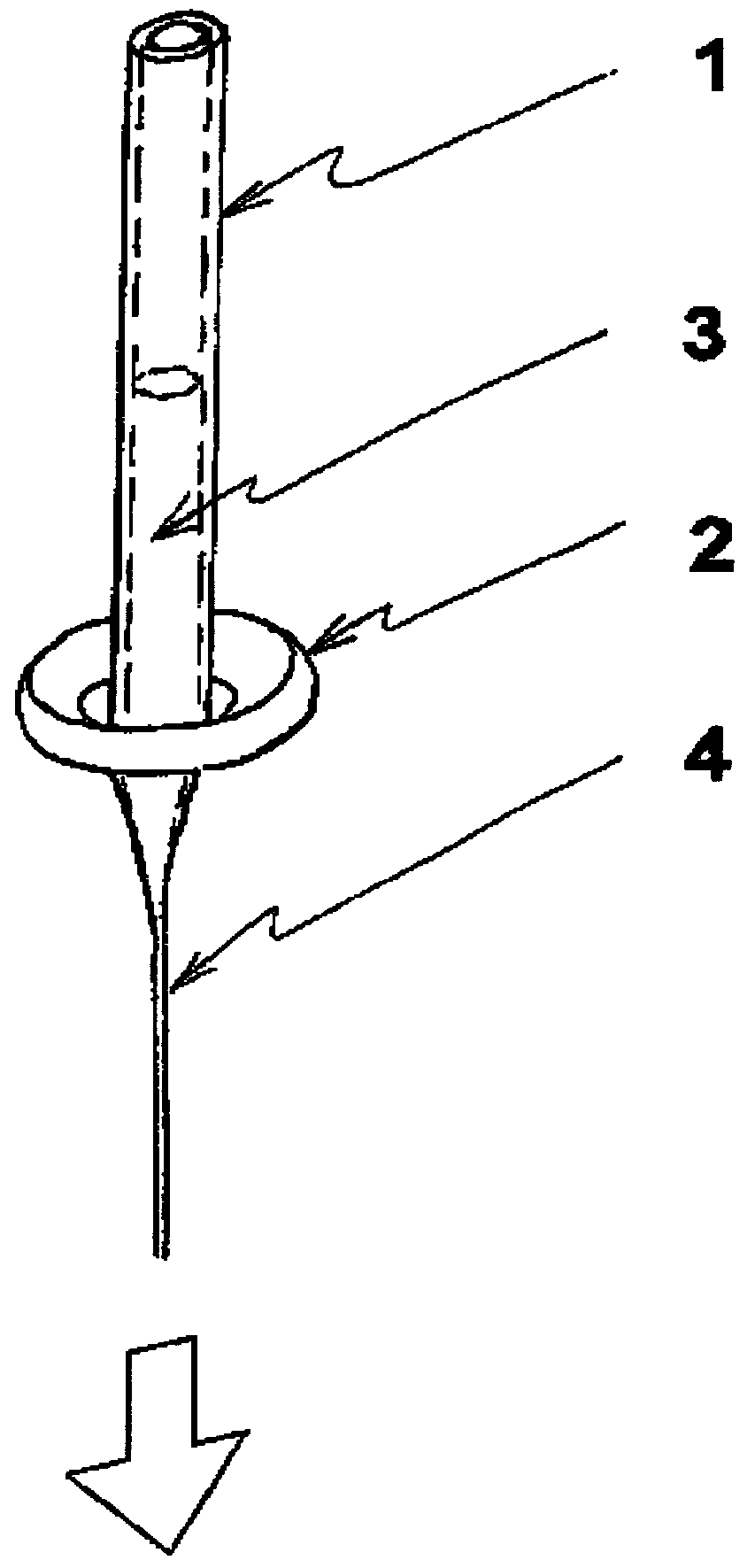
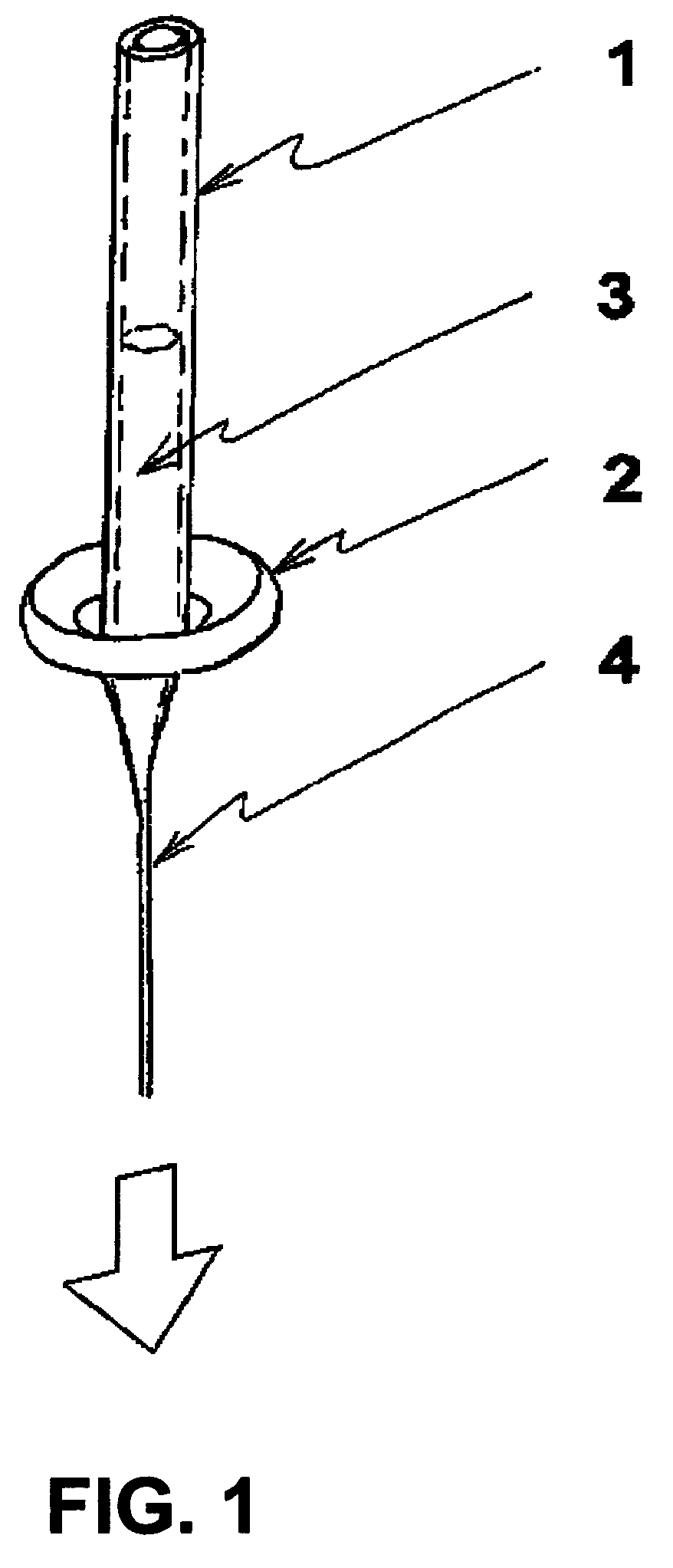
Patents
Literature
100 results about "Glass-coated wire" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
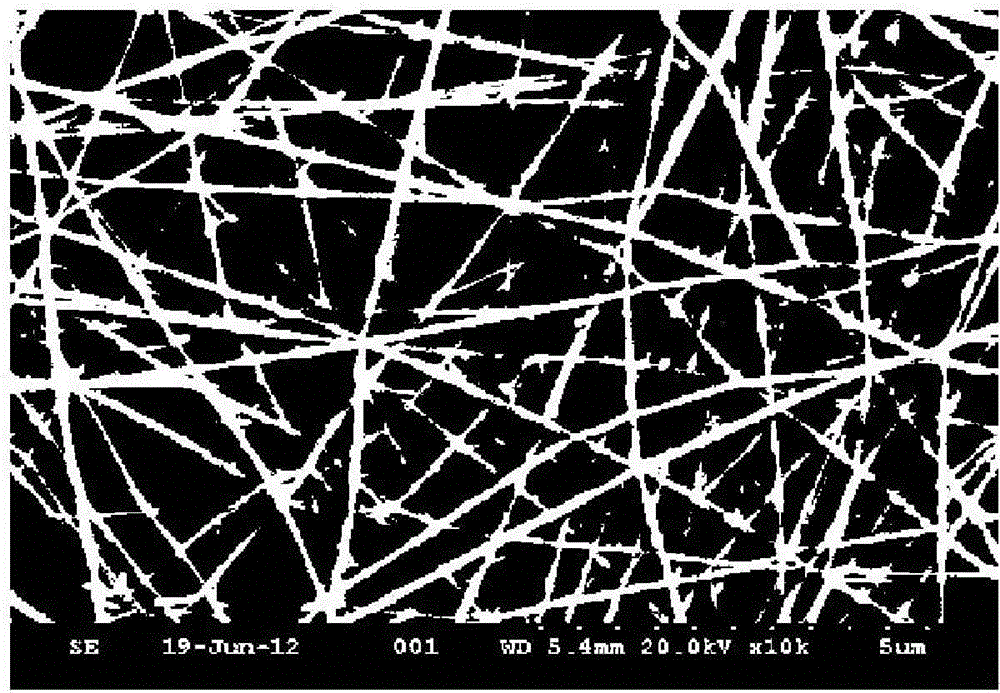
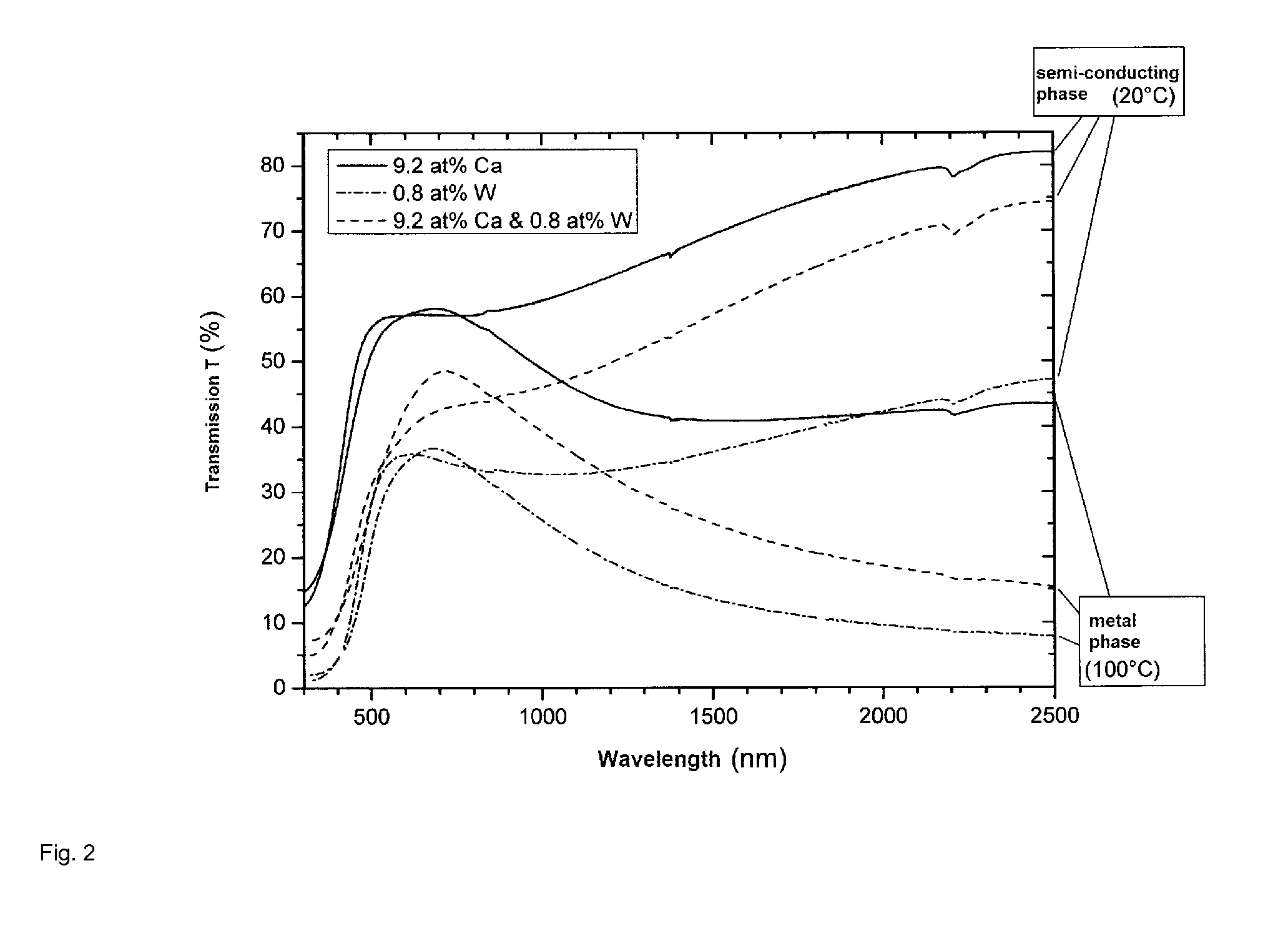
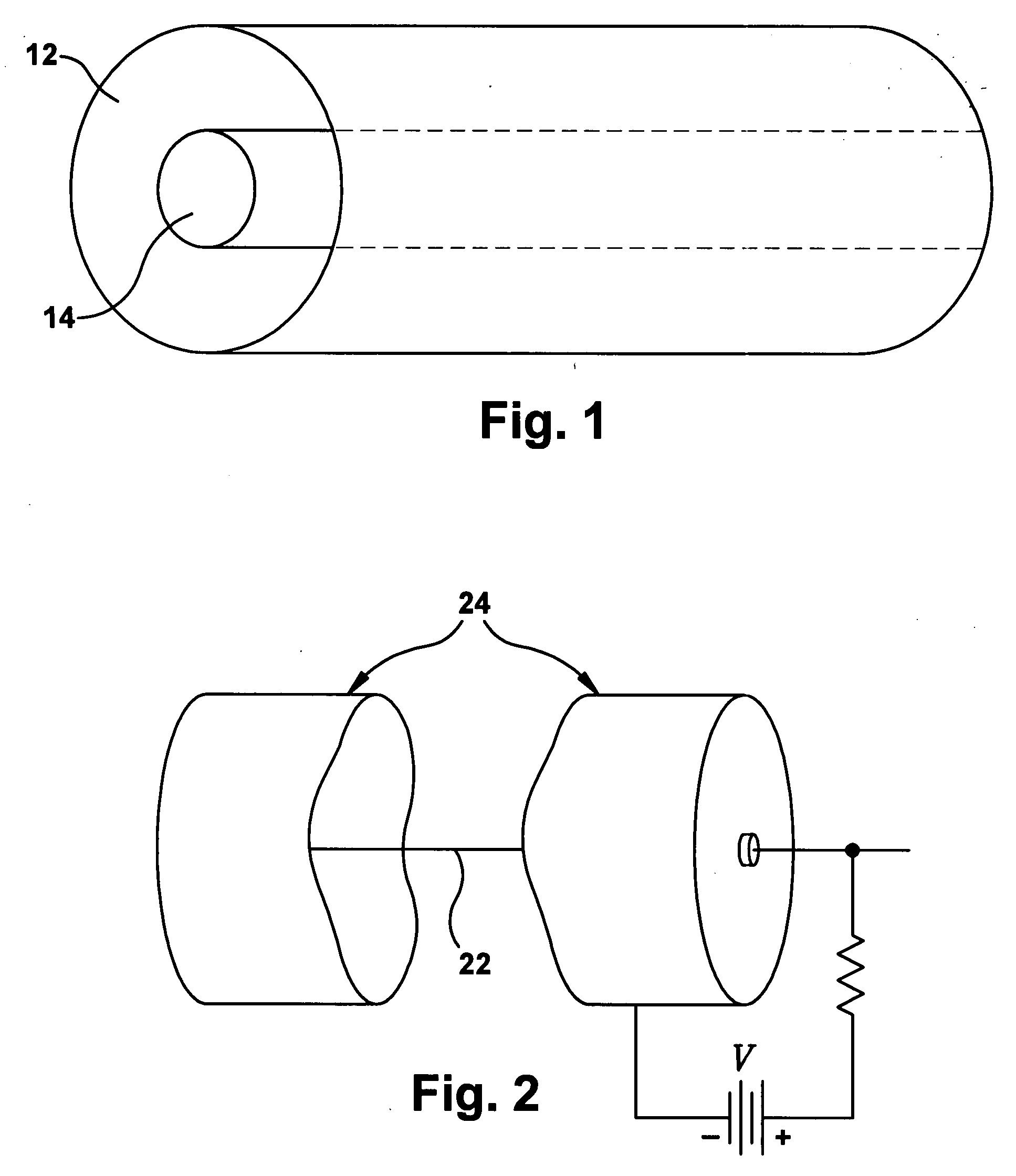
Glass-coating is a process invented in 1924 by G. F. Taylor and converted into production machine by Ulitovski for producing fine glass-coated metal filaments only a few micrometres in diameter. In this process, known as the "Taylor-wire" or "microwire process" or "Taylor-Ulitovski process", the metal to be produced in microwire form is held in a glass tube, typically a borosilicate composition, which is closed at one end. This end of the tube is then heated in order to soften the glass to a temperature at which the metal part is in liquid state and the glass can be drawn down to produce a fine glass capillary containing a metal core. In recent years the process was converted to continuous one by continuously feeding the metal drop with new material. Although this process is simple enough it requires a lot of factors to be met at the same time. The continuous flow of metal that is being coated by the glass has to be melted at the same temperature as the glass otherwise there may be consistency problems which could lead to a change in the properties of the wire. This means that metals that have a high melting temperature can not be used because it may prove difficult to match the high melting point of the metal to a high melting point in a glass. The rate at which the metal wire is pulled also has to be monitored due to the fact that a fluctuation in the speed of pulling may cause a difference of width in the wire. Not only does the wire need to be pulled at the same rate but it also needs to be cooled in a stable environment, which is normally conducted by moving the wire through a stream of cooled water or oil. However. there are some apparatuses that can bypass some of these problems by heating the glass and the metal in separate chambers which allows for the use of metals with high melting points. Around the 1950s the Taylor-Ulitovski process was changed to a continuous feeding process of the materials in order to make these wires on a mass production scale.
