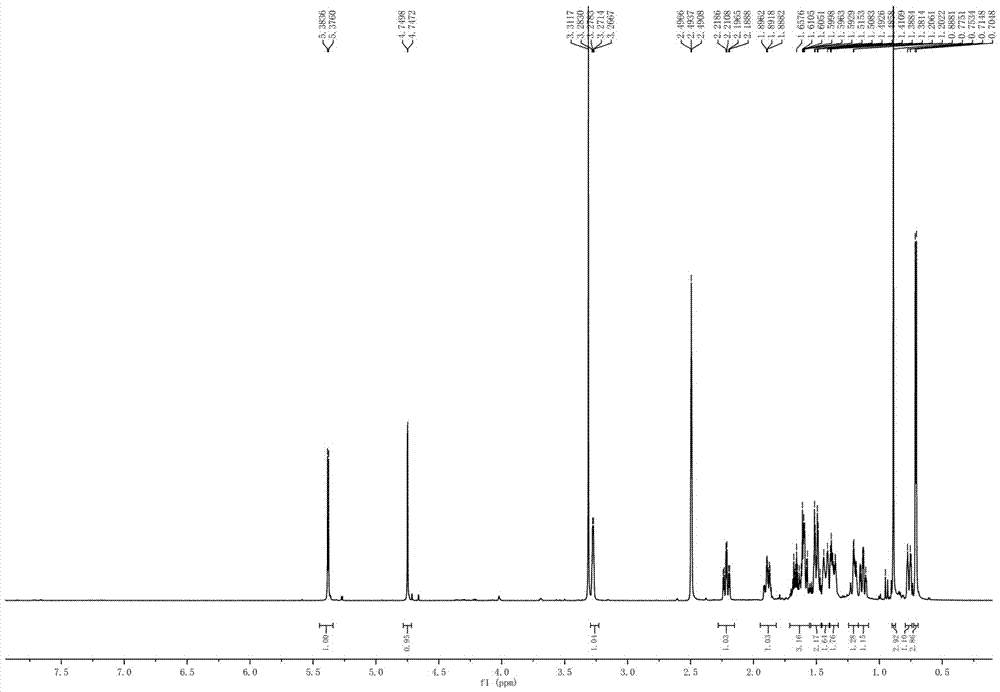
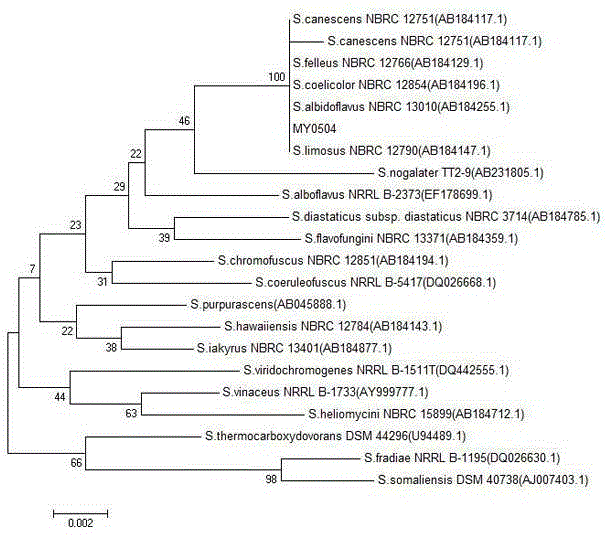
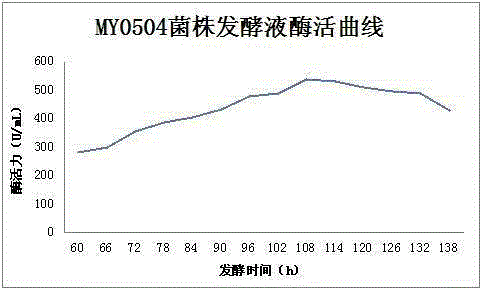
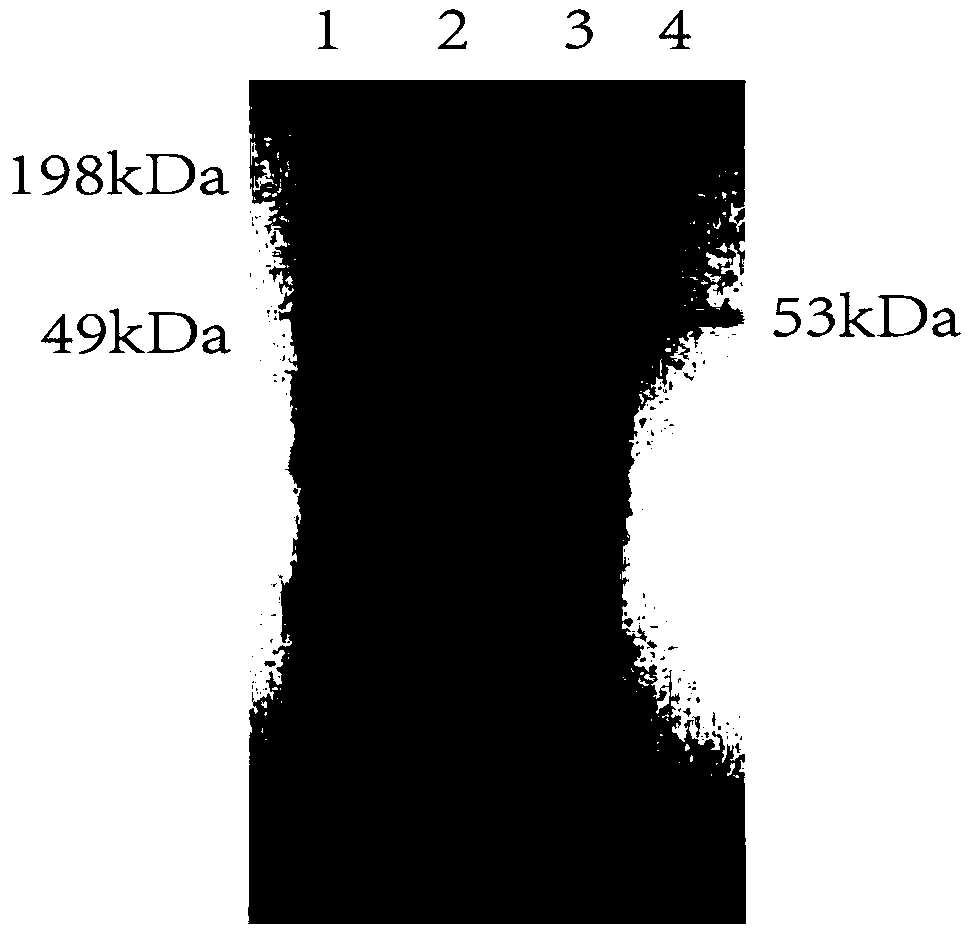Patents
Literature
54 results about "Streptomyces thermoautotrophicus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Streptomyces thermoautotrophicus is a thermophilic bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces thermoautotrophicus was claimed to be diazotrophic and to produce a new kind of nitrogenase, but new evidence suggests that it can´t fix N2 gas.
Streptomyces griseoflavus and application thereof in biological prevention and control of plant diseases
InactiveCN101822272ABroad antibacterial spectrumStrong antagonistic effectBiocideFungicidesPathogenic bacteriaPlant disease
The invention discloses application of streptomyces griseoflavus in biological prevention and control of plant diseases, particularly streptomyces griseoflavus NMG6-3-9 CGMCC No. 3441 in biological prevention and control of plant diseases. The provided strains have good antagonism effect on pathogenic bacteria of alfalfa root rot, can be used for the biological prevention and control of alfalfa root rot and other plant diseases, and have wide application potential in the field of biological prevention and control of plant diseases. The invention lays a foundation for the biological prevention and control of alfalfa root rot and further provides a scientific basis for the development and the application of a biological prevention actinomycete preparation.
Owner:GRASSLAND RES INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Bacillus stearothermophilus reverse transcription compositions and kits
The present invention relates to reverse transcription of RNA, and in particular to reverse transcription by thermostable DNA polymerases. Thermoactinomyces vulgaris and Bacillus stearothermophilus possess reverse transcriptase activity in the presence of magnesium or manganese ions. Methods, compositions, and kits for reverse transcription and RT-PCR are also provided.
Owner:PROMEGA CORP
Gopalamicin derivatives and application of same in inhibition of infection by drug-resistant bacteria and drug-resistant mycobacterium tuberculosis
ActiveCN103665071AHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsResistant bacteriaStreptomyces
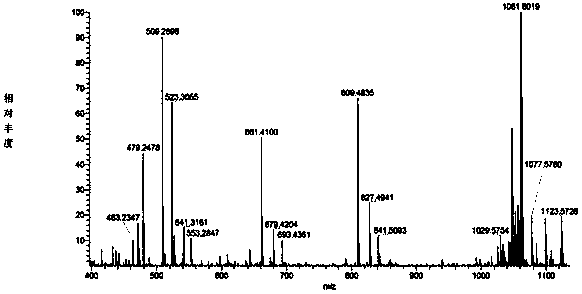
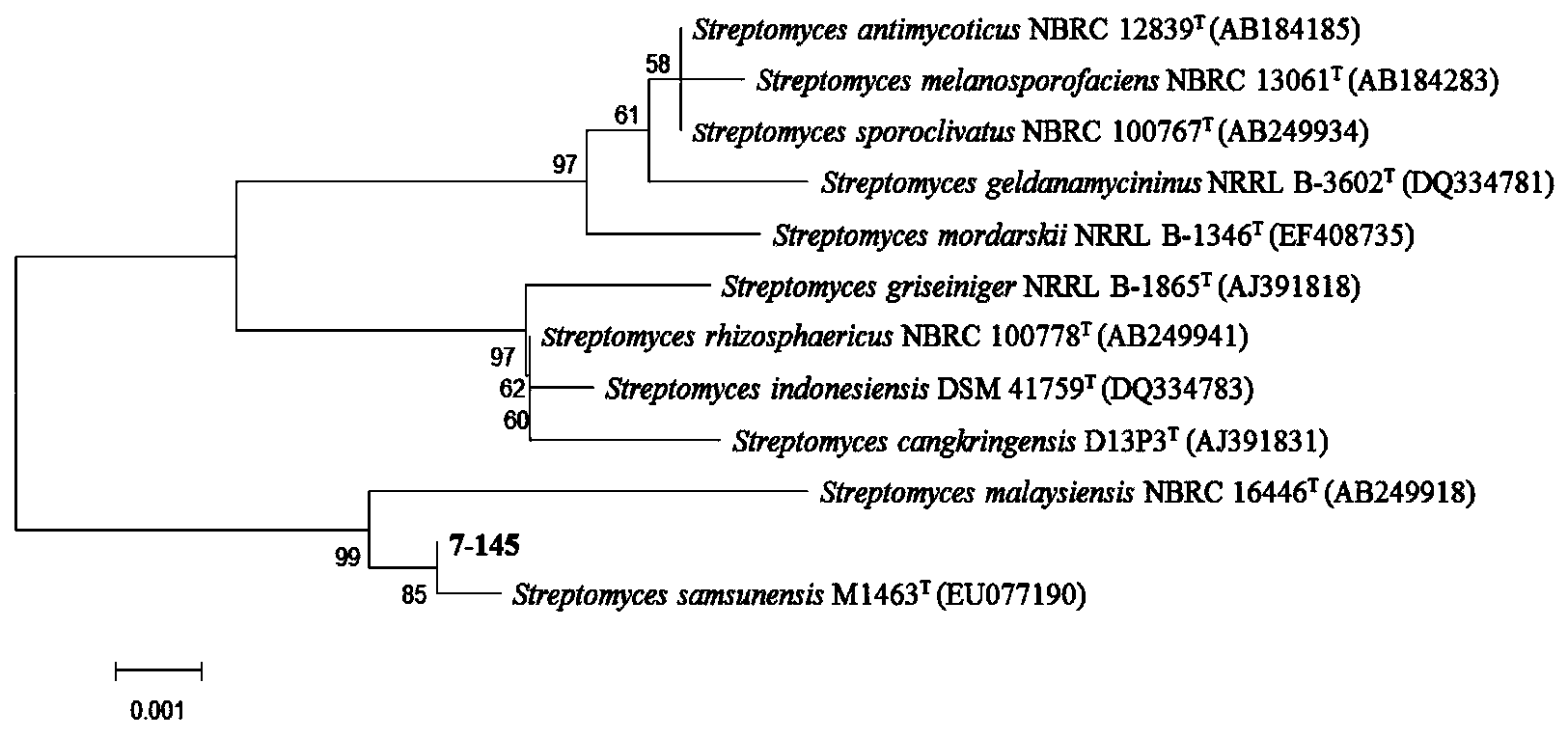
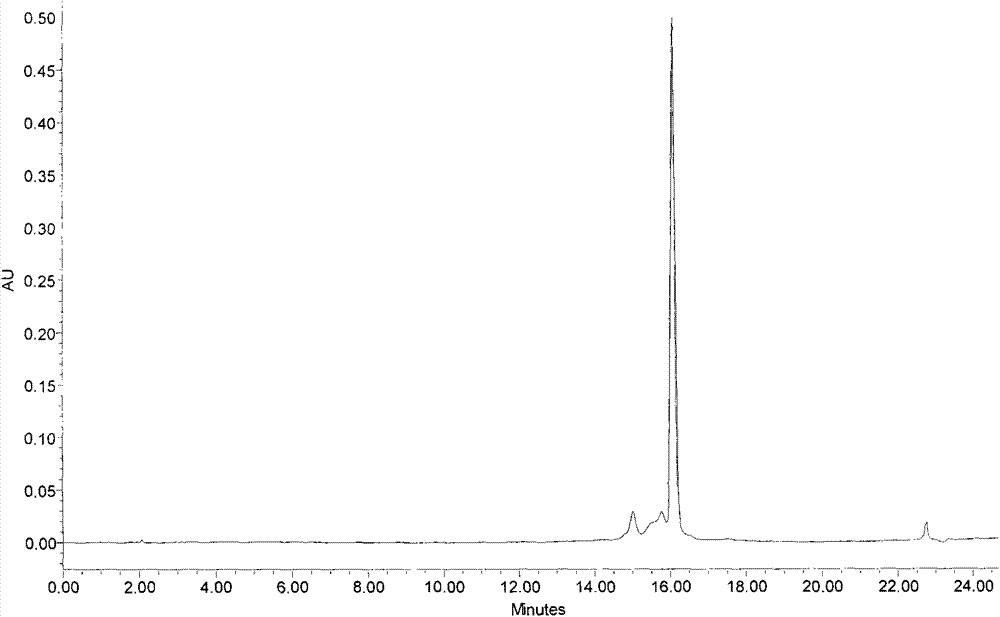
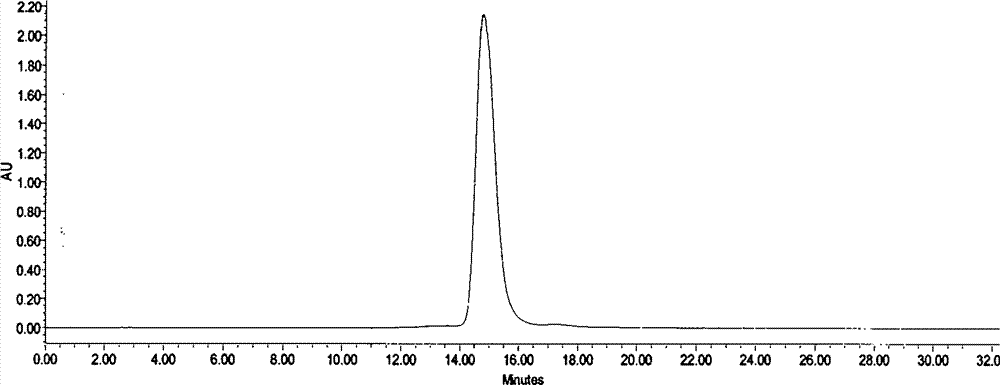
The invention relates to gopalamicin derivatives and application of the same in inhibition of infection by drug-resistant bacteria and drug-resistant mycobacterium tuberculosis. The derivatives are originated from fermentation products of marine actinomycete Streptomyces sp. 7-145. Results of experimental study show that discovered compounds with novel structures and known structures all have strong antibacterial activity on tested drug-resistant bacteria and drug-resistant mycobacterium tuberculosis and are expected to become clinically-useful novel drugs used for inhibition of infection by drug-resistant bacteria and drug-resistant mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Preparation methods and application of streptomyces parvulus OUCMDZ-2554 bacterial strain and product actinomycin D thereof
InactiveCN103665108AIncrease productionSimple separation processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyStreptomyces parvulus
