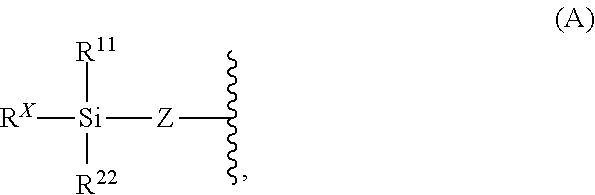Patents
Literature
437 results about "Molecular self-assembly" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Molecular self-assembly is the process by which molecules adopt a defined arrangement without guidance or management from an outside source. There are two types of self-assembly. These are intramolecular self-assembly and intermolecular self-assembly. Commonly, the term molecular self-assembly refers to intermolecular self-assembly, while the intramolecular analog is more commonly called folding.
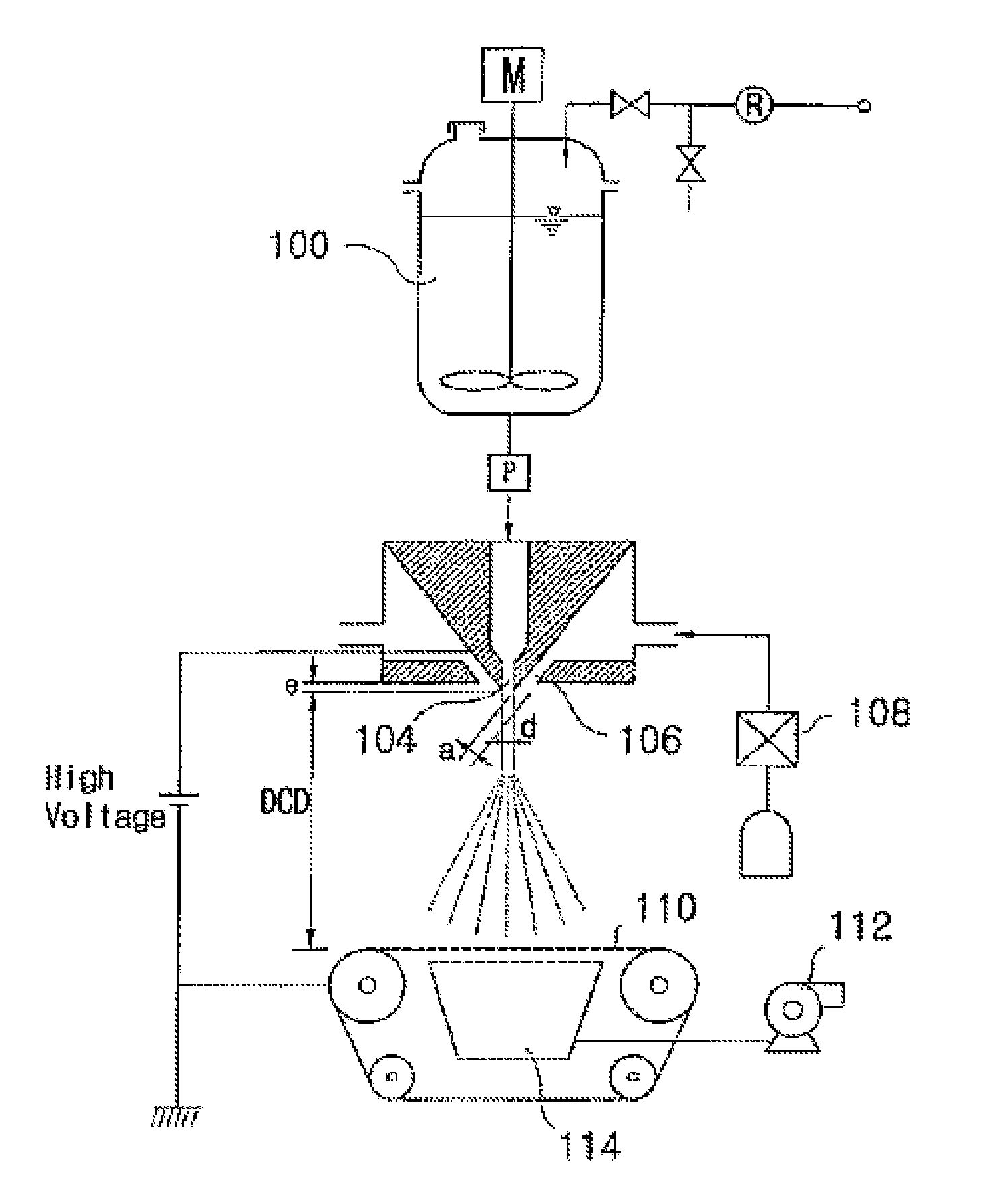
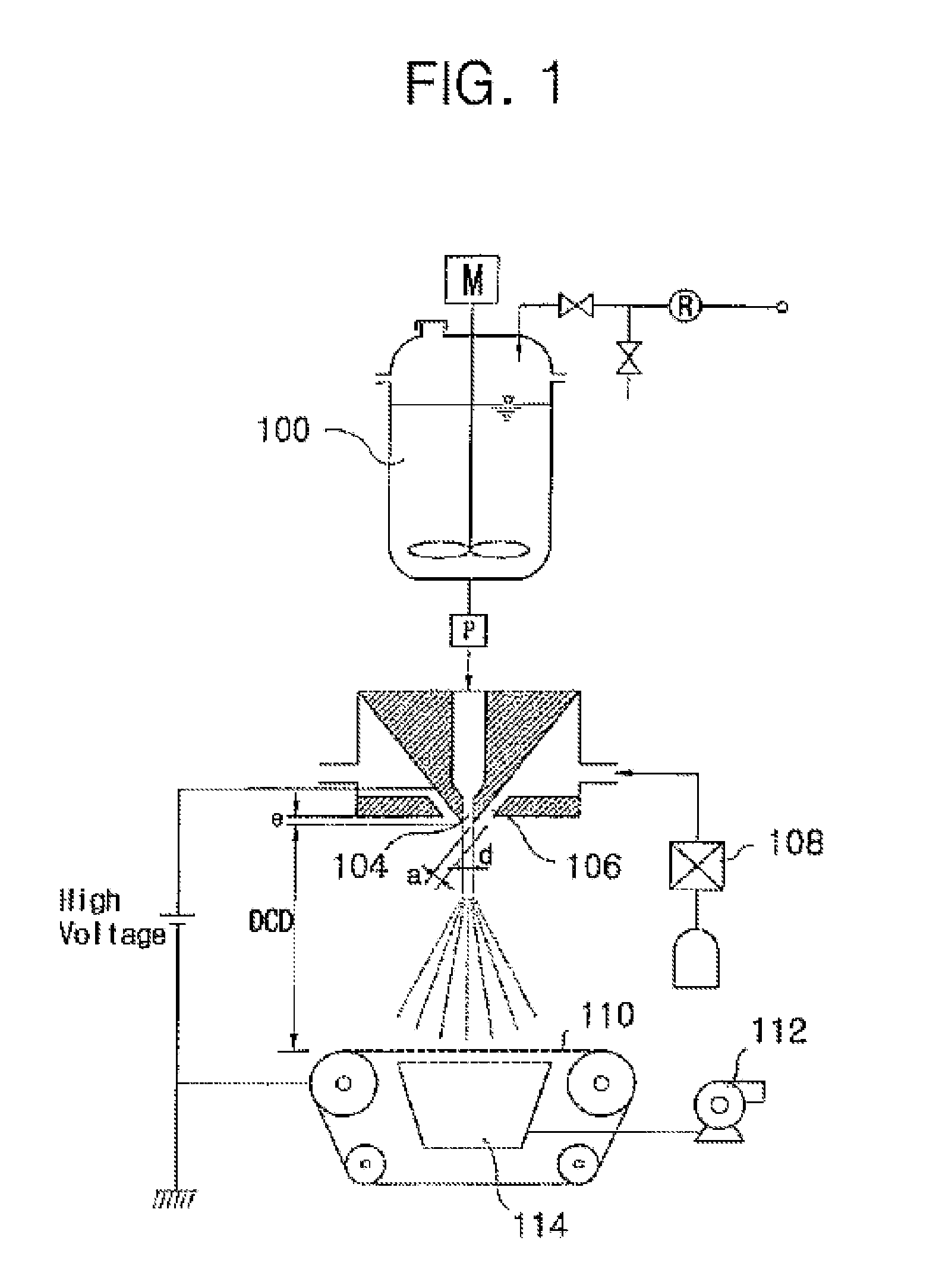
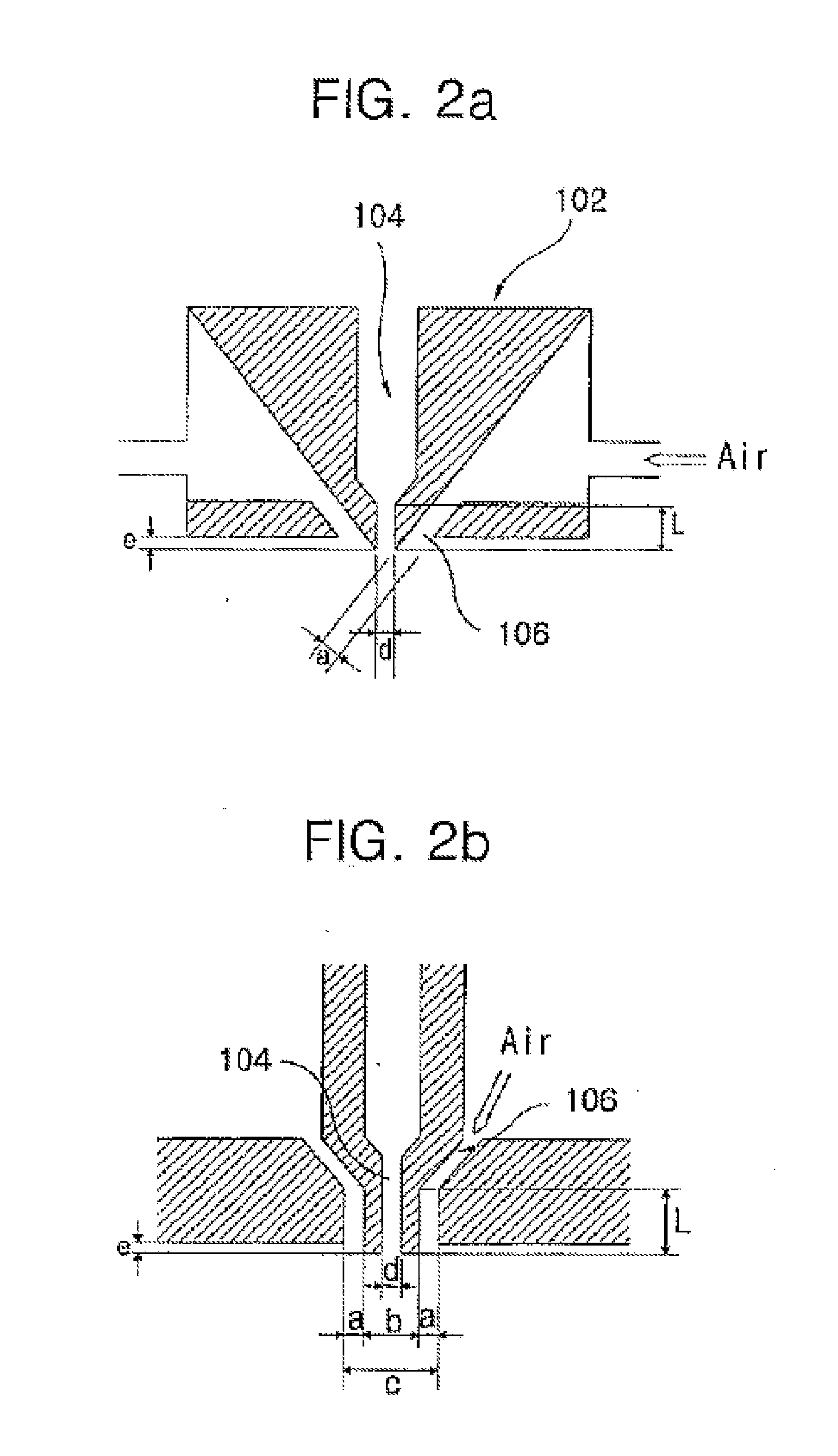
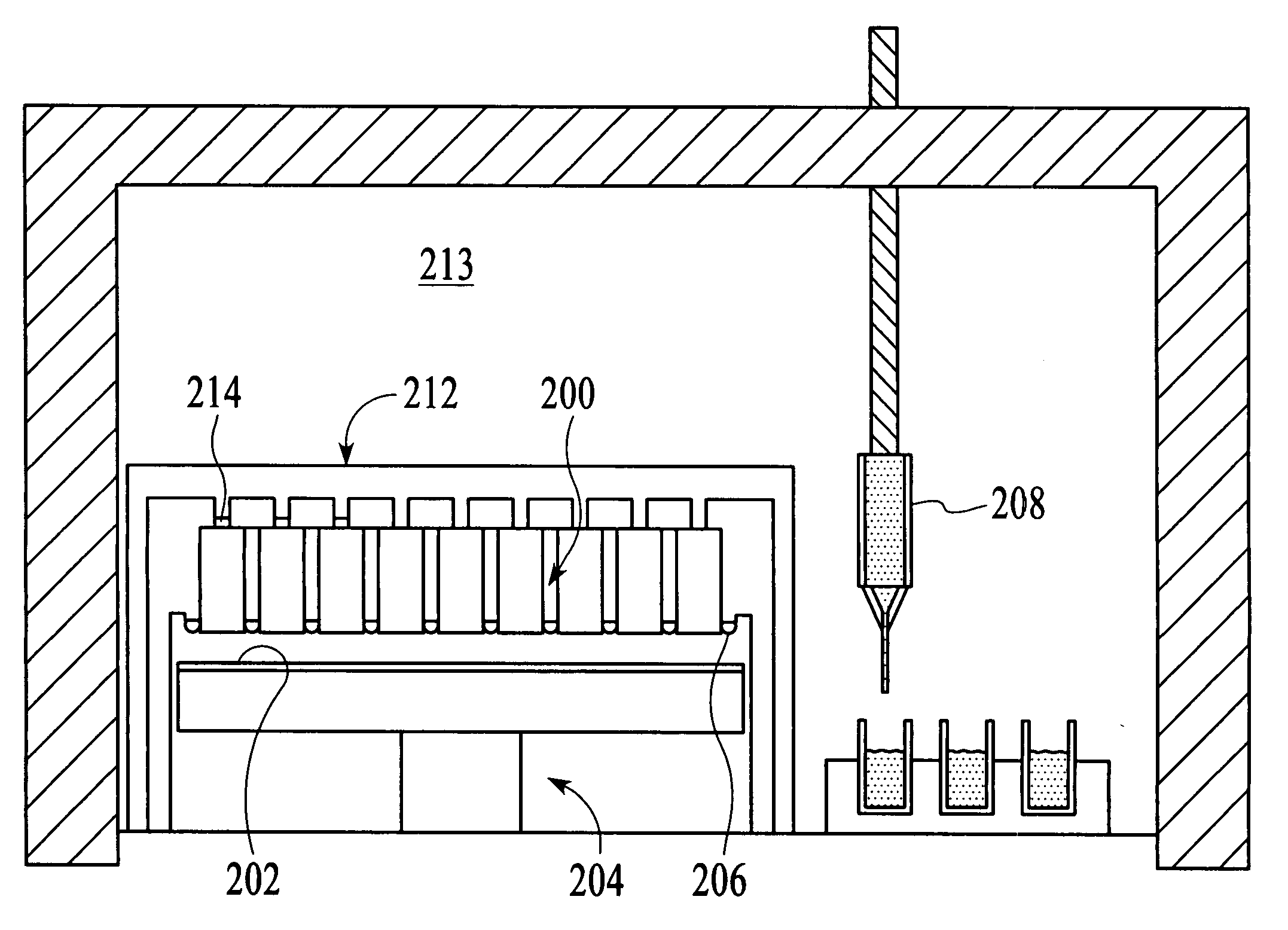
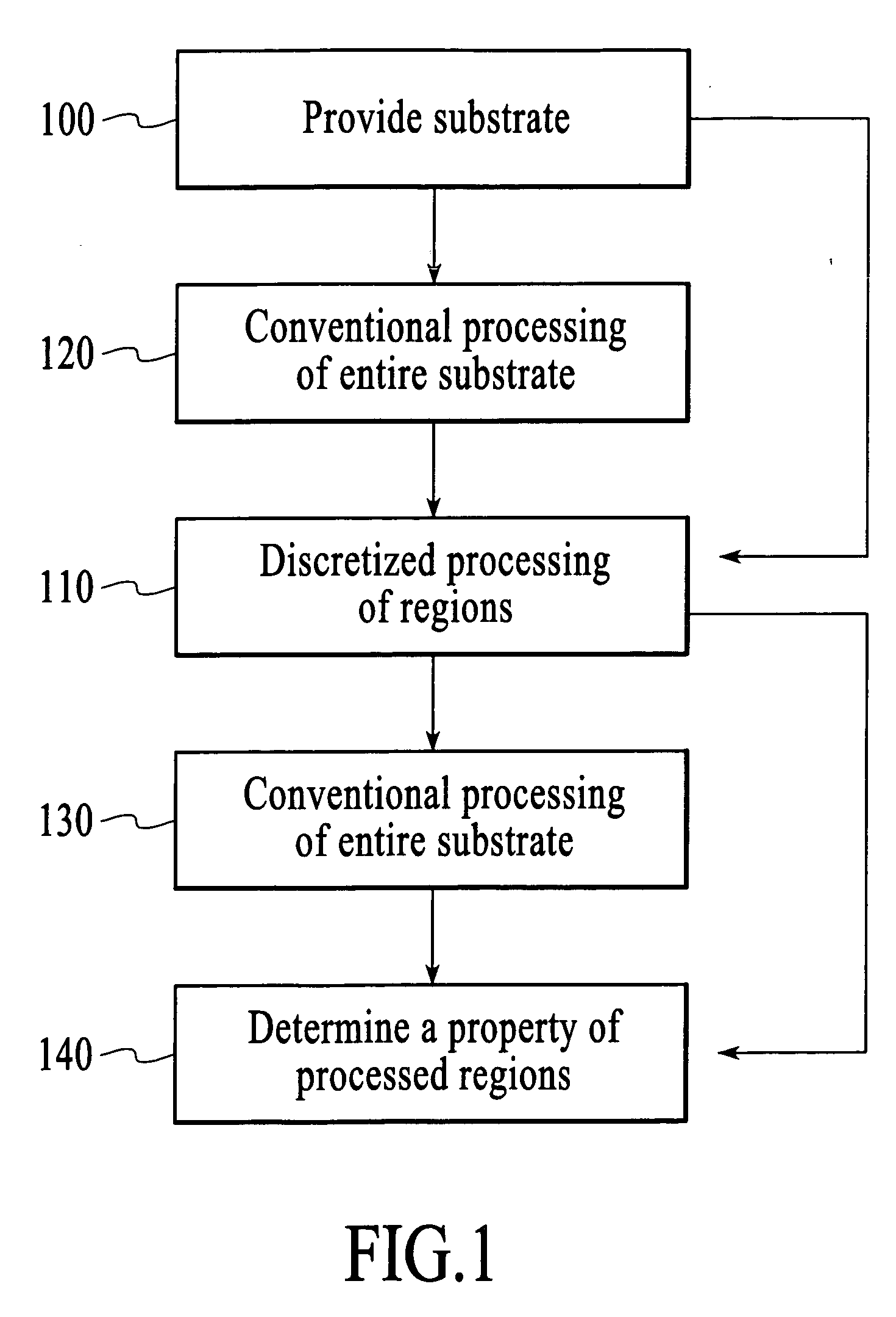
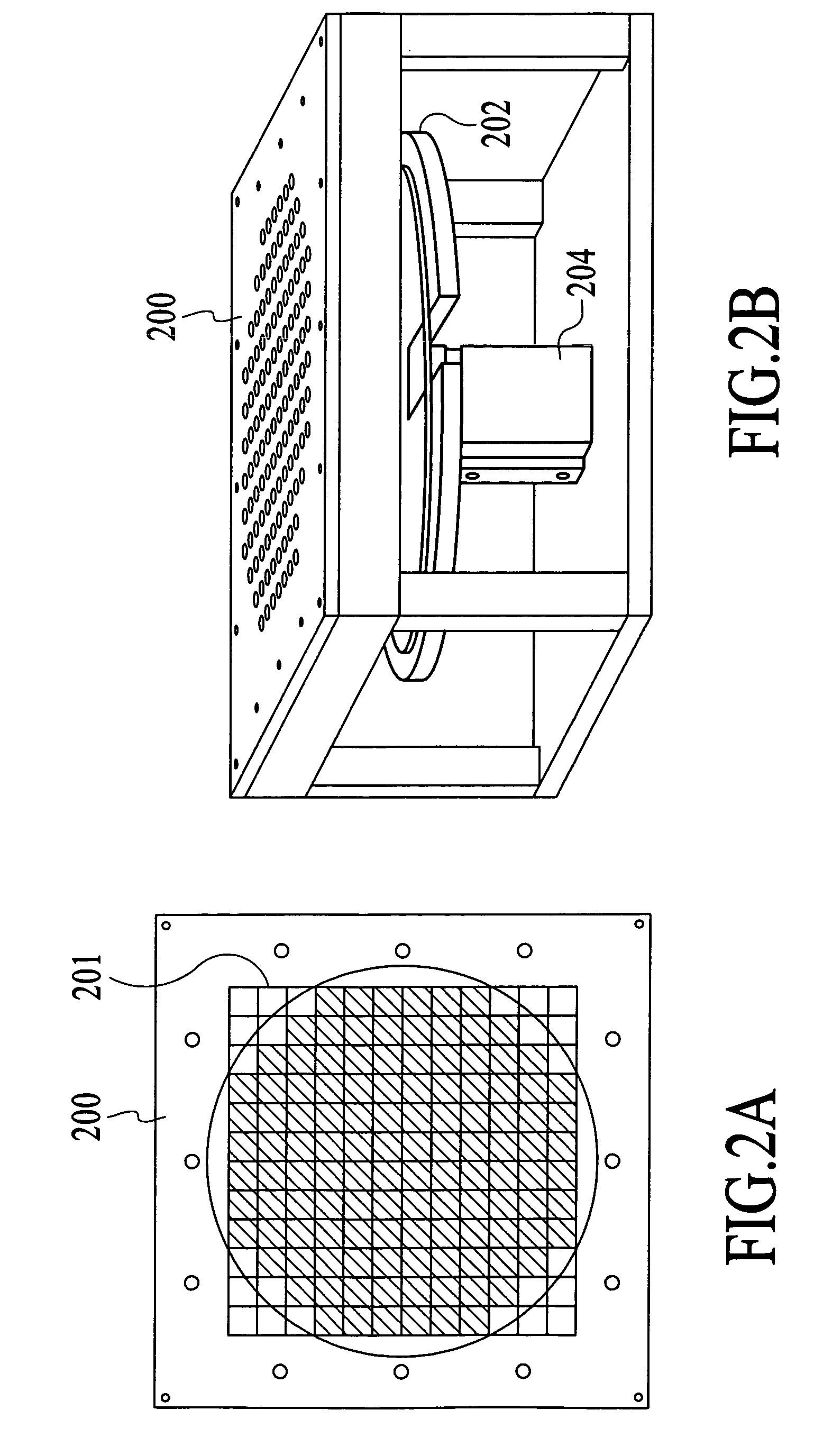
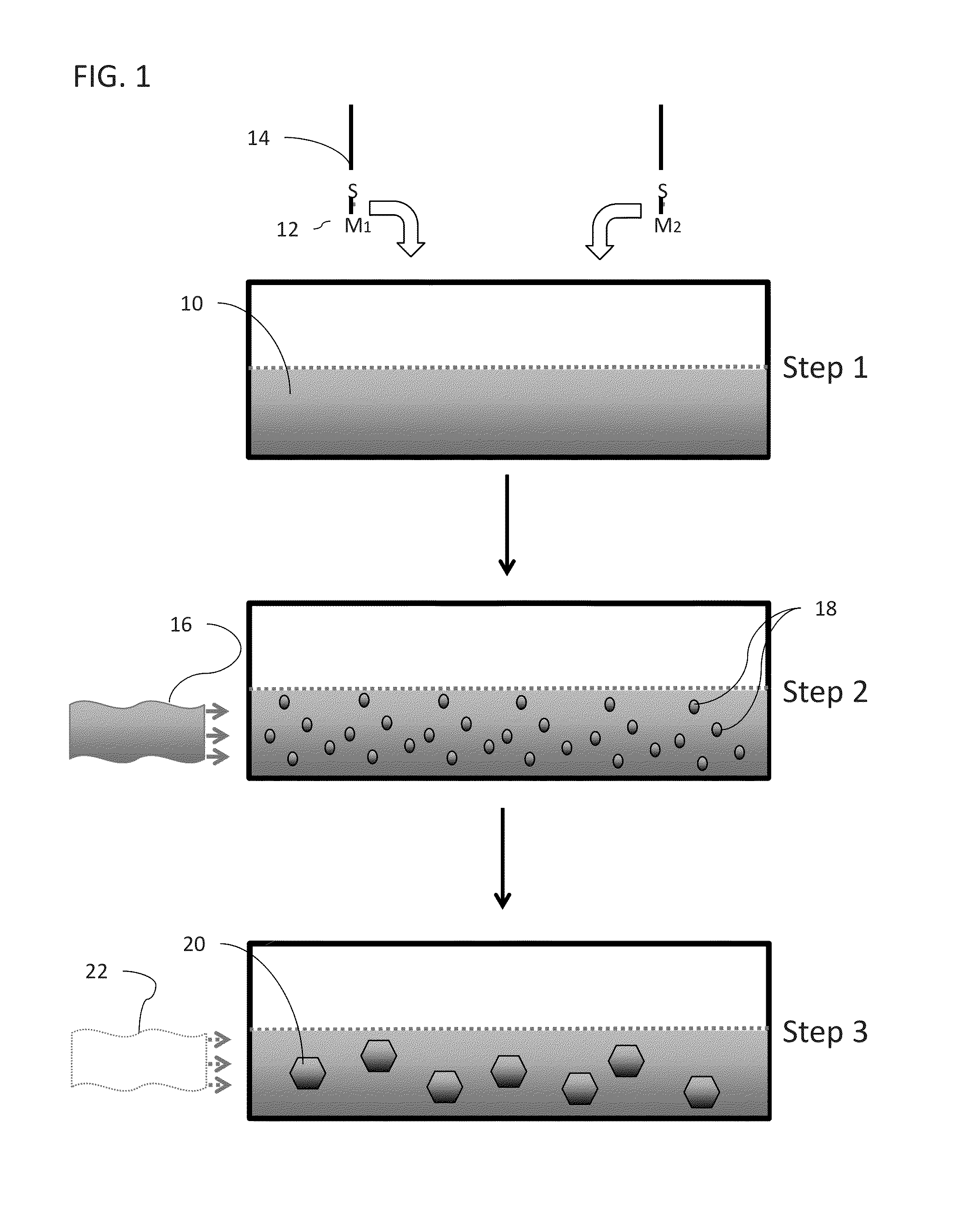
Systems and methods for sealing in site-isolated reactors
InactiveUS20070199510A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingComputer moduleEngineering
Substrate processing systems and methods are described for site-isolated processing of substrates. The processing systems include numerous site-isolated reactors (SIRs). The processing systems include a reactor block having a cell array that includes numerous SIRs. A sleeve is coupled to an interior of each of the SIRs. The sleeve includes a compliance device configured to dynamically control a vertical position of the sleeve in the SIR. A sealing system is configured to provide a seal between a region of a substrate and the interior of each of the SIRs. The processing system can include numerous modules that comprise one or more site-isolated reactors (SIRs) configured for one or more of molecular self-assembly and combinatorial processing of substrates.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Functional associative coatings for nanoparticles
InactiveUS20080089836A1Readily and efficiently optimizing propertyAvoid interactionBiocidePowder deliveryAmphiphileNanoparticle
Described herein are nanoparticles that are coated with a bilayer of molecules formed from surface binding molecules and amphiphatic molecules. The bilayer coating self assembles on the nanoparticles from readily available materials / molecules. The modular design of the bilayer coated nanoparticles provides a means for readily and efficiently optimizing the properties of the bilayer coated nanoparticle compositions. Also described herein are uses of such nanoparticles in medicine, laboratory techniques, industrial and commerical applications.