Cooking surface for cooking food having a glass ceramic surface with a glass coating thereon
InactiveUS6525300B1Reduction factorEasy to processCoil arrangementsHot plates heating arrangementsGlazeThermal expansion
The invention relates to lead- and cadmium-free glass for glazing, enamelling and decorating glasses or glass-ceramics which have a low coefficient of thermal expansion of less than 2x10-6 / K, having the composition (in % by weight) 0-6 Li2O, 0-5 Na2O, 0 to less than 2 K2O, where the sum Li2O+K2+Na2O is between 2 and 12, 0-4 MgO, 0-4 CaO, 0-4 SrO, 0-1 BaO, 0-4 ZnO, 3 to less than 10 Al2O3, 13-23 B2O3, 50-65 SiO2, 0-4 TiO2, 0-4 ZrO2 and 0-4 F, as replacement for oxygen and containing up to 30% by weight of a pigment which is resistant at the firing temperature, where the glass is suitable for glazing, enamelling and decoration in both primary and secondary firing, and both the full-area and sparse glaze, enamel or decoration layers have low abrasion susceptibility after firing, and it relates to processes for the production of a glass-ceramic coated therewith.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Phase change device
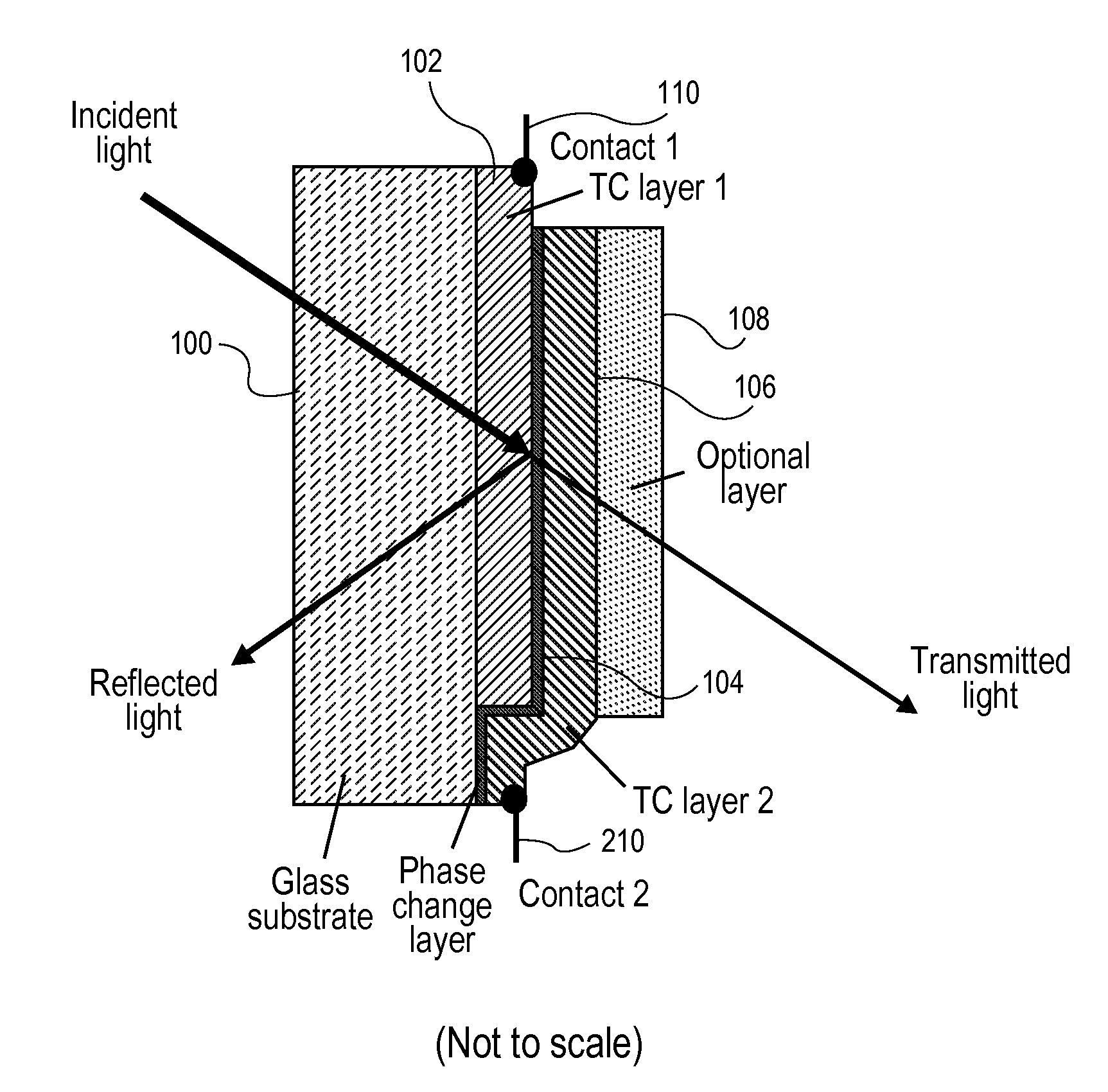
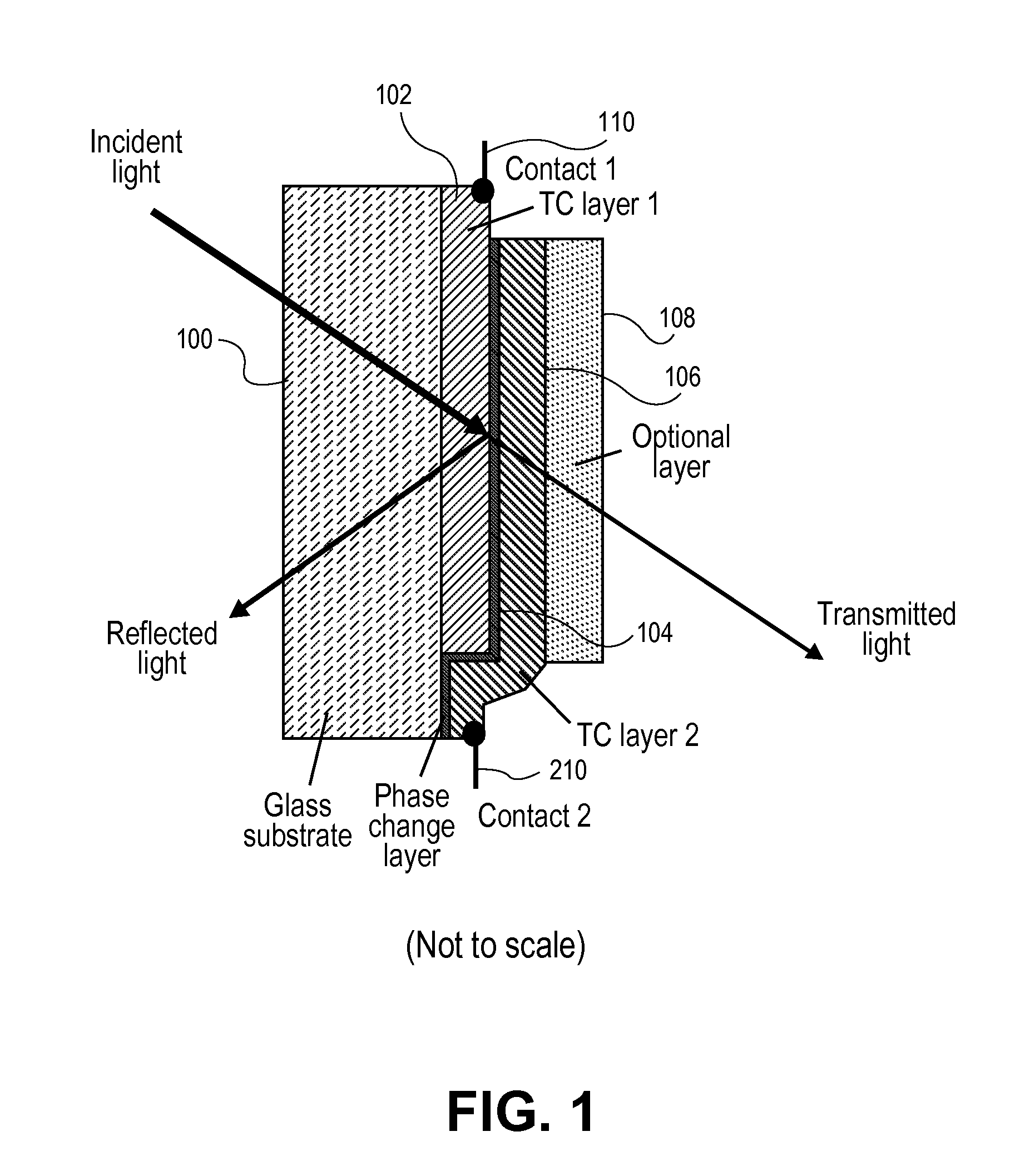
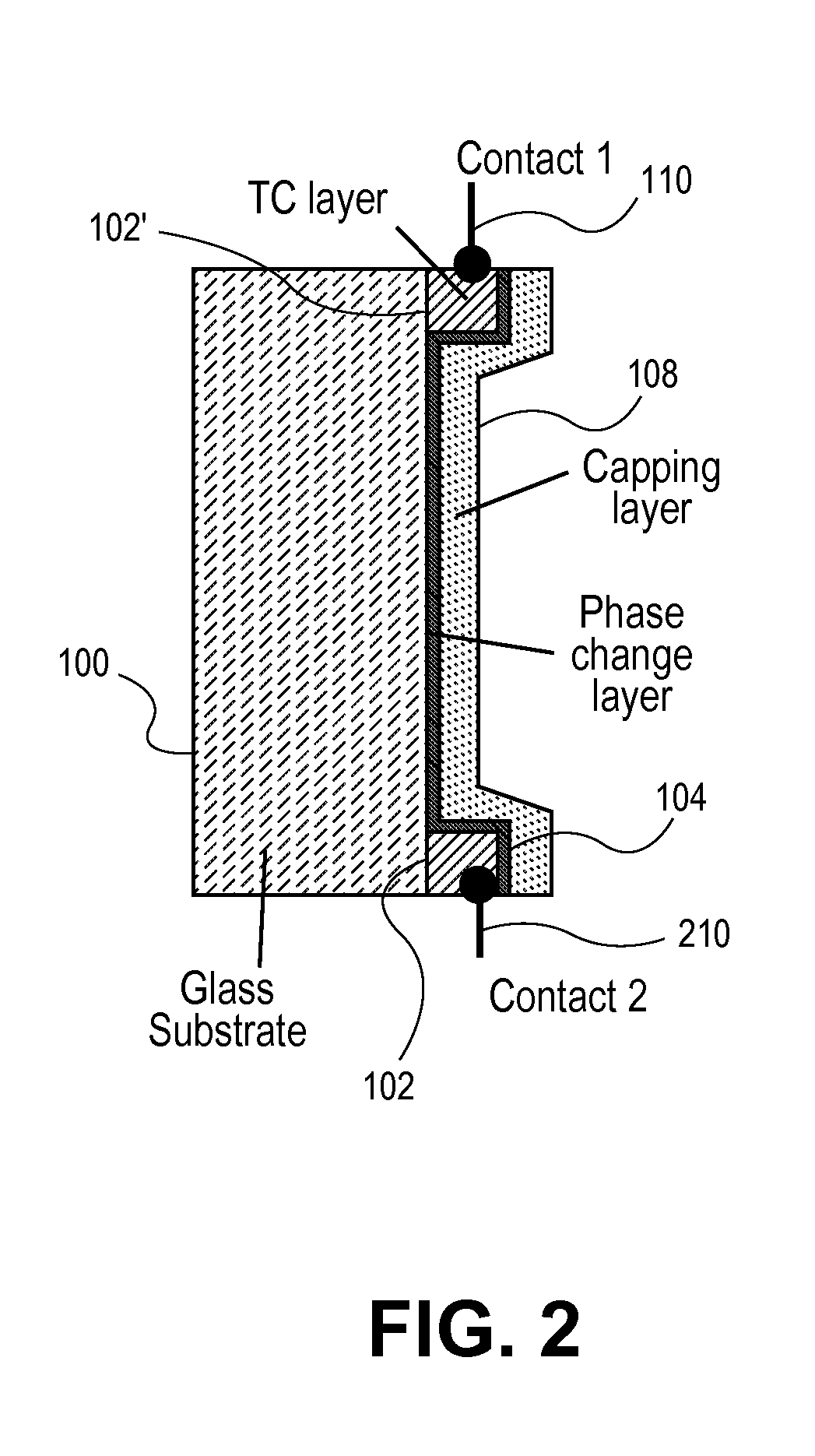
A phase change material is applied as a very thin film to a transparent substrate such as glass, which material when switched from the amorphous to the crystalline state and back again can affect the reflectivity / transmittance of the combined substrate-coating system. When used with glass panels in the fabrication of relatively large area window glass, the change in spectrally selective transmittance can be used to modulate the amount of sunlight passing through the glass, and thus reduce the amount of cooling required for an interior space in the summertime, and the amount of heating required of that same interior space in the wintertime, while also optimizing the use of visible daylight. Exemplary of a suitable phase change material for glass coating is GeSb or BiSn. Heating of the phase change material to initiate a change in phase can be provided by the application of electric energy, such as supplied from a pulsed power supply, or radiant energy, such as from a laser.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
High temperature resistant radar and infrared compatible stealth material based on double-layer metamaterials and preparation method of stealth material
ActiveCN106427115ALow emissivity characteristicEasy to implement reflection functionLaminationLamination apparatusFiberLow emissivity
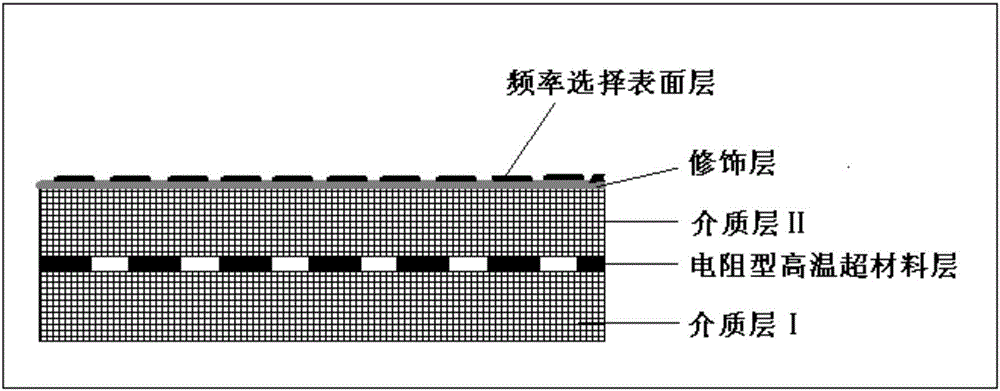
