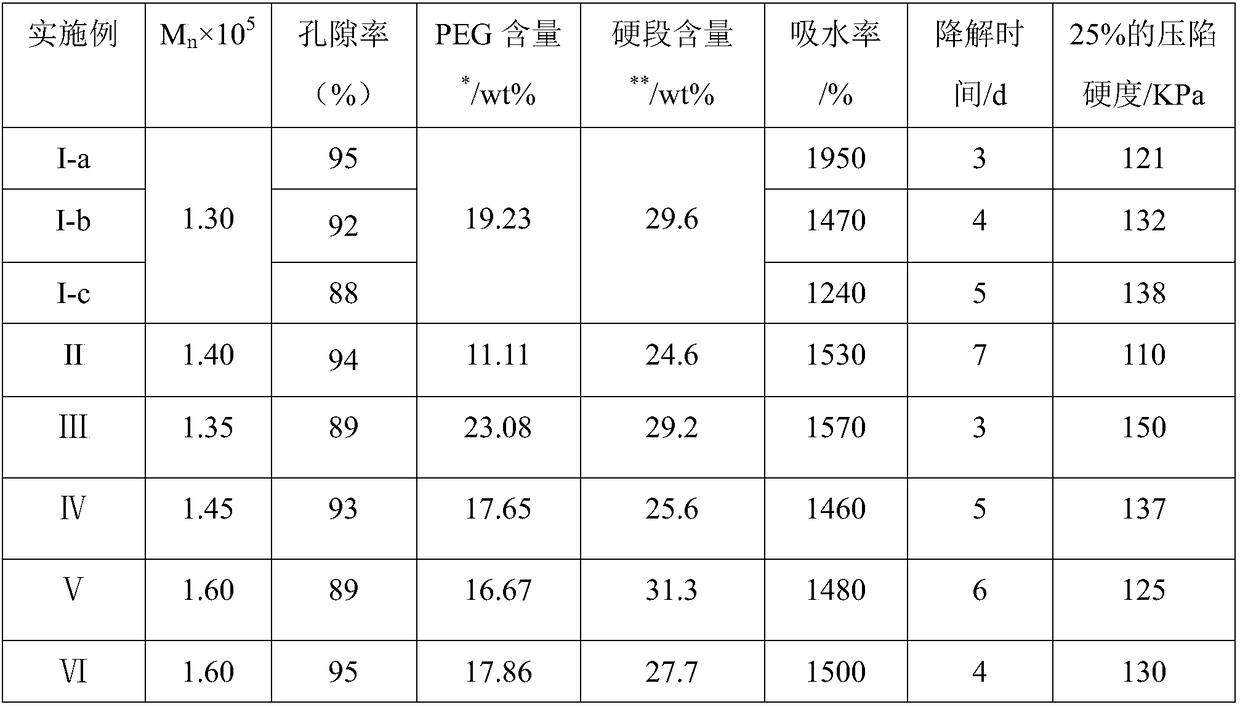
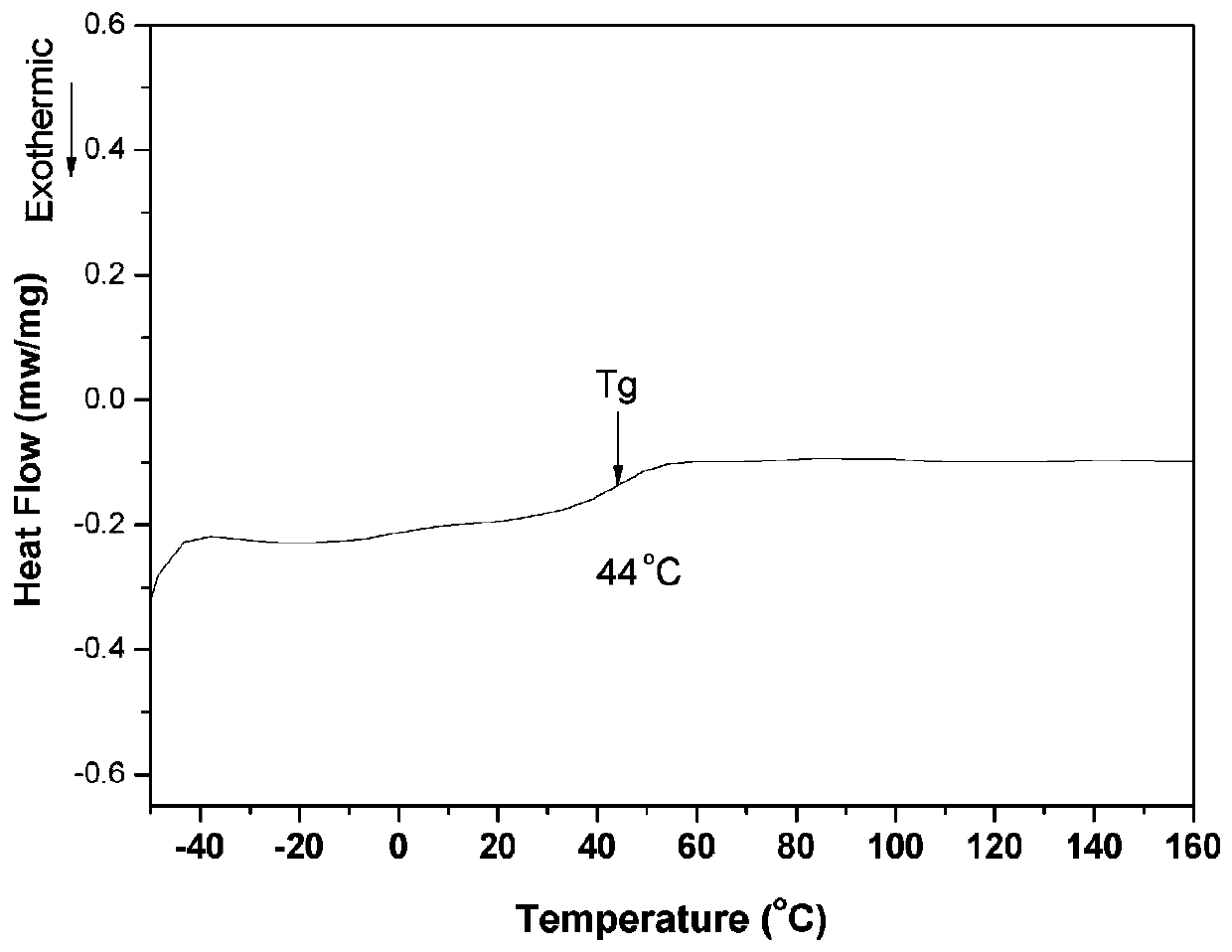
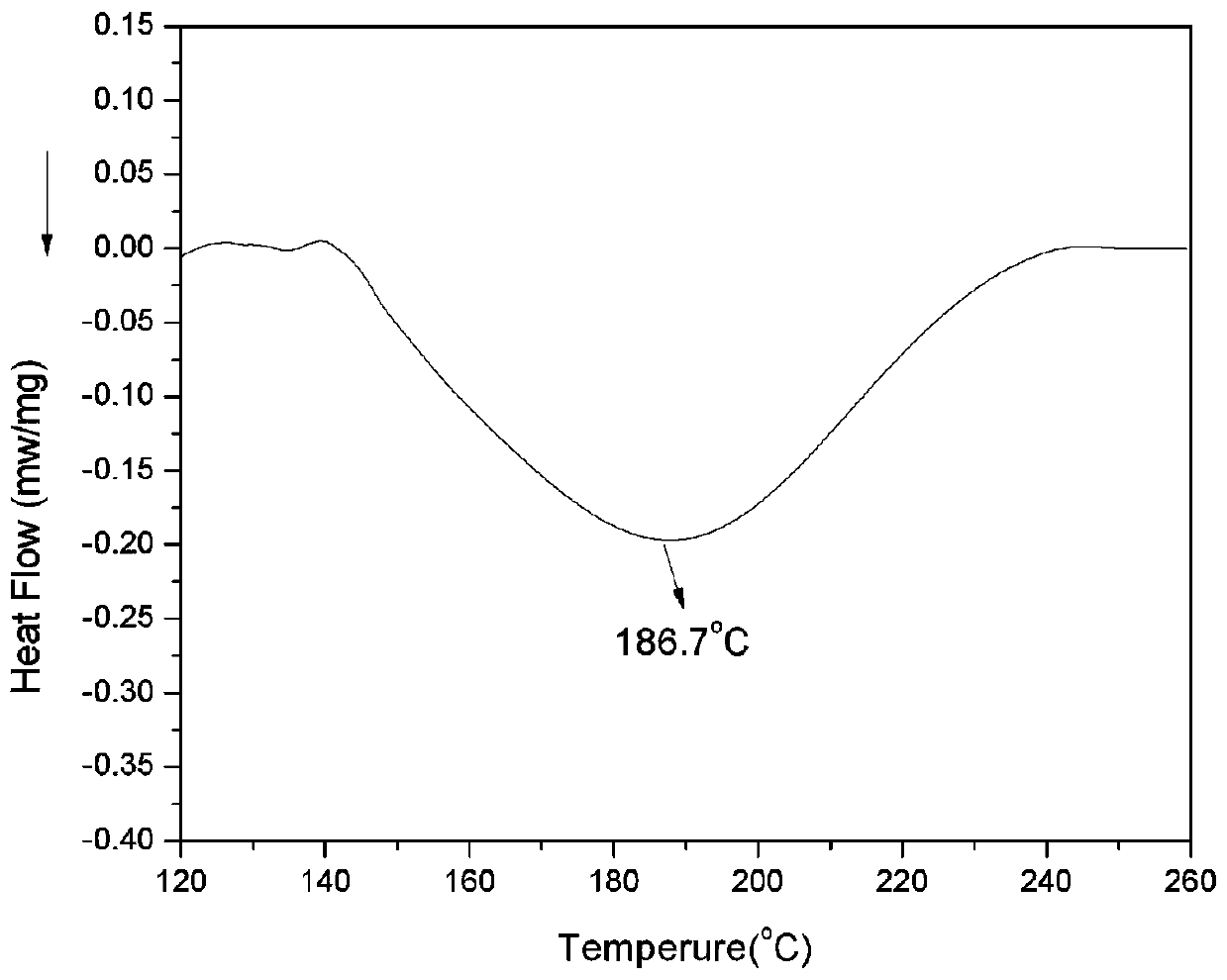
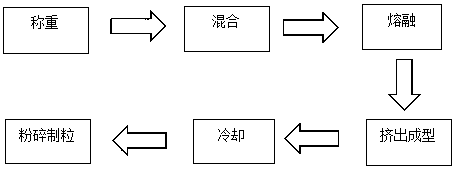
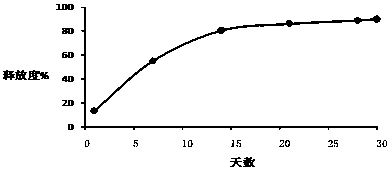
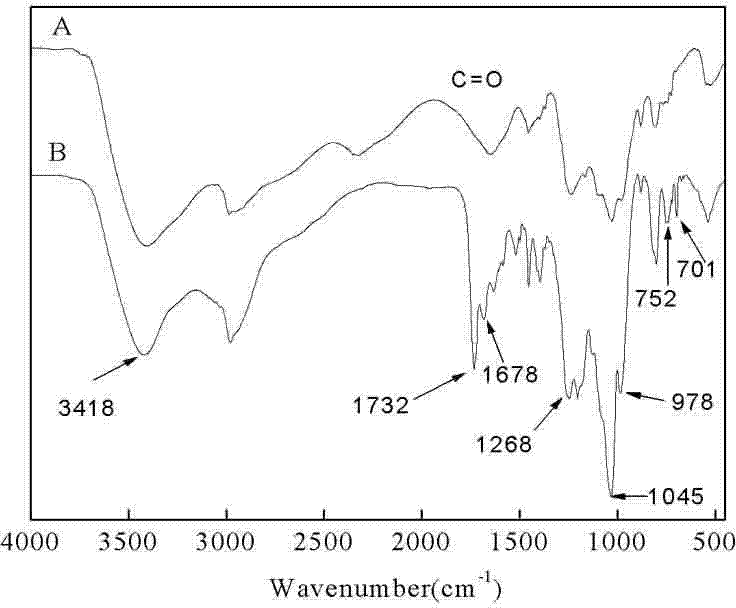
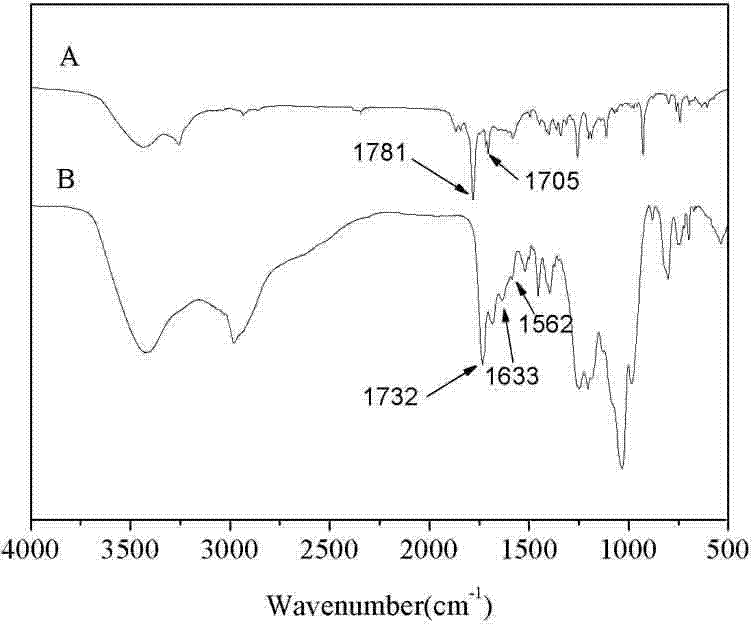
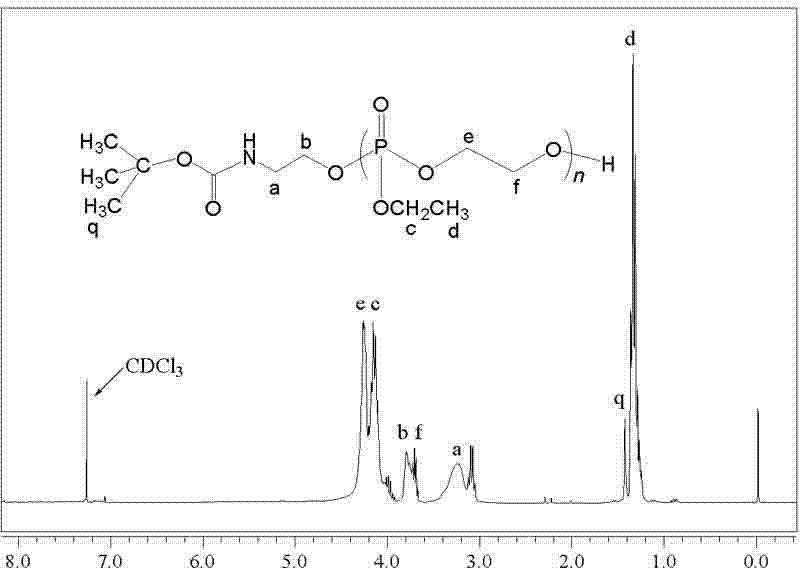
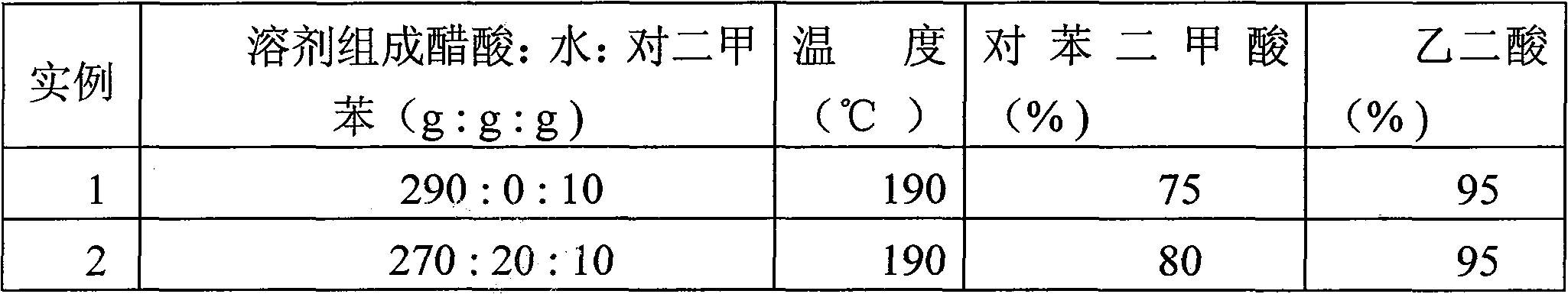
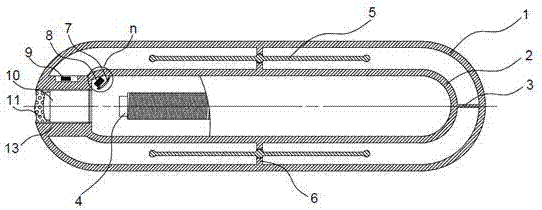
Patents
Literature
36results about How to "Adjust the degradation rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Porous active artificial bone and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a porous active artificial bone. In the porous active artificial bone, a calcium phosphate-based biological ceramic material is used as a matrix, and the porous active artificial bone comprises small pores, dense parts and directional pore channels and chelates with diphosphonate. A preparation method of the porous active artificial bone comprises the steps of preparing calcium phosphate precursor powder, compression molding a ceramic blank by using a pore-foaming agent, polyester fiber and the precursor powder, high temperature sintering into a calcium phosphate-based ceramic sintered body and forming the dense parts, the small pores distributed alternately; and immersing calcium phosphate-based ceramic sintered body in a diphosphonate solution to chelate with the diphosphonate so as to obtain the drug-loaded porous active artificial bone. The artificial bone provided by the invention has longitudinal directional pores and a porous structure suitable for osteoblast migration, propagation and growth metabolism, can slowly release small molecular drugs capable of promoting the growth of the osteoblast and inhibiting osteoclast, and is particularly suitable for the fields of treating bone defects of osteoporosis patients, dental restoration, and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN LANDO BIOMATERIALS
Bio-magnesium alloy with anti-bacterial function and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN107794424AWell mixedGuaranteed chemical activityAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyAnti bacterialBall mill
The invention relates to a bio-magnesium alloy with an anti-bacterial function and a method for manufacturing the bio-magnesium alloy by utilizing the laser selective smelting technology. The bio-magnesium alloy with the anti-bacterial function consists of a bio-magnesium alloy substrate and nanometer TiO2 distributed in the bio-magnesium alloy substrate; and in the bio-magnesium alloy with the anti-bacterial function, the mass percentage of the nanometer TiO2 is 3-7%. The manufacturing method comprises the steps that nanometer TiO2 powder and bio-magnesium alloy powder are prepared accordingto a designed ratio; the prepared powder is placed in a ball mill; in a protective atmosphere, mixed powder is obtained through high-speed ball milling; and then in the protective atmosphere, the bio-magnesium alloy with the anti-bacterial function is manufactured through laser selective smelting. The bio-magnesium alloy manufactured with the method has excellent anti-bacterial performance and cyto-compatibility, improved mechanical performance and a proper degradation rate; and the bio-magnesium alloy is advantaged compared with a current material when serving as an implant material.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Biological magnesium alloy with corrosion resistant function and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107739940AImprove corrosion resistancePlay a role in corrosion resistanceSelective laser meltingAlcohol