The invention relates to preparation methods and application of streptomyces parvulus OUCMDZ-2554 bacterial strain and a product actinomycin D thereof. The preservation number of the bacterial strain is CGMCC7907. The streptomyces parvulus OUCMDZ-2554 has high yield of single compound actinomycin D, and the yield is 0.25mg / mL. The bacterial strain obtained at home for the firstly time has high yield, the culture medium for the bacterial strain only uses one nutritional ingredient, so that the cost is low, the preparation method is simple and easy to operate, the fermentation period is short, a large quantity of active substances can be produced by fermentation in large scale, the problem of medicine source is fundamentally solved, and the bacterial strain can offer a precursor for structural modification of the compounds and study on structure-activity relationship.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Microbial agent and application for treating cultivating wastes
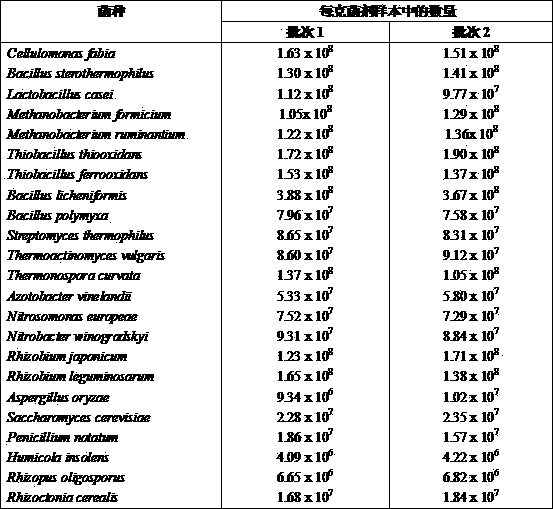
The invention provides a live microbial composition for fermentation treatment of cultivating wastes. The composition is characterized by consisting of bean fiber monad, bacillus stearothermophilus, lactobacillus, methanobacteria, thiobacillus, bacillus licheniformis, bacillus polymyxa, streptomycete, thermoactinomycete, thermomonospora, nitrogen-fixing bacteria, nitrated monad, nitrobacteria, rhizobium, Aspergillus oryzae, yeasts, moulds, humicola, rhizopus and glomus mosseae. In addition, the invention further provides an organic fertilizer generated by virtue of fermentation of the microbial composition as well as an application and a method thereof. In production of the organic fertilizer, cultivating wastes such as animal wastes are objectively treated.
Owner:宋彦耕
Application of microorganism bacterium agent in resisting of potato scab
InactiveCN104686583AIncrease profitImprove the ecological environmentBiocideDisinfectantsDactylosporangium sp.Ageing
The invention discloses application of a microorganism bacterium agent in resisting of potato scab. According to the microorganism bacterium agent, Bacillus subtilis CGMCC1.3382, Dactylosporangium sp. ACCC No.40661 and Streptomyces roseoflavus ACCC No.40400 are used as preparation strains; all the strains are prepared into fermented solutions respectively; and the fermentation solutions are mixed and then are deeply fermented to obtain the microorganism bacterium agent. The series of the strains reasonably utilize the mutual effect of microorganisms, and the product has the characteristics of strong adaptability, good stability, uneasiness in ageing, strong pathogenic bacteria antagonism and the like; and the pathogenic bacteria of the potato scab can be efficiently resisted, the growth of plants is stimulated and the quality of crops is improved, so that the aims of yield increasing and high yield are realized.
Owner:DALIAN SANKE BIO ENG
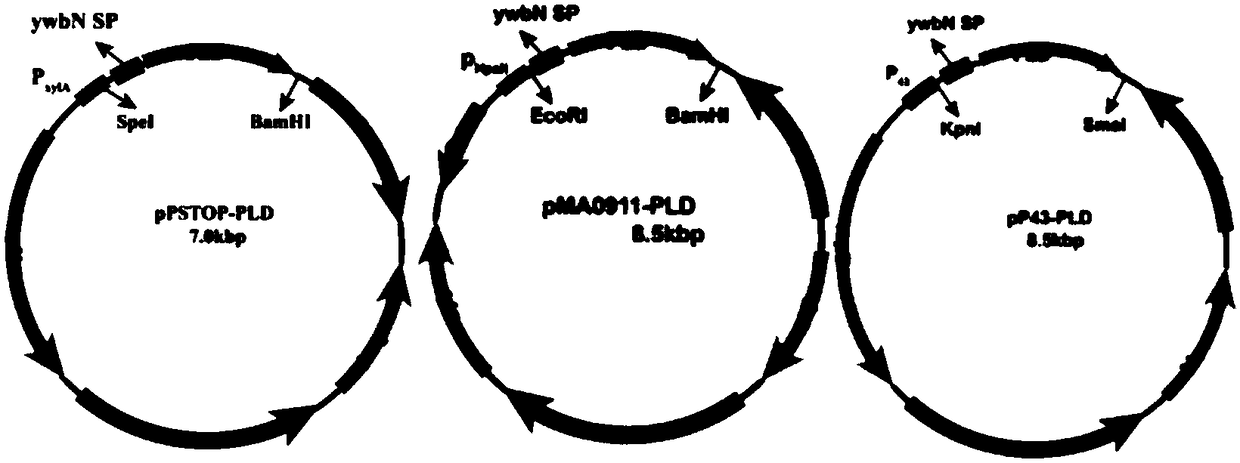
Engineering bacillus subtilis capable of expressing phospholipase D
InactiveCN108841770AAchieve secretory expressionHigh selectivityBacteriaHydrolasesPhospholipidStreptomyces peucetius
