Patents
Literature
221 results about "Sub micrometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
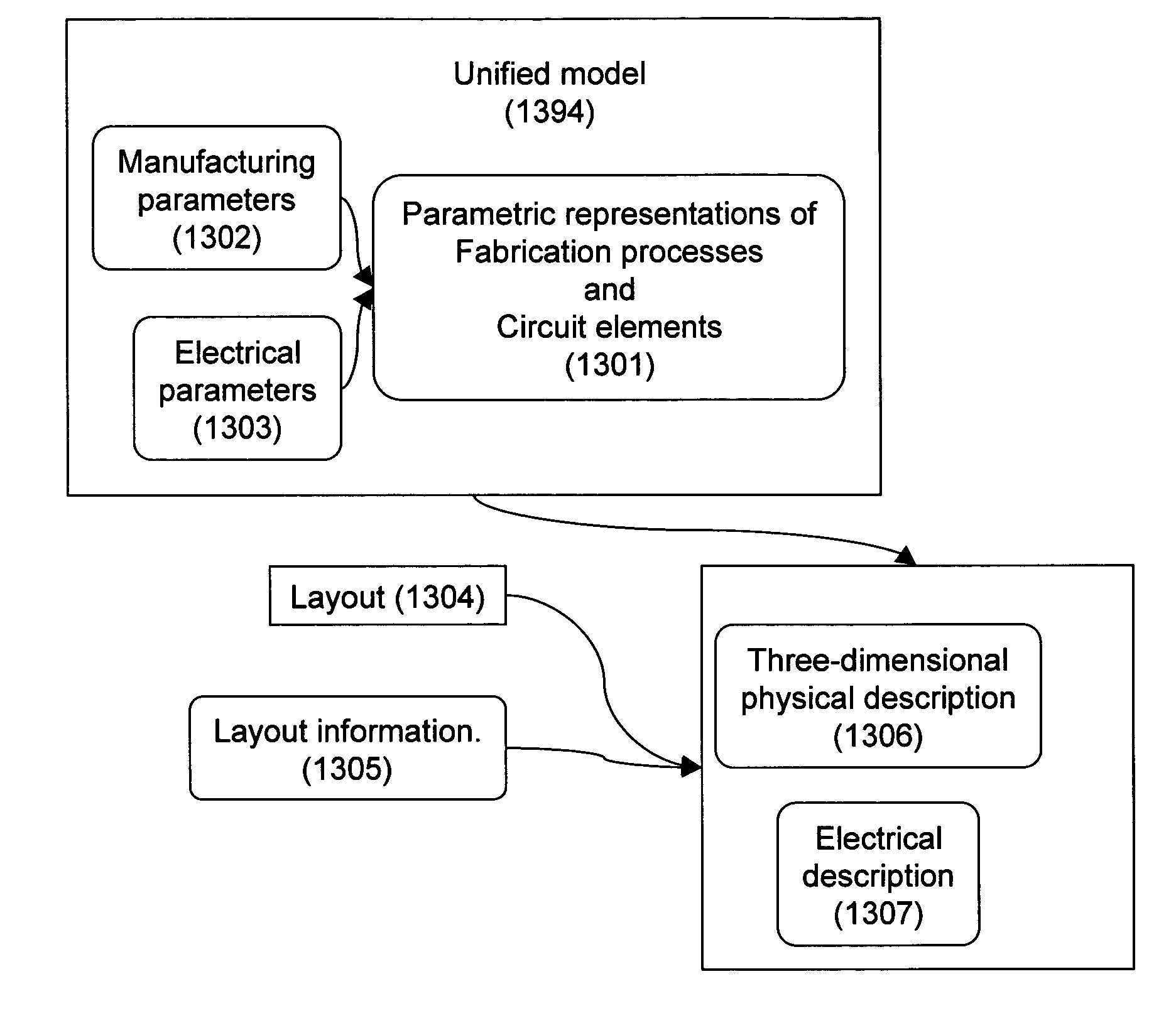
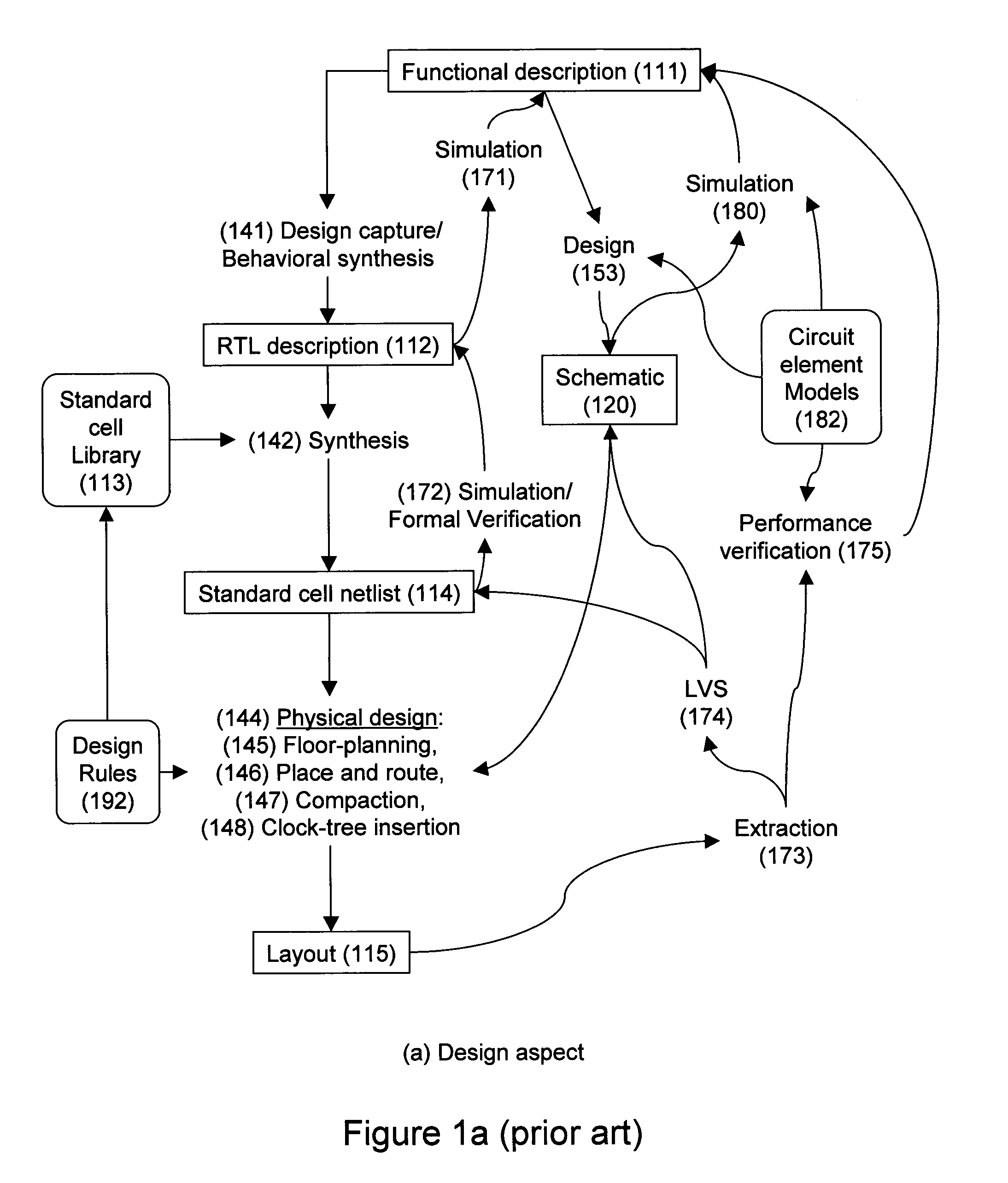
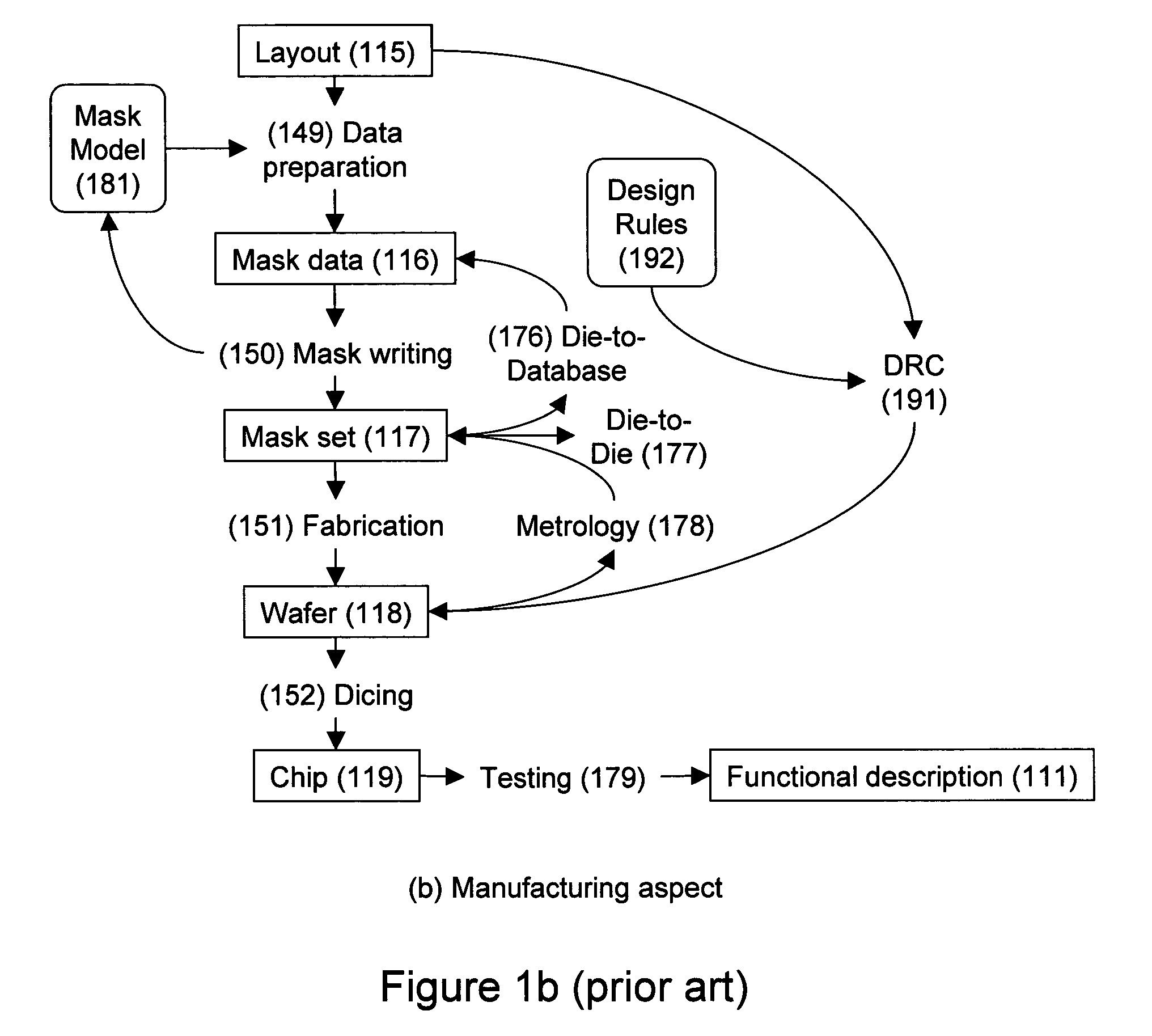
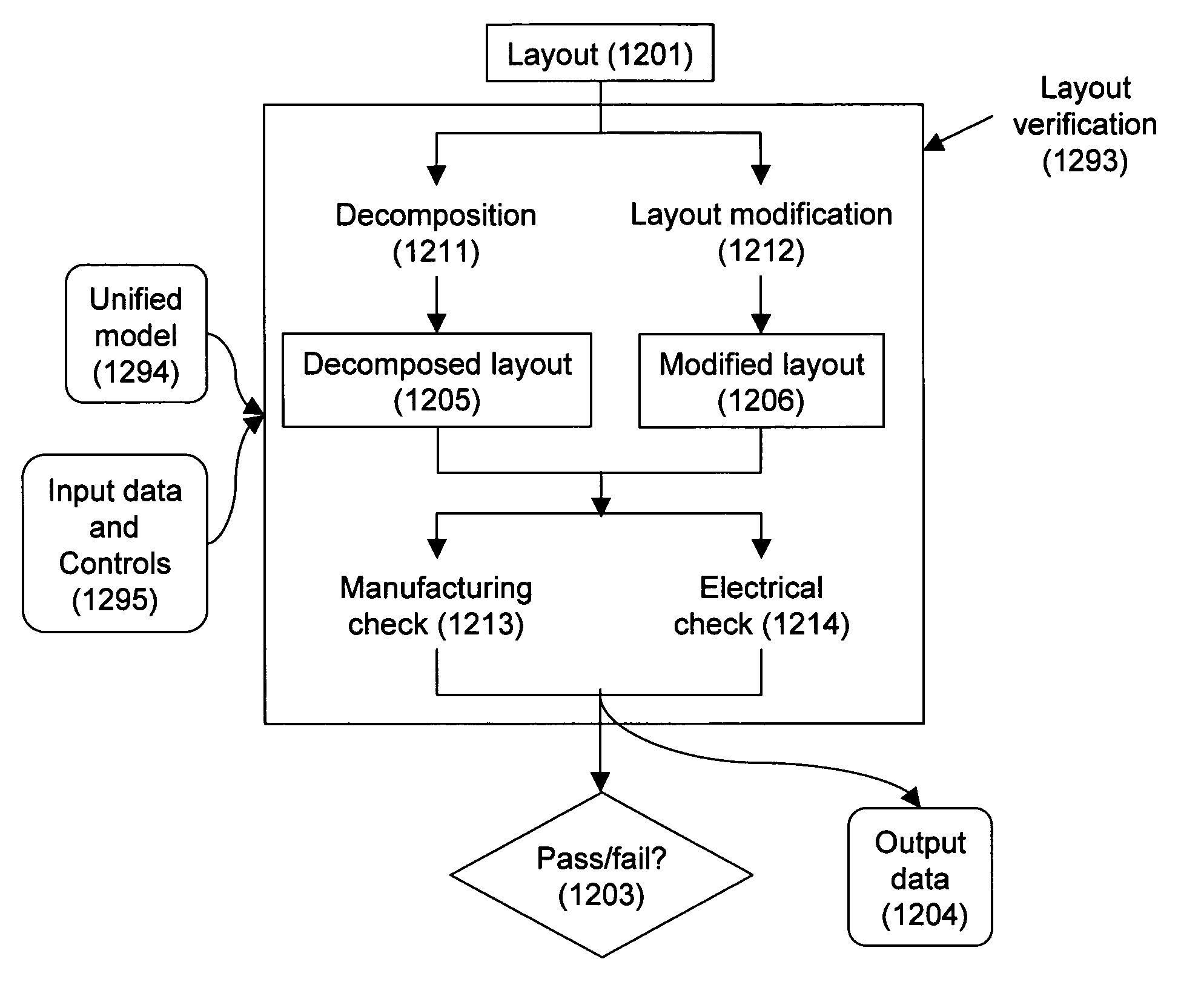
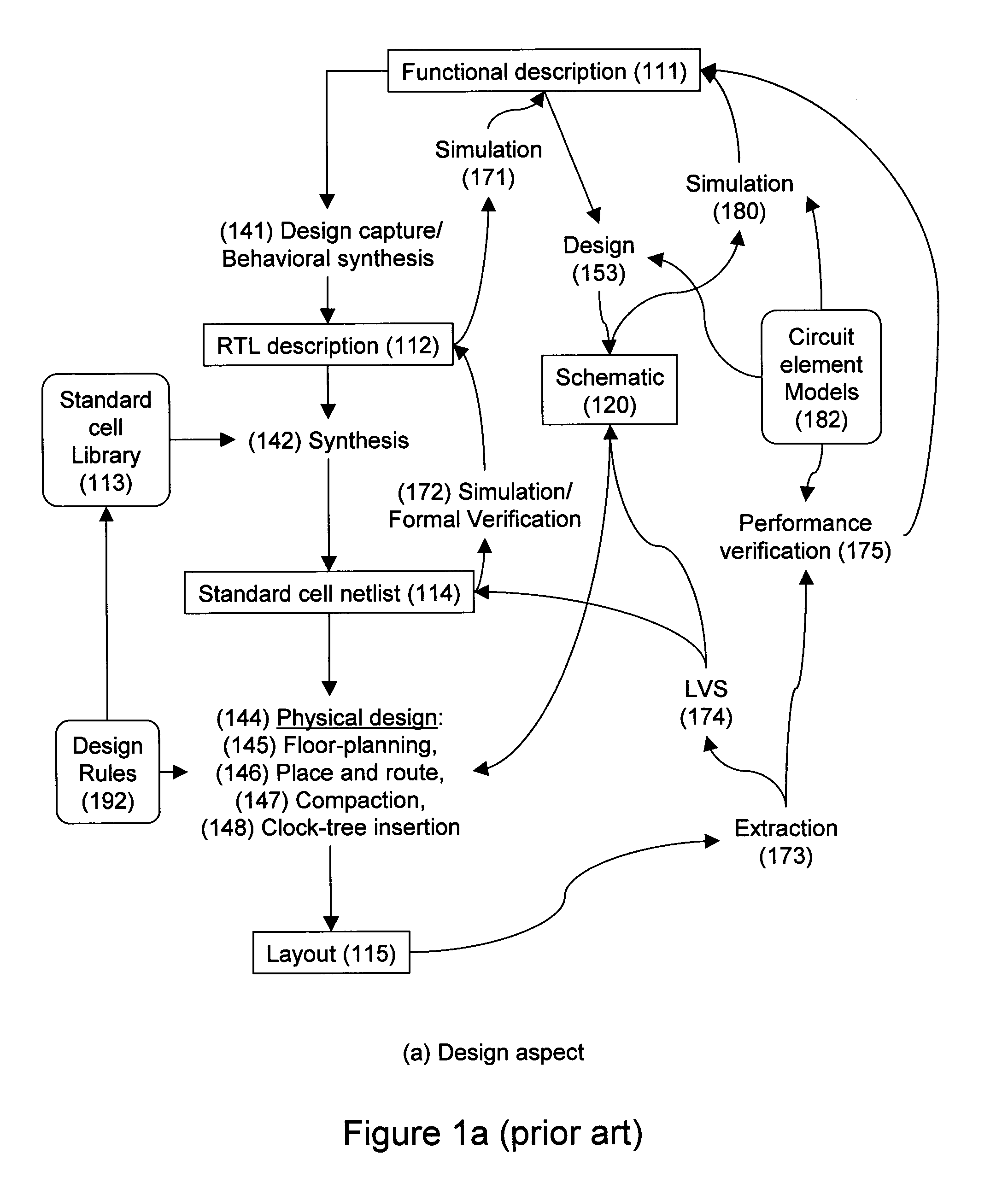
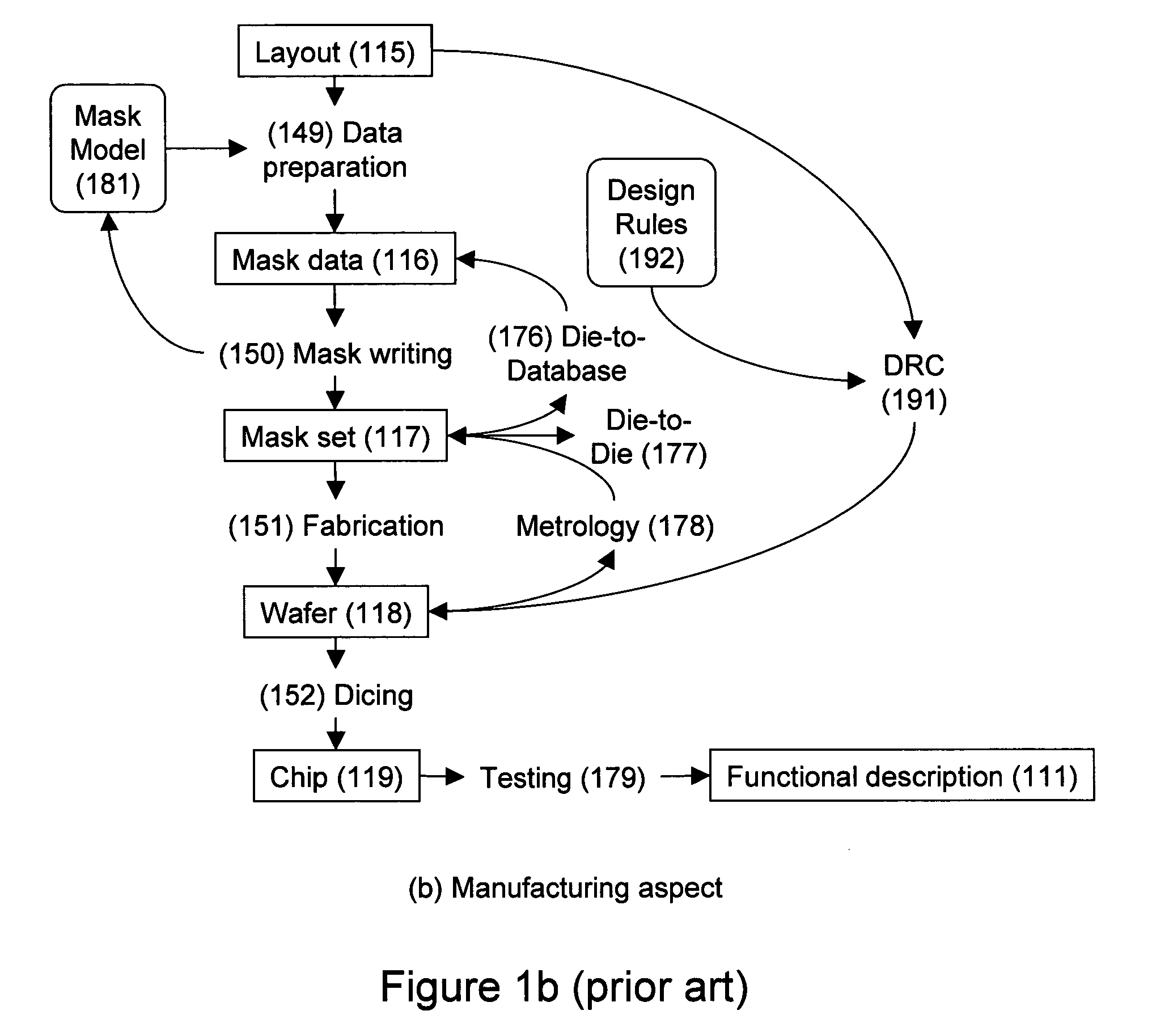
Design-manufacturing interface via a unified model
ActiveUS7155689B2Create additionalImprove accuracyCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsMiniaturizationEngineering
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Design-manufacturing interface via a unified model
ActiveUS20050076316A1Create additionalImprove accuracyCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationManufacturing technologyMiniaturization
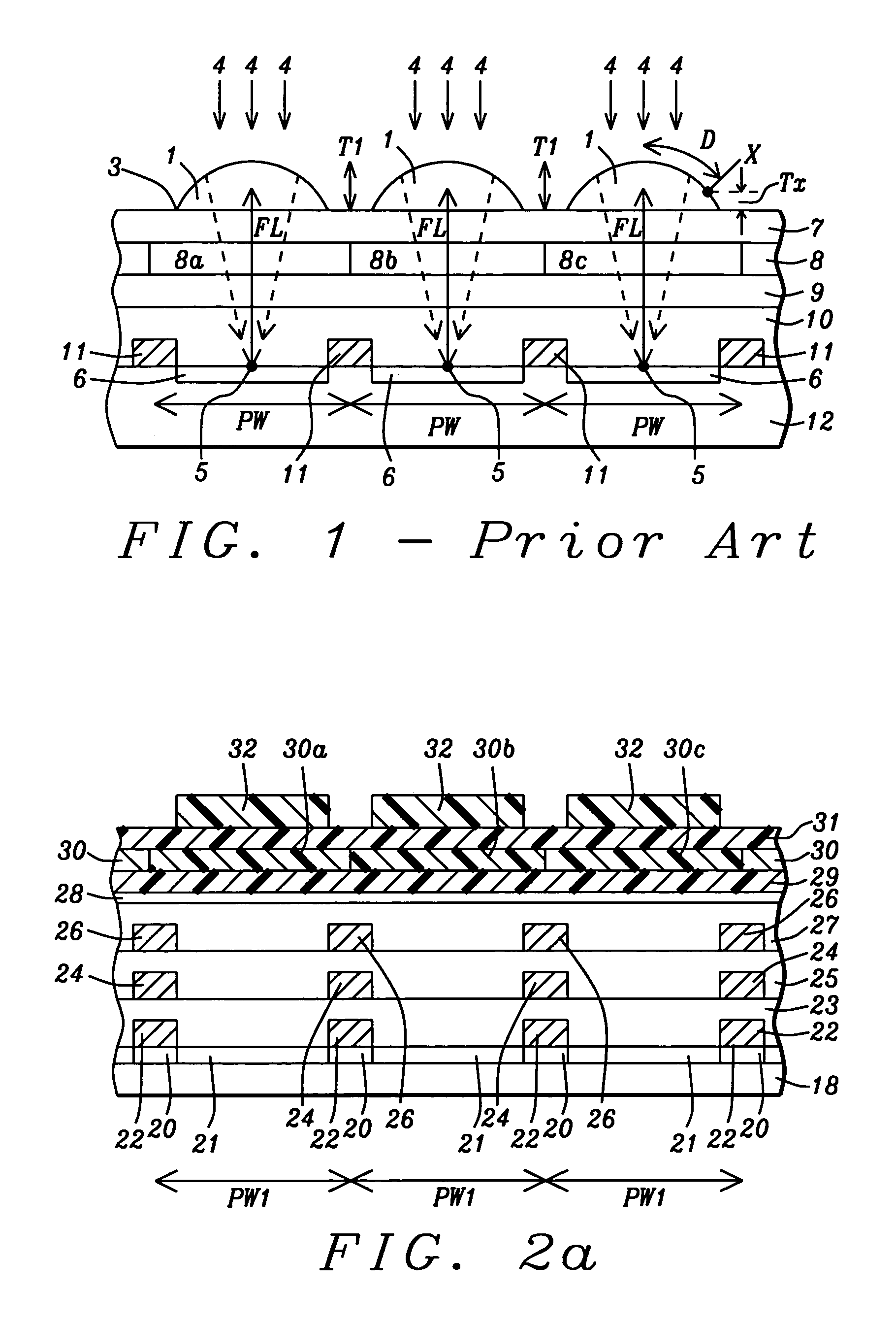
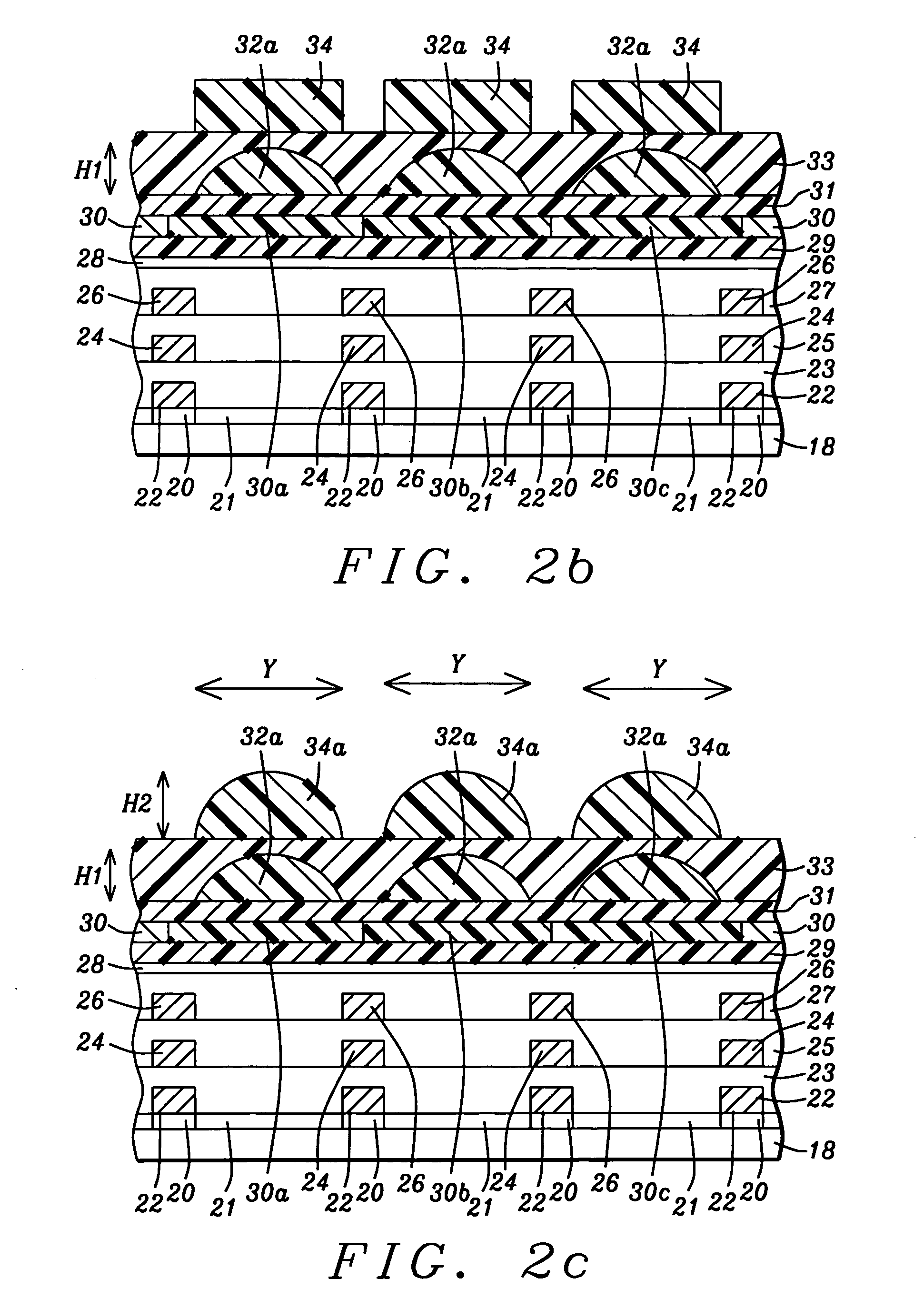
Subtleties of advanced fabrication processes and nano-scale phenomena associated with integrated circuit miniaturization have exposed the insufficiencies of design rules. Such inadequacies have adverse impact on all parts of the integrated circuit creation flow where design rules are used. In addition, segregation of the various layout data modification steps required for deep sub-micrometer manufacturing are resulting in slack and inefficiencies. This invention describes methods to improve integrated circuit creation via the use of a unified model of fabrication processes and circuit elements that can complement or replace design rules. By capturing the interdependence among fabrication processes and circuit elements, the unified model enables efficient layout generation, resulting in better integrated circuits.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
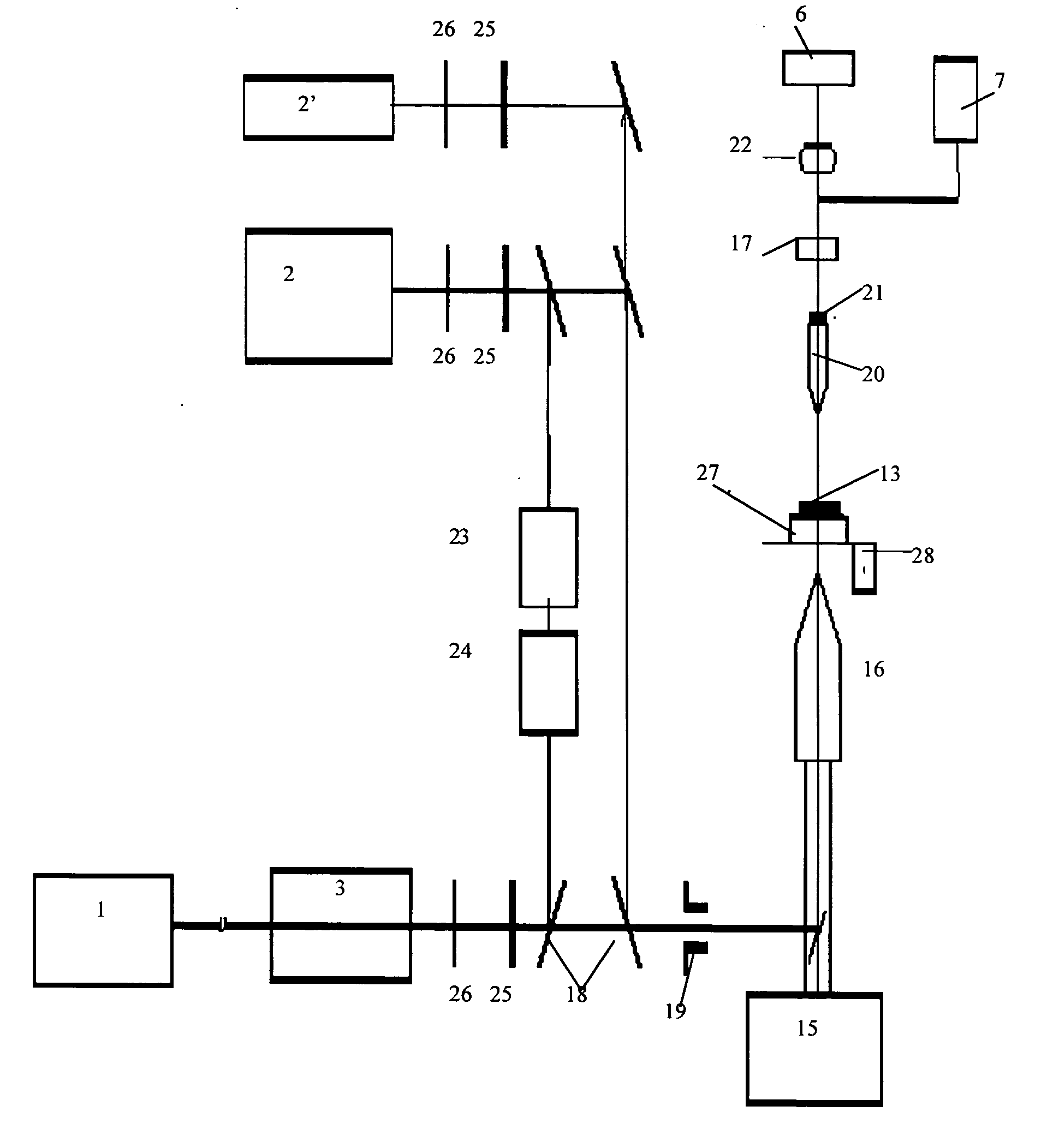
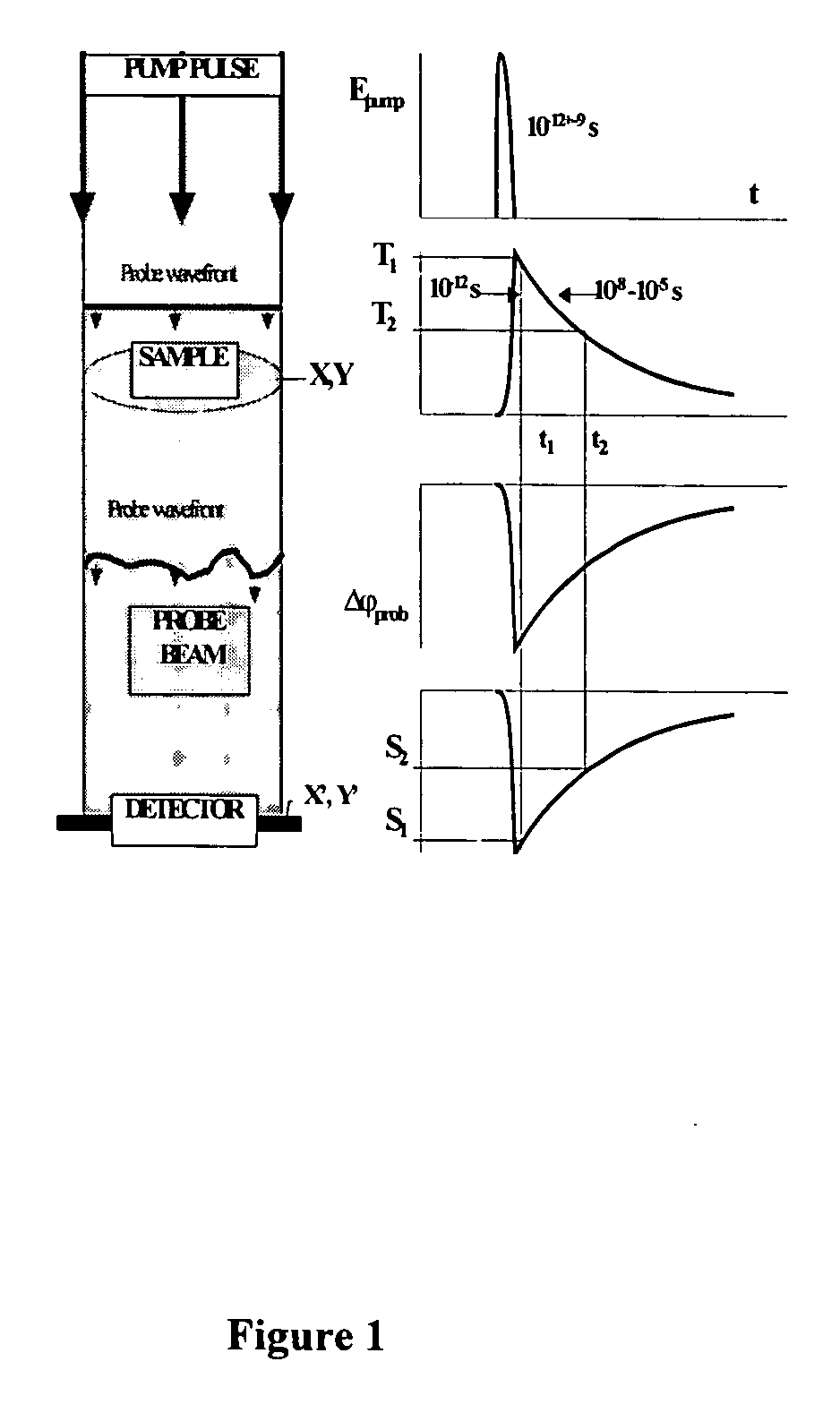
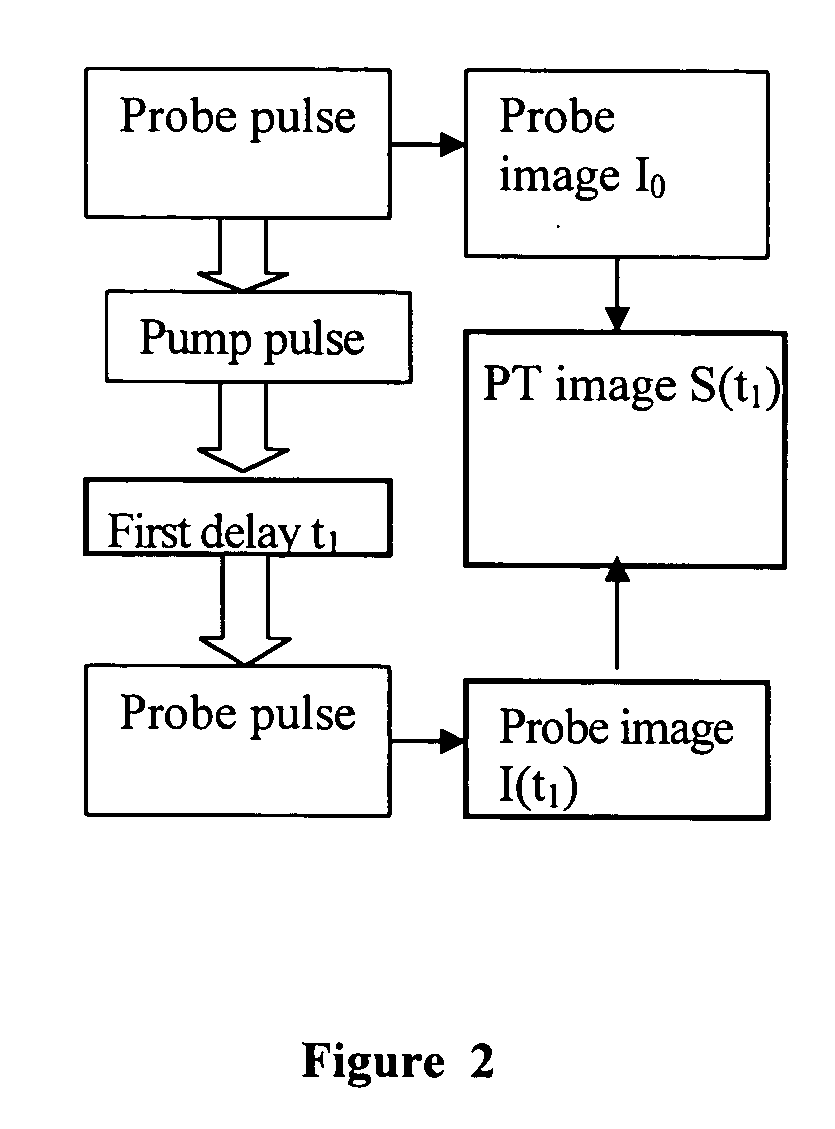
