the in-vivo engineering arterial blood vessel so as to replace lesion blood vessels. The method has the advantages that the in-vivo engineering arterial blood vessel has good biocompatibility, all the components are originated from autologous tissues, and therefore, the artificial blood vessel is non-toxic, free from immunogenicity, and incapable of causing inflammation; due to the existence of melt spinning fiber, the prepared in-vivo engineering blood vessel has good mechanical strength, tenacity and compliance, and is suitable for surgical sewing operation.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
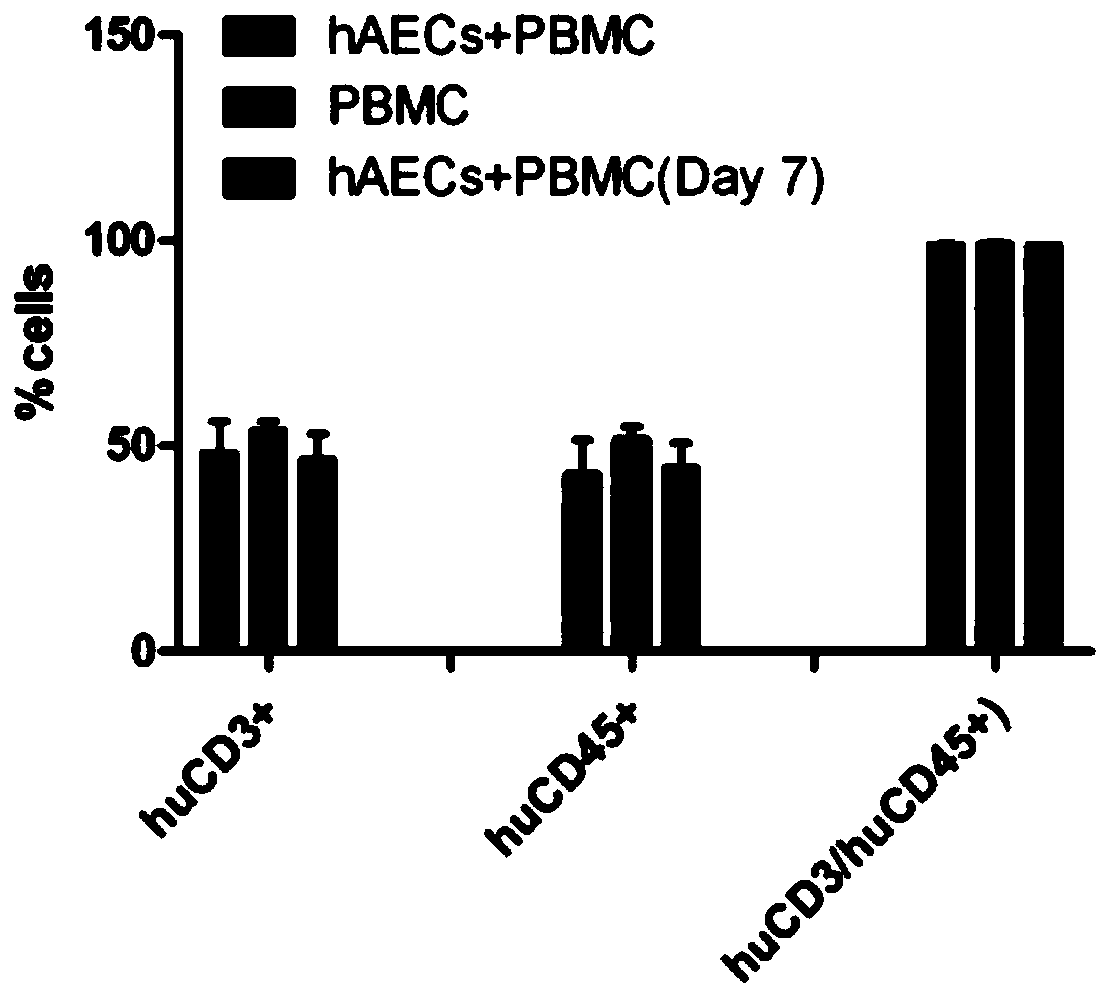
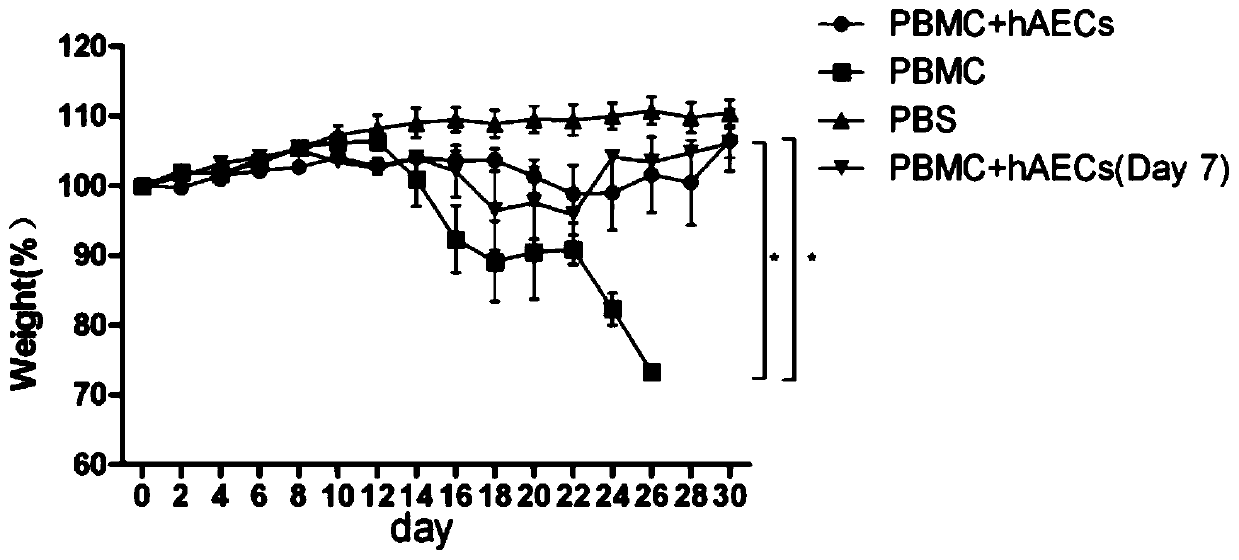
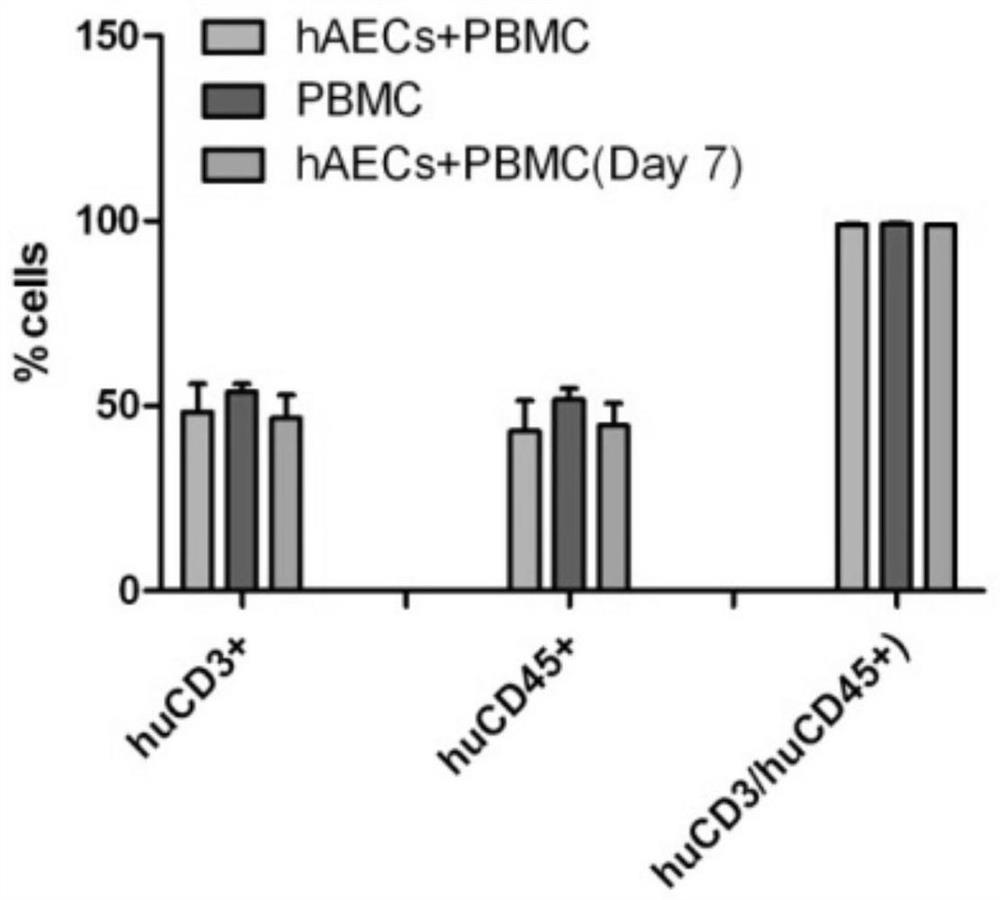
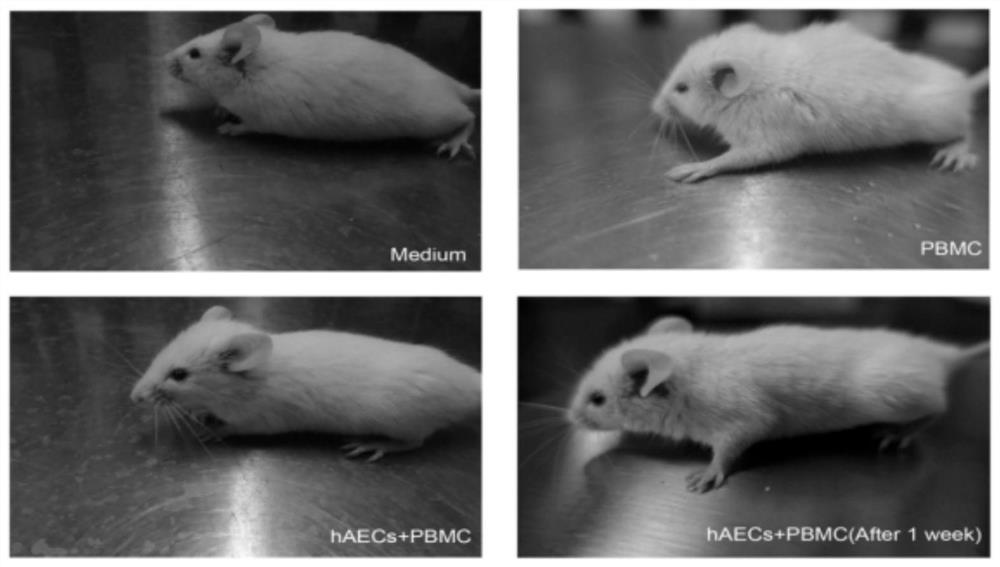
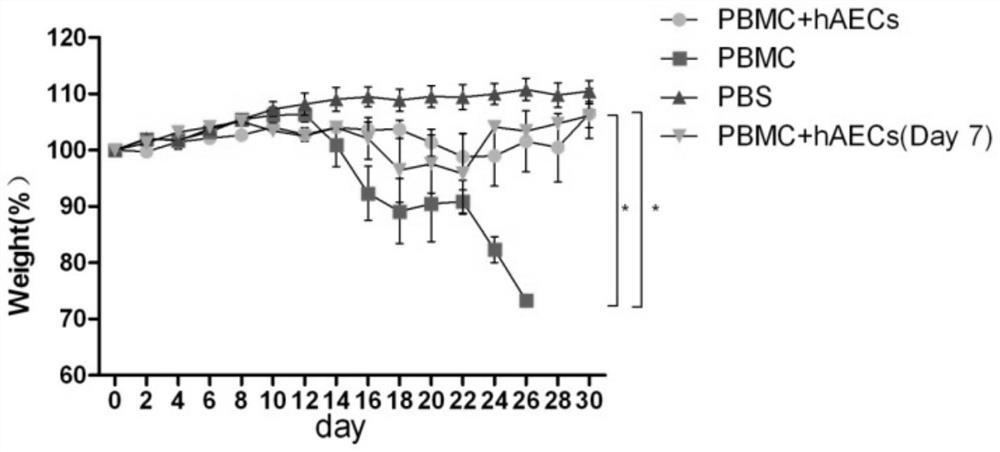
Use of human amniotic epithelial cells in treatment of graft-versus-host disease
ActiveCN110090227AReduce infiltrationReduce lesionsCell dissociation methodsEpidermal cells/skin cellsIntramedullary injectionIntravenous IG
The invention relates to a use of human amniotic epithelial cells (hAECs) in treatment of graft-versus-host disease (aGVHD). The invention discloses a method for treating and / or improving the graft-versus-host disease by using effective dose of the amniotic epithelial cells or a cell preparation containing the amniotic epithelial cells alone or in combination with other drugs. The amniotic epithelial cells can be given to patients by intravenous injection or intramedullary injection, the dosage range given at each time is about 10<3>-10<9> cells, the infiltration of inflammation cells caused by aGVHD to target organs can be effectively alleviated, the lesion of target organs is also significantly alleviated, the hAECs are found out to have an apoptosis-promoting effect on multiple leukemiacell lines and be used for treating the graft-versus-host disease.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
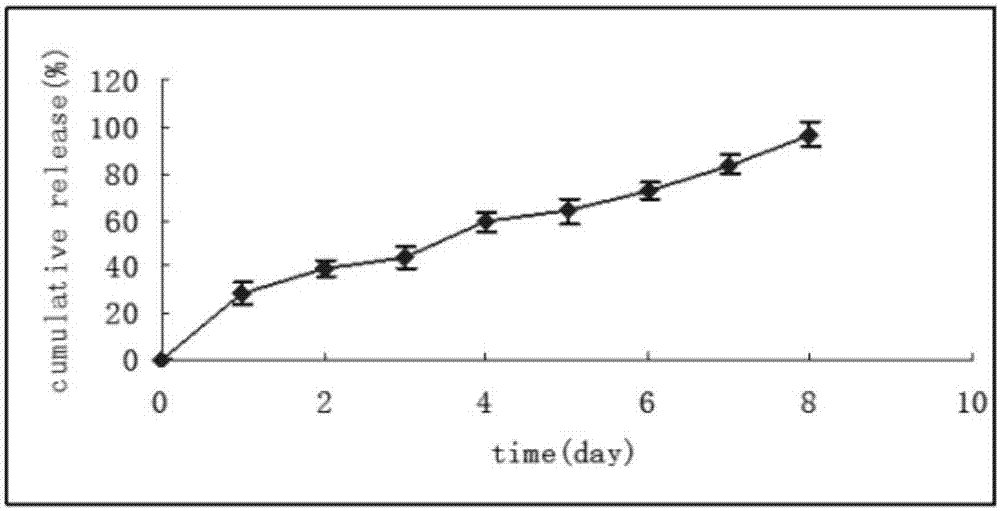
Multivesicular liposome for ocular vitreous injection and preparation method of multivesicular liposome
ActiveCN106924184AExtended release timeEase the pain of medicationSenses disorderAntibody ingredientsOrganic solventBevacizumab Injection
