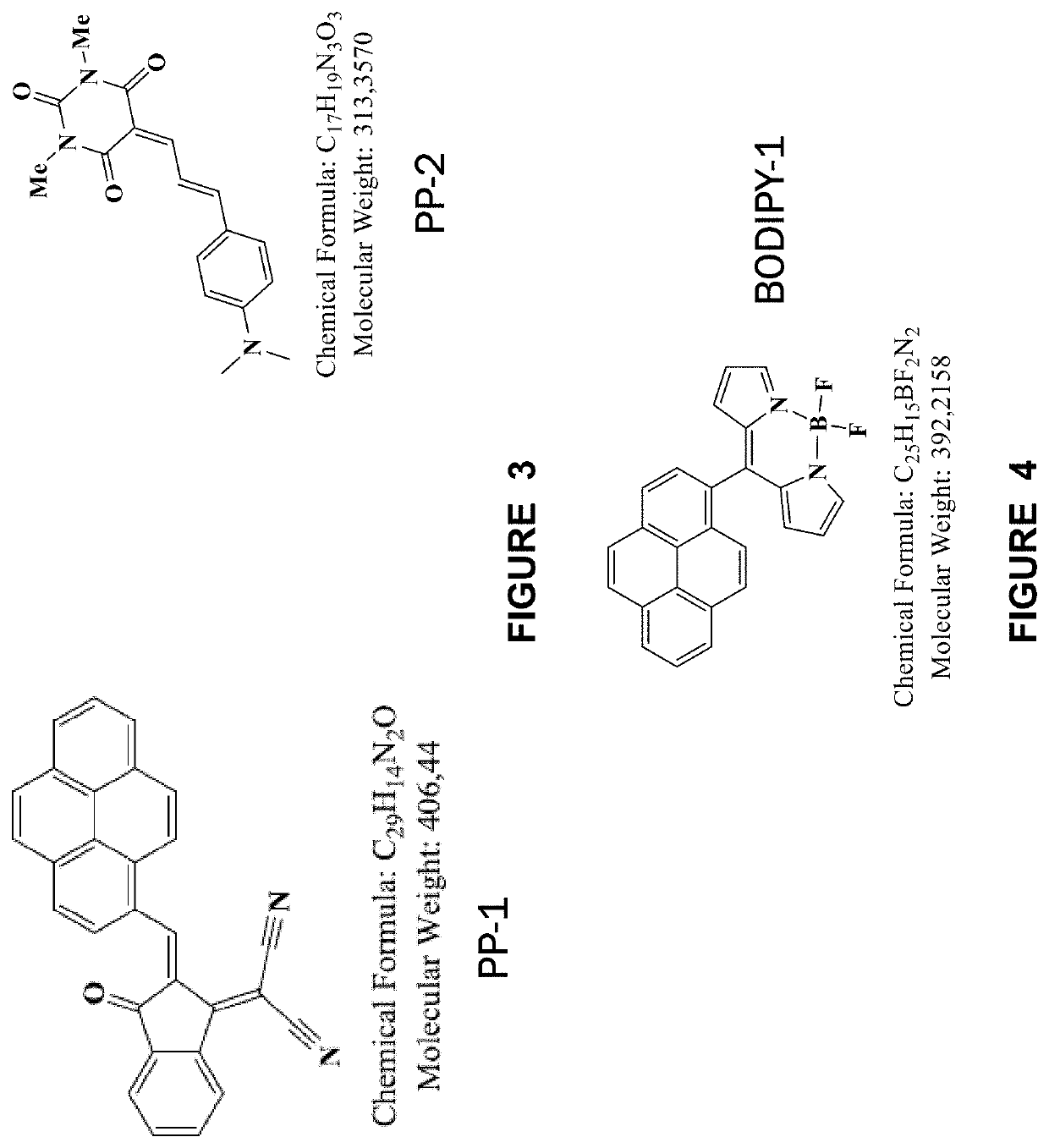
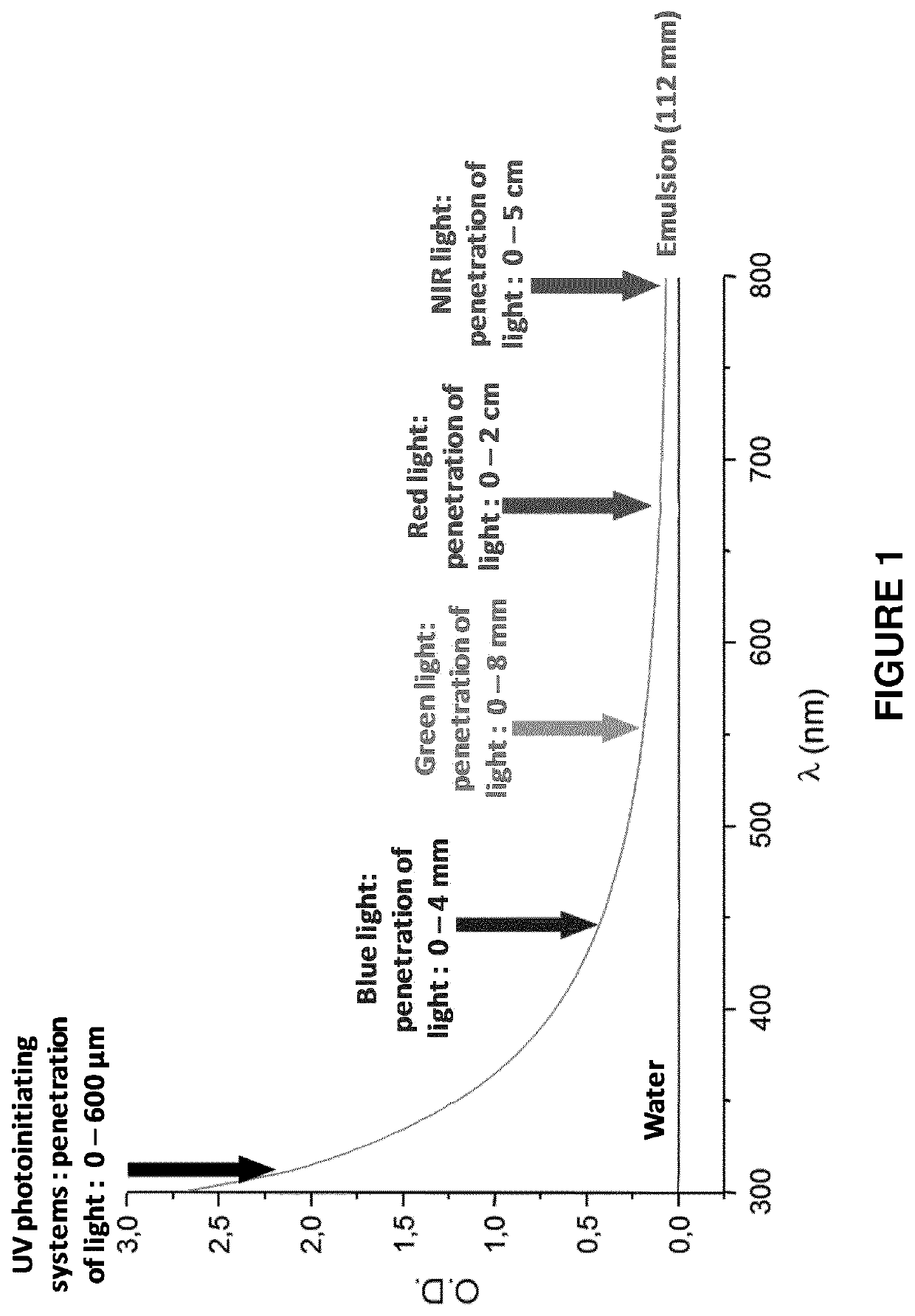
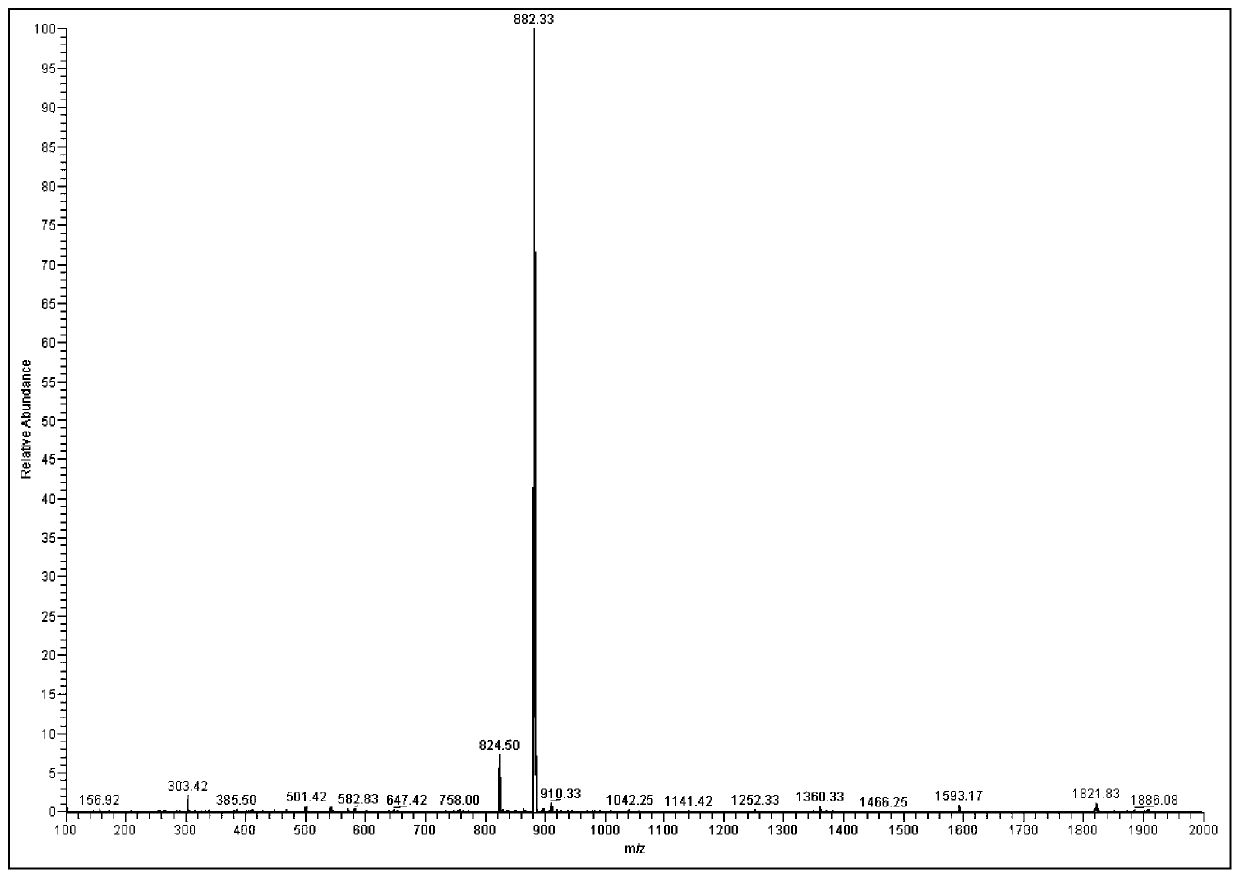
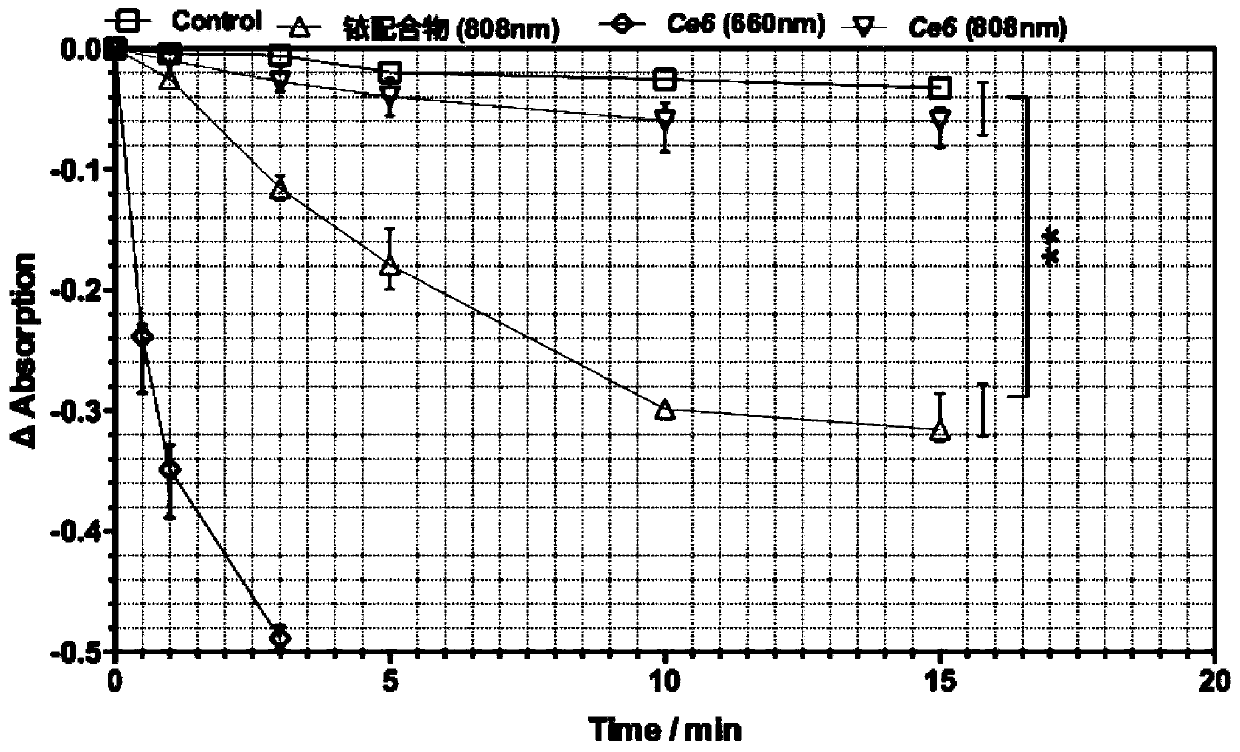
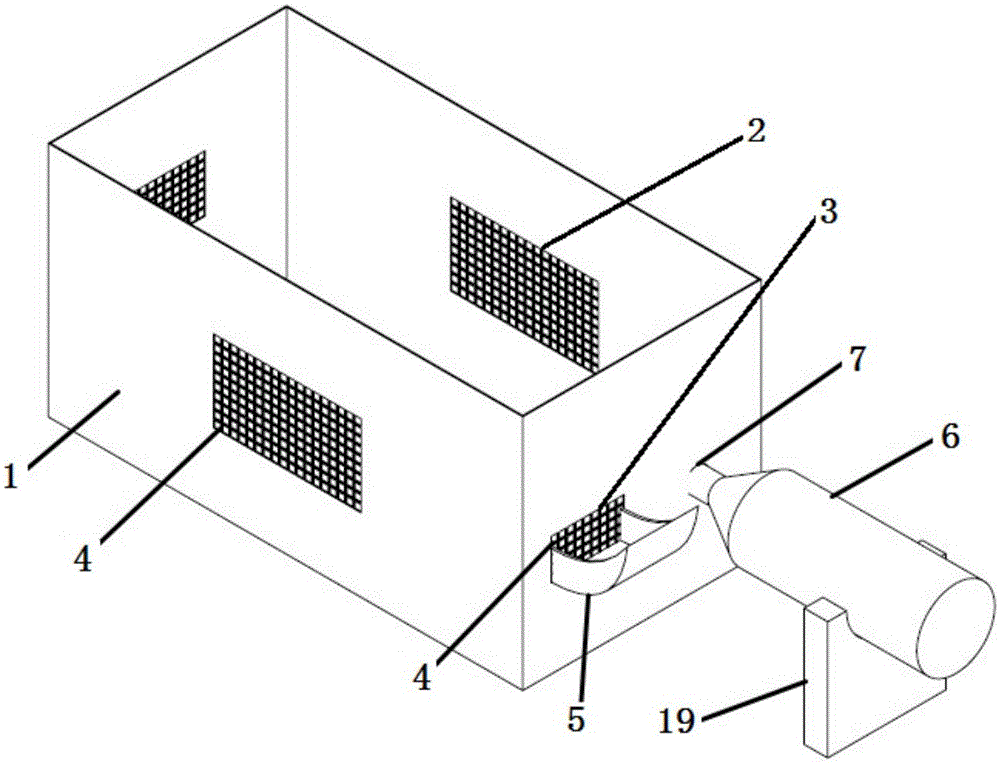
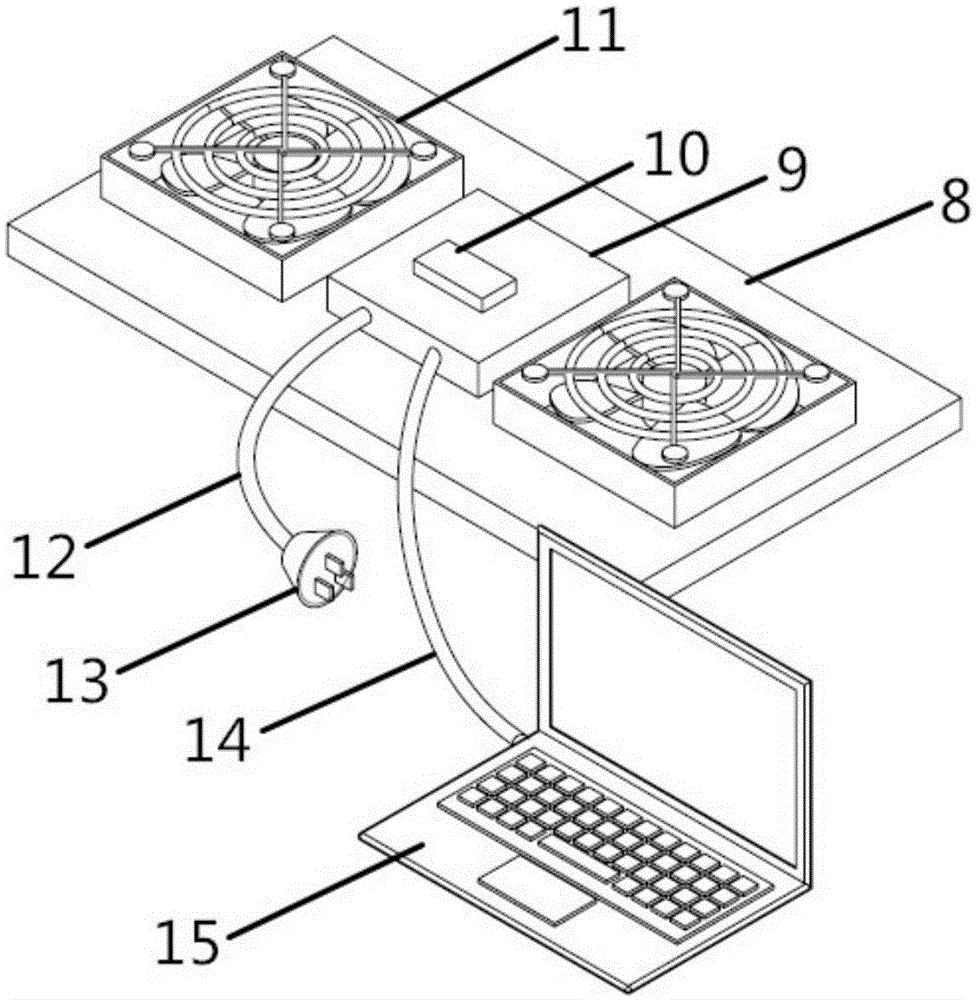
Patents
Literature
36 results about "Near infrared irradiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
NEAR INFRARED RADIATION. A portion of radiation that is just beyond the visible spectrum is referred to as near-infrared. Rather than studying an object's emission of infrared, scientists can study how objects reflect, transmit, and absorb the Sun's near-infrared radiation to observe health of vegetation and soil composition.
