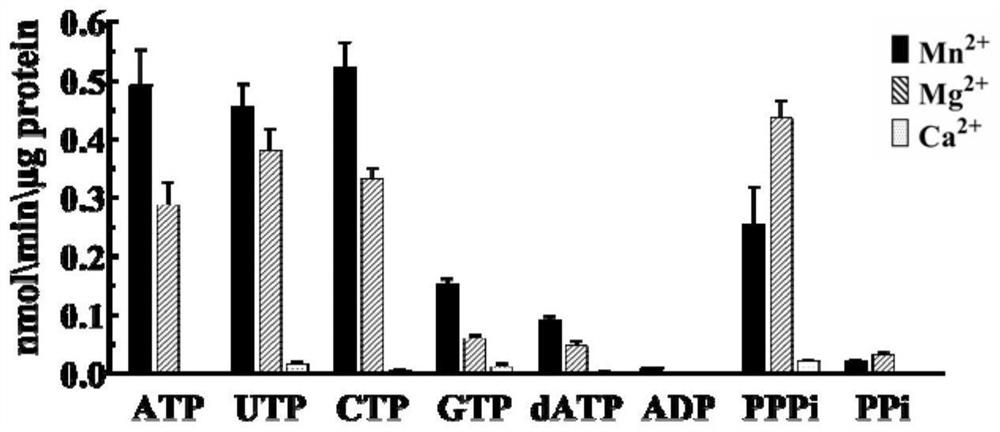
Patents
Literature
35 results about "Adenosine tri phosphate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
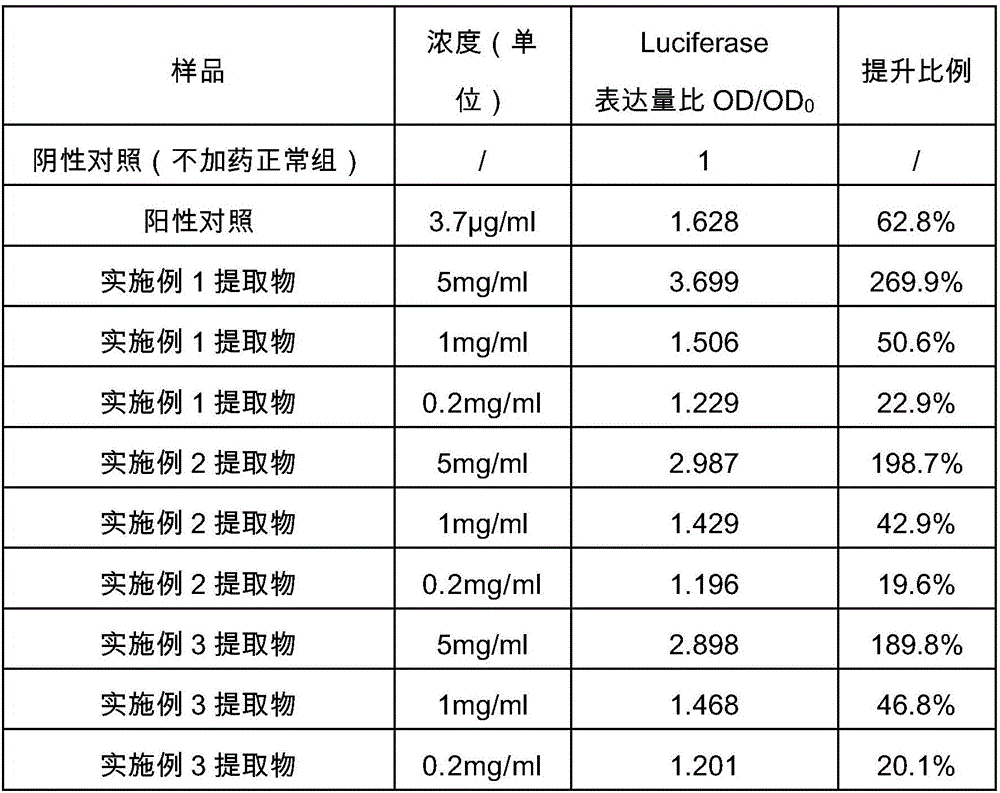
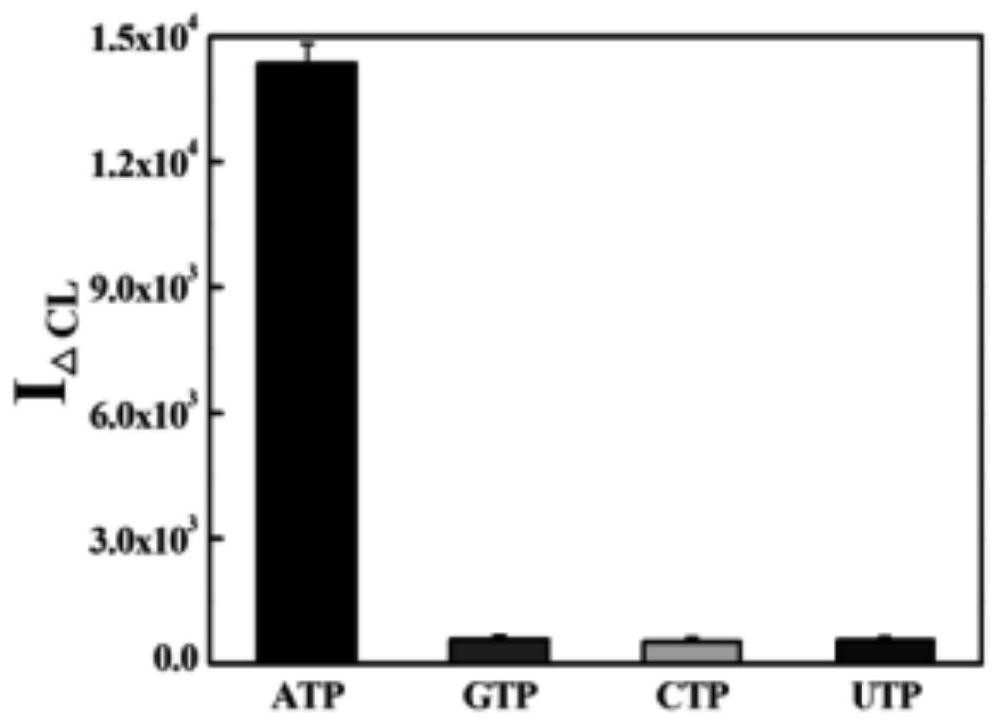
Adenosine triphosphate enables the movement of food through the digestive tract. Mitochondria generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a source of chemical energy. Adenosine triphosphate is a molecule that makes up DNA. Red light therapy may activate adenosine triphosphate.
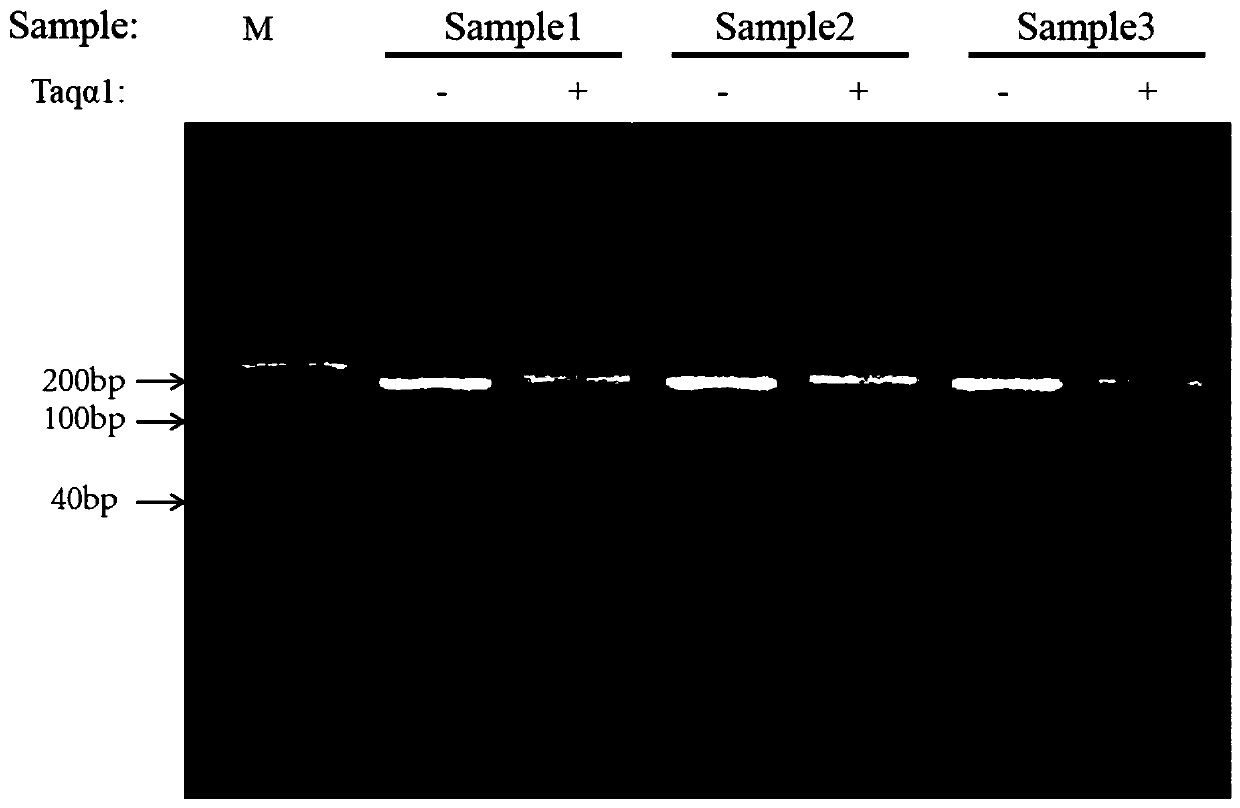
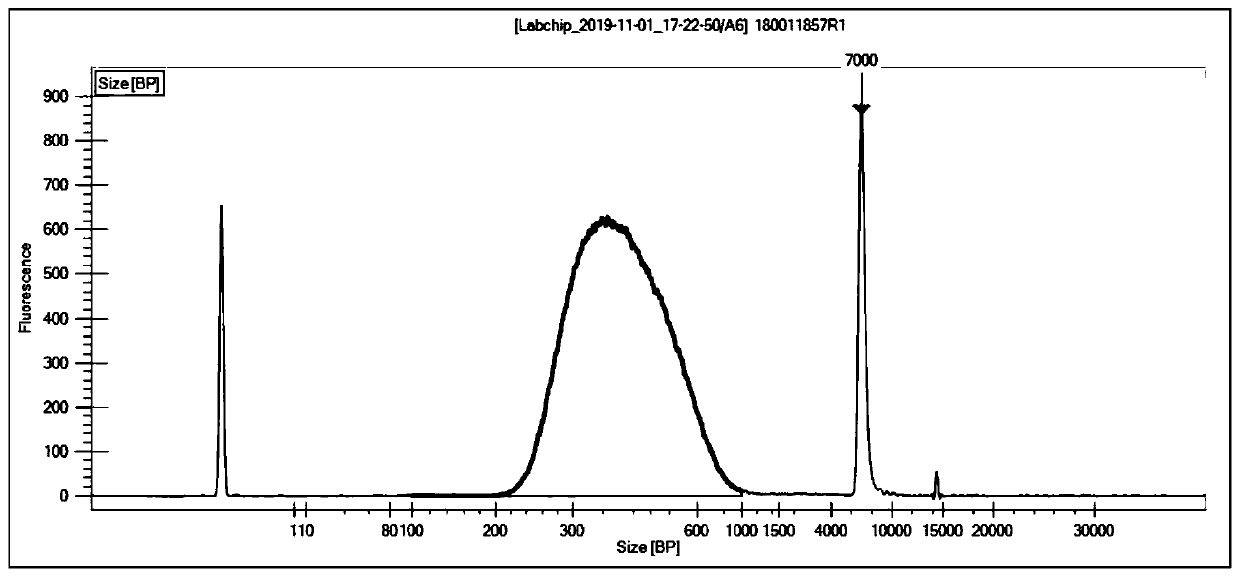
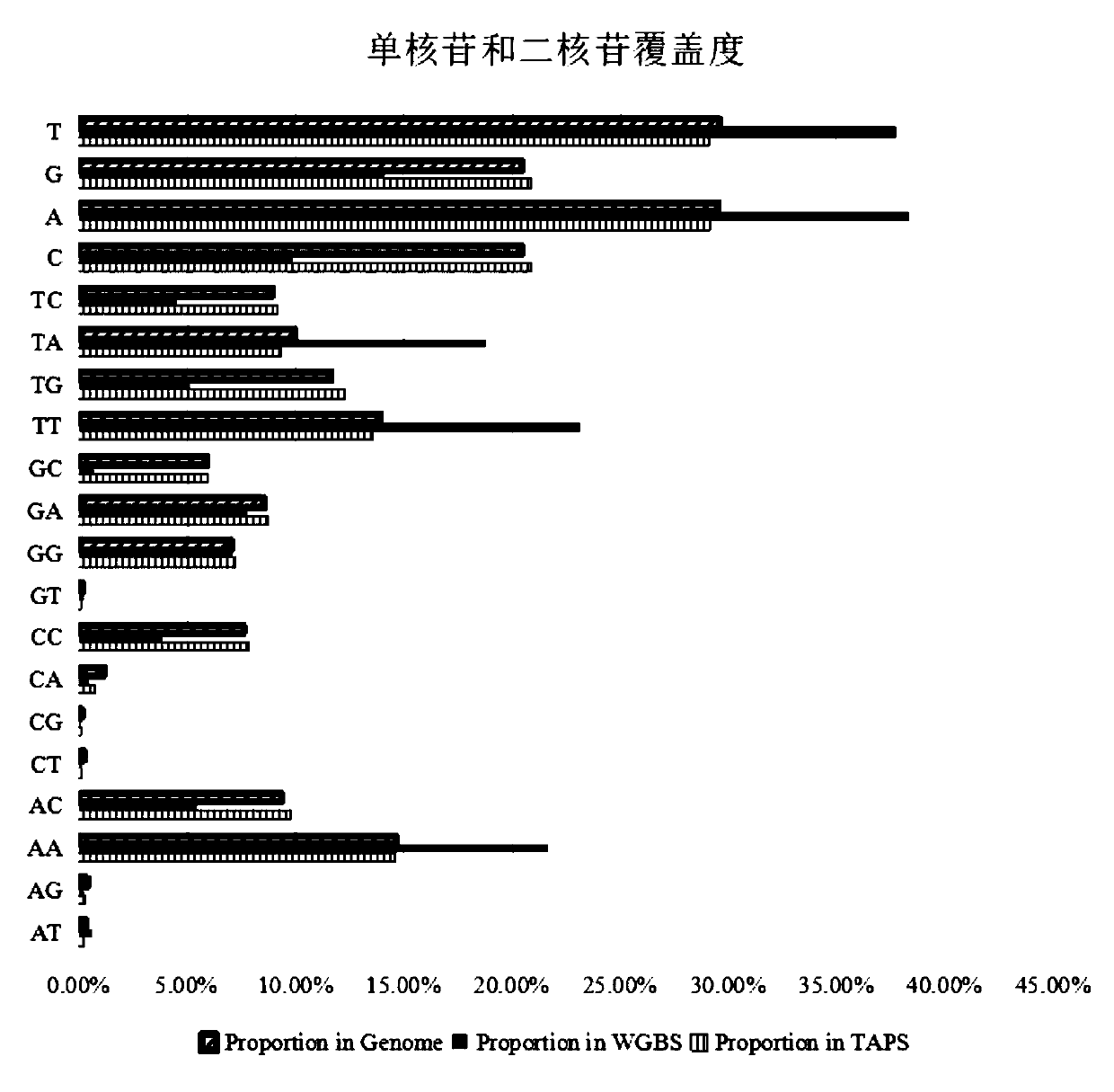
Whole-genome methylation non-bisulfite sequencing library, construction and applications thereof
InactiveCN110820050ASolve the defect of low usage rateReduce usageNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementDihydrouracilPhosphoric acid
The invention relates to the technical field of bioinformatics, particularly to a whole-genome methylation non-bisulfite sequencing library, a construction and applications thereof, wherein the sequencing library comprises a TET enzyme reaction solution, the TET enzyme reaction solution comprises the following independently packaged components: a TET enzyme oxidation buffer solution, and the TET enzyme oxidation buffer solution comprises, by micromole, (20-167)*10<3> parts of HEPES or Tris-Cl, (100-333)*10<3> parts of NaCl, 3.3*10<3> parts of alpha-KG or 2-oxoglutarate, 6.67*10<3> parts of ascorbic acid and 4*10<3> parts of adenosine triphosphate. According to the invention, by combining the kit, Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2 and TET enzyme, 5mc can be oxidized into 5cac, the 5cac is reduced into dihydrouracil under the action of a reducing agent, and T is identified through PCR sequencing, so that the the DNA methylation C-to-T conversion under the non-bisulfite condition is achieved, the defects ofbase imbalance and low sequencing data use rate of the existing methylation sequencing library constructed based on the bisulfite conversion are solved; and the formula further has effects of simplecomponents, extremely low TET enzyme use amount and significant cost reducing.