Owner:NANOPROBES
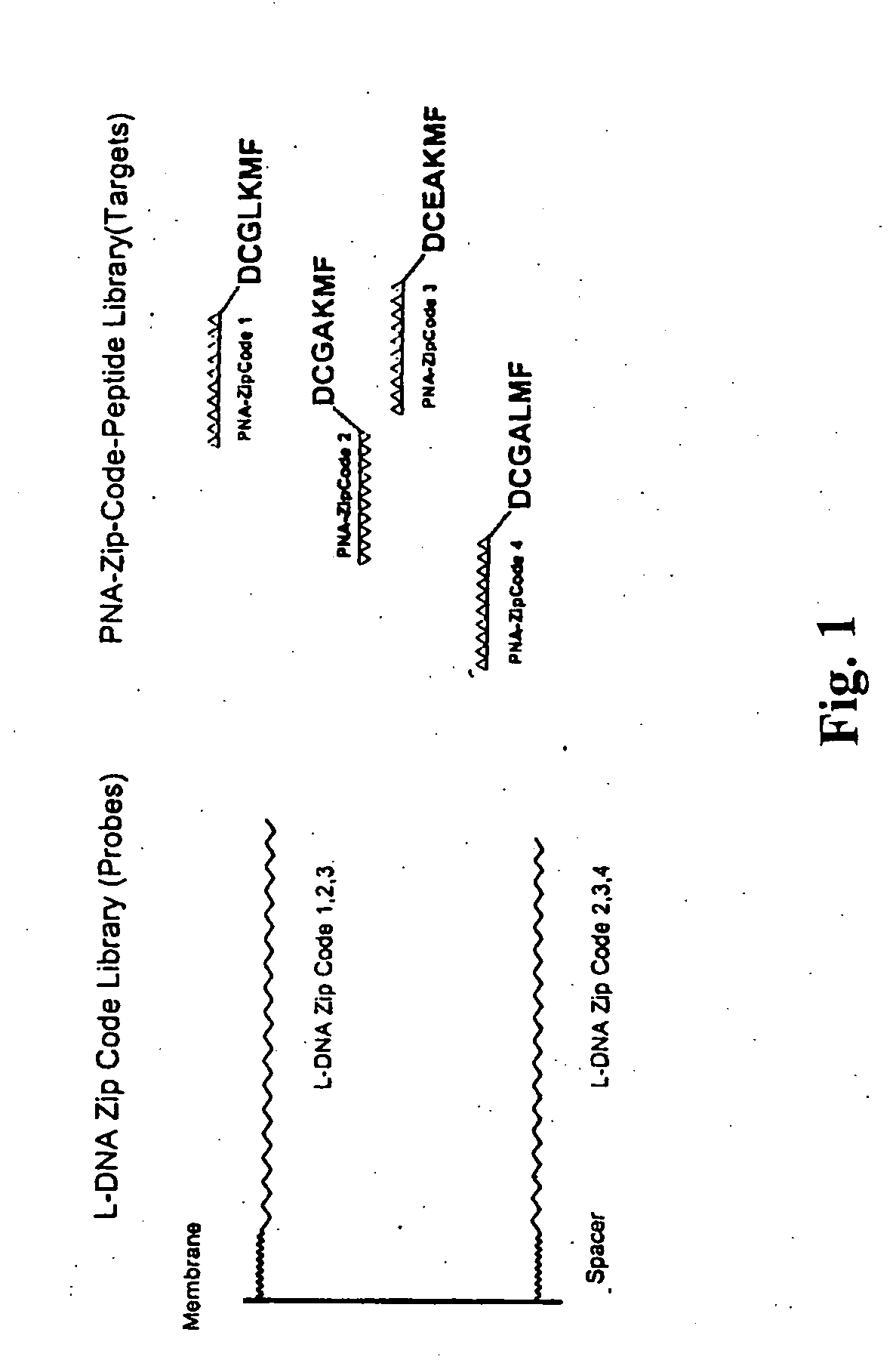
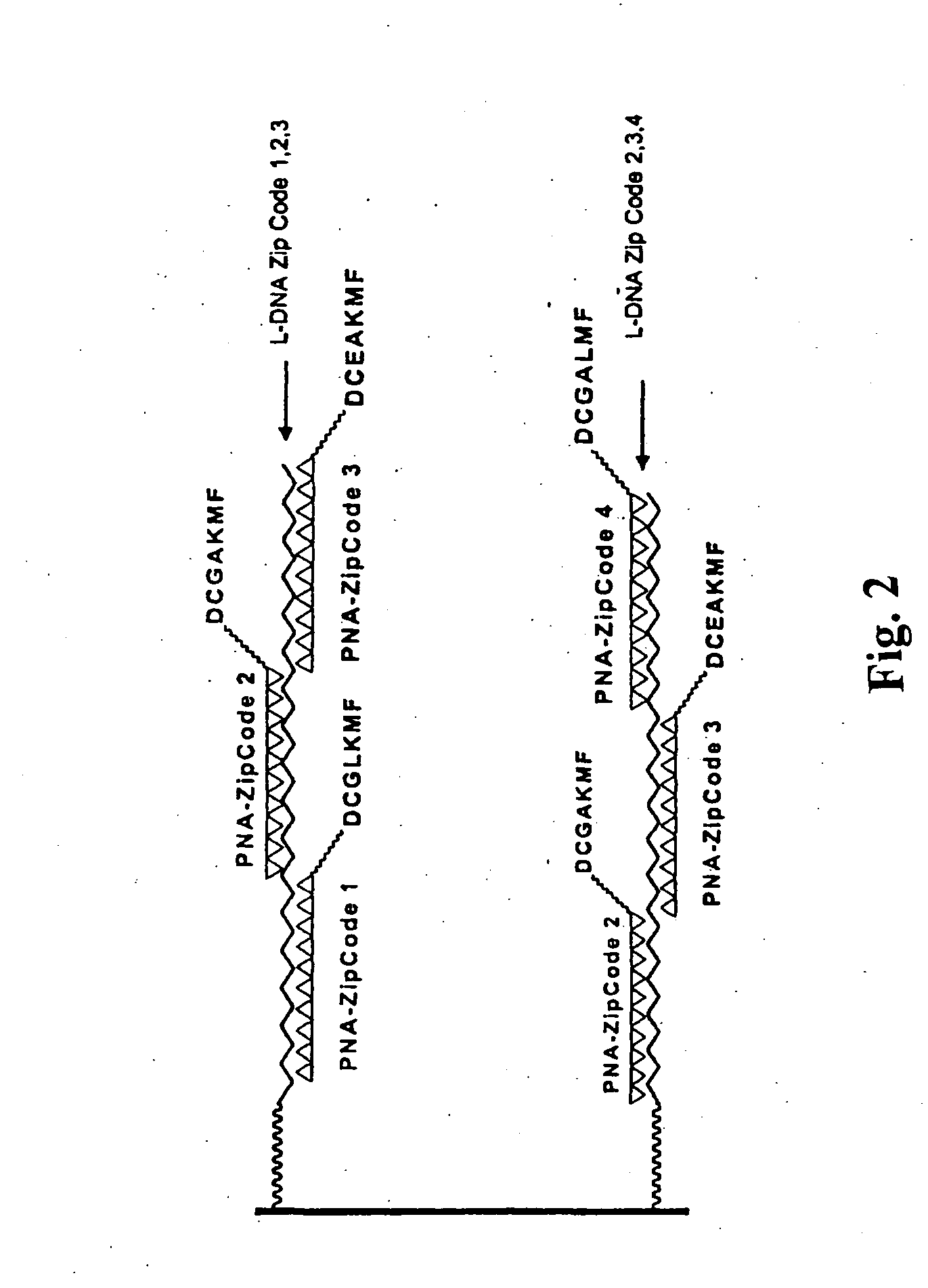
Self-assembly of molecules using combinatorial hybridization
InactiveUS20060199207A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsPeptide librariesNucleic acid sequencingBiology
Simple and convenient methods for arranging molecules of interest in a pre-determined pattern are described. The methods use combinatorial hybridization based on interactions between complementary nucleic acid sequences to arrange the molecules of interest. The resulting arrangements, kits containing the components used in the methods, and methods of using the resulting arrangements are also disclosed.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
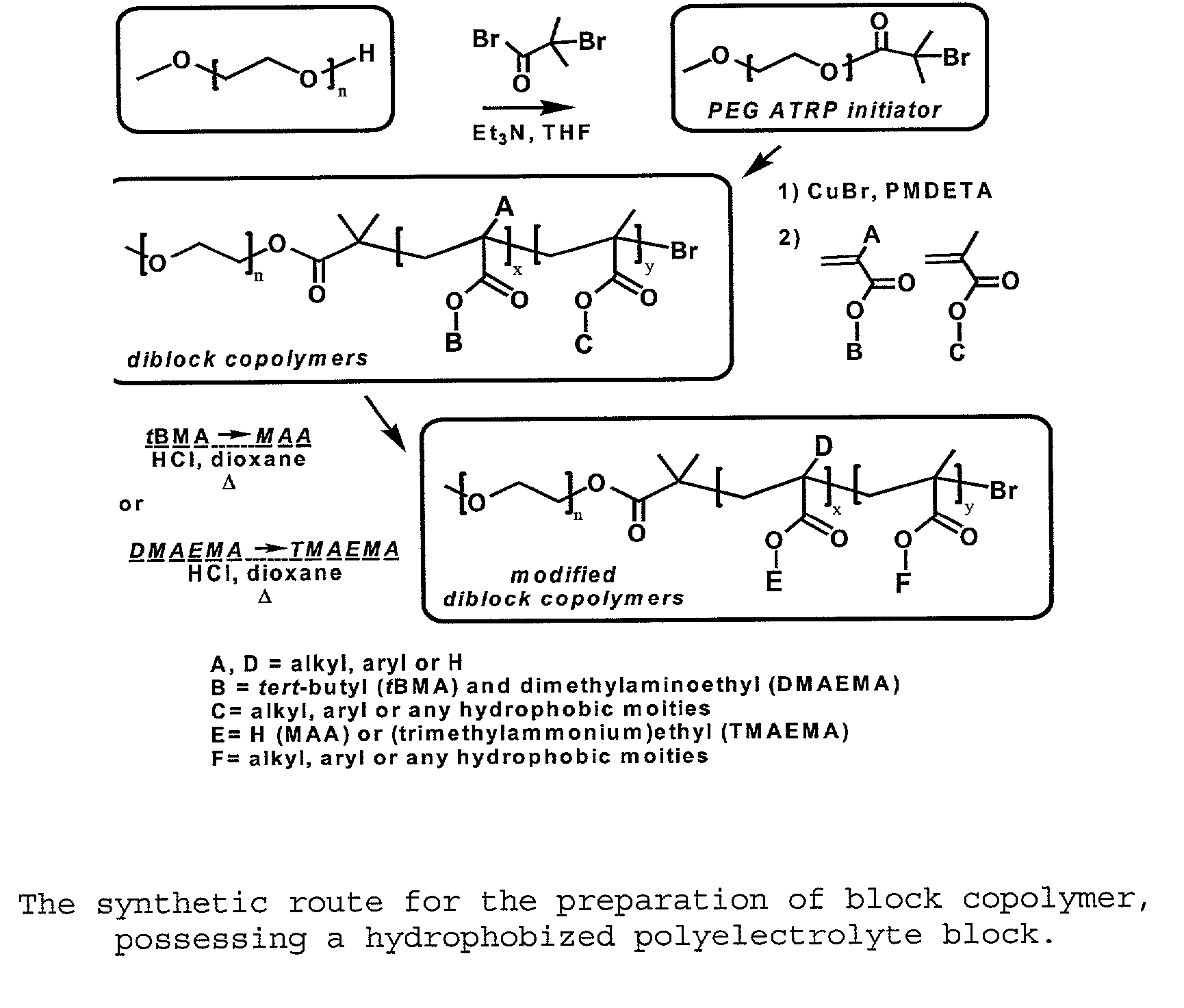
Water-soluble stabilized self-assembled polyelectrolytes
InactiveUS20030059398A1Pharmaceutical non-active ingredientsGranular deliveryPolyelectrolyteHydrophilic polymers
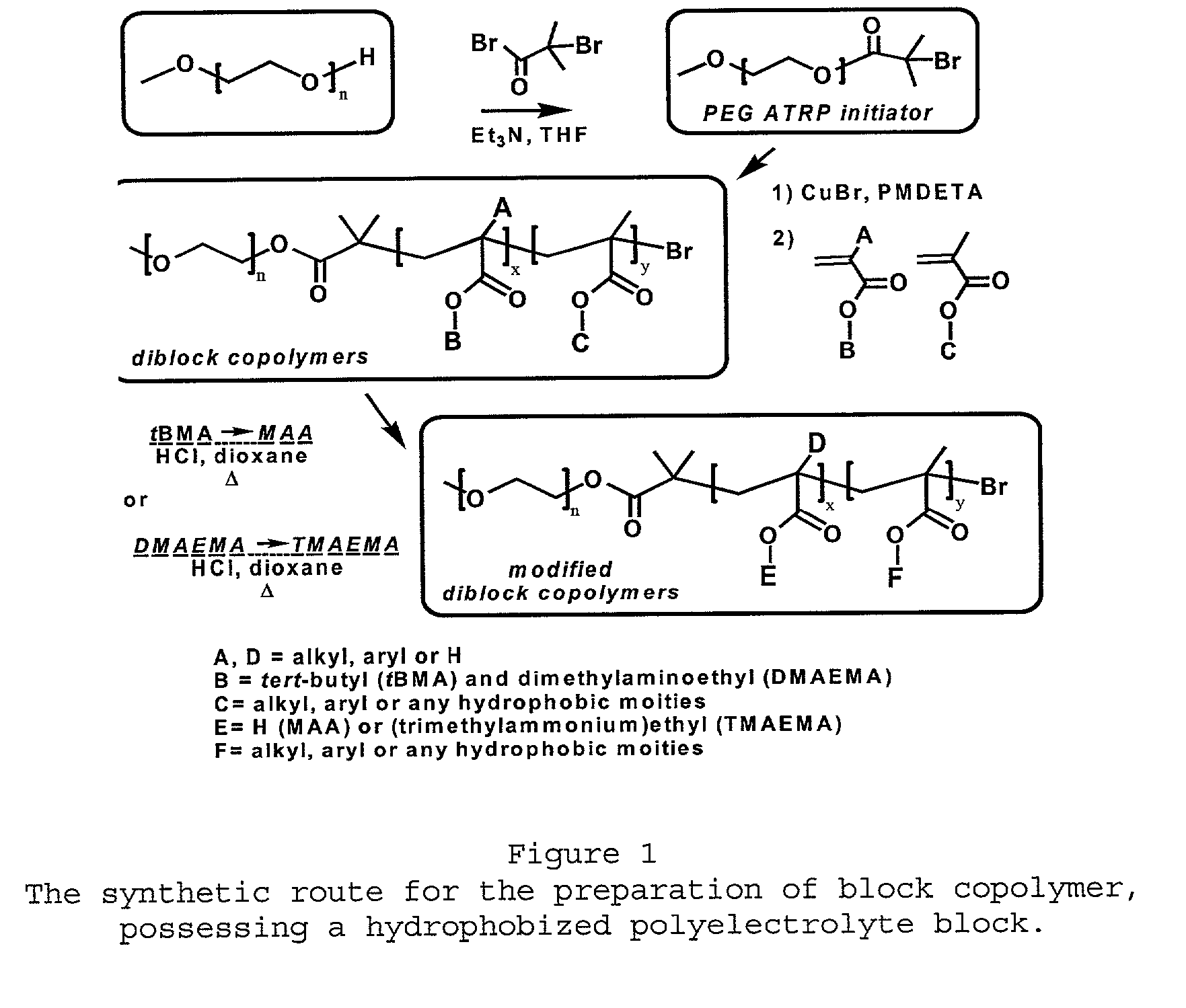
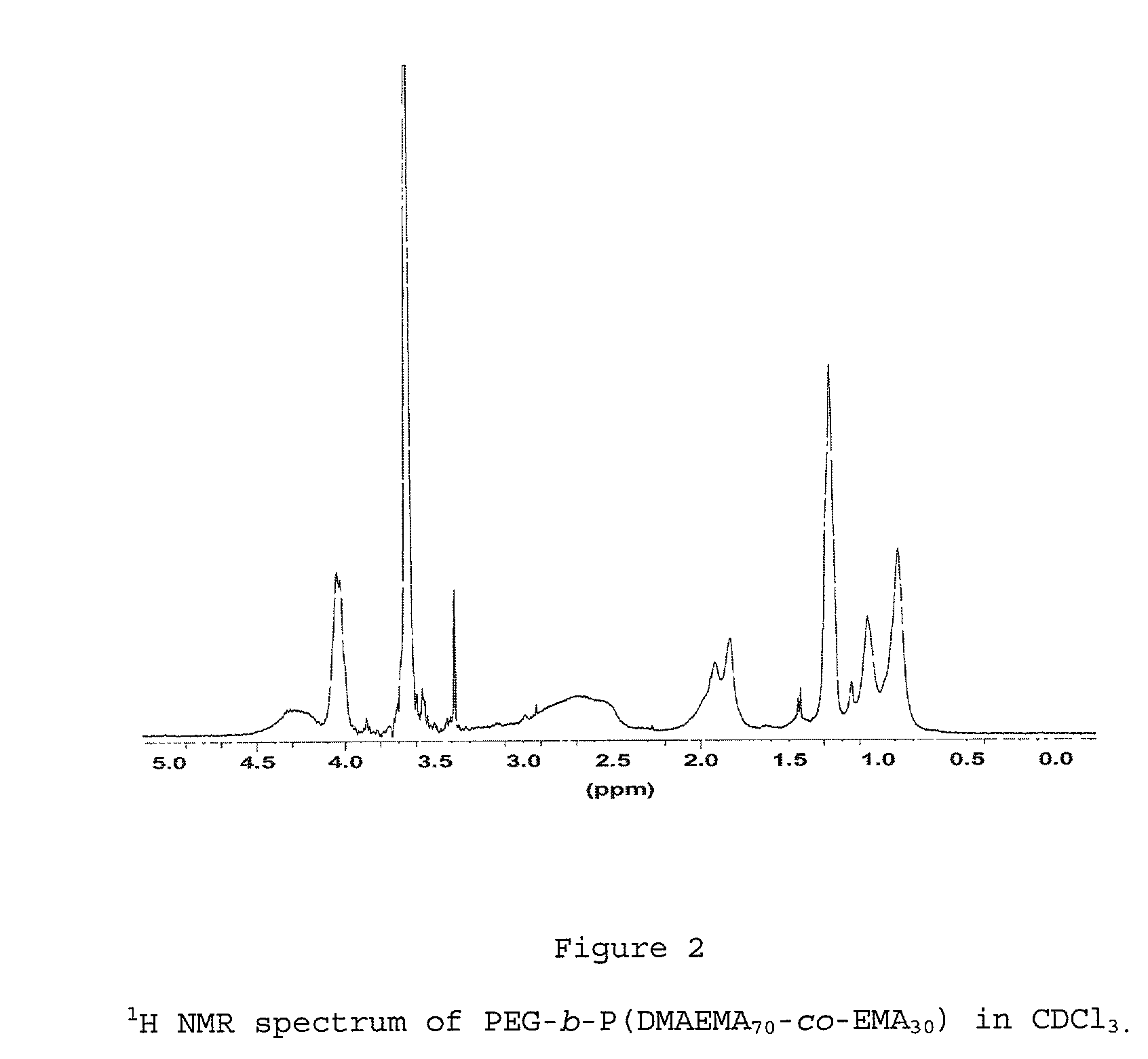
The present invention is directed toward water-soluble supramolecular self-assemblies and a process for their preparation via micellization of polyelectrolytes through the use of hydrophobic monomeric units. In this invention the polyelectrolyte segment ultimately forms the core of the supramolecular assembly whereas the shell consists of uncharged hydrophilic polymers or oligomers. It has been determined that the inclusion of the hydrophobic co-monomers to the polyelectrolyte segment forming the micelle core leads to a structure of enhanced stability.