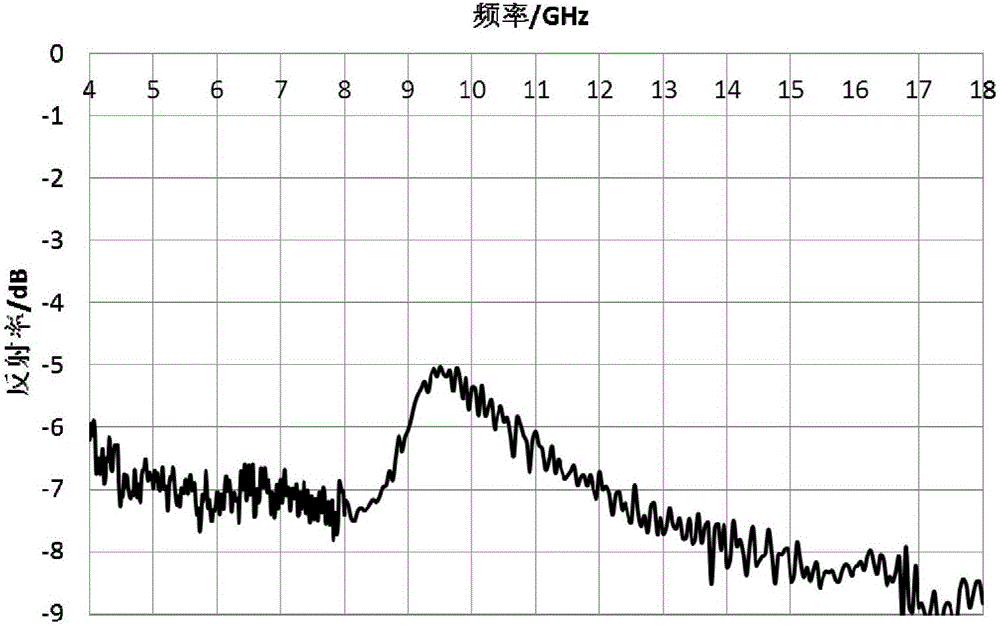
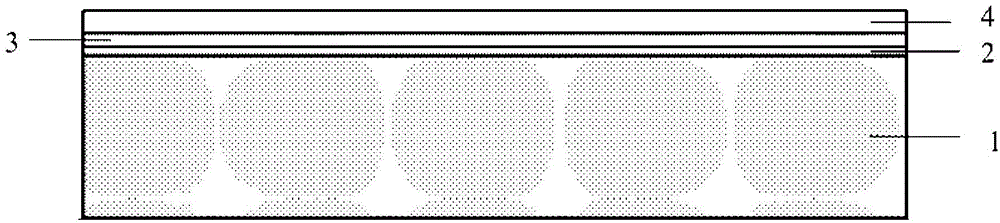
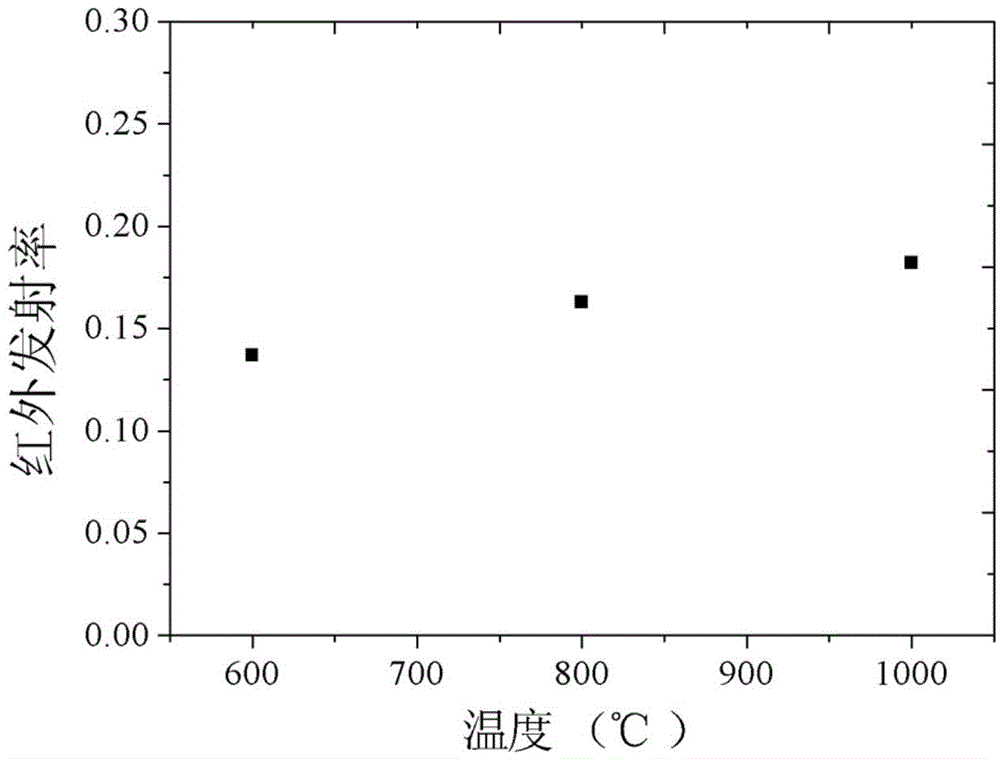
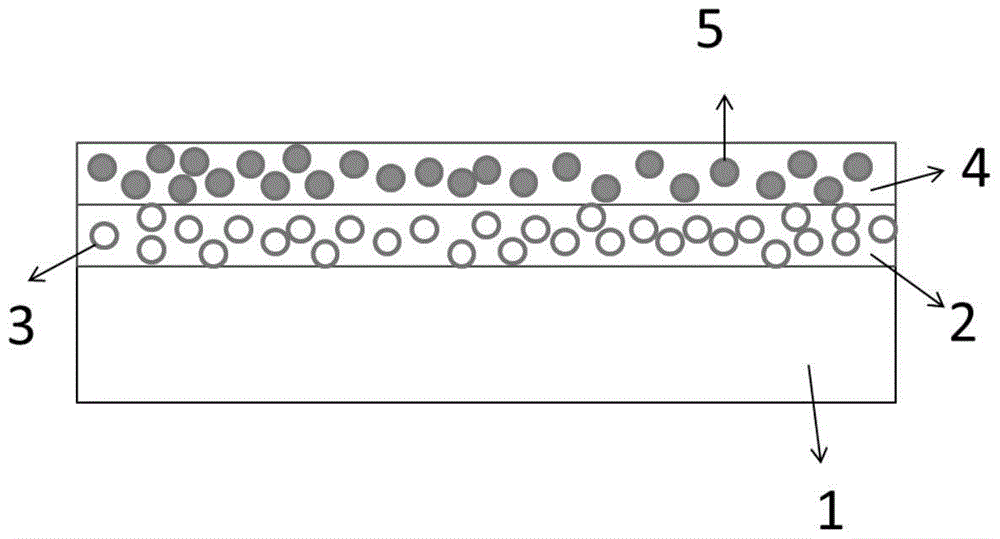
The invention discloses a high temperature resistant radar and infrared compatible stealth material based on double-layer metamaterials. The high temperature resistant radar and infrared compatible stealth material is of a layered structure sequentially comprises a dielectric layer I, a resistance-type high temperature metamaterials layer, a dielectric layer II, a decorative layer and a frequency selective surface layer from inside to outside, wherein both the dielectric layer I and the dielectric layer II are made of oxide fiber reinforced oxide-based composite materials, the resistance-type high temperature metamaterials layer mainly comprises a high temperature resistant resistor coating with periodic patterns, the decorative layer is made of glass coatings, and the frequency selective surface layer mainly comprises a high temperature resistant antioxidant and low infrared emissivity precious metal plating layer with periodic patterns. A preparation method is characterized in that the materials of the layers are prepared in a layered manner. The high temperature resistant radar and infrared compatible stealth material has high designability, the problem of radar and infrared compatible stealth contradiction can be effectively solved from the perspective of structural design by the aid of metamaterial technology, and the high temperature resistant radar and infrared compatible stealth material has good broadband wave-absorbing performance and low emissivity and can resist high temperature of 1000 DEG C or more.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH +1
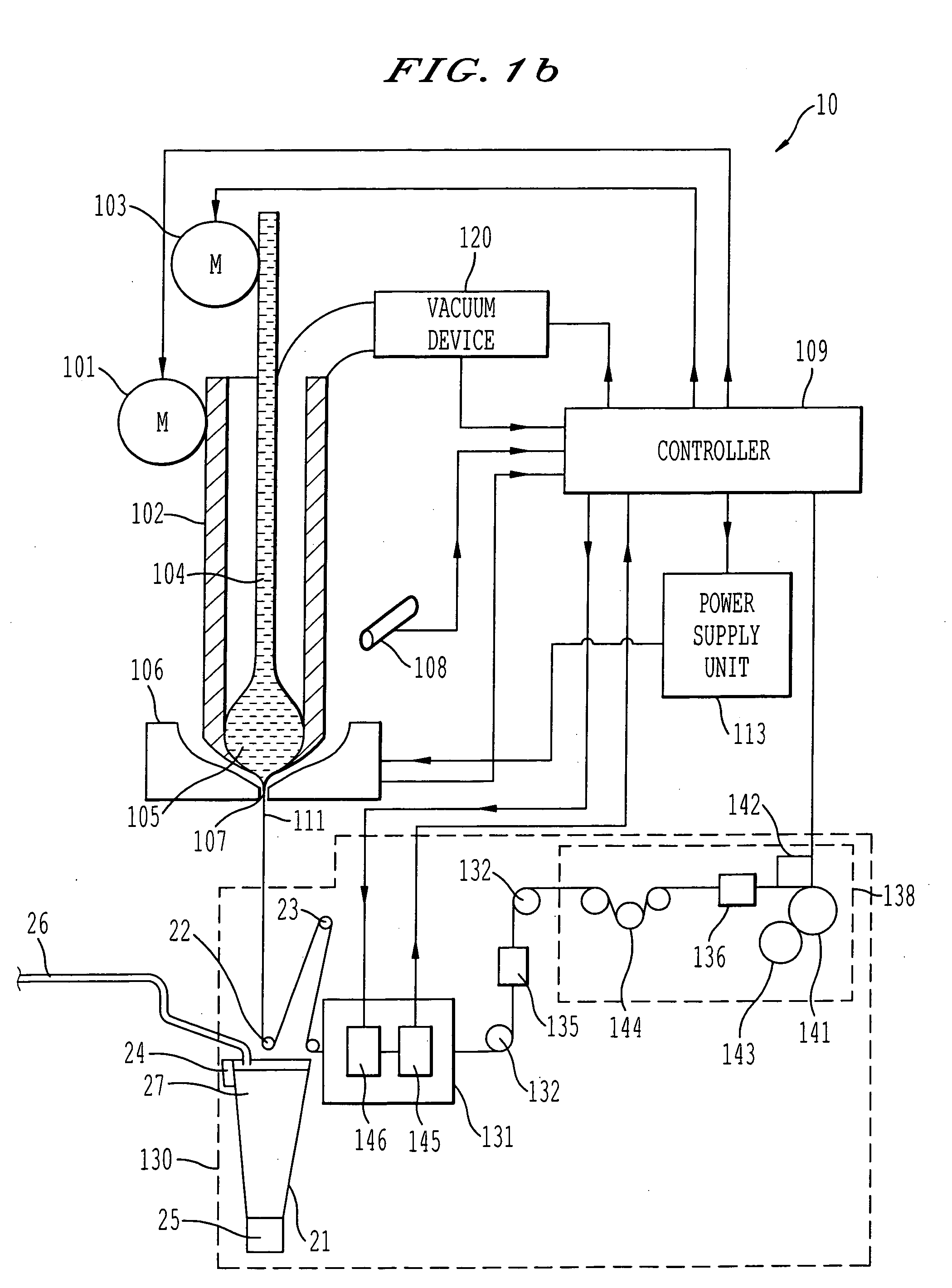
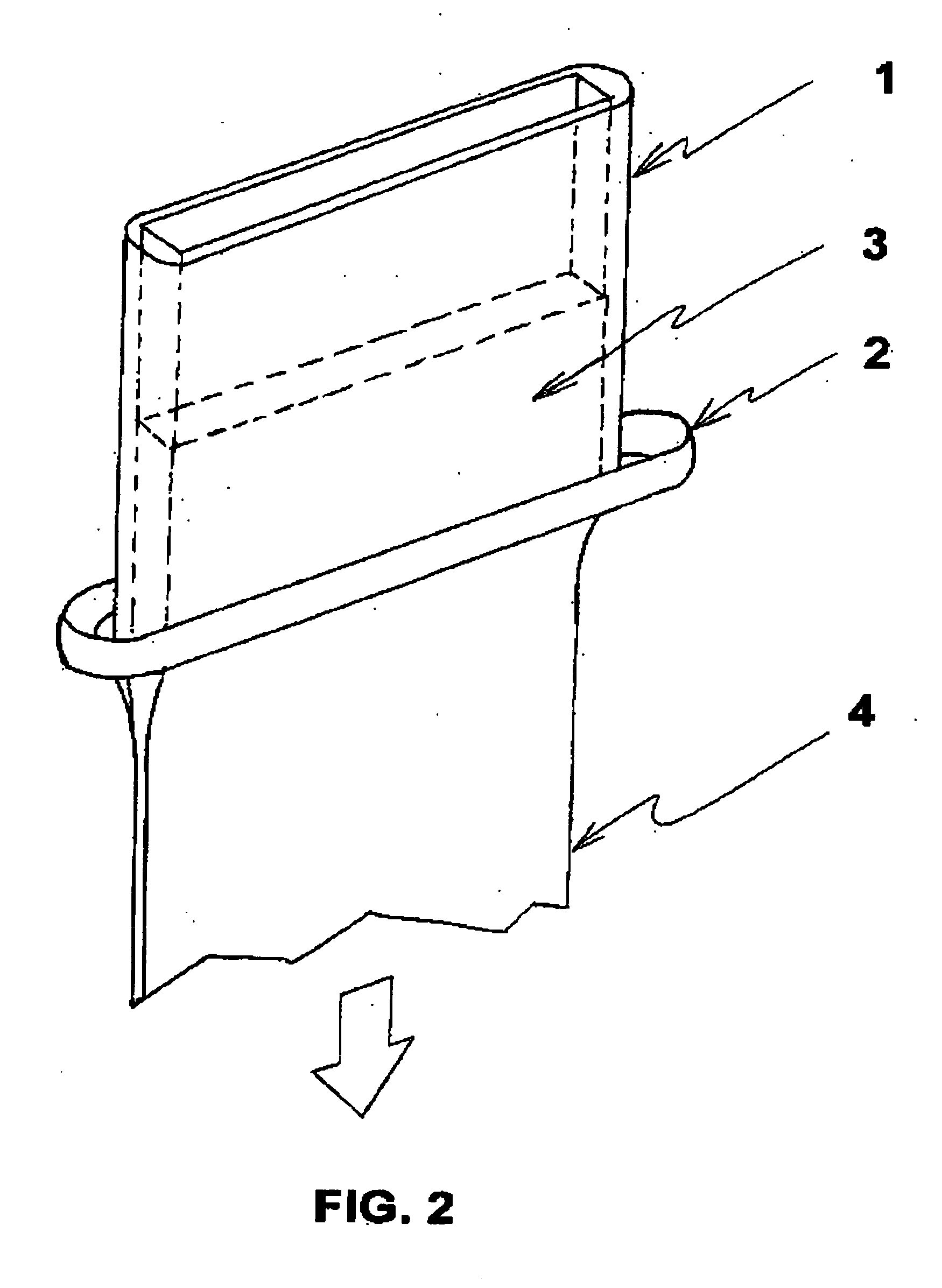
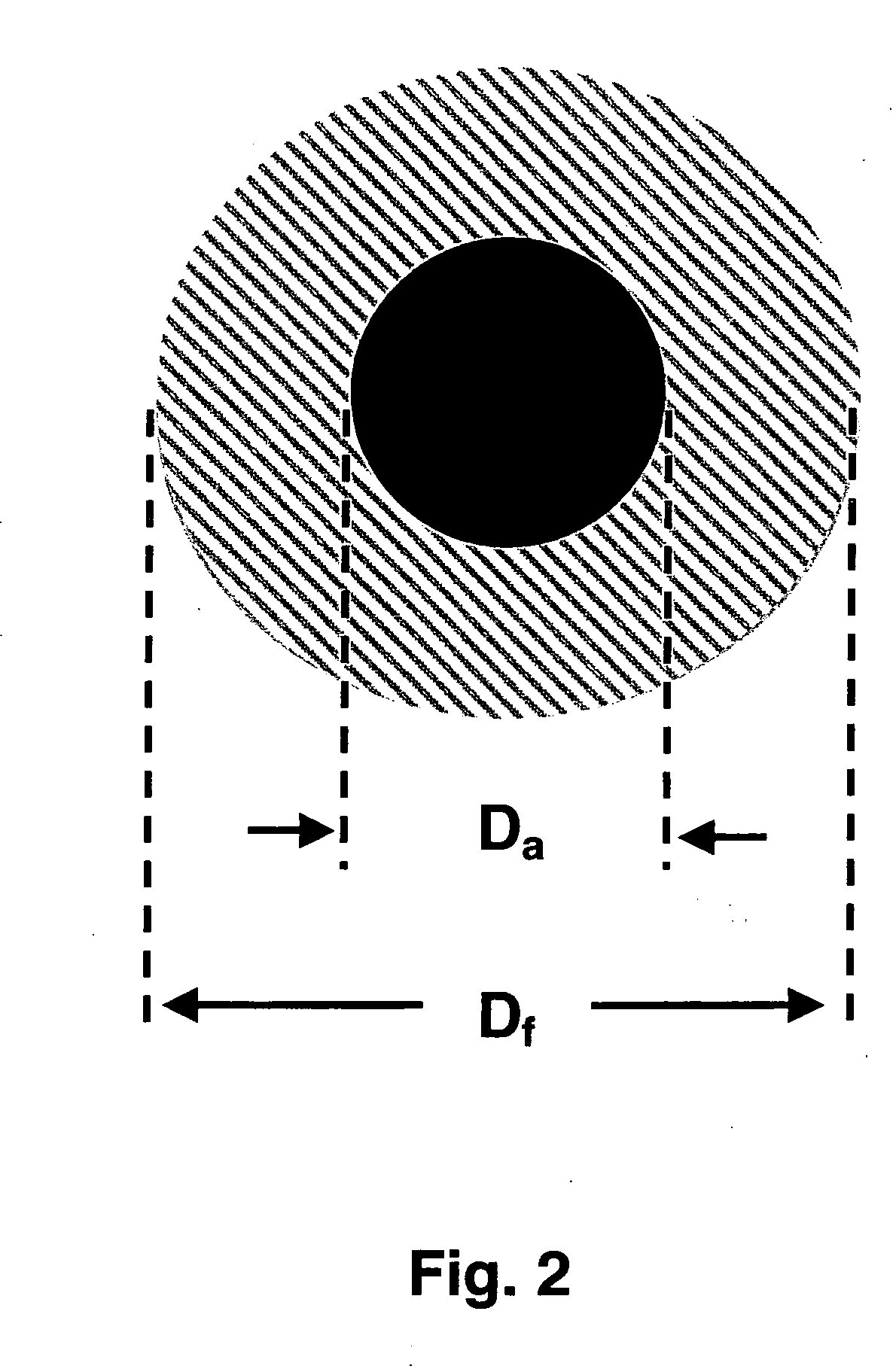
System and process for forming glass-coated microwires, including a cooling system and process
InactiveUS20060130995A1Minimize and overcomeReduce uniformityGlass rolling apparatusEngineeringCooling fluid
A system for generating glass-coating microwires that can particularly apply a uniform cooling to a glass tube filled with molten metal inserted into a tank including a cooling liquid. The uniform cooling allows the formation of a glass-coated microwire with a non-distorted and uniform glass coating.
Owner:GLOBAL MICRO WIRE TECH
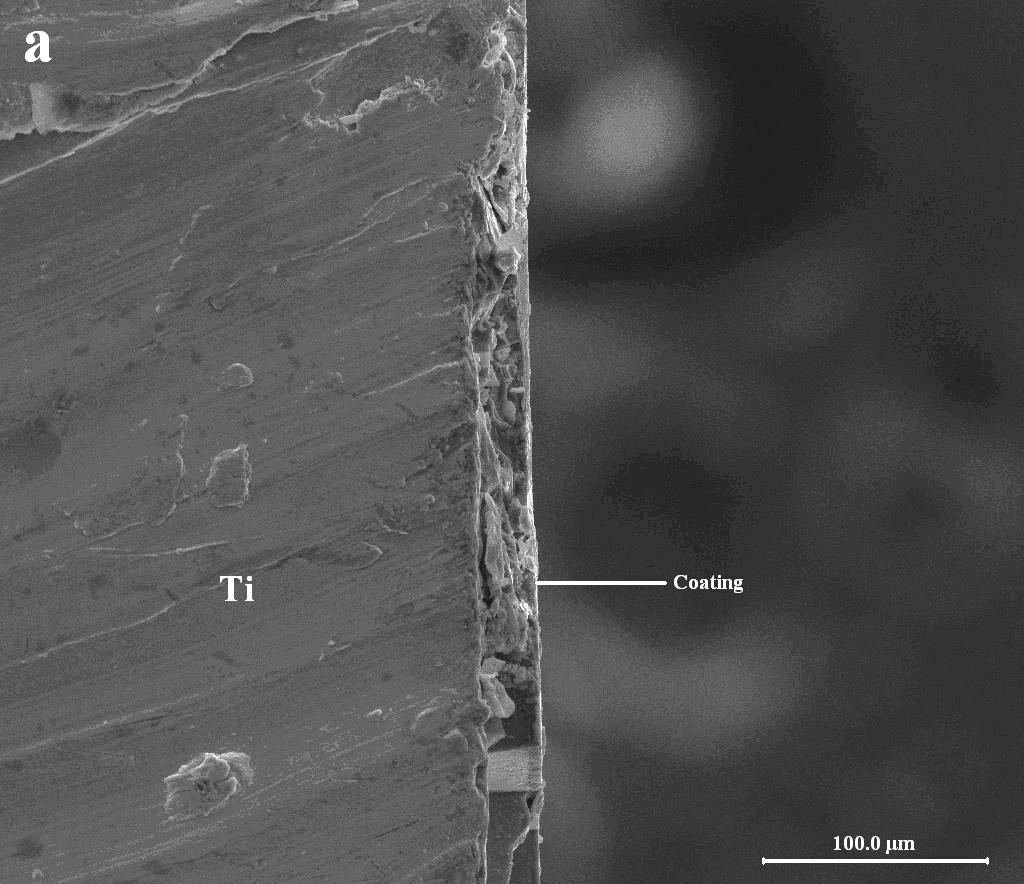
Preparation method and application of antibacterial glass coating of antibacterial bone fracture plate
