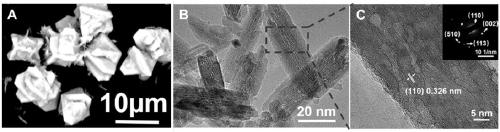
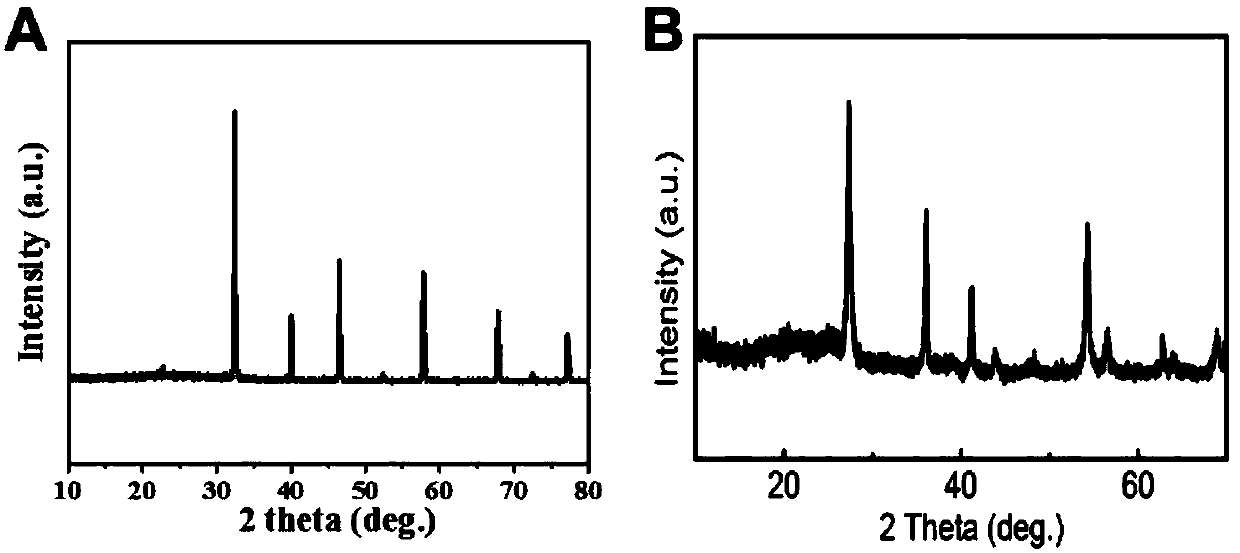
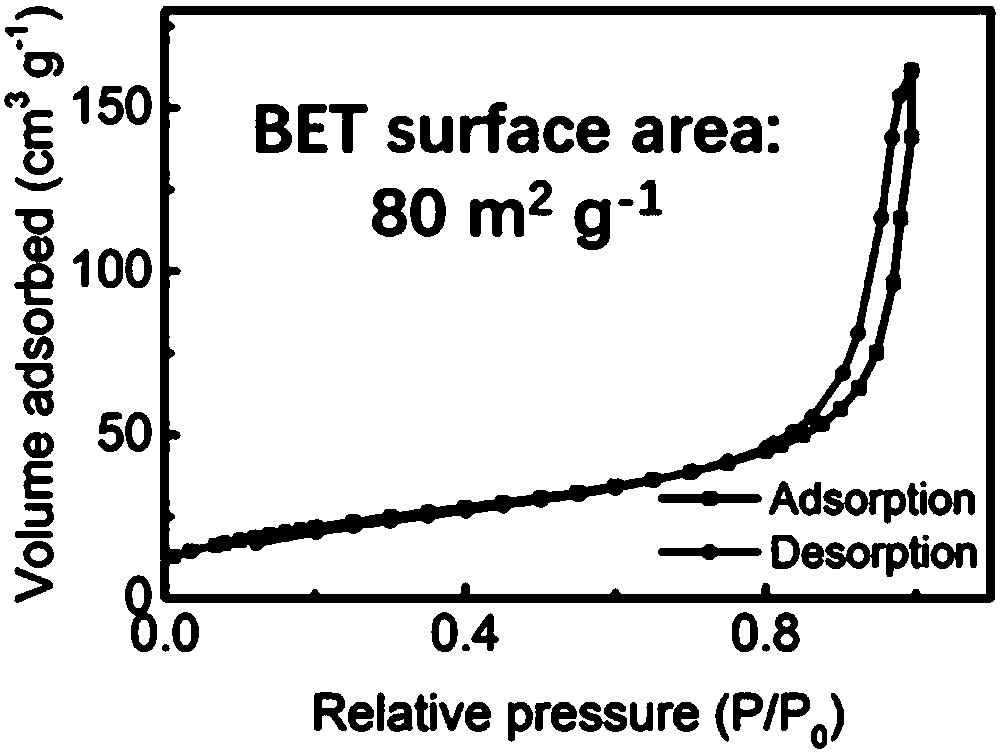
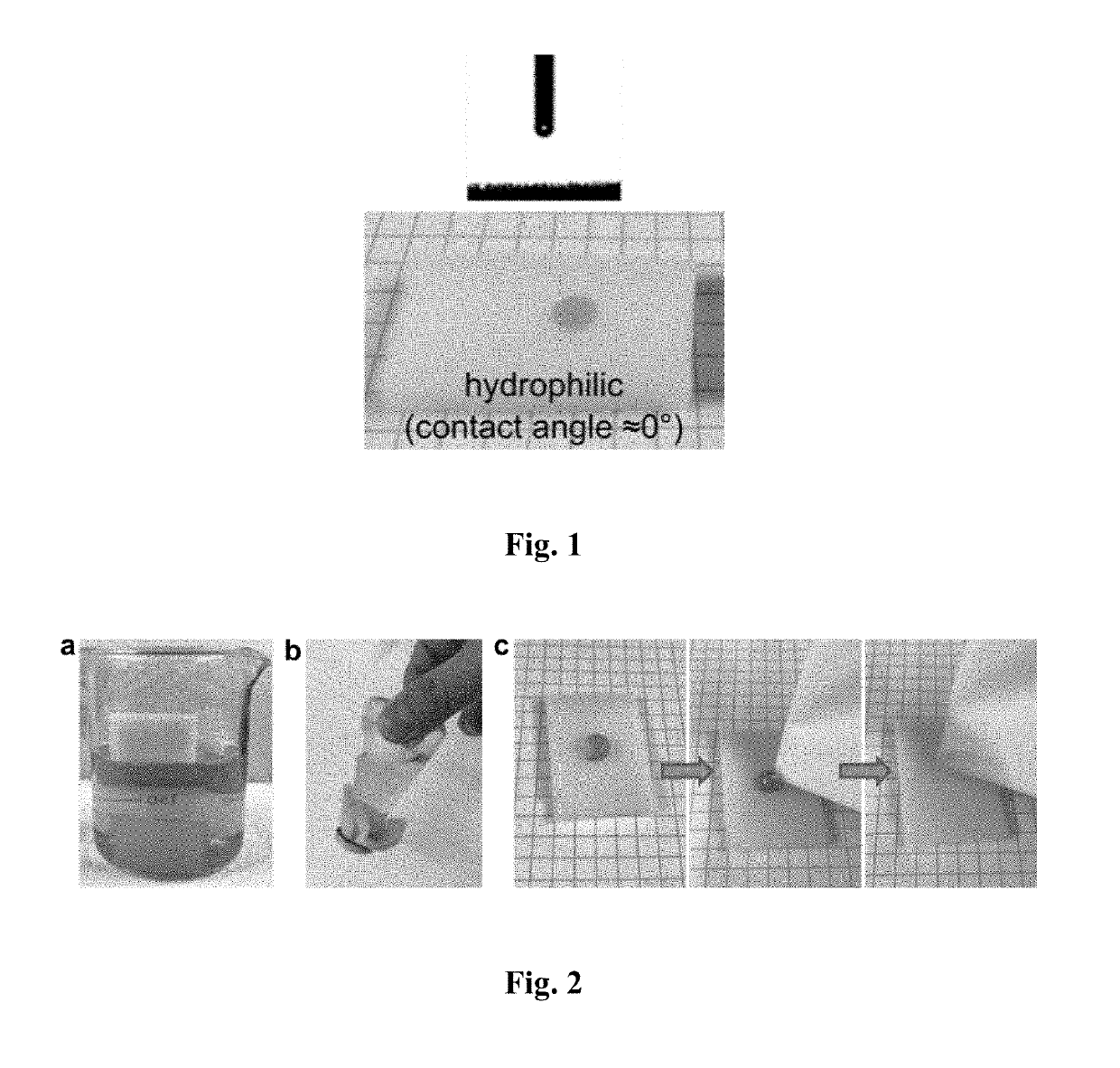
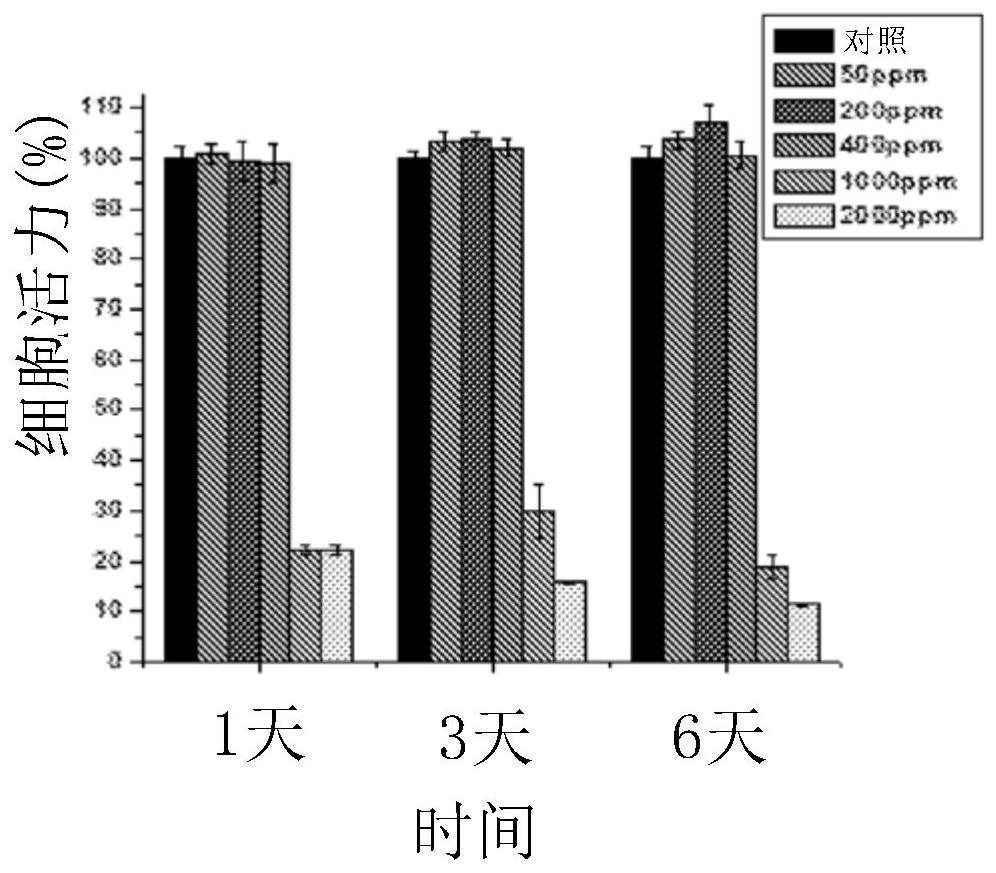
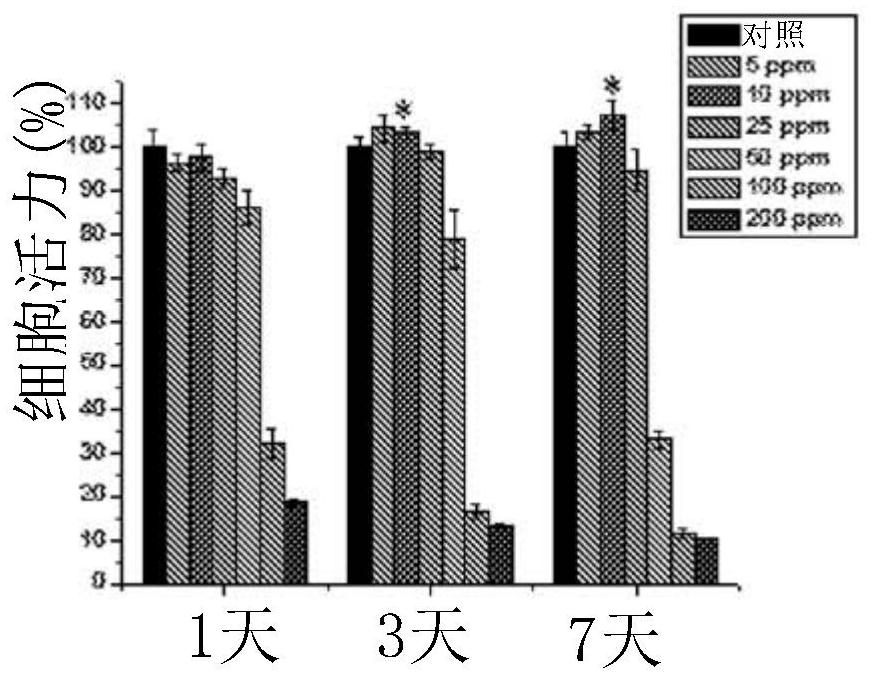
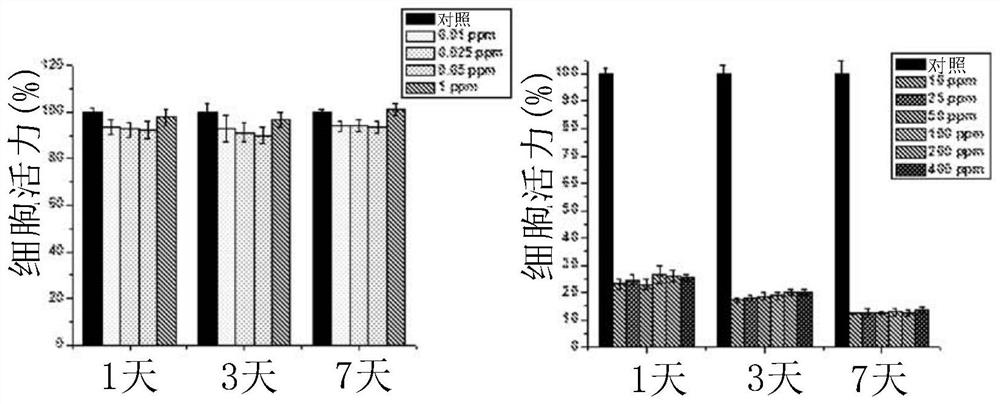
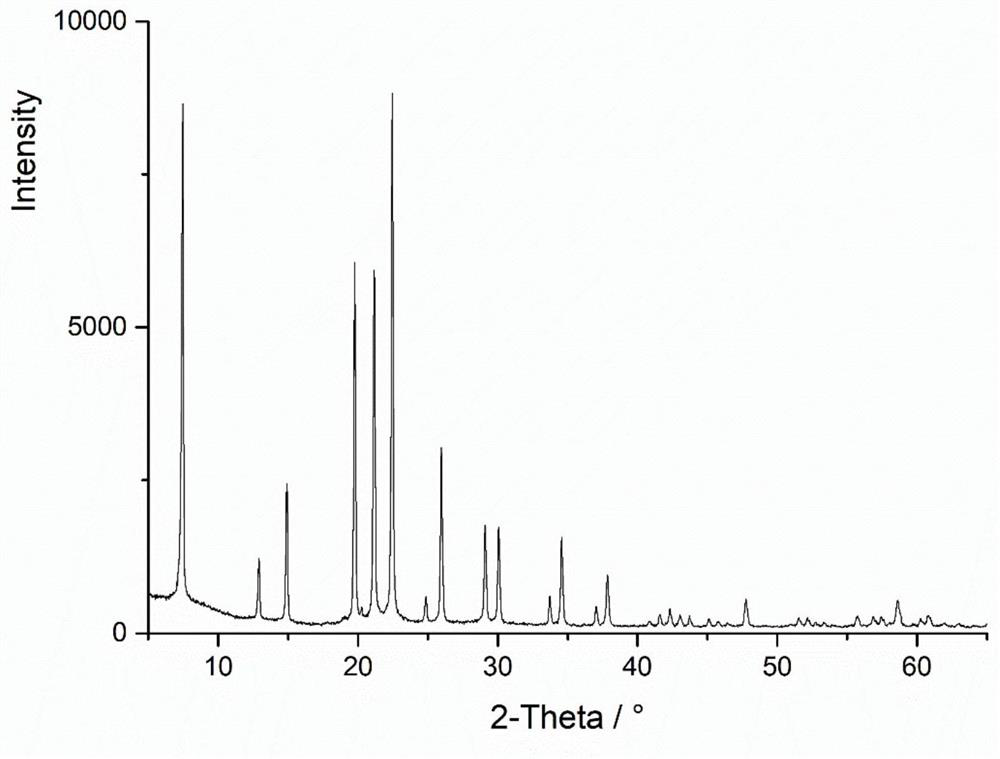
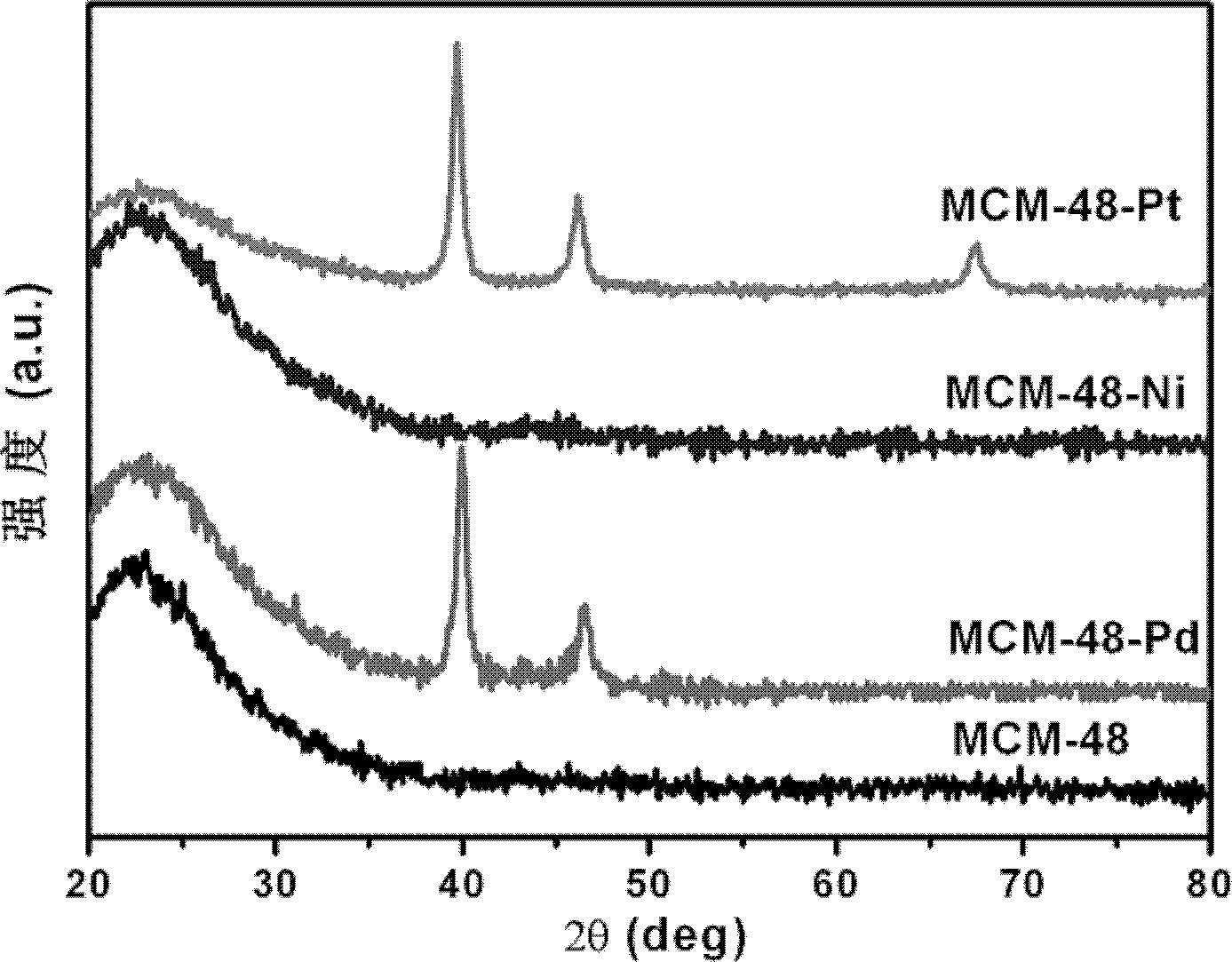
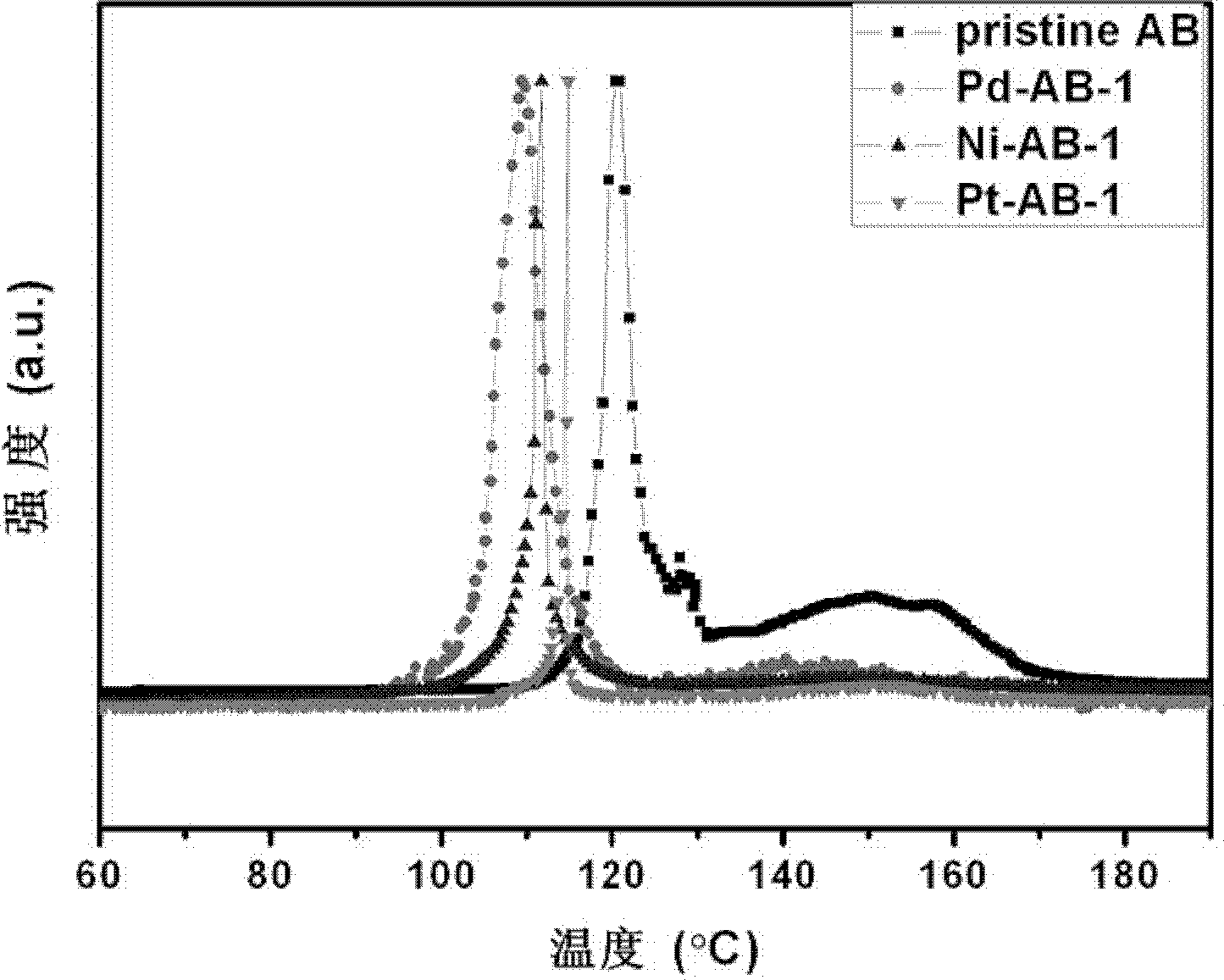
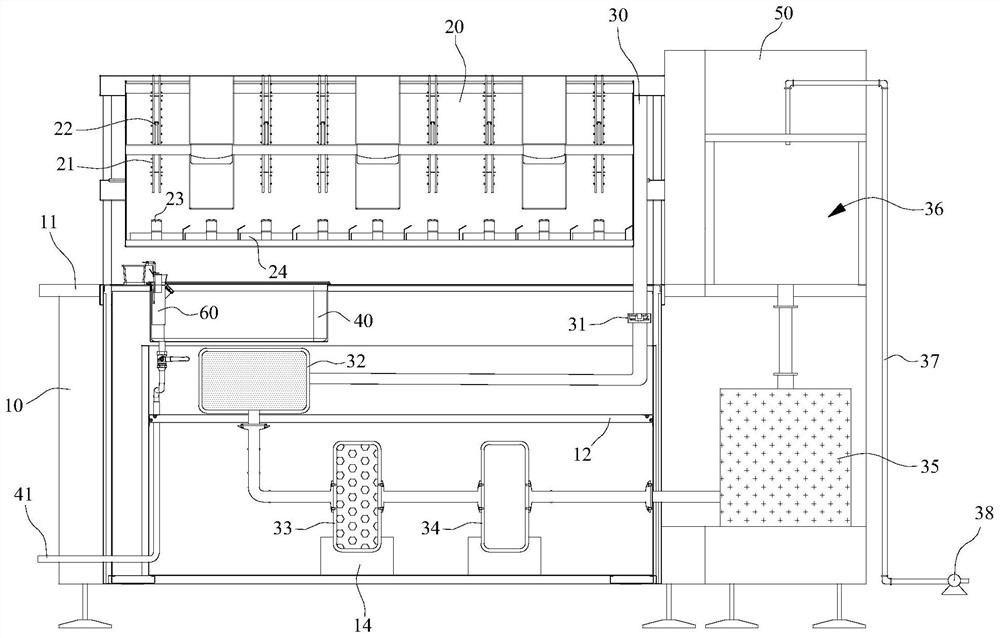
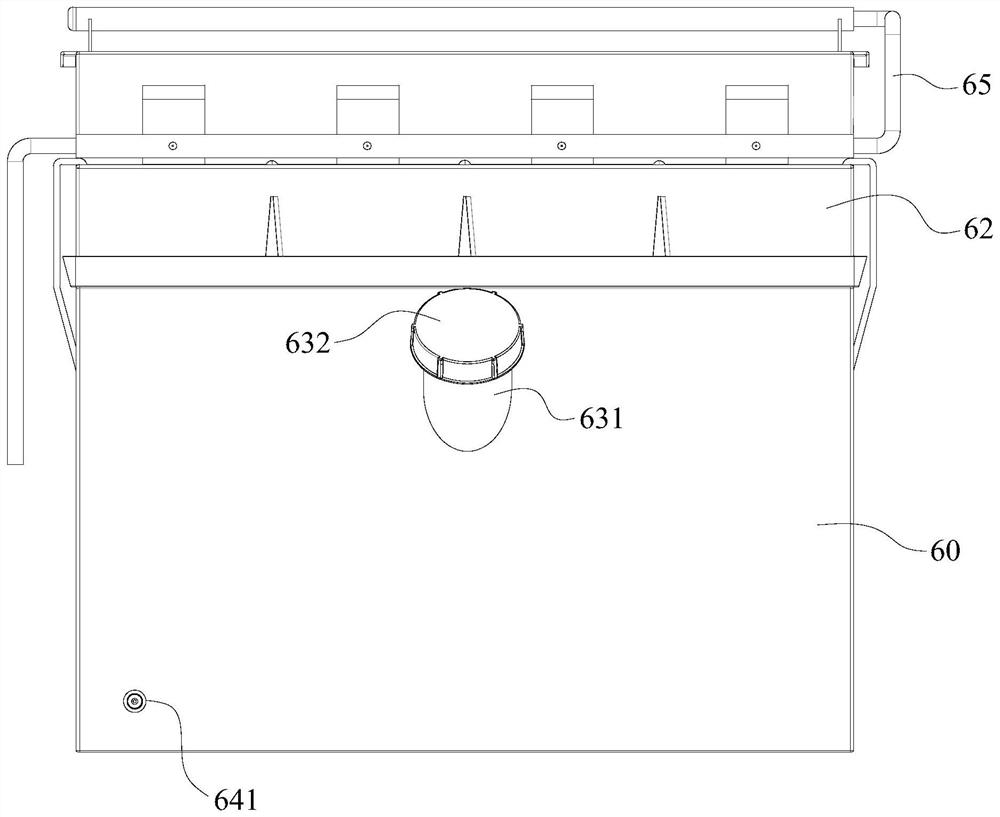
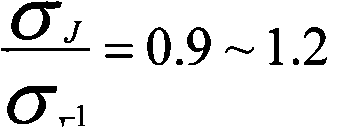Patents
Literature
37 results about "Classes of metals" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Class A metals are metals that form hard acids. Hard acids are acids with relatively ionic bonds. These metals, such as iron, aluminium, titanium, sodium, calcium, and the lanthanides, would rather bond with fluorine than iodine. They form stable products with hard bases, which are bases with ionic bonds. They target molecules such as phospholipids, nucleic acids, and ATP.