The invention relates to a multivesicular liposome for ocular vitreous injection. The multivesicular liposome is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 1 part of bevacizumab, 0.2-150 parts of lipid, 5-500 parts of an osmotic pressure regulator and 6-200 parts of a co-emulsifier. A preparation method of the multivesicular liposome for ocular vitreous injection comprises the steps of dispersing an inner water phase into a lipid phase according to the volume ratio of the inner water phase to the lipid phase of (1:1) to (1:10) to form a W / O primary emulsion; dispersing the W / O primary emulsion into an outer water phase according to the volume ratio of the W / O primary emulsion to the outer water phase of (1:1) to (1:5) to form a W / O / W compound emulsion; transferring the W / O / W compound emulsion to the outer water phase and removing an organic solvent in the compound emulsion; and centrifuging the obtained solution at 500-3,000rpm, taking lower sediments and adding normal saline for dispersion again to obtain the multivesicular liposome. According to the method provided by the invention, the prepared multivesicular liposome is high in encapsulation efficiency and has a good slow release effect, the particle sizes are 10-50 microns, the administration times are reduced and the compliance of a patient is improved.
Owner:YANTAI UNIV
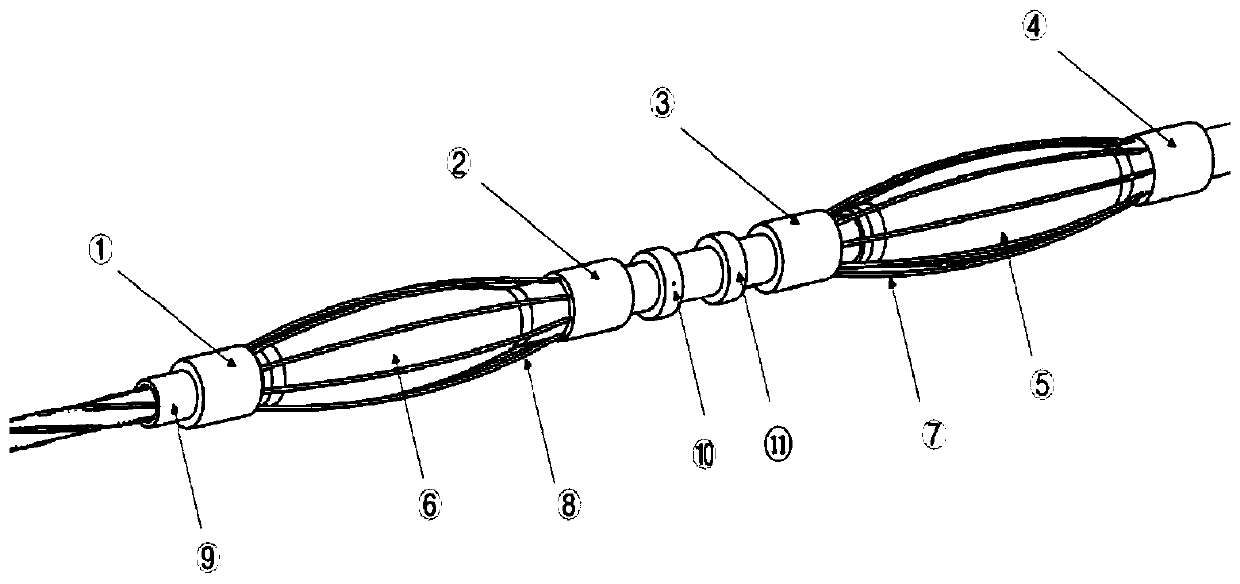
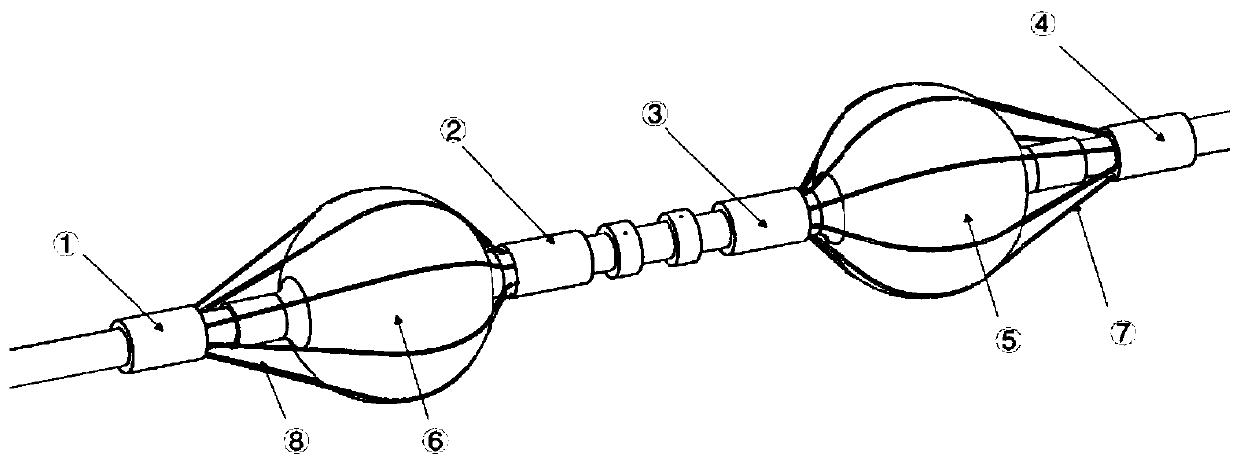
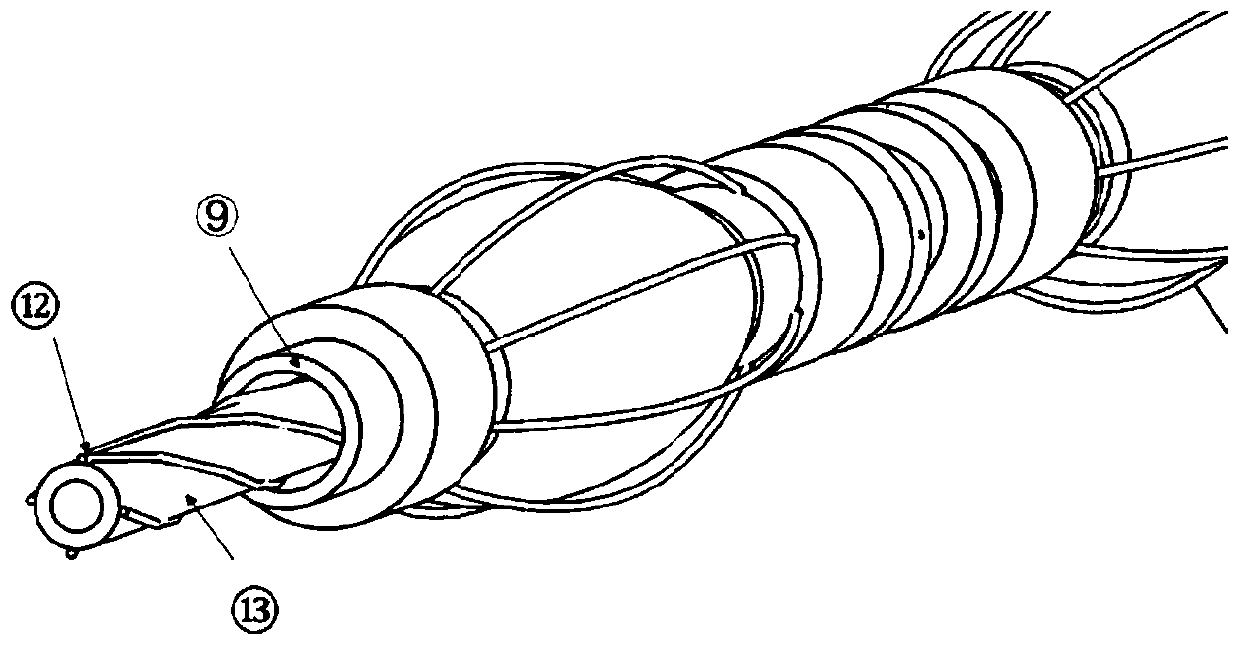
Saccule electrode duct for cavity tissue ablation
ActiveCN110693607AChanging treatment paradigmImproved prognosisSurgical instruments for heatingAnatomyCatheter
The invention relates to a saccule electrode duct for cavity tissue ablation. The saccule electrode duct comprises a duct a and a duct b arranged in the duct a, wherein an electrode sleeve ring a, a saccule b, an electrode sleeve ring b, a potential electrode a, a potential electrode b, an electrode sleeve ring c, a saccule a, and an electrode sleeve ring d are sequentially arranged on the outer surface of the duct a from left to right; a metal claw cage b is arranged between the electrode sleeve ring a and the electrode sleeve ring b; a metal claw cage a is arranged between the electrode sleeve ring c and the electrode sleeve ring d; the electrode sleeve ring b, the electrode sleeve ring c and the duct a are fixedly connected; the electrode sleeve ring a and the electrode sleeve ring d can freely slide in the duct a; the duct b is a flexible hollow columnar pipe body, and 4 conducting wires in spacing spiral wounding are arranged on the outer surface; and the conducting wires are respectively connected with the electrode sleeve ring b, the electrode sleeve ring c, the potential electrode a and the potential electrode b. The invention provides the saccule electrode duct which can perform safe and effective ablation radical cure treatment on malignant tumors.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF MEDICAL COLLEGE OF XIAN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for constructing engineered artery blood vessel in vivo by taking melt-spun fibers as framework