The invention discloses engineering bacillus subtilis capable of expressing phospholipase D, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The engineering bacillus subtilis capable of expressing the phospholipase D is constructed by taking bacillus subtilis (WB600) as an expression host and taking a phospholipase D encoding gene (PLD) from streptomyces racemochromogenes as a target gene.The activity of the phospholipase D produced by the engineering bacteria can be up to 5.916 U / mL and has an extremely high application value in the field of medicines, food and health care products;meanwhile, the phospholipase D adopted by the engineering bacteria is actinomyces-derived endogenous phospholipase D, which has high reaction activity, high phosphatidyl substrate selectivity and highorganic matter stability; furthermore, a catalysis structure is the most compact; the phospholipase D is more suitable for efficient synthesis of phospholipid and a phospholipid derivative in the industrial production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
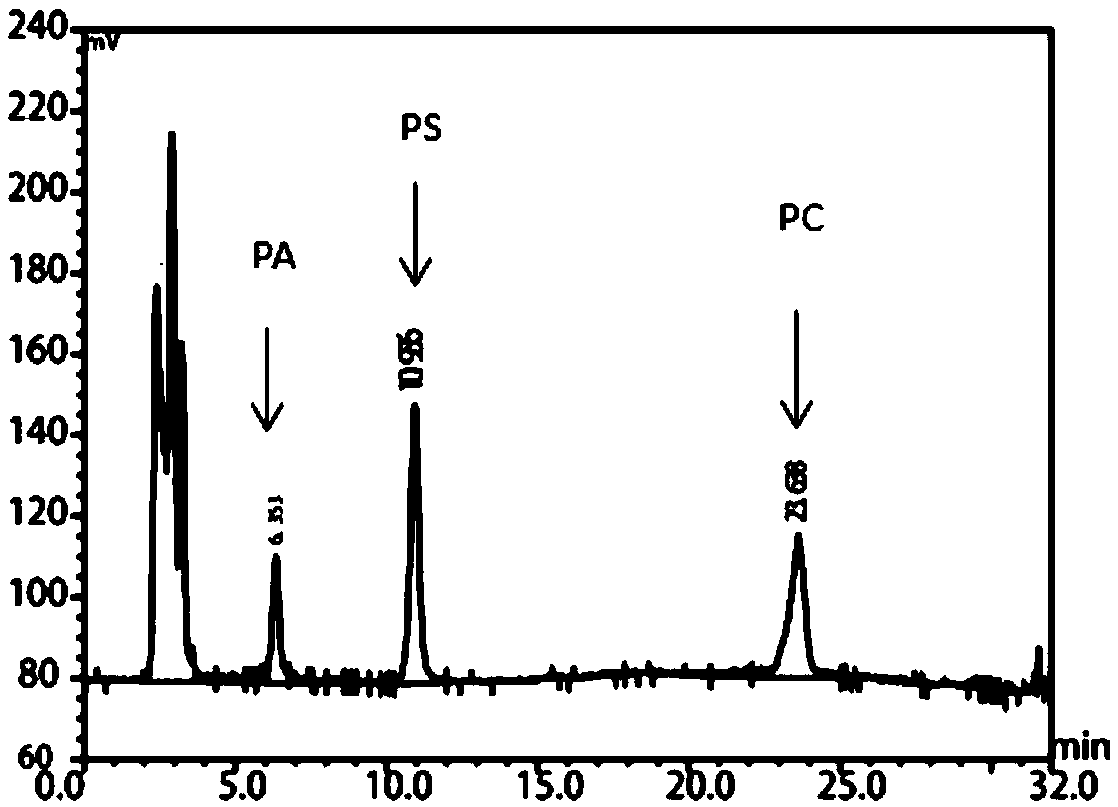
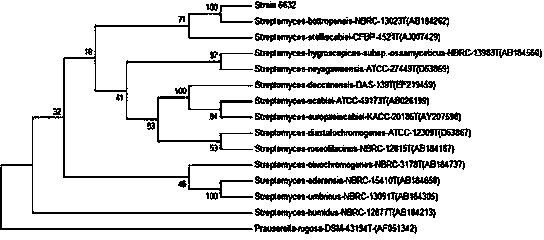
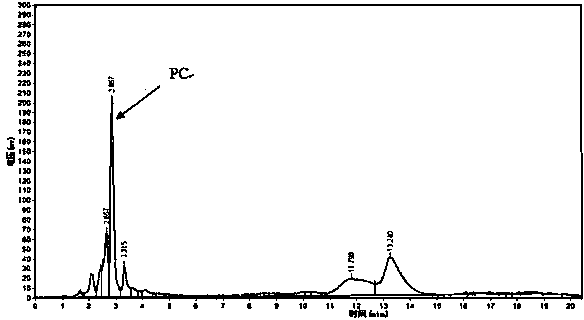
Actinomycete Streptomycesbottropensis and application thereof
The invention relates to actinomycete for production of phospholipase D and application thereof and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The phospholipase D produced by the actinomycetes after fermentation has catalytic action on soybean phosphatidylcholine and L-serine to efficiently produce phosphatidylserine through transesterification. The actinomycete is collected from a wellhead NO.1066 in Dongfeng town, Dawa County, Panjin city, Liaoning province, and is identified as Streptomycesbottropensis, preserved in the key laboratory for screening of new drugs in Liaoning province under the number of SYP-A-6632, and is preserved in CGMCC under the number of CGMCC No.6993. A screening method of the Streptomycesbottropensis includes: 1, activating strains to be activated; 2, preparing a screening plate; 3, screening and decomposing lecithin strains by a plate method; 4, detecting transesterification activity. The Streptomycesbottropensis has the advantages that the operation process is simple, implementation conditions are mild, phosphatidylserine can be bio-converted efficiently and quickly, and basis of industrial production of phosphatidylserine in future is laid.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Streptomyces virginiae and its application in transformation and degradation of steroid
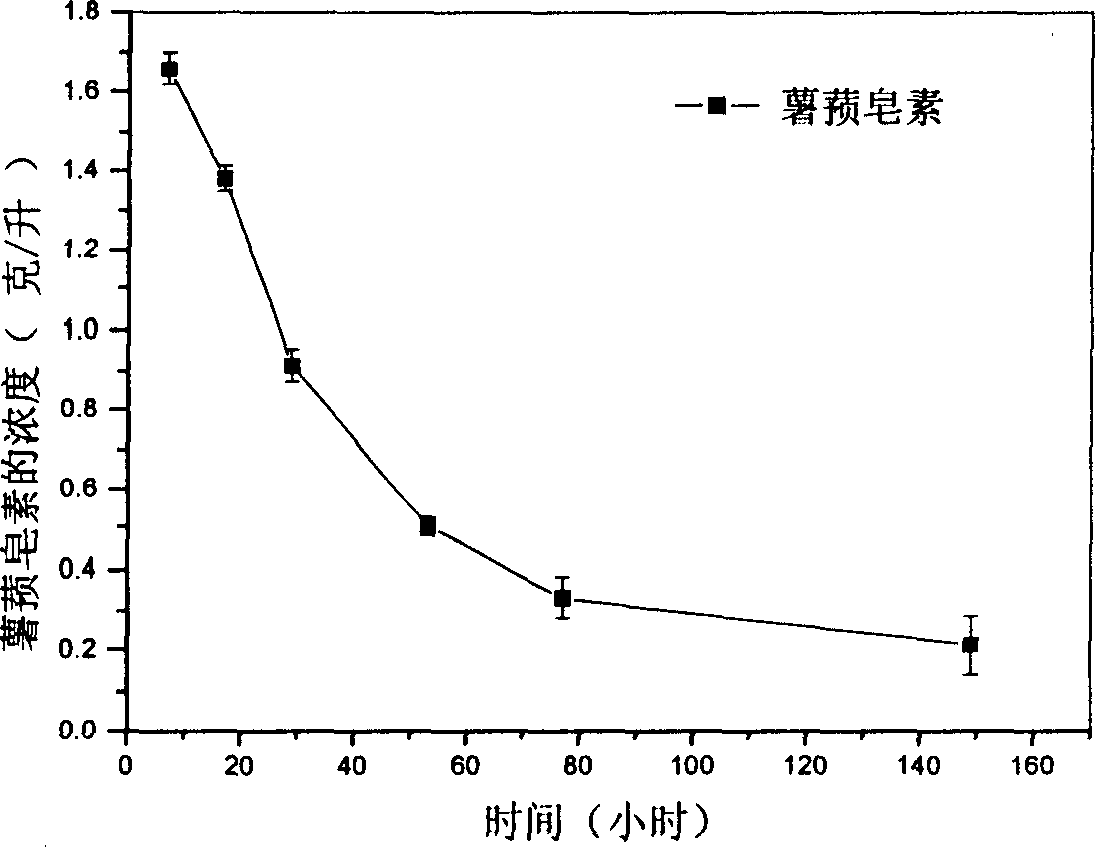
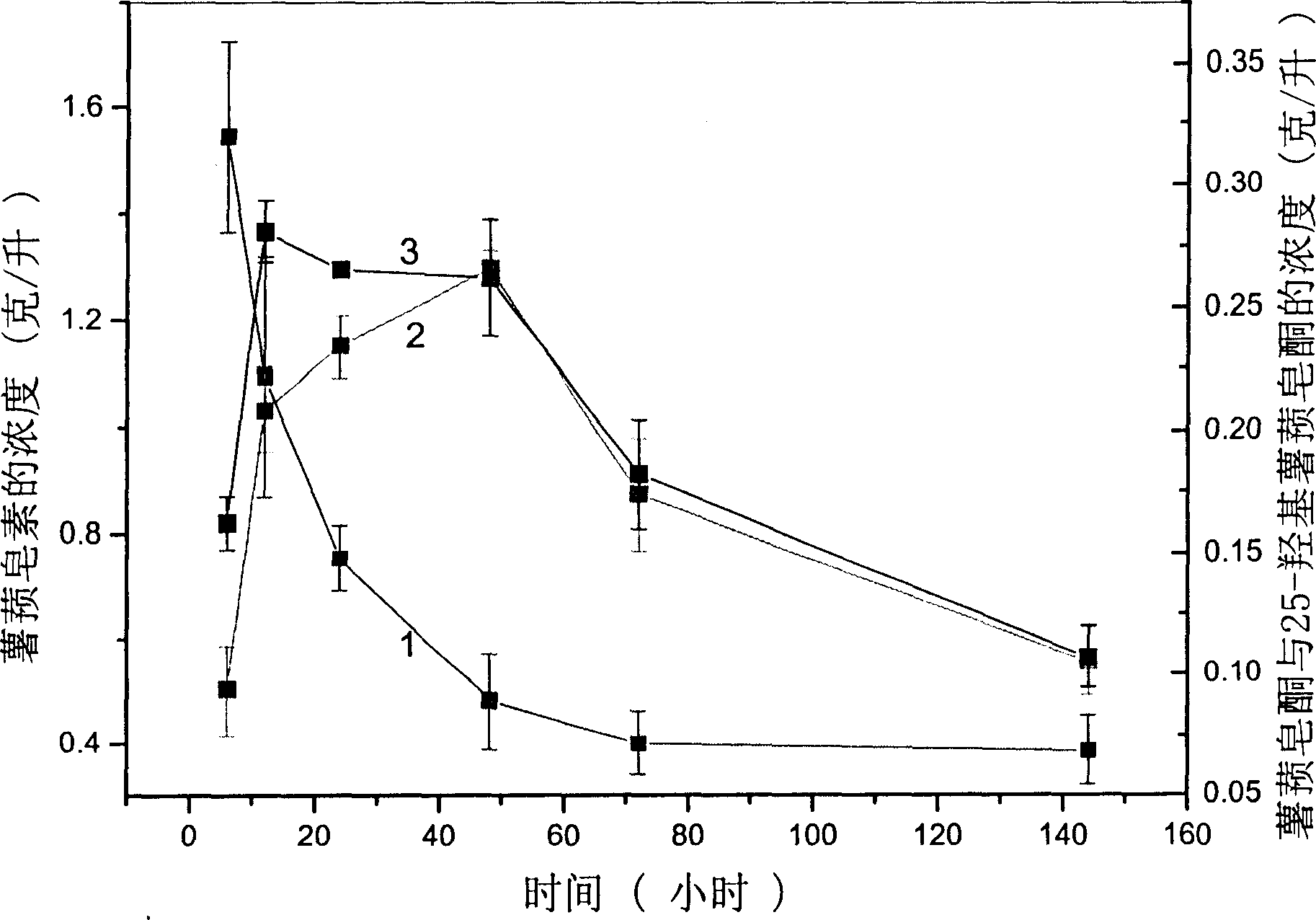
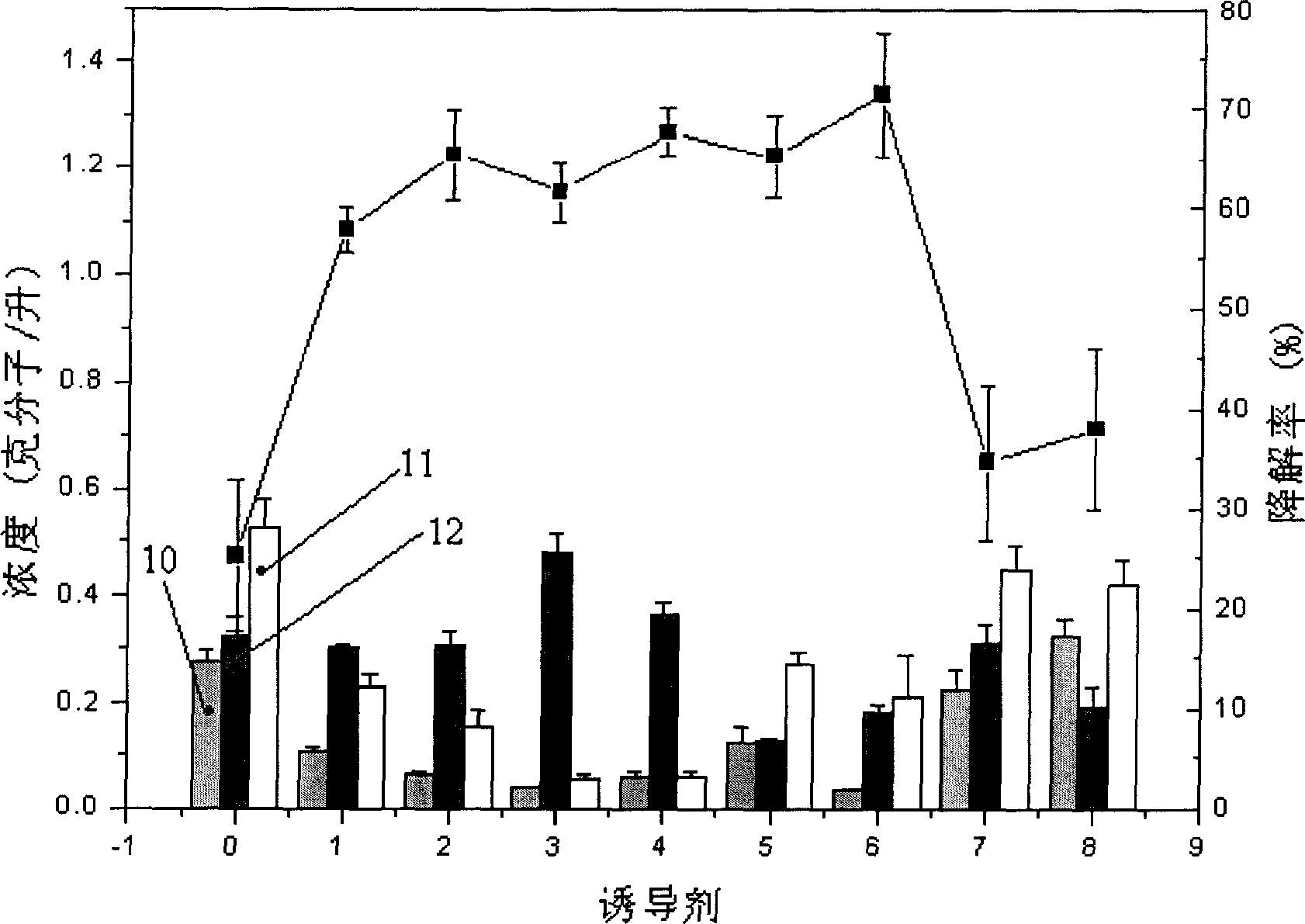
The invention relates to a Streptomyces virginiae and discloses Streptomyces virginiae IBL-14 CCTCC M 206045 and its application in converting and degrading the steroid compound. The bacterial of this invention can effectively convert and degrade almost all kinds of steroid compounds. This bacterial is an actinomycete which can widely exist in physical environment so that it can be used in environmental conservation domain to clear the steroid contaminant. The said bacterial of this invention can convert and degrade the steroid compound to produce some new compounds, which has potential pharmaceutical activity, for example, the said bacterial can convert yam saponin to produce 25-hydroxy dioscoreassapoketone.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel actinomycin A and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106905414AHigh antibacterial activityStrong anti-tumor cell activityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaResistant bacteriaExperimental research