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of an antibacterial glass coating of an antibacterial bone fracture plate. The method comprises the following steps: preparing sterile ion-containing borate bioactive glass, crushing the glass, and screening into glass powder with a certain size; adding a liquid-phase solvent, adhesive and stabilizer to the glass powder to prepare uniform glass slurry; coating the glass slurry to the surface of a titanium or titanium alloy bone fracture plate by utilizing a mechanical immersion method or a low temperature spraying method, drying with infrared ray or heat, and curing the slurry to the surface of the bone fracture plate; and volatilizing the solvent and the additives by virtue of high temperature sintering treatment, re-melting the residual glass powder to form molten glass, and adhering to the surface of the bone fracture plate to form the antibacterial glass coating capable of resisting bacteria and promoting tissue growth. The preparation method has the advantages of simple production process, easiness in operation, low cost and scale production; and the antibacterial glass coating has the functions of effective antibacterial performance and bioactivity in promotion of bone cell growth.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV +1
High-temperature-resistant high-bonding-strength low infrared emissivity composite coating, metal alloy material with coating and preparation method of metal alloy material
ActiveCN104818482AHigh bonding strengthMitigate Thermal MismatchMolten spray coatingSuperimposed coating processEmissivityMetal alloy
The invention discloses a high-temperature-resistant high-bonding-strength low infrared emissivity composite coating which sequentially comprises a NiCrAlY plasma spraying layer, a ZrO2 plasma spraying layer and ZrO2-Al2O3-SiO2 system containing AgPd alloy glass coating from inside to outside. The surface roughness of a metal alloy material coated with the coating is lower than 2.0 micrometers, the bonding strength of the metal alloy material exceeds 10MPa, the tolerable temperature of the coating is higher than 1000 DEG C, and the average infrared emissivity of the coating in a specified band is less than 0.3. A preparation method of the metal alloy material includes the steps: firstly, performing sand blasting for a base; secondly, sequentially spraying the NiCrAlY layer and the ZrO2 layer on the base by a plasma spraying process; finally, uniformly brushing or printing coatings on the ZrO2 layer, and drying and sintering the coatings to obtain the finished metal alloy material. The metal alloy material can be used in a high-temperature environment, infrared radiation of a high-temperature component is effectively reduced, and the metal alloy material is stable in performance and low in cost.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