InactiveCN108525015AConvenient and smoothGuaranteed unobstructedMelt spinning methodsNon-woven fabricsMedical equipmentIn vivo
The invention belongs to the field of medical equipment and in particular relates to a method for constructing an engineered artery blood vessel in vivo by taking melt-spun fibers as a framework. Theframework comprises a cylindrical receiver and a plurality of spun fibers which are wound on the cylindrical receiver; the diameter of the spun fibers is 5 to 200mu m; the spun fibers comprise warp fibers and weft fibers; a longitudinal included angle between the warp fibers and the weft fibers is alpha and the alpha is greater than or equal to 30 degrees and less than or equal to 130 degrees; thewarp fibers and the weft fibers are staggered for a plurality of layers up and down to form a cylindrical structure. According to the method provided by the invention, the finally-obtained melt-spunfiber framework has good mechanical strength, toughness and compliance through adjusting the diameter of the spun fibers, a winding angle and the winding density, and is suitable for surgical suturingoperation; the framework has good elasticity and can be shrunk or expanded along changes of blood pressure in an application process, the smoothness of the blood vessel is kept, the binary restenosisis reduced and arterial aneurysm is prevented from being formed.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
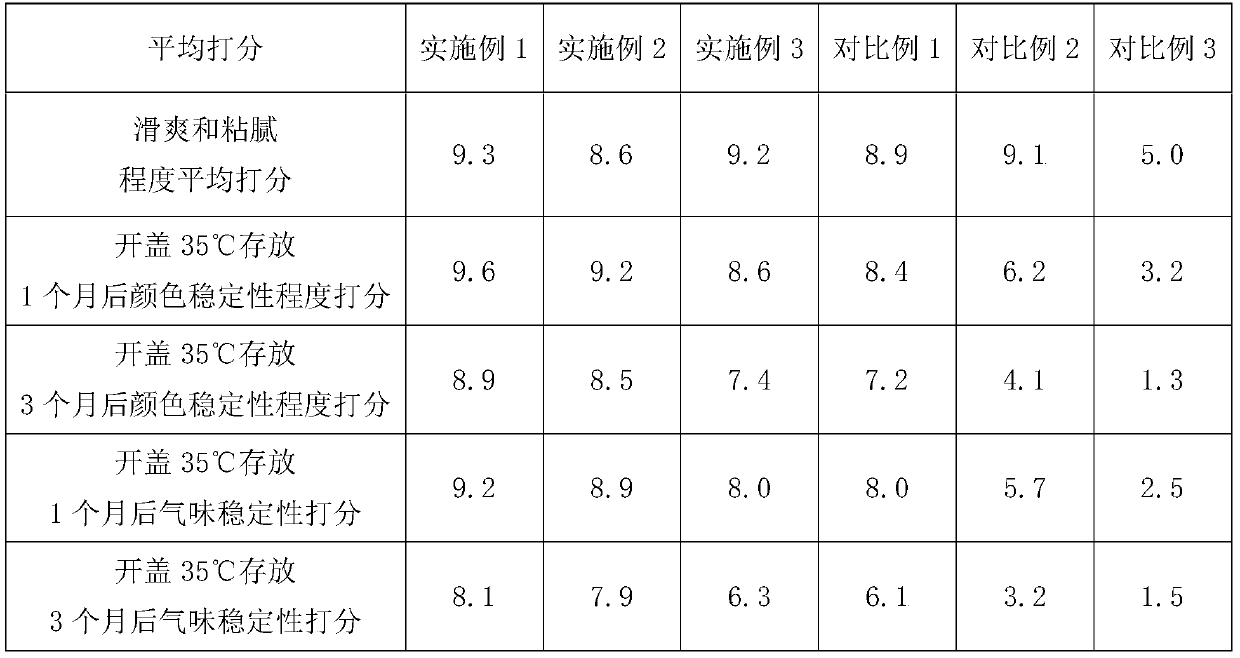
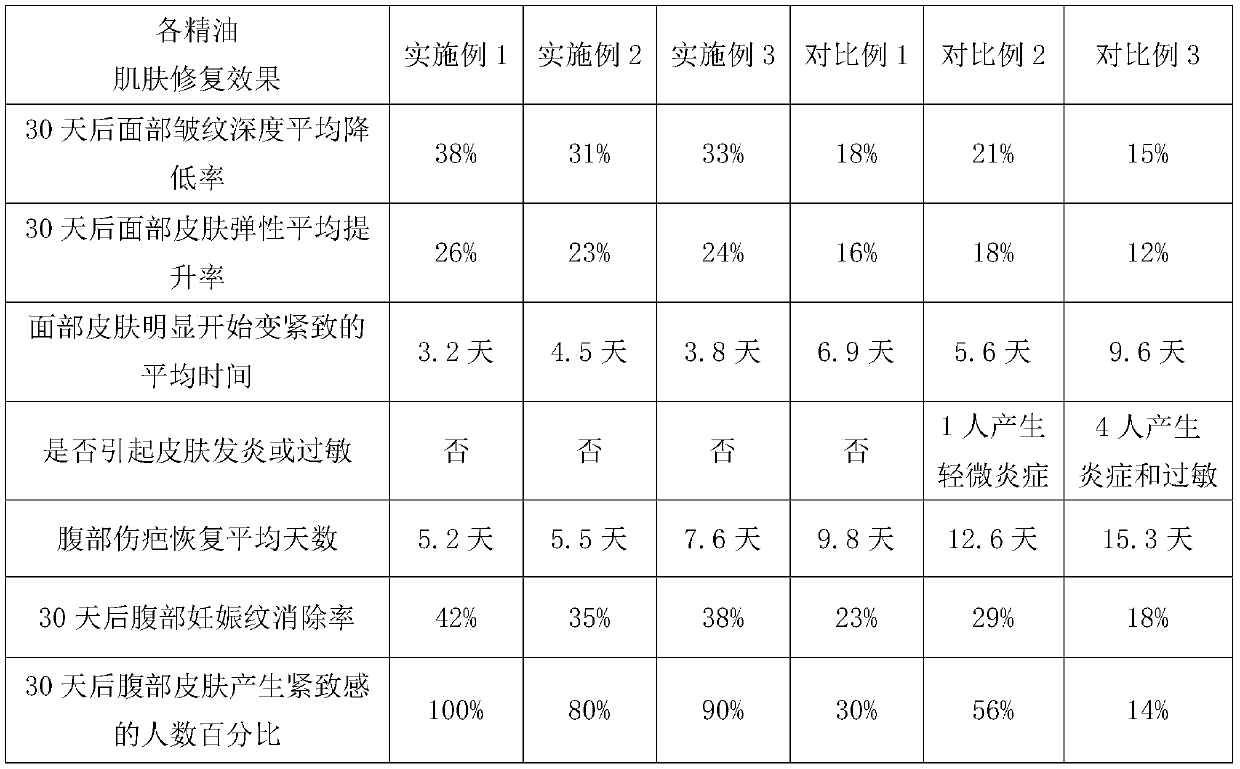
Skin-firming anti-oxidation compound essential oil
ActiveCN110090178AIncrease elasticityAntibacterialCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsEthylhexyl palmitateAloe barberae
The invention discloses a skin firming and anti-oxidation compound essential oil, which comprises the following raw materials of mass percentage: 50-80% of wheat germ oil, 5-15% of strawberry seed oil, 1.5-2.5% of a Selaginella tamariscina extract, 6-12% of oil ethylhexyl palmitate, and 0.5-1% of bisabolol; preferably comprises, 5-15% aloe oil and 3 to 5% of melaleuca alternifolia oil. The compound essential oil of the invention has smooth and non-sticky feel, good storage stability, and has the functions of antibacterial sterilization, anti-inflammatory and analgesic, is suitable for sensitive skin and skin with wounds, and can quickly wrinkle and remove scars and improve skin elasticity.
