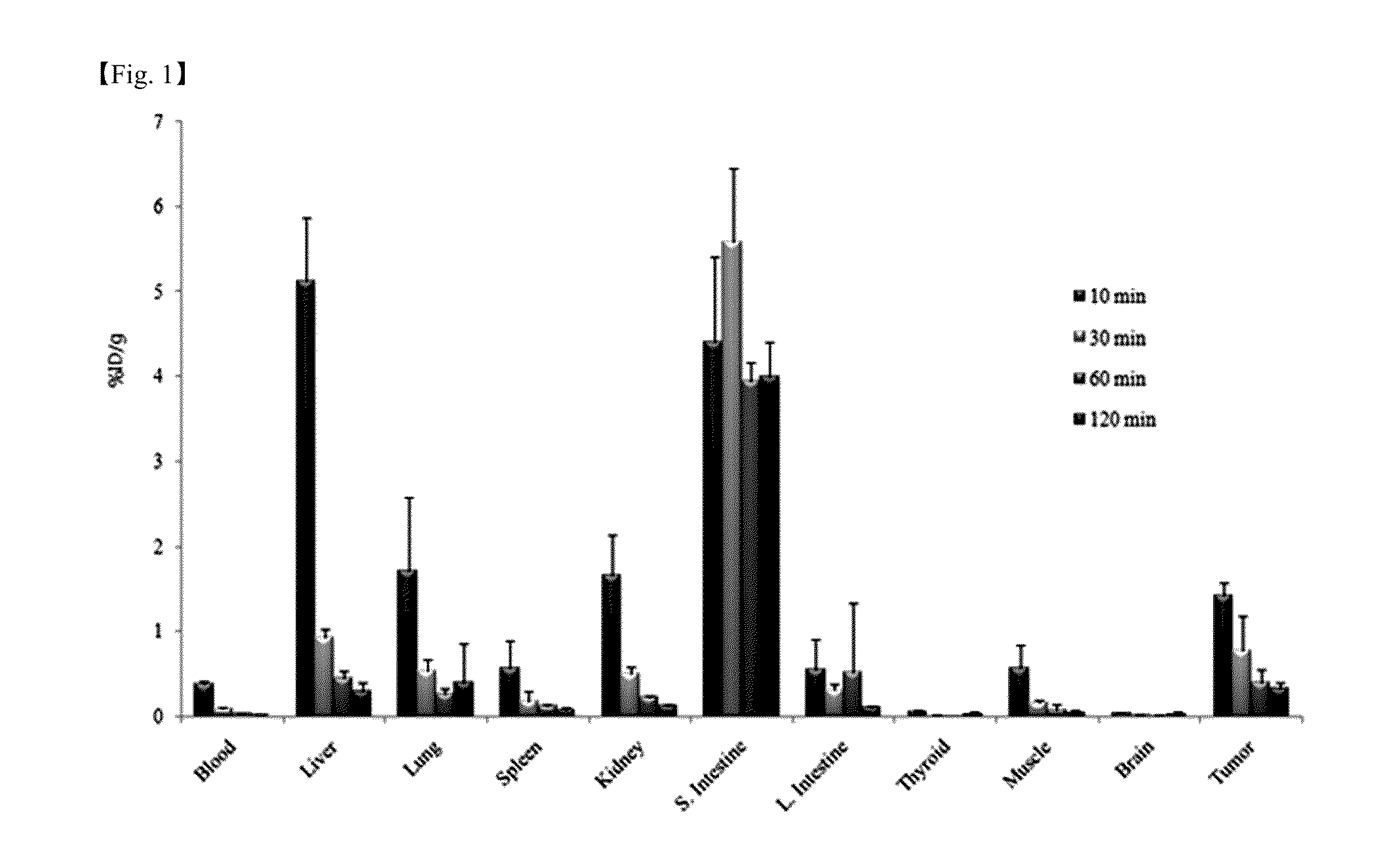
Patents
Literature
51 results about "Tail vein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tail vein or caudal vein is the largest vein in vertebrate animals' tail. It leads directly into the posterior cardinal vein in the posterior trunk in fishes. Mammal caudal vein (the middle caudal vein) leads to inferior vena cava.
Peptide Ligand Directed Drug Delivery
Provided is a novel peptide ligand (Leu-Ala-Arg-Leu-Leu-Thr) for binding to an EGFR surface pocket based on its 3D crystal structure. When conjugated to the distal end of liposome surface PEG moieties, the peptide ligand directs liposome binding and uptake by EGFR high expressing cancer cells (H1299 and SPCA1) specifically and efficiently. The targeted delivery of liposomal anticancer drug doxorubicin results in better therapeutic efficacy towards cells in vitro. In vivo, the targeted liposomes are injected via tail vein and the time course of their distribution and accumulation in xenograft tumor tissues are studied using a live animal fluorescence imaging system. The LARLLT targeted liposomes were seen to gradually concentrate at the tumor site and be preferentially retained more than 80 hours after injection.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Peptide ligand directed drug delivery
Provided is a novel peptide ligand (Leu-Ala-Arg-Leu-Leu-Thr) for binding to an EGFR surface pocket based on its 3D crystal structure. When conjugated to the distal end of liposome surface PEG moieties, the peptide ligand directs liposome binding and uptake by EGFR high expressing cancer cells (H1299 and SPCA1) specifically and efficiently. The targeted delivery of liposomal anticancer drug doxorubicin results in better therapeutic efficacy towards cells in vitro. In vivo, the targeted liposomes are injected via tail vein and the time course of their distribution and accumulation in xenograft tumor tissues are studied using a live animal fluorescence imaging system. The LARLLT targeted liposomes were seen to gradually concentrate at the tumor site and be preferentially retained more than 80 hours after injection.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Biological measuring method for dioxins compound in monitoring environment samples
InactiveCN1548945AReduce the numberSave operating timeMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceDioxin CompoundBiological Testing
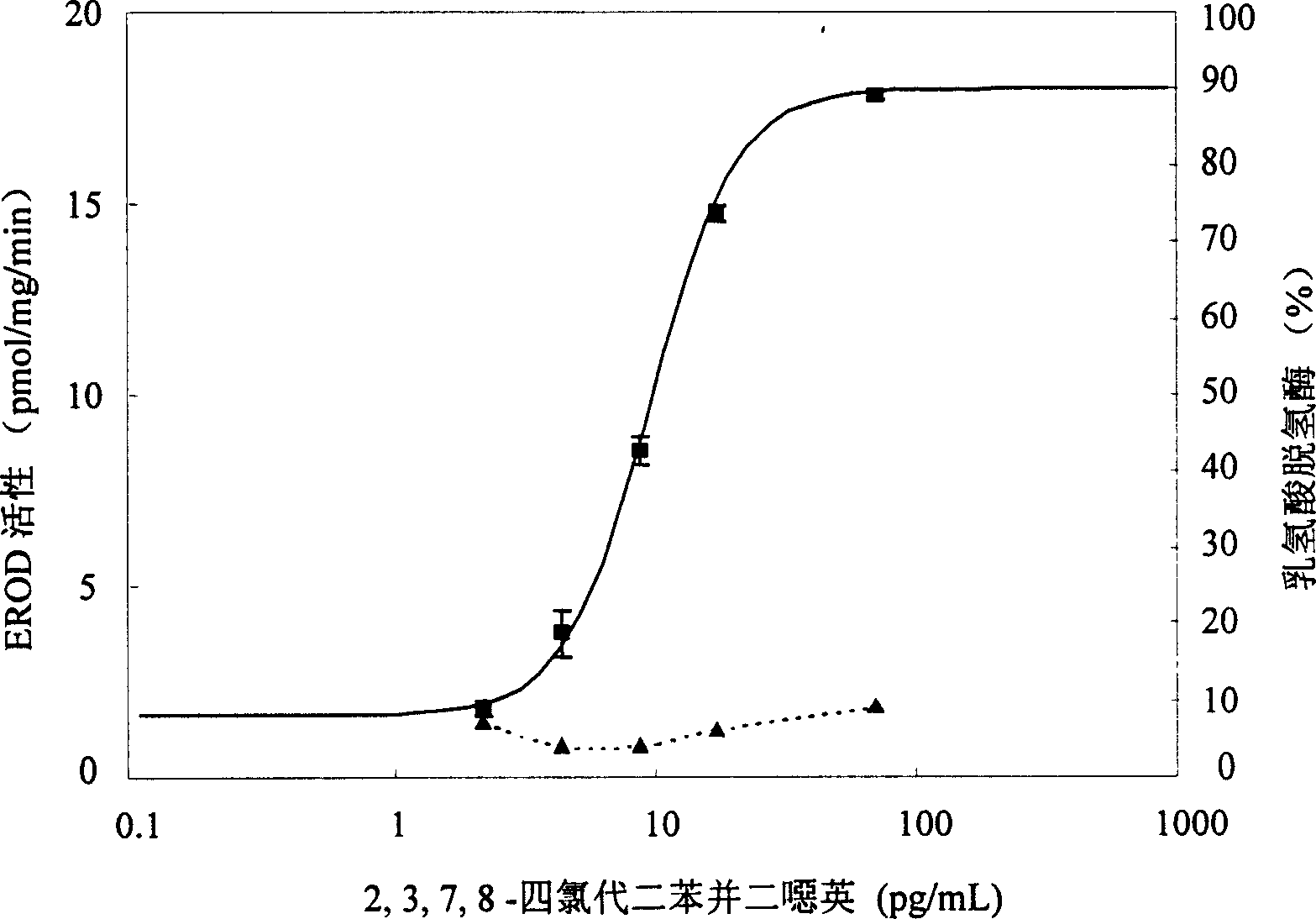
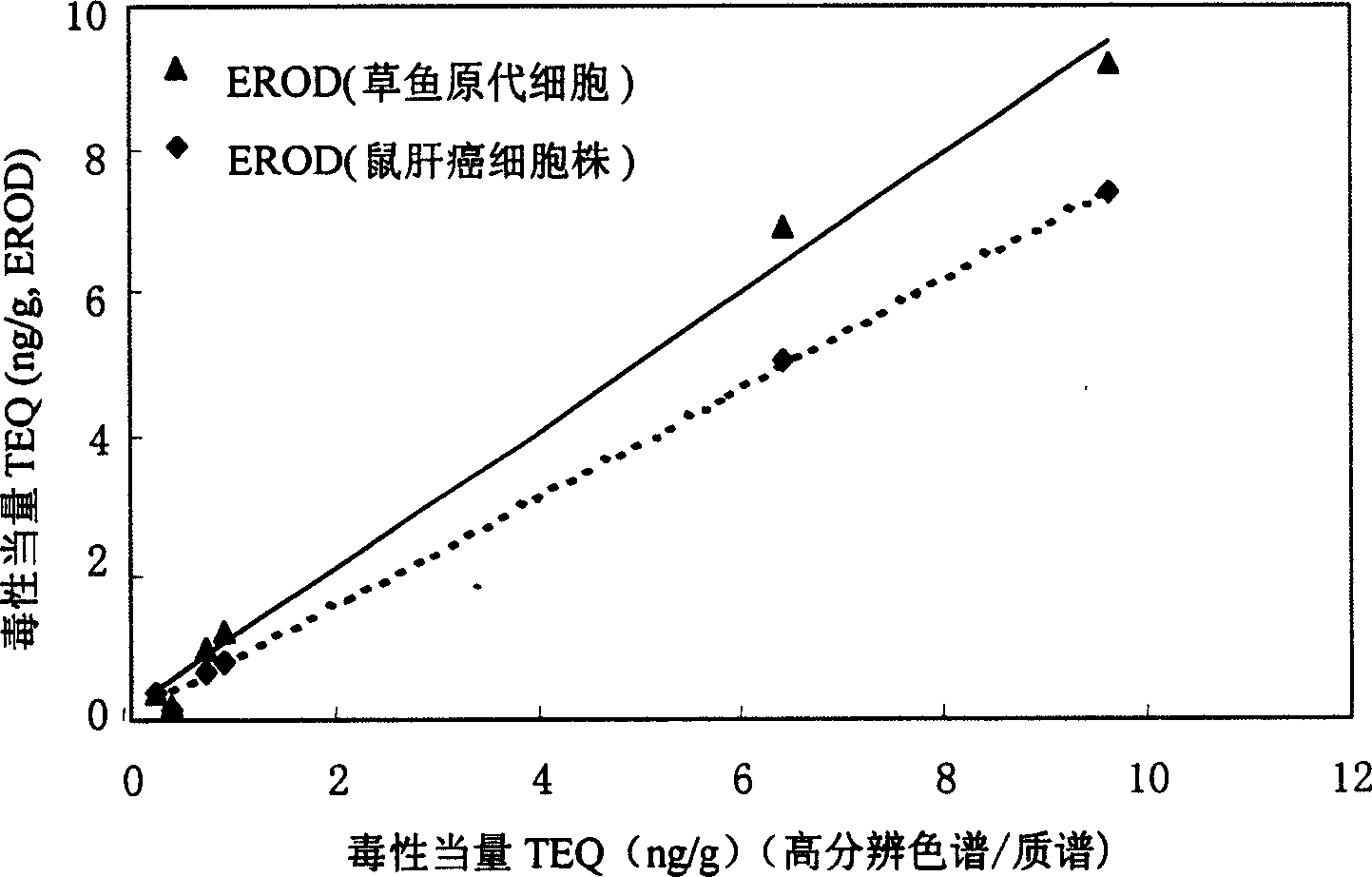
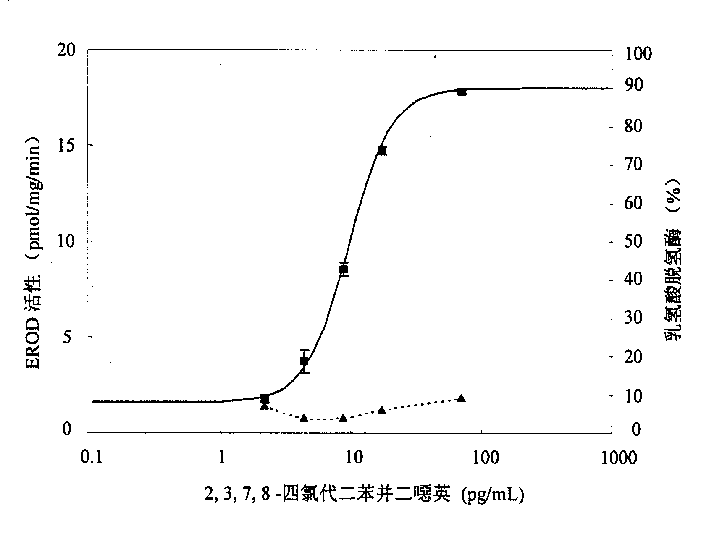
The present invention is the method of monitoring dioxins pollutant in environment sample with grass carp liver cell obtained via primary culture technology. Grass carp is blood eliminated via tail vein and its liver cell is primary cultured; the liver cell is then cultured together with 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzyl dioxins; reactant solution containing excessive 7-oxethyl-isophenol azolactone is then added; the fluorescent strength of the end product 7-hydroxy-isophenol azolactone is measured with fluorophotometer and the fluorescent strength is used as parameter for expressing EROD enzyme activity to draw the standard curve of dosage of EROD enzyme activity of primary liver cell vs 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzyl dioxins. The environment sample is detected similarly and through the comparison with standard curve the dioxins pollutant content in environment sample may be calculated.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Functional dendritic polymer gene vector system of targeted malignant cerebroma
InactiveCN101337076AGrowth inhibitionEfficient transfectionGenetic material ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCyclic peptidePolyamide
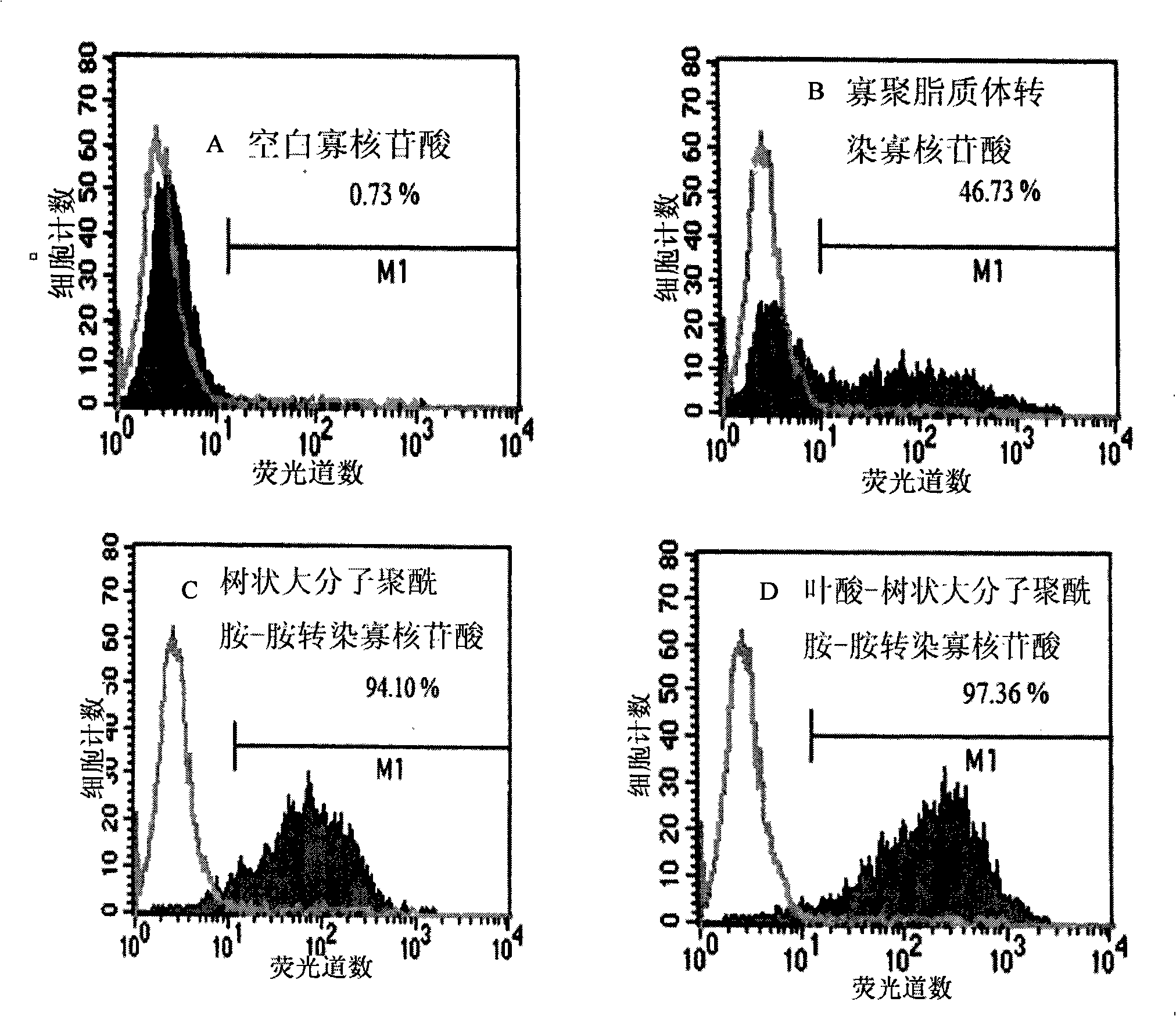
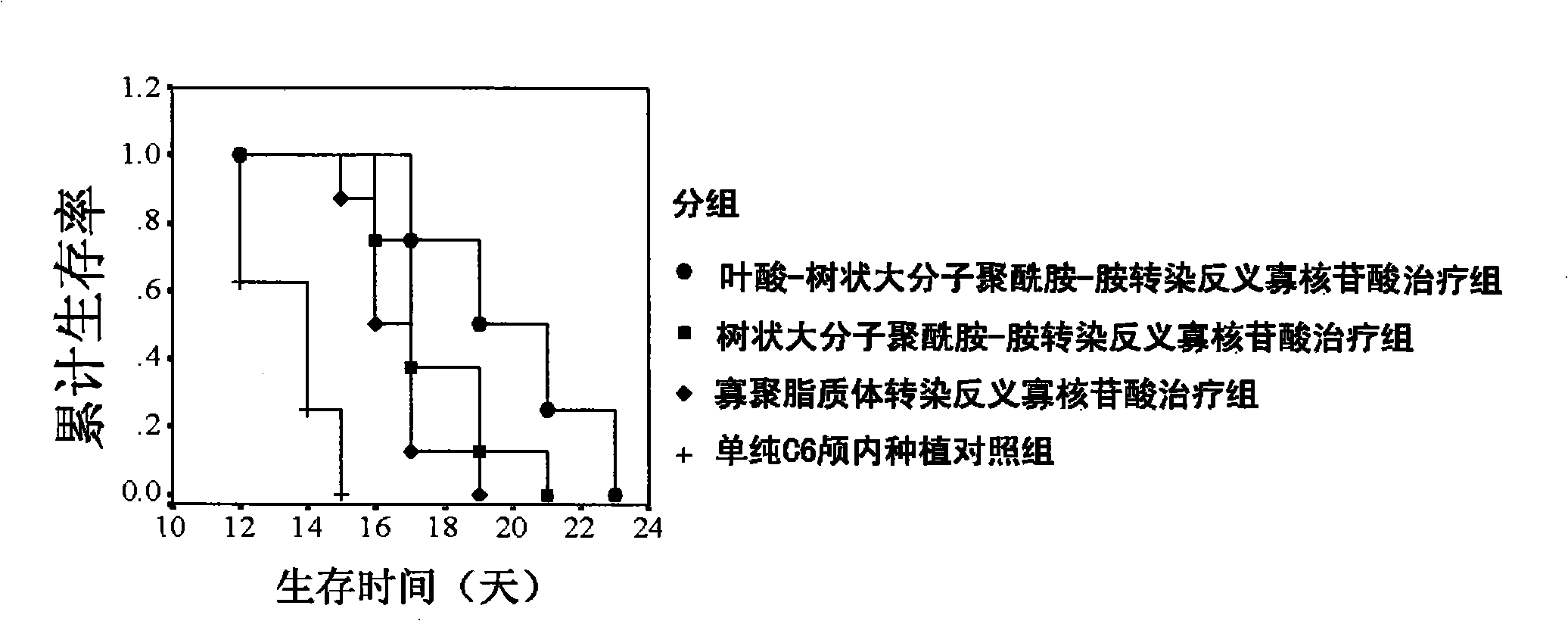
The invention relates to a functionalized arborescent macro radical carrier system for targeting malignant cerebroma. The functionalized arborescent macro radical carrier system is obtained by taking one or more of the following combinations as the targeting functional factor: transferrin and transferrin monoclonal antibody, or polyclonal antibody, folic acid (FA) and epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody, or polyclonal antibody and RGD cyclic peptide, chemically connecting the combinations to arborescent macro radical polyamide-amine (PAMAM) carrier system, and then compounding the combinations with treatment factor oligonucleotide, siRNA molecule or plasmid DNA. Through intra-tumor stereotactic injection, carotid injection or tail vein, the distribution of genes in the malignant cerebroma can be improved, high expression can be realized, and the effective cerebroma inhibition can be realized. Compared with the commercialized gene carrier Oligofectamin and unmodified PAMAM, the FA-PAMAM can remarkably improve the targeting delivery ability of the in vitro and in vivo genes.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