Owner:LABOPHARM BARBADOS LTD 36646
Device with chemical surface patterns
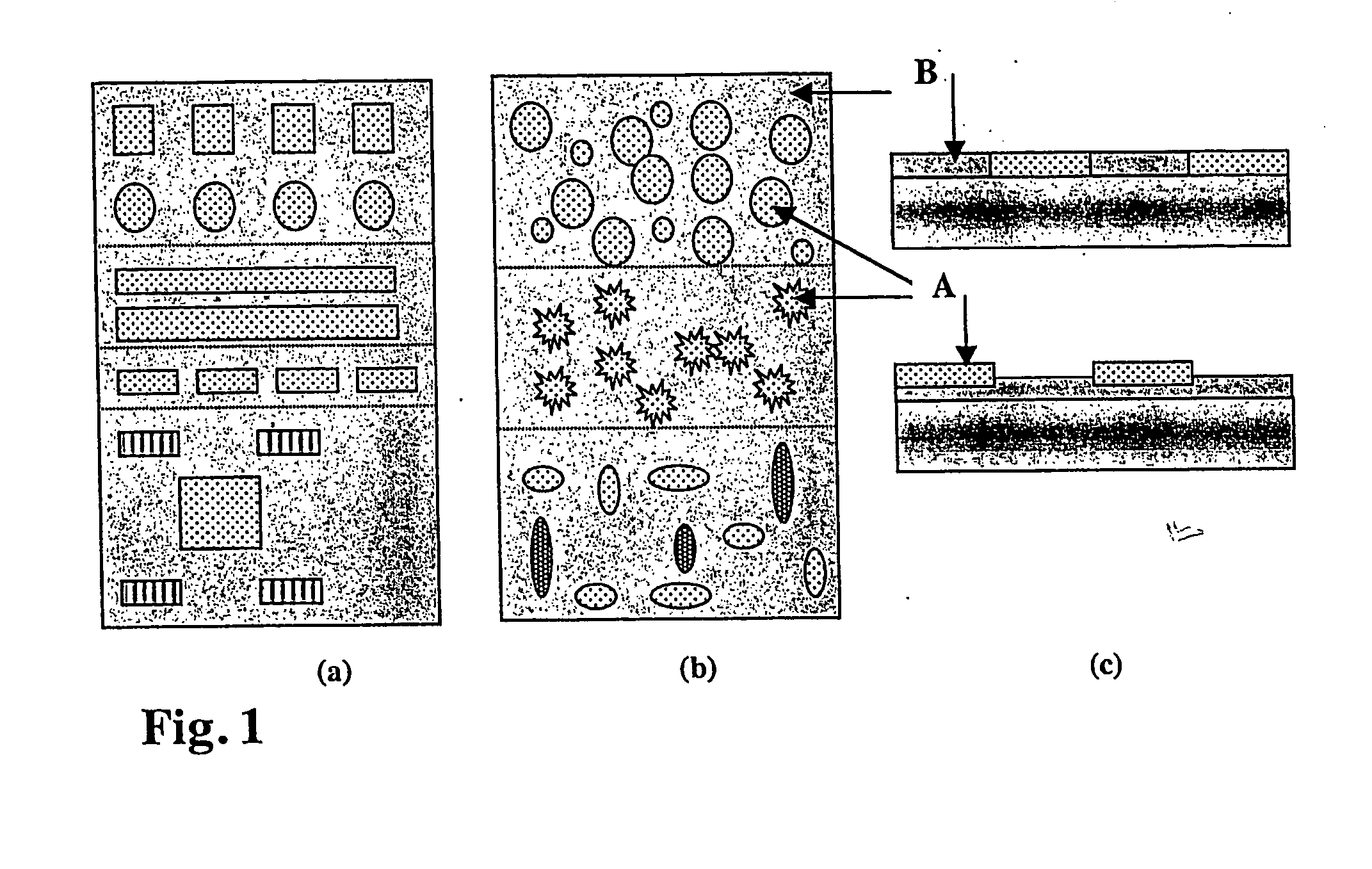
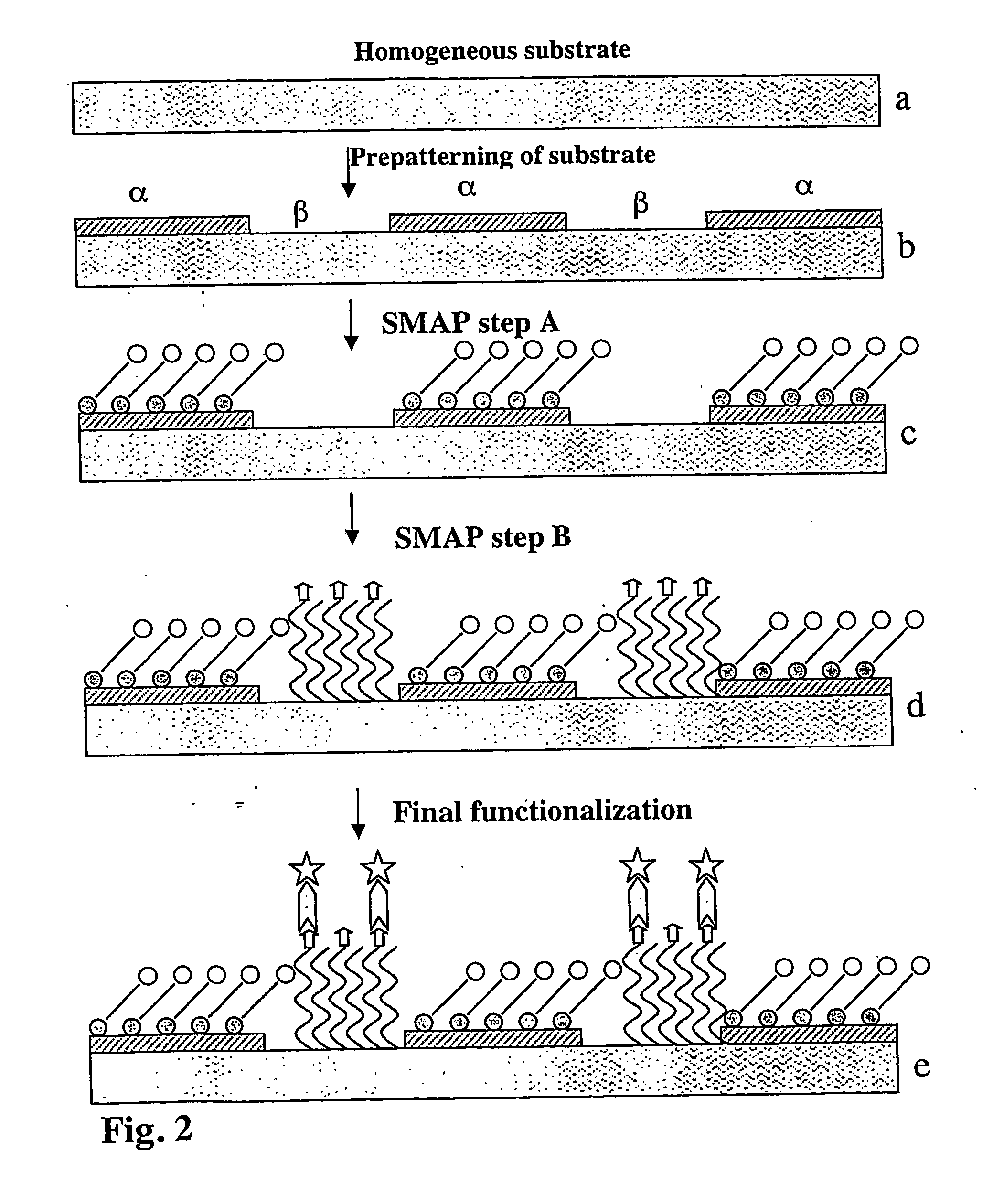
InactiveUS20050014151A1Retarded and prevented reactionSustained inflammationMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSurface patternChemical composition
A device with chemical surface patterns (defined surface areas of at least two different chemical compositions) with biochemical or biological relevance on substrates with prefabricated patterns of at least two different types of regions (α, β, . . . ), whereas at least two different, consecutively applied molecular self-assembly systems (A, B, . . . ) are used in a way that at least one of the applied assembly systems (A or B or . . . ) is specific to one type of the prefabricated patterns (α or β or . . . ).
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
Rapid self-assembly of block copolymers to photonic crystals
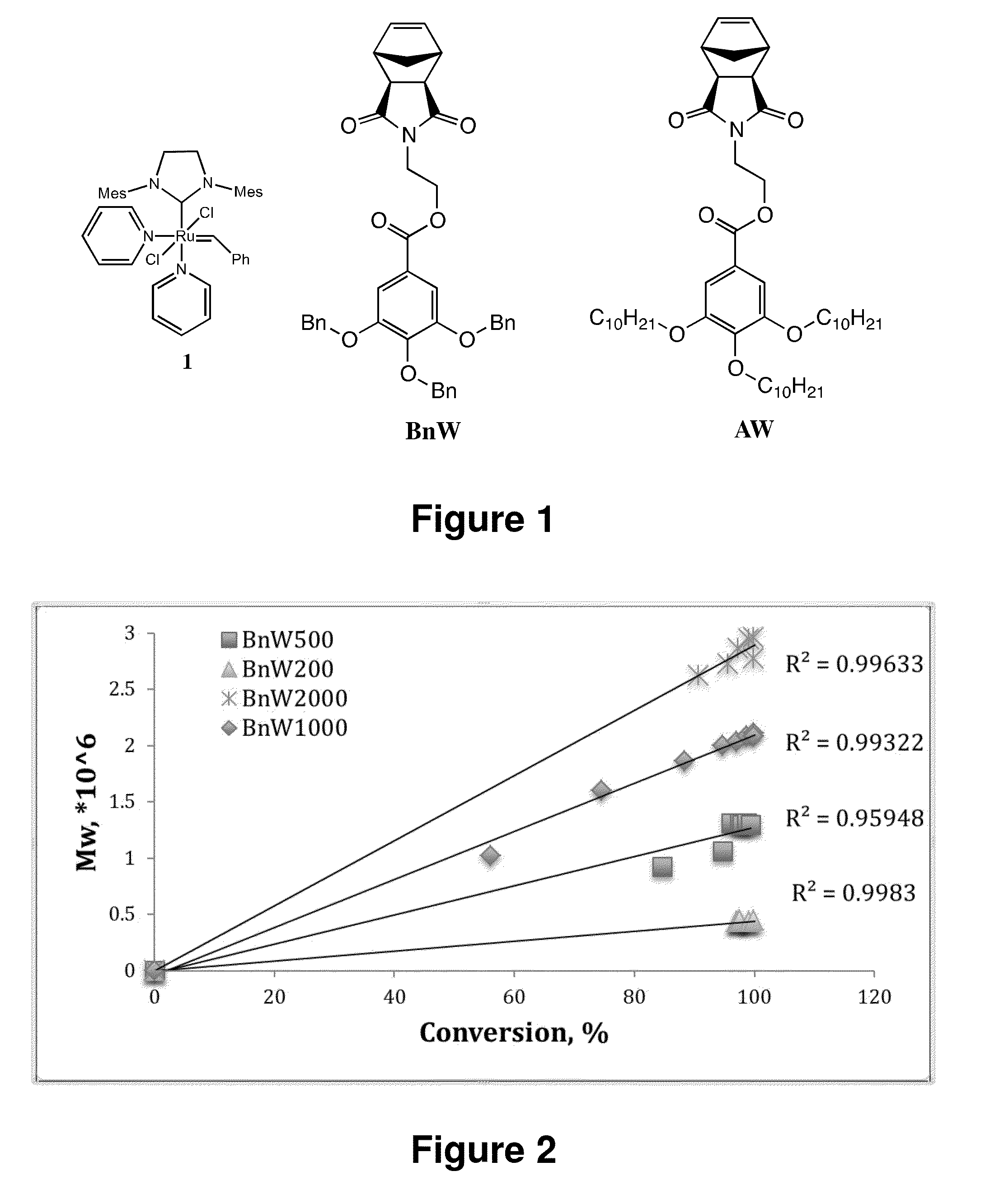
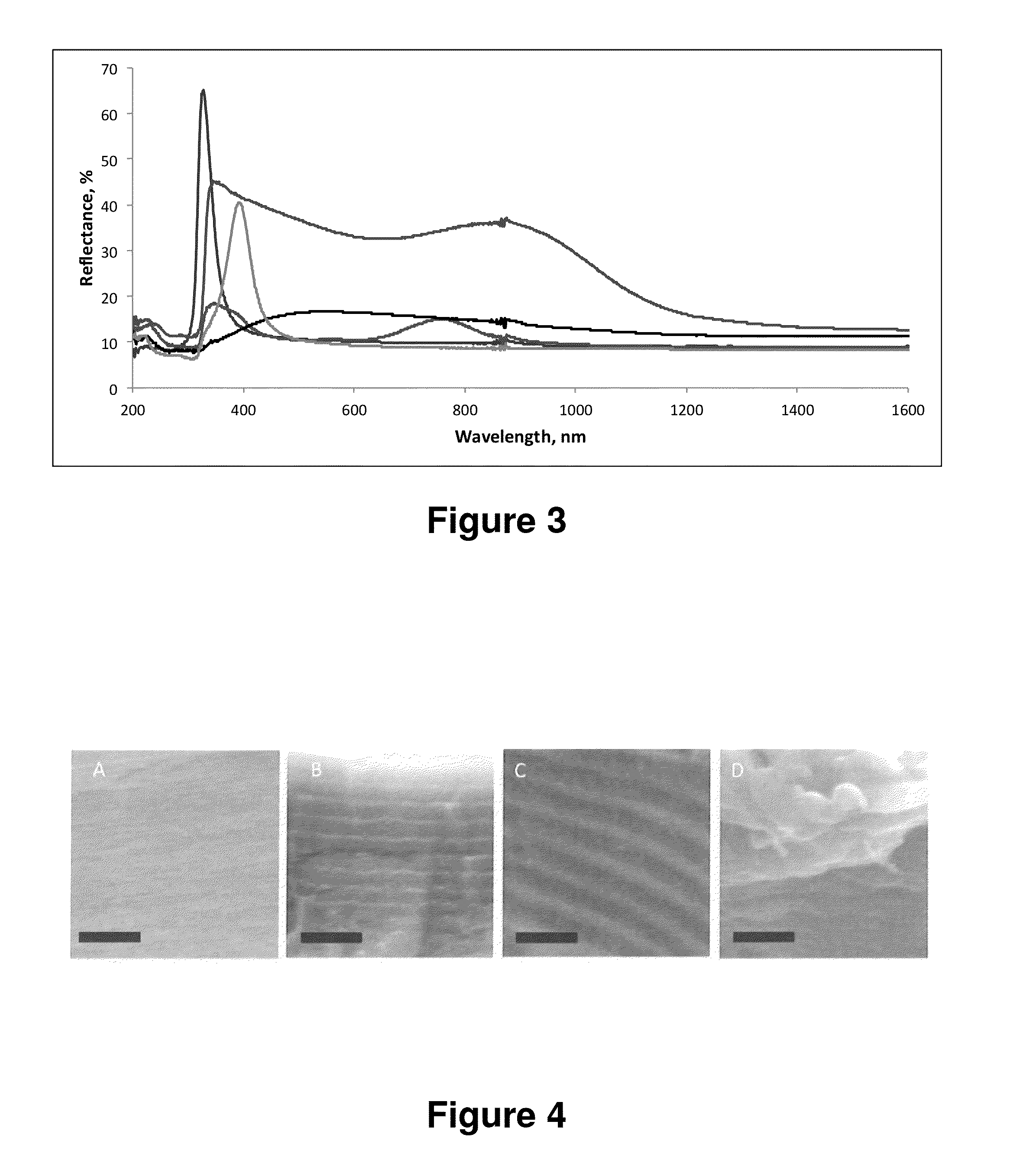
The invention provides a class of copolymers having useful properties, including brush block copolymers, wedge-type block copolymers and hybrid wedge and polymer block copolymers. In an embodiment, for example, block copolymers of the invention incorporate chemically different blocks comprising polymer size chain groups and / or wedge groups that significantly inhibit chain entanglement, thereby enhancing molecular self-assembly processes for generating a range of supramolecular structures, such as periodic nanostructures and microstructures. The present invention also provides useful methods of making and using copolymers, including block copolymers.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
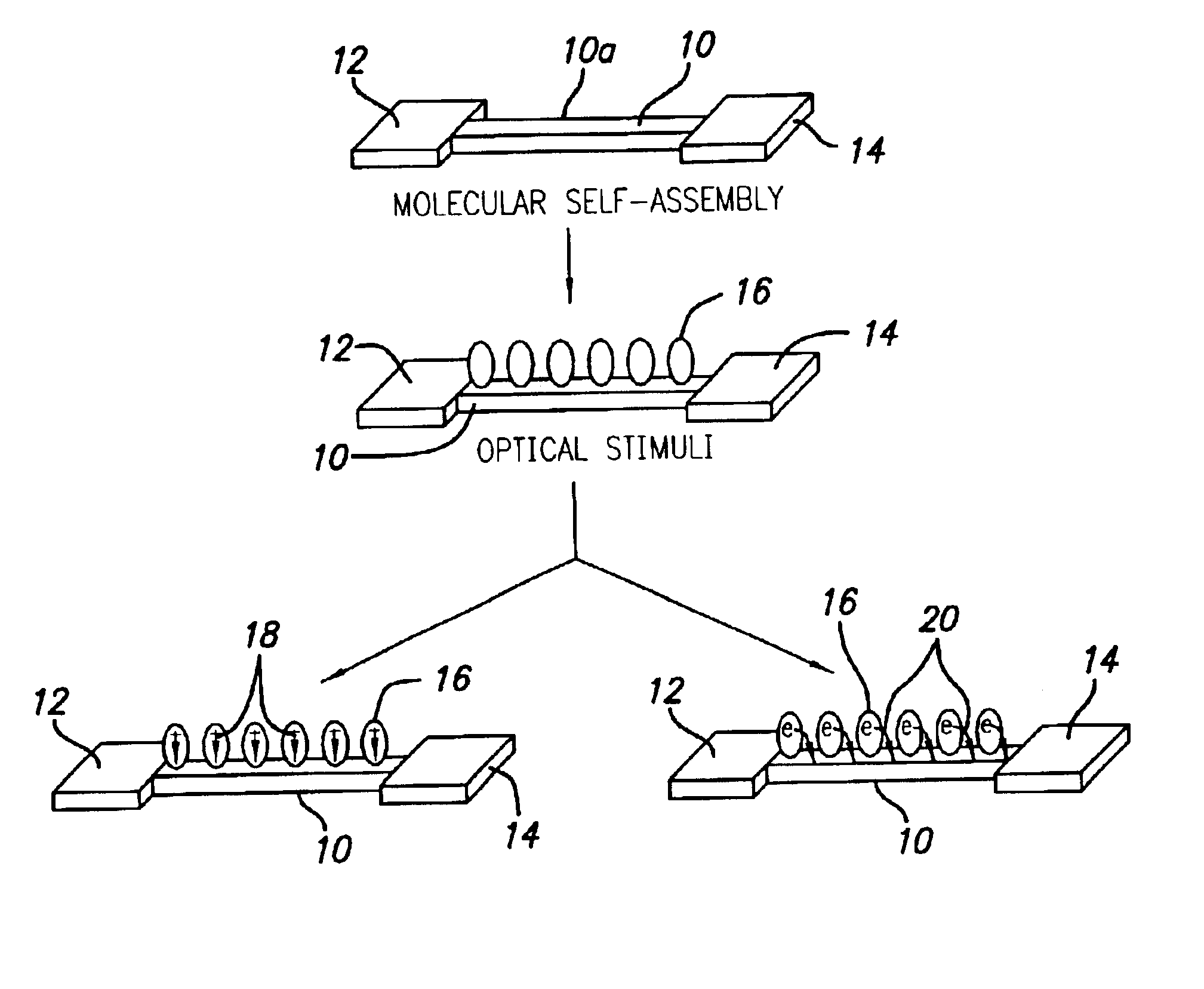
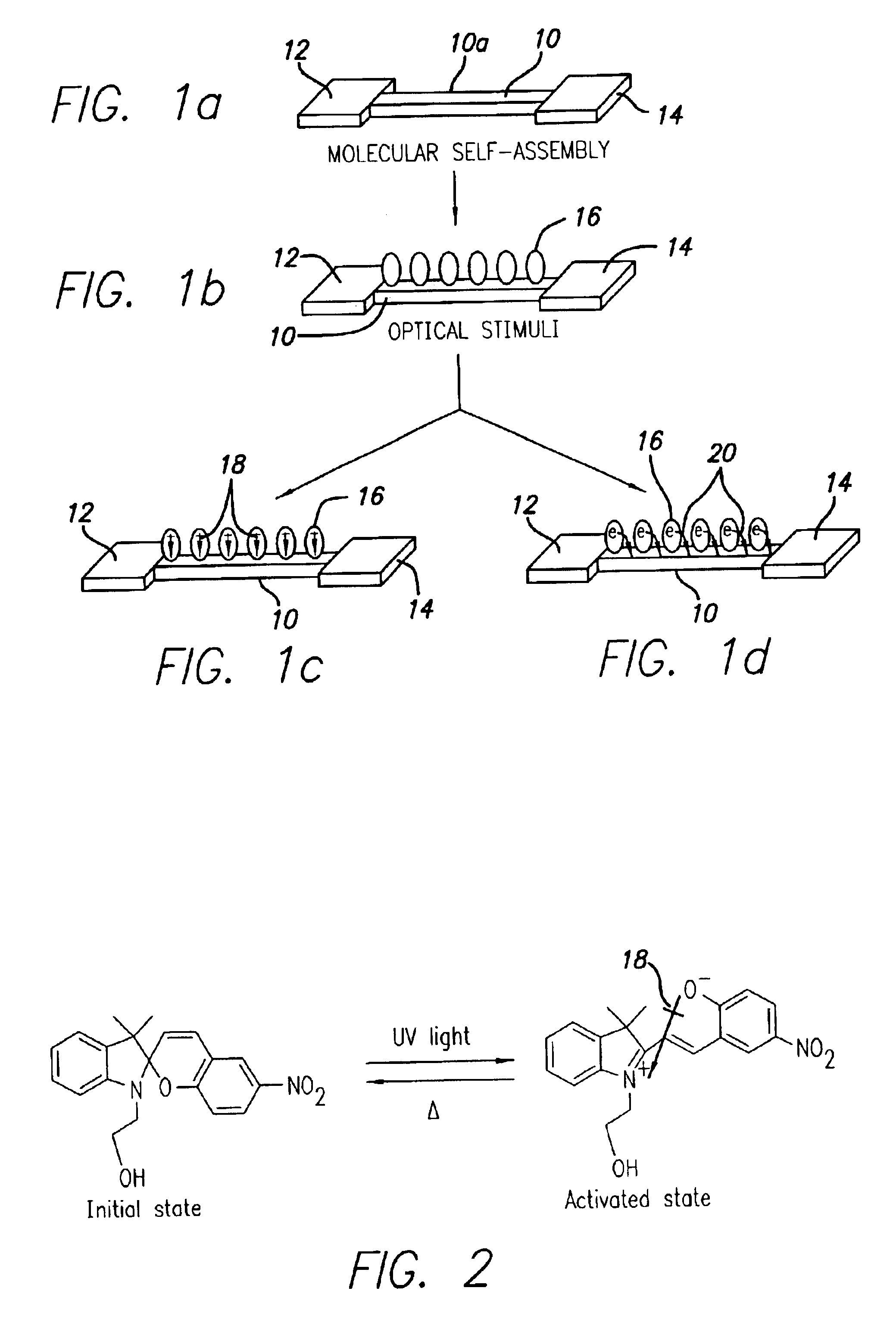
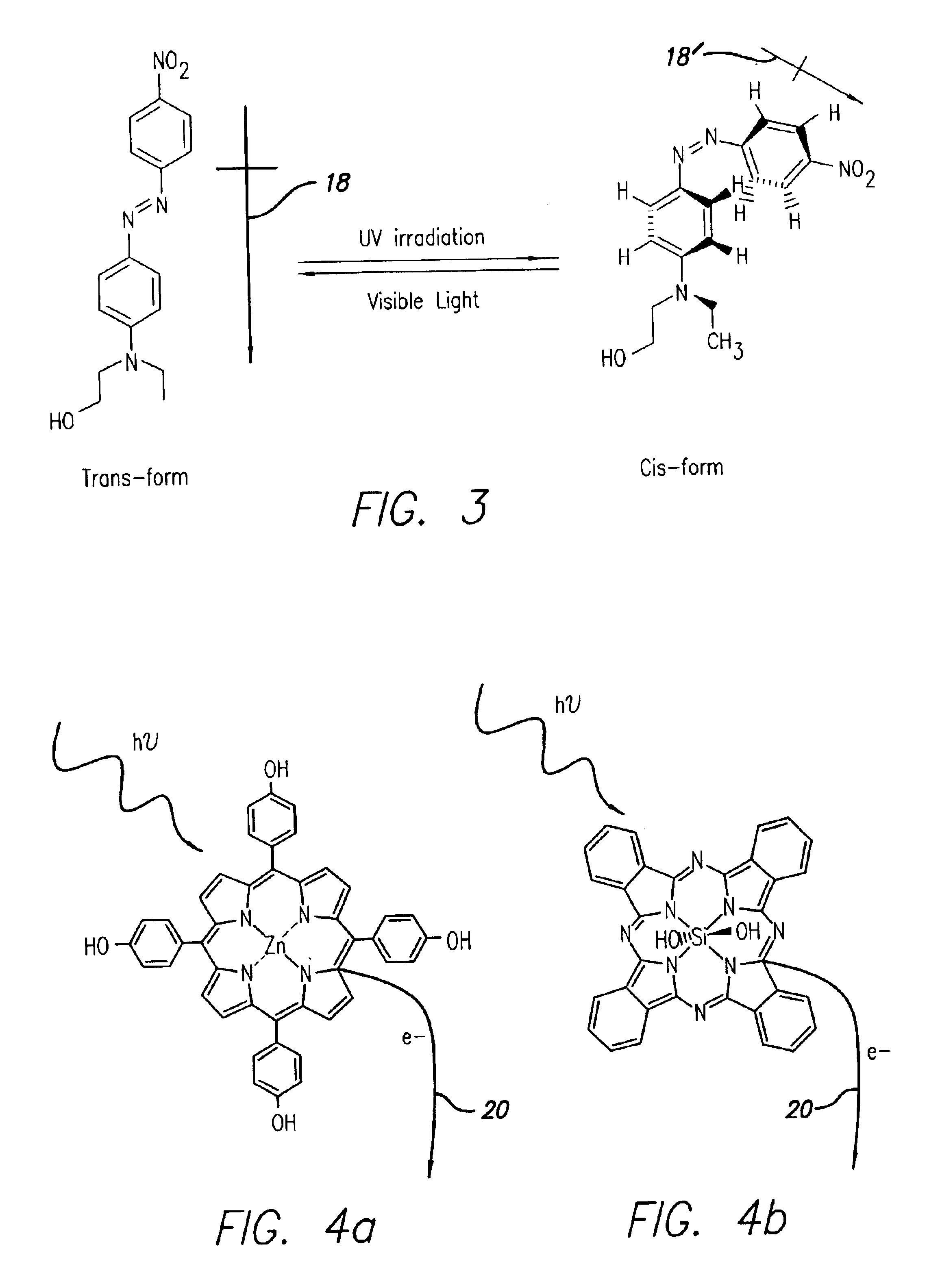
Nano optical sensors via molecular self-assembly
InactiveUS6815706B2High density and sensitivityIndividual molecule manipulationSolid-state devicesEnergy transferSilicon nanowires
An optical sensor is provided, comprising (a) a silicon nanowire of finite length having an electrical contact pad at each end thereof; and (b) a plurality of self-assembled molecules on a surface of the silicon nanowire, the molecules serving to modulate electrical conductivity of the silicon nanowire by either a reversible change in dipole moment of the molecules or by a reversible molecule-assisted electron / energy transfer from the molecules onto the silicon nanowire. Further, a method of making the optical sensor is provided. The concept of molecular self-assembly is applied in attaching functional molecules onto silicon nanowire surfaces, and the requirement of molecule modification (hydroxy group in molecules) is minimal from the point view of synthetic difficulty and compatibility. Self-assembly will produce well-ordered ultra-thin films with strong chemical bonding on a surface that cannot be easily achieved by other conventional methods.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Polymer micelle lyophilized agent encapsulating insoluble antitumor drug
ActiveCN102218027ASmall toxicityGood biocompatibilityOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPolyesterSide effect
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical agents, relates to a polymer micelle lyophilized agent encapsulating an insoluble antitumor drug as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The polymer micelle lyophilized agent is prepared by carrying out molecular self-assembly on a methoxy poly(ethylene glycol) 2000-polyester block copolymer to form micelles, and then encapsulating the insoluble antitumor drug in a hydrophobic core formed by the polyester. The lyophilized agent has high encapsulation rate, high drug loading and small particle size, can significantly improve the water solubility of the insoluble drug and result in passive targeting of more antitumor drugs to concentrate in the tumor tissues, thus improving an anti-tumor treatment effect and reducing the toxic and side effects of drugs, and can be used to prepare the drugs used for the treatment of lung cancer, intestinal cancer, mammary cancer, ovarian cancer, etc. The lyophilized agent can also be quickly dissolved and dispersed to form a transparent micellar solution after water for injection, normal saline solution and the like are added, and is used for the preparation of the drugs for treating primary intestinal cell carcinoma.