The invention discloses biological magnesium alloy with a corrosion resistant function. The biological magnesium alloy is prepared from a biological magnesium alloy matrix and graphene oxide, whereinthe graphene oxide is distributed on the grain boundary of the biological magnesium alloy matrix, and the graphene oxide wraps biological magnesium alloy grains so as to form a second phase of a nanohoneycomb structure. The invention further discloses a preparation method. The preparation method comprises the following steps of (1) respectively putting GO powder and biological magnesium alloy powder in absolute ethyl alcohol according to the design proportion for ultrasonic agitation so as to obtain a GO suspension and a biological magnesium alloy suspension; (2) slowly adding the GO suspension to the biological magnesium alloy suspension, continuing to perform ultrasonic agitation so as to obtain a mixed suspension, and performing vacuum filtration and drying treatment on the mixed suspension so as to obtain mixed powder with uniform dispersion; and (3) performing selective laser melting on the mixed powder in the protective atmosphere so as to prepare the biological magnesium alloywith the corrosion resistant function. According to the biological magnesium alloy with the corrosion resistant function, the second phase of the nano honeycomb structure constructed by utilizing GO can be used as a shield so as to isolate the biological magnesium alloy from body fluid, so that a galvanic corrosion effect of a conventional second phase is avoided, and the corrosion resistance is improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for preparing corrosion-resistant biological magnesium alloy
InactiveCN107760900AImprove degradation performanceIncreased number of grain boundariesAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyCorrosion resistantCrystallite
The invention discloses a method for preparing corrosion-resistant biological magnesium alloy. The method comprises the following steps: (1) putting calcium oxide powder and biological magnesium alloypowder in a specific ratio into a ball mill, and performing ball milling under protective atmosphere so as to obtain mixed powder; and (2) performing selective laser melting under protective atmosphere by taking the mixed powder as a raw material so as to prepare the corrosion-resistant biological magnesium alloy. In the preparation process, the laser power is controlled to be 60-90W, the scanning speed is controlled to be 100-500mm / min, and the spot diameter is controlled to be 40-100mu m. According to the method disclosed by the invention, calcium oxide is added to the biological magnesiumalloy through selective laser melting so as to generate an Mg / Al-Ca phase with a smaller volume; and by utilizing the characteristic of high setting rate of selective laser melting, the volume of thesecond phase of Mg / Al-Ca is refined, and simultaneously, the continuity of Mg / Al-Ca is improved, thereby coating magnesium alloy grains to form continuous second phase protection layers to prevent thecorrosion of body fluid.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Biological magnesium alloy with mold resistance and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107739939ASustained and highly effective antibacterial effectEvenly distributedAdditive manufacturing apparatusBall millLaser
