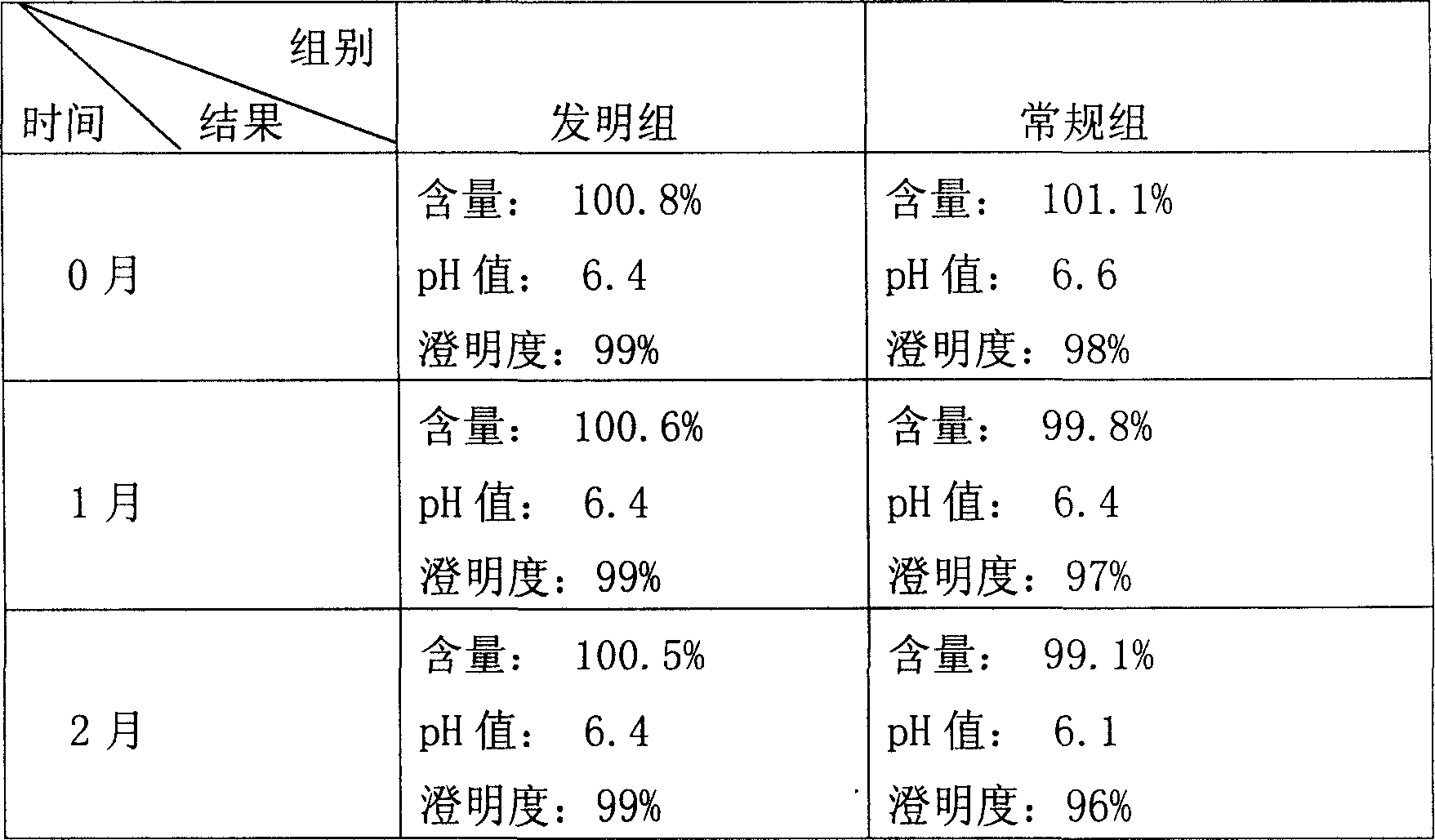
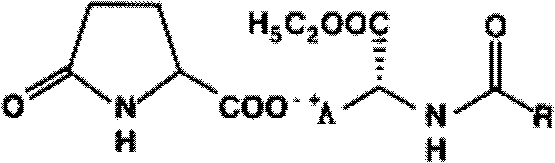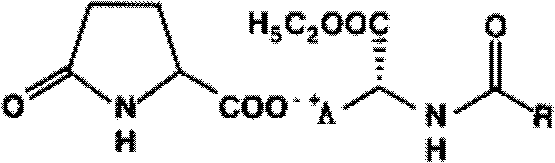Patents
Literature
58 results about "Trichomonas vaginalis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Trichomonas vaginalis is an anaerobic, flagellated protozoan parasite and the causative agent of trichomoniasis. It is the most common pathogenic protozoan infection of humans in industrialized countries. Infection rates between men and women are similar with women usually being symptomatic, while infections in men are usually asymptomatic. Transmission usually occurs via direct, skin-to-skin contact with an infected individual, most often through vaginal intercourse. The WHO has estimated that 160 million cases of infection are acquired annually worldwide. The estimates for North America alone are between 5 and 8 million new infections each year, with an estimated rate of asymptomatic cases as high as 50%. Usually treatment consists of metronidazole and tinidazole.
Therapeutic agents for inhibiting and/or treating vaginal infection
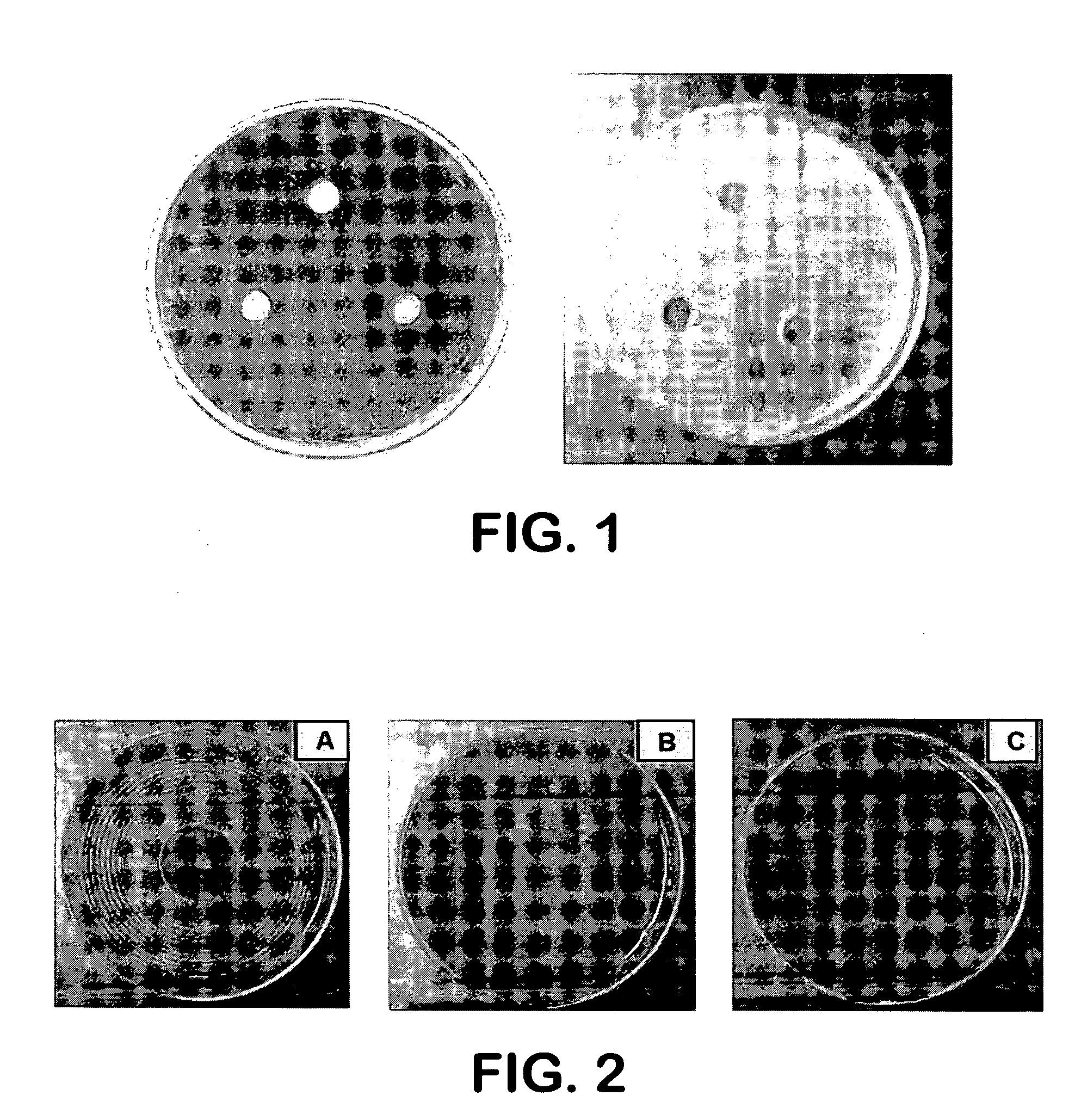
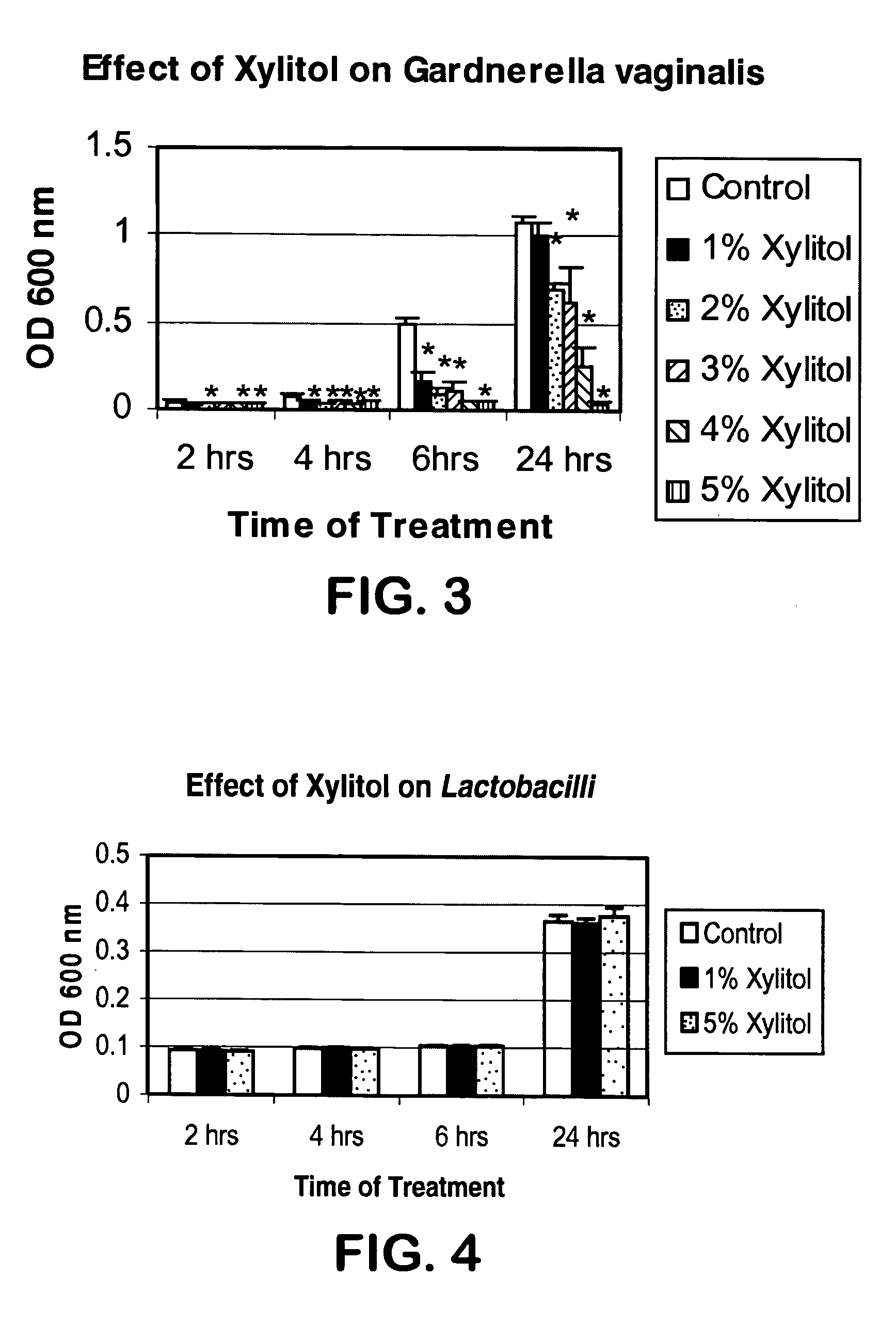
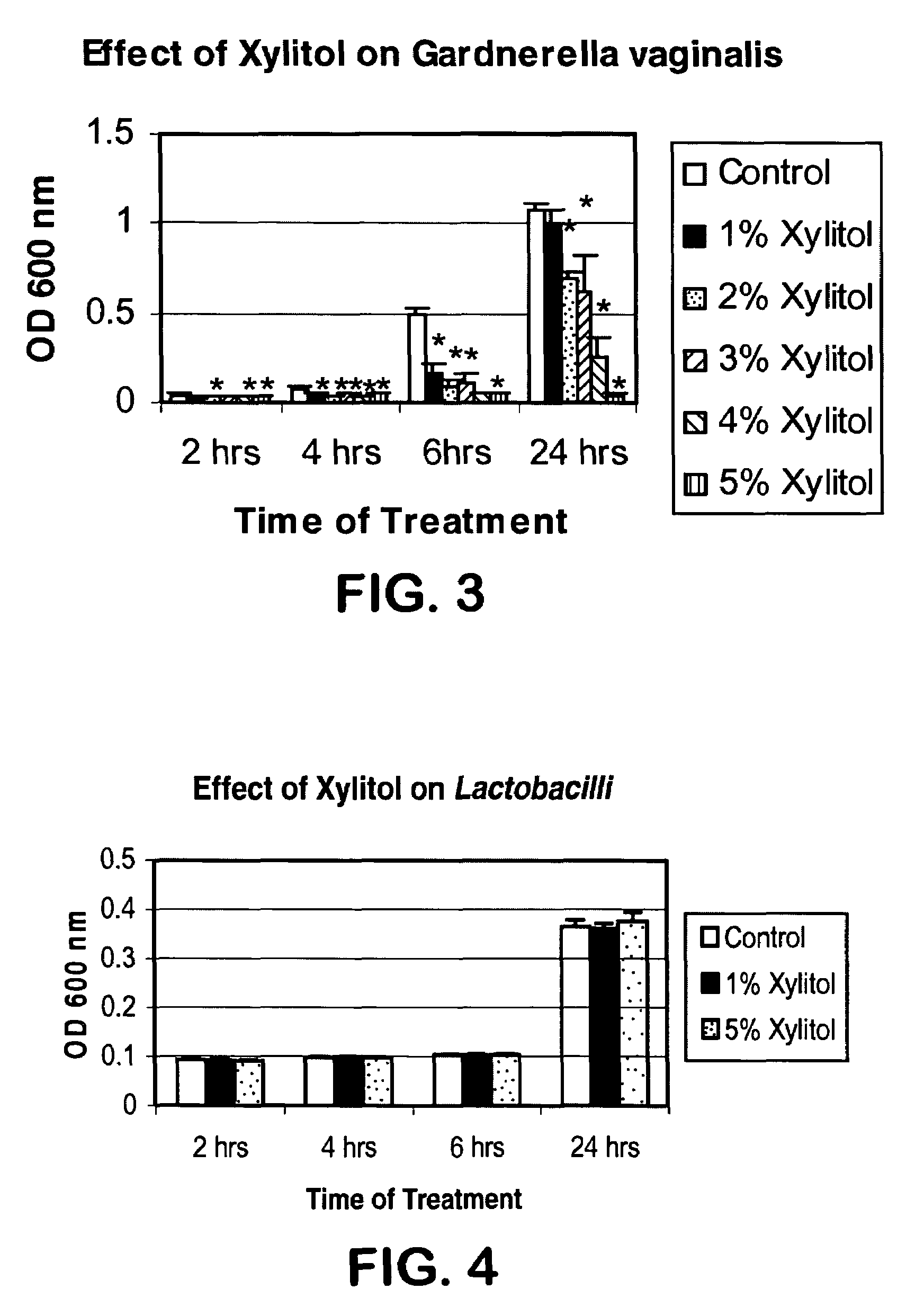
A vaginal treatment composition that employs a therapeutic agent to inhibit and / or treat vaginal infection is provided. The therapeutic agent is capable of inhibiting and / or killing Gardnerella (e.g., Gardnerella vaginalis), Candida (e.g., Candida albicans), and / or Trichomonas (e.g., Trichomonas vaginalis) pathogens. Desirably, such antimicrobial efficacy is achieved without substantially inhibiting the growth of Lactobacillus acidophilus. For instance, sugars and / or sugar alcohols may be employed in the present invention as a therapeutic agent for inhibiting and / or treating vaginal infection. In one particular embodiment, D-xylitol is used as the therapeutic agent.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
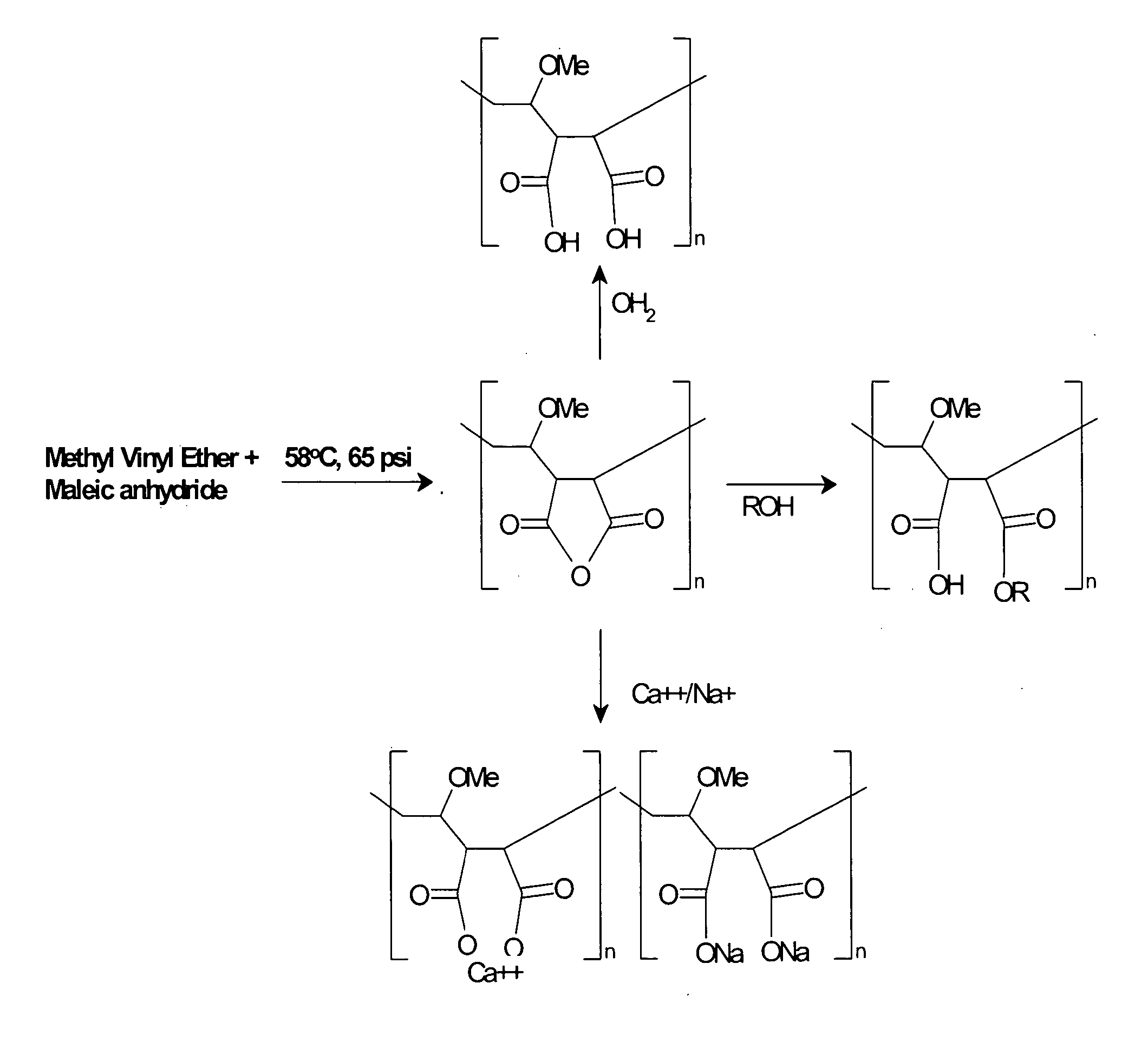
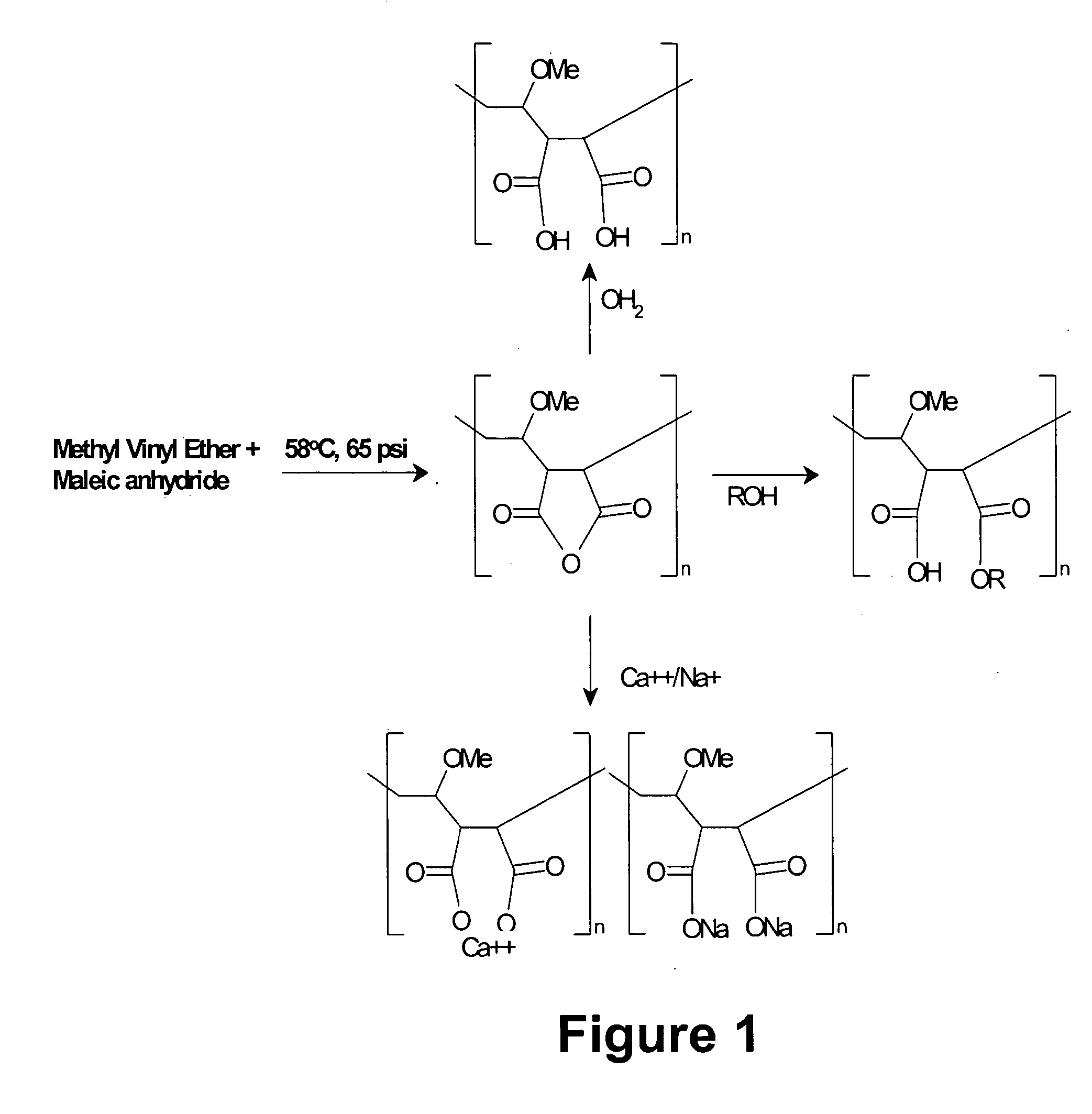
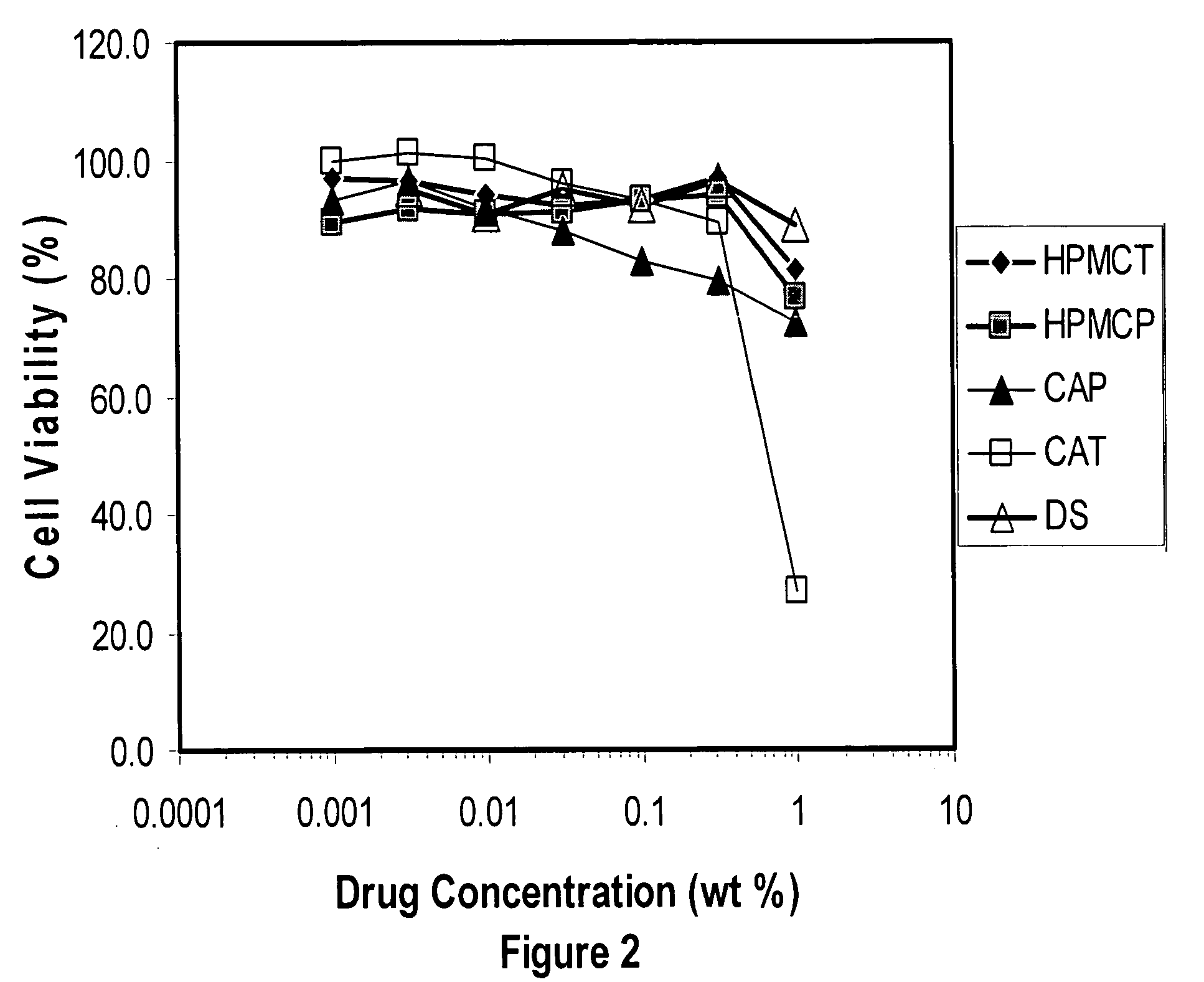
Methods, compositions, formulations, and uses of cellulose and acrylic-based polymers
InactiveUS20050244365A1Easy to chargeLow pKaAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsDisinfectantReverse transcriptase