Owner:上海谊众药业股份有限公司
Method for preparing composite graphene/silane film on surface of metal
ActiveCN103628050AImprove corrosion resistanceHigh bonding strengthLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingChemical LinkageComposite film
The invention relates to metal surface protection, and in particular relates to a method for preparing a composite graphene / silane film on the surface of metal. The method overcomes the defect that the binding strength of a graphene film and the metal is weak; a silane coupling agent with two different chemical functional groups is introduced as a transition film layer to prepare a composite film, and the composite film is prepared from graphene and the silane coupling agent. The chemical bond connection between the metal and graphene is achieved through the silane coupling agent, and the binding strength of graphene and the metal is improved; the prepared composite film is long in service life, and the anti-corrosion property of the metal is effectively improved.
Owner:扬中方略科技信息有限公司
Nanometer porous tungsten trioxide material and its prepn and application
InactiveCN1974890ALower surface energyImprove surface topographyPolycrystalline material growthSurface reaction electrolytic coatingPotassium fluorideStrong acids
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
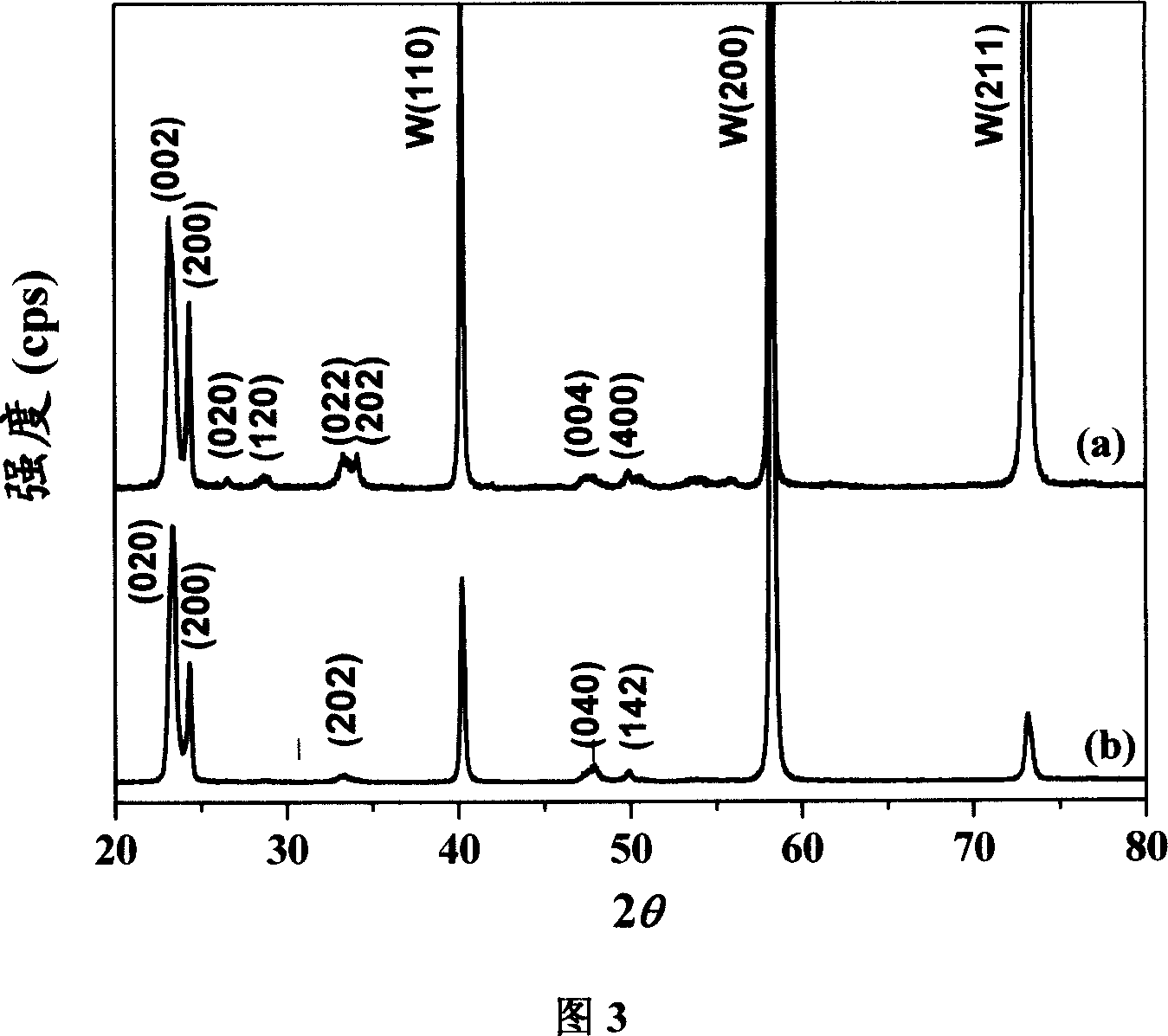
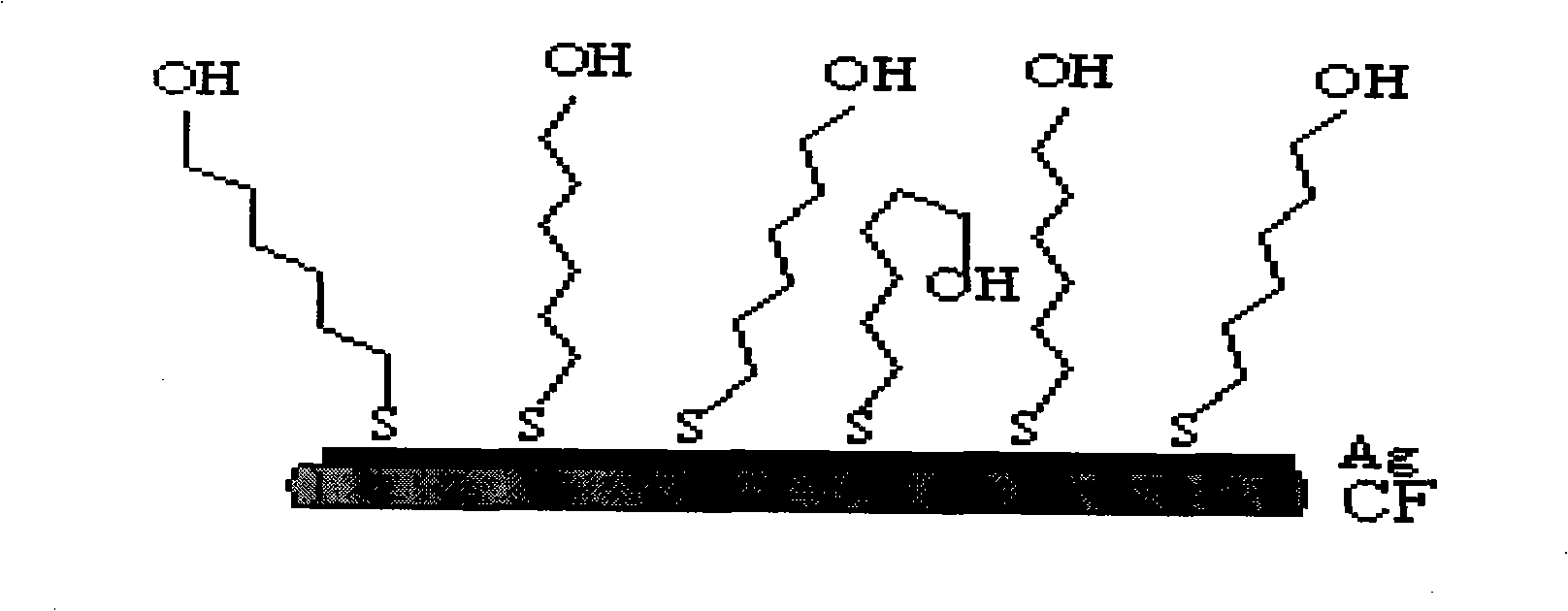
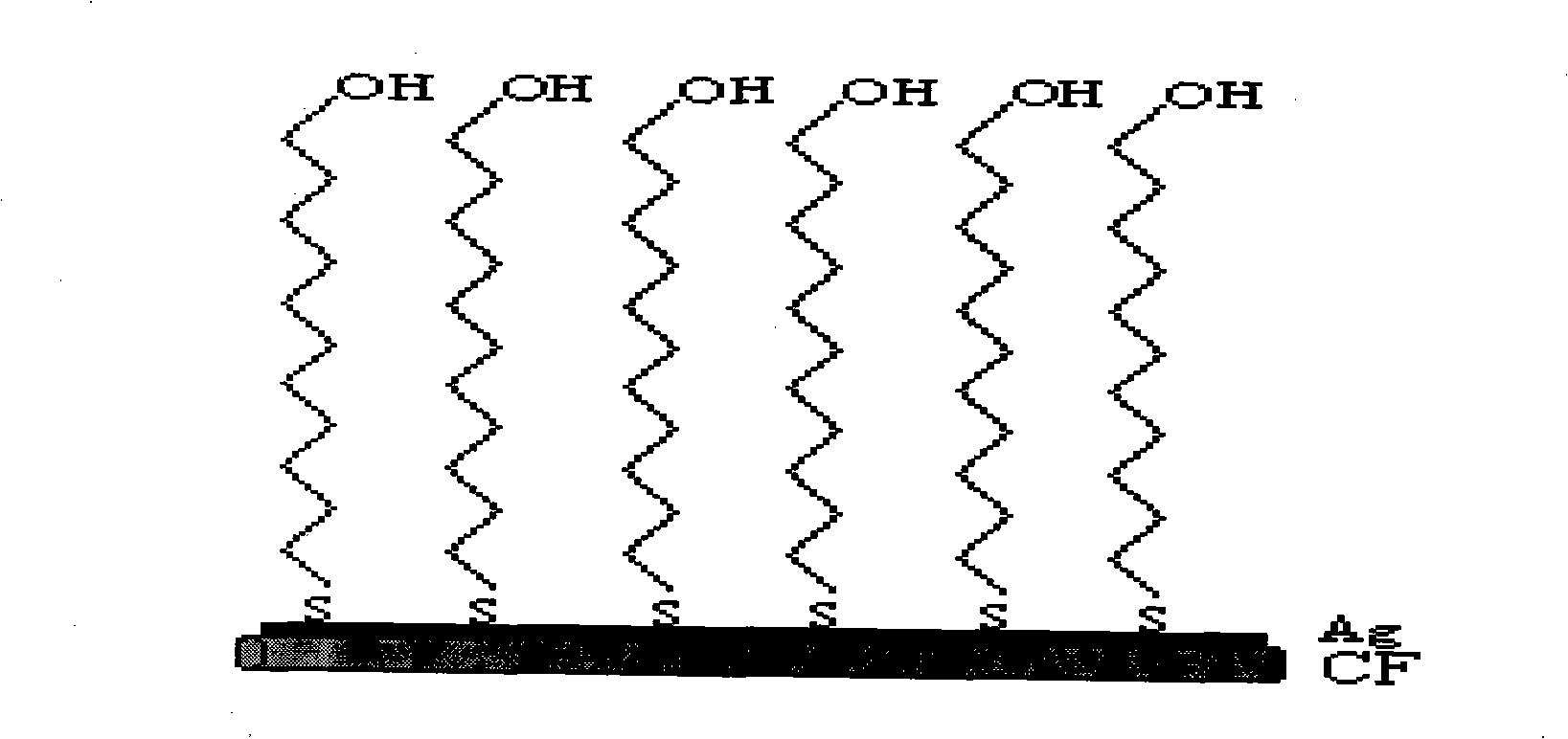
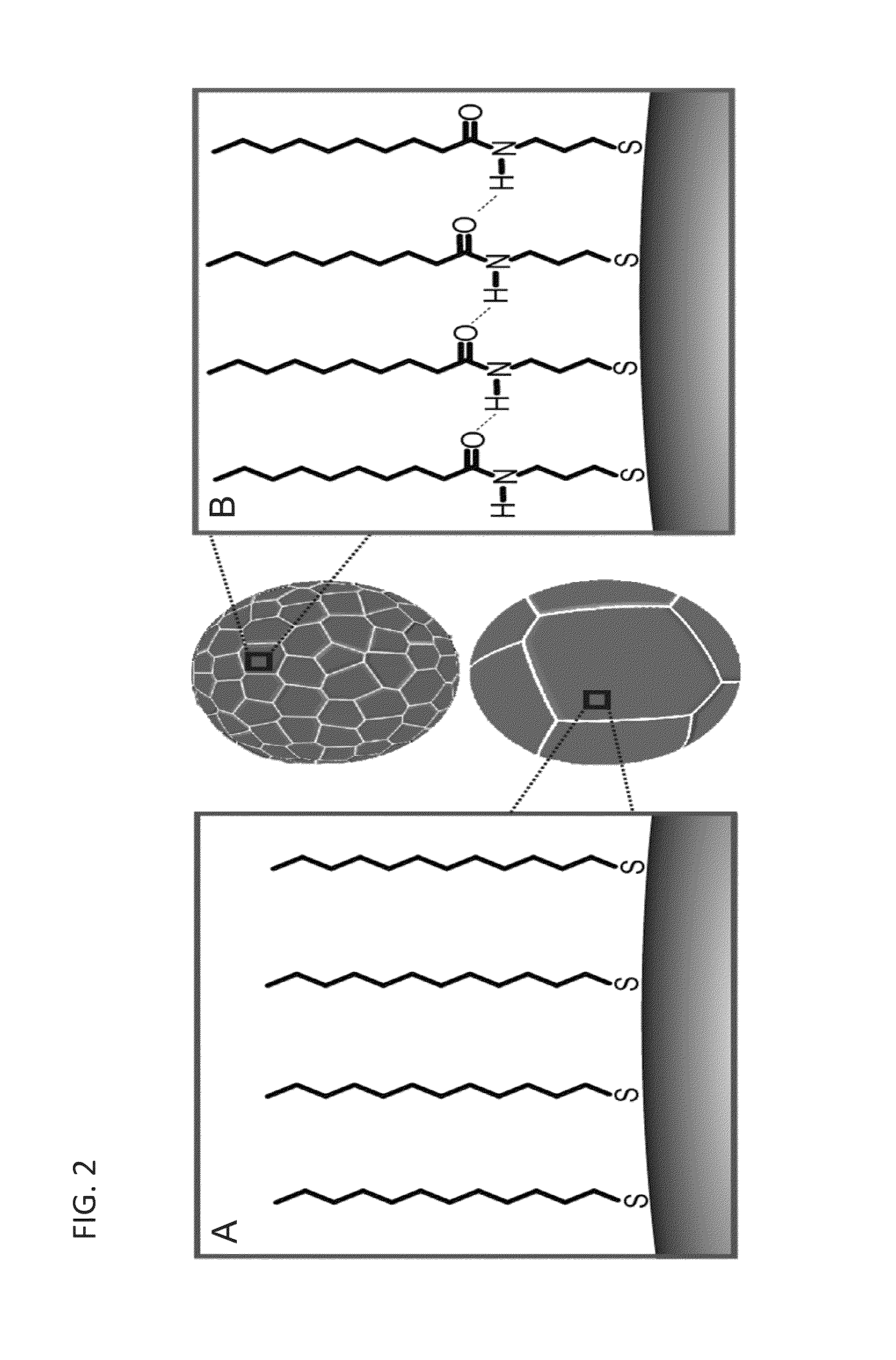
Carbon fiber surface modification method
The invention discloses a carbon fiber surface modification method, and relates to a carbon fiber modification method. The invention solves the problem of the uncontrollability of the distribution and arrangement of a carbon fiber surface functional group, which is not propitious to the study of the mechanism of a carbon fiber interface. The carbon fiber is plated with silver after surface pre-processing, then the carbon fiber with the silver-plated surface is infused in the dilute solution of thiol molecule containing sulfur element; depending on the coactions of the bonding reaction of sulfur atoms and metb and the force among self-assembly molecules, the thiol molecule has chemical absorption on the fiber surface and forms a closely arranged and ordered two-dimensional self-assembly single molecule membrane; two procedures are as follows: 1. the chemical plating of silver on the carbon fiber surface; and 2. the self assembly of molecules of organic sulfide on the silver-plating carbon fiber. The carbon fiber surface modification method has the advantages of realizing controllable, directional and ordered arrangement on the carbon fiber surface functional group from the molecule level, thus being beneficial to the study of the mechanism of the carbon fiber composite material interface.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
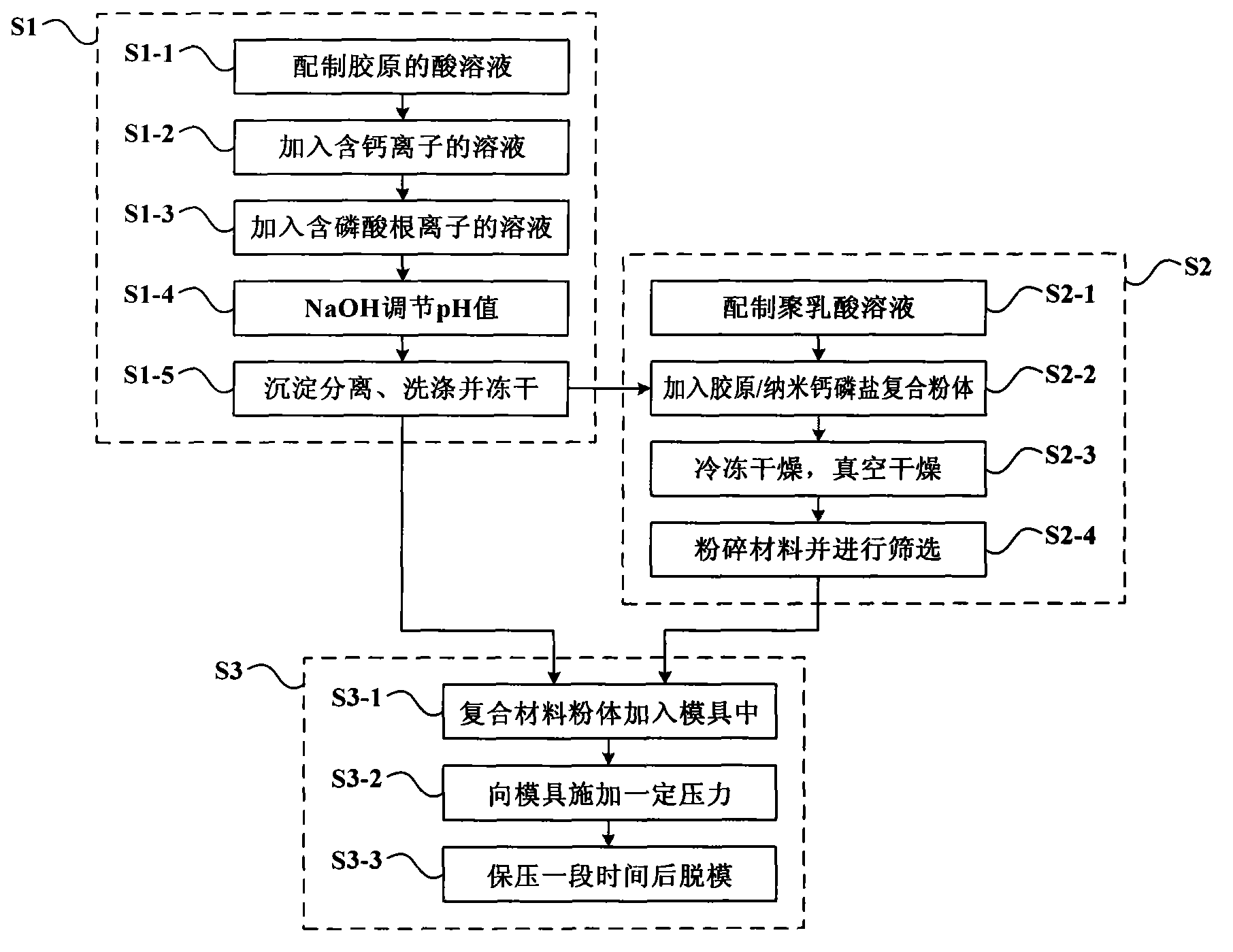
High-strength collagen base artificial bone repair material
ActiveCN103830775AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove biological activityProsthesisHuman bodyBone Cortex
The invention provides a high-strength collagen base artificial bone repair material which can be used for repairing the bone defect of bearing parts of a human body. The high-strength collagen base artificial bone repair material has chemical composition and structure formed by self-assembly of nanometer calcium phosphate and collagen molecules, so that the high-strength collagen base artificial bone repair material has a biomimetic mineralization structure similar to the natural bone tissue of the human body. In terms of mechanical properties, the material has the mechanical strength similar to that of the cortical bone of the human body and can be used for repairing the bone defect of the bearing parts of the human body. The invention also provides a preparation method of the high-strength collagen base artificial bone repair material.
