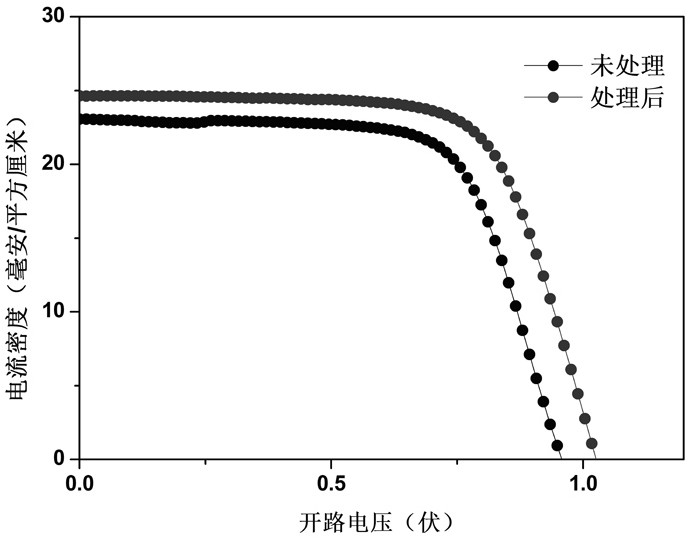
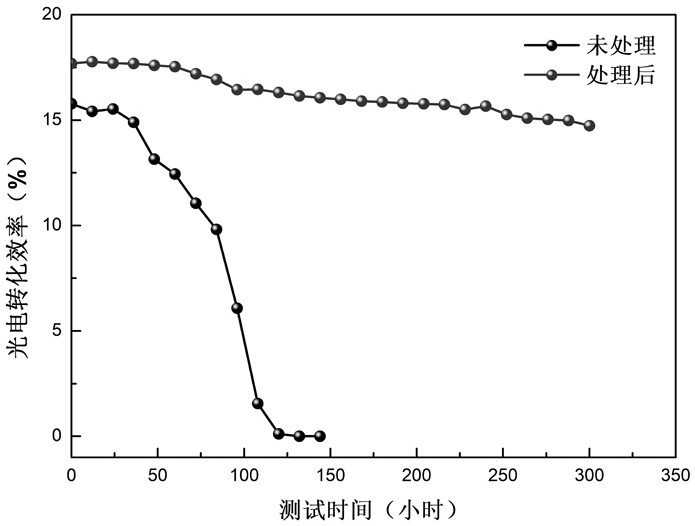
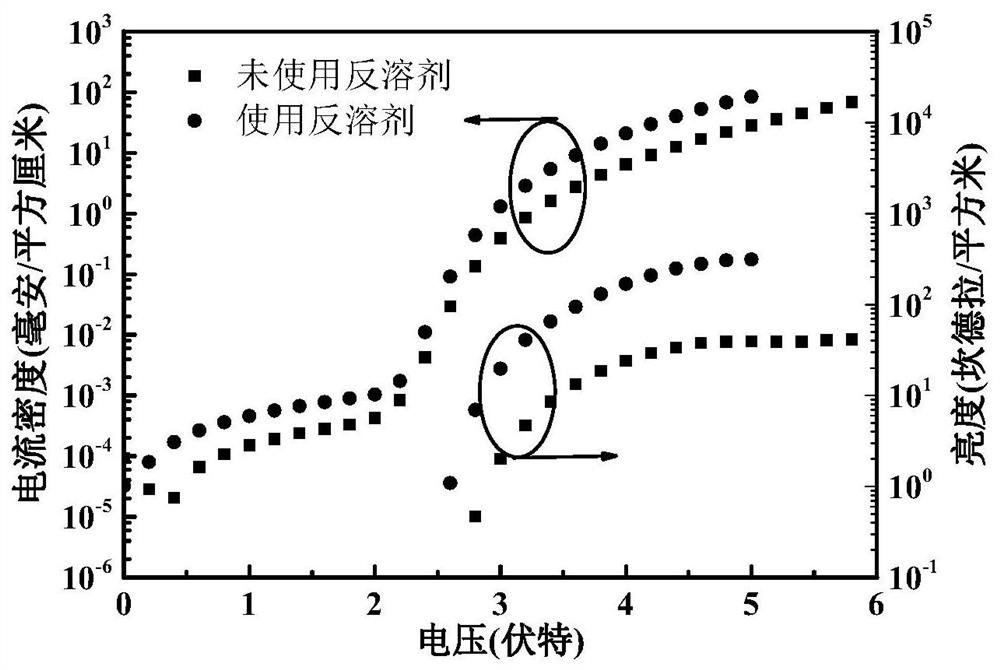
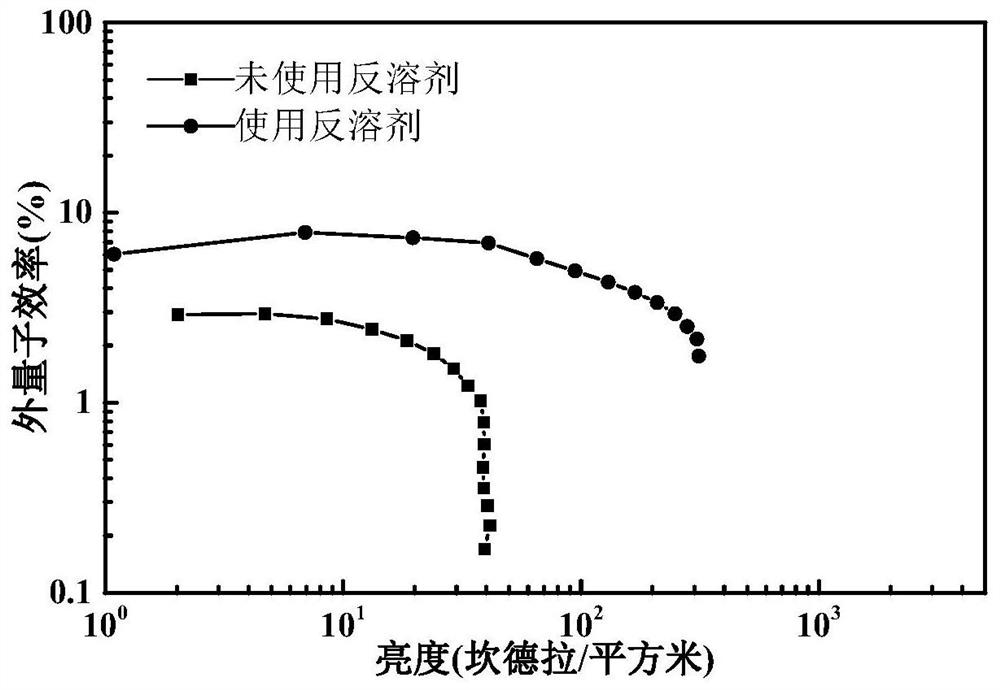
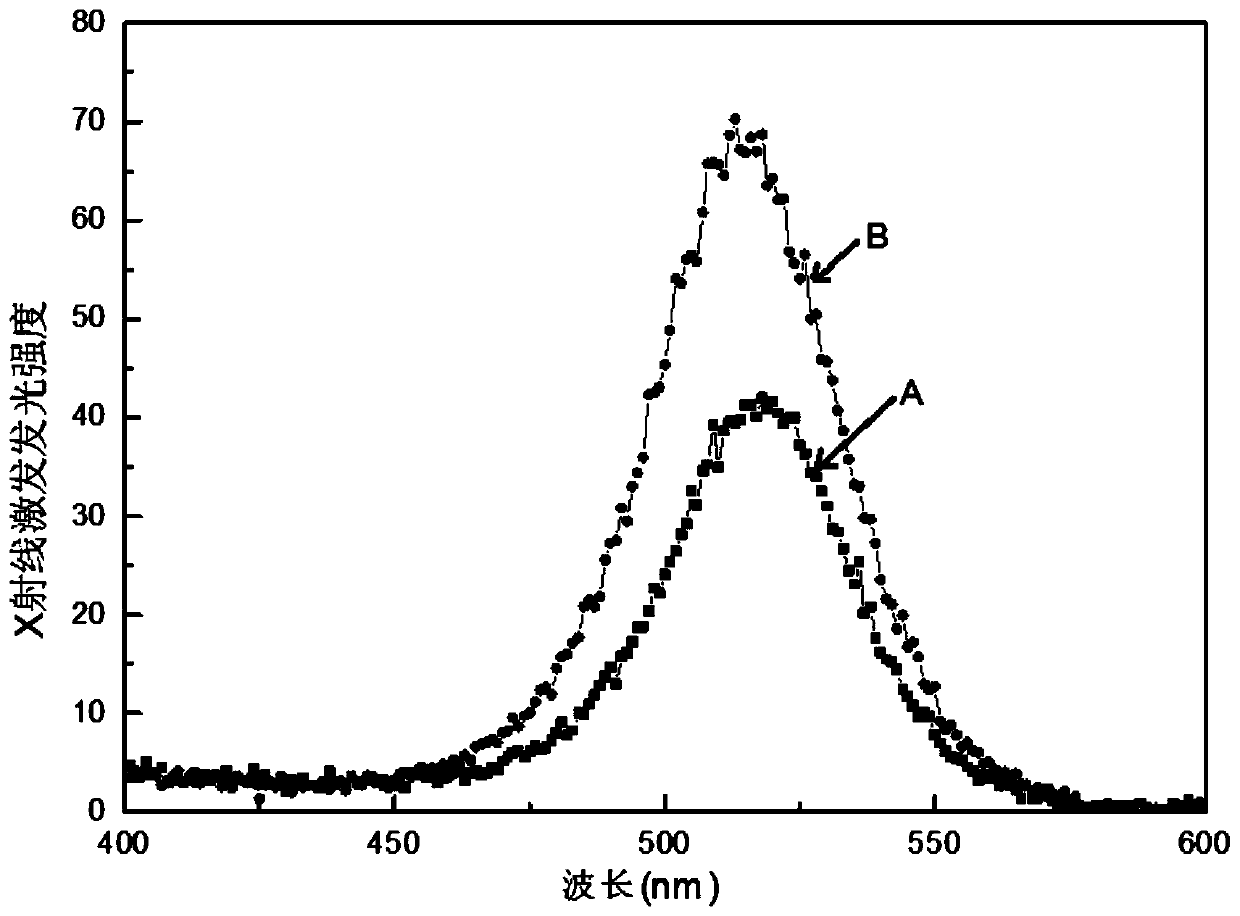
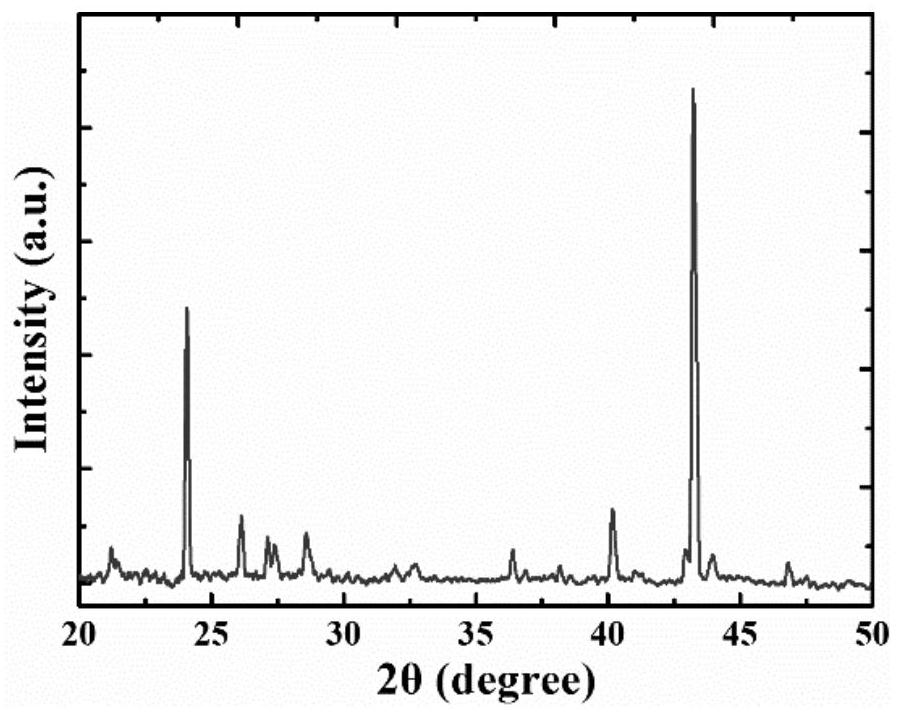
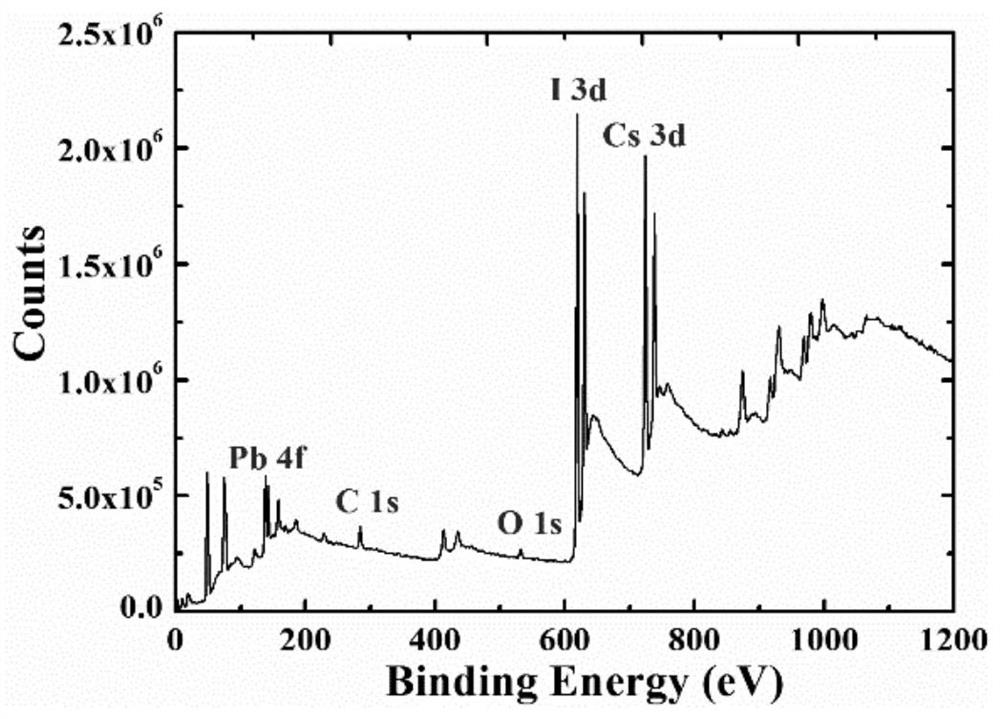
Patents
Literature
79 results about "Caesium iodide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
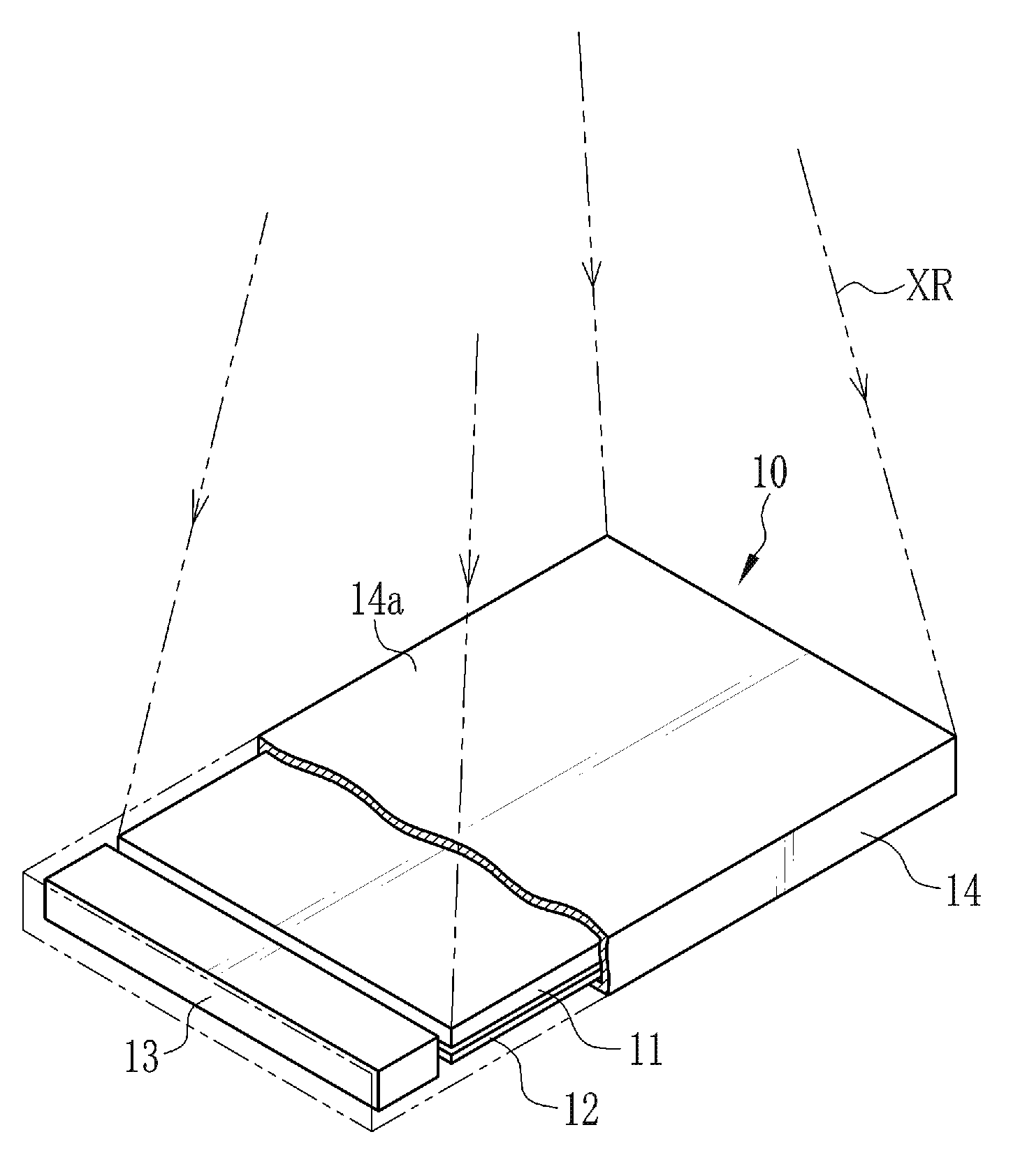
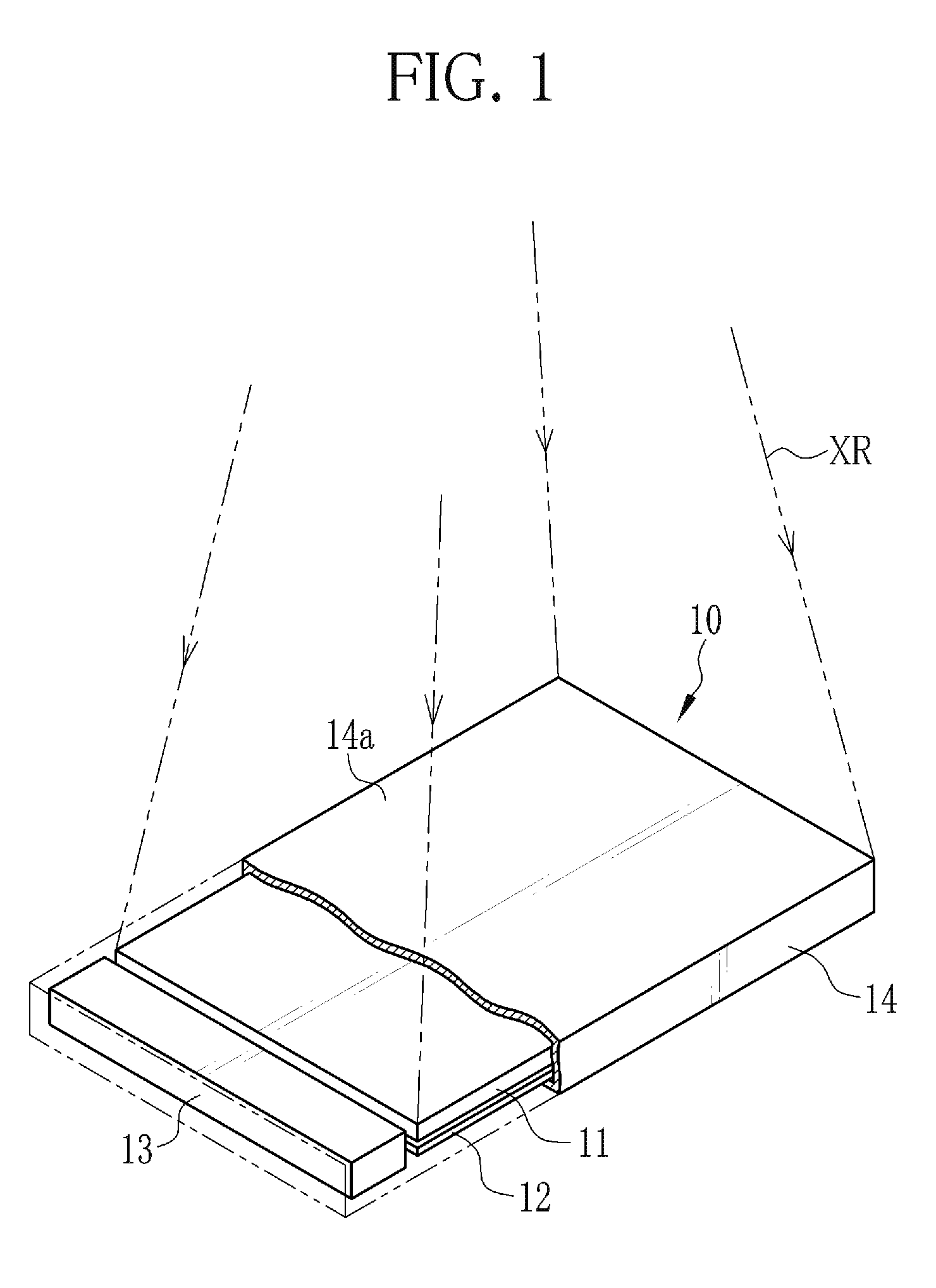
Caesium iodide or cesium iodide (chemical formula CsI) is the ionic compound of caesium and iodine. It is often used as the input phosphor of an X-ray image intensifier tube found in fluoroscopy equipment. Caesium iodide photocathodes are highly efficient at extreme ultraviolet wavelengths.