Compositions, formulations, and methods for the treatment or prevention, or decreasing the frequency of transmission of a virus (such as human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1), Herpes Simplex virus type 1 (HSV1), or Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 (HSV2), or other virus), or a bacterial infection (such as Trichomonas vaginalis, Neisseris gonorrhoeae Haemopholus ducreyl, or Chlamydia trachomatis, or other bacterial species), or a fungal infection, using an anionic cellulose- or acrylic-based oligomer, polymer, or copolymer. The present invention also includes administering a therapeutically effective amount of said oligomer, polymer, or copolymer, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or diluent, thereof. The invention relies on the unique biochemical substitution of the cellulose or acrylic backbone such that the resultant molecule can remain molecularly dispersed in solution (or gel or other formulation) and mostly dissociated over a wide range of physiological microenvironments, such as the low pH found within the vaginal lumen, preferably from a pH of 14 to below 3.5. These specific substitutions also impart on the resultant molecule potent antiviral, anti-bacterial, and anti-fungal properties. In addition, these compositions can be used as general disinfectants for human use such as in contact lens solutions, mouthwashes, toothpastes, suppositories, or as more generalized disinfectants found in soaps, household cleaning products, paints, water treatments modalities, or can be incorporated into cosmetic, and can be used as vehicles for drug delivery, an adjuvant in a therapeutic formulation, or as a preservative. These compounds can be delivered in a liquid or solid dosage form and can be incorporated into barrier devices such as condoms, diaphragms, or cervical caps, to help prevent the transmission of STDs. The compounds of this invention can also be used in combination therapies with other classes of antiviral, antibacterial, or antifungal agent having similar or differing mechanisms of action including, but not limited to, anionic or cationic polymers, copolymers, or oligomers, surfactants, protease inhibitors, DNA or RNA polymerase inhibitors (including reverse transcriptase inhibitors), fusion inhibitors, cell wall biosynthesis inhibitors, integrase inhibitors, or virus or bacterial attachment inhibitors.
