Patents
Literature
44 results about "Elemental chlorine free" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Elemental chlorine free (ECF) is a technique that uses chlorine dioxide for the bleaching of wood pulp. It does not use elemental chlorine gas during the bleaching process and prevents the formation of dioxins and dioxin-like compounds, carcinogens. The traditional ECF sequence is DEopDEpD using the common letter symbols for bleaching stages, though many improved sequences are available.
Method for preparing high-alkali value (TBN400) synthesized calcium alkyl benzene sulfonate
ActiveCN101318915AImprove cleanlinessGood dispersionAdditivesSulfonic acid preparationTotal Base NumberAlkaline earth metal
The invention provides a method for preparing high base number (TBN400) synthetic calcium alkyl-benzene sulfonate. The method comprises the following steps of: adopting a mixed acid of long-chain linear alkyl-benzene sulfonic acid and high-boiling heavy alkyl-benzene sulfonic acid, calcium oxide and / or calcium hydroxide, low-carbon alcohol, alkaline-earth metal halide or nitrate, and a mixture of alkaline-earth metal alkylphenol or alkaline-earth metal alkylphenate and polyisobutylene succinic anhydride for a neutralization reaction in the presence of a solvent and cutback oil at a temperature of between 40 and 80 DEG C; then, passing through carbon dioxide to a product of the neutralization reaction at a temperature of between 40 and 60 DEG C for a carbonation reaction; and producing high base synthetic alkyl-benzene sulfonate with a total base number (TBN) of 400mgKOH / g by adopting a process of a one-step method. The product is divided into high-base number (TBN400) synthetic alkyl-benzene sulfonate containing chlorine and high-base number (TBN400) synthetic alkyl-benzene sulfonate without the chlorine. The product produced by adopting the method with low viscosity, small turbidity, easy filtration, light color and no skin formation has the advantages of excellent high-temperature detergency, excellent anti-foaming property and excellent heat storage stability.
Owner:JINZHOU DPF TH CHEM CO LTD
Method of producing aluminum oxides and products obtained on the basis thereof
InactiveUS6841497B1Increase contentMaterial nanotechnologyPretreated surfacesNanoparticleCrystal structure
The invention relates to the field of technical ceramics and specifically relates to a method of synthesis for aluminum oxides of different crystalline structure and to the products obtained by the method. The aim of the invention is to provide a method of producing redispersible nanoparticulate corundum and nanoporous Al2O3 sintered products, the method using precursors and being viable on a commercial scale. To this aim, inter alia, a method of producing redispersible nanoparticulate corundum of an average particle size of D50<100 nm is used which method includes the addition of crystal nuclei. According to the method, organic or chlorine-free inorganic precursors are dissolved or processed to a sol and hydrolyzed. The substance is then dried and calcinated at temperatures of between 350 and 650° C. and is then further heated by increasing the temperature to ≦950° C. The aim of the invention is also attained by using a method of producing nanoporous Al2O3 sintered products according to which organic or chlorine-free inorganic precursors are dissolved or processed to a sol and hydrolyzed. The substance is then dried and calcinated at temperatures of between 350 and 750° C.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
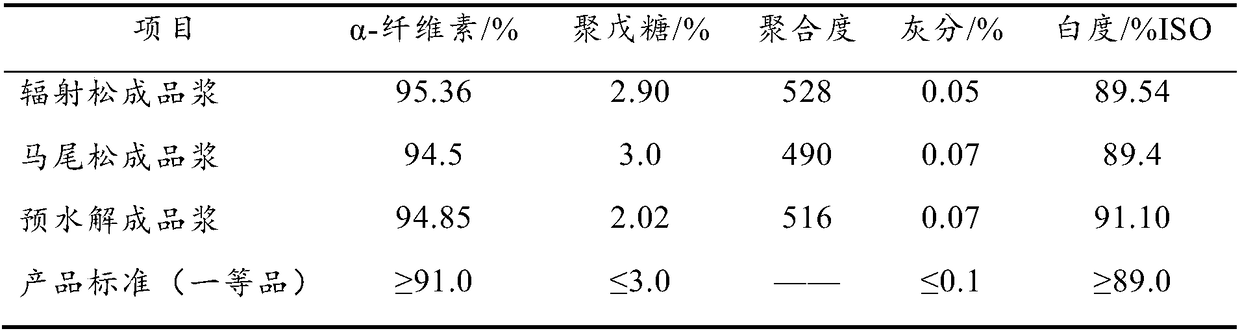
Production method of bamboo chemical dissolving pulp
ActiveCN101457494ASimple switching processHighly corrosiveWashing/displacing pulp-treating liquorsDigestersMaterial consumptionDissolving pulp
Aiming at the current situation of the cotton dissolving pulp and the wood dissolving pulp and the characteristics of the bamboo and the defects in the existing preparation of the dissolving pulp, the invention provides a method for preparing a chemical bamboo dissolving pulp. The chemical dissolving pulp produced can be widely applied in the cellulose derivative industries such as spinning viscose fiber, nitrocellulose and acetate fiber. The method comprises the following steps of: material preparation, cooking, screening, scrubbing, bleaching and paper making. The cooking procedure comprises two grades of cooking steps, wherein the primary cooking procedure is continuous cooking and the secondary cooking procedure is continuous cooking or intermittent cooking; and the bleaching procedure is elemental chlorine free bleaching or totally chlorine free bleaching. The invention solves the problems existed in the cooking and bleaching procedures. The chemical bamboo dissolving pulp can be prepared with high efficiency, low energy consumption, low material consumption and low pollution.
Owner:YIBIN GRACE GROUP CO LTD
Straw pulp bleaching technique
InactiveCN101463573AReduce generationReduce pollutionPulp bleachingOrganic chloride compoundChlorine dioxide
The invention discloses a bleaching process with low pollution used for straw pulp by virtue of elemental chlorine-free bleaching agents such as oxygen, chlorine dioxide, hydrogen peroxide and the like. The invention is characterized in that the process comprises the steps as follows: (1) on oxygen delignification section, sealing, sifting and washing are carried out; (2) on chlorine dioxide delignification section, washing is carried out; (3) on alkaline extraction section, washing is carried out; (4) on chlorine dioxide whitening section, washing and papermaking are carried out. The process of the invention is simple and feasible, applicable for reed pulps and the mixed pulp thereof and anaphalis yedoensis, the final brightness of the pulp of the reed pulps (ISO) reaches 78-85%, the brightness stability and the strength are good, and tear index is more than or equal to 8.0mN.m<2> / g; as no elemental chlorine joins the bleaching process, the generation amount of organic chloride during the bleaching process is greatly lowered and the pollution to ecological environment is reduced, thus having obvious social and economic benefits.
Owner:YUANJIANG PAPER
Genes, plasmid, bacterial strain and application of xylanase
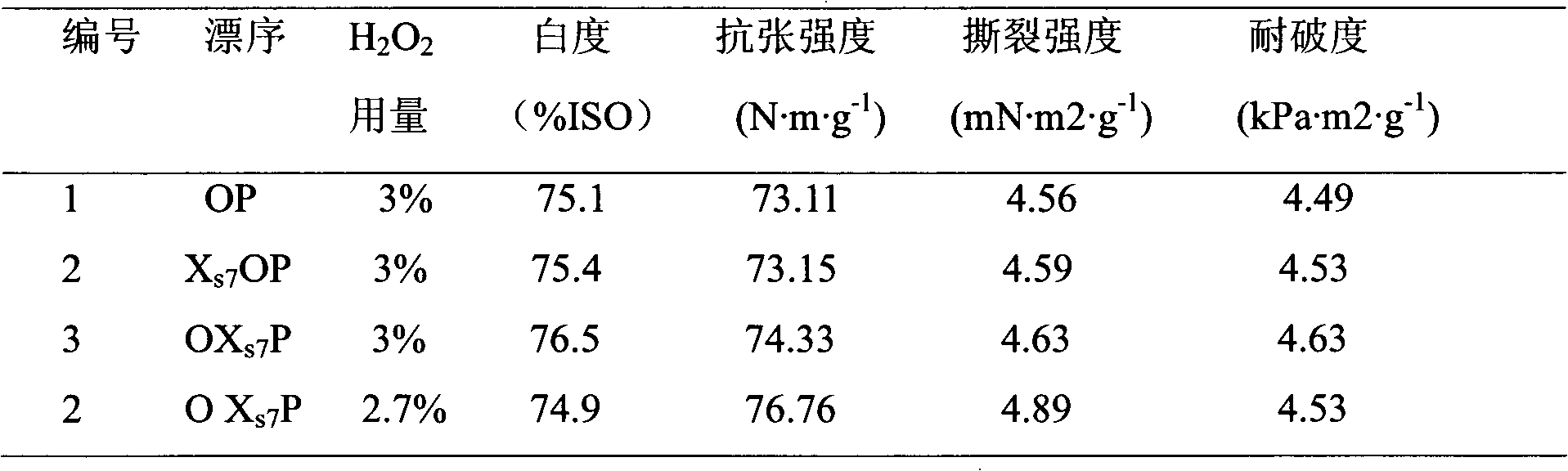
The invention provides genes, an expression vector, a production bacterial strain and application of xylanase with high temperature resistance, strong base resistance, high efficiency and stability in pulp bleaching. The genes of the xylanase provided in the invention realize high expression in Pichia pastoris by utilizing a codon optimizing and multi-copy technique; the expressed xylanase has no cellulase activity, high temperature resistance and high base resistance; and the xylanase can be applied to wheat straw pulp bleaching; when applied to an elemental chlorine free (ECF) bleaching procedure, the xylanase saves chlorine dioxide by 10%; when applied to a hydrogen peroxide (OP) bleaching procedure, the xylanase saves hydrogen peroxide by 10%.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for carrying out elemental chlorine free (ECF) multistage bleaching on masson pine kraft pulp by using glyoxal