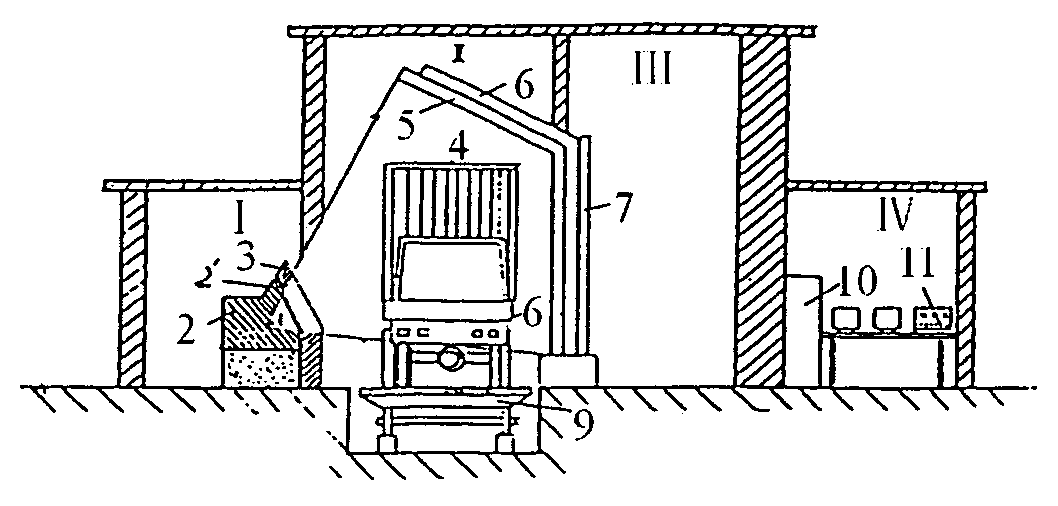
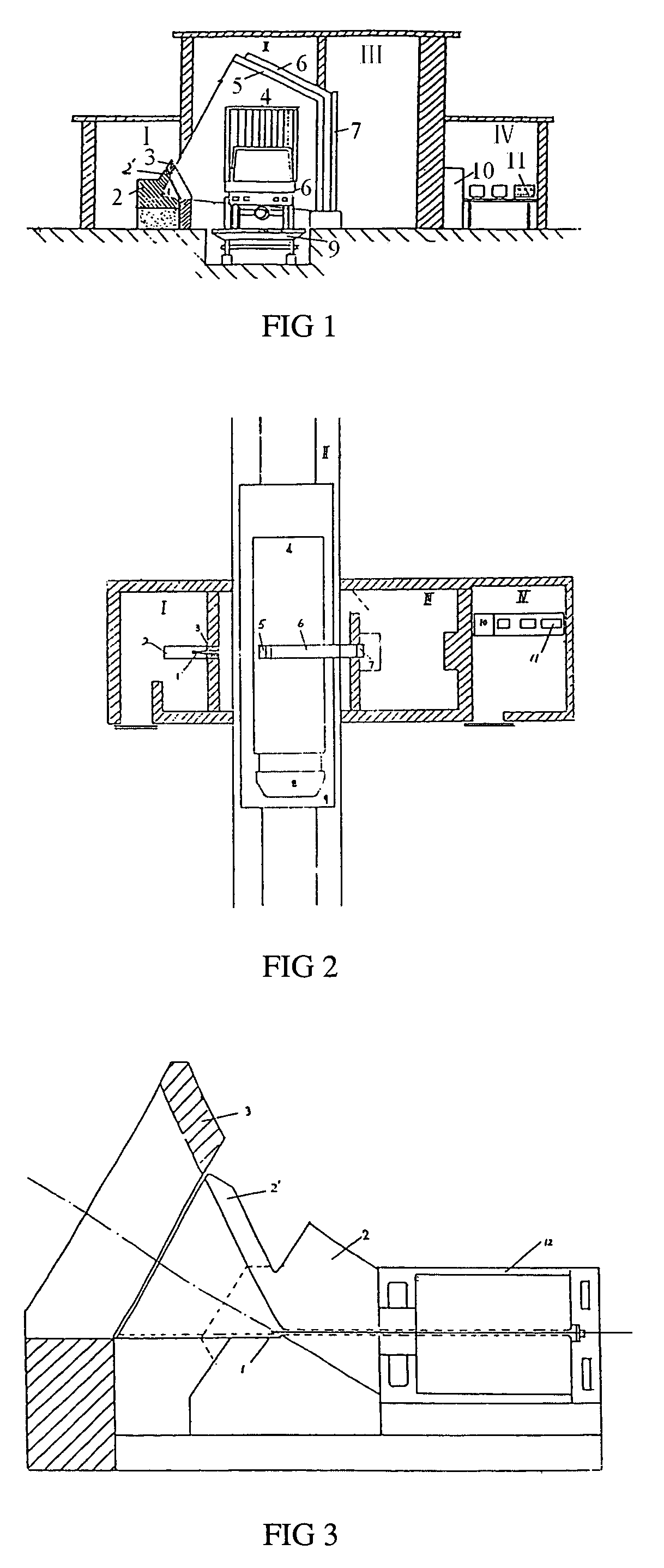
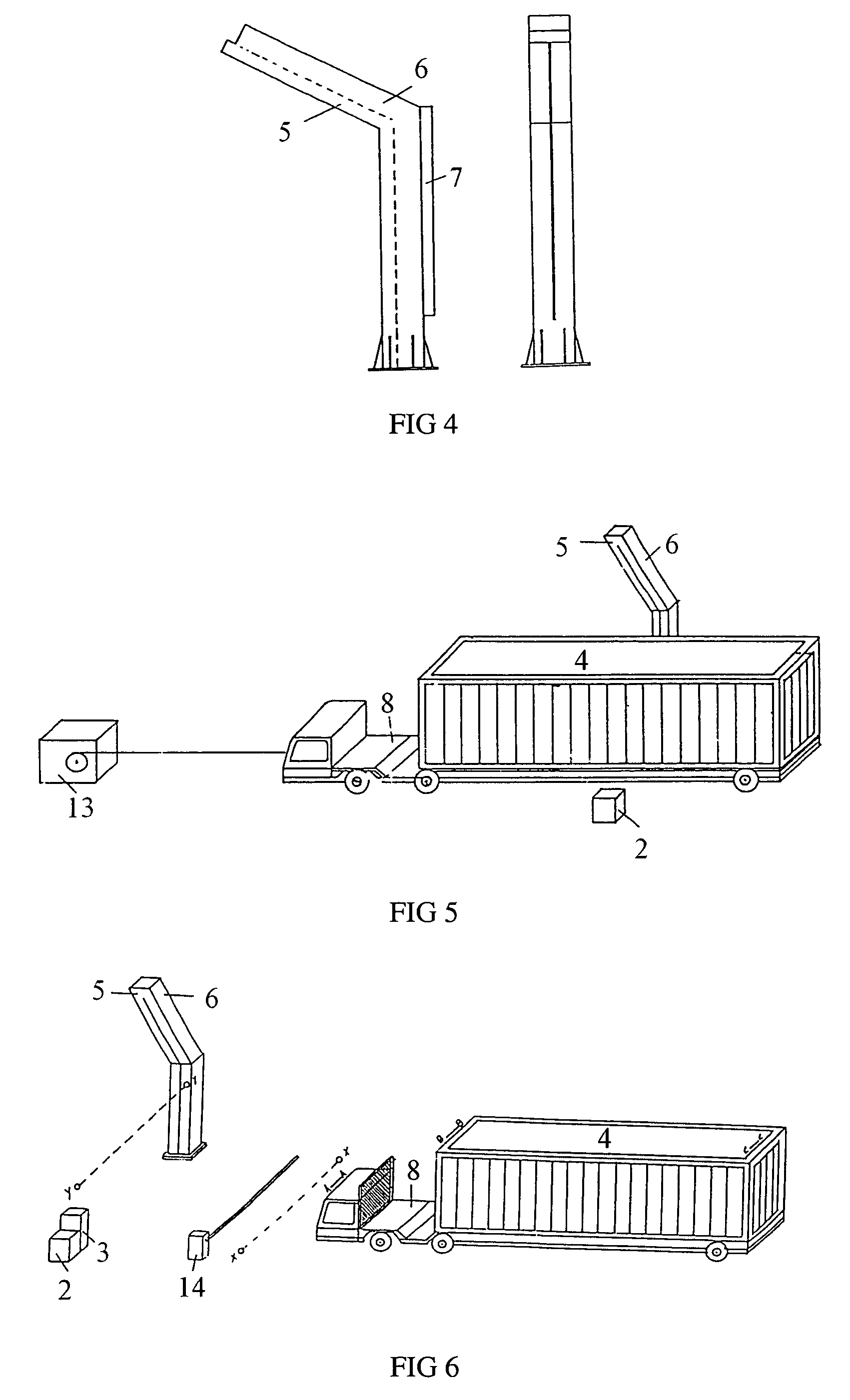
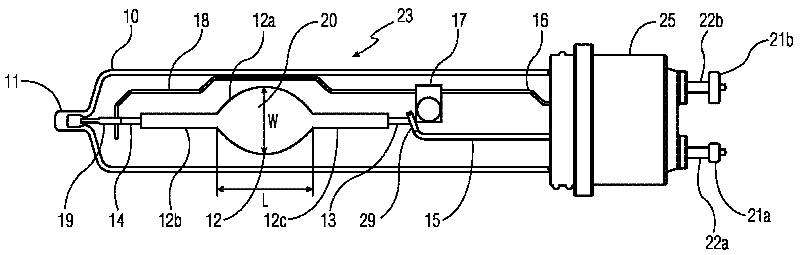
Container inspection system using cobalt-60 γ-ray source and cesium iodide or cadmium tungstate array detector
InactiveUS7082186B2Easy to produceLow costHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentAutomatic controlNuclear engineering
A container inspection equipment with cobalt-60 γ-ray source and cesium iodide or cadmium tungstate detector includes a cobalt-60 γ-ray source, a cask, a front collimator, a rear collimator, a cesium iodide or cadmium tungstate detector, signal and image processing systems, container trailer system, and automatic control system. The cask of the cobalt-60 γ-ray source, the beam shutter, and the front collimator are fixed on the same chassis to form an integration and placed in the source room. The rear collimator, cesium iodide or cadmium tungstate array detector and the radiation catcher are fixed on the same chassis to form an integration and placed in the detector room. A container inspection tunnel is formed between the source room and the detector room. The equipment is mainly used for inspecting smuggling goods and contrabands etc., in large containers, container trucks, train carriage and air containers. The equipment either can be installed in the sea port and land frontier customs or installed at the air port, vital communication line, and railway station.
Owner:BEIJING ISOTOPE NUCLEAR ELECTRONICS MACHINE
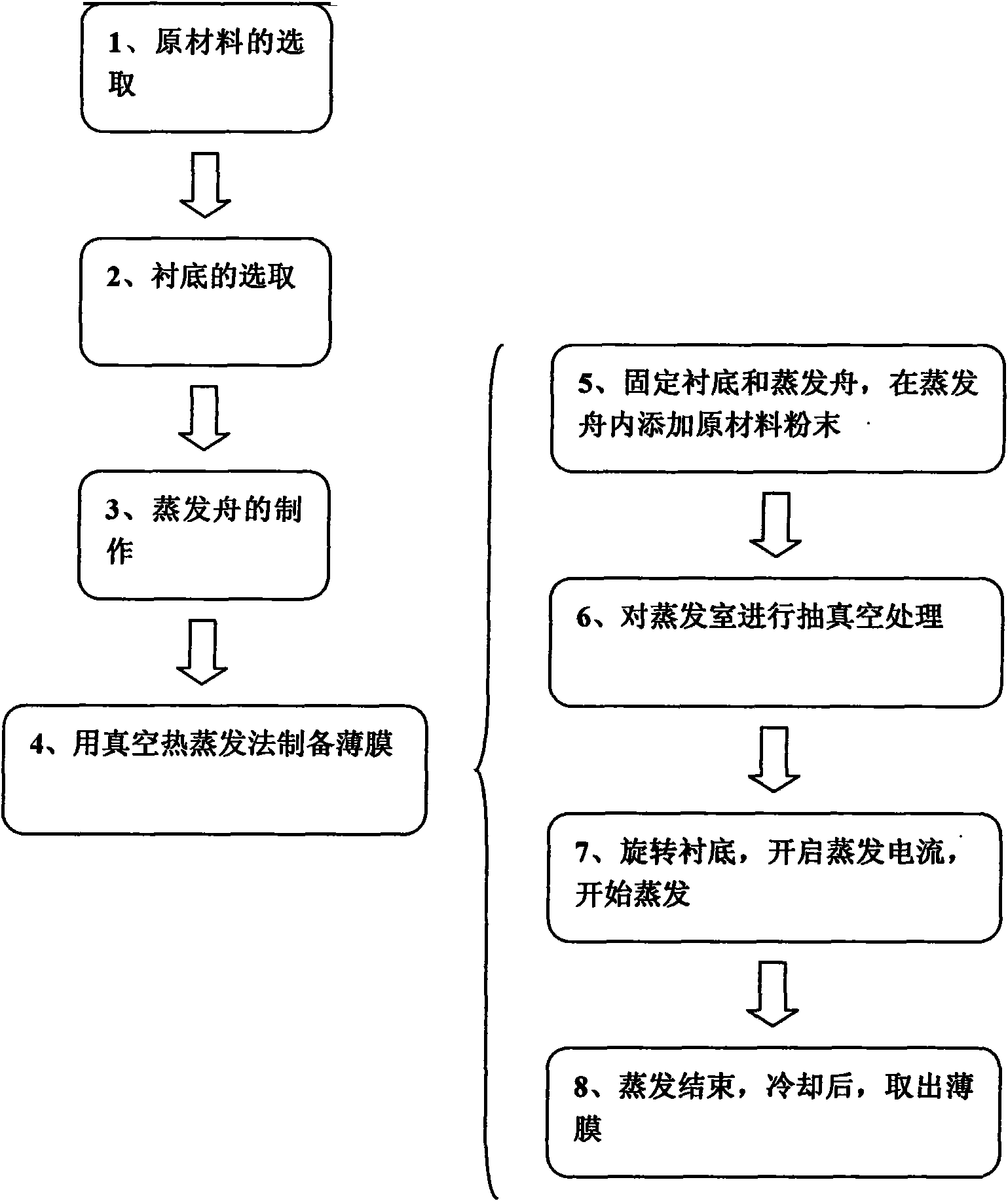
Method for preparing thallium-doped caesium iodide (CsI:T1) film
InactiveCN101967678AEasy to makeLow costPolycrystalline material growthFrom condensed vaporsCMOSPolymer science
The invention relates to a preparation technology of a functional film material and provides a method for preparing a thallium-doped caesium iodide (CsI:T1) film. According to the method, the high-performance 50-100 micrometer thallium-doped caesium iodide (CsI:T1) film which is attached to the substrate very well and compatible with a CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor transistor) process can be prepared on a substrate uniformly and compactly by adopting a thermal evaporation mode, and the thallium-doped caesium iodide (CsI:T1) film can be widely applied to X-ray detectors.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Radiotherapy Apparatus
ActiveUS20110142202A1Reduce skin doseAvoid insufficient thicknessX-ray tube electrodesHandling using diaphragms/collimetersHigh energyX-ray
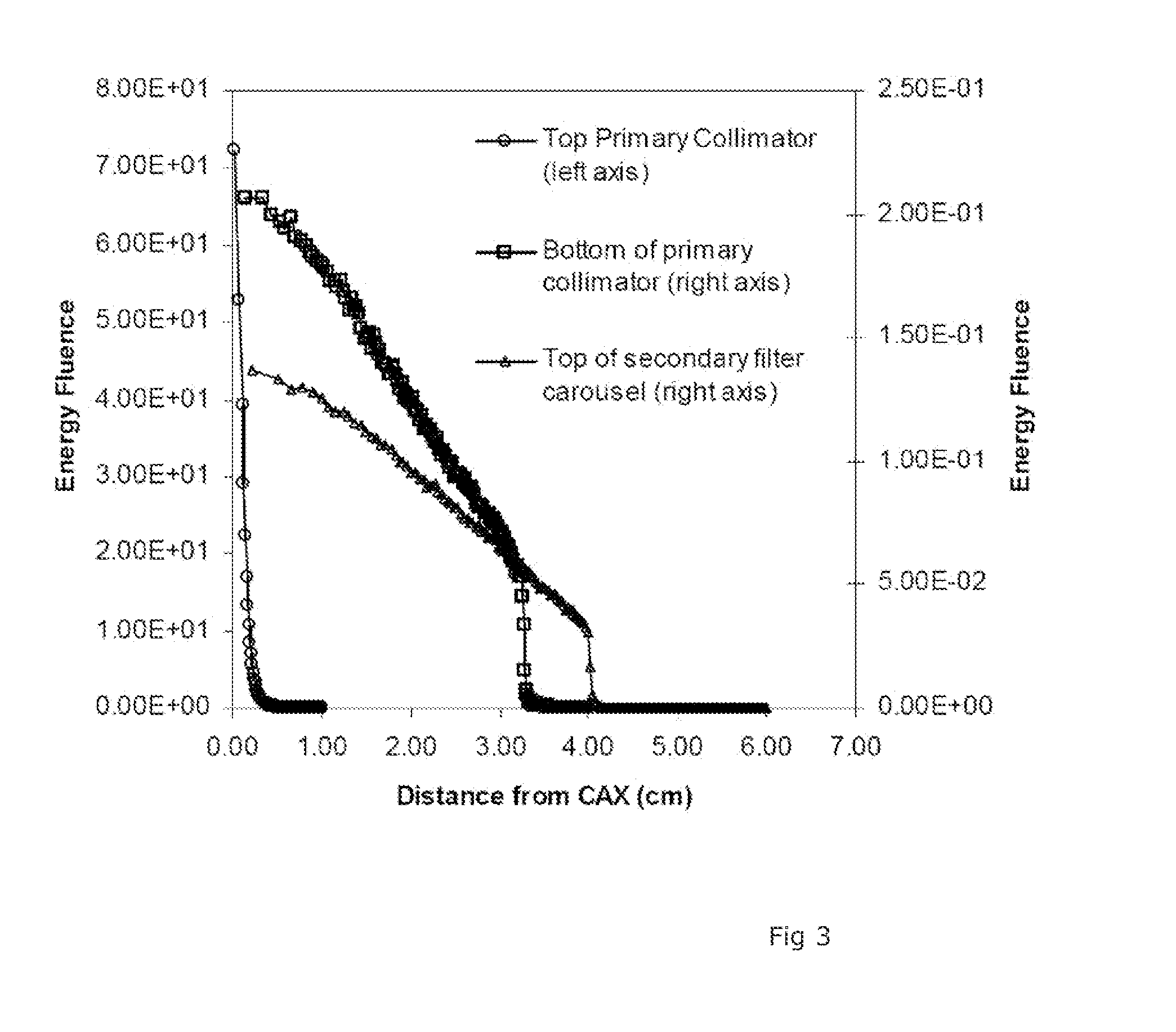
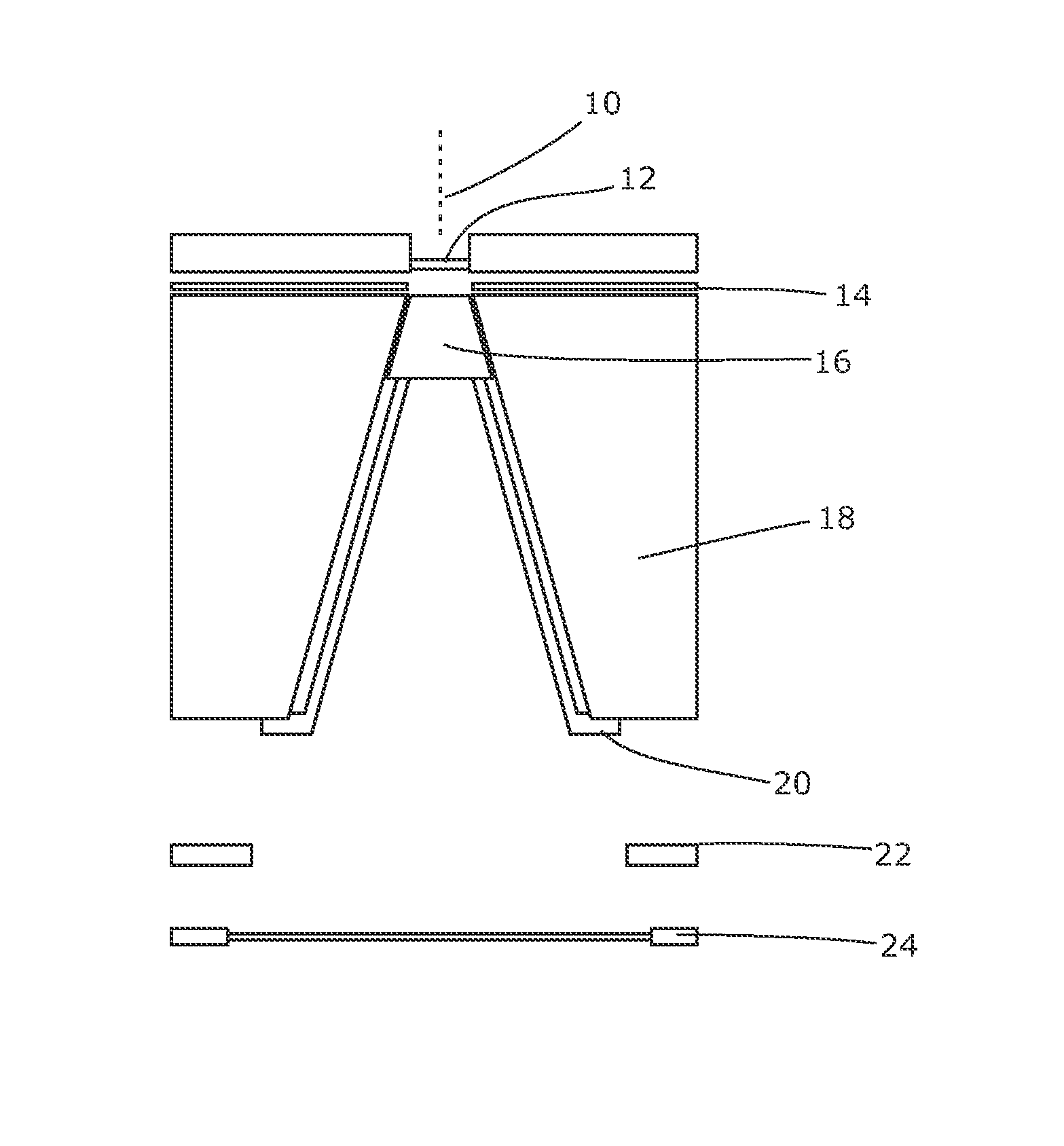
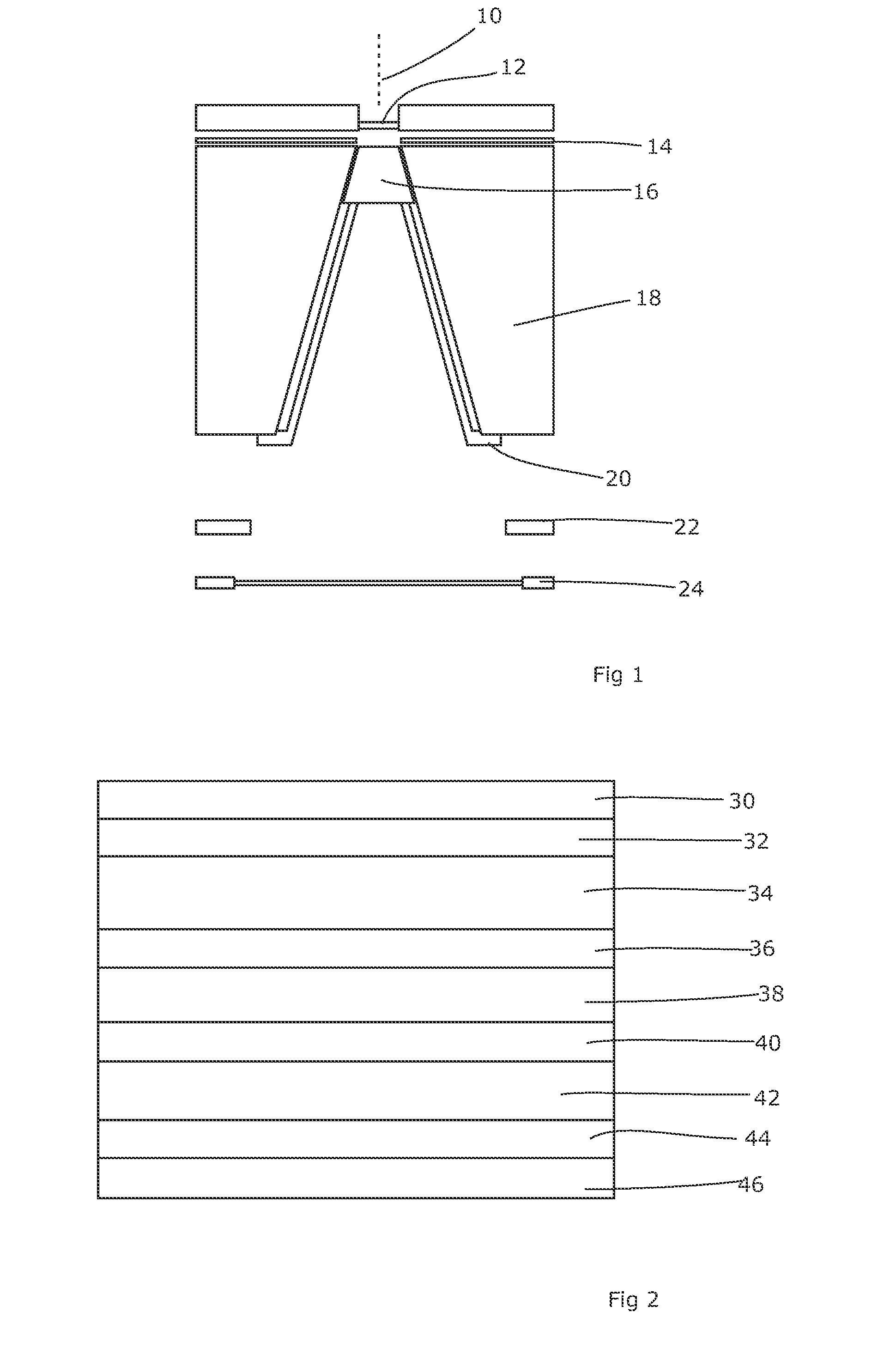
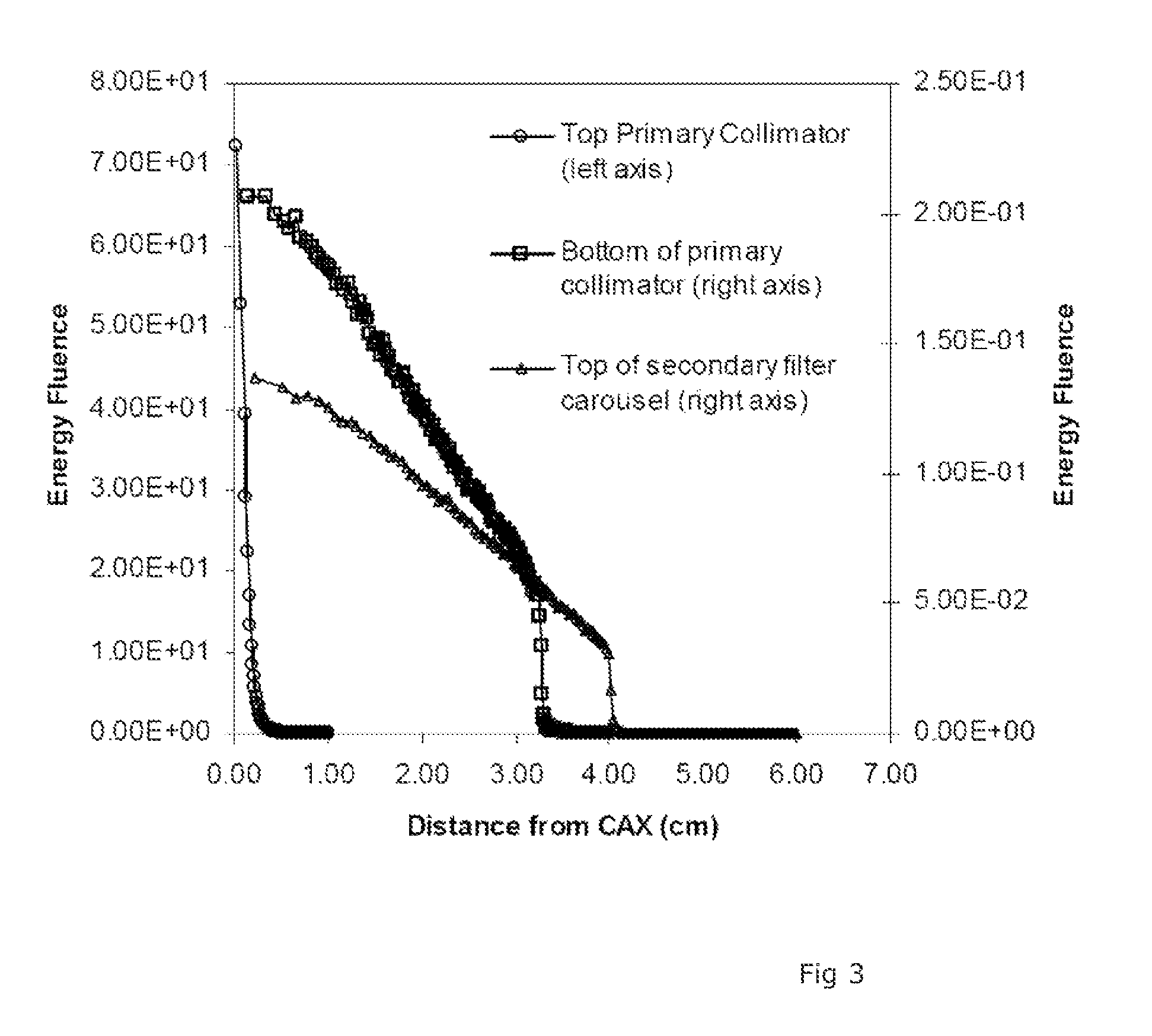
It is desirable to achieve a co-incident investigative kV source for a therapeutic MV source—a so-called “beams-eye-view” source. It has been suggested that bremsstrahlung radiation from an electron window be employed; we propose a practical structure for achieving this which can switch easily between a therapeutic beam and a beam-eye-view diagnostic beam capable of offering good image resolution. Such a radiation source comprises an electron gun, a pair of targets locatable in the path of a beam produced by the electron gun, one target of the pair being of a material with a lower atomic number than the other, and an electron absorber insertable into and withdrawable from the path of the beam. In a preferred form, the electron gun is within a vacuum chamber, and the pair of targets are located at a boundary of the vacuum chamber. The lower atomic number target can be Nickel and the higher atomic number target Copper and / or Tungsten. The electron absorber can be Carbon, and can be located within the primary collimator, or within one of a plurality of primary collimators interchangeably locatable in the path of the beam. Such a radiation source can be included within a radiotherapy apparatus, to which the present invention further relates. A flat panel imaging device for this source can be optimised for low energy x-rays rather than high energy; Caesium Iodide-based panels are therefore suitable.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