Owner:NOVAFLUX INC +1
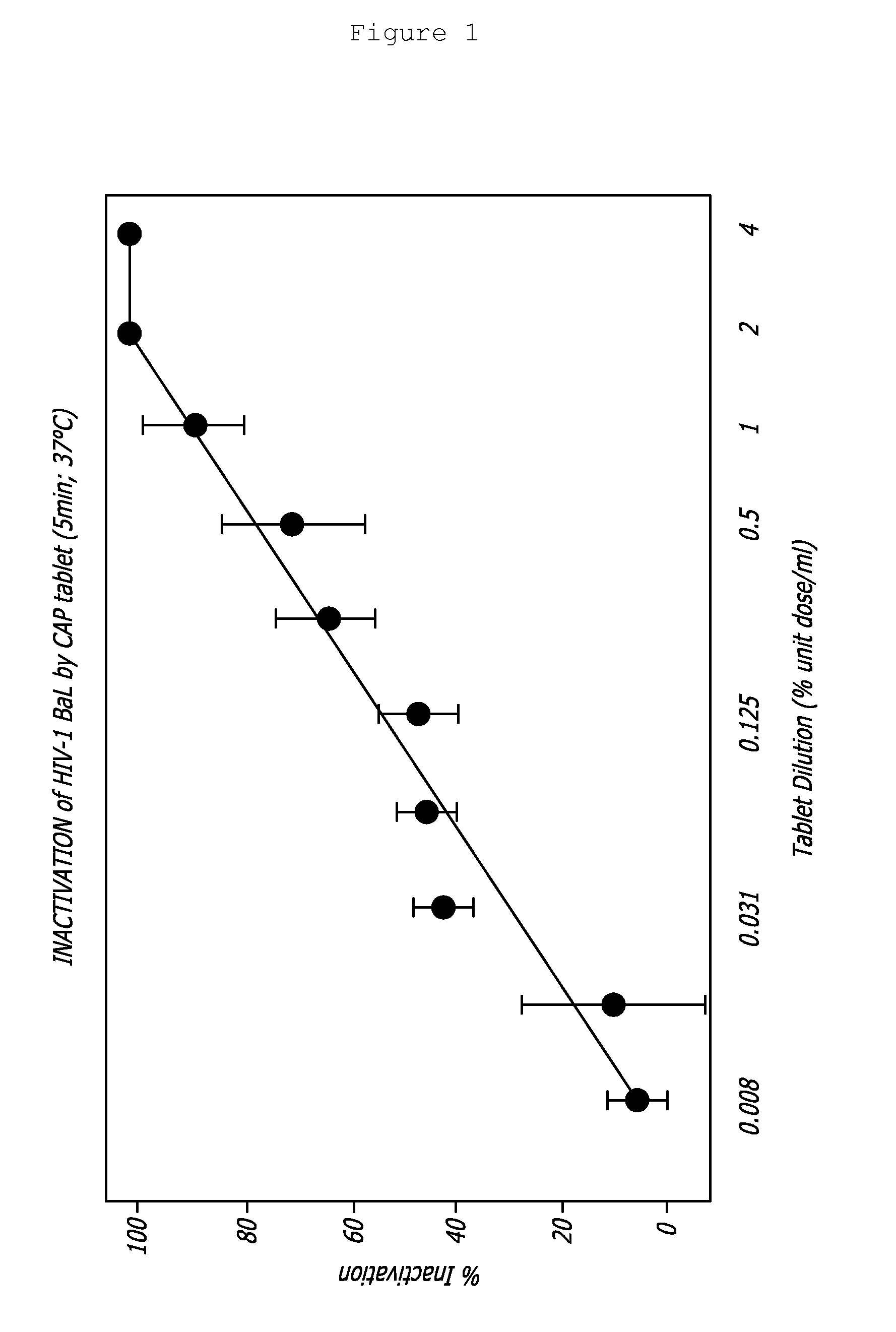
Rapidly dispersible vaginal tablet that provides a bioadhesive gel
InactiveUS20110159091A1Safe and relatively inexpensive methodAvoid spreadingAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacterial vaginosisSpiroplasma
A tablet for insertion into a vagina including 0.01 to 500 mg of a vaginal medication, such as a microbicide, such as cellulose acetate 1,2-benzenedicarboxylate (CAP); 100 to 500 mg of mannitol powder; 50 to 300 mg of inert microcrystalline cellulose; 10 to 80 mg of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose; 50 to 250 mg of glycerol and optionally 2 to 4 mg of at least one preservative which protects against microbicidal contamination and discourages the growth of yeast in the vagina. The tablet which includes CAP as the vaginal medication is vaginally administered before coitus in methods for preventing the sexual transmission of HIV-1, HIV-2, herpesvirus, or an infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis, Trichomonas vaginalis, Haemophilus ducreyi or Treponema pallidum. The tablet which includes CAP as the vaginal medication is vaginally administered to prevent or treat bacterial vaginosis.
Owner:NEW YORK BLOOD CENT
Gynecology lotion
The invention relates to a gynaecologic lotion relative to female pudendum, which is prepared by extracting glabrous greenbrier rhizome, radix stemonae, cave flower, common cnidium fruit, lightyellow sophora root, phellodendron, European vebena, densefruit pittany root-bark, broom cypress fruit, golden larch bark, shrubalthea bark, Chinese gall, pariphyllin, pericarpium zanthoxyli, indigo naturalis, borneol and white vitriol, and has the effects of reducing fever, detoxifying, eliminating dampness, diminishing inflammation, depriving body fluids, disinfesting insect, stopping leucorrhea, relieving itching, retracting, etc. The lotion can effectively kill pathogenic bacteria, such as trichomonas vaginalis, mucedine, gonococcus, chlamydia, etc., and has the effects of diminishing inflammation, eliminating dampness, stopping leucorrhea and relieving itching. The lotion has good curative effects on various colpitis, multi-colorea leucorrhea, pruritus vulvue, hysteroptosis, prolapse of uterus, vaginal looseness, etc.
Owner:丁绍余
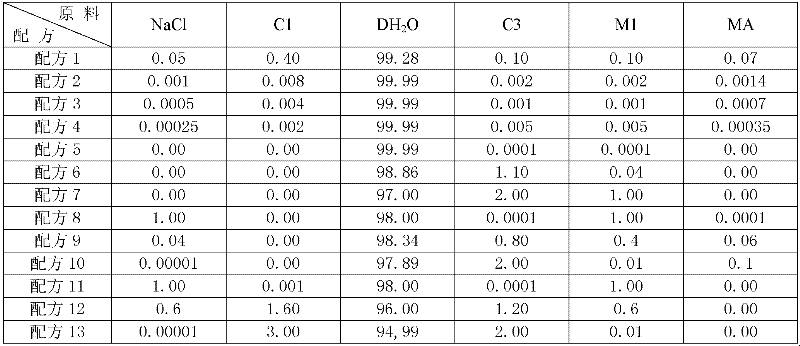
Broad-spectrum and high-efficiency antibacterial washing liquor
InactiveCN102416011ABroad spectrum killingEfficient killingAntibacterial agentsBiocideEscherichia coliArginine
The invention relates to a medicine, in particular to broad-spectrum and high-efficiency antibacterial washing liquor and a preparation method thereof. The invention is characterized in that the antibacterial washing liquor is prepared by the following materials according to the weight ratio: 0.0001-2.0 of N-coconut-oil fatty-acid acyl L-arginine ethyl ester DL-pyrrolidone carboxylate, 0.0001-1.0 of dodecyl dimethyl benzyl ammonium chloride, 10.0-99.995 of water, and the balance of auxiliary materials. The broad-spectrum and high-efficiency antibacterial washing liquor has the following characteristics and advantages that pathogenic microorganisms are killed in a broad-spectrum and high-efficiency manner; ureaplasma urealytium, gonococcocci and trichomonas vaginalis can be killed in one minute; the killing rate for escherichia coli, staphylococcus aureus and candida albicans is respectively more than 99%; non-toxic; no stimulation is caused to the skin; no allergic reaction is caused; no stimulation is caused to the eyes; no stimulation is caused to vaginal mucosa; and the pH value of a preparation is close to that in the normal vagina.
Owner:艾硕特生物科技(昆明)有限公司
