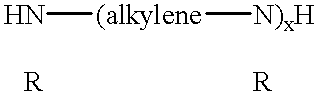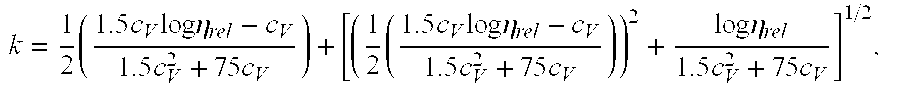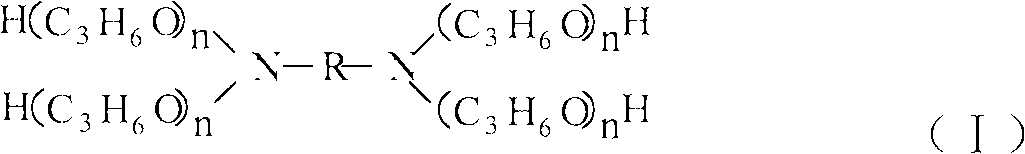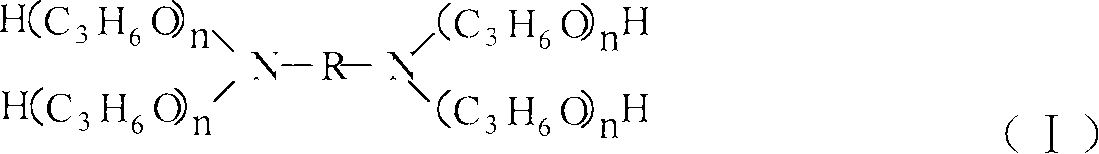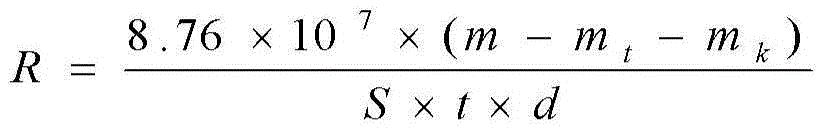Patents
Literature
48 results about "Ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
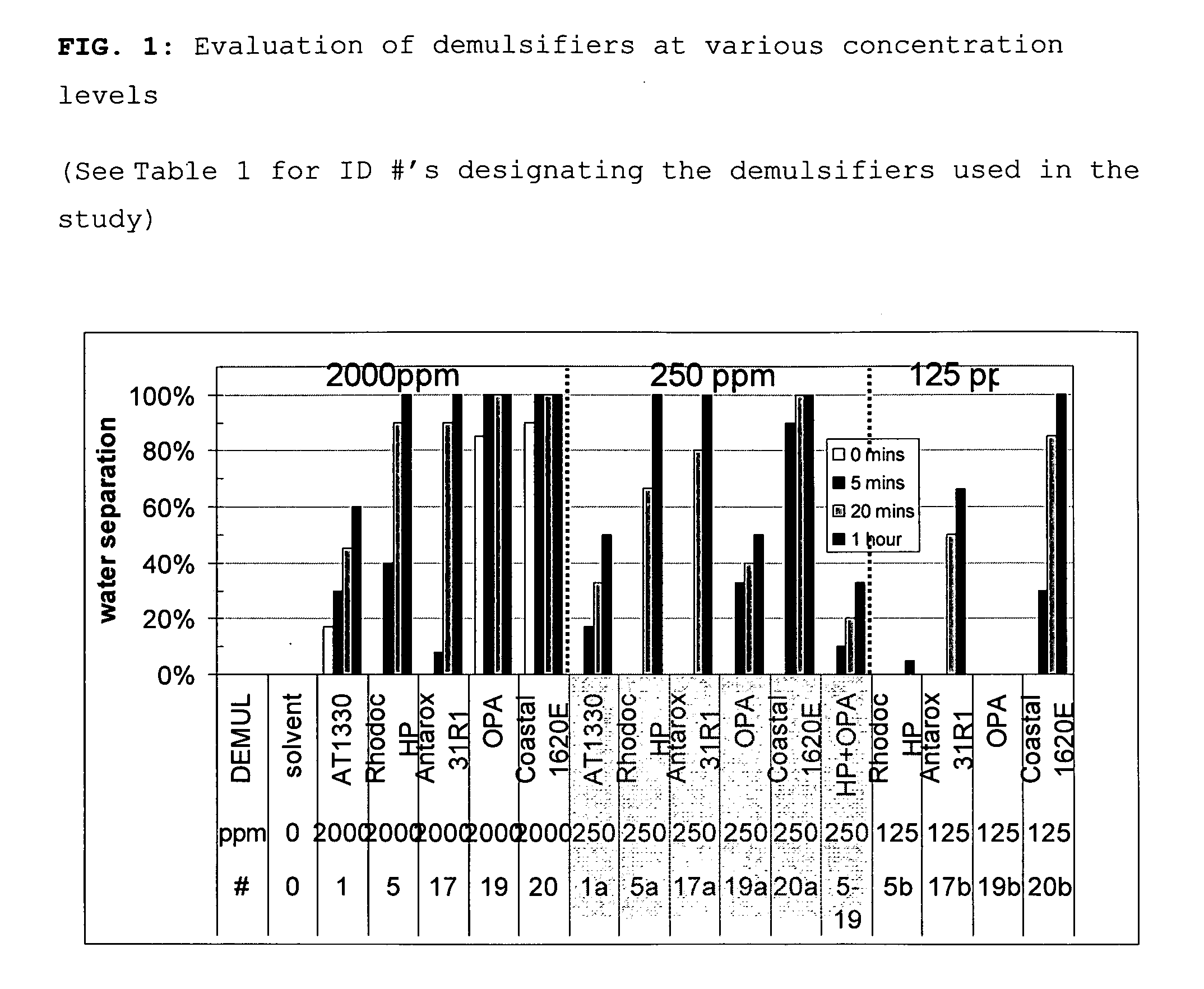
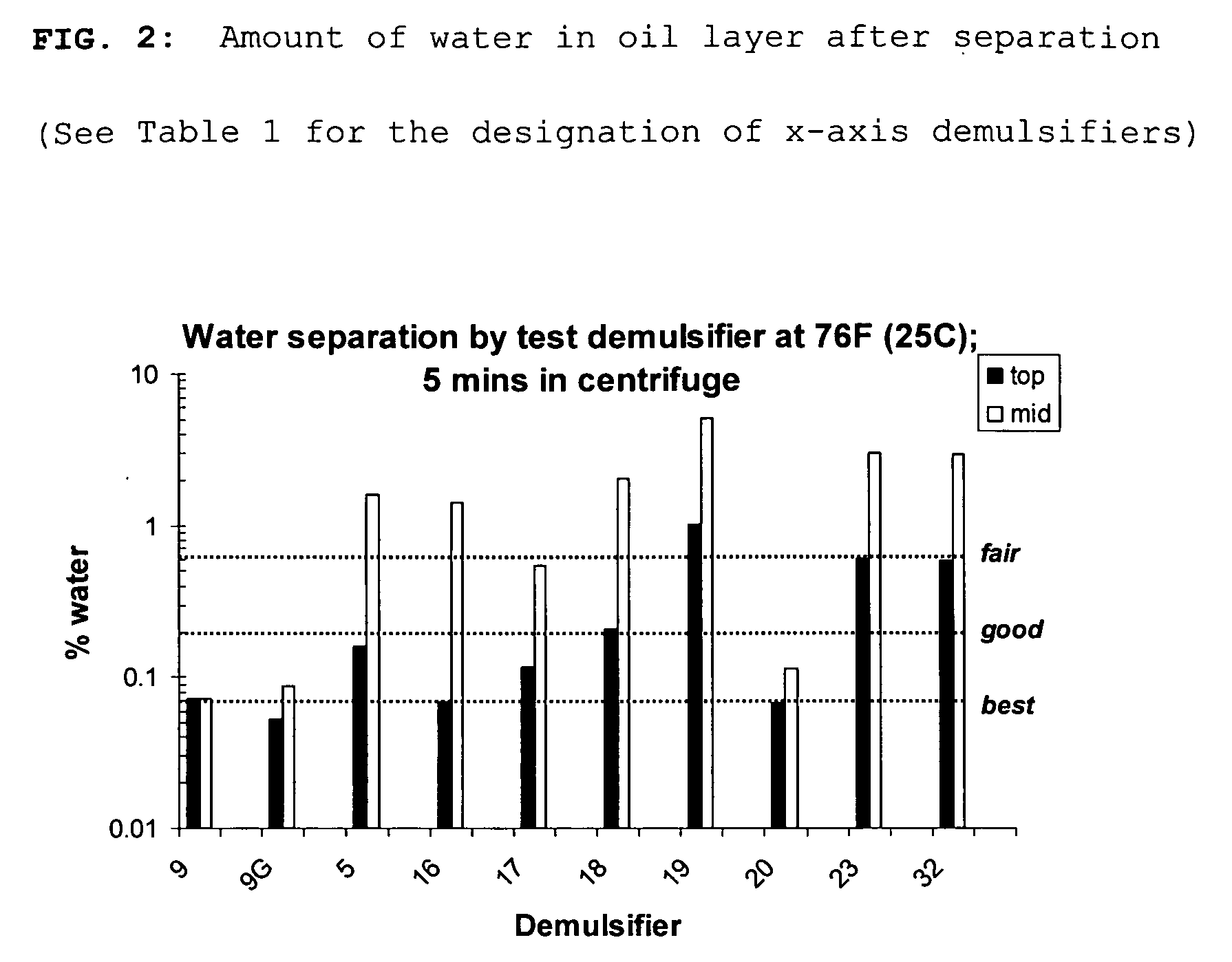
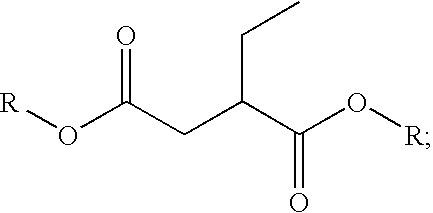
Demulsifiers in solvent base for separating emulsions and methods of use
InactiveUS20090149557A1Improve performanceGuaranteed to workOther chemical processesNon-miscible liquid separationPolymer scienceActive agent
Demulsifiers containing an anionic surfactant selected from alkylsulfosuccinates, alkylphosphonic acids, and their salts; a nonionic surfactant selected from ethylene oxide / propylene oxide copolymers, ethoxylated fatty acids of polyethylene glycol, terpene alkoxylates, and modified alkanolamides; and solvent bases comprising blends of dibasic esters. Methods for breaking emulsions using such demulsifiers and solvent bases are also disclosed.
Owner:RHODIA OPERATIONS SAS
Food Grade Lubricant Compositions
Novel non-aqueous water soluble food grade lubricant compositions comprising: (a) About 5% to about 50% of a polyalkylene glycol comprised of an ethylene oxide / propylene oxide copolymer, or polymer of propylene oxide, having molecular weight greater than 1,500; and (b) About 50% to about 95% of a polyethylene glycol having molecular weight of from about 200 to about 600; wherein said lubricating compositions have viscosities of about 28 to about 100% at 40° C. The novel non-aqueous water soluble food grade lubricant compositions are particularly useful in food processing and packaging equipment applications where low viscosity food grade lubricants with low pour points are desired, and in applications where there is a need for equipment and spill cleanup. These food grade lubricant compositions are also environmentally friendly due to their water solubility, rapid biodegradability, and low aquatic toxicity.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Machining fluid and method of machining
InactiveUS6316394B1Resists oil contaminationImprove the immunityWork treatment devicesAdditivesWater dispersiblePhosphate
A synthetic aqueous machining fluid admixture, that is free of sulfur containing and chlorine containing lubricants, and usable in heavy duty machining (e.g. stamping, punching and drawing) operations comprises a) water, b) a water soluble or dispersible fatty acid or water soluble or dispersible fatty acid salt, c) a water soluble or dispersible ethylene oxide propylene oxide copolymer having at least one terminal hydroxyl group or water soluble or dispersible derivative of an ethylene oxide propylene oxide copolymer and d) a water soluble or dispersible organic phosphate ester. Methods for heavy duty machining comprise the steps of applying a force to a workpiece by a tool contacting the workpiece and applying the synthetic aqueous fluid admixture to the interface between the tool and workpiece. The fluid exhibits safety and environmental advantages in use compared to prior art fluids comprising vanishing oils while providing equal or superior lubricity.