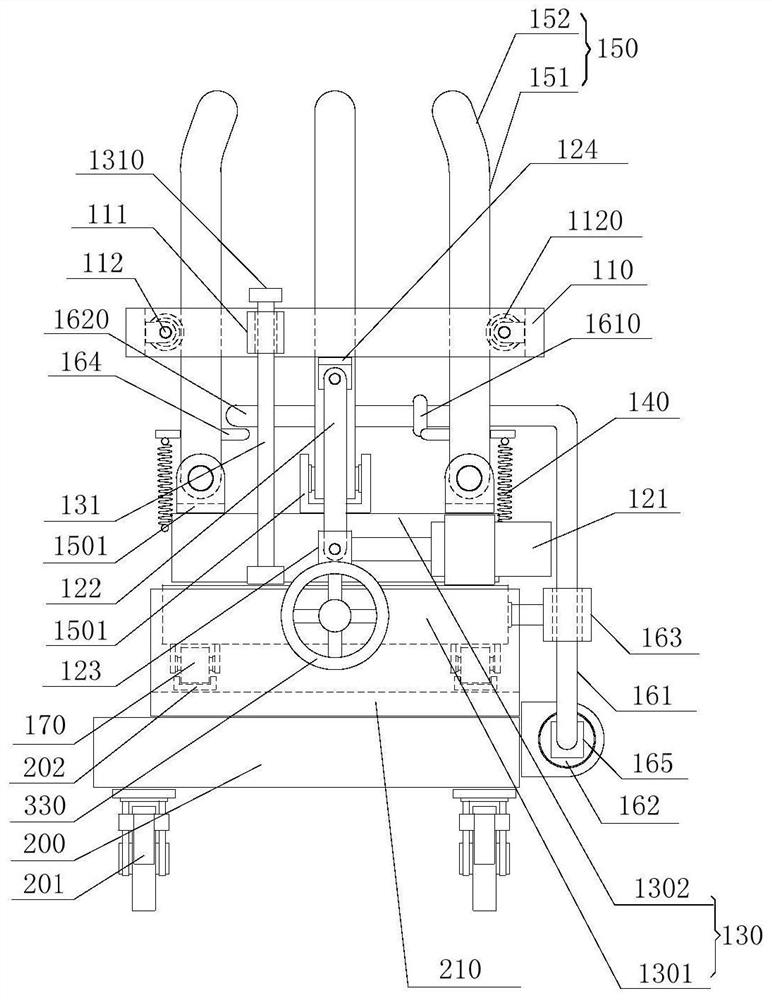
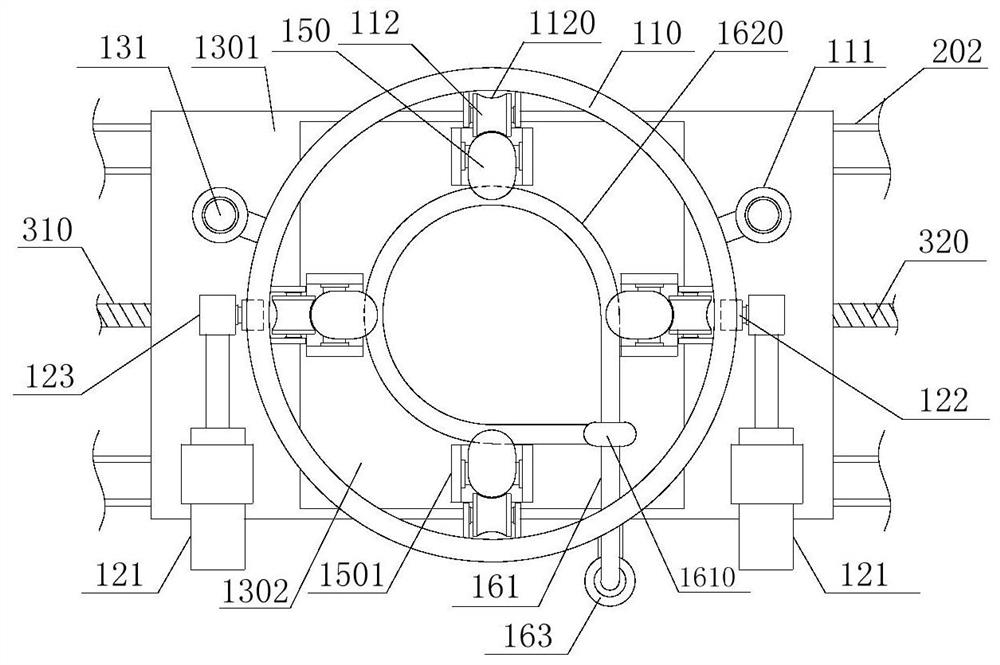
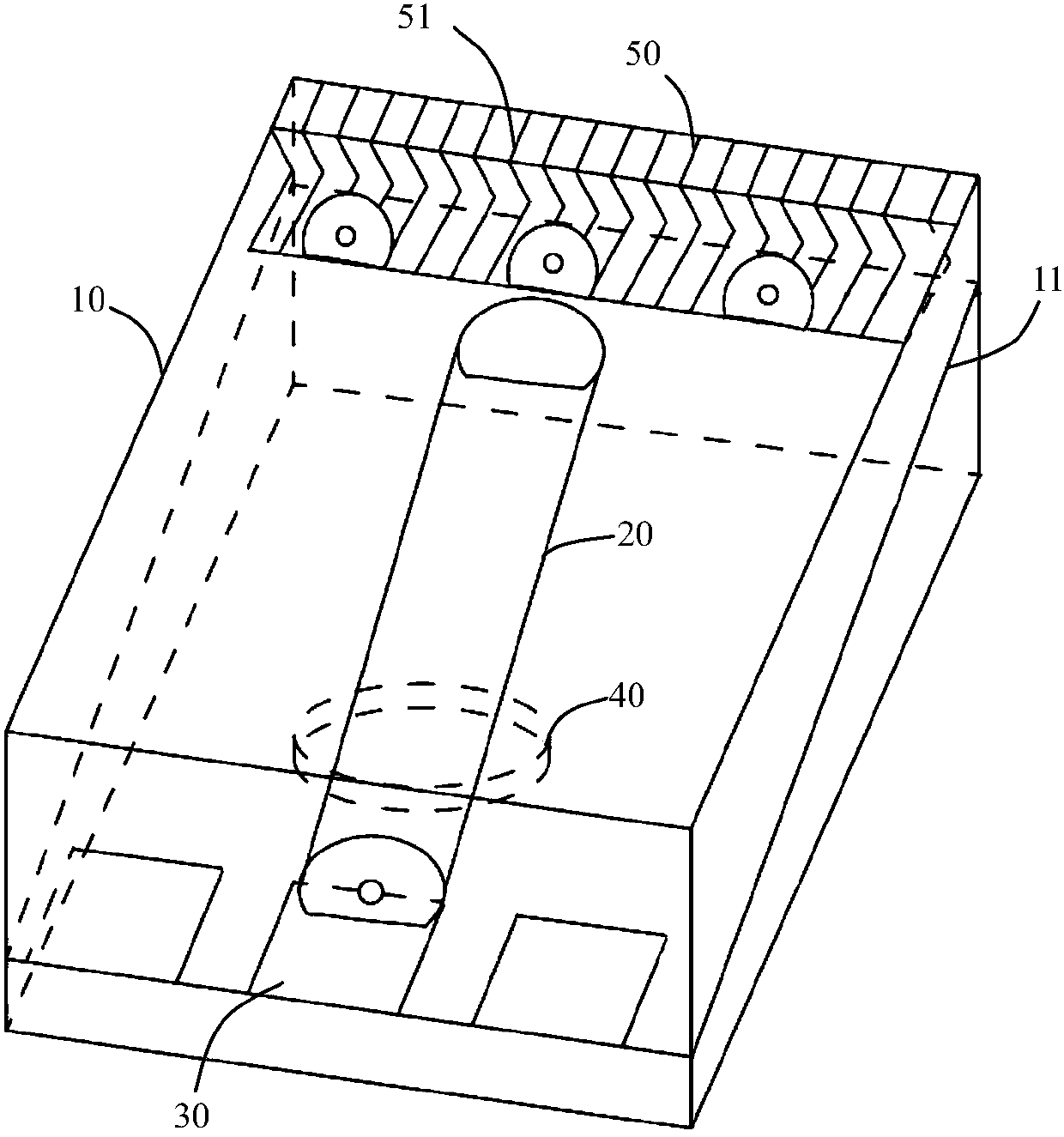
Device for animal tail vein injection
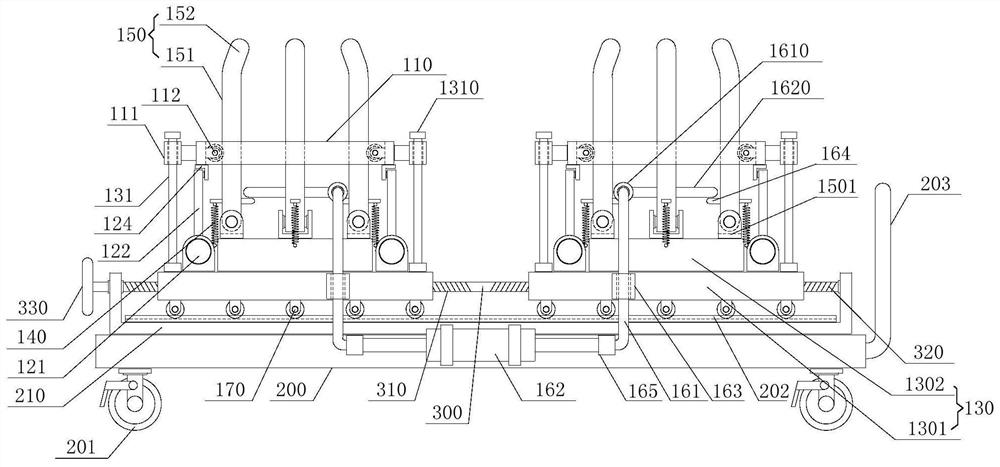
The invention provides a device for animal tail vein injection, and the device can effectively fix an animal body and facilitate animal tail vein injection. The device comprises a bottom plate and a semi-cylindrical cover body, the sealing end of the cover body is provided with a through hole through which an animal tail can stretch out, and the opening end of the cover body is provided with a piston, wherein the inner diameter of the piston is matched with that of the cover body, and non-slip rubber wraps the edge of the piston; a magnifying lens which is connected to the top of the cover body through a connecting rod and used for magnifying the animal tail is arranged over the through hole, and an auxiliary rod is connected to the connecting rod and provided with a lighting device. The device can be adjusted according to the body size of an experimental animal and is used for fixing the experimental animal without needing to fix the animal tail, and due to the fact that the magnifying lens is installed over the through hole and the lighting device is assembled, the vein of the tail is easier to see clearly; the device is suitable for tail vein injection of various animals with the smaller body size.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
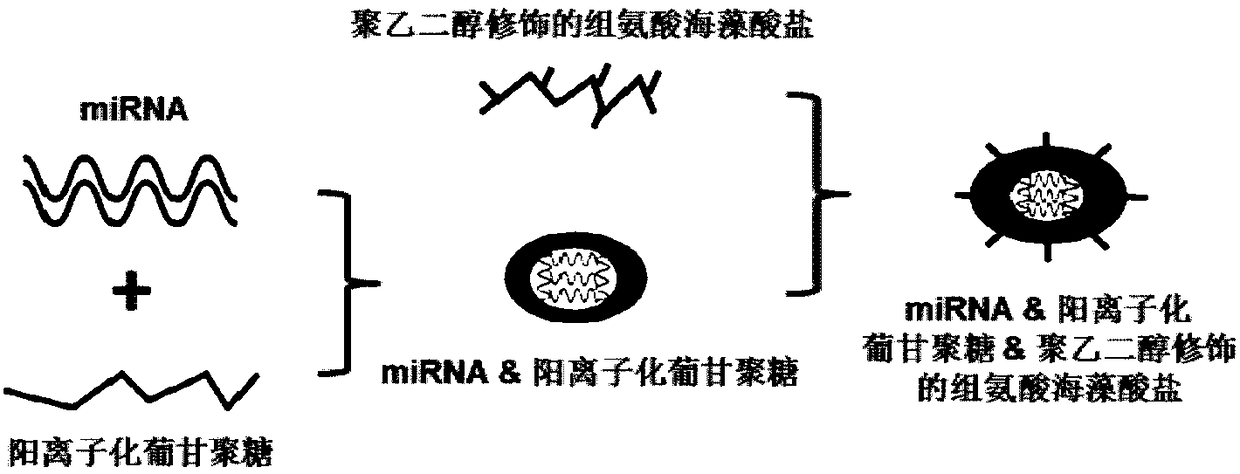
Drug delivering miRNA for suppressing tumor growth by targeting tumor-associated macrophages and application
InactiveCN108578386APromotes M1 activationGrowth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAbnormal macrophageBiological activation
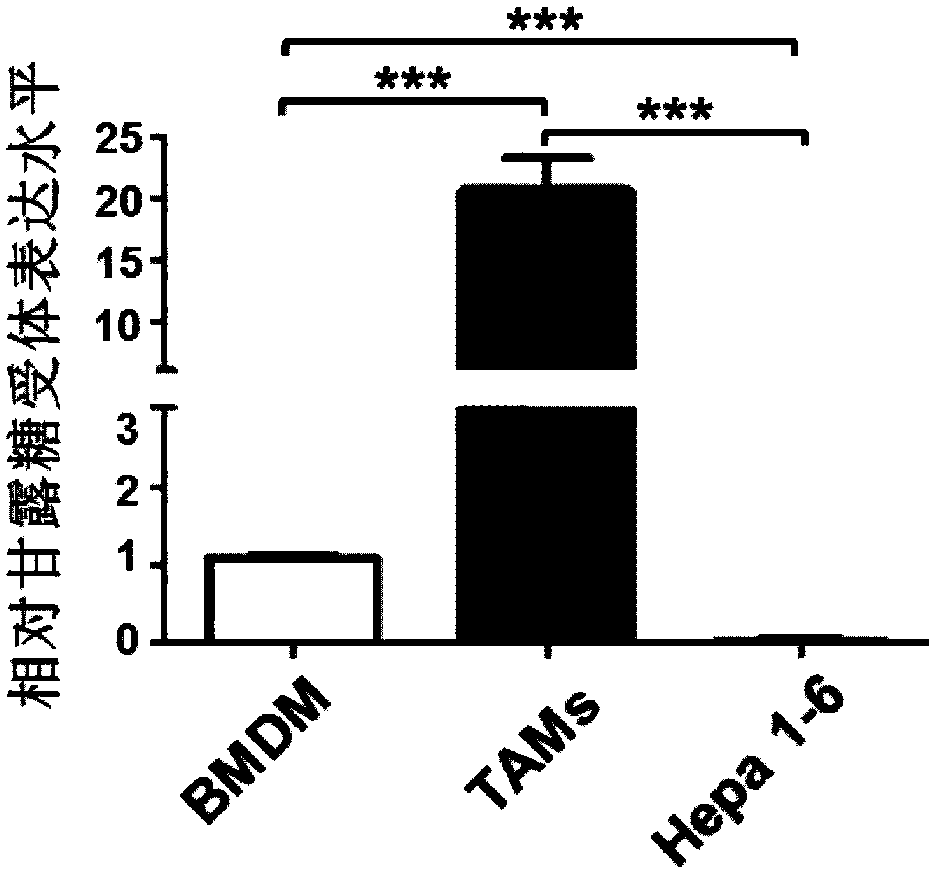
The invention provides a drug delivering miRNA for suppressing tumor growth by targeting tumor-associated macrophages and application. The drug comprises a drug carrier targeting the tumor-associatedmacrophages, miRNA wrapped in the drug carrier and cationized polysaccharide with mannose residues. The sequences of the miRNA are as shown in SEQ. ID. NO. 1 or SEQ. ID. NO. 2. Through an in vitro experiment, miR-99b-5p which can promote M1 type activation of the macrophages and can inhibit M2 type activation of the macrophages is discovered, nano-material targeting tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) is used for wrapping the miRNA, and the wrapped miRNA is directly transported to a mouse model of liver cancer through a tail vein, it is found that delivery of the miRNA to the targeted TAMs cansignificantly inhibit tumor growth, and delivery of the miR-99b-5p to the targeted TAMs has a better effect of inhibitory action on tumor growth than delivery of other miRNAs, such as miR-125a.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Model of outer marrow infiltration of leukemia-NOD/SCID mice and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN101548909AIncrease success rateProlong survival timeDiagnosticsSurgeryMolecular Targeted TherapiesScid mice
The present invention relates to a method for preparing model of outer marrow infiltration of leukemia-NOD / SCID mice, wherein the method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing a single karyocyte of marrow of leukemia patient, 2. preprocessing the NOD / SCID mice, 3. establishing a model, and 4. identifying the model. The invention firstly adopts a mode of injecting single karyocyte of marrow of leukemia patient through tail-vein injection for establishing the model of outer marrow infiltration of leukemia-NOD / SCID mice. Furthermore the prepared model of outer marrow infiltration of leukemia-NOD / SCID mice has the advantages of high success rate and long survival time. The invention can provide new animal model for researching the outer marrow infiltration mechanism of leukemia, sieving the leukemia medicine, and the targeted therapy of gene and molecule.