Method and device for photothermal examination of microinhomogeneities
InactiveUS20040085540A1Increase sensitivity and resolutionImprove resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansPhysicsRefractive index
The invention relates to optical microscopy, in particular to methods for photothermal examination of absorbent microinhomogeneities using laser radiation sources and can be widely used in laser engineering, industry and biomedicine for examining relatively transparent objects containing submicron impurities, including the detection of local inclusions and defects in ultrapure optical and semiconductor materials and the non-destructive diagnosis of biological samples on a cellular and subcellular level. The aim of the invention is to increase the sensitivity, spatial resolution and informativity of examination of local absorbent microinhomogeinities in transparent objects and to measure said microinhomogeinities even when they are less than the used emission wavelength. The inventive method consists in radiating a sample with a pumping laser beam. The duration of the radiation is equal to or less than a representative time for cooling the examined microinhomogeinity. The relatively large surface of the sample is radiated, the shape thereof being greater than the wavelength of the used pumping laser. Thermal variations of the refractive index occurring in the sample as a result of absorption produced with the aid of the pumping beam are recorded by measuring parameters of a test laser beam. The diameter of the test beam is chosen in such a way that it is equal to or greater than the diameter of the pumping beam. A diffraction-limited phase distribution along the cross-section of the testing laser beam is transformed into an amplitude image, the microinhomogeinity properties being determined by measuring said amplitude image.