Owner:MILACRON IND PROD
Rinse aid compositions and methods
InactiveUS20060046954A1Reduce generationEliminate needOrganic detergent compounding agentsPolymeric surface-active compoundsAdditive ingredientEthylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer
Rinse aid compositions and methods for using and methods for making the compositions for warewashing processes. In one aspect, the rinse aid composition includes ingredients listed on the FDA GRAS (“generally recognized as safe”) list, including 21 C.F.R. 172 and / or 21 C.F.R. 178; preferably, all the ingredients are listed on the GRAS list. The rinse aid composition includes at least two ethylene oxide-propylene oxide (EO / PO) copolymers, with at least one of those EO / PO copolymers being PO-terminated. The rinse aid composition can include two PO-terminated EO / PO copolymers.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Cement liquid grinding aid and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102153308AImprove finenessOptimized areaEthylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymerCarboxylic acid
The invention provides a liquid cement grinding aid, which mainly contains the following components in percentage by weight: 5-30% of triethanolamine, 5-30% of triisopropanolamine, 5-30% of glycol, 1-5% of adipate, 2-15% of ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer, 5-30% of polycarboxylic acid, 5-30% of molasses and the balance of water. The cement liquid grinding aid of the invention, in which the ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer having a densifying effect on cement concrete is in particular added, has the advantages of obviously improving the fineness and the specific surface area of the cement product, improving the grinding aid effect and improving the strength of a cement test block in each age; in addition, compared with the liquid grinding aid of the prior art, the cement liquid grinding aid can reduce the energy consumption while the same fineness and specific surface area are obtained. The invention also provides a method for preparing the cement liquid grinding aid.
Owner:北京金隅水泥节能科技有限公司
Recording Liquid, Liquid Cartridge Holding Recording Liquid and Liquid Emitting Apparatus and Method
InactiveUS20070263032A1Superior emission stabilityHigh quality printingDuplicating/marking methodsInksEthylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymerSolvent
Disclosed is a recording liquid for recording an image or a letter / character used for recording an image or a letter / character on a recording paper sheet P. The recording liquid contains a dye, a solvent for dissolving or dispersing the dye, at least one of specified ethylene oxide adducts of 2-ethyl-2-butyl-1,3-propanediol and at least one of specified ethylene oxide / propylene oxide copolymers.