Preparation method of biocompatible photo-thermal response self-healing conductive hydrogel
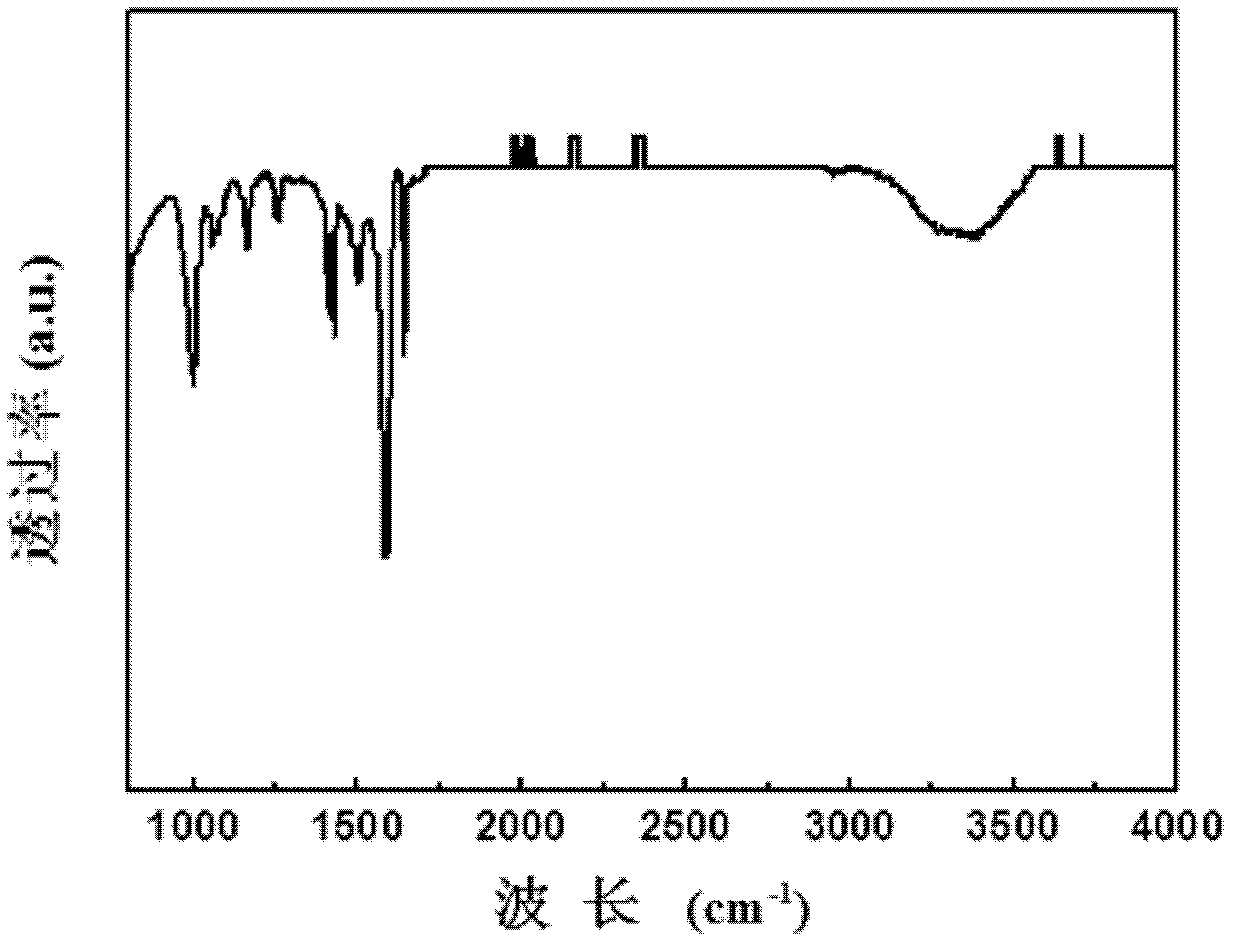
The invention relates to a preparation method of biocompatible photo-thermal response self-healing conductive hydrogel, which includes: preparing solution from N,N-dimethyl acrylamide monomer, potassium persulfate serving as initiator and N,N,N',N'-tetramethylethylenediamine serving as accelerator; then soaking graphene hydrogel into the monomer solution for solution displacement and standing; and finally, initiating polymerization reaction at the room temperature, so that the biocompatible photo-thermal response self-healing conductive hydrogel is prepared. The preparation method is simple in process, mild in reaction condition, short in reaction time and suitable for industrial production. The hydrogel uses the graphene as a three-dimensional network framework, the graphene is high in reduction degree, chemical stability, electric conductivity and mechanical strength and good in photothermal conversion effect, and the hydrogel shows good self-healing performance within the body temperature range and under near-infrared irradiation.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
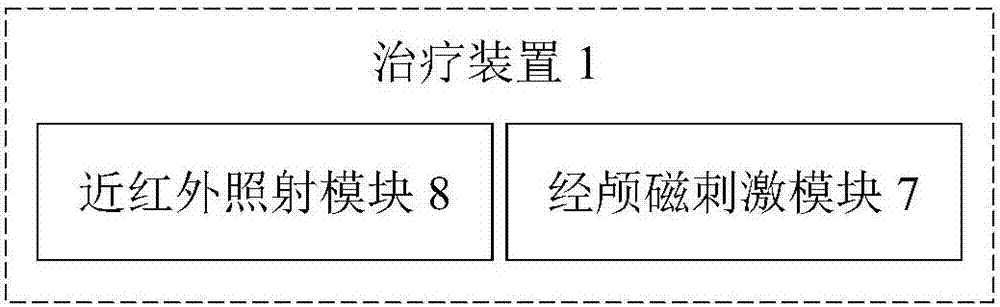
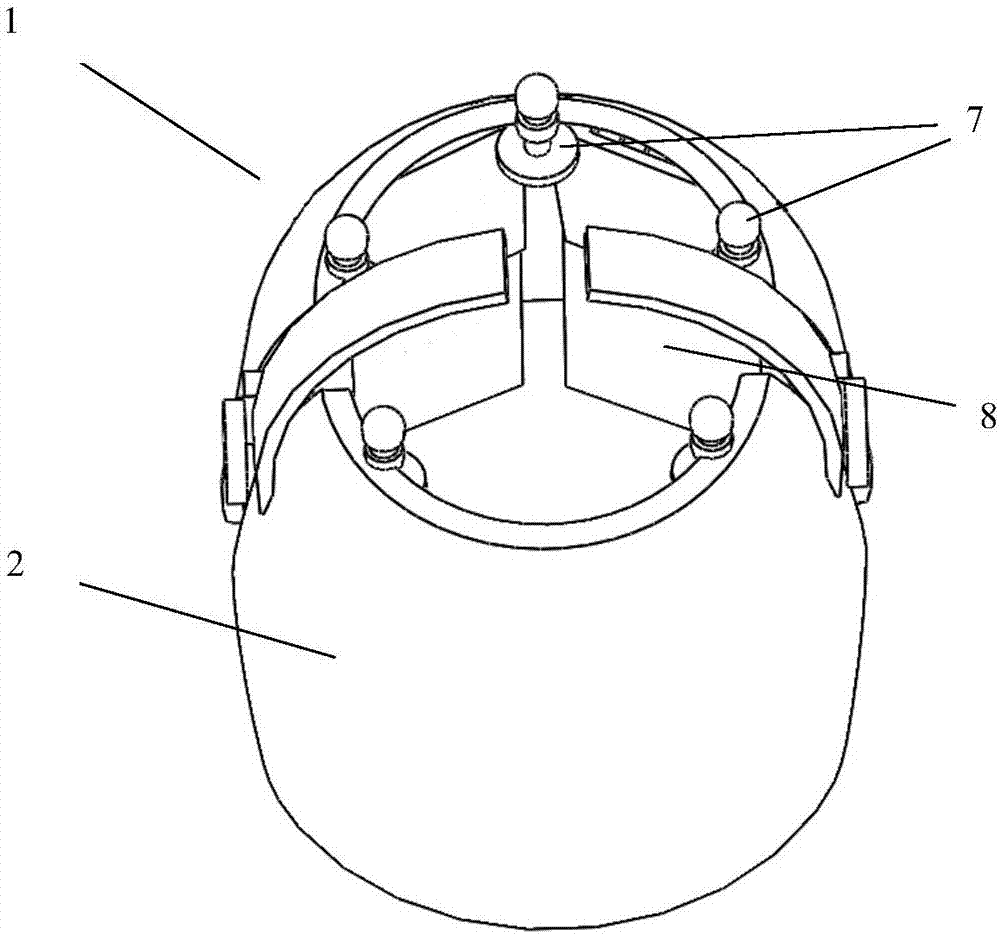
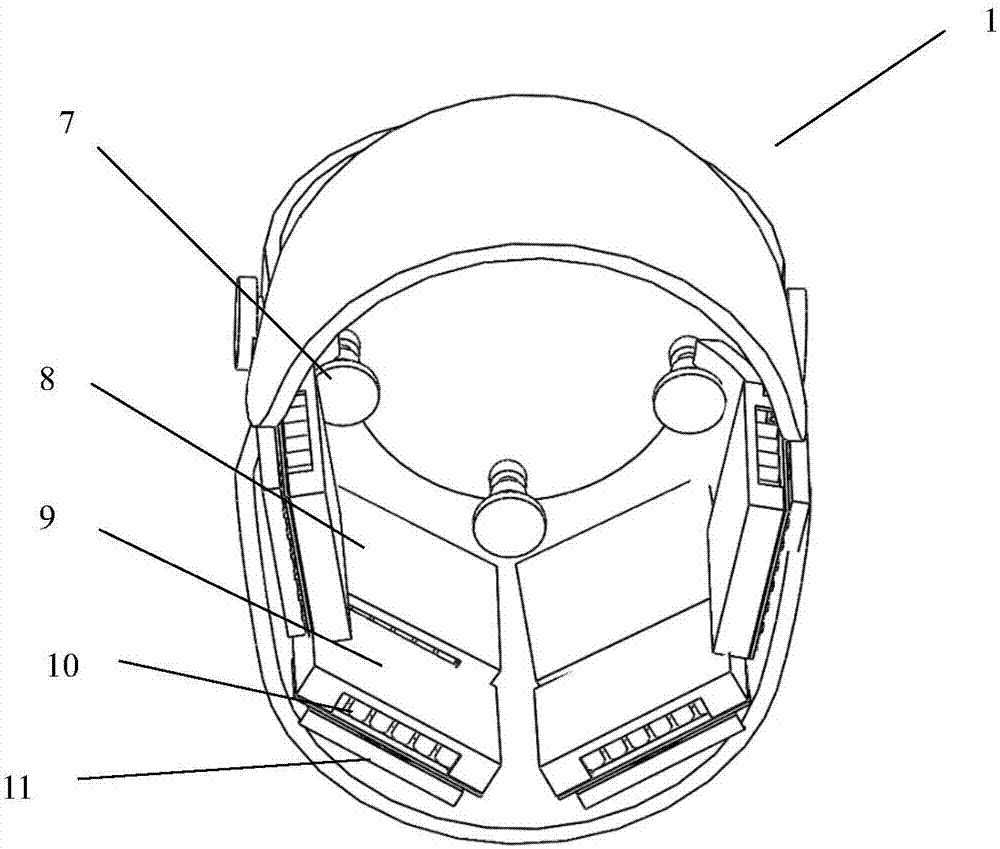
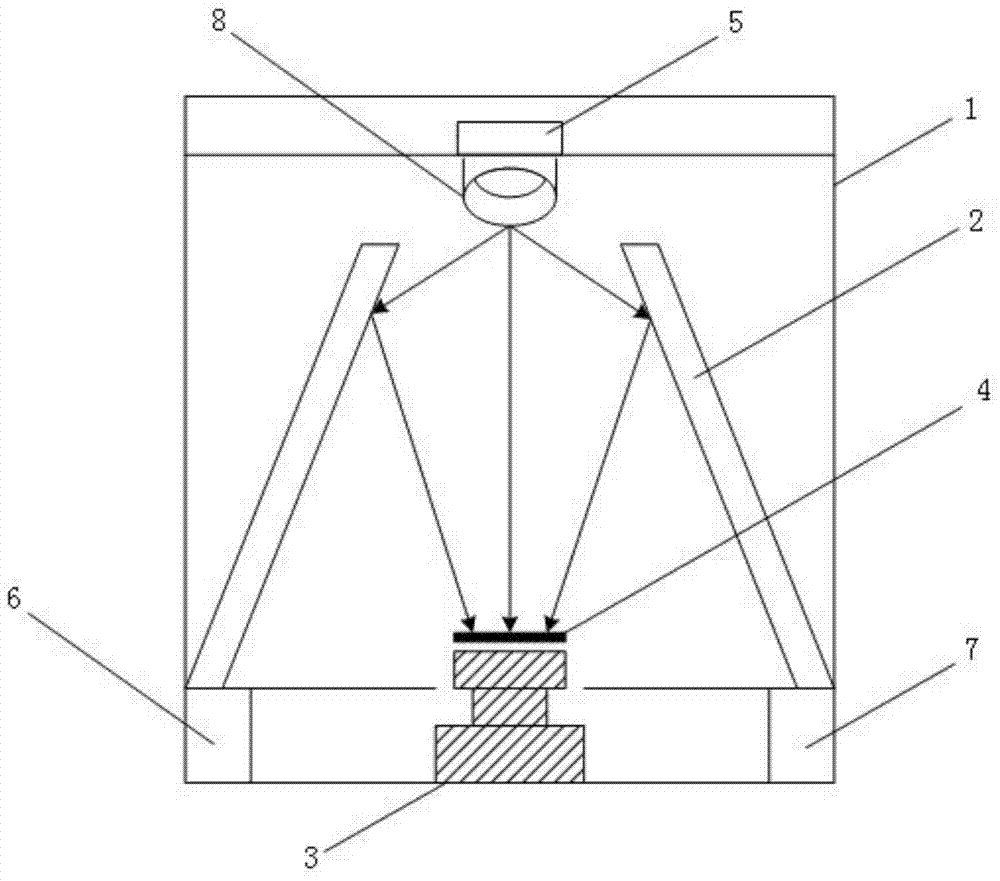
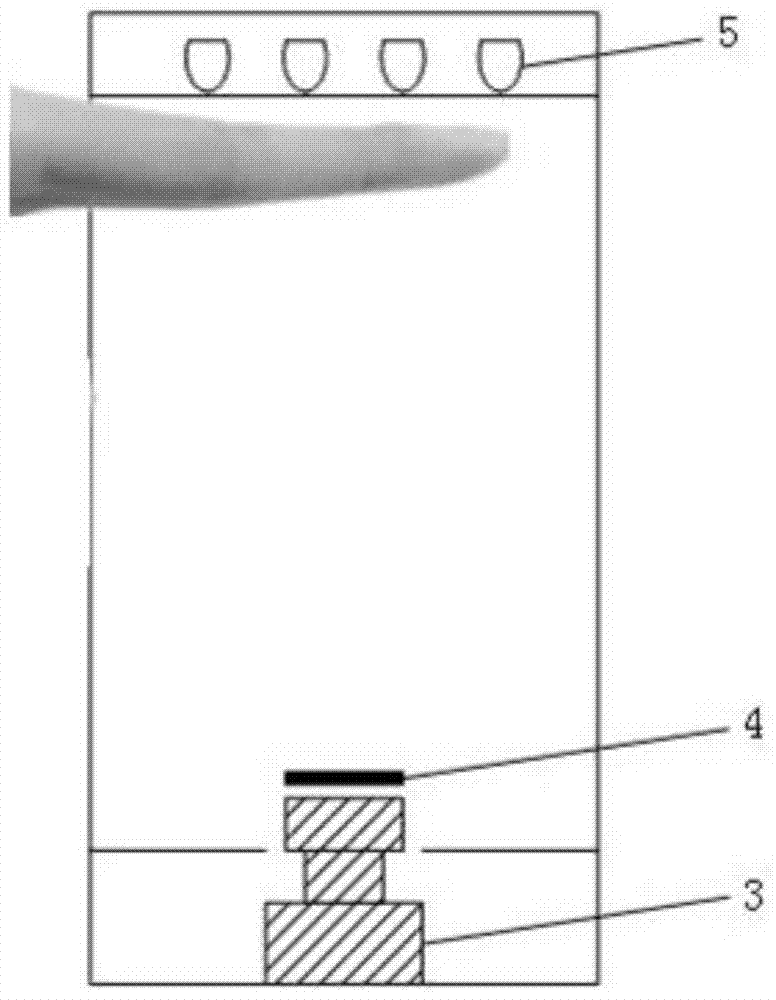
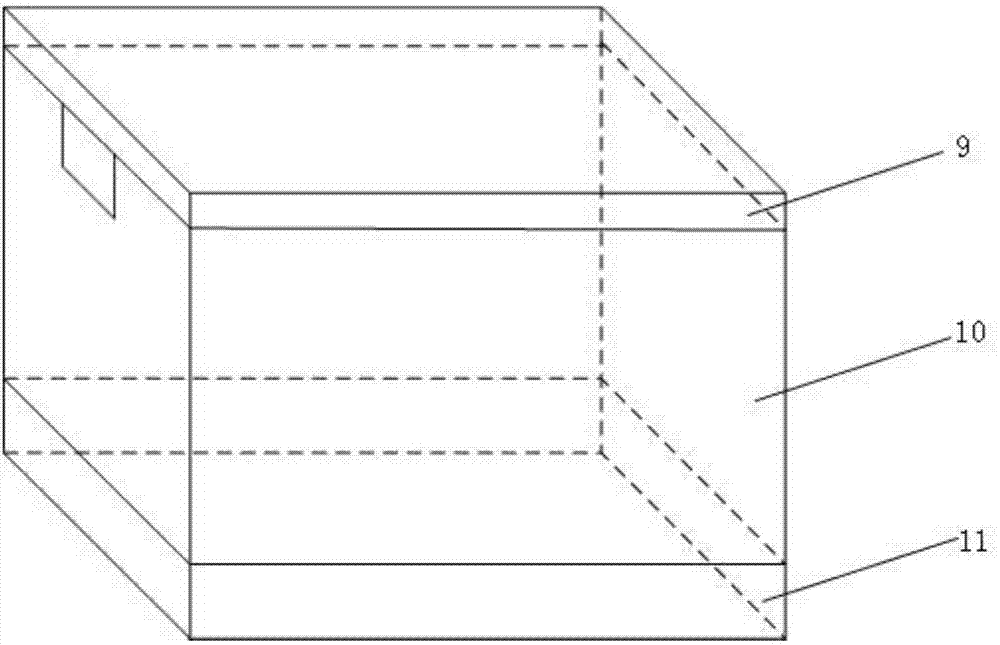
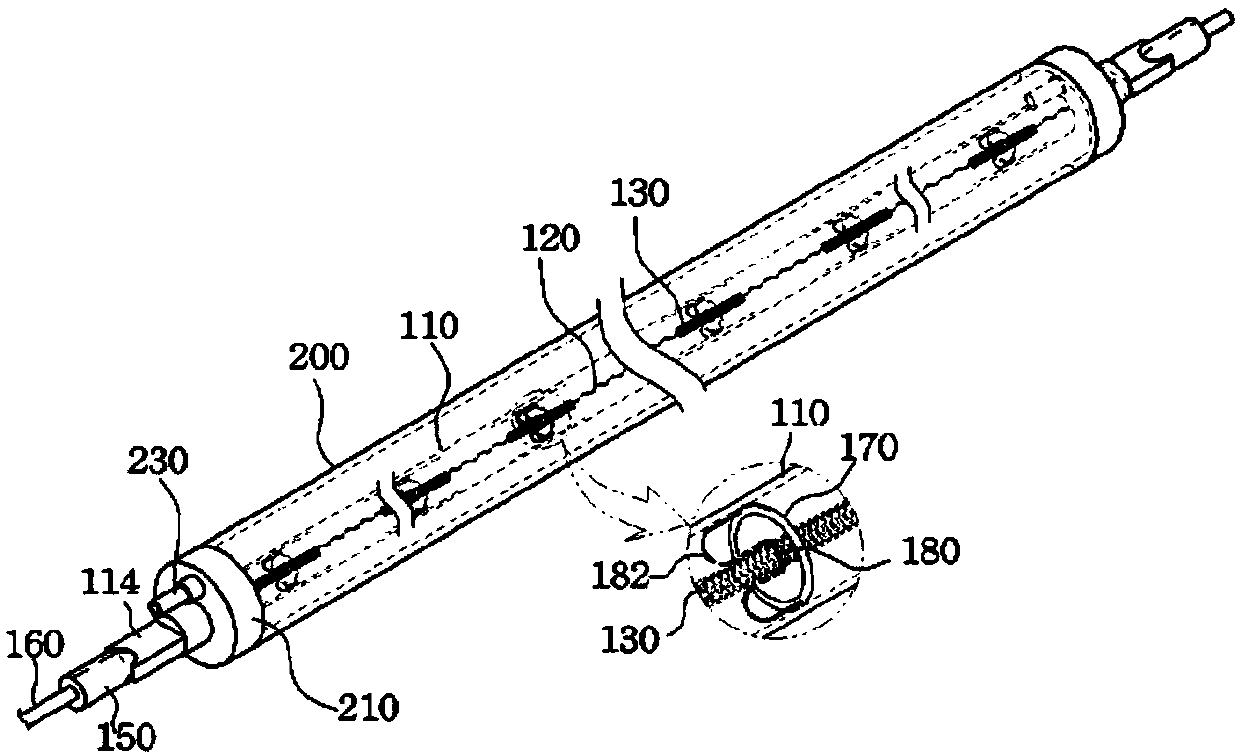
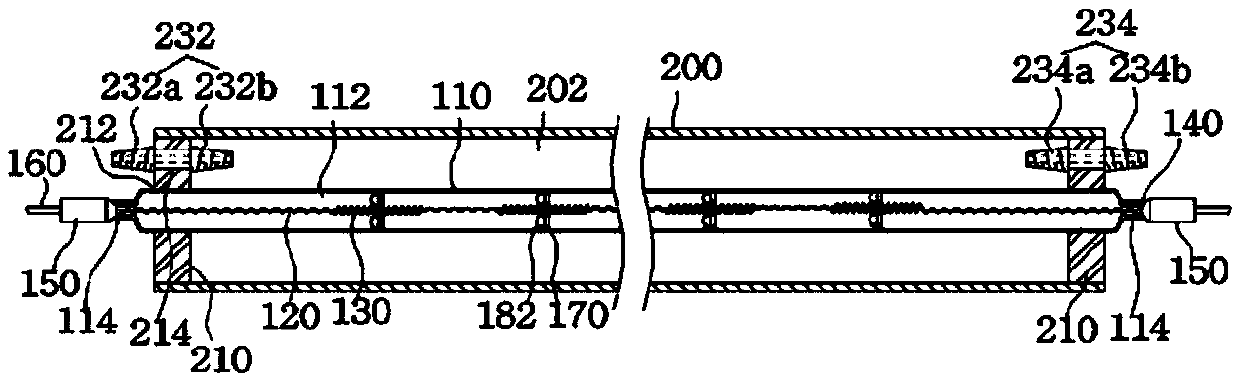
Therapeutic device and therapeutic equipment including therapeutic device
PendingCN107185113AElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsMedicineTherapeutic Devices
The invention provides a therapeutic device. The therapeutic device comprises a casing, magnets, a near-infrared irradiation module and a control module; the casing can be worn on the head by a user; the magnets are mounted on the casing; the near-infrared irradiation module is mounted on the casing and can emit near-infrared irradiation towards the internal of the casing; and the control module is coupled with the near-infrared irradiation module. The invention also provides therapeutic equipment including the therapeutic device.
Owner:ZHEJIANG BRAINHEALTH MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Living body recognizing device and method based on three-dimensional characteristics of finger venas
ActiveCN104778445APrevent cheatingImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionFinger vein recognitionComputer module
The invention discloses a living body recognizing device and method based on three-dimensional characteristics of finger venas. The device comprises a casing, wherein a finger extending-in hole is formed in the casing; a light source module, a camera and control circuit module and a reflecting board module are arranged in the casing, wherein the light source module comprises a plurality of near infrared irradiation sources and frosted glass scattering boards covering the surfaces of the near infrared irradiation sources, and the near infrared irradiation sources are arranged on the casing above a finger extending into the casing; the camera and control circuit module is arranged on the surface opposite to the infrared irradiation sources, and comprises a camera and an automatic light source control circuit, and an infrared filtering sheet covers the camera; the reflecting board module comprises a first reflecting board and a second reflecting board. The recognizing method based on the device comprises the step of comparing three finger images with the information of finger venas of an authenticated person registering in advance at the same time, so that the accuracy is improved, the check of whether an authenticated target is a living body or not can be realized in a short time, and the reliability of vena recognition of fingers is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
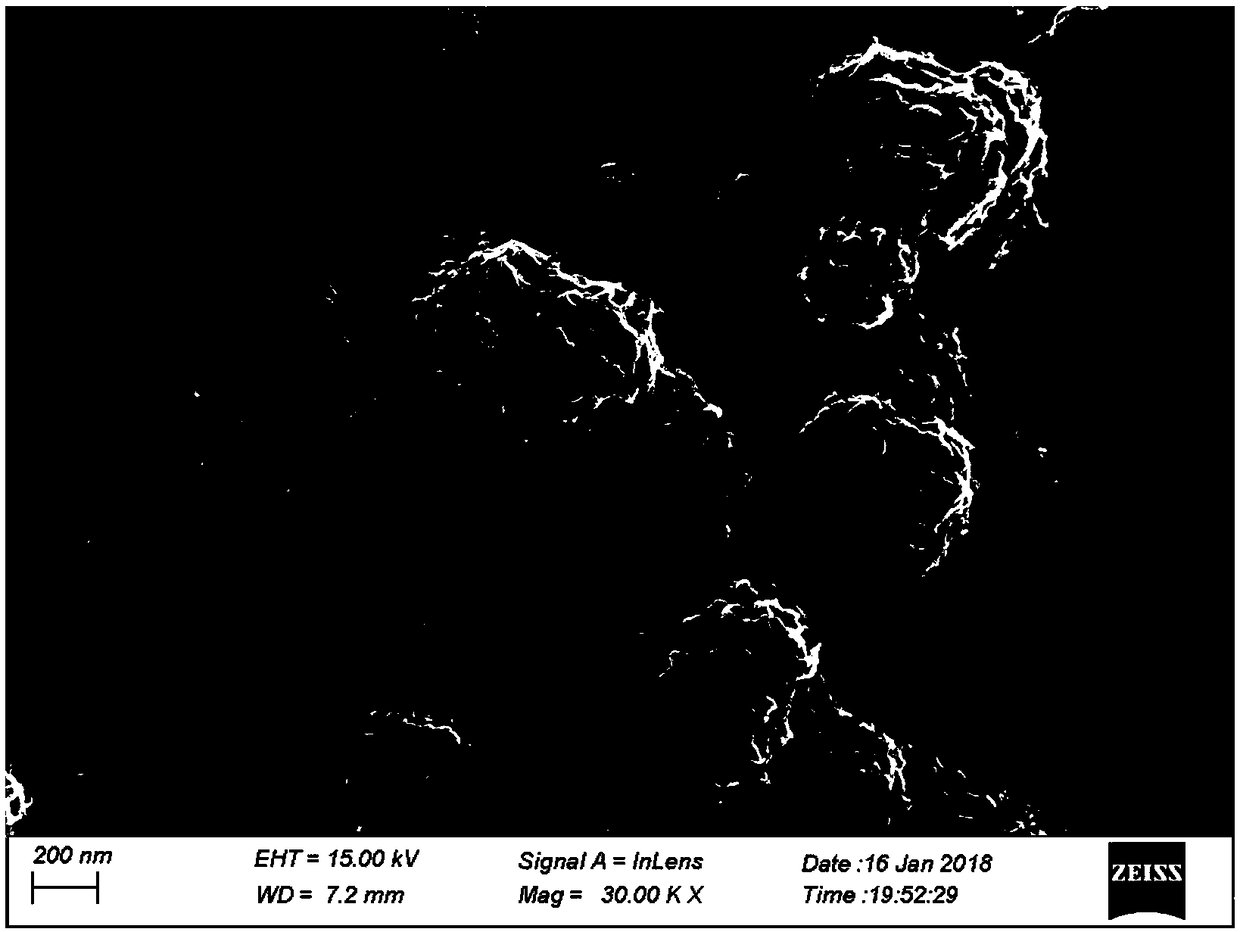
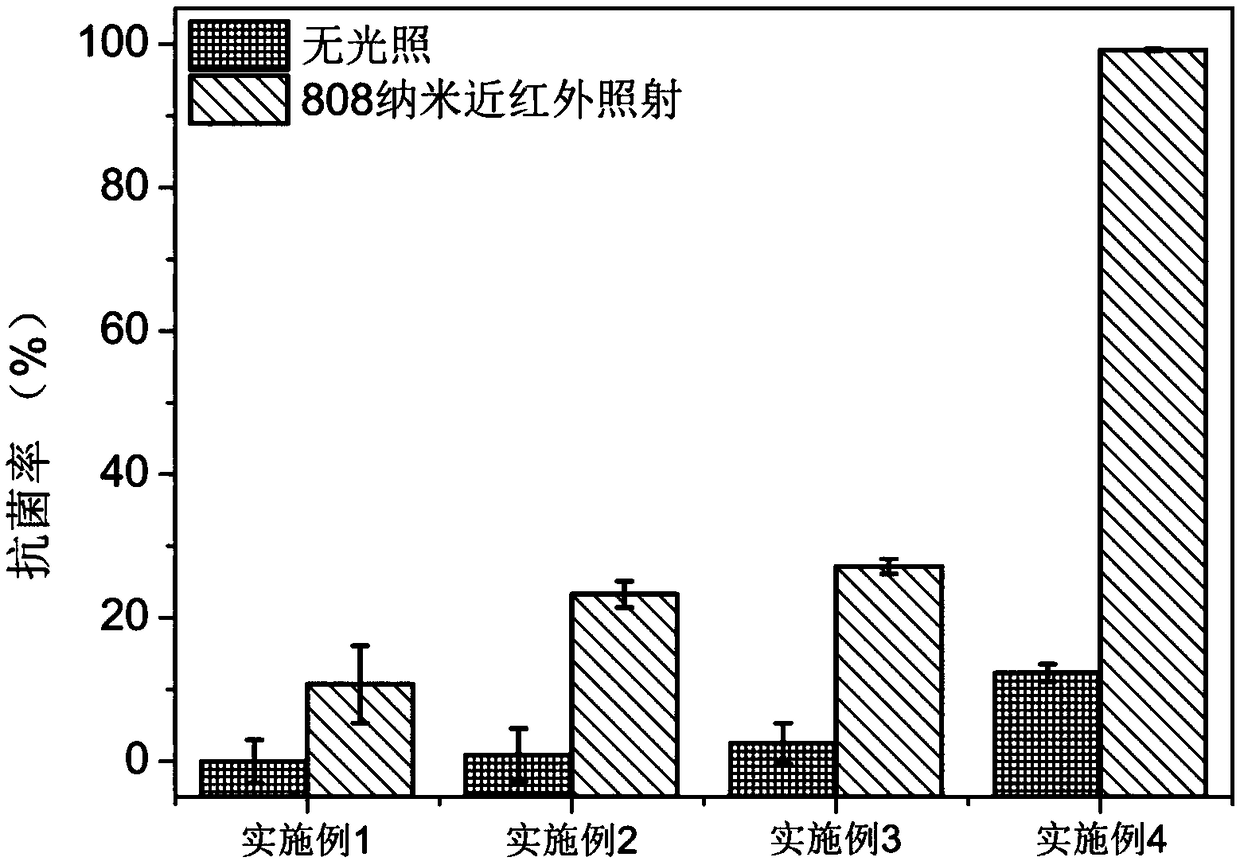
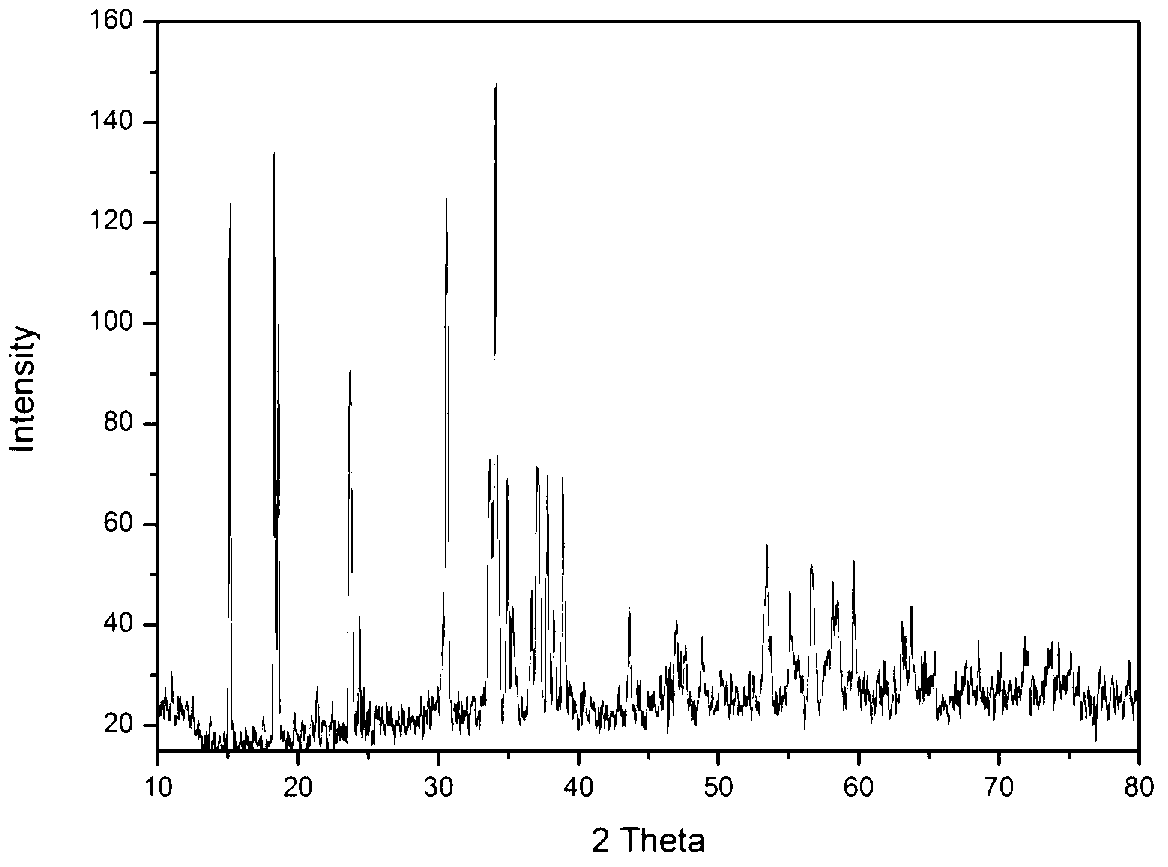
808 nanometer near-infrared excited composite antibacterial coating and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109260476AEasy to prepareGood photothermal effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDrug release rateTitanium surface