The invention discloses biological magnesium alloy with mold resistance. The biological magnesium alloy is composed of a biological magnesium alloy matrix and nano-silver evenly distributed in the magnesium alloy matrix, wherein the mass percent of nano-silver is 0.5-1.5%, preferentially, 0.75-1.25% and is 1% further preferentially. The invention further discloses a method for preparing the biological magnesium alloy with mold resistance. The method comprises the steps that 1, a specific amount of nano-silver powder and magnesium alloy powder are subjected to ball milling in a ball milling machine to obtain evenly-mixed mixed powder; and 2, the mixed powder is used as raw materials, and the biological magnesium alloy with mold resistance is prepared through laser selective melting. The nano-silver is added into the magnesium alloy matrix in a second phase mode, and mold resistance exists in the whole degradation process of the biological magnesium alloy.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
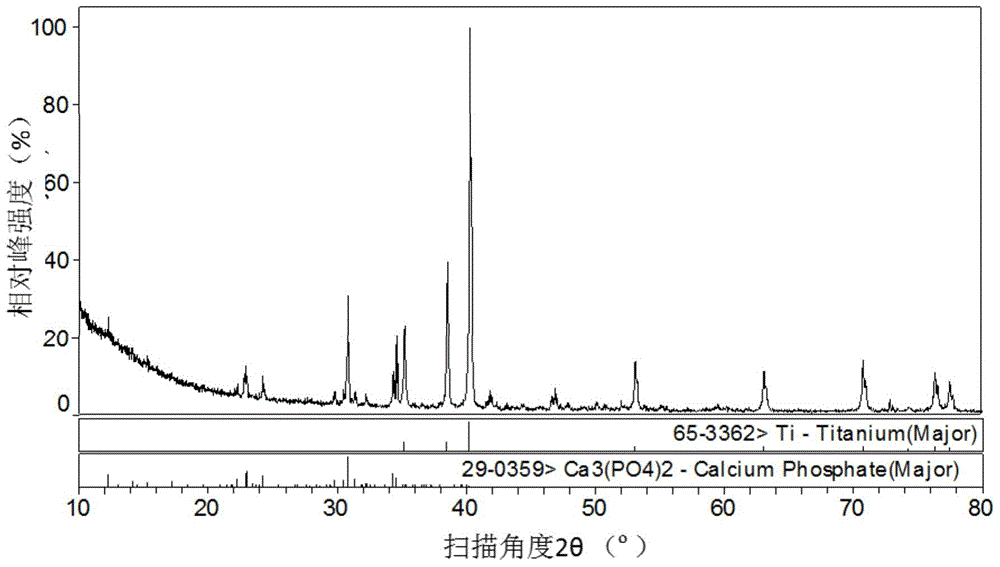
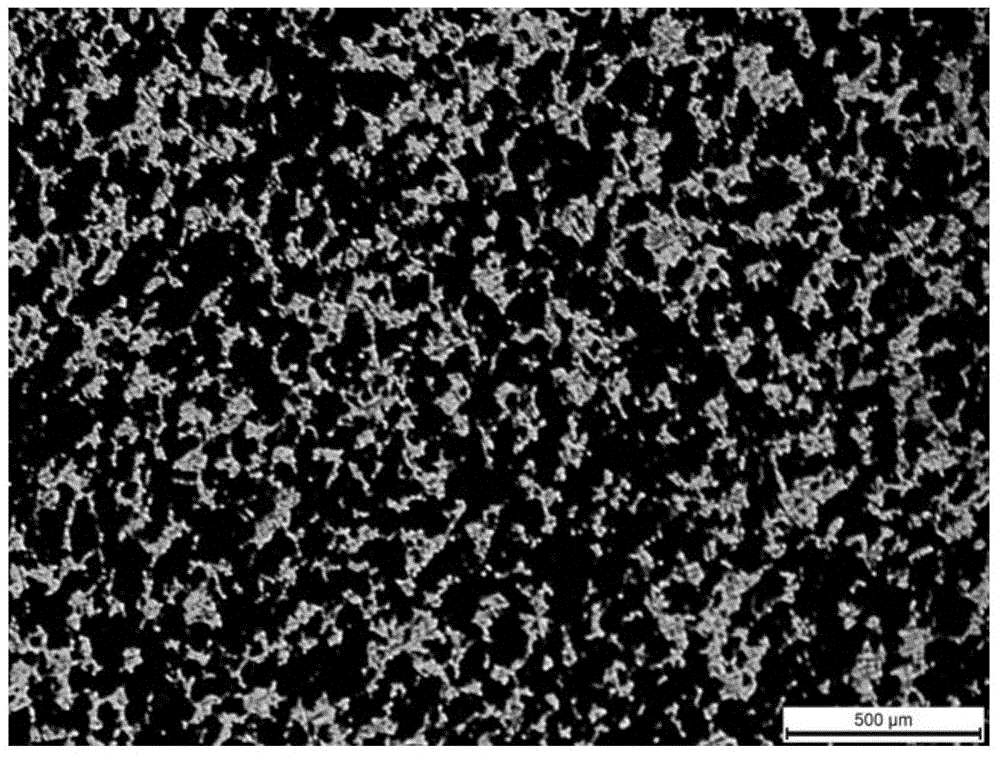
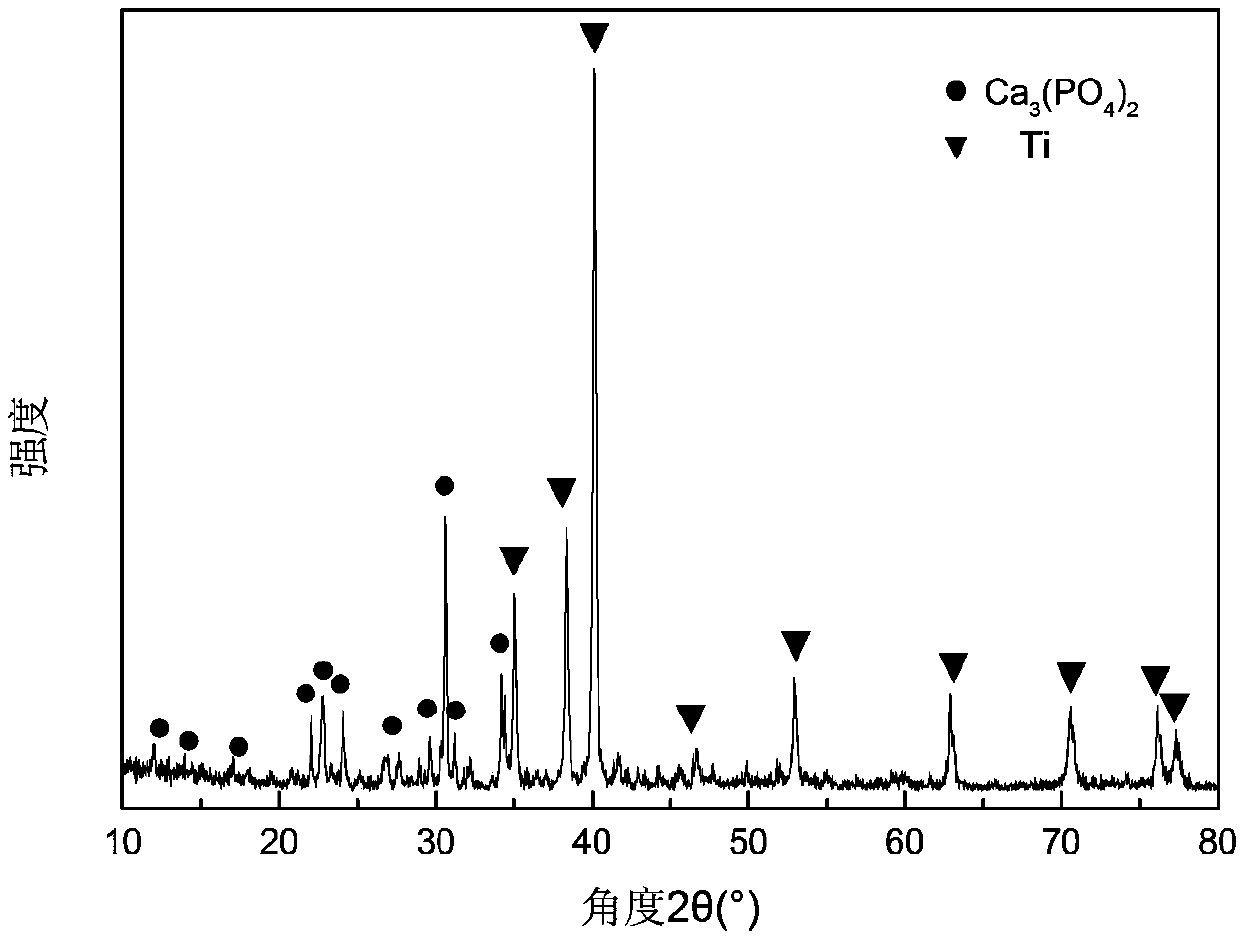
Titanium/tricalcium phosphate composite applied to bone implanting material and preparation method of titanium/tricalcium phosphate composite
InactiveCN104941003AGood mechanical propertiesReduce intensityProsthesisMass ratioTri calcium phosphate
The invention discloses a titanium / tricalcium phosphate composite applied to a bone implanting material. The titanium / tricalcium phosphate composite adopts a continuous network structure, tricalcium phosphate in the composite accounts for 10-50 wt% of the mass of the composite and is alpha-TCP or a mixture of alpha-TCP and beta-TCP, and the mass ratio of alpha-TCP to beta-TCP is (1-9): 1. A preparation method of the titanium / tricalcium phosphate composite comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a solution; (2) preparing tricalcium phosphate; (3) mixing and ball-milling titanium and tricalcium phosphate, and then preparing the titanium / tricalcium phosphate composite by the spark plasma sintering method. The titanium / tricalcium phosphate composite adopts a metal and ceramic continuous network structure, and has not only a favorable mechanical property, strength and an elastic modulus, which are close to human bones, but also excellent bioactivity and degradability.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for producing acetic acid by liquid phase catalytic degradation of waste polypropylene plastic
InactiveCN101279906AImprove oxidative degradation processMild reaction conditionsCarboxylic preparation by oxidationSolventPolypropylene