Owner:SONY CORP
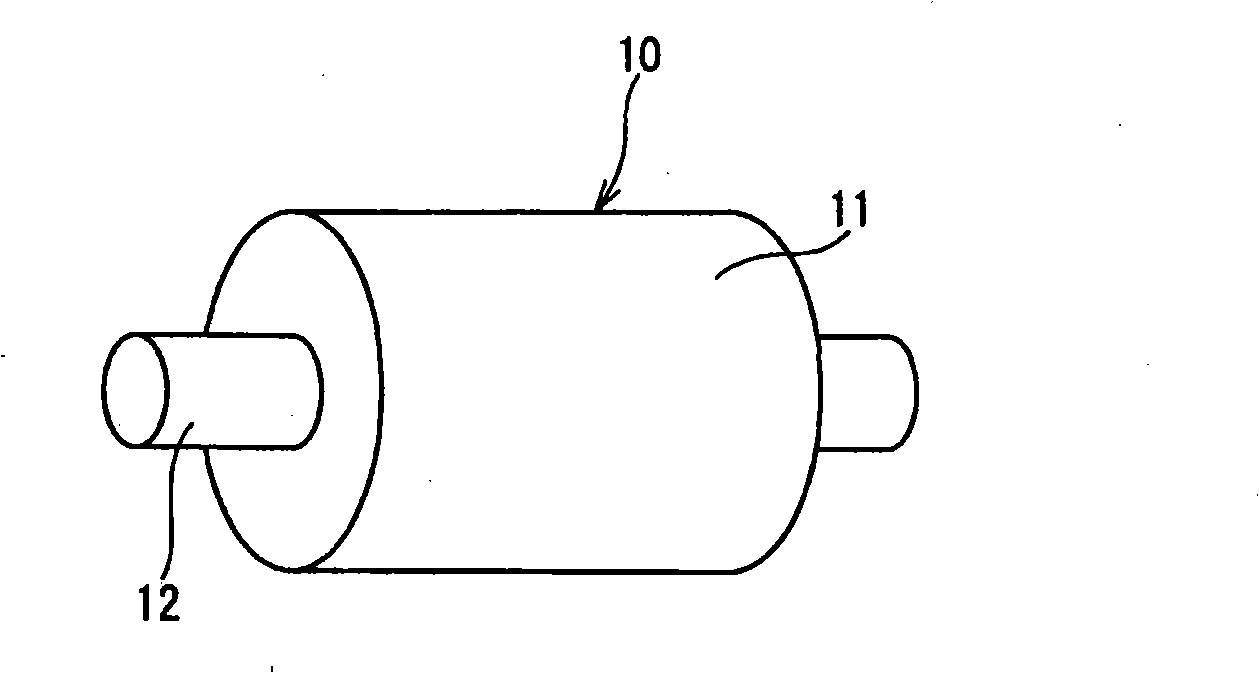
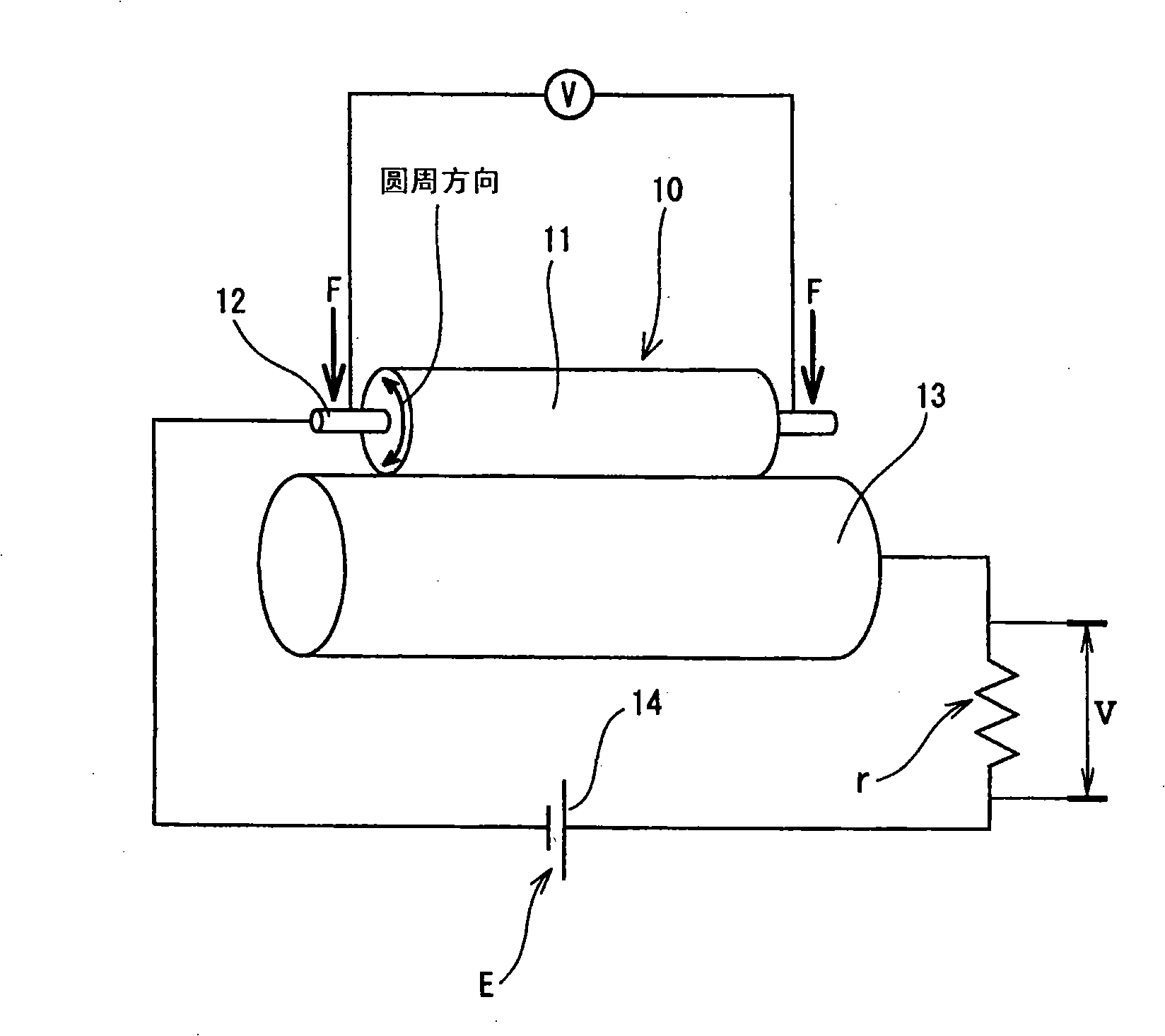
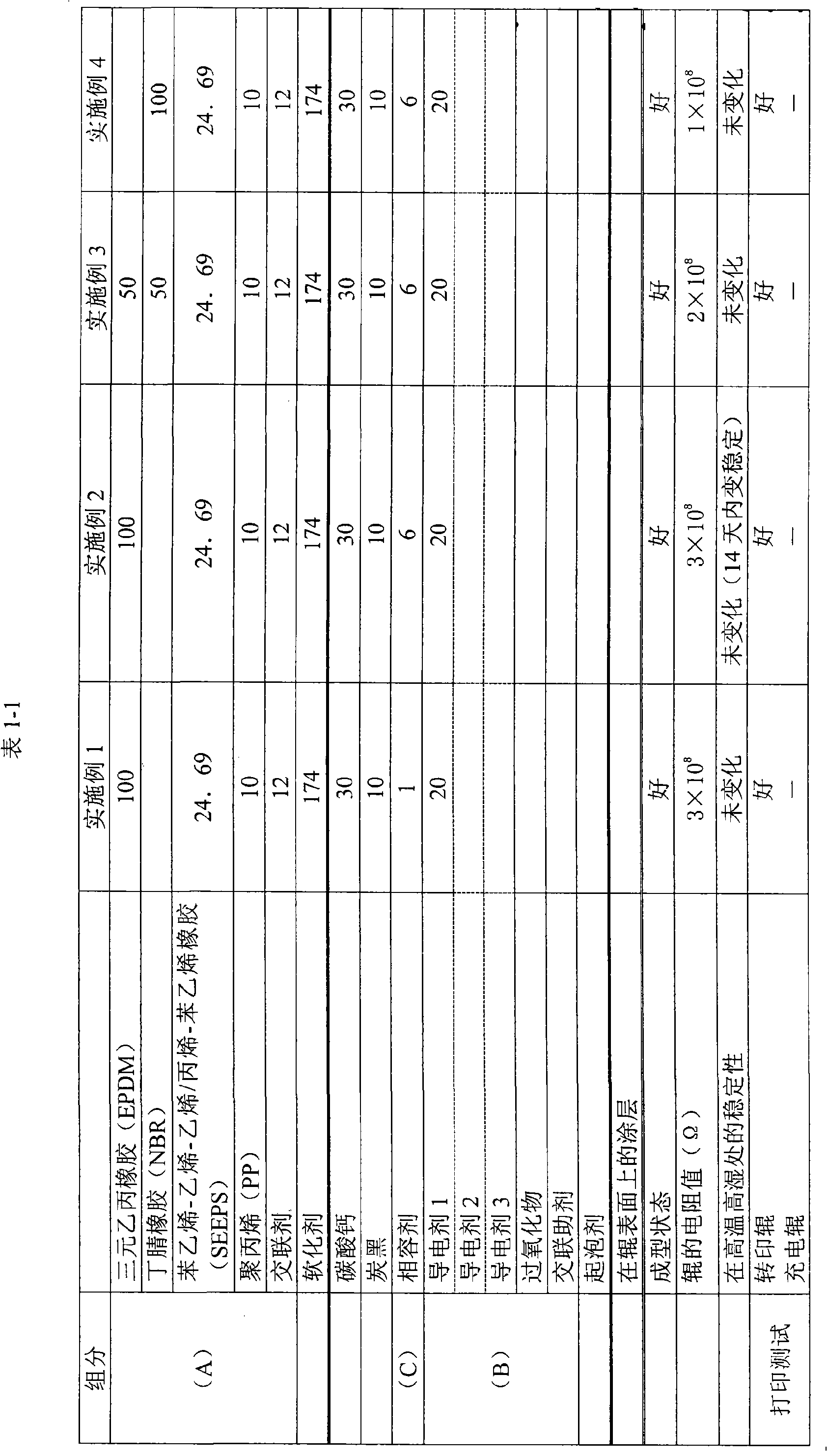
Conductive thermoplastic elastomer composition, method of producing same, and molding
InactiveUS7744781B2Good dispersionEasy to processConductive materialOrganic conductorsThermoplastic elastomerEthylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer
A conductive thermoplastic elastomer composition comprising a component (A) containing a thermoplastic resin or / and a thermoplastic elastomer; a component (B) comprising an ionic-conductive agent containing an ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer or / and an ethylene oxide-propylene oxide-allyl glycidyl ether copolymer and a metal salt contained in the ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer or / and the ethylene oxide-propylene oxide-allyl glycidyl ether copolymer; and a component (C) comprising an ethylene-acrylic ester-maleic anhydride copolymer.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Conductive thermoplastic elastomer composition, method of producing same, and molding
InactiveUS20080042108A1Good dispersionEasy to processConductive materialOrganic conductorsThermoplastic elastomerEthylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer
A conductive thermoplastic elastomer composition comprising a component (A) containing a thermoplastic resin or / and a thermoplastic elastomer; a component (B) comprising an ionic-conductive agent containing an ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer or / and an ethylene oxide-propylene oxide-allyl glycidyl ether copolymer and a metal salt contained in the ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer or / and the ethylene oxide-propylene oxide-allyl glycidyl ether copolymer; and a component (C) comprising an ethylene-acrylic ester-maleic anhydride copolymer.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Process for Preparing Vinyl Acetate-Ethylene Copolymers by Means of Emulsion Polymerization
ActiveUS20120015201A1Monocarboxylic acid ester polymer adhesivesSynthetic resin layered productsAcetic acidEmulsion polymerization
The invention provides a process for preparing vinyl acetate-ethylene copolymers by means of free-radically initiated emulsion polymerization of vinyl acetate and 18% to 34% by weight of ethylene, based on the total weight of the vinyl acetate and ethylene monomers, and, optionally, further comonomers, characterized in that polymerization takes place in the presence of at least one protective colloid and of 0.5% to 4% by weight, based on the total amount of monomers, of at least one nonionic, ethoxylated emulsifier with a branched or linear alkyl radical or in the form of ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymers, and in the absence of chain transfer agent, and, before the initiation of the