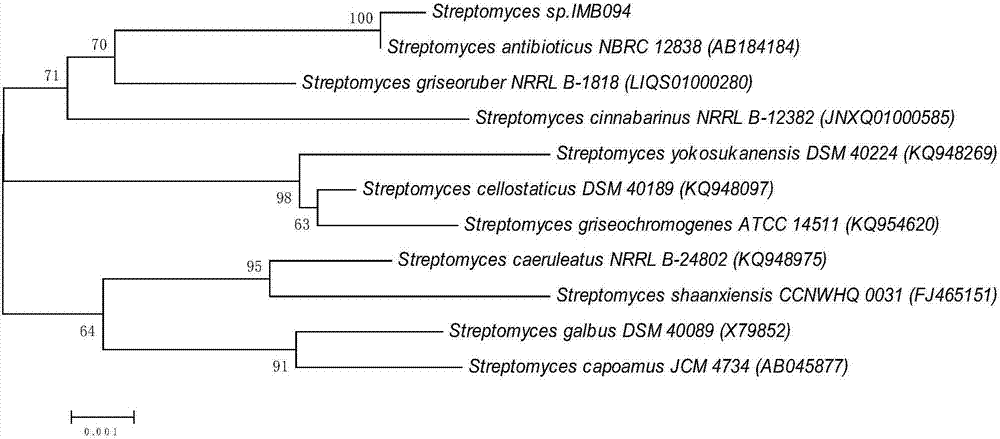
The invention relates to a novel actinomycin A, a preparation and synthesis method thereof and an application of a compound to anti-drug-resistant bacteria and tumor resistance. The novel actinomycin A is a fermentation product of a marine streptomyces IMB094 (Streptomyces sp. IMB094). Experimental research results show that the novel actinomycin A has high antimicrobial activities for tested Gram-positive resistant bacteria and high inhibiting effects on tested tumor cells, and novel actinomycin A is expected to be novel clinical useful anti-drug-resistant bacteria and tumor-resistant medicines.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Streptomyces sp. and screening method and application thereof
ActiveCN111363696AStrong antagonistic effectHigh-quality materialsBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a streptomyces sp. and a screening method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of microbiology. In order to improve the resistance of tomatoes to plant diseases, the invention provides a streptomyces sp. strain named NEAU-HV9 with a strain preservation number of CGMCC 19436. The invention also provides application of the strain in inhibiting activity of pathogenic bacteria causing plant diseases and producing actinomycin D, and the streptomyces sp. strain NEAU-HV9 can be used for preparing microbial agents which can be used for inhibiting plant tomato bacterial wilt. The invention provides a high-quality material for the research and development of environment-friendly actinomycetic inoculant.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
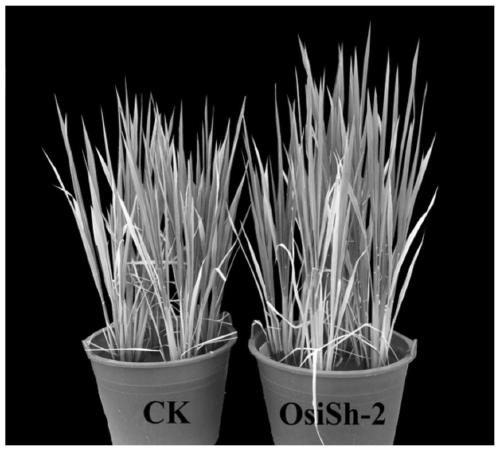
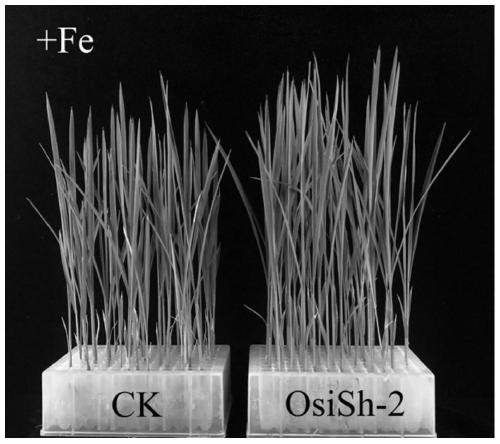
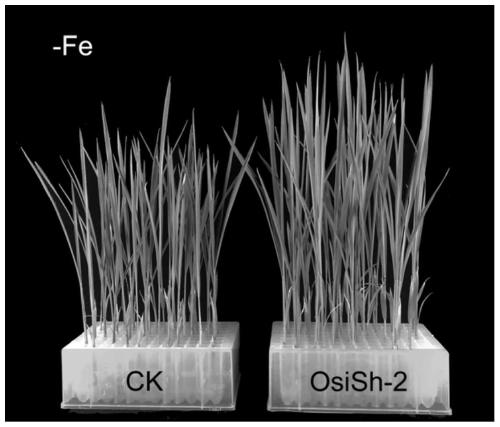
Method for promoting growth of rice and promoting rice to absorb iron element in iron deficiency environment
ActiveCN111466266APromote growthPromote absorptionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySporeling
The invention discloses a method capable of promoting growth of rice in a normal growth environment and capable of promoting the rice to absorb an iron element in an environment lacking of directly available iron. According to the method, a strain of Streptomycessp. OsiSh-2 is utilized, and a spore suspension thereof is employed; the rice under the normal condition can be treated with two different measures: (1) the spore suspension is sprayed on leaf surfaces of the rice, and (2) disinfected rice seeds are embedded with the spore suspension of Streptomycessp. OsiSh-2. The method disclosed bythe invention promotes the growth of the rice, and increases the chlorophyll content and the photosynthesis rate, and thus, rice biomass including plant height, root length, the fresh and dry weight of aboveground and underground parts and the like of the rice is significantly increased; and under the adverse situation of iron deficiency, the disinfected rice seeds are embedded with the spore suspension of Streptomycessp. OsiSh-2, so that the iron content in the rice is significantly increased, the normal growth of the rice under iron deficiency stress is guaranteed.