Owner:BEIJING ALLGENS MEDICAL SCI & TECH
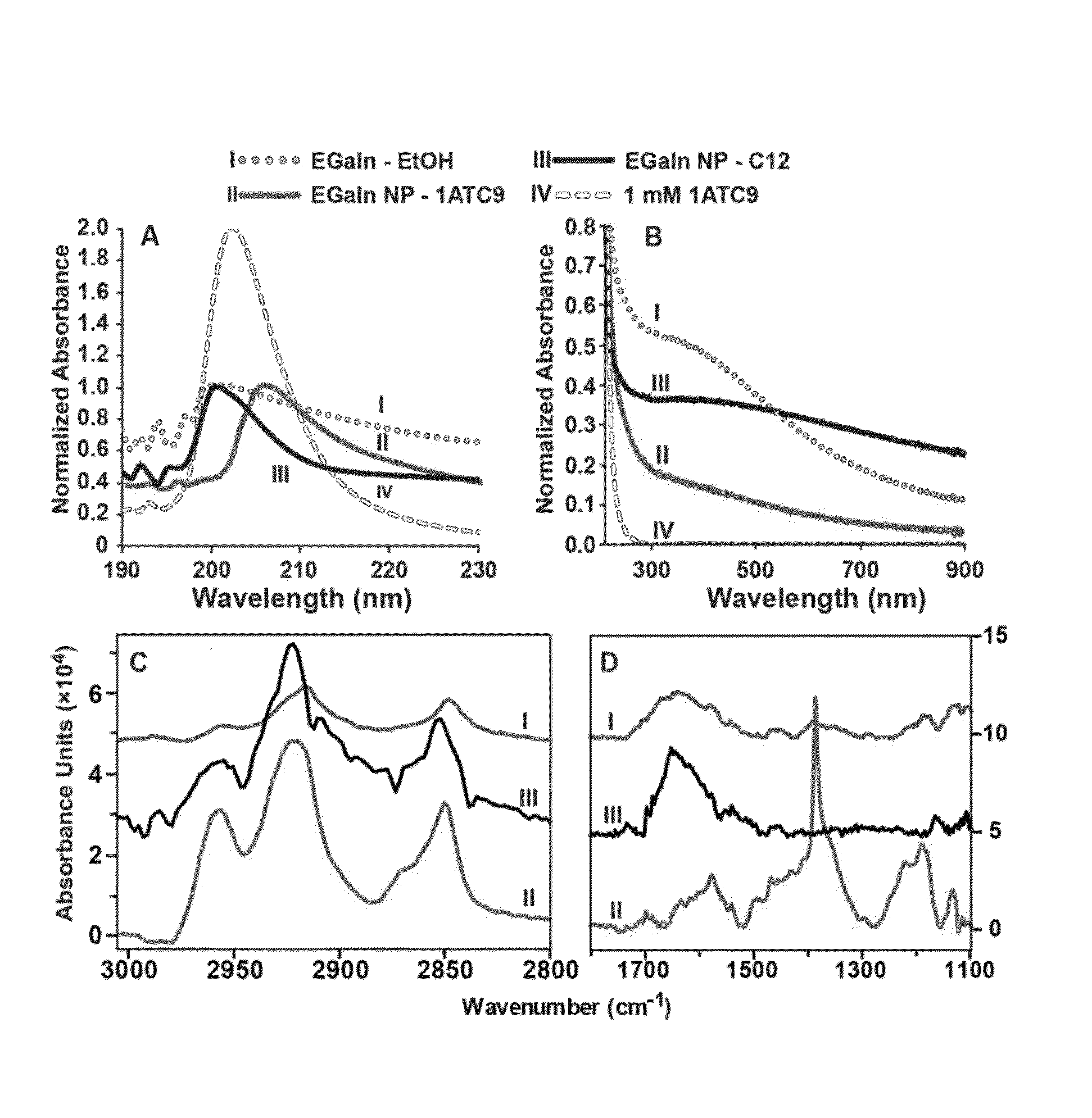
Metal alloy nanoparticle synthesis via self-assembled monolayer formation and ultrasound
ActiveUS20130244037A1Small sizeMaterial nanotechnologySynthetic resin layered productsIndiumSelf-assembled monolayer
Methods and assemblies for the construction of liquid-phase alloy nanoparticles are presented. Particle formation is directed by molecular self-assembly and assisted by sonication. In some embodiments, eutectic gallium-indium (EGaIn) nanoparticles are formed. In these embodiments, the bulk liquid alloy is ultrasonically dispersed, fast thiolate self-assembly at the EGaIn interface protects the material against oxidation. The assembly shell has been designed to include intermolecular hydrogen bonds, which induce surface strain, assisting in cleavage of the alloy particles to the nanoscale. X-ray diffraction and TEM analyses reveal that the nanoscale particles are in an amorphous or liquid phase, with no observed faceting.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Functional associative coatings for nanoparticles
InactiveUS7906147B2Readily and efficiently optimizing propertyAvoid interactionPowder deliveryIn-vivo radioactive preparationsAmphiphileNanoparticle
Described herein are nanoparticles that are coated with a bilayer of molecules formed from surface binding molecules and amphiphatic molecules. The bilayer coating self assembles on the nanoparticles from readily available materials / molecules. The modular design of the bilayer coated nanoparticles provides a means for readily and efficiently optimizing the properties of the bilayer coated nanoparticle compositions. Also described herein are uses of such nanoparticles in medicine, laboratory techniques, industrial and commercial applications.
Owner:NANOPROBES
Extruding organic polymers
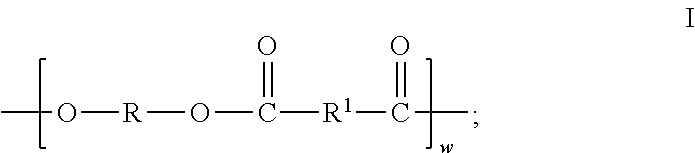
The instant invention generally provides a process for extruding a melt of a mixture comprising a molecularly self-assembling (MSA) material and at least one first rheological additive to give a shaped MSA material, a shaped MSA material produced by the process, and an article comprising the shaped MSA material. The instant invention also generally provides a composition comprising a MSA material and at least one second rheological additive, a process of electrospinning the composition, and a fiber prepared by the electrospinning process.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Periodic Nanostructures From Self Assembled Wedge-Type Block-Copolymers
ActiveUS20130296491A1Operation and useEfficient molecular self-assemblyNanotechnologyMicrostructural device manufacturePeriodic nanostructuresSelf assemble
The invention provides a class of wedge-type block copolymers having a plurality of chemically different blocks, at least a portion of which incorporates a wedge group-containing block providing useful properties. For example, use of one or more wedge group-containing blocks in some block copolymers of the invention significantly inhibits chain entanglement and, thus, the present block copolymers materials provide a class of polymer materials capable of efficient molecular self-assembly to generate a range of structures, such as periodic nanostructures and microstructures. Materials of the present invention include copolymers having one or more wedge group-containing blocks, and optionally for some applications copolymers also incorporating one or more polymer side group-containing blocks. The present invention also provides useful methods of making and using wedge-type block copolymers.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
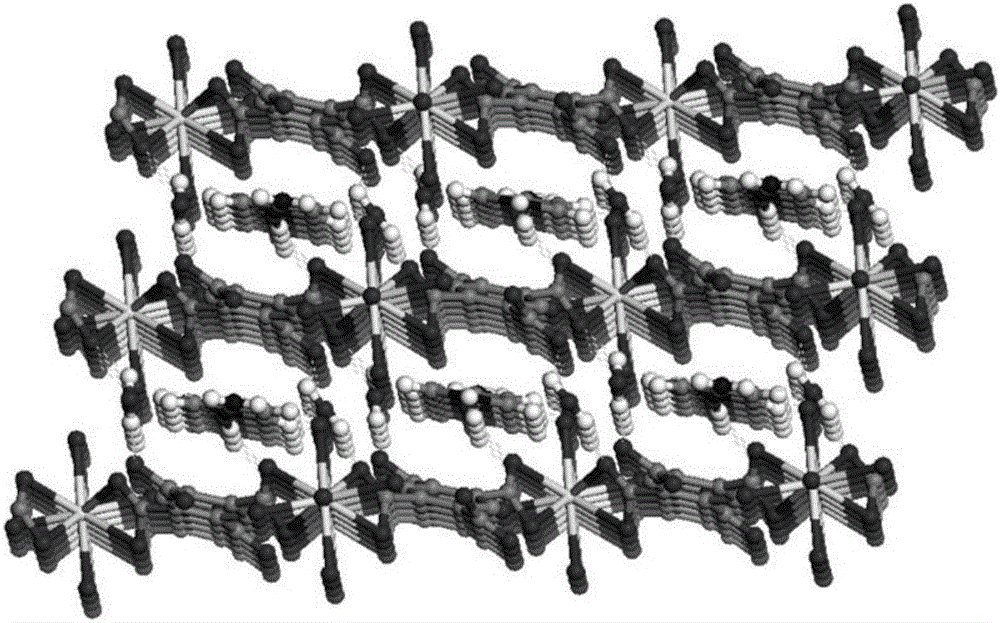
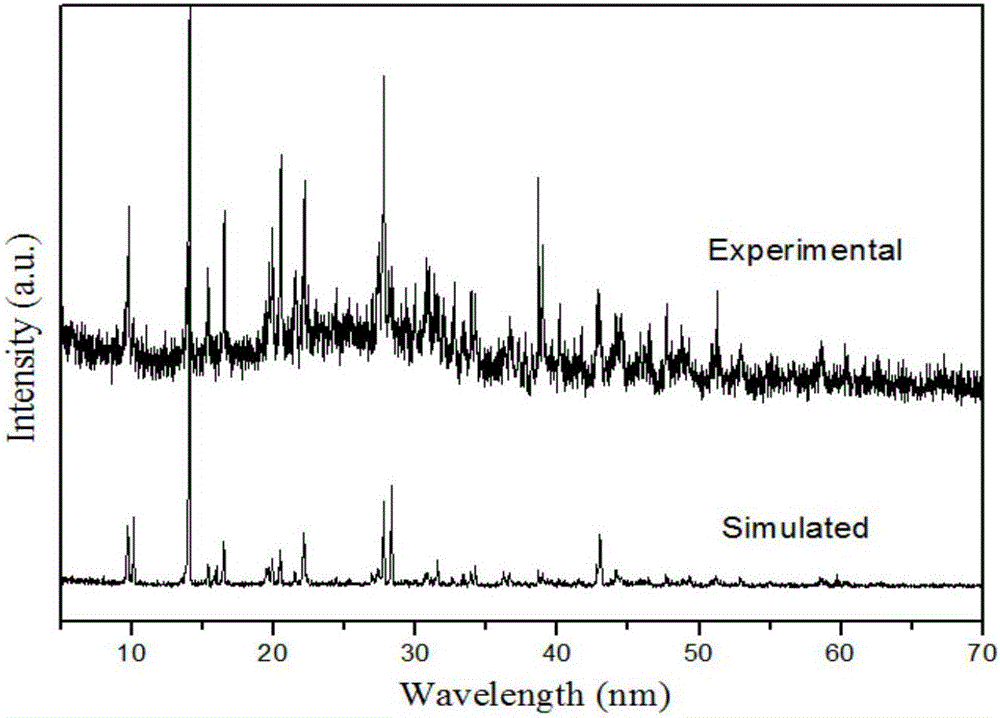
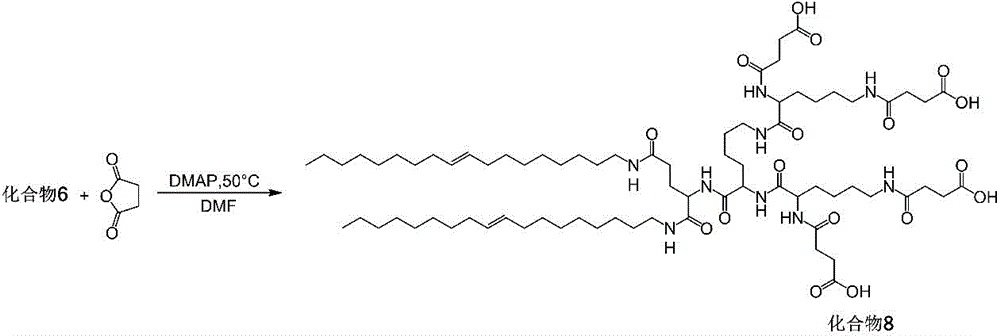
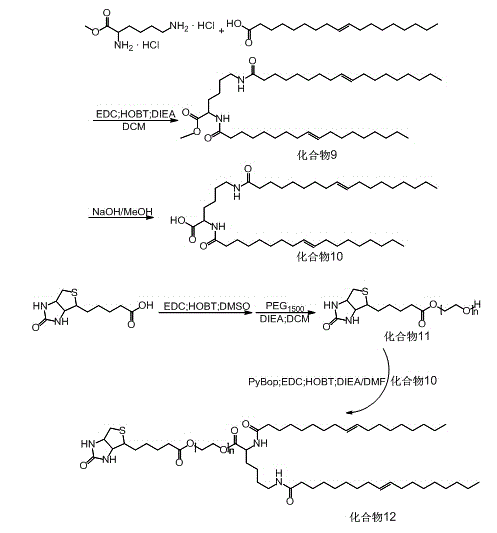
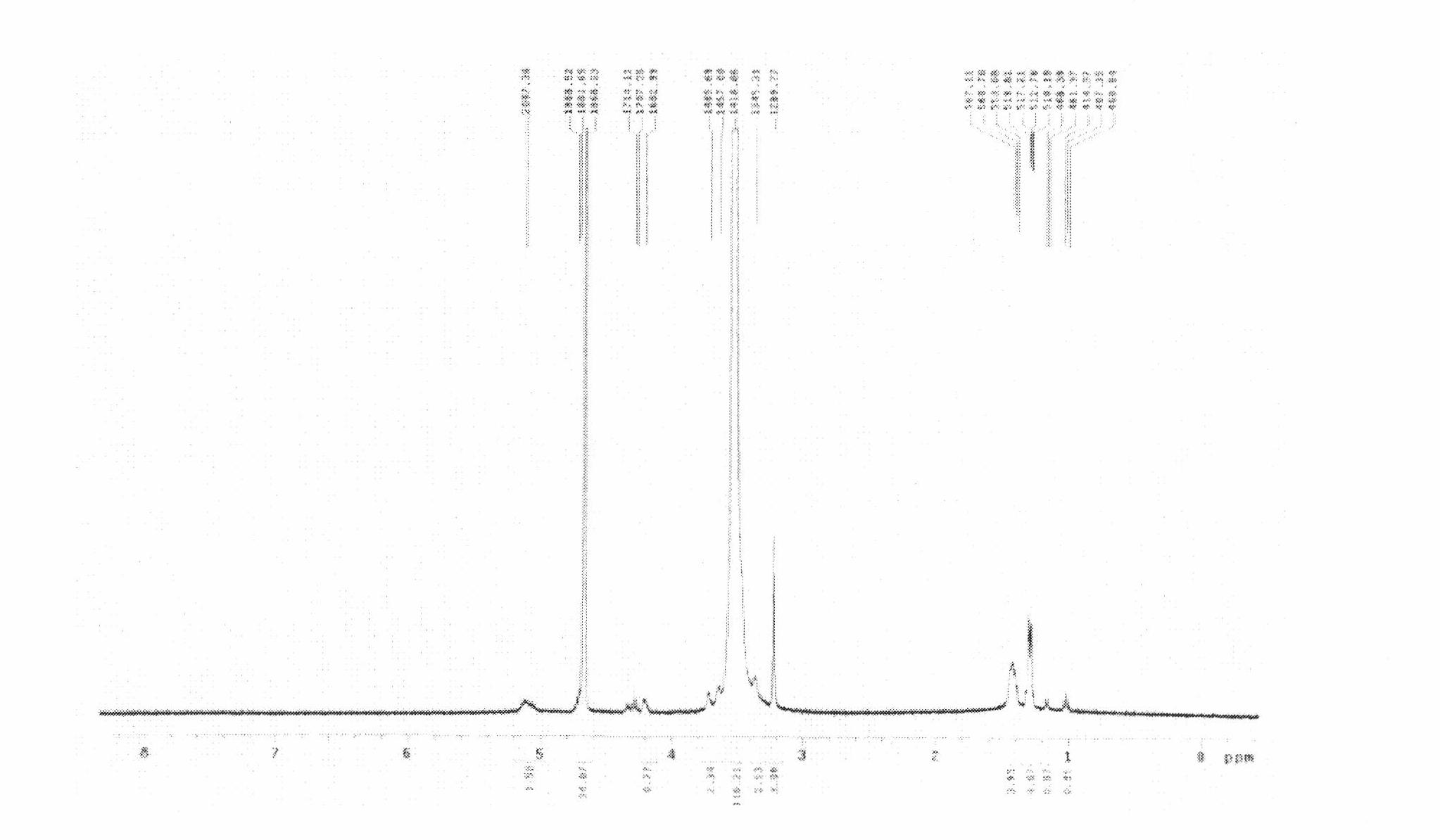
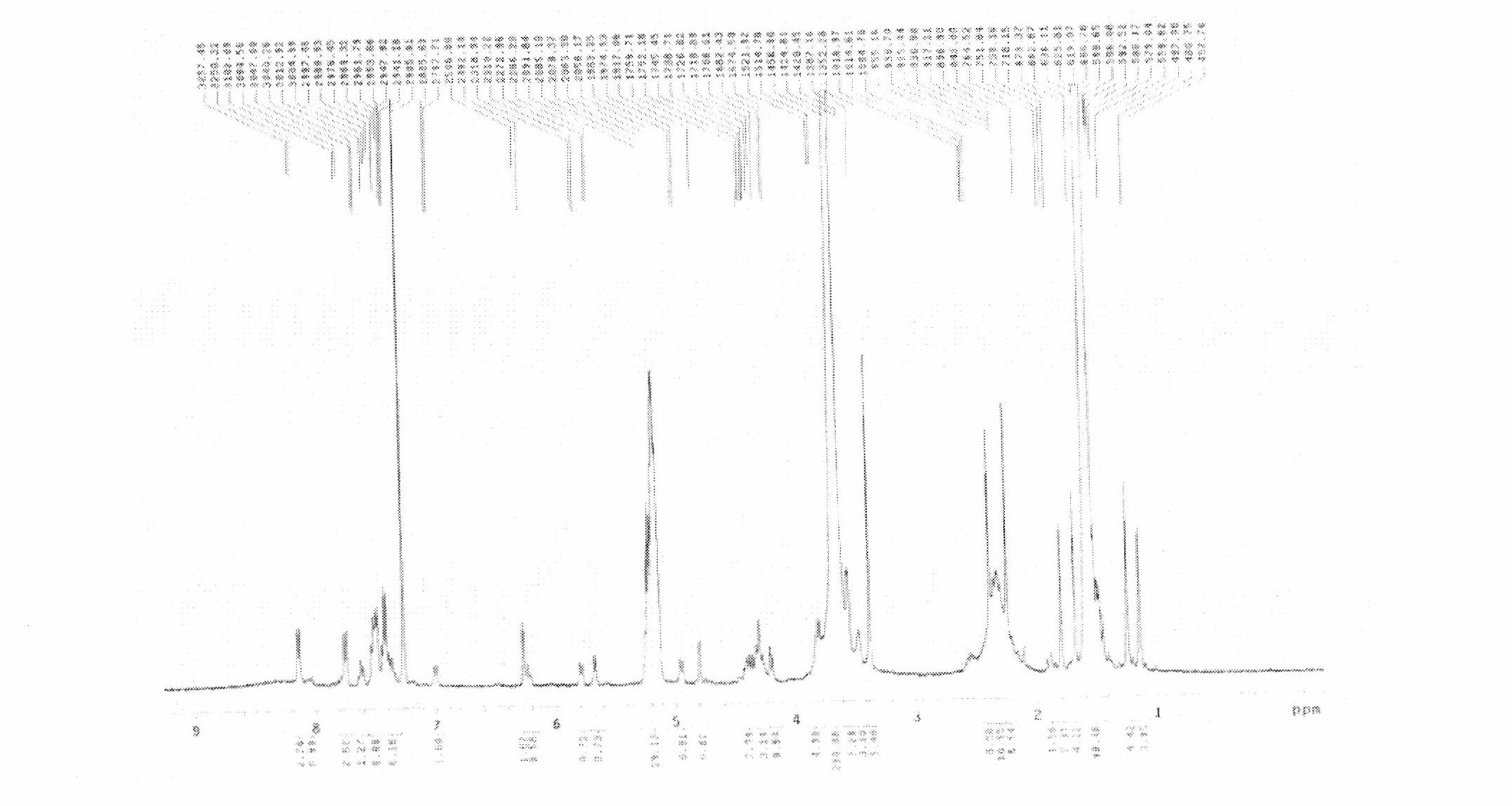
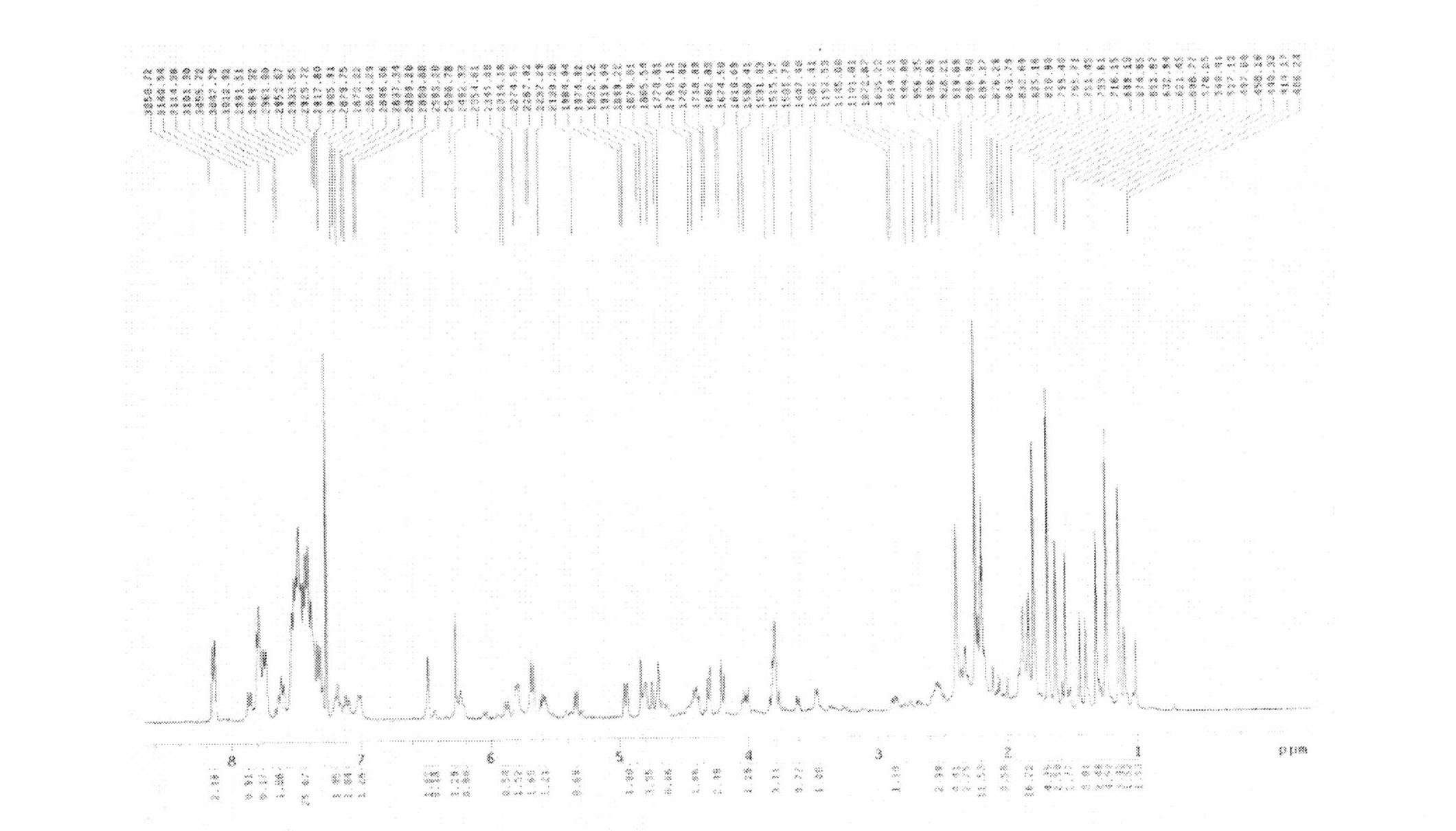
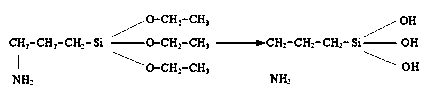
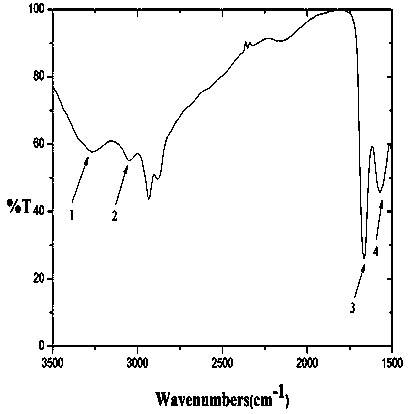
Cucurbit [7] uril [3] rotaxane as well as preparation method and application thereof
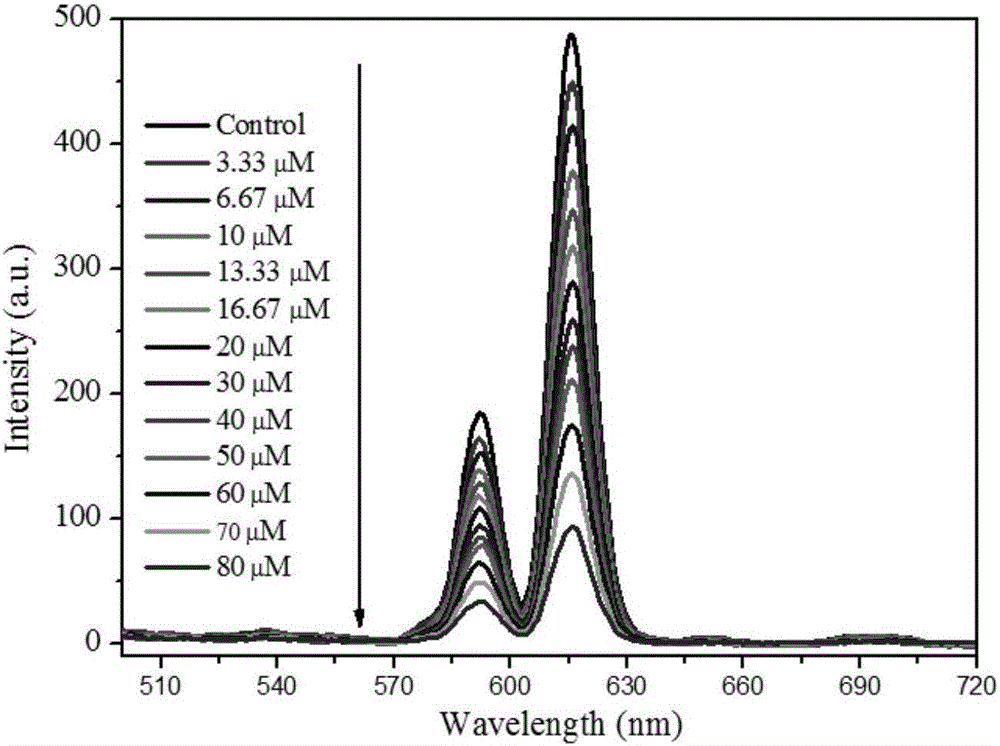
InactiveCN104447768ADecreased fluorescence intensityLow detection limitOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceArginineOrganic synthesis
The invention discloses a cucurbit [7] uril [3] rotaxane as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical fields of organic synthesis and analytical chemistry. A fluorescence probe cucurbit [7] uril [3] rotaxane prepared by the method can be applied to high-selectivity and high-sensitivity detection of lysine or arginine or a mixture of the lysine and the arginine. Under the medium condition of an aqueous solution, a trace amount of lysine or arginine or the mixture of the lysine and the arginine can be detected by taking cucurbit urils supramolecular self-assembly as a probe system by adopting a fluorescence emission spectrophotometry at high sensitivity and high selectivity. The invention also discloses a preparation method and a technological condition of the cucurbit [7] uril [3] rotaxane. The reacting fluorescence excitation wavelength of the cucurbit [7] uril [3] rotaxane and the lysine or the arginine or the mixture of the lysine and the arginine is 317nm; and the maximal emission wavelength is 375nm.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Electroblowing of fibers from molecularly self-assembling materials
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
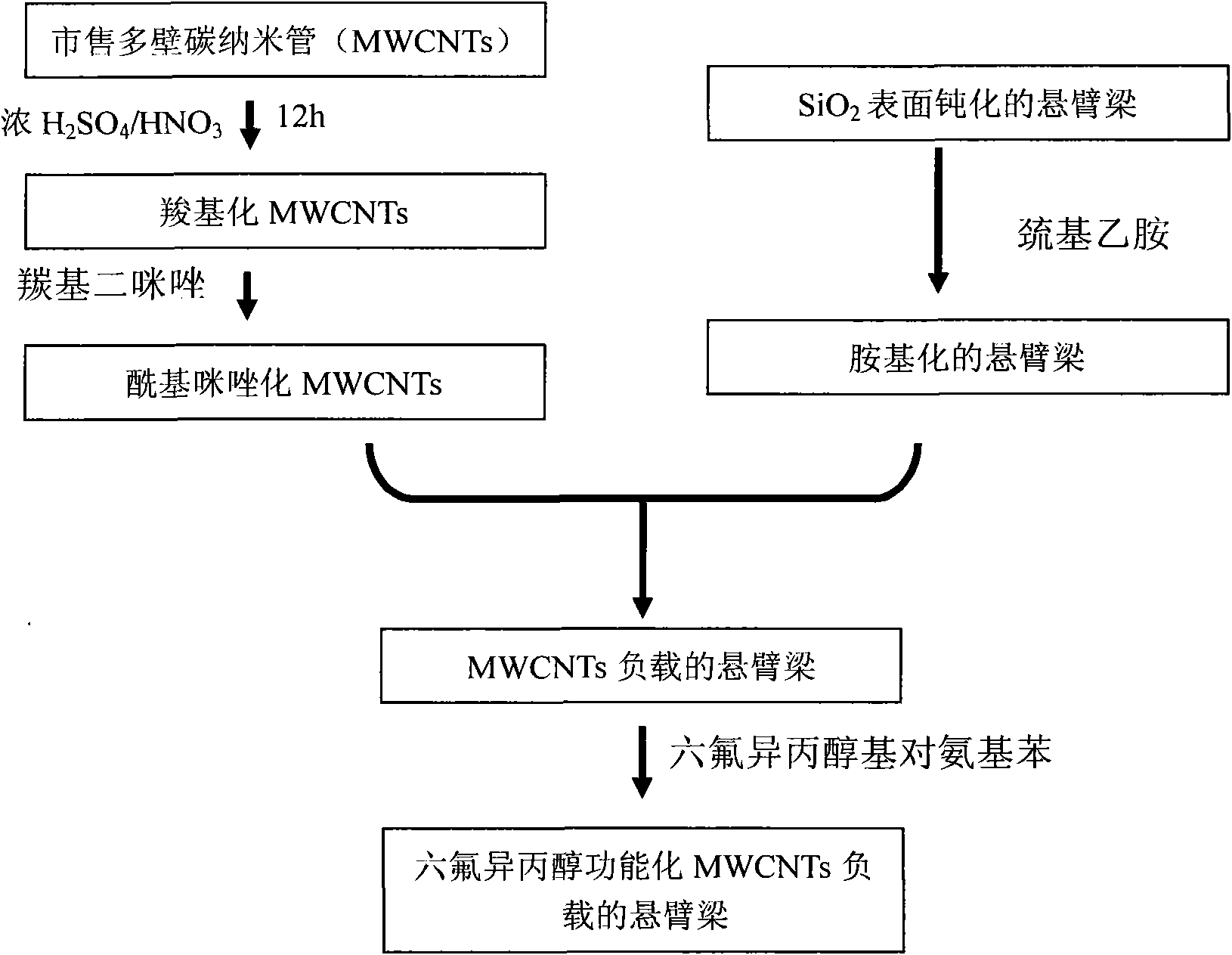
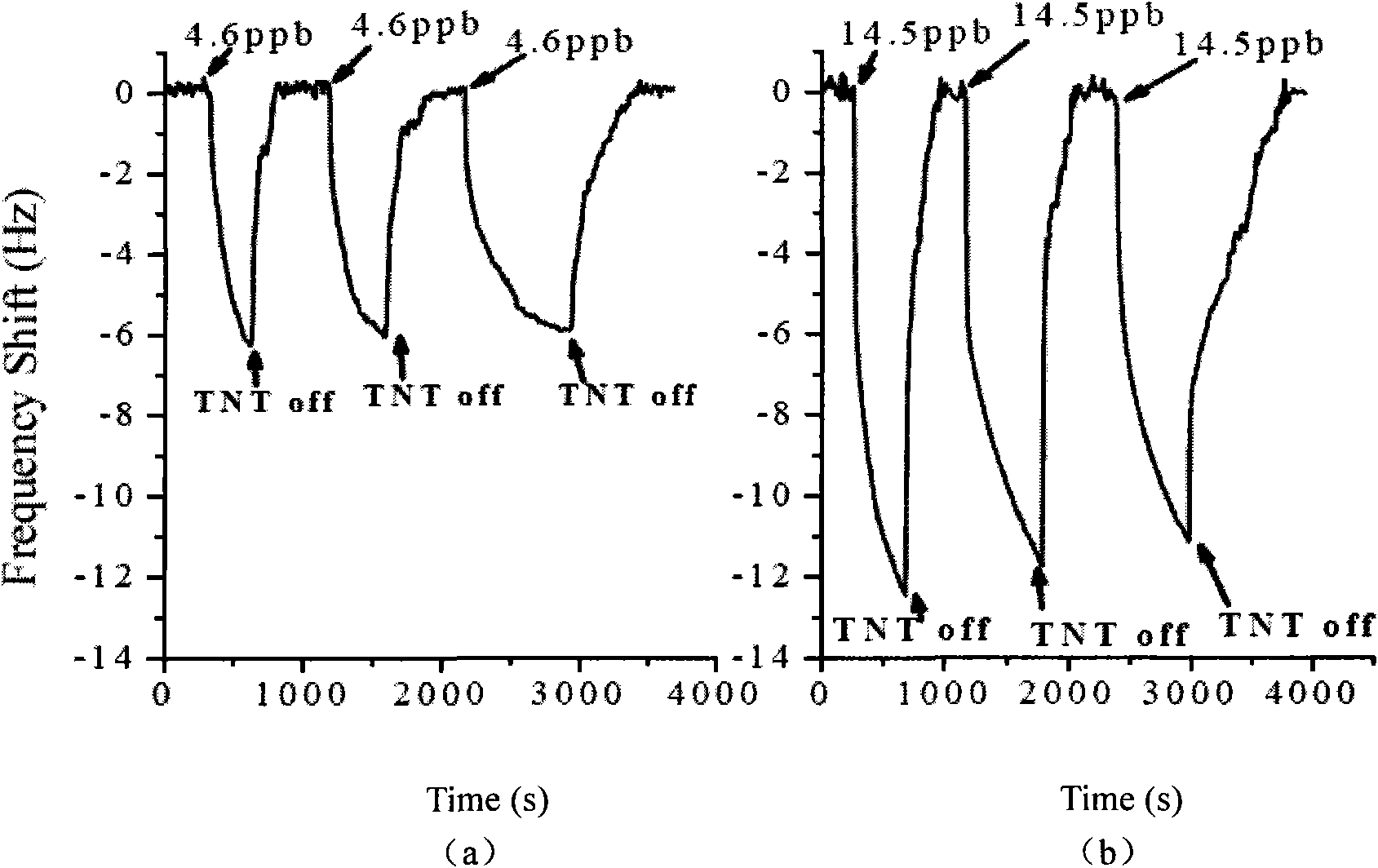
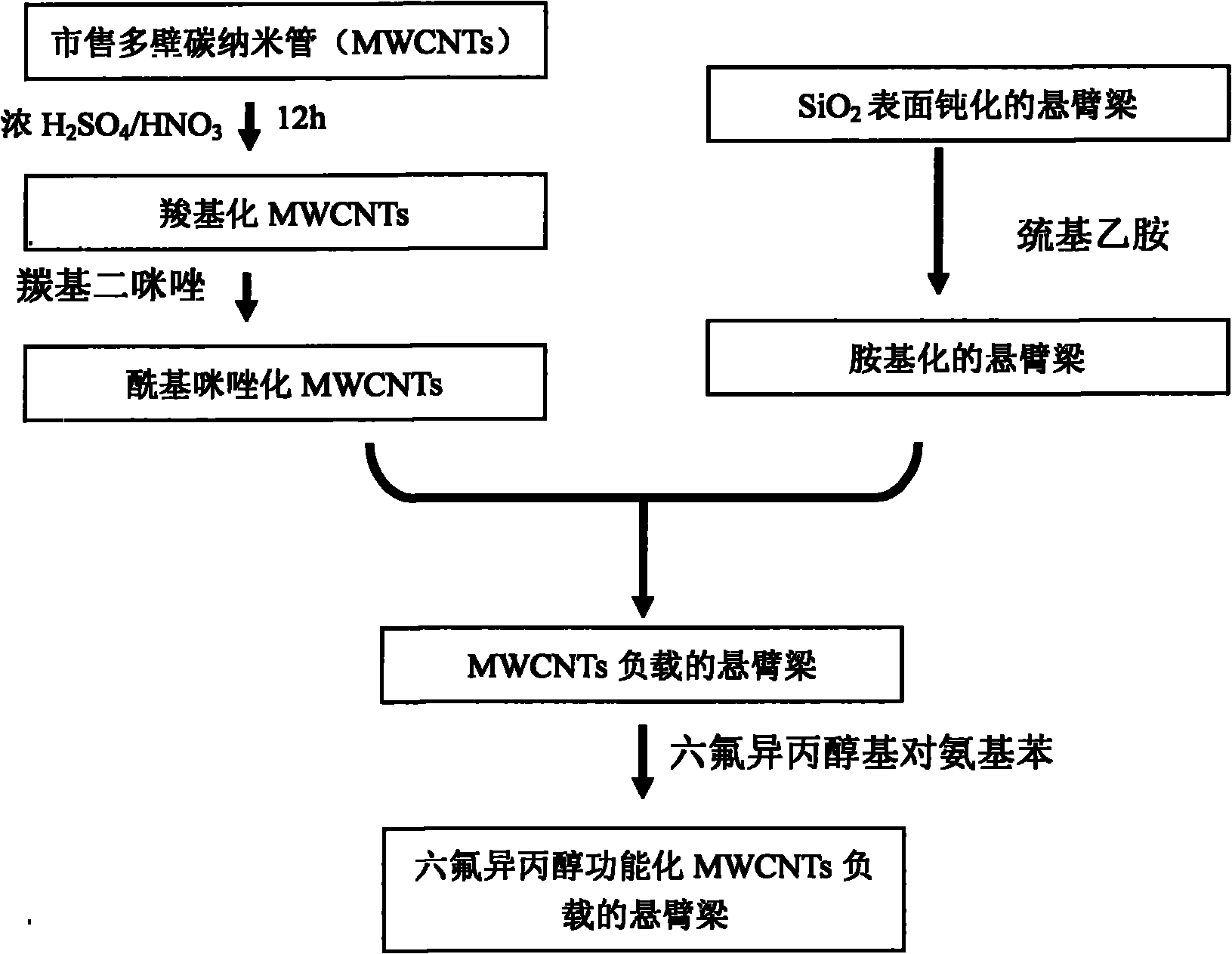
Method of micro cantilever beam sensor using functional carbon nano tubes as sensitive materials
ActiveCN101935008AEasy to operateLow costDecorative surface effectsFuel testingStrong acidsMems sensors
The invention relates to a manufacturing method of a micro cantilever beam sensor using functional carbon nano tubes as sensitive materials, belonging to the field of a micro-nano sensor. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: using multi-walled carbon nano tubes as manufacturing materials of the sensor, and pretreating with strong acid to form reaction-active points which can be functionally modified on the surfaces of the multi-walled carbon nano tubes; then, fixing the multi-walled carbon nano tubes onto the gold surface of the MEMS sensor according to the molecular self-assembly technology; and finally, carrying out functional group modification again on the carbon nano tubes fixed on the gold surface of the MEMS sensor according to chemical properties of target gas to be detected (for example, a certain hydrogen bonding effect and the like exist between ammonia gas and carboxyl as well as formaldehyde and amino group) based on the molecular design, and enabling the sensor to be used for the detection of special target gas.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