The invention discloses a method to produce acetic acid from waste polypropylene plastic through liquid-phase catalytic degradation. The method takes soluble cobalt salt, manganic salt, zirconium salt, cerium salt, bromide and organic base as activator(zirconium salt and cerium salt are used as catalyst accelerator) and mixes the activator with waste polypropylene plastic and inert solvent proportionally; then the waste polypropylene is oxidized and degraded by oxygen-containing gas to produce acetic acid under 100-350 DEG C and 0.4-.0 MPa. The reaction mother solution in the method can be recycled to the system for repeated use. The reaction is of mild condition, fast speed and high conversion rate; the method not only solves the social problem of white pollution, but also produces acetic acid which is a kind of fine chemical material to get more economic benefits; the degradation cost is low and the degraded products are of high added value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
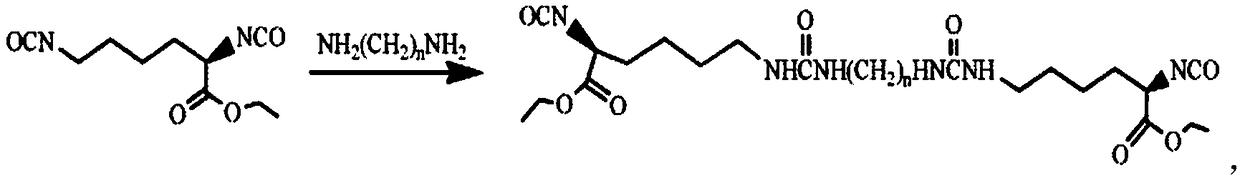
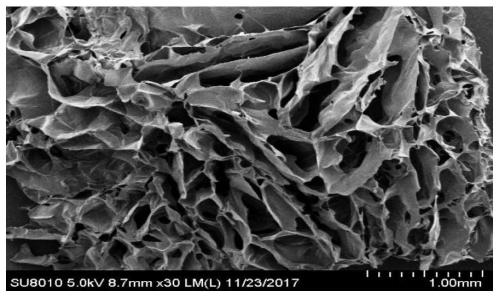
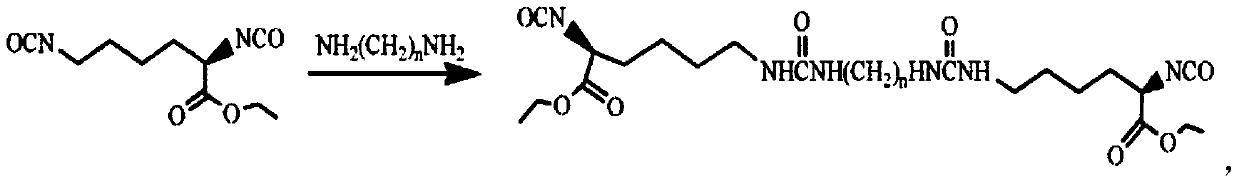
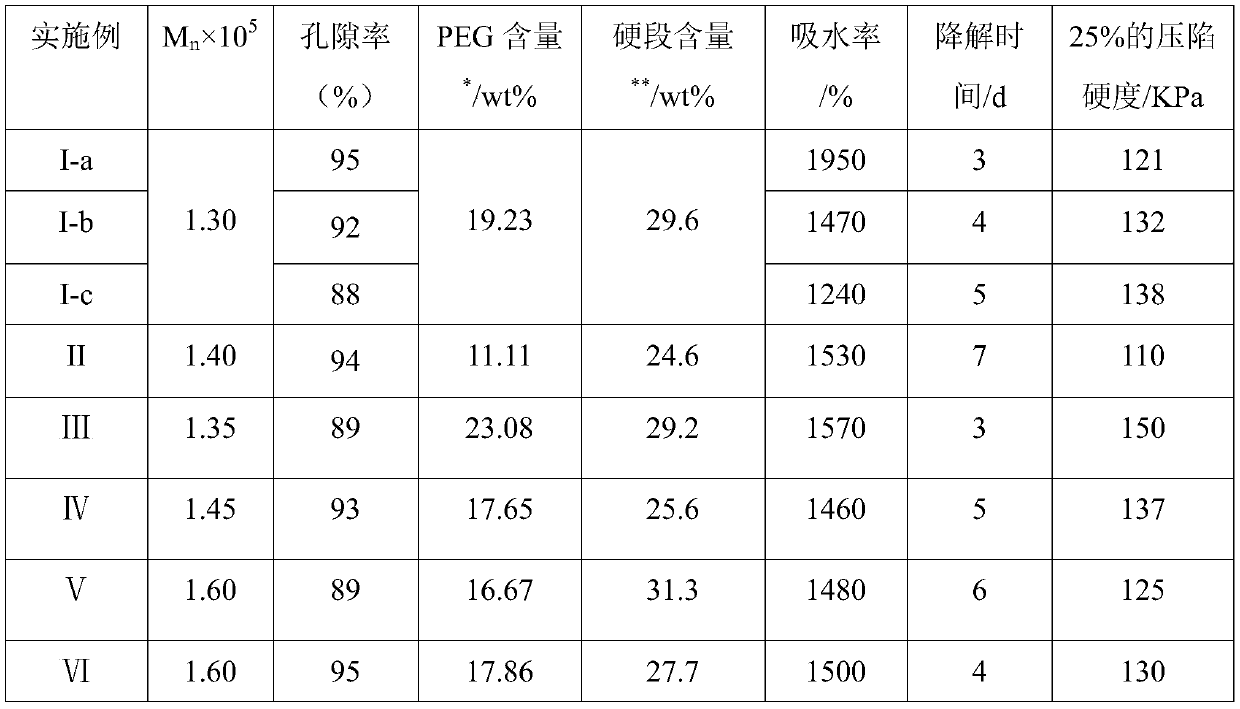
Biodegradable high-strength polyether ester type polyurethane urea foam and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108586293AEasy to purifyEasy to controlUrea derivatives preparationSurgical adhesivesLysine diisocyanatePolymer science
The invention relates to the technical field of biodegradable materials, specifically to a preparation method for a fully-synthetic biodegradable high-strength hemostatic foam applicable to hemostasisof cavities like ears and noses of human or animals. The biodegradable high-strength polyether ester type polyurethane urea foam is prepared from a polyether ester type polyurethane urea material through freeze-molding, wherein the polyether ester type polyurethane urea is prepared through chain extension of dihydroxy-terminal triblock prepolymer by using diisocyanate with a urea structure as a chain extender; the polyurethane urea material has a number average molecular weight of 1.1 x 105 to 1.8 x 105 and a dispersion coefficient of 1.18 to 1.51; and the diisocyanate chain extender containing the urea structure is selected from the group consisting of L-lysine diisocyanate-1,4-butadiamine-L-lysine diisocyanate and L-lysine diisocyanate-1,6-hexane diamine-L-lysine diisocyanate.
Owner:济南羽时信息科技有限公司
Graphene-modified starch multifunctional composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108384161AThermo-oxidative degradationInhibition affects the disintegration effectMaltitolPolyethylene glycol
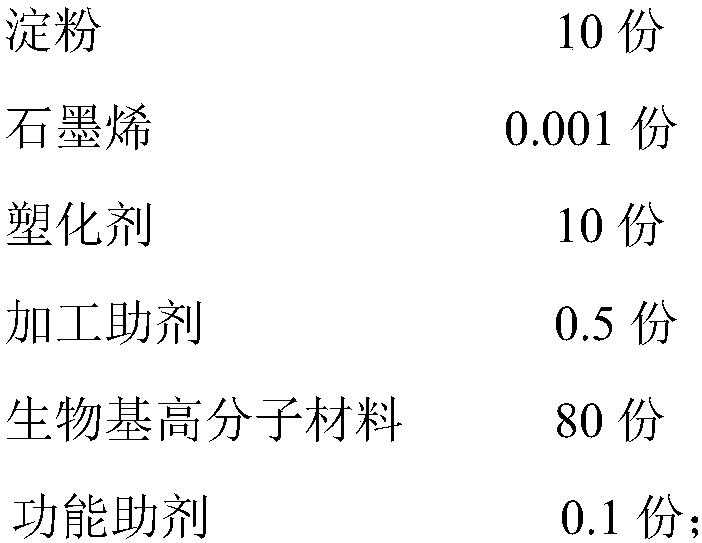
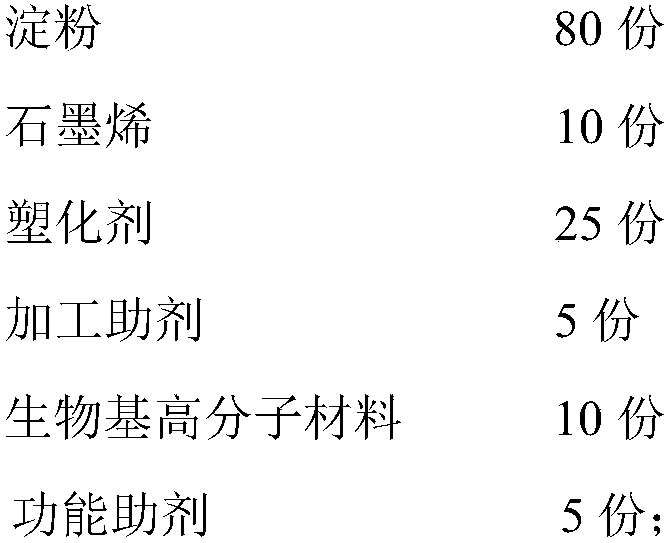
The invention relates to a graphene-modified starch multifunctional composite material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of starch material modification. The graphene-modified starch multifunctional composite material is prepared from the following raw materials of: in parts by weight, 10-80 parts of starch, 0.001-10 parts of graphene, 10-25 parts of plasticizers, 0.5-5 parts of a processing assistant, 80-10 parts of a bio-based polymer material and 0.1-5 parts of functional assistants, wherein the plasticizers are more than one selected from purified water,sodium alginate, ethylenebisformamide, glycerin, propylene glycol, ethylene glycol, polyethylene glycol, sorbitol, maltitol, chitosan, chitin, pentaerythritol, 1,4-butanediol and the like. The graphene-modified starch multifunctional composite material has complete biodegradability, and the invention provides the simple and easy preparation method, so that industrial production is facilitated.