The invention relates to an 808 nanometer near-infrared excited composite antibacterial coating and a preparation method thereof. The invention utilizes a hydrothermal method to synthesize uniform size polyethylene glycol modified molybdenum sulfide nano-flowers in one pot. Furthermore, chitosan encapsulated in gentamicin loaded polyethylene glycol modified molybdenum sulfide nanoparticles slowedthe drug release rate. The advantages of the invention are: the petal-like molybdenum disulfide grown on titanium surface has a larger specific surface area which can increase the loading of gentamicin, Molybdenum disulfide itself has a good photothermal effect under near-infrared irradiation. The drug is released quickly under the photothermal effect. The synergistic effect of photothermal and gentamicin can achieve higher antibacterial efficiency in a short period of time.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Near-infrared response photocatalysis material Cu2(OH)PO4 and preparation method
InactiveCN103127946AImprove photocatalytic performanceImprove performancePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationMicro nanoPhenol
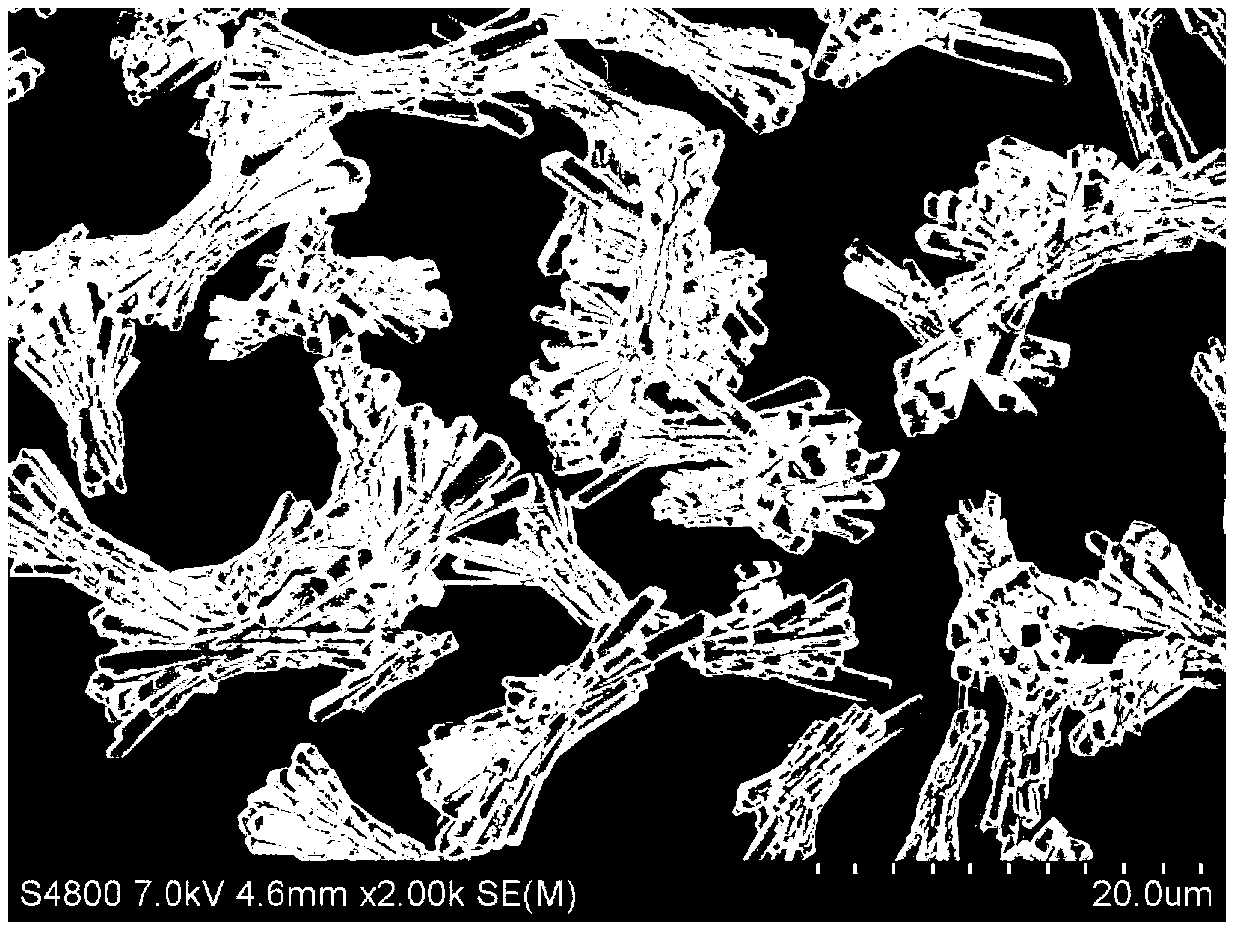
The invention relates to a near-infrared response photocatalysis material Cu2(OH)PO4 and a preparation method, the preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing Cu(NO3)2 and Na2HPO4 and adding in deionized water, adjusting the pH value of suspending liquid to 4-7, performing hydrothermal reaction for 6-12 hours at 120 DEG C, separating and purifying, and drying to obtain the product of micro-nano crystal having a quadrature structure, wherein the crystal length is 4-5 micrometers, the width is 1.4-1.6 micrometers, and the surface has ravine. The near-infrared response photocatalysis material Cu2(OH)PO4 has good photocatalysis performance under the near infrared irradiation (Lambda is greater than 800 nanometers), 90% of 2,4dichlorophenol can be degraded in six house, and the performance is excellent.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Preparation method and application of composite photo-thermal antimicrobial agent of antimicrobial peptide modified gold nanorod
ActiveCN107441489AImprove antibacterial propertiesAntibacterial agentsMaterial nanotechnologyMaterials preparationGold nanorod
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of a composite photo-thermal antimicrobial agent of an antimicrobial peptide modified gold nanorod, and belongs to the technical field of material preparation. Specifically, the invention provides the method that the gold nanorod is modified by virtue of antimicrobial polypeptide and synergistic and efficient sterilization is implemented on the basis of an antimicrobial effect of the antimicrobial peptide and a photo-thermal effect of the antimicrobial peptide generated under near-infrared irradiation, and the method mainly comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a gold seed; (2) preparing the gold nanorod; (3) preparing an antimicrobial polypeptide solution; (4) preparing a composite photo-thermal agent of the antimicrobial peptide modified gold nanorod; and (5) implementing photo-thermal bacterium resistance. According to the technology, the antimicrobial polypeptide is modified on the gold nanorod which has a strong NIR absorption effect and is applied to the photo-thermal bacterium resistance. A better synergistic and efficient antimicrobial effect can be achieved with relatively low energy input on the basis of the relatively good antimicrobial effect of the antimicrobial peptide and the photo-thermal effect of the antimicrobial peptide generated under the near-infrared irradiation.
Owner:兰州博林化工科技有限公司
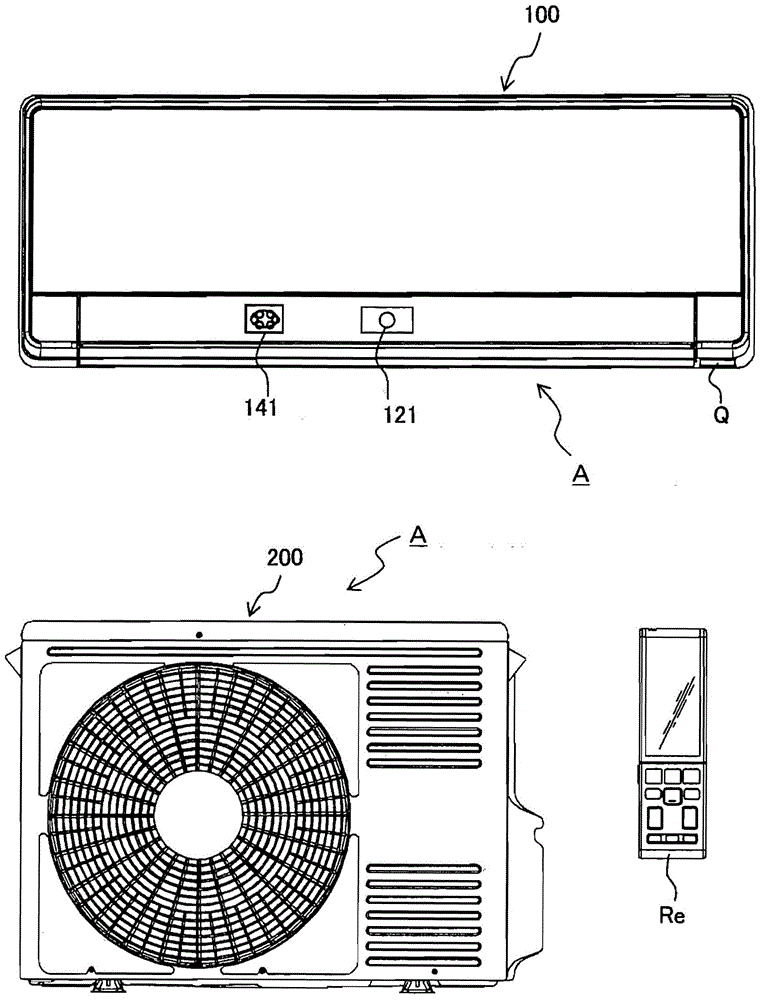
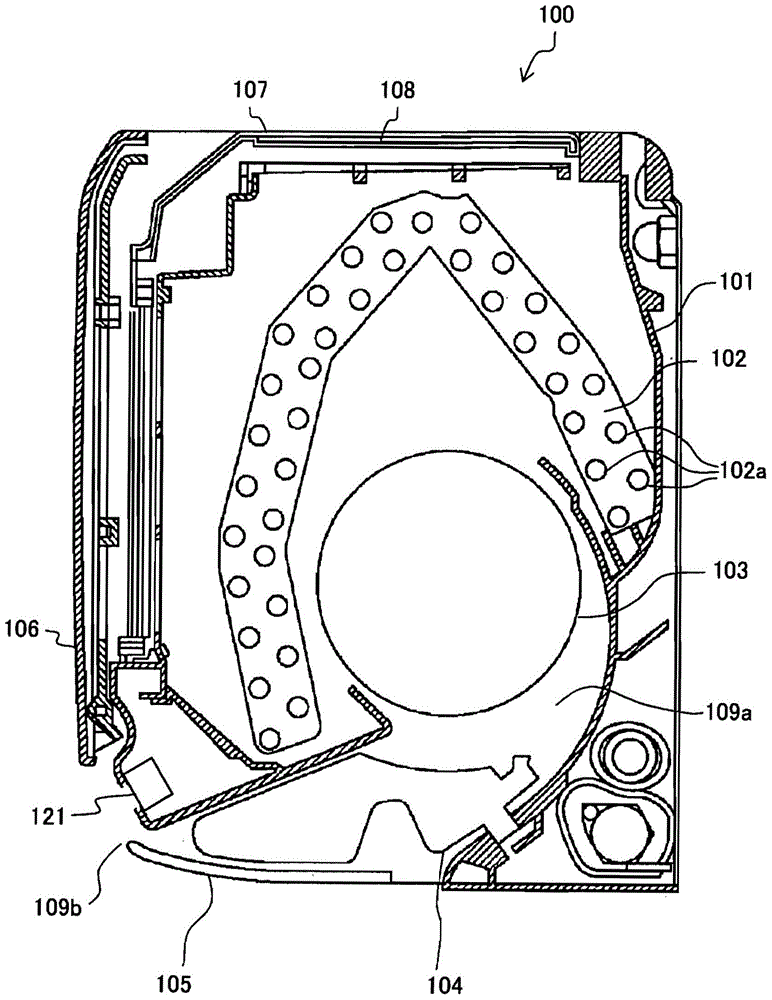
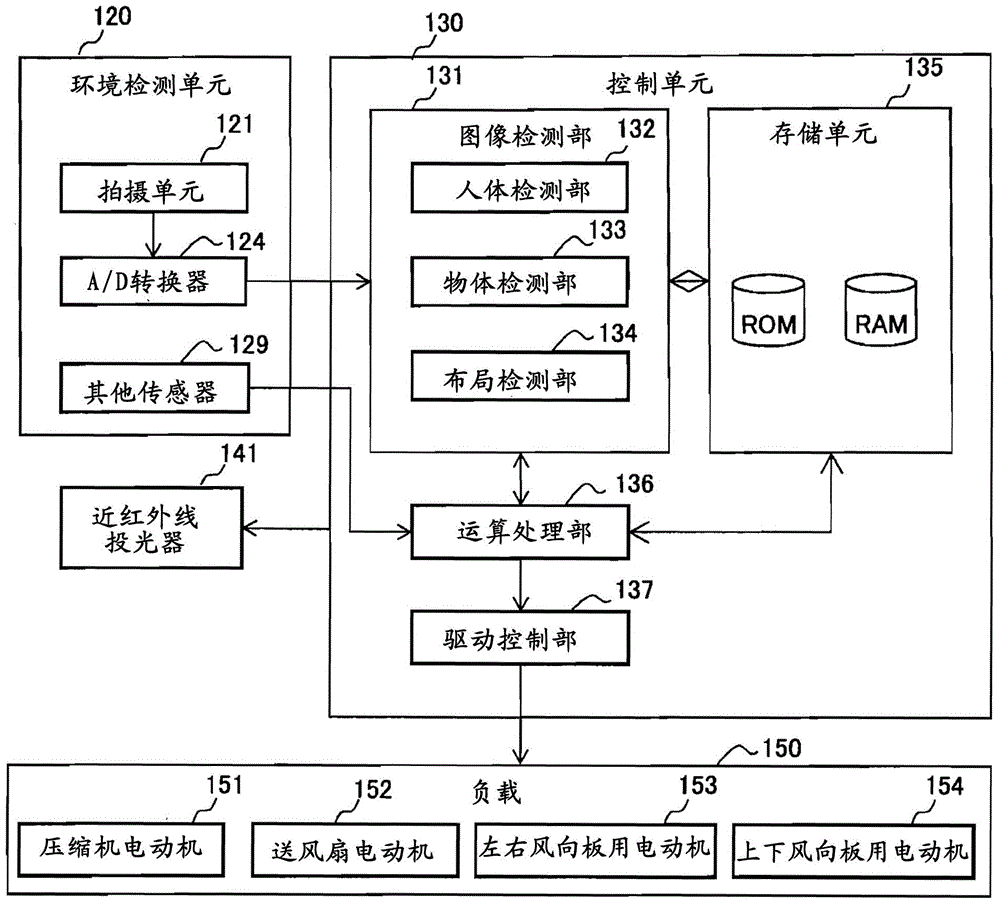
Air conditioner and control method thereof
InactiveCN105352028AHigh-precision detectionSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsLighting and heating apparatusInfraredImaging processing
The invention provides an air conditioner and a control method thereof. The air conditioner comprising a capturing unit and a near infrared irradiation unit can detect objects and / or a human body at high precision by image processing. The air conditioners (A) comprises the capturing unit (121) for capturing an air-conditioned room, a near infrared projector (141) having a near infrared light-emitting diode irradiating near infrared rays to the air-conditioned room, a drive control unit for controlling the air conditioning operation according to the captured result of the capturing unit (121), and a control unit (130) for enabling the capturing unit (121) to capture the air-conditioned room in both conditions that the near-infrared rays are not irradiated to the air-conditioned room through the near infrared projector (141) and that the near-infrared rays are irradiated to the air-conditioned room through the near infrared projector (141).