Owner:湖南新长山农业发展股份有限公司
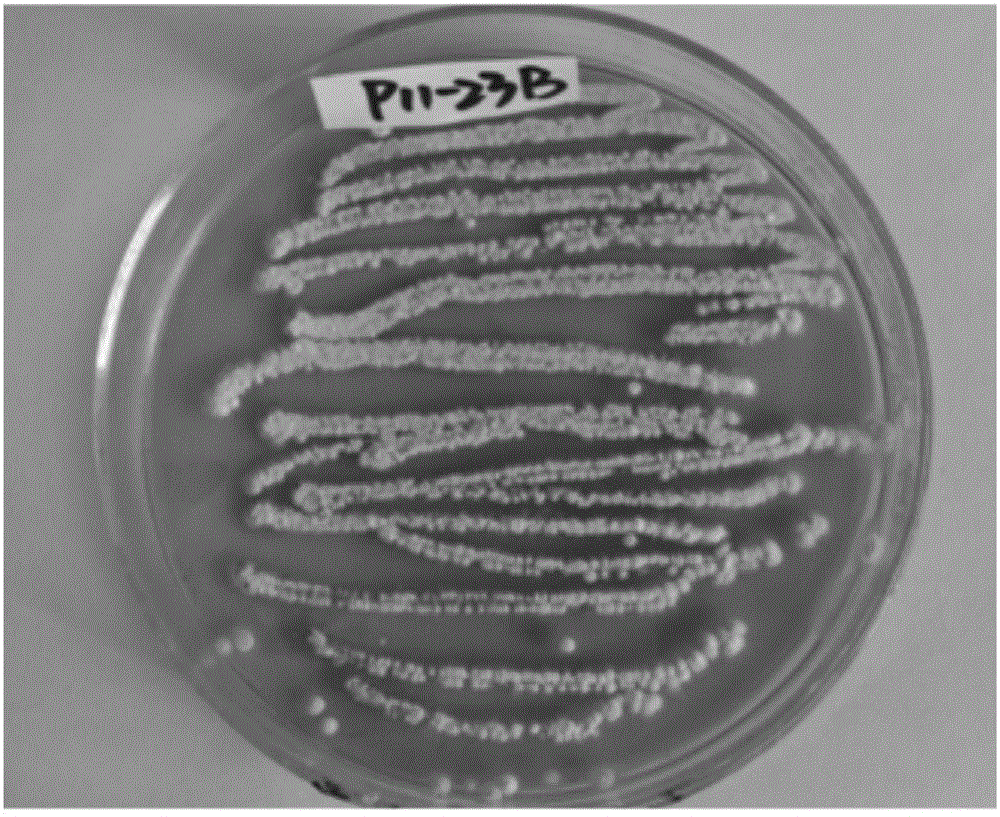
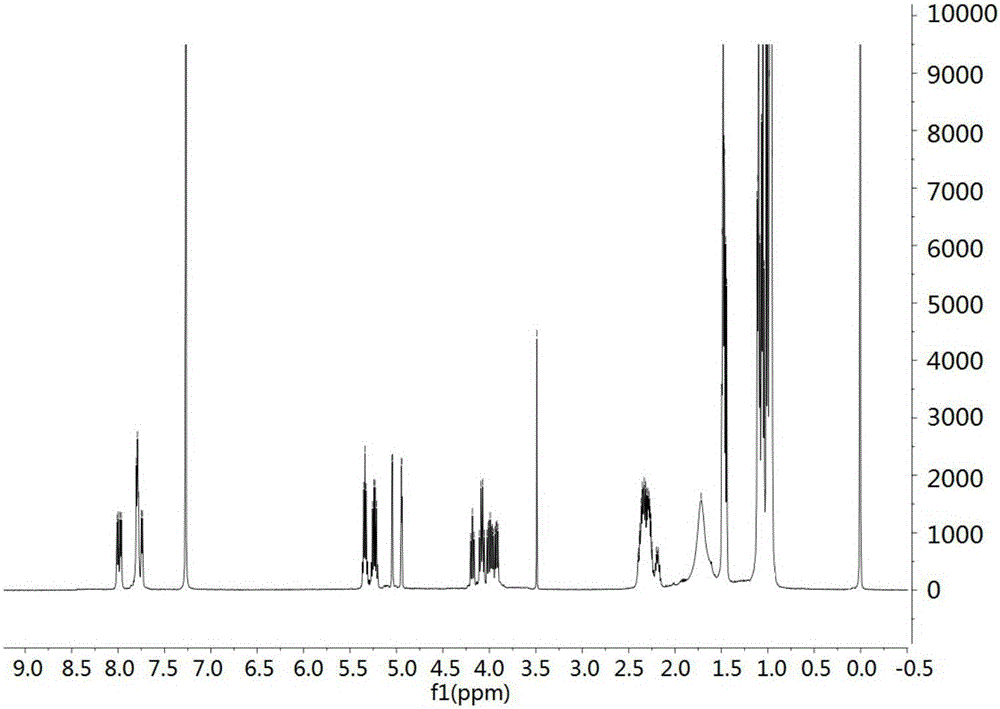
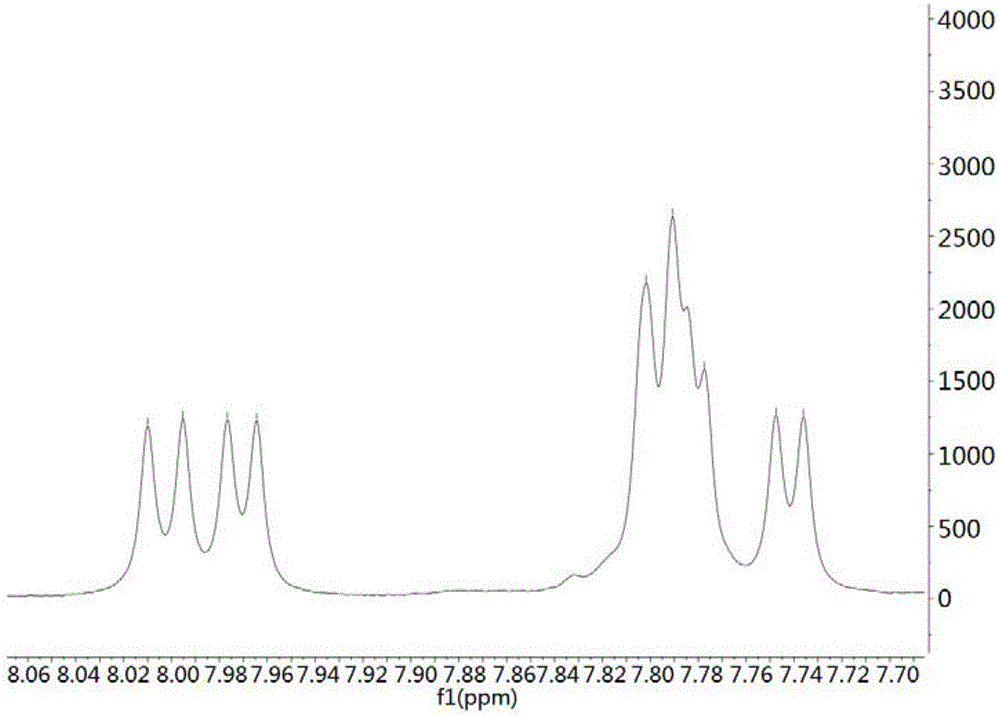
Anti-glioma active substance streptodepsipeptide P11B, preparation and applications thereof
The invention provides a compound streptodepsipeptide P11B having anti-glioma activity, wherein the streptodepsipeptide P11B is a marine natural active substance, and is obtained by carrying out separation culture purification in Streptomyces parvulus P11-23B. According to the present invention, the test results prove that the streptodepsipeptide P11B can significantly inhibit the proliferation of a variety of glioma cells, and can be used in preparation of drugs for glioma treatment, wherein the drugs comprise the separate streptodepsipeptide P11B active component and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, or the streptodepsipeptide P11B active component, other drugs or effective components, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier; the anti-glioma activity of the compound is firstly discovered, and the new way is provided for the preparation of the anti-glioma drug; and the chemical structure formula of the streptodepsipeptide P11B is defined in the specification.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A method for enhancing the gene editing efficiency of actinomycetes and its application
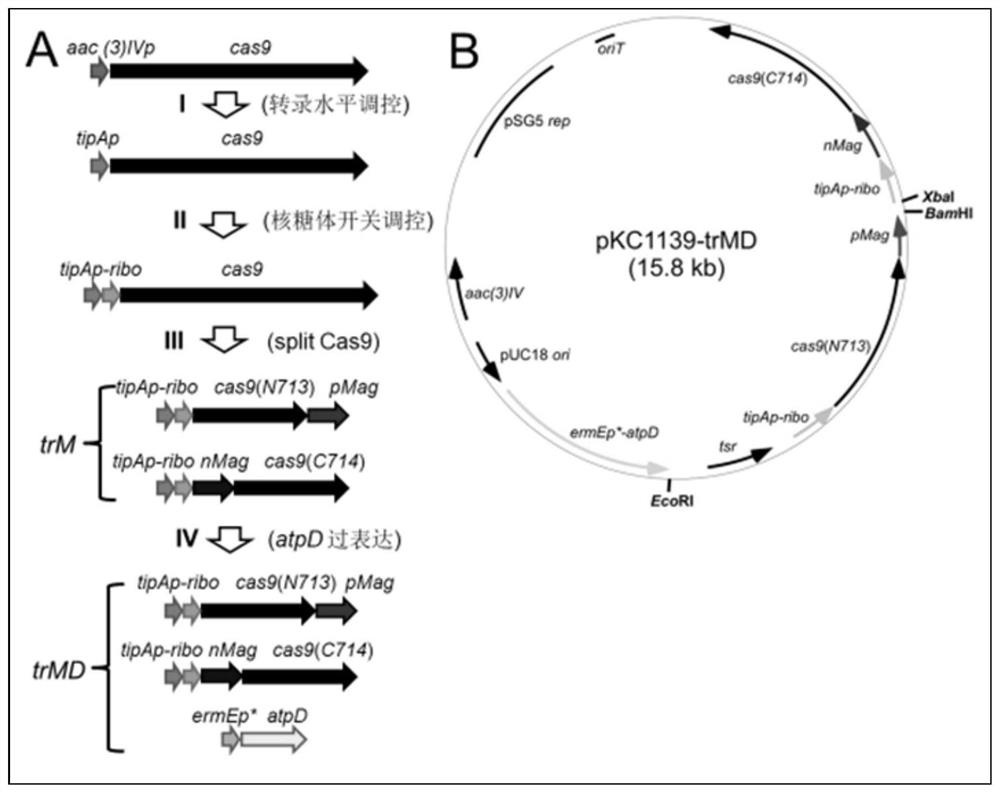
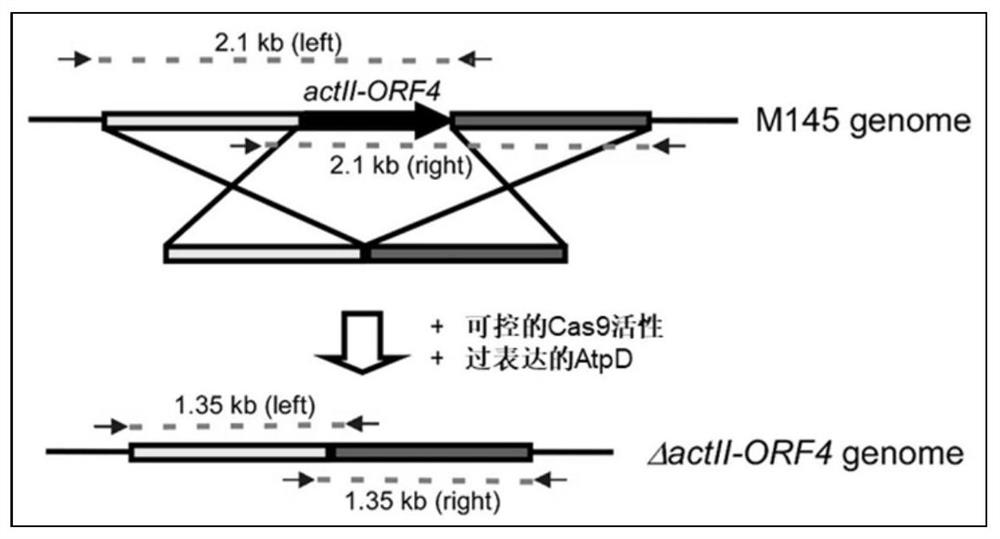
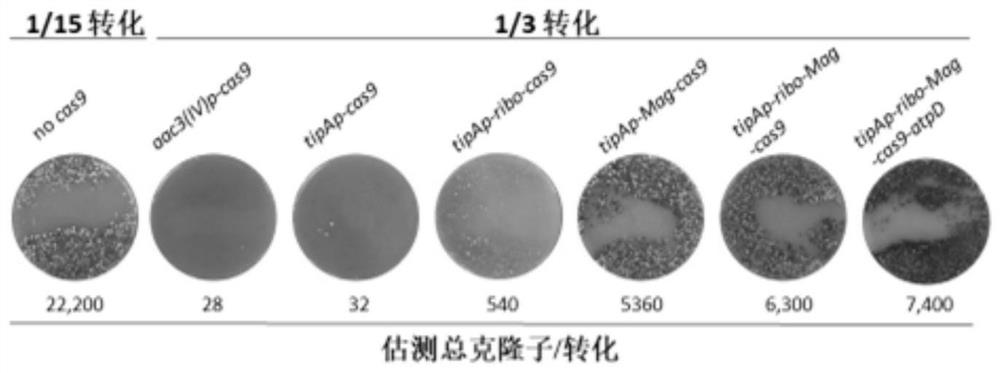
ActiveCN109811010BPrecise control of activityImprove editing efficiencyStable introduction of DNAMicroorganism based processesTransformation efficiencyStreptomyces thermoautotrophicus
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
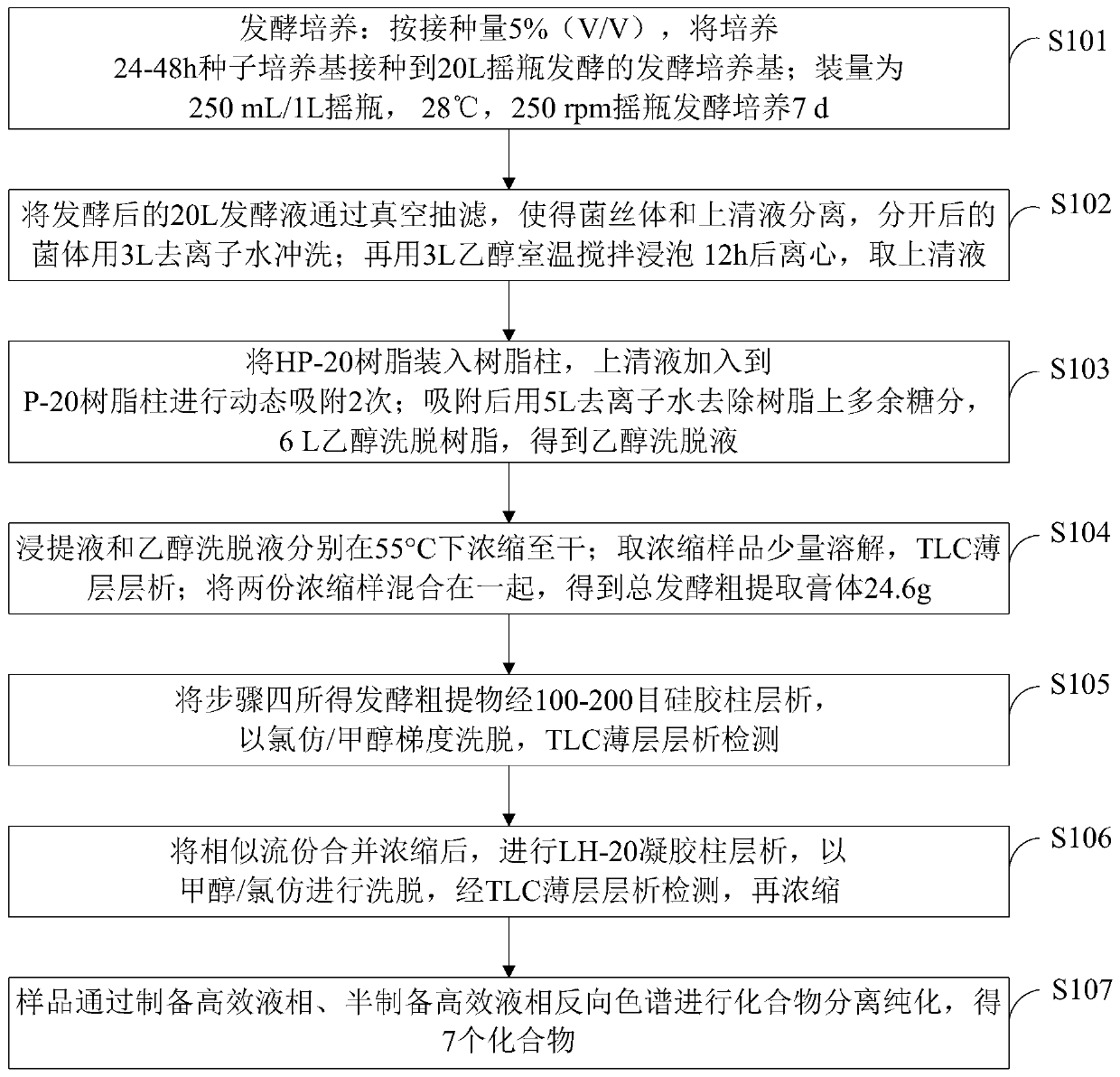
Method for separating and extracting secondary metabolites of streptomyces
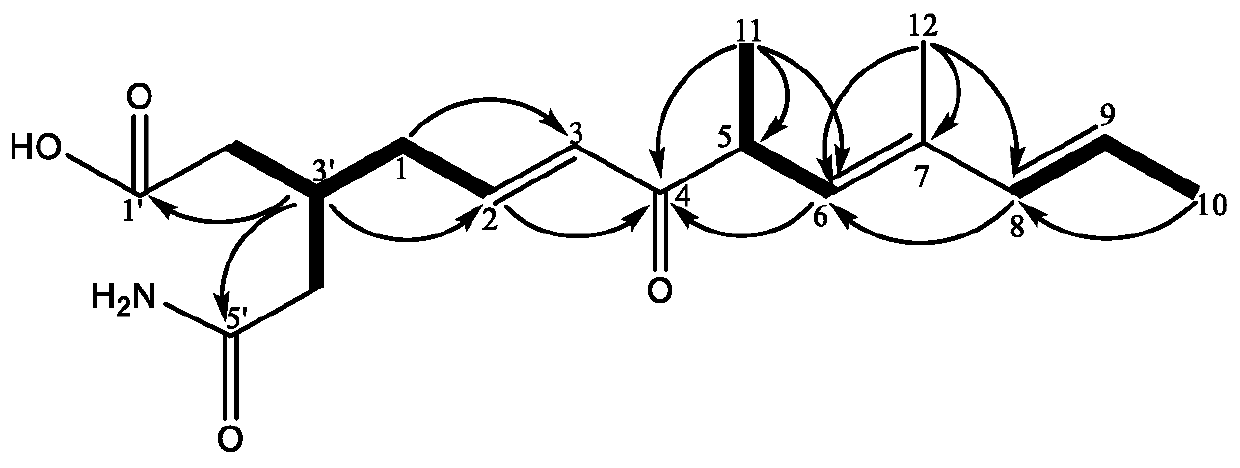
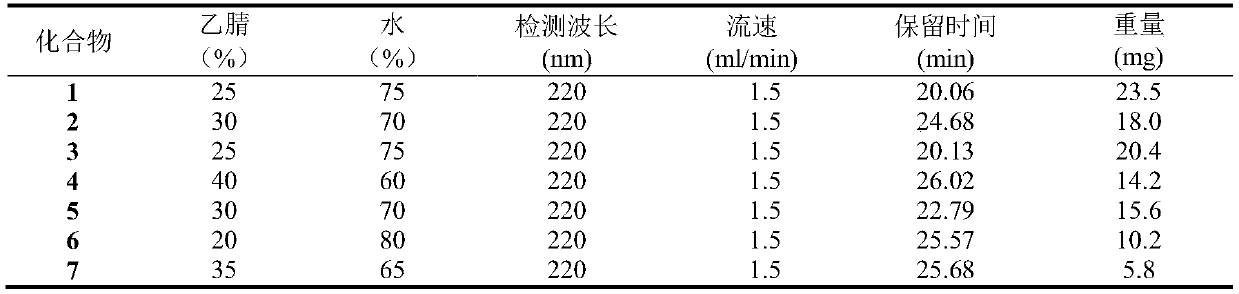
ActiveCN110452940ARapid and accurate separation and identificationRich diversityMicroorganism based processesCarboxylic acid amide separation/purificationChromatographic separationMetabolite
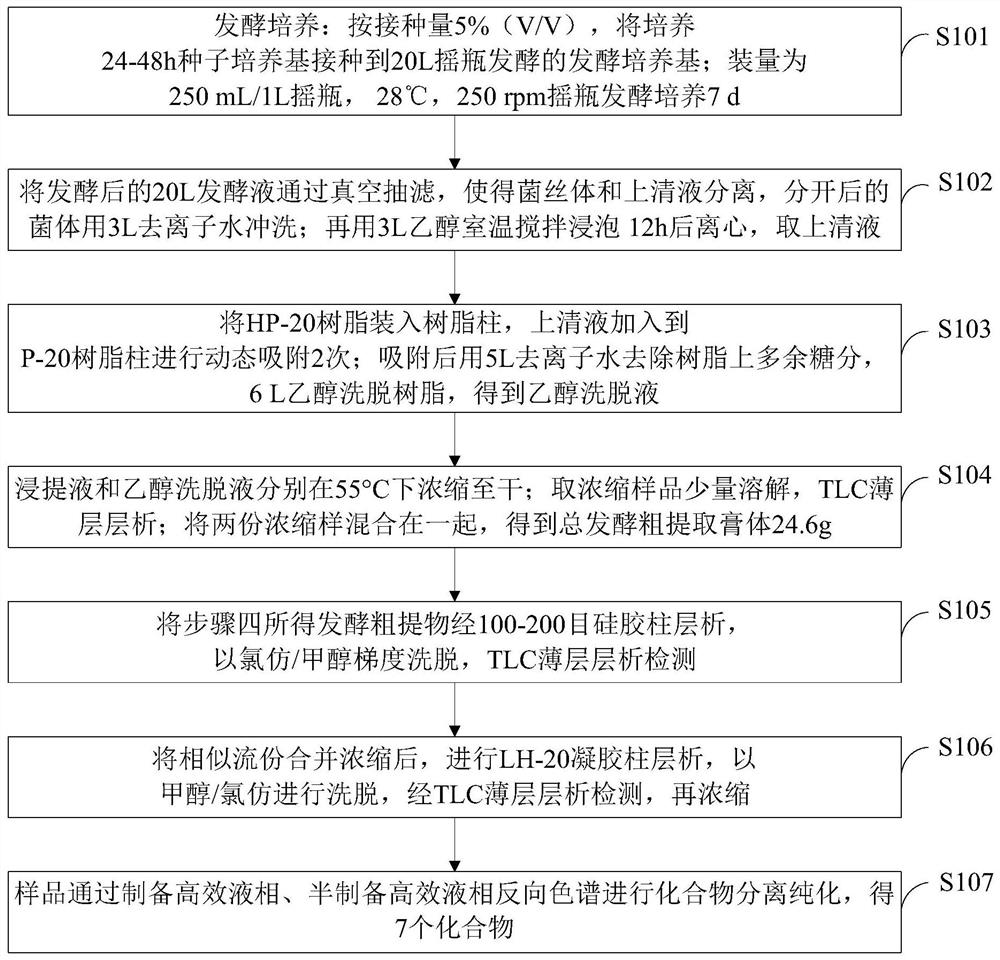