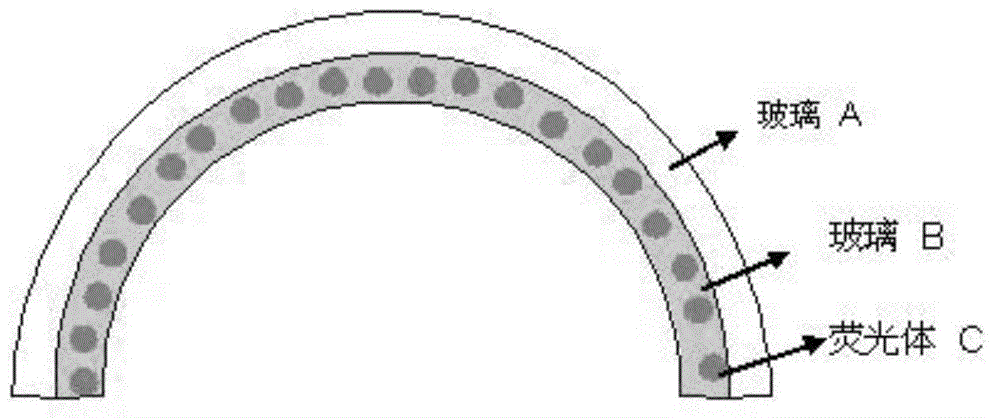
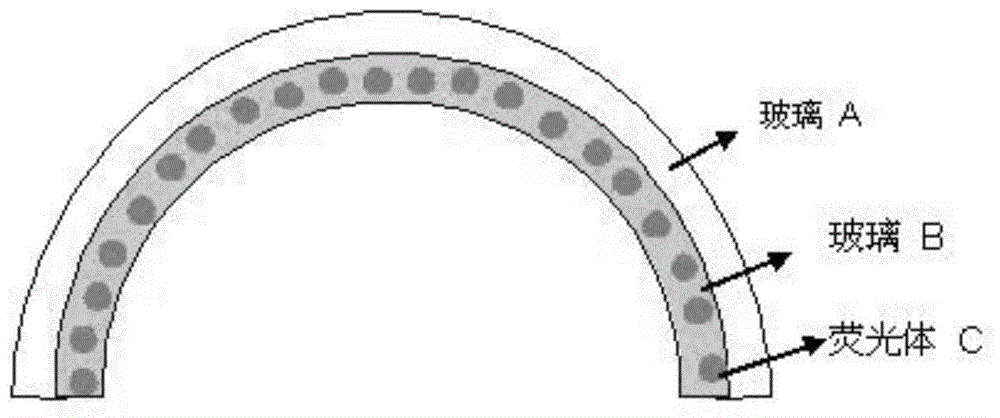
Preparation and application of reflecting type fluorescent glass light conversion assembly
A reflecting type fluorescent glass light conversion assembly comprises a glass substrate, a reflecting agent glass coating and a fluorescent glass coating, wherein the reflecting agent glass coating includes glass B powder and reflecting agent C according to the mass ratio of 150:1 to 100:150, a glass coating, containing a fluorescent body D, of the fluorescent glass coating is calcined on the glass substrate, and the thicknesses of the reflecting agent glass coating and the fluorescent glass coating each range from 0.3 mm to 3 mm.The reflecting agent C is an insulating body, has large optical energy band gaps and has the corresponding optical absorption wavelength of 420 nanometers or below.The reflecting agent C has a white appearance color.The assembly is prepared through the steps of mixing wide-band-gap reflecting agent powder and low-melting-point glass powder on the glass substrate to prepare a reflecting coating, then preparing the fluorescent glass coating on the reflecting coating, and fusing the reflecting coating, the fluorescent glass coating and the glass substrate into a whole through a thermal treatment process.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
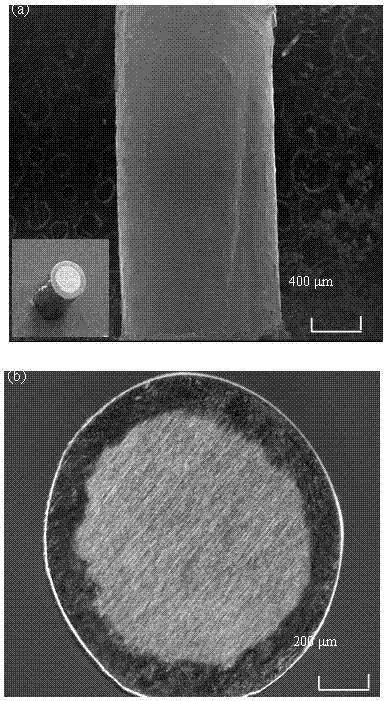
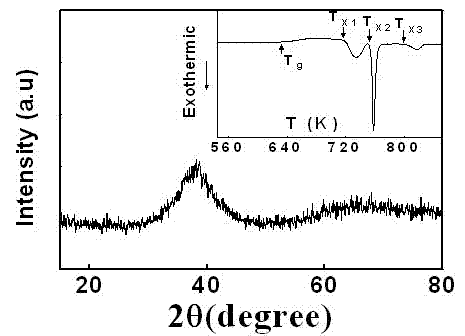
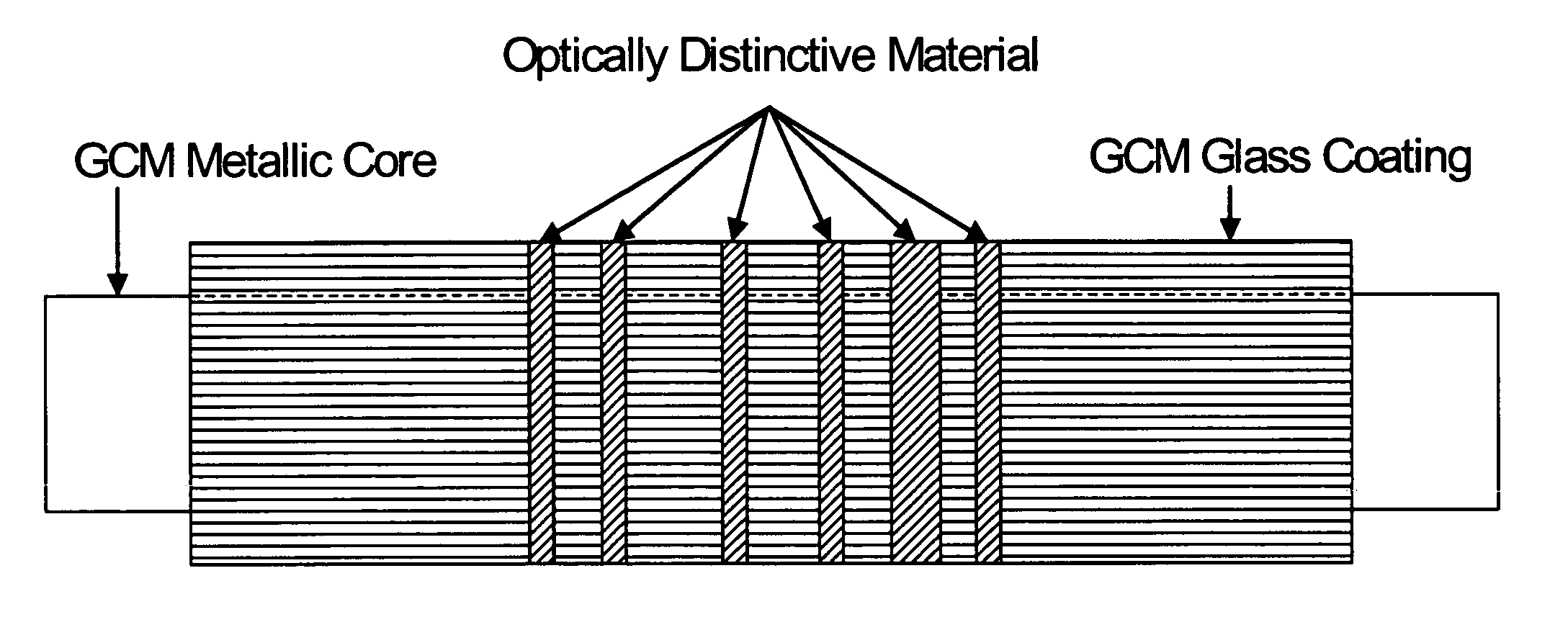
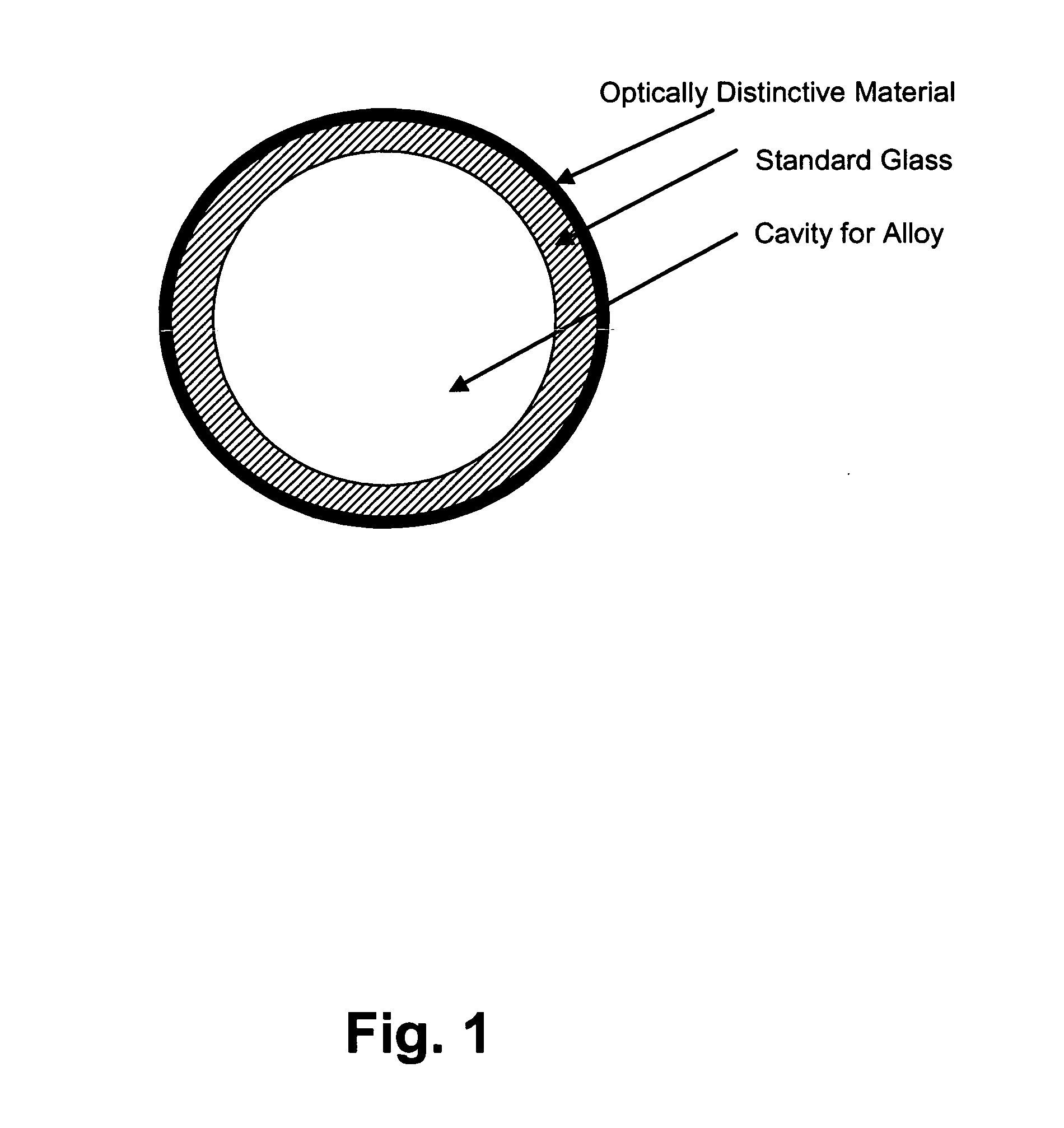
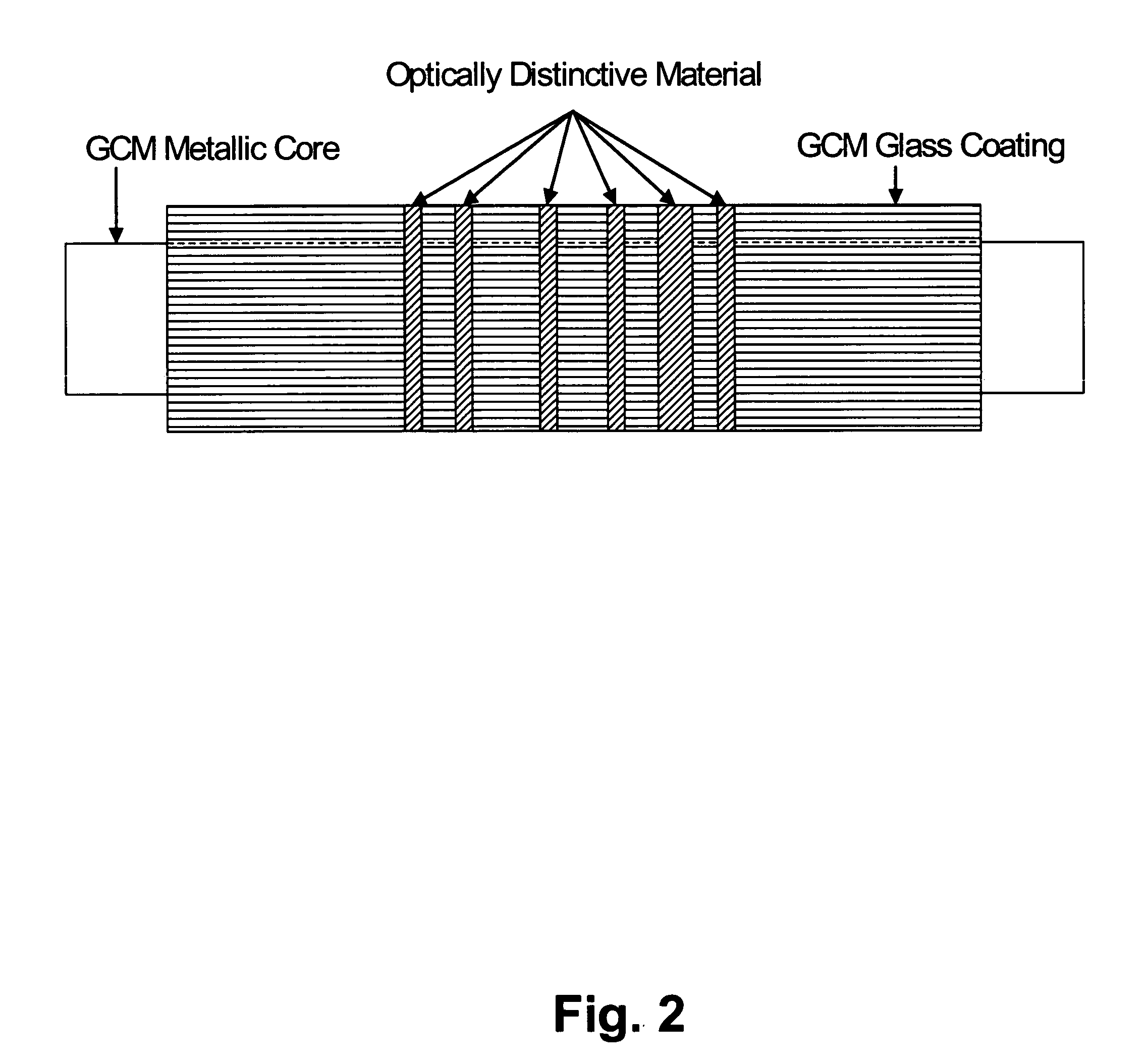
Amorphous and nanocrystalline glass-coated articles
InactiveUS20050000599A1Rapidly solidify molten alloyGlass making apparatusInorganic material magnetismDynamic balanceGlass vessel
A drawn glass-coated metallic member has a thermal contraction coefficient differential such that the thermal contraction coefficient of the glass is less than that of the metallic member. The thermal contraction coefficient differential is maintained within a predetermined range during drawing. The glass is placed under residual compression, interfacial bonding between said glass and said wire is substantially uniform, and surface cracking and bond breaks between metal and glass are substantially prevented. A dynamic balance is maintained between the surface tension of the molten alloy and the resistance to high temperature deformation by the glass vessel in which it is contained, enabling the production of glass-coated amorphous or nanocrystalline alloy members having predefined cross-sectional shapes.