Owner:天津中医药大学第一附属医院
Method used for identifying and detecting danhong injection in vivo metabolites
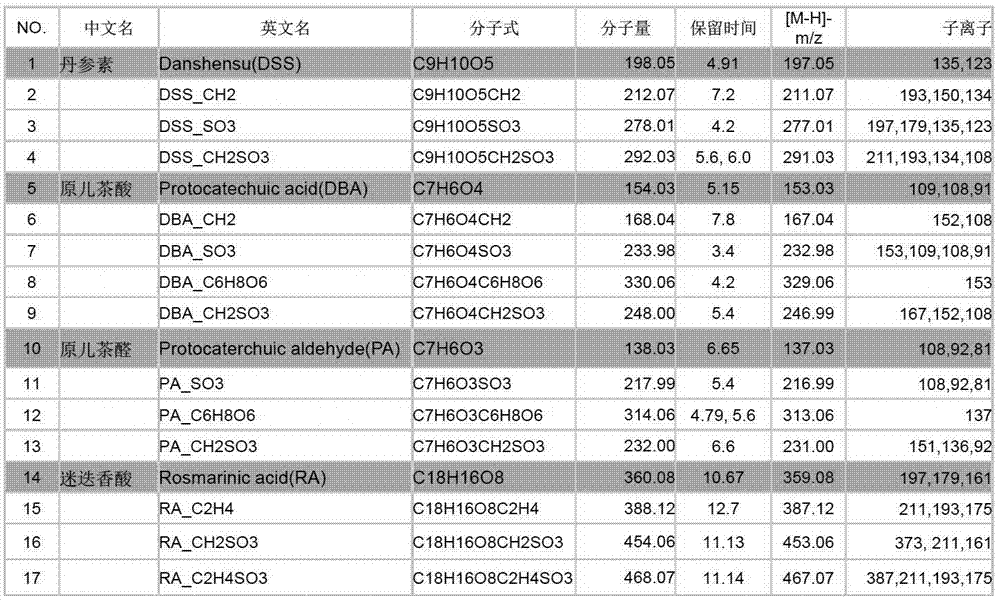
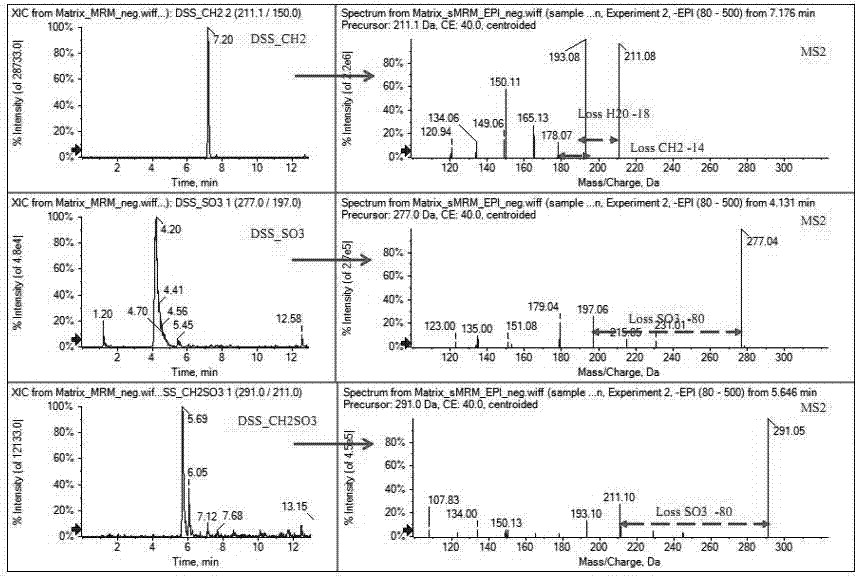
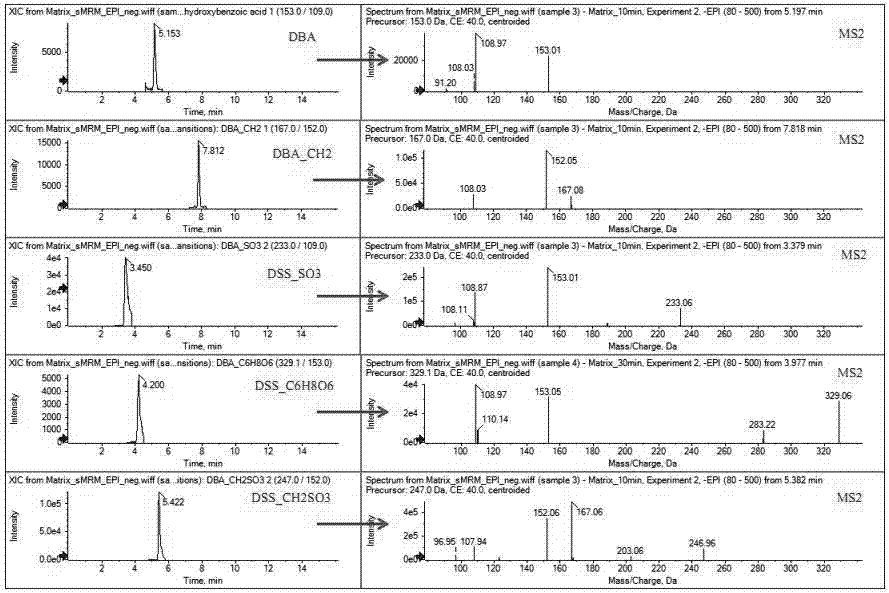
The invention discloses a method used for identifying and detecting danhong injection in vivo metabolites. The method comprises following steps: danhong injection is used for tail vein injection of SD rats, blood samples are collected at different time points, centrifugation is carried out so as to obtain blood plasma, the blood plasma is subjected to treatment, a Qtrap liquid chromatograph / mass spectrometer is adopted for gradient elution separation of obtained samples, and combination of a plurality of scanning modes, including EMS-IDA-EPI, (p)MRM-IDA-EPI, and NL / Pre-IDA-EPI, with MetabolitePilot<TM> metabolite idenfifying software is adopted for analysis of obtained metabolites. It is found that the II phase metabolites of active components, including tanshinol, protocatechuic acid, protocatechualdehyde, and rosmarinic acid, in the danhong injection are mainly a series of methylated, sulfated, methylated-sulfated, and glucuronidated metabolites. The metabolites change along with the passage of drug administration time, the concentations of most of the metabolites reaches C<max> in 10 to 30min, and most the original drug and the metabolites are eliminated in 6h. The method is simple, is high in repeatability and accuracy, is reliable, and is capable of providing basis for clinical applications of danhong injection.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHINESE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for constructing insulin resistance animal model
InactiveCN102228700AModeling method is simpleHigh molding ratePeptide/protein ingredientsBiological testingPhysiologyStatistical analysis
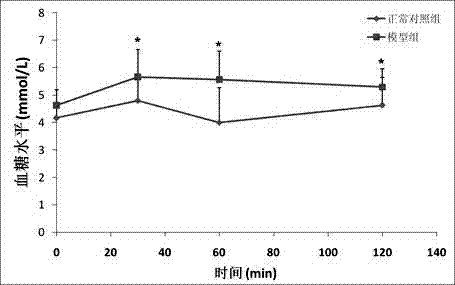
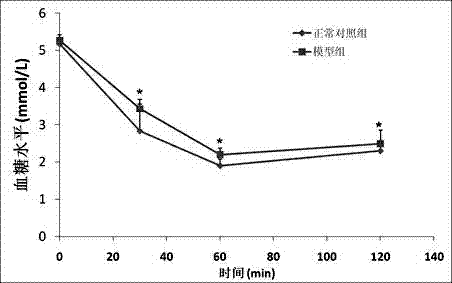
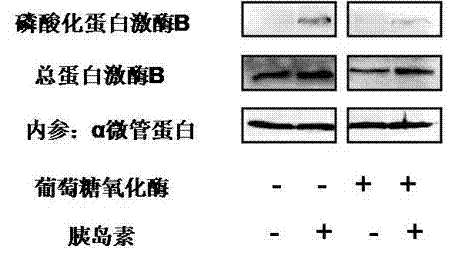
The invention relates to a method for constructing an insulin resistance animal model. A Sprague Dawley rat is injected with glucose oxidase (400U / kg weight) through tail vein injection to induce to generate insulin resistance. The statistical analysis of ghlcose tolerance and insulin tolerance and the detection of insulin signal transduction prove that the glucose oxidase constructed insulin resistance animal model is feasible, and can serve as a research model for insulin resistance, the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes and a medicine function mechanism. Compared with the conventional model constructing technology, the method has the advantages of simple modeling method, high modeling efficiency, low cost, short period, high repeatability and the like.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Protection device for tail vein blood sampling of livestock
PendingCN112336493ASimple structureEasy to operateAnimal fetteringBlood sampling devicesAnimal scienceMedicine
The present invention provides a protection device for tail vein blood sampling of livestock and relates to the field of medical devices of livestock. A special structure of the protection device is as follows: a plurality of leg protection stop levers are annularly distributed at intervals, and lower ends of the leg protection stop levers are hinged to supporting seats; an elastic energy storagepiece is connected between each leg protection stop lever and the supporting seat, and is configured to enable the corresponding leg protection stop lever to always have a movement trend of incliningfrom a middle part of the supporting seat to an edge part of the supporting seat from bottom to top; a plurality of the leg protection stop levers are sleeved with push rings; and push ring driving mechanisms are arranged on the supporting seats and are configured to drive the push rings to move upwards along a plurality of the leg protection stop levers to gather upper ends of a plurality of theleg protection stop levers and to drive the push rings to move downwards along a plurality of the leg protection stop levers to release the upper ends of a plurality of the leg protection stop levers.The protection device solves a technical problem that in the prior art, in a tail vein blood sampling process of cows or other medium and large livestock, a blood sampler has a risk of being kicked by rear legs of the livestock.
Owner:天康生物制药有限公司
Construction method of type I diabetes animal model
InactiveCN109718240AGood modelingHigh molding rateOrganic active ingredientsIntraperitoneal routeDiabetes model
The invention provides a construction method of a type I diabetes animal model. The method comprises the following steps: selecting C57BL / 6 mice, performing first tail vein injection, continuously performing intraperitoneal injection of a streptozotocin reagent for 5 days, performing ambrosia for 12 hours before injection, and allowing the mice to freely drink water. Two days after the injection procedure is completed, the ambrosia is carried out for 4 hours, and a glucometer is used for measuring blood glucose until the blood glucose value is 10 mmol / L or above. The statistical analysis of the blood glucose measurement result of the type I diabetes animal model shows that the C57BL / 6 mouse type I diabetes model constructed by using the streptozotocin is feasible and can be used for researching the diabetes pathogenesis and the anti-hyperglycemia intervention of medicaments and health-care foods. Compared with the prior art, the C57BL / 6 mouse type I diabetes model constructed by the invention has the advantages of high film forming rate, simple operation, no death of animals and good reproducibility.
Owner:贵州健安德科技有限公司 +1
Specific long-acting siRNA and application thereof to treatment of renal fibrosis