Oligonucleotides for amplifying trichomonas vaginalis-derived nucleic acid
ActiveUS20080234473A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementTest sampleTrichomonas vaginalis
Oligonucleotides useful for determining the presence of Trichomonas vaginalis in a test sample. The oligonucleotides may be incorporated into detection probes, helper probes, capture probes and amplification oligonucleotides, and used in various combinations thereof.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
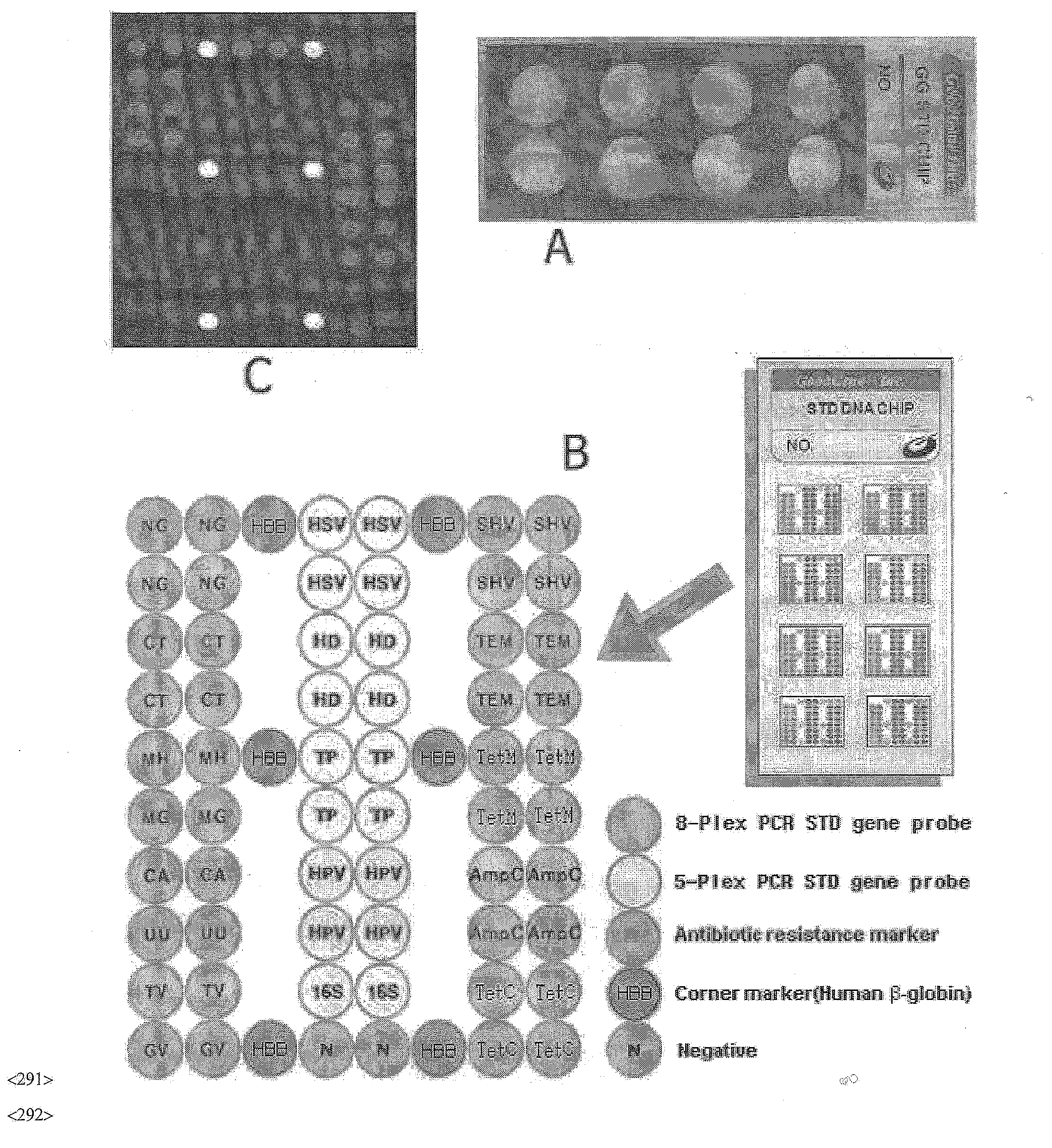
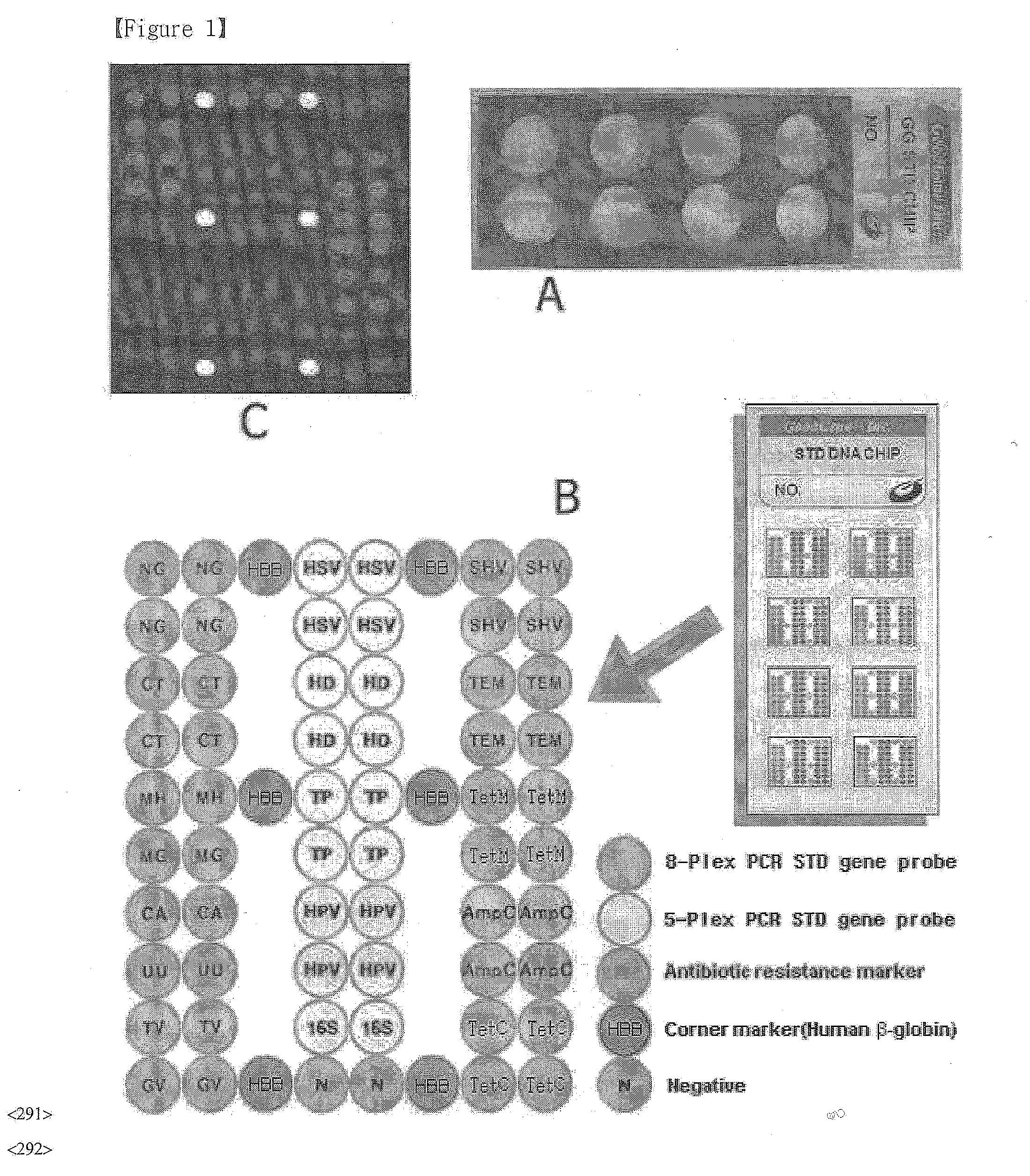
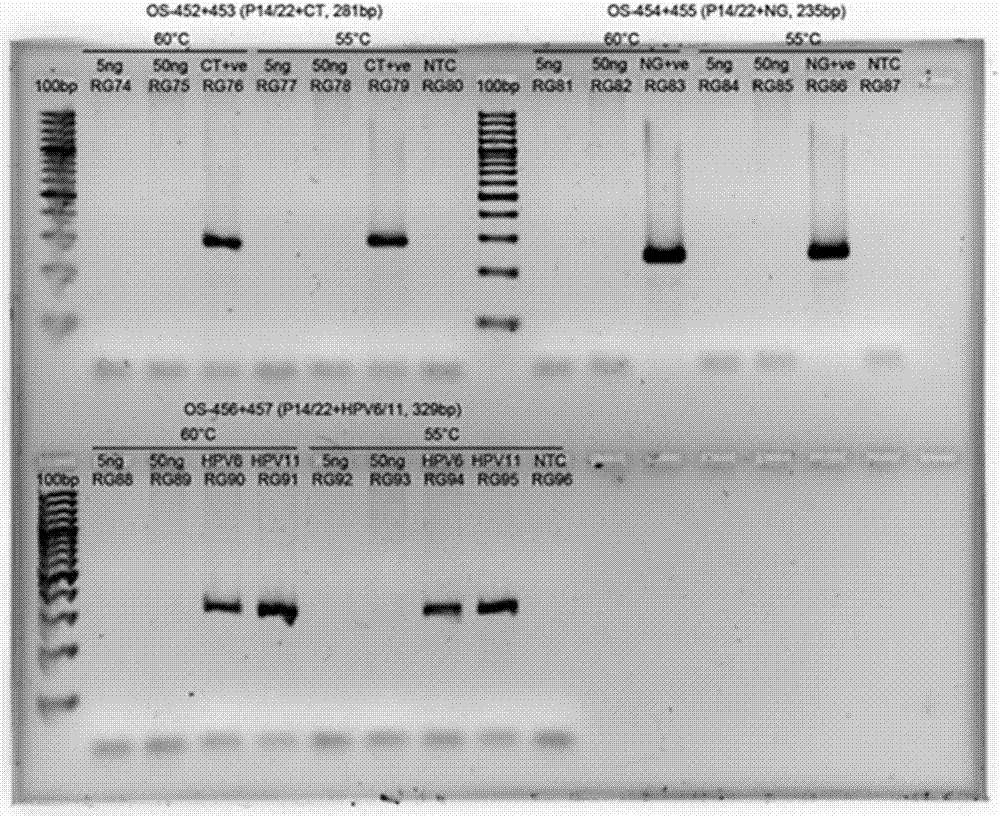
DNA chip, kit for detecting or genotyping bacteria causing sexually transmitted diseases, genotyping antibacterial drug resistance and detecting or genotyping method using the same
InactiveUS20120004113A1Quickly and accurately detectEasy to explainNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseEscherichia coli
Disclosed are a DNA chip and a kit capable of quickly and accurately detecting or genotyping the highly prevalent and important eleven microbes causing sexually transmitted diseases (STD) Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Mycoplasma genitalium, Mycoplasma hominis, syphilis-causing treponema, pallidum, chancroid-causing Haemophilus ducreyi, genital herpes-causing herpes simplex virus 1 and 2, human papillomavirus (HPV) and Trichomonas vaginalis and three related organisms Candida albicans, Gardnerella vaginalis and coliform bacteria and analyzing antibiotic resistance against tetracycline and lactam antibiotics, and a method for detecting or genotyping using the same. According to the present invention, the presence, genotype and antibiotic resistance of the fourteen organisms can be analyzed quickly and accurately from a DNA sample. With excellent sensitivity, specificity, reproducibility and accuracy of the 14 STD-causing and related microorganisms may be automatically identified quickly and accurately from multiple samples, and selection of antibiotics may be aided.
Owner:GOODGENE
Xylitol for treatment of vaginal infections
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Method and device for trichomonas detection
InactiveUS7291477B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsBacteriuriaBacterial Adhesins
A method and kit for detecting Trichomonas vaginalis infection in a human subject are disclosed. In the method, a body-fluid sample such as a vaginal swab sample or urine is obtained from the subject and contacted with an antibody specific against a Trichomonas adhesin peptide, forming an antibody-adhesin peptide complex if the subject is infected with Trichomonas. The presence or absence of the complex establishes, with a reliability of at least 80%, in the case of a vaginal swab sample, and with a reliability of at least 40% in the case of a urine sample, the presence or absence, respectively, of Trichomonas infection in the subject. A preferred test kit employs a dry-strip, sandwich assay, format.
Owner:XENOTOPE DIAGNOSTICS INC +1
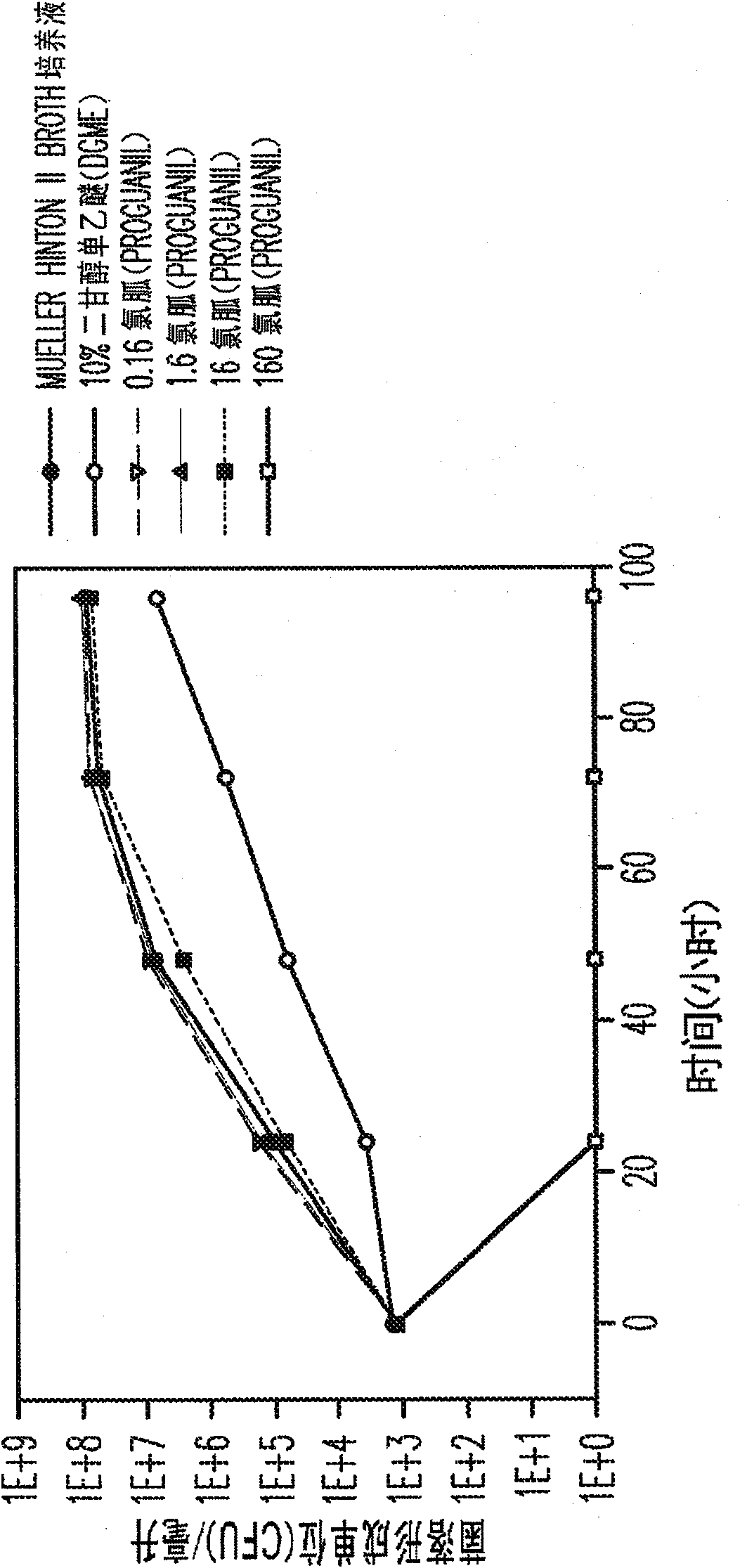
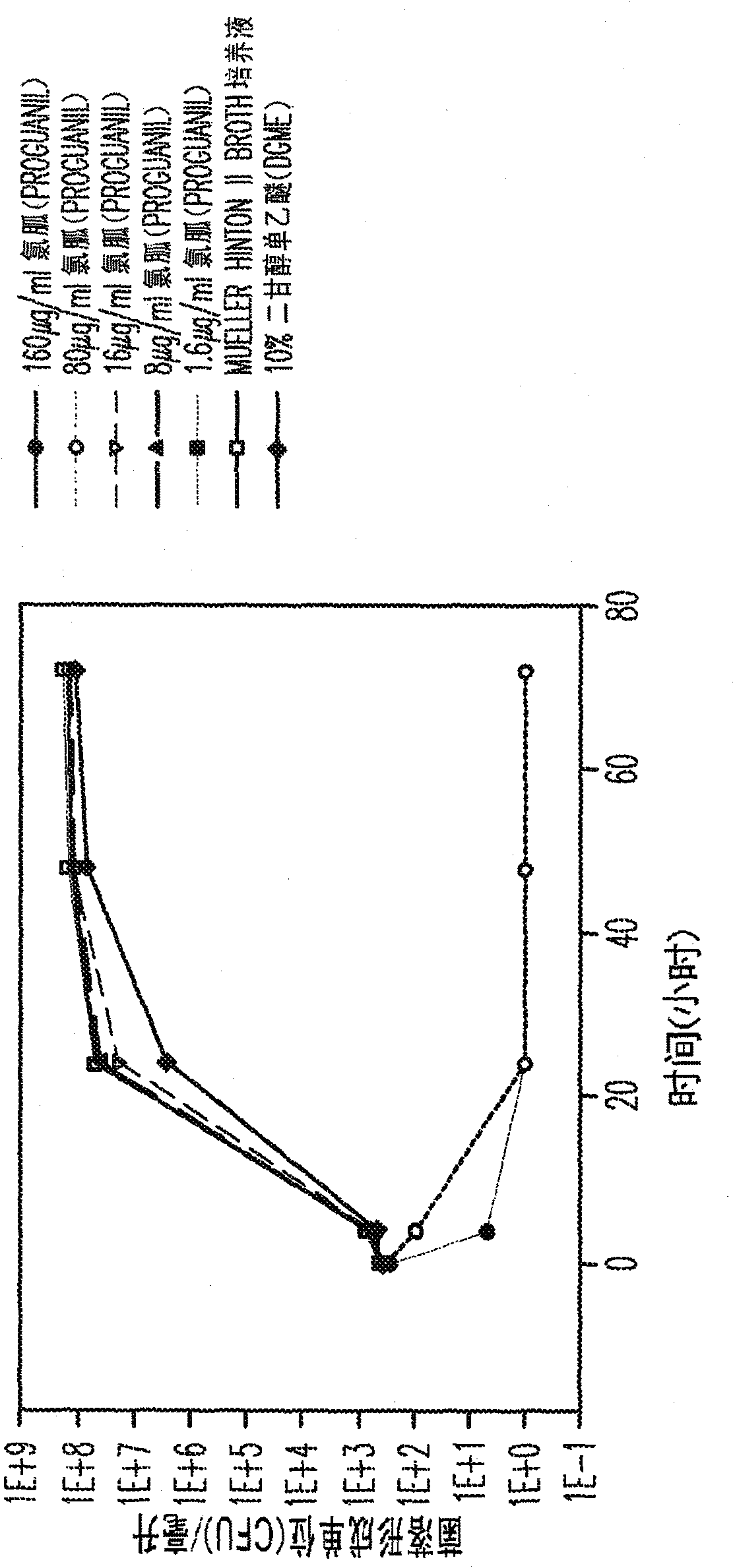
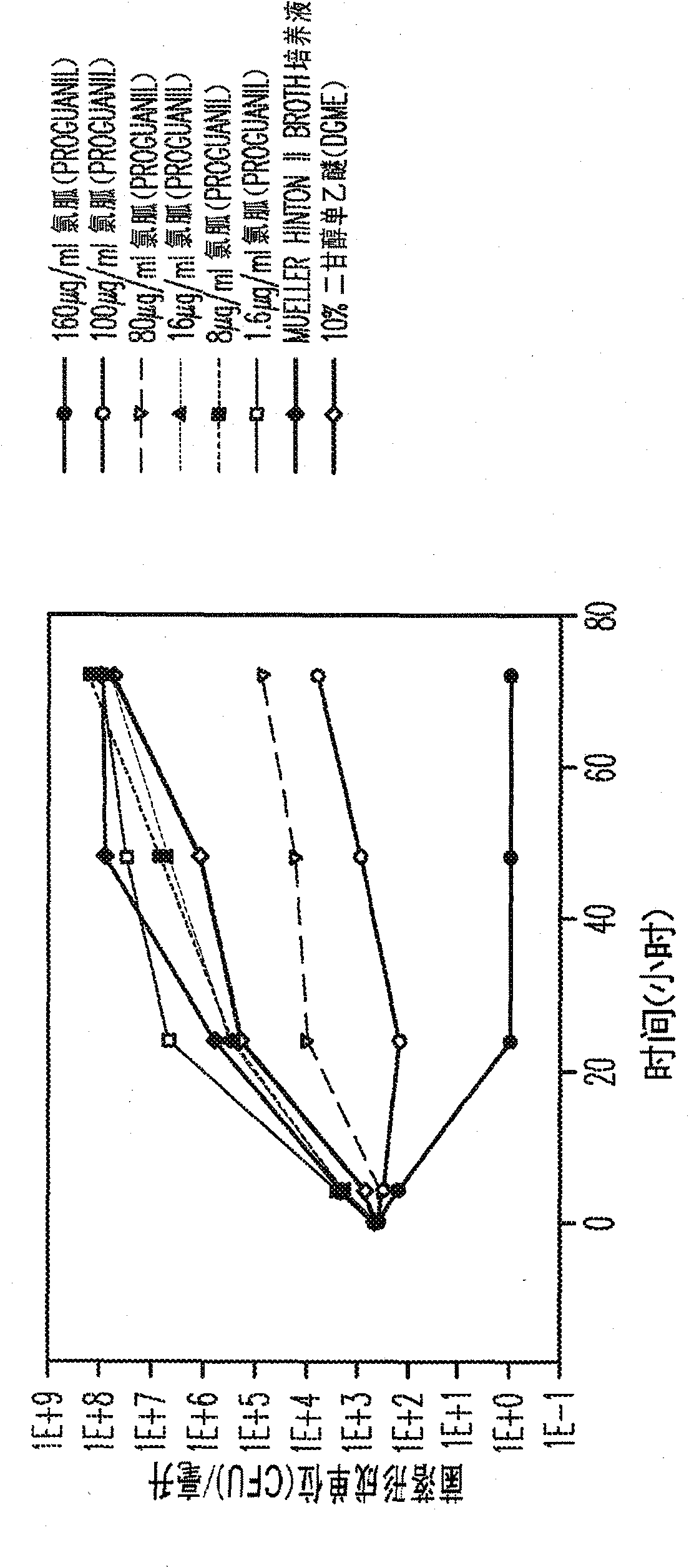
Proguanil to treat skin/mucosal diseases
Proguanil has been found to have rapid and effective killing activity against a variety of disease-causing micro organisms. For example, when applied topically, proguanil is particularly effective against Propionibacterium acnes, a bacteria that causes acne; Corynebacterium minutissimum, a bacteria that causes erythrasma, Gardnerella vaginalis, a bacteria that causes vaginosis; Trichomonas vaginalis, a protozoan that causes trichomoniasis and C. albicans, a fungus (a form of yeast).