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS HITACHI AIR CONDITIONING
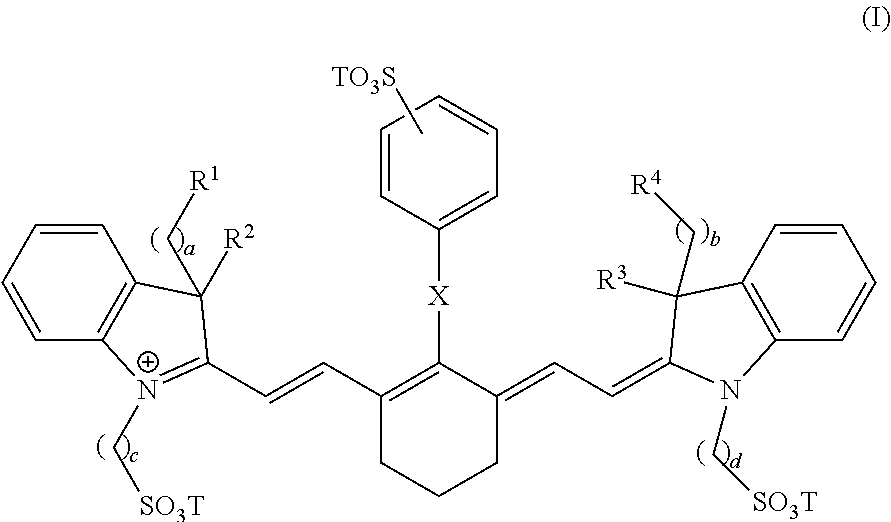
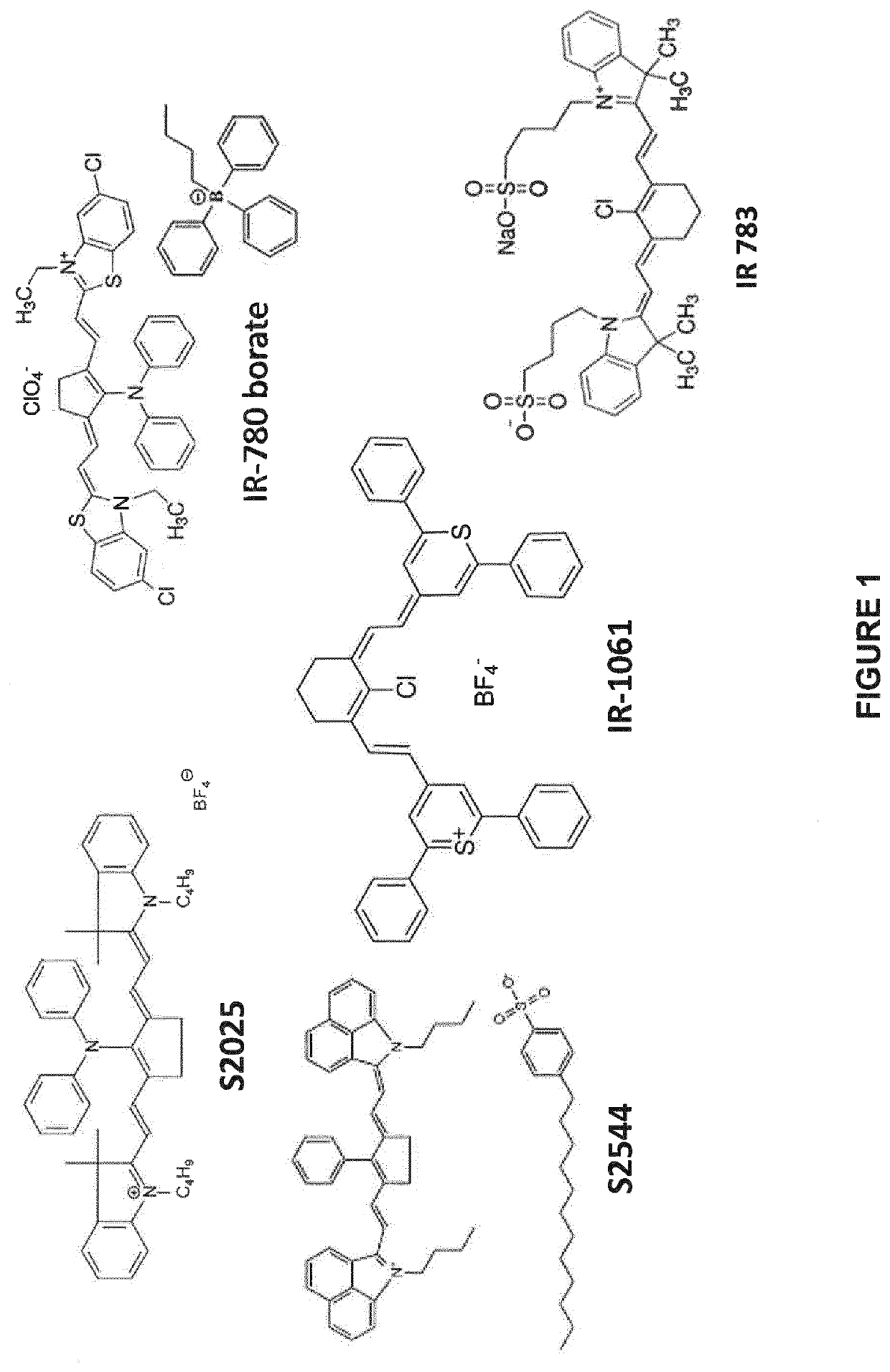
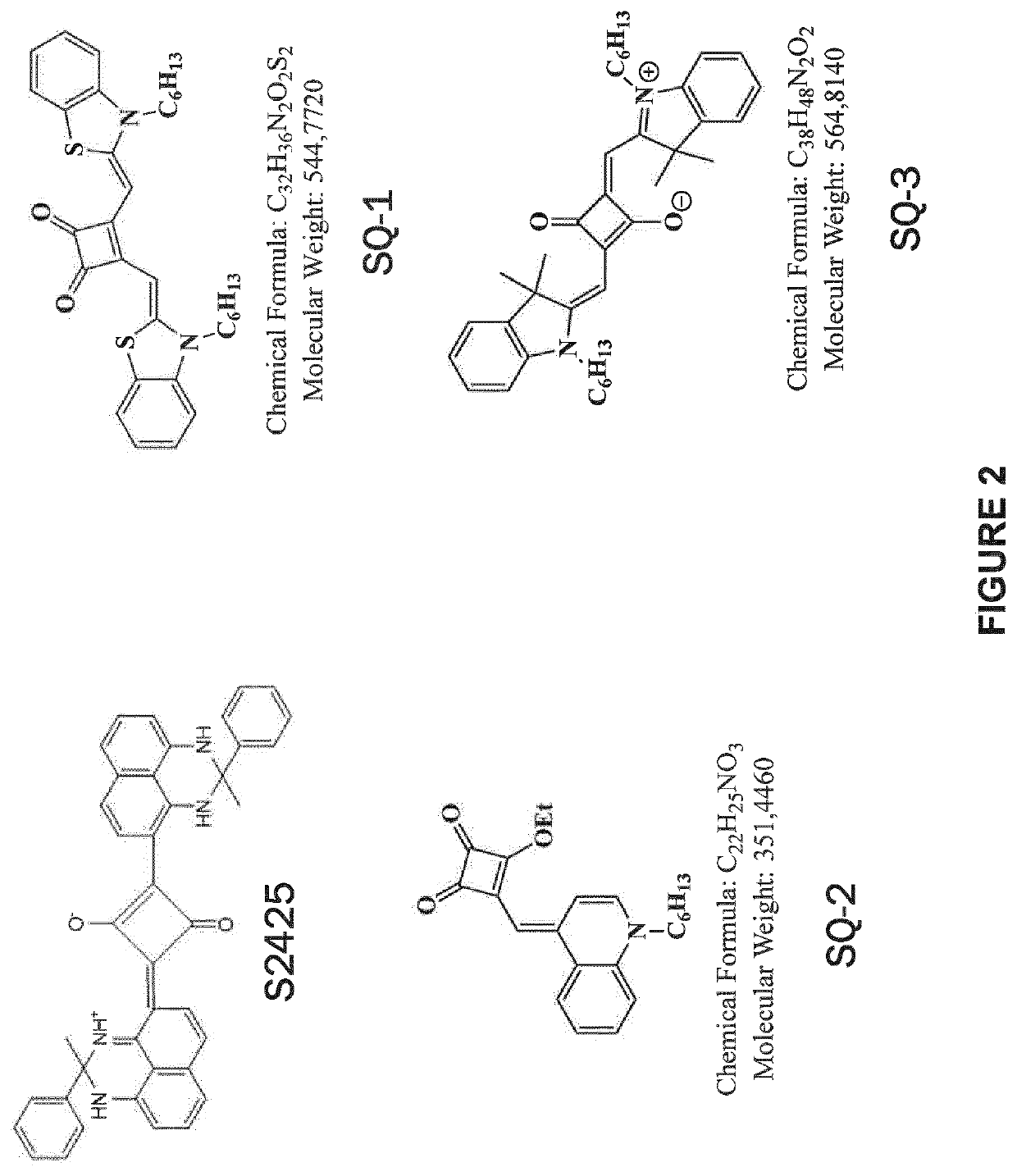
Pharmaceutical compositions of near ir closed chain, sulfo-cyanine dyes
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
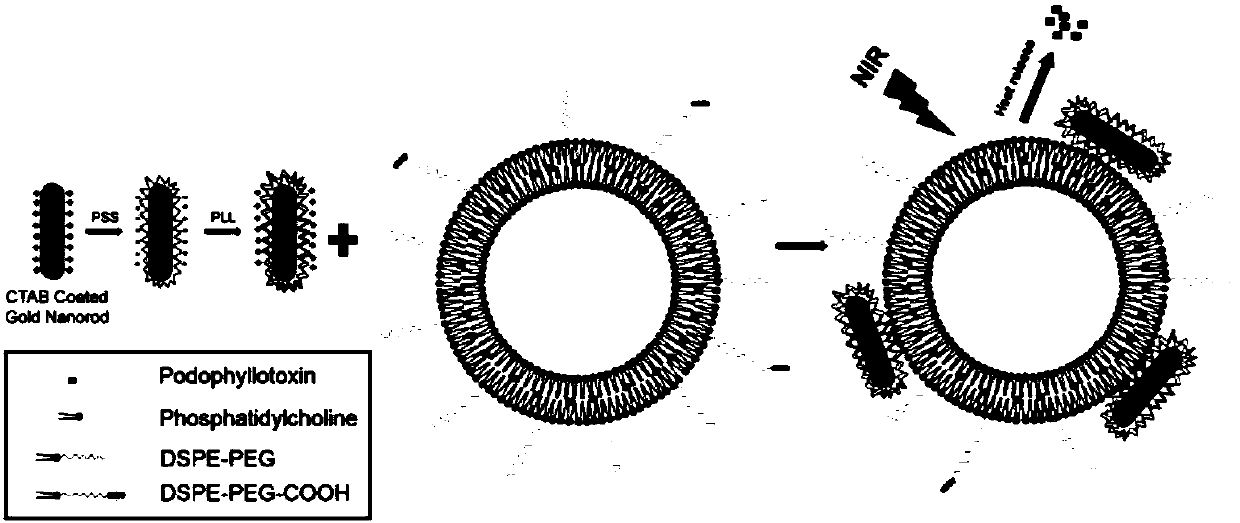
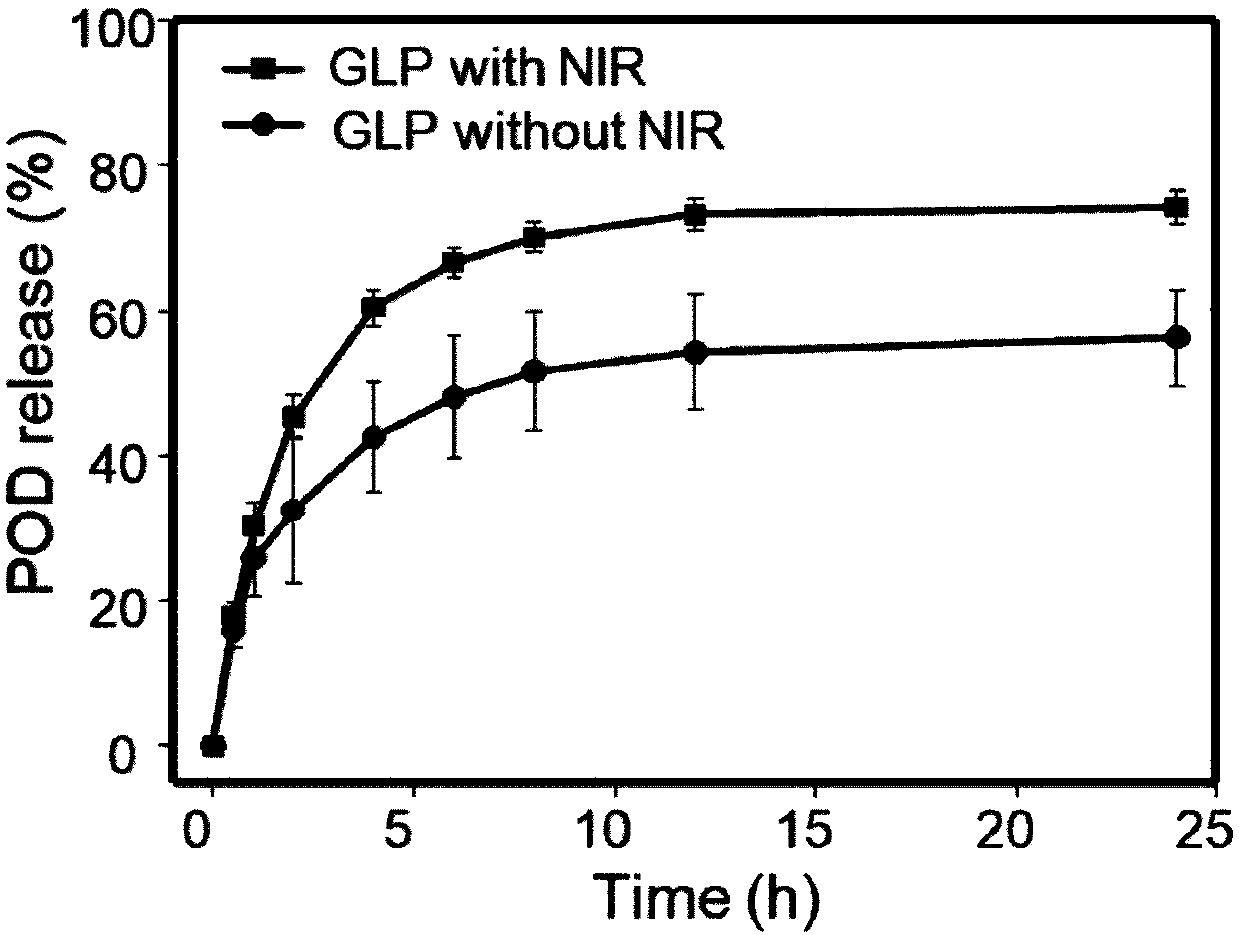
Gold nanorod podophyllotoxin liposome, preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN107670037AEffective absorptionImprove light-to-heat conversion efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsDrug photocleavageZeta potentialHemolysis
The invention discloses a gold nanometer podophyllotoxin liposome, a preparation method and use thereof. The gold nanometer podophyllotoxin liposome is a nano-composite obtained by causing a gold nanorod to be modified by a polyelectrolyte and then combined with the outer surface of the podophyllotoxin liposome containing carboxyl. The gold nanometer podophyllotoxin liposome is in a typical vesicle shape with a particle diameter of about 129.8 nm and a zeta potential of +15.7 mV, and has a high extinction coefficient (8.08Lg<-1>cm<-1>) and photothermal conversion efficiency (46.1%); and the gold nanometer podophyllotoxin liposome has no cytotoxicity and no hemolysis. The gold nanometer podophyllotoxin liposome has good photothermal stability under near-infrared irradiation and can achieverapid release; and the synergistic treatment of chemotherapy-photothermal therapy has a strong killing effect on tumor cells, and an effect thereof may not be limited to this.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Skin care apparatus using plasma and near infrared ray
InactiveUS20180008333A1Improve wrinklesIncrease skin elasticityElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingSkin contactMedicine
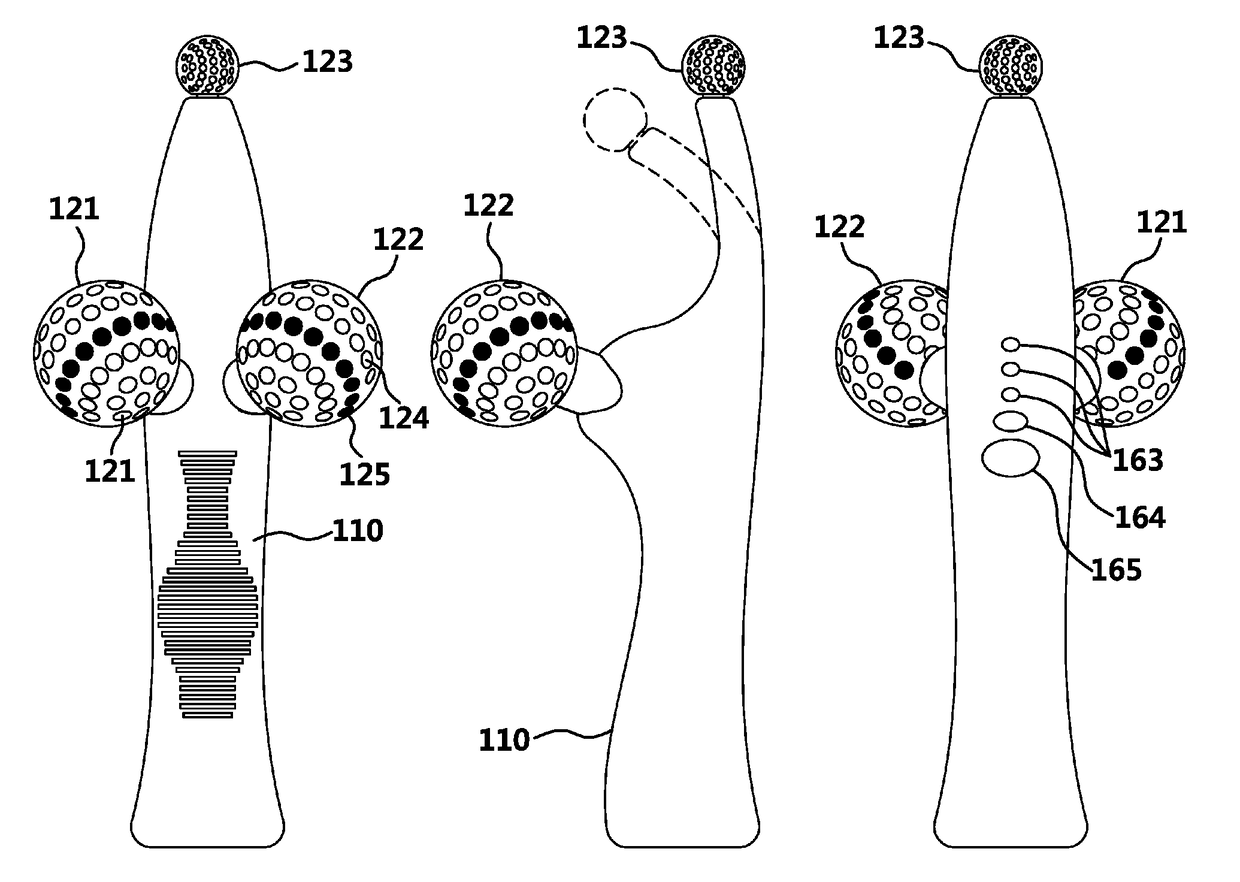
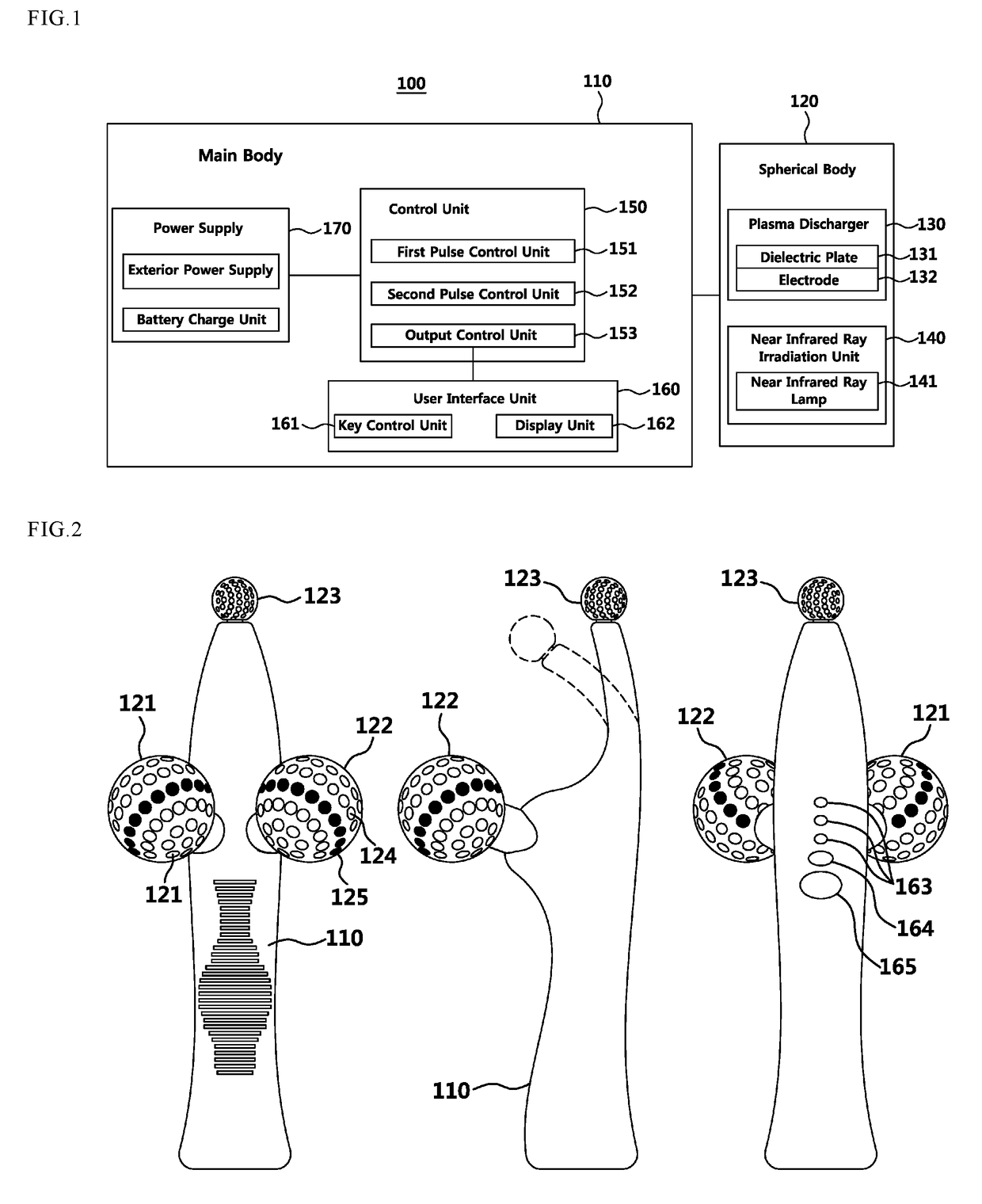
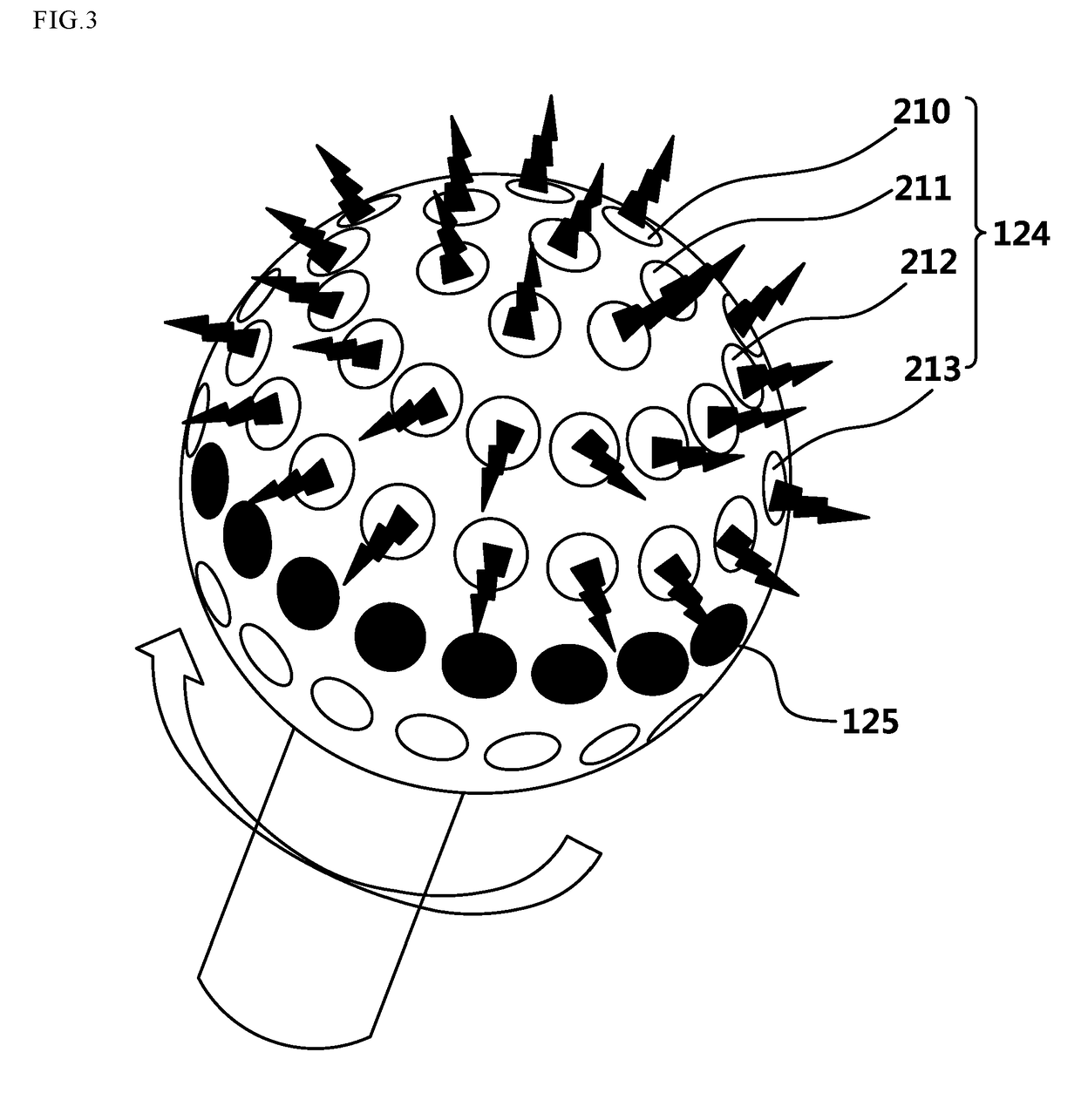
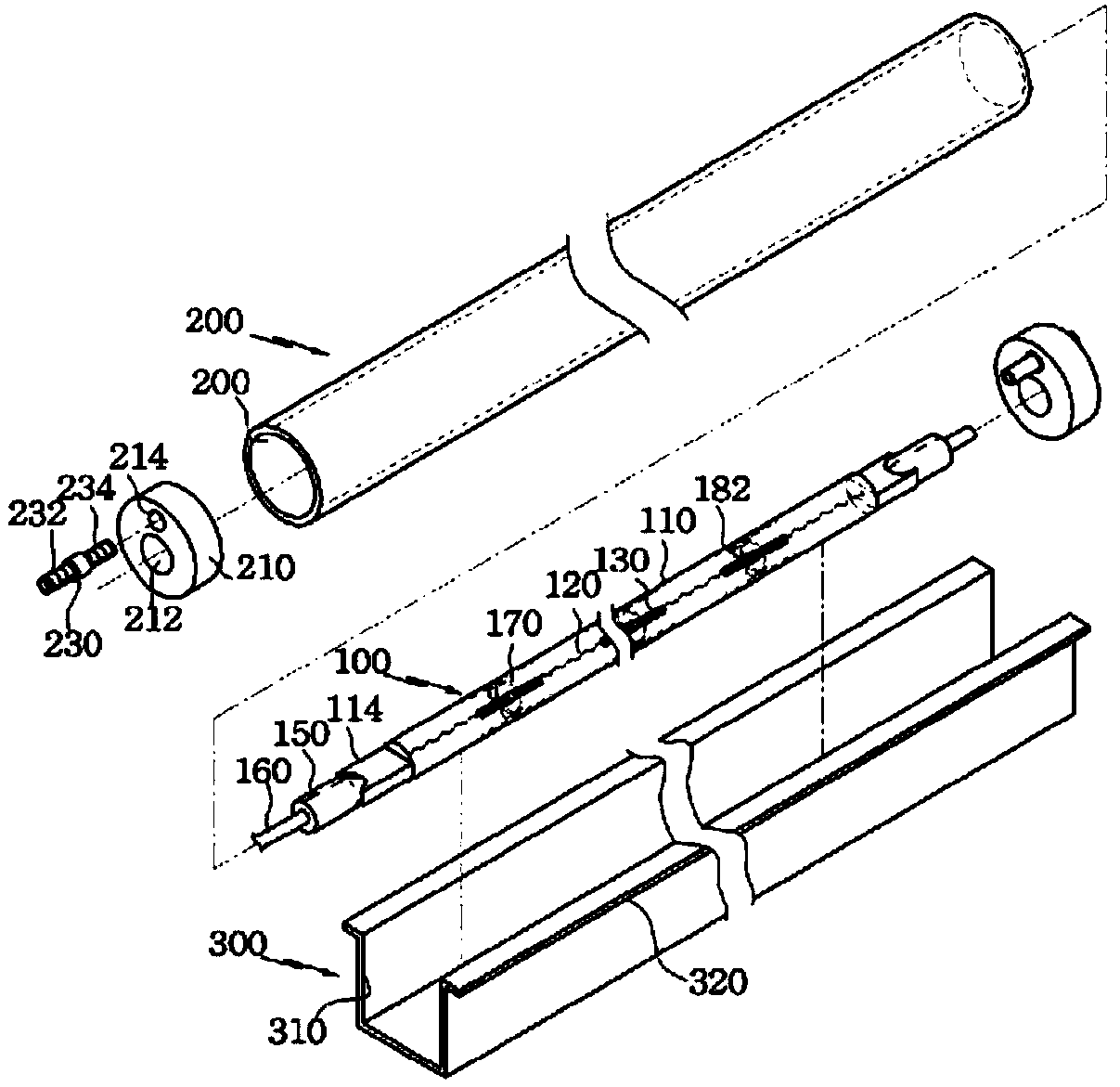
An exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure are directed to providing a skin care apparatus using plasma and near-infrared ray designed to provide effects of improving skin and lifting by irradiating plasma and near-infrared ray generated through dual electric generation on skin contacted by a spherical form. Further, the exemplary embodiments of the present disclosures are directed to providing a skin care apparatus using plasma and near-infrared ray that prevents skin contact or dual irradiation, which were used to happen in the conventional side contact structure, with the method of irradiating plasma and near-infrared ray by using dielectric barrier discharge for each of the plasma discharge groove and near-infrared irradiation groove that are different from the conventional contact structure, through a spot contact spherical body structure.