Owner:DEMODULATION
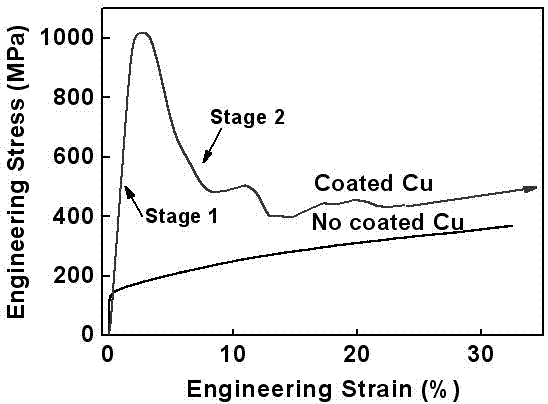
Metal wire for improving strength and corrosion resistance and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102779575ADoes not cause insect bitesDivide coins evenlyHot-dipping/immersion processesInsulated cablesElectric arc furnaceCopper wire
The invention discloses a metal wire for improving strength and corrosion resistance and a preparation method of the metal wire. A layer of metal glass coating is arranged on the surface of a metal wire main body. The preparation method comprises the following preparation steps of: 1) firstly, putting a metal glass ingot into an electric arc furnace filled with inert gas; continuously smelting the metal glass ingot by using electric arcs so that the metal glass ingot becomes liquid metal glass with uniform components; 2) enabling the metal wire to quickly pass through the liquid metal glass so that a layer of liquid metal glass coating is attached to the metal wire; and 3) quickly cooling the metal wire attached with the liquid metal glass coating so that the liquid metal glass coating forms a metal glass coating. According to the preparation method, the metal glass coating and the metal wire are closely combined without an insect biting effect caused by a potential defect. The mechanical strength and the strain property of a copper wire coated with metal glass alloy are obviously better than those of an uncoated copper wire. The corrosion resistance of the copper wire coated with the metal glass alloy is obviously better than that of the uncoated copper wire.
Owner:CHONGQING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
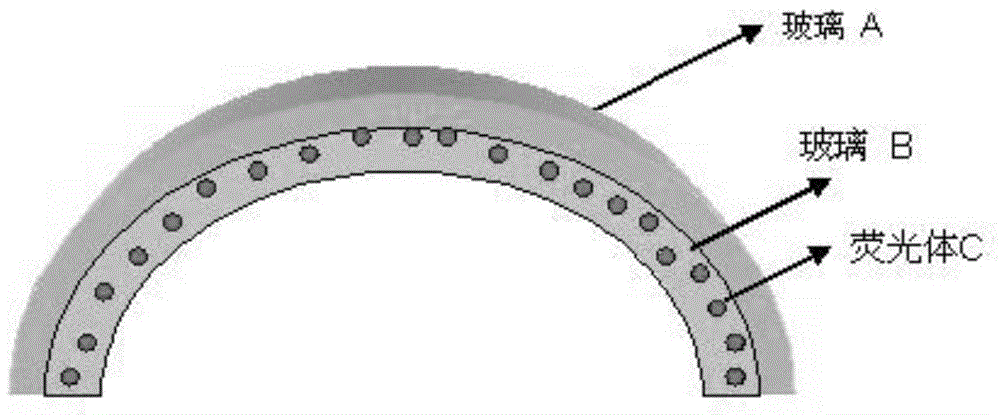
Phosphor glass coating for optical wavelength conversion and white light emitting device
InactiveCN102945914AAvoid light effect dropPhysical stabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesVitrificationFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a phosphor glass coating for optical wavelength conversion, which comprises the step of sintering and preparing a mixed layer of the powder of a phosphor C and glass B on a glass substrate A, specifically: (1) mixing the powder of the glass B and the phosphor C at a mass ratio of (100:1)-(100:150), binder and solvent into uniform paste, wherein the particle size of the powder of the glass B and the phosphor is 1-6 microns; (2) uniformly coating the paste on the glass substrate A and drying the glass substrate A coated with the paste to make the solvent volatilize completely; and (3) sintering the dried glass substrate A coated with the paste to obtain a glass B coating with the phosphor on the surface of the glass substrate A, wherein the sintering temperature of the phosphor glass coating is higher than the conversion temperature of the glass B in step (3).
Owner:JIANGSU MATERDIGE OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Super-hydrophobic glass coating and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a super-hydrophobic glass coating and a preparation method thereof. The super-hydrophobic glass coating comprises a nanoporous glass film and a low-surface-energy hydrophobic film which are attached to the glass surface sequentially from inside to outside, wherein the thickness of the nanoporous glass film is 150-1000 nm, the pore size thereof is 1-100 nm, the low-surface-energy hydrophobic film refers to siloxane or fluorinated siloxane with the thickness being 1-20 nm, and the surface energy of the low-surface-energy hydrophobic film is less than 40 mN / m. The preparation method includes sputtering a glass film on a glass substrate, performing heat treatment to enable the glass film to achieve phase separation and subjecting the glass film to acid