Owner:BEIJING GENEPLUS TECH +1
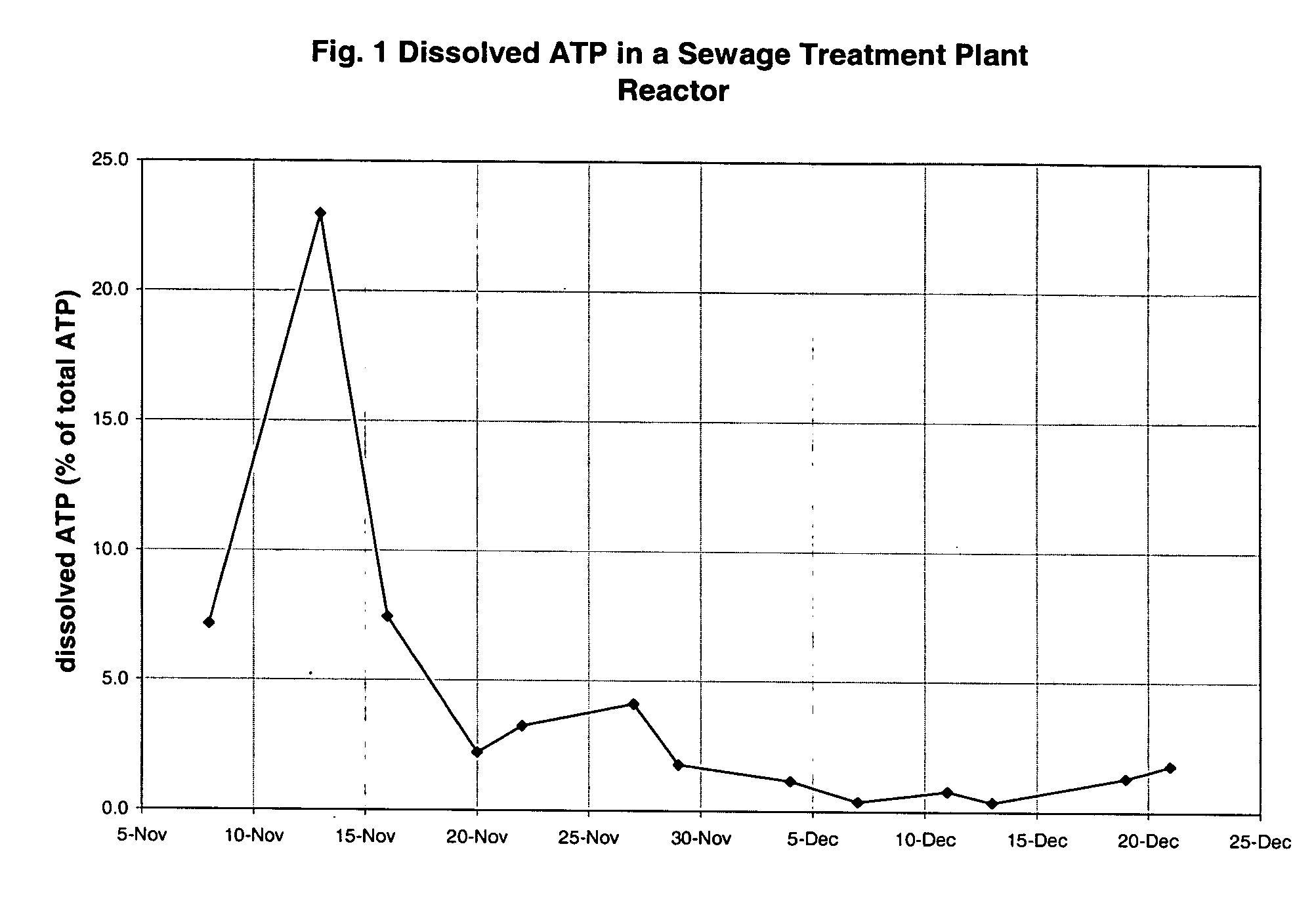
Reagent system and process for adenosine triphosphate monitoring
ActiveUS20060073537A1Efficient and reliable quantificationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsExtracellularLuciferin
A reagent system comprises a first reagent which includes a high pH phosphate buffer, and a second reagent which includes luciferase, luciferin, a magnesium salt and an enzyme stabilizer. The second reagent has a low pH and a buffer with a pK which is near the optimum pH for activity of luciferase. The reagent system may be used in a process for measuring total adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and / or dissolved extracellular ATP, in a fluid containing microorganisms. The reagent system may also be used in a microbiological remediation or production process.
Owner:LUMINULTRA TECH
Luminescence measuring apparatus
InactiveUS20080241871A1Optimize washing stepQuick and easy measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReagentLuminescent Measurements
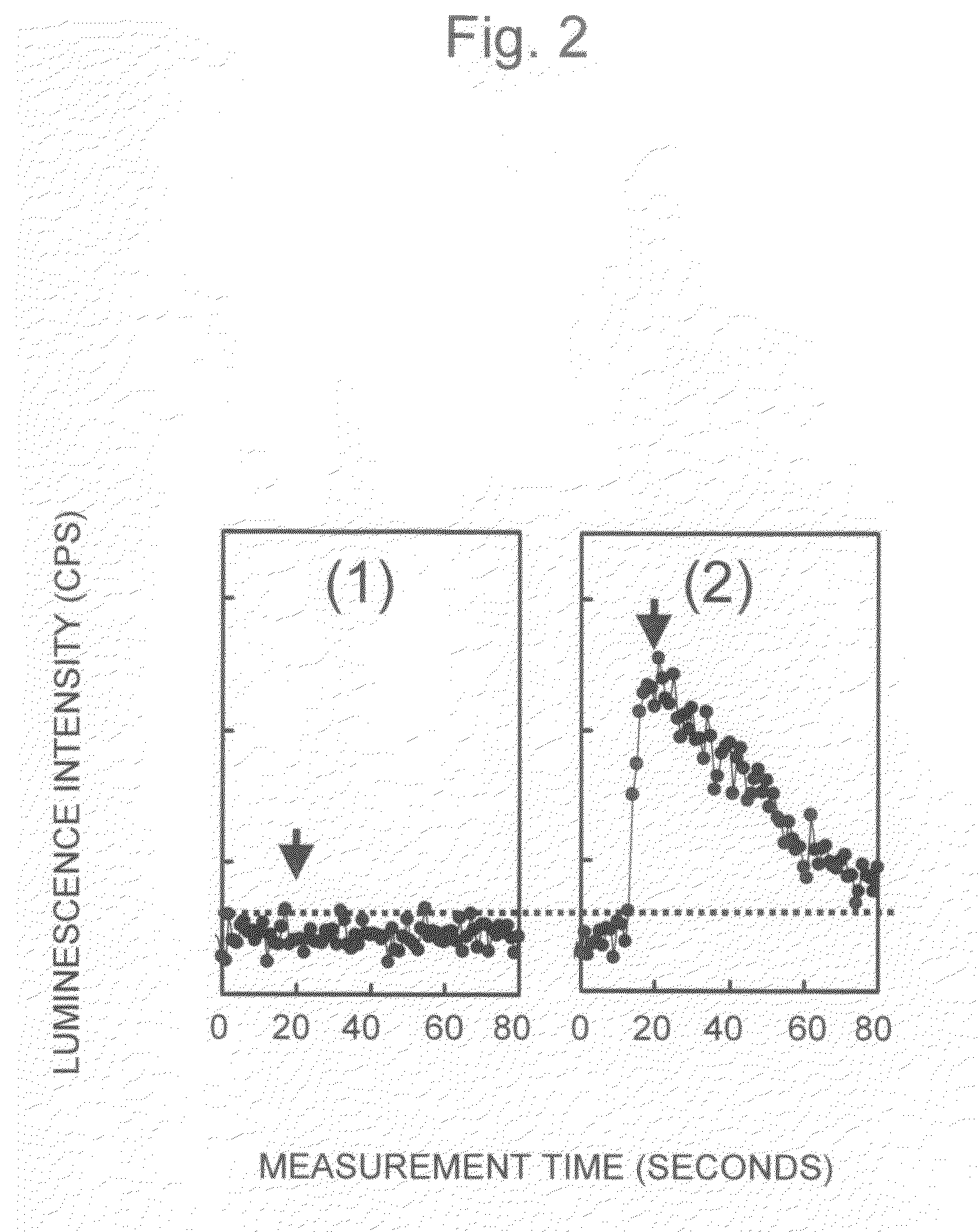
The present invention provides a luminescence measuring method that can be accurately and quickly carried out while inhibiting a possible background associated with viable bacteria adhering to a nozzle or Adenosine Tri Phosphate remaining in the nozzle, and an apparatus for the method. The present invention uses a washing apparatus characterized by including a nozzle, a lysys solution, a luminescence reagent solution, and a detection section, as well as a relevant washing method and a relevant luminescence measuring method. To remove viable bacteria adhering to the nozzle, the nozzle is immersed in the lysys solution and then in the luminescence reagent solution. The detection section monitors luminescence occurring during a washing process.
Owner:HITACHI PLANT TECH LTD
Hydrophilic metal ion immobilization affinity magnetic bead and preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN102760543AImprove hydrophilicityGood choiceNanomagnetismPeptide preparation methodsMagnetic beadAdenosine
The invention relates to a preparation method of a hydrophilic metal ion immobilization affinity magnetic bead, which comprises the following steps: the surface of an amino magnetic bead is subjected to amino activation through glutaral; the activated magnetic bead is connected with an adenosine disodium triphosphate molecule through a surface modification reaction; the surface of the activated magnetic bead is bonded with a hydrophilic functional molecule containing a plurality of phosphate and hydroxyl radicals, so as to be beneficial for subsequent metal ion immobilization; at last, the immobilization of a metal ion is realized in a solution containing the metal ion; and the preparation of the hydrophilic metal ion immobilization affinity magnetic bead is accomplished. The hydrophilic metal ion immobilization affinity magnetic bead has the advantages that the preparation method is simple; compared with other metal ion immobilization affinity chromatographic columns or magnetic beads, the hydrophilic metal ion immobilization affinity magnetic bead prepared by the method is high in hydrophily, good in selectivity, good in preparation repeatability and stable in performance, and has a good specific concentration ability to phosphorylated peptides; the operation is simple; the complicated centrifugation operation can be avoided; and the hydrophilic metal ion immobilization affinity magnetic bead has wide application prospects in proteomics, especially in phosphorylated proteomics.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Highly moisturizing biological cream good in stability performance and quite easy to absorb and preparation method of biological cream
ActiveCN108042462AFast absorptionDispersed droplets are smallCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsGlycyrrhiza glabra RootBetaine
The invention relates to the technical field of cosmetics, and discloses a highly moisturizing biological cream good in stability performance and quite easy to absorb. The biological cream consists ofthe following components in percentage by mass: 58.61% of water, 8% of glycerol, 8% of butanediol, 5% of whey, 3% of ceramide 2, 2.66% of grape seed oil, 2% of squalane, 2% of polyglycerol-3 polyricinolate, 2% of cetostearyl alcohol, 2% of betaine, 1% of a ginkgo biloba extract, 1% of hexapeptide-1, 1% of acetyl hexapeptide-1, 0.6% of ascorbic acid, 0.6% of oligopeptide-1, 0.5% of triphosadenine,0.5% of hyaluronic acid, 0.5% of a glycyrrhiza glabra root extract, 0.5% of a radix ginseng extract, 0.5% of phenoxyethanol and 0.03% of essence. According to the biological cream provided by the invention, the partial blue-light semitransparent micron-coated liquid whey, which is less than 200nm in grain size, is adopted, and the ceramide 2 is covered by the whey, and in coordination with the polyglycerol-3 polyricinolate which is a 100% natural emulsifying agent, a three-dimensional triangular structure is formed; dispersion liquid drops formed by the structure are relatively small, so thatbetter absorption to skin is guaranteed, and the biological cream, when used, is better in moistening and moisturizing effects.