Owner:TOLMAR INC
Nano iodine-chitosan cervical disease treating membrane agent and preparation method of membrane
InactiveCN102335462ALess discomfortImprove the bactericidal effectSurgerySynthetic polymeric active ingredientsDiseaseChlorhexidine Acetate
The invention discloses a nano iodine-chitosan cervical disease treating membrane agent and a preparation method of the membrane. The treating membrane is prepared by adding plasticizer and adsorbent to chitosan, povidone iodine, dialkyl quaternary ammonium salt and chlorhexidine acetate used as main effective ingredients. The treating membrane disclosed by the invention has killing activity to multiple pathogenic microorganisms, has no irrigation to mucosa, can relieve itching, arrest bleeding and promote the growth of epidermic tissues, can be used for treating colpitis, trichomonas vaginalis, cervicitis, cervical erosion and other gynecological diseases, has better repair action on vaginal and cervical injury, and can effectively prevent the propagation of venereal diseases such as gonorrhoea, syphilis, AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) and the like.
Owner:边俊杰
Use of Levo-Ornidazole For Preparing Anti-Parasitic Infection Drug
PendingUS20080177083A1Low toxicityImprove securityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDrugs preparationsTrichomonas vaginalis
The use of levo-ornidazole in the preparation of anti-parasitic infection drug is provided. It is demonstrated that levo-ornidazole is superior to dextro-ornidazole and racemic ornidazole in the therapeutic action against parasitization (especially trichomonas vaginalis infection and cecal amoeba infection), and thus it is more practicable to formulate L-ornidazole as anti-parasitic infection drugs, and particularly as drug preparations which are suitable for clinical uses, including oral preparation, intravenous preparation and vaginal preparation.
Owner:NANJING SANHOME PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Use of levo morpholine nidazole for preparing medicine for antiparasitic infection
The present invention provides an application of levomorpholinonidazol [R-(-)-1-(2-methyl-5nitroimidazole-1-group)-morpholinylpropane-2-alcohol] or its medicinal salt in preparation of medicine for resisting amoebic infection and resisting vaginal trichomonad infection.
Owner:NANJING SANHOME PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Probes for detecting the presence of trichomonas vaginalis in a sample
ActiveUS20110183339A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementTest sampleTrichomonas vaginalis
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
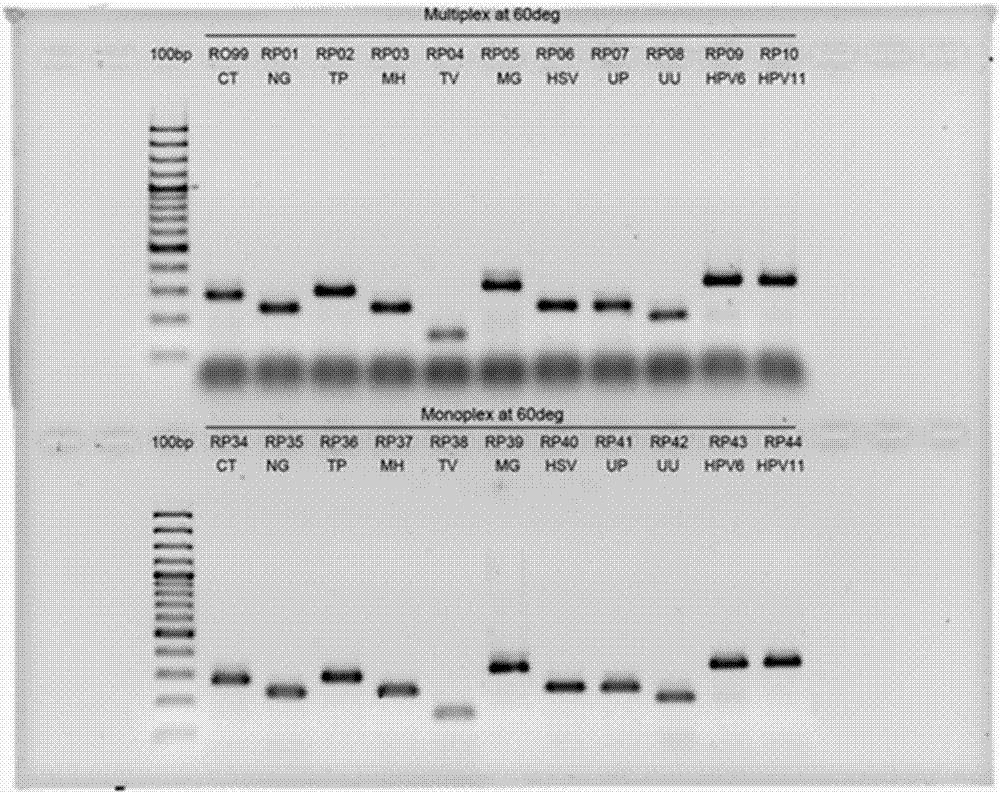
Rapid and sensitive genotype identification and nucleic acid detection
InactiveCN105392896AMicrobiological testing/measurementOrgan movement/changes detectionDiseaseUreaplasma parvum
The invention discloses a method, primer, probe and kit for identifying various gene mutations or substance genetic typing. In one embodiment, the disease is pathogenic. In the other embodiment, the invention is applied to detection of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis, hepatitis B virus, beta-globulin mutation, thrombophilia related mutation; or various sexually transmitted pathogens, consisting of Trichomonas vaginalis, Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Mycoplasma genitalium, Mycoplasma hominis, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Ureaplasma parvum, Treponema pallidum, Herpes simplex virus 1 , Herpes simplex virus 2, Human papillomavirus type 6, and Human papillomavirus type 1.
Owner:DIAGCOR LIFE SCI LTD
External medicine for treating toothache
InactiveCN102600248AEasy to makeLittle side effectsDigestive systemAluminium/calcium/magnesium active ingredientsSide effectTrichomonas vaginalis
The invention provides external medicine for treating toothache. The medicine is characterized by consists of the following raw material medicine in weight: 25g of alum and 120g of fresh snakeweed. A preparation method of the medicine comprises the following steps that: the alum is crushed and is screened by a sieve being 80 meshes, the snakeweed is cleanly washed, the alum and the snakeweed are uniformly mixed and are mashed into juices to be dripped into the auditory meatus. The medicine has the efficacies and beneficial effects that the alum is cold in property and is acerb in taste, a strong convergence effect is realized, and the efficacies of eliminating toxin, killing intestinal worms, removing dampness, relieving itching, stopping bleeding, stopping diarrhoica, clearing away the heat and dissolving the phlegm are realized. The alum also has antibacterium effect, anti-trichomonas-vaginalis effect and the like. The snakeweed has the effects of clearing away the heat, realizing diuresis, cooling the blood and eliminating the toxin. The medicine mainly treats heat accumulation of the bladder, dysuria, leucorrhea, summer damp diarrhea, nosebleed, hematuria, liver heat and hot eyes, swelling and pain in throat and swollen welling-abscess toxin and has the anti-inflammatory effect. The external medicine has the advantages that the preparation is simple, the side effect is small, and the external medicine is applicable to various kinds of toothache.
Owner:李三川
Immunochromatographic test strip for quickly detecting trichomonas vaginalis and its preparation method
The present invention relates to a testing bar, in particular to an immunity chromatographic test bar and the preparation method thereof for testing the trichomonas vaginalis. The present invention adopts the colloids metal immunity chromatographic test technology which is developed in the recent years and provided with the properties of strong specificity, high sensitivity, convenience and speediness. The immunity chromatographic test bar for quickly testing the trichomonas vaginalis is made by using 5 stems of monoclonal antibodies of the anti-recombination AP33 albumen screened out by the hybridoma technology, thus optimizing the best reaction mode by the monovalent parting of the different stems.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Primer and probe set and kit for multi-detection of gardnerella vaginalis, canidia albicans and trichomonas vaginalis and detection method
PendingCN110343780AReduce the problem of high detection costImprove the complicated operationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPathogenic microorganismFluorescence
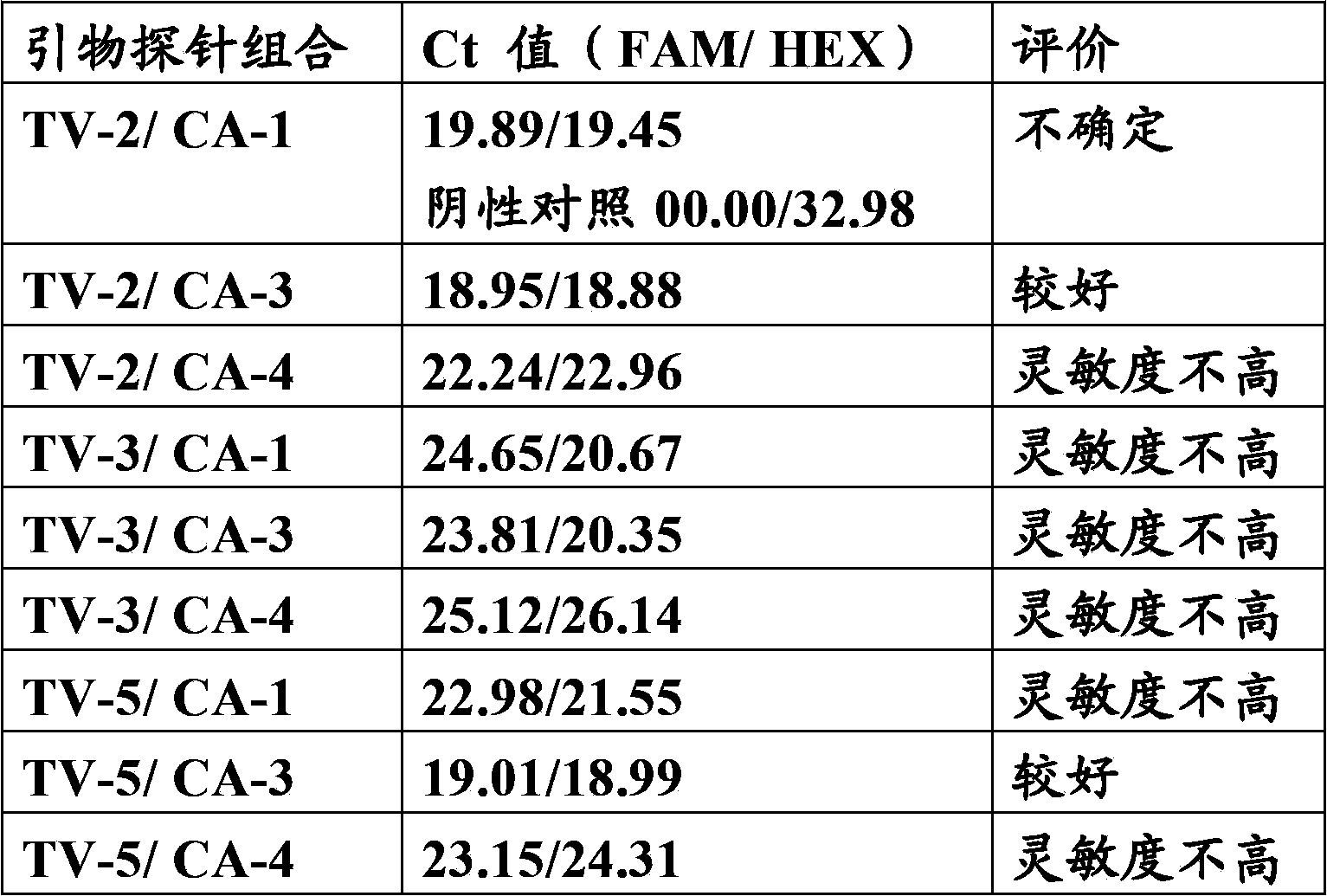
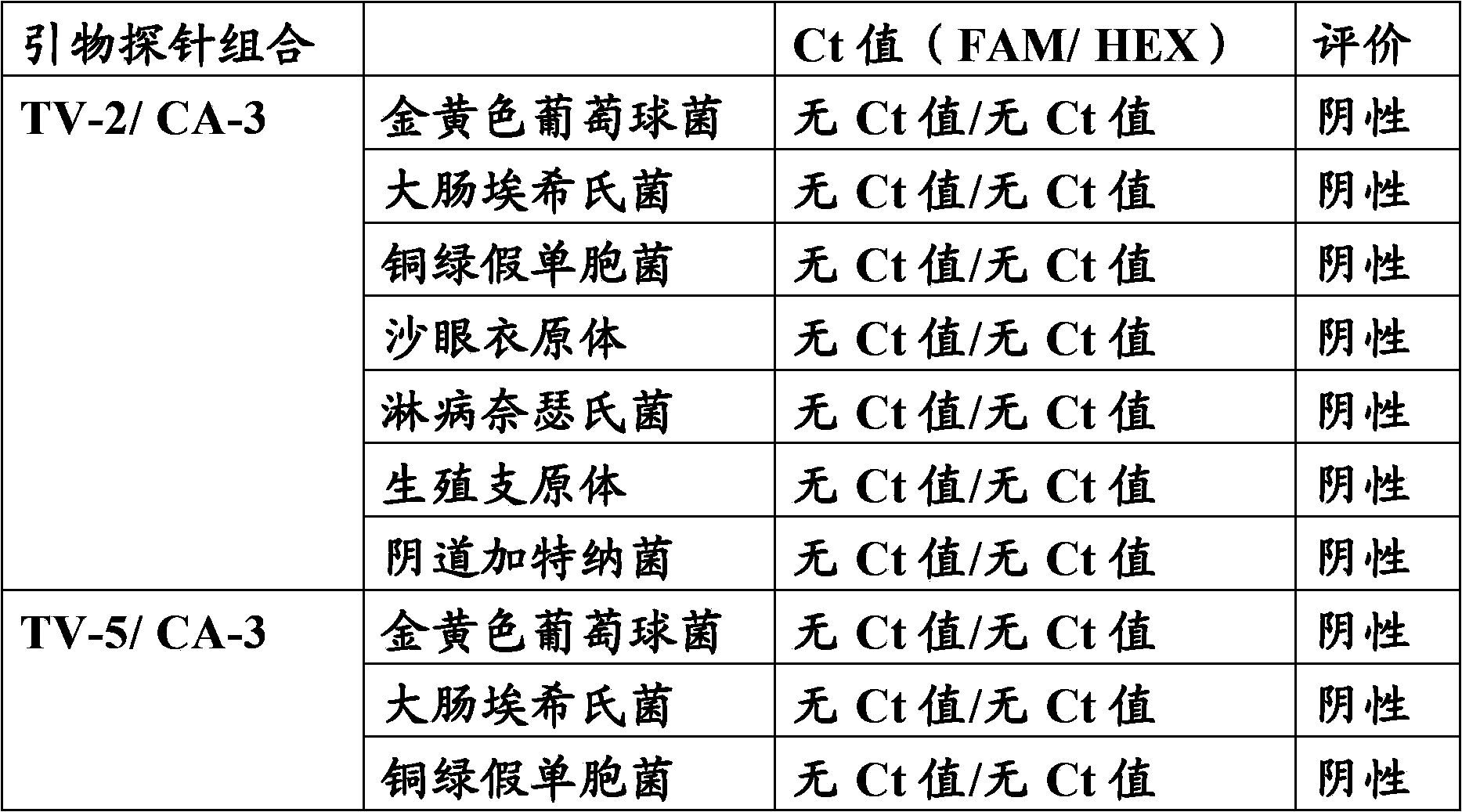
The invention relates to the technical field of detection of pathogenic microorganisms, in particular to a primer and probe set and kit for multi-detection of gardnerella vaginalis, canidia albicans and trichomonas vaginalis and a detection method. The kit comprises specific primer pairs and Taqman fluorescence probes for conservative areas of GD / CA / TV, and the kit can accurately detect samples infected with GD / CA / TV through real-time fluorescence quantification PCR and is high in sensitivity, good in specificity, high in repeatability and convenient and quick to use.