The invention provides a method for carrying out elemental chlorine free (ECF) multistage bleaching on masson pine kraft pulp by using glyoxal. The method is characterized by firstly adopting chlorine dioxide to carry out delignification on the unbleached masson pine kraft pulp; then utilizing sodium hydroxide to carry out alkali extraction on the masson pine kraft pulp after delignification; then using chlorine dioxide to carry out delignification on the masson pine kraft pulp; and finally adopting hydrogen peroxide to bleach the masson pine kraft pulp to obtain the masson pine ECF pulp with high whiteness and excellent physical indexes. The method has the following beneficial effects: the whiteness of the prepared masson pine kraft pulp can reach 88.36% ISO, the Kappa number is 5.02 and the yield is about 90.28%; and the masson pine kraft pulp bleached by DEDP is used for manufacturing the handsheet and the tensile index is 40.08N.m / g, the tear index is 12.80mN.m<2> / g and the burst index is 3.45kPa.m<2> / g, thus showing that the finished paper has better physical strength.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
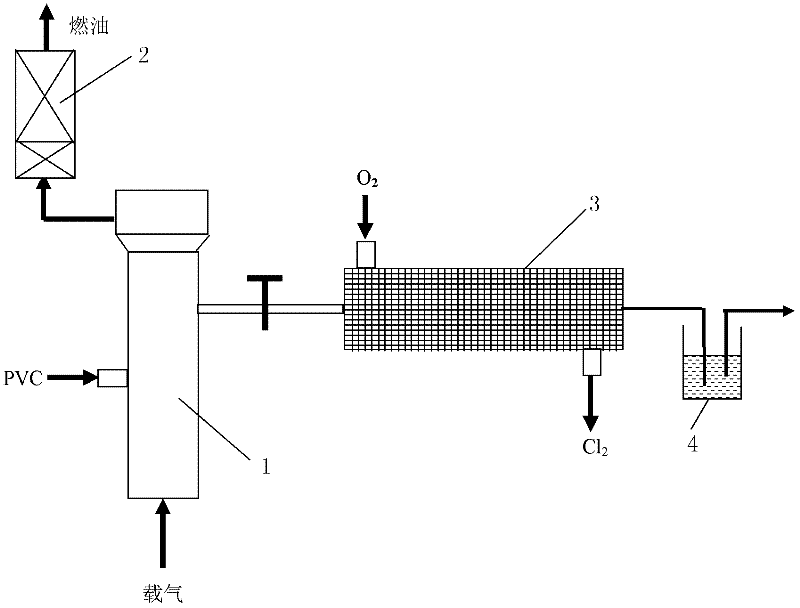
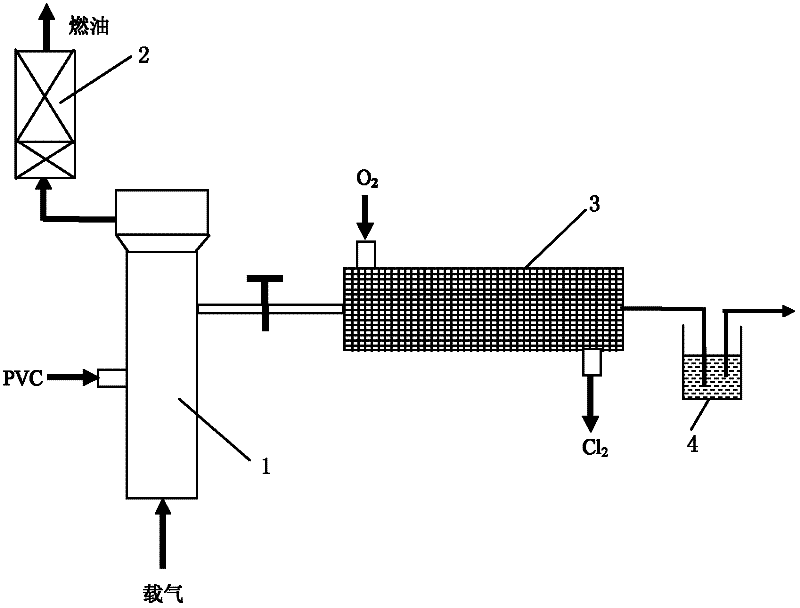
A method and device for efficient utilization of all components of chlorine-containing plastic waste
InactiveCN102268275AEfficient use ofHigh value utilizationSolid waste disposalPlastic recyclingCatalytic reformingResource utilization
The invention discloses a method and a device for efficient resource utilization of chlorine-containing plastic waste, which belong to the technical field of resource utilization of solid waste. Coupling the two processes of pyrolysis of chlorine-containing plastic waste to fuel oil and high value-added conversion of HCl generated by pyrolysis, so as to achieve the goal of efficient resource utilization of all components of chlorine-containing waste, and process chlorine-containing plastic in a fluidized bed cracking The HCl of the waste is removed by heat and further thermally cracked, while the capture and catalytic conversion of HCl to chlorine is carried out in the fixed bed of the monolithic catalyst. The catalytic tower is catalytically upgraded to obtain chlorine-free fuel. The invention can obtain chlorine-free high-quality fuel oil, and at the same time, the contained chlorine elements can be converted with high added value, thereby realizing efficient multi-component resource utilization of PVC chlorine-containing wastes.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
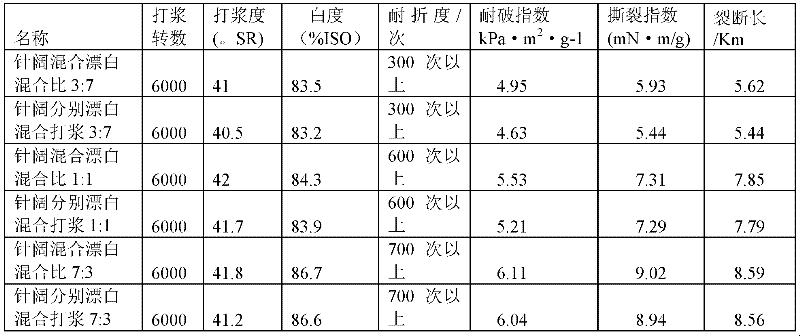
Process for bleaching needlebush and hardwood mixed chemical pulp stewed by using sodium hydroxide anthraquinone method
The invention relates to a process for bleaching needlebush and hardwood mixed chemical pulp stewed by using a sodium hydroxide anthraquinone method. The process comprises the steps of: mixing needlebush chemical pulp stewed by using the sodium hydroxide anthraquinone method with hardwood chemical pulp stewed by using the sodium hydroxide anthraquinone method in a mass ratio which ranges from 3:7to 7:3; and then performing high-whiteness bleaching by employing an ECF (elemental chlorine free) bleaching process having a bleaching working procedure of O1-O2-D0-OEP-D1-D2 or O1-O2-D0-OEP-D1. In the invention, the dosage of consumed chemicals in an entire process is equal to or a little lower than that of a process in which paper pulp is respectively stewed and respectively bleached. The two kinds of stewed crude pulp are similar in Kappa number, therefore other conditions of the bleaching process are milder, and the pulp provided by the invention is easier to bleach than the paper pulp with great hardness difference. Both the whiteness stability of the bleached paper pulp and various physical indexes such as burst index, fracture length, tearing index, folding strength and the like of made paper are better.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
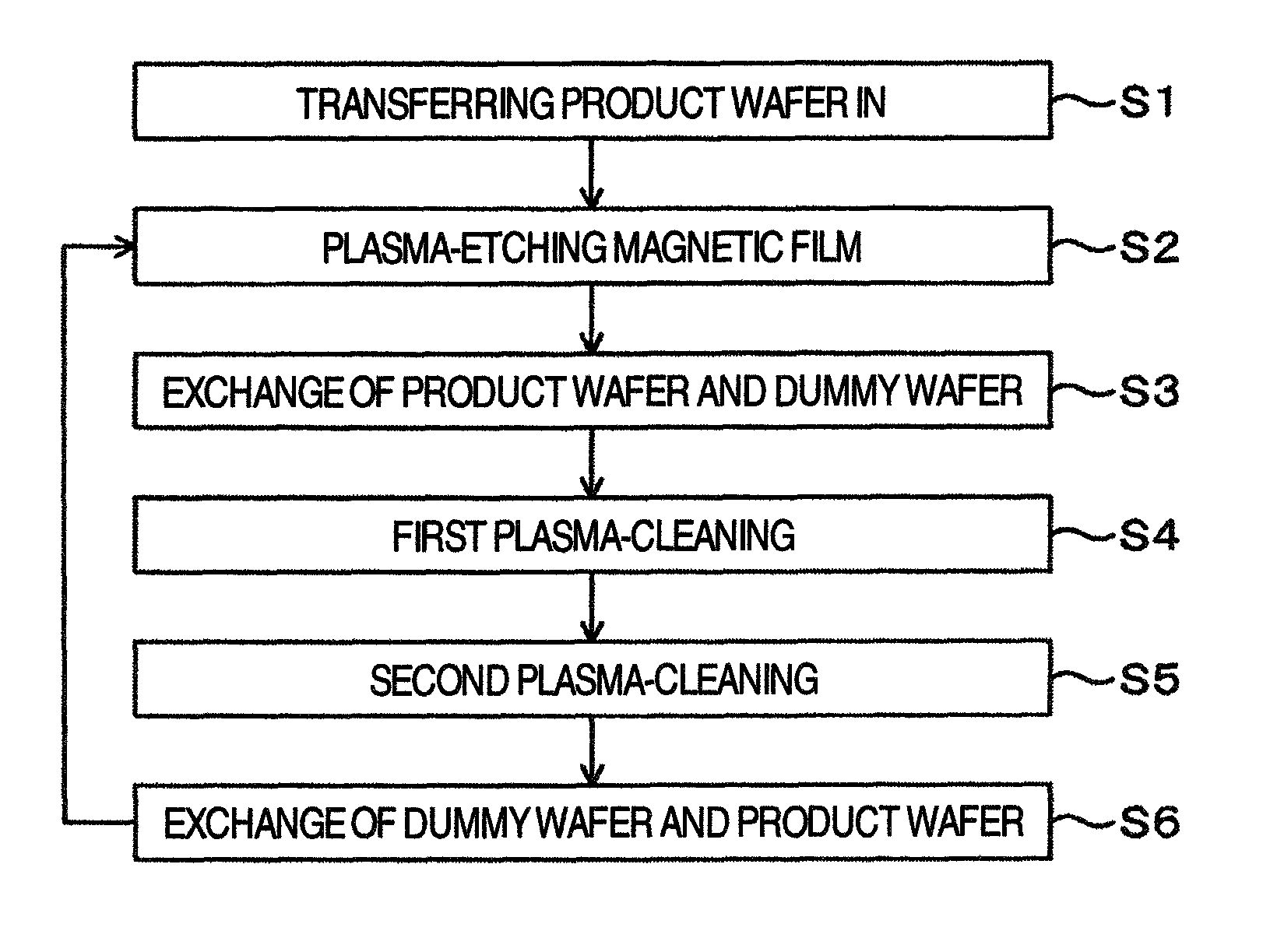
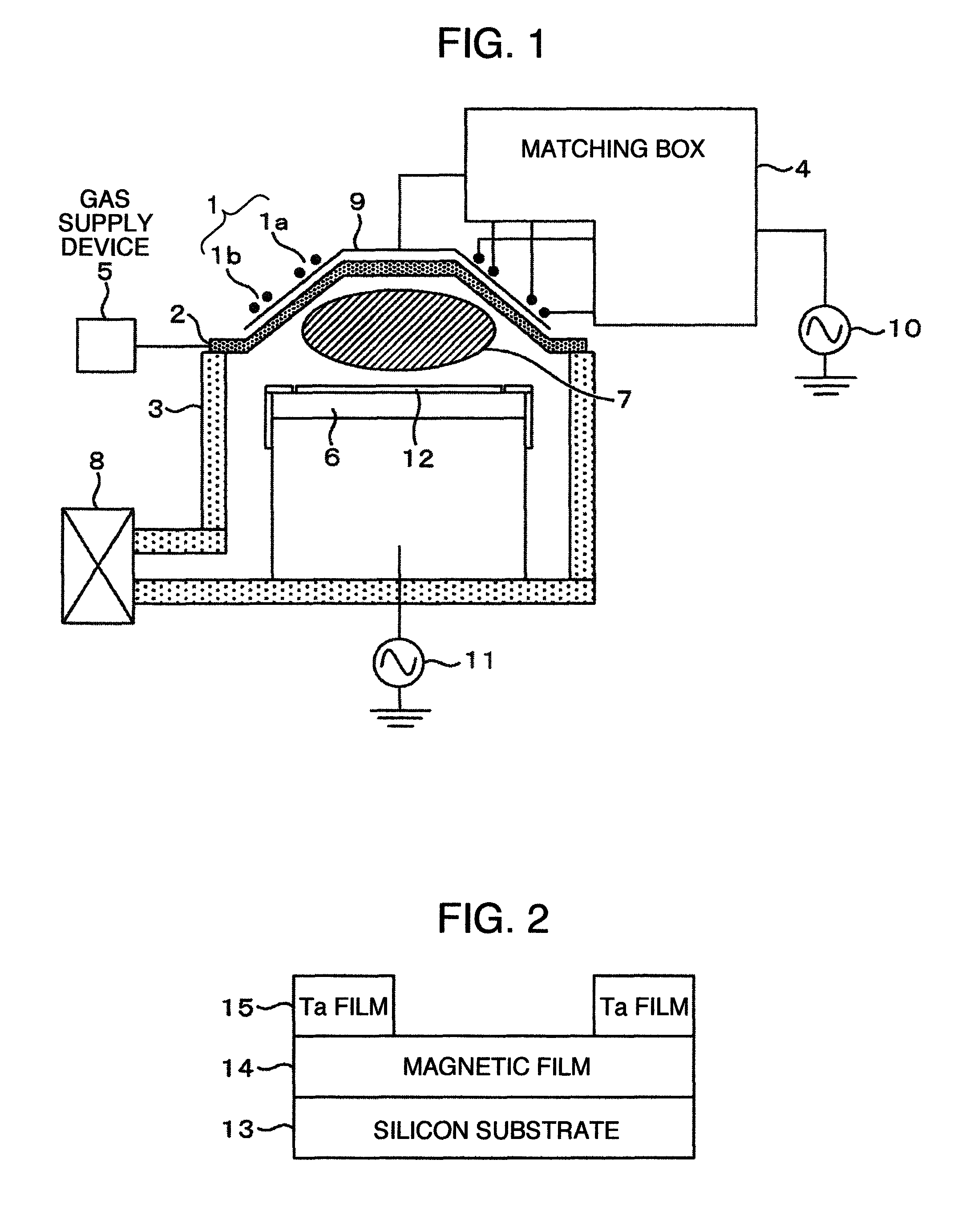
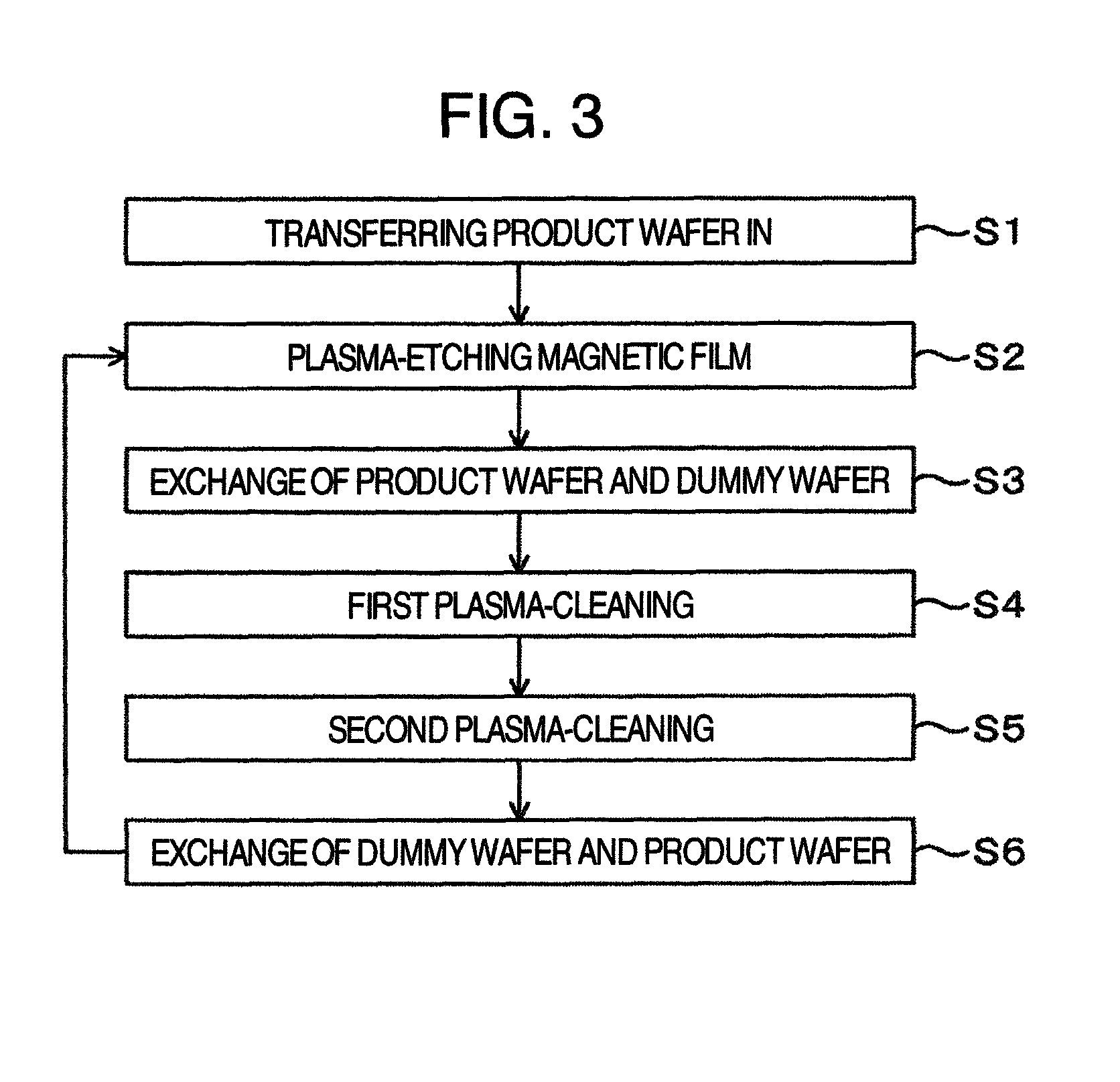
Plasma processing method
ActiveUS8591752B2Avoid corrosionEfficient removalElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsHydrogenPlasma processing
A method for plasma-etching a magnetic film and plasma-cleaning, in which deposits in an etching processing chamber are efficiently removed while corrosion of a wafer is suppressed, is provided. A plasma processing method for plasma-etching a to-be-processed substrate having a magnetic film in an etching processing chamber includes the steps of plasma-etching the magnetic film using a first gas not containing chlorine, transferring out the to-be-processed substrate from the etching processing chamber, first plasma-cleaning of the etching processing chamber using a second gas containing chlorine, and second plasma-cleaning using a third gas containing hydrogen after the first plasma cleaning.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Method for bleaching alkaline wheat straw pulp with medium-concentration DEP (diethyl phthalate)
The invention discloses a method for bleaching alkaline wheat straw pulp with medium-concentration DEP (diethyl phthalate). The method comprises the following steps of: dilignifying unbleached alkaline wheat straw pulp with chlorine dioxide; extracting alkali from the dilignified wheat straw pulp with sodium hydroxide; and bleaching the wheat straw pulp with hydrogen peroxide so as to obtain wheat straw ECF (Elemental Chlorine Free) pulp with high whiteness and high physical index. The whiteness of the obtained wheat straw pulp can reach 79.32 percent ISO (International Standardization Organization), Kappa number is 4.3, and yield is about 85.37 percent; the wheat straw pulp bleached by the DEP is manufactured into hand sheets with the tensile index of 48.41 N.m / g, the tear index of 5.21 mN.m<2> / g and the burst index of 2.64 kPa.m<2> / g. Finished paper has high physical intensity, and can meet the requirement for manufacturing of cultural paper.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for processing flexible OLED through printing micromolecule ink technology
InactiveCN104009189AImprove solubilitySimple processSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHole injection layerOptoelectronics
The invention relates to a method for processing a flexible OLED through the printing micromolecule ink technology. The method comprises the following steps that a hole injection layer, a hole transmission layer, a lighting layer and a cathode are prepared on an anode substrate material in an ink-jet printing mode, and hydrophilic PEDOT is adopted; the hole injection layer is prepared on an anode substrate material through PSS particle ink; lipophilic crosslinking and a arylamine composite are adopted to be dissolved in a aromatic solvent to serve as the ink, then the hole transmission layer is printed on the hole injection layer in the ink-jet printing mode; a high triplet state phosphorescence micromolecule material of host 1 and host 2 are adopted as a main lighting material, a dopant dye matched with the main material is adopted, the host 1, the host 2 and the dopant dye are mixed together in the solvent without chlorine to serve as a lighting micromolecule ink material, and the lighting layer is prepared on the hole transmission layer in the ink-jet printing mode.