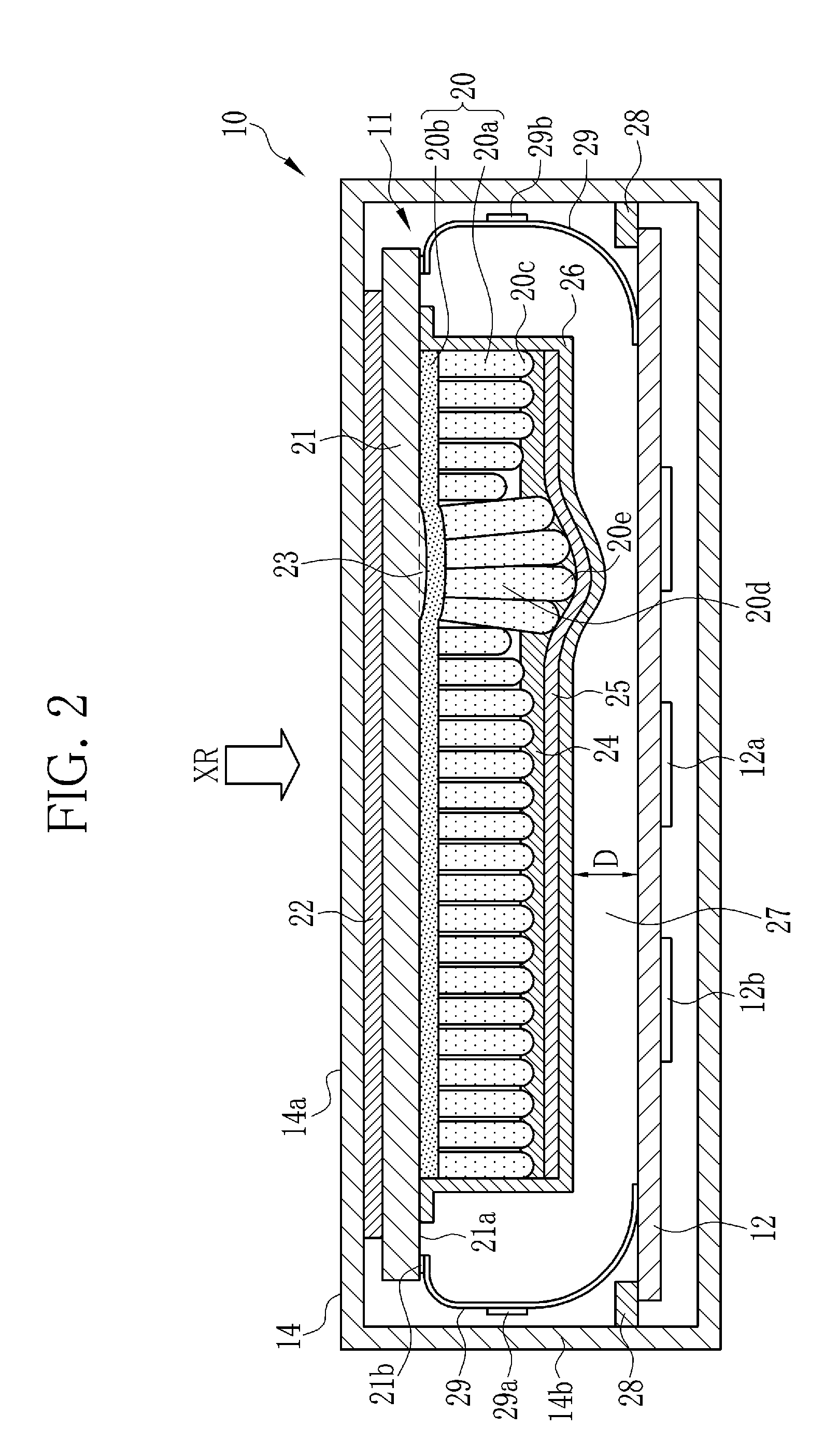
Radiographic image detection device
InactiveUS20150204987A1Material analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementImage detectionEngineering
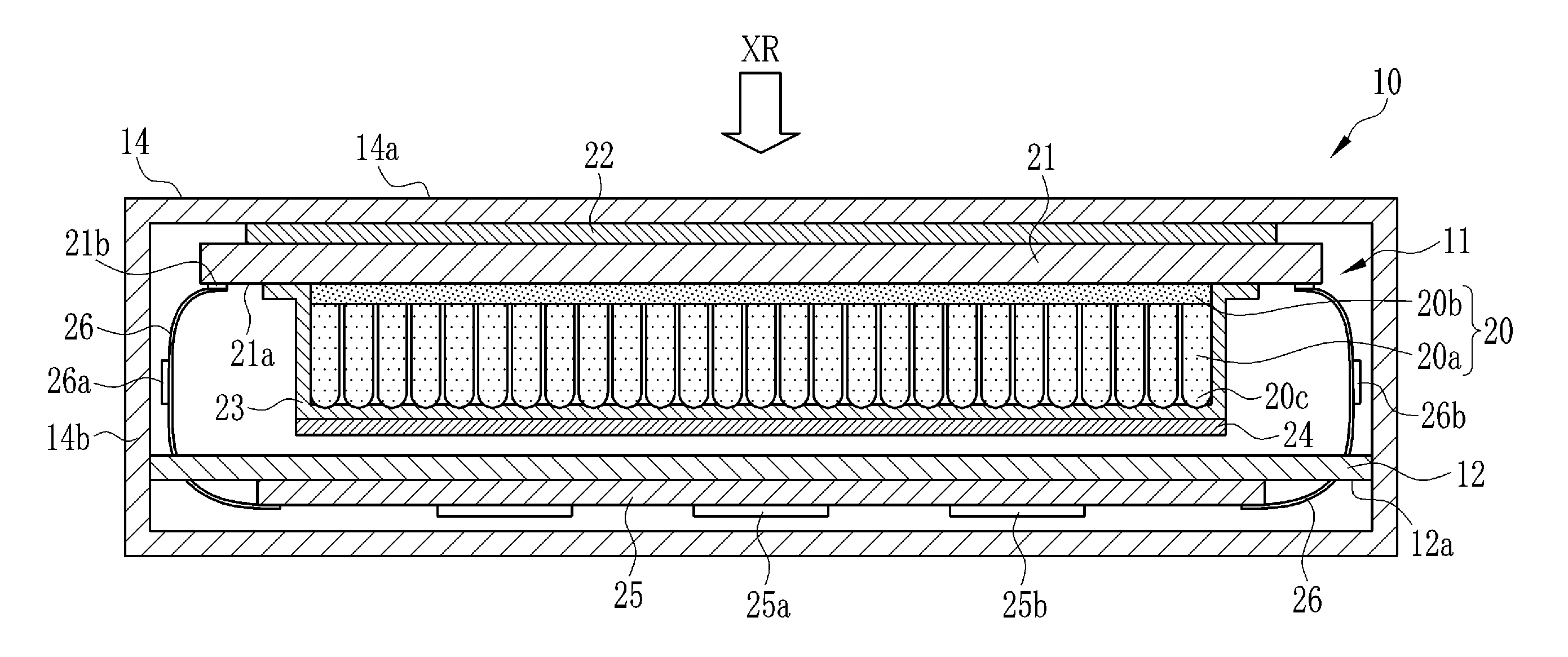
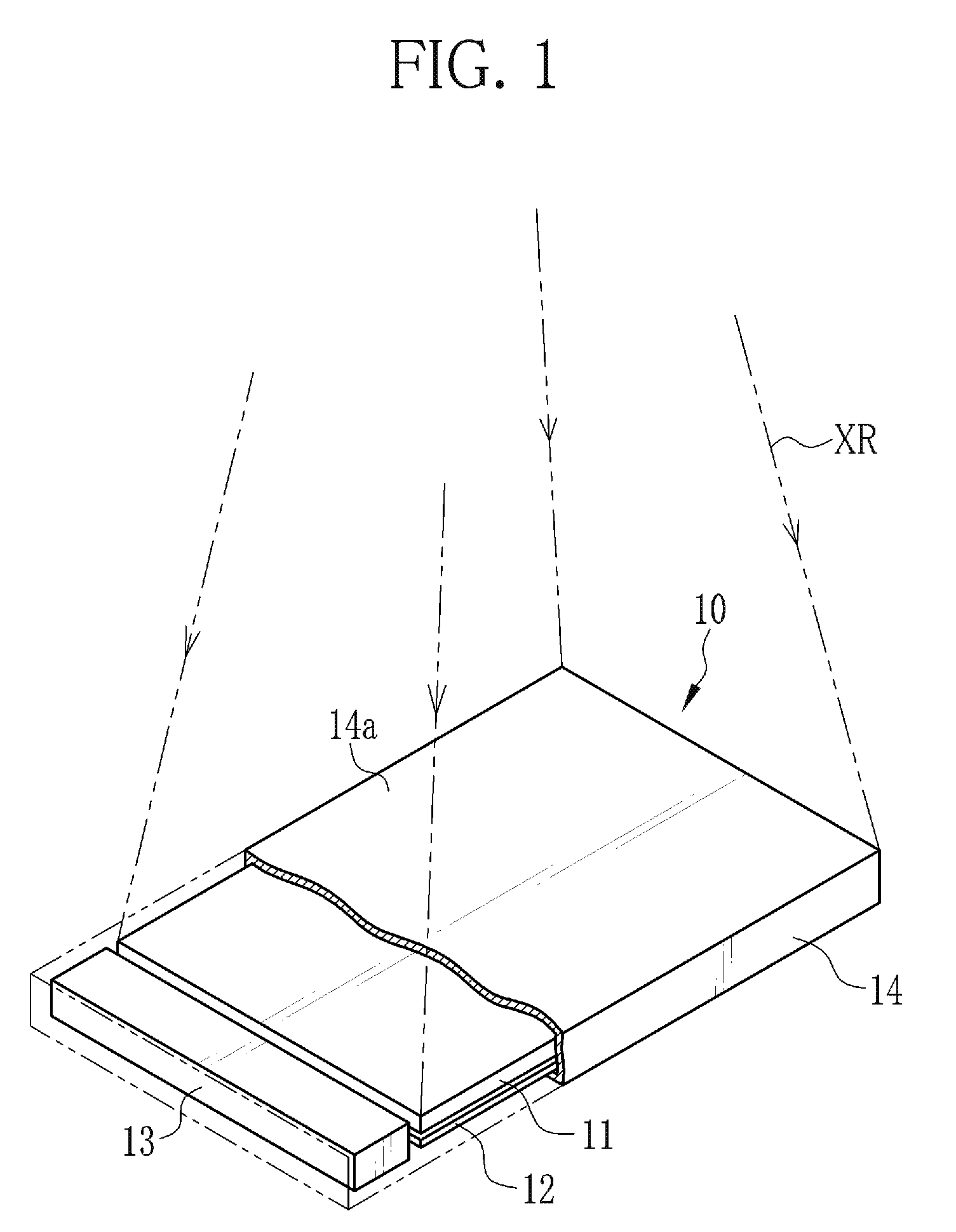
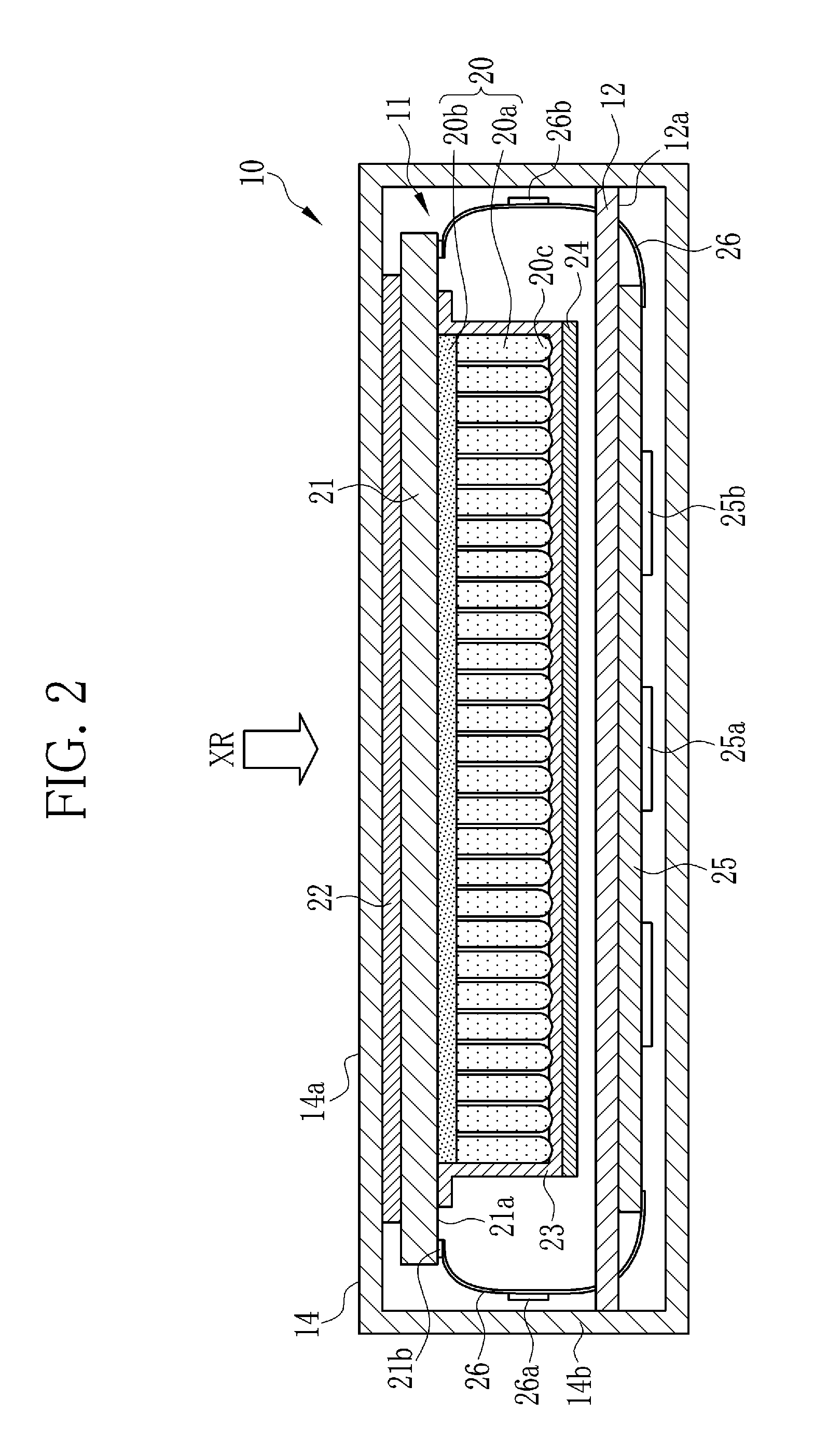
In a photoelectric conversion panel, a plurality of TFTs are formed over an insulating substrate. The TFTs are covered by a first planarizing film. A plurality of photodiodes are formed over the first planarizing film. The photodiodes and the first planarizing film are covered by a second planarizing film. A scintillator contains cesium iodide and is directly vapor-deposited over the photoelectric conversion panel. The scintillator is formed in an area, over the second planarizing film, extending to the outside of an area in which the TFTs and the photodiodes are formed and located inside edges of the first and second polarizing films.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
A preparation method of inorganic perovskite thin film and application in solar cell
InactiveCN109148642ALow annealing temperatureReduce lossFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationPorosityPerovskite solar cell
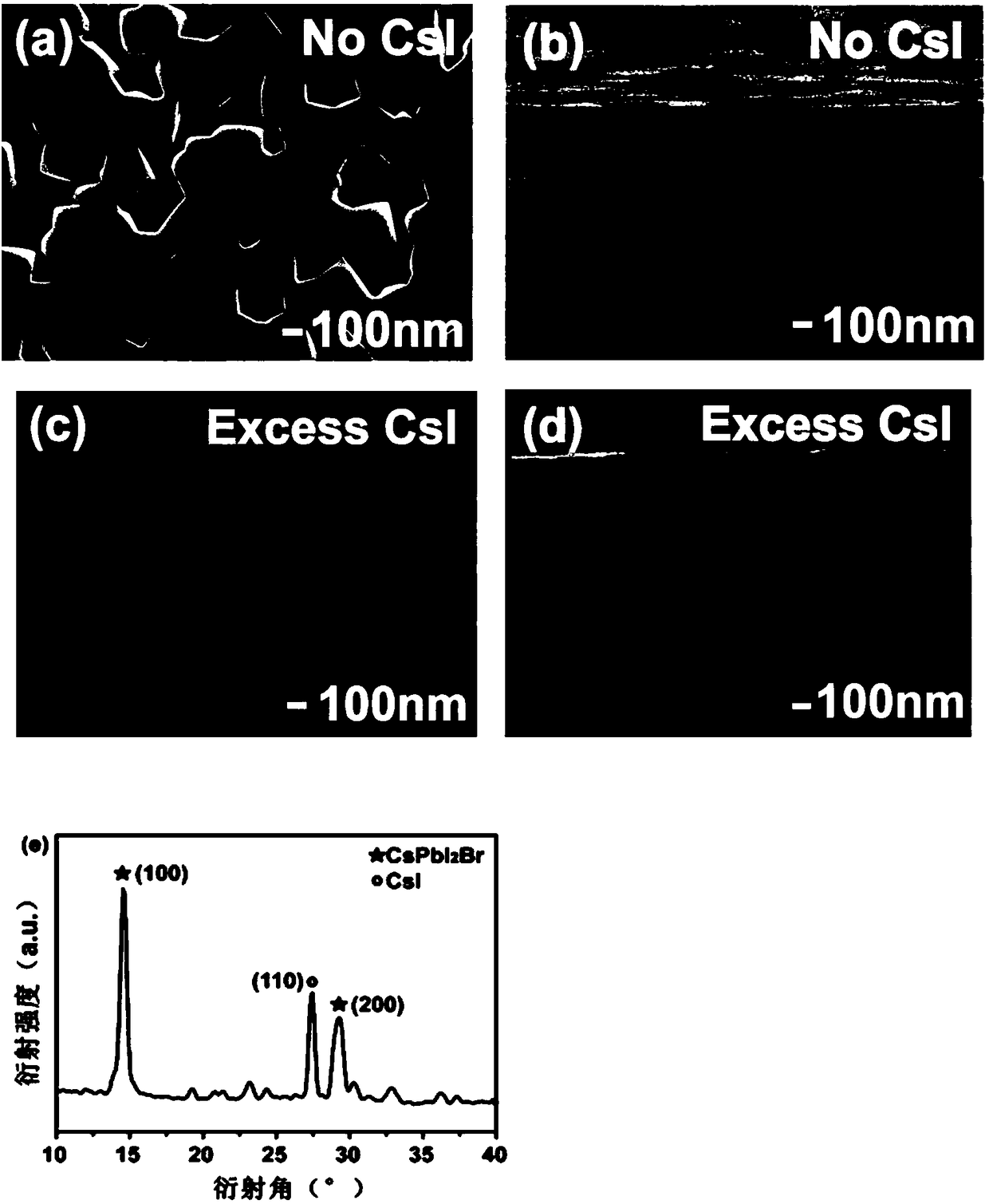
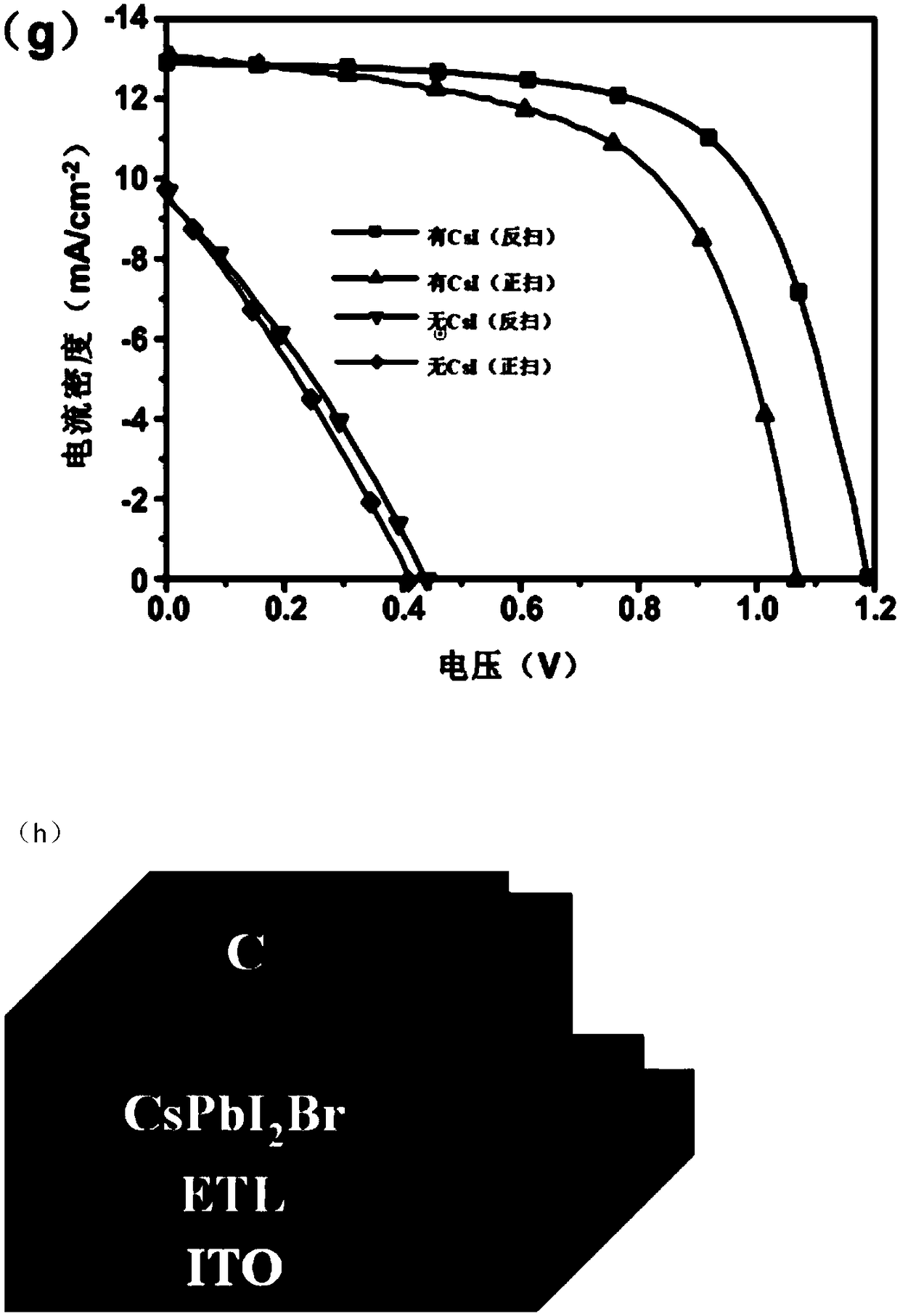
The invention relates to a preparation method of an inorganic perovskite thin film and an application in a solar cell, belonging to the technical field of solar cells. Excess cesium iodide is added asan additive to an inorganic perovskite solutio to deposite a high-quality inorganic perovskite film, the obtained thin film is used as light absorbing layer in the solar cell. The method can obtain the inorganic perovskite thin film with low porosity, uniform and compact, and greatly reduce the annealing temperature of the thin film and greatly reduce the energy consumption. The photovoltaic performance of inorganic halide perovskite solar cells can be greatly improved by applying the device to perovskite solar cells, and the prepared device has excellent environmental stability and repeatability, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production. As that technological condition such as the addition amount of the cesium iodide additive, the thickness of the active layer, the anneal temperature and the like are optimized, the invention is applied to a carbon-based all-inorganic perovskite solar cell, the photoelectric conversion efficiency can exceed 10%, and the photoelectric conversion efficiency has good stability.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
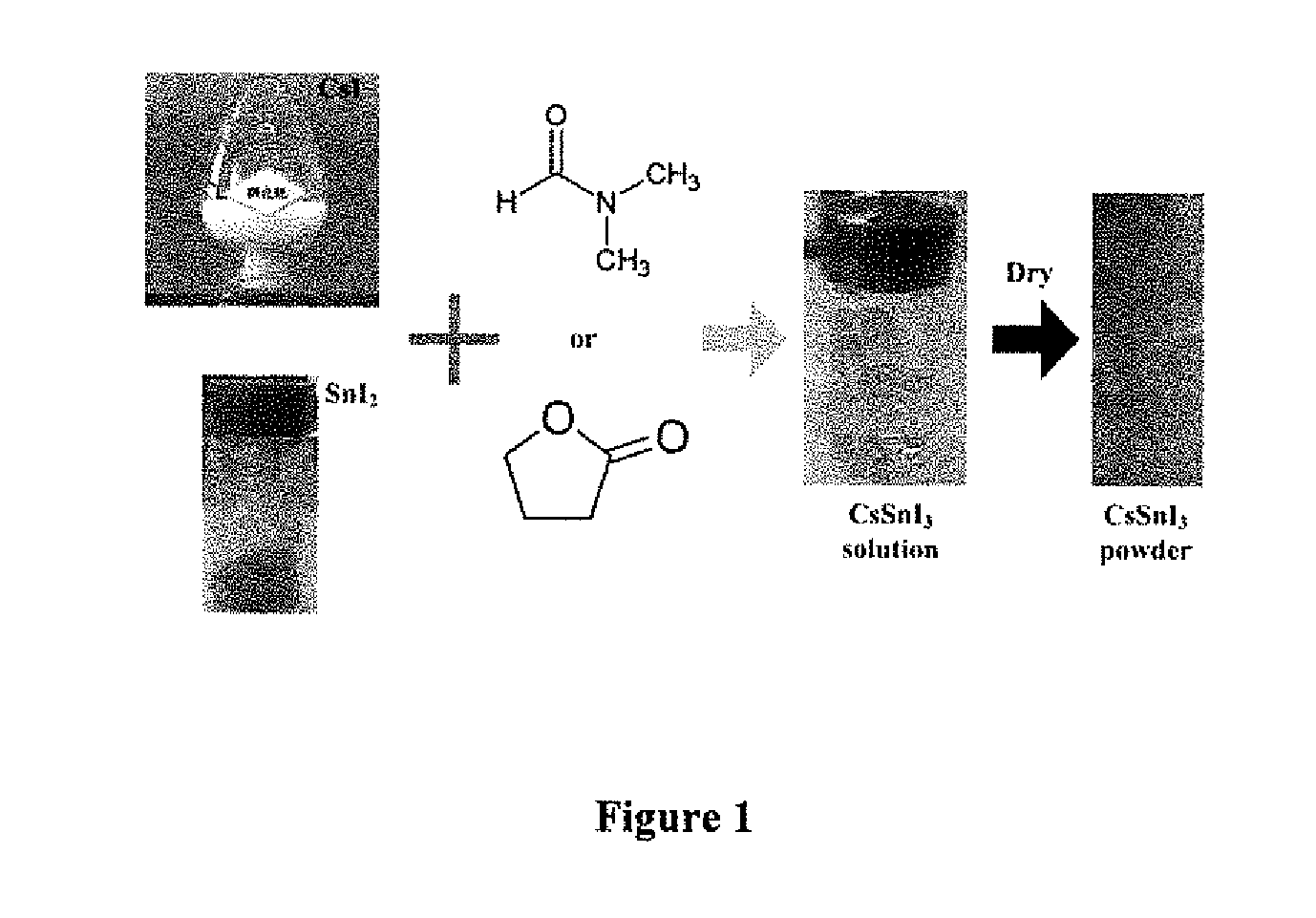
SYNTHESIS OF CsSnI3 BY A SOLUTION BASED METHOD
This invention discloses a solution based synthesis of cesium tin tri-iodide (CsSnI3). More specifically, the CsSnI3 is fabricated in an organic Perovskite precursor solvent. CsSnI3 are ideally suited for a wide range of applications such as light emitting and photovoltaic devices.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHANGYUE OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