Owner:中生方政生物技术股份有限公司
Rapid genotyping analysis and kits thereof
ActiveCN106906306AMicrobiological testing/measurementOrgan movement/changes detectionDiseaseMycobacterium tuberculosis
The present invention provides methods, primers, probes, and kits for identifying gene mutation or material genotyping. In one embodiment, the materials are disease-causing agents. In another embodiment, the present invention is applied to detecting multidrug-resistant mycobacterium tuberculosis, hepatitis B virus, beta-globulin mutation, thrombosis-related mutations; or multiple sexually transmitted diseases causing agents, including but not limited to, trichomonas vaginalis, chlamydia, neisseria gonorrhoeae, mycoplasma, mycoplasma hominis, ureaplasma urealyticum, Mycelia, Treponema pallidum, Herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 and human papilloma virus type 6 and type 11.
Owner:DIAGCOR LIFE SCI LTD
Preparation method of metronidazole freeze dried powder injection
InactiveCN1830439AImprove antibacterial propertiesPowerful killing of trichomoniasisAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsFreeze-dryingAnaerobic bacteria
A freeze-dried powder injection of metronidazole for treating anaerobe infection, Trichomonas vaginalis and amebiasis is prepared from metronidazole through depositing in water, cold storage, ultrafiltration, further preparing in dark condition and N2 atmosphere, pouring in containers, freeze drying and sealing.
Owner:巴里莫尔制药(通化)有限公司
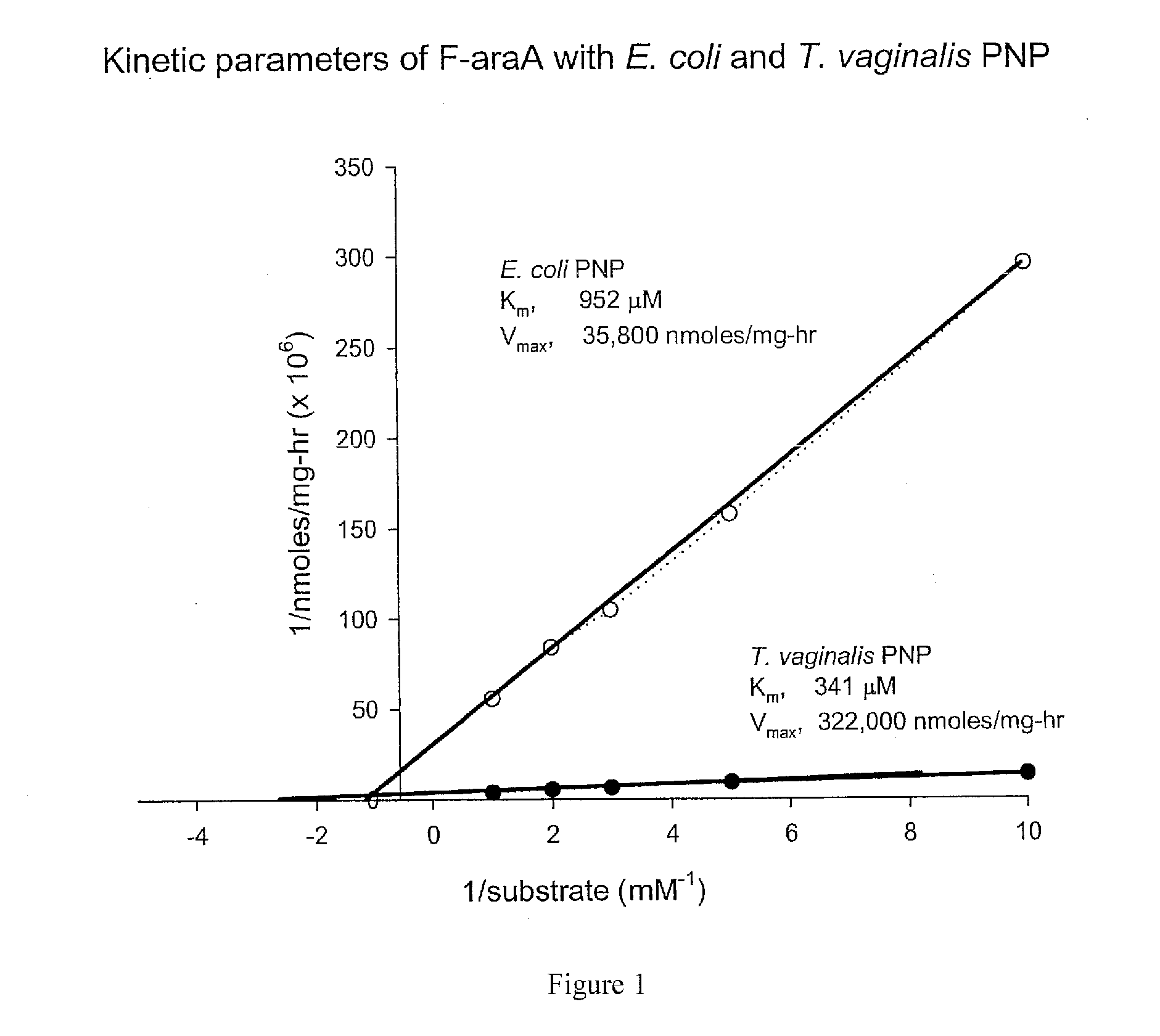
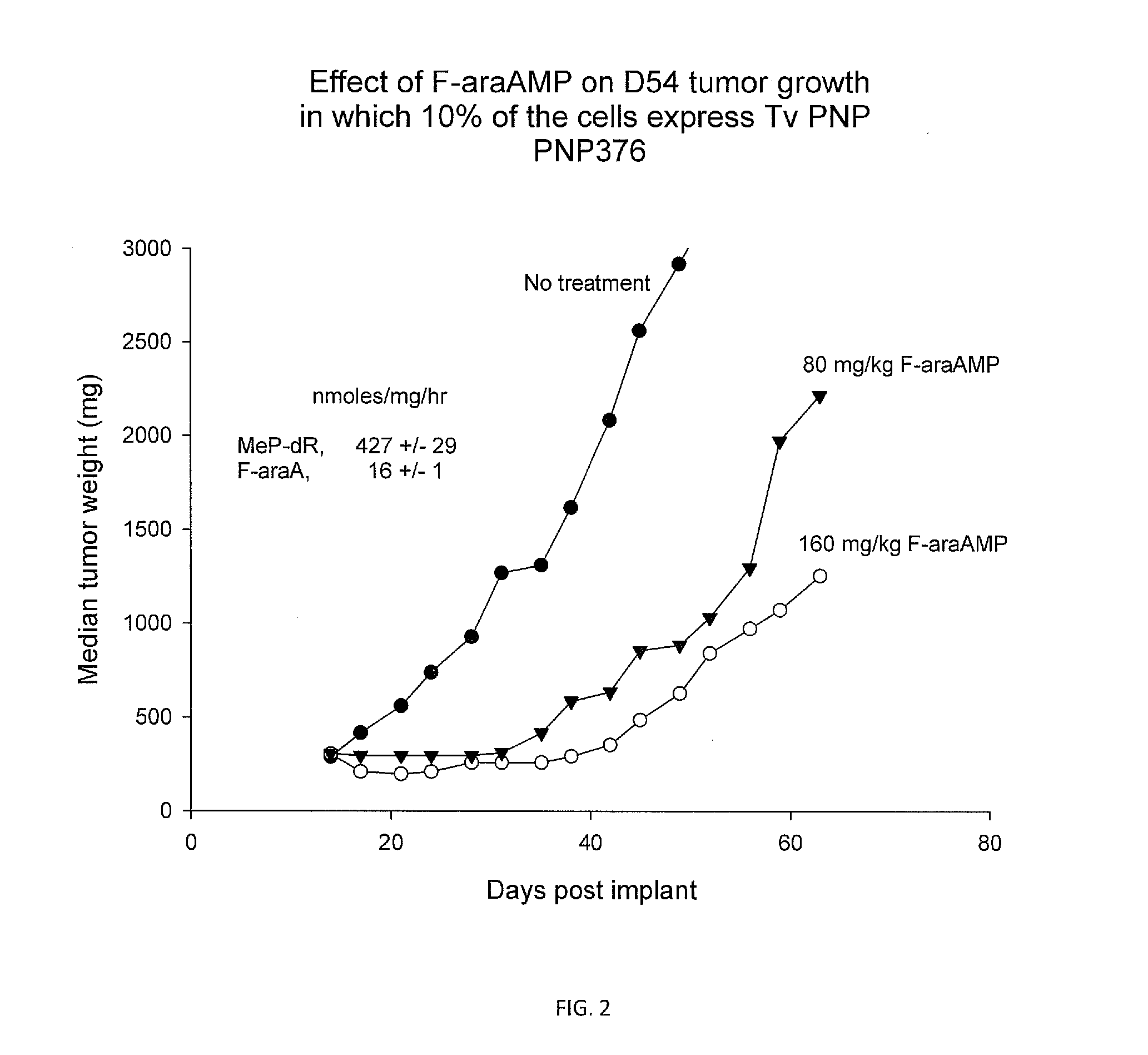
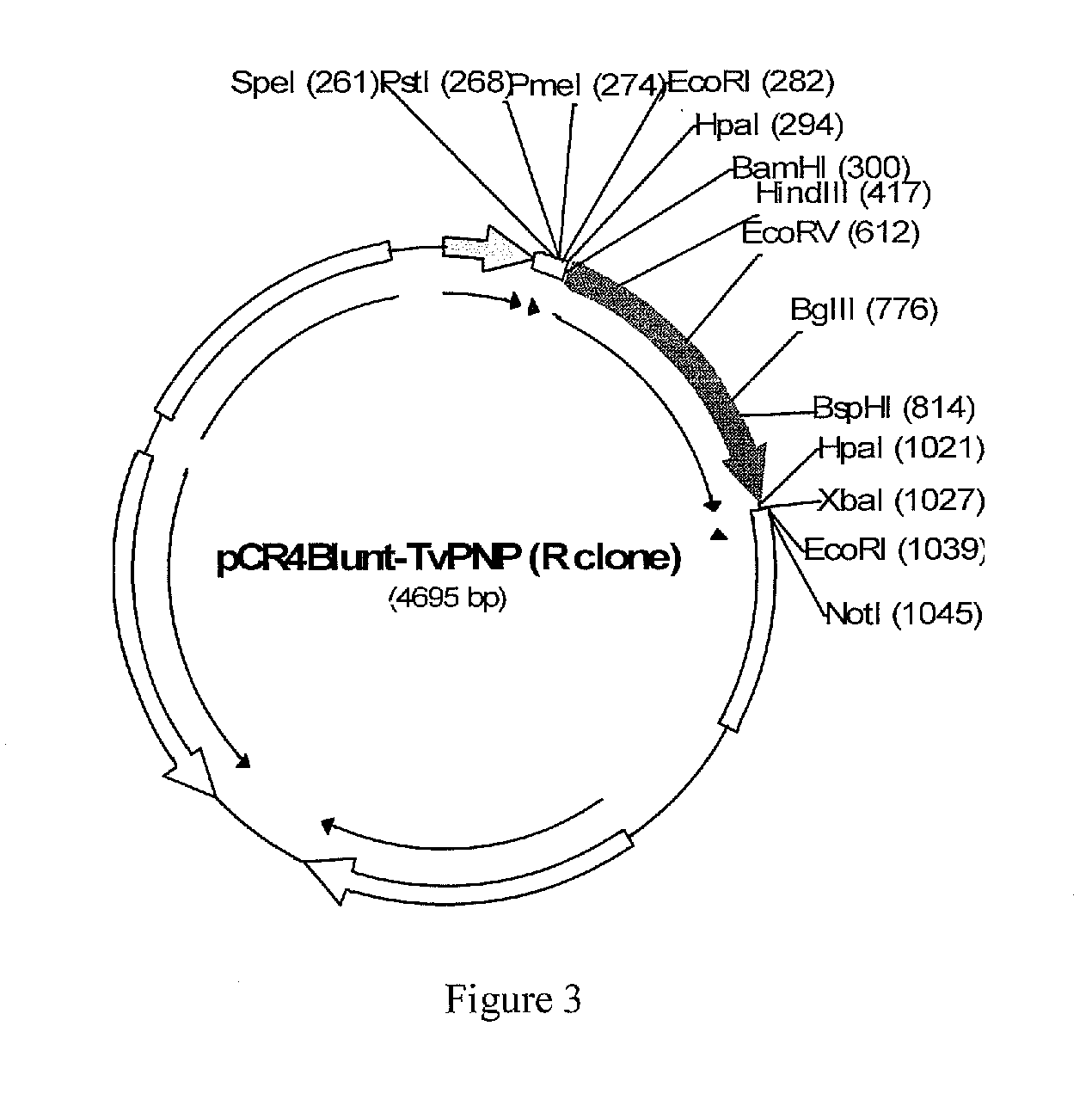
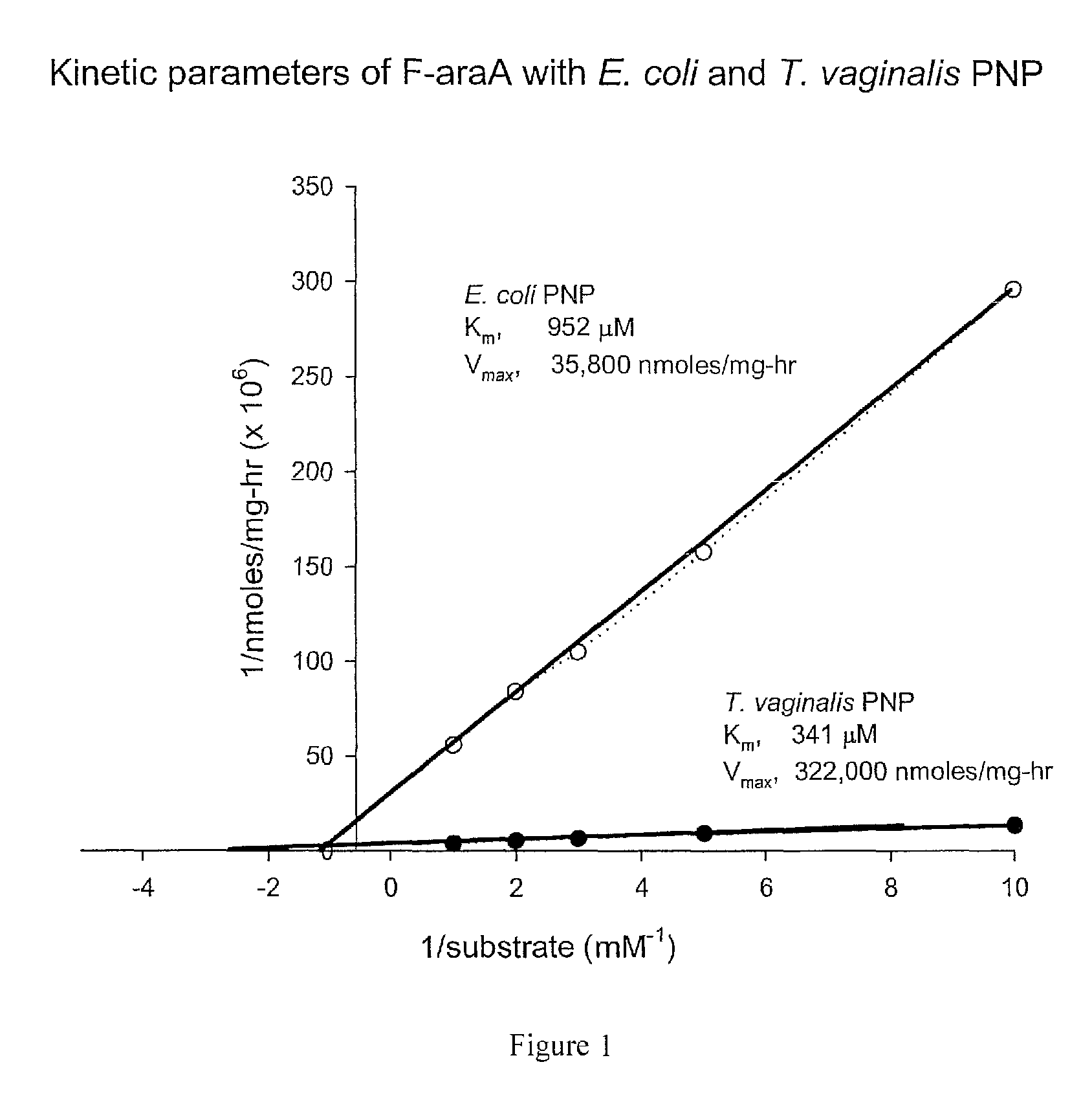