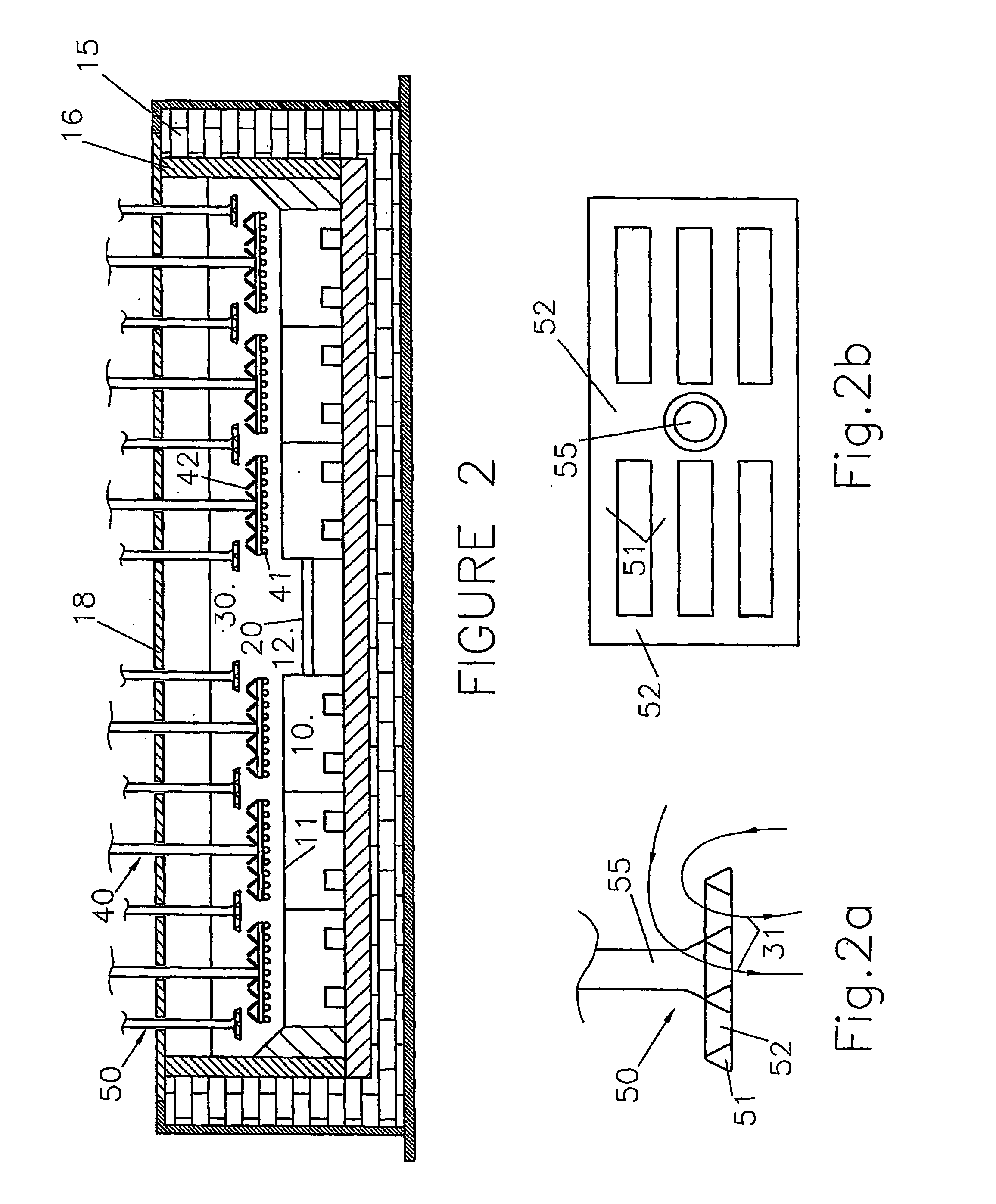
Titania-alumina mixed oxide hydrodesulfurization catalyst and preparing process thereof
ActiveCN101199935AGuaranteed qualityAssurance controlMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsRefining to eliminate hetero atomsAluminium chlorideHydrodesulfurization
The utility model relates to a synthesis of a titania-alumina mixed oxide material and a catalyst carrier of a supported deep hydrodesulfurization catalyst by taking the compound as the carrier. 1)take the tetrabutyl titanate and the aluminum chloride or the pseudo-boehmite as the raw material, prepare the mesoporous mixed oxide material of TiO2-Al2O3 with the sol-gel method, and use the material as the carrier of the diesel oil deep hydrodesulfurization catalyst; 2)use the dipping method by modifying the active metal variety and the dipping method to get highly dispersed supported mesoporous hydrodesulfurization catalyst of TiO2-Al2O3 compound material after baking; in the diesel oil hydrogenation deep desulfurization reaction, the desulfurization capability is good, and the desulfurization rate can reach 99 percent; if the reaction can be operated under a relative relaxative condition, the sulfur in the diesel oil can be desorbed from 1300ppm to below 15 ppm, or from the 430ppm to below 1ppm; the sulfur content in the product can meet the standard of Europe IV.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Catalyst and process for preparing the same