washing so as to obtain the nanoporous glass film; performing dip-coating of the low-surface-energy hydrophobic film so as to obtain the super-hydrophobic glass coating. The super-hydrophobic glass coating and the preparation method thereof have the advantages that a water contact angle is above 150 degrees, so that a super-hydrophobic surface can be obtained, and anti-fingerprint, anti-oil and hydrophobic effects are improved; the low-surface-energy material can be attached to the outer surface of the nanoporous glass film and the inner walls of nanoporous glass film layer pores, and accordingly the super-hydrophobic glass coating with the surface worn has the same super-hydrophobic performance.
Owner:安徽凯盛基础材料科技有限公司 +1
Method for preparing and coating reinforcing steel bar anticorrosive glass coating material
InactiveCN103848572ALow costHigh bonding strengthSurface reaction electrolytic coatingSilicon oxideSlurry
The invention discloses a method for preparing and coating a reinforcing steel bar anticorrosive glass coating material. The reinforcing steel bar anticorrosive glass coating material contains the following components in percentage by weight: 35-70% of silicon dioxide, 15-45% of boron oxide and 5-25% of sodium oxide. The preparation process of the material comprises the steps of blending according to a certain proportion, melting glass at a high temperature, maintaining the temperature for a certain period of time, and then performing water quenching to obtain a glass material; mixing the glass material with an appropriate amount of a mill addition, performing ball milling, and confecting a slurry; coating the slurry on the surface of a matrix subjected to pretreatment, and firing at a high temperature. The process method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that a steel base plate does not need nickel pre-plating, the preparation process is simple and convenient, and an obtained coating and an obtained base plate are good in cohesiveness and have excellent wear resistance and corrosion resistance.
Owner:周伟
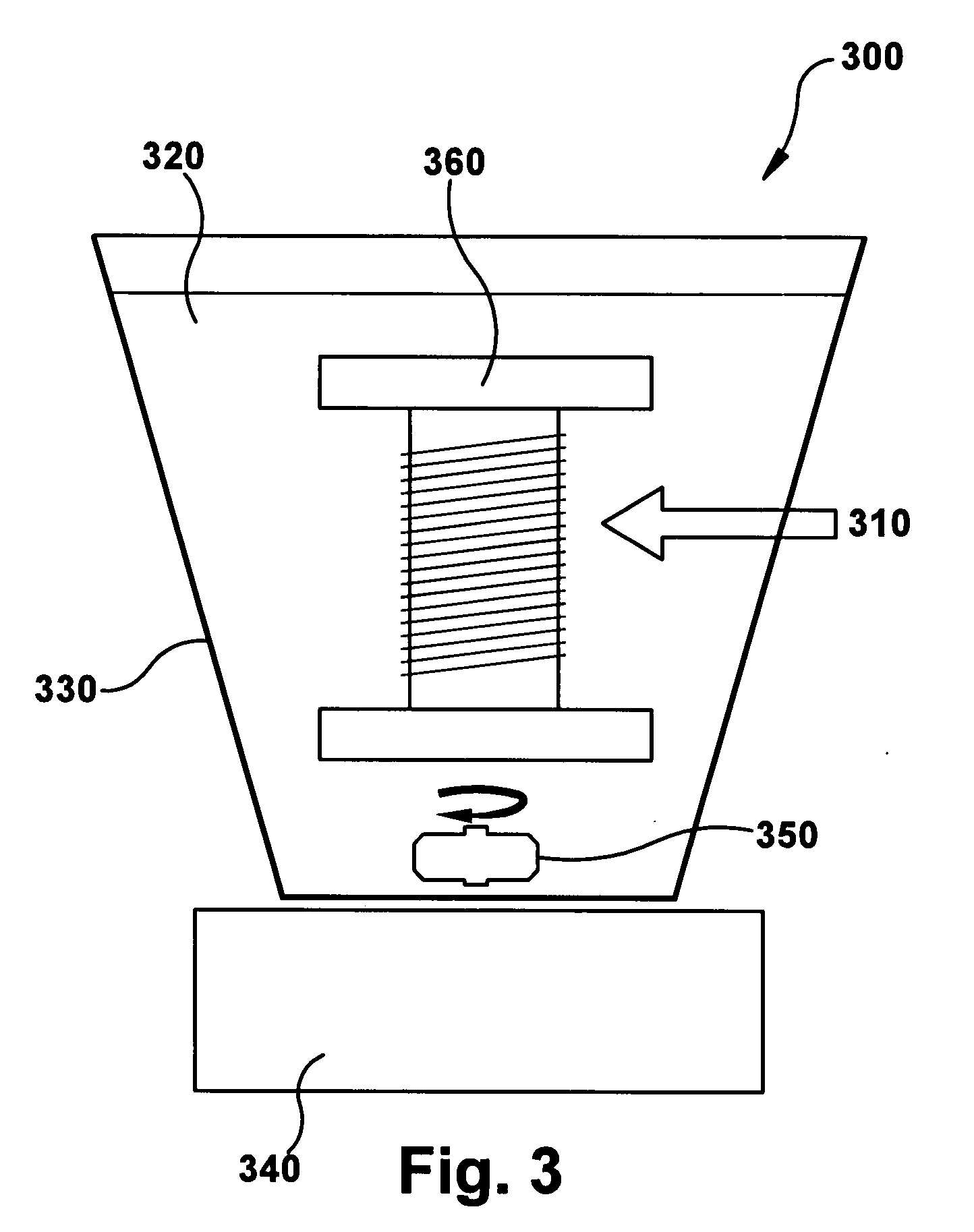
System and process for controllable preparation of glass-coated microwires
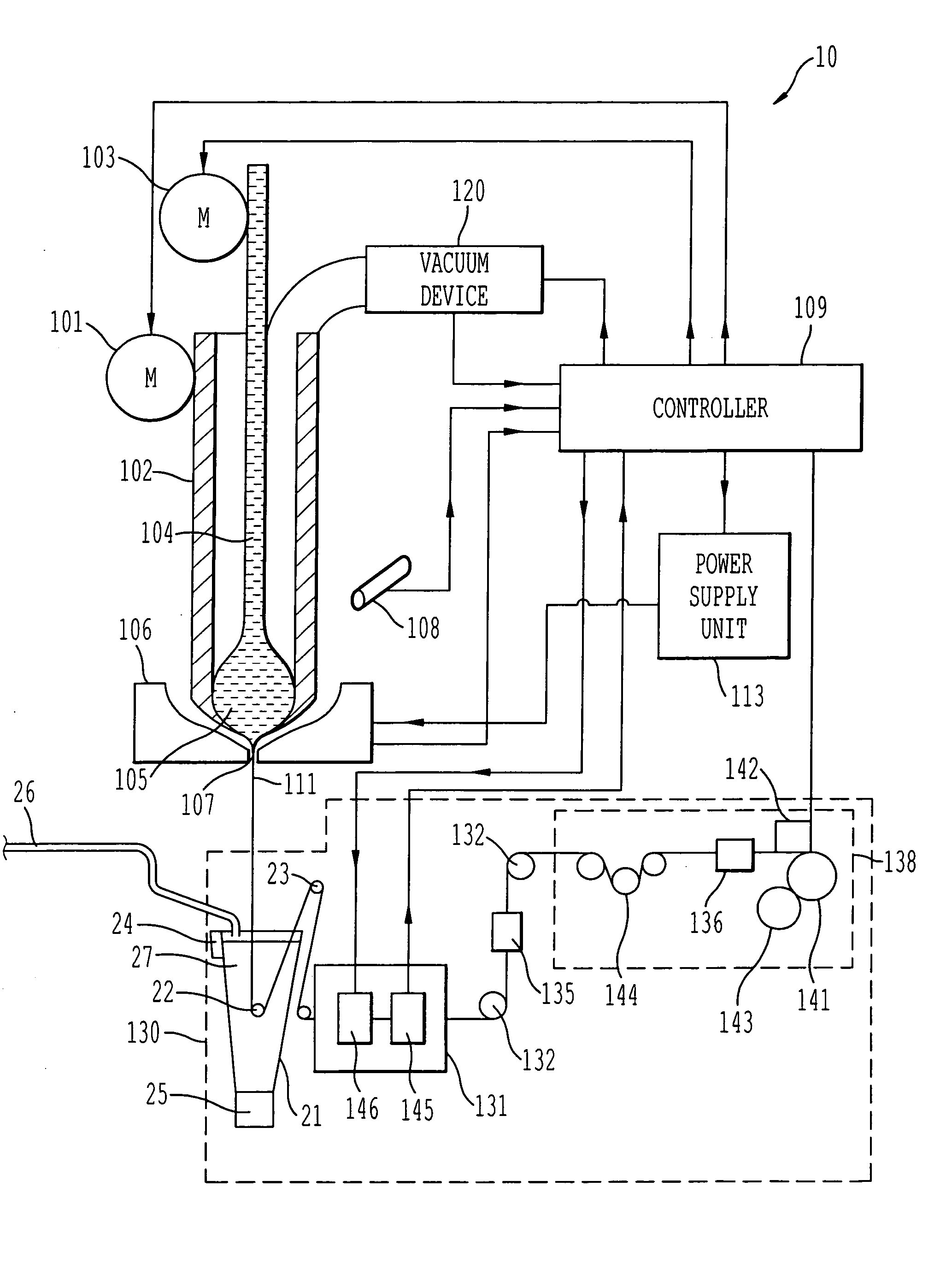
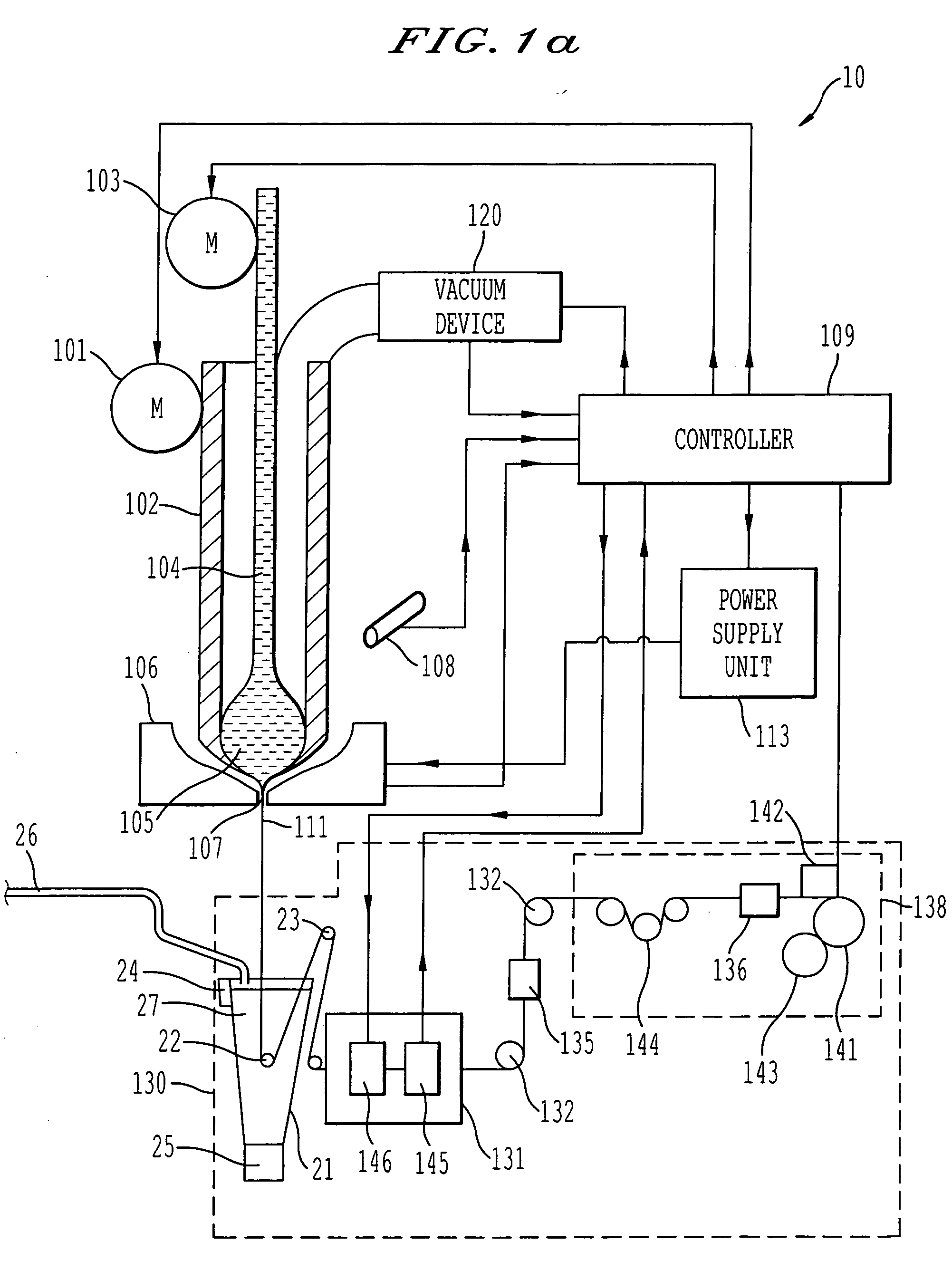
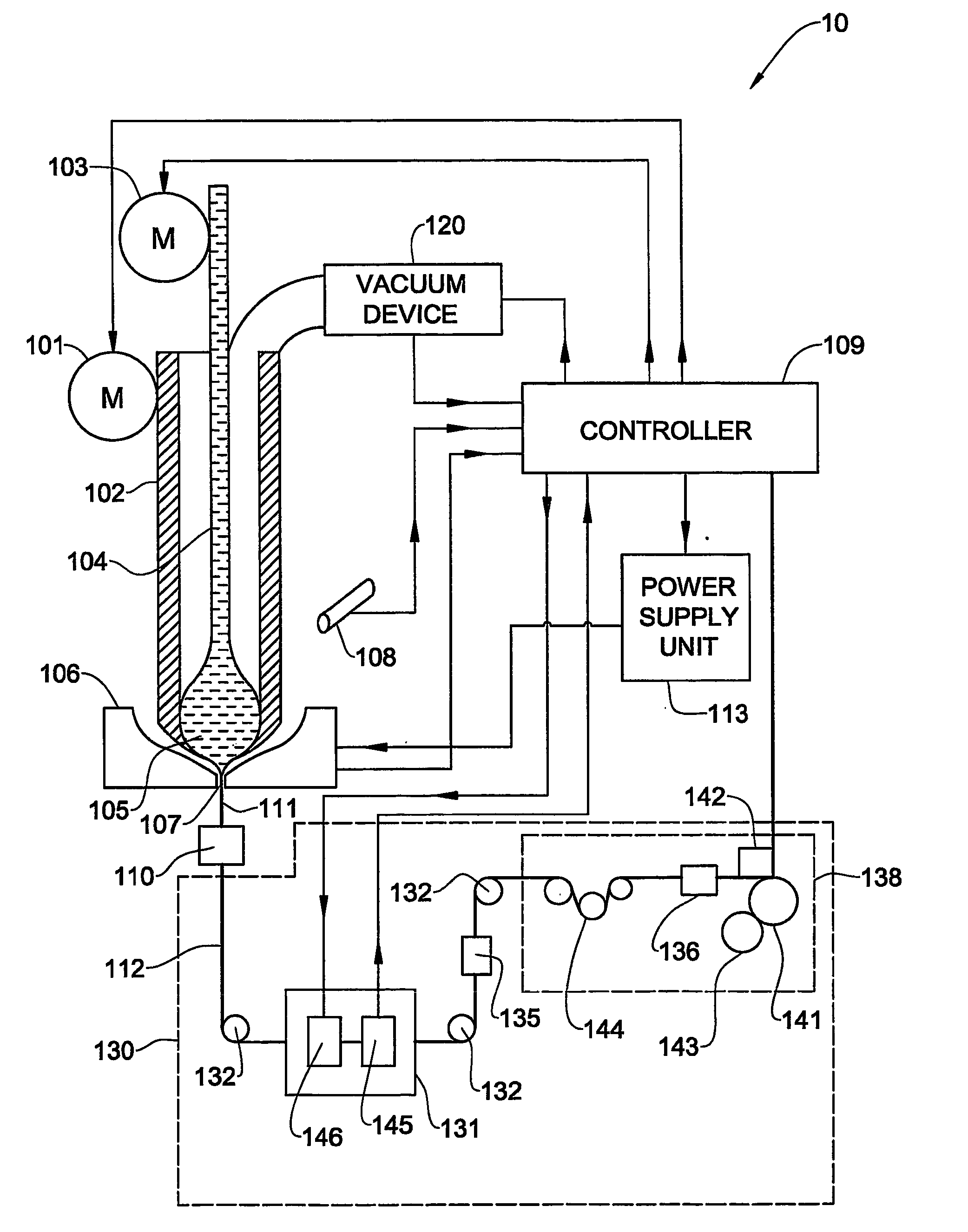
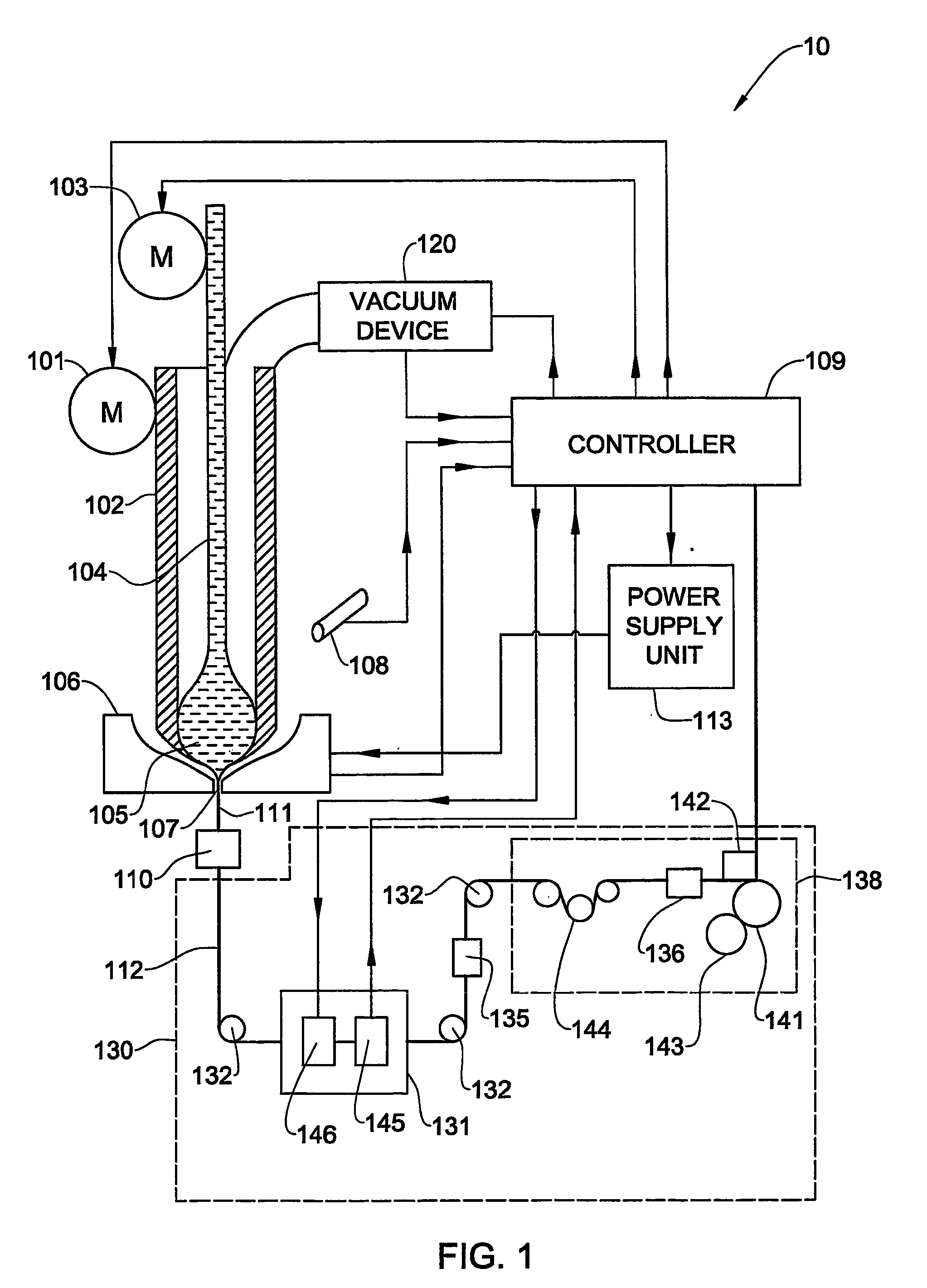
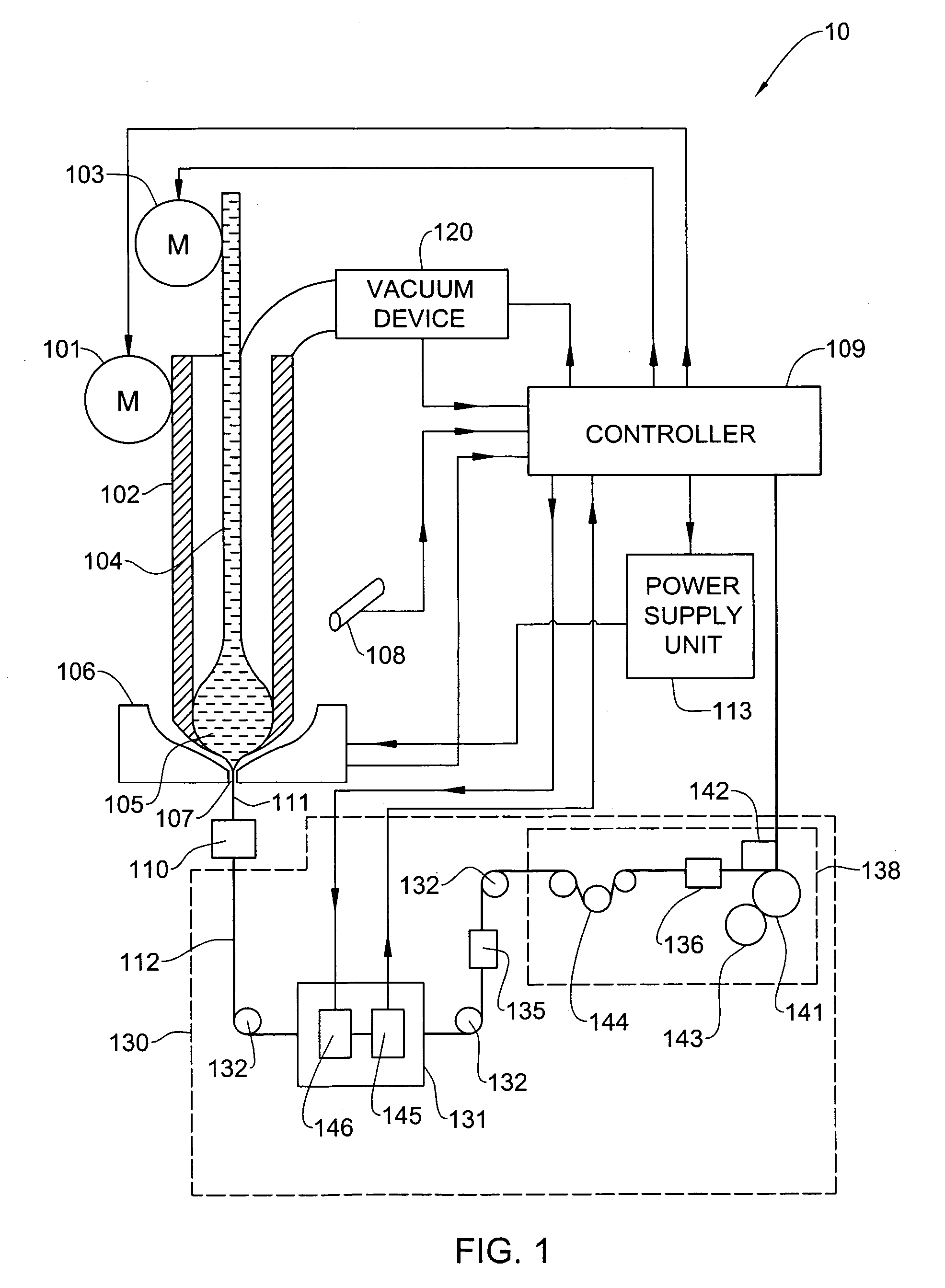
A process and system for controllable production of continuous lengths of microwire having a core covered by a glass coating are provided. According to the method of the invention, a glass tubing is loaded with a core material. Thereafter, the process includes the step of heating the tubing containing the core material for melting thereof, softening a tip of the glass tubing and forming a drop of the core material in the molten state surrounded by an outer glass shell. During the process, the gas is evacuated from the glass tubing in order to control elevation of the drop. The method includes drawing the heated outer glass shell into a continuous microwire filament and stabilizing the temperature and mass of the drop during the process. Accordingly, the system includes a suitable glass feeder mechanism, a rod feeder mechanism, a furnace configured for forming a drop of the core material in the molten state surrounded by an outer glass shell, controllable vacuum and cooling devices and a receiver section for receiving the microwire obtained after the cooling. The system also includes a controller and sensing means configured for producing signals representative of the gas pressure in the tubing, temperature temperature of the drop, the speed of the microwire, the value of the microwire diameter, the value of the spool diameter and other relevant parameters.