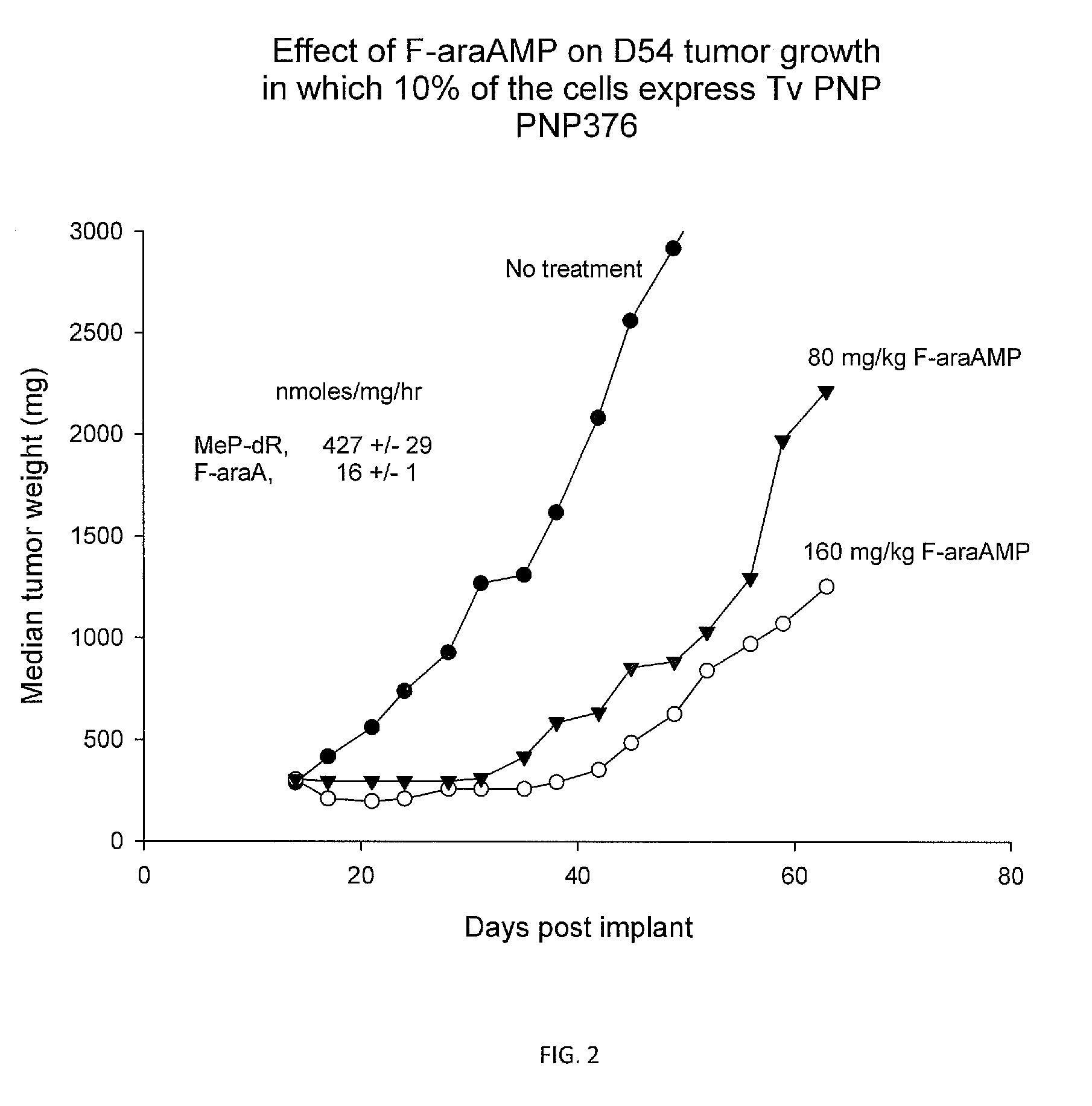
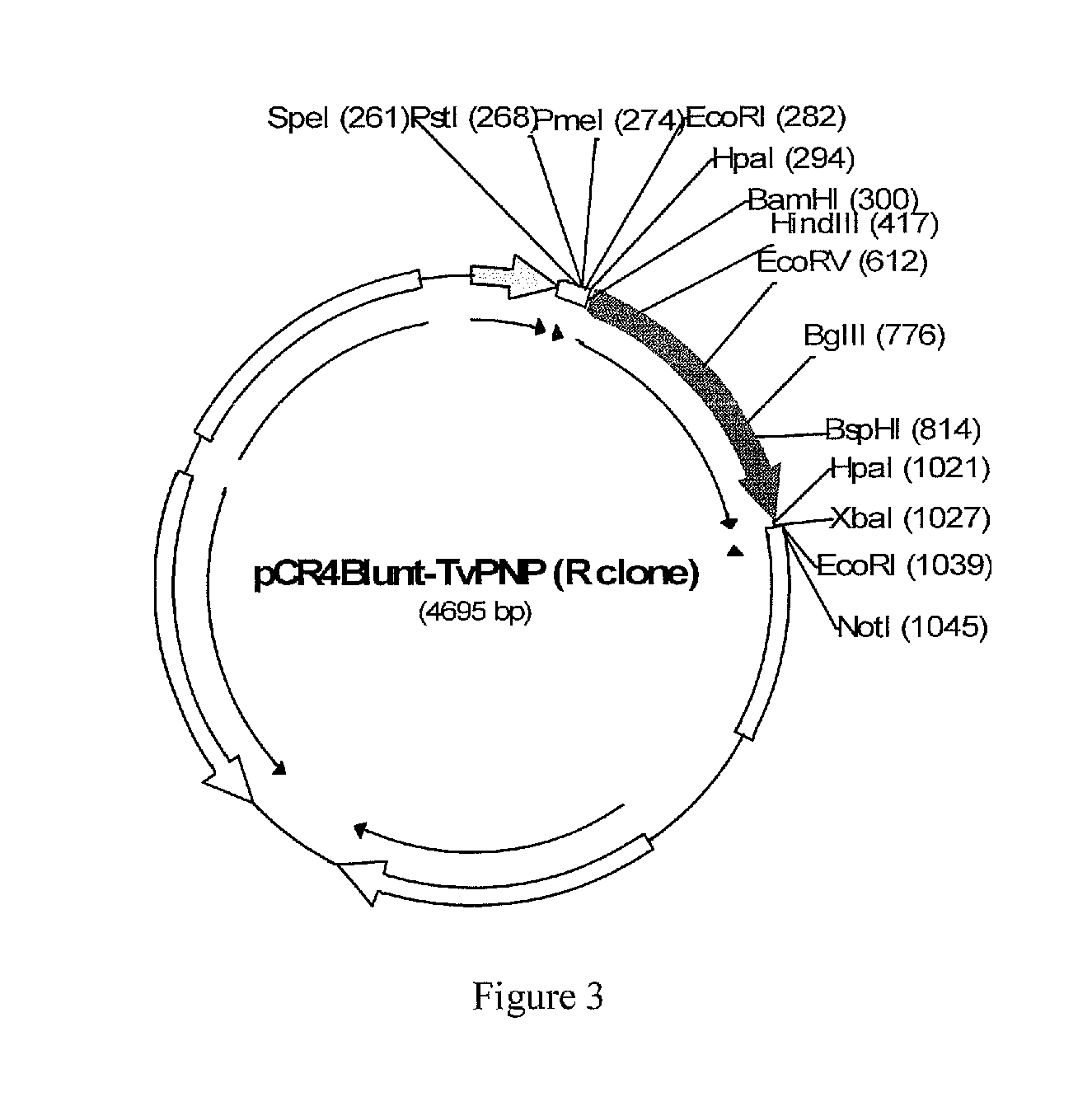
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase as enzymatic activator of nucleoside prodrugs
A process for inhibiting a mammalian cancerous cell or virally infected cell includes providing a Trichomonas vaginalis purine nucleoside phosphorylase enzyme or a tail mutant purine nucleoside phosphorylase enzyme in proximity to the mammalian cancerous cell or the virally infected cell and exposing the enzyme to a purine nucleoside phosphorylase enzyme cleavable substrate to yield a cytotoxic purine analog. The process includes introducing to the cell a vector containing the phosphorylase enzyme, or a DNA sequence coding for the same and delivering to the cell an effective amount of the substrate such as 9-(β-D-arabinofuranosyl)-2-fluoroadenine (F-araA).
Owner:SOUTHERN RES INST & IP +1
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase as enzymatic activator of nucleoside prodrugs
A process for inhibiting a mammalian cancerous cell or virally infected cell includes providing a Trichomonas vaginalis purine nucleoside phosphorylase enzyme or a tail mutant purine nucleoside phosphorylase enzyme in proximity to the mammalian cancerous cell or the virally infected cell and exposing the enzyme to a purine nucleoside phosphorylase enzyme cleavable substrate to yield a cytotoxic purine analog. The process includes introducing to the cell a vector containing the phosphorylase enzyme, or a DNA sequence coding for the same and delivering to the cell an effective amount of the substrate such as 9-(β-D-arabinofuranosyl)-2-fluoroadenine (F-araA).