Owner:东方爱堡(北京)母婴健康科技有限公司
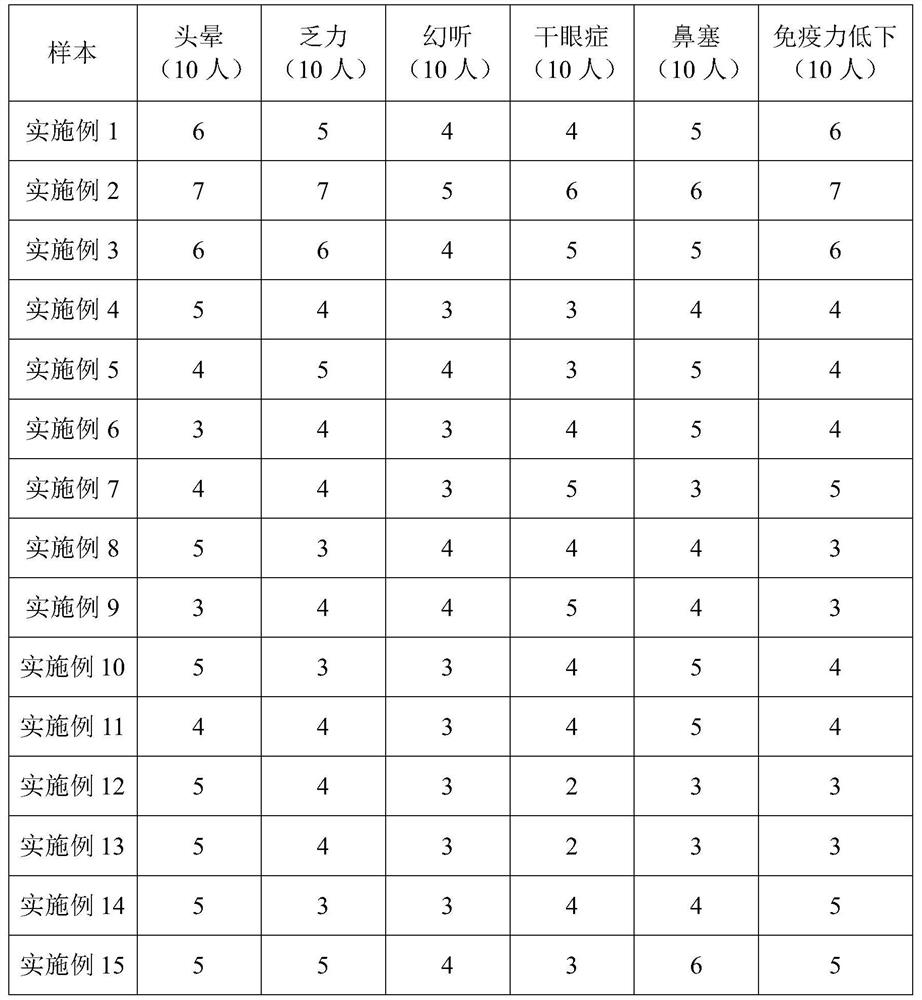
Maotai-flavor snuff and preparation method thereof
PendingCN114652790AWill not cause damageDoes not cause inflammationSenses disorderNervous disorderBiotechnologyXerophthalmia
The invention provides Maotai-flavor snuff and a preparation method thereof. The Maotai-flavor snuff is prepared from tobacco leaves, Maotai-flavor liquor and a traditional Chinese medicine composition. The Maotai-flavor snuff plays a role mainly through the nasal cavity and the airway mucosa, lung injury and inflammation cannot be caused, and therefore the Maotai-flavor snuff is safe and reliable to the health of a user; according to the Maotai-flavor snuff, the pressure of nervous tension can be relieved in the smoking experience, the tired body can have a temporary rest and relax, the refreshing effect can be achieved, the symptoms of dizziness, weakness, illusion, xerophthalmia and nasal obstruction can be obviously improved, the smoking amount of a smoker for a traditional burning cigarette is effectively reduced, and the smoking experience of the smoker is improved. Certain health-care and body immunity improving effects are achieved; according to the Maotai-flavor snuff, the Maotai flavor and the medicine flavor supplement each other, and the Maotai-flavor snuff is mellow, lingering, mild, relaxed and natural in taste and gives physiological enjoyment to smokers.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO JIANGSU INDAL
Method for preparing developing polyurethane
InactiveCN101392048BLong lasting developing effectExcellent developabilitySurgeryCatheterPolymer scienceNitrogen gas
The invention relates to a preparation method of developing polyurethane, which pertains to the technical field of high polymer material. The preparation method comprises the steps that: firstly, polymers, diatomic alcohol and diisocyanate are mixed; the mixture of the diatomic alcohol and the diisocyanate is stirred and reacts under the protection of nitrogen gas to obtain a prepolymer; after the temperature thereof is raised, the prepolymer is added with a chain extender and stirred for reaction; and the polymers are cured. As the chain extender contains developing atoms and developing groups are connected with the polyurethane by the effect of chemical bonds, the developing polyurethane prepared by the preparation method has long lasting development effect, good stability, biocompatibility and anticoagulant performance, arouses no inflammation in human bodies, is biological aging resistant and animalcule resistant, has good physical properties, can be sterilized by usual methods, is easy to be processed and takes advantages over non-developing polyurethane when being applied to heart valves, conduits and vascular stents. The preparation method is flexible, effective, simple andeasy to be realized.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