The invention belongs to the technical field of metabolite extraction, and discloses a method for separating and extracting secondary metabolites of streptomyces, which comprises the following steps:carrying out elution on a fermentation broth by using an HP-20 resin column, performing chromatographic separation by a silica gel column and a Sephadex LH-20 gel column, and performing analysis and purification of a compound by (semi) preparing a high performance liquid chromatography. Modern instrument spectrum analysis technologies such as nuclear magnetic resonance and high-resolution mass spectrometry are used for identifying the structure of the monomeric compound. According to the invention, actinomycetes which are separated from a soil sample and have antibacterial and anti-tumor cellactivity are fermented, and induction research is carried out on bioactivity of metabolites and part of products generated by the actinomycetes, so that diversity of microbial compounds is enriched; areference and theoretical basis is provided for research and exploration of active substances produced by other actinomycetes; meanwhile, a premise is provided for exploring and developing active natural compounds and commercial drugs.
Owner:台州市椒江唐宁贸易有限公司
Roof greening substrate
InactiveCN111903465AIncrease contentImprove the environmentGrowth substratesCulture mediaNutritionEngineering
The invention provides a roof greening substrate, and belongs to the field of food waste recycling. Particularly, food waste is used as a raw material, dry-wet separation is carried out, fermenting iscarried out by using thermoactinomycetes, ageing is carried out, inoculating of nitrogen-fixing bacteria and phosphate-solubilizing and potassium-solubilizing bacteria is carried out, and finally mixing with conventional materials such as peat is carried out, so that the roof greening substrate is obtained. The substrate provided by the invention is viable, is rich in nutrition and has a certaincapability of inhibiting infectious microbes, the nitrogen-fixing bacteria and the phosphate-solubilizing and potassium-solubilizing bacteria can rapidly grow and reproduce, nutrients are provided forplants, and the growth speed of the plants is high.