ActiveUS7169735B2High activityIncreased durabilityOther chemical processesDispersed particle separationIridiumPlatinum
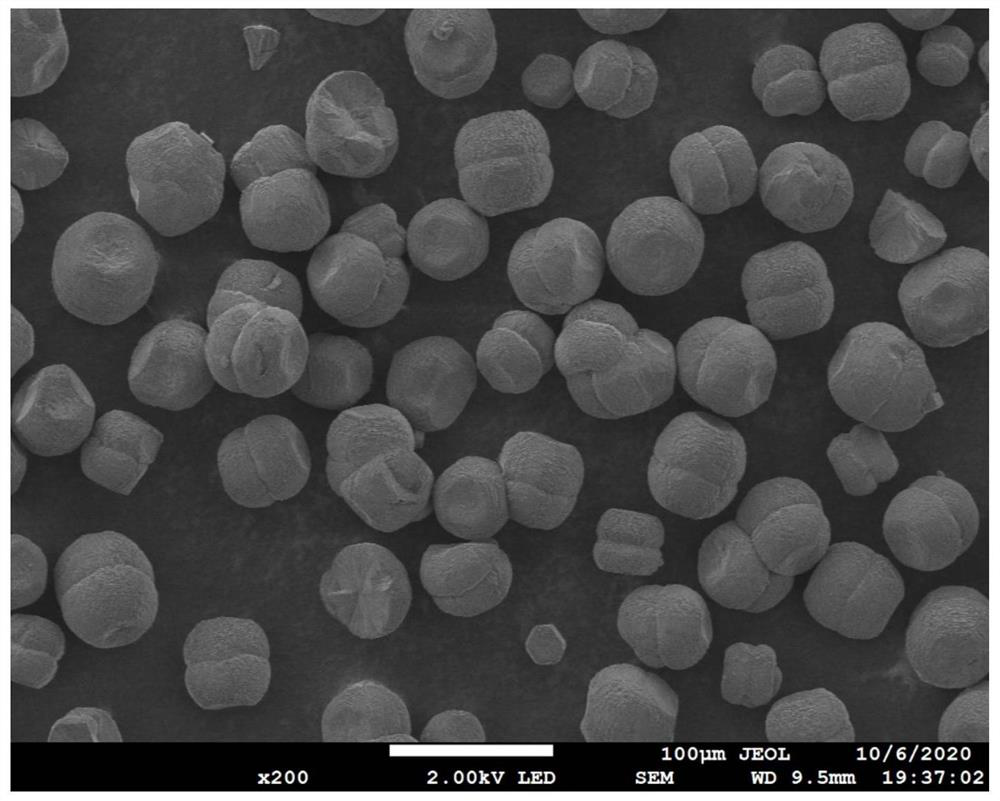
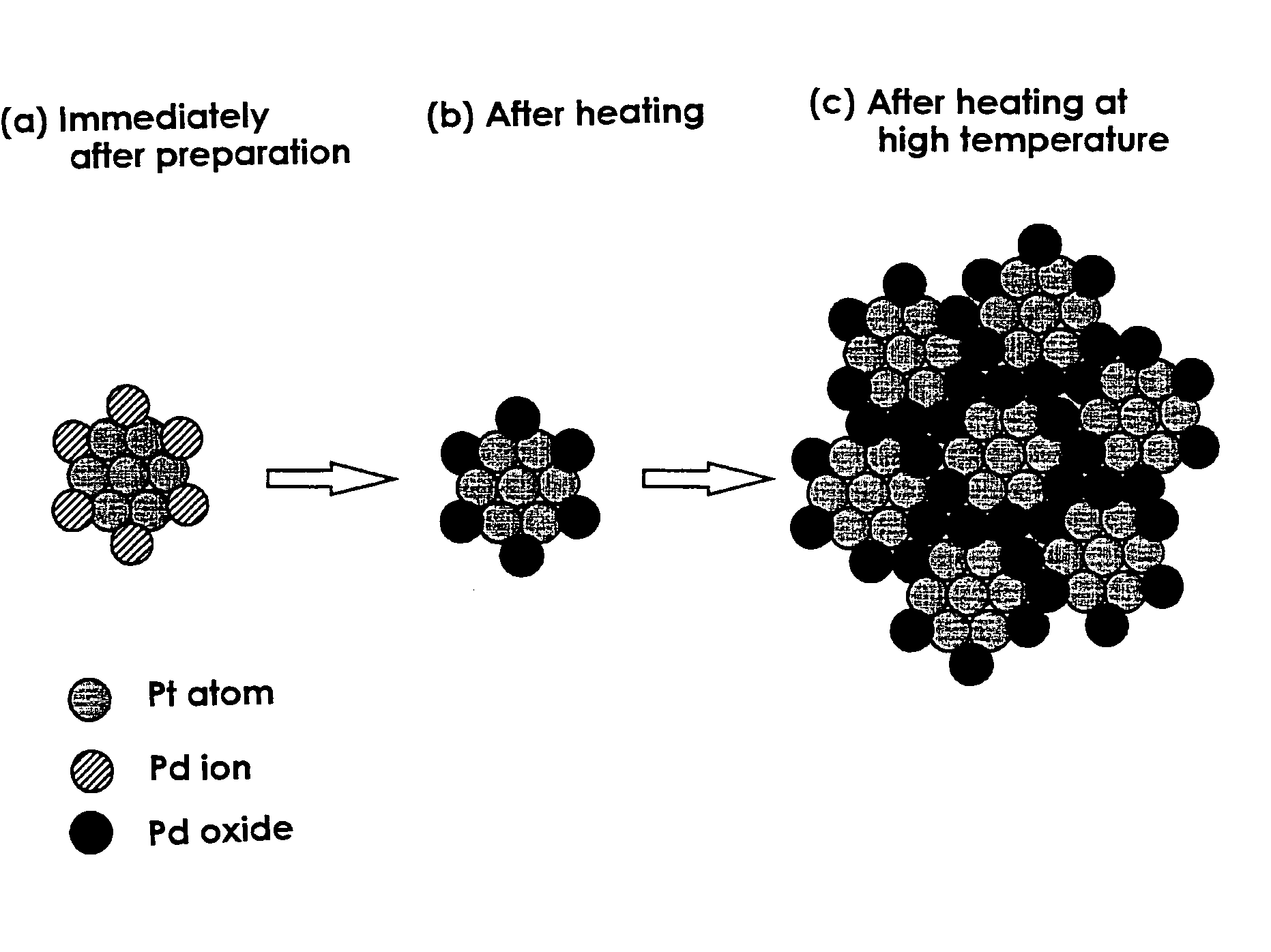
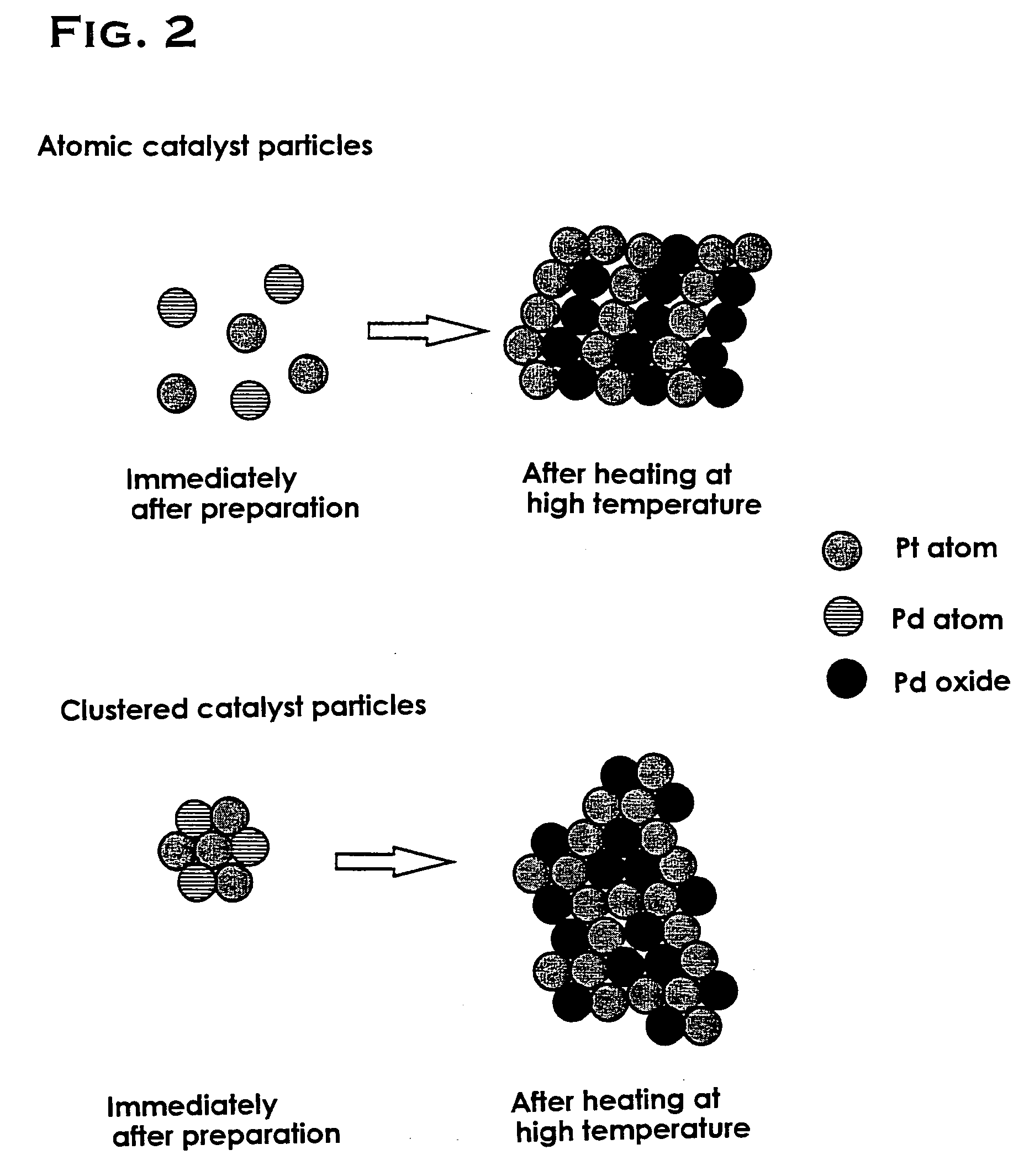
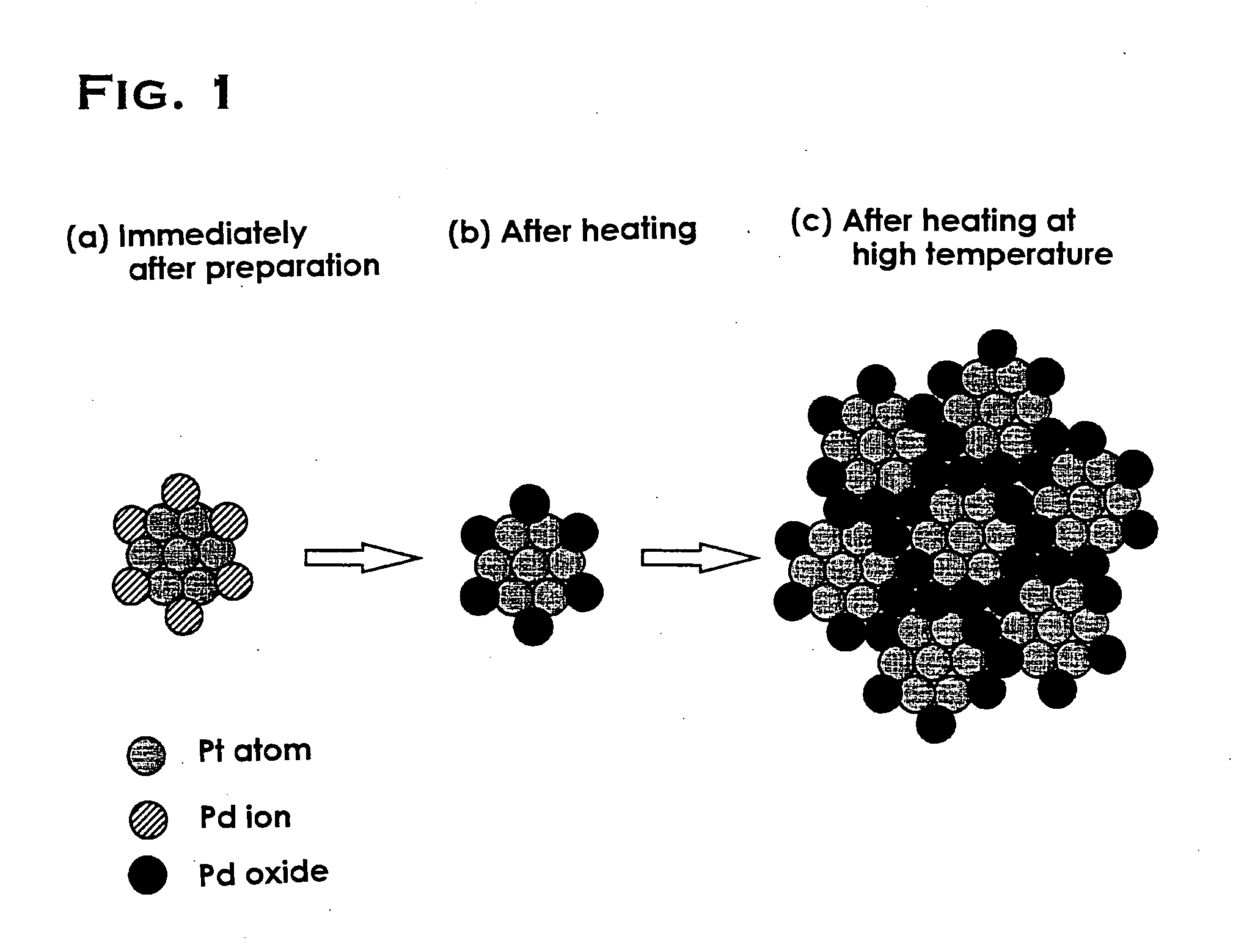
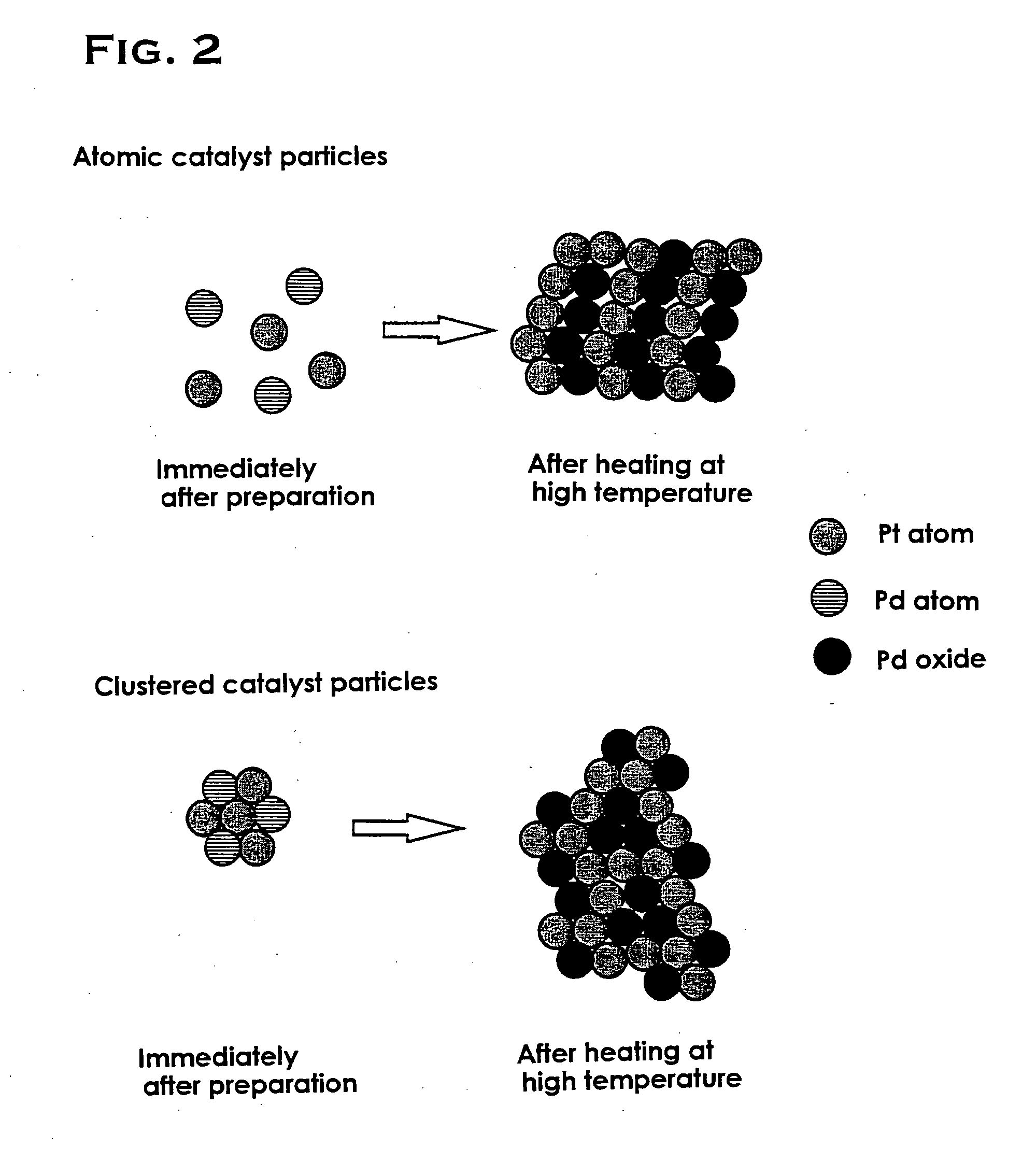
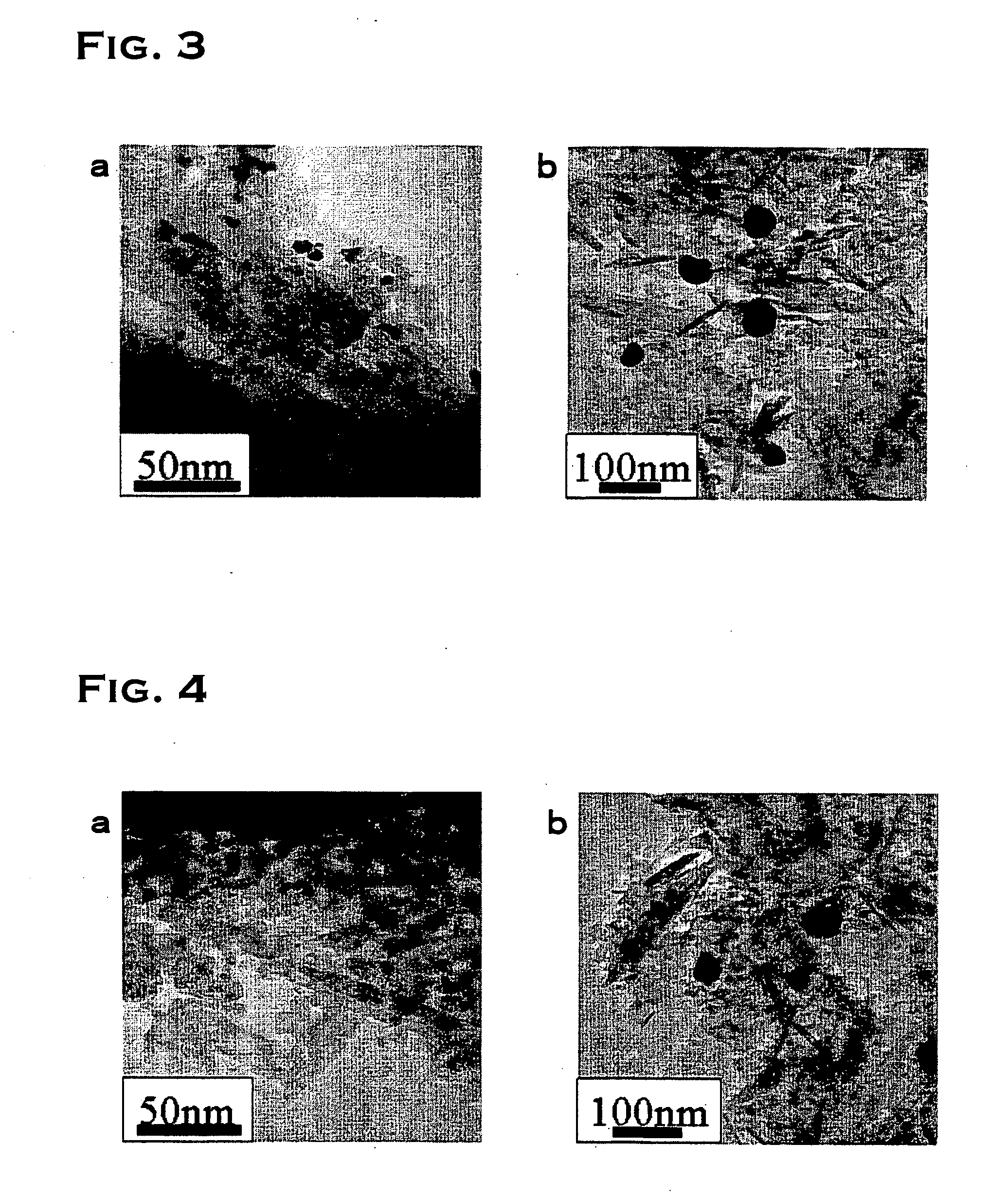
The object of the present invention is to provide a catalyst that is highly active and capable of maintaining its activity for a long period of time even in a high-temperature environment. The present invention is a catalyst including: a porous carrier which is comprised of one kind of or two or more kinds of metal oxides; and catalyst particles which are comprised of precious metals or precious metal oxides and supported on the above porous carrier, characterized in that the catalyst particles include: clustered particles formed by the aggregation of first precious metal atoms; and second precious metal ions bound to the above clustered particles. Preferably, the first precious metal and the second precious metal are different metal species which are selected from the group consisting of platinum, palladium, rhodium, ruthenium, silver, gold, iridium and osmium.