Owner:LAPOTKO TATIANA MS
Apparatus, methods and precision spray processes for direct write and maskless mesoscale material deposition
InactiveUS20040197493A1Reduce package sizeElectric discharge heatingVacuum evaporation coatingOptoelectronicsBiological materials
Apparatuses and processes for maskless deposition of electronic and biological materials. The process is capable of direct deposition of features with linewidths varying from the micron range up to a fraction of a millimeter, and may be used to deposit features on substrates with damage thresholds near 100° C. Deposition and subsequent processing may be carried out under ambient conditions, eliminating the need for a vacuum atmosphere. The process may also be performed in an inert gas environment. Deposition of and subsequent laser post processing produces linewidths as low as 1 micron, with sub-micron edge definition. The apparatus nozzle has a large working distance-the orifice to substrate distance may be several millimeters-and direct write onto non-planar surfaces is possible. This invention is also of combinations of precision spray processes with in-flight laser treatment in order to produce direct write electronic components, and additionally lines of conductive, inductive, and resistive materials. This development has the potential to change the approach to electronics packaging in that components can be directly produced on small structures, thus removing the need for printed circuit boards.
Owner:OPTOMEC DESIGN CO
Method and apparatus for characterizing solutions of small particles
A method and apparatus is described by which means molecules in suspension may be characterized in terms of the size and mass distributions present. As a sample solution is separated by centrifugal means, it is illuminated at a particular radial distance from the axis of rotation by a fine, preferably monochromatic, light beam. Despite the high resolution of such devices, a key problem associated with most separators based upon use of centrifugal forces is the difficulty in deriving the absolute size and / or molar mass of the separating molecules. By integrating means to detect light scattered, over a range of scattering angles, from samples undergoing centrifugal separation, molecular sizes in the sub-micrometer range may be derived, even in the presence of diffusion. Adding a second light beam at a displaced rotational angle, preferably of an ultraviolet wavelength, that intersects the sample at the same radial region as the first beam permits determination of the molecular concentration at that region. Combining the light scattering data with the associated concentration permits the determination of the associated molar mass. In a preferred embodiment, the light beam and detectors may be controlled to scan synchronously the sample radially during separation.
Owner:WYATT TECH
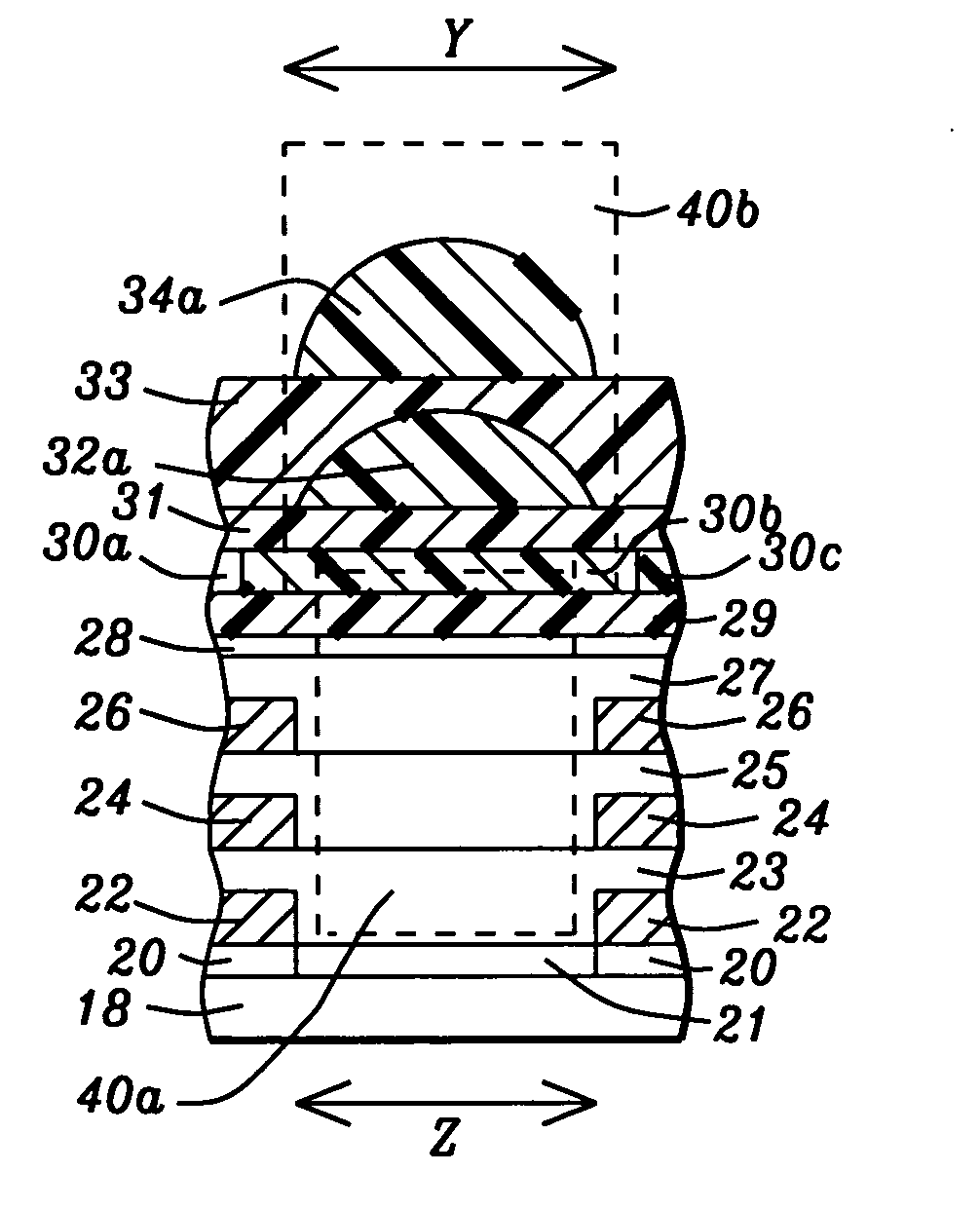
Effective method to improve sub-micron color filter sensitivity
ActiveUS20050242271A1High sensitivityLong focal lengthTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesColor gelPhotodiode
An image sensor device and method for forming said device are described. The image sensor structure comprises a substrate with photodiodes, an interconnect structure formed on the substrate, a color filter layer above the interconnect structure, a first microlens array, an overcoat layer, and a second microlens array. A key feature is that a second microlens has a larger radius of curvature than a first microlens. Additionally, each first microlens and second microlens is a flat convex lens. Thus, a thicker second microlens with a short focal length is aligned above a thinner first microlens having a long focal length. A light column that includes a first microlens, a second microlens and a color filter region is formed above each photodiode. A second embodiment involves replacing a second microlens in each light column with a plurality of smaller second microlenses that focus light onto a first microlens.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Closed-loop planar linear motor with integral monolithic three-degree-of-freedom AC-magnetic position/orientation sensor
InactiveUS6175169B1High quality positionEasy to manufactureDC motor speed/torque controlMagnetic circuitAir bearingLoop control
Owner:RALPH L HOLLIS JR
High accuracy miniature grating encoder readhead using fiber optic receiver channels
InactiveUS6906315B2Robust alignment toleranceHigh resolutionPhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A fiber optic encoder readhead for sensing the displacement of a scale grating is disclosed. The detector channels of the readhead are fiber optic detector channels having respective phase grating masks. The fiber optic encoder readhead is configured to detect the displacement of a self-image of the scale grating. In various exemplary embodiments, the fiber optic readhead is constructed according to various design relationships that insure a robust signal-to-noise ratio. Accordingly, high levels of displacement signal interpolation may be achieved, allowing sub-micrometer displacement measurements. The fiber optic encoder readhead may be assembled in a particularly accurate and economical manner and may be provided in a package with dimensions on the order of 1-2 millimeters.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Method and apparatus for characterizing solutions of small particles
A method and apparatus is described by which means molecules in suspension may be characterized in terms of the size and mass distributions present. As a sample solution is separated by centrifugal means, it is illuminated at a particular radial distance from the axis of rotation by a fine, preferably monochromatic, light beam. Despite the high resolution of such devices, a key problem associated with most separators based upon use of centrifugal forces is the difficulty in deriving the absolute size and / or molar. mass of the separating molecules. By integrating means to detect light scattered, over a range of scattering angles, from samples undergoing centrifugal separation, molecular sizes in the sub-micrometer range may be derived, even in the presence of diffusion. Adding a second light beam at a displaced rotational angle, preferably of an ultraviolet wavelength, that intersects the sample at the same radial region as the first beam permits determination of the molecular concentration at that region. Combining the light scattering data with the associated concentration permits the determination of the associated molar mass. In a preferred embodiment, the light beam and detectors may be controlled to scan synchronously the sample radially during separation.
Owner:WYATT TECH
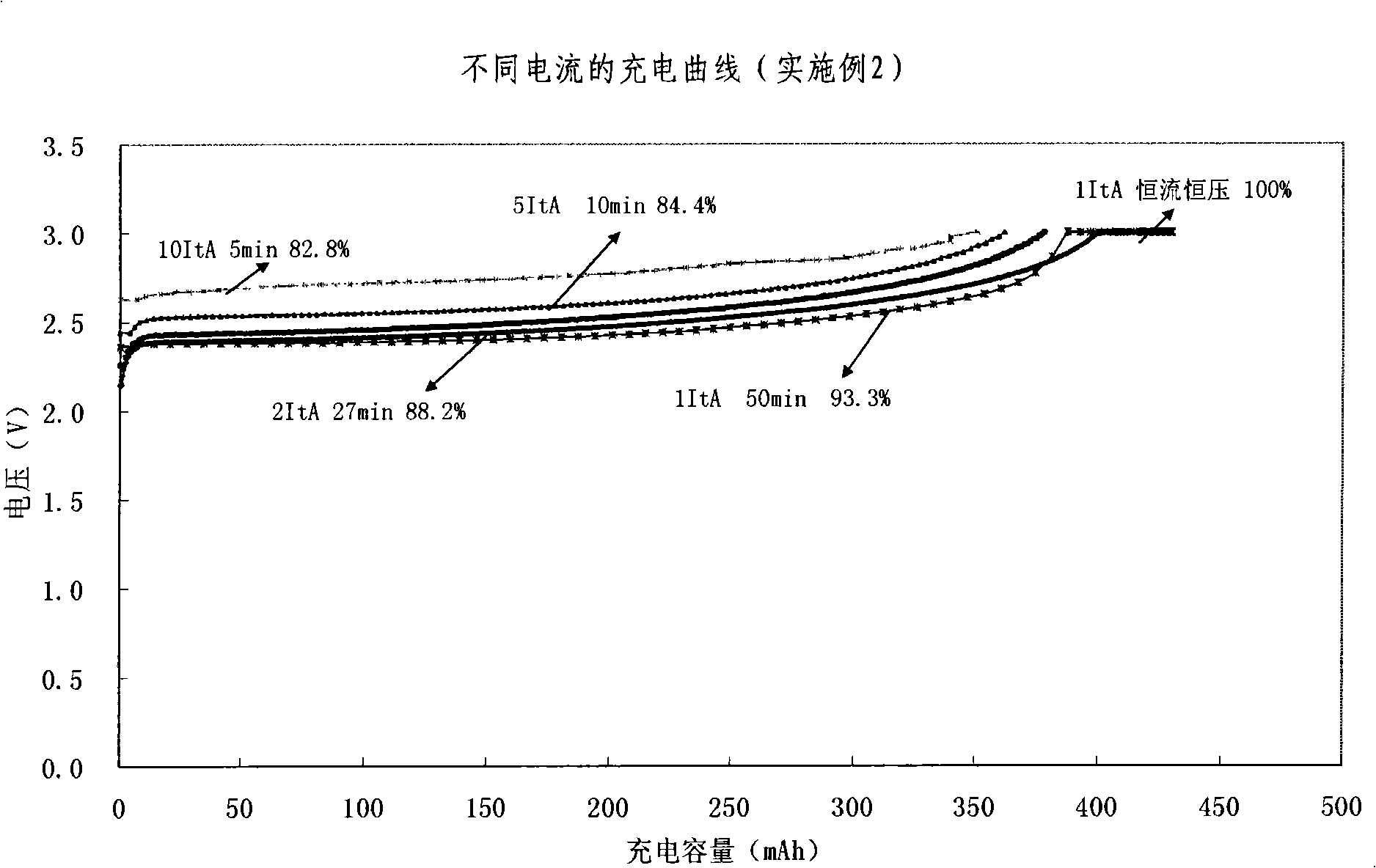
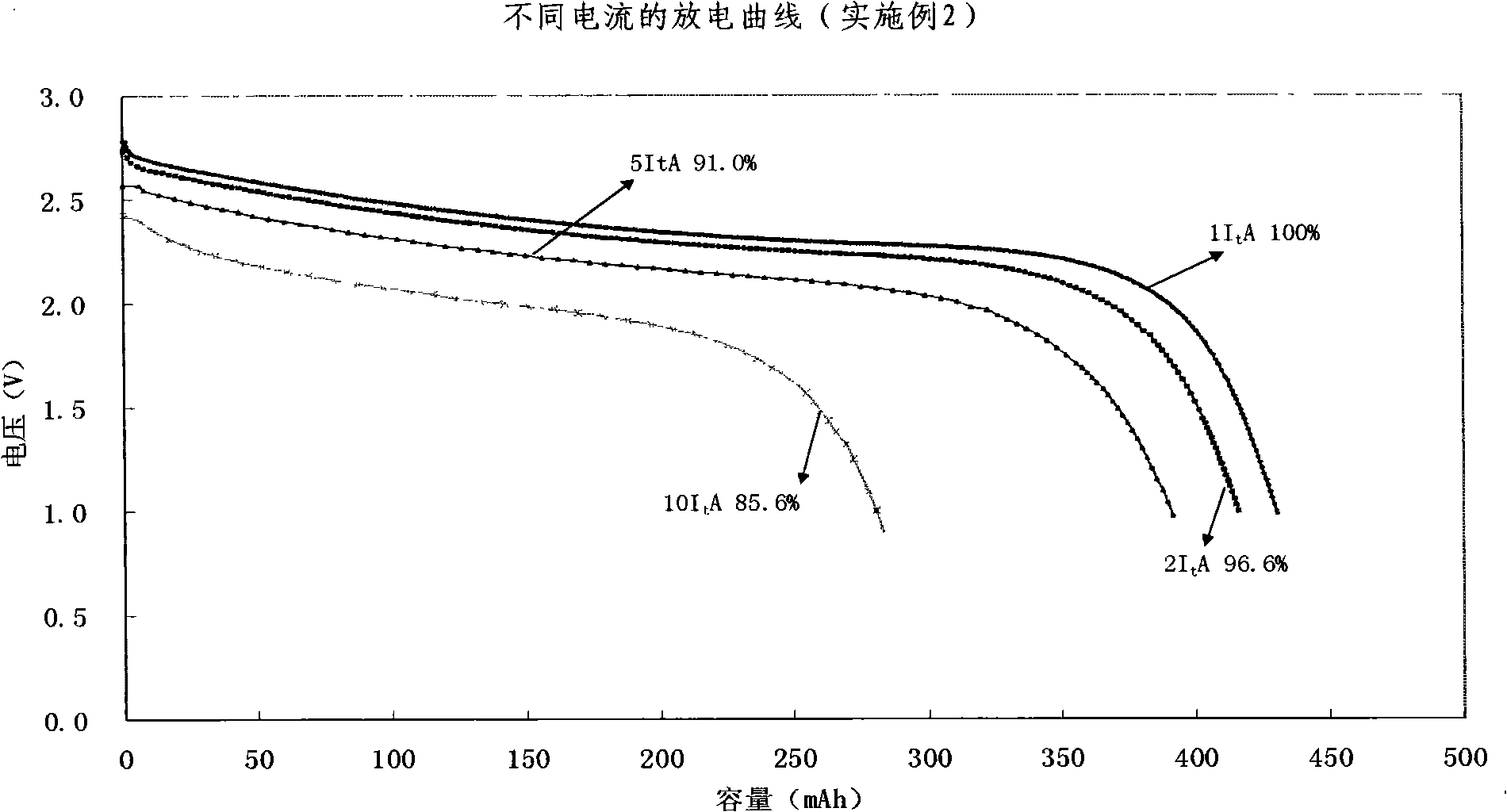
Quickly chargeable lithium ion battery and its making method
InactiveCN101262078AExcellent fast charge and discharge performanceCell electrodesFinal product manufactureMethyl carbonateManganate
The invention discloses a lithium-ion battery with fast charge property, which comprises an anode, a cathode, a diaphragm sandwiched between the anode and the cathode and an organic electrolyte, wherein, sub micrometer lithium titanate is used as the active substance of the cathode; one or several materials of lithium manganate (LiMn2O4), lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), lithium nickel cobalt oxide (LiNixCoyMzO2), ternary substance(LiNixMnxCo1-2xO2) are used as active materials of the anode, or a mixture of lithium cobalt (LiCoO2) and one of lithium manganate (LiMn2O4), lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), lithium nickel cobalt oxide (LiNixCoyMzO2), ternary substance(LiNixMnxCo1-2xO2) is adopted as the active materials of the anode; lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF6) is adopted as the electrolyte, and a multicomponent mixture of ethylene carbonate (EC), dimethylcarbonate(DMC), Ethyl Methyl Carbonate (EMC) is used as a solution. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the lithium-ion battery with fast charged property. The lithium-ion battery of the invention has excellent fast charging and discharging performance.