Owner:JIANGSU SHENGMEI IND TECH GRP
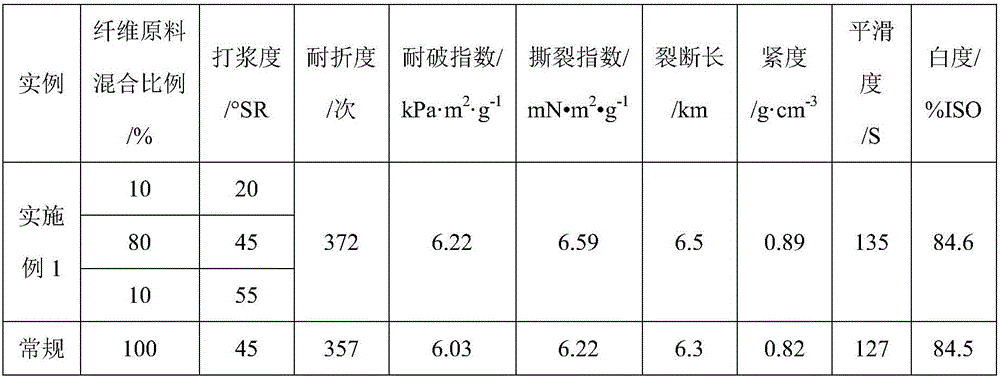
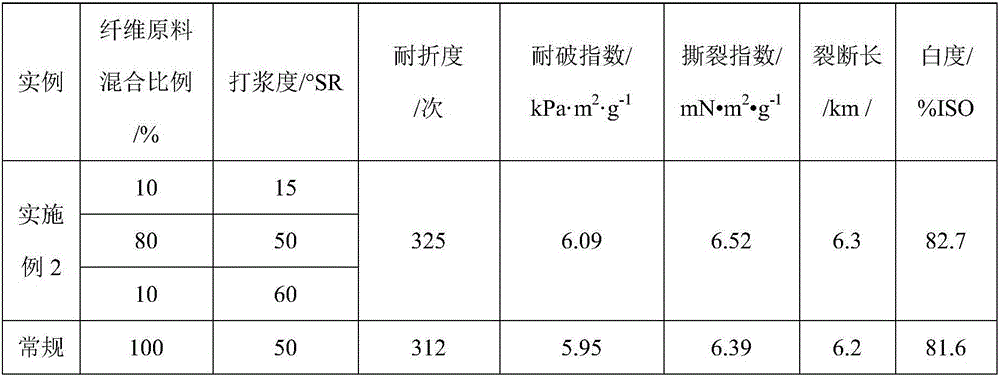
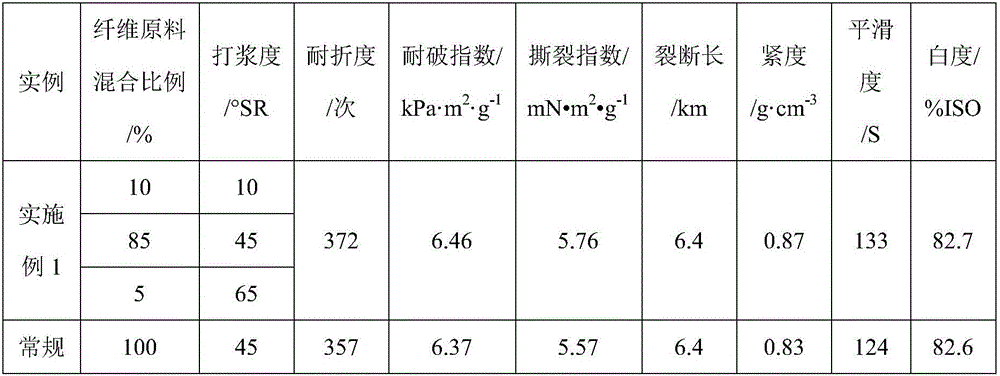
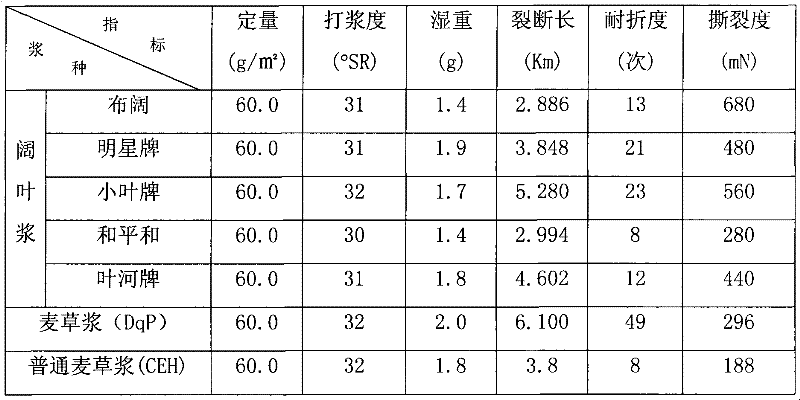
Method for preparing paper base by using needle and broad leaf-mixed sulfate elemental chlorine-free bleached chemical pulp
ActiveCN106676928AHigh tensile strengthImprove tightnessWashing/displacing pulp-treating liquorsPulp bleachingSulfatePaper based
The invention discloses a method for preparing paper base by using needle and broad leaf-mixed sulfate elemental chlorine-free bleached chemical pulp. The method comprises the following steps: (1) cooking by using a sulfate digestion method to obtain needle and broad leaf-mixed pulp as a pulp raw material, dividing the obtained needle and broad leaf-mixed pulp into three parts, and respectively pulping the three parts of pulp, wherein the beating degree of the first part of pulp is 10-20 degrees SR, the beating degree of the second part of pulp is 45-50 degrees SR, and the beating degree of the third part of pulp is 55-65 degrees SR; (2) mixing the three parts of pulp prepared in the step (1) together according to a certain proportion to obtain mixed pulp, wherein the mass ratio of the first part of pulp to the second part of pulp to the third part of pulp in the mixed pulp is equal to (10-20) to (60-85) to (5-10); (3) molding the mixed pulp obtained in the step (2) by lifting or pressing to obtain a paper base material.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
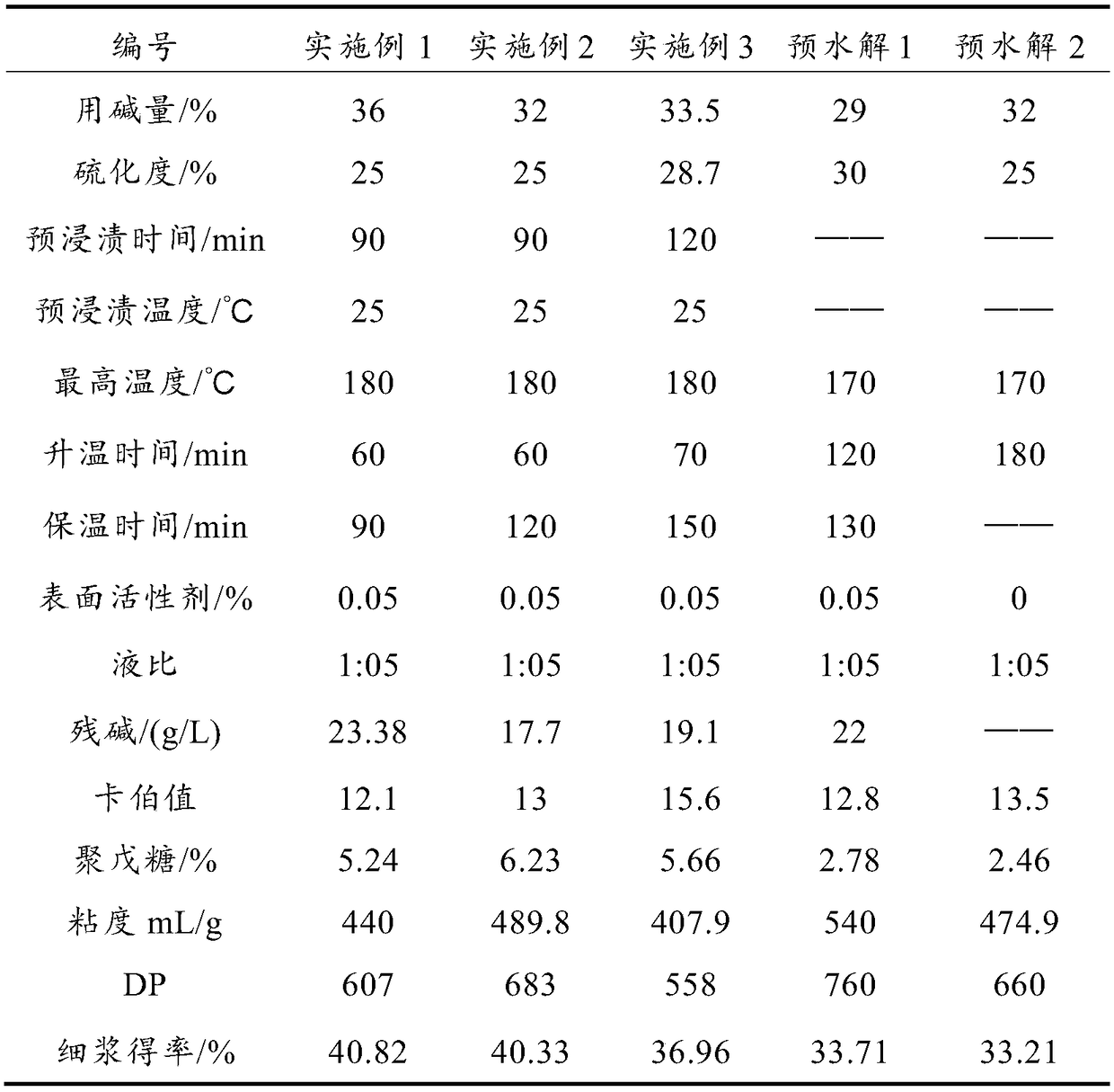
Pulping method of high-yield coniferous wood dissolving pulp and dissolving pulp prepared by pulping method
InactiveCN108867130ANo foulingIncrease product diversityDigestersPulp bleachingProduction lineSulfate
The invention provides a pulping method of high-yield coniferous wood dissolving pulp. The pulping method sequentially comprises the steps of cooking liquor presoaking, sulfate process cooking, cold alkali extraction and elemental chlorine free bleaching for the coniferous wood raw material, wherein the cooking liquor presoaking temperature is 20-100 DEG C, and the sulfate process cooking temperature is 170-185 DEG C. Compared with the traditional prehydrolyzed sulfate bleachable pulp, only a cold alkali extraction section needs to be added before bleaching of the prepared