Owner:朱春英 +1
Biomedical magnesium alloy with dual corrosion resistance and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109014184AImprove corrosion resistanceIsolated contactAdditive manufacturing apparatusTransportation and packagingTin dioxideSelective laser melting
The invention relates to a biomedical magnesium alloy with dual corrosion resistance and a preparation method thereof. The biomedical magnesium alloy with the dual corrosion resistance is composed ofa biological magnesium alloy matrix, inner layer graphene and outer layer stannic oxide, wherein the inner layer graphene and the outer layer stannic oxide are evenly distributed on a magnesium alloycrystal boundary, dual resistance is provided through the two-layer structure of graphene and stannic oxide, and thus the degradation resistance of the magnesium alloy is improved. The preparation method comprises the steps that firstly, magnesium alloy powder is soaked in an NaOH solution for etching, so that electronegative hydroxyl is formed on the particle surface; then the powder is soaked ina PDDA solution so that the particle surface can be electropositive; then the powder is soaked in a graphene oxide solution to obtain a PDDA-graphene oxide wrapping layer, and then the powder is soaked in an alkalescent stannic chloride aqueous solution, so that magnesium alloy powder wrapped with a graphene-stannic oxide two-layer structure is obtained; and finally, under a protective atmosphere, the biomedical magnesium alloy with excellent corrosion resistance is prepared through selective laser melting. According to the biomedical magnesium alloy with the dual corrosion resistance and thepreparation method thereof, magnesium alloy grains are wrapped with the graphene-stannic oxide two-layer structure so that a two-layer protection shield can be achieved to isolate contact between themagnesium alloy and a corroding medium, and the corrosion resistance is improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Degradable epoxy resin and preparation method thereof
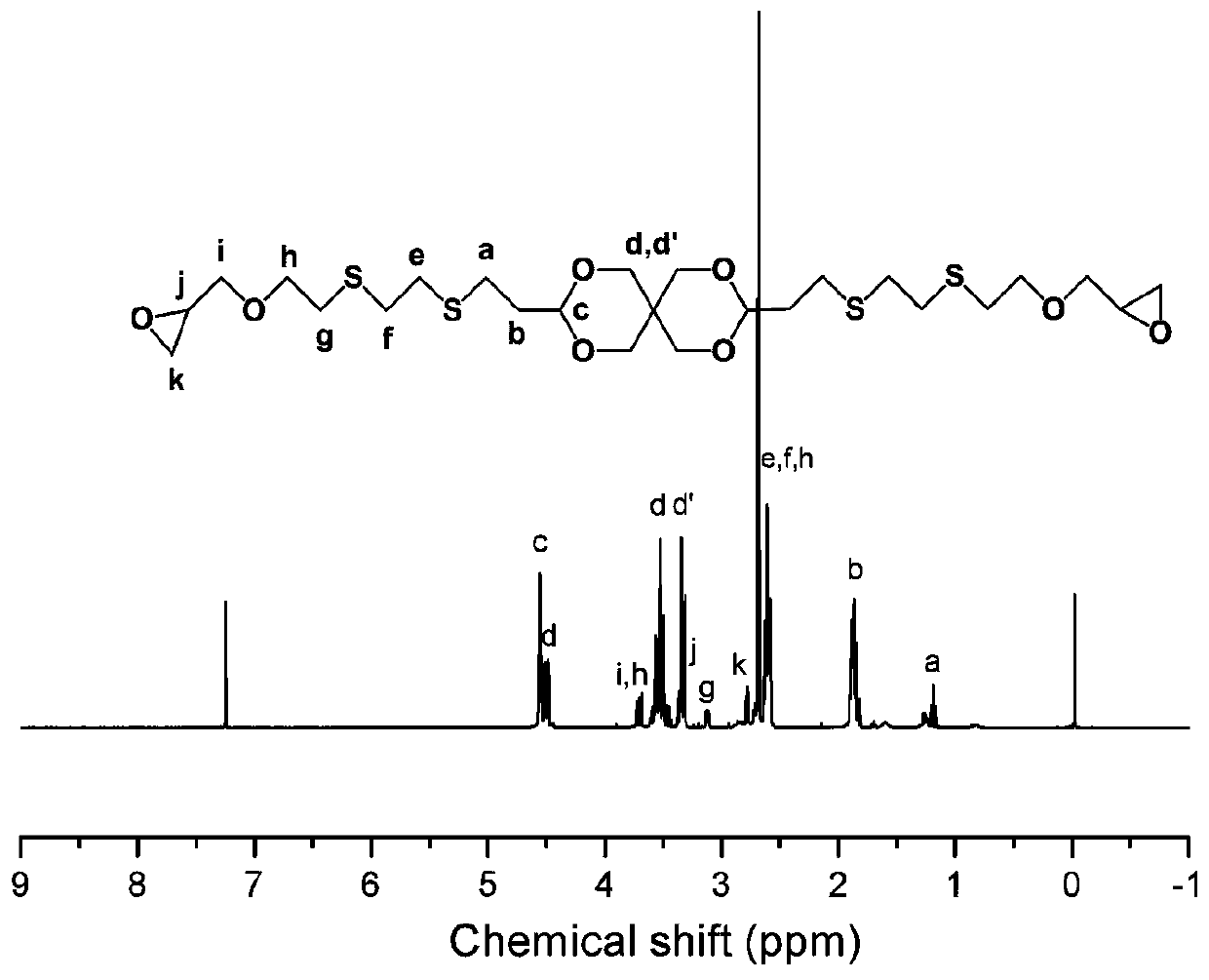
The invention belongs to the field of new materials, and particularly discloses a degradable epoxy resin and a preparation method thereof. The method is characterized in that a sulfydryl-terminated intermediate compound containing a spiro structure and the epoxy resin containing the spiro structure are synthesized through double sulfydryl-alkene addition reactions, and the molecular weight of theepoxy resin is about 600-5000 g / mol. The cured epoxy resin containing the spiro structure can be completely degraded within 36 h under an acidic condition at a temperature of above 40 DEG C. The method has the advantages of simple process, and rapidness in reaction, and the product has a high reaction activity, can be completely degraded, and is expected to be applied to the fields of epoxy resin-toughened and carbon fiber-reinforced composite materials.
Owner:TECHSTORM MATERIAL TECH SHANGHAI CO LTD
A kind of triptorelin sustained-release microparticles and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105267153BQuality assuranceStable physical and chemical propertiesPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMedicineTriptorelin
The invention relates to drug slow-release microparticles, in particular to triptorelin sustained-release microparticles and a preparation method thereof. The composition includes the following components by weight percentage: 0.5%-20% of triptorelin, 79%-99% of PLGA, and 0.1%-1% of poloxamer. The preparation method of the above-mentioned triptorelin sustained-release microparticles of the present invention comprises mixing each component and sending it into a hot-melt extruder, where heating and melting, extrusion and low-temperature pulverization are carried out. The praline sustained-release microparticles of the present invention have good shape, high encapsulation efficiency of the microparticles, good drug loading capacity and stable release. The synthesis process is simple, the product itself is non-toxic, and the product after degradation is non-toxic and stable in quality.