Owner:JIN SEOK
Integrated lamp unit and liquid-circulating dual pipe lamp having same
InactiveCN109691224ARealize replacement workSimple and convenient radiationBathing devicesHeating element shapesEngineeringFixed position
The present invention relates to an integrated liquid-circulating dual pipe lamp, and comprises: a lamp unit which has a plurality of coils and filaments thereinside, and which has a position-fixing ring for fixing positions of the filaments; a lamp housing which has the lamp unit thereinside, and which has a circulation hole formed thereon so that liquid circulates outside the lamp unit at a predetermined temperature; watertight members which seal both end parts of the lamp housing, and into / through which both end parts of the lamp unit are inserted and penetrate; a liquid-circulation memberwhich is coupled to the watertight member, which supplies a predetermined amount of liquid towards the circulation hole so as to circulate the same, and which discharges the circulating liquid according to the temperature of the liquid; and a reflection member in which the lamp housing is mounted, and which enhances the amount of near-infrared irradiation emitted from the lamp unit.
Owner:李宇宙
Device and method for living body recognition based on three-dimensional features of finger veins
ActiveCN104778445BPrevent cheatingImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionVeinFinger vein recognition
The invention discloses a living body recognizing device and method based on three-dimensional characteristics of finger venas. The device comprises a casing, wherein a finger extending-in hole is formed in the casing; a light source module, a camera and control circuit module and a reflecting board module are arranged in the casing, wherein the light source module comprises a plurality of near infrared irradiation sources and frosted glass scattering boards covering the surfaces of the near infrared irradiation sources, and the near infrared irradiation sources are arranged on the casing above a finger extending into the casing; the camera and control circuit module is arranged on the surface opposite to the infrared irradiation sources, and comprises a camera and an automatic light source control circuit, and an infrared filtering sheet covers the camera; the reflecting board module comprises a first reflecting board and a second reflecting board. The recognizing method based on the device comprises the step of comparing three finger images with the information of finger venas of an authenticated person registering in advance at the same time, so that the accuracy is improved, the check of whether an authenticated target is a living body or not can be realized in a short time, and the reliability of vena recognition of fingers is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
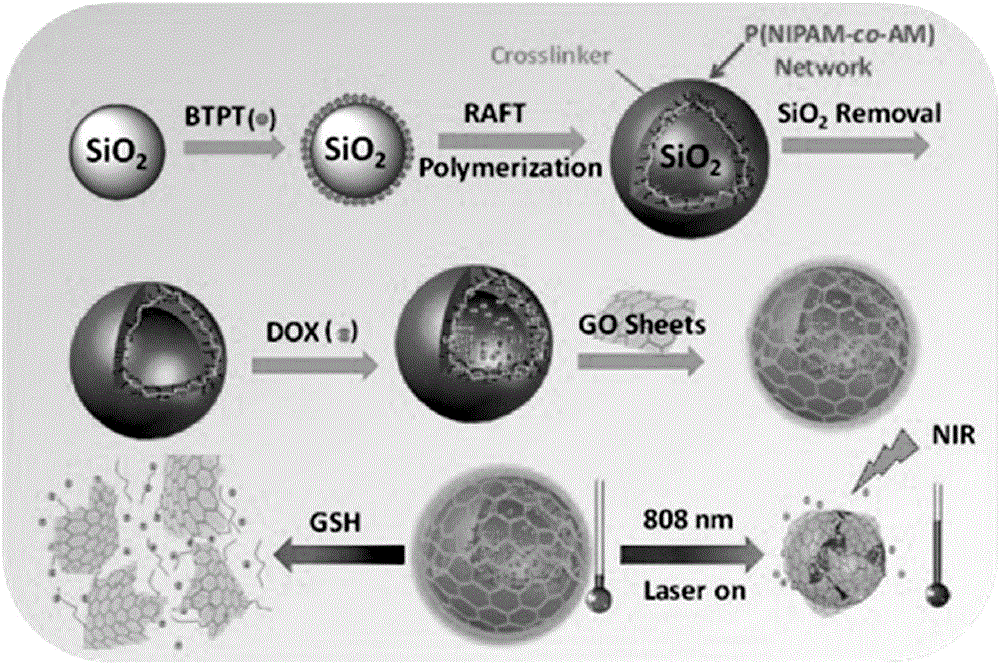
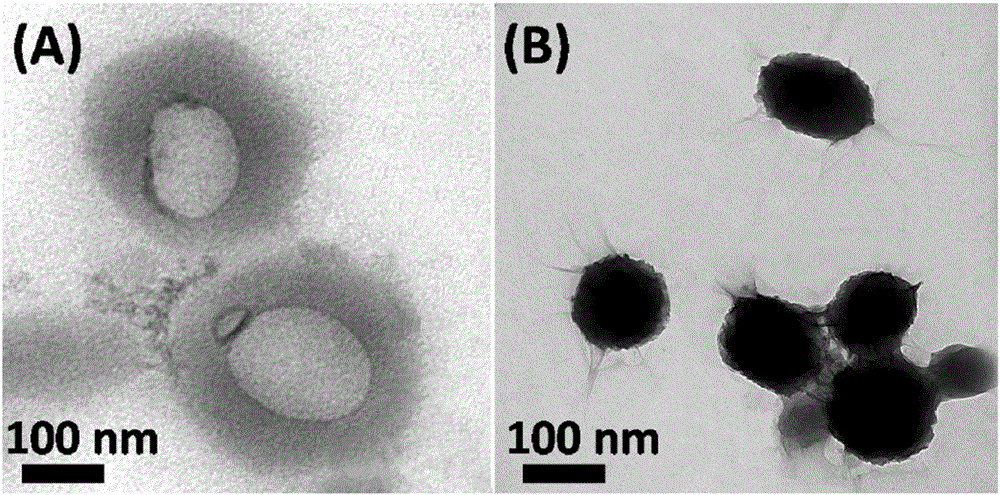
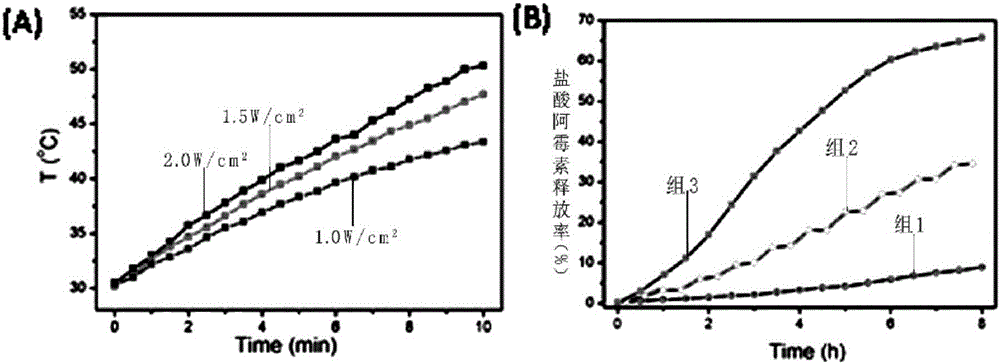
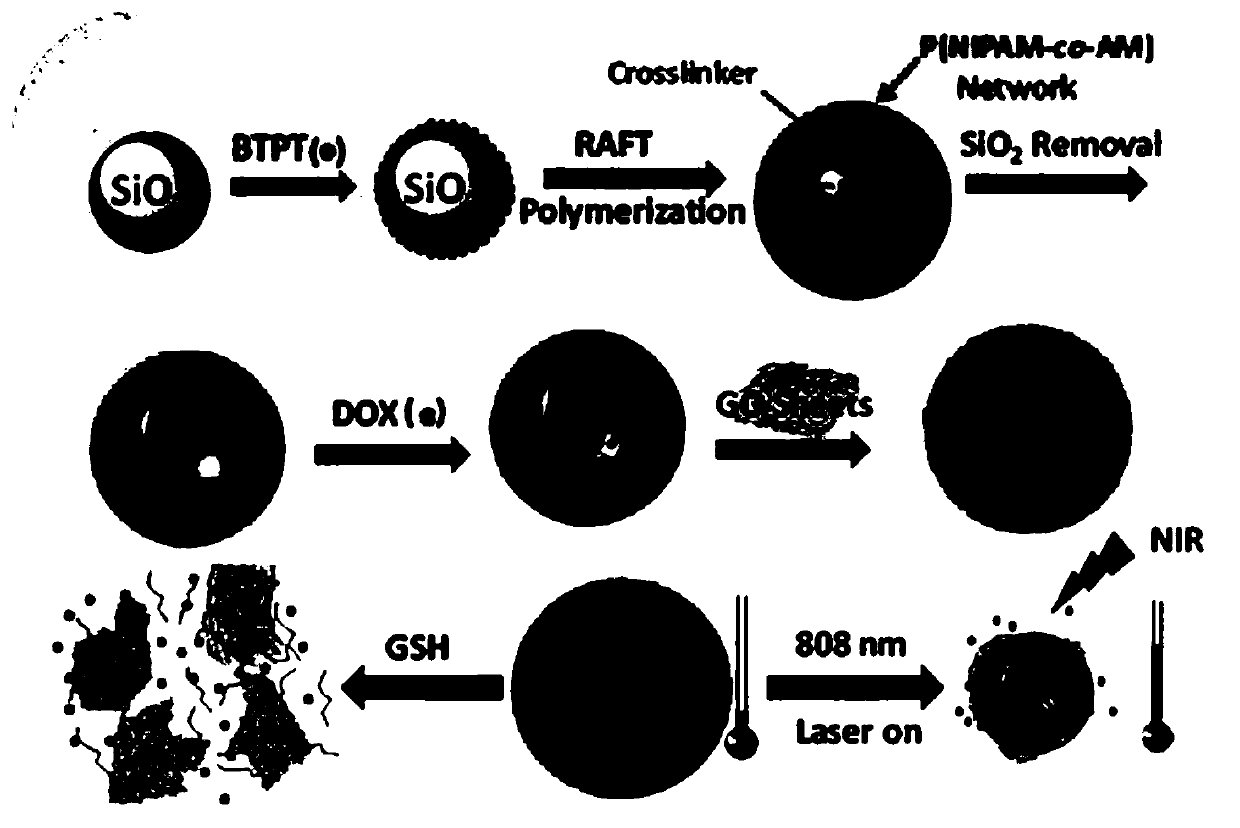
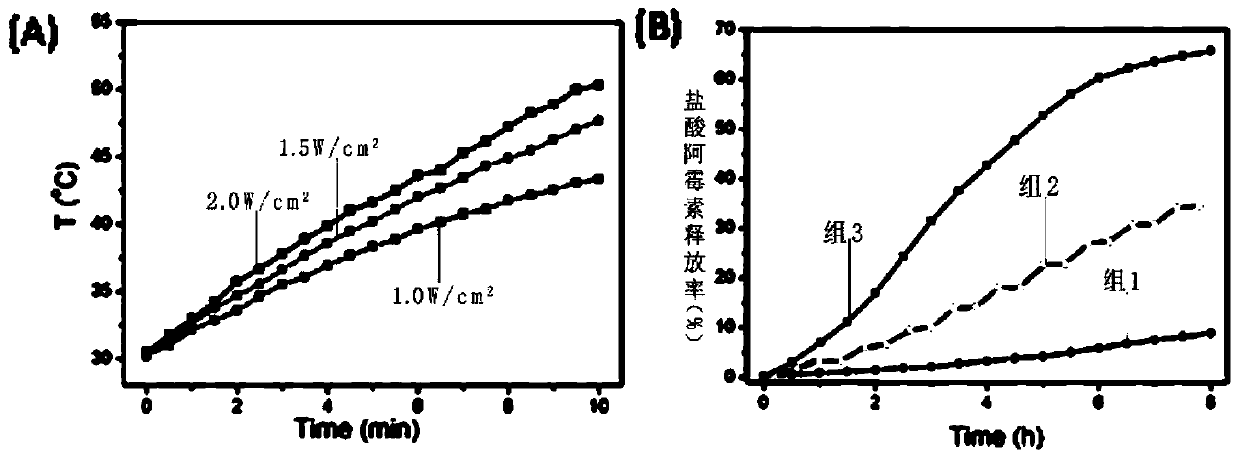
Temperature-sensitive polymer @ graphene oxide capsule drug carrier as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106390132APrevent pre-releaseImprove loading efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsEnergy modified materialsCross-linkDrug carrier
The invention discloses a temperature-sensitive polymer @ graphene oxide capsule drug carrier. According to the capsule drug carrier, silica spheres serve as a template, hollow cross-linked polymer capsules are prepared through reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer free radical polymerization, and meanwhile, graphene oxide covers the outer surfaces of the capsules. The invention also discloses a preparation method and an application of the temperature-sensitive polymer @ graphene oxide capsule drug carrier. The temperature-sensitive polymer @ graphene oxide capsule drug carrier provided by the invention has photo-thermal, temperature-sensitive and biodegradable properties, and controllable drug sustained release can be achieved by changing the temperature of the carrier through near-infrared irradiation; and the capsule drug carrier not only can show sensitive response to human physiological temperature but also can respond to bio-molecular glutathione in organism, so that the capsule drug carrier, which is decomposed into a small-lamella polymer chain, can be discharged out of a body easily; therefore, the toxic accumulation of the capsule drug carrier in the organism is reduced.
Owner:山东博润得农业科技有限公司
Preparation method of nanoparticles with magnetic targeting function and slow-release controllable photothermal-magnetothermal-anticancer drug synergy
ActiveCN109125725AEfficient killingImprove bioavailabilityOrganic active ingredientsEnergy modified materialsCancer cellTemperature sensitive