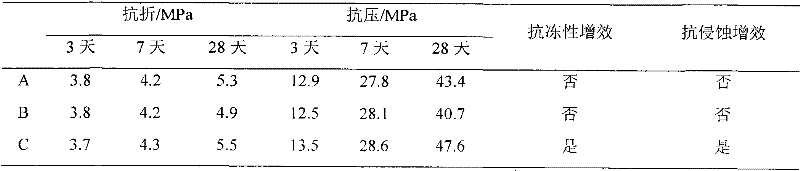
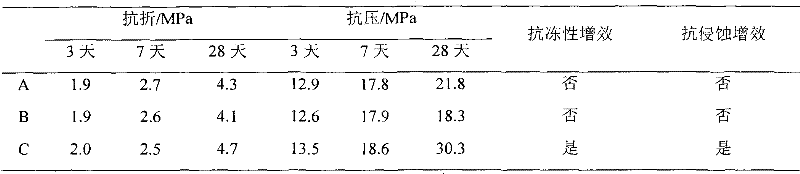
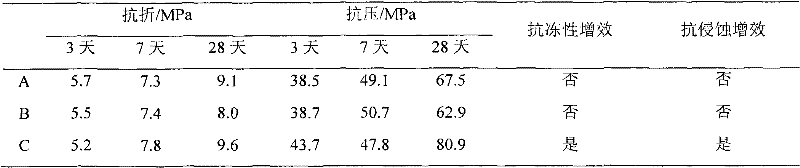
Preparation and application of cement material self-repairing molecular self-assembled microspheres
InactiveCN102049230ARealize controllable operationIntelligent self-healing functionMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationCross-linkBreaking strength
The invention discloses preparation of cement material self-repairing microspheres and application of the self-repairing microspheres in cement concrete. The microsphere preparation comprises the following steps: selecting repairing liquid with good repairing performance for cement and concrete; designing and screening self-repairing microsphere functional monomers; selecting cross-linking agent and porogen, and polymerizing the obtained functional monomers and the repairing liquid into microspheres with self-repairing function under proper conditions by using a molecular self-assembly technology; preparing self-repairing microspheres from the repairing liquid, the monomers, initiator, cross-linking agent, porogen and emulsifier under certain conditions in a certain proportion; and mixing the prepared cement material self-repairing microspheres in the cement and cement concrete to repair the material. By mixing the self-repairing microspheres, the breaking strength and compression strength of the cement concrete which cracks under stress are quickly recovered; and since the microspheres is added, the freezing resistance and erosion resistance of the cement concrete are remarkably improved.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
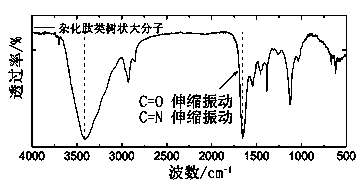
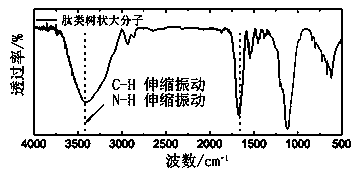
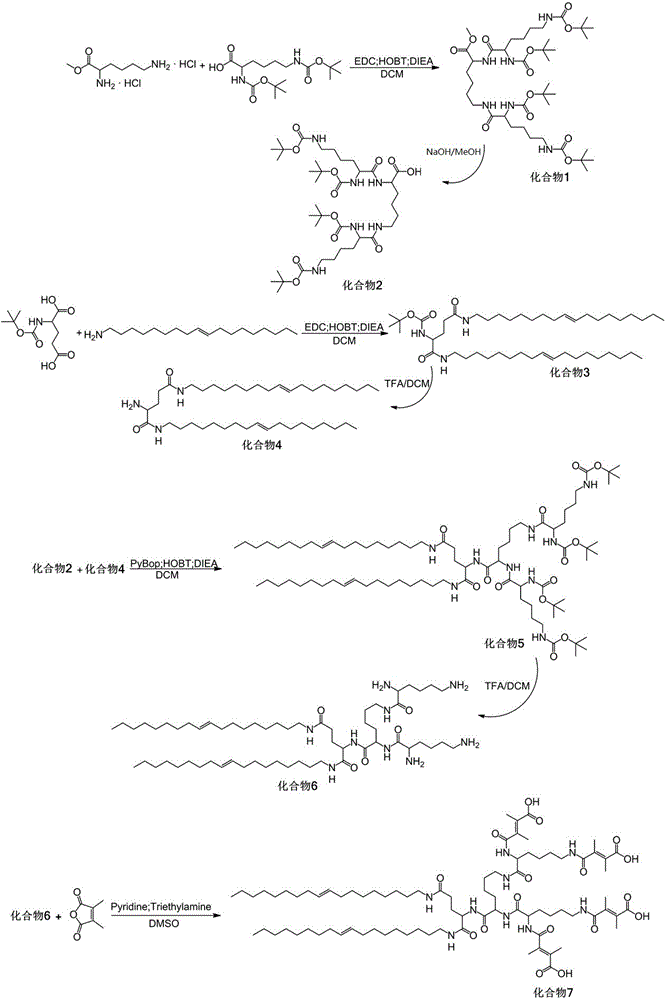
Supramolecular hybrid peptide dendric macromolecule self-assembly and preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104195176AStable structureGood dispersionOther foreign material introduction processesPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsInorganic nanoparticlesMacromolecule
The invention discloses a supramolecular hybrid peptide dendric macromolecule self-assembly and a preparation method and applications thereof. The supramolecular hybrid peptide dendric macromolecule self-assembly comprises an inorganic nanoparticle core and peptide dendritic macromolecules, wherein the peptide dendritic macromolecules are assembled at the periphery of inorganic nanoparticles by coordination interaction. Through the introduction of the coordination interaction, the peptide dendritic macromolecules are assembled on the surfaces of the inorganic nanoparticles. The coordination interaction is a relatively strong weak interaction, and an obtained supramolecular hybrid peptide dendric macromolecule self-assembly is stable in structure and good in dispersibility, and enriches the self-assembly strategy of dendritic macromolecules. By using the supramolecular self-assembly strategy, the spontaneous, rapid, green and efficient function integration of low-algebra dendritic macromolecules is realized, so that the highly branched structure of dendritic macromolecules is effectively amplified, and the function effect of the supramolecular hybrid peptide dendric macromolecule self-assembly reaches and is even higher than the function effect of classic high-algebra dendritic macromolecules.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Antireflection film used in all-angle and wide wavelength range and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101665014AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove smoothnessLayered productsCoatingsMicro structureRefractive index
The invention discloses an antireflection film used in the all-angle and wide wavelength range and a preparation method thereof. The film comprises a substrate, a first sol-gel layer, a silica nanoparticle layer and a second sol-gel layer. A first sol-gel film layer is prepared on the substrate by a pulling method, then a silica particle layer is prepared on the surface of the film by a molecularself-assembly technique, and finally a second sol-gel film layer is prepared on the surface of the film layer by the pulling method, wherein, the film on each layer is subjected to heat treatment. Byoptimizing the technological parameters, the film can have the following characteristics: the refractive index in the direction from the substrate to the air decreases progressively, the thickness matches and the surface micro-structure is two-dimensional ordered; therefore, the film realizes the antireflection effect in the all-angle and wide wavelength range and simultaneously has the ability of film forming in large area, the mechanical property and firmness of the whole antireflection film can be effectively improved, and the energy use ratios of the solar cells and the solar collector tubes are increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method for wettability controllable porous structure of titanium and titanium alloy surface
InactiveCN102345134AImprove bindingAchieve freedom of controlChemical vapor deposition coatingOsteoblast adhesionTitanium alloy
The invention discloses a preparation method for a wettability controllable porous structure of a titanium and titanium alloy surface, and belongs to the technical field of surface modification of biological implant materials. The method comprises the following steps of: performing roughening treatment on the titanium and titanium alloy surface by using a sand-blast, large-grit and acid-etch method (SLA) to prepare a super-hydrophilic surface with a micron-nano double-microcosmic pore structure; preparing a titanium oxide thin film with hydrophilic performance by using a plasma oxidation process, wherein osteoblast adhesion and proliferation experiments show that the surface prepared by the process method has excellent bioactivity; and finally, forming a hydrophobic surface on a rough titanium oxide surface by using a molecular self-assembly method and realizing mutual switching between hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity of the surface by using plasma treatment and ultraviolet irradiation. The hydrophilicity of the surface of an implant is obviously improved in the aspects of stability, durability and the like; and the binding force of the metal implant material and a surface coating can be obviously improved while the bioactivity of the titanium and titanium alloy surface is guaranteed.