high-temperature sulfate dissolving pulp to reduce the polypentose content to a suitable level, and the waste liquor of the cold alkali extraction section can be reused in the cooking stage so as to avoid cost increase.The process is universal for production of the dissolving pulp in a pulp mill having sulfate process pulping production lines, and different grades of pulp can be produced on the same production lineonly by changing the cooking strength to realize conversion of the produced pulp between paper pulp and dissolving pulp, so as to increase the product diversity of enterprises, so that the enterprisescan produce the pulp in different purposes at any time according to changes in the market so as to enhance the anti-risk capability of the enterprises.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
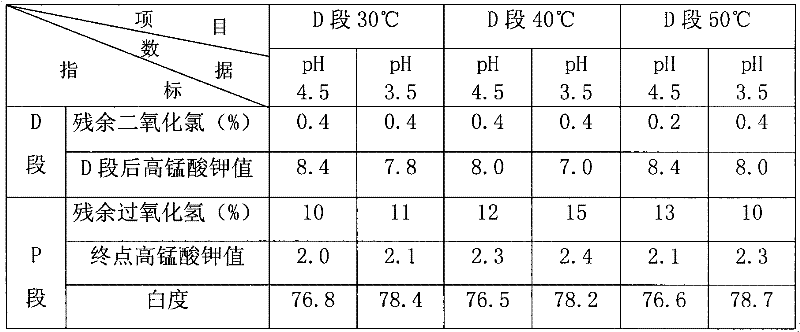
Elemental chlorine free bleaching method for plant fiber stuff
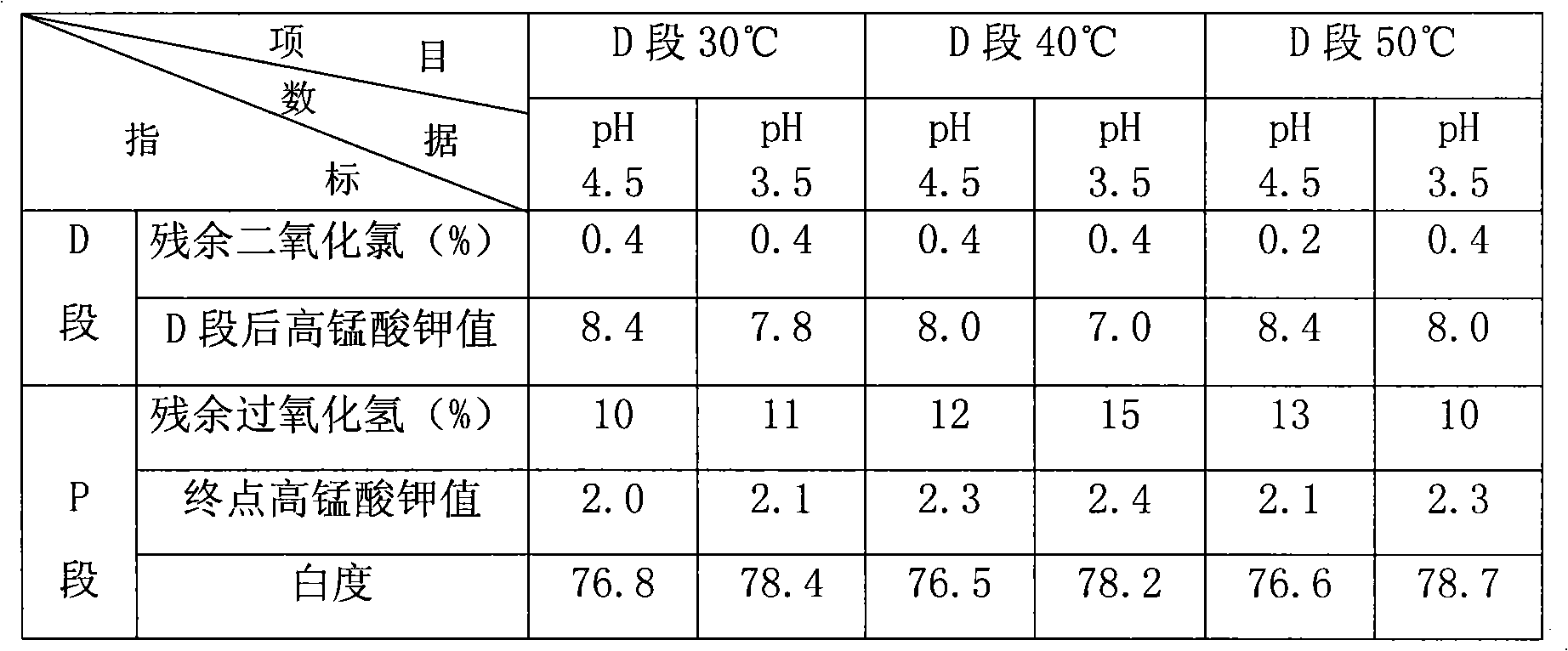
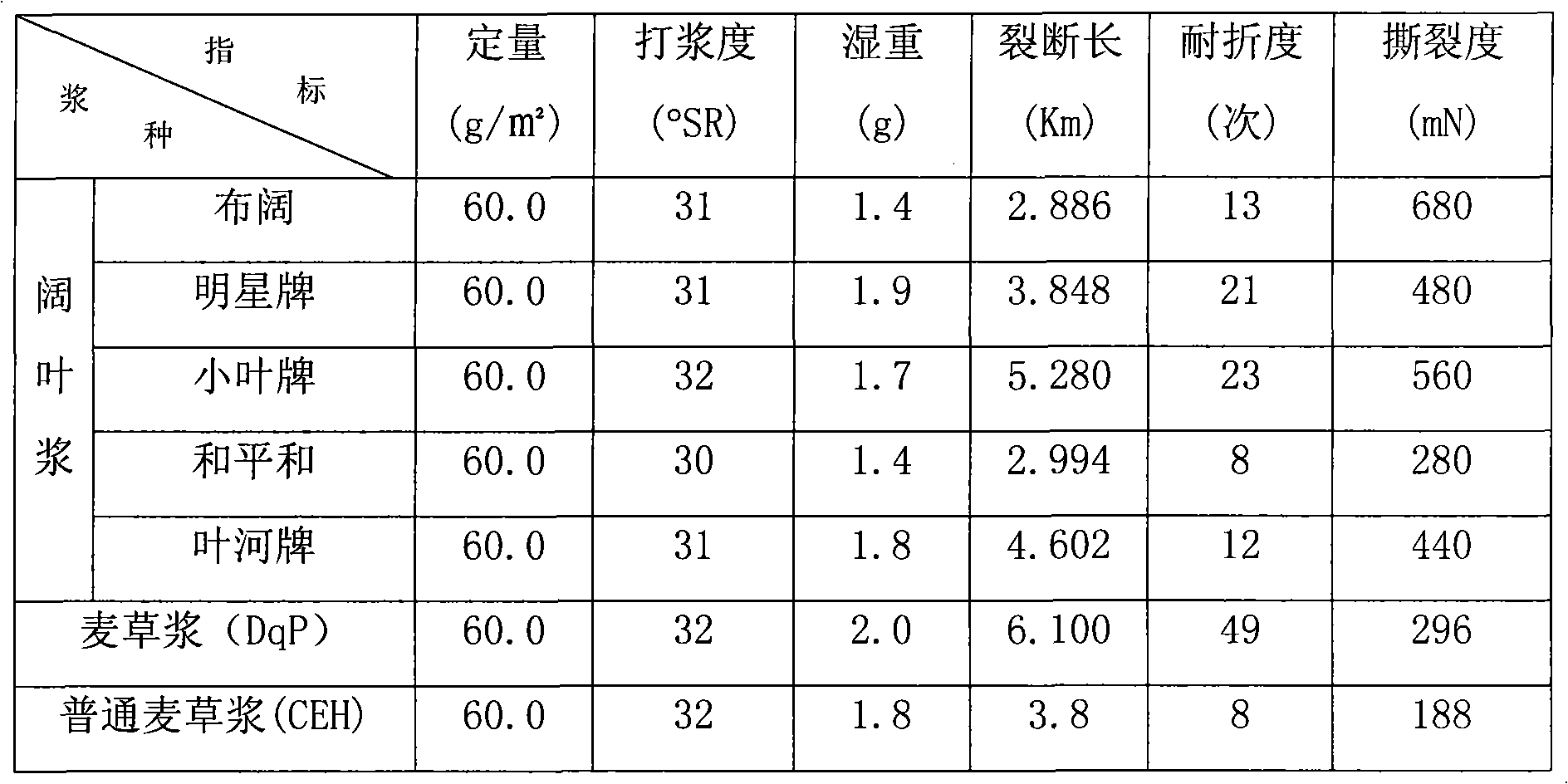
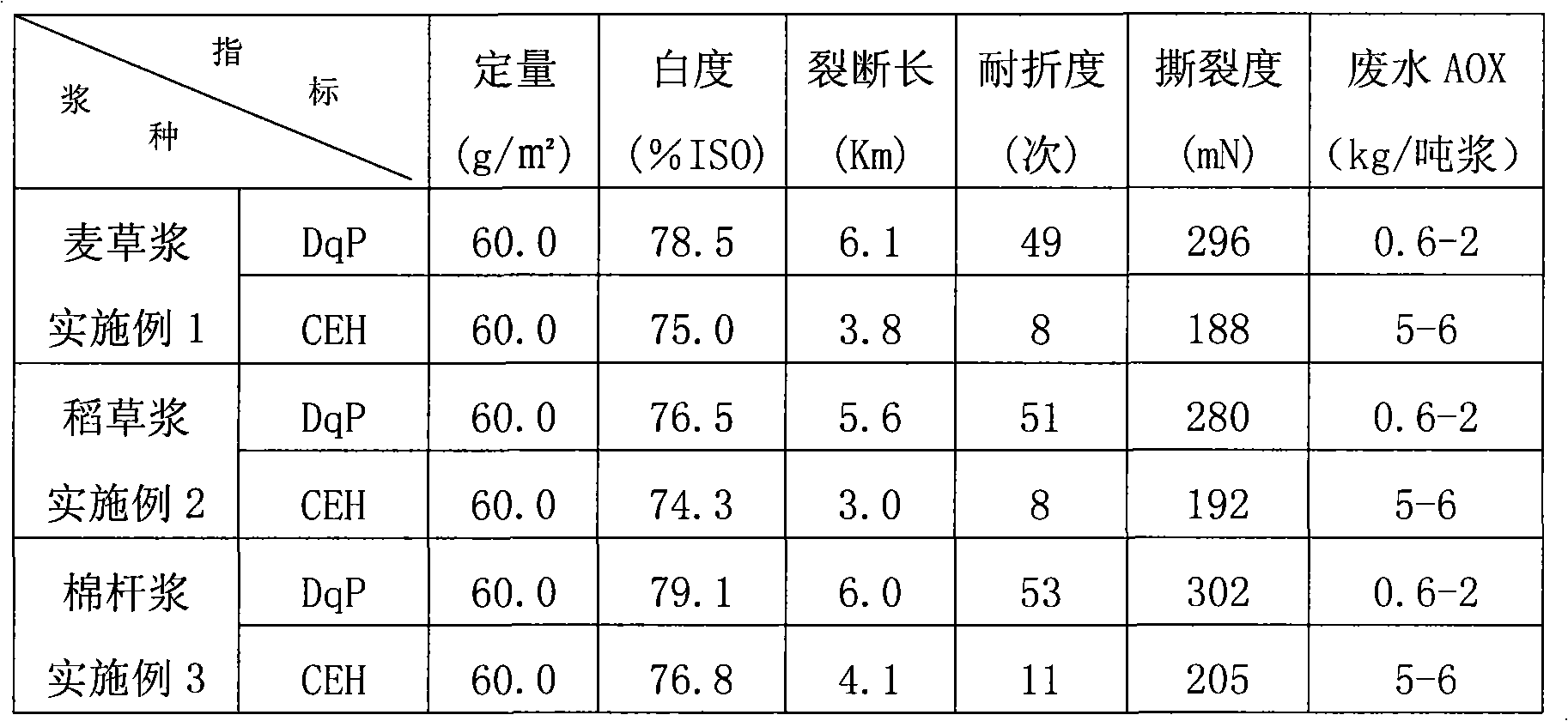
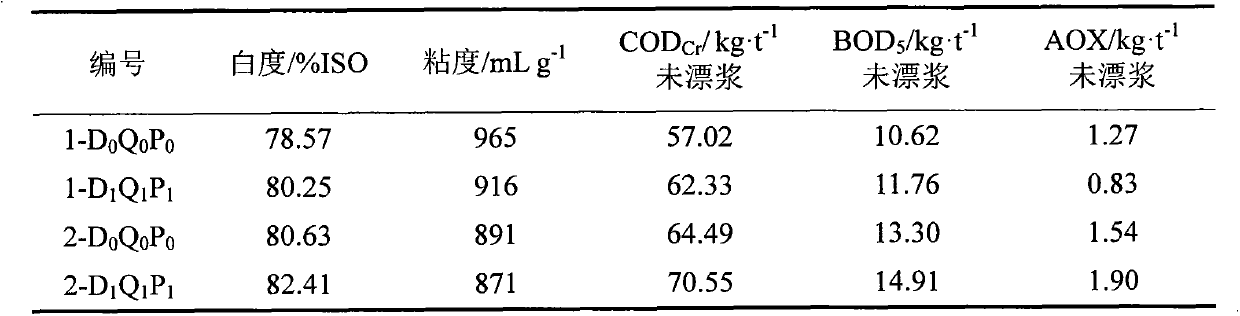
The invention relates to an elemental chlorine free bleaching method. In the method, dioxin and AOX are removed from the source by adopting D section bleaching and P section bleaching. The straw pulp is bleached by adopting the elemental chlorine free bleaching method, so that the problem that wastewater obtained by bleaching by the chlorine-containing bleaching method is most severely polluted is solved; and the bleaching process is simple and practicable. Each index of the bleached stuff can be compared with that of broadleaf wood pulp.
Owner:SHANDONG FUYIN PAPER & ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
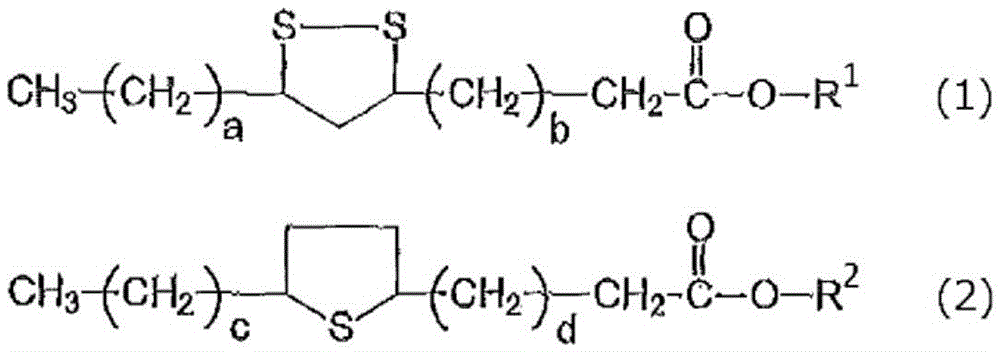
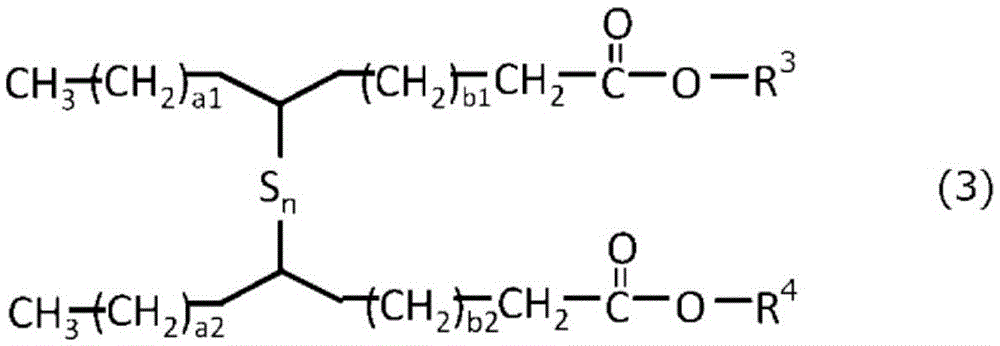
Lubricating oil composition for metal working
Provided is a lubricating oil composition for metal working, with which it is possible to achieve improved working efficiency and improved tool life, and which is an environmentally-friendly product containing no chlorine, wherein the lubricating oil composition for metal working contains a lubricating oil base oil, (A) a sulfate ester represented by a predetermined formula and / or a dialkylpolysulfide in which 50 mol% of the sulfur has 4 or more crosslinks, and (B) a metallic cleaner having a metal ratio of 6 or greater.