polymerization, 10% to 70% by weight of the vinyl acetate monomer and 40% to 100% by weight of the ethylene monomer are included in the initial charge, up to 100% by weight of the protective colloid fraction is included in the initial charge, at least 25% by weight of the emulsifier fraction is included in the initial charge, and the remaining fractions of monomers, protective colloid and emulsifier are metered in during the polymerization, the procedure being such that the criterion of process COP meets the condition2.5≦COP≦70, whereCOP=100×(ETM2.5×ETV1.25×EA2.5×EV1.5×VV−1), whereETM=MEt / MM, ETV=MEtV / MEt, EA=100 ME / MM, EV=MEV / ME and VV=MVacV / MVac, whereMEt=total mass of ethylene in kg, MM=total mass of monomer in kg, MEtV=mass of ethylene charge in kg, ME=total mass of emulsifier in kg, MEV=mass of emulsifier charge in kg; MVacV=mass of vinyl acetate charge in kg, and MVac=total mass of vinyl acetate in kg.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Biocidal compositions
InactiveUS20090325965A1Easy to useBiocideDead animal preservationPolymer scienceEthylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer
Compositions of 1-(3-chloroallyl)-3,5,7-triaza-1-azonia-adamantane chloride, and an optional second biocide, in copolymers of ethylene oxide / propylene oxide are provided. The compositions exhibit good color and phase stability.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Environmental-protection oriented silicon steel insulation layer
ActiveCN1978563ANo problem of moisture absorption and stickinessEpoxy resin coatingsInsulation layerAlkaline earth metal
The aqueous suspension of inorganic titanates containing meta titanates (M(II)TiO3), normal titanates (M(II)2TiO4) and mixed titanates (M(I)2Ti2O5), is an important components of the coating in this invention. The M stands for metals such as Potassium, Lithium and Sodium, the alkaline-earth metals such as Barium, Strontium, Magnesium and Calcium, as well as Zinc, Iron and Aluminium. The said aqueous suspension of inorganic titanates accounts 17.2-28.2% of the total weight ,the boric acid 0.17-13.9% and the ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymers 0.012-0.115%; the fillings such as Silicon dioxide, alumina and mica account for 0-20% and the rest is water. As an environment protective coating, it can be used to coat on the surface of the oriented silicon steel products. They contain no Chromium that does harm to environment and children, can be applied to products with demand of high security such as child toys and exported to the European Union and. Besides, this coating has no problem of moisture absorption and pastiness.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
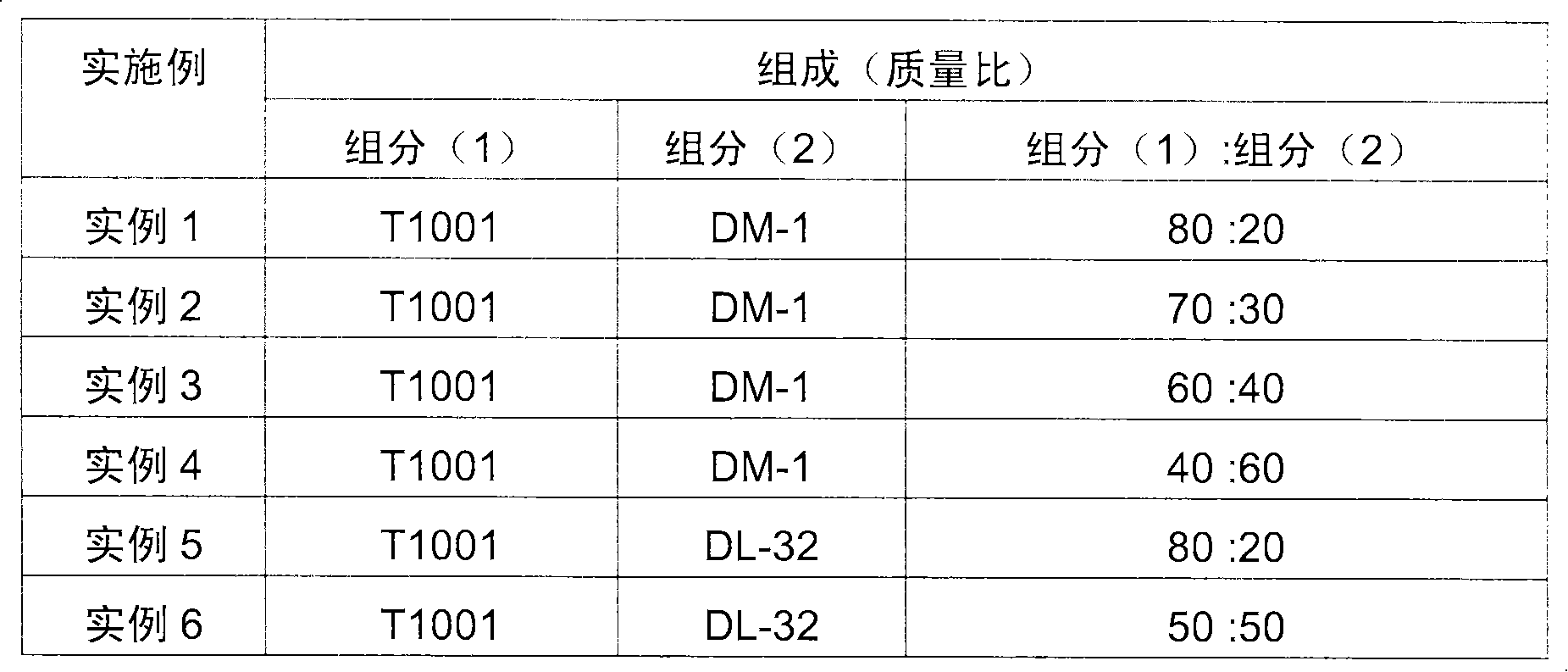
Lubricant anti-emulsifier composition and application thereof