Owner:TIANJIN B&M SCI & TECH
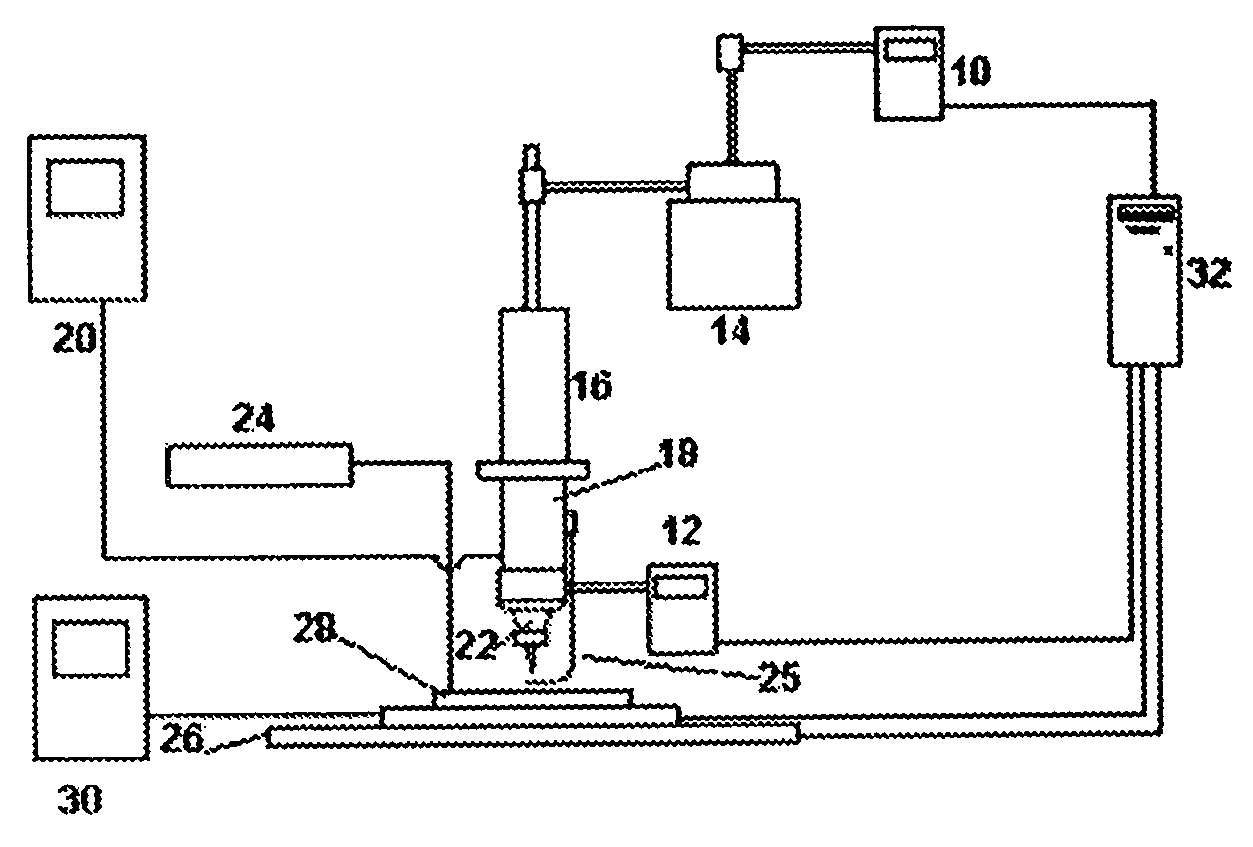
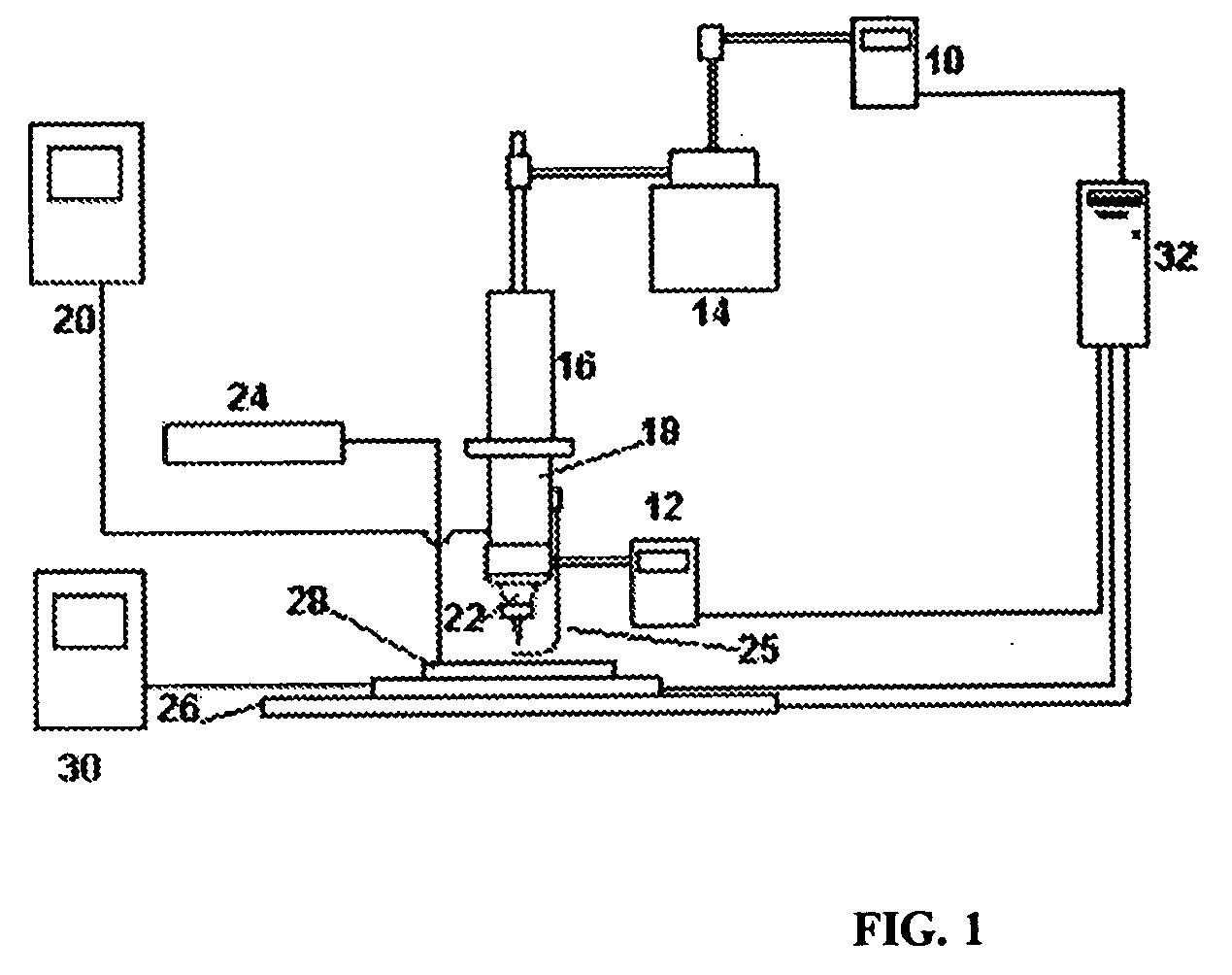
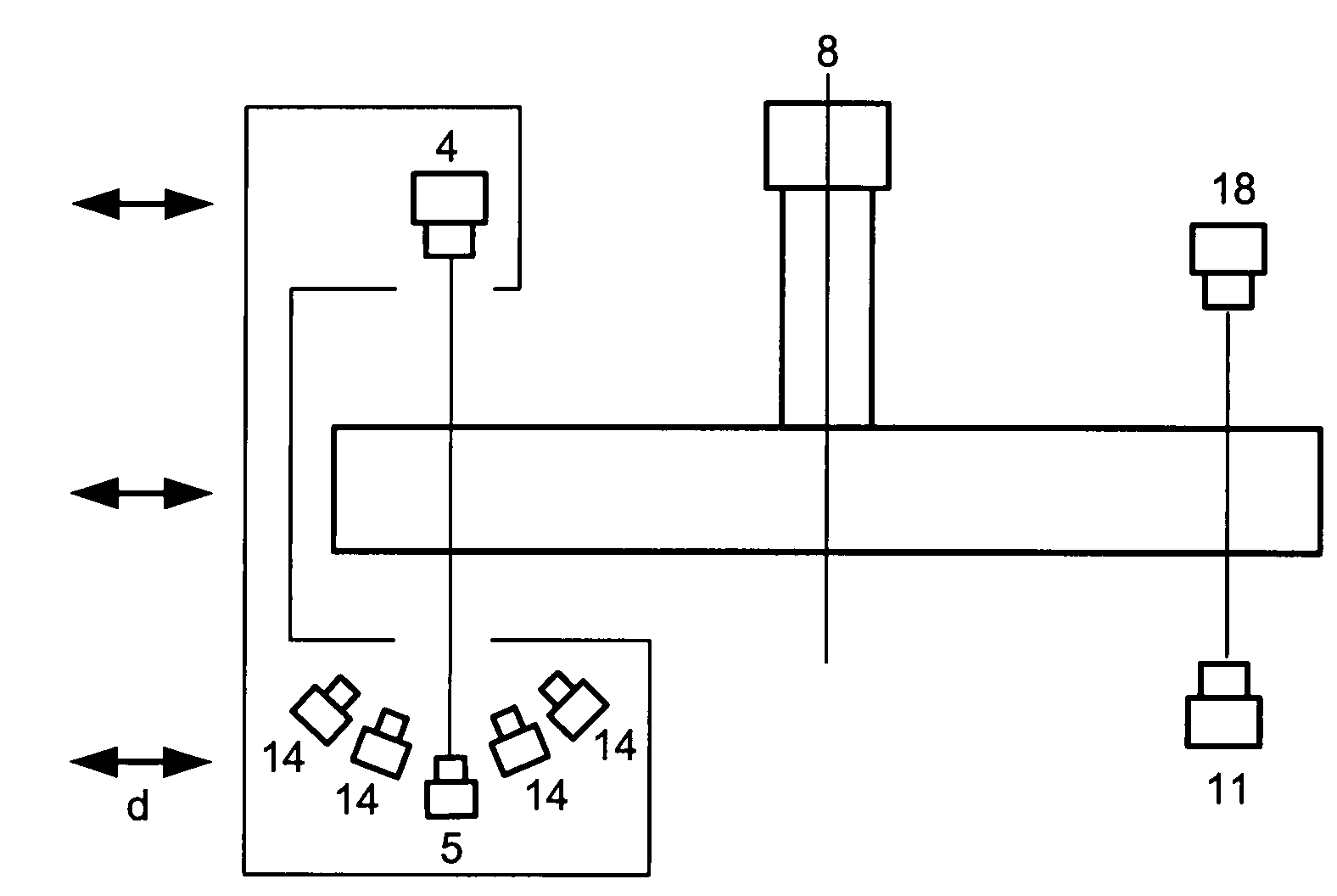
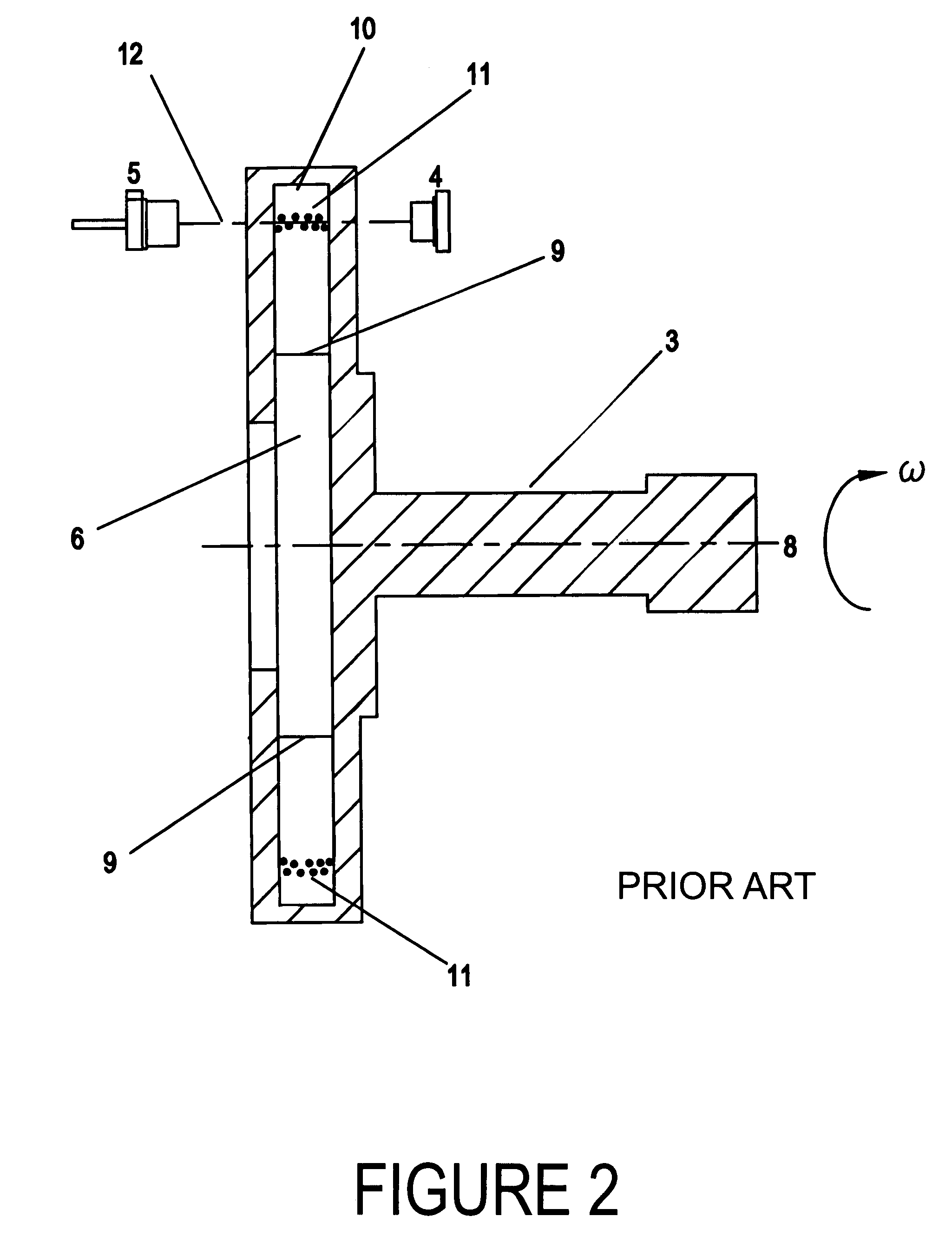
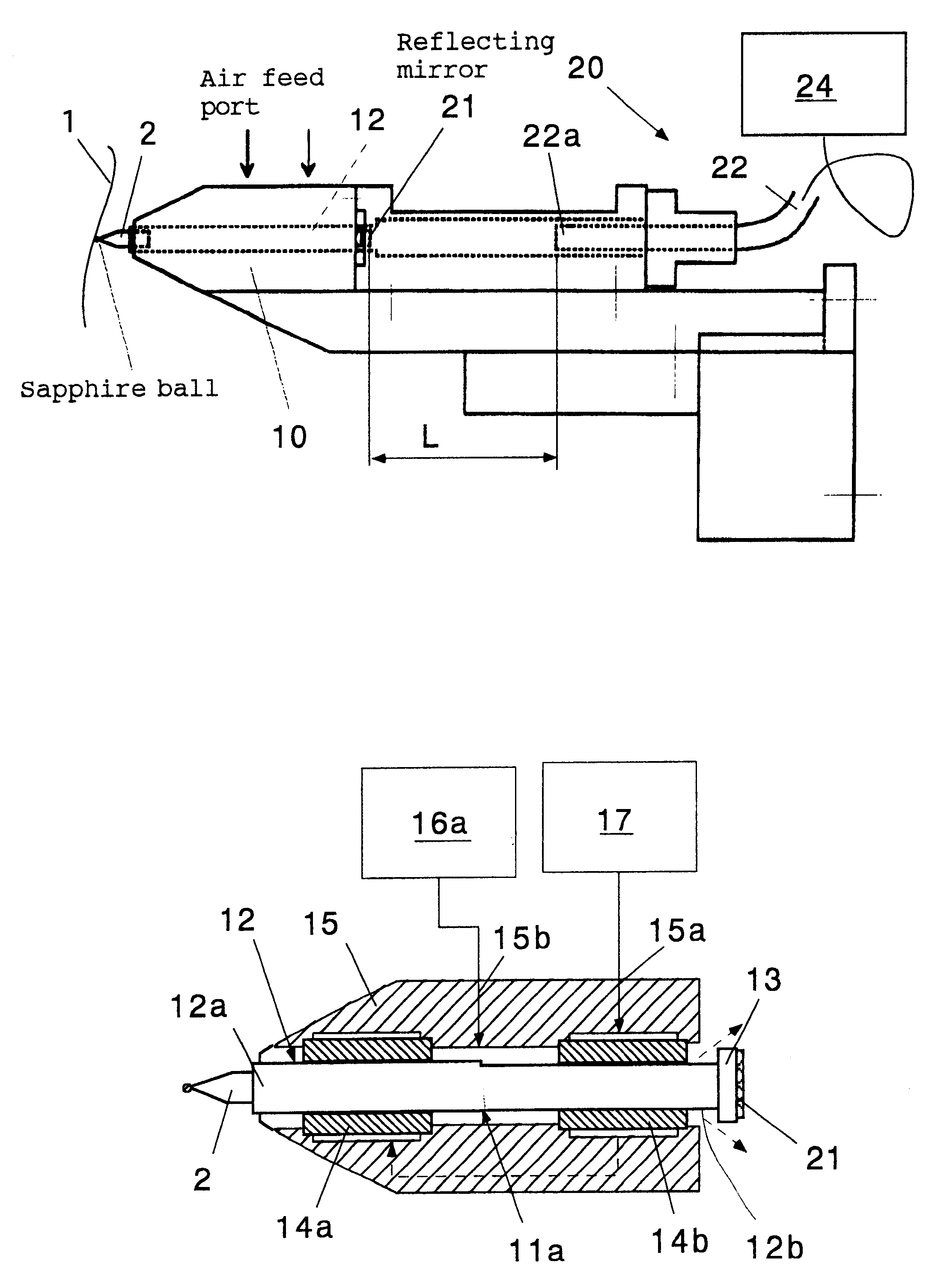
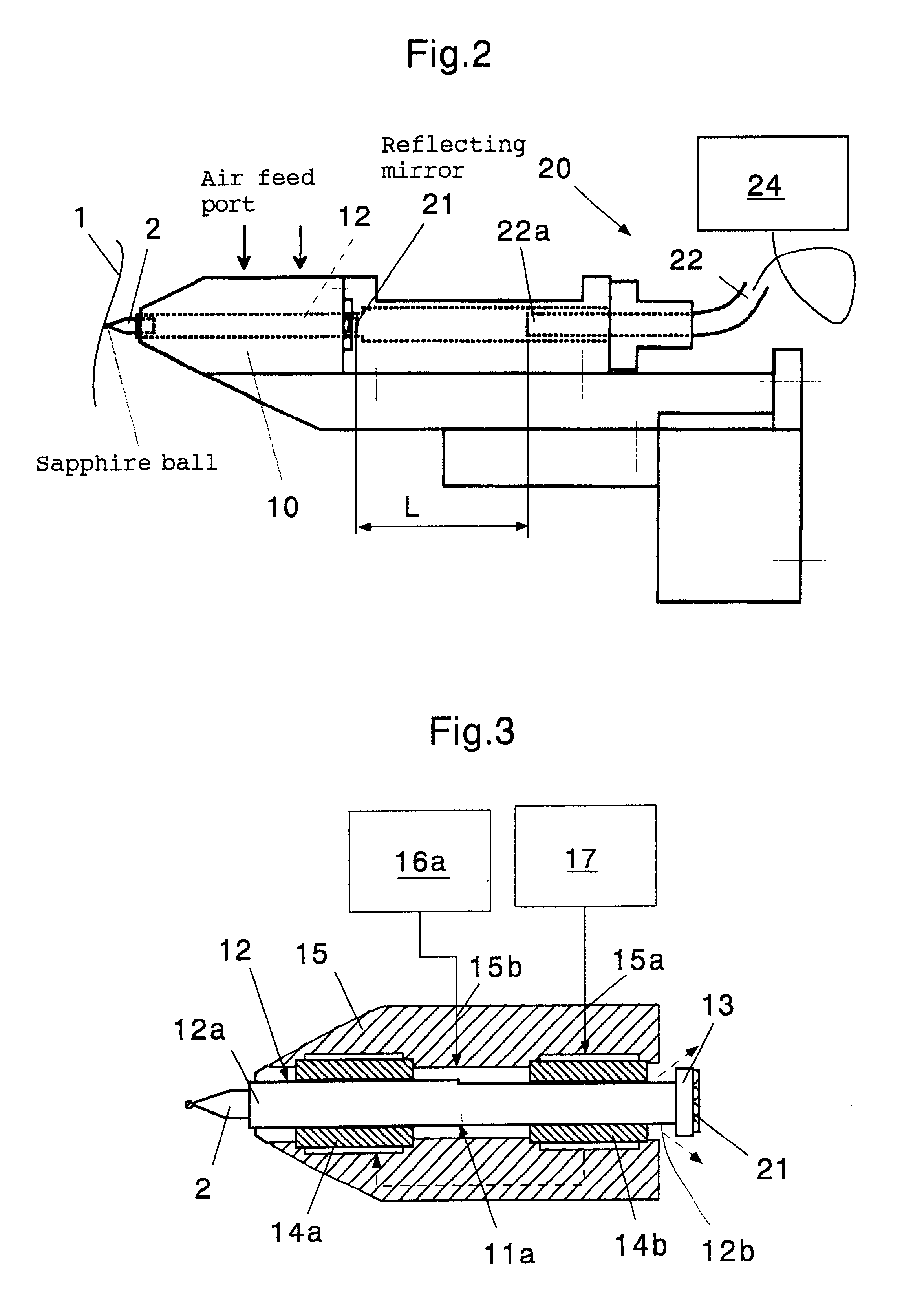
Probe type shape measuring sensor, and NC processing equipment and shape measuring method using the sensor
InactiveUS6539642B1Mechanical counters/curvatures measurementsUsing optical meansAir bearingHigh stiffness
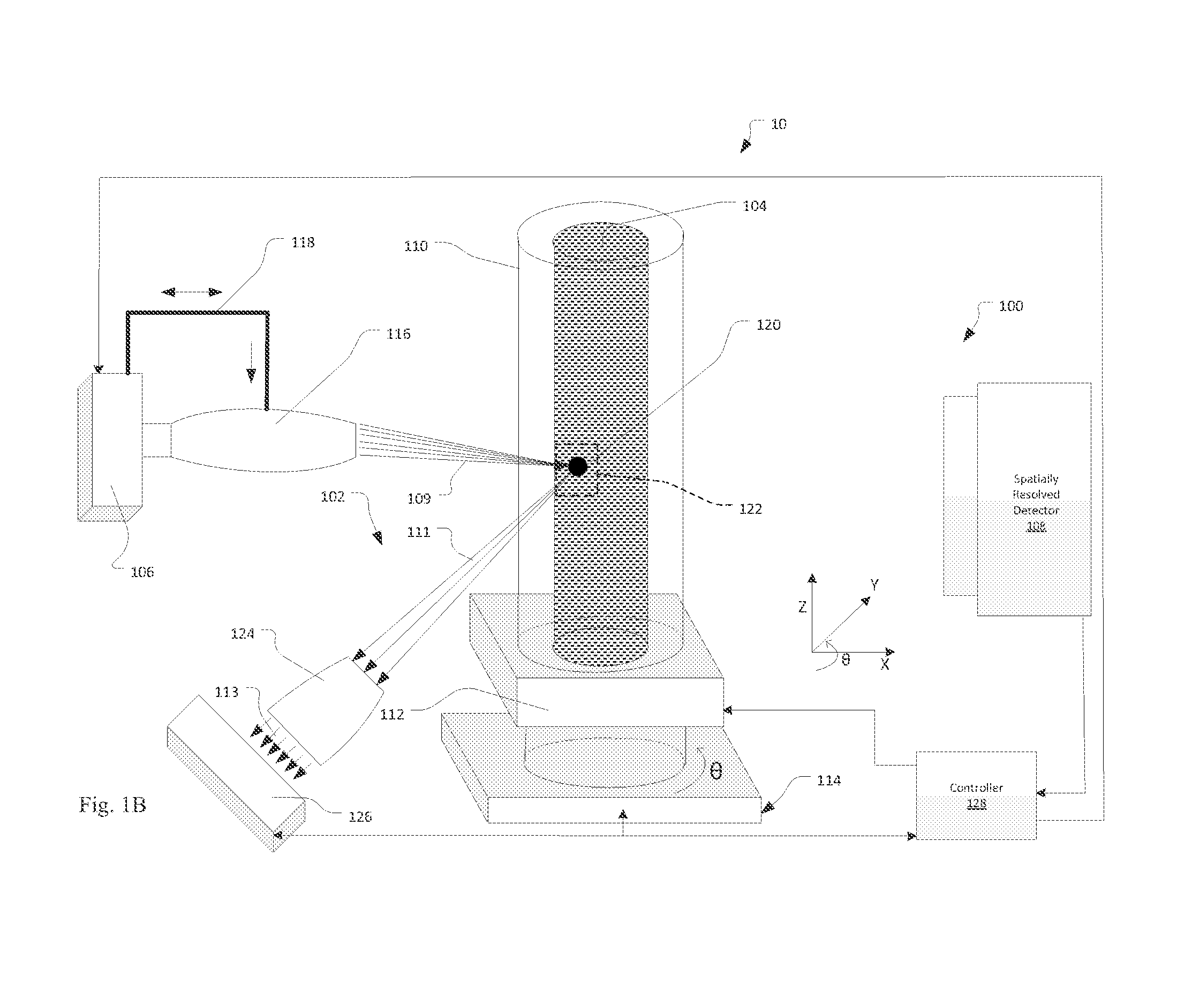
A probe head 10 and a laser interferometric displacement meter 20 are provided. The probe head supports a probe 2 that is capable of contacting a workpiece 1, that is free to move in the direction of the workpiece, and drives the probe towards the workpiece. The displacement meter measures the displacement of the probe with a high accuracy without contact. The probe head 10 is also provided with a probe shaft 12 with steps 11a, 11b at intermediate portions thereof and air bearings 14a, 14b that support the probe shaft on each side of the steps. The air bearings have a high stiffness in the radial direction, and the probe shaft is made to float by using compressed air, thus the resistance of the shaft to sliding is reduced. In addition, another compressed air is supplied to the location of the step and produces a driving force in the direction of the workpiece due to the difference of cross sectional areas on each side of the step, that provides a very small load within a predetermined range. Thereby, the measuring pressure can be adjusted to a constant very small load without reducing the stiffness of the bearings of the probe, and the measuring pressures can be varied freely. Therefore, a sub-micron accuracy of about 0.1 mum can be obtained, and the equipment can be made compact and is easily applied to on-machine measurements.
Owner:RIKEN
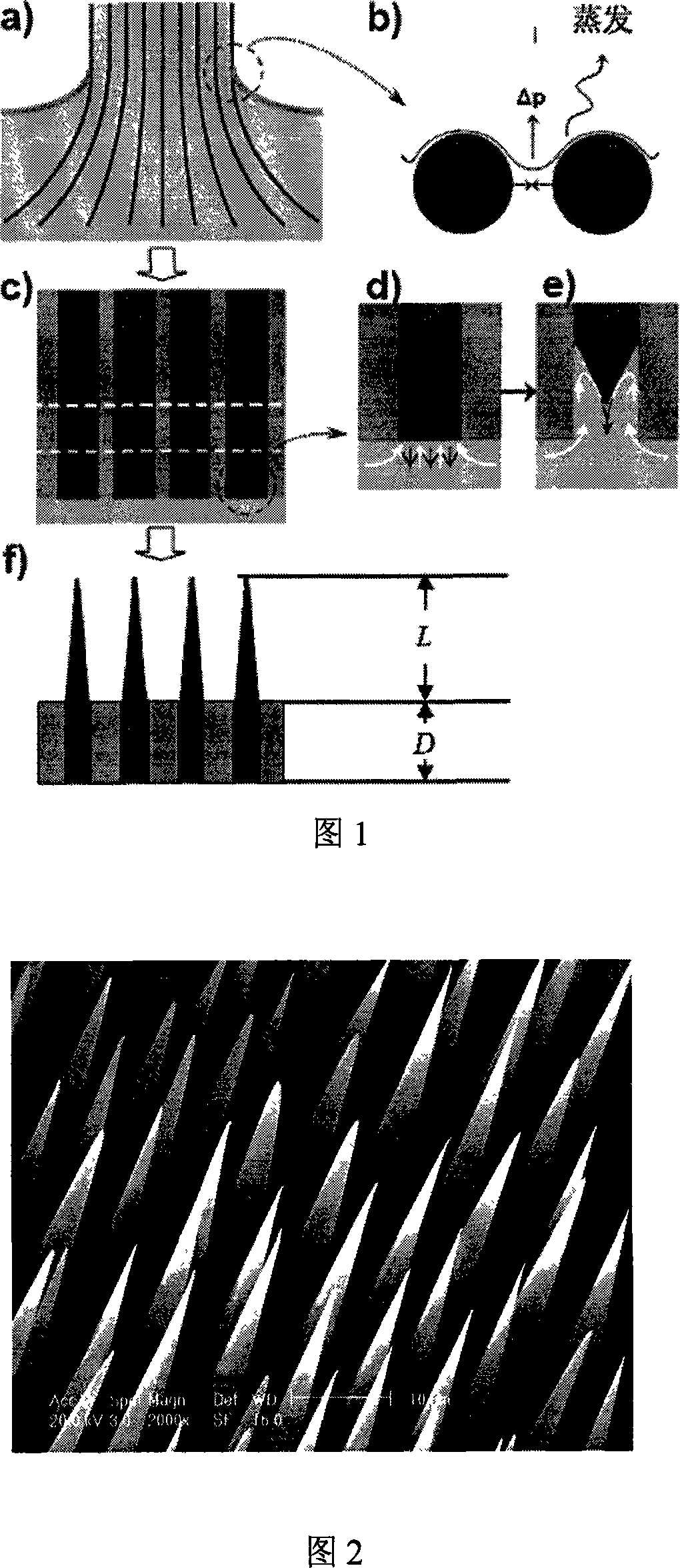
Method for preparing micrometer and submicron probe arrays
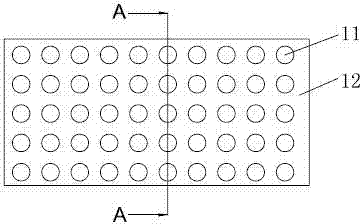
InactiveCN101143705AOrderly rowsReduce manufacturing costSemi-permeable membranesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesFiberMicrometer
The invention discloses a method of preparing a micrometer and sub-micrometer needle array. The method adopts the self-assembly technology and integrates the filling, cutting and controllable corrosion technologies. First, the self-assembly technology is adopted to technically assemble the micrometer / sub-micrometer fiber; and then the polymeric compound is filled, finally the micrometer and sub-micrometer needle array is prepared by the cutting and the controllable corrosion technologies. The invention has the advantages of low cost, no need of complicate equipments and technologies, capability of quick batch production, large area of needle array, smooth needle surface, adjustable diameter, length and taper, etc., and is widely applicable in the detecting, sensing, optical, biology and medicine fields, etc.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
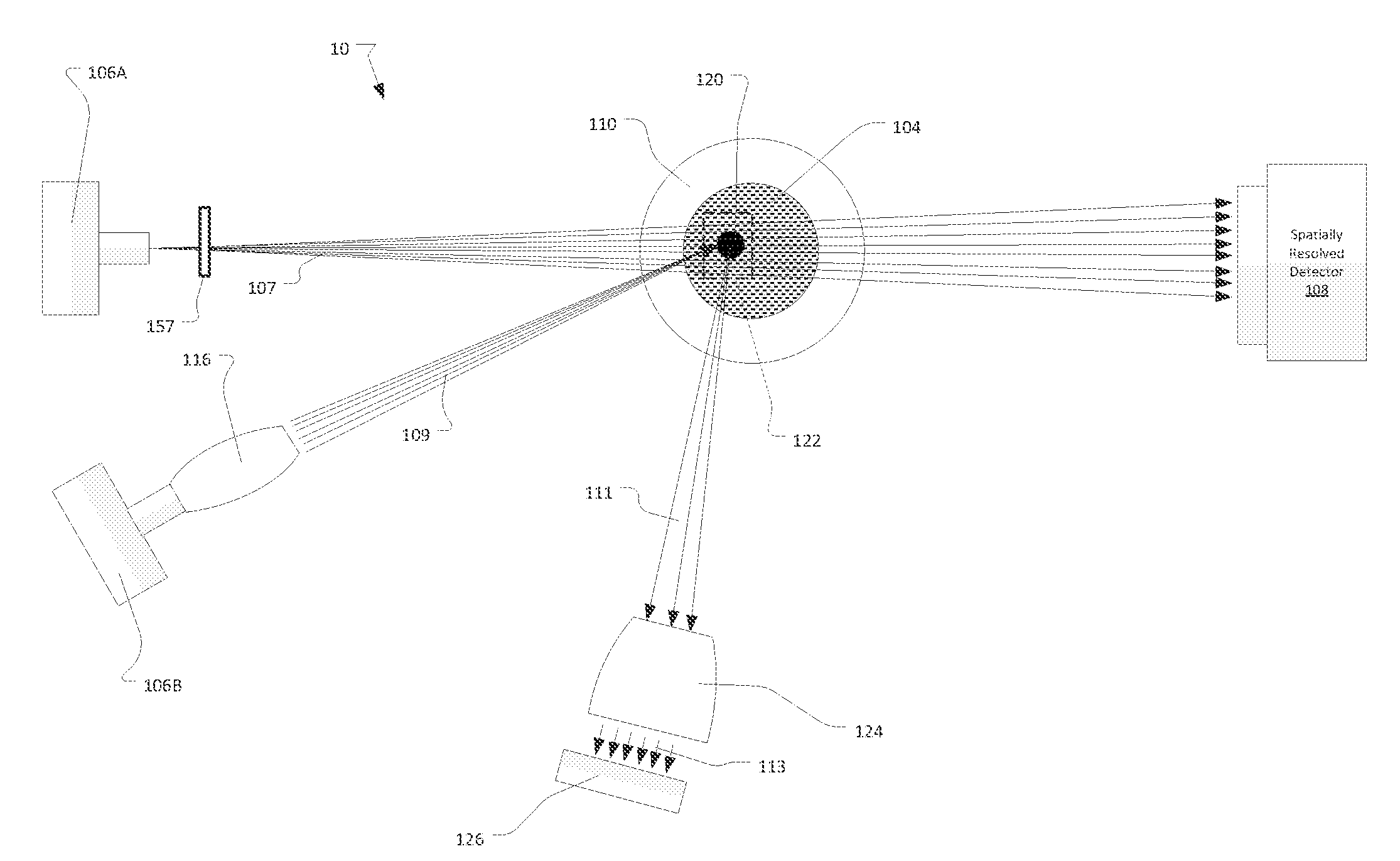
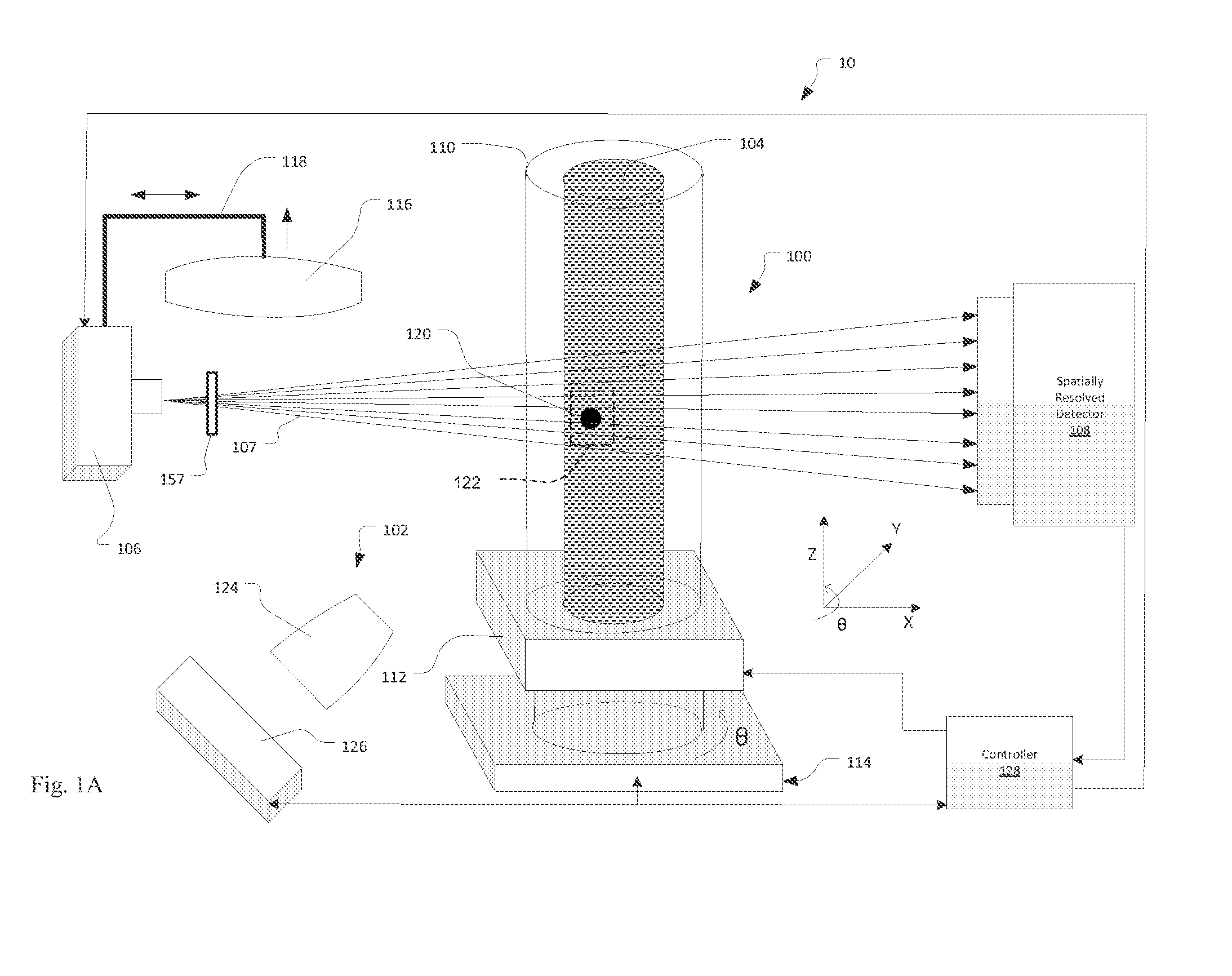
Confocal XRF-CT System for Mining Analysis
ActiveUS20140072095A1Easy to optimizeImproved financialRadiation/particle handlingEarth material testingElemental compositionImage resolution
A correlative evaluation of a sample using an x-ray computed tomography (CT) x-ray fluorescence (XRF) system and the method for analyzing a sample using x-ray CT and XRF is disclosed. The CT / XRF system includes an x-ray CT subsystem for acquisition of volume information and a confocal XRF subsystem for acquisition of elemental composition information. The CT / XRF system also includes a controller for managing the acquisitions by the x-ray CT subsystem and confocal XRF subsystem. Combining sub-micrometer spatial resolution 3-D imaging with elemental composition analysis in 3-D with ppm level sensitivity is important to elemental identification of precious metal grains in crushed and ground ores and floatation tailings in the mining industry.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Super-hydrophobic material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102950099ALow costSimple preparation processPretreated surfacesCoatingsCoatingSurface processing
The invention discloses a preparation method of a super-hydrophobic material. The preparation method includes firstly, etching to form a micrometer or sub-micrometer structure on the surface of a substrate by etching solution; secondly, forming a nano-coating layer on the surface of the substrate with the micrometer or sub-micrometer structure; and thirdly, preparing a low-surface energy substance layer on the nano-coating layer. The invention provides the super-hydrophobic material prepared by the preparation method. The super-hydrophobic material comprises a substrate with the surface having the micrometer or sub-micrometer structure, a nano-coating layer is formed on the surface of the substrate, and a low-surface energy substance layer is formed on the nano-coating layer. The preparation method with low cost is applicable to industrial production and glass surface processing, and the water contact angle of the super-hydrophobic material can be 150 degrees at least.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Method of fabricating imprint lithography template