Owner:JX NIPPON OIL & ENERGY CORP
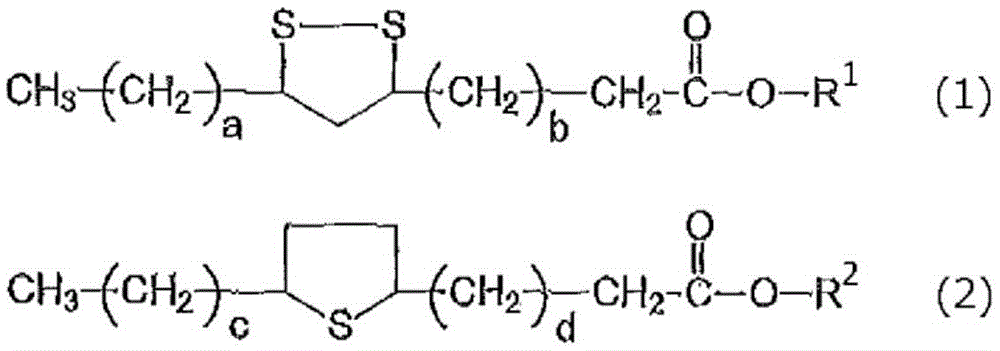
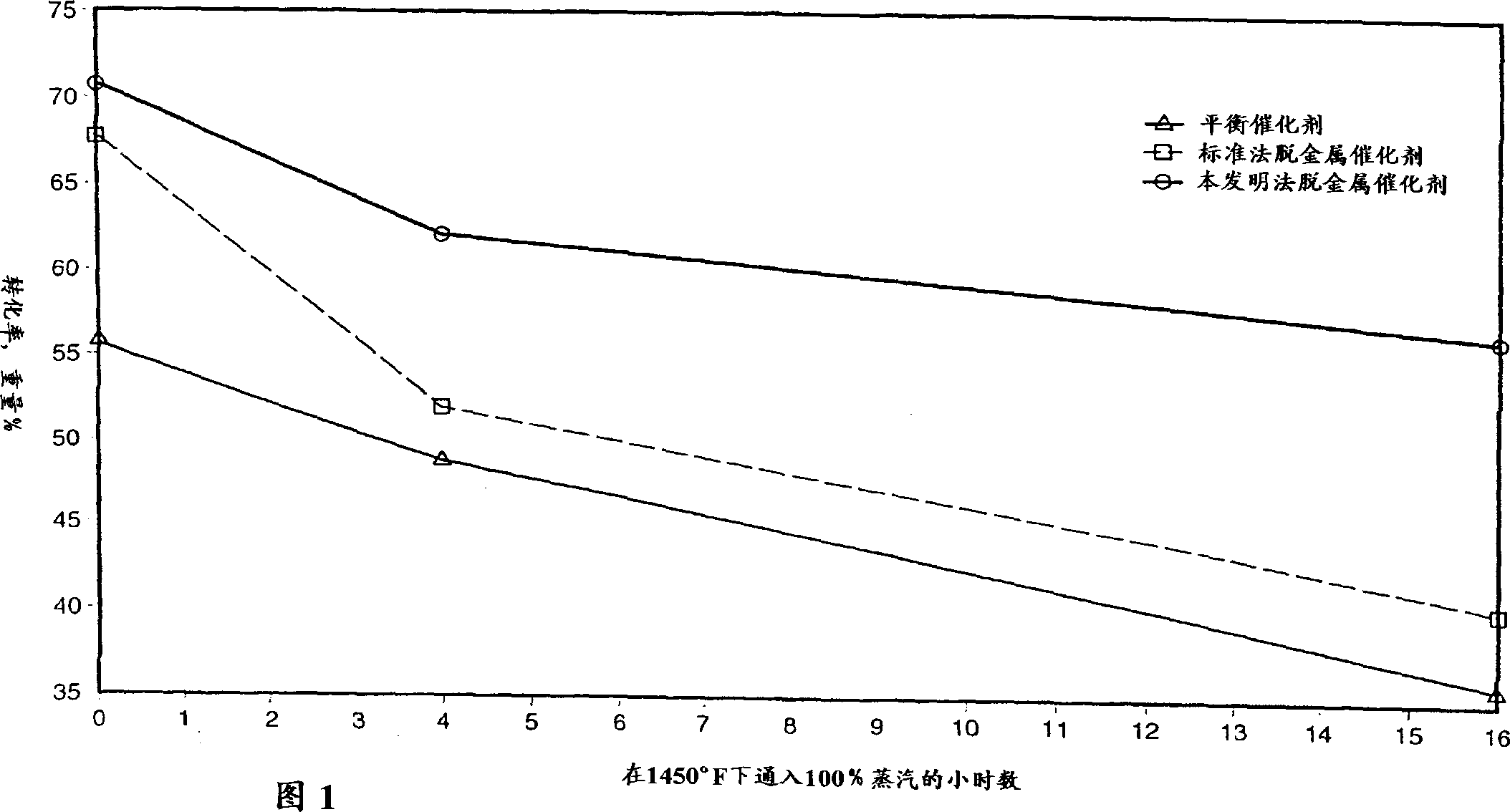
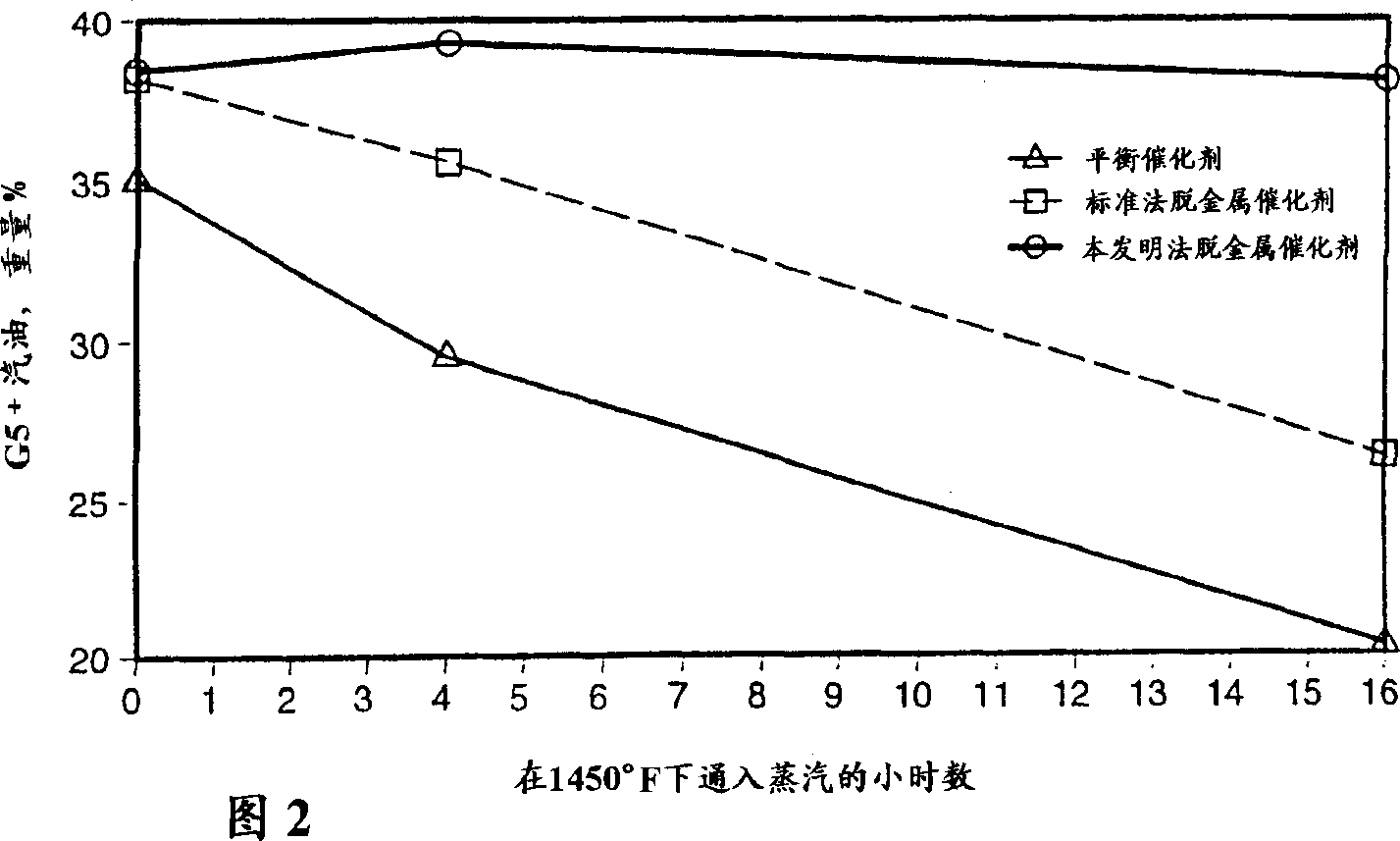
Methods for enhancing acid sites of FCC catalysts
InactiveCN1304330AHigh activityImprove stabilityCatalyst regeneration/reactivationCatalyst activation/preparationSlurryContamination
The present invention discloses aqueous methods for enhancing the acid sites of fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) catalysts. The methods comprise the steps of contacting an FCC catalyst, either spent or fresh, with an aqueous solution comprising water, an inorganic acid substantially free of chloride and aluminum. The acid is preferably sulfurous or sulfuric acid. The aluminum is provided by an aluminum source selected from the group consisting of the alumina trihydrates and aluminum oxide. Chloride contamination of the aluminum source should be minimal, preferably less than about 1000 ppm chloride, more preferably less than about 200 ppm chloride. The pH of the aqueous solution is adjusted to about 3-12 by the addition of a sufficient quantity of ammonium hydroxide. The FCC catalyst is added to this solution, preferably with stirring, in a weight ratio of about 1 part catalyst to about 1-10 parts water to prepare an aqueous slurry. Upon stabilization of the pH of the aqueous slurry, enhancement of the acid sites of the catalyst is achieved and the catalyst may be separated from the slurry and, if desired, washed. This simple, aqueous process reduces the level of many metal poisons on the FCC catalyst and produces a catalyst having an enhanced number of acid reaction sites.
Owner:COASTAL CATALYST TECH
Inorganic electrolytic coagulant and a method of transforming sludge by using this inorganic electrolytic coagulant
InactiveUS6843932B1Increase productionShorten operation timeScale removal and water softeningContaminated soil reclamationElectrolysisSludge
Contaminated sediments in such bodies of water as lakes and ponds, inner bays and rivers obtained by dredging are converted into favorable soils by adding to the contaminated sediments and aqueous solution formed by mixing an inorganic electrolytic coagulant obtained by mixing phosphonic acid and magnesium sulfate in a solvent not containing chlorine, stirring them for several minutes and then mixing aluminum sulfate and polyferric sulfate and stirring them for several minutes, together with a soil particle reinforcing agent and a pH controller.
Owner:KAWANO ICHIZO
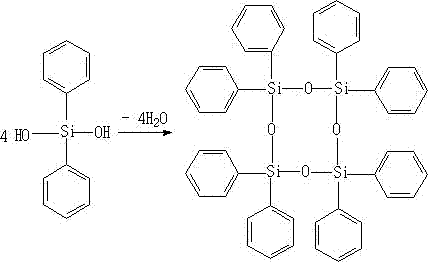
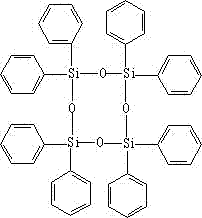
Preparation method for octaphenylcyclotetrasiloxane
ActiveCN106967108AAvoid it happening againAvoid introducingSilicon organic compoundsReaction temperatureDiphenylsilanediol
The invention discloses a preparation method for octaphenylcyclotetrasiloxane, belonging to the field of synthesis of organo silicon compounds. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding diphenylsilanediol and methanol in a certain mass ratio into a reaction container and carrying out stirring until diphenylsilanediol and methanol are totally dissolved; then adding an alkaline catalyst; carrying out heating to 60 to 65 DEG C and carrying out reflux for 4 to 6 h; then carrying out cooling to room temperature and standing for 5 to 8 h; and successively carrying out filtering and drying so as to obtain the acicular crystal octaphenylcyclotetrasiloxane. According to the invention, diphenylsilanediol free of chlorine is used as a raw material and introduction of chloride ions is avoided, so reaction temperature is mild, crystallization is carried out at normal temperature and the crystal is easy to filter and separate; solvents are recyclable and pose no influence to reaction effect; and the preparation method for octaphenylcyclotetrasiloxane is simple in process, and prepared octaphenylcyclotetrasiloxane has stable quality and high yield.