InactiveCN108060163AInhibition of Hippo signaling pathwayReduced expression levelOrganic active ingredientsUrinary disorderMedicineHippo signaling pathway
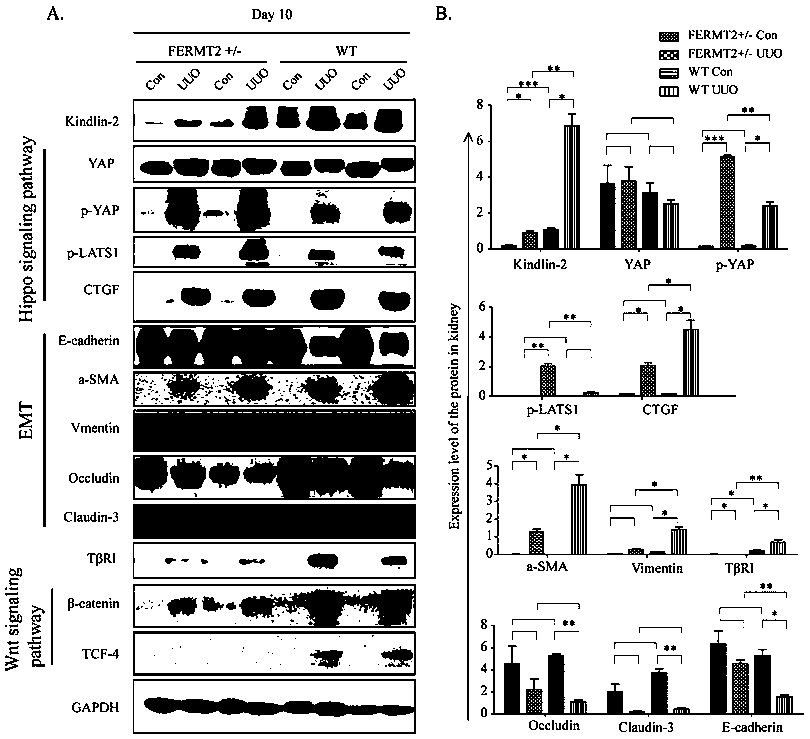
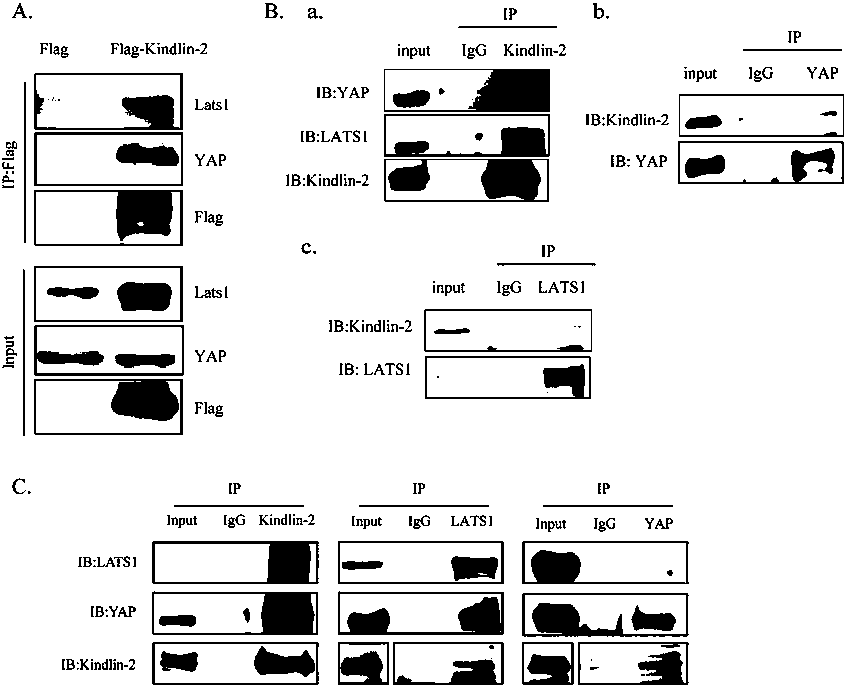
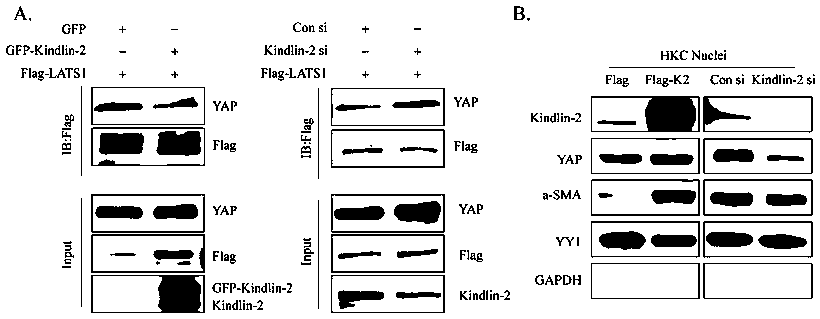
The invention discloses specific long-acting siRNA and application thereof to treatment of renal fibrosis. The specific long-acting siRNA specifically targets integrin-interacting protein Kindlin-2, can effectively reduce the expression level of the renal Kidlin-2 protein, and can effectively activate TGFbeta and Wnt signaling pathways in kidney and inhibit a Hippo signaling pathway so as to treatthe renal fibrosis and delay occurrence thereof; furthermore, animal experiments verify that tail vein injection of the specific long-acting siRNA after occurrence of UUO-induced fibrosis can effectively inhibit the progression of the fibrosis and alleviate the degree of the fibrosis and the effect of early medication is good.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Construction method of systemic lupus erythematosus animal model and application thereof
ActiveCN107693542AHigh induced molding rateRapid onsetMammal material medical ingredientsAnimal husbandryDiseaseDendritic cell
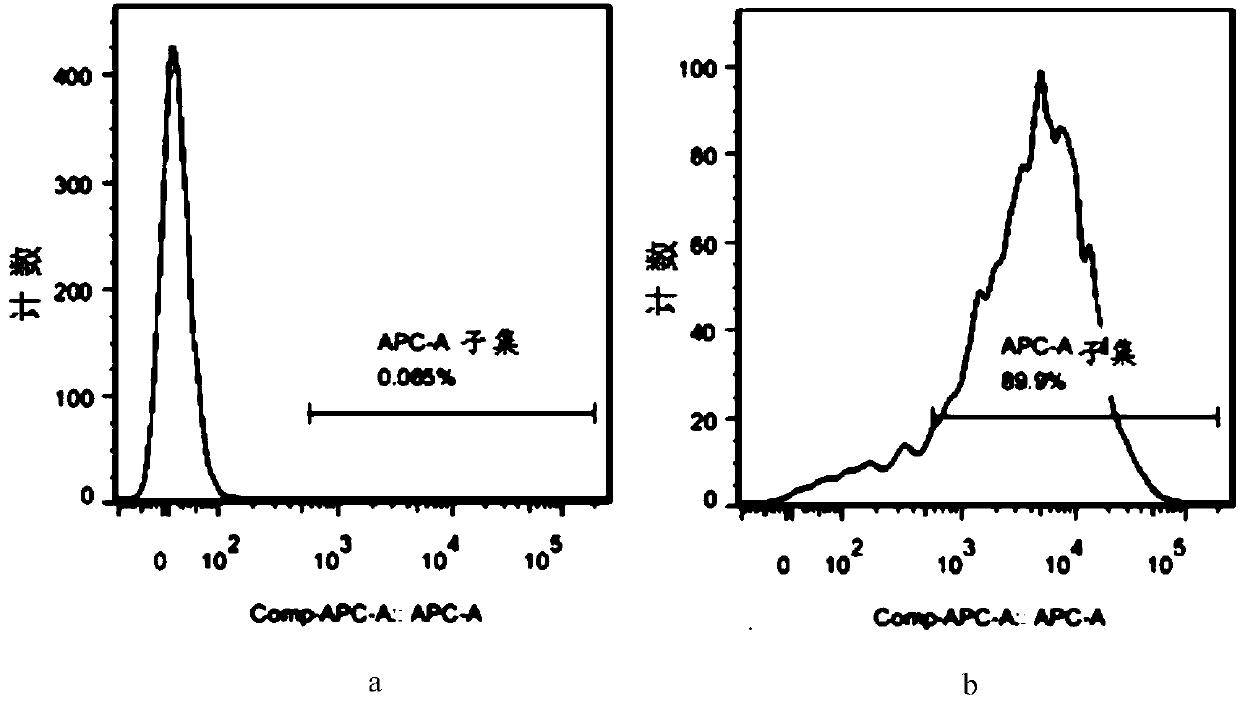
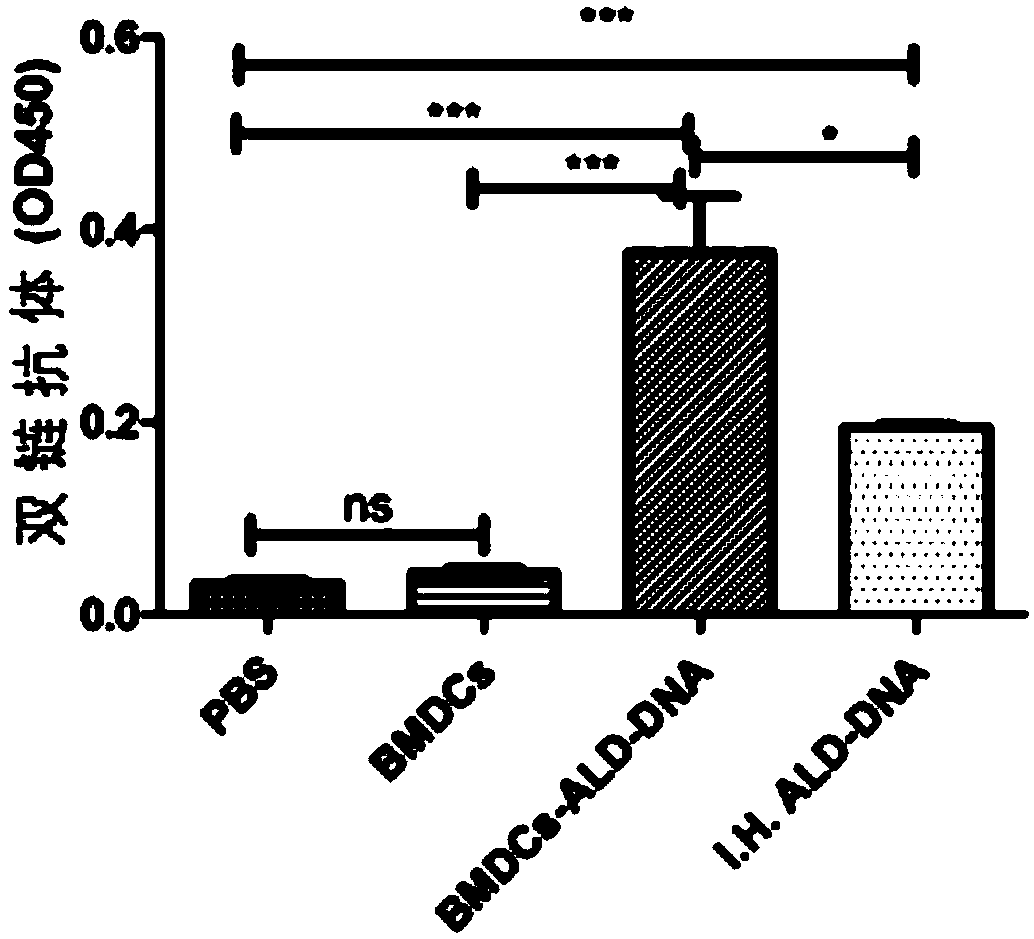
The invention discloses a method for constructing an animal model of systemic lupus erythematosus. According to the method, after dendritic cells of mice are coated in vitro with lymphocyte DNA in apoptosis state for 12 hours, the dendritic cells are tail-vein injected into mice body circulation to induce systemic lupus erythematosus in mice. Systemic lupus erythematosus disease in mice is evaluated by detecting the increase of autoantibody level in mice, hyperplasia and swelling of mice lymphoid tissues, and later changes in renal glomerular inflammation traits in mice. This method can help induce mice systemic lupus erythematosus within 2 weeks, and the induction model success rate reaches up to 100%. The method of the invention is a rapid, concise, efficient, immune cell and immunogen clear construction method of the systemic lupus erythematosus animal model, and can facilitate the exploration of the mechanism of systemic lupus erythematosus disease and the search for new and effective treatment methods.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
A pair of human stomach cancer cell lines having high metastasis towards livers and lungs and an establishing method thereof
InactiveCN103333857AClear genetic backgroundStable biological propertiesMicroorganism based processesTumor/cancer cellsLymphatic SpreadCancer metastasis
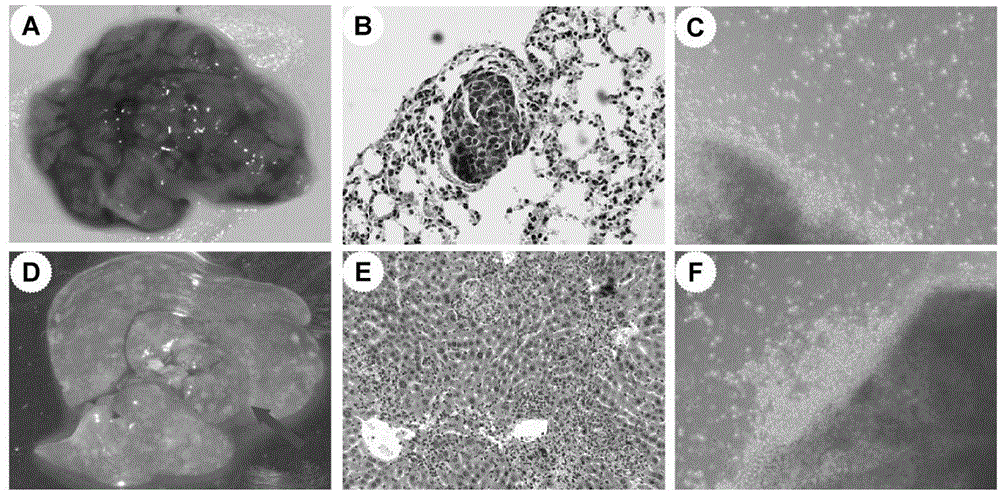
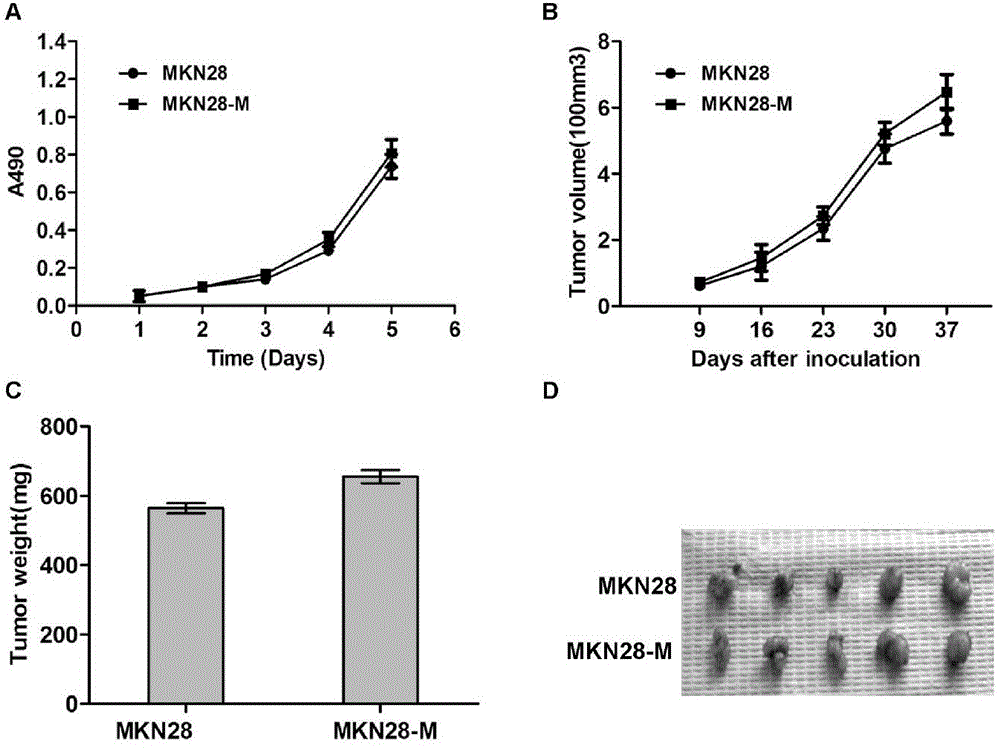
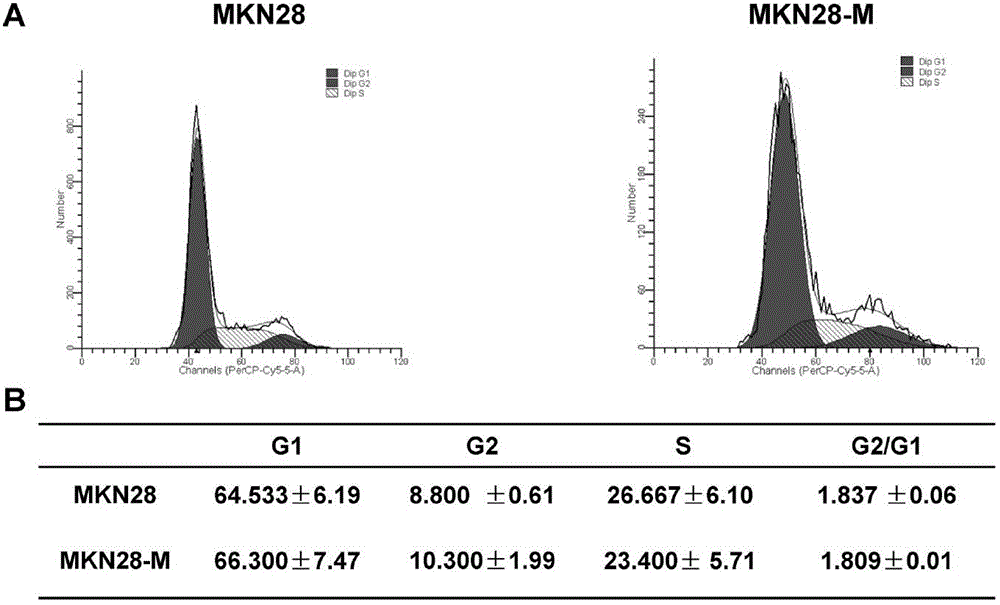
The invention belongs to the field of microorganism animal cell lines, and especially relates to a pair of human stomach cancer cell lines having high metastasis towards livers and lungs and an establishing method thereof. The human stomach cancer cell lines are characterized in that the human stomach cancer cell lines are MKN28-M and SGC7901-M respectively; the MKN28-M is assigned the accession number CGMCC No.6901; and the SGC7901-M is assigned the accession number CGMCC No.6902. The cell lines are humanized and have no obvious difference from parent cells in in-vitro growth and multiplication capacities, but have obviously enhanced migration, invasion and transfer capabilities over the parent cells. Results of nude mouse tail vein injection visceral metastasis experiments show that the average rate of metastasis towards livers and lungs is 70%. The cell lines have characteristics of high metastasis capacity and high malignancy degree. An animal model established based on the cell lines provides a good platform for further mechanism study of human stomach cancer metastasis. The animal model is an effective and feasible experiment model used for studying mechanisms of human stomach cancer metastasis and evaluating anti-cancer drug curative effects at present.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Construction method for suckling mouse model infected by hepatitis B virus and application of method
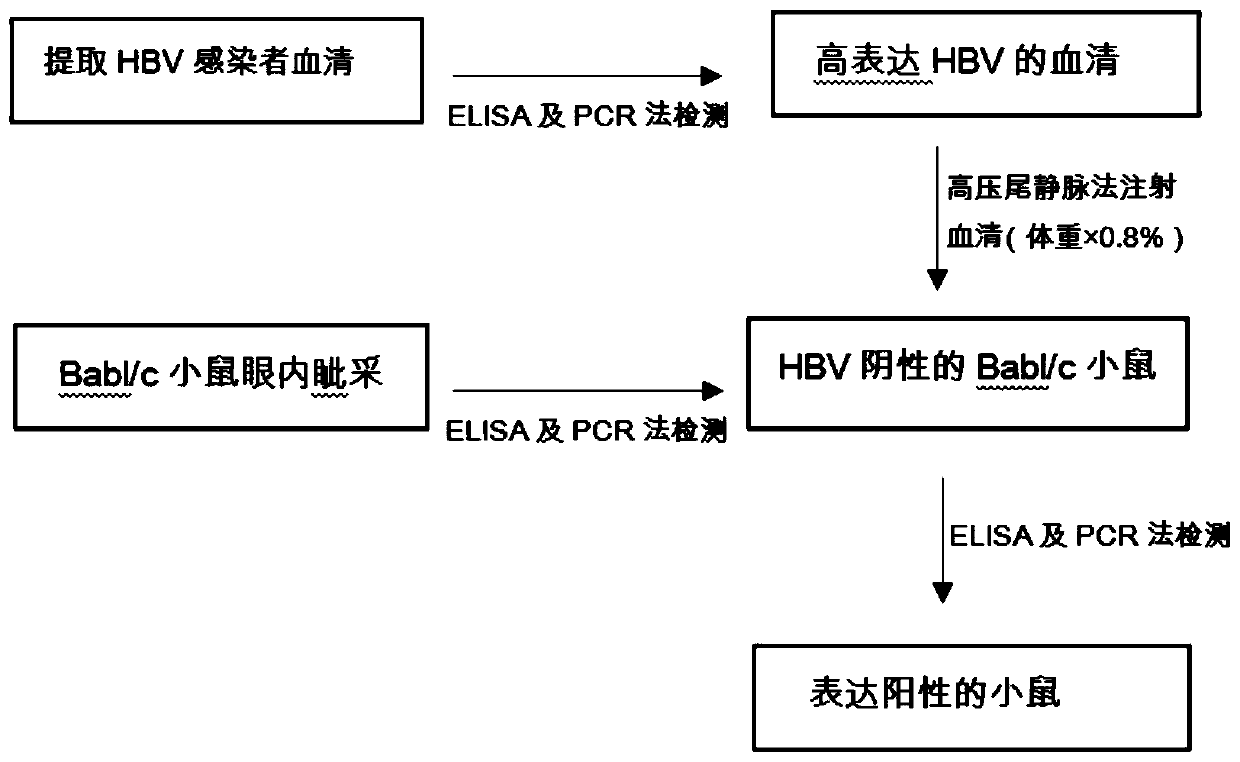
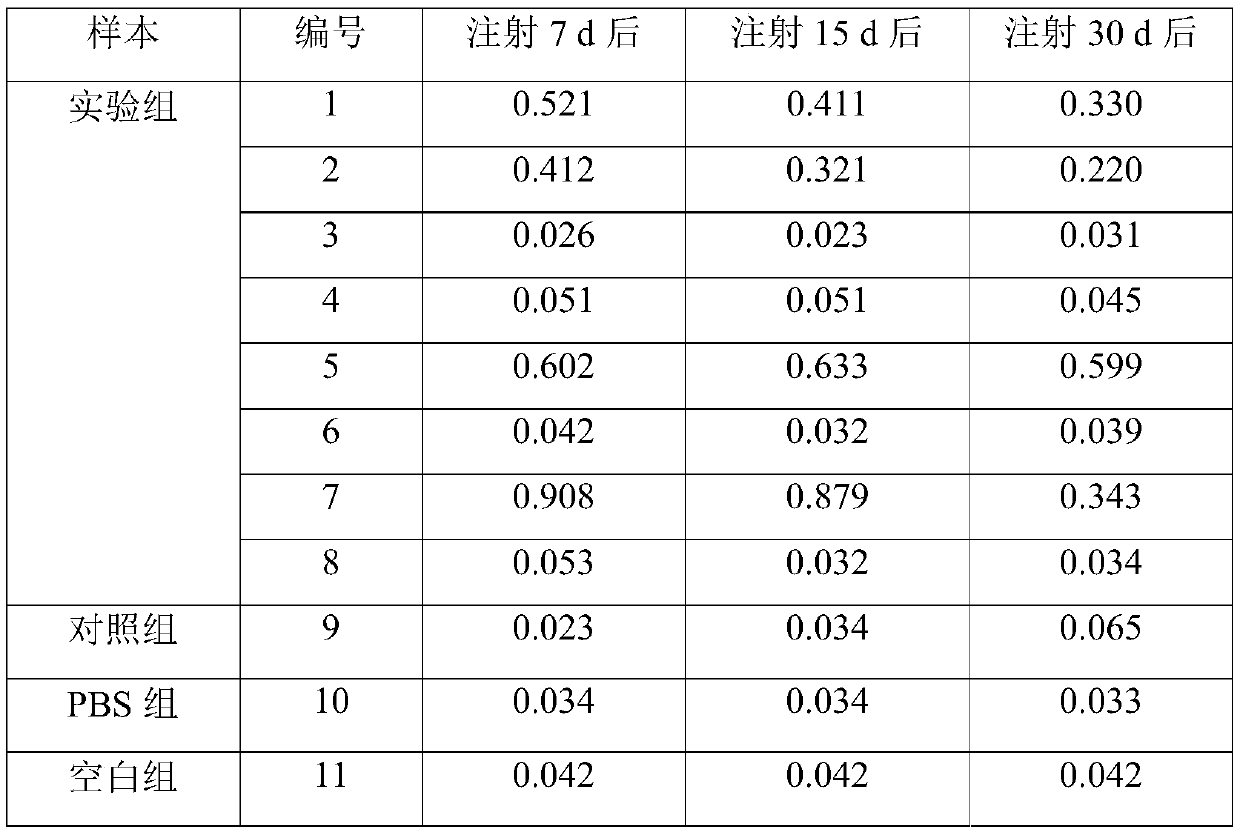
InactiveCN110199942ALow costNo ethical issuesCompounds screening/testingAnimal husbandryLaboratory mouseVein
The invention discloses a construction method for a suckling mouse model infected by hepatitis B virus and application of the construction method. The construction method comprises the steps of extracting serum of a patient with high expression infection, eliminating spontaneous infection of HBV in an experimental mouse, injecting the serum of the patient into the mouse by a high-pressure hydrodynamic tail vein method, respectively taking blood through an intraocular canthus vein of the mouse at 7, 15 and 30 days after injection to detect the concentration of HBs Ag, HBe Ag and HBV DNA, and determining that modeling is successful when the result is positive. The method provided by the invention can be used for successfully infecting suckling mice, it detects that the successfully modeled suckling mouse can permanently have the expression of HBV within one month, meanwhile, body temperature rising and body weight changing of the suckling mouse cannot be caused, the cost is low, ethicalproblems do not exist, the suckling mouse model can be used as an animal model for researching chronic HBV infection, and the requirements of current scientific research are met.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN THEATRE COMMAND OF PLA
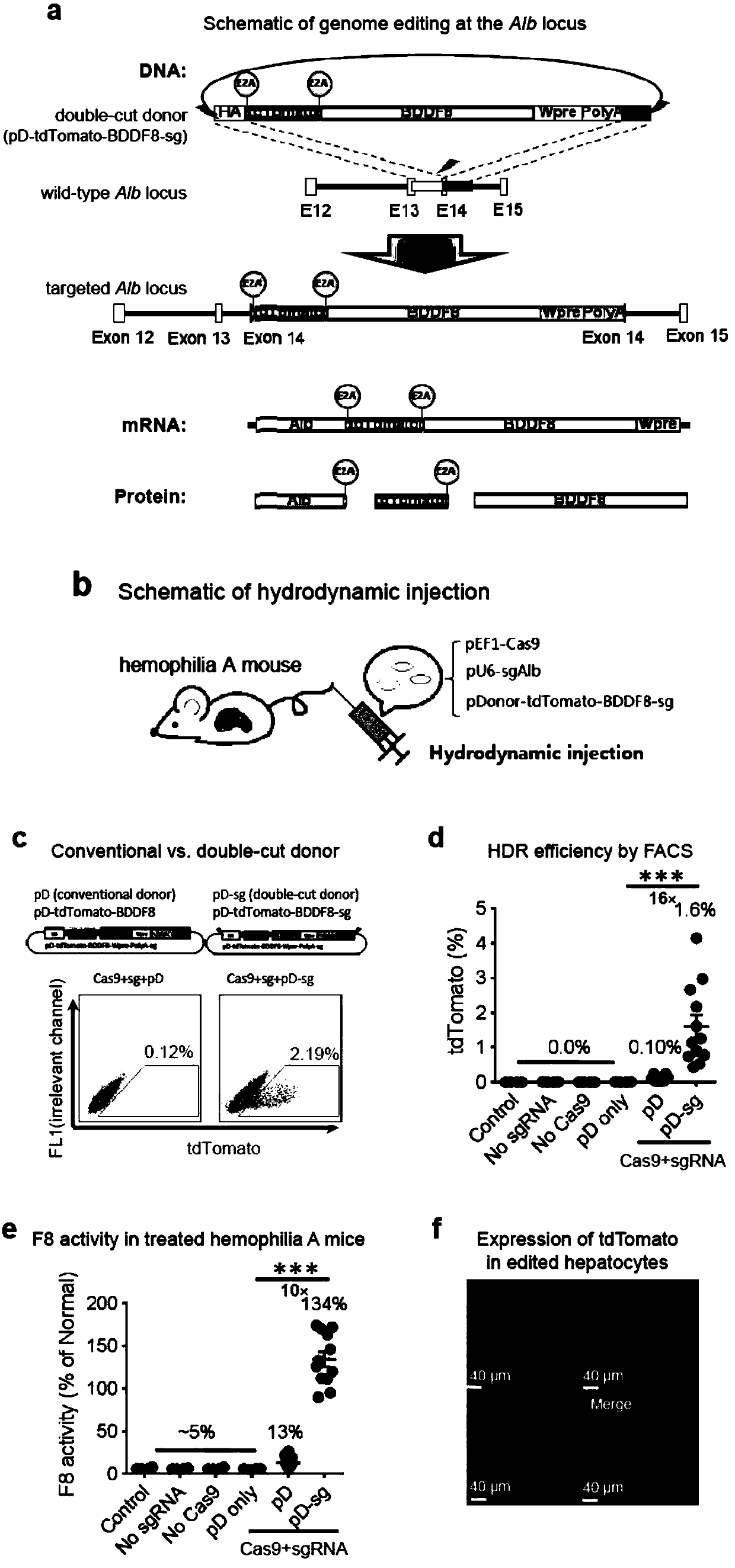
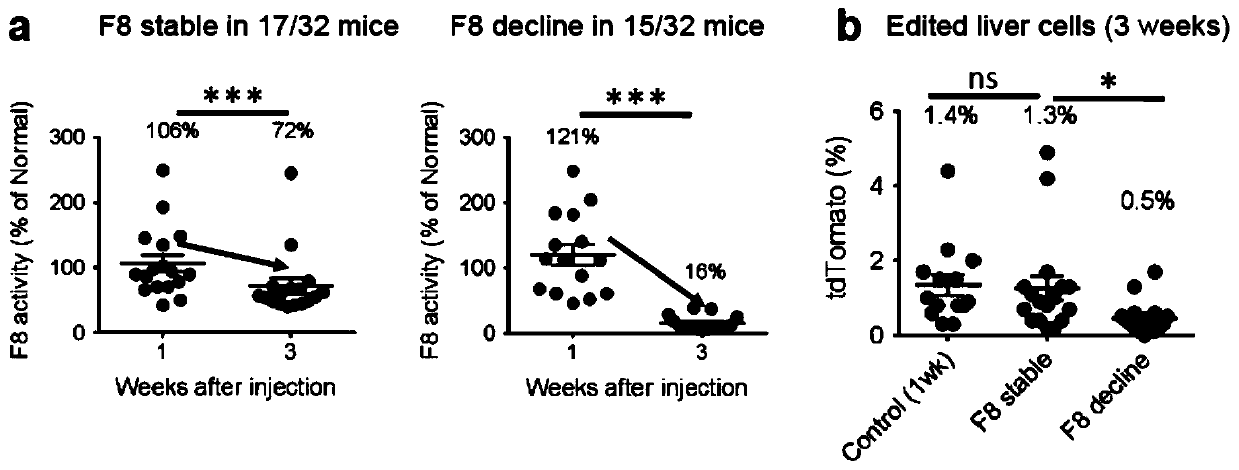
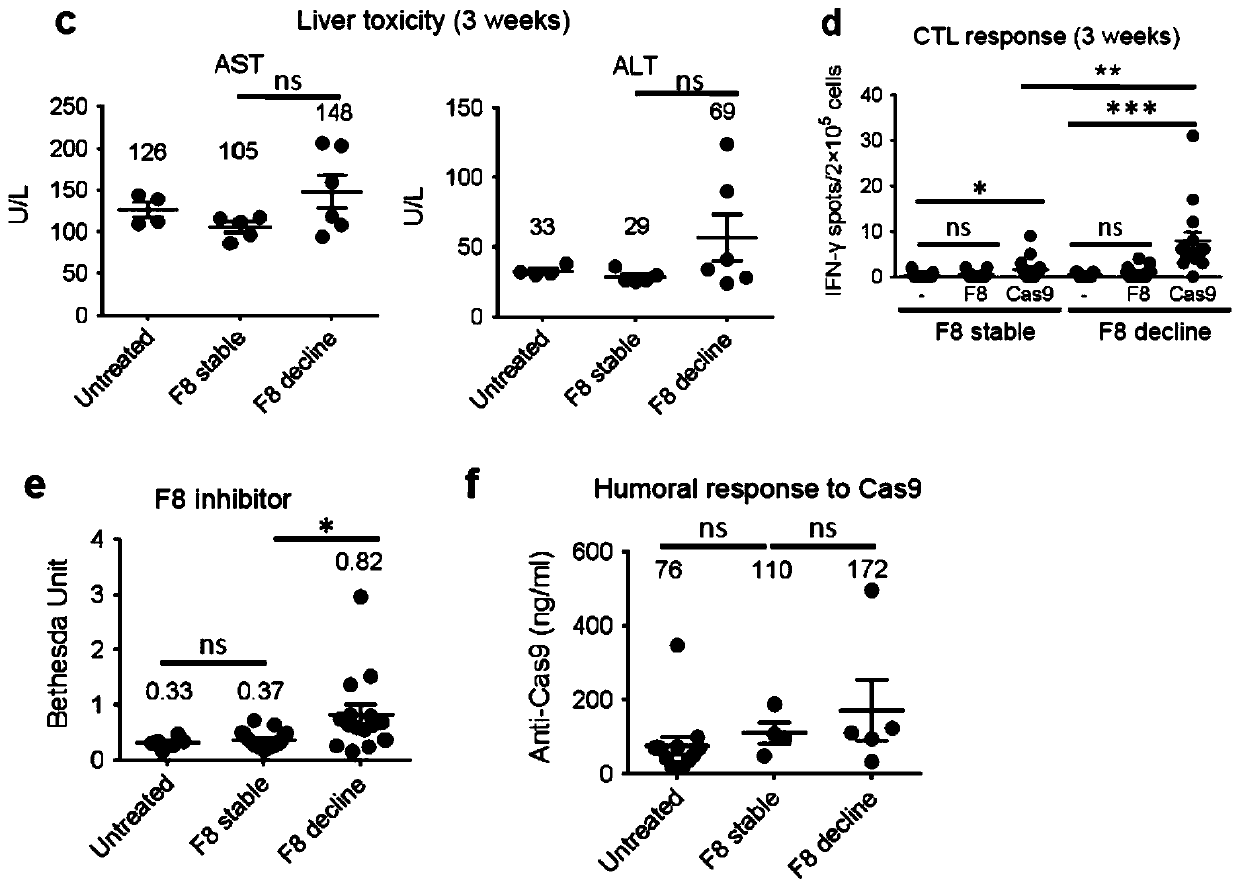
Double-cut donor for hemophilia A and medicine combination thereof