The invention provides a lubricant anti-emulsifier composition. The composition consists of a derivative (1) of alkylene diamine oxozone trimethylene and a copolymer (2) of ethylene oxide and propylene oxide, wherein the mass ratio of the component (1) to the component (2) is between 40:60 and 80:20. The anti-emulsifier composition is used for steam turbine oil to change the lypophile-hydrophile balance of the original emulsion and realize the quick separation of oil and water in a phase inversion process.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Electroconductive thermoplastic elastomer composition, its manufacturing method and molded product
InactiveCN101319072ADurableHas resistance valueThermoplastic elastomerEthylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer
A conductive thermoplastic elastomer composition comprising a component (A) containing a thermoplastic resin or / and a thermoplastic elastomer; a component (B) comprising an ionic-conductive agent containing an ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer or / and an ethylene oxide-propylene oxide-allyl glycidyl ether copolymer and a metal salt contained in the ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer or / and the ethylene oxide-propylene oxide-allyl glycidyl ether copolymer; and a component (C) comprising an ethylene-acrylic ester-maleic anhydride copolymer.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Solvent Compositions
ActiveUS20130037749A1Organic detergent compounding agentsOther chemical processesEthylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymerCarboxylic acid
Suggested are solvent compositions, comprising (a) Carboxylic acid dialkyl amides (b) Fatty acids or their salts, and (c) Ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymers.
Owner:COGNIS IP MANAGEMENT GMBH
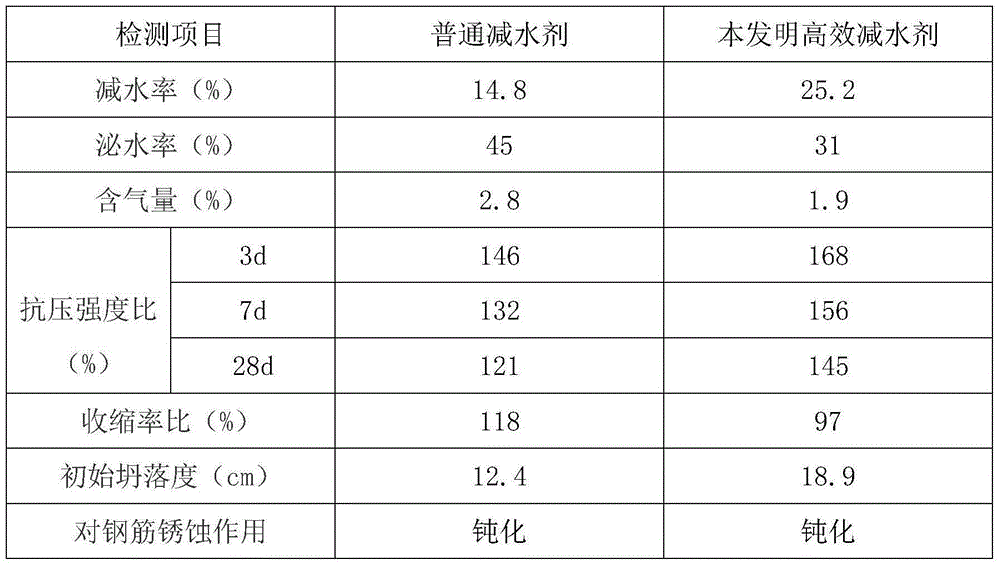
Superplasticizer
The invention discloses a high-efficiency water-reducing agent, which is prepared by the following raw materials in parts by weight: 50-60 parts of beta-naphthalene sulfonate formaldehyde condensate, 20-30 parts of poly(ethylene glycol) monomethyl ether methacrylate, 15-25 parts of calcium lignosulphonate, 10-15 parts of ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer, 2-4 parts of trehalose, 1.5-2.5 parts of silicone powder, 4-8 parts of shale ashes, 2.5-4.5 parts of sodium hydrogen sulfite, 5-10 parts of polyethylene oxide, 8-14 parts of aluminum tripolyphosphate, 2-3 parts of cocoanut oil diethanolamide, 1-2 parts of barium dinonyl naphthalenesulfonate, 2-3 parts of urotropine, and 3-5 parts of auxiliaries. The water-reducing agent is high in water-reducing rate, good in flowability, capable of obviously improving the flowability and working degree of the concrete, obvious in early-strength effect after being finally set, capable of greatly improving the strength of the concrete in all ages, and applicable to various concretes.