Owner:江西登云健康美业互联有限公司
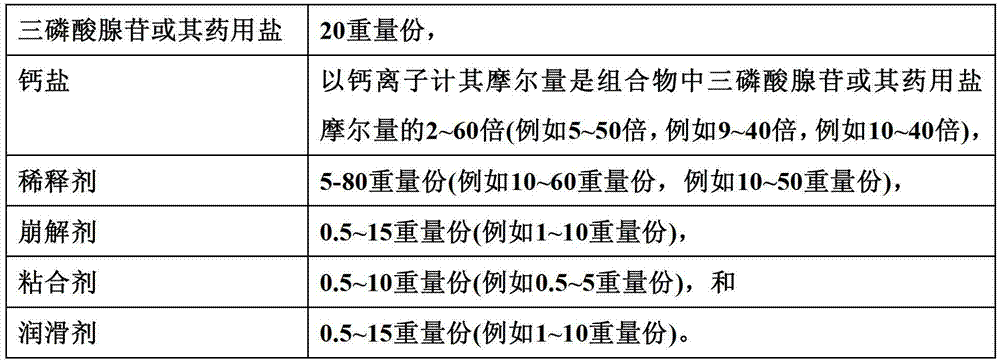
Disodium adenosine triphosphate troche medical composition
The invention relates to a disodium adenosine triphosphate troche medical composition, and in particular relates to use of calcium salt in preparation of stable triphosadenine or a solid medical composition of officinal salt thereof. The medical composition provided by the invention further stably comprises triphosadenine or the solid medical composition of officinal salt thereof. More specifically, the invention relates to the solid medical composition containing triphosadenine or the officinal salt thereof, wherein even if the medical composition is stored for a long time, the content of the effective components is still highly maintained to ensure the excellent stability. After the solid medical composition provided by the invention is placed at 20+ / -2 DEG C for 2 years, the residual ratio of active components, i.e., triphosadenine or officinal salt thereof in the composition is over 80%.
Owner:CHENGDU TIANTAISHAN PHARMA
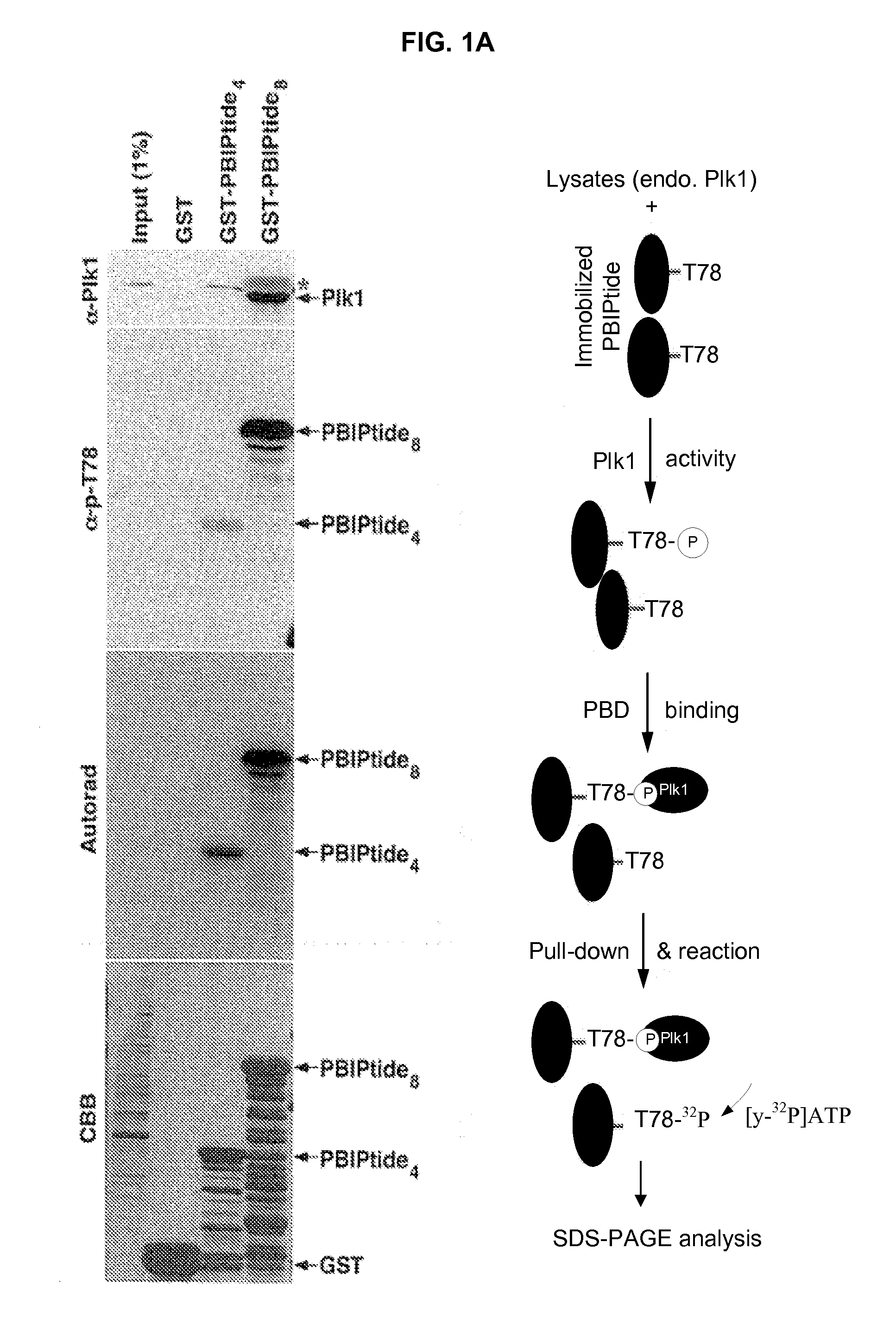
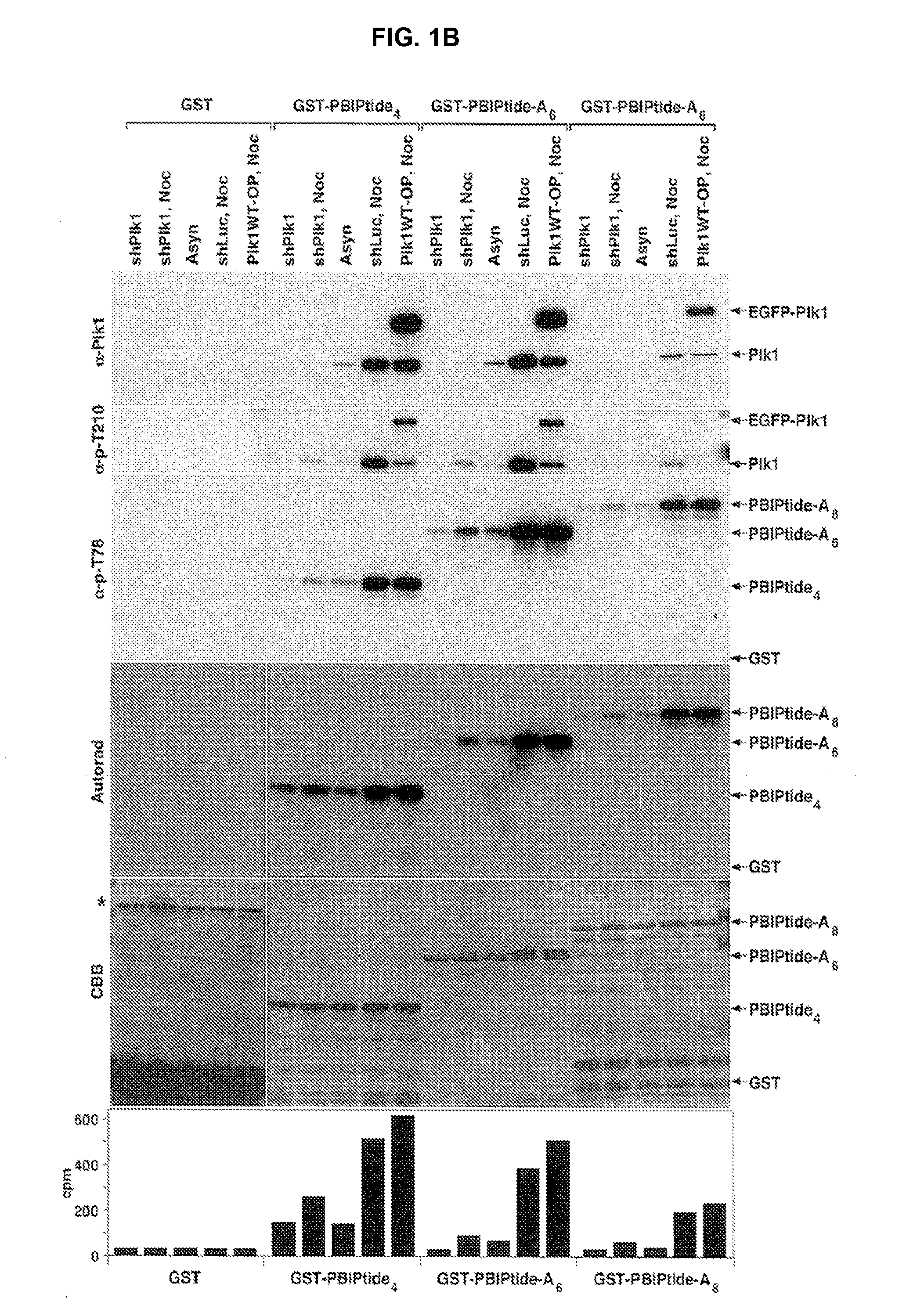
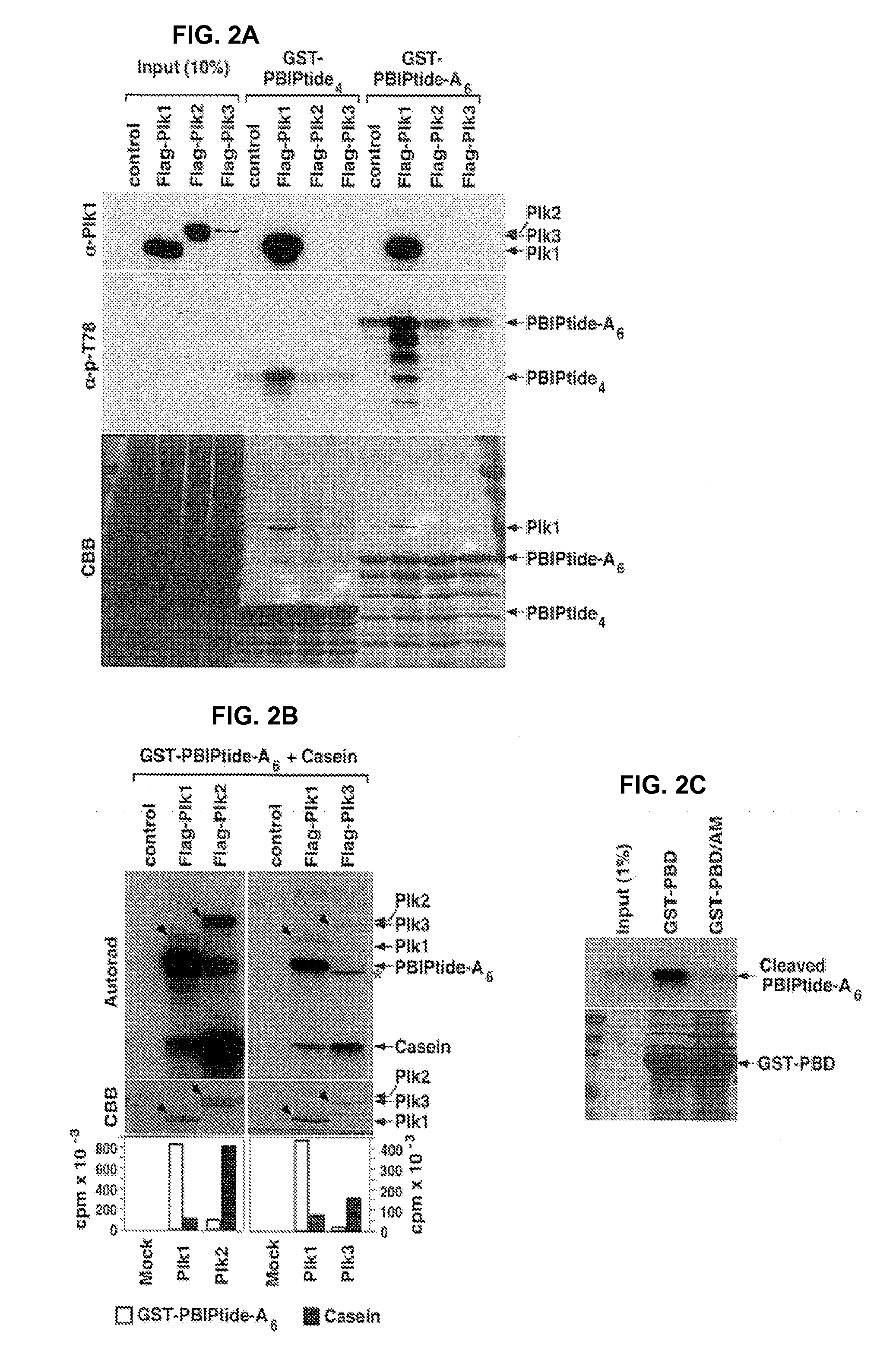
Method for detection and quantification of plk1 expression and activity
Isolated peptide substrates of Plk1 and nucleic acids encoding these peptides are disclosed. The peptides include two to ten repeats of the amino acid sequence set forth as X1X2AX3X4X5PLHSTX6X7X8X9X10X11X12 (SEQ ID NO: 1), in which within each repeat X1, X2, X6, X7, X8, X9, X10, X11, and X12 are each independently any amino acid or no amino acid, and X3 and X4 are each independently any amino acid. Methods of using these peptides to detect Plk1 activity in a sample are also disclosed. In some examples, the method includes contacting a sample with a disclosed peptide substrate of Plk1 in the presence of adenosine triphosphate, or an analog thereof, for a period of time sufficient for Plk1 to phosphorylate the PBIPtide. The presence and / or amount of the phosphorylated and / or the unphosphorylated peptide is detected, thereby detecting and / or quantitating Plk1 kinase activity in the sample.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Method for improving maturity of harvested fresh siraitia grosvenorii
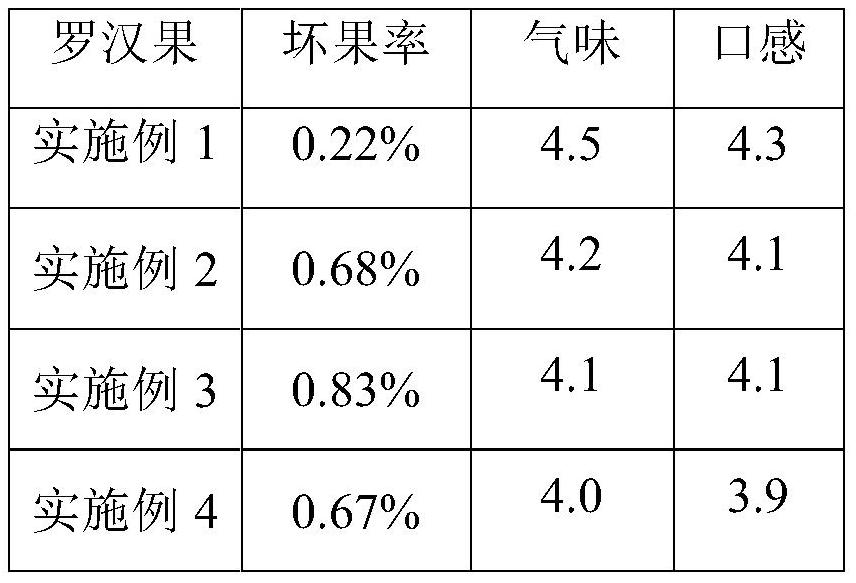
ActiveCN114176122APromote maturityReduce bad fruit rateFruit and vegetables preservationFood ingredientsRipenessMildew
The invention relates to a method for improving the maturity of harvested fresh siraitia grosvenorii, which comprises the following steps: (1) fruit selection and warehousing: firstly, the harvested fresh siraitia grosvenorii is divided into I) common fruits, II) old and green fruits and / or shed-sweeping fruits, intact, undamaged and mildew-free fruits are selected, the selected fruits are put into baskets, and the baskets are warehoused and stacked according to grades; (2) warehouse standard: setting a quick lime point and a saturated lime water point, and regularly ventilating; and (3) spraying adenosine triphosphate, methionine, jasmonic acid and / or a methyl ester solution of jasmonic acid in sequence, and standing for ripening. According to the method disclosed by the invention, for fresh fructus momordicae, particularly old and green fruits and shed-sweeping fruits, the quality of mature fructus momordicae can be obviously improved, and the fructus momordicae is good in taste and flavor and low in bad fruit rate.