ActiveCN110628816AIncrease insertion efficiencyImprove initial activityOrganic active ingredientsVectorsCombined useHigh pressure
The present invention provides a double-cut donor for hemophilia A. BDDF8 is located at a highly expressed Alb site in liver cells, sgAlb-PAM sequences capable of being recognized by Cas9-sgAlb are also arranged on both sides of a homologous arm, after high-pressure tail vein injection of a novel double-cut HDR donor plasmid encoding Cas9, sgAlb and pDonor plasmids, 1-2% of liver cells accuratelyintegrate BDDF8 at the Alb site. In addition, a combined use of an immunosuppressant enables the BDDF8 to be stably expressed in lifetime in 80% or more of mice, indicating that hemophilia A is completely cured in most mice.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD DISEASES HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
Melanin/Ce6 photodynamic nano drug with enhanced light absorption and preparation method of melanin/Ce6 photodynamic nano drug
ActiveCN107998392AGood biocompatibilityRealize nuclear magnetic detectionEnergy modified materialsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPhotodynamic therapyMedicine
The invention relates to a melanin / Ce6 photodynamic nano drug with enhanced light absorption and a preparation method of the melanin / Ce6 photodynamic nano drug. The melanin / Ce6 photodynamic nano drugis prepared from melanin nano particles serving as a carrier and Ce6 molecules loaded on the melanin nano particles; the mass ratio of the melanin nano particles to the Ce6 molecules is 1 to (0.01 to10). Compared with the prior art, the synthesized melanin / Ce6 photodynamic nano drug with enhanced light absorption has the advantages that the shortcomings such as short retention time of Ce6 in body, little enrichment in the diseased region and strong skin phototoxicity can be avoided, and is expected to be enriched on the tumor site after tail vein injection, so as to perform specific photodynamic therapy on local tumor and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
TRICARBONYL TECHNETIUM-99m OR RHENIUM-188 LABELED CYCLIC RGD DERIVATIVES, A PREPARATION METHOD THEREOF, AND A PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITION CONTAINING THE DERIVATIVES AS AN ACTIVE INGREDIENT FOR USE IN THE DIAGNOSIS OR TREATMENT OF ANGIOGENESIS-RELATED DISEASES
ActiveUS20130064766A1Reduce intakeHigh resolutionOrganic active ingredientsRadioactive preparation carriersIntestinal structureDisease
The present invention relates to tricarbonyl technetium-99m or rhenium-188 labeled cyclic RGD derivatives, a preparation method thereof, and a pharmaceutical composition containing the derivative as an active ingredient for use in the diagnosis or treatment (radiotherapy) of angiogenesis-related diseases. The tricarbonyl technetium-99m or rhenium-188 labeled cyclic RGD derivatives of the present invention has a high subnanomolar affinity to integrin αvβ3 (also called as a vitronectin receptor) that is activated in an angiogenic action induced by a tumor, reflects a high tumor image of the tricatvonyl technetium-99m labeled cyclic RGD derivative after initial intake in an animal in which cancer cells are transplanted, and acts exclusively upon cancer cells having selectively activated integrin αvβ3 because of a substantially low intake into the liver and intestines, compared to existing known radioactive isotope labeled cyclic RGD derivatives. These results show that the rhenium-188 labeled derivative, a therapeutic nuclide using the same precursor as used in the technetium-99m labeling, effectively inhibits the growth of a tumor and demonstrates therapeutic efficacy when administered via tail vein injection to an animal model bearing tumor, compared to a case where only saline has been injected, thereby making it useful as a medicine for the diagnosis or treatment of angiogenesis-related diseases.
Owner:BIK THERAPEUTICS INC
Construction method and application of gout animal model
ActiveCN110338139ATypical gout symptomsCompounds screening/testingAnimal husbandryIntraperitoneal routeClinical manifestation
The invention discloses a construction method and application of a gout animal model. The construction method comprises the steps of injecting a uricase inhibitor into the abdominal cavity of a rat every day for one week to inhibit the activity of uricase of the rat and meanwhile injecting uric acid salt crystals and ATP into the tail vein to make the rat spontaneously develop gouty arthritis. Theprovided construction method of the gout animal model can stably and rapidly induce gout in the rat, and the clinical manifestation and pathological characteristics of the model are completely matched with the characteristics of human gout. According to the gout model constructed by means of the method, massive uric acid salt crystals can be observed under a polarizing microscope in a diseased joint, and infiltration of massive neutrophilic granulocytes can be found through immunohistochemistry. In addition, the invention also relates to the application of the gout animal model constructed bymeans of the method in research on the occurrence and remission mechanisms of gout and related inflammation, screening and evaluation of therapeutic drugs and the like.
Owner:ANHUI PROVINCIAL HOSPITAL
Intravenous Drug Administration and Blood Sampling Model in the Awake Rat
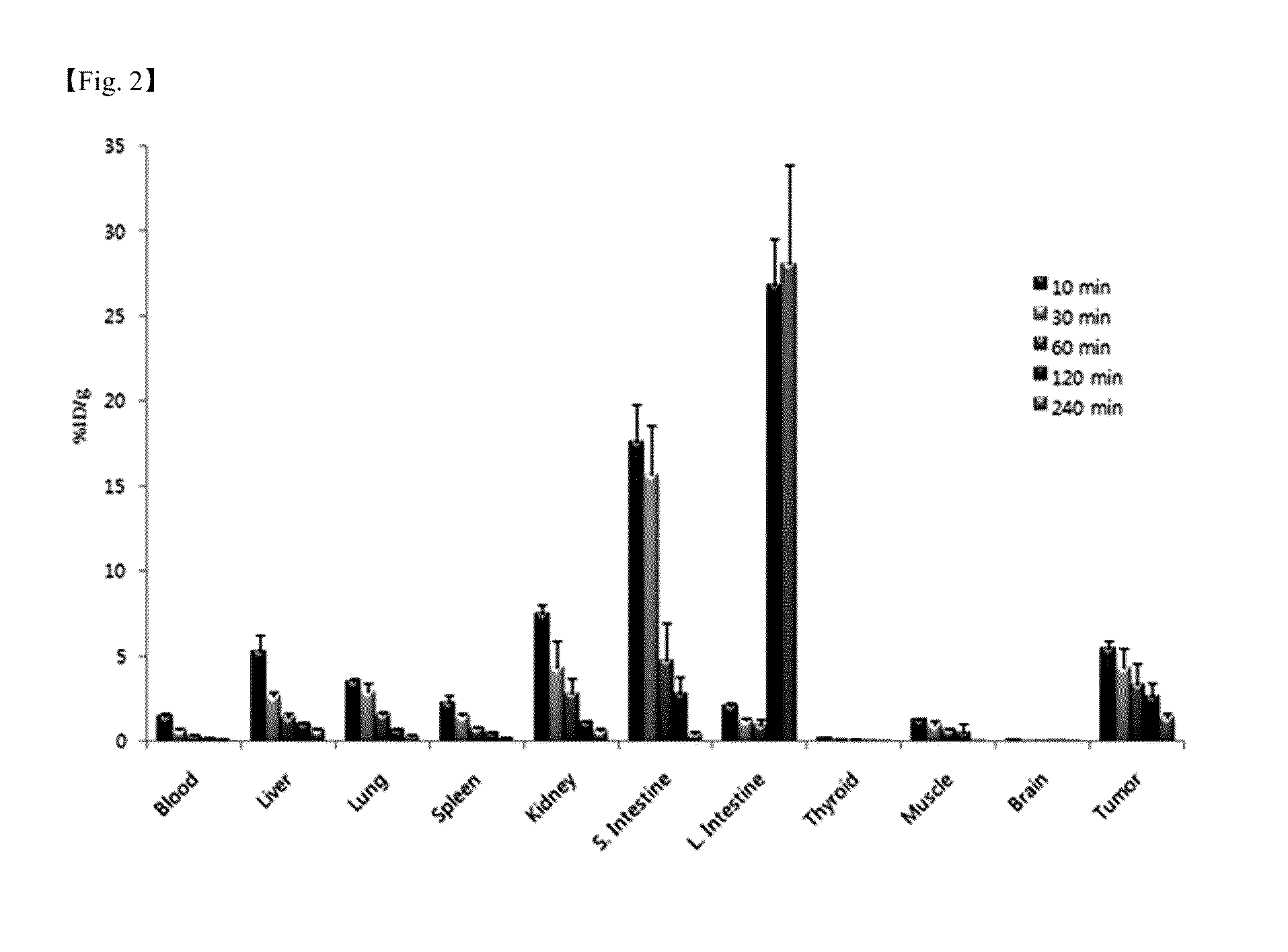
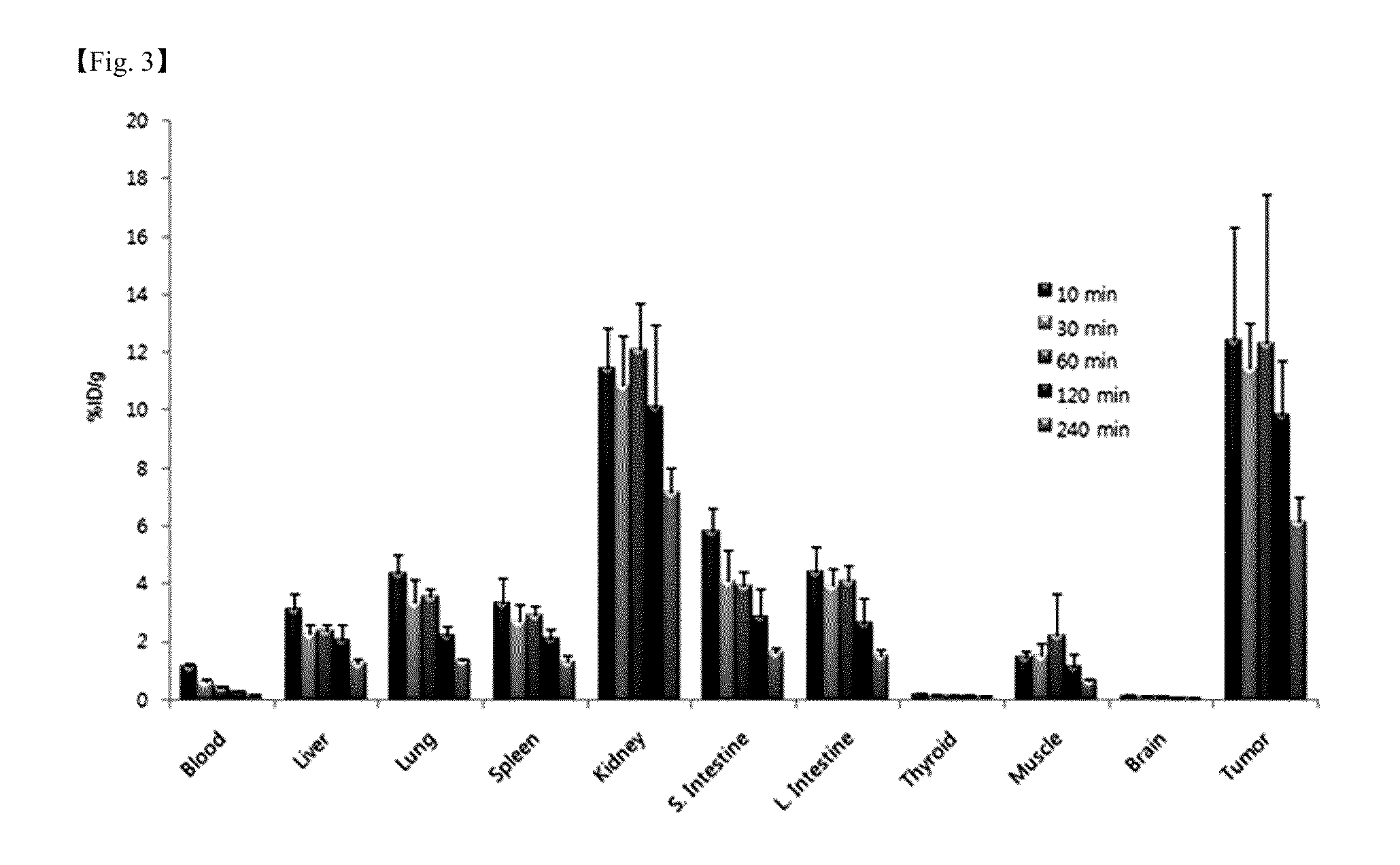
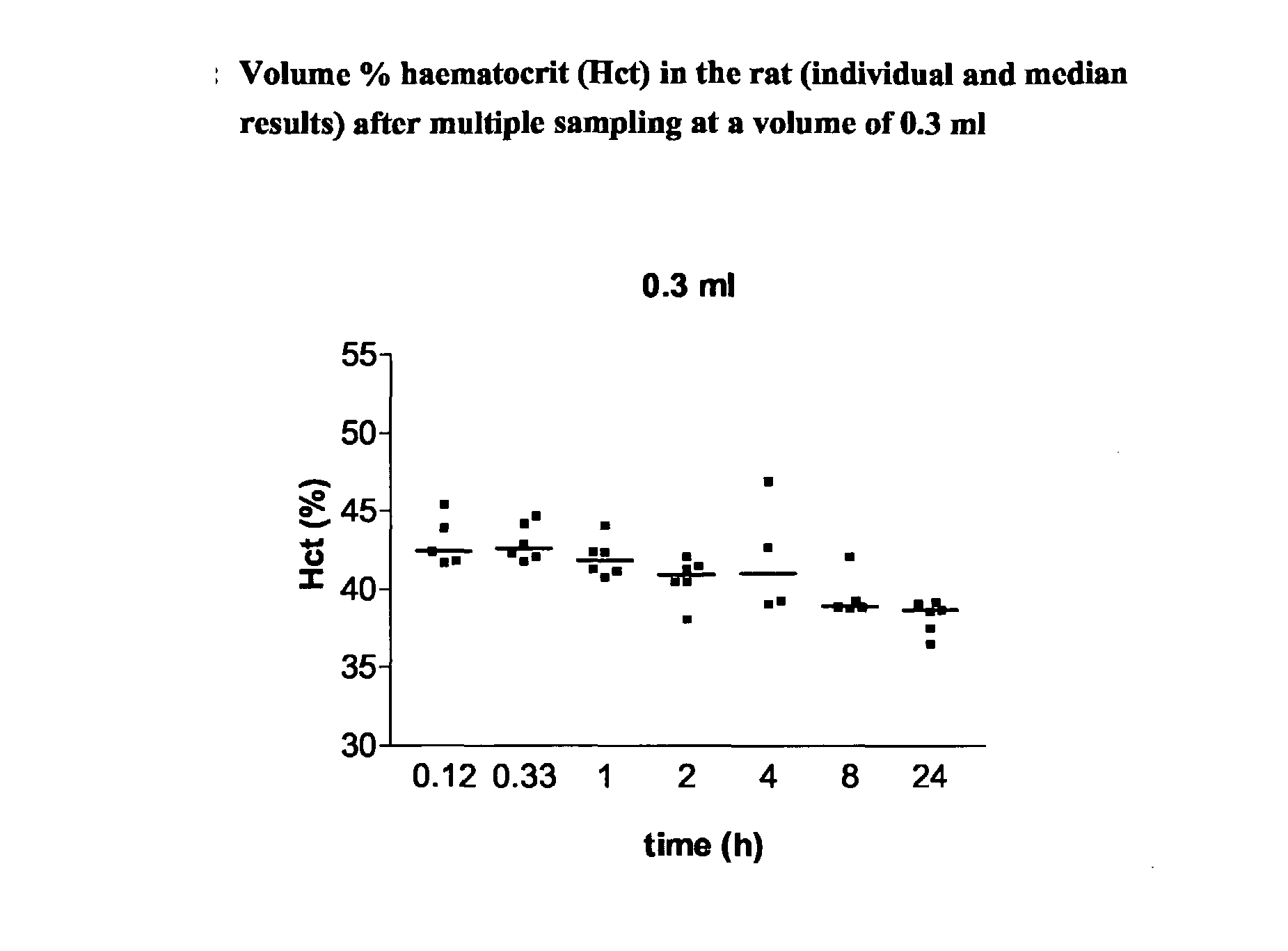
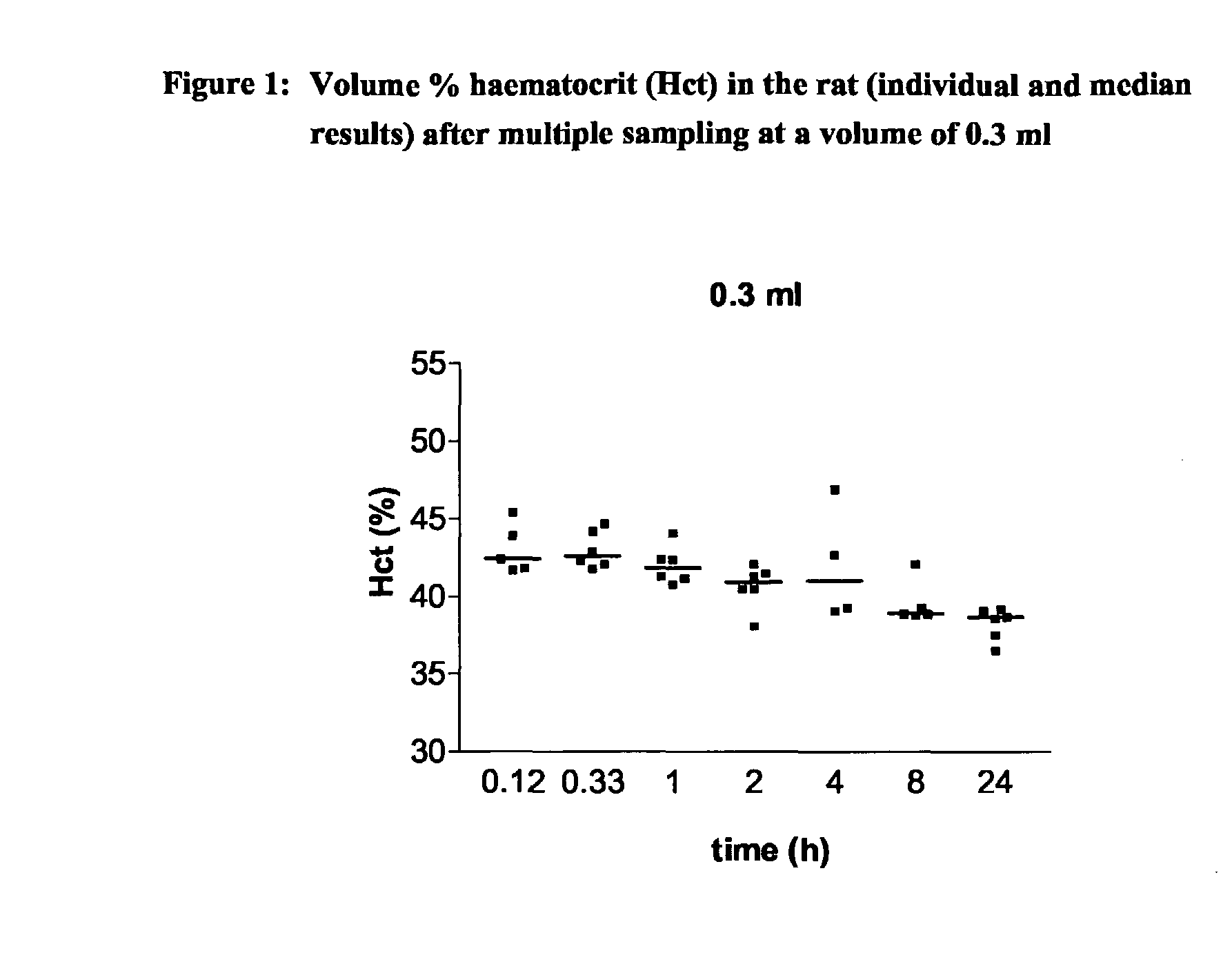
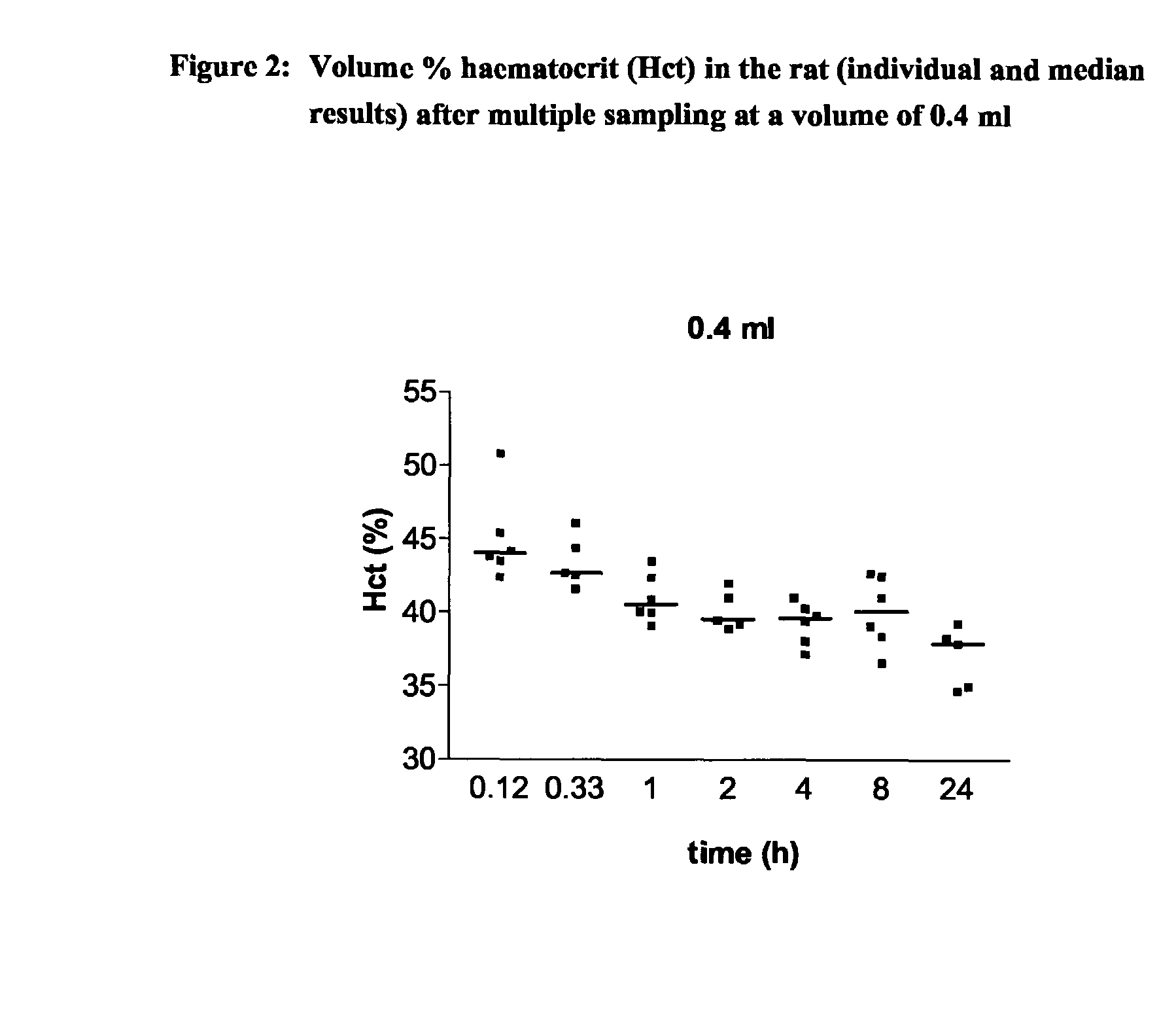