Owner:山东天酵源生物科技有限公司
Novel microorganism and its gene fragment order and application
InactiveCN101100653ANo killing effectAvoid destructionBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsDiseaseAdditive ingredient
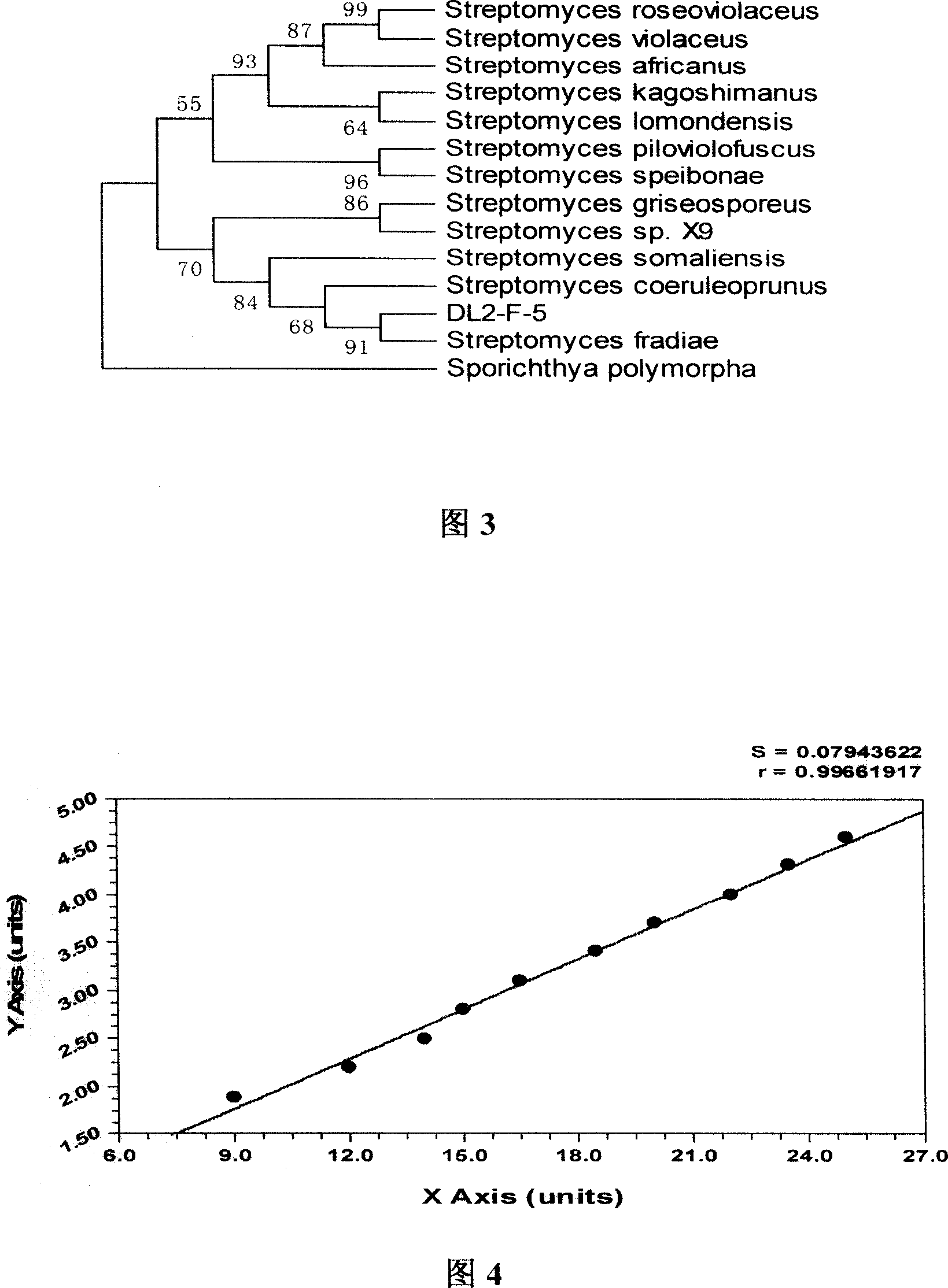
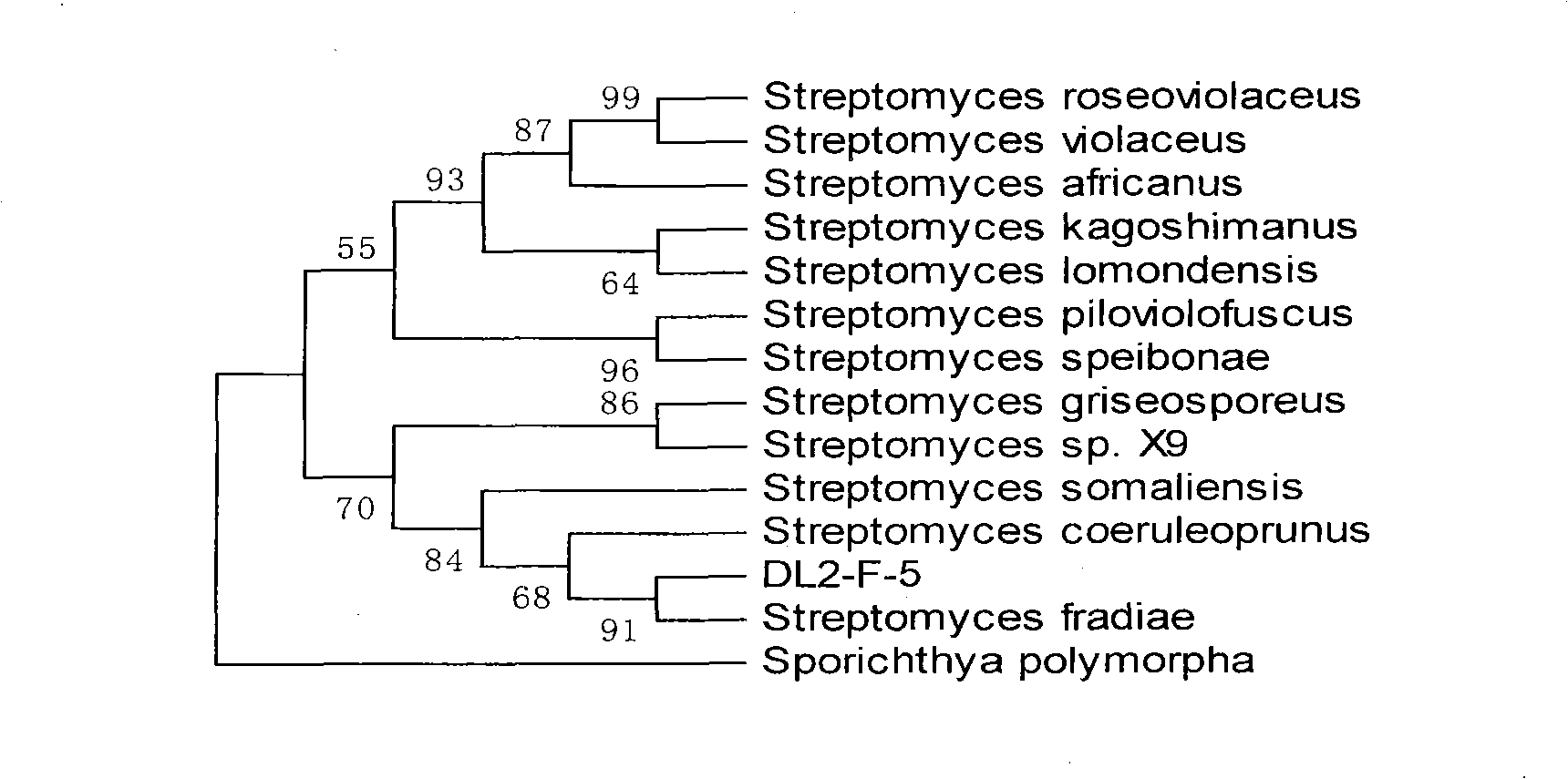
A streptomycesfradiae DL2-F-5 is separated from marine or fresh water microbe beneficial bacterial group. It can produce antibacterial substances or increase immune active ingredients, prevent aquatic animal diseases, avoid destruction for purified water environment by antiseptics, inhibit pathogenic bacteria multiplying, decompose organic pollutant and residual baits in water body and improve water-body environment. It can be used in medicine, food and feed additives production.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV +1
Aminosugar compound and process for production thereof
Disclosed is a compound useful as an active ingredient for a pharmaceutical composition having an a-amylase-inhibiting activity, particularly a pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of diabetes. Studies have been made for discovering a compound having an a-amylase-inhibiting activity among the compounds produced by Streptomyces sp. Strain 6982 which is a ray fungus belonging to the genus streptomyces, and it is confirmed that an aminosugar compound has an a-amylase-inhibiting activity. The aminosugar compound has an a-amylase-inhibiting activity, and therefore can be used as a prophylactic or therapeutic agent for diabetes, obesity, NASH (non-alcoholic steatohepatitis), particularly as an ameliorating agent for postprandial blood glucose elevation.
Owner:ASTELLAS PHARMA INC
Composite agricultural microorganism bacteria and method for applying composite bacteria to lotus root planting
InactiveCN105331555ARich varietyEasy to adaptBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyLysobacter antibioticus
The invention provides composite agricultural microorganism bacteria and a method for applying composite bacteria to lotus root planting. All strains of compound bacteria comprise, by weight, 20% of rhodospirillum, 10% of nitrospira, 10% of azotobacter, 10% of bacilli, 10% of thermoactinomyces, 10% of xanthomonas, 10% of lysobacter, 10% of acidophilic bacteria and 10% of novosphingobium. The composite bacteria are used for lotus root planting, the yield of lotus roots is increased, and the quality of the lotus roots is improved.
Owner:NANPING CP OREEZYME BIOTECH DEV CO LTD
Lipase L-1 and coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses lipase L-1 and a coding gene and application thereof. The lipase gene l-1 is obtained from Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 13580 in a cloned mode, the nucleotide sequence of the lipase gene l-1 is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, the overall length of the lipase gene l-1 is 1005 bp, and the amino acid sequence of the coded lipase L-1 is shown as SEQ ID NO.2 and contains 334 amino acids in all. The lipase gene l-1 is cloned and connected with an expression vector pET-28a(+), then conversion is performed to obtain escherichia coli BL21 (DE3), and after culture and induced expression, the recombinant expression lipase L-1 is obtained. The lipase L-1 serving as a catalyst catalyzes a reaction between cinnamyl alcohol and an acyl donor, and cinnamyl acetate is prepared, wherein the yield of the obtained cinnamyl acetate can reach 48.3%. The lipase L-1 has the advantages of being high in stability and catalysis efficiency and can be applied to the fields of biological medicine, cosmetics, fine chemical engineering and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Streptomyces rubiginosohelvolus capable of producing actinomycin D through fermentation and applications thereof
ActiveCN112680387AEfficient fermentationIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention belongs to the field of microorganisms, specifically relates to streptomyces rubiginosohelvolus capable of producing actinomycin D through fermentation, and further discloses applications of the streptomyces rubiginosohelvolus in producing the actinomycin D through fermentation. Through an atmospheric and room temperature plasma mutagenesis technology, the streptomyces rubiginosohelvolus FIM-Z19-12 capable of highly yielding the actinomycin D can be obtained through screening; the strain can efficiently ferment the actinomycin D; in fermentation experiments, the potency of the streptomyces rubiginosohelvolus FIM-Z19-12 producing the actinomycin D through fermentation can reach up to 1383 mg / L, so that the yield of the actinomycin D can be greatly increased; and therefore, the streptomyces rubiginosohelvolus can be applied to industrial fermentation production.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF MICROBIOLOGY
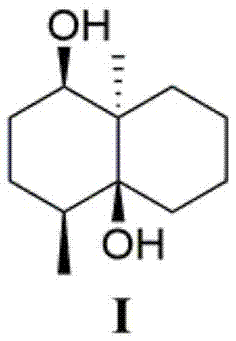
Preparation method for novel antifungal compound and antifungal application
The invention relates to a preparation method for a novel antifungal compound and an antifungal application. The invention discloses a novel compound with a structure formula I as follows, wherein the novel compound is prepared by separating Streptomyces-albolongus which is used as a source; the chemical name is (1beta, 4beta, 4abeta, 8a alpha)-4,8a-dimethyloctahydronaphthalene-1,4a(2H)-diol; the molecular formula is C12H22O2. The invention also provides a preparation method and an application of the compound. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: performing fermenting culture on the strain S.albolongus, and then centrifuging, thereby acquiring a culture solution; absorbing the culture solution by a macroreticular resin column, reducing pressure and concentrating the 95% alcohol eluting part, thereby acquiring a crude extract; treating the crude extract with normal phase silica gel, dextrangel LH-20 and reverse phase silica gel column chromatography, thereby acquiring a monomer compound shown as structure I; and adopting nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum and mass spectrum for identifying the structure as the novel compound. An in vitro antifungal activity research proves that the compound I provided by the invention has obvious inhibiting effect to various pathogenic fungi, including candida albicans, candida parapsilosis and cryptococcus neoformans and is expected to be developed into a novel antifungal drug.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV +1
Ocean actinomycetes strain producing plasmin, application and plasmin prepared from same and application of plasmin
The invention discloses an ocean actinomycetes strain producing plasmin, a preparation method and application of same and the plasmin prepared from same and application of the plasmin. The strain is from sludge of Bohai Bay and is identified as Streptomyces sp. through 16SrRNA, and the preservation number of the strain is CGMCC No. 10664. The actinomycetes strain can produce the plasmin through liquid culture and fermentation, the plasmin is one type of principal medicine for clinically treating thrombotic diseases, the plasmin is low in molecular weight, great in fibrous protein specificity and not prone to hemorrhage reaction, and the good application prospect in thrombotic disease treatment is achieved.