The invention relates to the field of pharmacy, in particular to a preparation method of nanoparticles with a magnetic targeting function and slow-release controllable photothermal-magnetothermal-anticancer drug synergy. Graphite fluoride is used as a raw material to prepare part of graphene fluoride first; iron oxide is modified with an amino group; the graphene fluoride is then modified with themodified iron oxide; the anticancer drug mitoxantrone is then loaded to the modified graphene fluoride is loaded to obtain iron oxide-graphene fluoride-mitoxantrone nanoparticles; with the nanomaterial serving as a core material and the temperature-sensitive materials, polyvinylpyrrolidone and Arabic gum, as a wall material, the nanoparticles with the magnetic targeting function and slow-releasecontrollable photothermal-magnetothermal-anticancer drug synergy are prepared. The nanoparticles can target at an affected part under the action of a magnetic field, can raise the ambient temperaturethrough magnetic heat and optical heat under orthogonal magnetic field and near-infrared irradiation, can release an anticancer drug under the temperature-sensitive action of the wall material, polyvinylpyrrolidone and Arabic gum, and can then cooperate with the anticancer drug to efficiently and quickly kill cancer cells.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Tumor self-targeting photo-isomerization nano-carriers and preparation method thereof
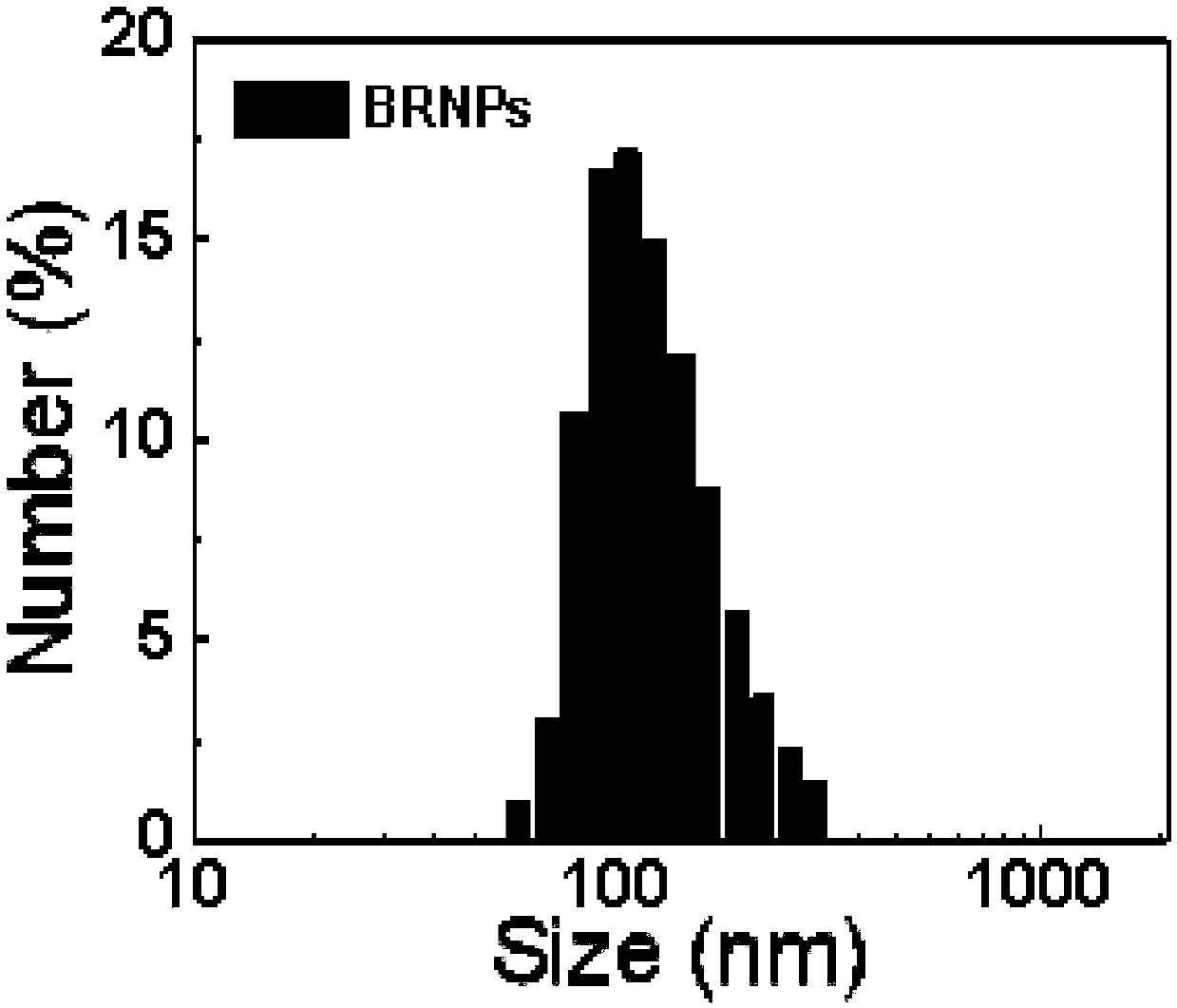
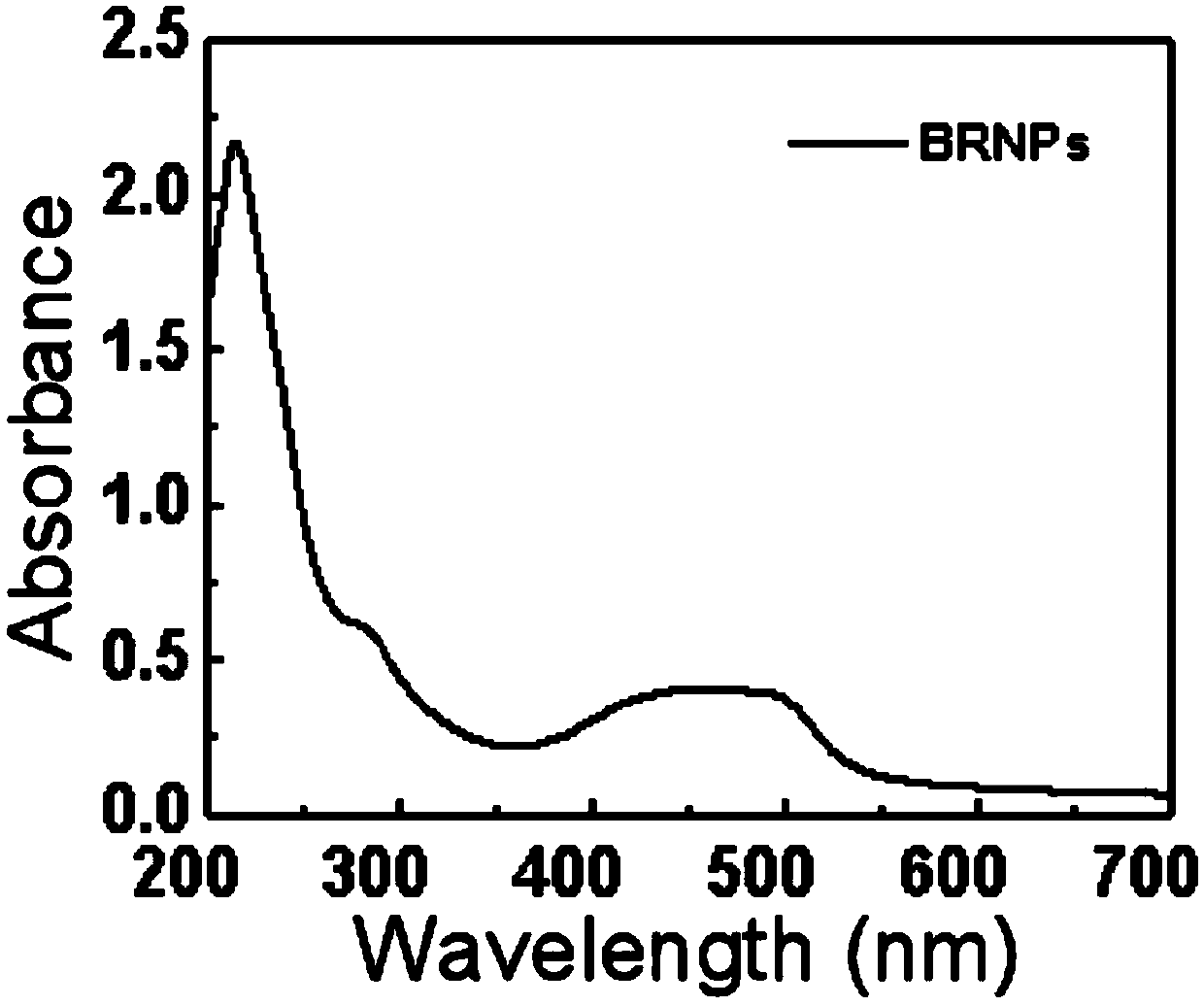
ActiveCN110898228AGood biocompatibilityImprove solubilityOrganic active ingredientsDrug photocleavageHydroxyethyl starchCell membrane
The invention discloses tumor self-targeting photo-isomerization nano-carriers and a preparation method thereof. Nano assembly bodies BRNPs are formed through the self-assembling of bilirubin, 3-aminophenylboronic acid and hydroxyethyl starch; and nano-carriers DBC3NPs coated with HeLa cell membranes are obtained by coating HeLa cell membrane debris on the surfaces of the BRNPs loaded with adriamycin through a continuous extrusion method. The tumor-specific target enrichment of the nano-carriers can be realized under the self-targeting action of the cell membranes; and near infrared irradiation can make nano-particles generate photo-isomerization, thus, the rapid near infrared light releasing of drugs at tumor tissue sites can be realized, and the efficient treatment of tumors can be achieved as well.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
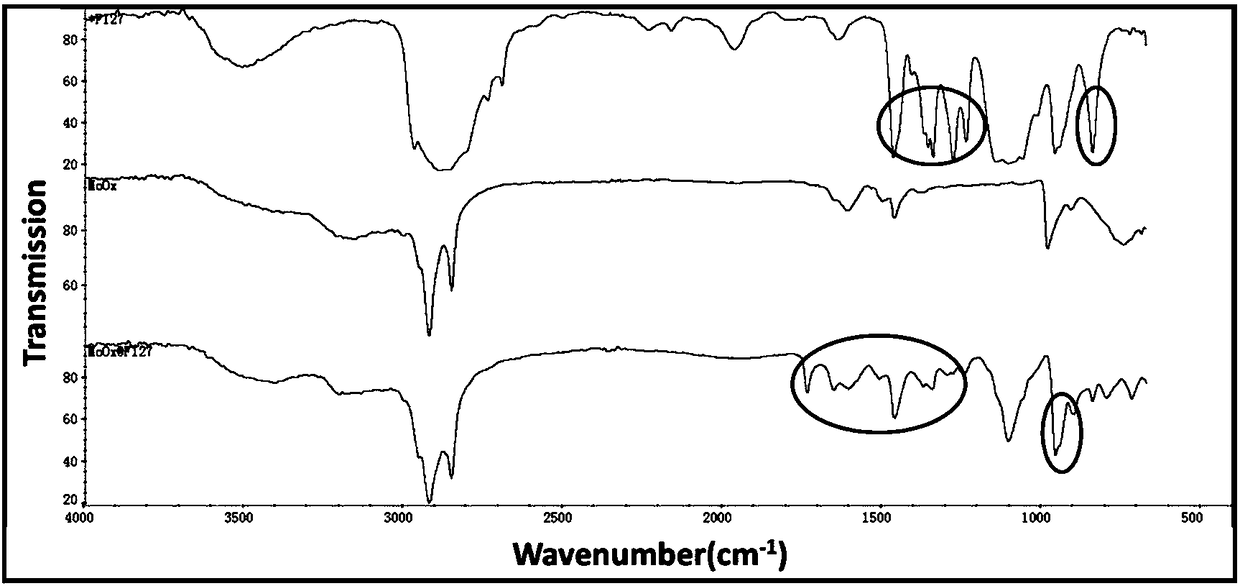
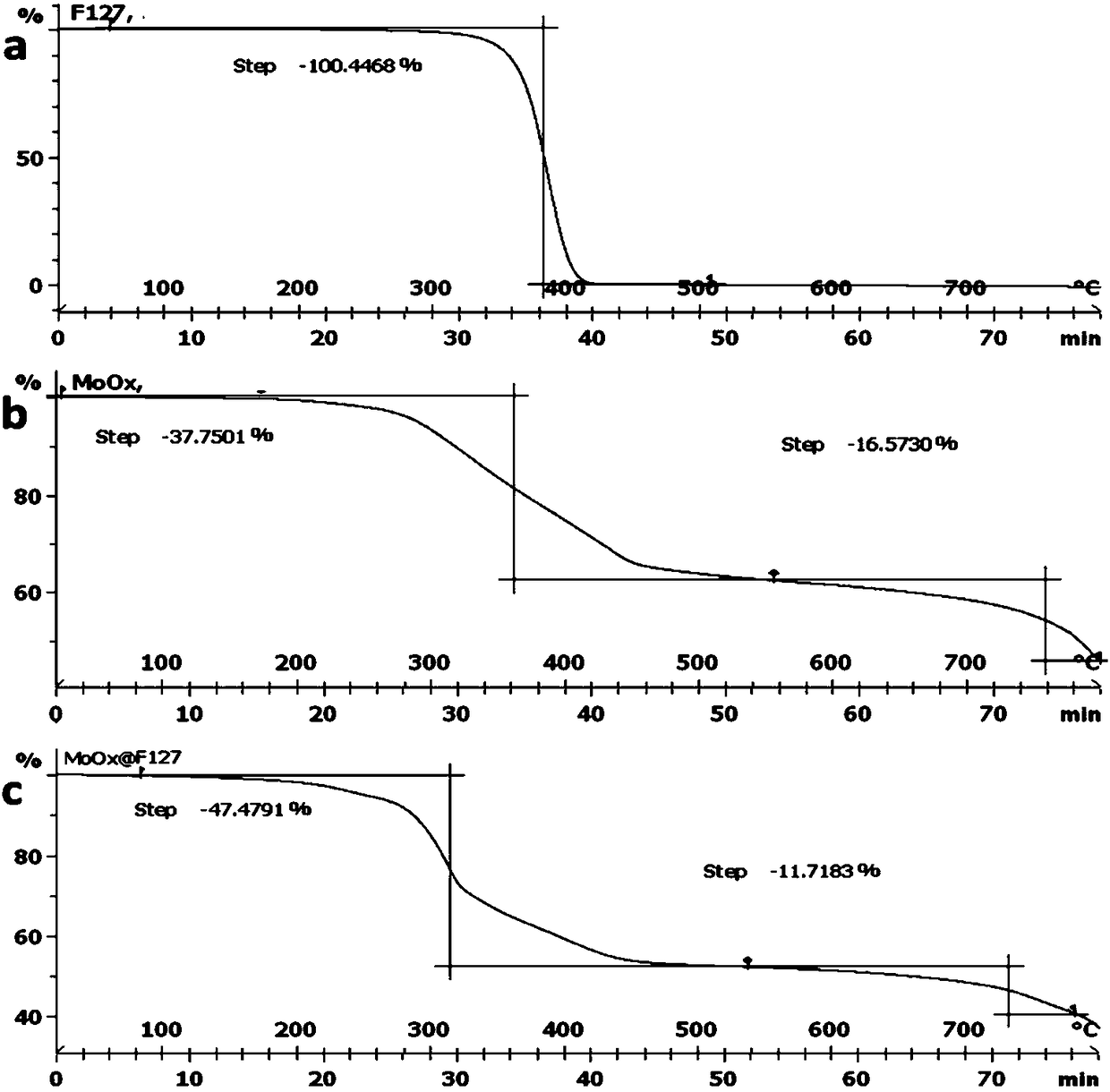
Pluronic-modified molybdenum oxide nano-sheet as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108451932AGood treatment effectImprove solubilityOrganic active ingredientsEnergy modified materialsTumor targetSolubility
The invention discloses a Pluronic-modified molybdenum oxide nano-sheet as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The Pluronic-modified molybdenum oxide nano-sheet has good biological safety, strong photo-thermal conversion effect, high drug loading capacity and PH-dependent biodegradability and can be used as a drug carrier to increase the solubility of a hydrophobic anti-cancer drug and improve the distribution of the hydrophobic anti-cancer drug in a body; the tumor target enrichment ability of the Pluronic-modified molybdenum oxide nano-sheet is improved; the tumor photo-thermal therapy or the chemotherapy-the photo-thermal combined therapy can be realized in combination with near-infrared irradiation, so that the tumor therapeutic effect is improved, and toxic and sideeffects are reduced.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
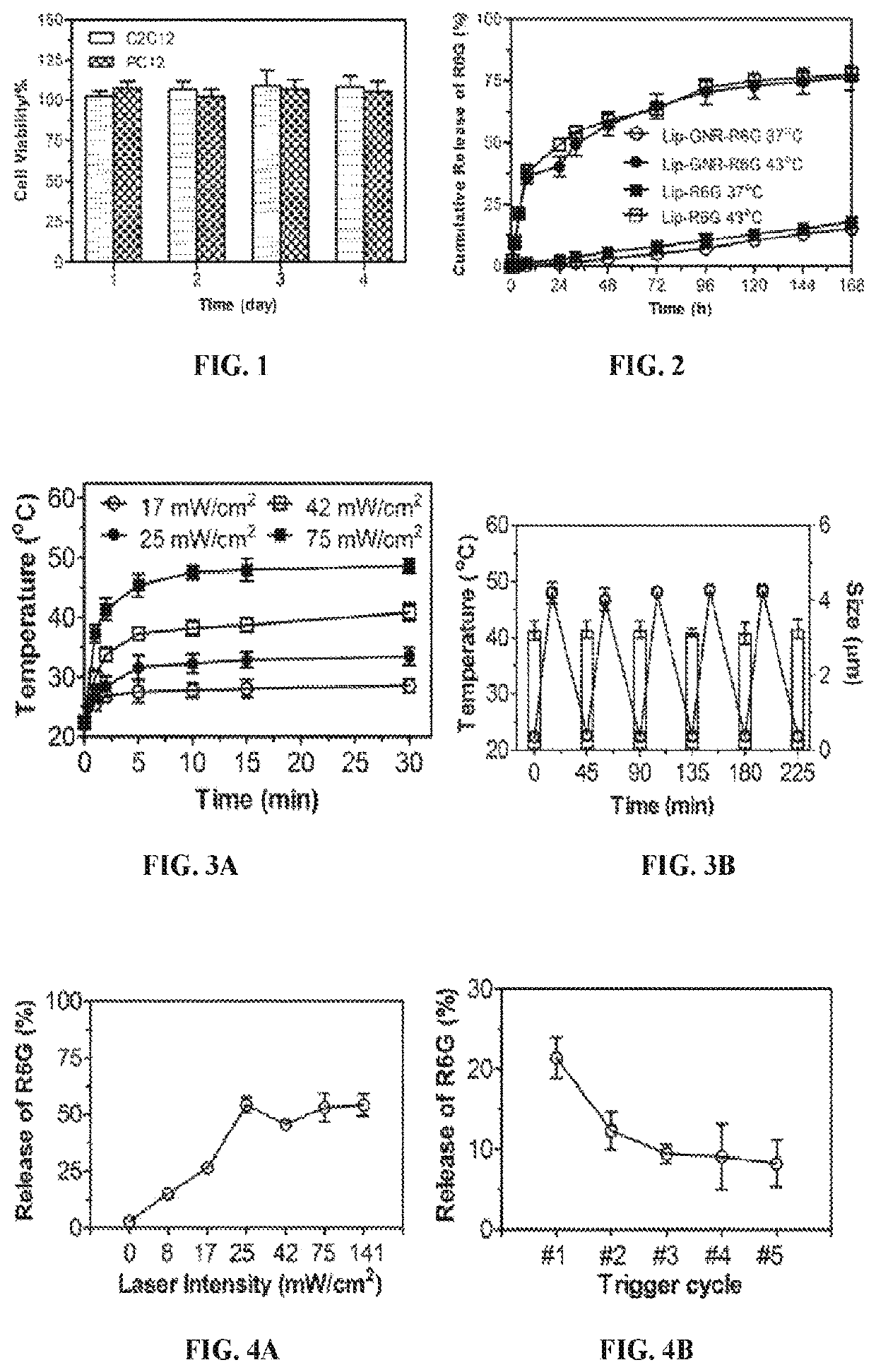
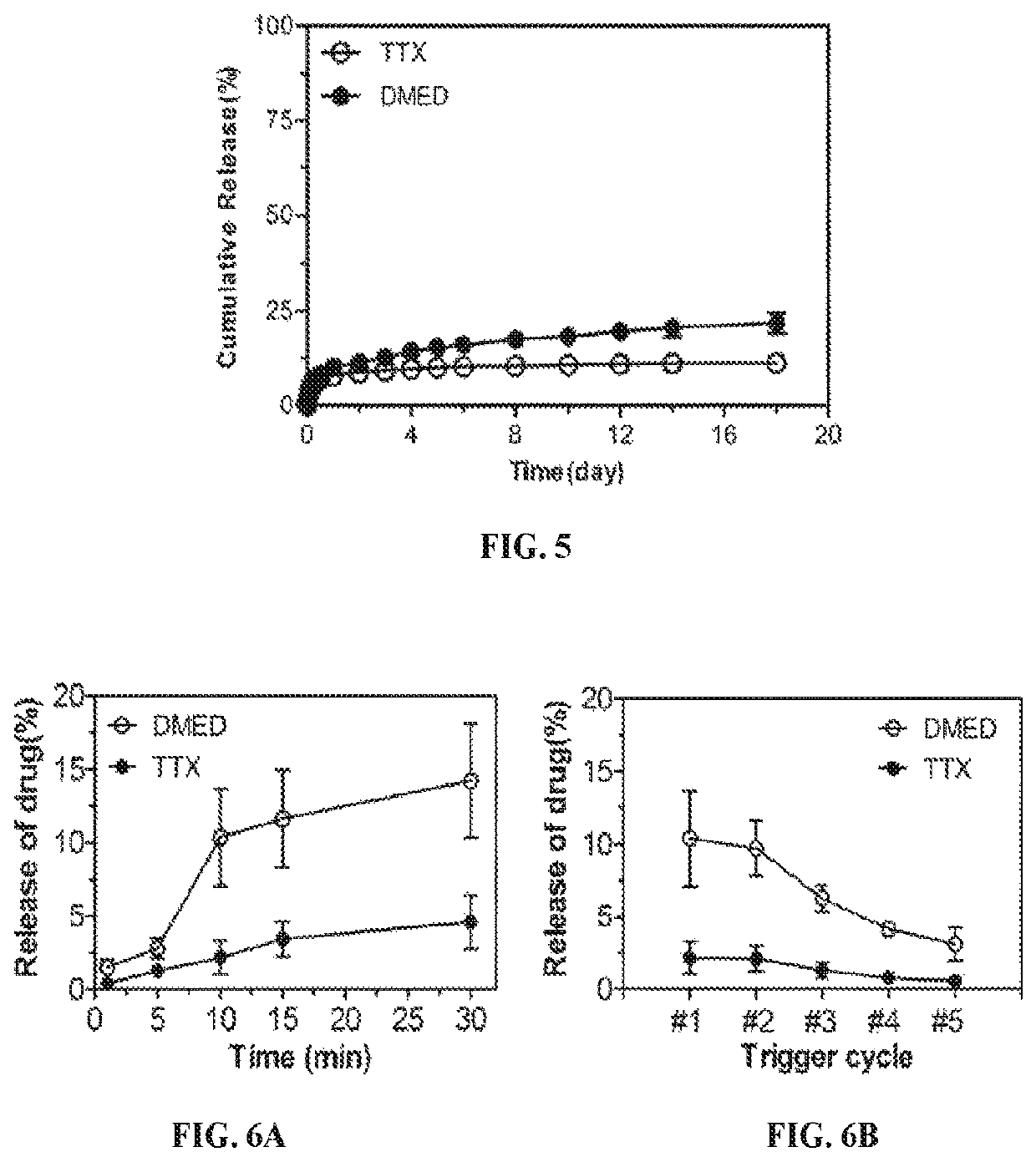
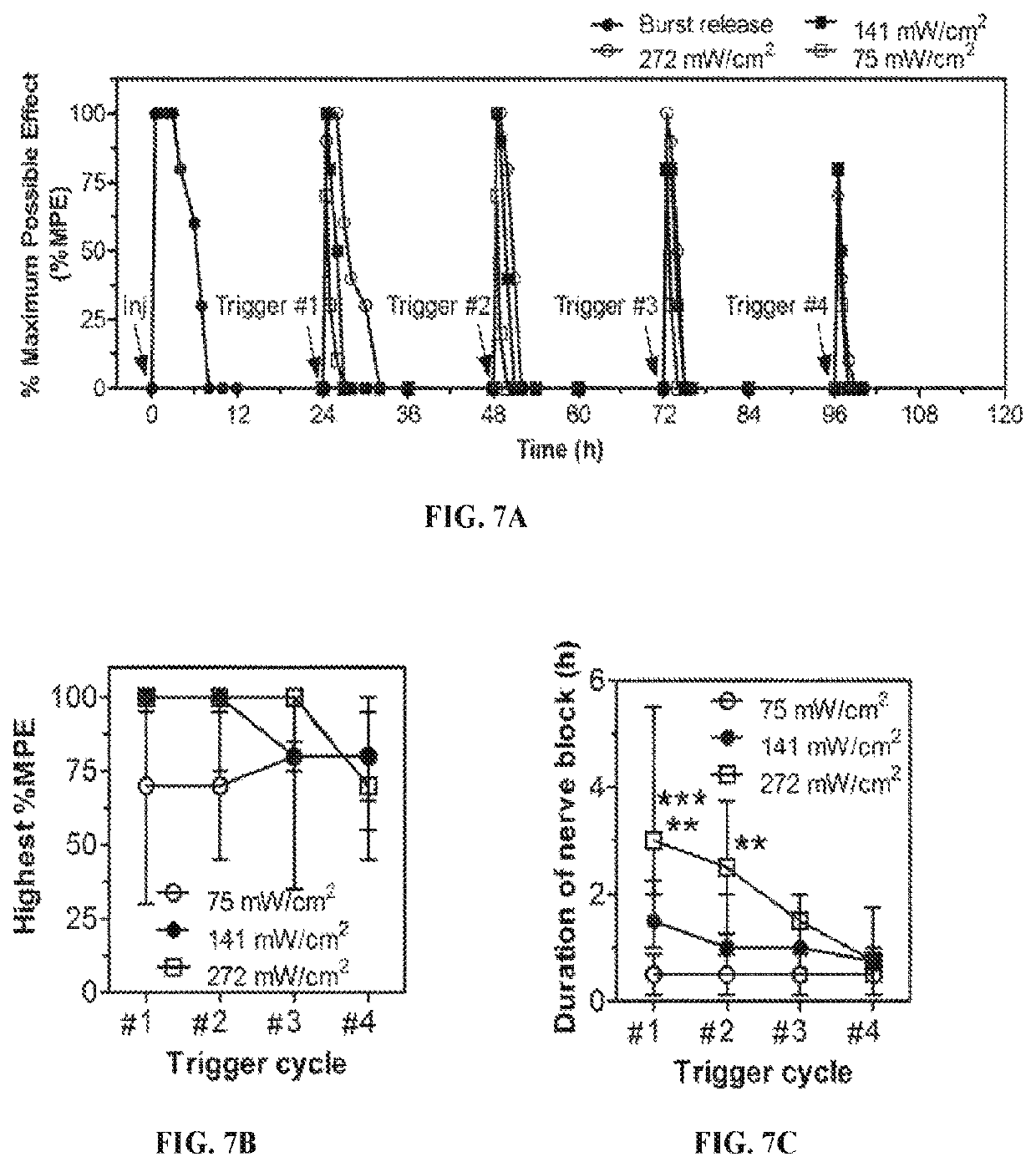
Compositions and Methods for On-Demand High-Efficiency Triggerable Anesthesia
ActiveUS20190070115A1Extended durationIncrease the number ofOrganic active ingredientsAnaestheticsAnesthetic AgentSingle injection
Compositions and methods for administration of local anesthetics that are delivered by a single injection and enable repeated on-demand or high influx analgesia over extended periods have been developed. Pharmaceutical compositions including an effective amount of one or more sodium channel blockers including site 1 sodium channel blockers, optionally one or more alpha-2-adrenergic agonists, which are optionally encapsulated in liposomes, particles or microbubbles, and one or more triggerable elements are provided. The triggerable elements allow delivery of the encapsulated anesthetic drugs when an appropriate triggering stimuli are applied. Exemplary triggering agents or stimuli include near-infrared irradiation, UV- and visible light, ultrasound and magnetic field. In one embodiment, ultrasound is used to trigger a burst of microbubbles to enhance penetration of local anesthetic.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