There is a continuing need for increased throughput in the examination of new chemical entities (NCEs) in terms of the pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters. The aim was to validate a new study method which allows a higher throughput, the examination of inter-animal variability and a reduction in the numbers of animals needed for routine bioavailability studies of NCEs in awake rats. The design uses a new method for intravenous (iv) administration via the saphenous vein in combination with serial blood sampling via the tail vein. The multiple sampling method was compared with single sampling (decapitation) and the effect on haematocrit (Hct) levels was studied. Direct injection in the saphenous vein was compared to iv administration using an indwelling jugular catheter. Using structural different CE's, it was shown that a combination of direct injection via the saphenous vein and multiple sampling from the tail vein produces comparable plasma concentrations and subsequent PK results to the comparator methods. Furthermore, Hct levels remained within recommended levels using a total blood sampling volume of up to 2.1 ml per day. The new technique increases throughput by reducing the time required for preparative surgery, increases the quality by allowing inter-animal comparison of major PK parameters as concentration time curves can be collected from each animal and reduces the number of animals required.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
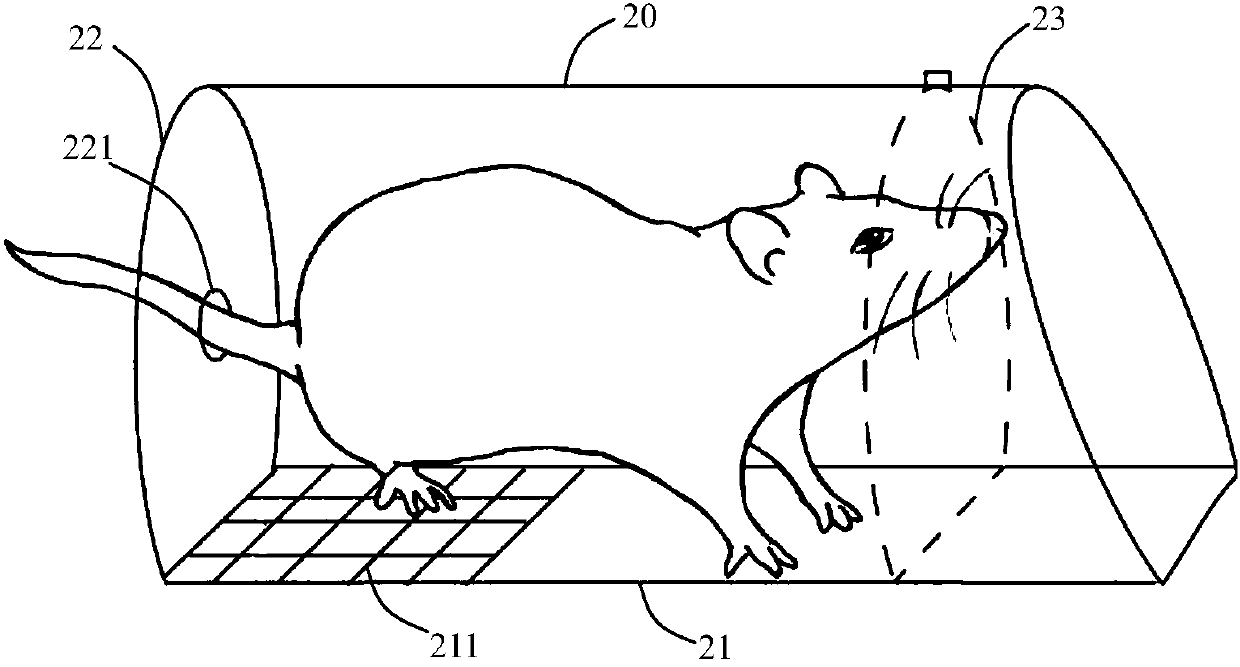
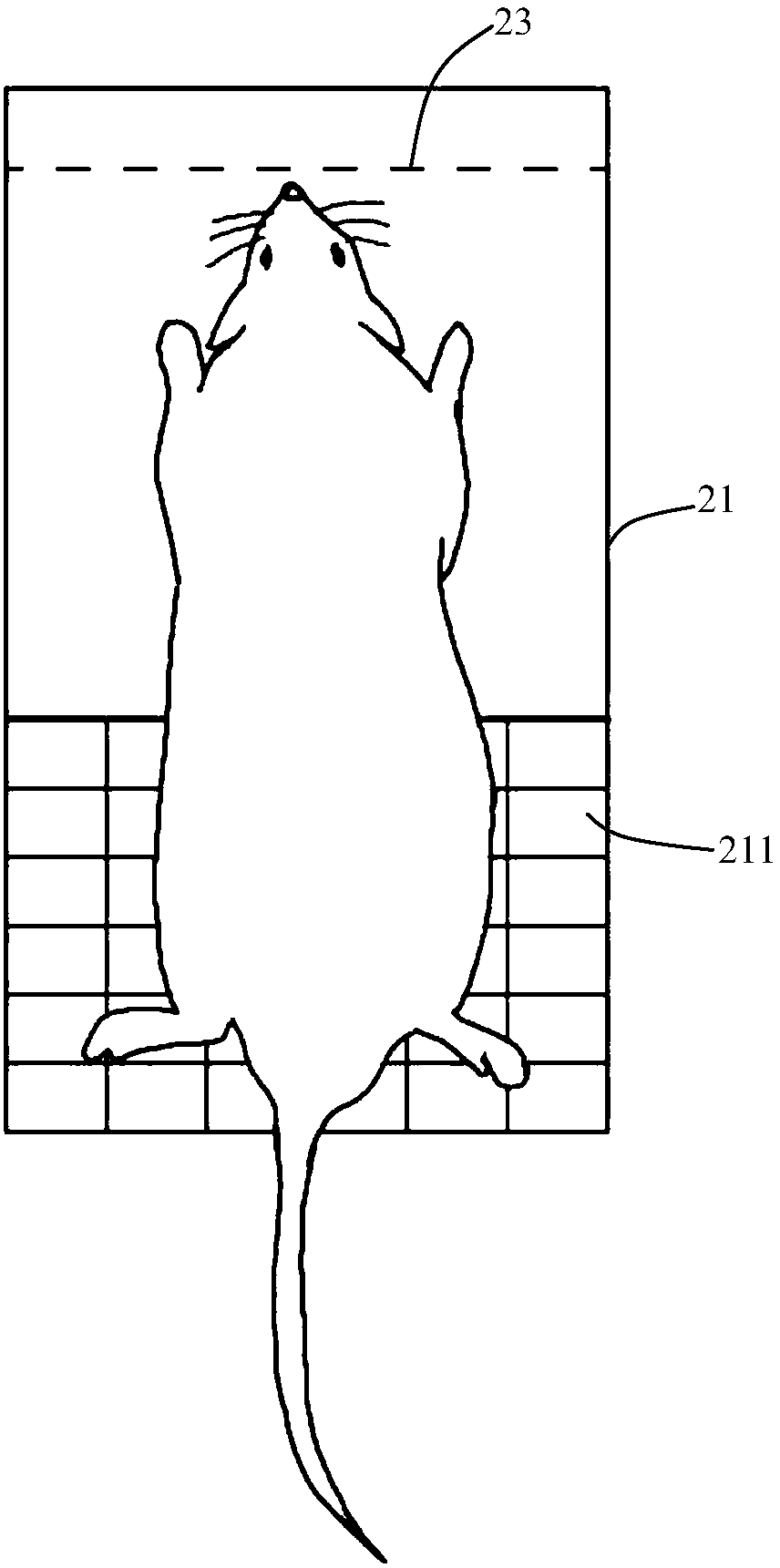
Mouse tail vein blood sampling and injection clamp
The invention discloses a mouse tail vein blood sampling and injection clamp. The mouse tail vein blood sampling and injection clamp comprises a fixing device and a handle device; the fixing device comprises magnetic fixing plates, a fixing opening and a bolster sheet, the magnetic fixing plates can fix the mouse tail to a magnetic panel or a metal plate, the fixing opening is located between a connecting shaft and the front-end magnetic fixing plates, and the rubber bolster sheet is placed in an inner groove of the fixing opening, and is thin at front and thick at back in the horizontal direction of the inner groove; the handle device comprises a spring sheet, handles and the connecting shaft, and the spring sheet is fixed to the inner sides of the handles and used for pressurizing the handles. The mouse tail vein blood sampling and injection clamp has the advantages that that the mouse tail vein blood sampling and injection clamp is simple in structure, small in size and convenient to carry; the rubber bolster sheet is arranged in the clamp and is thin at front and thick at back in the horizontal direction of the inner groove, which conforms to the physiological curvature of themouse tail; the clamp is convenient to operate, and capable of fixing the mouse tail from multiple angles and quickly filling the vein of the mouse tail, tail vein puncturing is facilitated, the timeis saved, the labor can also be saved, and the mouse tail vein blood sampling and injection success rate is increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI TONGJI HOSPITAL
Method for establishing renal dysfunction model of mice with IgA nephropathy
InactiveCN108935316AImprove hypothermiaReduce mortalityCompounds screening/testingPeptide/protein ingredientsBALB/cMortality rate
The invention relates to a method for establishing a renal dysfunction model of mice with IgA nephropathy. The method comprises the steps of selecting BALB / C mice as animal models; the experiment comprises the steps that 1, an oral low-endotoxin bovine serum albumin acidified aqueous solution is used for intragastric administration every other day for five weeks; 2, in the sixth week, tail veins are injected with 0.2mL of a 2% BSA buffer solution once a day for 3 consecutive days; 3, general states of the mice are observed from the ninth week to the eleventh week; in the 12th week, 0.2mL of the SEB buffer solution is injected into the tail veins at a dose of 0.8 mg / kg per mouse once a week for 3 weeks; the 15th week is the end point of the experiment. The method has the advantages that (1)the method effectively reduces the mortality of the mice with the IgA nephropathy; (2) the model can better simulate the pathogenesis of human IgA nephropathy and further screen for drugs for treating the IgA nephropathy; (3) technical operation is easy and convenient, the animal models have a high success rate, and the method has a good application prospect.
Owner:SHUGUANG HOSPITAL AFFILIATED WITH SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
Therapeutic effect of forsythin on rats with sepsis
InactiveCN105878262AReduce mortalityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAdditive ingredientInternational market
The invention relates to the field of treatment of sepsis, specifically to a medicine capable of reducing mortality and relatively prolonging survival time. It is found through current researches that a forsythia extract has effects of destroying bacterial endotoxin and inhibiting various positive and negative bacteria. But the mechanism of action hasn't been completely illustrated clearly, thus affecting the promotion of the forsythia extract to the international market. By silica gel column chromatography, Saphadex LH-20 column chromatography, recrystallization and the like, the substance is separated from 50% forsythia ethanol extract. By chemical identification, H NMR spectroscopy, C NMR spectroscopy, thin-layer chromatography, high performance liquid chromatography and the like, structural identification is carried out on a substance, and its structure and name are determined. By replication of cecal ligation perforation animal model, the pathological process of human sepsis is simulated. Tail vein injection is carried out for drug delivery, and postoperative survival rate of rats is observed after operation. According to the invention, forsythin is used as a main component to prepare an injection which is used for treatment of sepsis.