Owner:SHANGHAI SOHO YIMING PHARMA
Nanometer carbon micro-crystal modified polylactic acid-based orthopedic material and method for preparing same
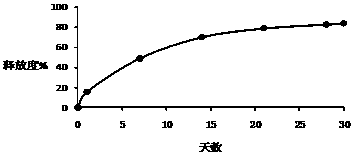
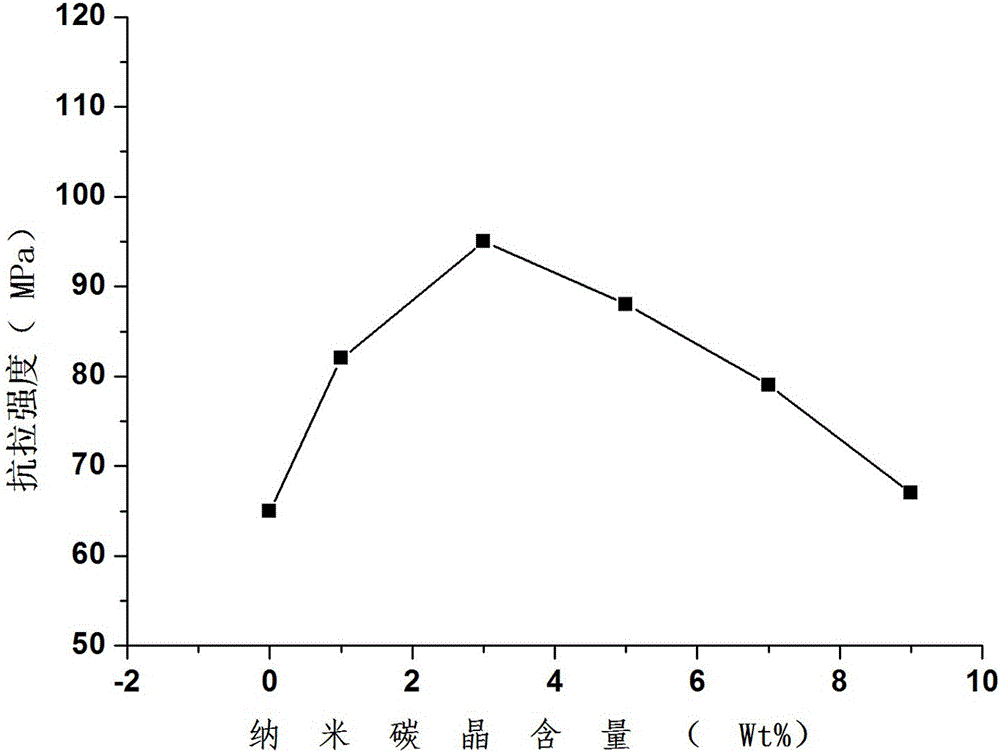
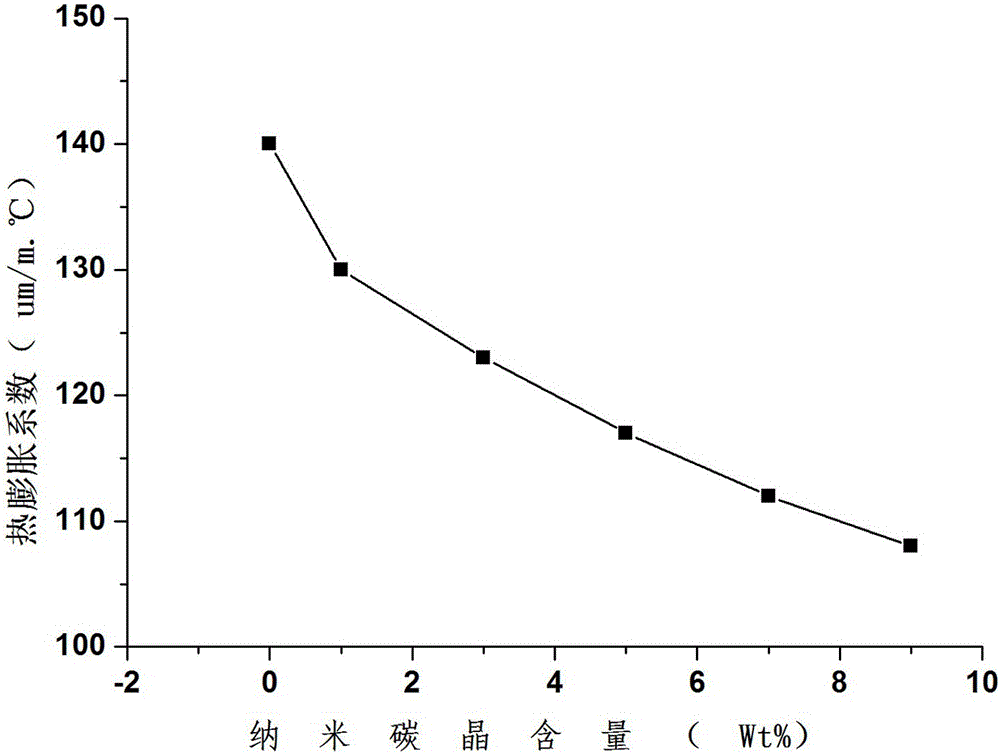
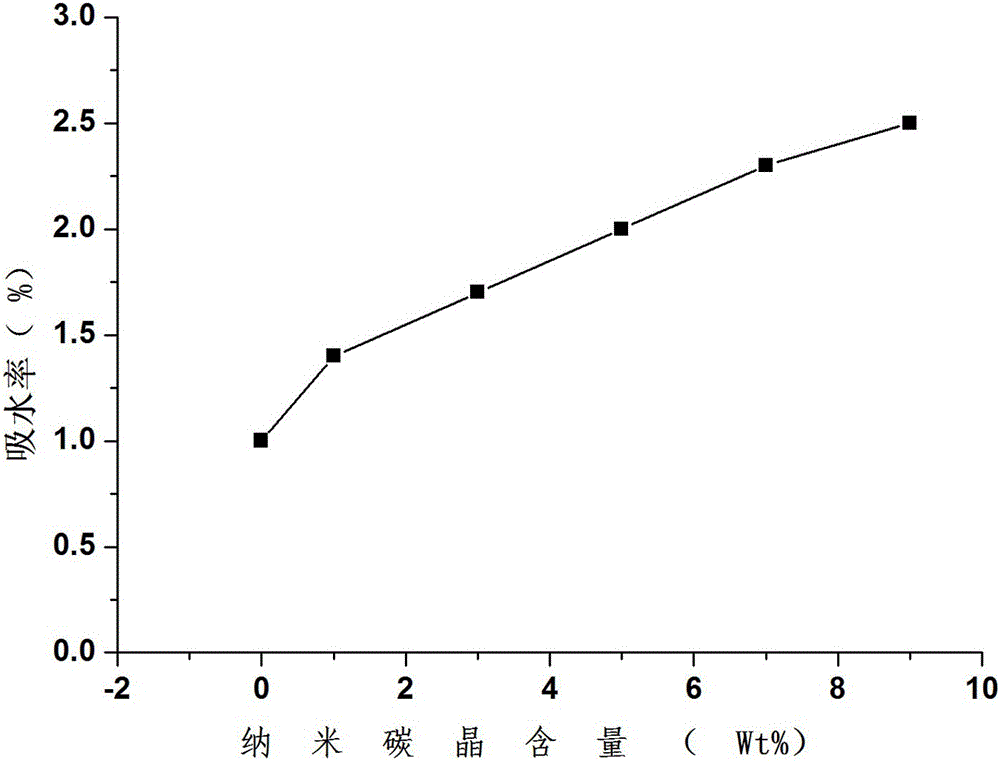
InactiveCN106806944AHigh tensile strengthImprove water absorptionPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationBiological bodyLactide
The invention belongs to the field of preparation of orthopedic materials, and particularly relates to a nanometer carbon micro-crystal modified polylactic acid-based orthopedic material and a method for preparing the same. The nanometer carbon micro-crystal modified polylactic acid-based orthopedic material is made of raw materials including, by weight, 89-98 wt% of lactide, 0.3-2 wt% of catalysts and 1-10 wt% of nanometer carbon micro-crystals. The nanometer carbon micro-crystal modified polylactic acid-based orthopedic material and the method have the advantages of high tensile strength and organism affinity and good dimensional stability.
Owner:HENAN YUXING MICRON DIAMOND CO LTD
Synthesis method of poly-benzyl L-glutamate/ethyl polyphosphate block copolymer
ActiveCN102731777AGood water solubilityAdjust the degradation ratePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolymer sciencePhosphoric acid
The invention relates to a synthesis method of a poly-benzyl L-glutamate / ethyl polyphosphate block copolymer. The technical scheme is as follows: the synthesis method comprises the following steps: respectively dissolving moderate amino-terminated ethyl polyphosphate and benzyl L-glutamate amino acid anhydride into CH2Cl2, mixing, stirring and reacting at room temperature for 12-48 hours, after reaction is completed, dropping a product into diethyl ether to precipitate, standing at 2 DEG C for 12-18 hours, filtering, precipitating at 30 DEG C, and drying in vacuum to obtain a target product. Through the invention, the amphiphilic poly-benzyl L-glutamate / ethyl polyphosphate block copolymer is obtained, a micelle with a hydrophobic core and a hydrophilic shell is self-assembled in aqueous solution, a hydrophobic medicine molecule is assembled in the hydrophobic core, the circulating time of the medicine in the blood is improved, and the poly-benzyl L-glutamate / ethyl polyphosphate block copolymer has good application prospect in the biomedical field of controlled release of the medicine, targeted medicine transfer and the like.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
A biomedical magnesium alloy with double corrosion resistance and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109014184BImprove corrosion resistanceIsolated contactAdditive manufacturing apparatusTransportation and packagingMg alloysCorrosion resistant
The invention relates to a biomedical magnesium alloy with dual corrosion resistance and a preparation method thereof, which is composed of a biomagnesium alloy substrate, an inner layer of graphene and an outer layer of tin dioxide uniformly distributed on the grain boundaries of the magnesium alloy, and uses graphene and The double-layer structure of tin dioxide provides double resistance, thereby improving the degradation resistance of magnesium alloys. First, the magnesium alloy powder is immersed in NaOH solution for etching to form negatively charged hydroxyl groups on the surface of the particles; then immersed in PDDA solution to positively charge the surface of the particles; Then immerse in the graphene oxide solution to obtain the PDDA-graphene oxide coating layer, and then immerse in the weakly alkaline tin chloride aqueous solution to obtain the magnesium alloy powder wrapped by the graphene-tin dioxide double-layer structure; finally, under the protective atmosphere, pass Preparation of biomedical magnesium alloy with excellent corrosion resistance by selective laser melting. The present invention utilizes the graphene-tin dioxide double-layer structure to wrap the magnesium alloy crystal grains, and serves as a double-layer protective shield to isolate the contact between the magnesium alloy and the corrosive medium, thereby improving the corrosion resistance.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Process for preparing terephthalic acid and ethane diacid by degrading waste polyethylene glycol terephthalate plastic
InactiveCN101284777BSolve pollutionPromote oxidative degradationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationReaction rateOrganic base