Zero-dimensional Cs3Cu2I5 perovskite scintillation crystal and application thereof
ActiveCN112048764AHigh transparencyImprove stabilityPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsScintillation crystalsCesium iodide
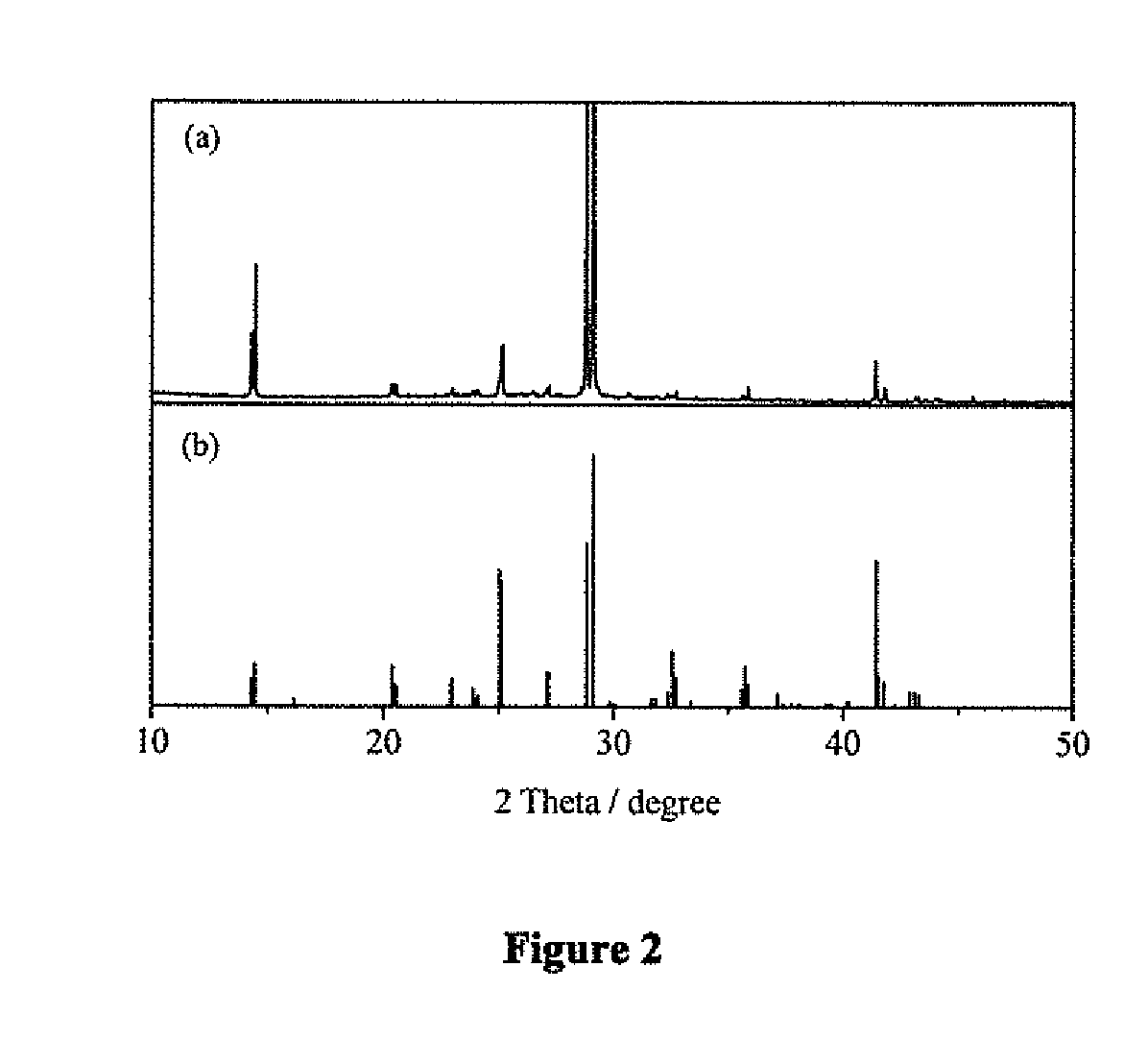
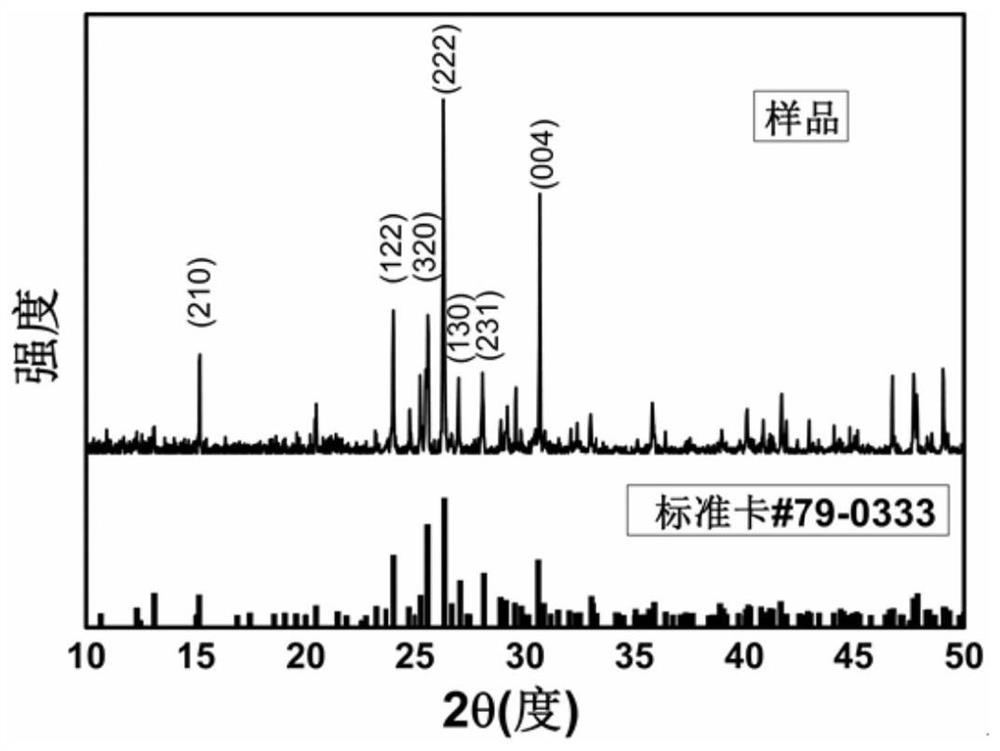
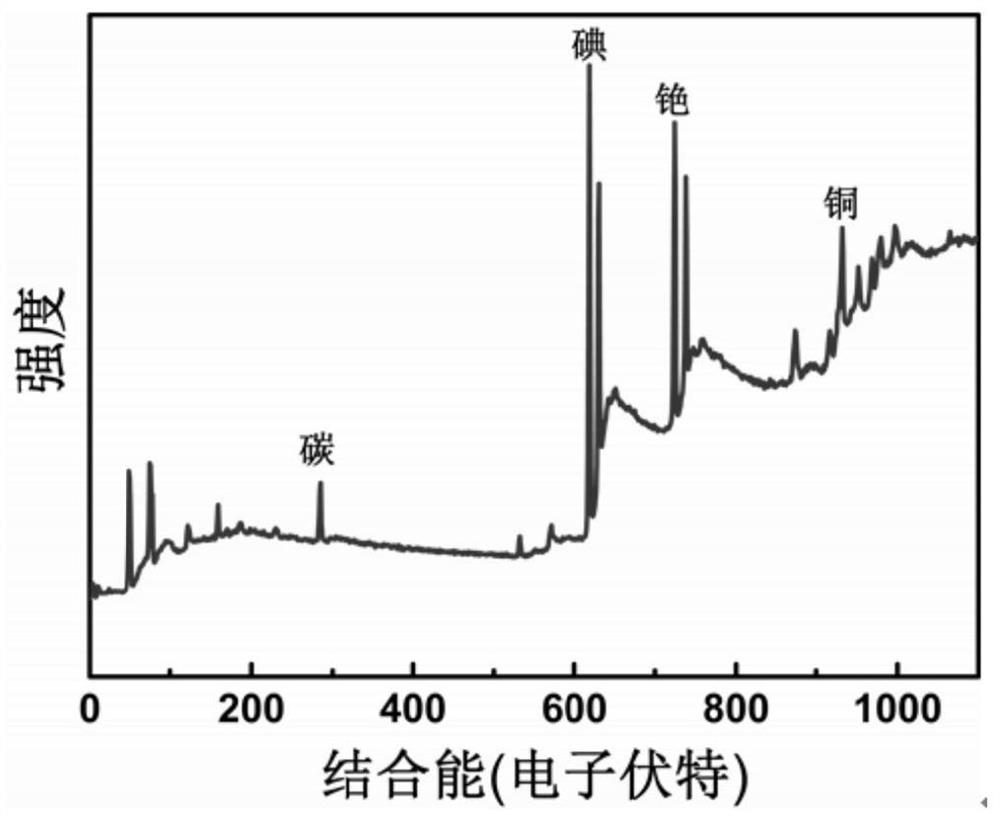
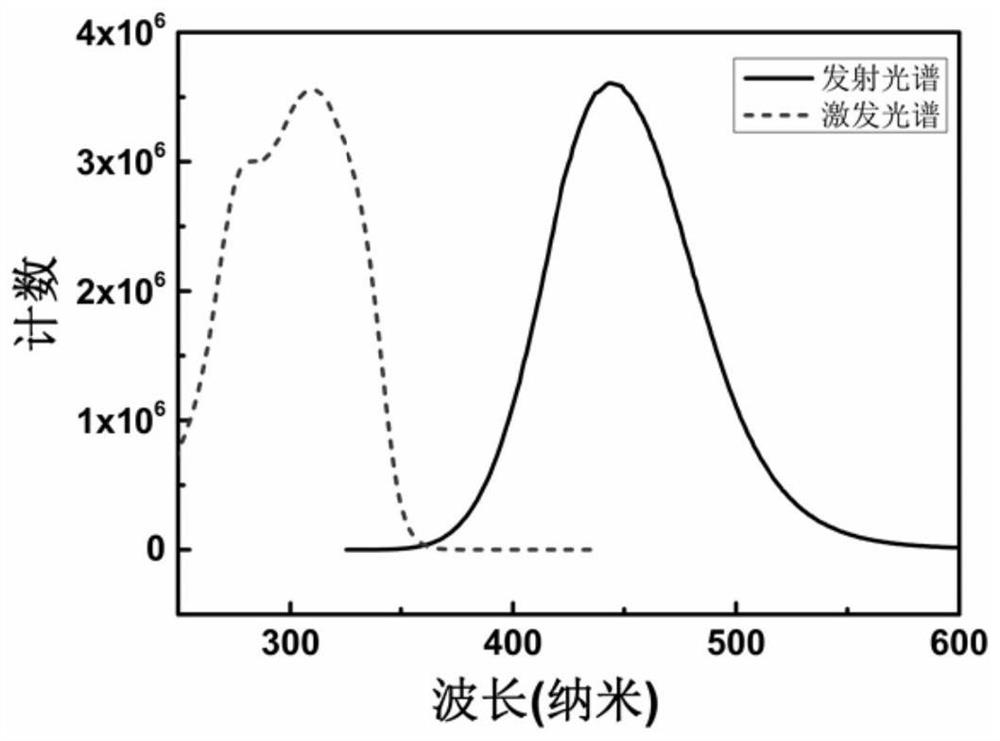
The invention discloses a zero-dimensional Cs3Cu2I5 perovskite scintillation crystal and application thereof. The zero-dimensional Cs3Cu2I5 perovskite scintillation crystal is prepared through the steps that firstly, N, N-dimethylformamide and dimethyl sulfoxide are mixed evenly to prepare a mixed solution, cesium iodide and cuprous iodide are added into the mixed solution, stirring is conducted to prepare a supersaturated precursor solution, and finally crystal growth is conducted through an inverse temperature crystallization method after the supersaturated precursor solution is filtered. When the Cs4PbI6 perovskite crystal is prepared, the inverse temperature crystallization method is adopted, operation is easy, controllability is high, repeatability is good, and large-scale industrialproduction can be achieved; meanwhile, the crystal prepared by the method is good in transparency, good in stability, high in quantum luminous efficiency and high in responsivity, and can be used fornuclear radiation detection.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Radiotherapy apparatus
ActiveUS8355482B2High contrast imageEasy to switchX-ray tube electrodesHandling using diaphragms/collimetersHigh energyX-ray
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Perovskite precursor solution for improving stability of perovskite solar cell
ActiveCN111740015AImprove stabilityPoor uniformityFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesSolar batteryCesium iodide
The invention discloses a perovskite precursor solution for improving the stability of a perovskite solar cell, and the method comprises the steps of adding ioformamidine and cesium iodide into a solvent, adding bromomethylamine after stirring, adding lead iodide and 3, 4-dichloroaniline after stirring, and obtaining the perovskite precursor solution for improving the stability of the perovskite solar cell through stirring; spin coating the perovskite precursor solution for improving the stability of the perovskite solar cell on a substrate, and obtaining a perovskite thin film through thermalannealing as a light absorption layer of the solar cell. The perovskite precursor solution for improving the stability of the perovskite solar cell prepared by the invention replaces an existing perovskite layer, the defects in the existing perovskite mineralization technology are solved, and a perovskite stability improvement means that has low requirements for the process environment, is convenient in preparation method, can realize the long-time stable performance in a common environment and is used for the cell preparation process, is provided.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Red perovskite light emitting diode based on mixed halogen and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111916571ASuppress generationReduce movementSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCesium iodideLight-emitting diode