Owner:HUNAN HUACHENG BIOTECH
Applications of At-ACA8 gene of arabidopsis thaliana for enhancing plant stress resistance and regulating plant growing development
InactiveCN102643856AImprove the ability to resist adversityStrong resistanceVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsATPaseBiotechnology
The invention provides an application of an arabidopsis thaliana calcium ion transported-ATP (Adenosine Tri-Phosphate) enzyme gene At-ACA8. The application comprises an application of the gene on aspects of regulating plant growing development and resisting adverse circumstance stress, and an application of the gene in an aspect of an adverse circumstance stress resisting transgenic plant variety. A T-DNA (Transforming-Deoxyribonucleic Acid) inserting mutant aca8 of the At-ACA8 gene obtained from an arabidopsis thaliana biological resource center is utilized as a target and an experiment result confirms that the mutant has obvious resistances on adverse circumstances of low temperature, high temperature, penetration compelling and the like; a seed germination phase is sensitive to whether sucrose exists or not; the germination of seeds is seriously inhibited under the condition of not adding the sucrose and a growing phase is more sensitive to the raising of the concentration of the sucrose; the seed germination phase is sensitive to a hormone ABA (Abscisic Acid); and less ABA is applied to obviously inhibiting the germination of the seeds. The invention discloses responding functions of regulating the plant growing development and resisting stress of the calcium ion conduction system and provides a good-quality gene for the variety improvement of the plants; the invention represents a new method and a mechanism which are used for improving the resisting adverse circumstance resisting capability and have good resisting variety and important economic meanings and application values.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
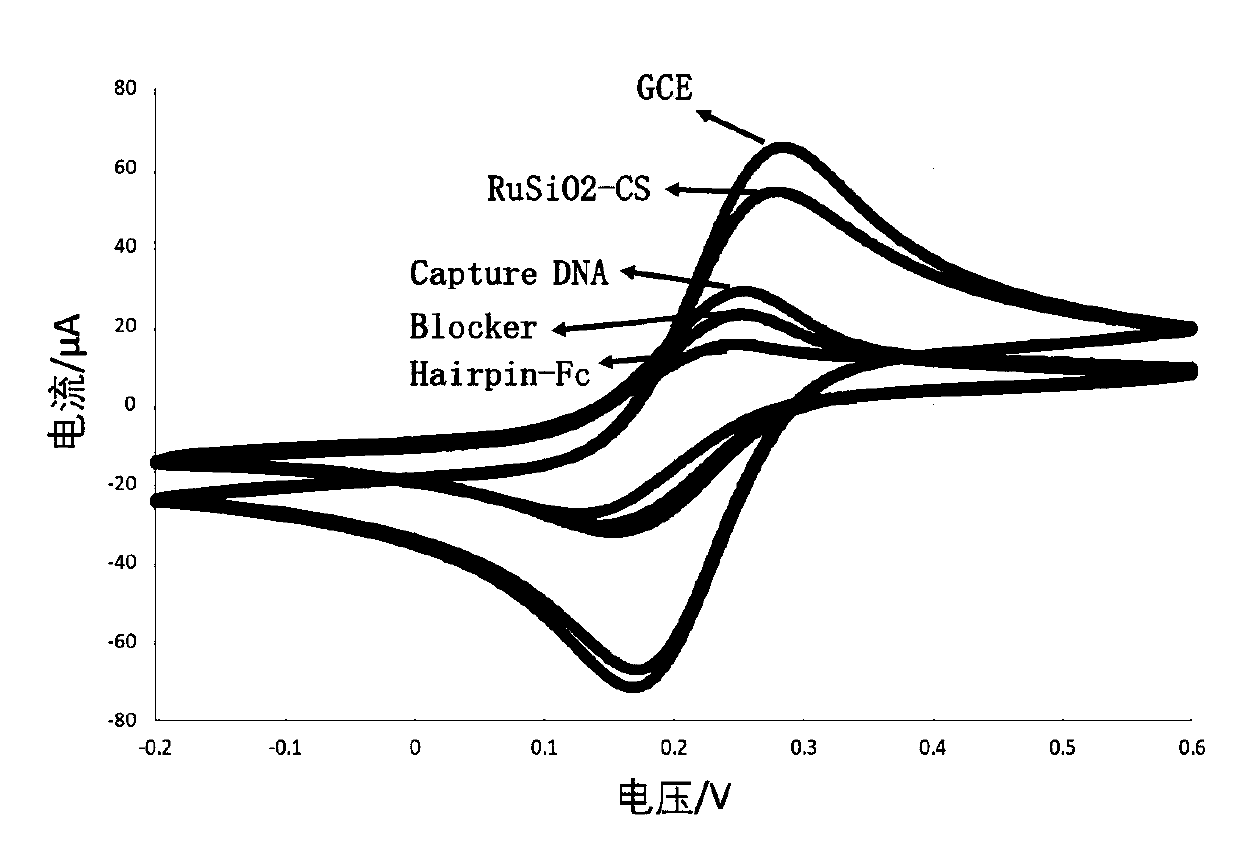
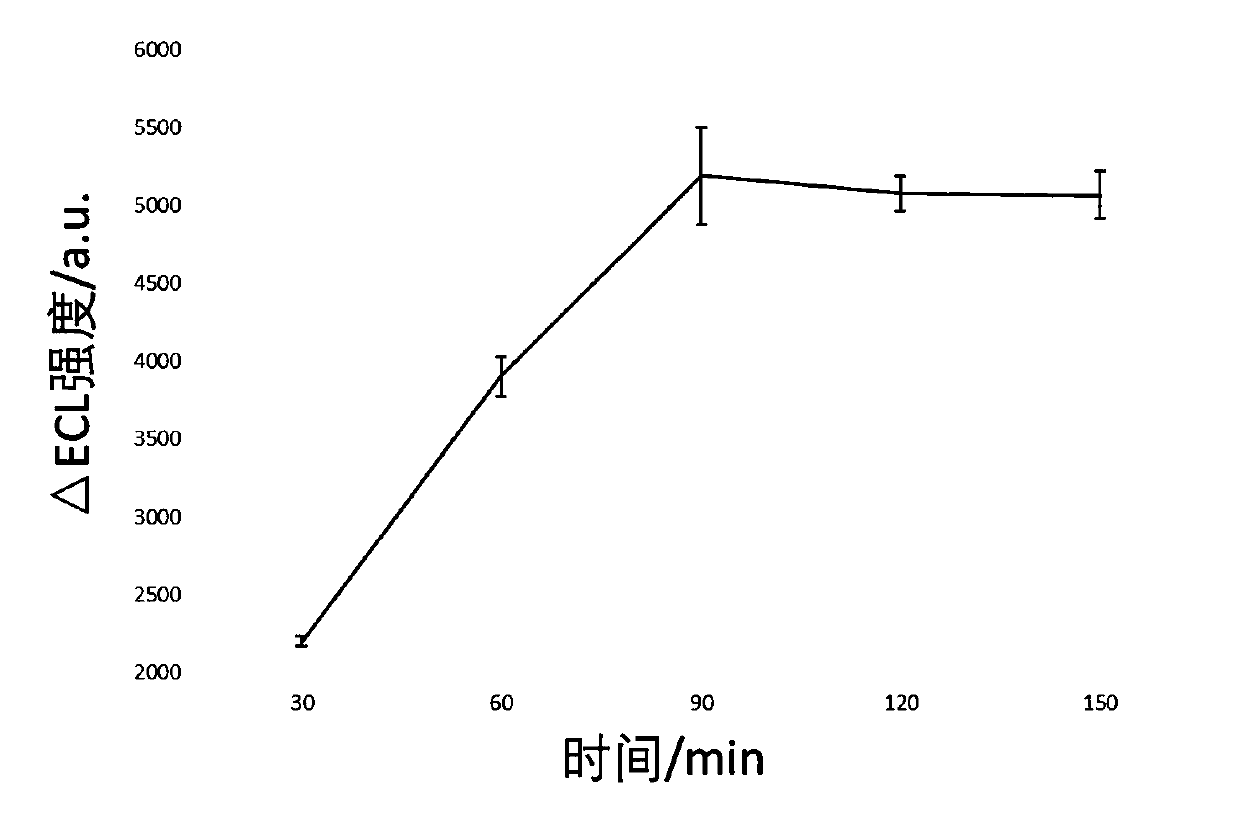
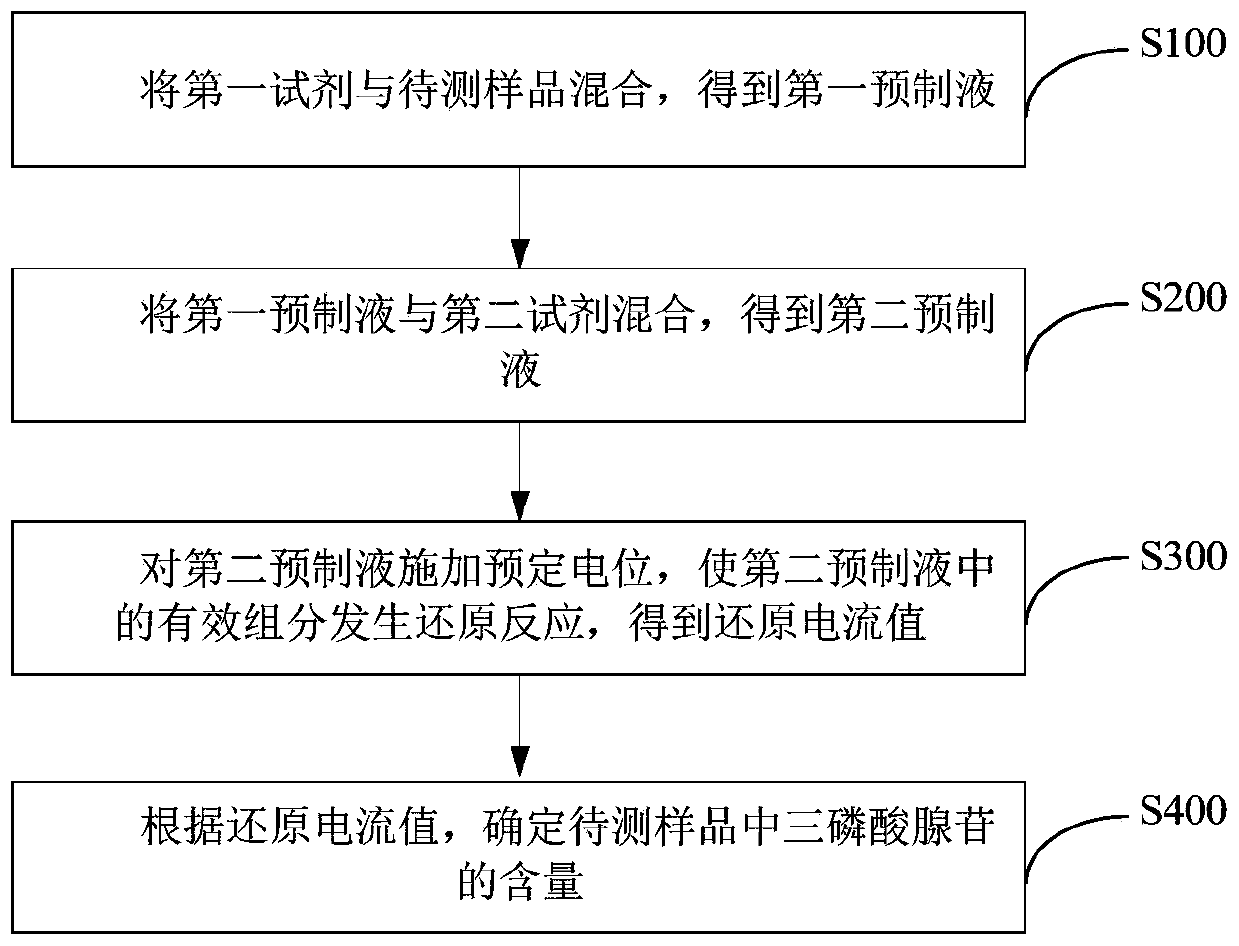
Electrochemical luminescence sensor system for determining adenosine triphosphate and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111020006AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAdenosineA-DNA
The invention discloses an electrochemical luminescence sensor system for determining adenosine triphosphate and a preparation method and application thereof. The system is composed of a magnetic probe for amplifying an adenosine triphosphate concentration signal and an electrochemical luminescence sensor for determining Triger DNA. The magnetic probe is formed by compounding Fe3O4 nano particles,gold nano particles, a DNA substate and aptazyme in sequence. The electrochemical luminescence sensor is obtained by connecting amino-modified Capture DNA to the surface of a RuSiO2-CS-modified working electrode through glutaraldehyde cross-linking action. According to the invention, adenosine triphosphate participates in an isothermal amplification reaction guided by the magnetic probe and a large amount of intermediate Trigger DNAs are generated; and then, the intermediate Triger DNAs are quantitatively detected through the electrochemical luminescence sensor; and finally, the purpose of indirectly and quantitatively detecting adenosine triphosphate is achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
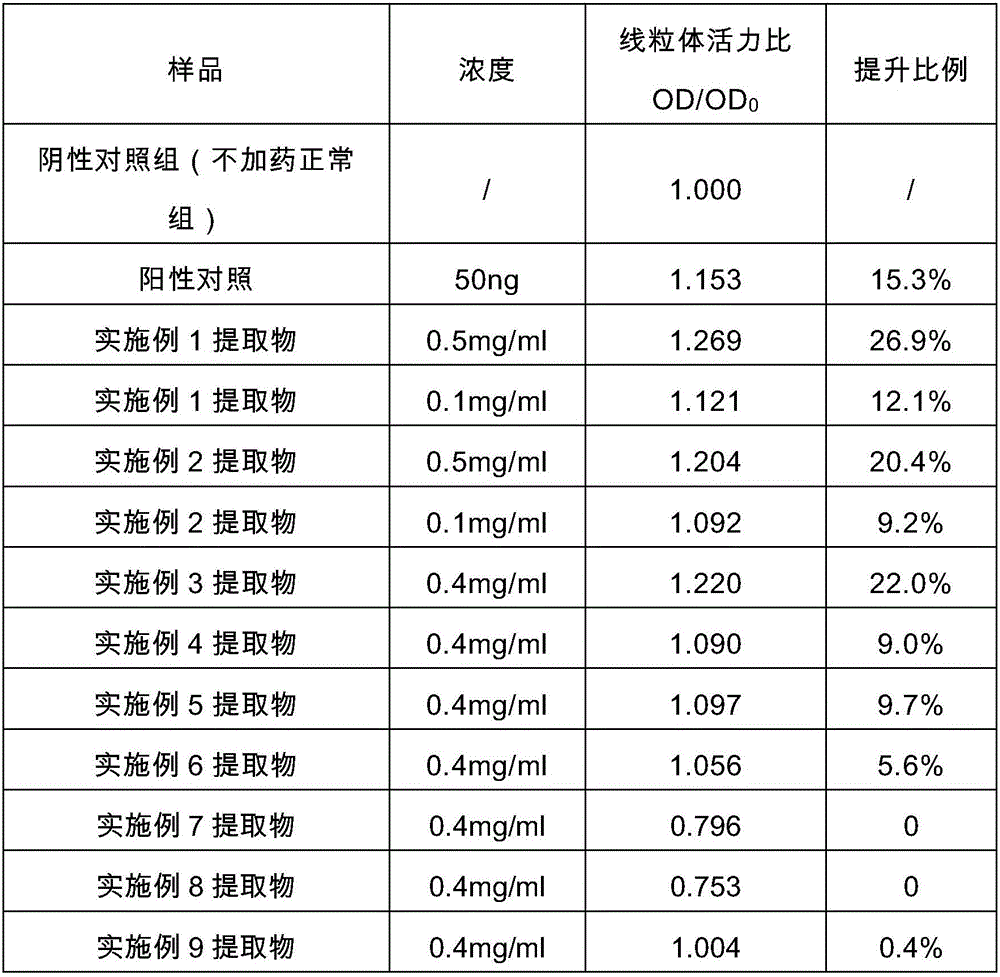
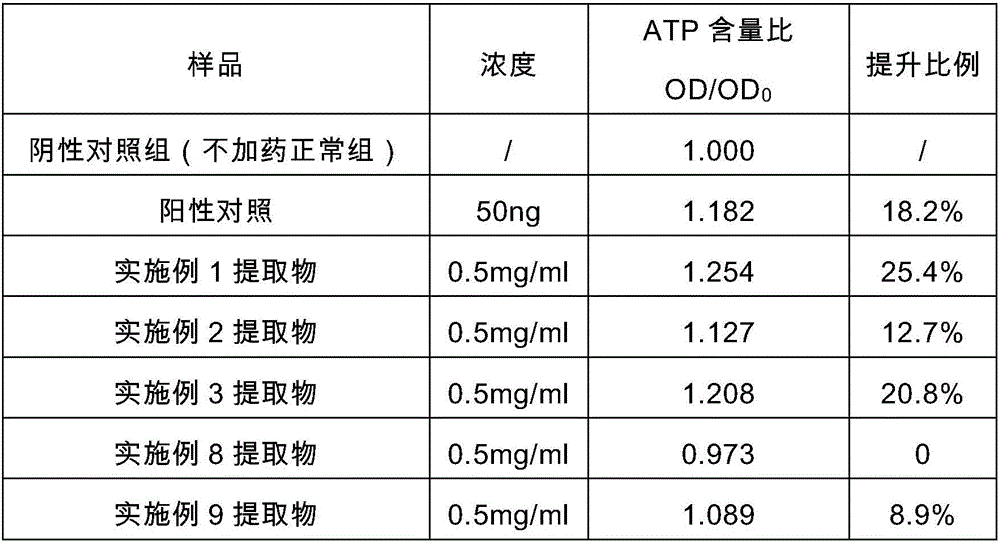
Compound extract of rhizoma polygonati and Chinese wolfberry fruits, as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a compound extract of rhizoma polygonati and Chinese wolfberry fruits, as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The compound extract is prepared from rhizoma polygonati and Chinese wolfberry fruit extract, wherein the weight ratio of rhizoma polygonati to Chinese wolfberry fruit raw materials is 1:5-5:1, and the crude herbal concentration of the extract is 0.1mg / mL-5mg / mL. The compound extract can be used for enhancing expression of peroxire-doxin in cells and / or ROS content in fibroblasts after UVA radiation and increasing the mitochondria activity of epidermal keratinocytes and / or the content of adenosine triphosphate in the epidermal keratinocytes. The compound extract is added into a skin externally applied preparation as a functional additive for skin care.