Owner:唐山砼科建筑科技有限公司
High-performance polycarboxylate water reducer and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a high-performance polycarboxylate water reducer and a preparation method thereof. The high-performance polycarboxylate water reducer is prepared from the following raw materials: acrylic acid, mercaptoacetic acid, isoamylene alcohol polyoxyethylene ether, hydrogen peroxide, vitamin, white sugar, sodium dodecyl sulfate, solid naphthalene, concentrated sulfuric acid, formaldehyde, caustic soda liquid, polyethylene glycol monoethylether methacrylic ester, calcium lignosulphonate, an ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer, trehalose, shale ash, sodium hydrogen sulfite, polyoxyethylene, aluminum triphosphate, oleic acid diethanolamide, dinonylnaphthalene sulfonic acid, urotropin, an additive, acetone, sodium sulfite, acrylamide, an initiating agent and water. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing the isoamylene alcohol polyoxyethylene ether and the like; after the solid naphthalene is processed, adding a silicone powder into the processed solid naphthalene and stirring the mixture; processing the acrylamide and the like; finally, mixing products obtained in the former three steps, so as to obtain the high-performance polycarboxylate water reducer. The high-performance polycarboxylate water reducer has the advantages that the corrosion resistance and the water reducing rate can be improved, and the slump loss is smaller.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DADONGWU GROUP CONSTR OF THE NEW MATERIAL
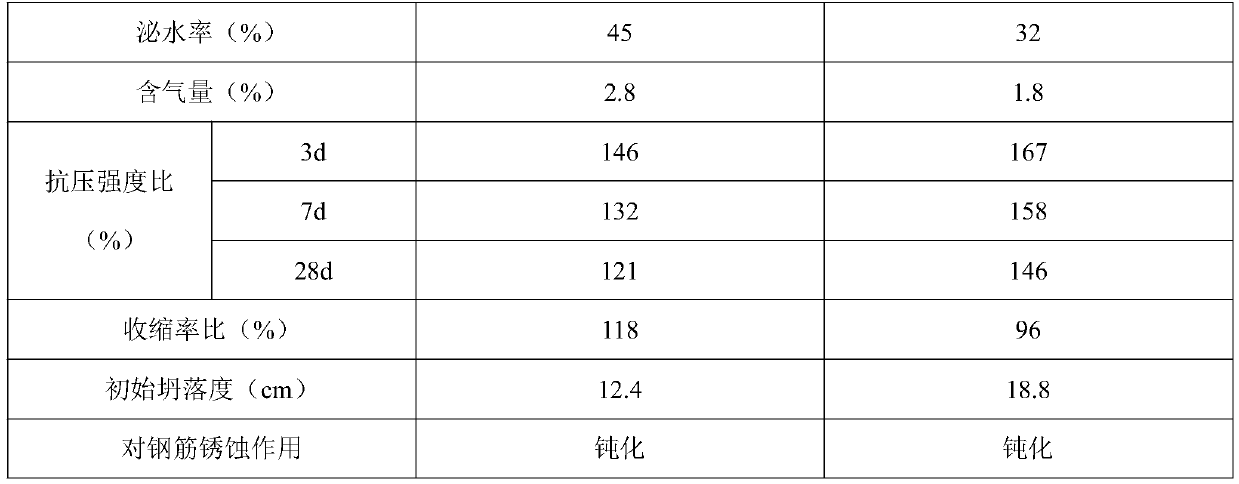
Underwater-non-dispersing non-shrinking grouting material
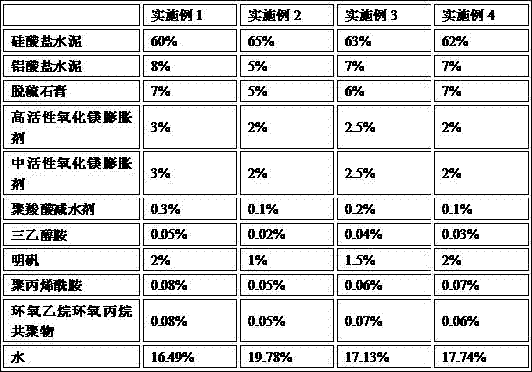
Disclosed is an underwater-non-dispersing non-shrinking grouting material. The raw material formula of the grouting material is as follows: 60-65% of Portland cement, 5-8% of aluminate cement, 5-7% of desulphurization gypsum, 2-3% of a high-activity magnesia expansive agent, 2-3% of a medium-activity magnesia expansive agent, 0.1-0.3% of a polycarboxylic acid water reducing agent, 0.02-0.05% of triethanolamine, 1-2% of alum, 0.05-0.08% of polyacrylamide, 0.05-0.08% of an ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer and the balance of water. The grouting material provided by the invention has a good flow ability and groutability, and is not dispersed or segregated during direct grouting construction underwater. The hardened grout body has good strength both in the early and later period. The grout body has comparatively high volume stability and does not shrink, and the durability is improved obviously.
Owner:XUZHOU ZHONGLIAN CONCRETE CO LTD
Test strip for detecting low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in serum, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107402209AThe test result is accurateRapid responseMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorLow density lipoprotein cholesterolChemical reaction
The invention relates to a test strip for detecting low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in serum. The test strip includes a dry chemical reaction chip, the dry chemical reaction chip is prepared by soaking a reagent pad in a chemical reagent and then drying the reagent pad, and the chemical reagent is prepared from cholesterol esterase, cholesterol oxidase, peroxidase, metal salt, a color developer, polyoxyethylene ether and an ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer having preferable concentrations according to a preferable ratio. The test strip has the advantages of low cost, easiness in preparation and obtaining, quickness in reaction and convenience in operation.
Owner:LUMIGENEX (SUZHOU) CO LTD
Efficient stain-removing windshield washer fluid
InactiveCN108165386AGuaranteed clarityClear visionOrganic detergent compounding agentsAmpholytes/electroneutral surface-active compoundsBetaineAlkyl polyglycoside
The invention relates to an efficient stain-removing windshield washer fluid, which comprises the following raw materials by mass: 50-70 parts of deionized water, 2-5 parts of ethanol, 1-3 parts of sodium dodecyl sulfate, 1-2 parts of sodium olefinsulfonate, 0.5-1.5 parts of sodium polyoxyethylene fatty alcohol sulfate, 1-5 parts of alkylolamide, 1-3 parts of alkyl polyglycoside, 0.5-1.5 parts ofalkyl betaine, 1-3 parts of alkyl sodium sulfonate, 1-3 parts of an ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer, 0.2-0.3 part of ethylene glycol, and 1-5 parts of a defoamer. The defoamer adopted by theinvention is emulsified silicone oil, can inhibit the formation of bubbles during use, and ensure that the windshield glass clear and transparent. In addition, the formula adopted by the invention canefficiently and quickly remove dust, bird droppings and stubborn stains formed after collision of animal insects on the surfaces of automobile front windshields and headlamp glass.
Owner:LUOYANG MINGLI TECH DEV
Use of polypropylene oxide or ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymers in combination with starch ether derivatives as additive in dry mortar compositions
ActiveUS20150166413A1Good redispersibilityStarch dervative coatingsStarch derivtive adhesivesAlkali saltEther
The use of an adhesion-promoting additive combination composed of one or more polyalkylenoxides out of the group comprising polypropylene oxides and ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymers, and of one or more starch ether derivatives out of the group comprising carboxyalkyl starch ethers and their alkali salts, and hydroxyalkyl starch ethers, in mortar compositions comprising mineral binders and water-redispersible polymer powders.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Clean preparation method of high-quality and high-purity natural-color bamboo fluff pulp
ActiveCN106192542AKeep it pureKeep naturalWashing/displacing pulp-treating liquorsMachine wet endBursting strengthFluff pulp
The invention belongs to the pulping field, and particularly relates to a clean preparation method of high-quality and high-purity natural-color bamboo fluff pulp. The method comprises the following steps that natural-color KP bamboo pulp is fully and uniformly defiberized; the defiberized pulp is diluted and then fed into a heat disperser, and sodium hydroxide is added for alkali extraction; the pulp subjected to heat dispersion is diluted with water and enters a flotation machine for flotation, and meanwhile a trapping agent oxirane-epoxypropane copolymer is added; the pulp obtained after flotation is washed and shrunk through a vacuum pulp washer, and generated washing waste liquid is drained; the pulp enters a pulp board papermaking workshop after being washed. The natural-color bamboo fluff pulp prepared through the technology has the advantages that the technological process is simple, the production efficiency, the production capacity, the finished pulp yield rate and the raw material utilization rate are high, investment is low, adopted chemicals are clean and environmentally friendly, a fluff pulp board has the low bursting strength, flexibility, comfort and elasticity are achieved, the liquid absorbing property is good, raising and dissociating are easily achieved, dust is little, and the hygienic indexes such as the good bacterium inhibiting property, antibacterial property and antianaphylaxis meet the requirement.