The invention discloses a red perovskite light-emitting diode based on mixed halogen and a preparation method thereof. The light-emitting diode sequentially comprises a transparent substrate, an anode, a hole injection layer, a hole transport layer 1, a hole transport layer 2, a perovskite light-emitting layer, an electron transport layer, an electron injection layer and a cathode, wherein the perovskite light-emitting layer is prepared by spin-coating a perovskite precursor solution; dropwise adding an anti-solvent in the spin coating process, wherein the perovskite precursor solution is prepared by dissolving cesium iodide CsI, cesium bromide CsBr, lead bromide PbBr2, lead iodide PbI2, organic ammonium bromide salt LBr and organic ammonium iodide salt LI in a polar solvent. By combininglarge-size organic cations with mixed halogens, the generation of a non-luminous active perovskite phase is inhibited, the movement of halogen ions is reduced, and the spectral stability is realized while the brightness and efficiency of the red perovskite LED are improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Radiographic image detection device
ActiveUS20150204986A1Avoid damageMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation diagnosticsImage detectionEngineering
A monocoque-structured housing accommodates a photoelectric conversion panel, a scintillator, and a circuit board in this order from an X-ray incidence side. The scintillator contains cesium iodide and converts X-rays into visible light. The scintillator is vapor-deposited on the photoelectric conversion panel. A plurality of pixels that photoelectrically convert the visible light into charges are formed in the photoelectric conversion panel. A signal processor, which reads out the charge from each pixel and generates image data, is mounted on the circuit board. A gap layer is formed between the scintillator and the circuit board.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Thallium-doped caesium iodide scintillator and application thereof
InactiveCN104762657AHigh flicker efficiencyReduce afterglowPolycrystalline material growthVacuum evaporation coatingRadiation imagingSingle crystal
The invention discloses a thallium-doped caesium iodide scintillator and an application thereof; the thallium-doped caesium iodide scintillator is thallium-ytterbium co-doped cesium iodide and has the following composition general formula: (Cs1-x-yTlxYby)(I1-yM2y) or (Cs1-x-yTlxYby)(I1-yM3y), wherein M is I, Br, Cl or F, 0<x<=0.05, and 0<y<=0.05. A thallium-doped caesium iodide thin film and a single-crystal fiber prepared by the thallium-doped caesium iodide scintillator have excellent properties of high scintillation efficiency and low afterglow, and can be widely applied in the field of X-ray radiation imaging.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
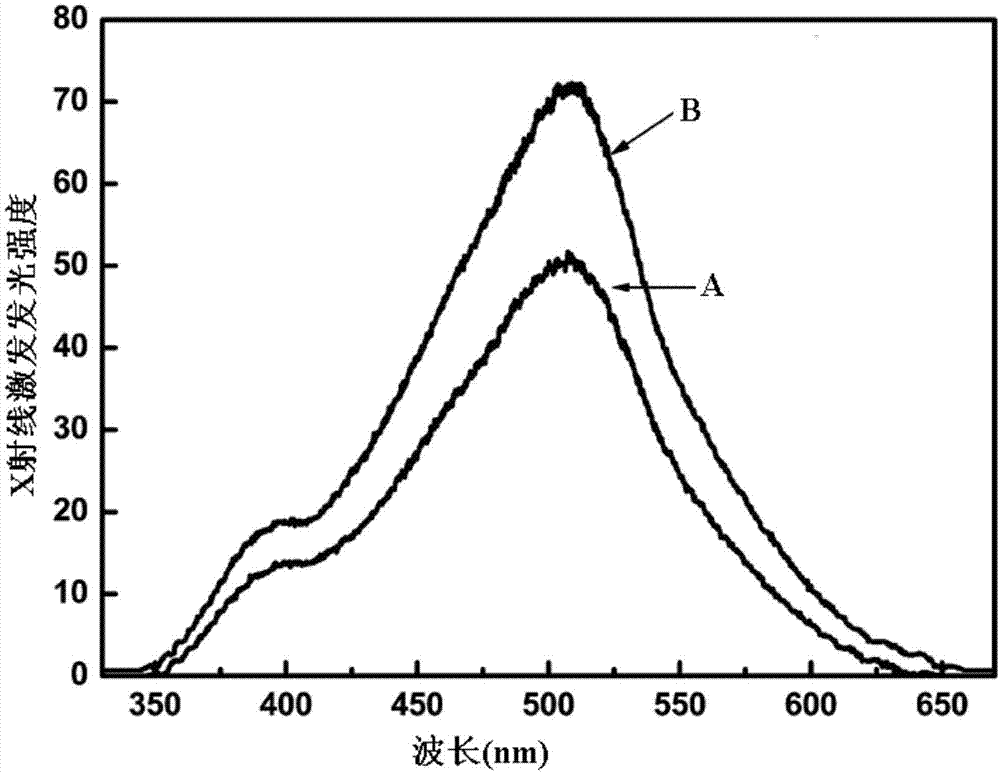
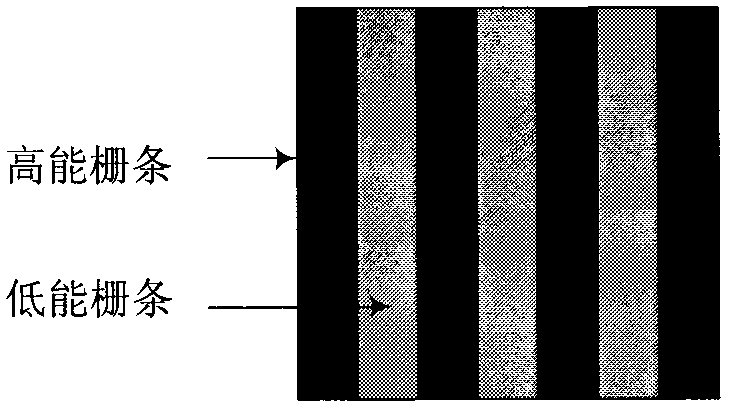
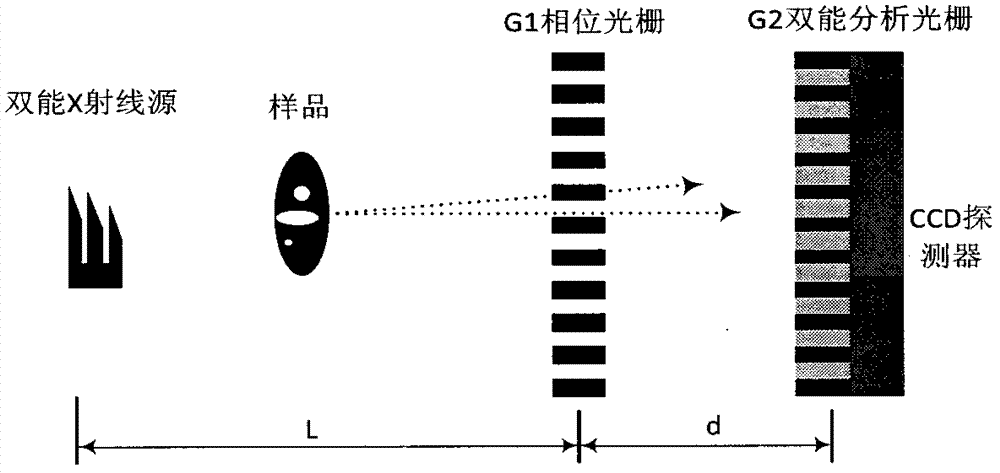
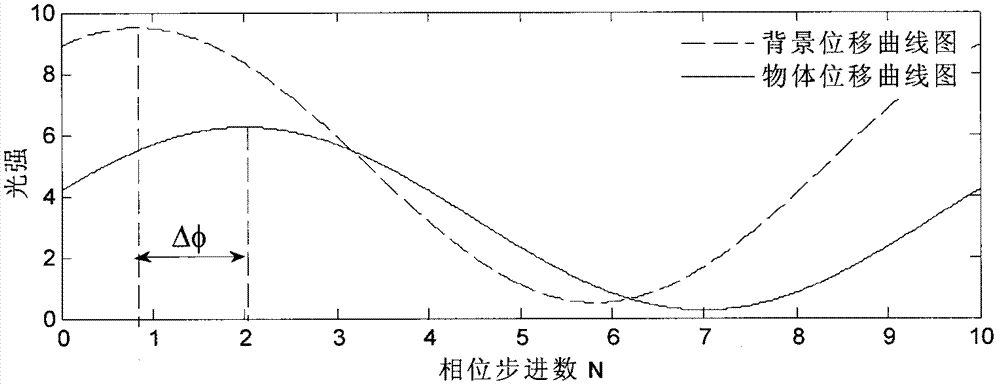
Dual-energy analysis grating
PendingCN107290359AReduce radiationSimple calculationMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationX-rayEngineering
The invention relates to a dual-energy analysis grating. The dual-energy analysis grating mainly comprises high-energy grate bars and low-energy grate bars. The high-energy grate bars can be used for converting high-energy X rays into visible light and screening low-energy X rays, and the low-energy grate bars can be used for converting the low-energy X rays into the visible light and screening the high-energy X rays. The grating is made from caesium iodide (CsI) and bismuth (Bi). According to the dual-energy analysis grating, the defects of the traditional analysis gratings are overcome, and the dual-energy analysis grating is used for converting the X rays of different energies instead of stepping; by applying the dual-energy analysis grating to a dual-energy imaging system, steps of imaging are reduced, the requirements on mechanical accuracy are lowered, and the imaging system is simplified.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