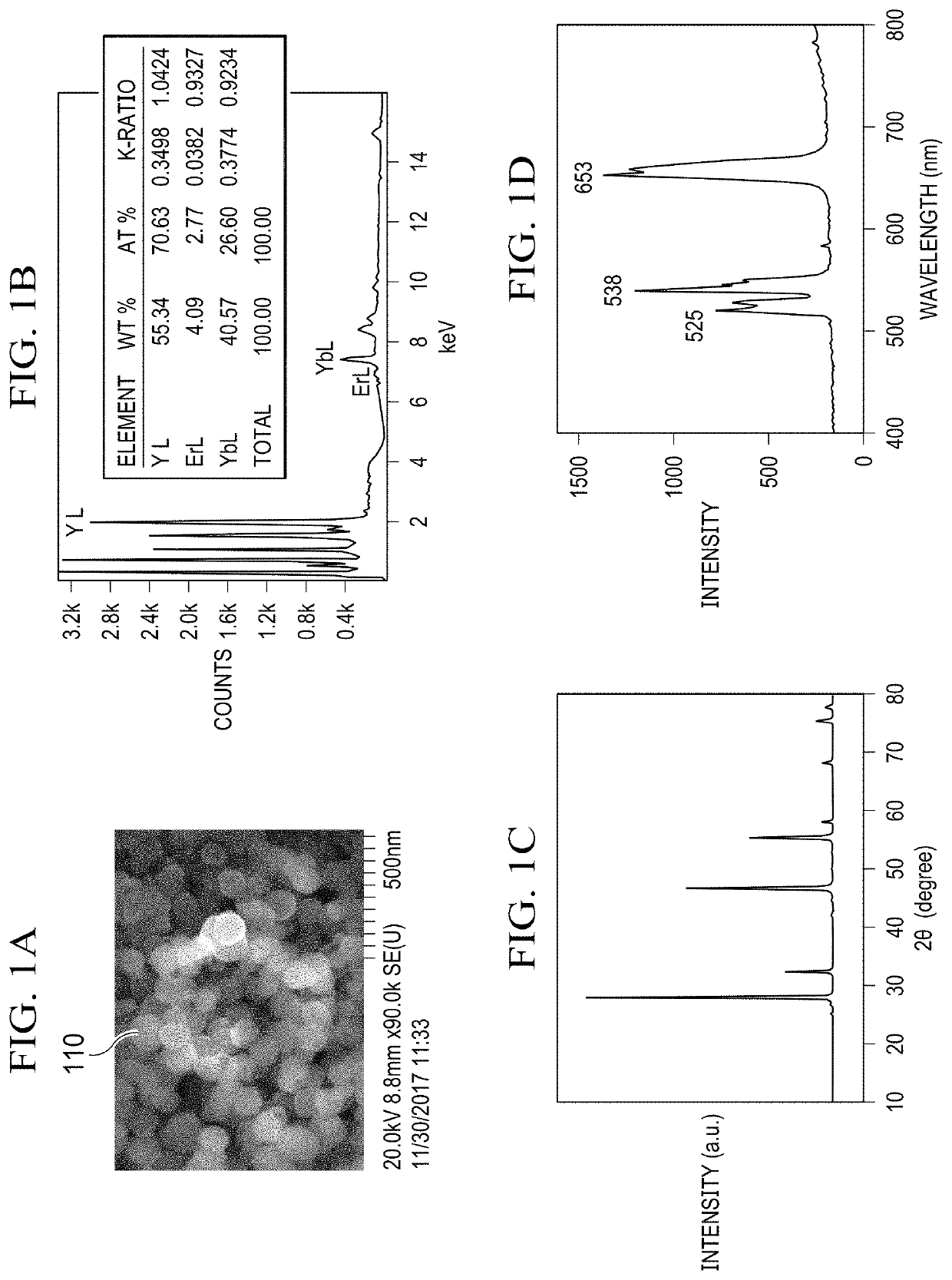
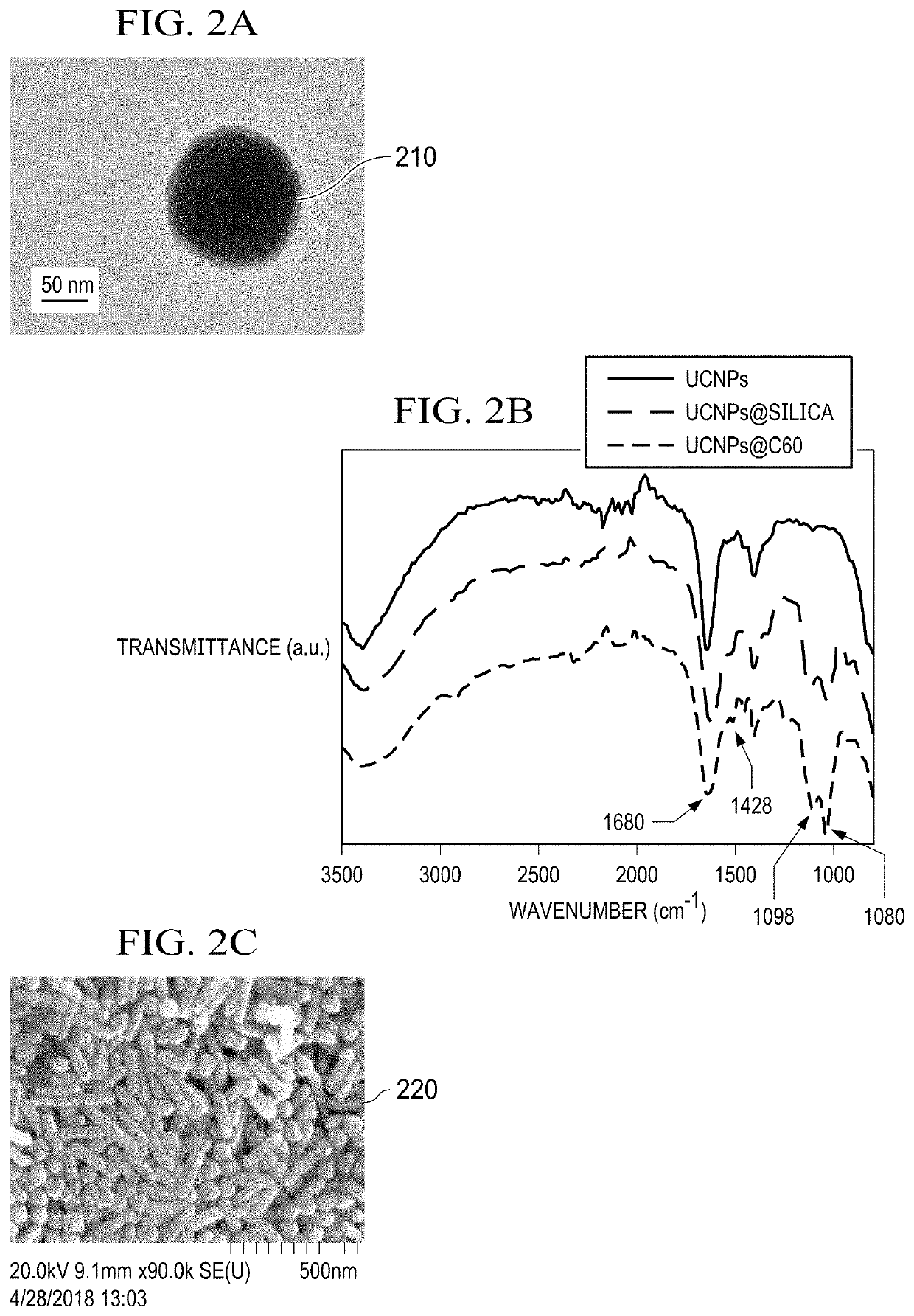
Single nir irradiation triggered upconversion NANO system for synergistic photodynamic and photothermal cancer therapy
A composition includes a photon upconversion nanoparticle coupled to a photosensitizer nanoparticle that can absorb light and convert tissue oxygen into reactive oxygen species. A low temperature hydrothermal method of making photon upconversion nanoparticles includes dispersing Yb(NO3)3, Y(NO3)3, and Er(NO3)3 in water to prepare a mixture; adding an ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and NaF with sonication to make a solution; adjusting a pH of the solution to approximately 3.5 using HNO3 and NaOH; treating the solution hydrothermally at approximately 130° C. for approximately 4 hours; quenching to approximately 20° C.; collecting and washing the photon upconversion nanoparticles. A near infrared triggered photon upconversion method for synergistic photodynamic and photothermal cancer therapy includes administering a nanocomposite comprising a photon upconversion nanoparticle coupled to a photosensitizer nanoparticle that can absorb light and convert tissue oxygen into reactive oxygen species; and exposing the mammal and the nanocomposite to a near infrared source of actinic radiation.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
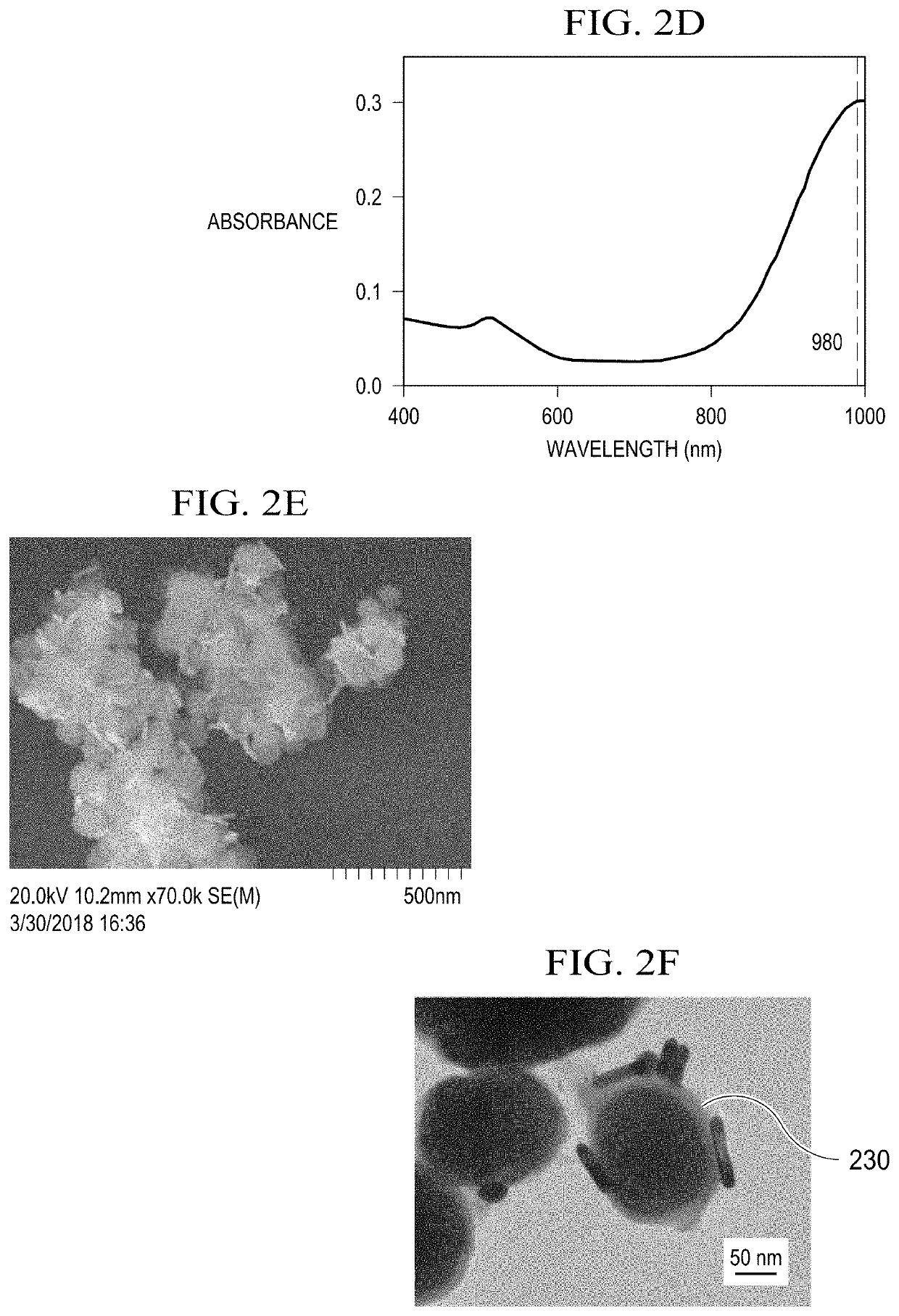
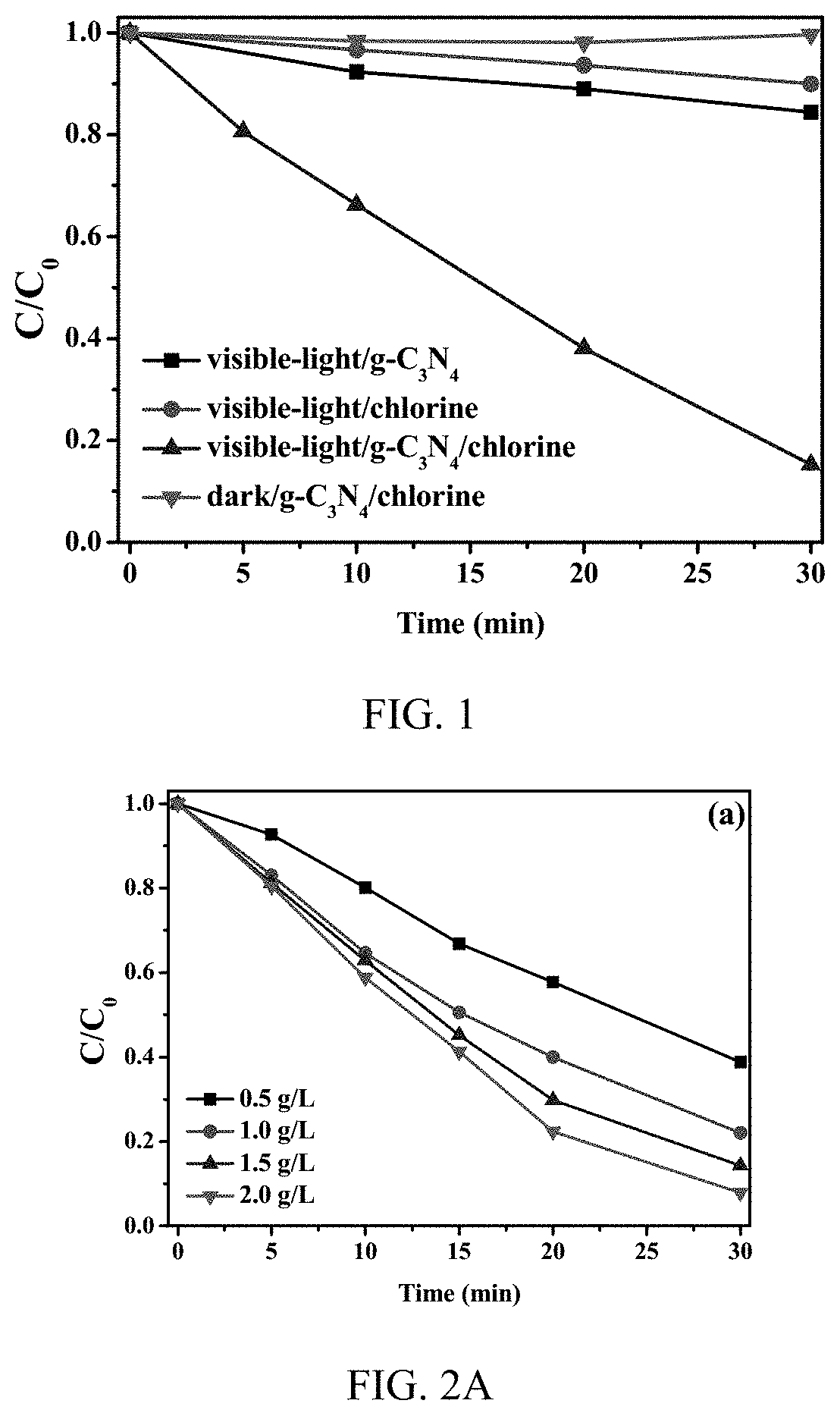
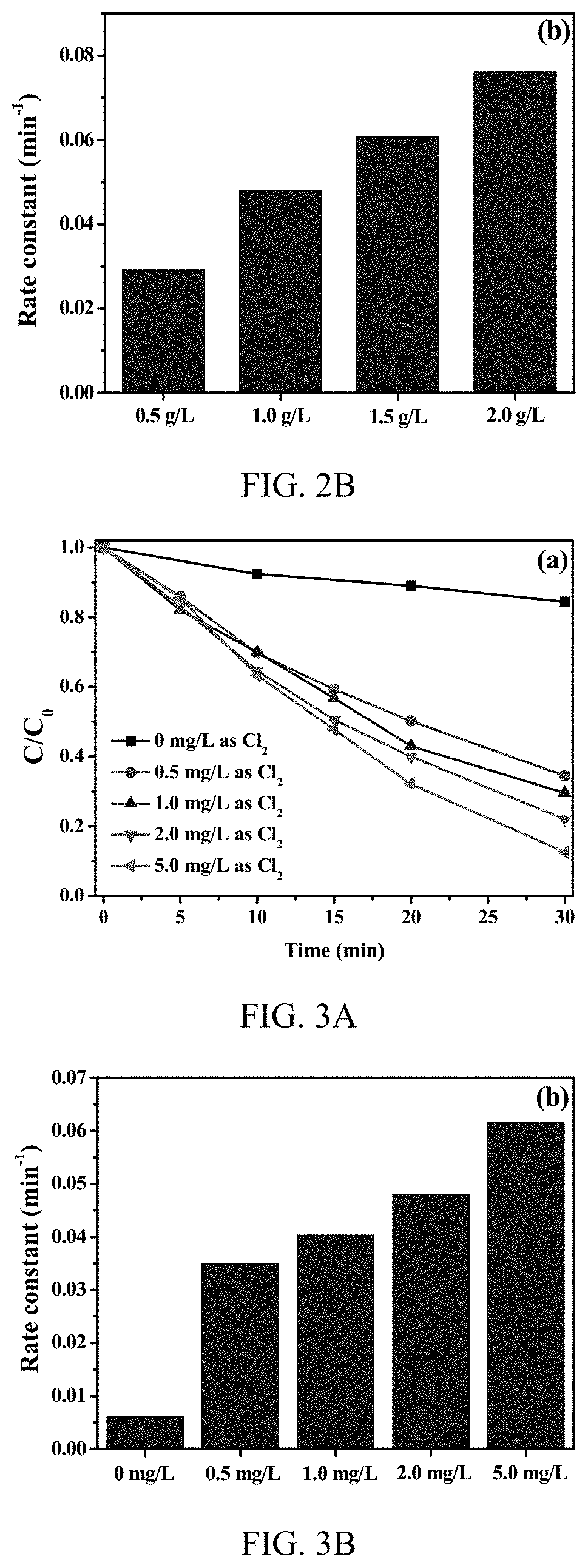
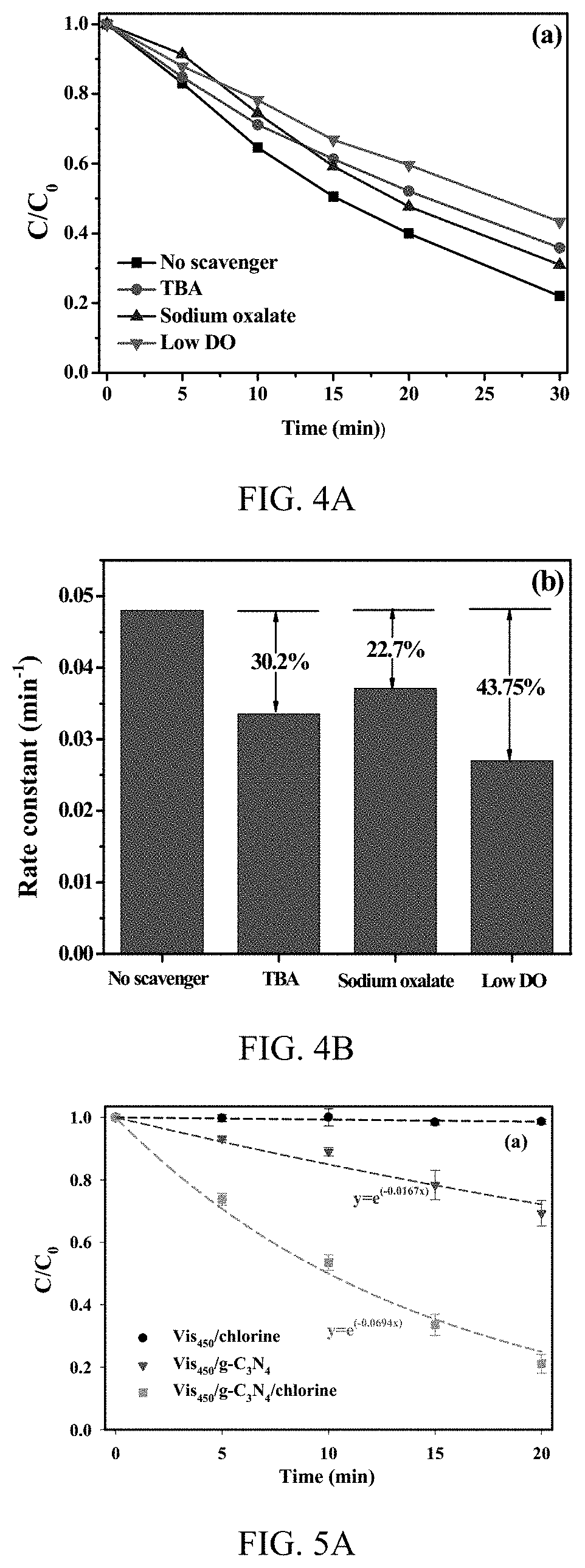
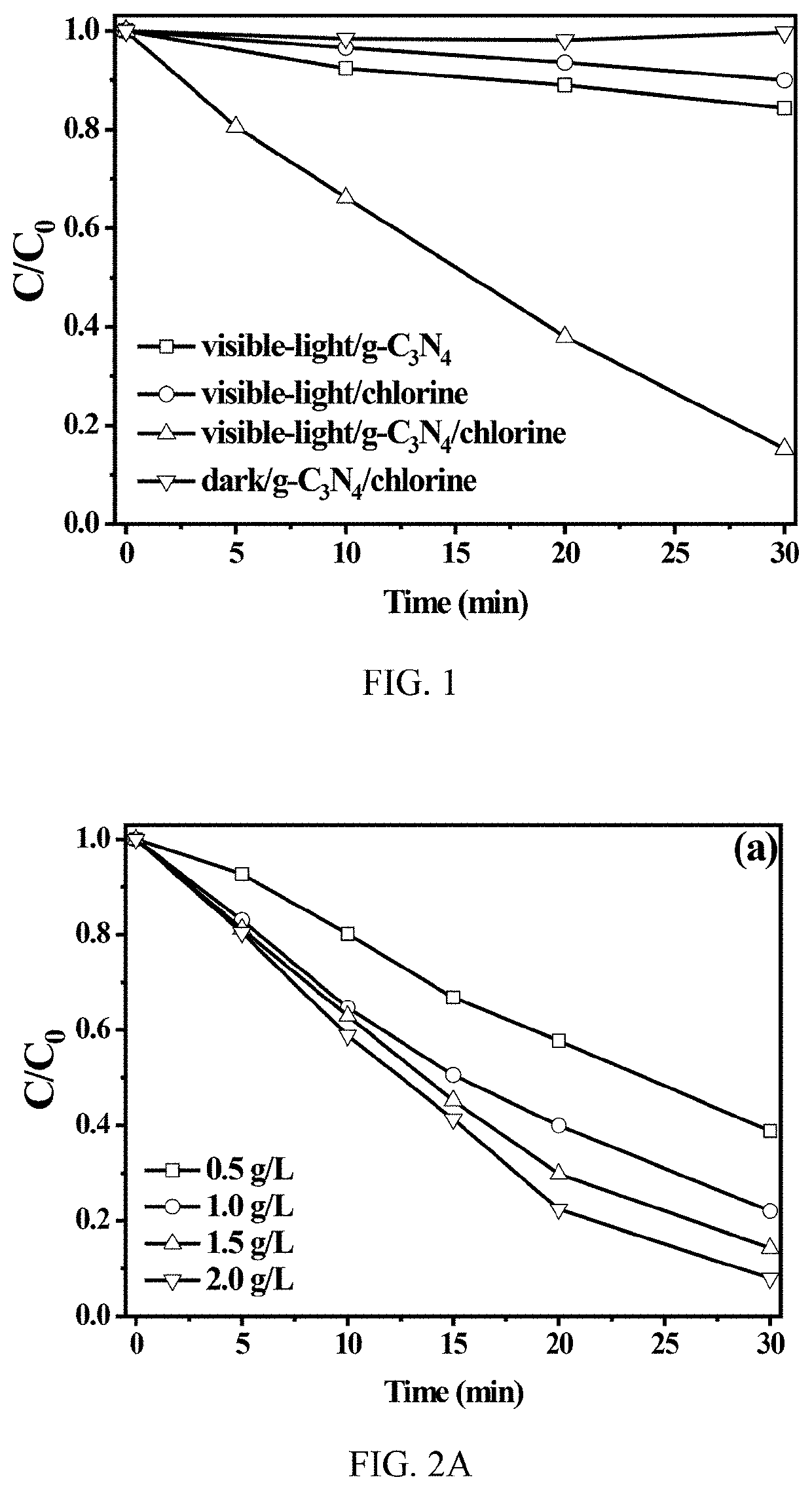
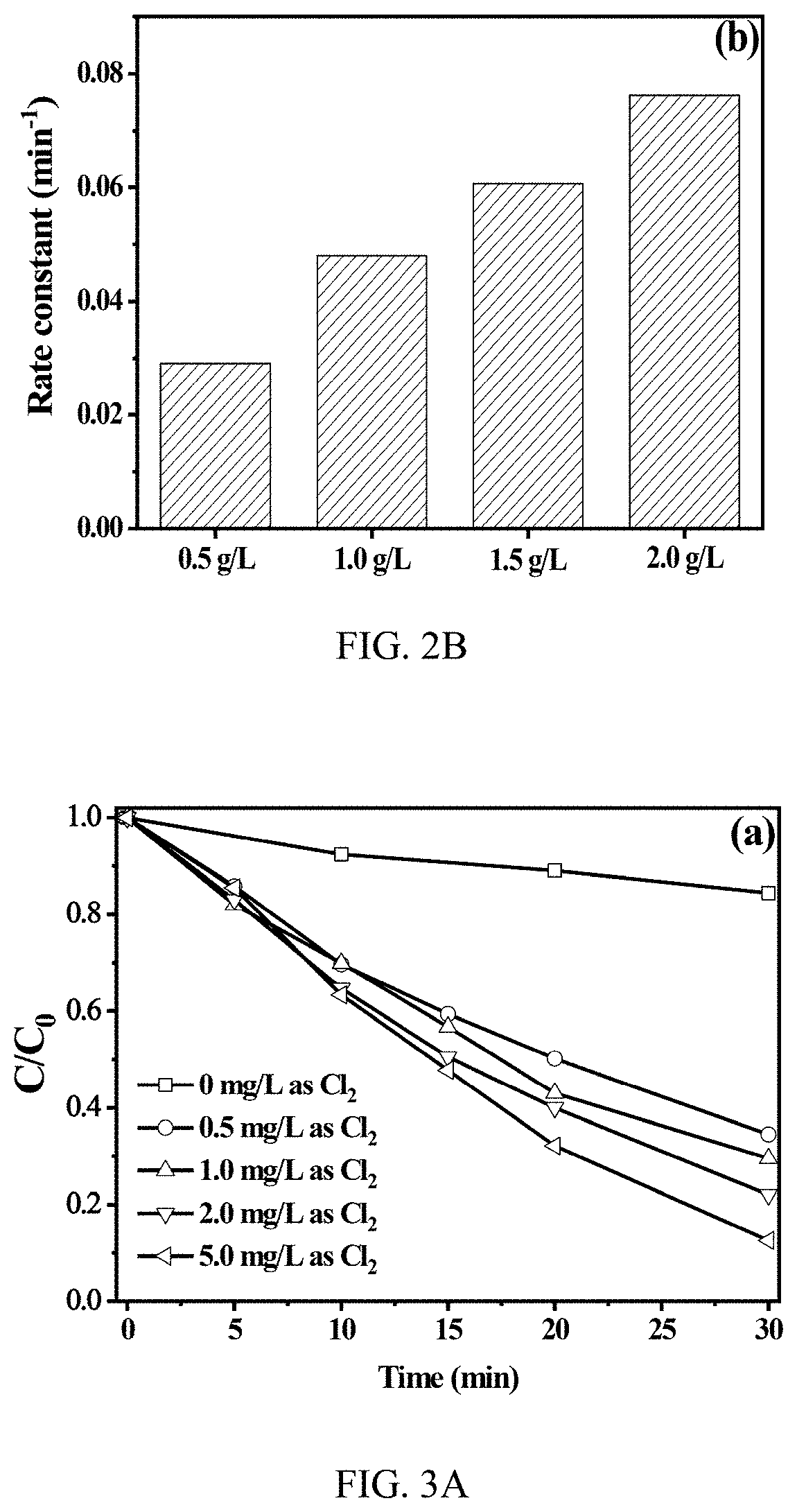
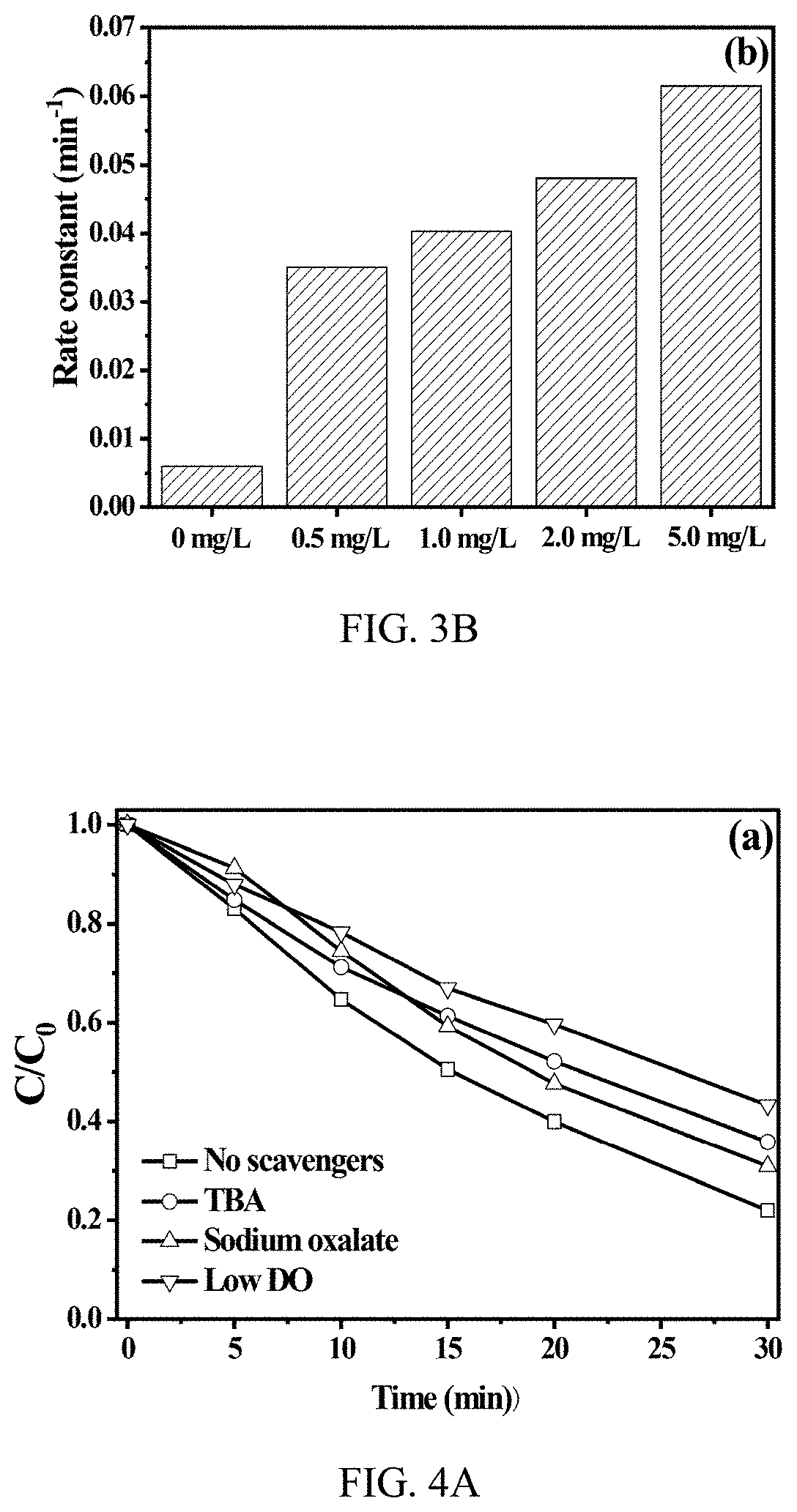
Production of reactive oxidative species by photocatalytic activation of chlorine (i) under ultraviolet/visible light/near infrared irradiation
A system to produce reactive oxidative species in a fluid medium containing a source of Cl(I) by irradiating a solid photocatalyst suspended in the fluid medium or residing on a surface that is contactable by the fluid with electromagnetic radiation. The electromagnetic radiation can be in the UV, near-UV, visible, or near-IR consistent with the photocatalyst employed. The source of Cl(I) in certain embodiments is Cl2, HOCl, or H2NCl. The photocatalyst is g-C3N4, TiO2, BBiOBr, or any other solid insoluble photocatalyst.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Thermal amplification of free radical polymerization induced by red to near-infrared irradiation
ActiveUS11384167B2Less energyEasy to controlMethine/polymethine dyesPhotomechanical apparatusOrganic chemistryPolymer chemistry
The present invention relates to compositions thermally curable on demand by red to near infrared irradiation, method of using same for thermal amplification of free radical polymerizations, and articles obtained by such method. The invention also relates to the use of a heat-generating dye in association with a thermal initiator for controlling the onset of thermal free radical polymerization.
Owner:UNIVERSITE DE HAUTE ALSACE +2
Ultrafast Cyclic Ether-Amine Photopolyaddition And Uses Thereof
PendingUS20210363286A1OptimizationSure easyPhotomechanical apparatusCoatingsPolymer scienceCyclic ether
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
A kind of photosensitizer with double photodynamic therapy effect and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106581675BLow toxicityDouble damage effectPhotodynamic therapyAntineoplastic agentsFluorescenceTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses a photosensitizer having dual photodynamic therapy effects and a preparation method thereof, wherein the photosensitizer having the dual photodynamic therapy effects has the structural formula described in the specification. With cheap and easy-to-obtain 2-phenylpyridine, iridium trichloride and ethyl benzoate terpyridine as raw materials, and through mild reaction conditions, a target product-iridium complex is simply and efficiently synthesized. Research results indicate that the iridium complex has two-photon excited fluorescence emission in a near infrared region and can be used as a photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy. Confocal development is used for tracking the photodynamic therapy process, the photosensitizer iridium complex can be obviously observed to migrate from cell nucleuses to mitochondria under illumination, and secondary damage of the cells is caused. Animal experiments also prove that the iridium complex has quite good inhibitory effects on tumor growth under a near infrared irradiation condition and has low toxicity to animal bodies in dark environments.