Owner:广东省科学院产业技术育成中心
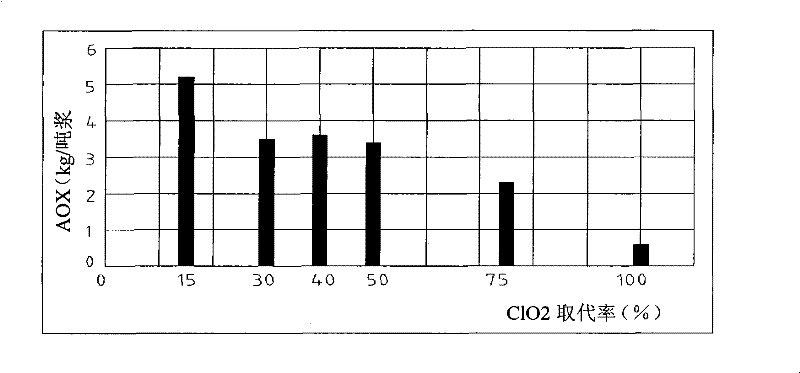
Method for reducing generation of AOX in bleaching process of bagasse pulp with chlorine dioxide by optimizing alkali extraction section
The invention discloses a method for reducing generation of AOX in a bleaching process of bagasse pulp with chlorine dioxide by optimizing an alkali extraction section. According to the method, the bagasse pulp is taken as a raw material, elemental chlorine-free bleaching is adopted, chlorine dioxide is taken as a main bleaching agent, a D0EpD1 three-section bleaching process is used, an assistant, namely sodium sulfide, is added in the Ep section, the using amount of sodium sulfide is 0.25-1.00% of the mass of absolutely dry bagasse pulp, and the ISO whiteness of the pulp after bleaching and the content of AOX in bleaching wastewater are detected. Compared with the prior art, the ISO whiteness of the pulp after bleaching is slightly reduced, and meanwhile, the content of AOX in the bleaching wastewater is greatly reduced.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Method for reducing content of AOX in chlorine dioxide bleaching wastewater of bagasse pulp
InactiveCN105350371AReduce AOX contentPulp bleachingCellulose material pulpingState of artChlorine dioxide
The invention discloses a method for reducing the content of AOX in chlorine dioxide bleaching wastewater of bagasse pulp. With bagasse as a raw material, bagasse is treated by using hot water pre-extraction technology; pretreated bagasse enters an elemental chlorine-free bleaching phase after a cooking and steaming procedure, and chlorine dioxide is used as a main bleaching agent; and after a section of chlorine dioxide bleaching procedure, wherein the usage amount of chlorine dioxide is 1.6% of the mass of absolute dry bagasse pulp, the content of AOX in bleaching wastewater is detected. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention has the advantage that the content of AOX in bleaching wastewater is greatly reduced.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Fine powder of mixed plastic and its production process
The present invention provides a method for producing mixed plastic micropowder, which includes the following steps: by increasing or decreasing at least one plastic selected from the group consisting of chlorine-containing plastics and chlorine-free plastics, to prepare plastics with a chlorine concentration of 2-2 20% by mass of the mixed plastic; stirring the mixed plastic under melting, and performing dechlorination until the chlorine concentration is 0.9% by mass or less; cooling and solidifying the dechlorinated stirred material; and A step of pulverizing the cured product. By applying this method, as long as the chlorine concentration is within a specified range, increasing the chlorine concentration in waste plastics can promote stirring and dehydrochlorination of molten waste plastics, and therefore, fine waste plastic powders with very low chlorine concentrations can be obtained. Therefore, plastics discarded in daily life and industrial activities can be reused as reducing agents, fuels, etc.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Phenol resin foam body and method for producing same
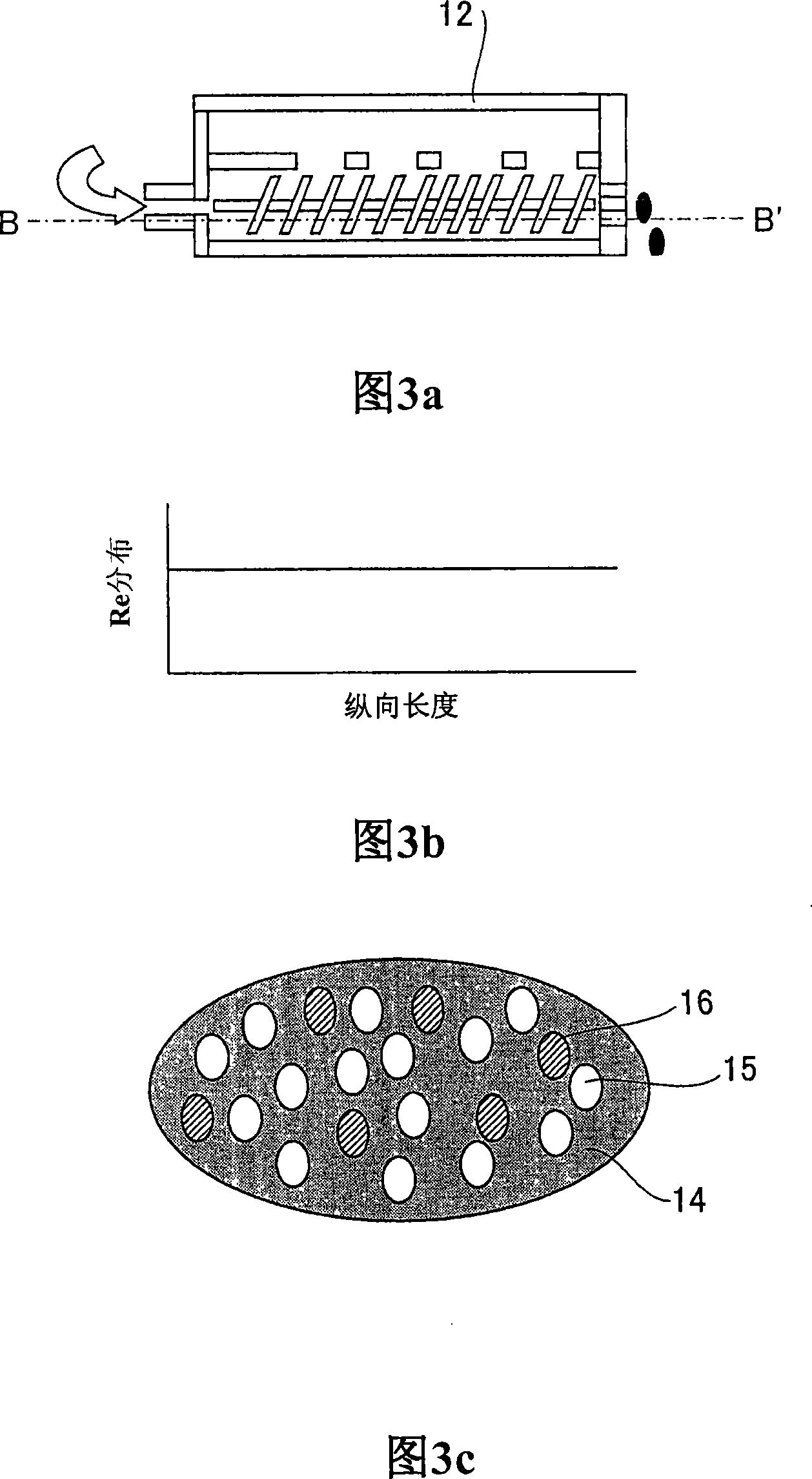
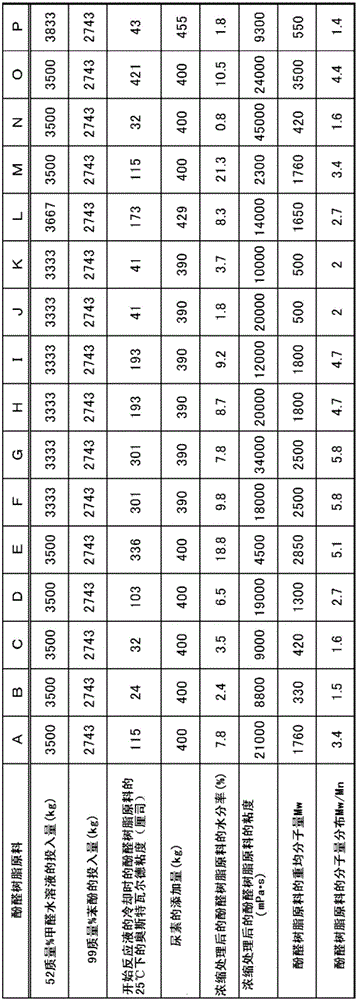
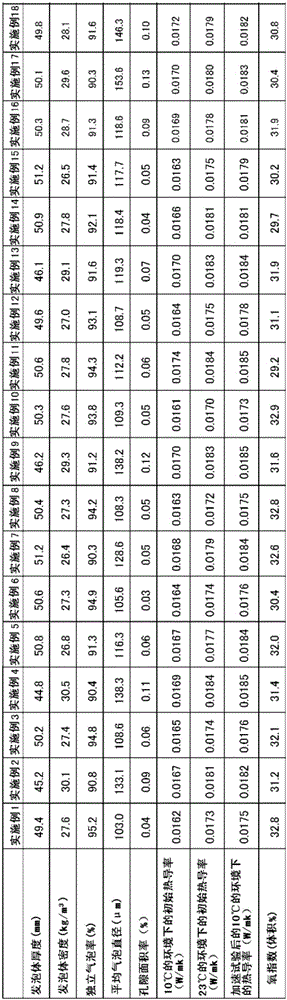
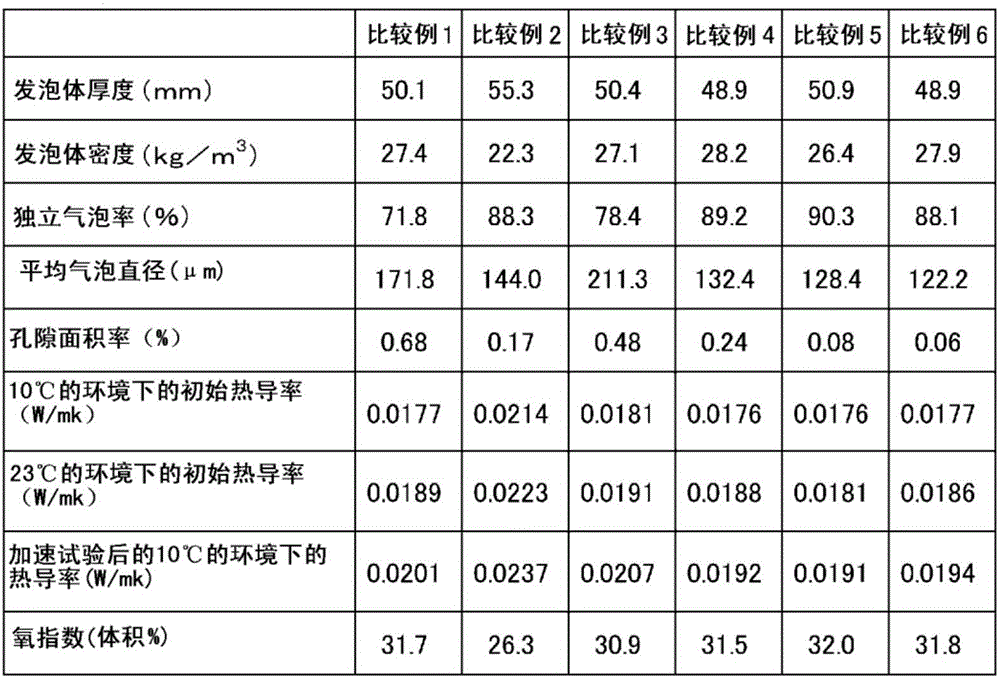
ActiveCN106414573ALow global warmingGood insulation performancePaper/cardboard layered productsConstructions elementsFoaming agentHydrofluoroolefin
Provided is a phenol resin foam body which comprises a phenol resin and a foaming agent that includes a chlorinated hydrofluoroolefin and / or a non-chlorinated hydrofluoroolefin. The phenol resin foam body has a density of 10 to 150 kg / m3, a thermal conductivity in a 10 DEG C environment of 0.0175 W / m.k or less, and a thermal conductivity in a 23 DEG C environment of 0.0185 W / m.k or less.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS CO LTD
Elemental chlorine free bleaching method for plant fiber stuff
The invention relates to an elemental chlorine free bleaching method. In the method, dioxin and AOX are removed from the source by adopting D section bleaching and P section bleaching. The straw pulp is bleached by adopting the elemental chlorine free bleaching method, so that the problem that wastewater obtained by bleaching by the chlorine-containing bleaching method is most severely polluted is solved; and the bleaching process is simple and practicable. Each index of the bleached stuff can be compared with that of broadleaf wood pulp.
Owner:SHANDONG FUYIN PAPER & ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Wheat straw pulp elemental-chlorine-free bleaching wastewater recycling method
InactiveCN104179056APerformance is not affectedReduce bleach dosagePulp bleachingChlorine dioxideWastewater
The invention discloses a wheat straw pulp elemental-chlorine-free bleaching wastewater recycling method which is characterized in that a paper pulp bleaching mode is DQP three-section bleaching, and the whole washing wastewater of pulp from hydrogen peroxide (P) section bleaching is reused, without being processed, in washing pulp from chlorine dioxide (D) section bleaching. The specific method is as follows: after the washing wastewater of pulp from the P section bleaching is reused in the D section bleaching, the pulp is diluted to the washing pulp concentration of 0.5-2%; the pulp is fully mixed and washed and then is concentrated to 15-18%; and the concentrated pulp is diluted with clear water and then is processed in a Q section. The amount of residual bleached chemicals in washing water from the P section is no less than 40%. By the method of directly recycling P-section bleaching wastewater in washing pulp from D-section bleaching without being processed, water consumption during the wheat straw pulp bleaching process and yield of bleaching wastewater can be reduced effectively. In addition, dosage of a bleaching agent can be decreased remarkably, pollution load can be reduced, and performance of the bleached pulp is basically not influenced. Heat energy of wastewater from the P section also can be utilized, and energy consumption of the bleaching section can be reduced effectively.
Owner:CHINA NAT PULP & PAPER RES INST CO LTD
Method of manufacturing glass preforms for optical fibers
A method of manufacturing a fluorine-doped glass preform for an optical fiber, comprising: exposing a soot preform (11) in a first elongated chamber (28; 44) of a first furnace (30; 40) to an atmosphere containing In an atmosphere of fluorine gas and substantially free of chlorine to obtain a fluorine-doped soot preform, the first elongated chamber (28; 44) has a single isothermal hot zone maintained at a doping temperature of 800°C to 1200°C (33; 53); exposing the fluorine-doped soot preform (11) in a second elongated chamber (61) of a second furnace (60) to an atmosphere comprising a gas containing chlorine and substantially free of fluorine to make It dehydrates, and the second elongated chamber has an upper thermal zone (66') at a dehydration temperature of 1000°C to 1350°C and a lower thermal zone (67') at a consolidation temperature of 1500°C to 1650°C, wherein Dehydration takes place in the upper hot zone (66') of the second furnace, and the fluorine-doped soot preform (11) is consolidated by moving it down into the lower hot zone of the second furnace to obtain fluorine-doped Glass preforms.