High-fluorescence-efficiency inorganic lead-free perovskite material and preparation method thereof
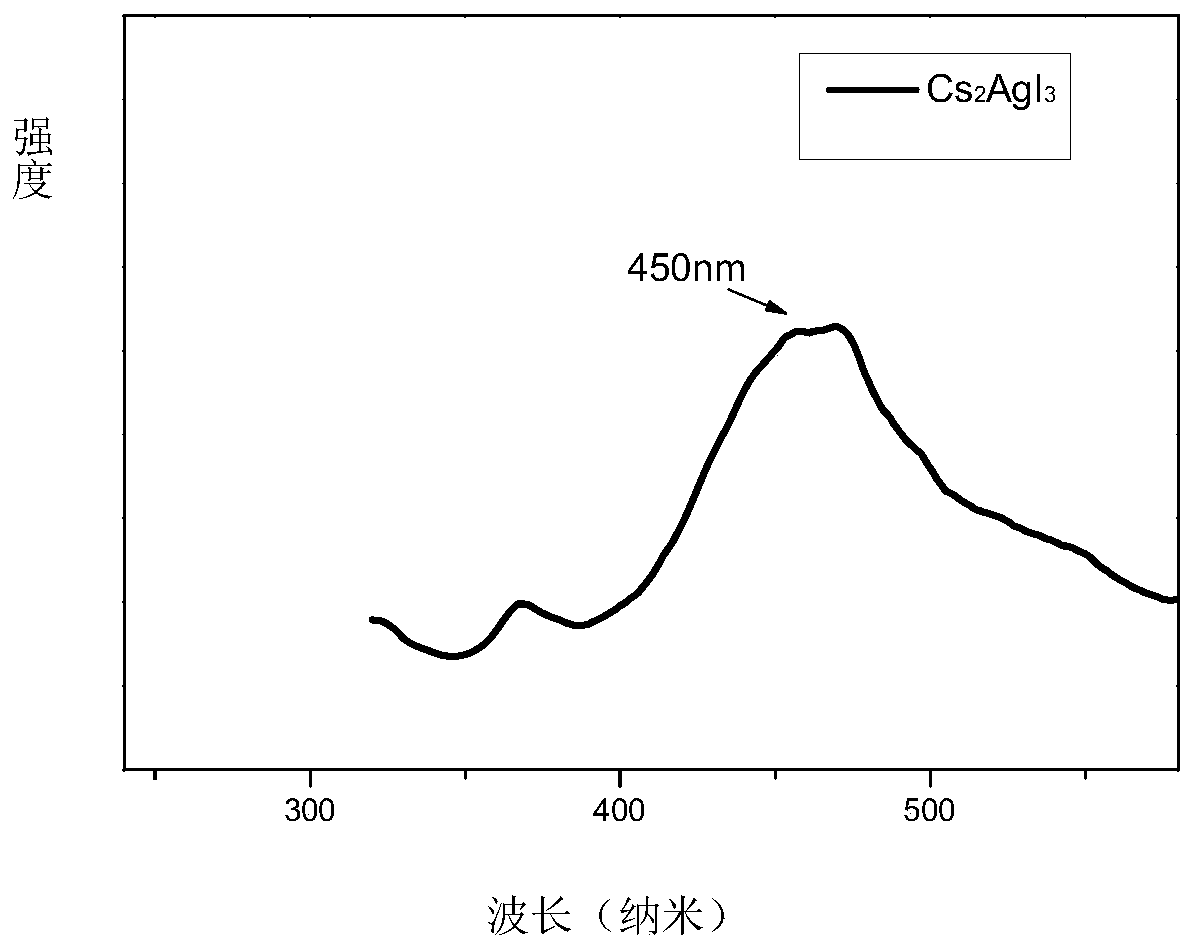
ActiveCN112480911AImprove fluorescence efficiencyWeak glowLuminescent compositionsSilver iodideFluorescence
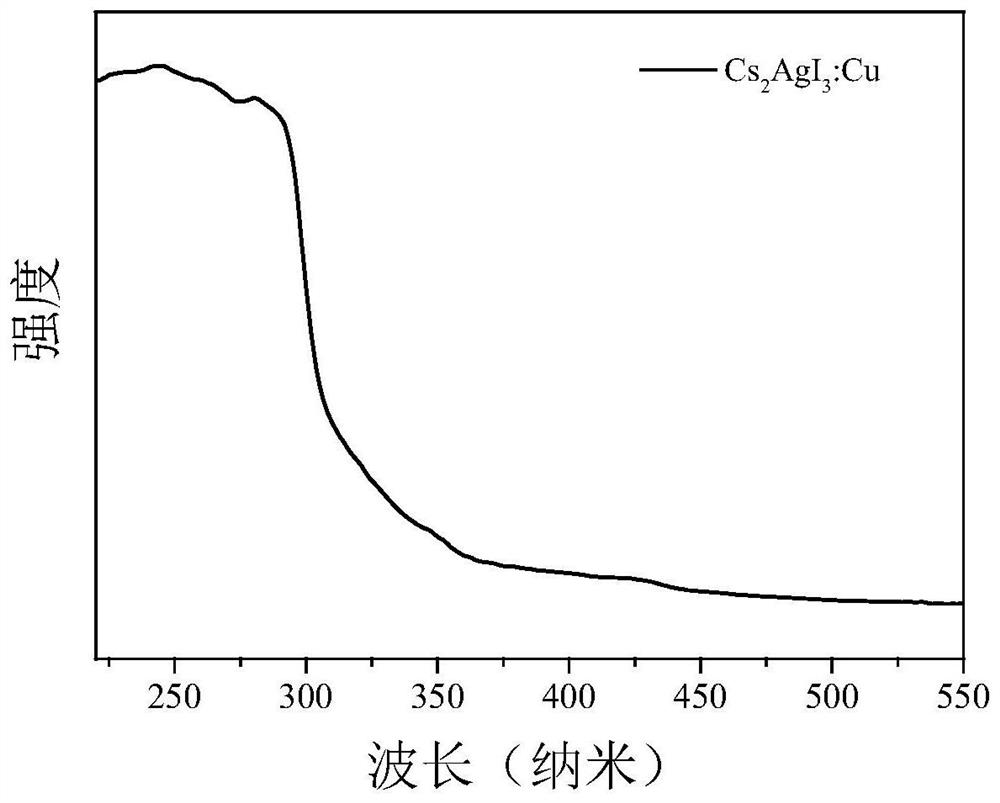
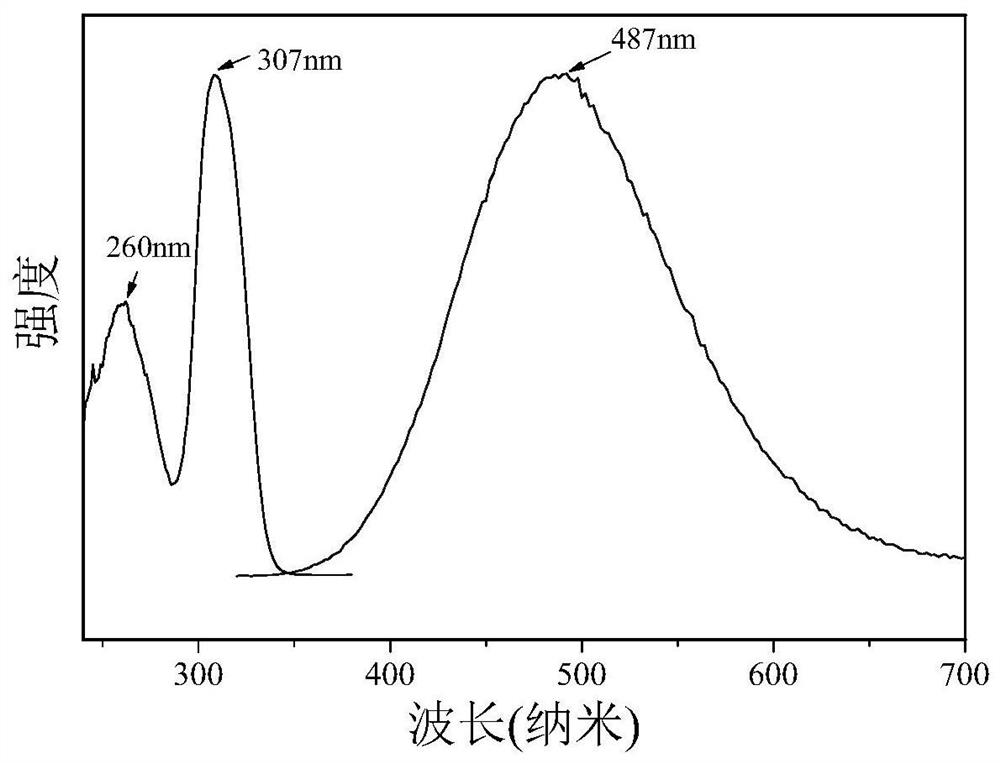
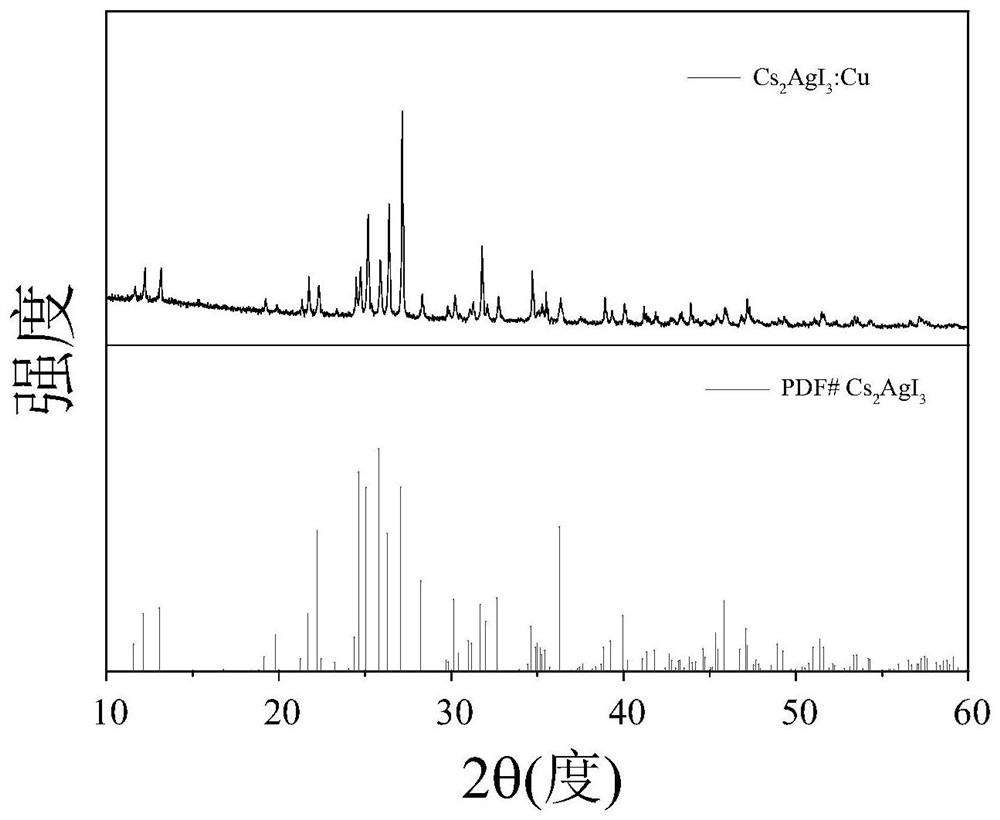
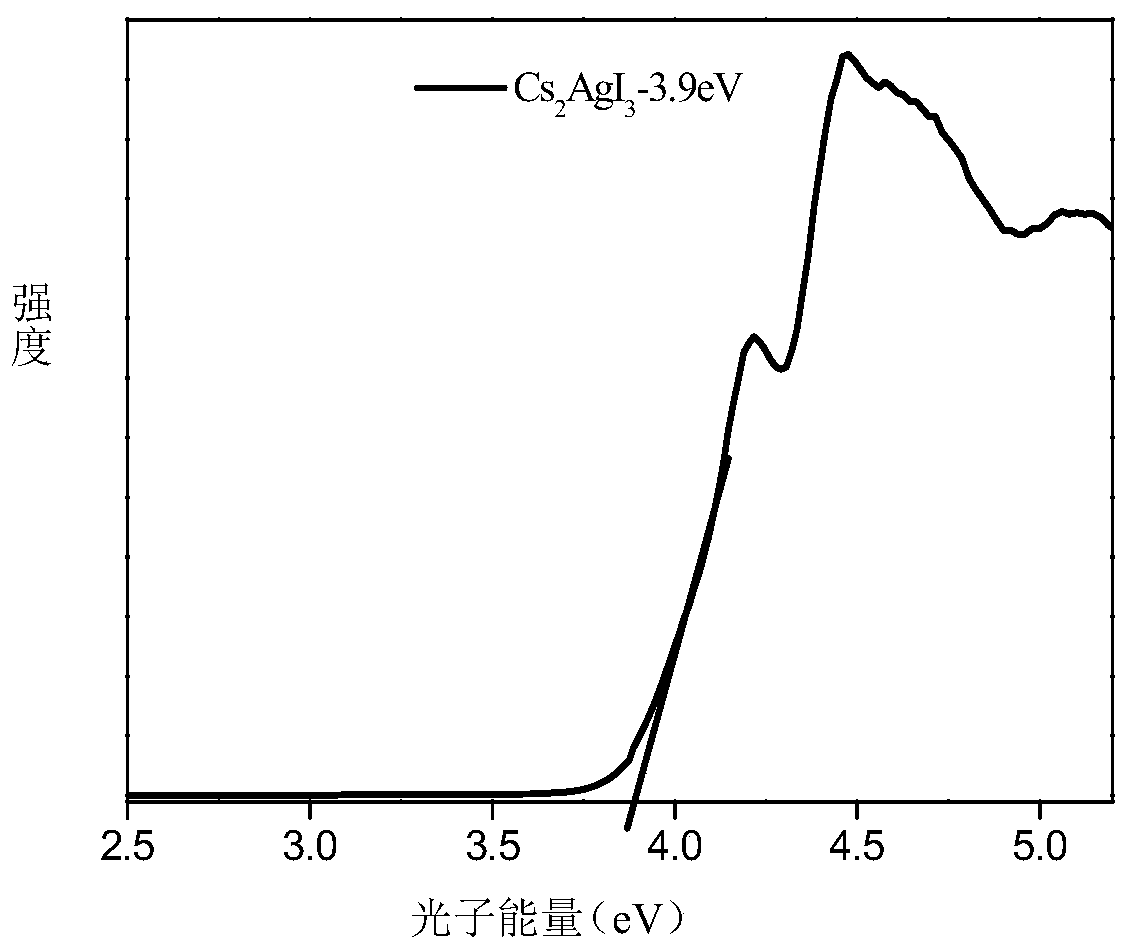
The invention discloses a high-fluorescence-efficiency inorganic lead-free perovskite material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of perovskite crystal material preparation. The high-fluorescence-efficiency inorganic lead-free perovskite material is Cu-doped Cs2AgI3 perovskite, and the doping amount of Cu is 0.09%. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing cesium iodide and silver iodide, carrying out ball milling, adding cuprous iodide, hydroiodic acid and microliter hypophosphorous acid, carrying out sealed heating to 150-200 DEG C, cooling to room temperature, annealing, and carrying out cooling treatment at -10 to -35 DEG C for 1-3 hours. The Cs2AgI3: Cu crystal with high purity and enhanced fluorescence efficiency is obtained, emitsbright blue fluorescence under the excitation of a 302 nm ultraviolet lamp, and has the advantages of no lead or chromium, high quantum efficiency, environmental stability and the like.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
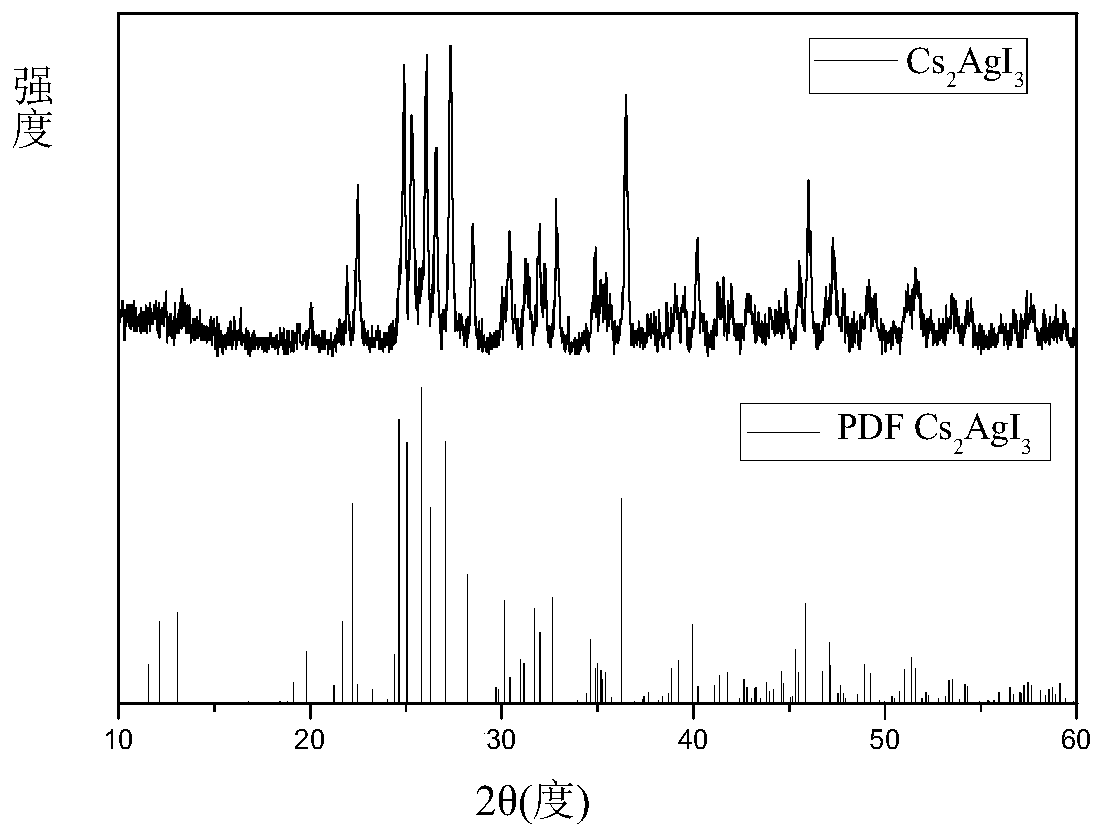
Simple and efficient method for synthesizing Cs2AgI3 perovskite
The invention discloses a simple and efficient method for synthesizing Cs2AgI3 perovskite, and belongs to the technical field of semiconductor nanomaterial preparation. First cesium iodide and silveriodide are mixed at a molar ratio of 1:1 and then1-dodecanethiol is added for grinding, during the grinding process, a 254 nm ultraviolet lamp is used for monitoring, the grinding is stopped when thebrightness of the product is no longer increased, the obtained product is subjected to heat treatment in a vacuum oven at 120-350 DEG C for 3 h, and the white product obtained after heat treatment issubjected to freezing treatment at -10 DEG C to -50 DEG C for 1-3 h to obtain the Cs2AgI3 non-lead all-inorganic perovskite with improved fluorescence yield. The method realizes preparation of the pure phase Cs2AgI3 by mechanical grinding for the first time. At the same time, the method has the advantages of convenient operation, simple method, easy realization of industrialized production, and the like.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Substrate for growing caesium iodide scintillator
InactiveCN103645493AImprove brightness effectImprove image qualityX-ray/infra-red processesConversion screensProduction rateOptoelectronics
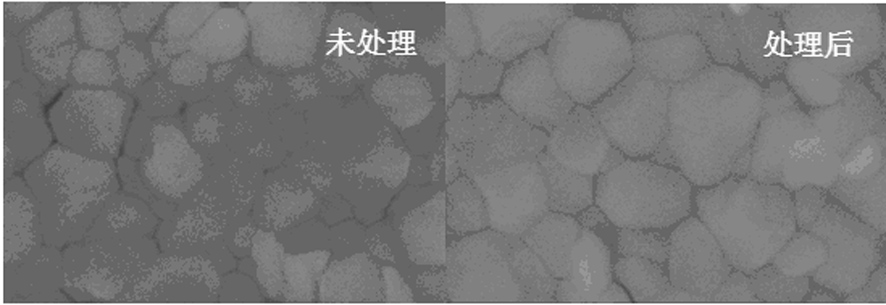
The invention discloses a substrate for growing a caesium iodide scintillator. The substrate comprises a substrate body. The upper surface of the substrate body is provided with a smooth leveling layer; the lower surface of the substrate body is provided with an unevenly accidented diffuse reflection layer; and the substrate body is a transparent substrate body. Through such a mode, by using the substrate provided by the invention, the caesium iodide scintillator growing on the substrate can be sealed by use of a common waterproof metal film so that the waterproof sealing cost of the scintillator can be substantially saved, and the production efficiency of the scintillator is improved.