A kind of preparation method of skin-friendly liquid absorbent material
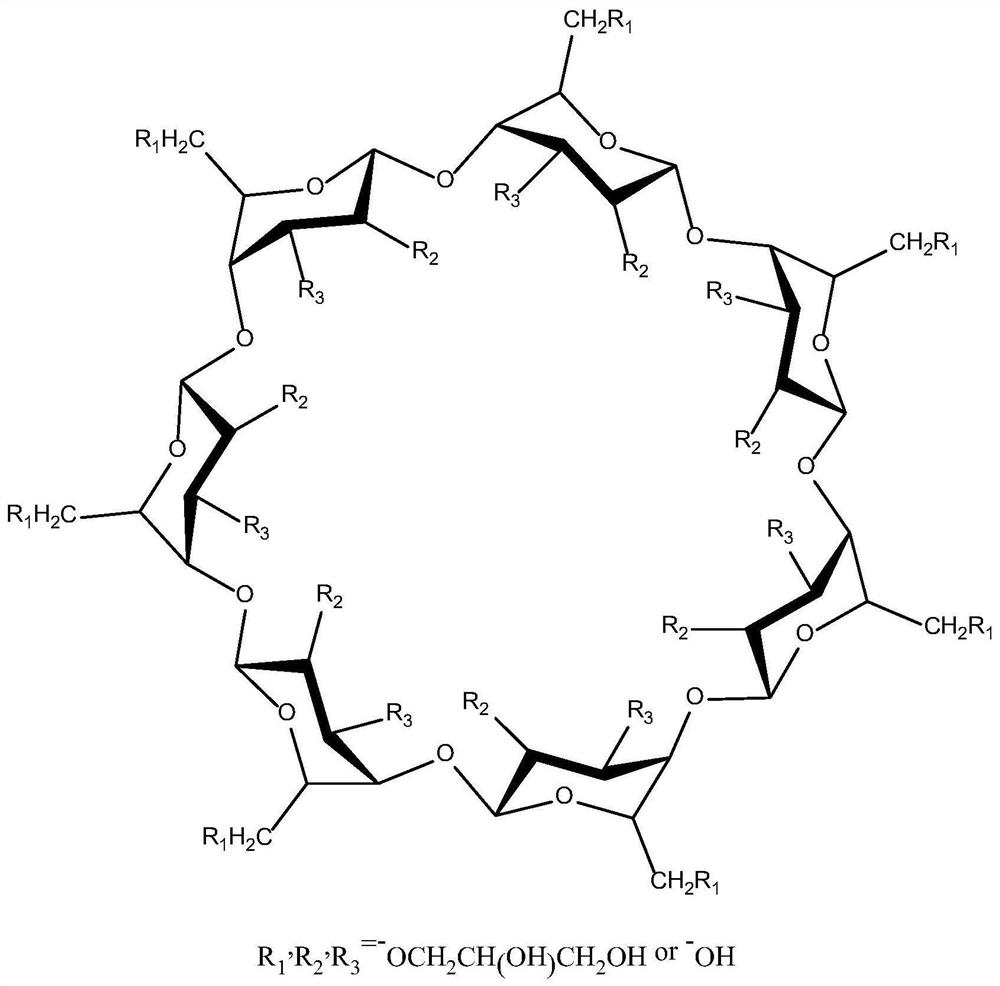
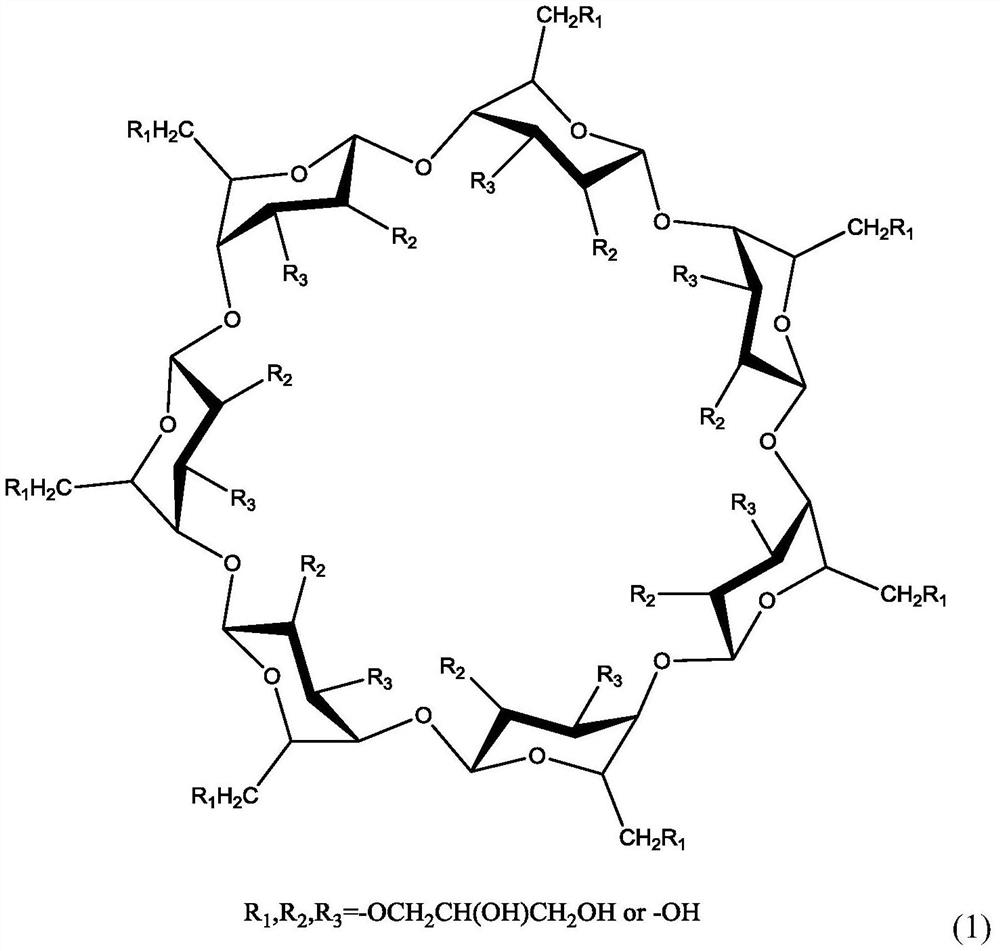
ActiveCN111617305BDo no harmHigh liquid absorptionCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsIRRITATION SKINSkin contact
The present invention relates to a liquid-absorbing material, in particular to a method for preparing a skin-friendly liquid-absorbing material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) modifying β-cyclodextrin by introducing a double bond; 2) modifying β-cyclodextrin and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin with different Ds are dissolved in lye; 3) adding monomer and initiator to the mixed solution in step 2) for pre-crosslinking; 4) increasing drop by drop Add the sodium alginate solution dropwise to the reaction solution in step 3) to continue cross-linking; 5) keep it warm and dry it. The skin-friendly liquid-absorbent material prepared according to the method of the present invention is friendly to the skin, does not irritate the skin, does not cause adhesion after contact with the skin, does not cause inflammation, has relatively excellent liquid-absorbent performance, and has satisfactory Mechanical effect, its degradability is excellent, and it is friendly to the environment.
Owner:杭州千芝雅卫生用品有限公司
Use of human amniotic epithelial cells in the treatment of graft-versus-host disease
ActiveCN110090227BReduce infiltrationReduce lesionsCell dissociation methodsEpidermal cells/skin cellsHost diseaseThelial cell
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Preparation method of high-adhesiveness degradable fiber protein adhesive
PendingCN110368516AHigh bonding strengthPromote degradationSurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismFiberCross-link
The invention belongs to the technical field of adhesive materials and relates to a preparation method of a high-adhesiveness degradable fiber protein adhesive. The high-adhesiveness degradable fiberprotein adhesive is prepared by adopting glutaraldehyde as a cross-linking agent for cross linking with glucan molecules, adopting fibrin glue as a raw material and adopting glucose modified polyurethane as an adhesive. The hydroxyl-containing glucan molecules are available for direct reaction with glutaraldehyde under violent