Owner:蔺增
Crosslinked silane-modified molecularly self-assembling material
InactiveUS20130255490A1Satisfactory acid gasImprove permeabilitySemi-permeable membranesMembranesPolymer scienceSilanes
The present invention generally relates to a crosslinked silane-modified molecularly self-assembling material, cured manufactured article comprising the crosslinked silane-modified molecularly self-assembling material, semipermeable membrane comprising the crosslinked silane-modified molecularly self-assembling material, method of using the semipermeable membrane to separate an acid gas from a separable gas mixture comprising the acid gas and a permeation-resistant gas, and method of preparing the cured manufactured article from a curable manufactured article comprising a shaped reactive silane-modified molecularly self-assembling material.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Preparation method and application of europium coordination polymer for visible detection on p-nitrophenol and iron ion
InactiveCN105837830AExcellent fluorescence sensing performanceImprove luminosityFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical recyclingFluorescenceNitrophenol
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a europium coordination polymer for visible detection on p-nitrophenol and iron ions, and belongs to the technical field of novel materials. The preparation method comprises the following step: under a hydrothermal or solvothermal condition, performing molecular self-assembly on metal europium ions, organic ligand and a structure-directing agent with additives, thereby synthesizing the europium coordination polymer. The europium coordination polymer is excellent in fluorescent sensing property for the p-nitrophenol and the iron ions; a piece of detection test paper can be prepared from the synthesized europium coordination polymer and a carrier in a compounding manner, and rapid, simple, convenient and visible detection on the p-nitrophenol and the iron ions can be achieved. Compared with the prior art, the prepared europium coordination polymer and the test paper can achieve selective detection on the p-nitrophenol and the iron ions, have the characteristics of low preparation cost and rapid and accurate detection, and have good application prospects.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Supramolecular self-assembly biological chip, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102539777ARich varietyReduce non-specific adsorptionMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalysis by material excitationPolyrotaxaneThree-dimensional space
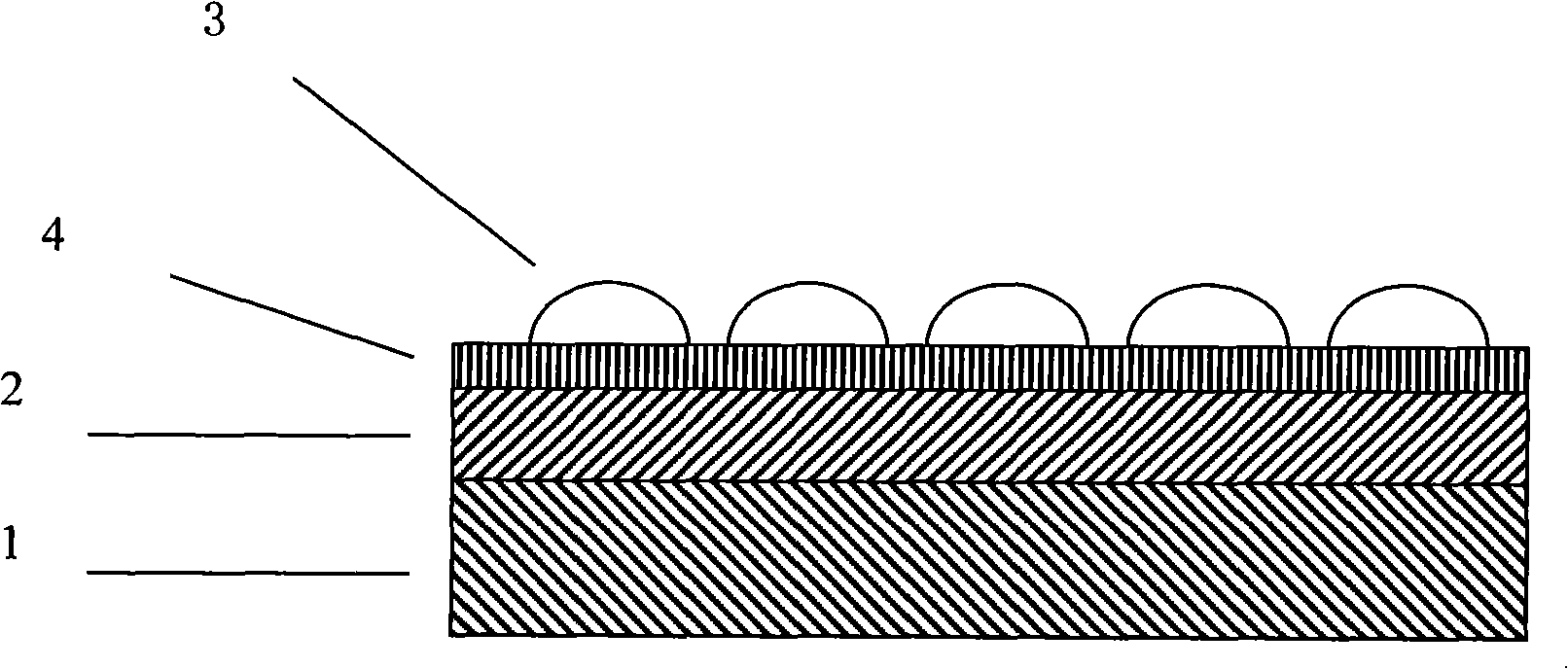
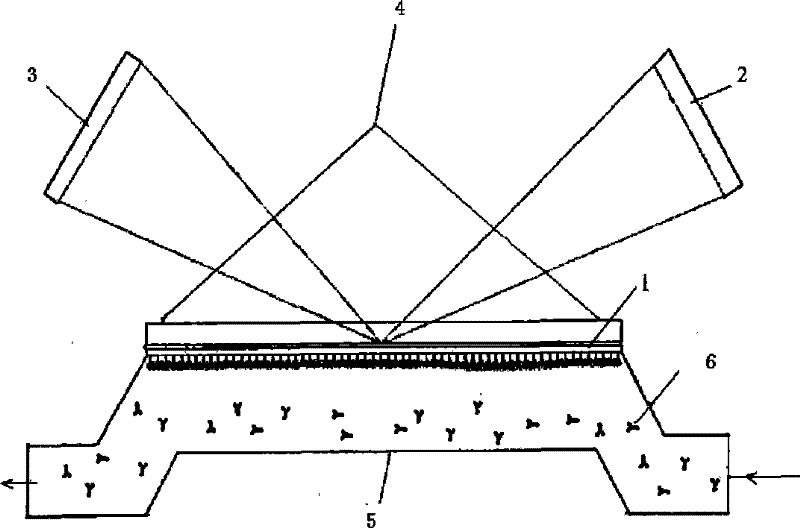
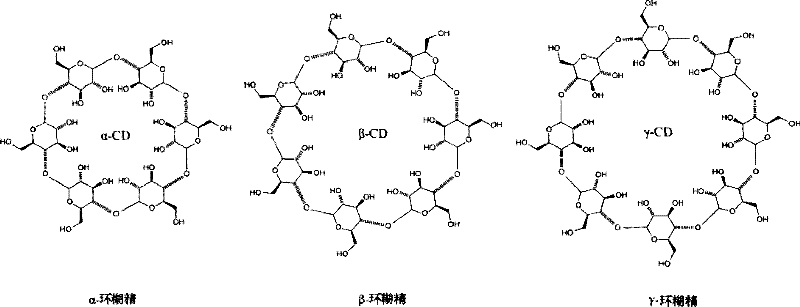
The invention provides a supramolecular self-assembly biological chip. The supramolecular self-assembly biological chip comprises a substrate (1), first chain molecules (3) which are fixed on the surface of the substrate, and second chain molecules (4) which are fixed on the surface of the substrate, wherein the first chain molecules and the second chain molecules are fixed on the substrate at intervals; part of one end, which is far away from the substrate, of each first chain molecule is included by cyclodextrin (2); the cyclodextrin comprises a functional group which can be directly or indirectly bound with protein molecules; and each second chain molecule is not longer than each first chain molecule. Poly(pseudo)rotaxane which is formed by coating the cyclodextrin and the first chain molecules and the second chain molecules which are arranged uniformly at the intervals are arranged on a self-assembly layer on the surface of the biological chip, a three-dimensional space has a dense, controllable and changeable structure, and compared with a two-dimensional surface, the three-dimensional space can fix more detection molecules such as the protein molecules. Moreover, the invention also provides a preparation method and application of the biological chip.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
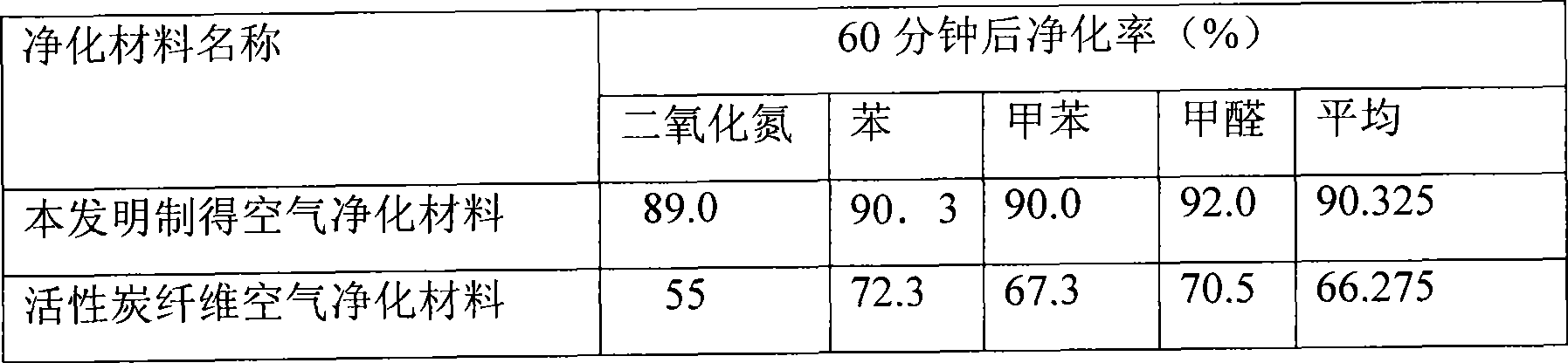
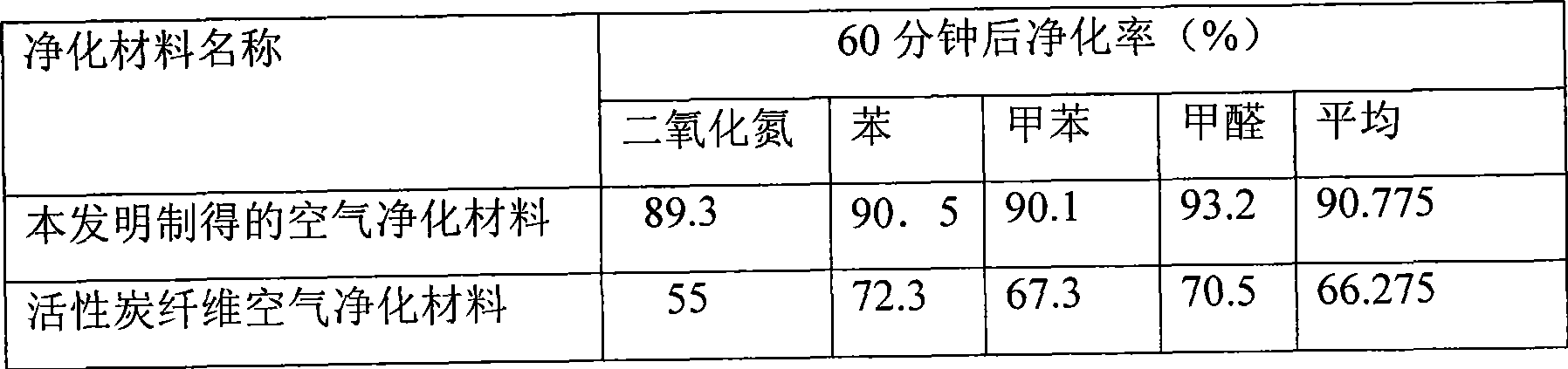
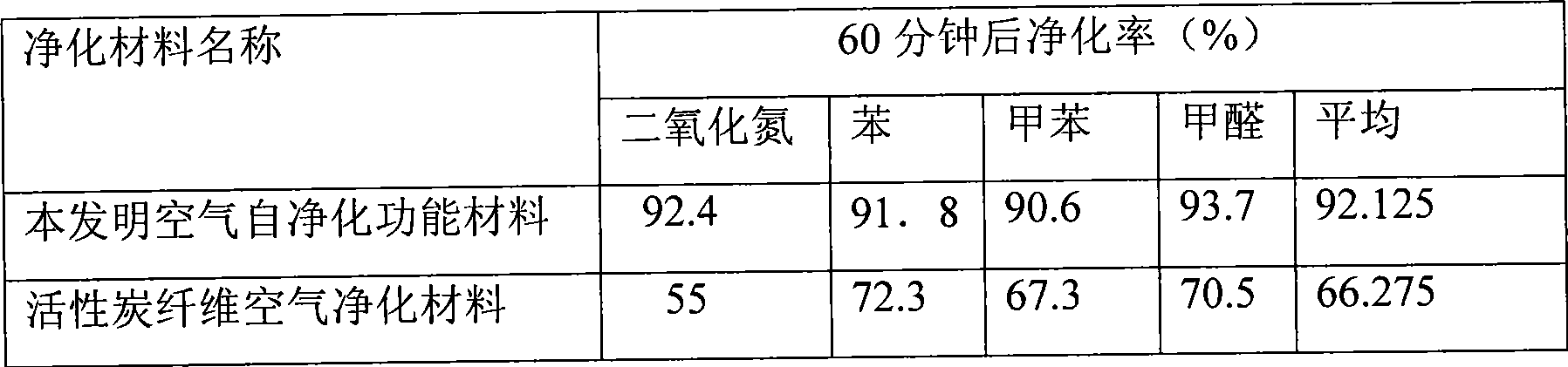
Method for preparing molecular self-assembly porous vermiculite air purification material
InactiveCN101496994AImprove photocatalytic efficiencyImprove adsorption capacityCatalyst carriersMolecular sieve catalystsAlcoholPhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a method for preparing a molecular self-assembly porous vermiculite air purifying material. The method comprises that: (1) vermiculite is subjected to acid cleaning, alkali cleaning and alcohol cleaning sequentially; and finally, the vermiculite is washed by deionized water and dried; (2) the vermiculite is soaked in a 0.01 to 0.1mol / l surfactant solution; after the surface of the vermiculite is assembled with a layer of organic unimolecule film, the vermiculite is taken out; a surface physical adsorption composition is washed out; and the vermiculite is dried in vacuum; (3) the vermiculite is soaked in 0.15 to 0.35 mol / L sol; an SnCl2 solution is taken out and injected to the sol; PdCl2 is taken out and dripped to the sol; the mixture is kept stand, stirred and separated; a loose layer is washed out; and the mixture is dried; and (4) the step (2) and the step (3) are repeated for three to four times; and the mixture is calcined to obtain the molecular self-assembly porous vermiculite air purifying material. The preparation method is simple, easy to operate and suitable for industrial scale production; and the prepared air purifying material has good air purifying effect.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Transparent electrode based on ultra-thin metallic film and preparation method and application thereof