Owner:李文俊
Fatty alcohol block polyether, dispersant for aqueous pesticide suspension, preparation method of dispersant, and aqueous pesticide suspension
ActiveCN110408017AWith low temperature antifreeze performanceEasy to useBiocideFungicidesEndcappingPolyethylene oxide
The invention provides a fatty alcohol block polyether, a dispersant for an aqueous pesticide suspension, a preparation method of the dispersant, and the aqueous pesticide suspension. The polyether chain segment of the fatty alcohol block polyether comprises a polypropylene oxide block, a polybutylene oxide block, an ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer block and a polyethylene oxide block which are sequentially connected. The fatty alcohol block polyether adopts the polypropylene oxide block as a starting block, and the polybutylene oxide block is located in the middle of the polyether chain segment, so the fatty alcohol block polyether has a good low temperature antifreeze property; ethylene oxide and propylene oxide form the block in the manner of the copolymer, so a molar ratio ofthe ethylene oxide to propylene oxide in order to adjust the HLB value of the fatty alcohol block polyether, thereby the fatty alcohol block polyether is suitable for different systems with hydrophilic and lipophilic properties; and the fatty alcohol block polyether is terminated with the polyethylene oxide block to improve the integral hydrophilicity of the fatty alcohol block polyether, so the fatty alcohol block polyether is convenient for being used in an aqueous phase system.
Owner:JIAHUA CHEM TECH DEV SHANGHAI CO LTD
Method for separating carnosine and histidine
The invention discloses a carnosine and histidine separation method which comprises the following steps: adding a mixture containing carnosine and histidine into an aqueous two-phase system for extraction to realize separation of carnosine and histidine; wherein the aqueous two-phase system comprises a heavy phase serving as an extraction agent and a light phase serving as a detergent, the heavy phase consists of inorganic salt and water, and the light phase consists of a polymer and water or an organic solvent and water; the inorganic salt is at least one of sulfate, phosphate, carbonate andchloride; the polymer is at least one of polyethylene glycol, polypropylene glycol, polyvinyl pyrrolidone and an ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer; wherein the organic solvent is at least one of low-carbon alcohol with the carbon number of 1-5, acetone and acetonitrile. According to the method, an aqueous two-phase system is used as a separation medium, efficient separation of carnosine andhistidine is achieved, the operation process is simple, and amplification is easy.
Owner:QUZHOU RES INST OF ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
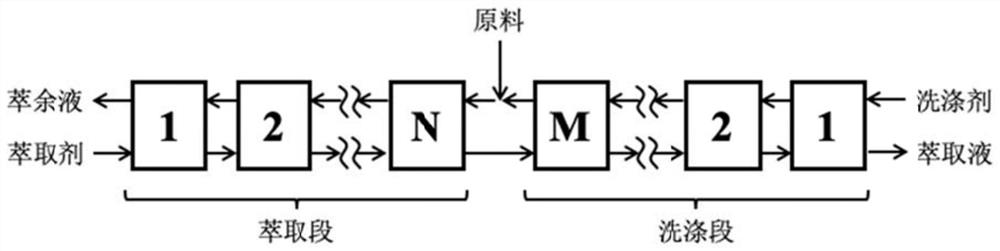
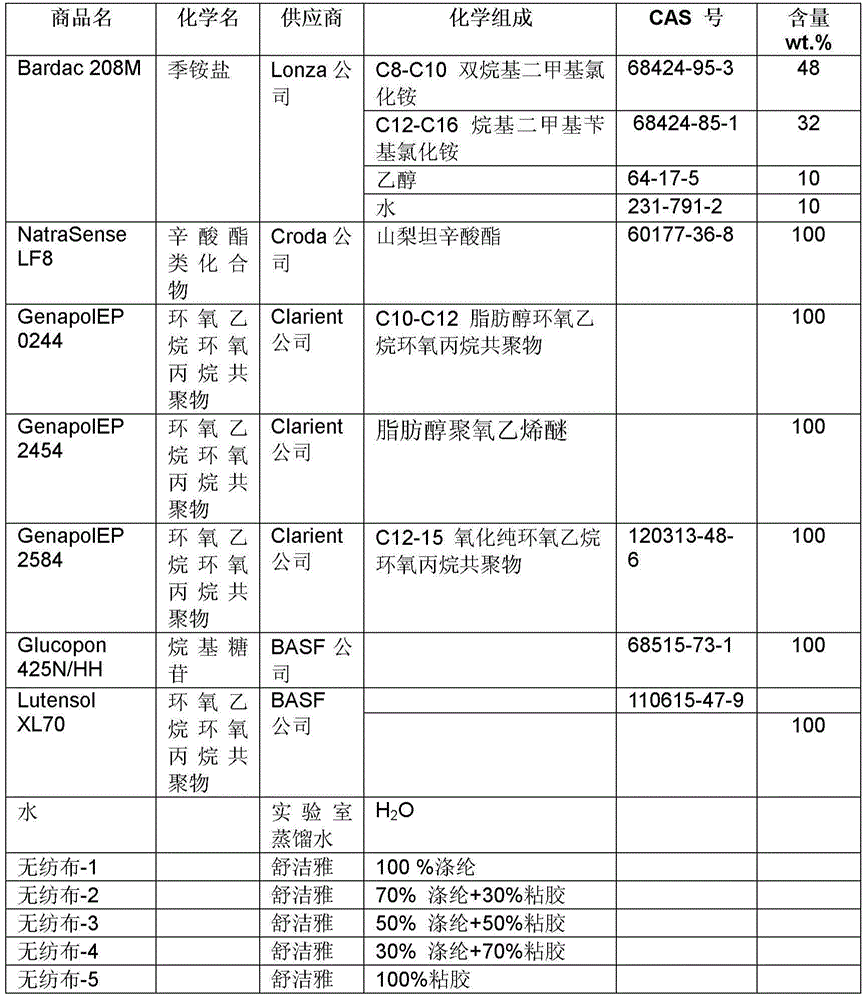
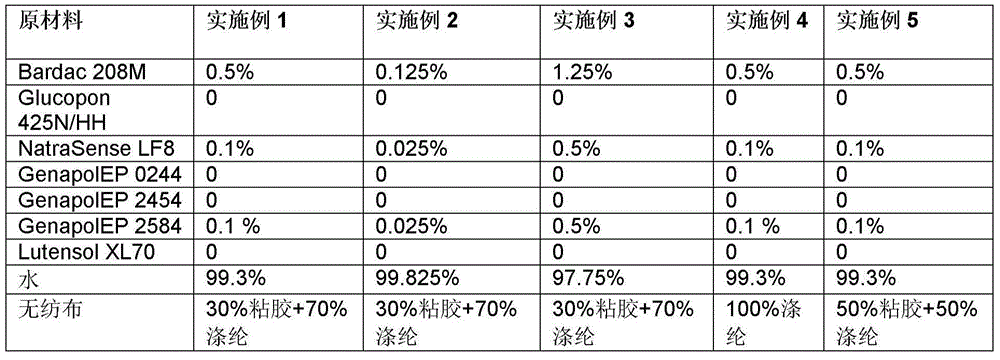
Disinfectant, nonwoven fabric containing disinfectant, preparation method and application
The invention relates to disinfectant. The disinfectant comprises the following components by weight percent (according to 100 percent of total weight): 0.1 to 1 percent of quaternary ammonium salt; 0.01 to 1 percent of octoate compound; 0.01 to 1 percent of oxide alcohol oxacyclopropane epoxypropane co-polymer; 37 to 99.88 percent of water; and 0 to 60 percent of alcohol. The disinfectant has good sterilizing capacity, low corrosion to the metal, rapid drying speed after being used for scrubbing the surface of an object and good compatibility with nonwoven fabric.