The invention discloses a method for producing diethylene glycol terephthalate and oxalic acid by degrading the waste polyethylene glycol terephthalate plastic. The method adopts soluble cobalt salt, manganese salt, zirconium salt, cerium salt and bromide and organic base as the catalysts (zirconium salt and cerium salt as the promoters), paraxylene as the pro oxidant, the catalysts and the pro oxidant are mixed with waste PET plastic and indifferent solvent proportionally, and under the conditions of the temperature of 100 to 350 DEG C and the pressure of 0.4 to 4.0 MPa, oxidative degradation is performed to the waste PET by adopting the gas containing oxygen molecule to produce diethylene glycol terephthalate and oxalic acid. The reaction conditions are mild; the reaction rate is high; the conversion rate is high; the method has the social benefit to solve the problem of white pollution; the diethylene glycol terephthalate and oxalic acid, and other fine chemically raw materials can be produced to obtain higher economic benefit; and the method has the advantages that the degradation cost is low, and the added value of the degradation products is high, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Titanium/tricalcium phosphate/titanium mesh composite material for bone implantation material, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106983911AImprove mechanical propertiesHigh compressive strengthTissue regenerationProsthesisNetwork structureTri calcium phosphate
The invention provides a titanium / tricalcium phosphate / titanium mesh composite material for a bone implantation material. The titanium / tricalcium phosphate / titanium mesh composite material has a continuous network structure, wherein a mass ratio of titanium powder to tricalcium phosphate in the composite material is 5:5-8:2, and the titanium mesh accounts for 10-20% of the mass of the composite material. The invention further provides a preparation method of the composite material. The preparation method comprises: adding a calcium salt solution into a phosphate solution in a dropwise manner, carrying out stirring, centrifuging or suction filtering separation to obtain a precipitate, drying and calcining the precipitate, grinding to obtain alpha-TCP powder, mixing the alpha-TCP powder and titanium powder to obtain titanium / tricalcium phosphate mixed powder, loading the titanium / tricalcium phosphate mixed powder into a titanium mesh skeleton, and performing spark plasma sintering to produce the titanium / tricalcium phosphate / titanium mesh composite material. According to the present invention, the prepared titanium / tricalcium phosphate / titanium mesh composite material has the continuous network structure of the metal and the ceramic, and has advantages of excellent mechanical property, elastic modulus close to human bone, excellent biological activity, and excellent degradability.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
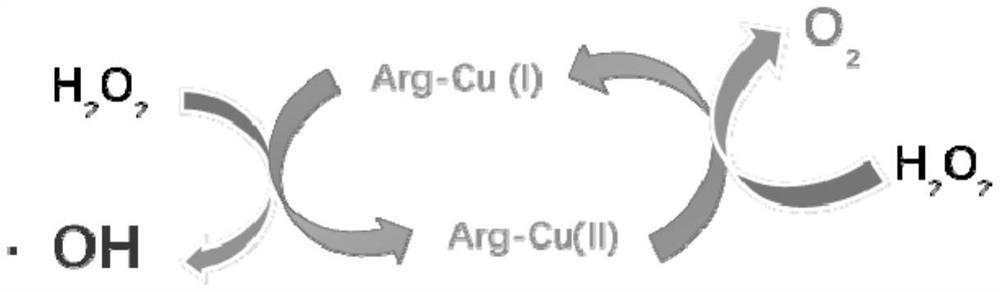
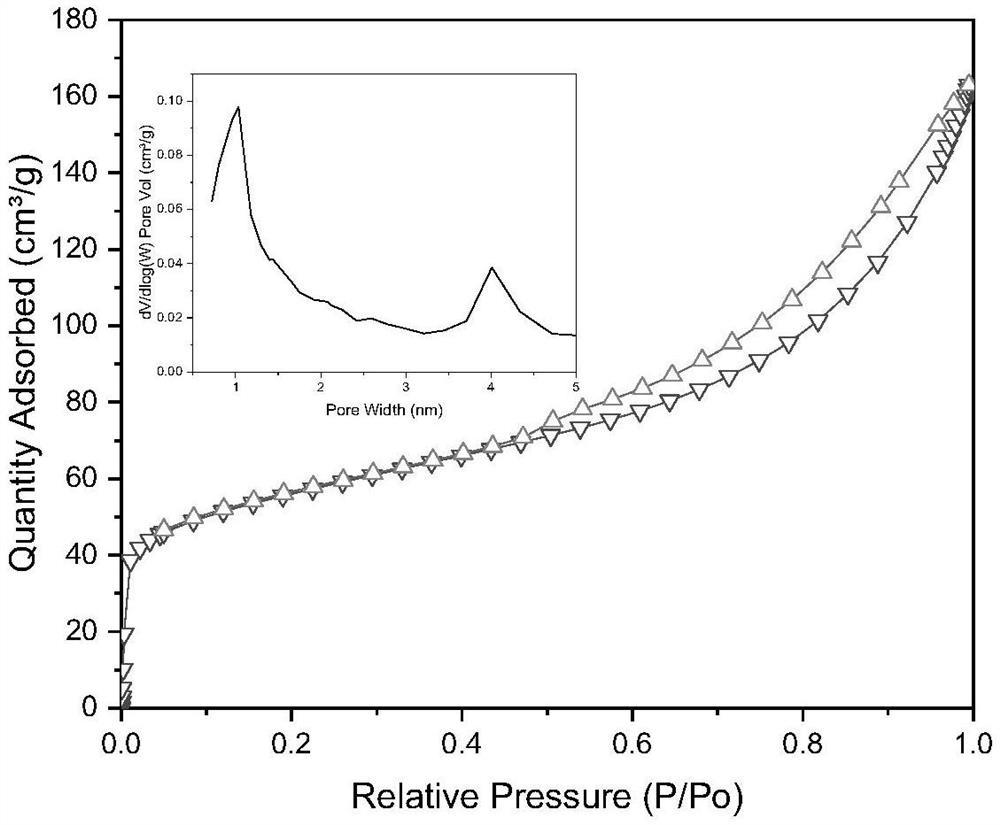
Composite mimetic enzyme gel for degrading organic pollutants and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN112619707BAdjust the degradation rateLong-term degradationWater treatment compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCu2 ionsEngineering
The invention relates to a composite simulated enzyme gel for degrading organic pollutants and its preparation method and application. The method comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving amino acid in deionized water to form an amino acid solution, adding acid to adjust pH=6.5 -7.5, add an equal volume of copper ion solution drop by drop, continue to adjust the pH=6.5-7.5 and stir, after washing several times, freeze-dry the product to obtain simulated enzyme; Add simulated enzymes to the mixture to obtain a mixed solution; adjust pH=3.5-7.5 after stirring and dissolving, and age to obtain a composite simulated enzyme gel containing mesoporous or micropores for degrading organic pollutants, and used to degrade phenols and / or phenols in the environment or dye-like organic pollutants. Compared with the prior art, the present invention controls the speed of enzyme degradation by adjusting the pore size without causing additional pollution to the environment, so as to achieve long-term, stable and efficient degradation effects, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Biodegradable zinc (or zinc alloy) and porous biphase calcium phosphate composite material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102727937BGood biocompatibilityFix compatibility issuesProsthesisPorosityBiphasic calcium phosphate
The present invention provides a biodegradable zinc (or zinc alloy) and porous biphase calcium phosphate composite material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material comprises porous biphase calcium phosphate and zinc or a zinc alloy, wherein the zinc or the zinc alloy is arranged in the porous biphase calcium phosphate through suction casting, the porosity of the porous biphase calcium phosphate is 60-95%, the HA content is 10-70%, the beta-TCP content is 30-90%, and the zinc or the zinc alloy is zinc, a zinc-magnesium alloy, a zinc-yttrium alloy, a zinc-calcium alloy, a zinc-magnesium-manganese alloy, a zinc-magnesium-calcium alloy or a zinc-magnesium-yttrium alloy. The composite material is non-porous at the initial stage, and has good mechanical stability and good mechanical strength; after the composite material is implanted a certain time, the composite material is degraded, and the portion which is degraded slowly maintains the mutually-penetrated porous structure so as to prompt the bone to grow in the structure; and the composite material is gradually degraded along with the gradual growth of the bone in the structure, and the composite material is completely degraded when the bone is healed, such that the good coordination of the biodegradability of the composite material and the osteoinductive is provided.