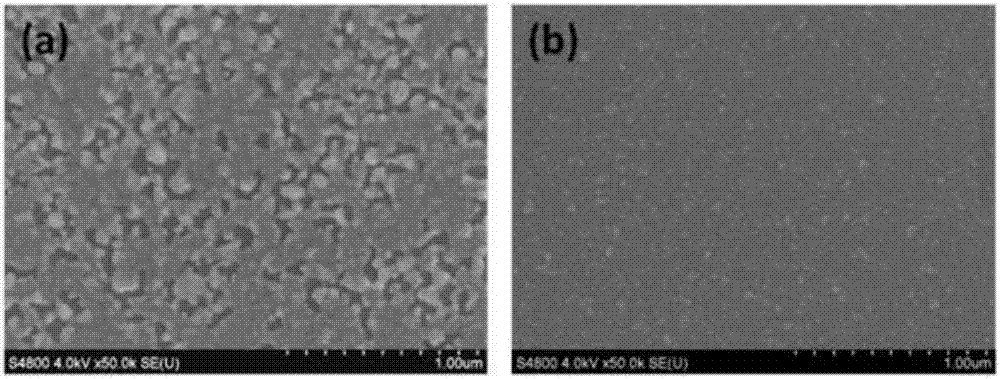
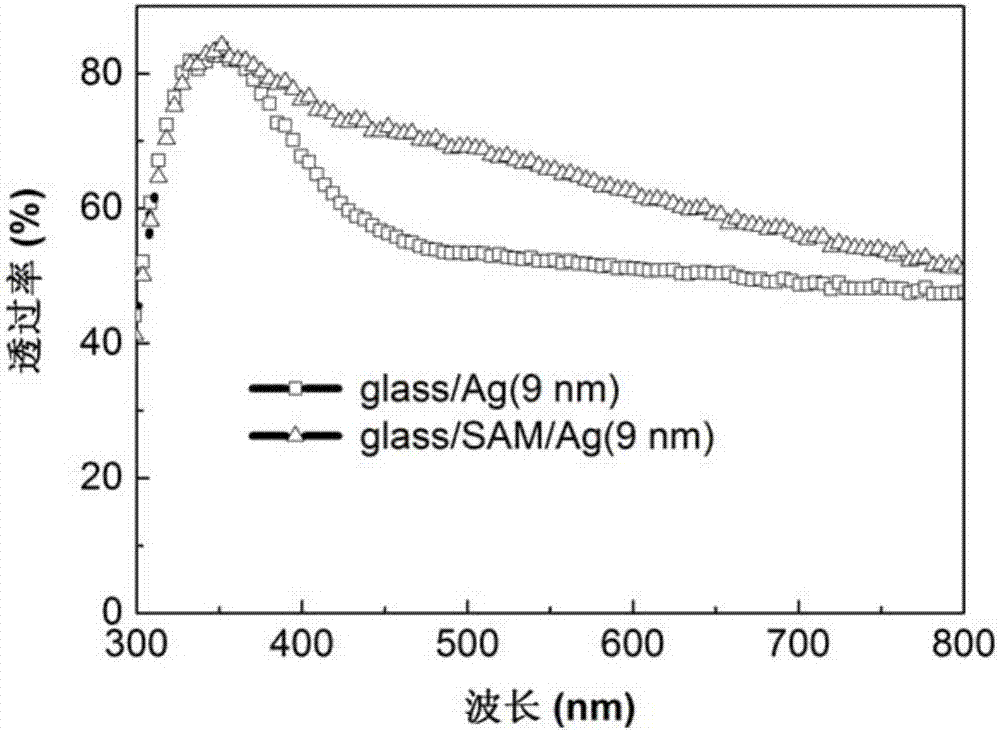
ActiveCN107393979AGood optical performanceControl conductivityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesThin metalSystem structure
The invention discloses a transparent electrode based on an ultra-thin metallic film. The transparent electrode orderly comprises a transparent substrate, a metal layer and a metal oxide layer from bottom to top, wherein the thickness of the metal layer is 3 to 12nm. The substrate is modified by a monomolecular self-assembled layer; an ultra-thin metal layer is directly deposited on the substrate, and the continuity and conductivity of the ultra-thin metallic film are improved through the function of the monomolecular self-assembled layer; or through the co-deposition of metals, the continuous growth of the ultra-thin metallic film is realized directly on the substrate; and a metal oxide layer is deposited on the substrate as an antireflection layer, then a double-layer film system structure is obtained, and through the design and optimization of the double-layer film system structure, the maximization of transmittance is realized. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the transparent electrode based on the ultra-thin metallic film and an application thereof in photoelectric devices, wherein the transparent electrode can have good conductivity and high transmittance at the same time.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
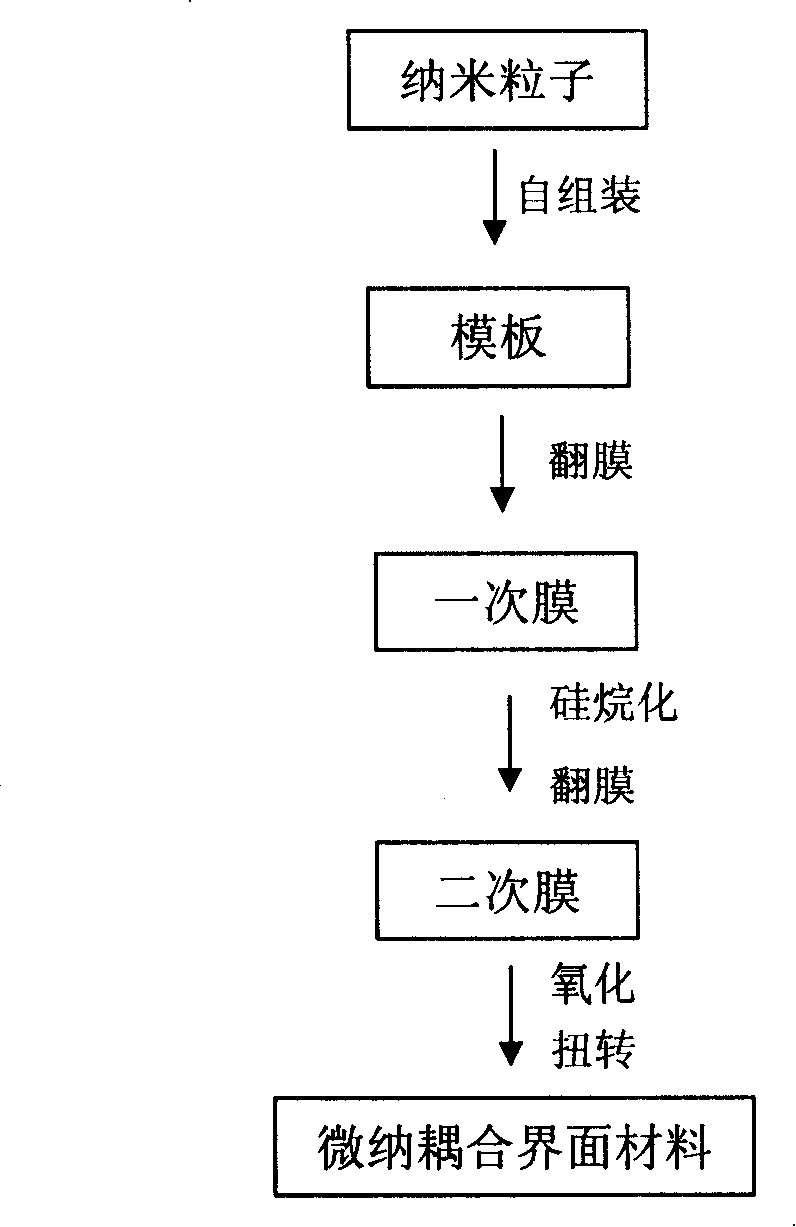
Blood compatibility material with micro nano coupling interface structure and its manufacturing method
InactiveCN101190344AGood blood compatibilityReduce adhesionPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingMicro nanoHemocompatible Materials
The invention relates to a material with blood compatibility and a structure of micro-nanometer coupling interfaces, and surface structure of the material consists of folds in microns and heaves in nanometers, wherein, the heaves in nanometers are scattered randomly on the folds and in the places between adjacent folds. The preparation method of the material with blood compatibility includes following steps: firstly, a template with nanometer particles closely arranged is constructed on a substrate by using a method of molecular self-assembly of a solution; secondly, liquid macromolecules are poured on the template and solidified; a macromolecule film is separated from the template and placed into a hydrophobing agent for soaking, and then taken as a first film; the first film is taken as a template for making a second film; the second film is oxidized in a plasma cleaner; finally the second film is twisted to get the material with blood compatibility and a structure of micro-nanometer coupling interfaces of the invention. From testing experiments, the fact that activated blood platelet hardly adheres to the structure of micro-nanometer coupling interfaces can be seen, which greatly reduces possibility of blood coagulation and the formation of thrombosis, and consequently blood compatibility of the material is markedly improved.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Programmed multi-target tree-shaped macromolecular assembled body medicine conveying system as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104906076AImprove stabilityHigh mechanical strengthOrganic active ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsPharmaceutical drugDrug carrier
The invention discloses a programmed multi-target tree-shaped macromolecular assembled body medicine conveying system as well as a preparation method and application thereof and belongs to the field of biomedical materials. The medicine conveying system taking an amphipathic tree-shaped macromolecular assembled body as a carrier is used for realizing programmed multi-target through responding a tumor micro-environment, so that main biological obstacles met in a process of transferring the medicine carrier in a body are overcome, and finally, medicines are conveyed to the destination. The obtained self-assembled body has a multi-target effect through the functionalization effect of a plurality of types of terminal groups. On one hand, tree-shaped molecules are used as the medicine carrier and have the advantages of good stability, high mechanical strength, multivalent terminal groups, hyper-branched structures, and intracellular conveying of echoviruses; on the other hand, a multi-element cooperated self-assembling policy is integrated with the advantages of all functional groups on a tree-shaped macromolecular self-assembled unit, so that the assembled body can be conveyed by the multifunctional and efficient medicine system. The system is particularly suitable for conveying anti-tumor medicines.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com



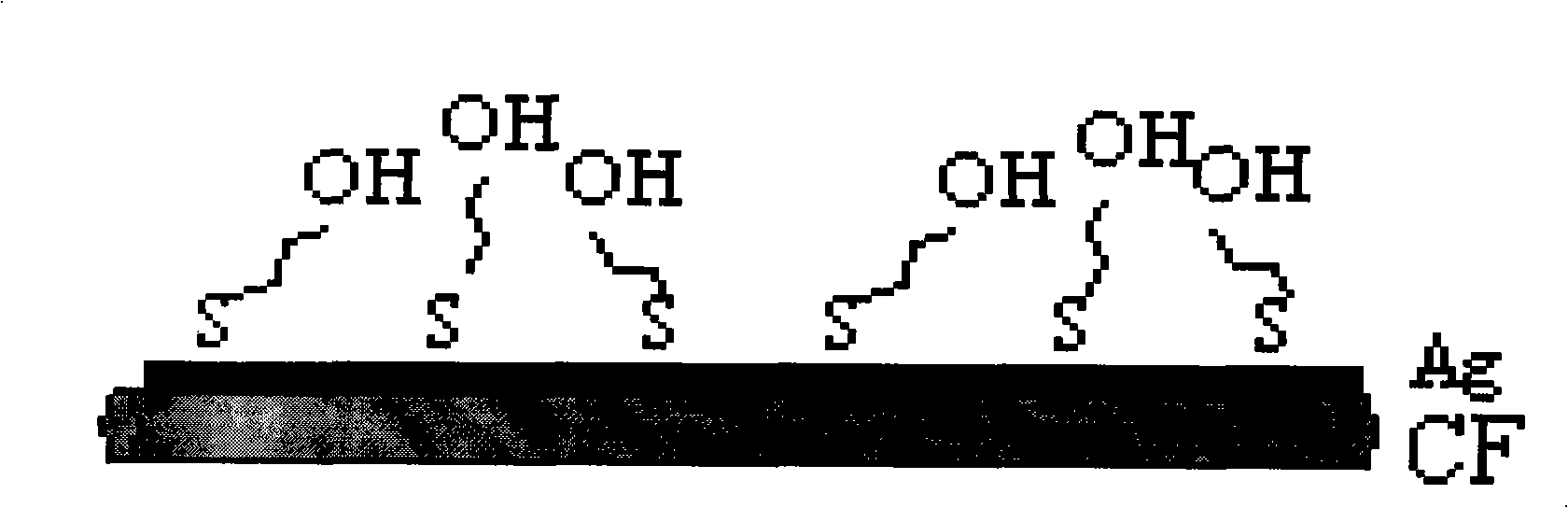
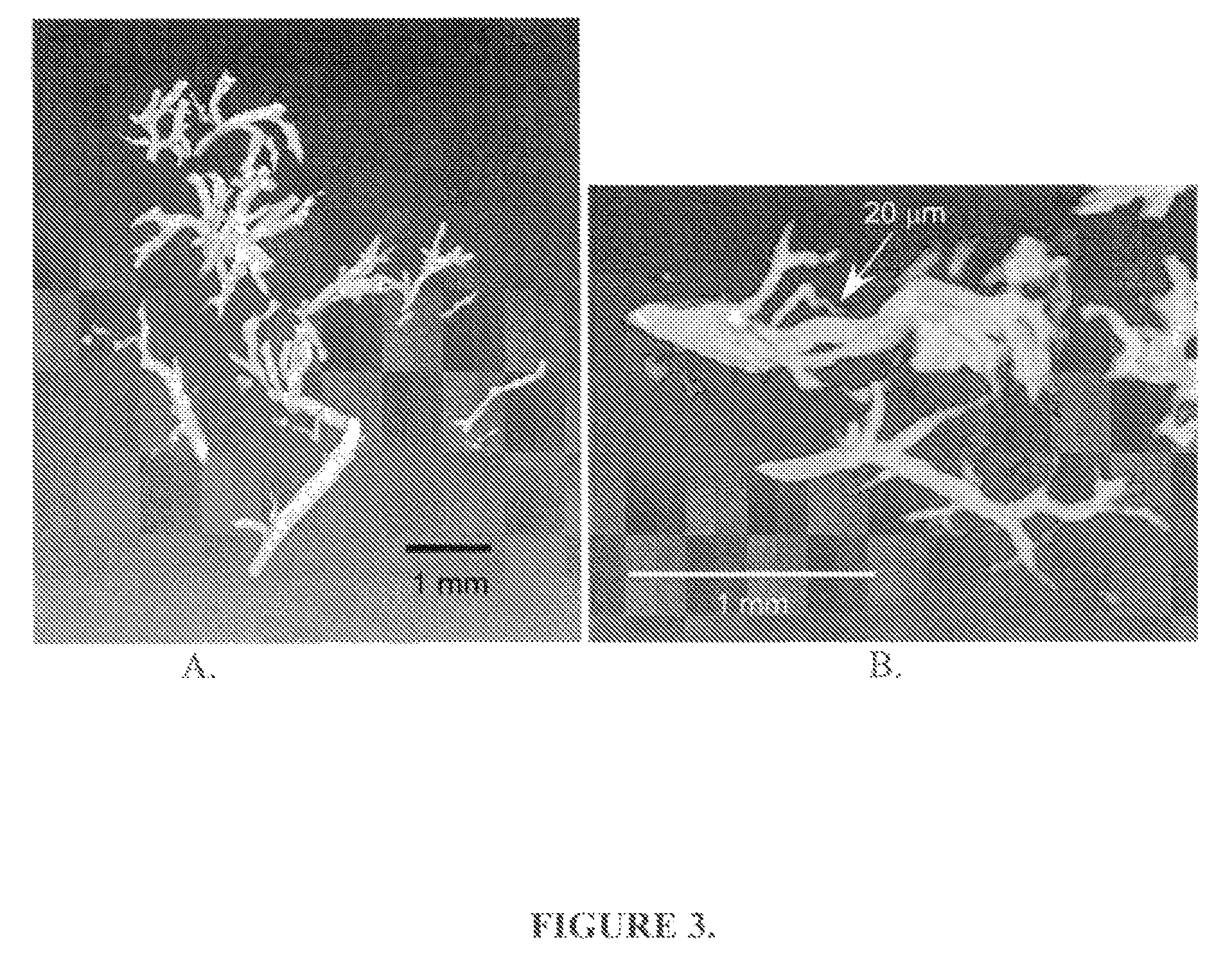
![Cucurbit [7] uril [3] rotaxane as well as preparation method and application thereof Cucurbit [7] uril [3] rotaxane as well as preparation method and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/f5cfb341-3563-4d21-97d3-1224b9056f79/130923152944.PNG)
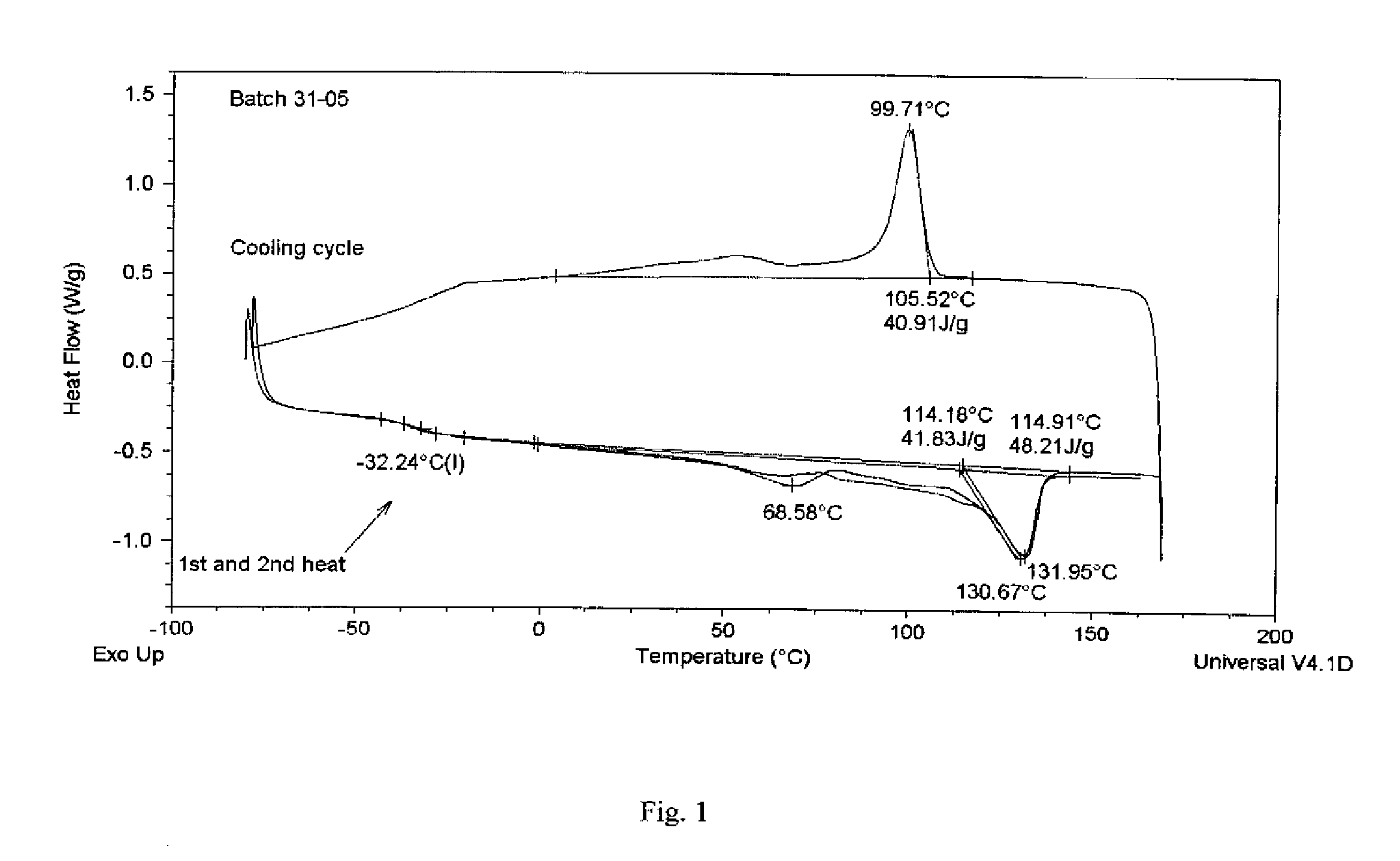
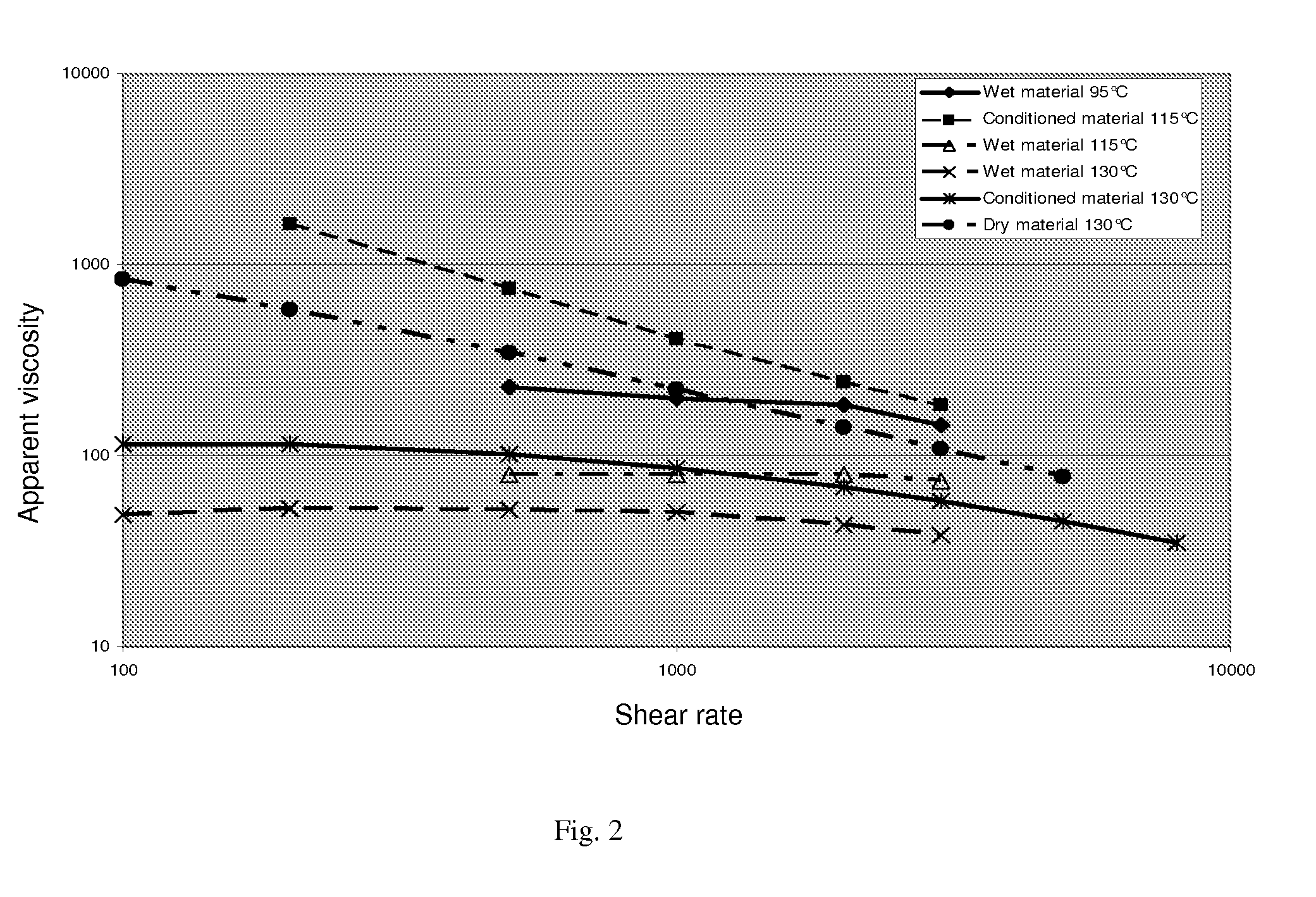
![Cucurbit [7] uril [3] rotaxane as well as preparation method and application thereof Cucurbit [7] uril [3] rotaxane as well as preparation method and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/f5cfb341-3563-4d21-97d3-1224b9056f79/130923152948.PNG)
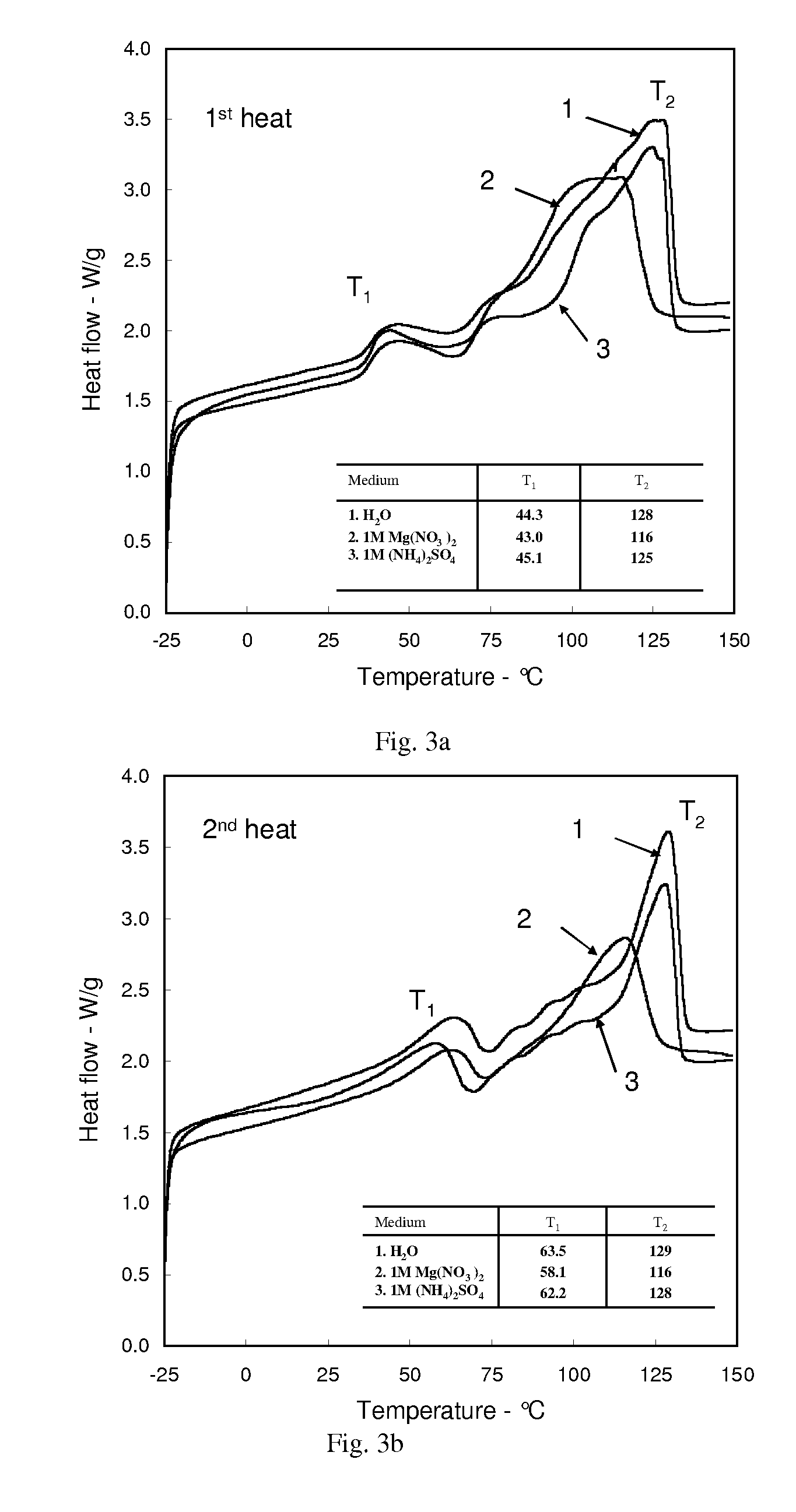
![Cucurbit [7] uril [3] rotaxane as well as preparation method and application thereof Cucurbit [7] uril [3] rotaxane as well as preparation method and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/f5cfb341-3563-4d21-97d3-1224b9056f79/130923152951.PNG)