Owner:明尼苏达矿业制造医用器材(上海)有限公司
Cleaning solution for engine
The invention relates to a cleaning solution and particularly relates to a cleaning solution for an engine. The cleaning solution is prepared from the following substances in parts by weight: 15-25 parts of coconut high-carbon fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether, 18-25 parts of polyoxyethylene nonylphenol ether, 3-5 parts of polyisobutene amine, 2-5 parts of methacrylic acid, 15-25 parts of fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether sulfate, 3-5 parts of potassium polyoxyethylene laurylether phosphate MAEPK, 1-5 parts of ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymers, 25-45 parts of sulfonated castor oil, 0.05-0.08 part of an ethylene glycol-ethyl ether mixed solution, 4-6 parts of sodium silicate, 15-25 parts of ethyl acetate and 45-55 parts of water. The cleaning solution for the engine, disclosed by the invention, can generate a great number of randomly moving colloidal suspended particles together with oil stains, dust, oil dirt and rust in the engine after being added into the engine so as to emulsify and decompose dirt and the like; and due to the addition of a great deal of dispersing agent, the dispersed particles cannot be caked and can be dispersed into an organic solvent so as to be directly discharged out of the engine.
Owner:青岛城轨交通装备科技有限公司
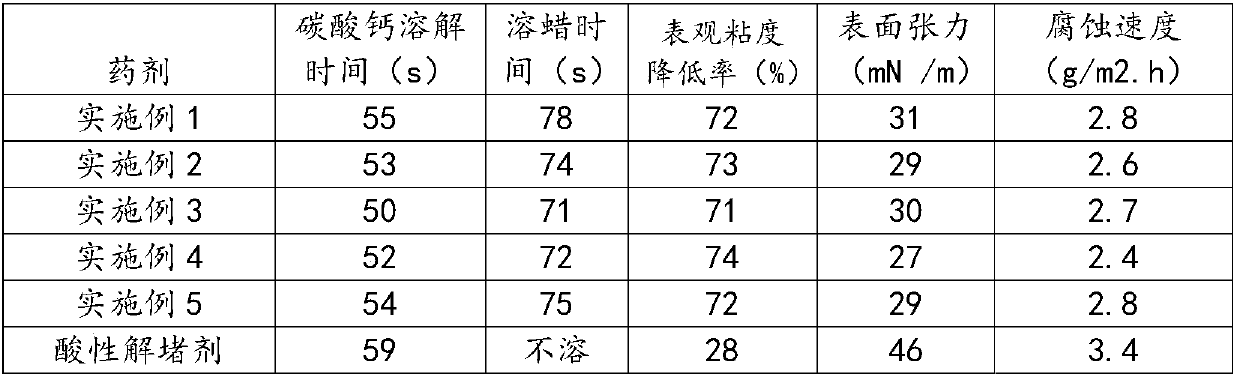
Agent for purifying gas wells and draining and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107674663AImprove purification effectPurification adapts to a wide rangeDrilling compositionBorehole/well accessoriesPyrazineEthylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer
The invention provides an agent for purifying and draining gas wells and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the field of gas well purification. The agent comprises, by weight, 30 to 80 partsof alkyl methylamino carboxylic acid, 5 to 20 parts of polyoxyethylene ether, 5 to 20 parts of ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer, 0.1-1 part of perfluoroalkyl ammonium chloride and 0.1 to 2 parts of 2,5-alkyl pyrazine. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing the alkyl methylamino carboxylic acid with water, heating to 45-55 DEG C, under the conditions of stirring at the constant temperature of 45-55 DEG C, mixing with the polyoxyethylene ether, the perfluoroalkyl ammonium chloride and the 2,5-alkyl pyrazine, stirring at the constant temperature for 20 to 40 minutes, mixing with the ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer, completely dissolving and cooling. The agent has strong purification efficiency, wide purification adaptability and strong foaming capability, and effectively improves the purification effect of the wellbores of the gas wells.
Owner:成都华阳兴华化工有限公司
Use of polypropylene oxide or ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymers in combination with starch ether derivatives as additive in dry mortar compositions
ActiveUS9593046B2Starch dervative coatingsStarch derivtive adhesivesPolymer scienceEthylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer
The use of an adhesion-promoting additive combination composed of one or more polyalkylenoxides out of the group comprising polypropylene oxides and ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymers, and of one or more starch ether derivatives out of the group comprising carboxyalkyl starch ethers and their alkali salts, and hydroxyalkyl starch ethers, in mortar compositions comprising mineral binders and water-redispersible polymer powders.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Green printing and dyeing auxiliary agent and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a green printing and dyeing auxiliary agent and a preparation method thereof. The green printing and dyeing auxiliary agent comprises 3-9 parts of an ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer, 2-4 parts of amino polysiloxane, 1-3 parts of amide ethyl imidazoline, 3-5 parts of ethylene oxide, 1-3 parts of diester quaternary ammonium salt, 10-14 parts of polyacrylamide, 5-9 parts of sodium sulfite, 1-3 parts of sodium carbonate and 1-3 parts of a nonionic surfactant. The invention belongs to the technical field of printing and dyeing auxiliary agents, and particularly provides the green printing and dyeing auxiliary agent which is healthy in raw material, environment-friendly and pollution-free, has good color protecting and color increasing functions on textiles, enables the textiles not to fade easily, and improves the flexibility and color fixing performance of the textiles, and the preparation method of the green printing and dyeing auxiliary agent.
Owner:威海允祯服饰有限公司
High-efficiency water reducer
InactiveCN110467375AHigh water reduction rateImprove liquidityCoconut diethanolamideSuperplasticizer
The invention provides a high-efficiency water reducer. The high-efficiency water reducer is prepared through mixing, by weight, 45-65 parts of a beta-naphthalenesulfonate-formaldehyde condensate, 15-25 parts of polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether methacrylate, 20-30 parts of calcium lignosulphonate, 15-20 parts of an ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer, 3-5 parts of trehalose, 1.8-2.8 partsof silicone powder, 3-7 parts of shale ash, 3-5 parts of sodium bisulfite, 4.5-9.5 part sof polyoxyethylene, 7-13 parts of aluminum tripolyphosphate, 2.5-3.5 parts of coconut diethanolamide, 1.5-2.5parts of barium dinonylnaphthalenesulfonate, 2.5-3.5 parts of urotropine and 2.5-5.5 parts of an assistant. The water reducer of the invention has the advantages of high water reducing rate, good fluidity, obvious improvement of the fluidity and workability of concrete, significant early strength effect after final setting, great improvement of the strength of the concrete at all ages, and suitableness for various concretes.
Owner:徐州巨龙新材料科技有限公司
Novel rapid cleaning agent for stickers
InactiveCN106398882AEasy to cleanWon't hurtInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsAdhesiveEthyl acetate
The invention relates to the technical field of chemical products and discloses a novel rapid cleaning agent for stickers. The novel rapid cleaning agent is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 5 percent to 10 percent of soda, 25 percent to 45 percent of ethanol, 4 percent to 10 percent of ethyl acetate, 2 percent to 5 percent of rosin water, 10 percent to 20 percent of turpentine oil, 1 percent to 2 percent of benzene, 2 percent to 4 percent of toluene, 5 percent to 10 percent of acetone, 1 percent to 5 percent of kerosene, 3 percent to 6 percent of an ethylene oxide-propylene oxide copolymer, 1 percent to 6 percent of a fluorine-containing surfactant and the balance of water. The novel rapid cleaning agent for the sticker is reasonable in formula and has a good cleaning effect on a plurality of types of stickers; the cleaning speed is rapid and materials adhered to an adhesive are not damaged, so that the novel rapid cleaning agent is environment-friendly and safe.
Owner:CHENGDU FANXINJIA TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com