Owner:江苏龙信电子科技有限公司
Metal oxide and halide perovskite quantum dot heterojunction visible-light-driven photocatalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113275026AEasy to operateMild reaction conditionsGas treatmentPhysical/chemical process catalystsHeterojunctionHydration reaction
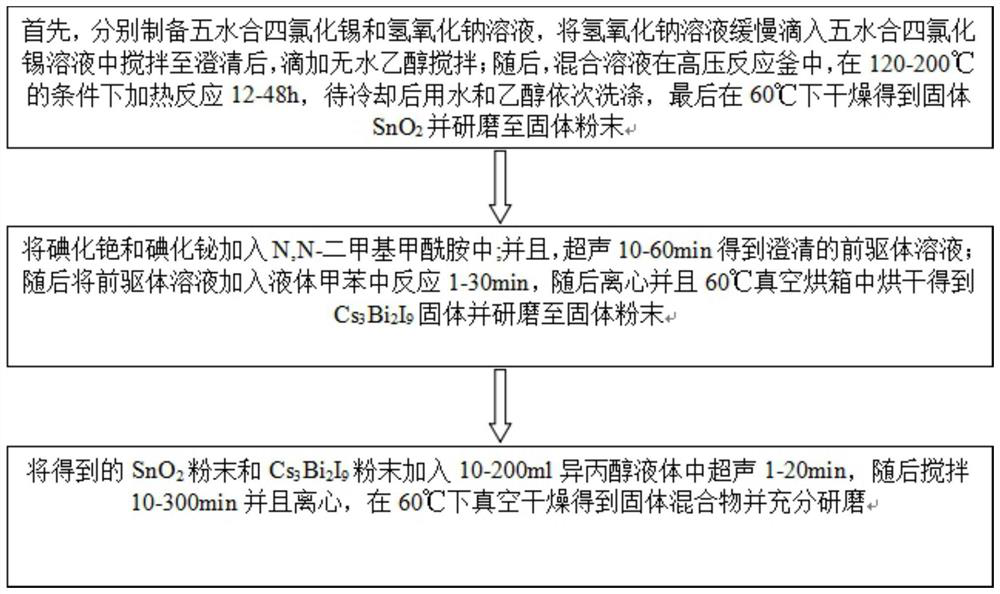
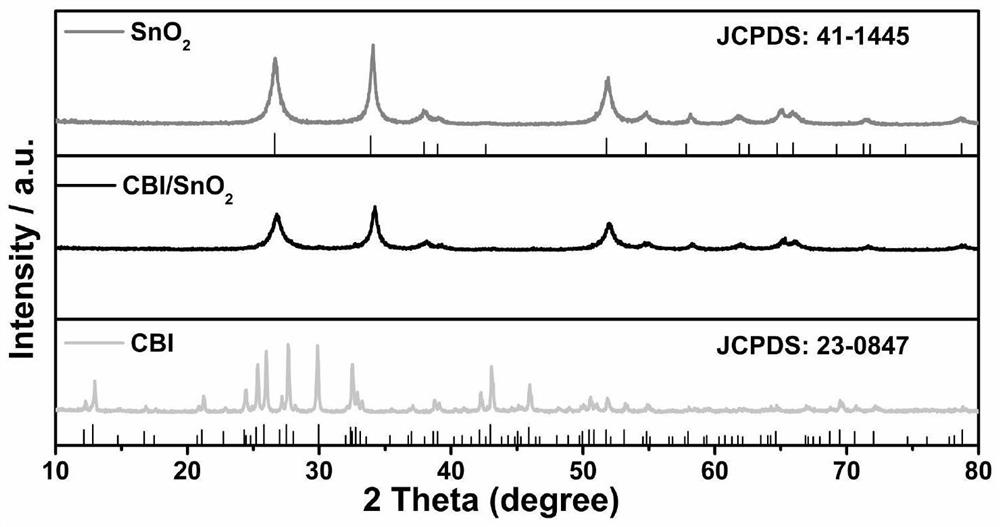
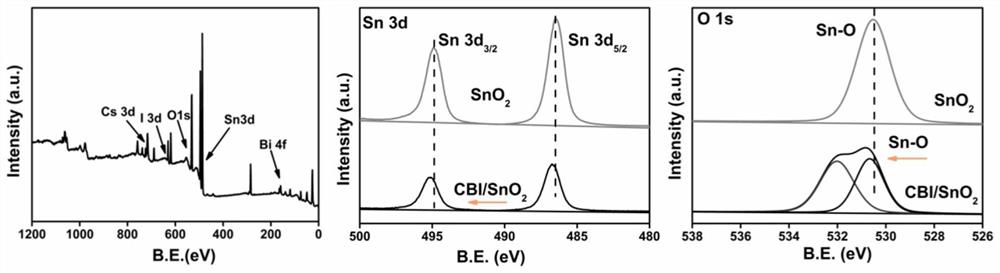
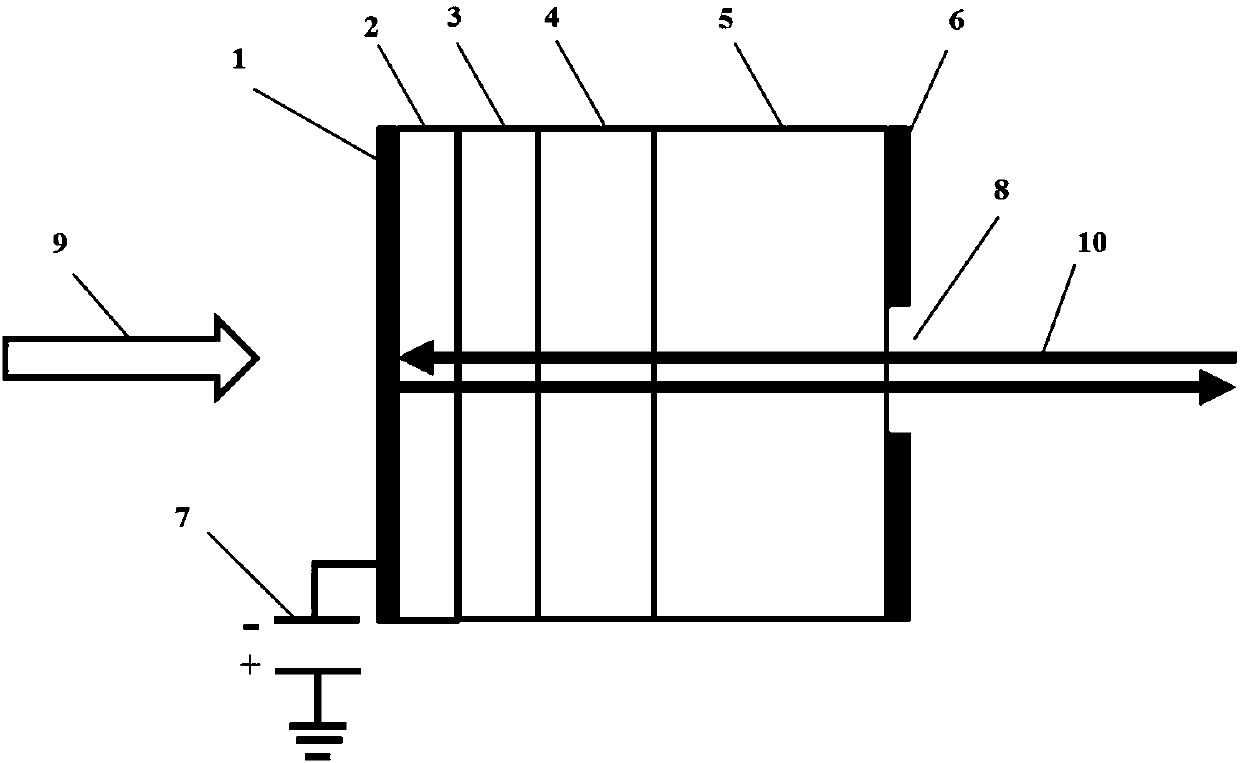
The invention discloses a preparation method of a metal oxide SnO2 and halide perovskite quantum dot Cs3Bi2I9 heterojunction visible-light-driven photocatalyst, which comprises the following steps of (1) preparing a tin tetrachloride pentahydrate solution and a sodium hydroxide solution, dropwise adding the sodium hydroxide solution into the tin tetrachloride pentahydrate solution, stirring, dropwise adding absolute ethyl alcohol, stirring, heating, reacting, then washing, drying and grinding, (2) adding cesium iodide and bismuth iodide into N, N-dimethylformamide, and performing ultrasonic treatment to obtain a precursor solution, then adding the solution into toluene for reaction, and then centrifuging, drying and grinding, and (3) adding the two kinds of powder into isopropanol liquid for ultrasonic treatment, then stirring and centrifuging, drying and grinding to obtain the heterojunction visible-light-driven photocatalyst. The method for preparing the heterojunction photocatalyst is easy to operate, mild in reaction condition, low in equipment requirement and free of a complex synthesis device, and the catalyst is applied to nitrogen oxide degradation and can remarkably improve the nitrogen oxide removal efficiency.
Owner:YANGTZE DELTA REGION INST OF UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINE HUZHOU +1
Optical refractive index change-based ultra-wideband neutron detector
PendingCN107894608AImplement detectionEnables radiation detectionMeasurement with semiconductor devicesUltra-widebandSemiconductor materials
The invention discloses an optical refractive index change-based ultra-wideband neutron detector and belongs to the technical field of nuclear radiation detection. The optical refractive index change-based ultra-wideband neutron detector comprises a detection unit composed of a hydrocarbon material layer, a cesium iodide layer, a semiconductor and a substrate which are sequentially fixed, a high-voltage power supply and a neutron beam. A first metal film and a second metal film are respectively electroplated on the outer surface of the hydrocarbon material layer and the outer surface of the substrate. The first metal film is electrically connected with the negative electrode of the high-voltage power supply. After the neutron beam is incident on the detection unit, neutrons collide with protons in the hydrocarbon material layer to generate back-flushing protons. The back-flushing protons enter the cesium iodide layer to generate free electrons. Under the electric field action of a negative high voltage between the first metal film and the second metal film, generated free electrons in the cesium iodide layer are injected into the semiconductor, so that the optical refractive indexof the semiconductor is changed. The detector can convert the neutron beam into the refractive index change of the semiconductor material. Based on the optical interference, the refractive index change of the semiconductor material is measured, and then the intensity information of the neutron beam is obtained.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
High-stability all-inorganic CsPbI2Br perovskite thin film and preparation method thereof
PendingCN111792851AHigh crystallinityGood lookingCoatingsPhotovoltaic energy generationCrystallinityCesium iodide
The invention discloses a high-stability all-inorganic CsPbI2Br perovskite thin film and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: processing an FTO conductive glass substrate material, and preparing a TiO2 layer on an FTO conductive glass substrate; preparing an anti-solvent, and adding cesium iodide, lead iodide and lead bromide into an organic solvent to prepare a perovskite precursor solution; coating an FTO / TiO2 substrate with the perovskite precursor solution to obtain a CsPbI2Br perovskite precursor thin film; coating the perovskite precursor thin film with an anti-solvent methylamine bromide solution; and annealing to form the all-inorganic CsPbI2Br perovskite thin film. According to the CsPbI2Br thin film prepared by the method, the crystallinity and the morphology of the thin film are improved, and the stability of the thin film is further improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Scintillation screen structure for X-ray radiation detector
ActiveCN103344984AImprove waterproof performanceGood light transmissionX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentTransmittanceCesium iodide
The invention relates to a scintillation screen structure for an X-ray radiation detector. The scintillation screen structure comprises a silicon substrate. A cesium iodide hybrid film is deposited on the silicon substrate through the laser evaporation process. The cesium iodide hybrid film is a cesium iodide thick film doped with thallium and boron. A transparent water blocking film is deposited on the cesium iodide thick film. The visible light transmittance of the transparent water blocking film is larger than or equal to 90%. The water vapor transmittance of the transparent water blocking film is smaller than or equal to 0.01g / m<-2>.day<-1>. The scintillation screen structure for the X-ray radiation detector is compact, even in component and good in cohesiveness with the substrate, and has good water blocking and waterproof performance.
Owner:SHENZHEN BASDA MEDICAL APP
Charged particle detector of white neuron source charged particle detecting spectrometer
ActiveCN109459454ARealize switchingImplement switch detectionX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionPolyesterIodide
The invention discloses a charged particle detector of a white neuron source charged particle detecting spectrometer. The charged particle detector of the white neuron source charged particle detecting spectrometer comprises a delta E-E detector and an ionization chamber detector, wherein the delta E-E detector is a compound gas-solid detector and composed of a small multiwire proportional chambergas detector and a cerium iodide solid detector, which are mutually independent, and provided with a 0.5 mu m thick polyethylene film particle beam window; the ionization chamber detector is providedwith a 8 mu m thick polyimide film or polyester film particle beam window. According to the charged particle detector of the white neuron source charged particle detecting spectrometer, the delta E-Edetector is provided with the 0.5 mu m thick polyethylene film particle beam window, allowing charged particles to easily pass through and meanwhile avoiding being cracked under 5000 Pa pressure; theparticle beam window of the ionization chamber is made of 8 mu m thick polyimide film or PET (polyethylene), thereby allowing easy penetration of the charged particles and bearing 1 atm pressure.
Owner:DONGGUAN NEUTRON SCI CENT
Indium and thallium co-doped cesium iodide scintillator and application thereof
ActiveCN109705854AHigh flicker efficiencyImprove stabilityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingChemical compositionIndium
The invention discloses an indium and thallium co-doped cesium iodide scintillator and an application thereof. The chemical composition general formula of the scintillator is (Cs1-x-yTlxIny)I1+2y, x is more than 0 and not more than 0.05, and y is more than 0 and not more than 0.05. The indium and thallium co-doped cesium iodide scintillator can be applied to the preparation of an indium and thallium co-doped cesium iodide film, and the film is prepared through a thermal evaporation process. The indium and thallium co-doped cesium iodide film prepared by using the indium and thallium co-doped cesium iodide scintillator has a high scintillation efficiency and a high stability, and has great values in the promotion of the wide application of CsI scintillation materials in the high-resolutionX imaging field due to the improvement of the stability.