Owner:TANAKA PRECIOUS METAL IND
Catalyst and process for preparing the same
ActiveUS20050261125A1High activityIncreased durabilityOther chemical processesDispersed particle separationIridiumPlatinum
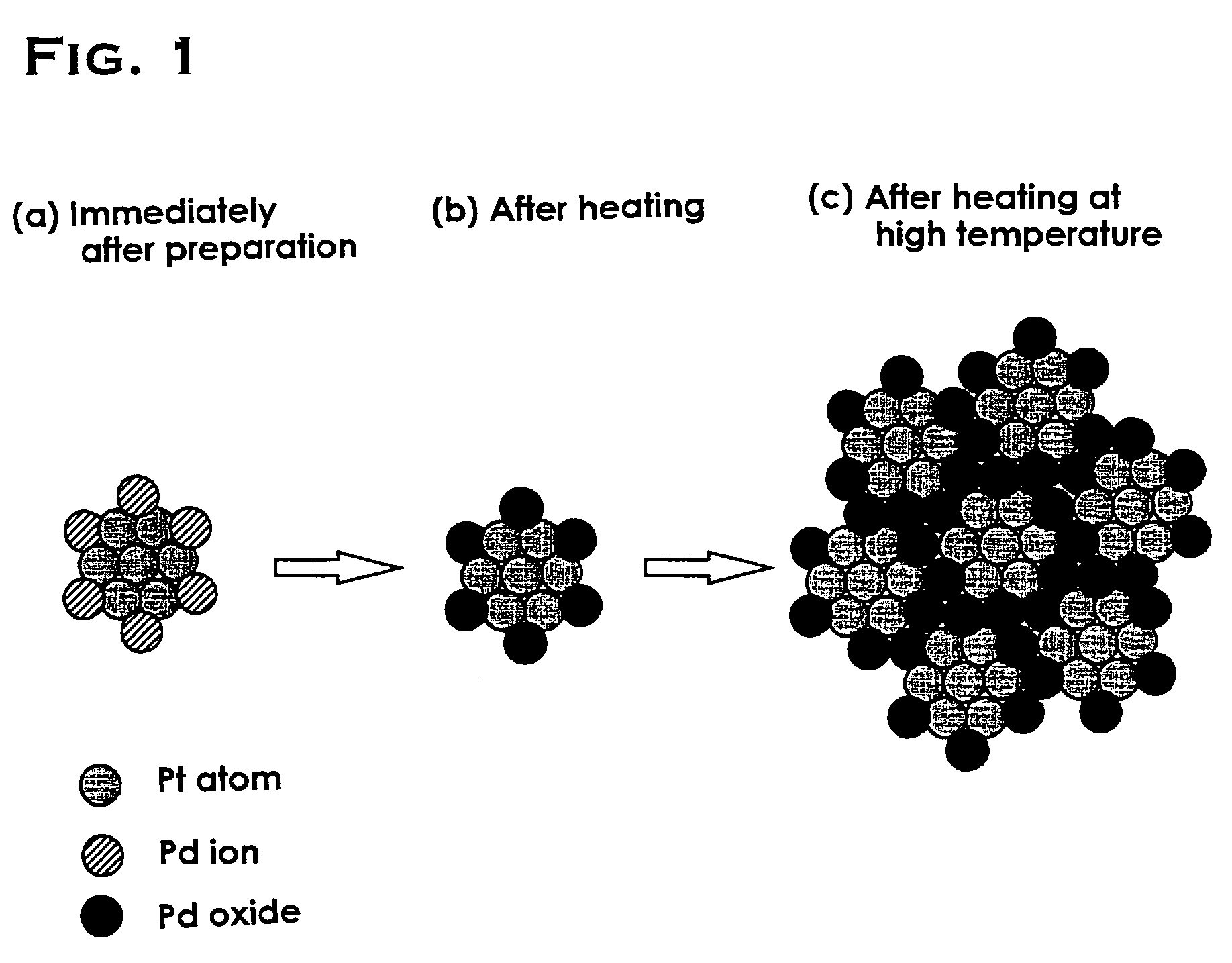
The object of the present invention is to provide a catalyst that is highly active and capable of maintaining its activity for a long period of time even in a high-temperature environment. The present invention is a catalyst including: a porous carrier which is comprised of one kind of or two or more kinds of metal oxides; and catalyst particles which are comprised of precious metals or precious metal oxides and supported on the above porous carrier, characterized in that the catalyst particles include: clustered particles formed by the aggregation of first precious metal atoms; and second precious metal ions bound to the above clustered particles. Preferably, the first precious metal and the second precious metal are different metal species which are selected from the group consisting of platinum, palladium, rhodium, ruthenium, silver, gold, iridium and osmium.
Owner:TANAKA PRECIOUS METAL IND
Preparation method of covalent organic framework material derivative carbon skeleton loaded metallic monatomic composite material
PendingCN110368931AFacilitate the realization of industrial applicationSimple preparation processCatalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsMaterials scienceSolid phases
The invention discloses a preparation method of a covalent organic framework material derivative carbon skeleton loaded metallic monatomic composite material. The preparation method comprises the following steps that firstly, a covalent organic framework material is synthesized through a room-temperature solid phase method, then the covalent organic framework material and a transition metal salt are mixed, stirred and dried, and a precursor is obtained; and finally, the precursor is calcinated through an in-situ pyrolysis method under protection of inert gas, and thus a target product is obtained. According to the preparation method, the monatomic catalytic material with high catalytic activity site dispersion and high catalytic stability is successfully constructed, the coverage of the metal types is wide, the cost is low, the operation steps are simple, reaction process conditions are easy to adjust and control, expensive equipment, special raw materials and complex processes are notneeded, and large-scale production can be achieved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Austempering ductile iron (ADI) supercharged diesel engine six-cylinder crankshaft and production method
Owner:长春怀林机械工程材料科技有限公司
Soluble metal hydride/transition metal dichalcogenide alloys
InactiveUS6143359ALiquid surface applicatorsAlkali/alkaline-earth/beryllium/magnesium hydridesOrganic solventAlloy
A new class of metal hydride alloy and processes for forming these alloys is disclosed. The alloys are comprised essentially of organically soluble metal hydrides and single molecular layer type transition metal dichalcogenides. They are produced via a non-metallurgical route in organic solvents under mild conditions. These alloys have exhibited improved qualities in battery applications.
Owner:LIGHTYEAR TECH
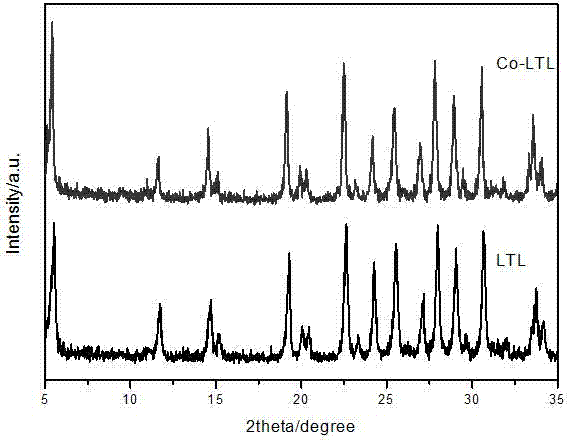
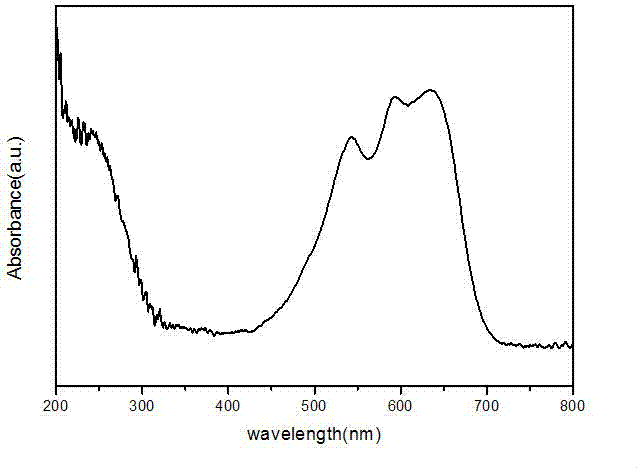
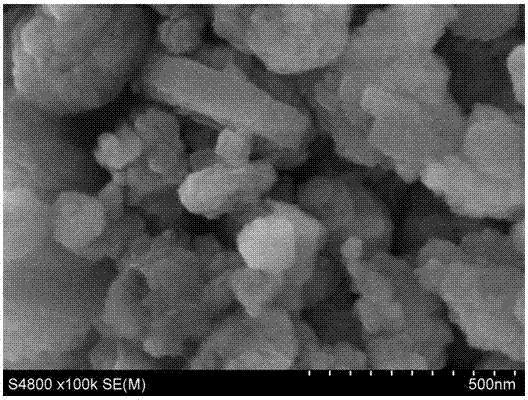
Method for synthesizing molecular sieve containing transition metal heteroatom LTL structure
ActiveCN103936025ARich varietyWide range of sources and cheapMolecular sieve catalystsAluminosilicate zeolite type-LMolecular sievePhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a molecular sieve containing a transition metal heteroatom LTL structure. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: mixing a heteroatom metal source, a coordinating complexing agent, an aluminum source, potassium hydroxide, a silicon source and water according to the atomic molar ratio of (0.001-0.1): (0.1-1.0): (0.04-0.2): (0.7-1.2): 1.0: (12-50), uniformly stirring, then performing crystallization reaction at the temperature of 150-180 DEG C for 24-72h, performing suction filtration and washing on a reaction solution, and then drying at the temperature of 100-200 DEG C to prepare a product, namely the molecular sieve containing the transition metal heteroatom LTL structure. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of simple process, a variety of applicable heteroatom metals, extensive raw material sources and low cost, and can better solve the difficult problem of precipitation of a heteroatom transition metal source under strong alkaline conditions, thereby being a preparation process for synthesizing the molecular sieve containing the transition metal heteroatom LTL structure, which is easy to realize industrial implementation, mild in reaction conditions and environment-friendly.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A class of metal oxide materials with special microstructure, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110092414ARich varietyMaterial nanotechnologyRuthenium/rhodium/palladium/osmium/iridium/platinum oxides/hydroxidesIndiumNew energy