reaction conditions, and by cross linking of hydroxyl and formyl, the prepared high-adhesiveness degradable fiber protein adhesive can be quickly polymerized to realize form adhesion while degradability is realized; by adoption of glucose for modification of polyurethanewith unique advantages of high bonding strength, resistance to water, solvents and low temperature, availability for low-temperature curing and the like, polyurethane is endowed with high degradability. Therefore, high bonding strength and a soft-hard transition layer with great physical properties can be formed between substrates by the prepared high-adhesiveness degradable fiber protein adhesive.
Owner:袁斯曼
Ocimum basilicum type snuff and preparation method thereof
PendingCN114794523AWill not cause damageDoes not cause inflammationTobacco preparationNervous disorderNasal congestionSweet Basil
The invention provides basil type snuff and a preparation method thereof. The basil type snuff is prepared from tobacco leaves, basil and a traditional Chinese medicine composition. The basil type snuff provided by the invention plays a role mainly through a nasal cavity and an airway mucosa, and does not cause lung injury and inflammation, so that the basil type snuff is safe and reliable to the health of a user; the basil snuff provided by the invention can relieve the pressure of nervous tension in the smoking experience, so that a tired body can temporarily rest and relax, and the basil snuff can also refresh and restore consciousness, obviously improve the symptoms such as dizziness, weakness, nasal obstruction, restlessness and the like, effectively reduce the smoking amount of a smoker on a traditional burning cigarette, and improve the smoking experience of the smoker. Certain health-care and body immunity improving effects are achieved; the sweet basil type snuff provided by the invention is cool in smell, sweet in aftertaste, mellow and lingering in fragrance, relaxed and natural, and gives taste enjoyment to a smoker.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO JIANGSU INDAL
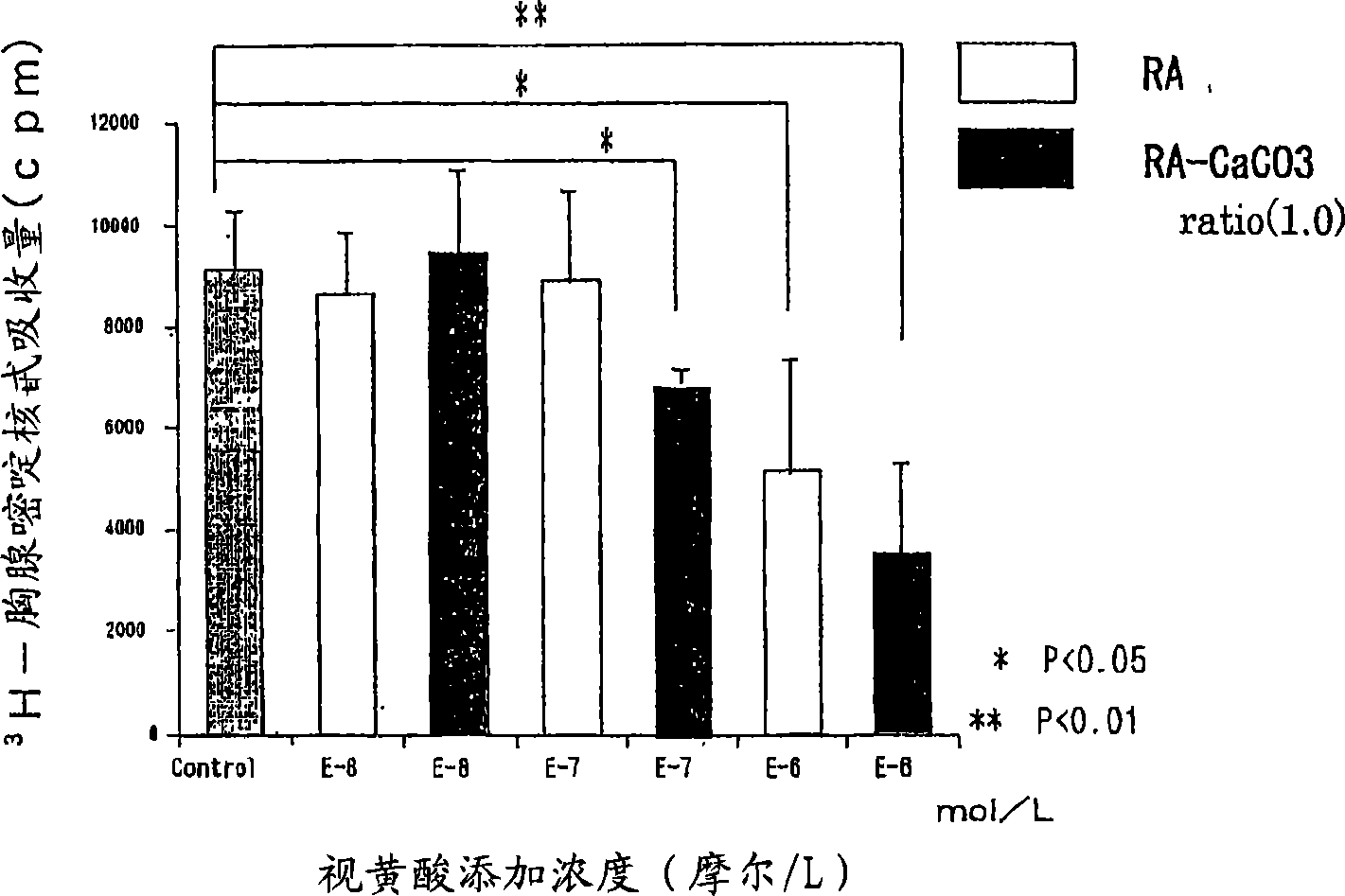
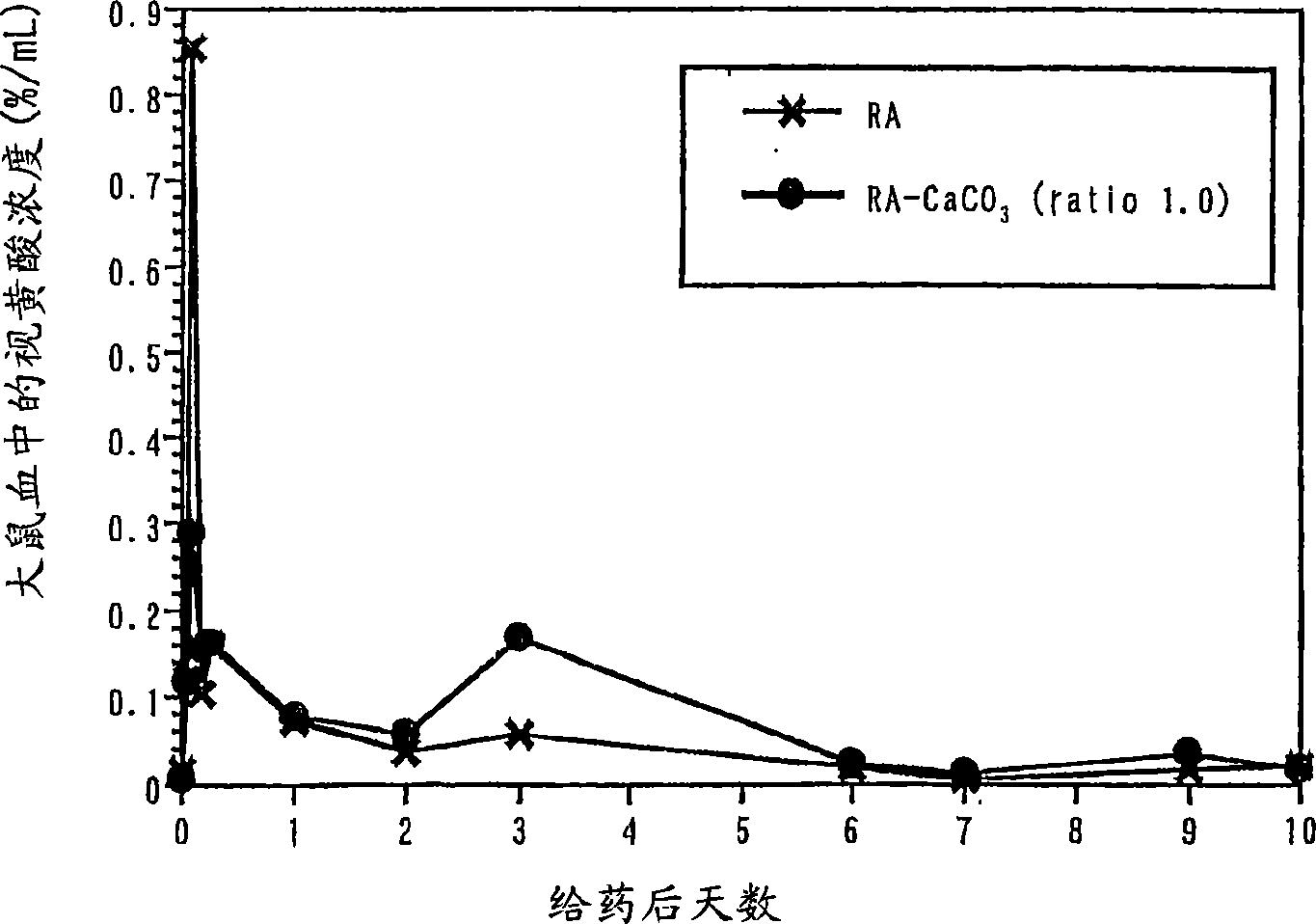
Composition containing retinoic acid nanoparticles coated with polyvalent metal inorganic salt
InactiveCN1859906AIncrease irritationLess irritatingCosmetic preparationsHydroxy compound active ingredientsIrritationBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Owner:NANOEGG RES LAB
Developable film for implanting medical device and preparation method of developable film
PendingCN114225123AGood biocompatibilityEasy to observeSurgical navigation systemsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismBiomedical engineeringAdhesive