Owner:SOUTHERN RES INST & IP +1
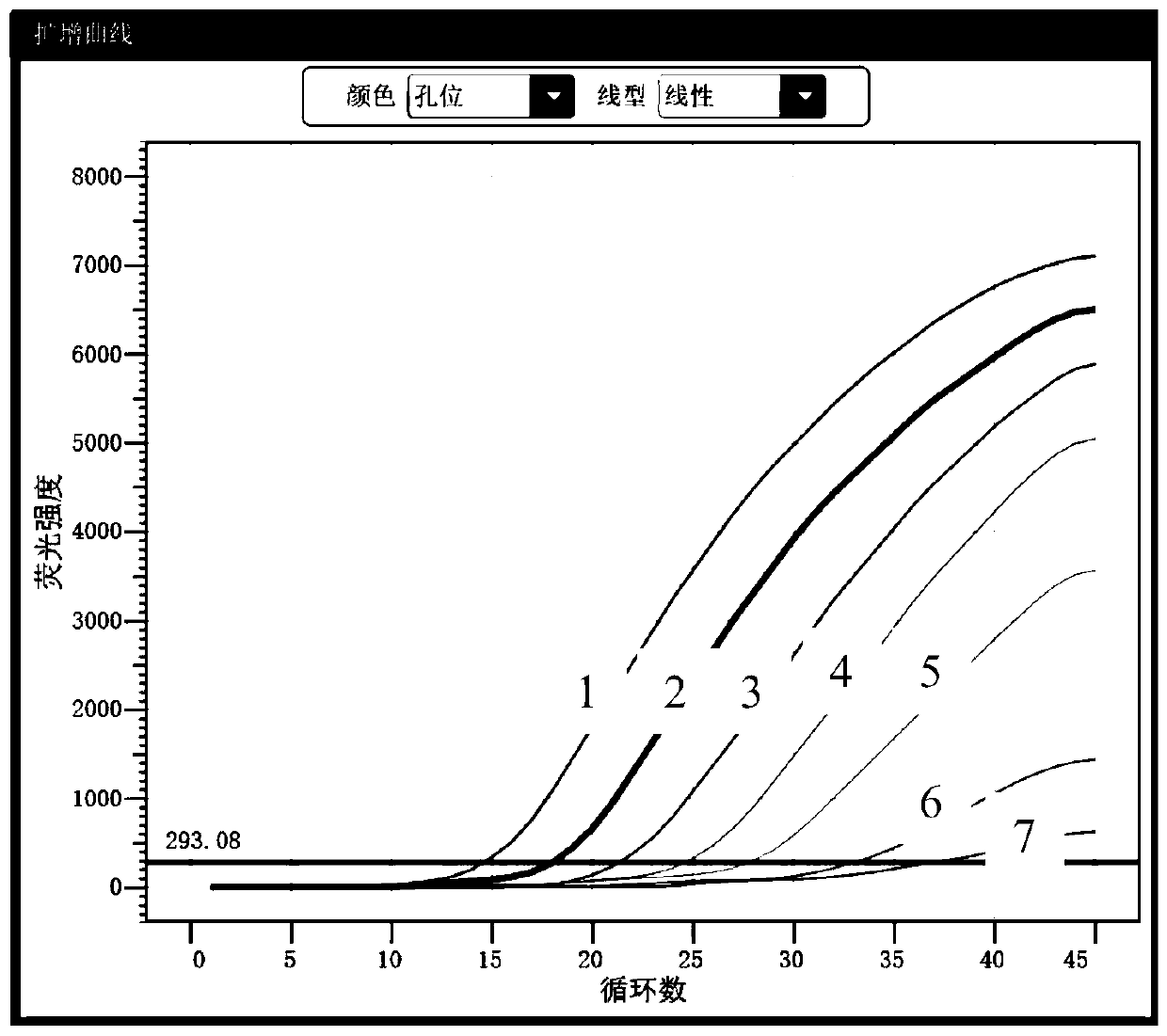
Trichomonas vaginalis and candida albicans two-channel fluorescence PCR detection method and kit thereof
ActiveCN102719529BAvoid samplingTest sample diversificationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFluorescenceCandida famata
The invention relates to primers and TaqMan probes used for carrying out two-channel fluorescence PCR detection of trichomonas vaginalis viruses and candida albicans viruses. The primers and the TaqMan probes are trichomonas vaginalis virus primers and trichomonas vaginalis virus TaqMan probes designed based on a trichomonas vaginalis virus conserved area and candida albicans virus primers and candida albicans virus TaqMan probes designed based on a candida albicans virus conserved area. Simultaneously, the primers and the TaqMan probes are used for detecting whether trichomonas vaginalis virus RNA and candida albicans virus DNA exist in a sample to be detected. The invention further comprises a detection method employing the primers and the TaqMan probes and a kit containing the primers and the TaqMan probes.
Owner:北京新沿线医药科技发展有限公司
Application of botanical medicinal composition in the preparation of gynecopathy treating medicine
InactiveCN1541659AImprove itchingGood pain reliefAnthropod material medical ingredientsAntipyreticDiseaseTraditional medicine
The present invention is Chinese medicine composition for treating women's diseases and its production process. The externally applied medicine is used in treating women's inflammation caused by trichomonas vaginalis, fungus and bacteria. The Chinese medicine composition contains honeysuckle, sessile stemona root, phellodendron bark and other plant medicine materials, borax and borneol.
Owner:LANZHOU FOCI PHARM CO LTD
Novel veterinary anti-inflammation agent and preparation method of same
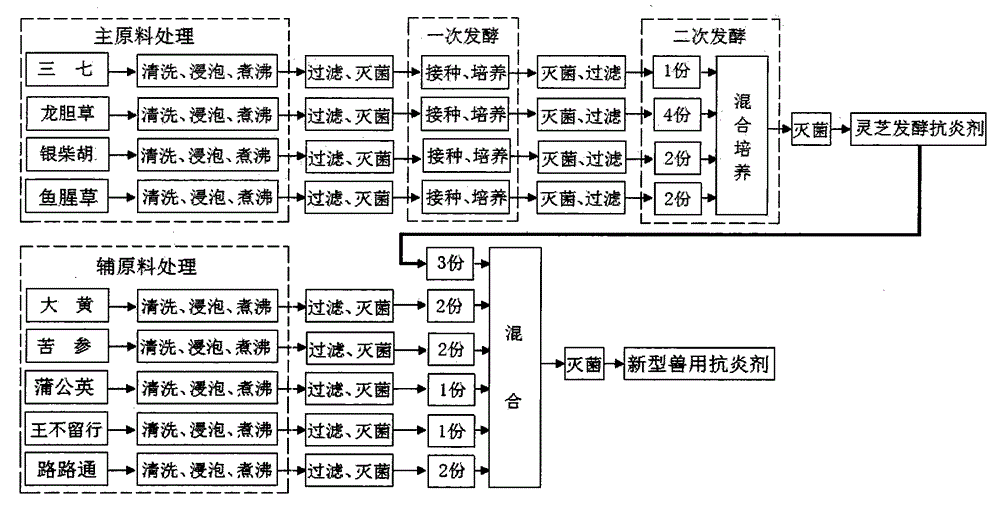
A novel veterinary anti-inflammation agent and a preparation method of the same. The multifunctional veterinary anti-inflammation agent is prepared by extracting effective components from following traditional Chinese medicine raw materials including: pseudo-ginseng, gentiana scabra, radix stellariae, herba houttuyniae, rhubarb, sophora flavescens, dandelion, cowherb seeds and liquidambar formosana and the like, by means of a bio-fermentation engineering technology and a bio-chemical engineering technology according to a special process and a special formula. The anti-inflammation agent can safely, high-effectively, quickly and synchronously kill six categories of pathogenic microorganisms including bacteria, fungus, viruses, mycoplasma, chlamydia and protozoons (including staphylococcus aureus, escherichia coli, candida albicans, herpes virus vaginalis, mycoplasma urealytium, chlamydia vaginalis, trichomonas vaginalis and the like). The anti-bacterial range of the anti-inflammation agent greatly exceeds a limit that conventional antibiotics only can kill and inhibit bacteria. The anti-inflammation agent is free of generation of polluting substances not only in production but also in use, is low in production cost, is good in effects and is free of toxic and side effects, can be used for replacing the antibiotics to eliminate damage on human body and livestock due to "antibiotic-milk" and "antibiotic-meat", can effectively prevent and treat inflammation ingenital tract and mammary gland of cattle, horses, sheep, pigs, dogs, wild animals and pets, and is very wide in market prospect.
Owner:YUNNAN MINGSHIDA SCI TECH CO LTD
Kit for quantitatively detecting trichomonas vaginalis by chemiluminiscence method and detecting method thereof
InactiveCN110487779AGood dispersionImprove bindingChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceColor/spectral properties measurementsAntigenQuantum yield
The invention provides a kit for quantitatively detecting trichomonas vaginalis by a chemiluminiscence method. In use, a trichomonas vaginalis antigen in a sample reacts with a reagent in the kit to generate a neutral avidin microsphere-capture antibody-antigen-detection antibody-acridinium ester compound; washing is carried out to remove substances which do not participate in the reaction; and when acridinium ester is in an alkaline H2O2 solution, molecules are attacked by hydrogen peroxide ions, unstable dioxane is generated, the dioxane is decomposed into CO2 and N-methyl acridone in an electron excited state, photons are emitted when acridinium ester returns to a ground state, and a light-emitting signal measuring instrument is used for measuring the light quantum yield for measurement. Meanwhile, a quantitative standard curve is fitted through a calibrator, and the concentration of trichomonas vaginalis is calculated by substituting the light signal measurement result of the sample into the quantitative standard curve. The kit provided by the invention is used for quantitative detection of trichomonas vaginalis, the sensitivity is high, the specificity is good, and the concentration of trichomonas vaginalis in the sample can be accurately detected.
Owner:江苏美克医学技术有限公司
An in-vitro trichomonas vaginalis treating vaginal suppository and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN1879628AHigh insecticidal rateGood curative effectSuppositories deliveryAntiparasitic agentsVaginal SuppositoryTrichomonas vaginalis
The invention relates to a suppository for treating vaginal trichomonas in vitro and its preparation, wherein the main compositions of the suppository include metronidazole 0.8-1.2 parts, dihydro-artemisinin 1.6-2.4 parts, cocoa bean grease 40-60 parts.
Owner:JIUJIANG UNIVERSITY +2
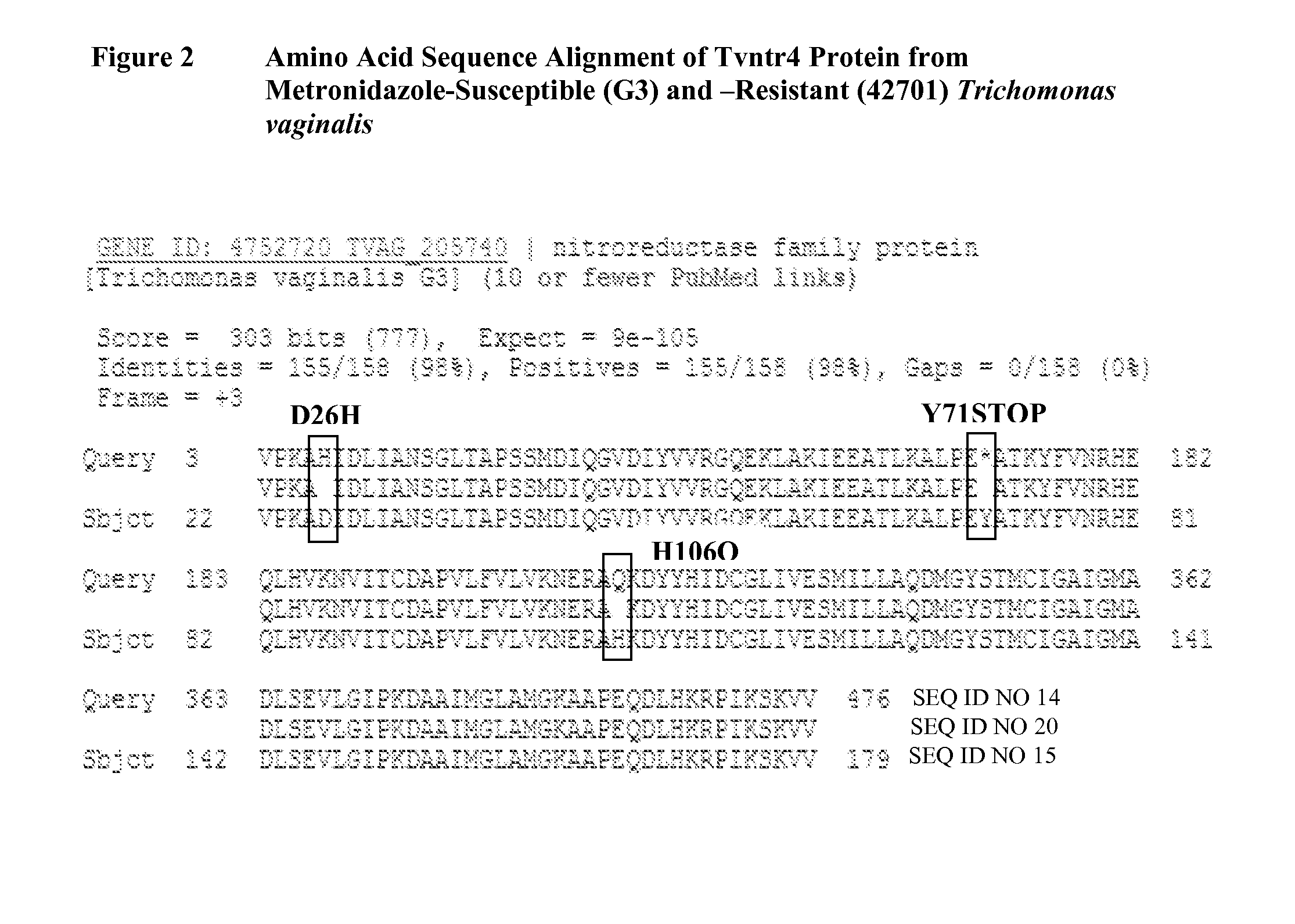
Metronidazole resistance in trichomonas vaginalis and single nucleotide polymorphisms
ActiveUS20130130253A1Reduce medical costsEffective patient treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideTrichomonascus
The present invention is directed to the discovery of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the presence of metronidazole-resistant Trichomonas vaginalis. The presence of G76C, C213G, or C318A (SNP) in tvntr 4 or the presence of A238T, G427C, or T476C (SNP) in tvntr6 provides a reliable biomarker for the presence of metronidazole-resistant Trichomonas vaginalis. The present invention further provides reagents used for detecting the SNPs to screen subjects for metronidazole resistance in Trichomonas vaginalis.
Owner:MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC LAB
Metronidazole resistance in trichomonas vaginalis and single nucleotide polymorphisms
ActiveUS8741563B2Effective treatmentReduction in repeated physician visitsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideBiomarker (petroleum)
The present invention is directed to the discovery of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the presence of metronidazole-resistant Trichomonas vaginalis. The presence of G76C, C213G, or C318A (SNP) in tvntr 4 or the presence of A238T, G427C, or T476C (SNP) in tvntr6 provides a reliable biomarker for the presence of metronidazole-resistant Trichomonas vaginalis. The present invention further provides reagents used for detecting the SNPs to screen subjects for metronidazole resistance in Trichomonas vaginalis.
Owner:MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC LAB
Multiplex detection of vulvovaginal candidiasis, trichomoniasis and bacterial vaginosis
Methods and compositions for detection of vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC), trichomoniasis and bacterial vaginosis (BV) are disclosed herein. In some embodiments, the presence or absence of VVC-associated Candida, Trichomonas vaginalis, and a plurality of BV-related bacteria in a sample is determined using multiplex nucleic acid-based testing methods.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com