The invention relates to a class of metal oxide materials with a special microstructure, and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of materials. A purpose of the present invention isto solve the problem of large-scale and low-cost production of high-performance metal oxides for energy storage and catalysis. According to the present invention, a multi-component metal oxide AxMyOz(A represents one or a plurality of elements selected from elements with strong metallicity, M represents one or a plurality of elements selected from transition metal elements or germanium, antimony,indium and other elements with weak metallicity, and O represents oxygen) is used as a raw material, and is subjected to A site element removing through etching with an acidic solution (an aqueous solution or organic solution with a pH value of less than 7) to prepare the metal oxide material, wherein a variety of microstructures such as an amorphous porous material, a mono-dispersed nano-crystalmaterial, a self-assembled nanometer hairball-like material, a porous nano-crystal material, a hollow material, a core-shell structure material and the like can be obtained by controlling experimental conditions. According to the present invention, the method is simple and effective, and does not require complicated post-treatment process, and the product can be widely used in the fields of industrial reaction catalysts or catalyst carriers and new energy.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Welding flux for soldering and soldering paste composition
InactiveCN101138816AQuality improvementImprove wettabilityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaClasses of metalsOxygen
A soldering flux contains a base resin and an activating agent. The soldering flux contains, as the activating agent, an oxygen-containing heterocyclic compound having at least one carboxyl group in a molecule. A solder paste composition contains the abovementioned soldering flux and the solder alloy powder. These enable exhibition of excellent wettability to lead-free metals and plating, irrespective of the type of the metals.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
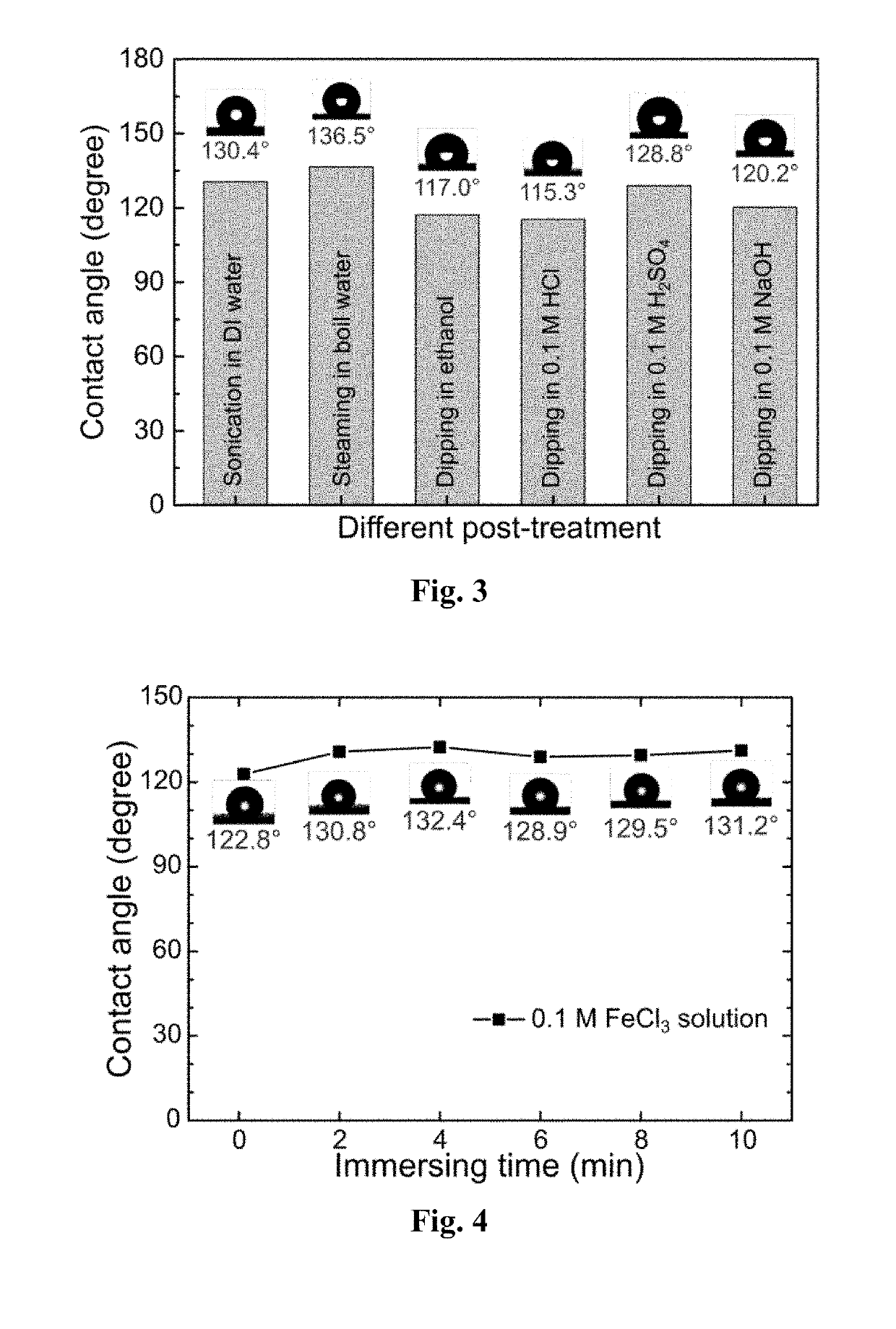
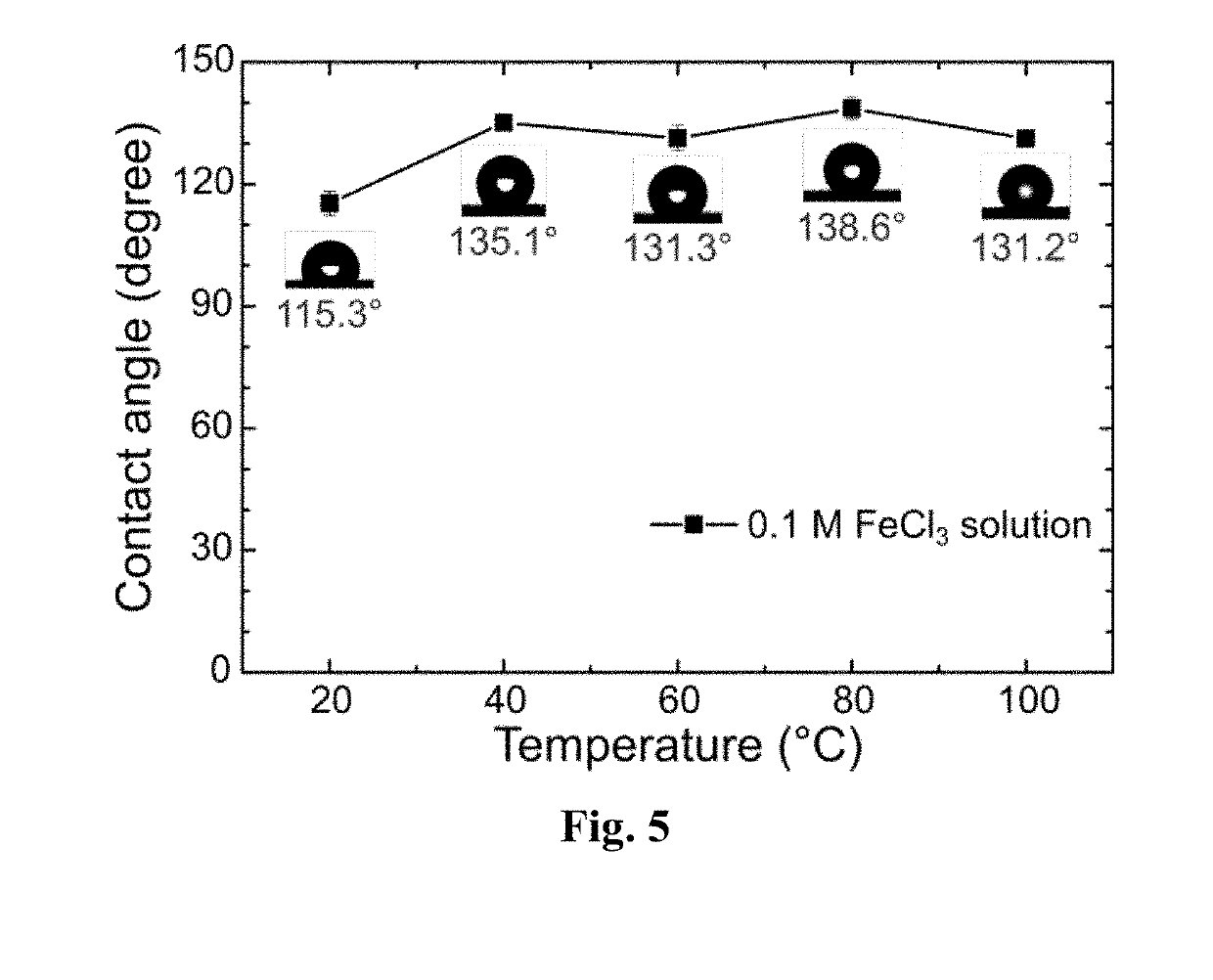
Highly hydrophobic and oleophilic melamine resin via metal-ion induced wettability transition, application, and preparation thereof
This disclosure is related to a class of metal-ion induced hydrophobic polymers and method of producing such class of compounds by a one-step solution immersion process. Specifically, a metal-ion Induced hydrophobic polymer or melamine sponge (MII-HMS) is disclosed. Such polymer or sponge is demonstrated to be highly hydrophobic and oleophilic and exhibits excellent oil absorption capabilities, being able to absorb a wide range of oils and organic solvents up to 71 to 157 times of its own weight.
Owner:SOUTH DAKOTA BOARD OF REGENTS
Texture corrosion liquid medicine
The invention provides texture corrosion liquid medicine which comprises 3-9 parts of ferric chloride, 4-15 parts of copper chloride, 5-16 parts of the mixture of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid, 3-7 parts of potassium dichromate, 2-4 parts of picric acid, 5-15 parts of a sodium metabisulfite aqueous solution and 30-40 parts of deionized water. The texture corrosion liquid medicine can corrode various kinds of metal and has the good corrosion effect on common steel, high-strength steel, stainless steel and alloy steel, additional high-temperature heating is not needed, and corroded textures are clear and uniform.
Owner:模德模具(苏州工业园区)有限公司
Metal electrowinning cell with electrolyte purifier
ActiveUS20060185984A1High purityAvoid attenuationCellsIsotope separationElectrolysisReduction potential
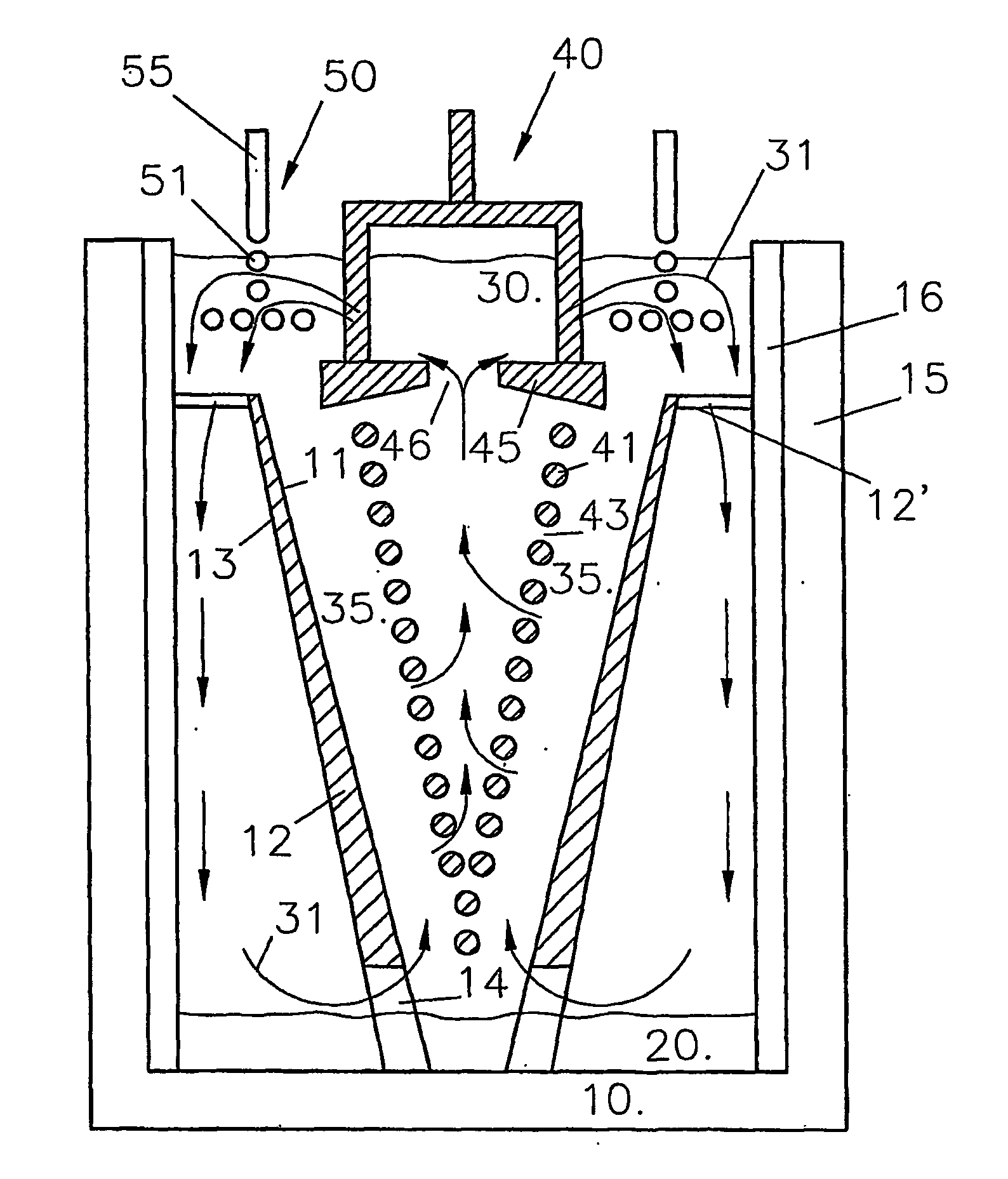
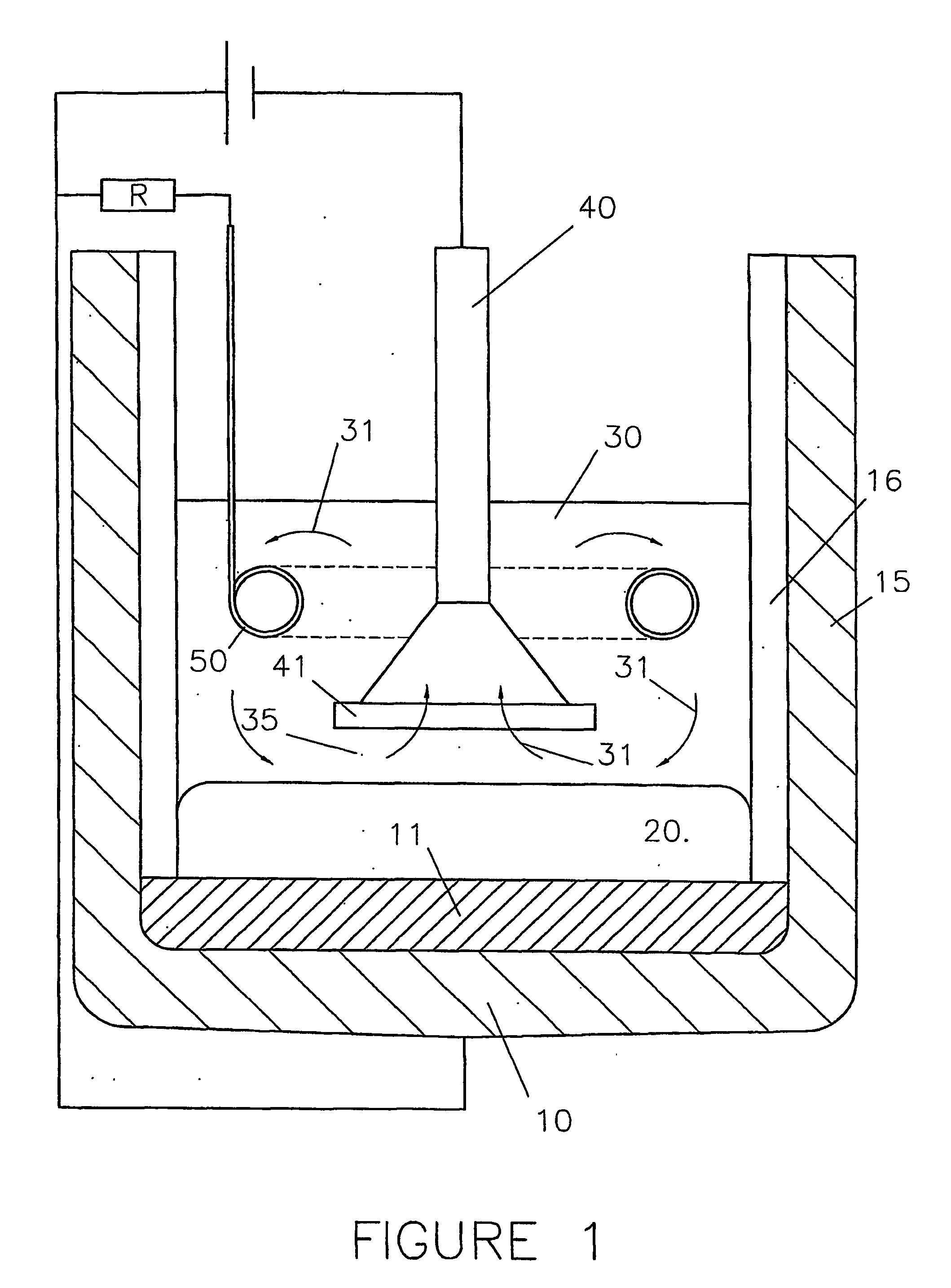
A cell for electrowinning a metal, in particular aluminium, from a compound thereof dissolved in an electrolyte (30) comprises an anode (40) and a cathode (10,11) that contact the electrolyte (30), the cathode (10,11) being during use at a cathodic potential for reducing thereon species of the metal to be produced from the dissolved compound. The electrolyte (30) further contains species of at least one element that is liable to contaminate the product metal (20) and that has a cathodic reduction potential which is less negative than the cathodic potential of the metal to be produced. The cell further comprises a collector (50) for removing species of such element (s) from the electrolyte (30). During use the collector (50) is at a potential that is: less negative than the cathodic potential of the produced metal (20) to inhibit reduction thereon of species of the metal to be produced; and at or more negative than the reduction potential of the species of said element(s) to allow reduction thereof on the collector (50). The cell is so arranged that species of said element(s) are reduced on the collector (50) rather than on the cathode (10,11) so as to inhibit contamination of the product metal (20) by said element(s).