Owner:SHANGHAI JAHWA UNITED +1
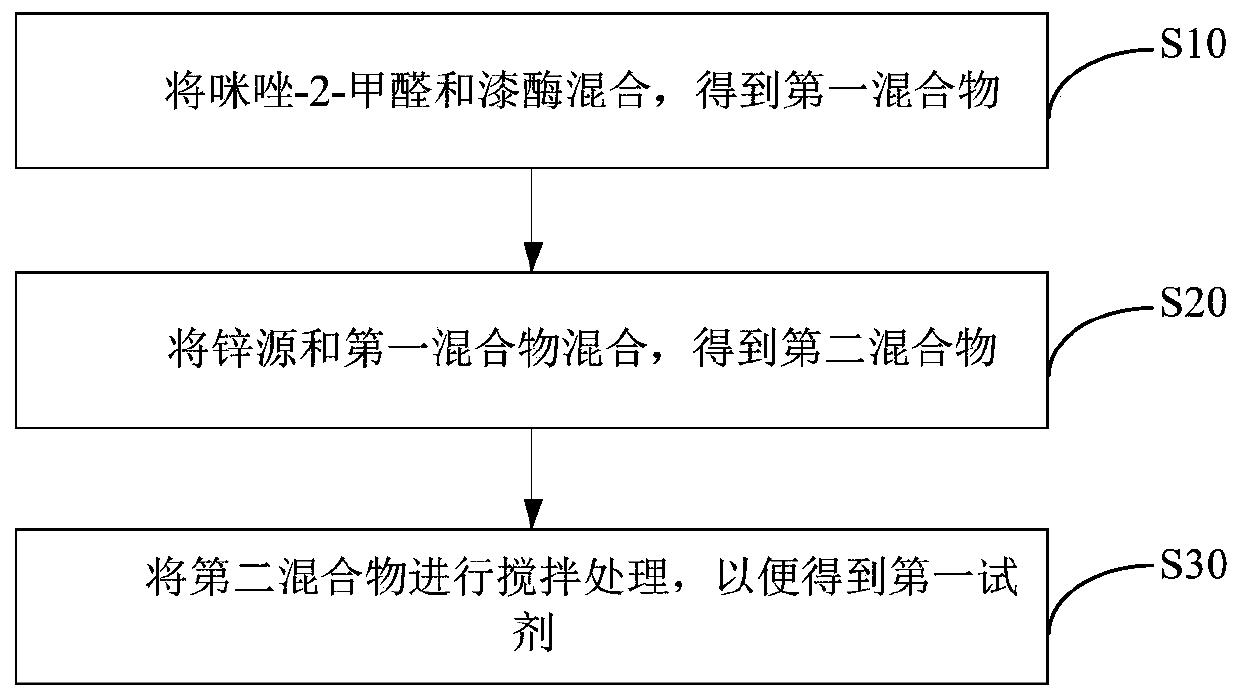
Detection reagent for detecting adenosine triphosphate, preparation method of detection reagent, and method and device for detecting adenosine triphosphate by using detection reagent
ActiveCN111253758AEasy to operateEasy to implementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAdenosineCrystal structure
The invention provides a detection reagent for detecting the content of adenosine triphosphate, a preparation method of the detection reagent, and a method and a device for detecting the content of adenosine triphosphate by using the detection reagent. The detection reagent comprises a first reagent and a second reagent, wherein the first reagent comprises ZIF-90 crystal grains and laccase, the laccase is embedded in the crystal structure of the ZIF-90 crystal grain, and the second reagent comprises dopamine. The detection reagent is simple in preparation process, readily available in raw materials, relatively low in cost, and easy in industrial production; when the detection reagent is used for detecting the content of adenosine triphosphate, the detection reagent has particularly outstanding anti-interference capability, has the advantages of wide linear range, complete coverage of the physiological concentration range of adenosine triphosphate, low detection limit, high sensitivity,strong stability and good reproducibility, can realize rapid, real-time and continuous detection of adenosine triphosphate in a to-be-detected sample, and is especially suitable for detection of adenosine triphosphate in the physiological process of living brain nerves.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of branch type walking machine aptamer electrochemical sensor for adenosine triphosphate detection
ActiveCN112763562AHigh sensitivityGood repeatabilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAdenosineSignalling molecules
The invention relates to a preparation method of a branch type walking machine aptamer electrochemical sensor for adenosine triphosphate detection, which comprises the following steps: preparing an acanthosphere-shaped bimetallic oxide / functionalized carbon nano composite material by adopting a hydrothermal synthesis method, and constructing a branch-type walking machine by self-designing complementary pairing of bases, constructing a branch walking machine / acanthosphere bimetallic oxide / functionalized carbon nano composite material / film gold electrode through covalent bonding, and reflecting the content of a target object adenosine triphosphate by signal change generated by T-DNA marked by signal molecules, so that the signal-reduced electrochemical aptamer sensor for detecting adenosine triphosphate is obtained. Compared with other electrochemical sensors for detecting the content of adenosine triphosphate, the prepared branch type walking machine aptamer electrochemical sensor has the advantages of high sensitivity, good repeatability and high accuracy.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography filler, chromatographic column and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113499761ASimple preparation stepsGood repeatabilityOther chemical processesSolid sorbent liquid separationPhosphoric acidChromatography column
The invention discloses an immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography filler, a chromatographic column and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: mixing and stirring potash water glass, gamma-glycidyl ether oxypropyl trimethoxy silane and water-dissolved adenosine disodium triphosphate, then adding water-dissolved formamide, stirring to obtain a reaction solution, reacting and curing to obtain a solid material, and then washing to obtain the immobilized metal ion affinity chromatographic column filler. The ATP modified immobilized metal ion affinity capillary monolithic column prepared through a one-step reaction method is simple and rapid in preparation step, high in repeatability and yield and low in preparation cost. The product can be obtained by uniformly mixing the raw materials and then carrying out one-time baking reaction, and is good in physical and chemical stability, and has relatively good reproducibility after being used for multiple times.