InactiveUS20080131822A1Improve stabilityHigh hardnessNanoinformaticsPhotomechanical apparatusResistLithographic artist
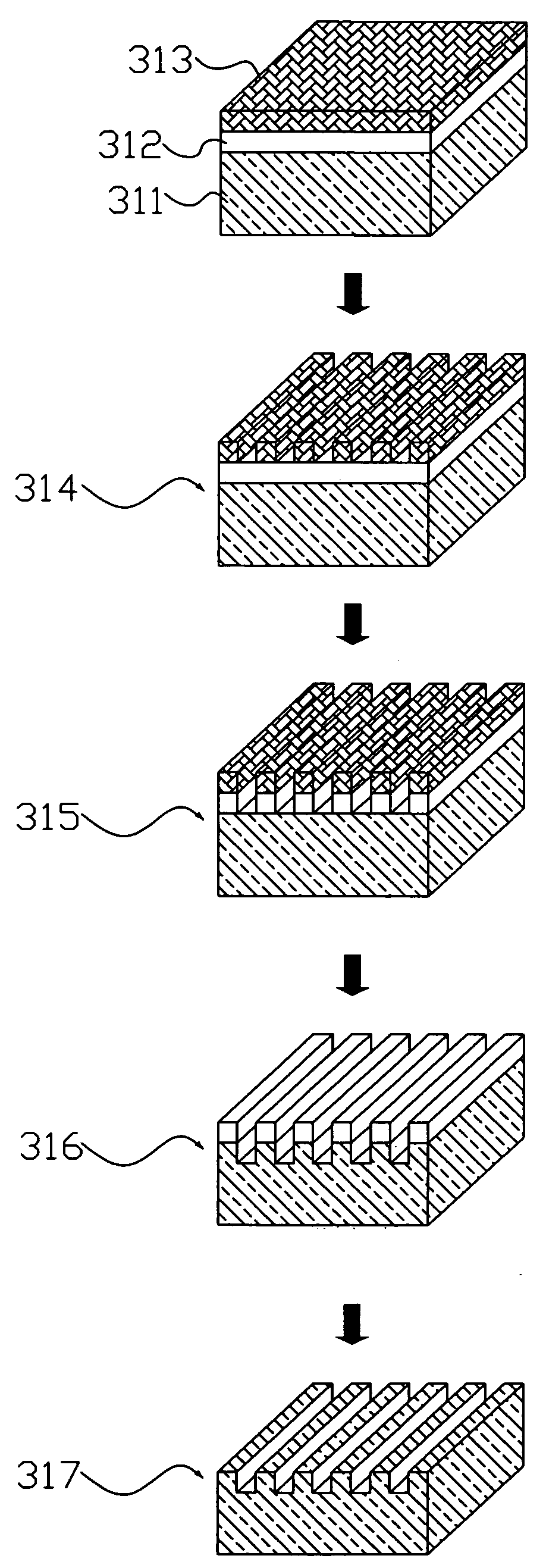
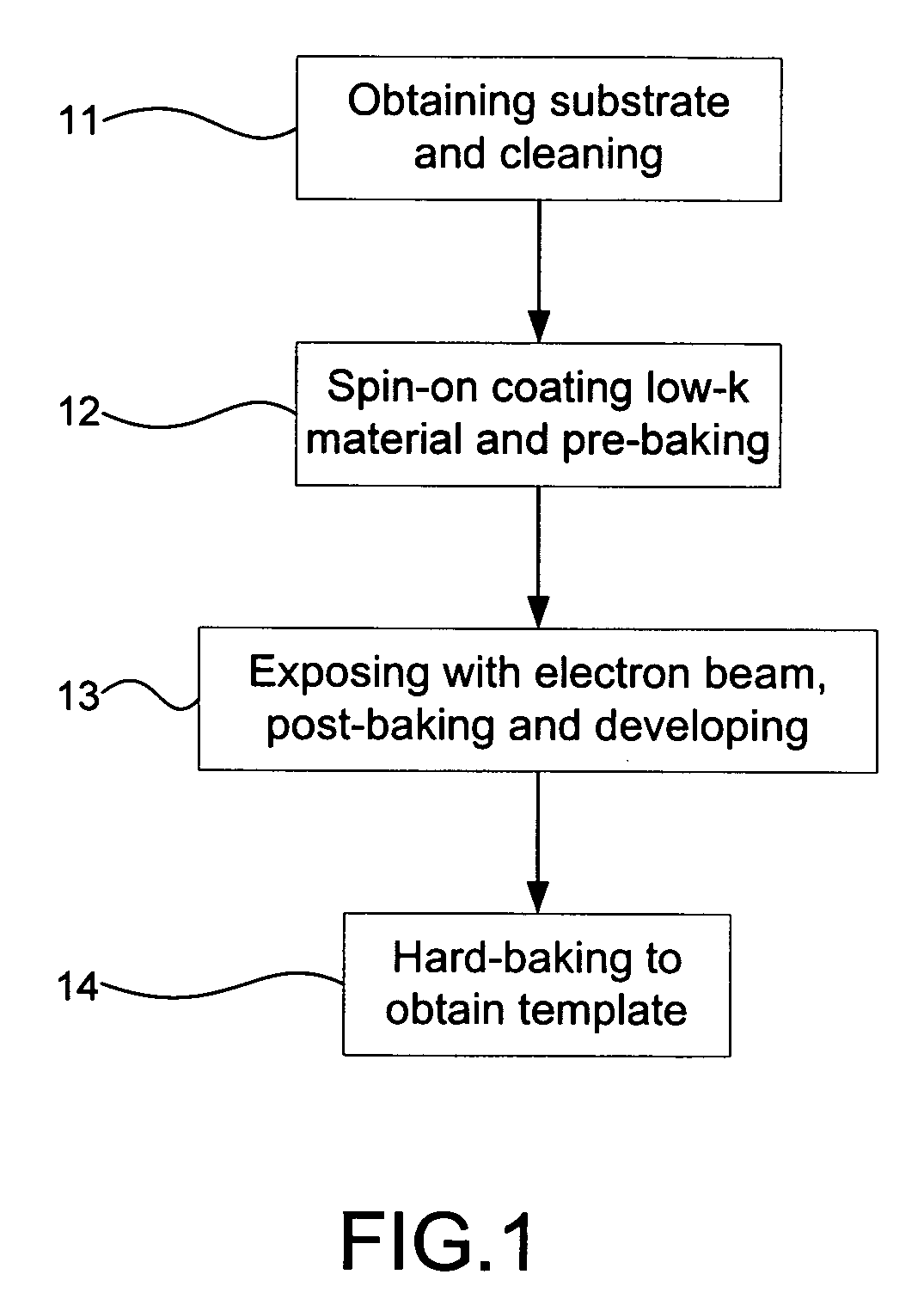
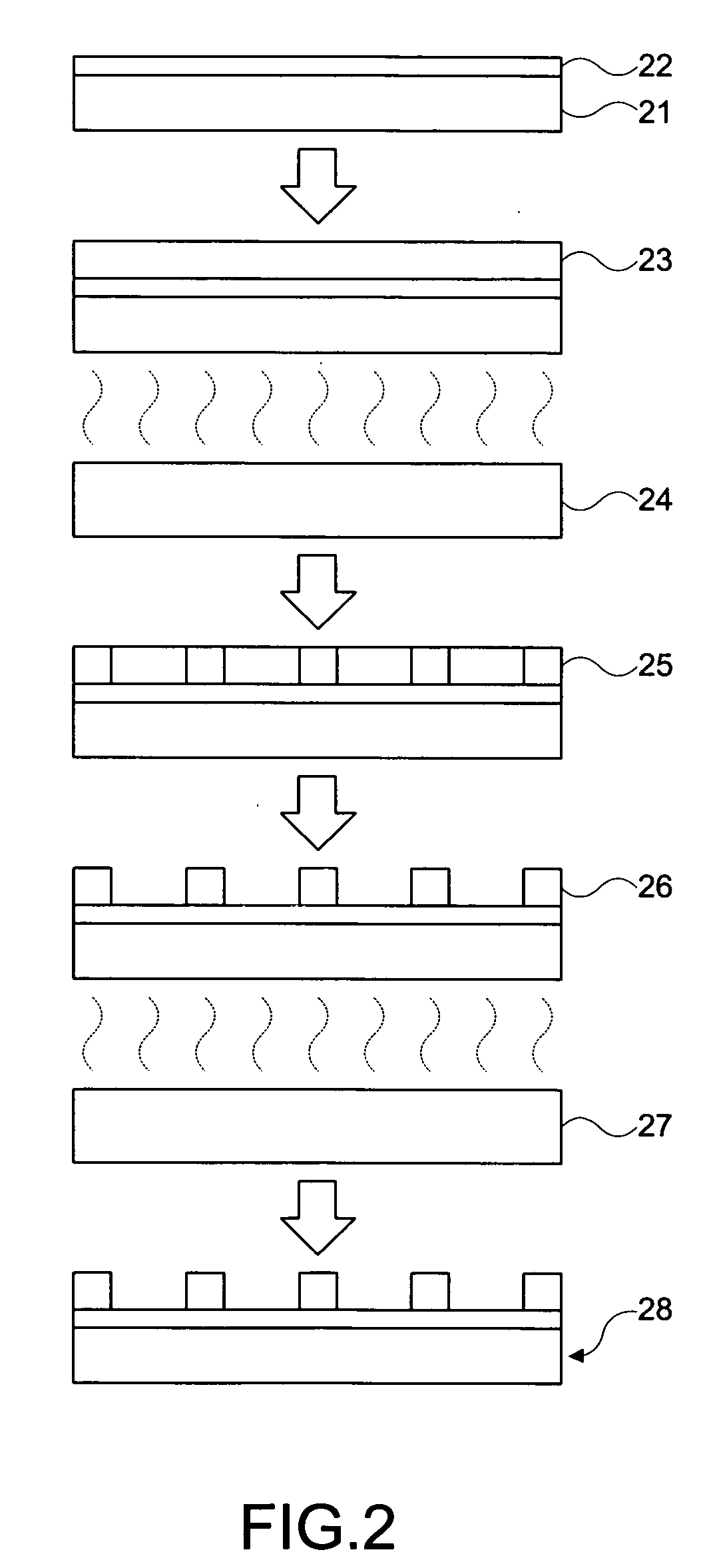
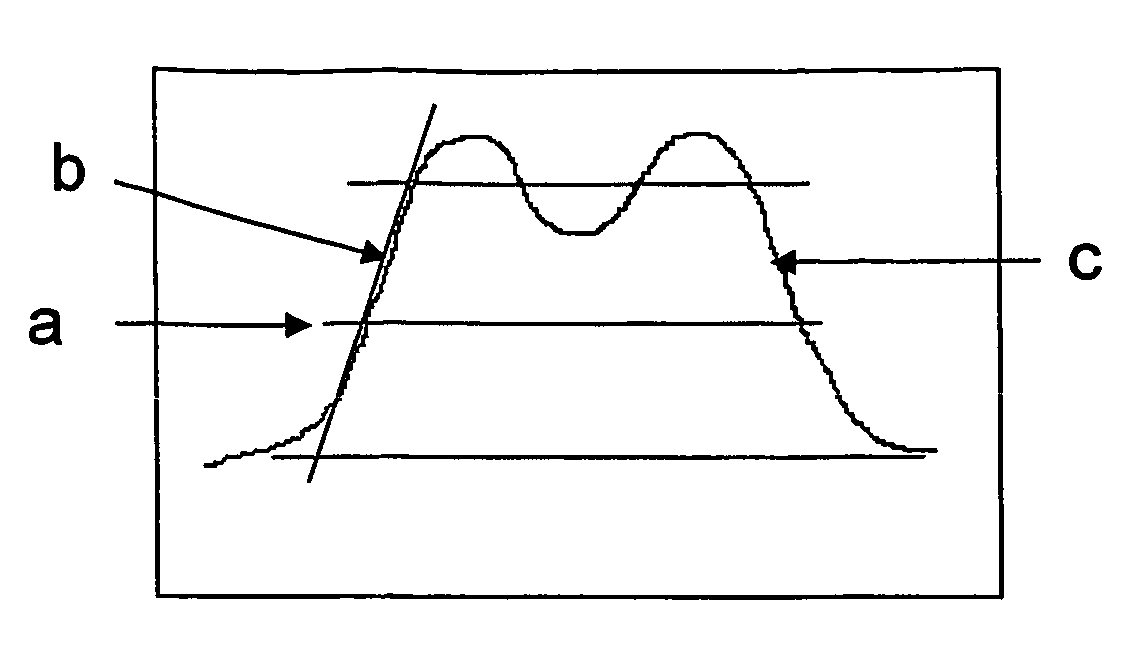
A template, stamp or mold is fabricated by using a low-k material. The structure of the low-k material is transformed when it is baked in a novel heating process. Thus, the template is fabricated to obtain a high hardness and a high aspect-ratio with a low dose of electron beam lithography and an optimized baking process. Consequently, the residual; layer at photoresist bottom is reduced and the time for reactive ion etching is saved. In the end, the stability and the integrity is improved. Hence, the present invention is a solution for fabricating a template, stamp or mold with the feature size from sub-micrometer down to nanometer level.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Method for Particle Size and Concentration Measurement
ActiveUS20080037004A1High resolutionGood concentration sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansParticle size analysisGaussian laser beamSignal mapping
The present invention provides method of particle size and concentration measurement that comprises the steps of: providing a focused, synthesized, non-Gaussian laser beam, causing the beam to interact with the particles, measuring the interaction signal and the number of interactions per unit time of the beam with the particles, and using algorithms to map the interaction signals to the particle size and the number of interactions per unit time to the concentration. The particles are fluid borne, airborne, or on a surface and have a size ranging from sub-micron to thousands of microns. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the focused, synthesized, non-Gaussian laser beam is a dark beam. The non-Gaussian beam can be generated by employing a mask over a Gaussian laser beam or by directly modifying the laser cavity or by combining the beams from several lasers. The measurements can be made using the duration of interaction with a scanning beam, including dark field. The invention further provides a system for particle size and concentration measurement.