Owner:JIANGYIN BIODEGRADE MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
A kind of biological magnesium alloy with antibacterial properties and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107739939BSustained and highly effective antibacterial effectEvenly distributedAdditive manufacturing apparatusBall millLaser
The invention discloses biological magnesium alloy with mold resistance. The biological magnesium alloy is composed of a biological magnesium alloy matrix and nano-silver evenly distributed in the magnesium alloy matrix, wherein the mass percent of nano-silver is 0.5-1.5%, preferentially, 0.75-1.25% and is 1% further preferentially. The invention further discloses a method for preparing the biological magnesium alloy with mold resistance. The method comprises the steps that 1, a specific amount of nano-silver powder and magnesium alloy powder are subjected to ball milling in a ball milling machine to obtain evenly-mixed mixed powder; and 2, the mixed powder is used as raw materials, and the biological magnesium alloy with mold resistance is prepared through laser selective melting. The nano-silver is added into the magnesium alloy matrix in a second phase mode, and mold resistance exists in the whole degradation process of the biological magnesium alloy.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A kind of biological magnesium alloy with antibacterial function and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107794424BWell mixedGuaranteed chemical activityAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyAnti bacterialBall mill
The invention relates to a bio-magnesium alloy with antibacterial function and a method for preparing the bio-magnesium alloy by laser selective melting technology. The bio-magnesium alloy with antibacterial function consists of a bio-magnesium alloy matrix and nano-TiO uniformly distributed in the magnesium alloy matrix. 2 Composition; In the bio-magnesium alloy with antibacterial function, nano-TiO 2 The mass percentage content is 3-7%. The preparation method is as follows: according to the design ratio, mix nano-TiO 2 Powder and bio-magnesium alloy powder, the prepared powder is placed in a ball mill, and the mixed powder is obtained by high-speed ball milling under a protective atmosphere; then, a bio-magnesium alloy with antibacterial function is prepared by selective laser melting under a protective atmosphere. The bio-magnesium alloy prepared by the invention has both excellent antibacterial performance and cell compatibility, improved mechanical properties and proper degradation rate. When used as an implant material, it has advantages over existing materials.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A long-term physical marking device for cuttlefish based on endoskeleton octopus
ActiveCN107372272BHigh strengthImprove stress resistancePisciculture and aquariaEngineeringSilicone grease
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
A method for preparing corrosion-resistant bio-magnesium alloy
InactiveCN107760900BPromote degradationPromote nucleation productionAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyMg alloysBall mill
The invention discloses a method for preparing a corrosion-resistant bio-magnesium alloy, which comprises the following steps: (1) placing a specific ratio of calcium oxide powder and bio-magnesium alloy powder in a ball mill, and ball milling to obtain a mixed powder under a protective atmosphere; ( 2) Using the above mixed powder as raw material, under a protective atmosphere, the corrosion-resistant bio-magnesium alloy was prepared by selective laser melting; during the preparation process, the laser power was controlled at 60-90W, the scanning speed was 100-500mm / min, and the spot diameter was 40 -100 μm. In the present invention, calcium oxide is added to the bio-magnesium alloy through laser selective melting to generate Mg / Al-Ca phase with smaller volume, and utilizes the characteristics of rapid solidification speed of laser selective area to refine the volume of the second Mg / Al-Ca phase at the same time Improve its continuity, and then wrap the magnesium alloy grains to form a continuous second-phase protective layer to prevent the erosion of body fluids.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Long-acting physical cuttlefish marking device based on endoskeleton cuttlebone
ActiveCN107372272AHigh strengthImproves balance and swimming speedPisciculture and aquariaRadio frequencyLong acting
The invention discloses a long-acting physical cuttlefish marking device based on an endoskeleton cuttlebone. The long-acting physical cuttlefish marking device comprises an inner housing and a radio frequency chip arranged in the inner housing, wherein the inner housing is connected with an outer housing through a supporting rod and a connecting sleeve, diluted heat-conducting silicone grease is filled between the inner housing and the outer housing, a threaded plug is connected in the connecting sleeve, the outer side of the threaded plug is filled with a sealant, a supporting ring is arranged between the surface of the middle of the inner housing and the outer housing, a spherical hole is formed in the supporting ring, and a balancing rod is arranged in the spherical hole. The long-acting physical cuttlefish marking device has the advantages that a positioner is arranged on the connecting sleeve and real-time positioning and tracing to marked cuttlefishes can be kept. The device is simple in structure, easy to manufacture, convenient to mark, low in cost and suitable for the research of a large individual quantity, the service life of the chip is long, and periodical research can be conducted on marker lives. The device has excellent biocompatibility, does not affect normal growth of cuttlefishes and has excellent corrosion resistant performance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Preparation method of cohesive composite microsphere porous scaffolds
InactiveCN101579539BAperture adjustablePorosity adjustableMicroballoon preparationProsthesisTissue repairFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a preparation method of cohesive composite microsphere porous scaffolds, which comprises the steps as follows: 1) nano hydroxyapatite and polylactic acid are adopted as raw materials, and composite microspheres are obtained by ultrasonic blending, suspension balling, solvent volatilization and freeze drying; and 2) the composite microspheres are subjected to grain size screening, mold feeding, air flow smoothening, polylactic acid solution dropwise adding and cohesion, solvent volatilization by air flow, vacuum heat insulation and sintering, demoulding and washing so asto obtain the porous scaffolds. The preparation method has simple process; the porosity factor of the composite microsphere is high; the aperture of the scaffold and the porosity factor can be adjusted; the moulding of the scaffold is convenient; the shape designability is strong; other cohesive phases are not introduced; and the heating time at high temperature is short. The prepared scaffold has good three-dimensional interlocking pores, good mechanical property and biocompatibility, can meet the demands of tissue engineering scaffold materials, and has potential and wide practical value inthe field of tissue repair in bone tissue engineering.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF ARTS & SCI
Method for preparing high-porosity three-dimensional calcium alginate gel scaffolds by virtue of pulsed ultrasonic wave
InactiveCN104593327AEasy to prepareMeet the needs of different organizational structure shapesTumor/cancer cellsCross-linkPorosity
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-porosity three-dimensional calcium alginate gel scaffolds by virtue of a pulsed ultrasonic wave, and belongs to the technical field of performance optimization for a three-dimensional scaffold material. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: directly moulding three-dimensional calcium alginate gel scaffolds with different mechanical strengths by a cross-linking synthesis method; carrying out an applied voltage test on the Young moduli of the three-dimensional gel scaffolds prepared in the step 1 at room temperature, and primarily selecting the three-dimensional gel scaffolds with stable mechanical properties; irradiating the obtained scaffolds by a low-intensity pulsed ultrasonic wave to prepare the high-porosity three-dimensional gel scaffolds, wherein the sound pressure of the low-intensity pulsed ultrasonic wave is 0.055MPa, and the irradiation time is 20min. The three-dimensional gel scaffolds prepared by the method disclosed by the invention are high in porosity and good in permeability, and has a great promotion role on cell growth.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
A kind of biodegradable high-strength polyetherester type polyurethane urea foam and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108586293BEasy to purifyEasy to controlUrea derivatives preparationSurgical adhesivesLysine diisocyanatePolymer science
Owner:济南羽时信息科技有限公司
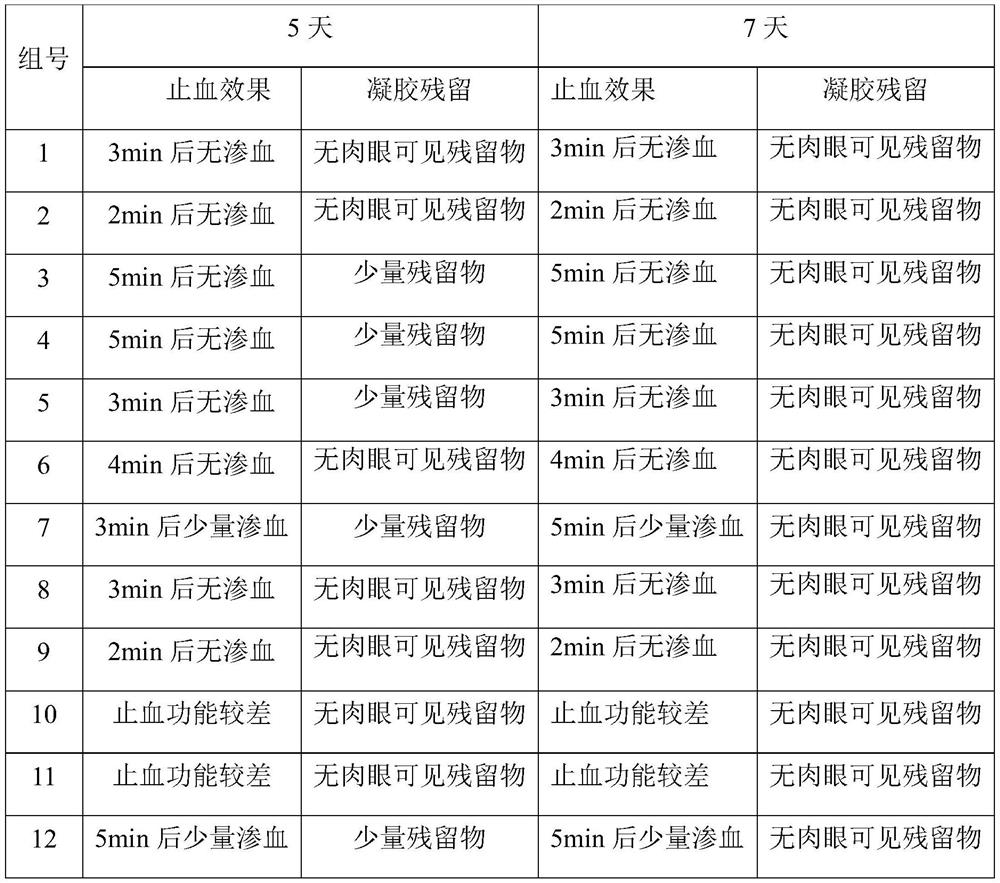
Preparation method and application of self-thickening bone wound hemostatic gel
ActiveCN110464869BAdjust the degradation rateReduce compositionSurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismWound healingPolymer science
The invention discloses a self-thickening bone wound hemostatic gel and its preparation method and application. The gel includes a zwitterion-polysaccharide polymer brush, a solvent matrix, and blood coagulation factor components. First, the zwitterion-polysaccharide polymer brush is prepared , then, the zwitterionic-polysaccharide polymer brush is mixed with the solvent base, stirred to obtain a pre-gel, and finally, blood coagulation factors are added to the pre-gel, and stirred to obtain a self-thickening bone wound hemostatic gel, the present invention The bone wound hemostatic gel has simple components, does not need to add thickeners, excipients and other components, and has a good hemostatic effect, is easy to absorb, and does not affect wound healing.
Owner:BOZHOU CITY THE NEW HEALTH TECH CO LTD
A kind of biological magnesium alloy with anti-corrosion function and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107739940BImprove corrosion resistancePlay a role in corrosion resistanceSelective laser meltingAlcohol
The invention discloses biological magnesium alloy with a corrosion resistant function. The biological magnesium alloy is prepared from a biological magnesium alloy matrix and graphene oxide, whereinthe graphene oxide is distributed on the grain boundary of the biological magnesium alloy matrix, and the graphene oxide wraps biological magnesium alloy grains so as to form a second phase of a nanohoneycomb structure. The invention further discloses a preparation method. The preparation method comprises the following steps of (1) respectively putting GO powder and biological magnesium alloy powder in absolute ethyl alcohol according to the design proportion for ultrasonic agitation so as to obtain a GO suspension and a biological magnesium alloy suspension; (2) slowly adding the GO suspension to the biological magnesium alloy suspension, continuing to perform ultrasonic agitation so as to obtain a mixed suspension, and performing vacuum filtration and drying treatment on the mixed suspension so as to obtain mixed powder with uniform dispersion; and (3) performing selective laser melting on the mixed powder in the protective atmosphere so as to prepare the biological magnesium alloywith the corrosion resistant function. According to the biological magnesium alloy with the corrosion resistant function, the second phase of the nano honeycomb structure constructed by utilizing GO can be used as a shield so as to isolate the biological magnesium alloy from body fluid, so that a galvanic corrosion effect of a conventional second phase is avoided, and the corrosion resistance is improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Preparation method for polypropylene film
The invention provides a preparation method for a polypropylene film. The preparation method comprises the steps that (1) a raw material is heated to 120-180 DEG C; (2) the heated raw material is rolled through a pulley block; and (3) the temperature is gradually lowered to the normal temperature. A traditional film making technology is replaced, the pulley block is adopted for rolling, accordingly, the problem that polypropylene films prepared through the traditional preparation technology have gaps is solved, that is, the obtained polypropylene film is in a real film form instead of a woven silk form, and the water leakage phenomenon is avoided when the polypropylene film is made into a bag, a heat preservation film and other products.
Owner:广东乐将生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com