Owner:AGRO BIOLOGICAL GENE RES CENT GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
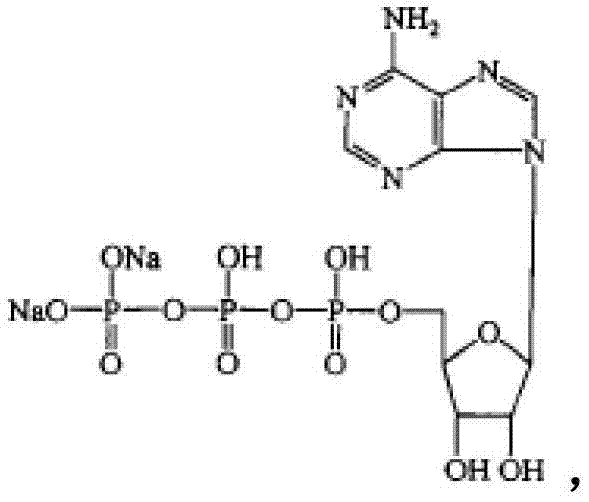
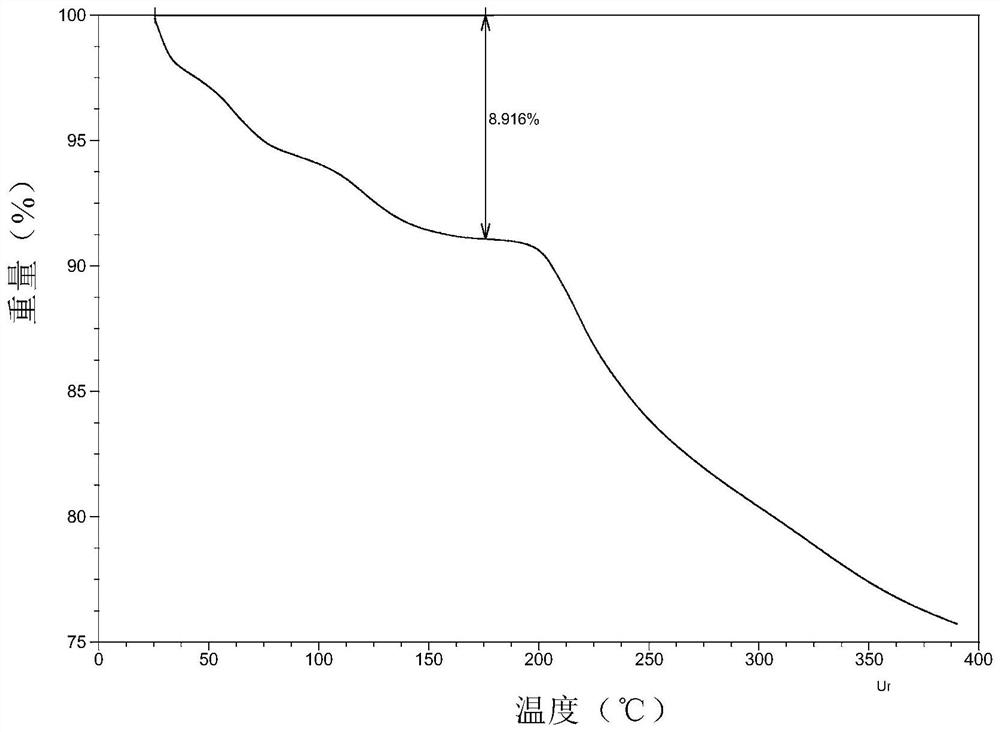
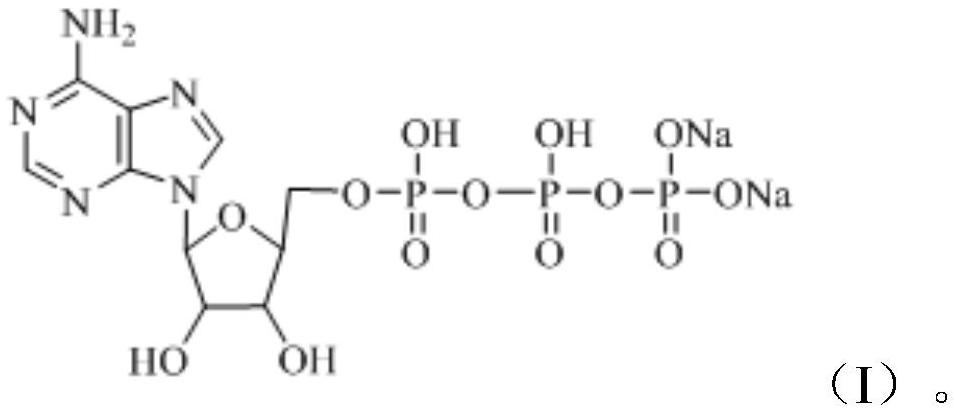
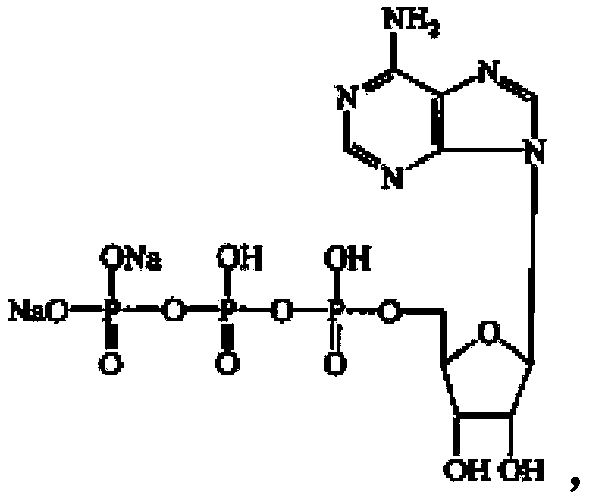
Trihydrate crystal of disodium adenosine triphosphate and preparation method thereof
PendingCN114539338AHigh purityImprove stabilityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAdenosinePhosphoric acid
The invention provides an adenosine disodium triphosphate trihydrate crystal and a preparation method thereof. Specifically, the invention provides a crystal of a compound as shown in a formula I, and the crystal is a trihydrate crystal. The crystal is high in stability, simple in preparation process, high in yield and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:苏州赜文医药科技有限公司
Disodium adenosine triphosphate troche medical composition
The invention relates to a disodium adenosine triphosphate troche medical composition, and in particular relates to use of calcium salt in preparation of stable triphosadenine or a solid medical composition of officinal salt thereof. The medical composition provided by the invention further stably comprises triphosadenine or the solid medical composition of officinal salt thereof. More specifically, the invention relates to the solid medical composition containing triphosadenine or the officinal salt thereof, wherein even if the medical composition is stored for a long time, the content of the effective components is still highly maintained to ensure the excellent stability. After the solid medical composition provided by the invention is placed at 20+ / -2 DEG C for 2 years, the residual ratio of active components, i.e., triphosadenine or officinal salt thereof in the composition is over 80%.
Owner:CHENGDU TIANTAISHAN PHARMA
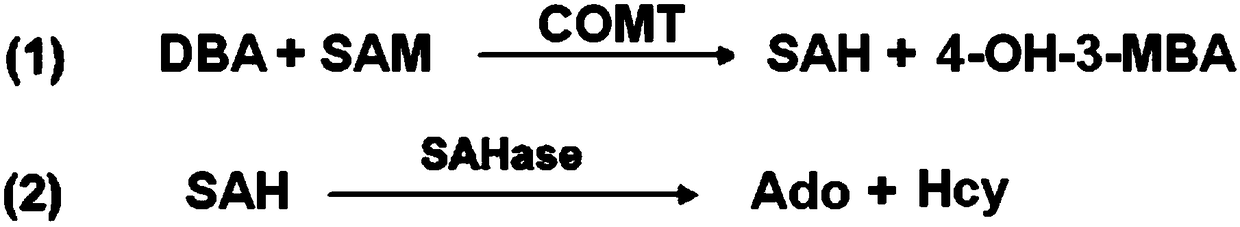
A kind of catechol-o-methyltransferase enzyme activity detection kit
ActiveCN105734114BEarly processing is simpleLow technical requirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisS-Adenosyl-l-methionineCatechol-O-methyl transferase
The invention provides a combined product for detecting activity of catechol-O-methyl transferase. The combined product comprises S-adenosine-L-methionine or an enzyme reaction system generating S-adenosine-L-methionine, and the enzyme reaction system comprises triphosadenine, methionine, S-adenosine methionine synthetic enzyme, methyl receptor and S-adenosine-L-homocysteine hydrolase. Preferably, the combined product is in the form of a kit, and each ingredient is in a state of reagent existing independently. The combined product can be used on semi-automatic or full-automatic analysis and detection equipment, and is high in detection sensitivity, high in specificity and simple and convenient to operate, thereby being capable of being popularized and applied truly.
Owner:山西盈科正欣生物科技有限公司
Topical compositions and methods
ActiveUS20210369596A1Improve antioxidant capacityReduce glycationCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAdenosineMatricaria
The present invention relates generally to cosmetic compositions and methods that can be used to increase skin hydration, increase adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production in skin, increase antioxidant capacity of skin, reduce glycation of skin, or a combination thereof. In particular, topical application of the compositions to skin increases adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production in skin by at least 10%, increases antioxidant capacity of skin, and / or reduces glycation of skin by at least 50%. In particular, the compositions can include Chamomilla recutita (Matricaria) flower extract, Vitis vinifera (Grape) seed extract, hydrolyzed sodium hyaluronate, Natural Moisturizing Factors (NMF), and optionally carnosine.
Owner:MARY KAY INC
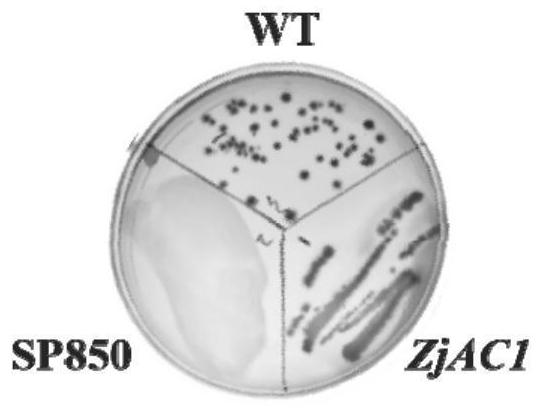
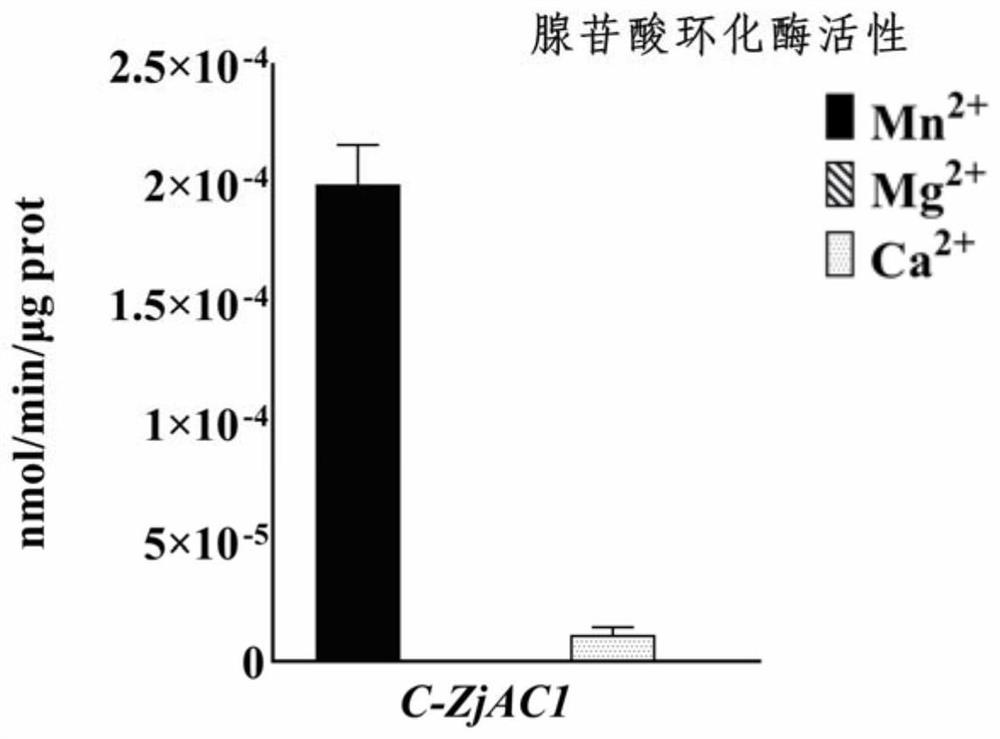
Coding gene sequence with adenosine triphosphate tunneling metalloenzyme activity
PendingCN113462705APossesses NTP hydrolase activityHas tripolyphosphatase activityHydrolasesGenetic engineeringAdenosineTripolyphosphatase activity
The invention discloses a coding gene sequence with adenosine triphosphate tunneling metalloenzyme activity, a gene for coding adenosine triphosphate tunneling metalloenzyme is ZjAC1, and the ZjAC1 has a DNA sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 in a sequence table. According to the invention, the coding gene sequence with adenosine triphosphate tunnel metalloenzyme activity is adopted, and the coded protein has the activity of adenylate cyclase, NTP hydrolase activity, triphosphatase activity and relatively weak pyrophosphatase activity.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
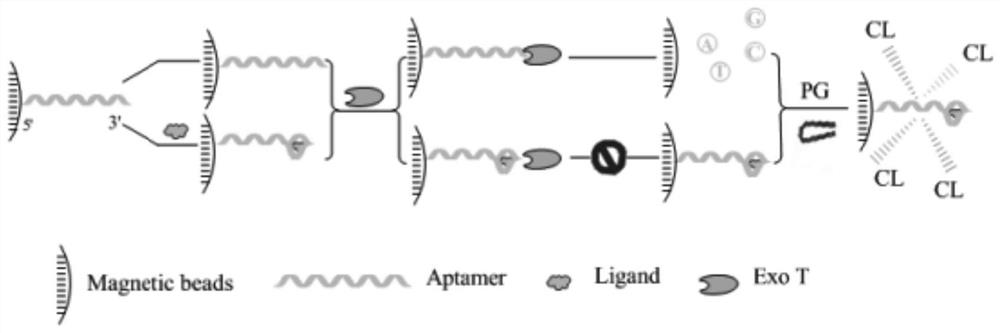
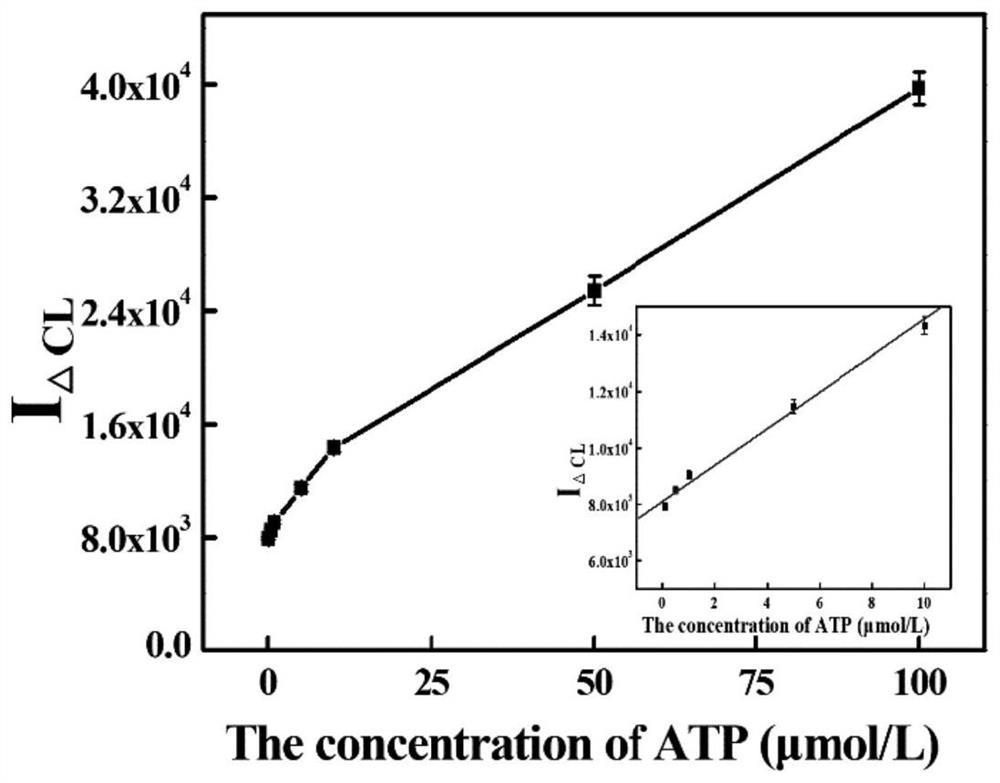
ATP chemiluminiscence detection method based on enzyme digestion assisted label-free aptamer sensor
ActiveCN112067602AStrong specificityGuaranteed specificityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAptamerEnzyme digestion