Owner:李志军
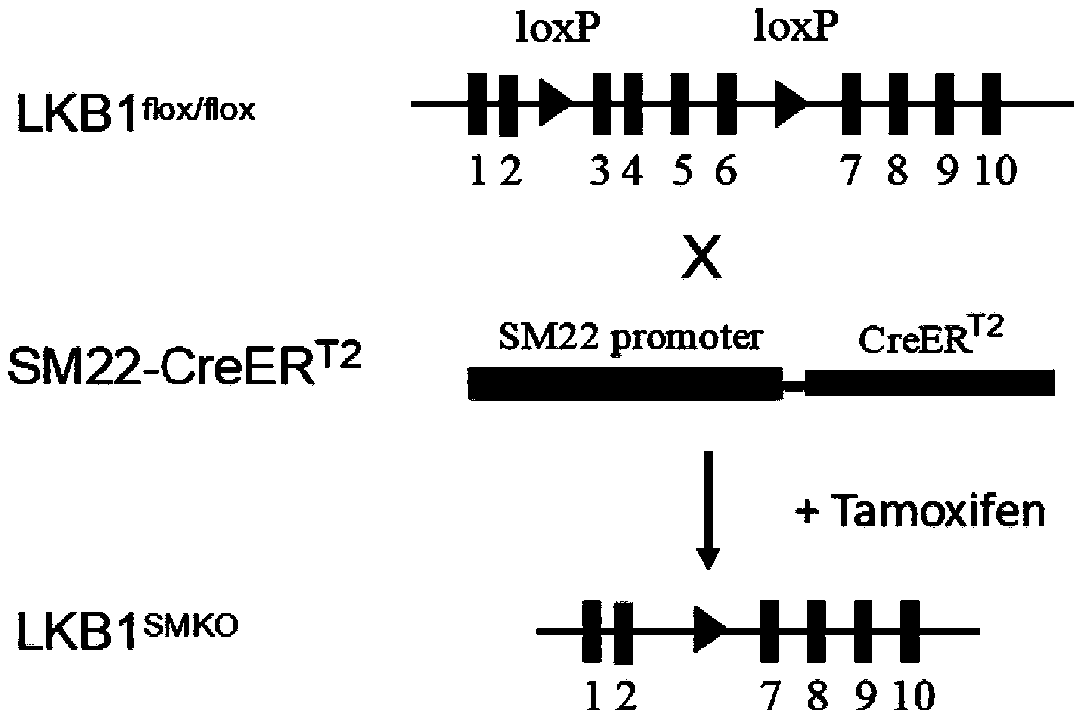
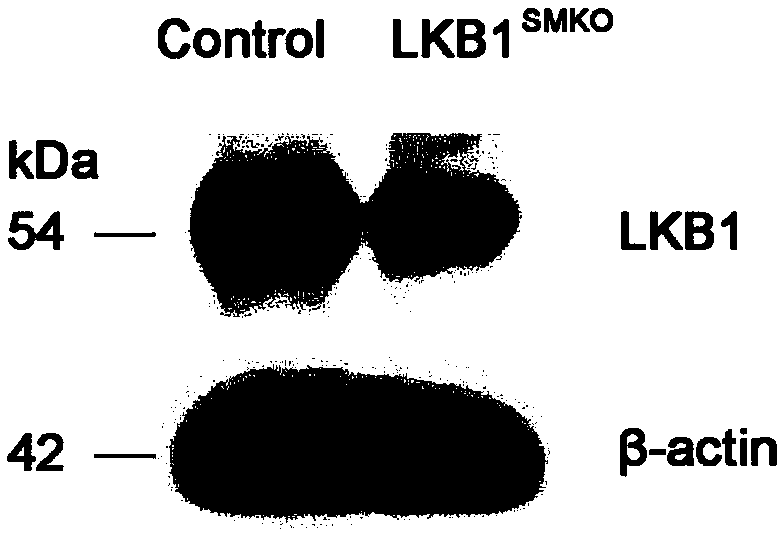
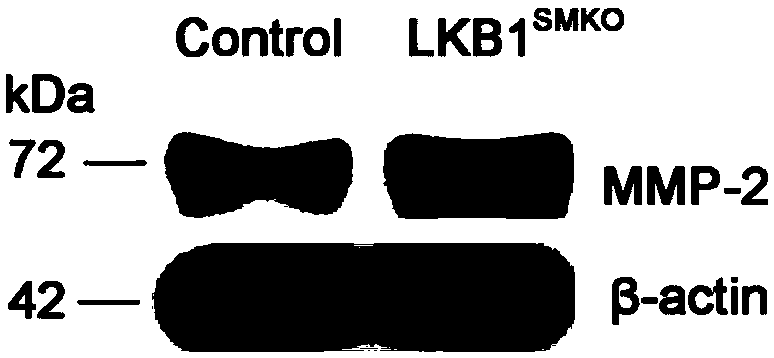
Application of LKB1 gene in preparation of anti-abdominal-aortic-aneurysm drugs
ActiveCN109602918AReduce morbidityHigh expressionAntineoplastic agentsGene therapySmooth muscleCancer research
The invention relates to application of a LKB1 gene in preparation of anti-abdominal-aortic-aneurysm drugs. According to the application of the LKB1 gene in preparation of the anti-abdominal-aortic-aneurysm drugs, important role of the LKB1 gene in regulating expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 in smooth muscles is disclosed by constructing gene knockout mice with LKB1 gene specifically knocked-out in smooth muscles; and significantly increased incidence of abdominal aortic aneurysm in the LKB1-gene-knockout mice is discovered by constructing abdominal aortic aneurysm models in mice by performing subcutaneous infusion of angiotensin II (Ang II). In addition, lentiviruses with the LKB1 gene are further prepared by the invention. Being injected into tail veins of mice, the lentiviruseswith the LKB1 gene are capable of significantly reducing incidence of abdominal aortic aneurysm in the mice. The anti-abdominal-aortic-aneurysm drugs prepared or screened by using the LKB1 gene as a target according to the invention are of great significance to treatment on abdominal aortic aneurysm.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV QILU HOSPITAL
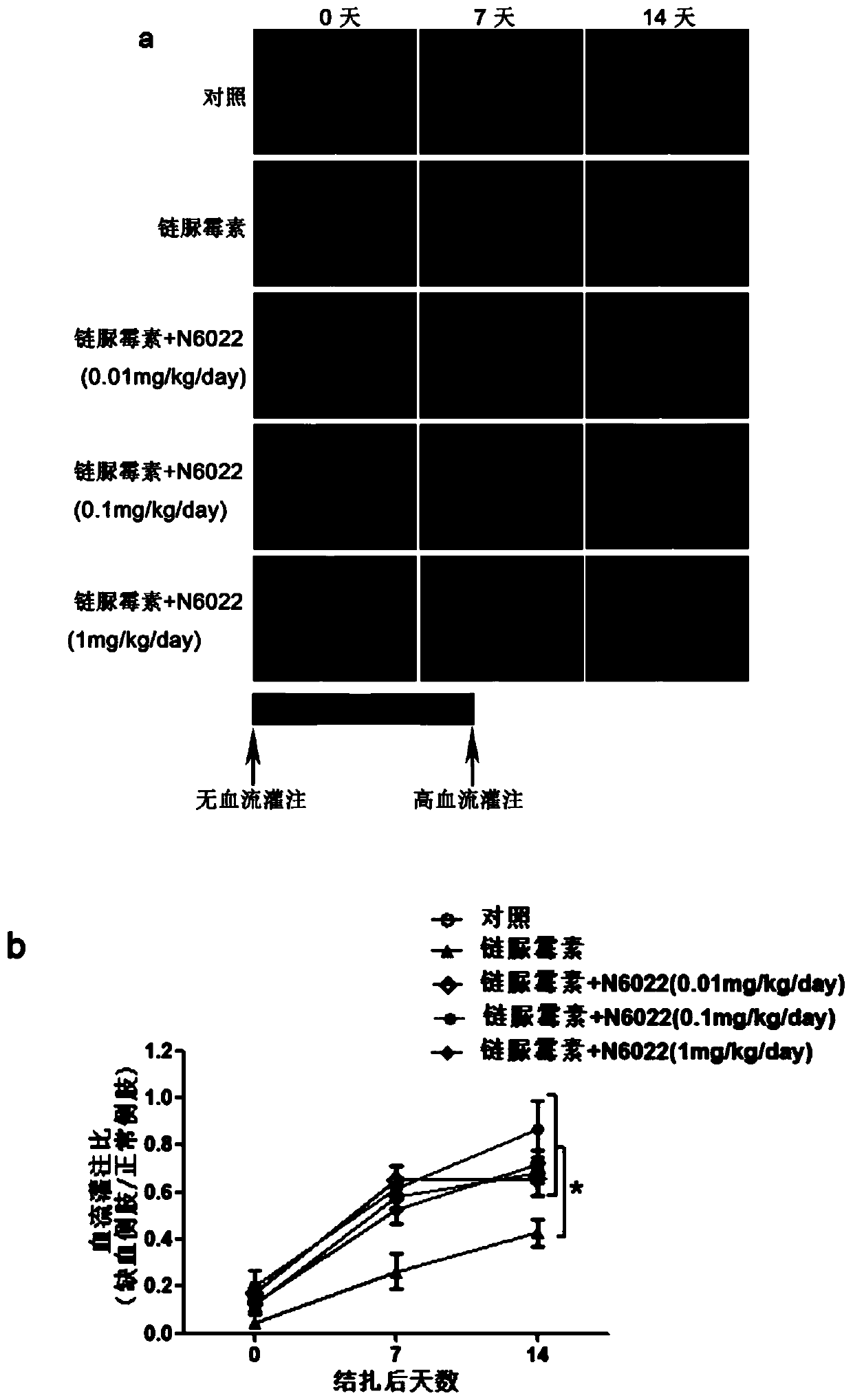
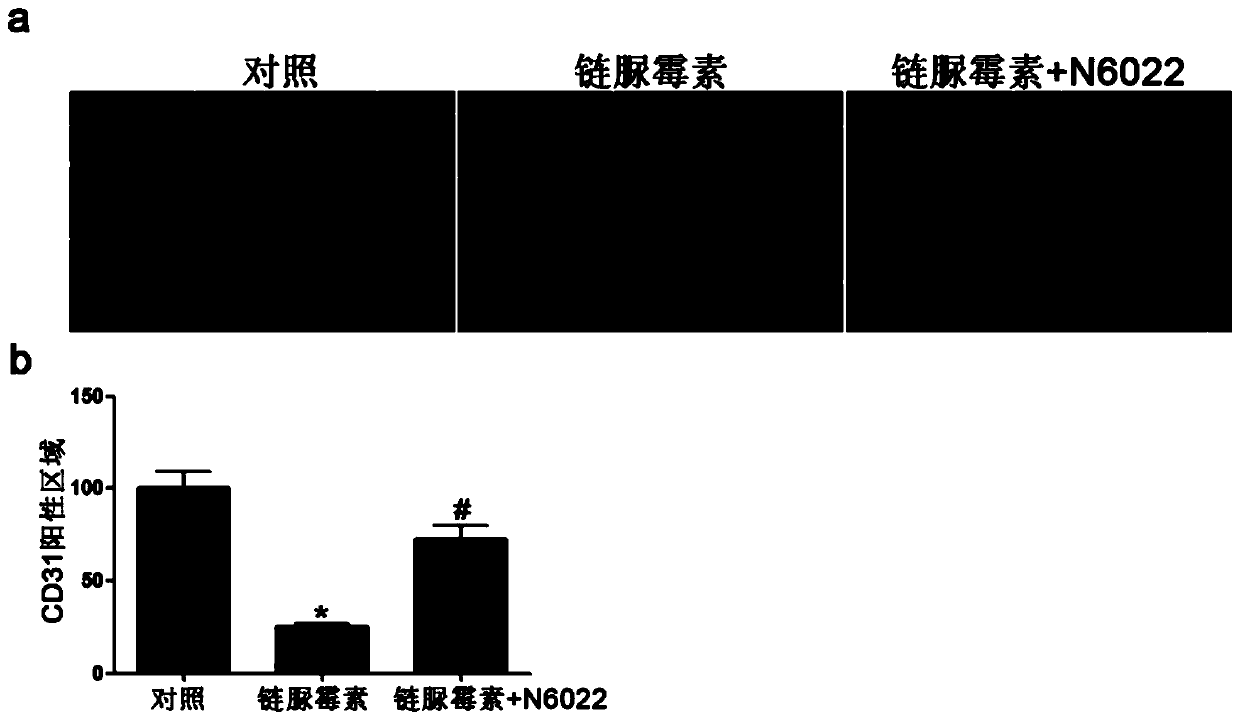
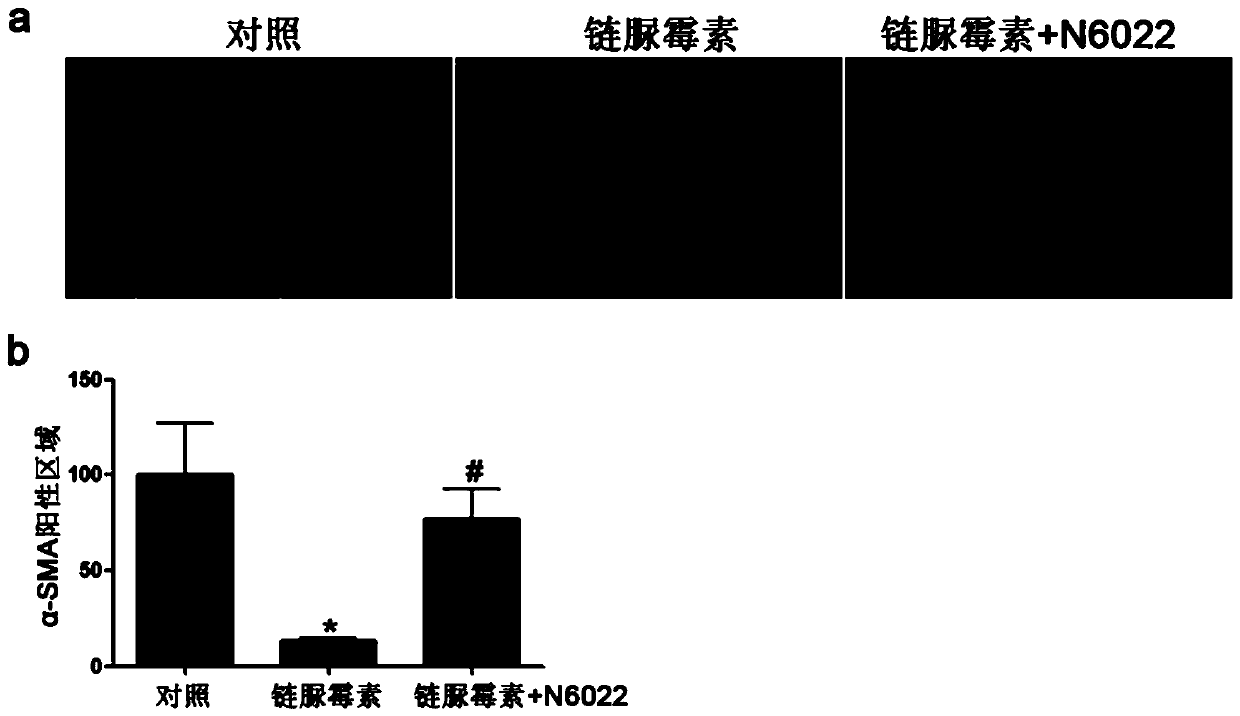
Medical use of n6022 in the treatment of diabetic peripheral arterial disease
ActiveCN109999029BImproved blood flow restorationPromote migrationOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderLimb ischemiaDisease
The invention relates to medical application of N6022 in treating diabetic peripheral arterial diseases, and relates to the cardiovascular field. At an animal level, in a diabetic mouse side limb ischemia model, by means of tail vein injection of N6022, blood flow recovery can be improved, angiogenesis of skeletal muscles can be improved, and the diabetic peripheral arterial diseases can be alleviated. At a cell level, by giving a GSNOR inhibitor, N6022 can alleviate reduction, caused by high glucose, of the human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) migration capacity and vessel formationcapacity. A new application field of N6002 is exploited, and a meaningful reference is provided for treating the diabetic peripheral arterial diseases and improving diabetic vascular lesion conditions.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
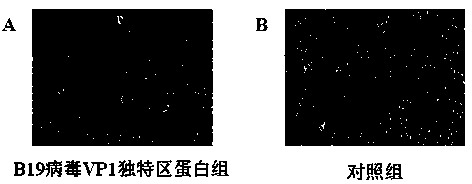
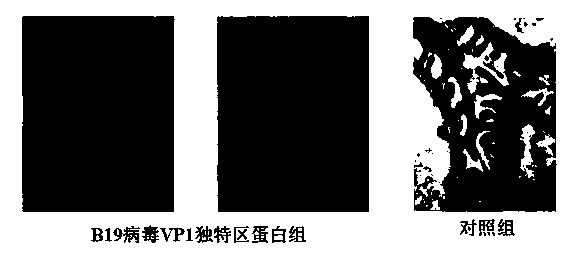
Application of B19 virus VP1 unique protein to construct viral nephropathy model
InactiveCN104083753AGuaranteed to successfully buildImprove securityPeptide/protein ingredientsBALB/cKidney
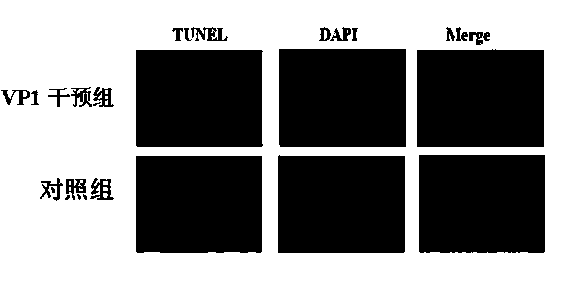
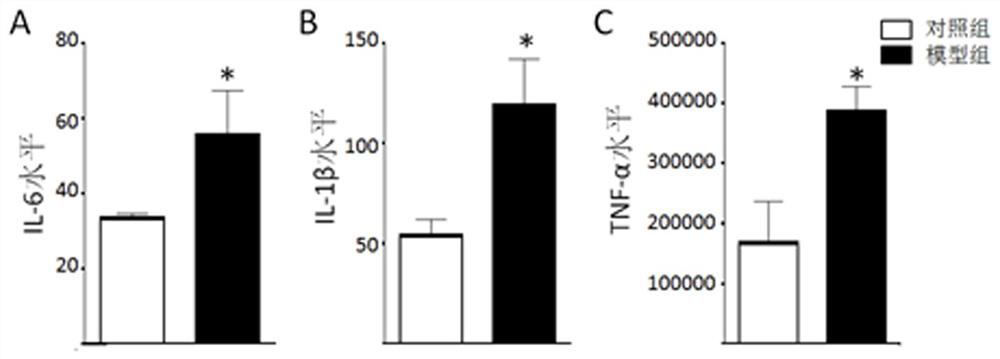
The invention discloses application of B19 virus VP1 unique protein to construct a viral nephropathy model. The application comprises: injecting purified B19 virus VP1 unique protein into BALB / c mouse via tail vein for three times with the interval of 10 day, and taking a sample for correlated detection after 10 days of performing the final injection; and performing analysis on kidney tissue respectively by utilizing a light microscope, an electron microscope and TUNEL immunofluorescence, and performing routine analysis on urine and peeing. The results show that B19 virus VP1 unique protein is capable of causing change of kidney tissue and urine, and therefore the B19 virus VP1 unique protein can be used to successively construct the viral nephropathy model. There is certain risk by using a common active virus to establish the viral nephropathy model through infection, while the technical scheme of utilizing B19 virus VP1 unique protein to construct the viral nephropathy mode has the characteristics of good safety, good maneuverability and high success rate.
Owner:FUZHOU GENERAL HOSPITAL OF NANJING MILITARY COMMAND P L A
A device for animal tail vein injection
The invention provides a device for animal tail vein injection, and the device can effectively fix an animal body and facilitate animal tail vein injection. The device comprises a bottom plate and a semi-cylindrical cover body, the sealing end of the cover body is provided with a through hole through which an animal tail can stretch out, and the opening end of the cover body is provided with a piston, wherein the inner diameter of the piston is matched with that of the cover body, and non-slip rubber wraps the edge of the piston; a magnifying lens which is connected to the top of the cover body through a connecting rod and used for magnifying the animal tail is arranged over the through hole, and an auxiliary rod is connected to the connecting rod and provided with a lighting device. The device can be adjusted according to the body size of an experimental animal and is used for fixing the experimental animal without needing to fix the animal tail, and due to the fact that the magnifying lens is installed over the through hole and the lighting device is assembled, the vein of the tail is easier to see clearly; the device is suitable for tail vein injection of various animals with the smaller body size.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
HDAC5 as a peripheral marker in a rat model of progeny infected during pregnancy
ActiveCN112400799BAbnormal expression phenomenon earlyMicrobiological testing/measurementAnimal husbandryAbnormal expressionIntravenous IG
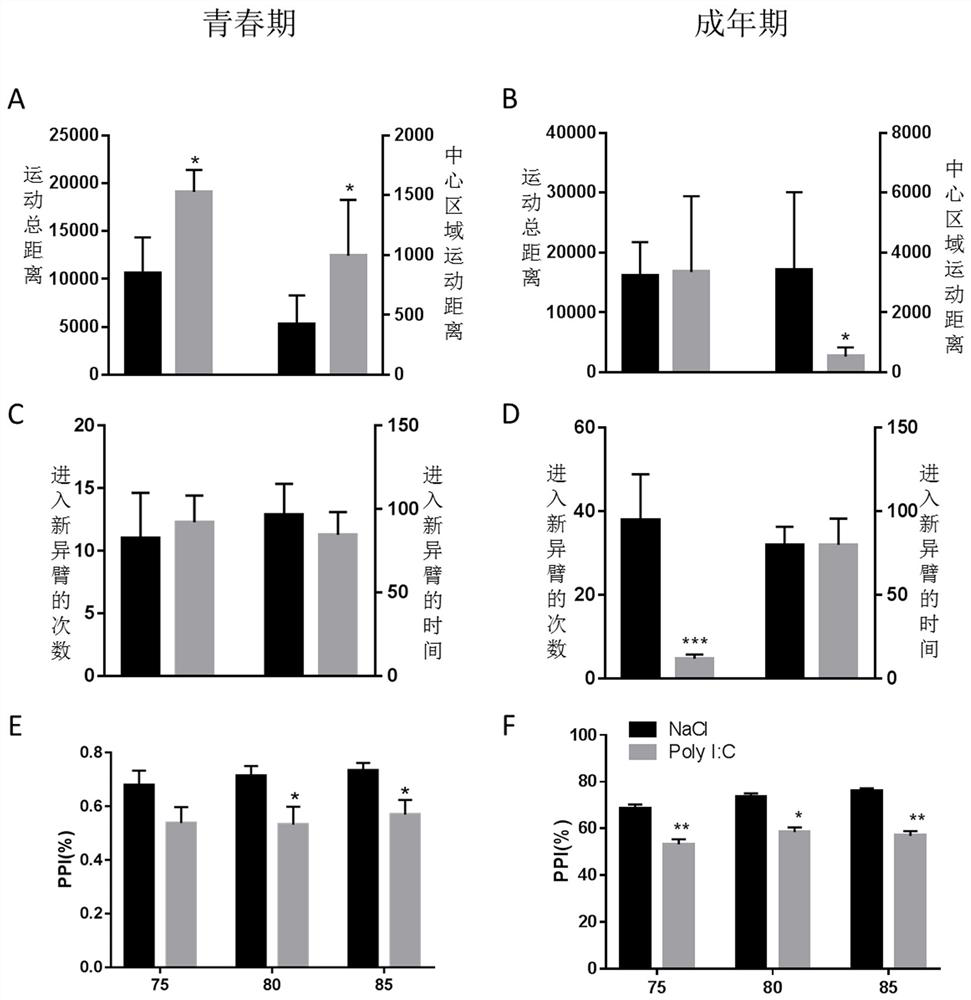
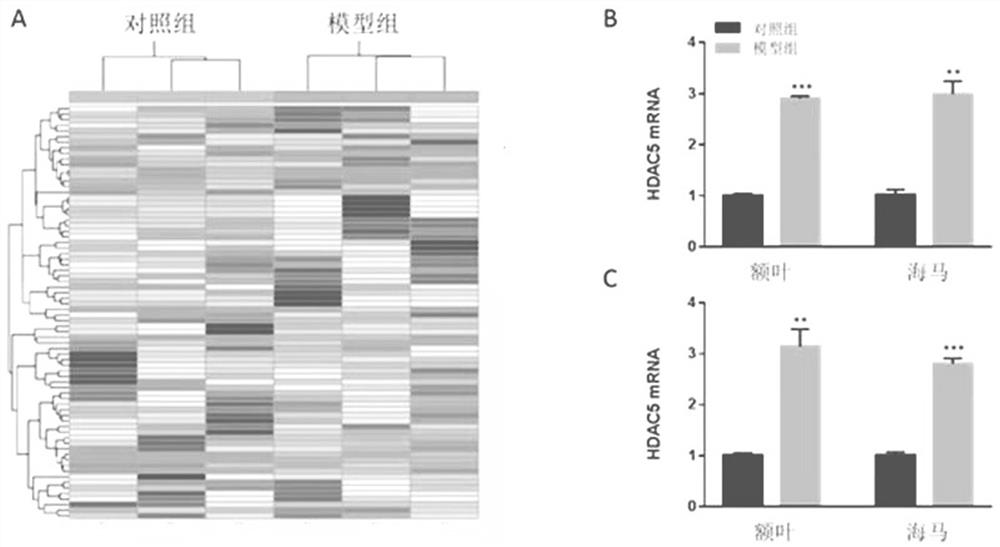
The present invention provides a test method for evaluating HDAC5 as an early peripheral marker of the quality of the offspring rat model infected during pregnancy, by injecting Poly I:C into the tail vein on the 9th day of pregnancy to activate the immune response of pregnant mice to prepare the offspring rat model infected during pregnancy, Comprehensive behavioral and HDAC5 expression analysis, found that the abnormal expression of HDAC5 in model rats appeared earlier than its abnormal behavior, and the change of HDAC5 expression in peripheral blood was consistent with the central reaction, so HDAC5 can be used as a tool for evaluating the quality control of offspring rat models infected during pregnancy Early peripheral marker molecules. The invention has ingenious conception and scientific scheme, and is of great significance to human epidemiological research and drug research and development.