Owner:RIOTINTO ALCAN INT LTD
Coated metal plate with excellent corrosion resistance and reduced environmental impact
InactiveCN1890089AGood adhesionAccelerated corrosionLiquid surface applicatorsElectrolytic coatingsCrazingMetal sheet
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Method for production of catalyst and catalyst produced by the method
ActiveUS20100041547A1Avoid scratchesDispersed particle separationCatalyst activation/preparationSaline waterClasses of metals
A method for producing a catalyst of the present invention is characterized by sequentially performing the steps of: (i) dipping an end face portion of a carrier structure having a catalytic component carried thereon in an aqueous metal salt solution at a concentration of 2.7 to 3.88 mol / L in terms of mole of the metal; (ii) drying the dipped end face portion; (iii) dipping the dried end face portion again in an aqueous metal salt solution whose metal species is the same as that in the aqueous metal salt solution at a concentration of 2.7 to 3.88 mol / L in terms of mole of the metal; and (iv) performing a calcination treatment to harden the catalytic end face.
Owner:HITACHI ZOSEN CORP
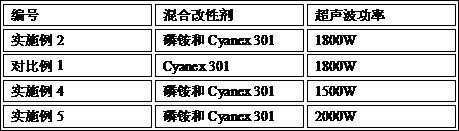
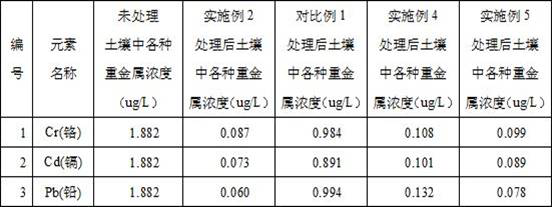
Modifier for repairing heavy metal contaminated soil and preparation method and application of modifier
The invention discloses a modifier for repairing heavy metal contaminated soil. The modifier is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight; 30 to 60 parts of modified zeolite; 10-50parts of lime, 5-10 parts of blast furnace slag; 10-15 parts of organic fertilizer, 5-10 parts of humic acid and 5-10 parts of a microbial agent, wherein the modified zeolite is formed by mixing calcined zeolite and a mixed modifier, the mass of the mixed modifier accounts for 10-20 wt% of the mass of the modified zeolite, and the mixed modifier is formed by mixing phosphate and Cyanex 301 according to the mass ratio of (2-4): 1; the invention further discloses a preparation method of the modifier and application of the modifier in remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil. The modifier prepared by the method is suitable for various heavy metal contaminated soils, and has the advantages of multiple acting metal varieties, low cost, resource reutilization, ecological environmental protection, short remediation period, good effect, high efficiency, soil fertility increase and the like.
Owner:SHENGSHI LANDSCAPE GRP CO LTD
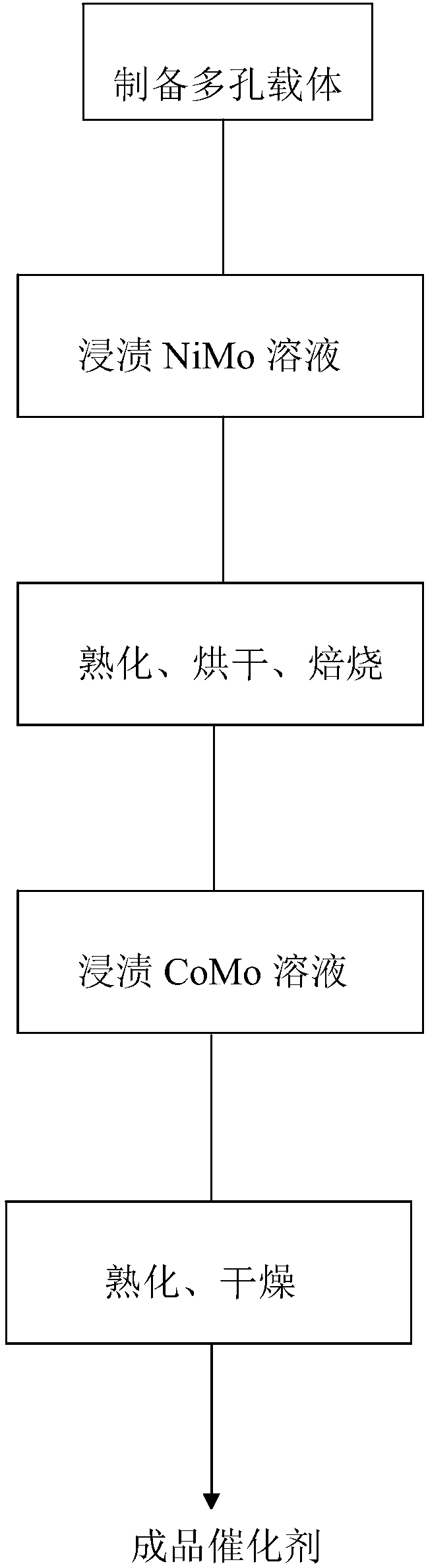
Preparing method for hydrotreating catalyst with desulfurization activity
ActiveCN110064405AHigh desulfurization activityMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsRefining to eliminate hetero atomsHydrogenReactive site
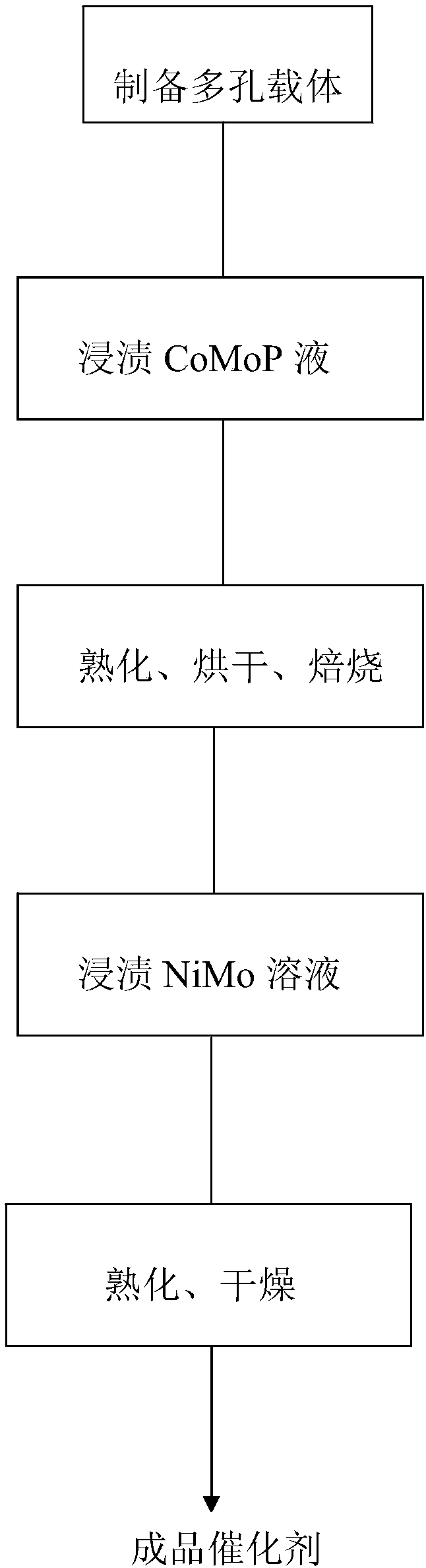
The invention discloses a preparing method for a hydrotreating catalyst with the desulfurization activity. The preparing method includes the following steps that 1, a macroporous carrier of a phosphorus-containing aluminum oxide or phosphorus-modified aluminum oxide material is prepared; 2, a porous carrier is soaked with a I-class metallic solution, curing, drying and roasting are conducted, anda catalyst precursor is obtained, and the I-class metallic solution is a NiMo solution containing a Ni element and a Mo element; 3, the catalyst precursor is soaked with a II-class metallic solution containing an organic assistant, then curing and drying are conducted, a roasting process is not required, and a final catalyst is obtained; the II-class metallic solution is a CoMo solution containinga Co element and a Mo element, and the I-class metallic solution and the II-class metallic solution are not simultaneously the NiMo solution or the CoMo solution. The method adopts a metallic-solution step-by-step soaking, and active site combinations with different metal-class combinations and different types are provided, so that the hydrotreating catalyst generates the higher hydrogen desulfurization activity than a traditional pure I-type catalyst and a pure II-type catalyst.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Preparation method of ammonia borane-metal catalyst composite hydrogen storage material
InactiveCN103011074AImprove catalytic performanceRich varietyMolecular sieve catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationOrganic solventMetal catalyst
The invention discloses a preparation method of an ammonia borane-metal catalyst composite hydrogen storage material. The preparation method comprises that through magnetron sputtering, metal atoms having catalytic effects are uniformly deposited on a mesoporous material base so that catalyst powder is obtained; the catalyst powder and ammonia borane are mixed uniformly in an anhydrous organic solvent; and the organic solvent is volatilized so that the ammonia borane-metal catalyst composite hydrogen storage material is obtained. The catalyst in the ammonia borane-metal catalyst composite hydrogen storage material has good catalytic effects on a thermolysis hydrogen desorption reaction of ammonia borane so that a hydrogen desorption temperature of ammonia borane is reduced and foreign gas escape can be inhibited effectively and hydrogen desorption dynamic features can be improved. The preparation method adopts simple equipment, and has a fast synthesis speed and a low cost. The ammonia borane-metal catalyst composite hydrogen storage material obtained by the preparation method has good product dispersibility, a wide metal selection range and obvious catalysis performances, can be massively produced easily and has a good application prospect.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Antimicrobial Exfoliated Vermiculite Composite Material and Methods for Preparing the Same
An antimicrobial exfoliated vermiculite composite material is synthesized by impregnating the interlayers of exfoliated vermiculite through cation exchange and surface absorption with at least one of the following metal species: copper, silver, zinc, and manganese. Alternately, the antimicrobial material is synthesized by impregnating interlayers of unexfoliated vermiculite with said metal species and exfoliating the product thereafter. The metal species can be in ionic state, nanometer particles, and in the form of metal oxides, metal hydroxides, metal nitrides, metal carbides, metal phosphates, metal silicates, metal borides, metal sulfides, metal halides, metal hydrides, metal nitrates, metal carbonates, and metal sulfadiazines. Any mixture of these metal species in the exfoliated vermiculite can provide protection against a broad spectrum of pathogens. This antimicrobial material in any desired form, in whole or as an additive, can effectively self-decontaminate various materials or products as the antimicrobial metal ions slowly diffuse to the surface of the products.
Owner:LI BOWEN +1
Method for production of catalyst and catalyst produced by the method
ActiveUS7825060B2Avoid scratchesImprove propertiesDispersed particle separationCatalyst activation/preparationSaline waterClasses of metals
A method for producing a catalyst of the present invention is characterized by sequentially performing the steps of: (i) dipping an end face portion of a carrier structure having a catalytic component carried thereon in an aqueous metal salt solution at a concentration of 2.7 to 3.88 mol / L in terms of mole of the metal; (ii) drying the dipped end face portion; (iii) dipping the dried end face portion again in an aqueous metal salt solution whose metal species is the same as that in the aqueous metal salt solution at a concentration of 2.7 to 3.88 mol / L in terms of mole of the metal; and (iv) performing a calcination treatment to harden the catalytic end face.