Owner:BIOLOGY INST OF HEBEI ACAD OF SCI
Preparation and application of a composite microbial agent for coal gangue artificial ecological matrix
ActiveCN110982748BRich varietyHigh temperature resistantFungiBio-organic fraction processingBiotechnologyAmylase
The invention discloses a compound microbial bacterial agent used for coal gangue artificial ecological matrix, including 5 kinds of actinomycetes: Streptomyces violaceum ( Streptomyces thermoviolaceus ), Streptomyces thermophilus ( S.thermodiastaticus ), Streptomyces carbon monoxide ( S.thermocarboxydus ), Streptomyces albus ( S. albidoflavus ) and Streptomyces vulgaris ( S. thermovulgaris ), 1 bacteria: Pseudomonas ( Pseudomonas sp.), and 1 mold: Penicillium oxalicum ( Penicillium oxalicum ). The preparation process of the bacterial agent includes four steps: activation of the bacterial strain, preparation of the seed liquid, preparation of the liquid composite bacterial agent, and preparation of the solid bacterial agent. The technology of the invention solves the problem that the coal gangue lacks microorganisms and the nutrients are not conducive to plant absorption and utilization, and provides a new way for the resource utilization of the coal gangue and landscaping waste.
Owner:北京优生基生态科技有限公司
Application of high-temperature-resistant streptomycete in agricultural waste compost
InactiveCN104355690APromote degradationImprove conversion abilityBio-organic fraction processingExcrement fertilisersBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention discloses a high-temperature-resistant actinomycete which can efficiently degrade and convert rice straw and nitrogen in pig manure. The actinomycete disclosed by the invention belongs to streptomyces griseorubens with the preservation number of CGMCC No. 5706. The actinomycete can strongly degrade methyl cellulose in the rice straw, further can quickly convert nitrate nitrogen and organic nitrogen in the pig manure, and tolerates the high temperature of more than 70 DEG C; the actinomycete can be added to the mixed compost of rice straw and pig manure to obviously rise the compost temperature, shorten the fermentation cycle, and improve the quality and the yield of the organic fertilizer; in addition, the organic fertilizer inoculated with the solid bacteria agent can quickly fertilize soil, so as to increase the content of the organic fertilizer, total nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen, activate the soil enzyme activity, and finally increase the yield of the crop.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Thermophilic streptomyces hygroscopicus cDNA library construction, and expression and expression methods of two greenhouse farmer's lungpathopoiesia antigen polypeptides
The invention provides thermophilic streptomyces hygroscopicus cDNA library construction, and expression and expression methods of two greenhouse farmer's lung pathopoiesia antigen polypeptides. The problem needed solving is that: the thermophilic streptomyces hygroscopicus cDNA library is constructed, two greenhouse farmer's lung pathopoiesia virulence genes with virulence effects need screening out for cloning in vitro and inducing expression of the two greenhouse farmer's lung pathopoiesia antigen polypeptides. The key point of construction of the thermophilic streptomyces hygroscopicus cDNA library comprises: acquiring 978 sense sequences and 347 single genes, wherein the homology of two gene fragments respectively with actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae outer membrane protein and transferrin B is 51% and 42%, and the open reading frame length of the two gene fragments respectively is 1554 bp and 726 bp, and 517 and 241 amino acids are respectively encoded. The applications of the thermophilic streptomyces hygroscopicus cDNA library comprise that: from the thermophilic streptomyces hygroscopicus cDNA library, the two greenhouse farmer's lung pathopoiesia virulence genes with virulence effects are screened out for cloning in vitro and inducing expression of the two greenhouse farmer's lung pathopoiesia antigen polypeptides, and theoretical basis and practical basis are provided for subsequent development of new diagnosis methods for farmer's lung diseases.
Owner:中国医科大学附属第四医院
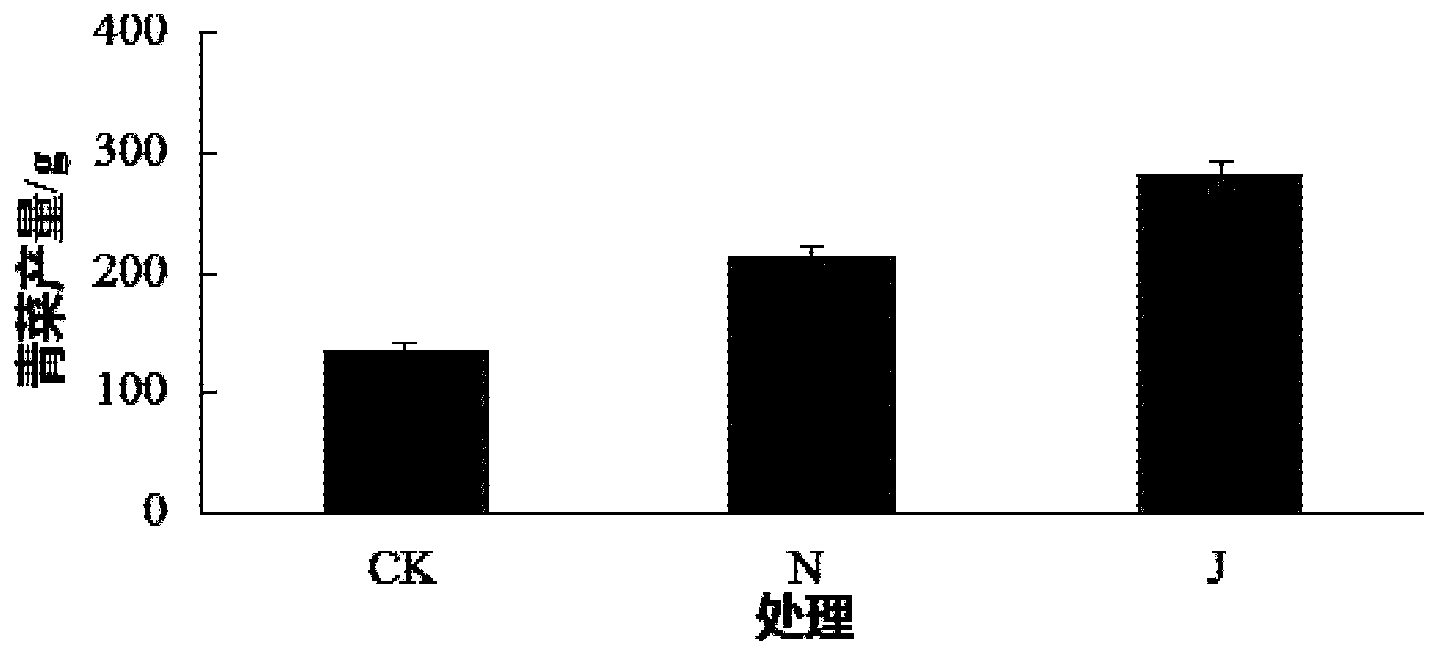
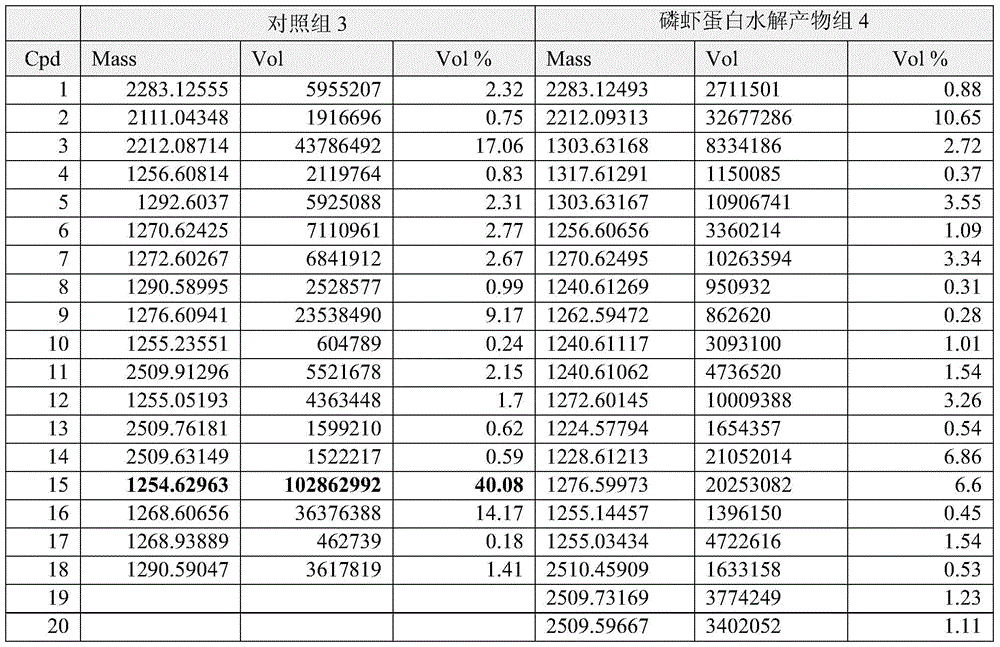
Preparation and application of protein hydrolyzate of chilled Antarctic krill
ActiveCN103834711BRich sourcesHigh protein contentMicroorganism based processesFermentationStreptomyces thermoautotrophicusStreptomyces thermodiastaticus
The invention relates to a method of preparing protein hydrolysate of chilled Antarctic krill. The method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing chilled Antarctic krill raw material with water in a ratio of 1-3L water per kilogram raw material, grinding and homogenizing, adding alkaline protease, and performing enzymolysis for 1-5 hours at the temperature of 35-55 DEG C; (2) performing solid-liquid separation to obtain clear liquor, concentrating and drying the clear liquor to obtain the protein hydrolysate, wherein the content of fat is 0%, and the total content of peptides and amino acid is more than 60%. The total yield of actinomycin produced through fermentation by virtue of streptomycete in an Antarctic krill protein hydrolysate group is equivalent to the yield of the existing commercialization nitrogen source group, and high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrum analysis results show that the diversity of analogue of actinomycin D produced through fermentation in the Antarctic krill protein hydrolysate group is better.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
A microbial agent against potato scab
ActiveCN103725630BIncrease profitImprove the ecological environmentBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a microbial agent which adopts bacillus subtilis CGMCC1. 3382, dactylosporangium sp. ACCC No. 40661 and streptomyces roseoflavus ACCC No. 40400 as preparation bacteria; all bacteria are prepared to form fermentation liquors, the fermentation liquors are mixed, and the mixture is subjected to submerged fermentation to prepare the microbial agent. The microbial agent utilizes the interaction among microorganism in a reasonable manner, has the characteristics of high adaptability, excellent stability, and high antagonism to pathogenic bacteria, and difficulty in aging, can realize efficient antagonism to the potato common scab, stimulate growth of the potatoes, and improve the quality of the potatoes so as to achieve the purposes of production increasing and high yield.
Owner:DALIAN SANKE BIO ENG
Novel microorganism and its gene fragment order and application
InactiveCN100529058CNo killing effectAvoid destructionBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsBiotechnologyAquatic animal
A streptomycesfradiae DL2-F-5 is separated from marine or fresh water microbe beneficial bacterial group. It can produce antibacterial substances or increase immune active ingredients, prevent aquatic animal diseases, avoid destruction for purified water environment by antiseptics, inhibit pathogenic bacteria multiplying, decompose organic pollutant and residual baits in water body and improve water-body environment. It can be used in medicine, food and feed additives production.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV +1
A method for separating and extracting secondary metabolites of streptomyces
ActiveCN110452940BRapid and accurate separation and identificationRich diversityMicroorganism based processesCarboxylic acid amide separation/purificationMetaboliteNatural compound
The invention belongs to the technical field of metabolite extraction, and discloses a method for separating and extracting secondary metabolites of streptomyces, which comprises the following steps:carrying out elution on a fermentation broth by using an HP-20 resin column, performing chromatographic separation by a silica gel column and a Sephadex LH-20 gel column, and performing analysis and purification of a compound by (semi) preparing a high performance liquid chromatography. Modern instrument spectrum analysis technologies such as nuclear magnetic resonance and high-resolution mass spectrometry are used for identifying the structure of the monomeric compound. According to the invention, actinomycetes which are separated from a soil sample and have antibacterial and anti-tumor cellactivity are fermented, and induction research is carried out on bioactivity of metabolites and part of products generated by the actinomycetes, so that diversity of microbial compounds is enriched; areference and theoretical basis is provided for research and exploration of active substances produced by other actinomycetes; meanwhile, a premise is provided for exploring and developing active natural compounds and commercial drugs.
Owner:台州市椒江唐宁贸易有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com