Owner:XUZHOU NADIA ELECTRONICS TECH
Cesium-tin-iodine film as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112054126AGood crystalline phaseHigh phase puritySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysical chemistryTin(IV) iodide
The invention discloses a cesium-tin-iodine film and a preparation method and application thereof, and the preparation method of the Cs2SnI6 film comprises the following steps: (1) adding cesium iodide and tin iodide into DMSO or a mixed solvent of DMSO and DMF, stirring and dissolving at 20-70 DEG C to prepare a Cs2SnI6 precursor solution; (2) standing and aging the precursor solution prepared inthe step (1) in an N2 atmosphere for 3 days to 10 days, and spin-coating and depositing the precursor solution on a substrate to obtain a precursor film; (3) placing the precursor film obtained in the step (2) on a heating stage with the temperature of 30-70 DEG C, and standing for 1.0 min to 40 min; then putting the film on a spin coater, dripping 40 microliters to 100 microliters of supplementary solution, and spin-coating to be dry after dripping the solution; and (4) annealing the film obtained in the step (3) to obtain the Cs2SnI6 film.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
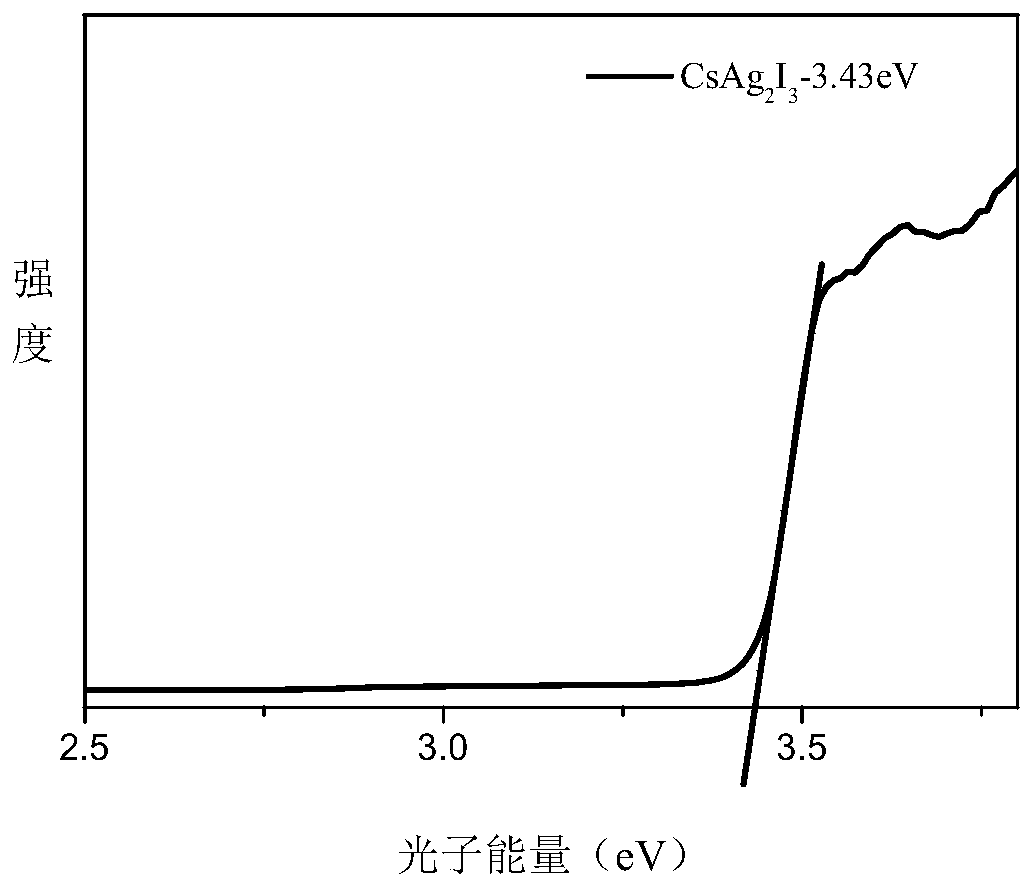
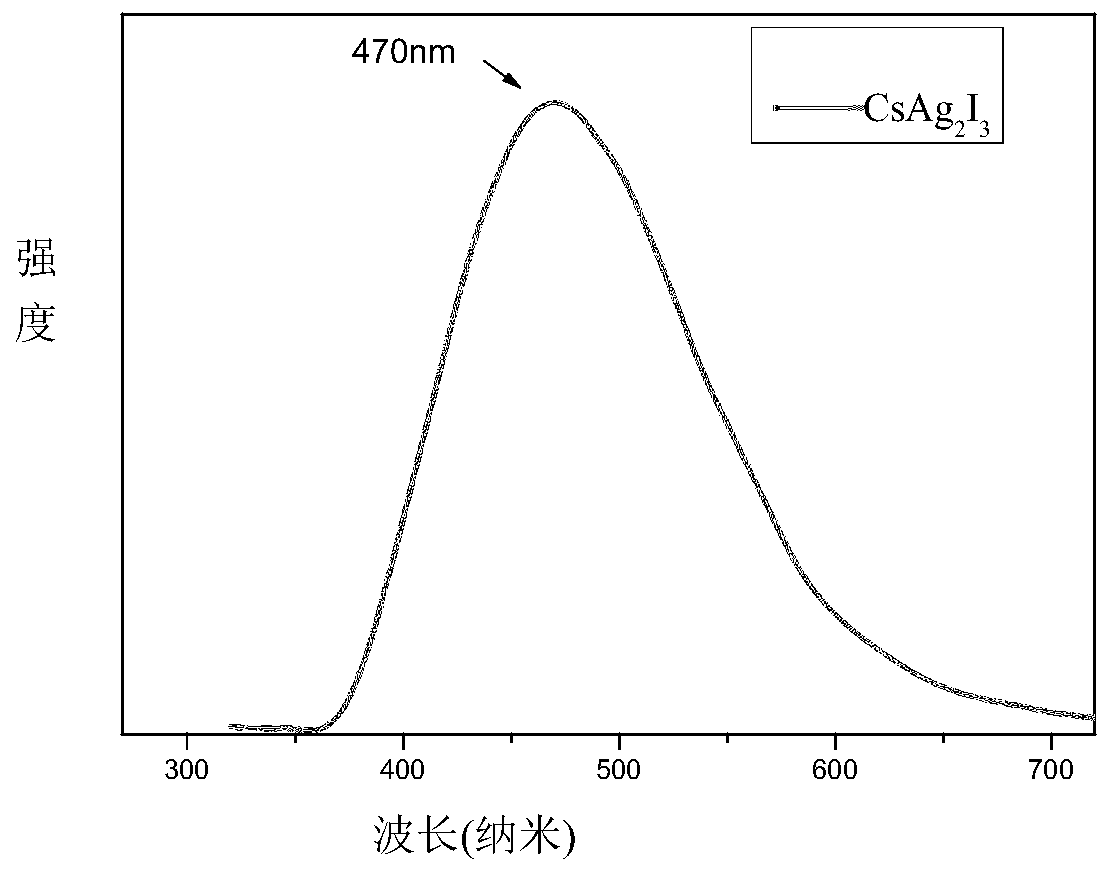
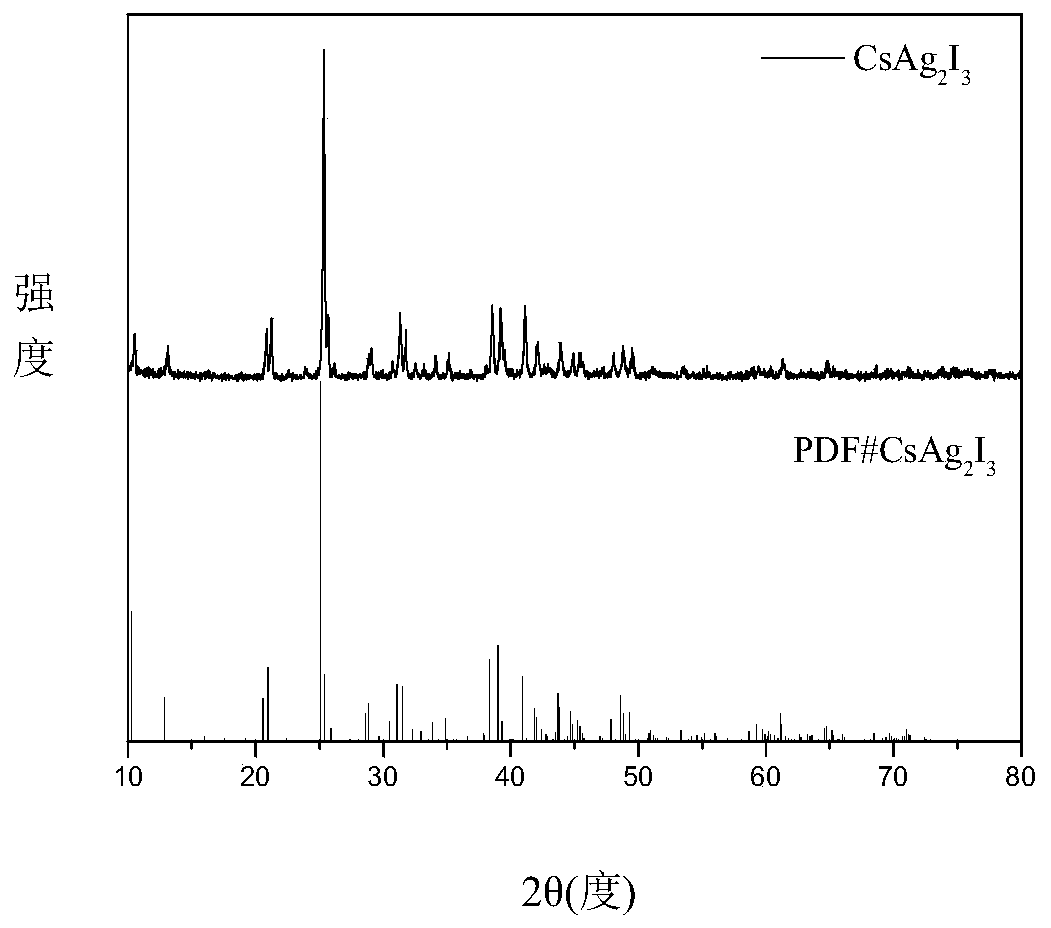
Method for simply synthesizing CsAg2I3 pure phase inorganic non-lead perovskite
InactiveCN110790299AHigh fluorescence efficiencySimple methodLuminescent compositionsSilve compoundsSilver iodidePhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a method for simply synthesizing CsAg2I3 pure phase inorganic non-lead perovskite, and belongs to the technical field of semiconductor nanomaterial preparation. First cesium iodide and silver iodide are mixed at a molar ratio of 1:2 and then 1-dodecanethiol is added for grinding, with the passing of ball-milling time, the mixture first gradually becomes dense from a fluffygray-white powder and adheres to the container wall, and finally is turned into a fluffy gray-white powder again, ball-milling is stopped, the product is directly put into a vacuum oven, and heat treatment is performed at 60-300 DEG C for 2 h; and then cooling treatment is performed at -15 DEG C to -40 DEG C for 1 h-2 h to obtain the CsAg2I3 perovskite with high purity and high fluorescence efficiency. The method has the advantages that the method is simple, the operation is easy, the time consumption is short, the energy consumption is small, the synthesized CsAg2I3 is a pure phase substance, and the like, and has important significance.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
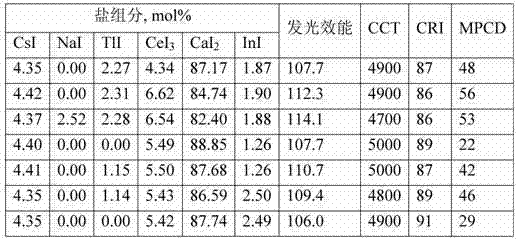
Ceramic gas discharge metal halide lamps with high color temperature
InactiveCN102282643AGood lumen maintenanceHigh color temperatureGas discharge lamp detailsAquarium lightingIndium
A ceramic gas discharge metal halide (CDM) lamp (23) with a high color temperature (higher than 4500K) having a prolate spherical PCA discharge vessel (12) containing an inert gas, mercury and A filling of a metal halide salt mixture of: at least about 62 mole percent calcium iodide (CaI2); up to about 8 mole percent cerium iodide (CeI3); up to about 15 mole percent % mole percent cesium iodide (CsI); and up to about 15 mole percent other halides selected from the group consisting of lithium (Li), sodium (Na), indium (In), manganese (Mn) , lead (Pb), praseodymium (Pr), europium (Eu), gallium (Ga) and thallium (Tl) halides, and the amount of sodium (Na) halide is less than about 5 mole percent, and thallium halide (Tl ) in an amount of less than about 5% by mole. This light is particularly suitable for horticultural applications, as well as sports lighting, aquarium lighting and other specialty lighting applications.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
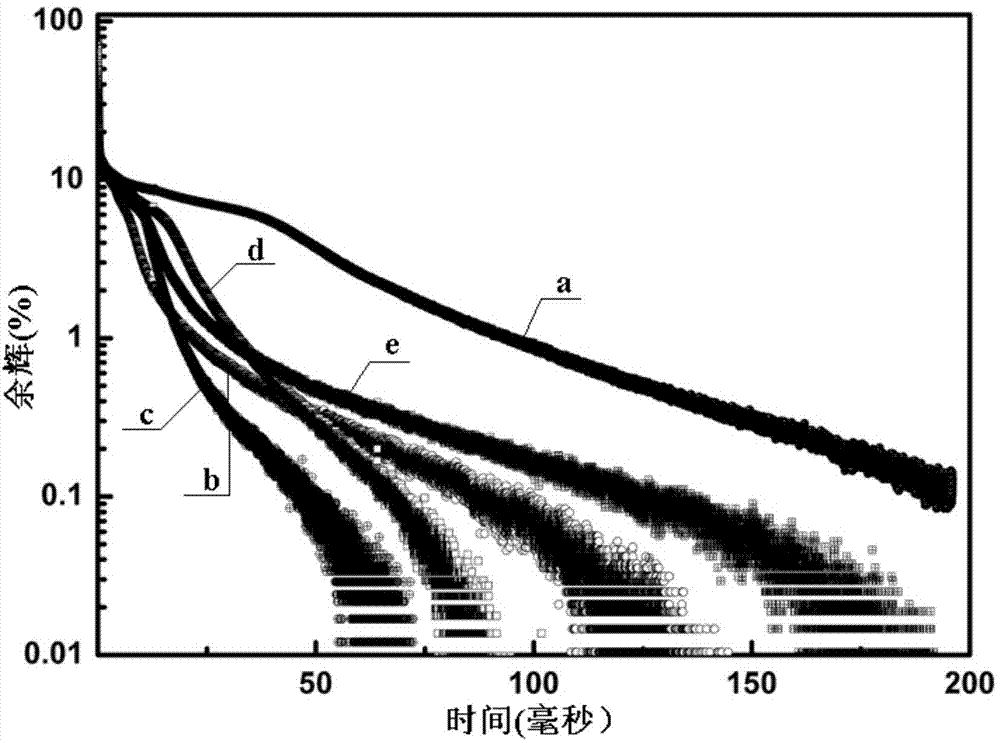
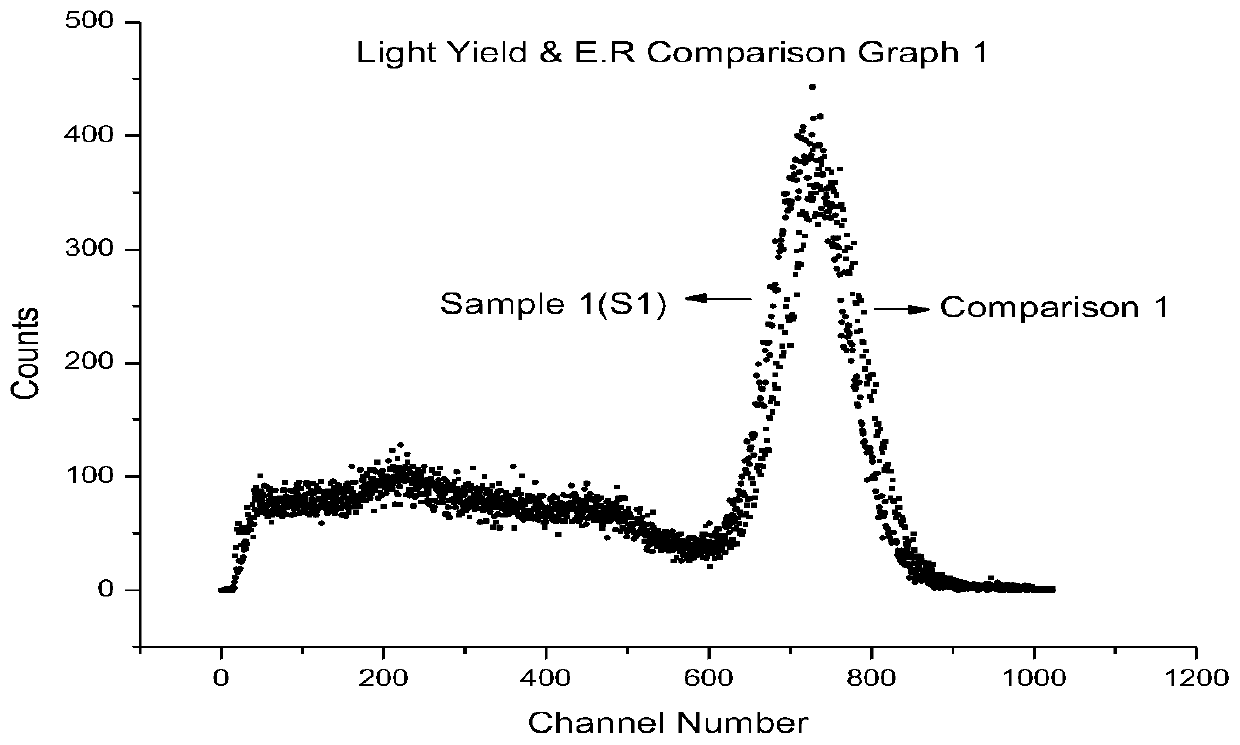
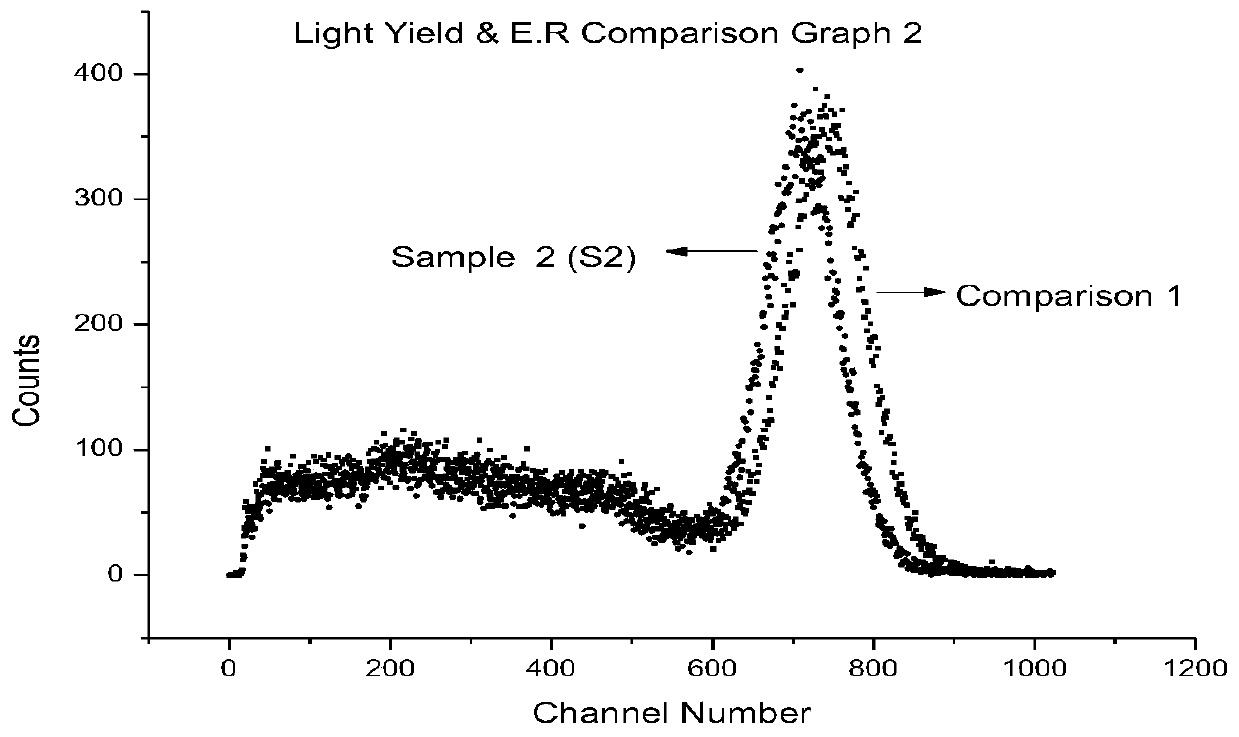
Scintillation crystal, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN111593405AHigh purityLow content of harmful impuritiesPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsScintillation crystalsCesium iodide
The invention relates to the technical field of artificial scintillation crystals, and concretely relates to a scintillation crystal, and a preparation method and application thereof. The chemical formula of the scintillation crystal is CsI:T1(x):Cu(y), wherein x is more than or equal to 0.05 and less than or equal to 0.1; and y is more than or equal to 0.01 and less than or equal to 0.1. The cesium iodide crystal prepared by adopting a co-doping formula and an improved descending method not only can keep the original light yield, but also can effectively reduce the afterglow, particularly, the afterglow in the first 50 ms time period after irradiation rays are turned off is remarkably improved, and the requirement of high-speed ray imaging detection can be met.
Owner:上海御光新材料科技股份有限公司
Method for high-pressure solid-phase synthesis of iodine-copper-cesium lead-free quantum dot
ActiveCN111792665AThe preparation process is simple and controllableSmall grain sizeNanoopticsCopper compoundsPhotoluminescencePhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a method for high-pressure solid-phase synthesis of an iodine-copper-cesium lead-free quantum dot. The method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing CsI and CuI according to a molar ratio of 3: 2, conducting tabletting, and carrying out treating at a high pressure not lower than 1 GPa to obtain an iodine-copper-cesium quantum dot nanomaterial. According to the invention, copper iodide and cesium iodide are used as precursors, high-pressure solid-phase synthesis is adopted, process is simple and controllable, inert atmosphere protection is not needed in the preparation process, and the obtained copper-cesium iodide quantum dot has high photoluminescence intensity.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Illuminant pill for metal halide rare-earth lamp
InactiveCN101477934AExtended service lifeImprove luminous efficiencyGas discharge lamp detailsIndiumSodium iodide
The invention discloses a luminous pill of a metal halide rare-earth lamp, which contains sodium iodide, thallium iodide, indium iodide, dysprosium iodide, caesium iodide, iridium iodide and berkelium iodide. Compared with the prior art, the prepared metal halide rare-earth lamp is characterized by good luminous efficiency being more than 100Lm / w, and long service life lasting for 10000 hours.
Owner:芜湖兴华照明电器有限公司
Illuminant pill for metal halide rare-earth lamp
InactiveCN101477936AImprove luminous efficiencyReduced luminous efficiencyGas discharge lamp detailsIridiumIndium
The invention discloses a luminous pill of a metal halide rare-earth lamp, which contains sodium iodide, thallium iodide, indium iodide, dysprosium iodide, caesium iodide and iridium iodidee. Compared with the prior art, the prepared metal halide rare-earth lamp is characterized by good luminous efficiency being more than 100Lm / w.
Owner:芜湖兴华照明电器有限公司
Cs4PbI6 perovskite crystal as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN112064115AQuality improvementHigh transparencyPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsOctahedronCesium iodide
The invention discloses a Cs4PbI6 perovskite crystal as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The perovskite crystal is an inorganic cation Cs<+> surrounded [PbI6]<4-> octahedron. Thepreparation method comprises the following steps of: uniformly mixing N, N-dimethylformamide and dimethyl sulfoxide, adding lead iodide and cesium iodide to prepare a supersaturated precursor solution, filtering the supersaturated precursor solution, heating to carry out crystal growth, and stopping growth until other impurities grow in the solution. The Cs4PbI6 perovskite crystal disclosed by theinvention is high in quality, regular in appearance, good in transparency, good in stability, high in quantum luminous efficiency and high in responsivity, and can be used for nuclear radiation detection; and meanwhile, an inverse temperature crystallization method is adopted during preparation, the operation is simple, the controllability is high, the repeatability is good, and large-scale industrial production can be realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com