Owner:HITACHI ZOSEN CORP
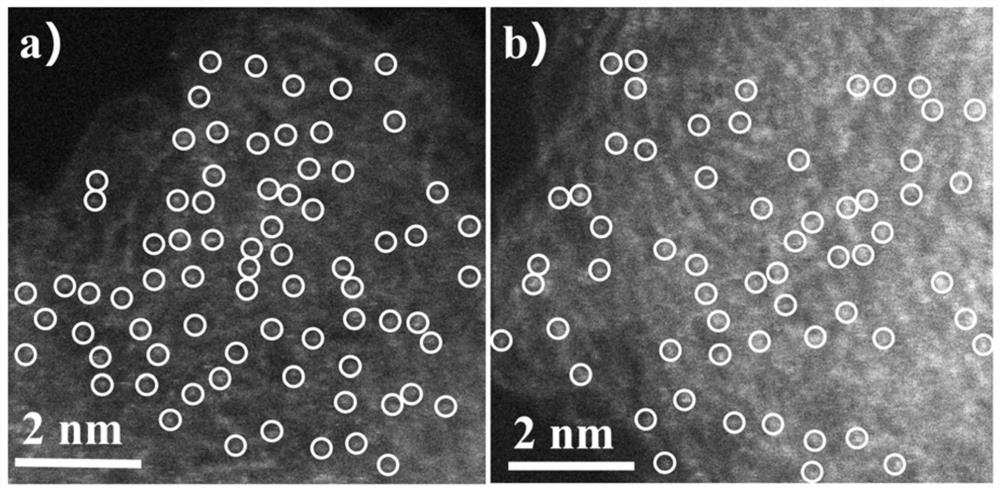
Method for quasi-continuous synthesis of monatomic catalyst
ActiveCN111604081AAvoid gatheringGood reproducibilityMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystMaterial synthesis
The invention discloses a method for quasi-continuous synthesis of a monatomic catalyst. According to the preparation method, a metal precursor is encapsulated in chitosan / lauryl sodium sulfate hydrogel encapsulation through a microcapsule technology, and the metal monatomic catalyst is synthesized through further pyrolysis. According to the preparation method, a hanging drop method in a microcapsule technology is adopted, and the technology can continuously generate homogeneous microcapsules, so that quasi-continuous preparation of the monatomic material is realized. The quasi-continuous synthesis process provided by the invention solves the problems of poor reproducibility, amplification effect and the like caused by batch synthesis. Besides, the method has good expansibility, solves theproblems of few metal types, low metal content and the like in the prior art, and enriches the research in the related fields of metal monatomic material synthesis methodology and the like.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
A corrosion test device for low-magnification inspection of dendrite corrosion
ActiveCN109211646BAvoid damageEasy to handlePreparing sample for investigationCopper nitrateWater chlorination
The invention relates to an etchant for low-magnification inspection of dendrite corrosion, which belongs to the technical field of chemical analysis and detection. The components in the etchant include: 0.01% to 1.0% of copper chloride and 0.01% to 1.5% of copper nitrate in sequence according to mass percentage , 0.01% to 1.5% of magnesium chloride, 0.01% to 3.0% of ferric chloride, 0.01% to 2.0% of ferrous chloride, 1.0% to 4.0% of hydrochloric acid, 40% to 50% of absolute ethanol, and the balance is water. The above technical solution improves the detection range of ferrous metal species by optimizing the selection of the components of the corrosive agent. The present invention also relates to a waste liquid treatment system for the corrosive agent. Aiming at the problem that the hydrochloric acid contained in the corrosive agent has a high concentration and escapes into the air during the corrosion process, a fume hood is designed as a set, and it is suitable for the corrosion process. The hydrochloric acid in the air is extracted to avoid damage to the operator's respiratory tract; at the same time, the waste acid generated during the corrosion process is collected centrally through the integrated treatment box to facilitate waste acid treatment.
Owner:SHENYANG QIGUANG TECH CO LTD
Multi-mineral supplement for improved bone density
InactiveCN111787928AIncrease bone densityIncrease in sizeInorganic boron active ingredientsMetabolism disorderBone densityMedicine
Owner:AVALON BONE SUPPLEMENT HK LTD +1
A cobalt-based polymetallic single-atom isomorphously substituted phosphorus-aluminum molecular sieve meapo-5 and its preparation method
ActiveCN112850734BGood dispersionHigh yieldMolecular-sieve aluminophosphatesMolecular-sieve and base-exchange phosphatesMolecular sievePhysical chemistry
The invention provides a cobalt-based polymetallic single-atom isomorphously substituted phosphorus-aluminum molecular sieve MeAPO-5 and a preparation method thereof. The method uses aluminum source, phosphorus source, template agent, cobalt source, other doping metal sources and mineralizer as basic synthesis raw materials, and the maximum number of metal types that can be doped at the same time is 5. After fully mixing all the raw materials uniformly through a specific feeding sequence, the cobalt-based polymetallic single-atom MeAPO‑5 molecular sieve is prepared by two short-term crystallization methods. The process of the present invention is easy to operate, strong in practicability, and good in raw material compatibility. The prepared MeAPO-5 molecular sieve has high yield, many types of doped metals, high dispersion of metal sites, and the doped metals are in a single atomic state. The product has the characteristics of high particle size uniformity.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Titania-alumina mixed oxide hydrodesulfurization catalyst and preparing process thereof
ActiveCN100548479CGuaranteed qualityAssurance controlMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsRefining to eliminate hetero atomsAluminium chlorideHydrodesulfurization
The utility model relates to a synthesis of a titania-alumina mixed oxide material and a catalyst carrier of a supported deep hydrodesulfurization catalyst by taking the compound as the carrier. 1)take the tetrabutyl titanate and the aluminum chloride or the pseudo-boehmite as the raw material, prepare the mesoporous mixed oxide material of TiO2-Al2O3 with the sol-gel method, and use the material as the carrier of the diesel oil deep hydrodesulfurization catalyst; 2)use the dipping method by modifying the active metal variety and the dipping method to get highly dispersed supported mesoporous hydrodesulfurization catalyst of TiO2-Al2O3 compound material after baking; in the diesel oil hydrogenation deep desulfurization reaction, the desulfurization capability is good, and the desulfurization rate can reach 99 percent; if the reaction can be operated under a relative relaxative condition, the sulfur in the diesel oil can be desorbed from 1300ppm to below 15 ppm, or from the 430ppm to below 1ppm; the sulfur content in the product can meet the standard of Europe IV.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Oxide cathode for picture tube
InactiveCN1267953CStable jobProlonged Diffusion PathwayCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesDischarge tube/lamp detailsCold cathodeAlkaline earth oxides
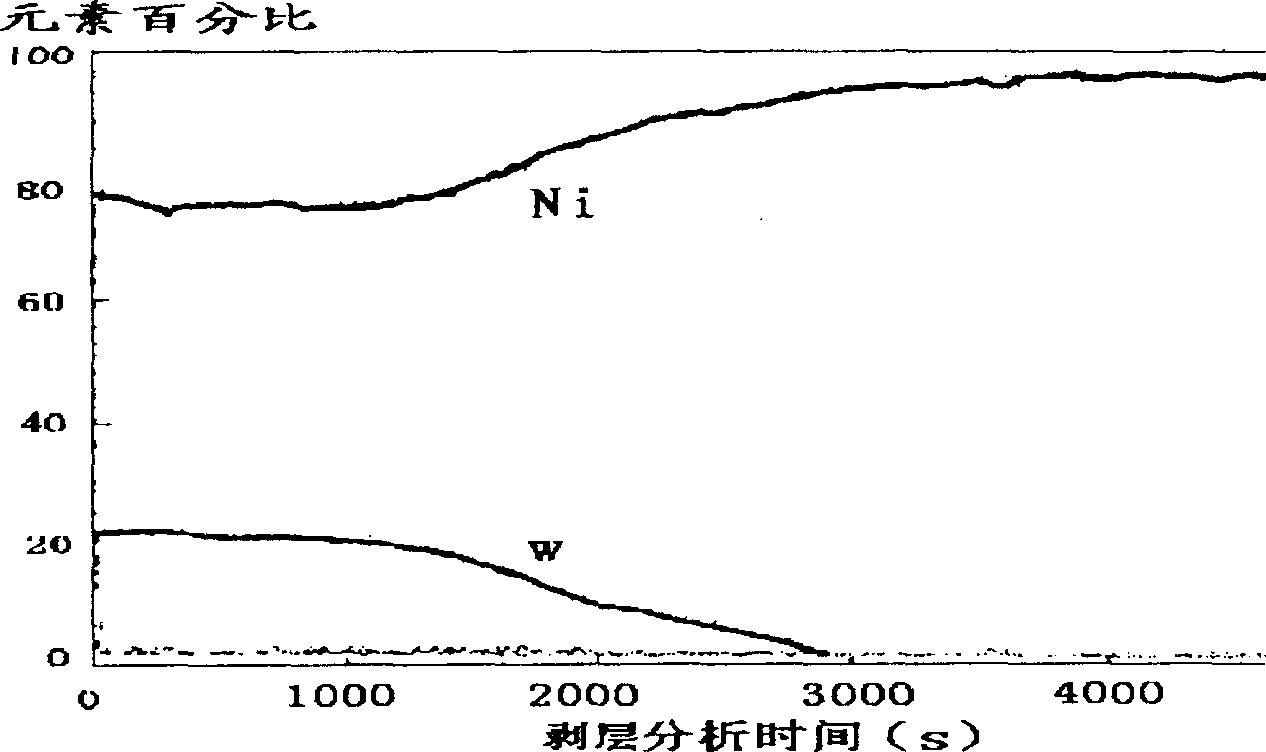
The cathode includes base metal and sleeve press-fitted with the base metal. There are one or two sleeves including inner and outer sleeve. Heating unit is setup inside sleeve i.e. at lower part of base metal, and electronic emission layer is spray-coated on upper part of the base metal. The said electronic emission layer includes two sub layers. Based on main component alkali-earth oxide, two classes of metal powders are doped into the first sub layer. The said one metal powder is Ni powder without reducing power, and the other is W powder having reducing power. Main component of second electronic emission layer is alkali-earth oxide. Comparing with traditional cathode of oxide, the disclosed cathode possesses fine performance under large current for long stable operation.
Owner:SHANGHAI NOVEL COLOR PICTURE TUBE
Preparation method of ammonia borane-metal catalyst composite hydrogen storage material
InactiveCN103011074BImprove catalytic performanceRich varietyMolecular sieve catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationOrganic solventMetal catalyst
The invention discloses a preparation method of an ammonia borane-metal catalyst composite hydrogen storage material. The preparation method comprises that through magnetron sputtering, metal atoms having catalytic effects are uniformly deposited on a mesoporous material base so that catalyst powder is obtained; the catalyst powder and ammonia borane are mixed uniformly in an anhydrous organic solvent; and the organic solvent is volatilized so that the ammonia borane-metal catalyst composite hydrogen storage material is obtained. The catalyst in the ammonia borane-metal catalyst composite hydrogen storage material has good catalytic effects on a thermolysis hydrogen desorption reaction of ammonia borane so that a hydrogen desorption temperature of ammonia borane is reduced and foreign gas escape can be inhibited effectively and hydrogen desorption dynamic features can be improved. The preparation method adopts simple equipment, and has a fast synthesis speed and a low cost. The ammonia borane-metal catalyst composite hydrogen storage material obtained by the preparation method has good product dispersibility, a wide metal selection range and obvious catalysis performances, can be massively produced easily and has a good application prospect.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Corrosive agent for dendritic crystal corrosion macroscopic examination
PendingCN112649270AAvoid damageEasy to handlePreparing sample for investigationCopper nitrateWater chlorination
The invention relates to a corrosive agent for dendritic crystal corrosion macroscopic examination, and belongs to the technical field of chemical analysis and detection. The corrosive agent comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 0.01%-1.0% of copper chloride, 0.01%-1.5% of copper nitrate, 0.01%-1.5% of magnesium chloride, 0.01%-3.0% of ferric chloride, 0.01%-2.0% of ferrous chloride, 1.0%-4.0% of hydrochloric acid, 40%-50% of absolute ethyl alcohol and the balance of water. According to the technical scheme, the components of the corrosive agent are optimally selected, so that the detection range of ferrous metal types is widened. The invention further relates to a waste liquid treatment system for the corrosive agent. According to the invention, aiming at the problems that the concentration of hydrochloric acid contained in the corrosive agent is relatively high and hydrochloric acid escapes into air in the corrosion process, an air draft cabinet is designed in a matched manner to pump out hydrochloric acid in air in the corrosion process, so that the respiratory tract of an operator is prevented from being injured; and waste acid generated in the corrosion process is collected in a centralized mode through the integrated treatment box, and waste acid treatment is facilitated.
Owner:沈阳市启光科技有限公司
Polycondensed amino-acid coordinated SOD simulatives
InactiveCN1281742CGood water solubilityModerate molecular weightPeptide/protein ingredientsEnzymesElemental analysisDivalent metal ions
The invention discloses a kind of SOD simulant coordinated by polycondensed amino acid, and prepares a kind of polycondensed amino acid metal complex-polycondensed ferrous aspartate complex by using amino acid condensate as a ligand and different divalent metal ions in aqueous solution And polycondensed aspartic acid manganese complexes. Firstly, after dissolving polycondensed aspartic acid in ammonia water, add manganese sulfate solution under the condition of adjusting pH to be neutral to reflux reaction to obtain polycondensed aspartic acid manganese complex; add ferrous sulfate and ferrous sulfate under acidic conditions Equimolar hydroxylamine hydrochloride, reflux reaction to obtain polycondensation aspartic acid ferrous complex. The chemical composition and structure of the complex were characterized by elemental analysis and infrared spectroscopy, and its catalytic O 2 ・- SOD-like activity for disproportionation reactions. The SOD simulant of the invention has the characteristics of moderate molecular weight, good water solubility, non-toxicity, high activity, etc., and has broad application prospects.
Owner:北京联合大学职业技术师范学院
A kind of refining method of pentane
ActiveCN107573204BThe refining method is simpleReduce energy consumptionOther chemical processesAdsorption purification/separationMolecular sieveUnsaturated hydrocarbon
The invention provides a pentane refining method. The pentane refining method comprises the following steps: mixing a pentane raw material and a metal-modified HZSM-5 molecular sieve, and refining toobtain refined pentane, wherein in the metal-modified HZSM-5 molecular sieve, modifying metal is copper or silver. According to the invention, the metal-modified HZSM-5 molecular sieve is used as a pentane refining agent, the refining method is simple, the energy consumption is low, and after refining, the content of unsaturated hydrocarbon is lower than 10 ppm; in addition, the pentane refining agent provided by the invention is recyclable, a pentane product obtained after recycling meets index requirements of the unsaturated hydrocarbon, the recycling condition is mild, and the recycling time is short.
Owner:SHANDONG CHAMBROAD PETROCHEMICALS CO LTD
A method for quasi-continuous synthesis of single-atom catalysts
ActiveCN111604081BIncrease productionGood reproducibilityMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystMaterial synthesis
The invention discloses a method for quasi-continuously synthesizing a single-atom catalyst. The invention encapsulates the metal precursor in the chitosan / sodium lauryl sulfate hydrogel encapsulation through the microcapsule technology, and further pyrolyzes and synthesizes the metal single-atom catalyst. The present invention adopts the pendant drop method in microcapsule technology, which can continuously produce homogeneous microcapsules, thereby realizing the quasi-continuous preparation of single-atom materials. The quasi-continuous synthesis process of the invention solves the problems of poor reproducibility, amplification effect and the like caused by batch synthesis. In addition, the present invention has good expandability, solves the problems of few metal types and low metal content in the prior art, and enriches the research in related fields such as metal single-atom material synthesis methodology.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com