Owner:PARTICLE MEASURING SYST
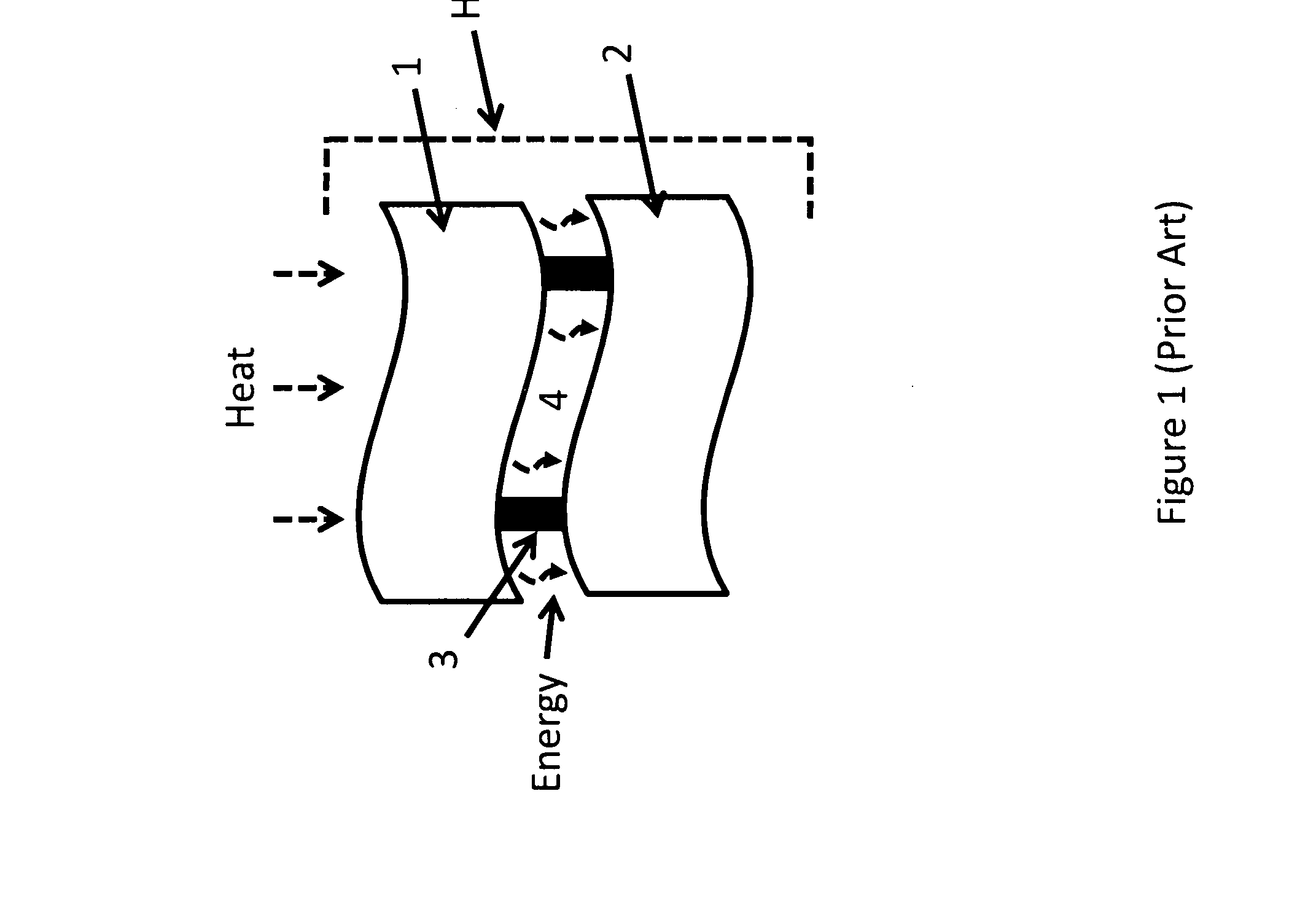
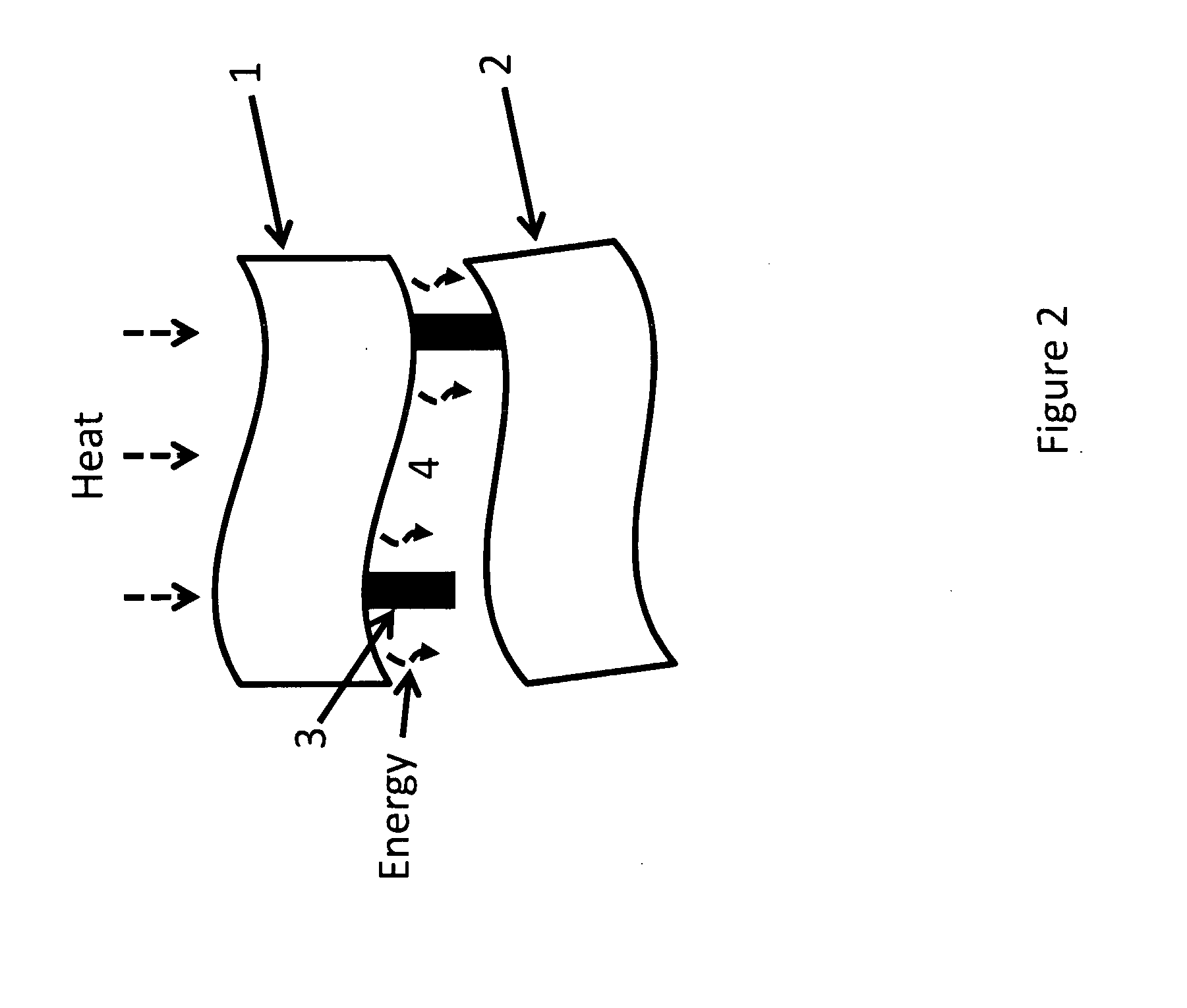
Sub-micrometer gap thermophotovoltaic structure (MTPV) and fabrication method therefor
ActiveUS20100319749A1Reduce manufacturing costPrecise and uniform setting of gap dimensionPV power plantsThermoelectric device detailsEngineeringThermophotovoltaic
An MTPV thermophotovoltaic chip comprising a photovoltaic cell substrate, micron / sub-micron gap-spaced from a juxtaposed heat or infrared radiation-emitting substrate, with a radiation-transparent intermediate window substrate preferably compliantly adhered to the photovoltaic cell substrate and bounding the gap space therewith.
Owner:MTPV POWER CORP
Surface plasmon crystal transducer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101551330AStructural parameters are adjustableSimple preparation processIndividual molecule manipulationScattering properties measurementsMicrosphereTransducer
The invention discloses a surface plasmon crystal transducer and a manufacturing method thereof. The transducer comprises a quasi-three-dimensional metal hemispherical shell membrane with periodic fluctuation surface; the metal hemispherical shell membrane is formed by metal nano hollow hemispherical shells and forms two-dimensional hexagonal close piling arrangement; the adjacent hemispherical shells are connected with each other; and microscopic holes are arranged among any three adjacent hemispherical shells. The manufacturing method of the transducer comprises the following steps of: adopting colloidal crystal obtained by micron or submicron medium microspheres through self-assembly technology as a template; utilizing a physical or chemical deposition method to deposit metal nanoparticles on the surface of the microspheres of the template till the deposition amount of the metal leads the nanoparticles to form a continuous metal hemispherical shell membrane; and utilizing a physical or chemical method to remove the colloidal crystal template so as to obtain the surface plasmon crystal transducer formed by the metal nano hollow hemispherical shells. The invention has the advantages of simple manufacturing process, low cost, good stability, high sensitivity, repeatability and simple operation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method of fabricating a trench capacitor
InactiveUS6251722B1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceEngineering
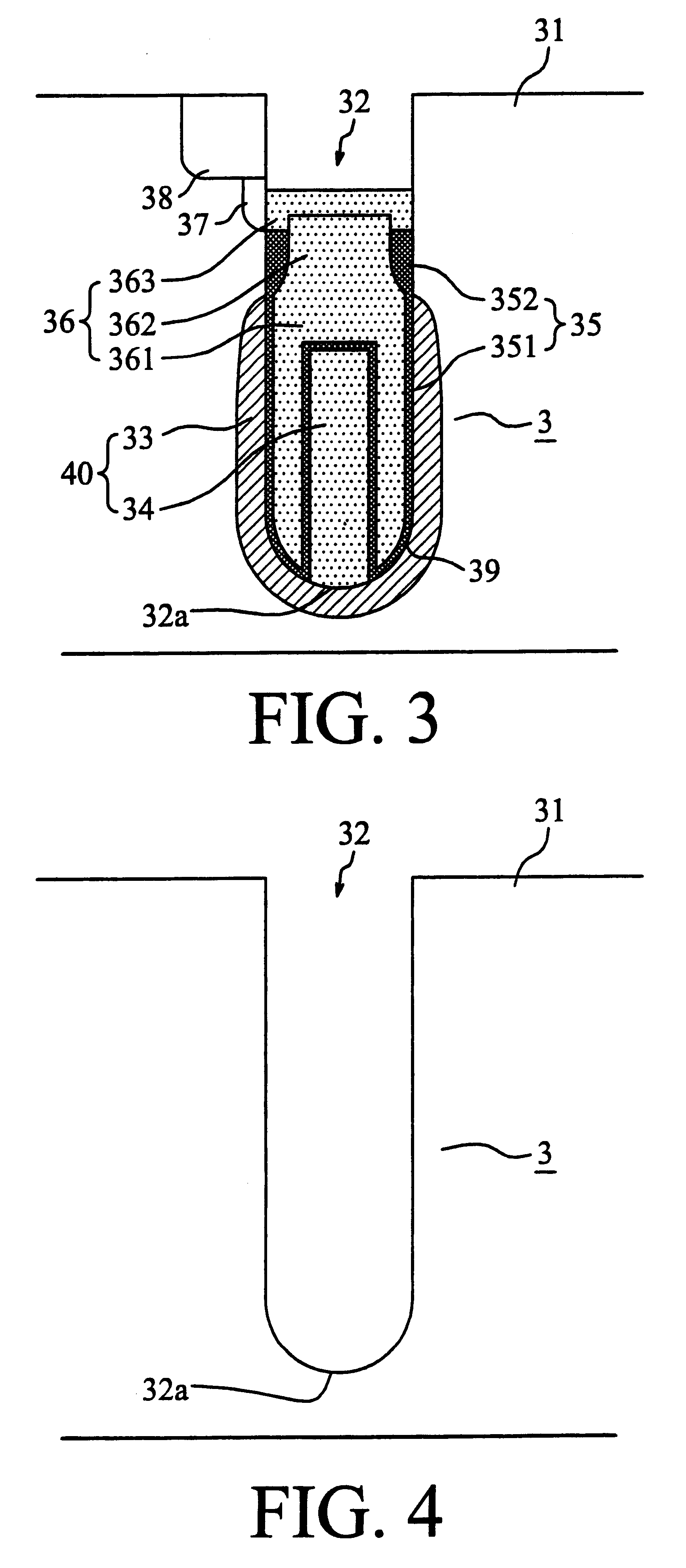
A method of fabricating a trench capacitor having high capacitance for ULSI technology below the sub-micrometer scale is provided. The method includes: form a trench on a semiconductor substrate. The trench has a bottom portion and at least one sidewall on the semiconductor substrate. Then, form a diffusion layer in the silicon substrate for circumscribing the bottom portion of the trench and a predetermined region of its sidewall. After that, form a first polysilicon layer on the bottom portion of the trench and in a manner that a portion of the first polysilicon layer does not contact with the sidewall. Then, form a first dielectric layer to completely cover the first polysilicon layer and the diffusion layer. Then, form an upper electrode layer on top of the trench to at least completely cover the first dielectric layer. Eventually, the contact area between the diffusion layer and the dielectric layer has been largely increased so as to maintain sufficient capacitance.
Owner:PROMOS TECH INC
Detersive compositions containing hydrophobic benefit agents pre-emulsified using sub-micrometer-sized insoluble cationic particles
InactiveUS20060154836A1Improve stabilityIncrease depositionInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsCosmetic preparationsEdge surfaceNitrogen
A cationic oil-in-water emulsion for addition to detersive compositions comprising a hydrophilic cationic polymer, an oil-soluble anionic polymer, and a hydrophobic benefit agent in the oil phase made by adding the benefit agent to a hydrophobic liquid; thickening the oil phase with an organophillic smectite clay reacted at clay platelet surfaces to make the clay platelet surfaces hydrophobic while the edge surfaces of the clay remain hydrophilic, such that the benefit agent is adsorbed at an oil / water interface in the emulsion, wherein the anionic polymer is capable of adsorbing the hydrophobic benefit agent at an oil / water interface of the emulsion, and the a hydrophilic, cationic polymer has a cationic nitrogen content of at least 6% by weight, that is incompatible with anionic surfactants, being insoluble in anionic-surfactant solutions containing an amount of 3% or higher of an anionic surfactant, and the hydrophilic cationic polymer has a cationic nitrogen content of at least 0.1% by weight and has a molecular weight of at least 600,000 Dalton.
Owner:AMCOL INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Apparatuses and methods for maskless mesoscale material deposition
InactiveUS20060233953A1High resolutionPretreated surfacesLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingLine widthEngineering
Apparatuses and processes for maskless deposition of electronic and biological materials. The process is capable of direct deposition of features with linewidths varying from the micron range up to a fraction of a millimeter, and may be used to deposit features on substrates with damage thresholds near 100° C. Deposition and subsequent processing may be carried out under ambient conditions, eliminating the need for a vacuum atmosphere. The process may also be performed in an inert gas environment. Deposition of and subsequent laser post processing produces linewidths as low as 1 micron, with sub-micron edge definition. The apparatus nozzle has a large working distance—the orifice to substrate distance may be several millimeters—and direct write onto non-planar surfaces is possible.
Owner:OPTOMEC DESIGN CO
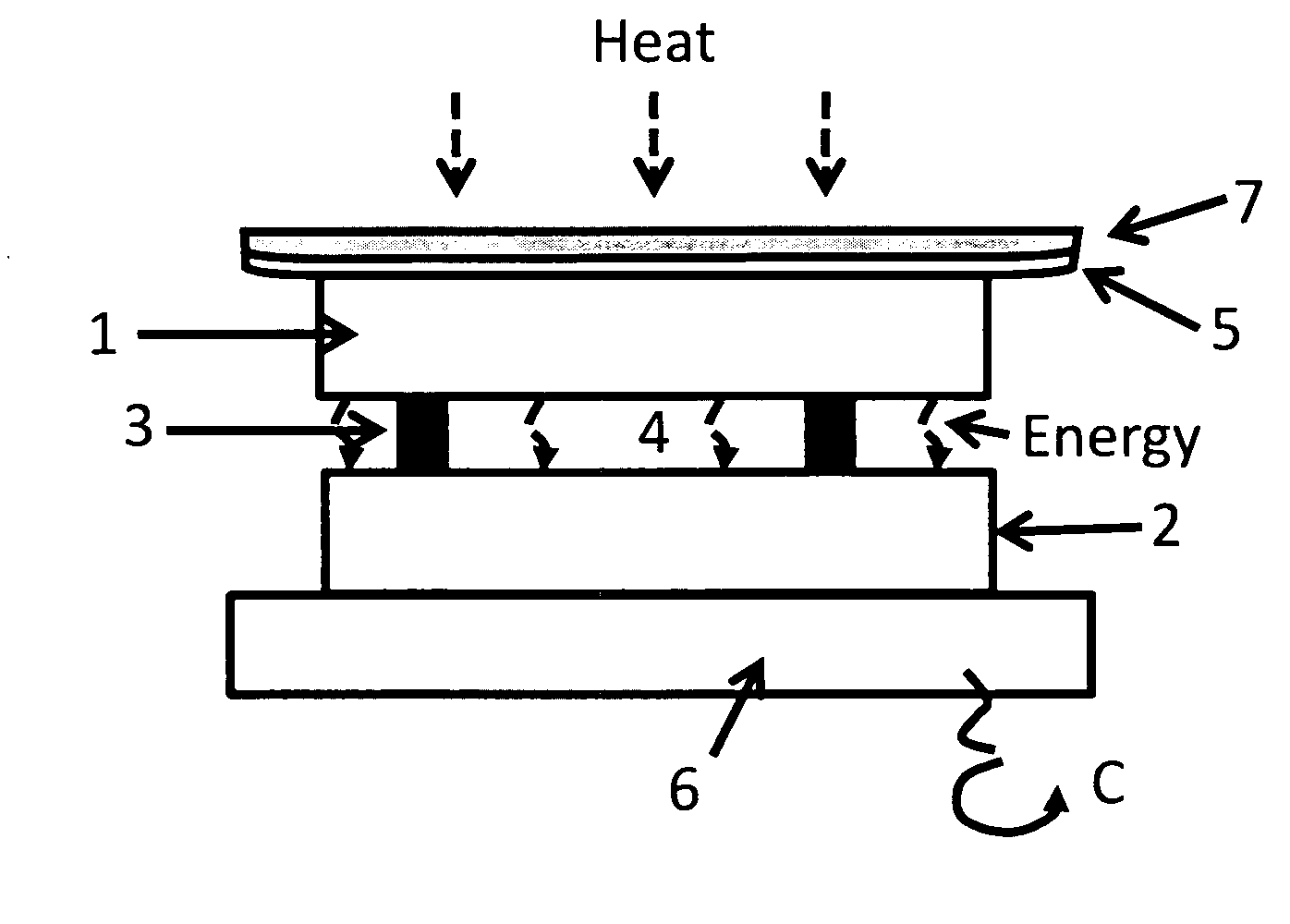
Method and structure, using flexible membrane surfaces, for setting and/or maintaining a uniform micron/sub-micron gap separation between juxtaposed photosensitive and heat-supplying surfaces of photovoltaic chips and the like for the generation of electrical power
ActiveUS20090277488A1Thermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentPV power plantsLight CellField energy
A near-field energy conversion structure and method of assembling the same, utilizing a sub-micrometer “near field” gap between juxtaposed photocell infrared radiation receiver and heat emitter surfaces, wherein compliant membrane structures, preferably fluid-filled, are interposed in the structure.