Owner:PRYSMIAN SPA
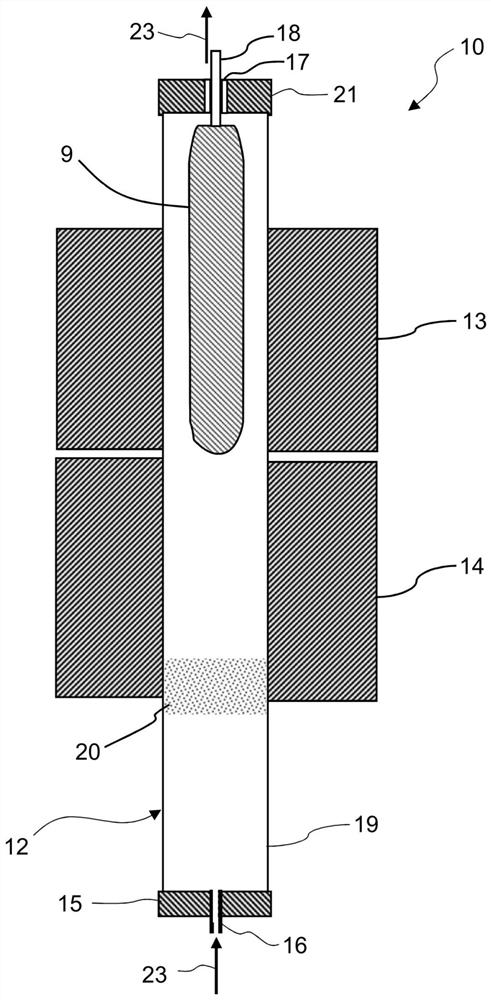
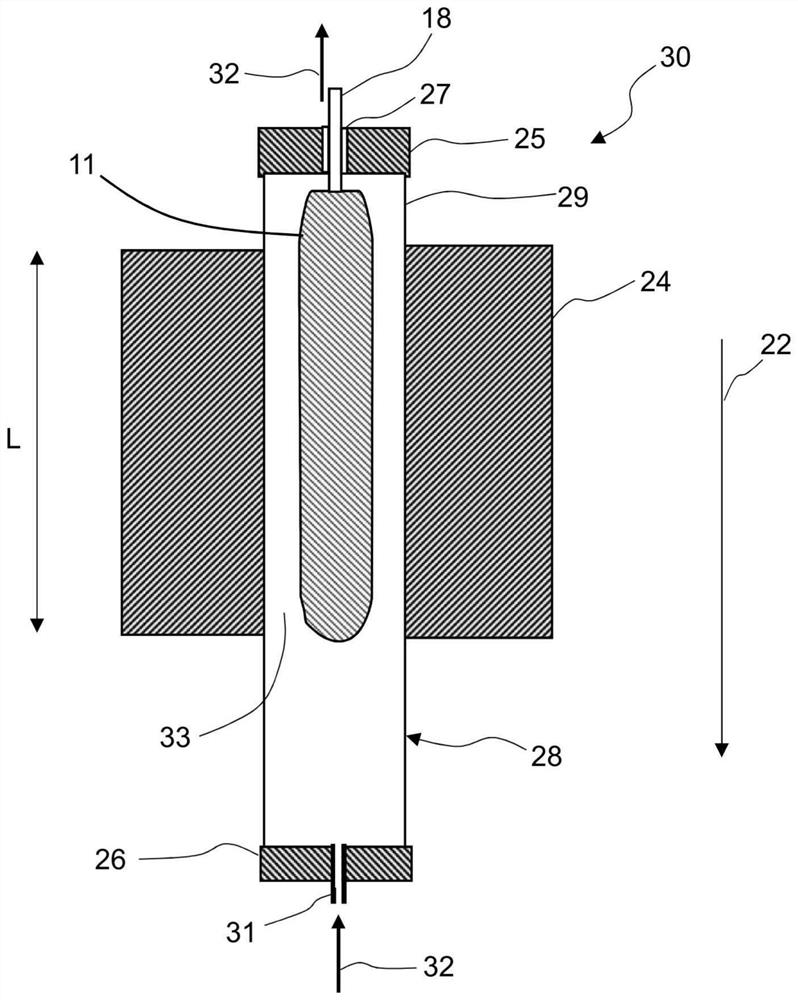
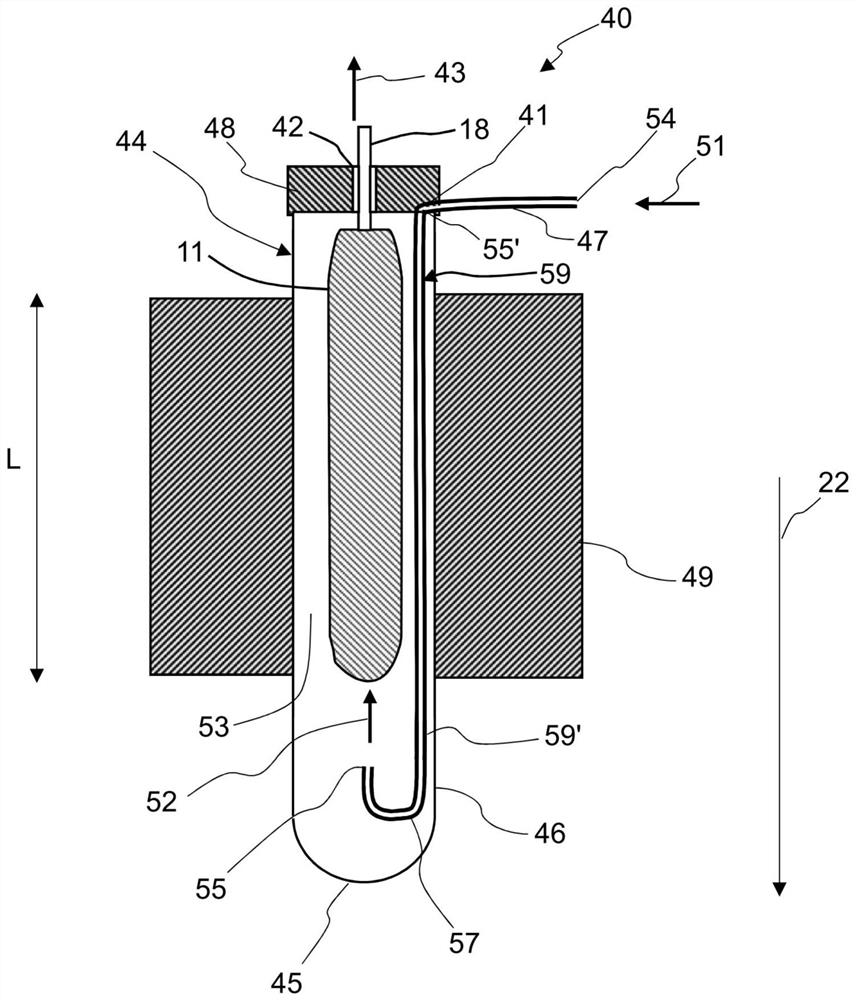
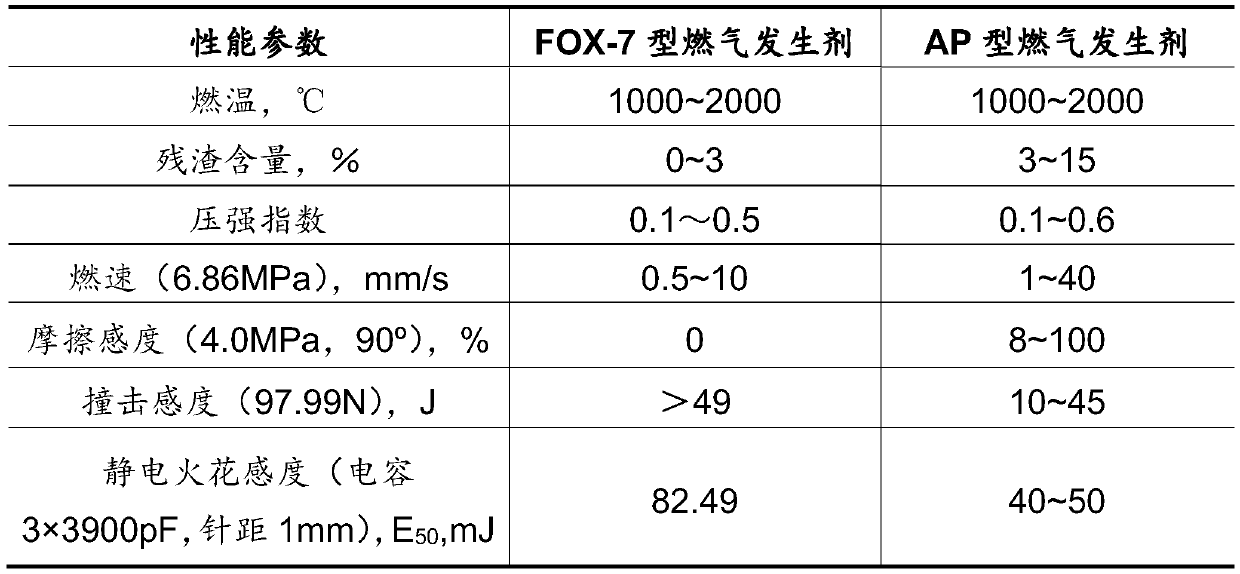
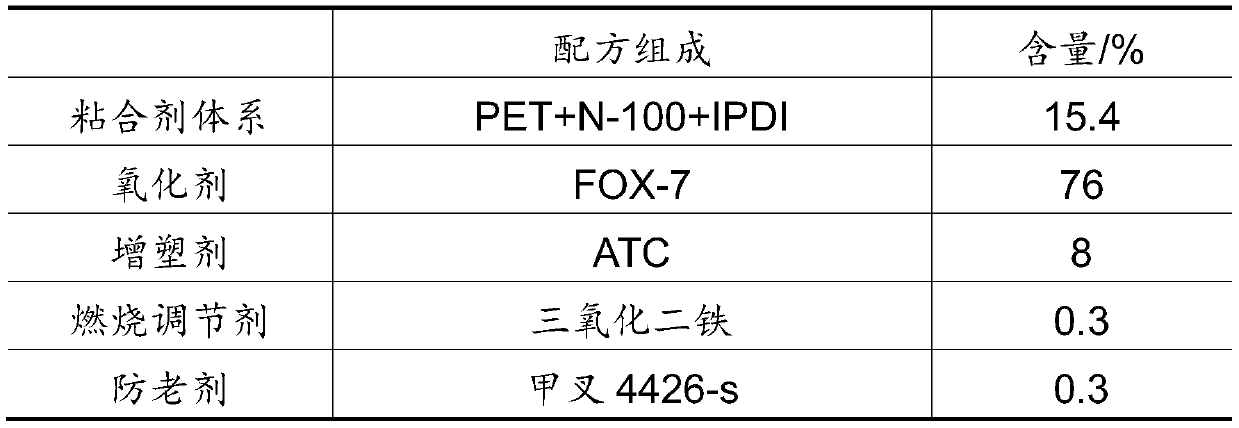
Clean fuel gas generating agent
The invention relates to a clean fuel gas generating agent, which is characterized in that chlorine-free 1,1-diamino-2,2-dinitroethylene is introduced into a formula of the fuel gas generating agent,and serves as a clean oxidizing agent to replace ammonium perchlorate, and the problems that the fuel gas generating agent is large in combustion smoke and large in residue amount are solved. The clean fuel gas generating agent disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of being clean in gas, low in residue, low in characteristic signal, safe, insensitive and the like. The fuel gas generating agent is applied to a power source of an aircraft, so that the combat effectiveness and the war survival ability of the aircraft are greatly improved, and the fuel gas generating agent has an extremely wide application prospect.