Owner:合肥欧申福德生物科技有限责任公司
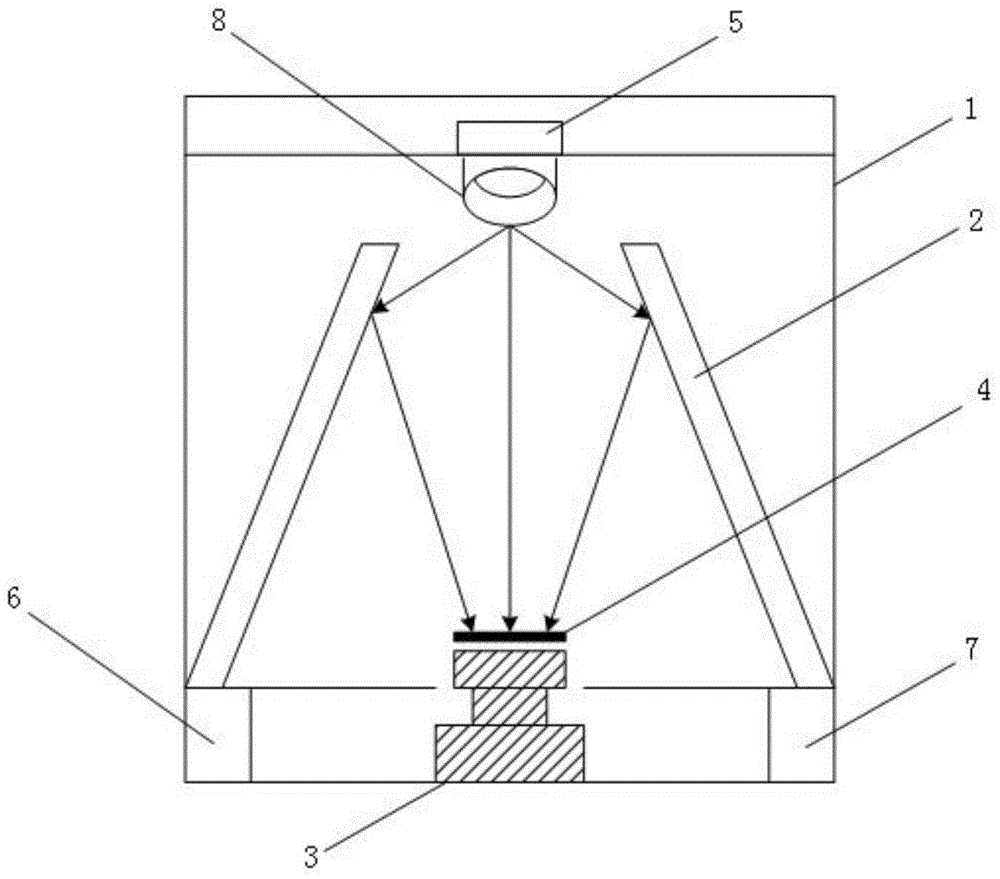
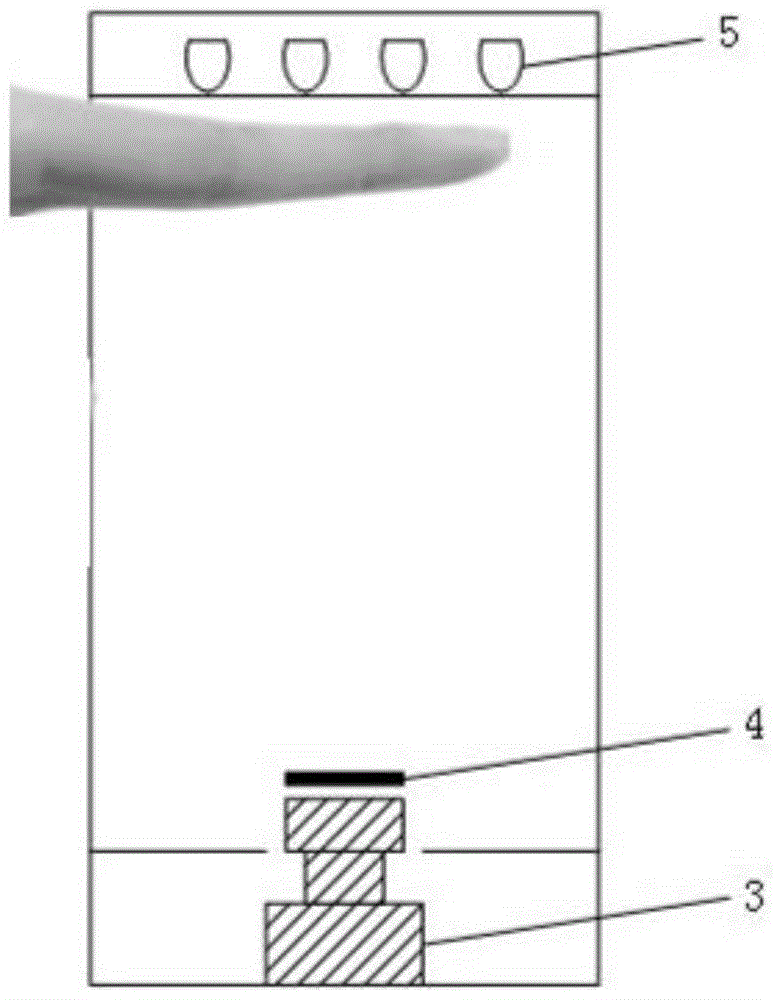
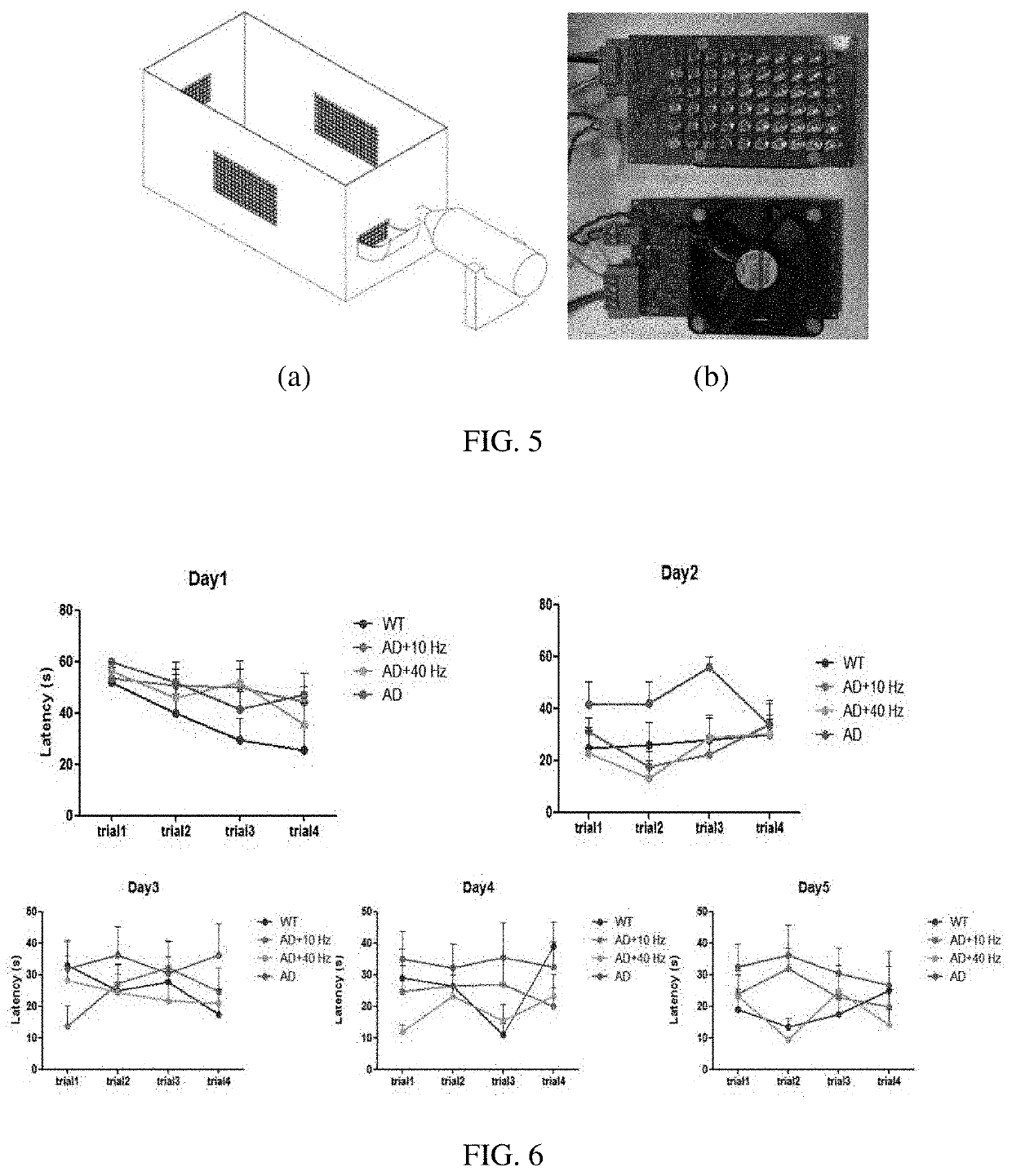
Experimental device for verifying the treatment effect of near-infrared light on Alzheimer's disease and application of the device
ActiveCN105148411AImprove efficiencyImprove accuracyLight therapySpecial data processing applicationsLight therapyElectricity
The invention relates to an experimental device for verifying the treatment effect of near-infrared light on Alzheimer's disease and an application of the device. The experimental device includes an experimental container, a near-infrared irradiation unit arranged at the top of the experimental container and forming an experimental cavity together with the experimental container, and a circuit control unit electrically connected with the near-infrared irradiation unit. During the experiment, an experimental mouse is arranged in an enclosed experimental cavity, the on and off time and the illumination frequency of the near-infrared irradiation unit are automatically adjusted through the circuit control unit, the experimental mouse is subjected to near-infrared illumination treatment, and then is taken out after the near-infrared illumination treatment is completed to be subjected to subsequent verification experiments. Compared with the prior art, the experimental device is simple in structure, economic and practical to use, and convenient to operate, can realize the intelligent control of near-infrared illumination treatment, effectively reduce the experimental errors and the workload of experimental personnel, is high in experiment accuracy, safe and reliable, and has great application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG BRAINHEALTH MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
A thermosensitive polymer@graphene oxide capsule drug carrier and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN106390132BPrevent pre-releaseImprove loading efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsEnergy modified materialsCross-linkSilicon dioxide
Owner:山东博润得农业科技有限公司
Intelligent window and preparation method thereof
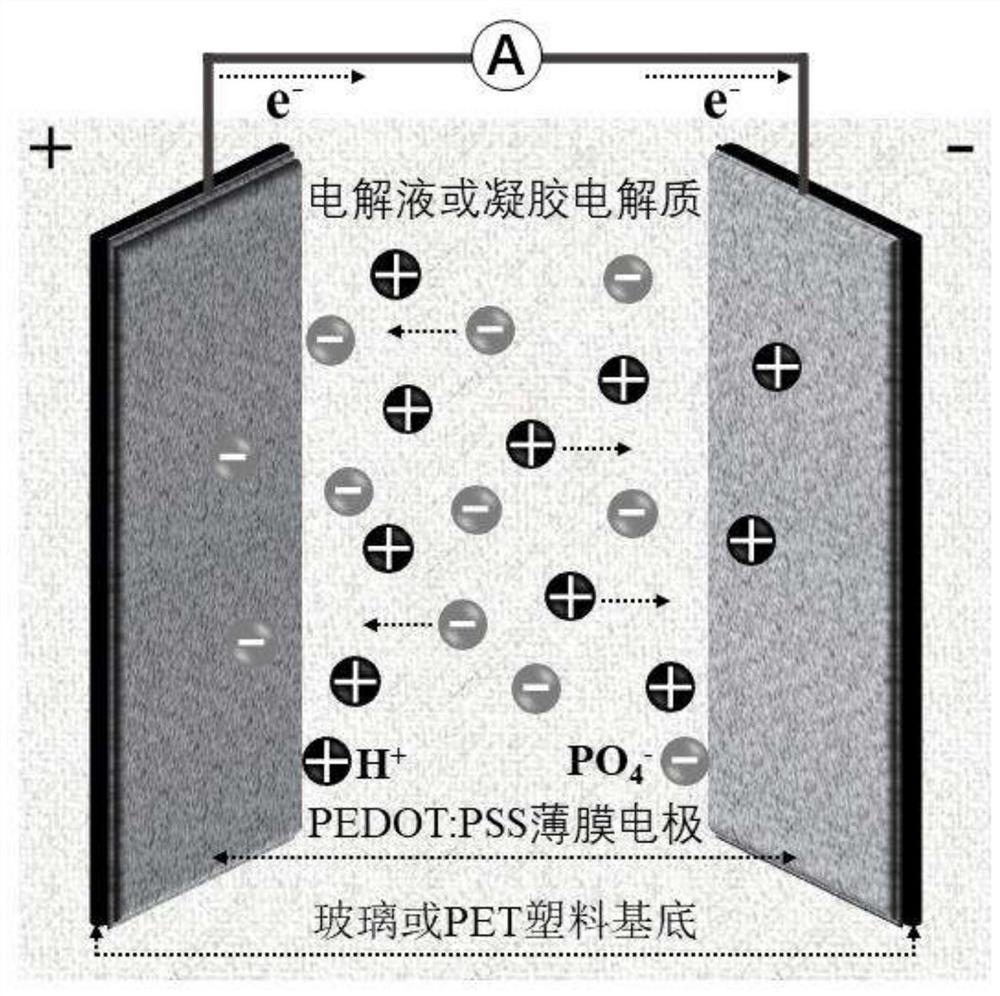
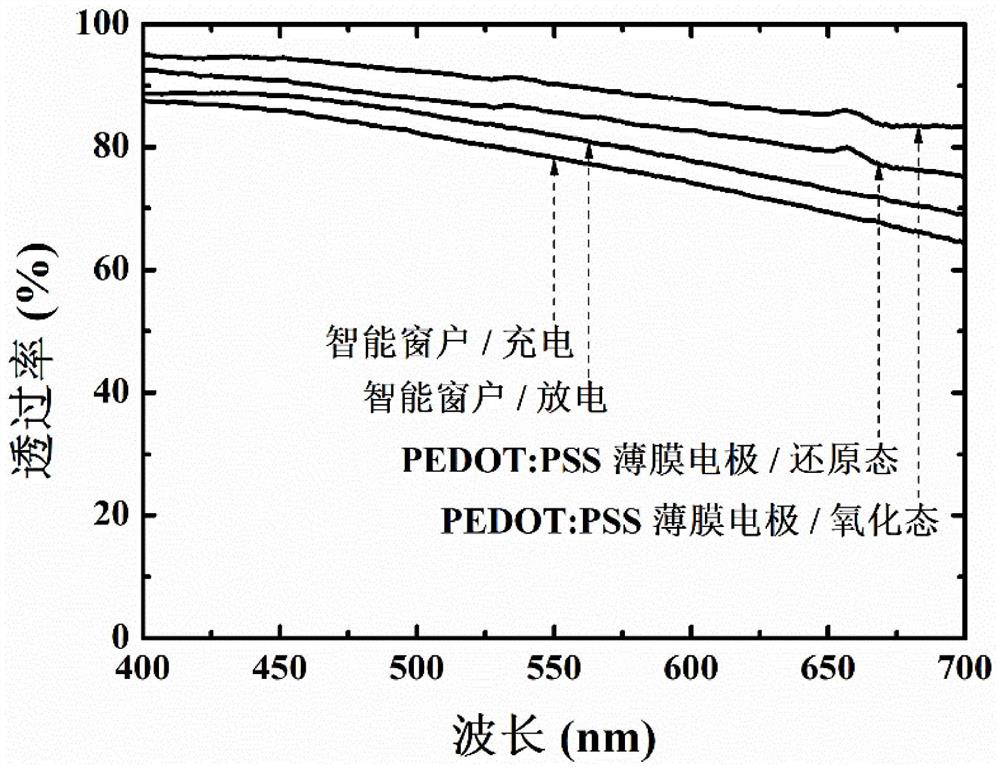
PendingCN114320133AHigh transparencyImprove the living environmentLight protection screensNon-linear opticsElectrolytic agentO-Phosphoric Acid
The invention provides an intelligent window and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the field of new materials. The intelligent window comprises two PEDOT: PSS film electrodes and an electrolyte packaged between the two PEDOT: PSS film electrodes, each PEDOT: PSS film electrode comprises a substrate and a PEDOT: PSS suspension liquid coating arranged on the surface of the substrate, PEDOT: PSS suspension liquid is prepared from ethylene glycol, PH1000 and a fluorine-containing surfactant, the electrolyte comprises a phosphoric acid electrolyte or a phosphoric acid gel electrolyte, and the PEDOT: PSS suspension liquid coating is coated on the surface of the substrate. The phosphoric acid electrolyte is prepared from a phosphoric acid solution, deionized water and ethylene glycol, and the phosphoric acid gel electrolyte is prepared from polyvinyl alcohol and the phosphoric acid electrolyte. According to the intelligent window, the transmittance of solar near-infrared radiation energy can be remarkably regulated and controlled, electrochemical energy storage can be achieved, the visible light transparency is high, all-weather work can be achieved, and the stability is good.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
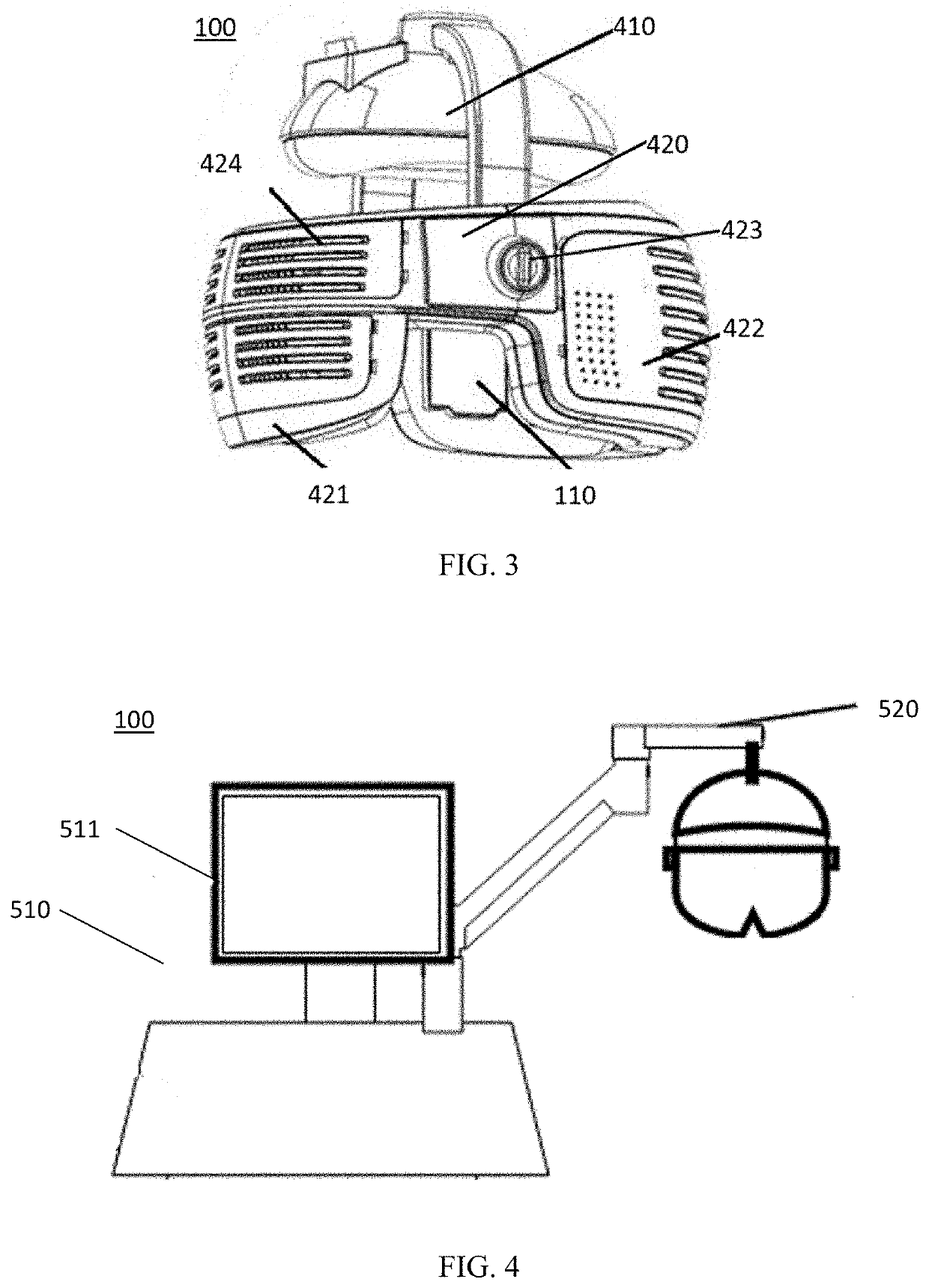
Phototherapy device and phototherapy instrument used for irradiation of the head, and therapy method thereof
A phototherapy device (100) and a phototherapy instrument (500), comprising a near infrared irradiation module (110) used for emitting near infrared light to the head, and a control component (120) used for controlling the operation of the near infrared irradiation module (110) and coupled to the near infrared irradiation module (110). A method for using near infrared light for therapy, which comprises applying a first, optional second, optional third or more near infrared lights to the head of a patient. The device and method are used for treating Alzheimer's disease, improving brain mitochondrial function and ATP levels, promoting amyloid beta protein (Aβ) decomposition, reducing Aβ deposition, reducing damage to nerve cells, improving nerve tissue repair and regeneration capabilities, improving cognitive ability etc. A therapy method using the phototherapy device (100) or the phototherapy instrument (500), and a computer readable recording medium controlling required near infrared light.
Owner:ZHEJIANG BRAINHEALTH MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Compositions and methods for on-demand high-efficiency triggerable anesthesia
ActiveUS11344498B2Extended durationIncrease the number ofPowder deliveryAnaestheticsAdrenergic receptor agonistsSingle injection
Compositions and methods for administration of local anesthetics that are delivered by a single injection and enable repeated on-demand or high influx analgesia over extended periods have been developed. Pharmaceutical compositions including an effective amount of one or more sodium channel blockers including site 1 sodium channel blockers, optionally one or more alpha-2-adrenergic agonists, which are optionally encapsulated in liposomes, particles or microbubbles, and one or more triggerable elements are provided. The triggerable elements allow delivery of the encapsulated anesthetic drugs when an appropriate triggering stimuli are applied. Exemplary triggering agents or stimuli include near-infrared irradiation, UV- and visible light, ultrasound and magnetic field. In one embodiment, ultrasound is used to trigger a burst of microbubbles to enhance penetration of local anesthetic.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
An electrochromic film for effectively modulating sunlight transmittance and its preparation method
The invention discloses an electrochromic film for effectively modulating sunlight transmittance. The electrochromic film contains Cs x WO 3 A nano-lattice embedded amorphous tungsten oxide composite film, wherein x is 0.06-0.2, the grid point diameter is 80-300nm, the distance between adjacent grid points is 200-600nm, and the grid point height is 30-80nm. The thin film solves the problems that the commercial electrochromic thin film has a narrow adjustable wavelength range of sunlight and cannot independently adjust near-infrared radiant heat. The preparation method first uses laser interference combined with photosensitive sol-gel method to prepare Cs x WO 3 The nano lattice is then filled with an amorphous tungsten oxide matrix in the gaps of the lattice by a sol-gel method to form a composite film. The preparation method has the characteristics of controllable process and large-area film formation, and is very suitable for industrialized mass production.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Thermal amplification of free radical polymerization induced by red to near-infrared irradiation
ActiveUS20200362061A1Less energyEasy to controlMethine/polymethine dyesDuplicating/marking methodsOrganic chemistryPolymer chemistry
The present invention relates to compositions thermally curable on demand by red to near infrared irradiation, method of using same for thermal amplification of free radical polymerizations, and articles obtained by such method. The invention also relates to the use of a heat-generating dye in association with a thermal initiator for controlling the onset of thermal free radical polymerization.
Owner:UNIVERSITE DE HAUTE ALSACE +2
Production of reactive oxidative species by photocat alytic activation of chlorine (I) under ultraviolet/visible light/near infrared irradiation
ActiveUS11046592B2BiocideWater/sewage treatment by irradiationElectromagnetic radiationRadiation exposure
A system to produce reactive oxidative species in a fluid medium containing a source of Cl(I) by irradiating a solid photocatalyst suspended in the fluid medium or residing on a surface that is contactable by the fluid with electromagnetic radiation. The electromagnetic radiation can be in the UV, near-UV, visible, or near-IR consistent with the photocatalyst employed. The source of Cl(I) in certain embodiments is Cl2, HOCl, or H2NCl. The photocatalyst is g-C3N4, TiO2, BBiOBr, or any other solid insoluble photocatalyst.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com