Owner:MTPV POWER CORP
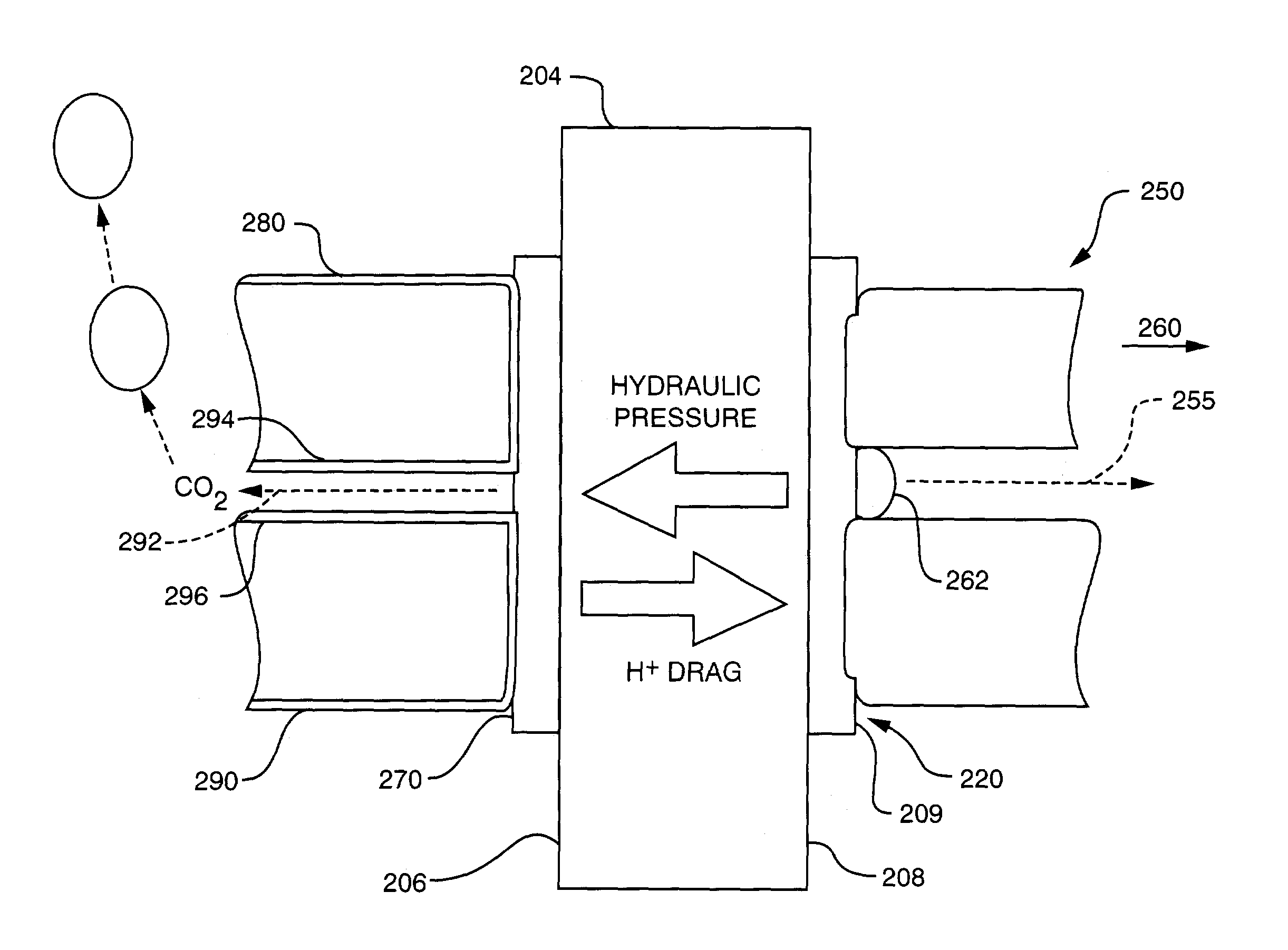
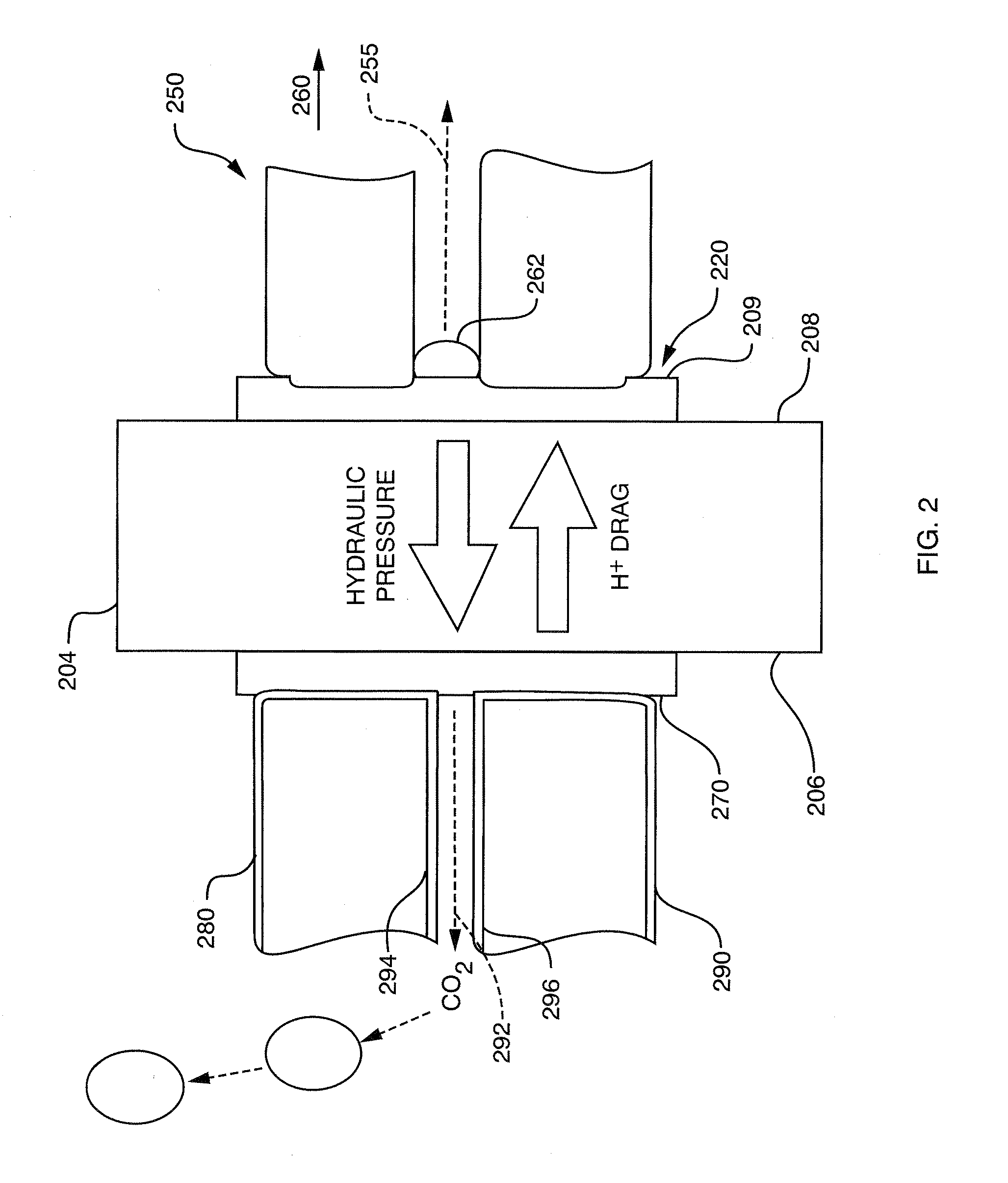
Passive water management techniques in direct methanol fuel cells
InactiveUS7282293B2Increase water flowConvenient paymentWater management in fuel cellsActive material electrodesWater vaporLiquid water
Passive water management techniques are provided in an air-breathing direct oxidation fuel cell system. A highly hydrophobic component with sub-micrometer wide pores is laminated to the catalyzed membrane electrolyte on the cathode side. This component blocks liquid water from traveling out of the cathode and instead causes the water to be driven through the polymer membrane electrolyte to the cell anode. The air-breathing direct oxidation fuel cell also includes a layer of cathode backing and additional cathode filter components on an exterior aspect of the cell cathode which lessen the water vapor escape rate from the cell cathode. The combination of the well laminated hydrophobic microporous layer, the thicker backing and the added filter layer, together defines a cathode structure of unique water management capacity, that enables to operate a DMFC with direct, controlled rate supply of neat (100%) methanol, without the need for any external supply or pumping of water. The cell anode is provided with a hydrophilic backing layer. When the water is driven through the polymer membrane electrolyte from the cell cathode to the cell anode chamber, it is available for the anodic reaction, and any excess water is carried out along CO2 ventilation channels to the outside environment.
Owner:MTI MICROFUEL CELLS
Method and device for laser-assisted separation of a portion from a sheet glass element
ActiveUS20180134606A1Easy to cleanGlass severing apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesFiberFlat glass
A method for separating a portion from a sheet glass element having a thickness of at least 2 millimeters along an intended separation line that divides the sheet glass element into the portion and a remaining main part is provided. The method includes producing filamentary damages comprising sub-micrometer hollow channels in a volume of the glass sheet element adjacently aligned along the separation line; and heating and / or cooling the glass sheet element to cause expansion and / or contraction so that the portion detaches from the main part along the separation line. The portion and the remaining main part each remain intact as a whole. The step of producing the filamentary damages includes generating a plasma within the volume with laser pulses of an ultrashort pulse laser; and displacing points of incidence of the laser pulses over a surface of the glass sheet element along the separation line.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Method for affirming fatal fault in deep-sub-micrometer semiconductor device
InactiveCN1801470AQuickly assess damageQuickly assess critical flaws that have failedSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationThermodynamicsElectron microscope
The confirmation method for critical defect in semiconductor device of deep sub-micron comprises: step S101, using TEM to qualitative and local detect device sample to determine whether there is silicon crystal defect / dislocation defect and defect type; step S102, if there is defect, using SEM to detect sample, eroding with solution the sample; step S103, detecting sample section with SEM to confirm the film layer position of defect and whether it is fetal. Wherein, the SEM detecting sample erosion solution comprises HNO3, CH3COOH, HF and Cu(NO3)2.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
Methods and apparatus of aligning surfaces
ActiveUS20070195084A1Improperly formedCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputation using non-denominational number representationPhotonicsEngineering
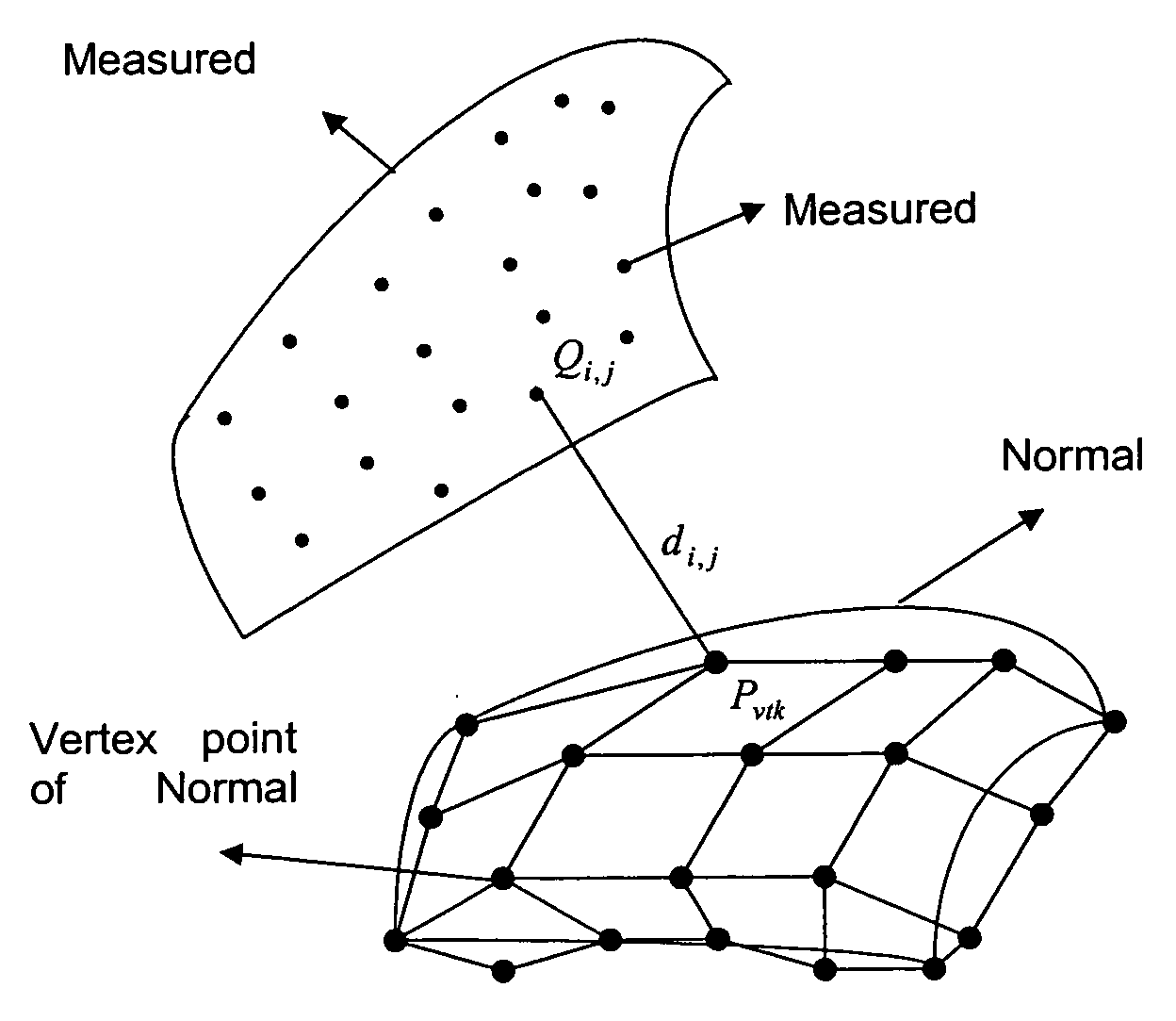
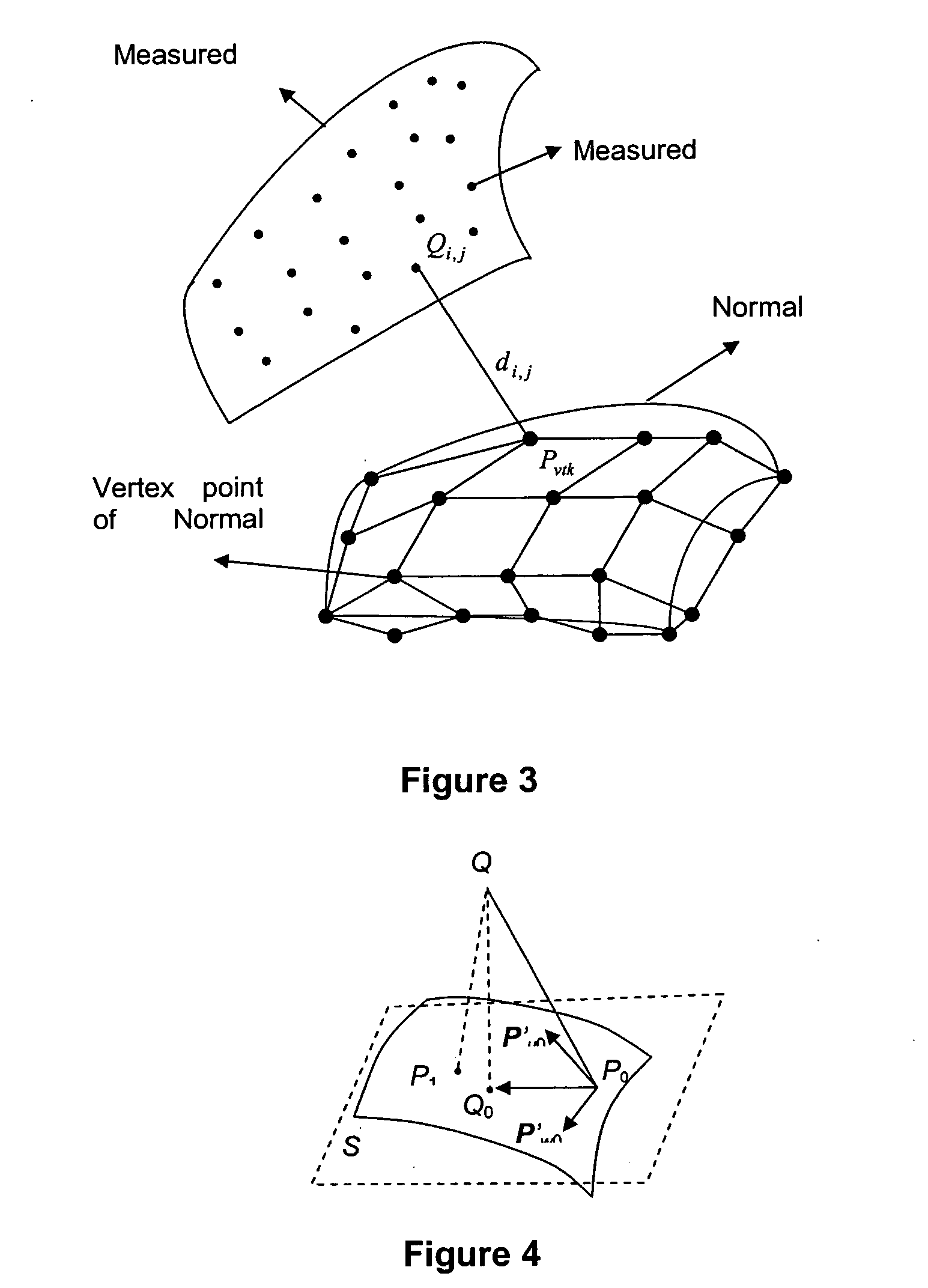
Ultra-precision freeform surfaces are important to the development of complex and micro-optical-electro-mechanical devices used in many photonics and telecommunication products such as F-theta lenses for laser printers. These surfaces are complex and large scale surface topologies with shapes that generally possesses no rotational symmetry. Due to the geometrical complexities of these ultra-precision freeform surfaces, it is difficult to characterize the form accuracy and surface quality of freeform optical surfaces. The method of this invention is based on feature-point pre-fixture, and iterative precision alignment algorithm, which can provide sufficient capability of form characterization for ultra-precision freeform surfaces with form accuracy down to below sub-micrometer range
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Interferometric miniature grating encoder readhead using fiber optic receiver channels
ActiveUS20050068539A1Highly accurate and economical and high configurationOvercome disadvantagesMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansFiberPhase grating
An interferometric fiber optic encoder readhead for sensing the displacement of a scale grating is disclosed. The detector channels of the readhead are fiber optic detector channels having respective phase grating masks. The fiber optic encoder readhead is configured to detect the displacement of interference fringes arising from the scale grating. In various exemplary embodiments, the fiber optic readhead is constructed and operably positioned according to various design relationships that insure a compact mounting and a relatively ideal sinusoidal signal as a function of displacement. Accordingly, high levels of displacement signal interpolation may be achieved, allowing sub-micrometer displacement measurements. The fiber optic encoder readhead may be assembled in a particularly accurate and economical manner and may be provided in a package with dimensions on the order of 1-2 millimeters.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Passive water management techniques in direct methanol fuel cells
InactiveUS20080032182A1Neat, or highly concentrated methanol fuel supplyOvercome disadvantagesWater management in fuel cellsActive material electrodesWater vaporLiquid water
Passive water management techniques are provided in an air-breathing direct oxidation fuel cell system. A highly hydrophobic component with sub-micrometer wide pores is laminated to the catalyzed membrane electrolyte on the cathode side. This component blocks liquid water from traveling out of the cathode and instead causes the water to be driven through the polymer membrane electrolyte to the cell anode. The air-breathing direct oxidation fuel cell also includes a layer of cathode backing and additional cathode filter components on an exterior aspect of the cell cathode which lessen the water vapor escape rate from the cell cathode. The combination of the well laminated hydrophobic microporous layer, the thicker backing and the added filter layer, together defines a cathode structure of unique water management capacity, that enables to operate a DMFC with direct, controlled rate supply of neat (100%) methanol, without the need for any external supply or pumping of water. The cell anode is provided with a hydrophilic backing layer. When the water is driven through the polymer membrane electrolyte from the cell cathode to the cell anode chamber, it is available for the anodic reaction, and any excess water is carried out along CO2 ventilation channels to the outside environment.
Owner:MTI MICROFUEL CELLS
One-step wet black silicon preparation and surface treatment method
ActiveCN106024988AReduce the probability of electric leakageImprove absorption efficiencyAfter-treatment detailsFinal product manufactureSilicon cellPolymer
The invention provides a one-step wet black silicon preparation and surface treatment method, which comprises the steps of enabling a silicon wafer with a surface damage layer being removed to be immerged into a corrosive liquid so as to prepare black silicon through reaction, wherein the corrosive liquid is a mixed aqueous solution of a metal ion containing concentrated hydrofluoric acid, an oxidizing agent and a high-molecular polymer; and enabling the black silicon to be immerged into a surface treatment corrosive liquid so as to carry out surface optimization treatment, and acquiring a silicon wafer with a sub-micrometer structure and uniform texturing, wherein the surface treatment corrosive liquid is an additive containing mixed acid aqueous solution. The wet black silicon preparation method provided by the invention is simple in process and low in cost, the texturing surface of the black silicon after corrosion treatment is uniform and has no sharp boundary, and the reflectivity is 7-15%. The one-step wet black silicon preparation and surface treatment method greatly improves the absorption efficiency of a silicon cell for light, a solar cell prepared by using the black silicon prepared according to the method has low cell electric leakage rate, stable open-circuit voltage and high conversion efficiency.
Owner:湖州三峰能源科技有限公司
Hydrophilic-underwater oleophobic polymer porous membrane, preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN104368247AHigh mechanical strengthEfficient separationSemi-permeable membranesFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesMicro nanoEngineering production
The invention discloses a hydrophilic-underwater oleophobic polymer porous membrane, a preparation method and applications thereof. The hydrophilic-underwater oleophobic polymer porous membrane is a polymer matrix membrane. The membrane surface has a coarse micro-nano level porous structure. Nano level, micrometer level and / or sub-micrometer level tunnels are distributed in the membrane. The static contact angle between the membrane and water is less than 10 degrees, and the underwater static contact angle between the membrane and oil is greater than 130 degrees. The provided membrane can be used to separate and purify oil-water mixture and emulsified oil-water generated by chemical engineering production, daily life, crude oil leakage accidents, and the like, and has a very important application value and wide application range.
Owner:SUZHOU BINARY CENTURY NANO TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com