Owner:河南省精神病医院
Use of fat emulsion as photoacoustic imaging contrast agent
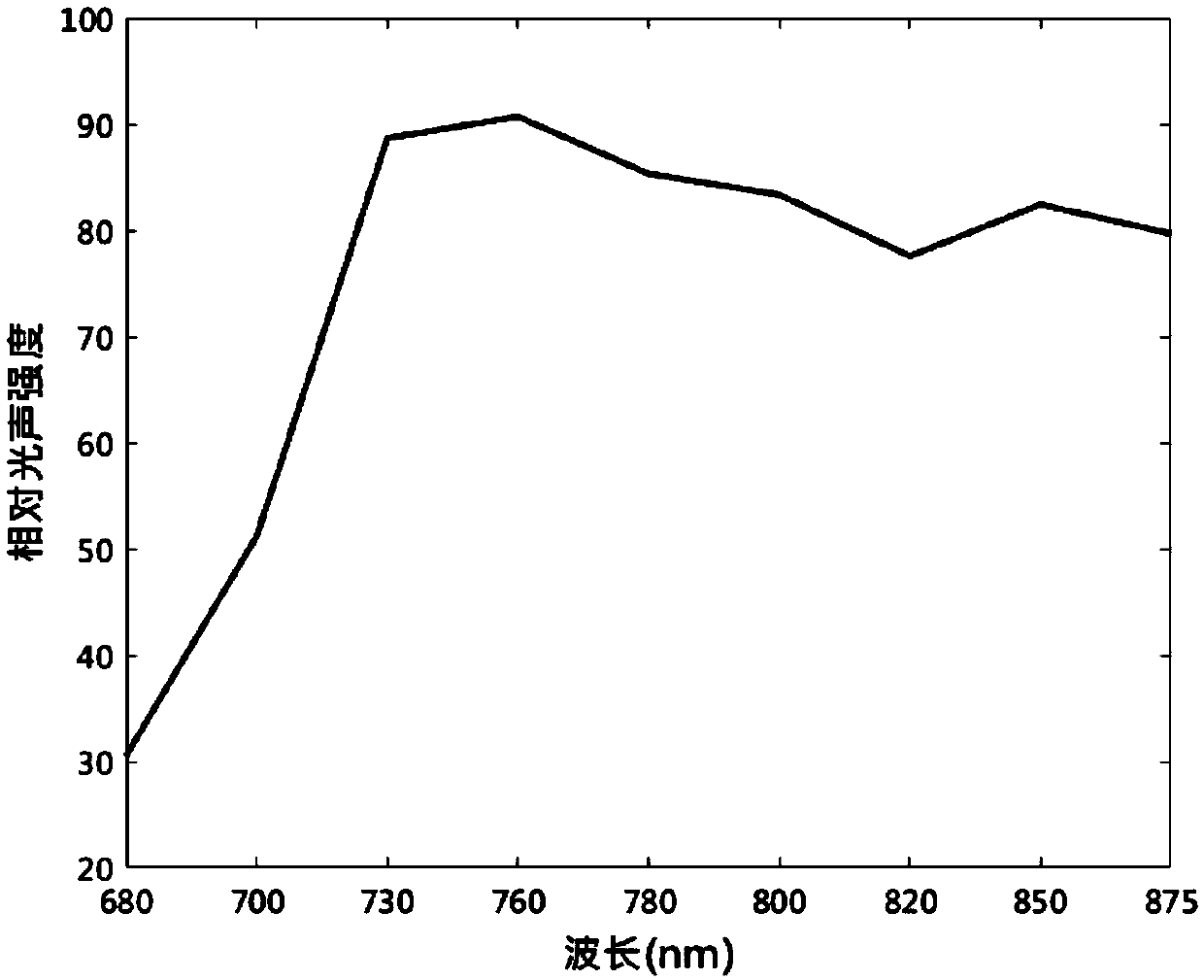
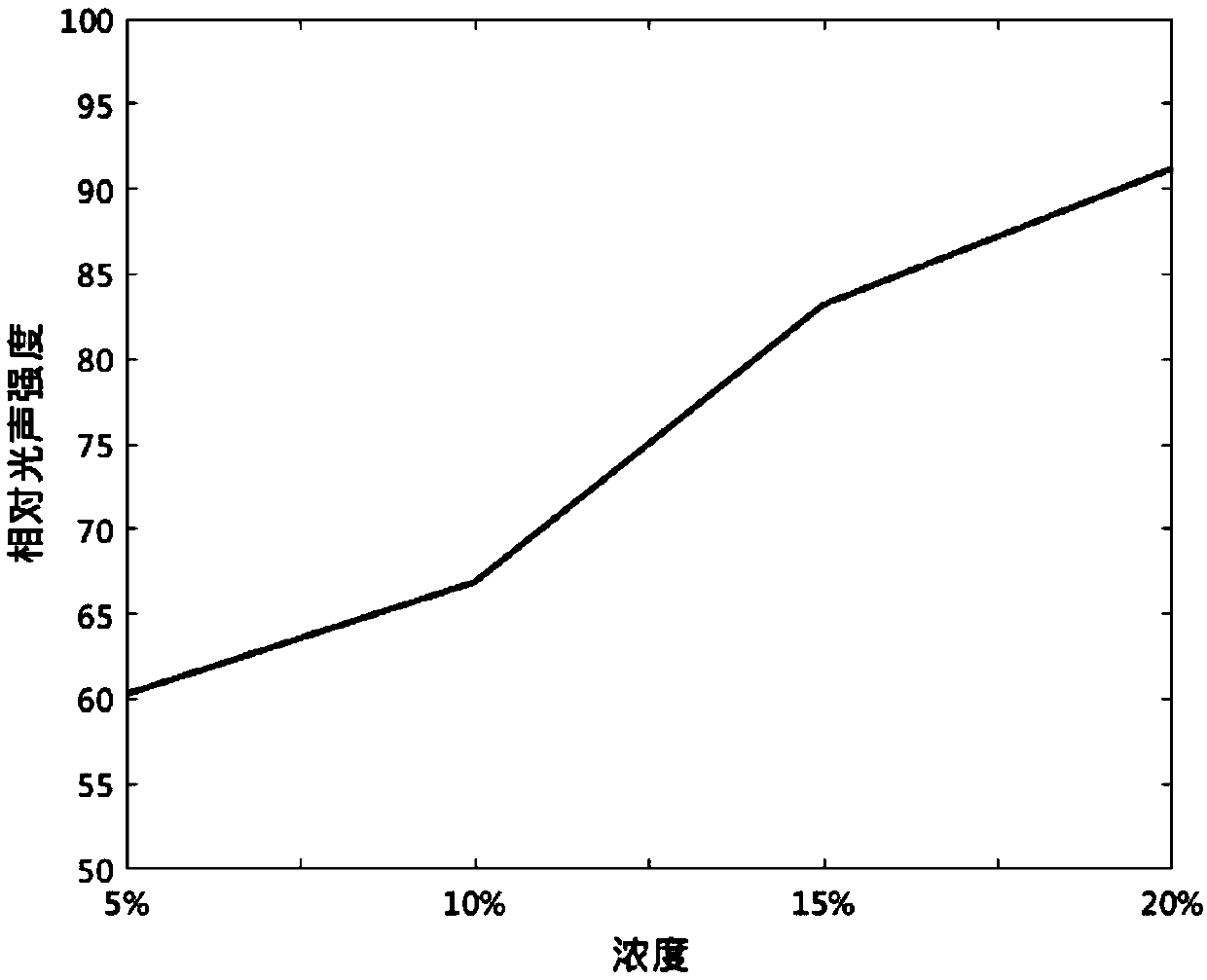
InactiveCN109529061AEasy to prepareLow costEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsGlycerolAnimal imaging
The invention proposes the use of a fat emulsion as a photoacoustic imaging contrast agent, and belongs to the fields of biology and optics. The fat emulsion enhances the contrast ratio of a tissue photoacoustic signal and image. The fat emulsion is used for imaging animals or humans; for animal imaging, the fat emulsion is injected into animals through tail veins; and for human imaging, the fat emulsion is intravenously injected into the human body. The fat emulsion consists of soybean oil, lecithin and glycerin, and each 1000 ml of 20% fat emulsion contains 200 g of soybean oil, 12 g of lecithin, and 22 g of glycerin. The use of the fat emulsion as the photoacoustic imaging contrast agent can significantly enhance the contrast ratio of tissue photoacoustic imaging. In addition, the fat emulsion is often used as a supplement for intravenous nutrition in clinical practice. Compared with other photoacoustic imaging contrast agents, the fat emulsion is simple to manufacture, low in cost,and high in biosafety and has great potential for application as the imaging contrast agent.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Animal experimental facility
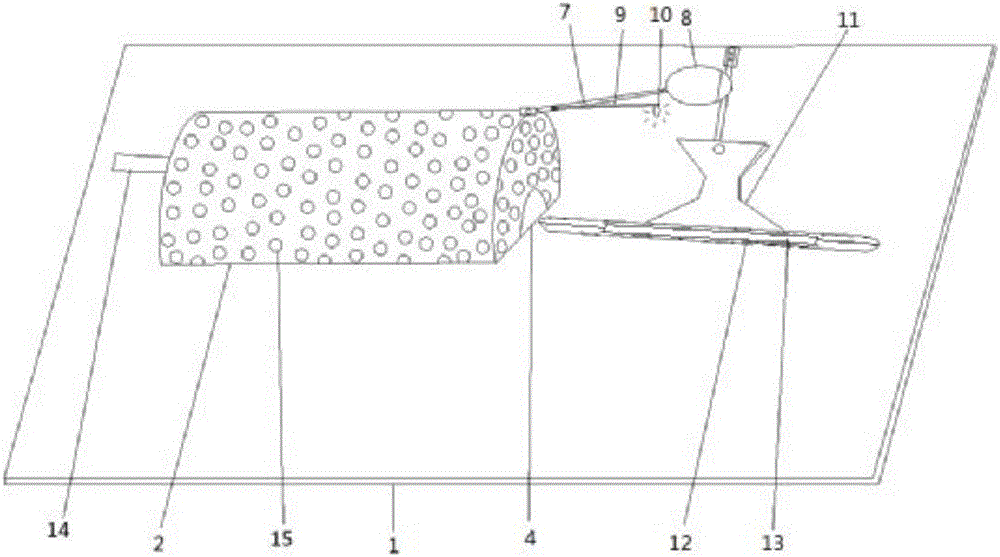
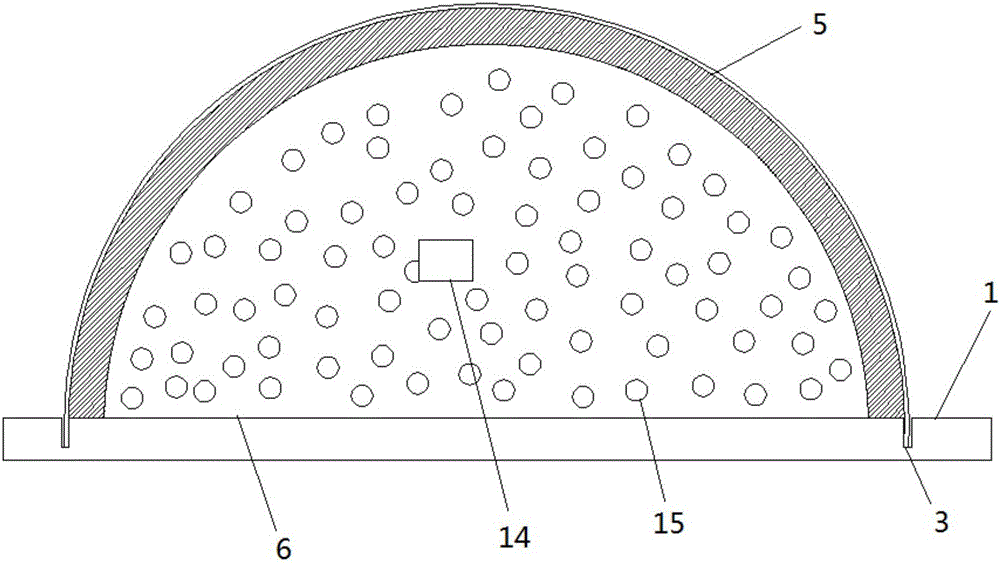
PendingCN107890380ADoes not affect dietDoes not affect drinking waterDiagnostics using lightSurgeryBlood collectionEngineering
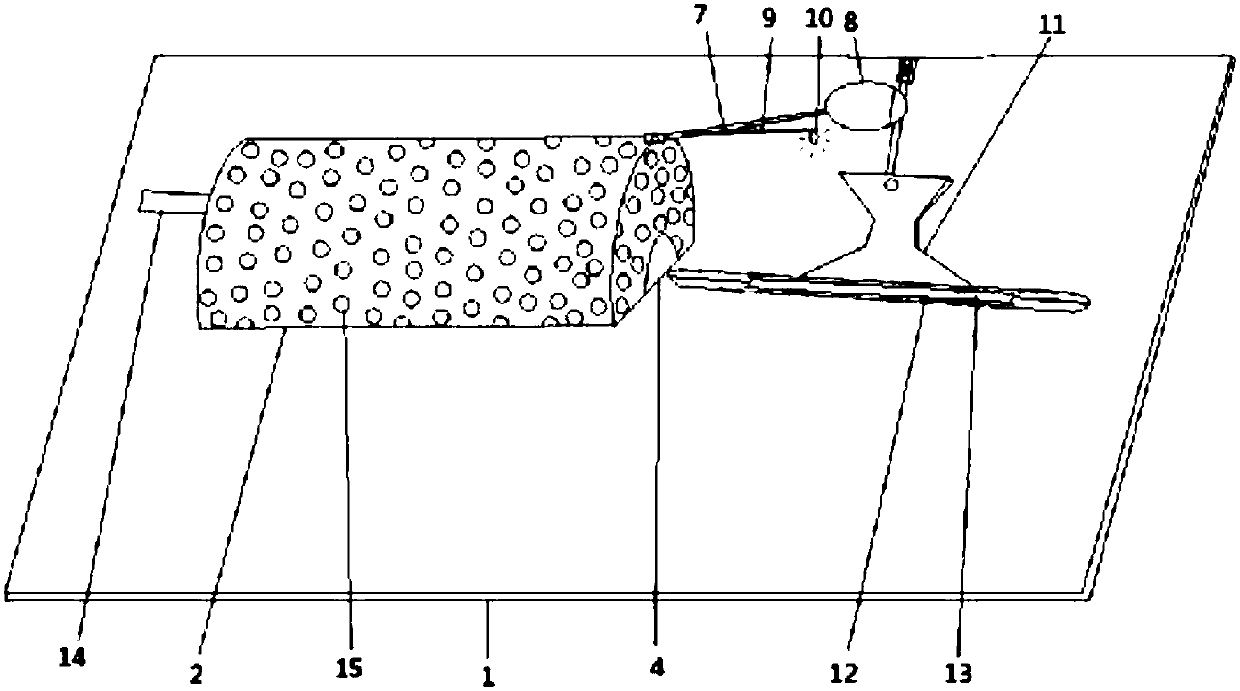
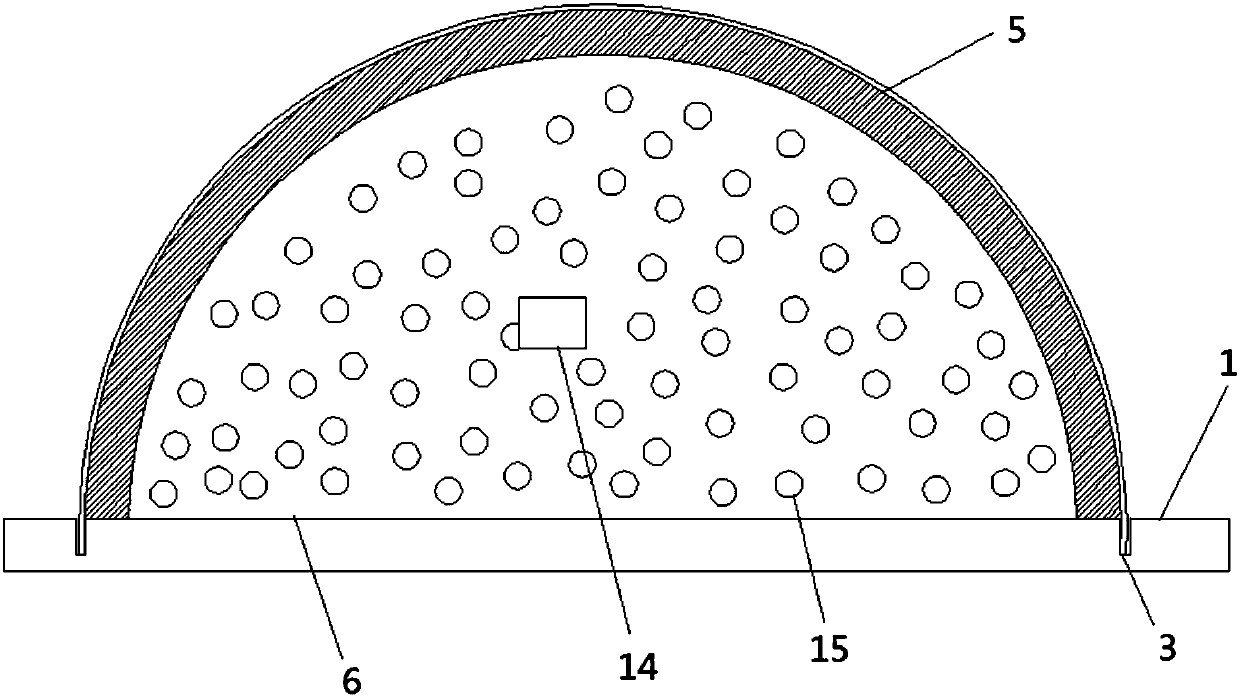
The invention discloses an animal experimental facility. The animal experimental facility comprises a body frame and a fixed barrel used for containing an experimental animal, wherein a partition board is arranged in the body frame, and the fixed barrel is fixed on the partition board; a cover plate is arranged at the rear end of the fixed barrel, and a through hole used for enabling a tail of theexperimental animal to pass through is formed in the cover plate; and an infrared light source which can irradiate the tail of the experimental animal is arranged on the partition board. By adoptingthe animal experimental facility disclosed by the invention, an injector can be easily pricked into a caudal vein of the animal, caudal vein injection or continuous blood sampling operation can be carried out, repeated operation does not need to be carried out for grabbing and fixing the animal, and stress reaction caused by repeated grabbing of the animal and negative influence on experimental study are avoided to the utmost extent.
Owner:上海市生物医药技术研究院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com