The invention discloses a developable film for an implanted medical device and a preparation method of the developable film. The developable film can be developed or visible under X-ray irradiation, the developable film comprises a film base material and a developing component, and the mass ratio of the developing component to the film base material is (1-30): 100; the developable film is prepared by the following steps: (1) carrying out plasma surface treatment on the surface of a film substrate; (2) coating the developing component or a mixture of the developing component and a high polymer material on the surface of the film base material, and fixing the developing component on the surface of the film base material by a drying, active energy ray irradiation or heating sublimation method; or, the developing component and the film base material are combined together by using an adhesive. The developable membrane disclosed by the invention can be degraded by a human body, has good biocompatibility, does not cause inflammation of a patient, and is convenient to observe.
Owner:MALLOW MEDICAL SHANGHAICO LTD
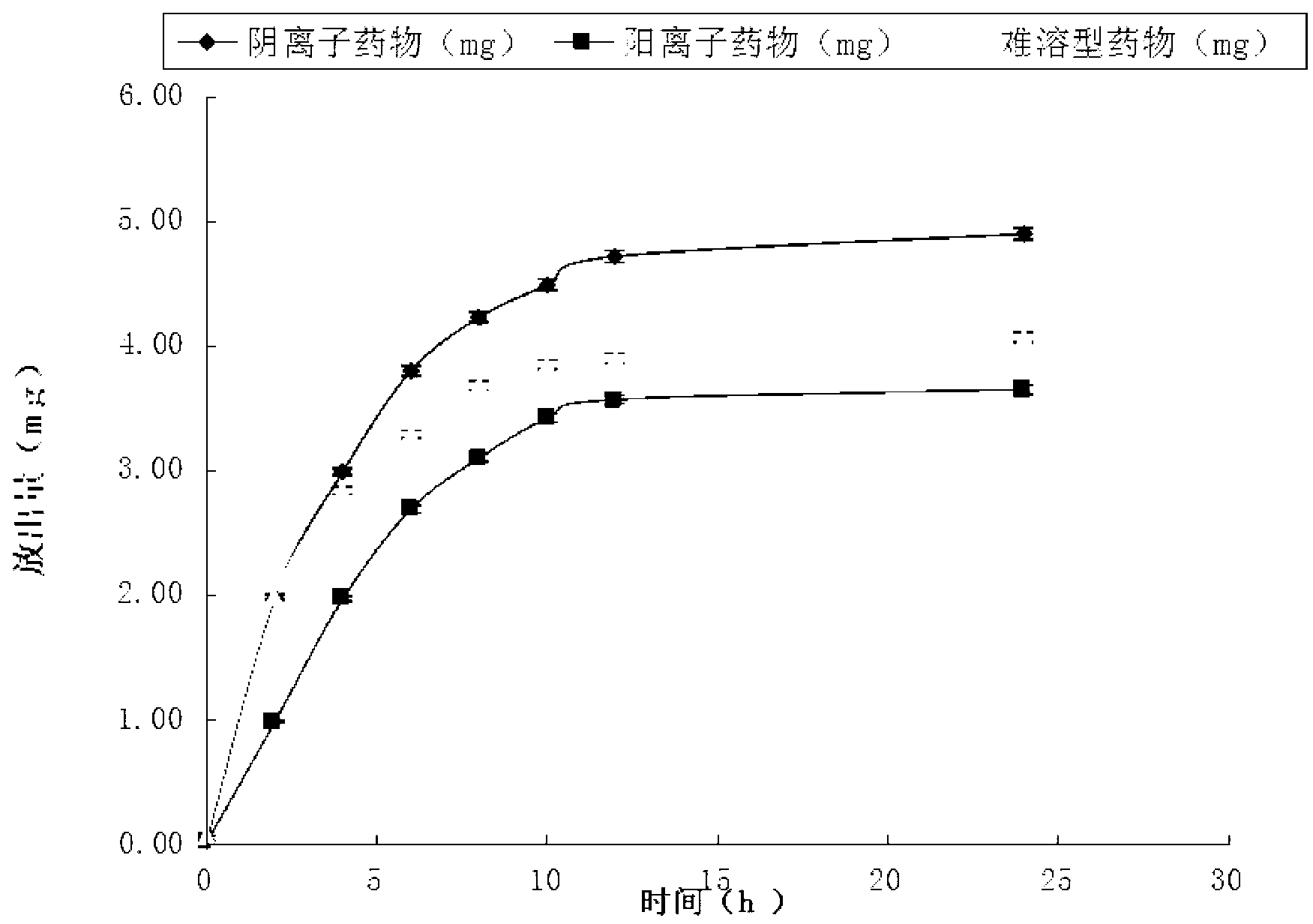
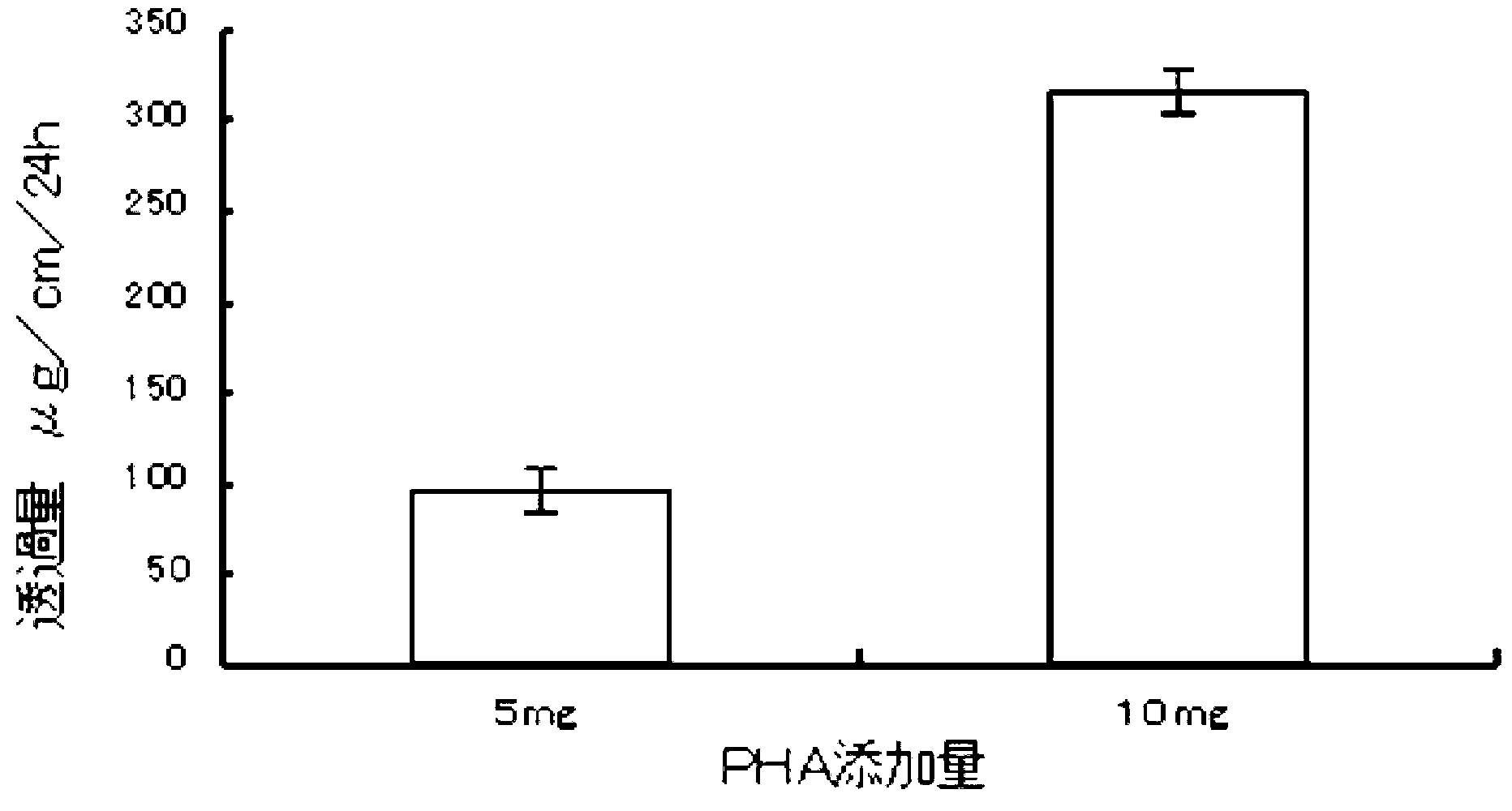
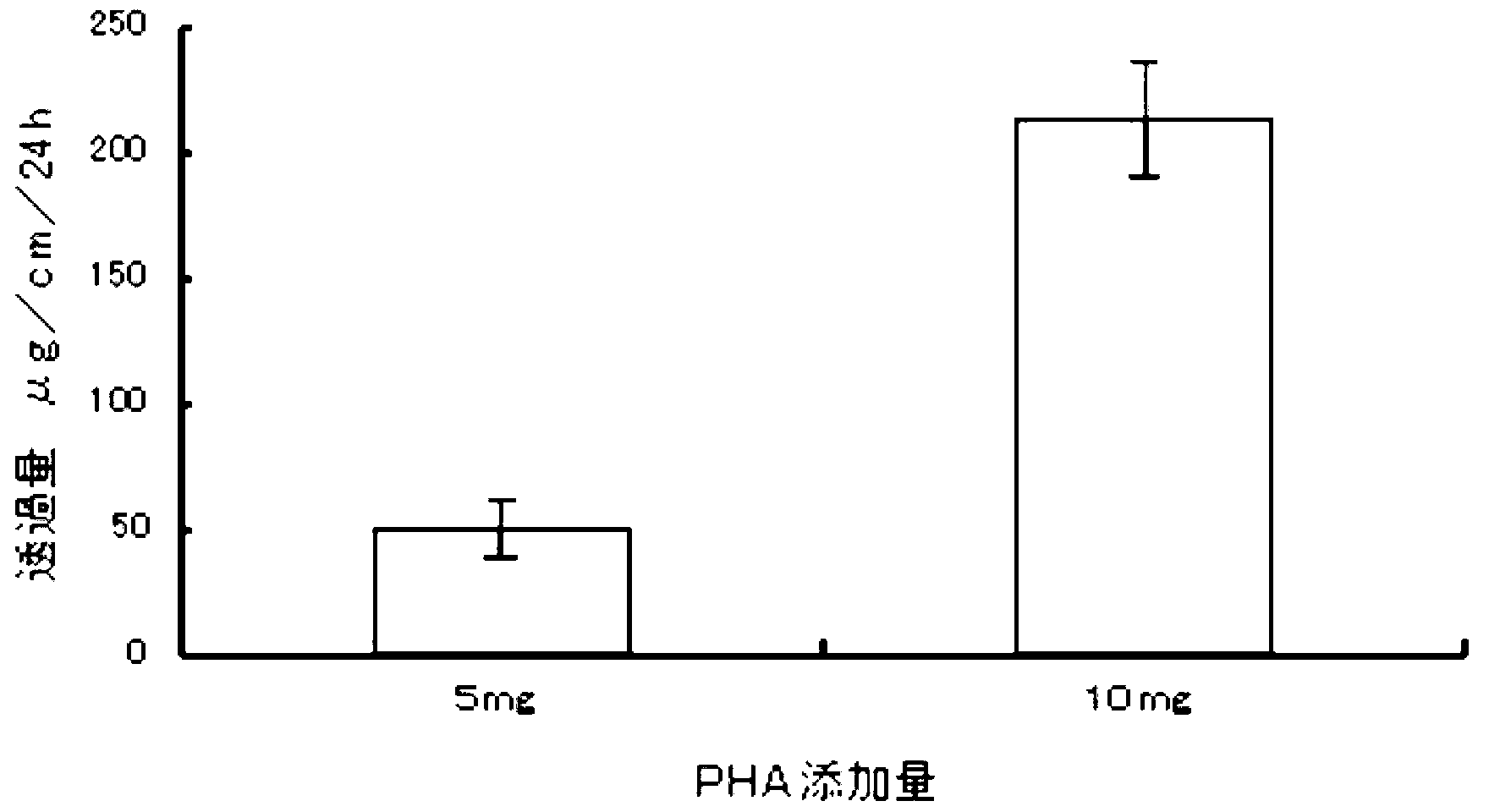
Preparation method of transdermal drug delivery system (TDDS)
InactiveCN103230385AReduce the amount entering the bodyReduce allergic reactionsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsPharmaceutical active ingredientsMedicineAdhesive
The invention provides a preparation method of a transdermal drug delivery system (TDDS). The preparation method comprises the following steps that 1. adding midchain PHA (polyhydroxyalkanoate) to chloroform solution to be mixed to obtain solution A; 2. adding drugs to dimethyl sulfoxide solution to be mixed to obtain solution B; and 3. mixing the solution A with the solution B uniformly, then coating the mixture on glass paper and drying the glass paper, thus obtaining the final product, namely the TDDS. The preparation method has the beneficial effects that the biodegradable material PHA obtained by synthesizing microorganisms is utilized as one of the raw materials and can replace adhesives and micromolecular accelerants in the existing TDDSs; PHA is combined with ionic and insoluble drugs respectively by utilizing the physiochemical properties of PHA, thus forming the TDDS; with slow release property, PHA can control drug release; and the TDDS has high transmittance, obvious effects, simple steps and better application prospect and is easy to operate.