Owner:HUBEI INST OF AEROSPACE CHEMOTECHNOLOGY
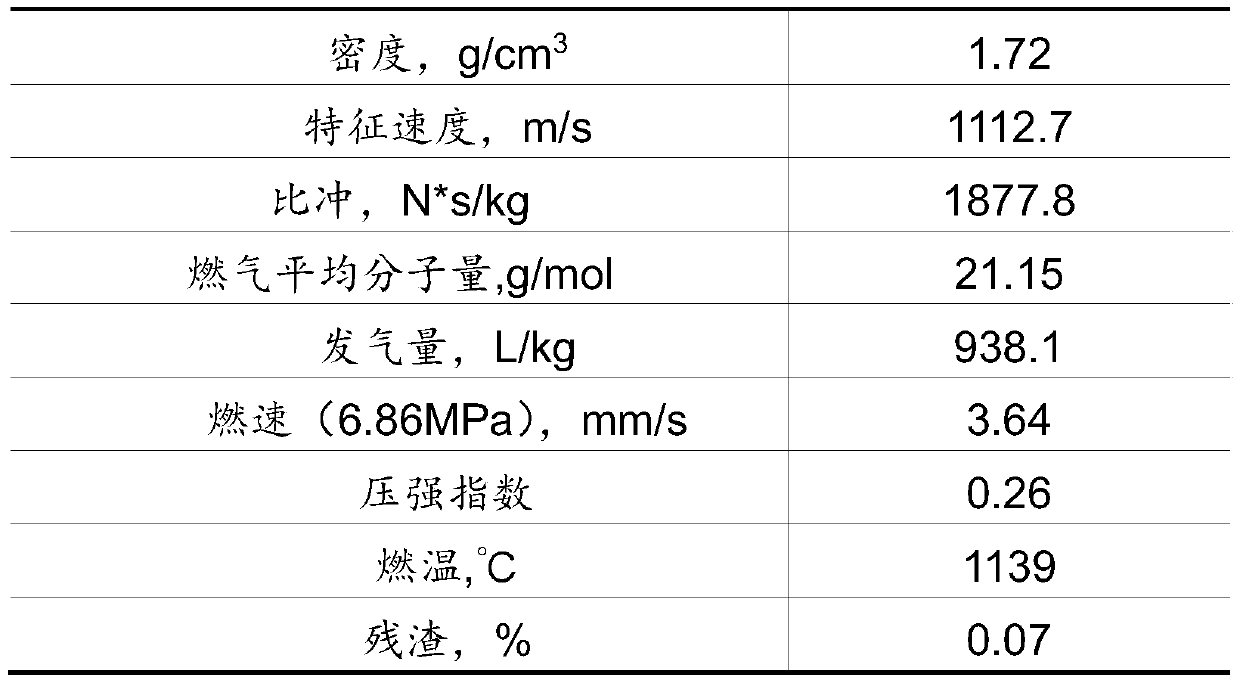
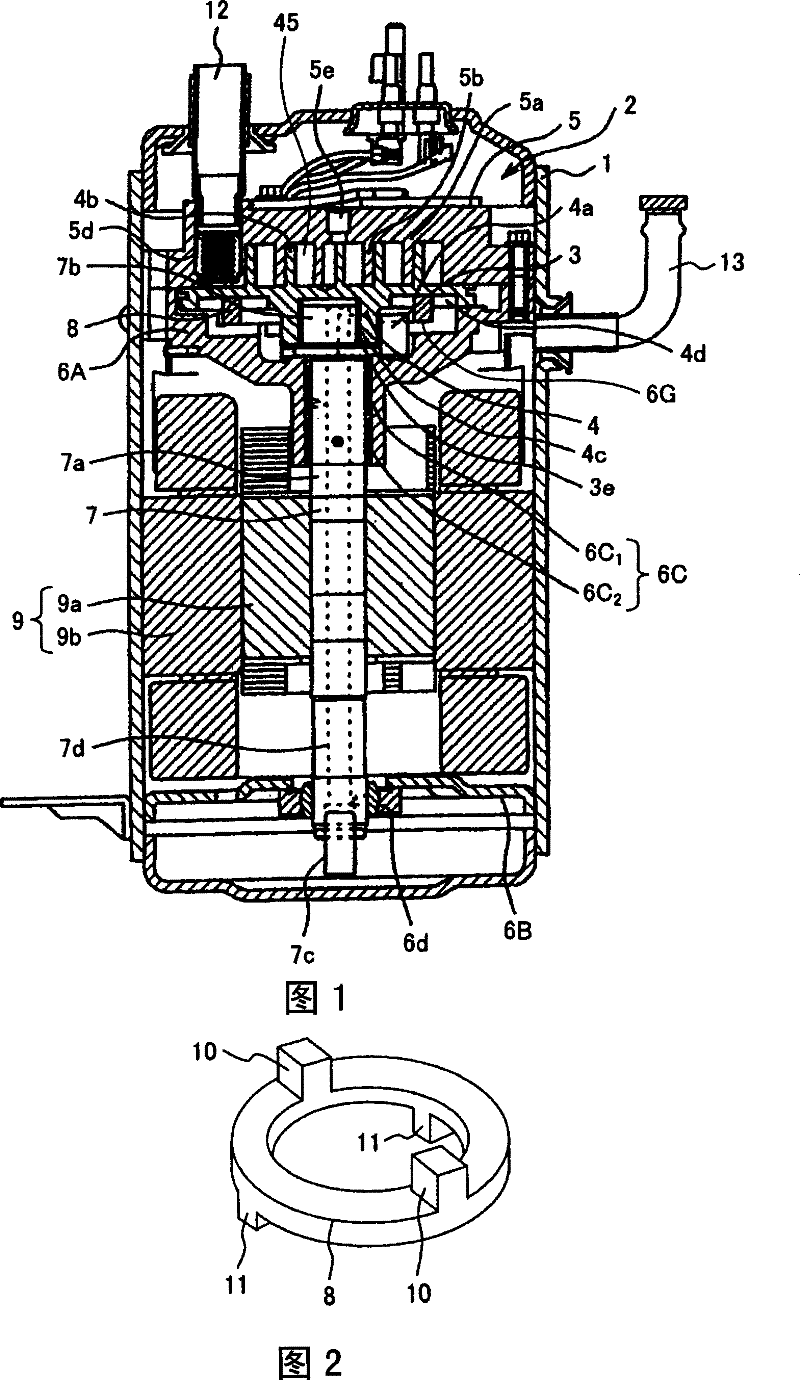
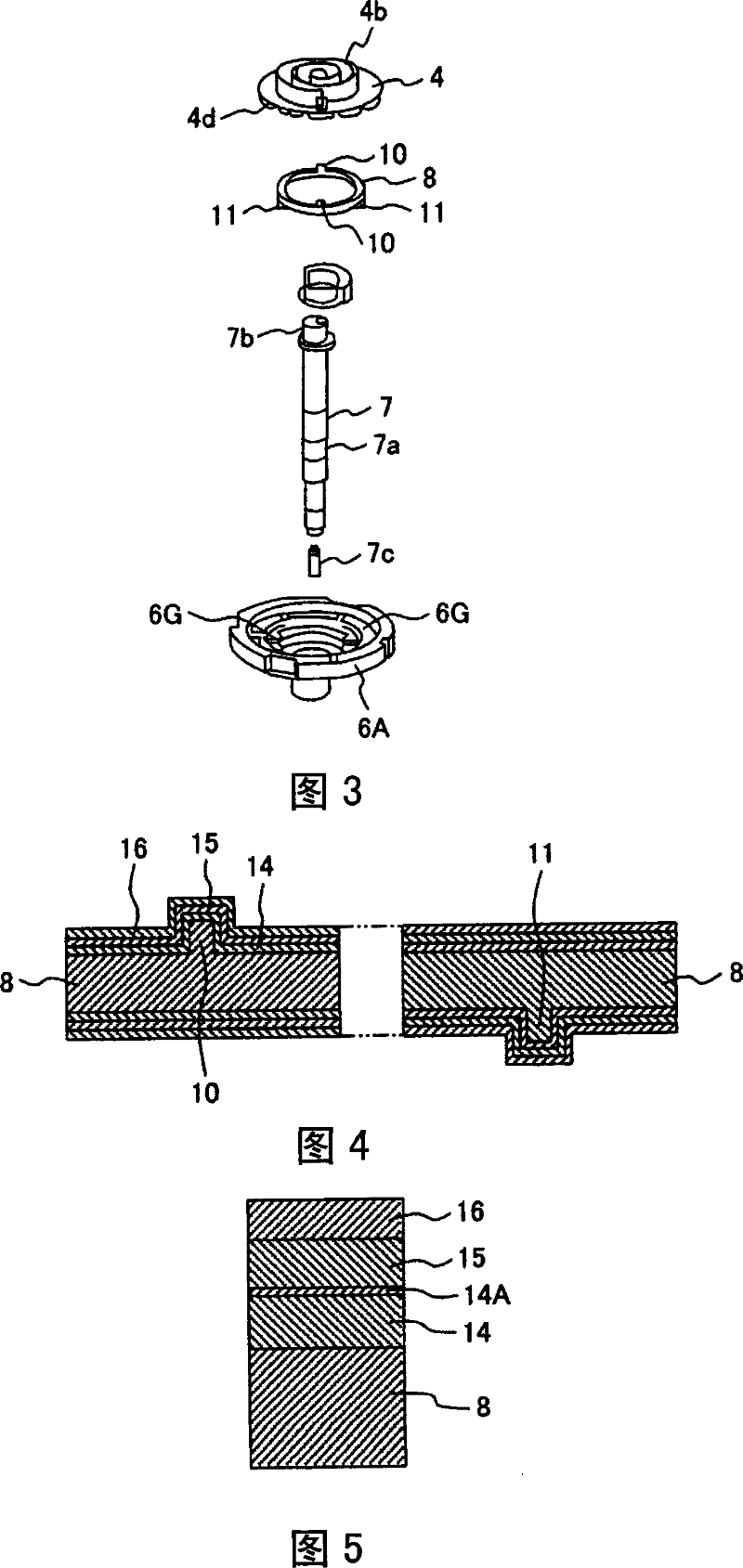
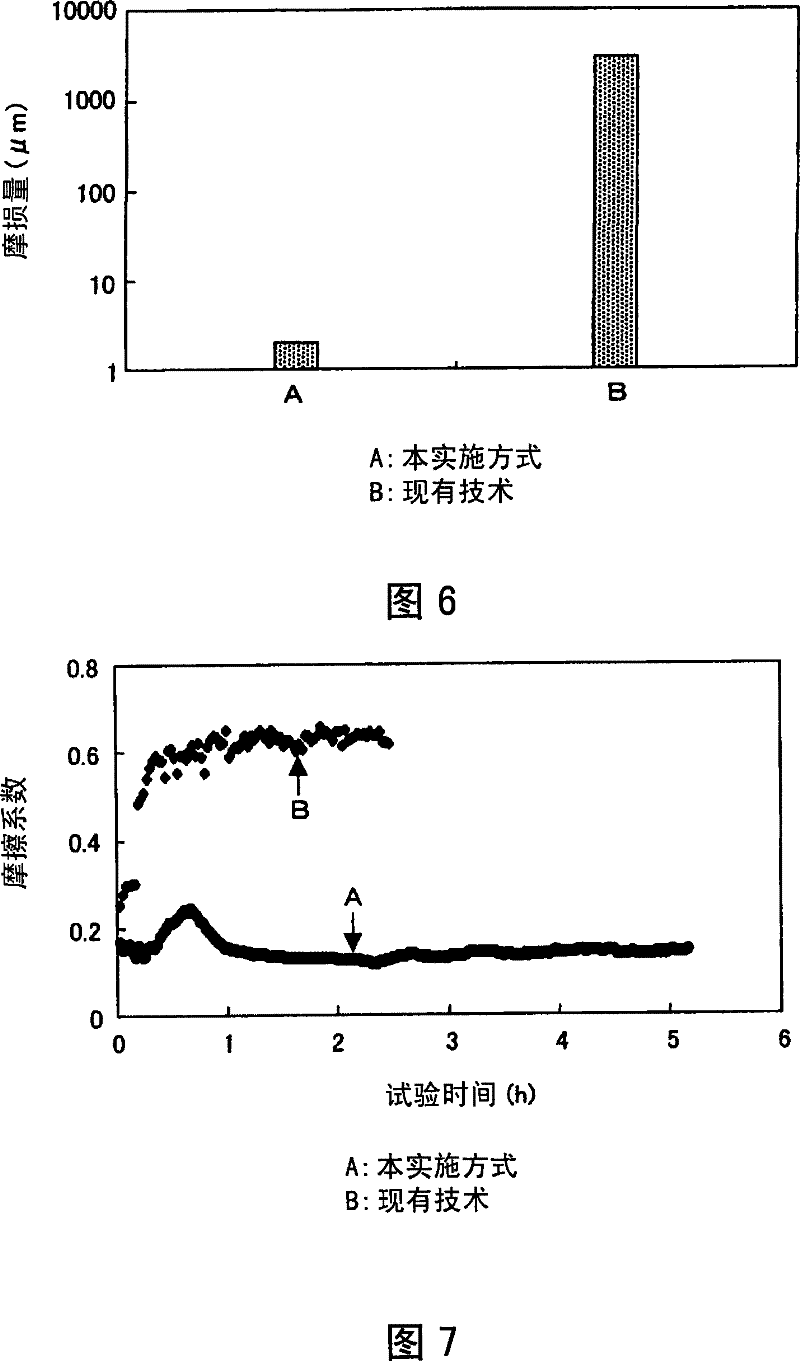
Sliding component and swirl motor compressor using the same
ActiveCN101285469BImprove wear resistanceReduce frictionLayered productsVacuum evaporation coatingThermodynamicsEngineering
The invention provides a sliding member which is able to further improve wearability and is not maintained for a long time by using substitute refrigerant without chlorine or natural refrigerant and a scroll motor compressor using the sliding member. The invention forms an oxydizing membrane layer (14) on the surface of the sliding member (8) formed by sintered iron, and forms an intermediate layer (15) on the oxidizing membrane layer (14), and forms an oxide layer (14A) and forms a hard carbon membrane layer (16) on the intermediate layer (15). As above, the surface of the sliding member (8)is orderly formed with the oxydizing membrane layer (14), the oxide layer (14A), the intermediate layer (15) and the hard carbon membrane layer (16), so as to contact the hard carbon membrane layer (16) with excellent wearability and low friction with the surface of the sliding member (8) and not to maintain for a long time.
Owner:HITACHI JOHNSON CONTROLS AIR CONDITIONING INC
Environment-friendly chlorine-free stainless steel rust removal cleaning agent and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to an environment-friendly chlorine-free stainless steel rust removal cleaning agent and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of stainless steel surface treatment. The stainless steel rust removal cleaning agent comprises the following raw material components in percentage by mass: 5-10% of sulfinic acid, 3-5% of fluoride, 10-20% of glycolic acid, 8-15% of citric acid, 8-15% of sodium alkyl amino propionate, 5-10% of acrylic polymer and the balance of water. The stainless steel rust removal cleaning agent does not contain strong acid, heavy metal and nitrous acid substances, does not have pungent smell, and overcomes the defect that a traditional rust removal agent containing hydrochloric acid quickly returns rust after being washed with water. The cleaning agent is widely applied to cleaning processes such as dipping, ultrasonic wave and scrubbing, and can quickly remove rust, decompose various oil stains and form a clean and short-term rust-proof surface.
Owner:苏州盈得化学科技有限公司
Inorganic electrolytic coagulant and method for modifying mud using said inorganic electrolytic coagulant
InactiveCN1454111AImprove protectionConducive to sustainable useSludge treatmentContaminated soil reclamationAluminium sulfateElectrolysis
Owner:河野市藏 +2
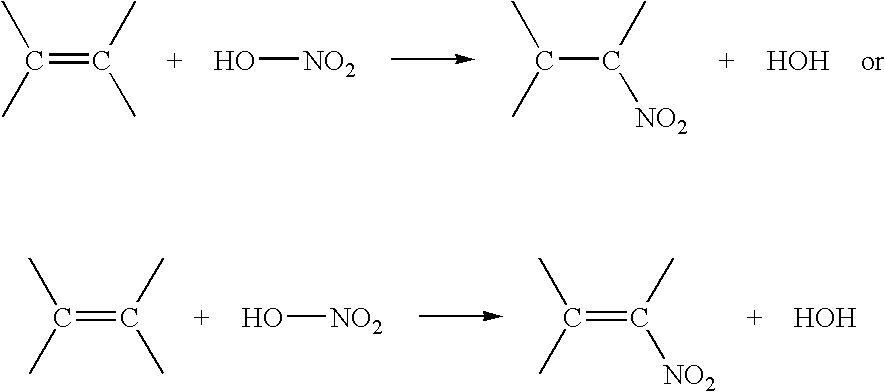
Nitrated extreme pressure additives and blends
InactiveUS8664171B2Organic chemistryLiquid carbonaceous fuelsNitro compoundInternal combustion engine
Owner:DOVER CHEM CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com