The invention provides an ATP chemiluminiscence detection method based on an enzyme digestion assisted label-free aptamer sensor, which comprises the following steps: immobilizing an aptamer on the surface of a magnetic microsphere, and specifically binding the aptamer with adenosine triphosphate, then, degrading the single-stranded DNA specifically and gradually into a free basic group from the 3' end by utilizing exonuclease T, and reducing a background signal remarkably based on the exonuclease, so that a quantitative relation between the quantity of the aptamer detected on the surface of the magnetic microsphere and the concentration of the ATP to be detected is obtained; and finally, carrying out chemiluminiscence detection on the aptamer sensor. Based on the principle that guanine base (G) on an ATP aptamer chain and a chemiluminescence reagent benzoyl formaldehyde (PG) are subjected to an instantaneous derivatization reaction to generate chemiluminescence, the marking link of other chemiluminescence markers is omitted, the operation steps are simplified on the basis of ensuring the sensitivity, the detection time is shortened, and the detection efficiency is improved. In addition, the used chemiluminescence analysis method is wide in linear range, simple in equipment and easy to operate, so that full-automatic detection is expected to be realized.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Disodium adenosine triphosphate external medicine for preventing and treating myopia as well as preparation method and application of disodium adenosine triphosphate external medicine
PendingCN114569546AEliminate or reduce astigmatismImprove distance visionOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderMuscular asthenopiaAdenosine
The invention discloses an adenosine disodium triphosphate external medicine for preventing and treating myopia as well as a preparation method and application of the adenosine disodium triphosphate external medicine. The externally applied medicine comprises an adenosine disodium triphosphate eye drop and an adenosine disodium triphosphate eye patch, wherein the adenosine disodium triphosphate eye patch comprises an eye patch liquid and a spunlace non-woven fabric for the eye patch; the invention further discloses a medicine for preventing and treating myopia. The medicine comprises an oral medicine and an external medicine, the disodium adenosine triphosphate eye drop and the disodium adenosine triphosphate eye patch liquid both comprise disodium adenosine triphosphate, L-methionine and a pH regulator. According to the disodium adenosine triphosphate eye patch, the prevention and treatment effects of disodium adenosine triphosphate on eye asthenopia, myopia and myopic amblyopia are effectively exerted, and side effects caused in the use process are effectively avoided. According to the invention, a lengthened part of the ocular axis can be shortened, astigmatism of a crystalline lens can be removed or relieved, the distant vision of naked eyes can be improved, the functions of optic nerves and retina can be improved, and some asthenopia and systemic discomfort symptoms caused by myopia can be relieved.
Owner:裴丽林
Preparation and application of non-immobilized photoelectric sensor for detecting ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
PendingCN114740067AImplement encapsulationAchieve releaseEnergy inputAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionAptamerAdenosine
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a non-immobilized photoelectrochemical sensor for detecting ATP (adenosine triphosphate), and belongs to the technical field of photoelectric biosensing analysis. The method comprises the following steps: synthesis of a magnetic MOFs material for packaging AA, namely Fe3O4 ZIF-90 AA, construction of a photoelectric sensor system, and photoelectrochemical analysis and detection of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The method has the characteristics that a photoelectrochemical biological analysis method with the advantages of simple equipment, high response speed, high sensitivity and the like is combined with a specific response mechanism between the ATP and Zn < 2 + > in the ZIF-90, so that the dependence on a nucleic acid aptamer is eliminated, the interference of layer-by-layer modification on an electrode is avoided, and finally, the non-immobilized sensitive detection of the ATP is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
A kind of adenosine triphosphate disodium composition powder injection
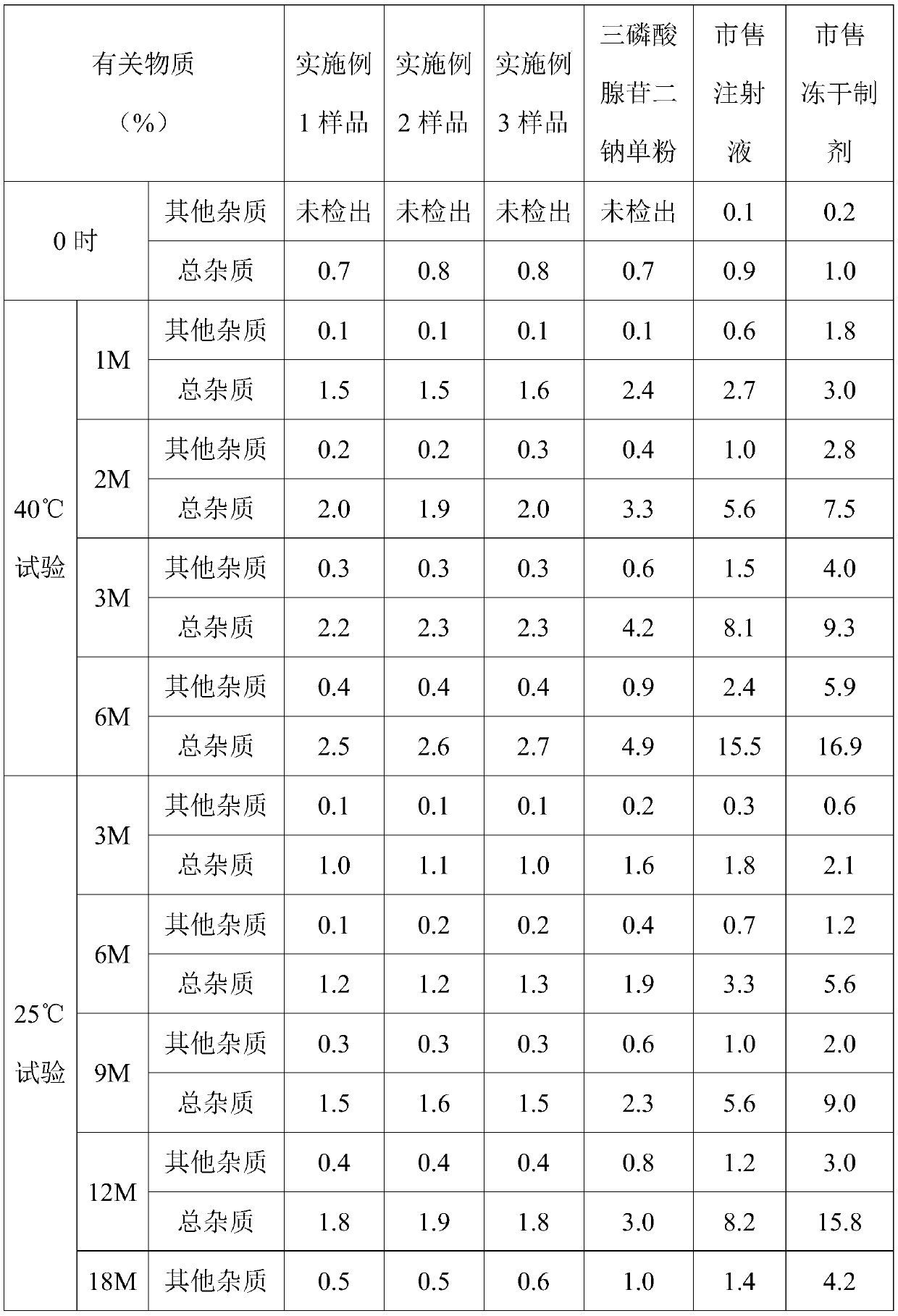
ActiveCN107890460BGood quality and stabilityLong shelf lifeOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryAdenosinePharmaceutical industry
The invention relates to an adenosine disodium triphosphate compound powder injection, belonging to the field of the pharmaceutical industry. The adenosine disodium triphosphate compound powder injection is composed of adenosine disodium triphosphate and a stabilizing agent in a mol ratio of 1: 0.5-2, wherein the stabilizing agent is anhydrous sodium carbonate, anhydrous sodium citrate, or a mixture thereof. The adenosine disodium triphosphate compound powder injection is good in quality stability; in a validity period of the adenosine disodium triphosphate compound powder injection, the content of other impurities in related substances are smaller than 1.0%, and the total content of impurities is less than 5%; and the adenosine disodium triphosphate compound powder injection is simple toprepare and low in cost, lowers the medical cost of patients and produces good social benefits.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BAIYUSN TIANXIN PHARMA
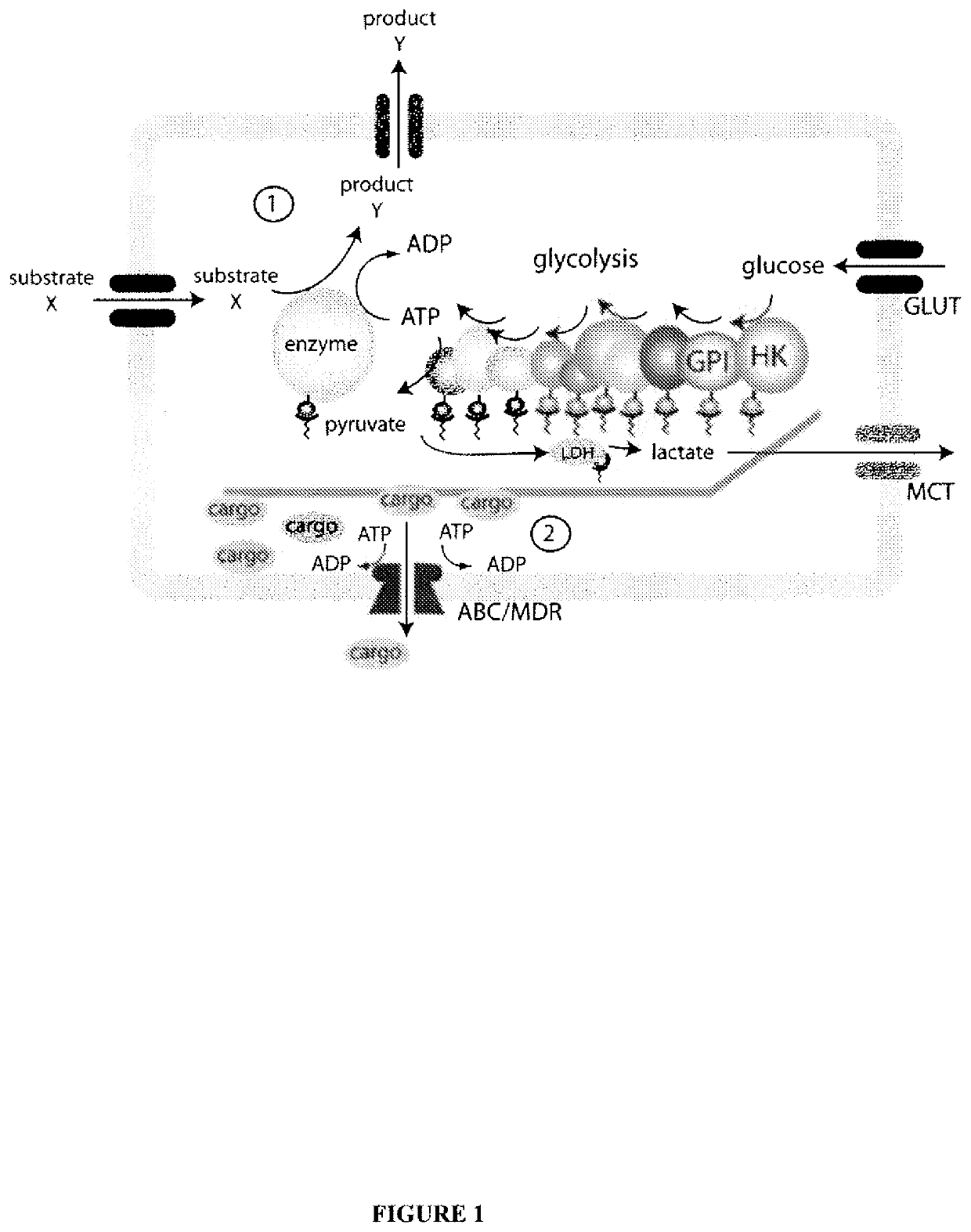
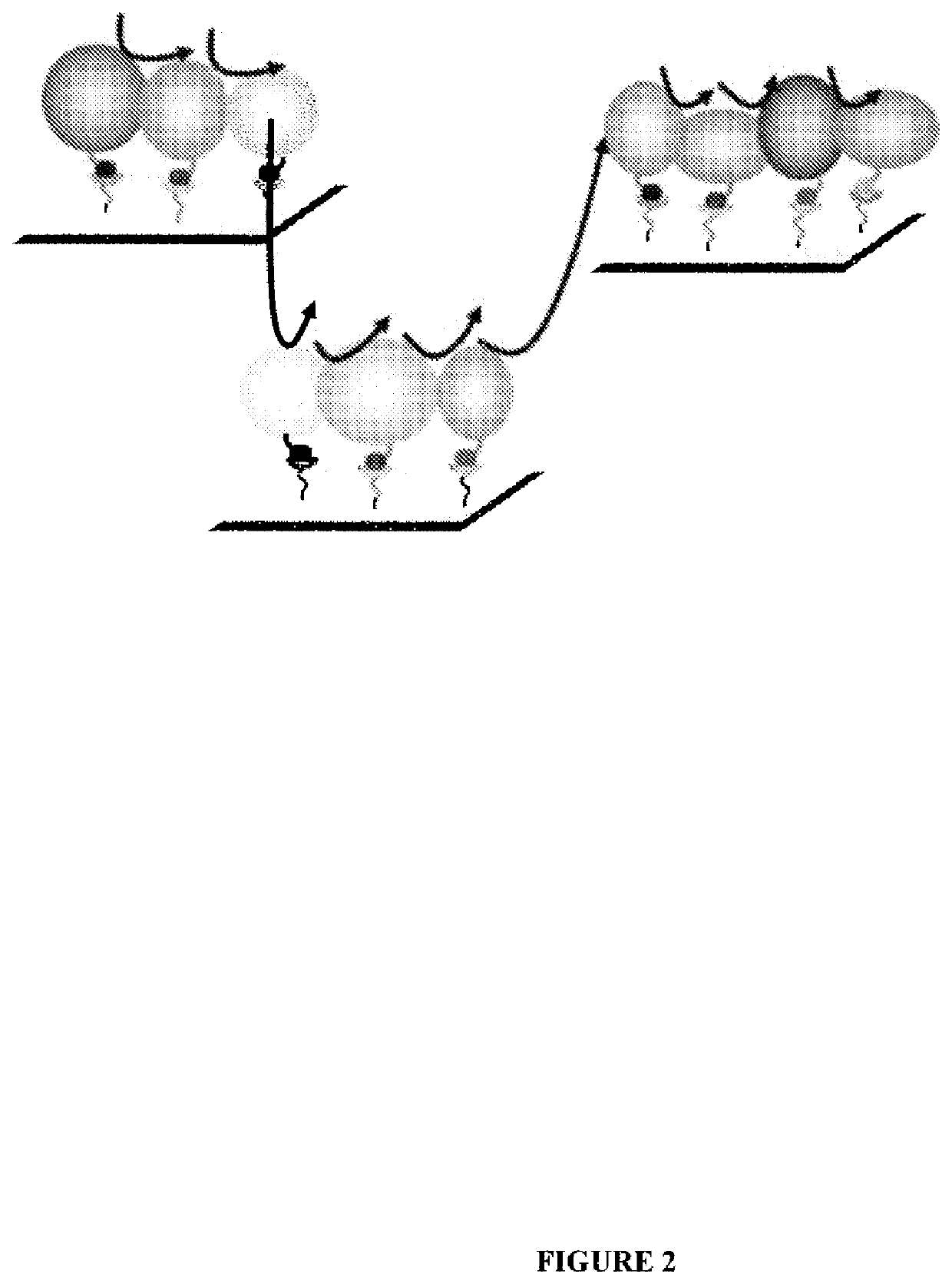
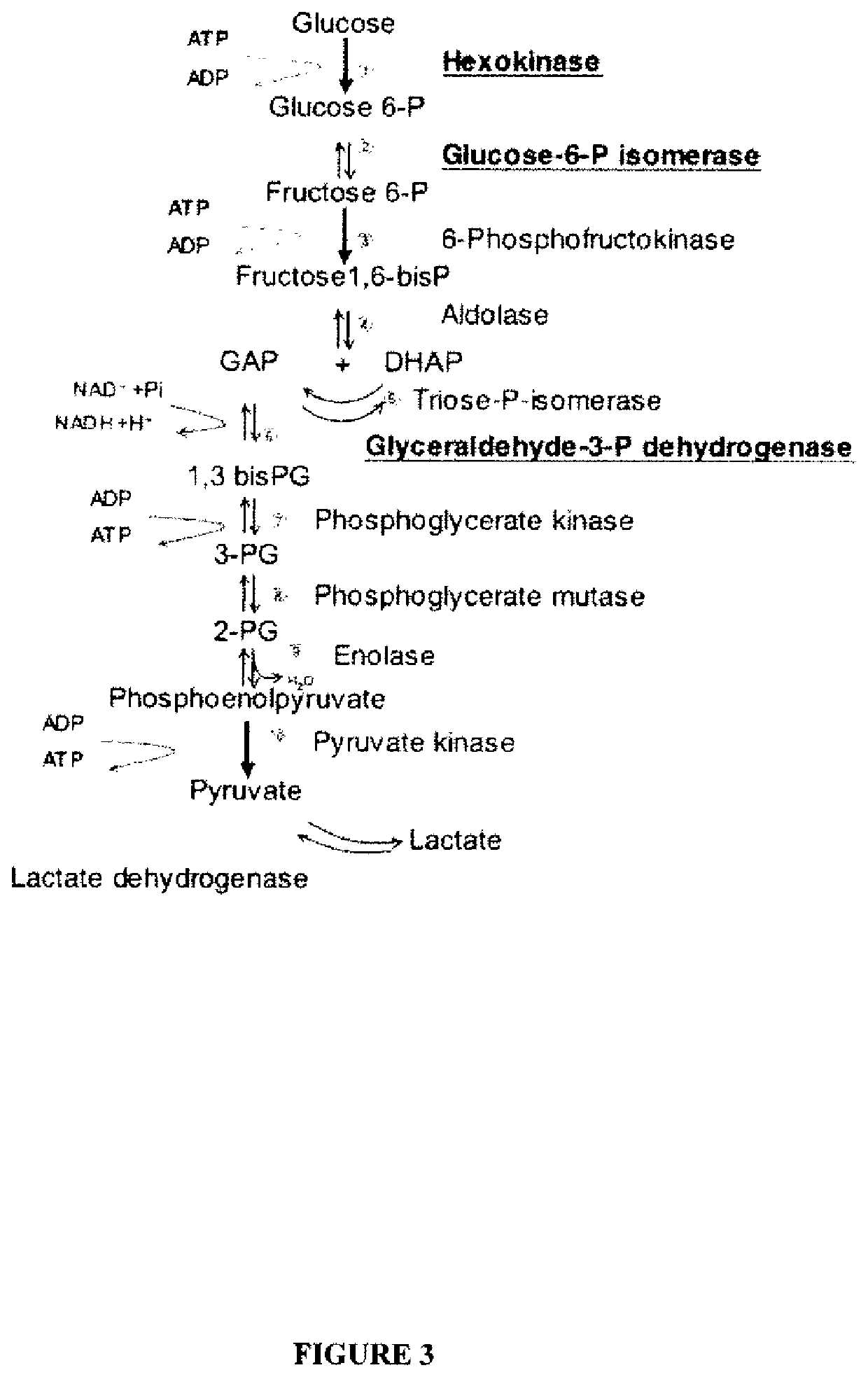
System for production of adenosine triphosphate