Owner:SHANGHAI MEDICAL INSTR COLLEGE
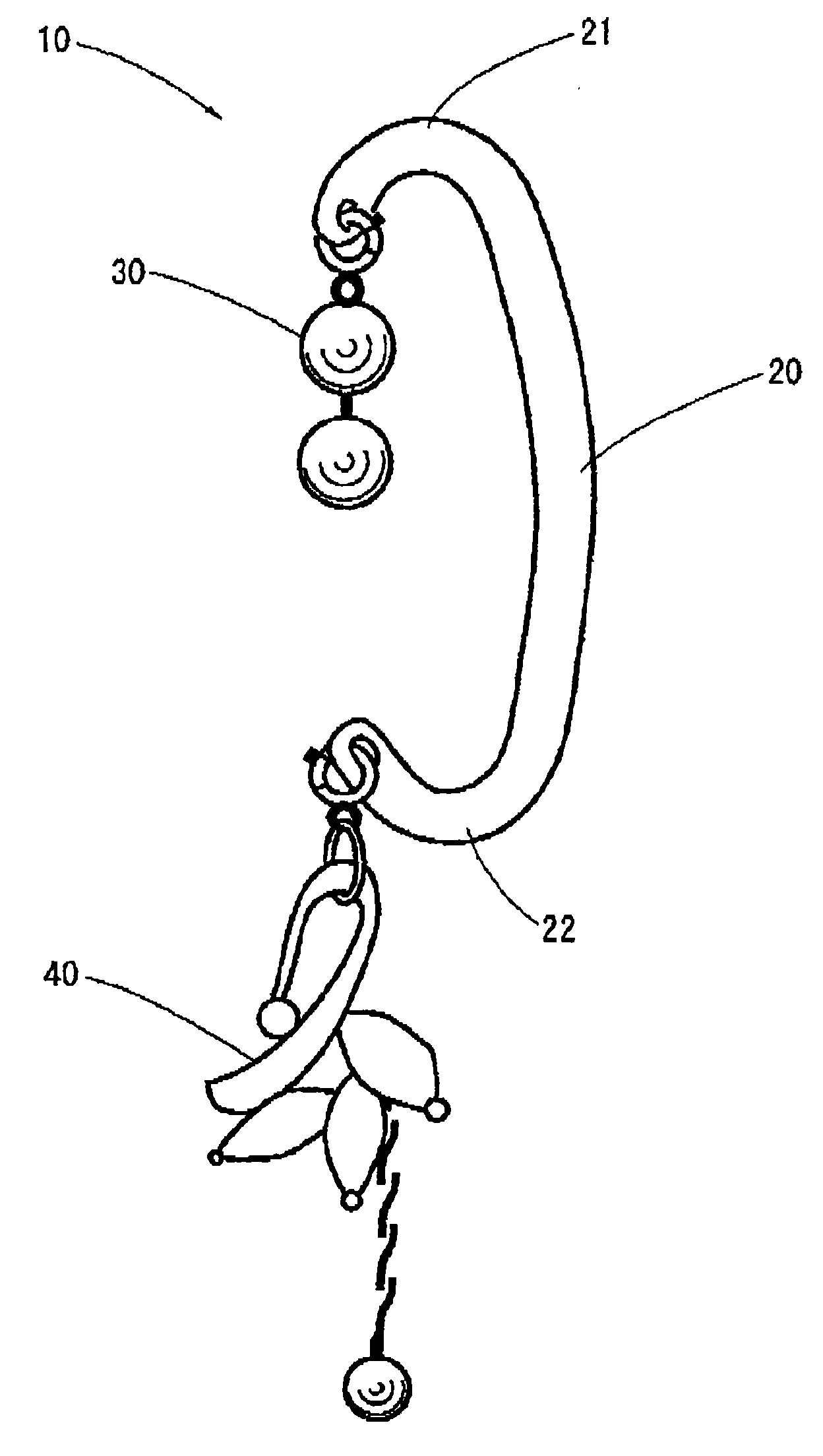
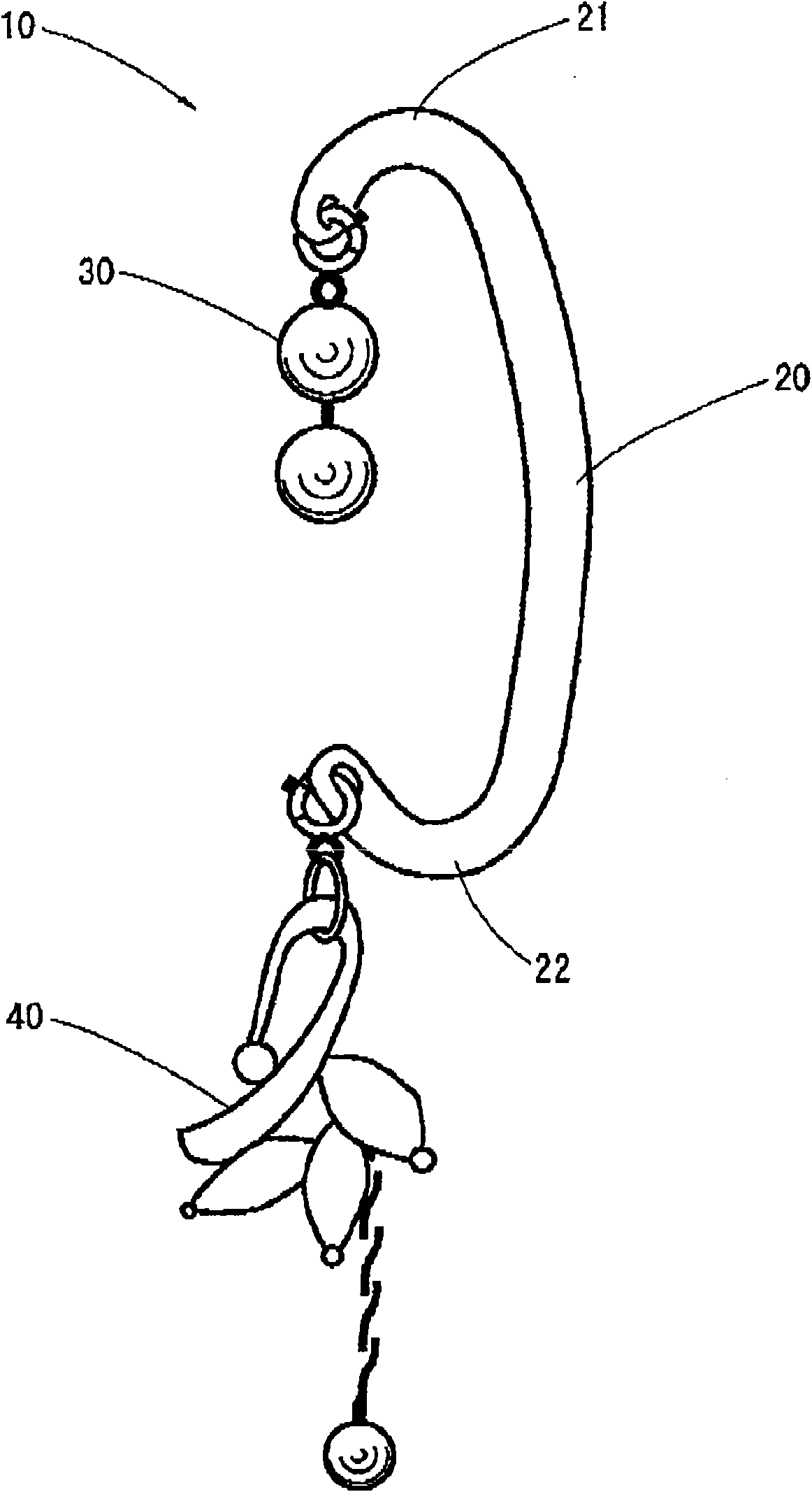
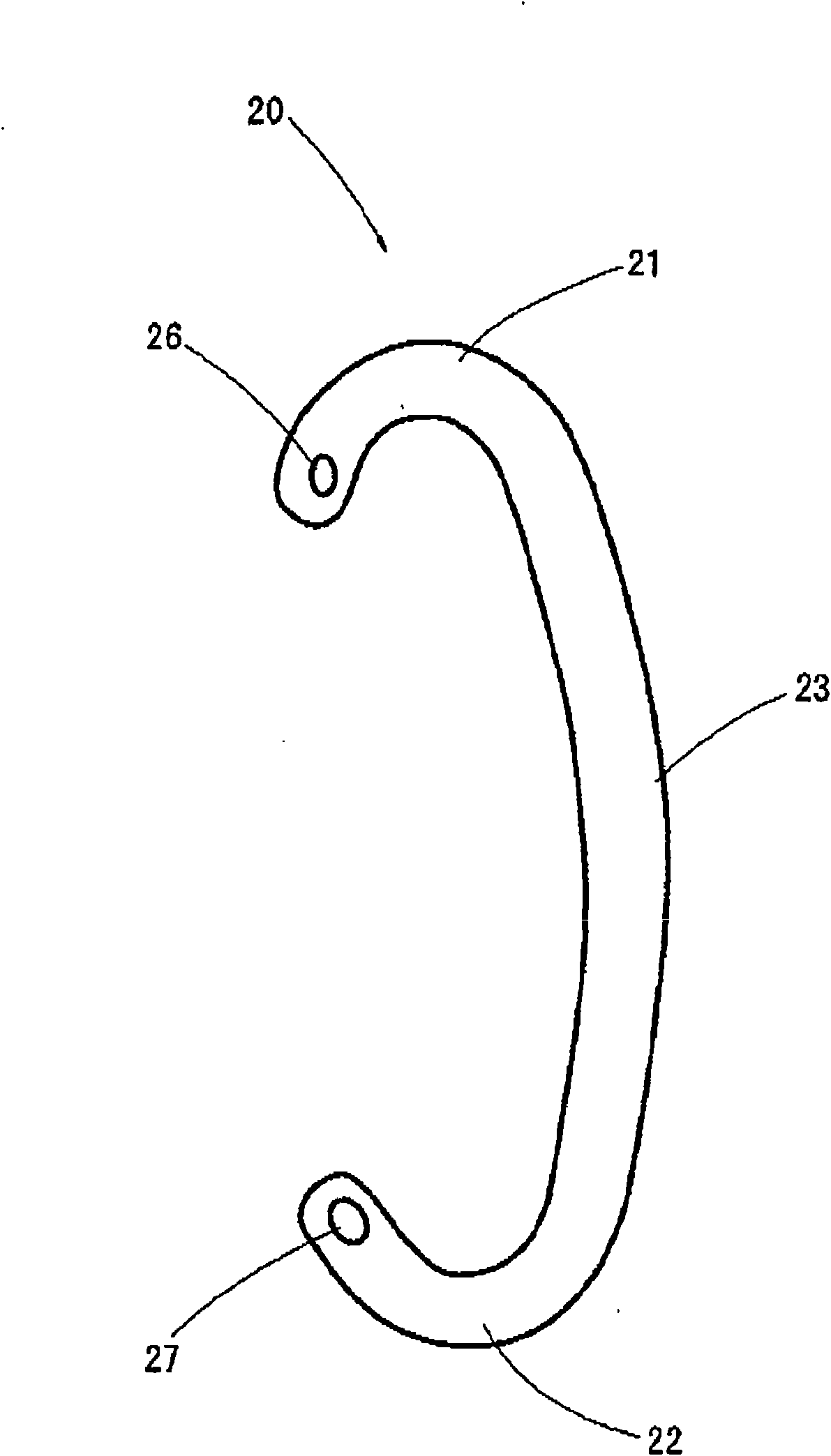
Earring
An earring that can be easily put on an ear without coming off during a use thereof and causes no pains in the earlobe of the ear is provided. Moreover, the earring can give a gorgeous decorative feeling. The earring includes a supporting portion formed in a shape of a letter C to be put along a root of a human ear and a decorative body provided at an end of the supporting portion, wherein one end of the supporting portion is caught by an upper end of the ear, and a central part of the supporting portion abuts against a reverse side of the root of the ear. The decorative body is exchangeable.
Owner:并木敏贵
Biosoluble ultrafine glass wool and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108658457AThin diameterLow thermal conductivityGlass making apparatusGlass fiberBiological body
The invention discloses biosoluble ultrafine glass wool and a preparation method thereof. The biosoluble ultrafine glass wool comprises the following chemical components by mass: 60-68 parts of SiO2,0 to 3 parts of Al2O3, 6 to 12 parts of CaO and MgO, 15 to 20 parts of Na2O and K2O, 4 to 4.9 parts of B2O3, 3 to 5 parts of BaO, and no more than 4 parts of Fe2O3, SO3, ZrO2 and CeO2, wherein the content of CeO2 is not less than 0.5 part. The biosoluble ultrafine glass wool has good biosolubility and thermal insulation properties; the ultrafine glass wool has a small fiber diameter and a low thermal conductivity (wherein thermal conductivity at room temperature can be as low as 0.03 W / (m.K)), and is good in heat preservation effect; once the glass wool is inhaled into a respiratory system byan organism, or even enters the lung, the half-life of the glass wool is less than 40 days, and the glass wool can be quickly dissolved by the lung fluid of the organism and does not cause any inflammation.
Owner:CHONGQING MAGU FIBER NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com