The present invention relates to a system for production of ATP. This system is comprised of a support and one or more enzymes coupled to that support which are capable of collectively producing ATP from glucose or fructose metabolism. The present invention is additionally directed to a device, which includes the system, and to a method for carrying out a reaction involving the conversion of ATP to ADP using the system.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Preparation method and application of spherical crystal of disodium adenosine triphosphate
PendingCN114560895AUniform particle sizeHigh purityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderCrystallographyAdenosine
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a spherical crystal of disodium adenosine triphosphate. Specifically, the invention provides a spherical crystal of a compound as shown in a formula I. The crystal is uniform in particle size, high in purity, good in fluidity, not prone to coalescence, high in bulk density and convenient to separate and dry.
Owner:苏州赜文医药科技有限公司
Preparation of a gold@graphene oxide composite nanomaterial and its application in the detection of adenosine triphosphate
ActiveCN110343522BSmall particle sizeLow densityMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon compoundsAdenosineOxide composite
The invention discloses the preparation of a gold@graphene oxide composite nanomaterial and its application in the detection of adenosine triphosphate. Graphene aqueous solution; stir and mix a certain volume of graphene oxide aqueous solution and gold nanoparticle solution at room temperature, then ultrasonically mix, and then filter with a filter membrane; strip gold@graphene oxide from the filter membrane, and dilute it with distilled water to the desired concentration. Concentration is required for storage at low temperature. Experiments show that there is a good linear relationship between the recovery of the silver nanocluster fluorescence signal and the concentration of adenosine triphosphate in the range of 5.0 pmol / L to 2.5 nmol / L. The gold@graphene oxide composite nanomaterial prepared by the present invention can achieve a good combination of gold and graphene oxide characteristics, and has more excellent characteristics, and has good biocompatibility and high stability, and can be used as an effective fluorescence quencher Quantitative detection of biomolecules using incinerators.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Application of disodium adenosine triphosphate in preparation of drug for treating diabetic foot
The invention belongs to the field of chemicals, relates to a novel pharmaceutical purpose of drugs, and particularly relates to an application of a disodium adenosine triphosphate drug in preparation of a drug for treating a diabetic foot. The invention discloses an application of disodium adenosine triphosphate in preparation of a drug for treating a diabetic foot. The disodium adenosine triphosphate medicine is disodium adenosine triphosphate for injection, a disodium adenosine triphosphate injection, or a disodium adenosine triphosphate tablet, or disodium adenosine triphosphate magnesium chloride or a disodium adenosine triphosphate-magnesium chloride injection or a disodium adenosine triphosphate enteric capsule.
Owner:陈钏黄
Steam system working technology in adenosine disodium triphosphate production
PendingCN111018925AReduce pollutionLarge air volumeSugar derivativesDistillation in boilers/stillsThermodynamicsAdenosine
The invention discloses a steam system working technology in adenosine disodium triphosphate production. The technology involves (1) a biomass steam boiler system, (2) a steam pipeline system and (3)an ethanol distillation recovery system.
Owner:GUANGXI PUBEI PHARMA FACTORY +1
Marine product preservative with antibacterial peptide loaded on gliadin nanoparticles and preparation method thereof
PendingCN112514980AImprove performanceImprove antibacterial propertiesVegetable proteins working-upMeat/fish preservation using chemicalsNanoparticleNisin
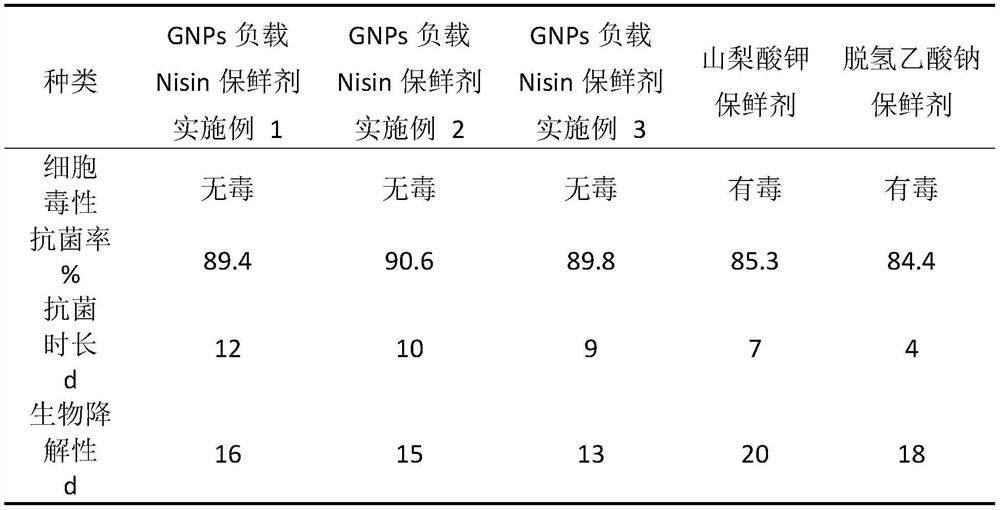
The invention provides a preparation method of a marine product preservative with antibacterial peptide (Nisin) loaded on Gliadin Nanoparticles (GNPs). The preparation method comprises the following steps of: mixing extracted gliadin with Nisin to obtain gliadin-Nisin nanoparticles; and mixing the obtained gliadin-Nisin nanoparticle solution with an impurity-removed nano chitin whisker (ChNW) solution to obtain the marine product preservative with antibacterial peptide loaded on gliadin nanoparticles. The marine product preservative is prepared by taking Nisin as a main raw material and otheraids as auxiliary materials, and the stability and bioavailability of Nisin are improved by embedding Nisin with GNPs. Meanwhile, the stability of GNPs is improved by adding ChNW into the GNPs solution. Nisin acts on a cytoplasmic membrane to cause exudation of cytoplasm such as adenosine triphosphate, namely matrix in cytoplasm is damaged to lose activity, so that the bacteriostatic and bactericidal effects are achieved. Experimental results show that the marine product preservative has excellent performances, has indexes exceeding those of commercially available common preservatives, has excellent antibacterial property, is short in biodegradation time, is safe and environment-friendly, and can completely replace the existing common preservatives.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com