Owner:GLOBAL MICRO WIRE TECH
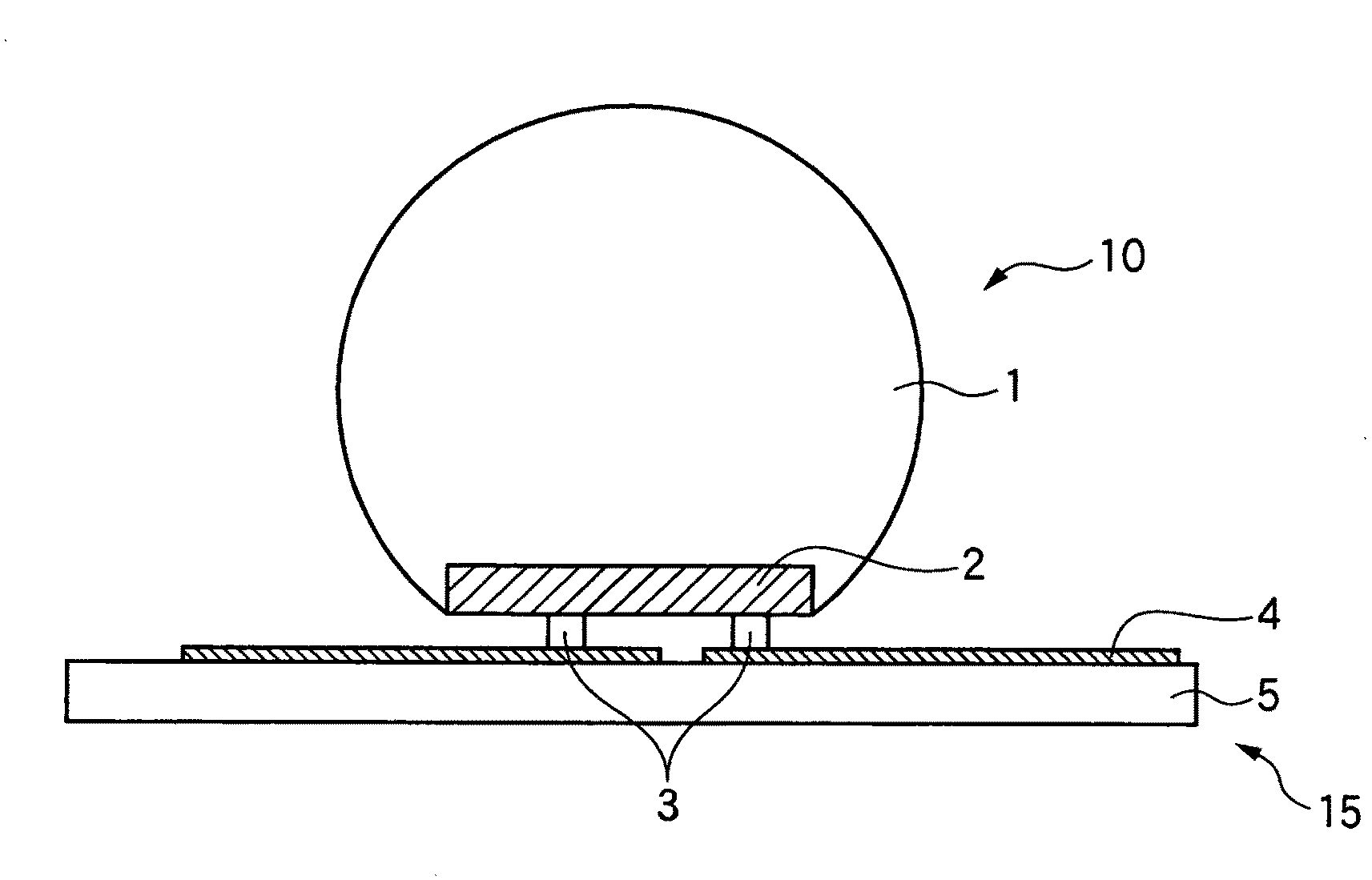
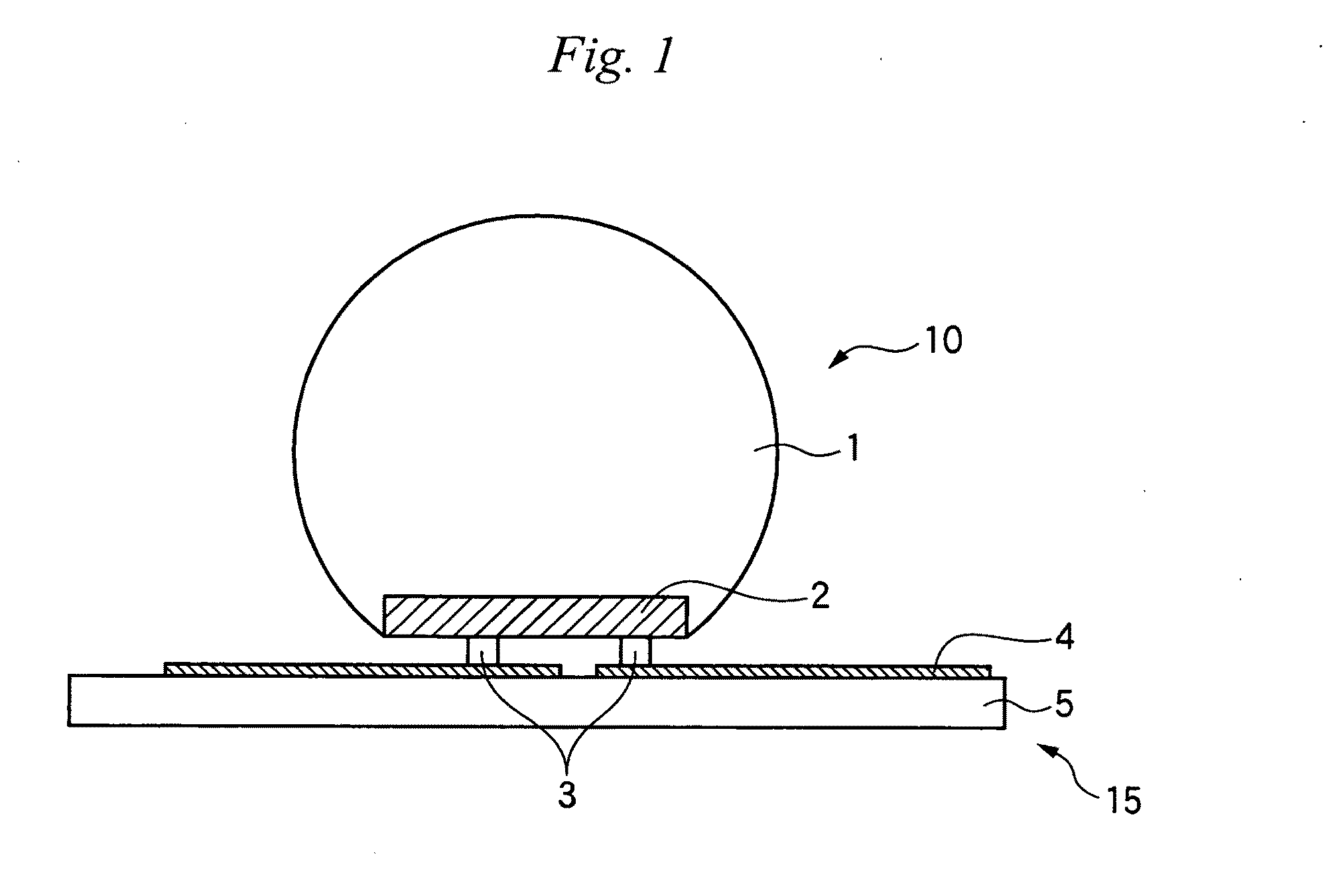
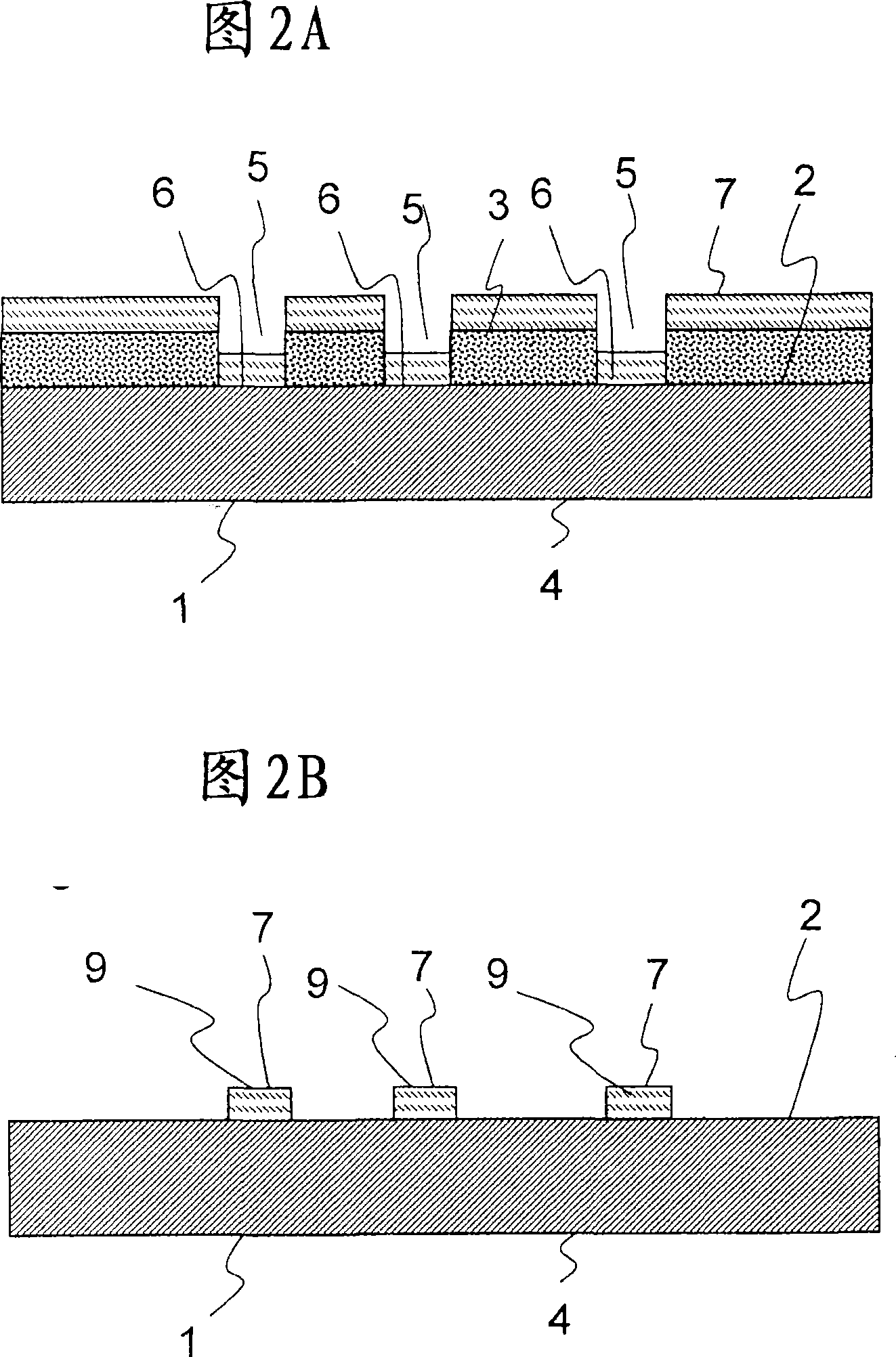
Glass-coated light-emitting element, light-emitting element-attached wiring board, method for producing light-emitting element-attached wiring board, lighting device and projector
InactiveUS20090239318A1Improve directivityReduce the amount requiredSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMaximum diameterLight pipe
A glass-coated light-emitting element 10 of the invention has a semiconductor light-emitting element 2 having a surface on which no electrode is formed is coated with a glass 1, in which a surface of the glass 1 constitutes a part of a spherical surface broader than a hemispherical surface, the refractive index of the glass 1 at an emission peak wavelength of the semiconductor light-emitting element 2 is 1.7 or more, and the ratio of the diameter of the above-mentioned spherical surface to the maximum diameter of a surface of the semiconductor light-emitting element 2 on which electrodes are formed is 1.8 to 3.5, whereby light emitted from the light-emitting element can be efficiently introduced into a light control unit, and alignment with a lens or a light pipe, which has hitherto been made, becomes unnecessary.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Glass coating and film technology for reducing platinum rhodium alloy bushing plate loss
InactiveCN102352143AReduce volatilityWill not affect the production processPretreated surfacesCoatingsPlatinumMetallurgy
A glass coating for reducing platinum rhodium alloy bushing plate loss provided by the invention comprises glass and Suzhou soil in a mass ratio of 9-15:1; a film technology employs a sol-gel film method, which is simple; and the coating raw material is cheap and with a utilization rate. Small size (nanometer level) oxide particles with high specific surface area and high activity can be obtained; and the coating has high uniformity, and multiple ingredient uniform oxide coating is easily prepared.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Air purifying device
InactiveCN102462857AIncrease oxygen enrichmentReduce inhalationDeodrantsRadiationOrganic compoundTitanium oxide
The invention belongs to the field of air purification and disinfection, and provides an air purifying device, which comprises at least two layers of glass sheets, wherein a gap is formed between any two adjacent layers of glass sheets; the side face of any layer of glass sheet is provided with a photocatalyst coating; at least one layer of glass sheet is provided with an ultraviolet ray generator; and the photocatalyst coating consists of nanoscale platinum particles and nanoscale titanium dioxide particles. In the invention, molecules of organic compounds in the air are decomposed and split into atoms through nanoscale platinum coated on glass, ultraviolet rays of which the wavelengths are 365-400 nanometers are irradiated onto the glass coating through an ultraviolet ray emitter, and the atoms are reduced into water, carbon dioxide and oxygen once again under the photocatalysis action of the titanium oxide on the coating. The air purifying device can be used for treating formaldehyde, toluene, dimethylbenzene, ammonia, radon, ether, heterocyclic organic matters, dioxin, viruses, pollen and the like in the air.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHENGZENG TECH DEV
Composite agitator
ActiveUS11311847B2Light weightGood chemical resistanceTransportation and packagingRotary stirring mixersEngineeringAgitator
A mixing agitator, for industrial use in mixing processes, that overcomes disadvantages associated with glass coated mixing agitators in the prior art. In particular, the mixing agitator includes a glass coated metal hub radially symmetrical about a central axis. The hub is at least partially embedded within a fluorinated polymer. The fluorinated polymer extends beyond the hub and forms agitator blades that may be reinforced. The hub has a centrally located receiving portion for receiving a drive shaft for rotating the agitator. The agitator is lighter weight than prior art glass coated steel agitators yet still has excellent chemical resistance and good temperature resistance. The agitator of the invention reduces likelihood of glass damage and permits agitator blade shapes not useable by glass coated agitators in the prior art. The invention also includes a mixing apparatus incorporating the hub and a method for mixing using the agitator.
Owner:GMM PFAUDLER US INC
Thermochromic glass comprising a coating of neutral-colour vanadium dioxide
ActiveUS20150203398A1High degreeVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingVanadium dioxideAlkaline earth metal
Owner:JUSTUS LIEBIG UNIV
Engineered glasses for metallic glass-coated wire
InactiveUS7354645B2Increased gating distanceGood magnetic responseGlass making apparatusQuartz/glass/vitreous enamelsGlass fiberChemical composition
Owner:DEMODULATION
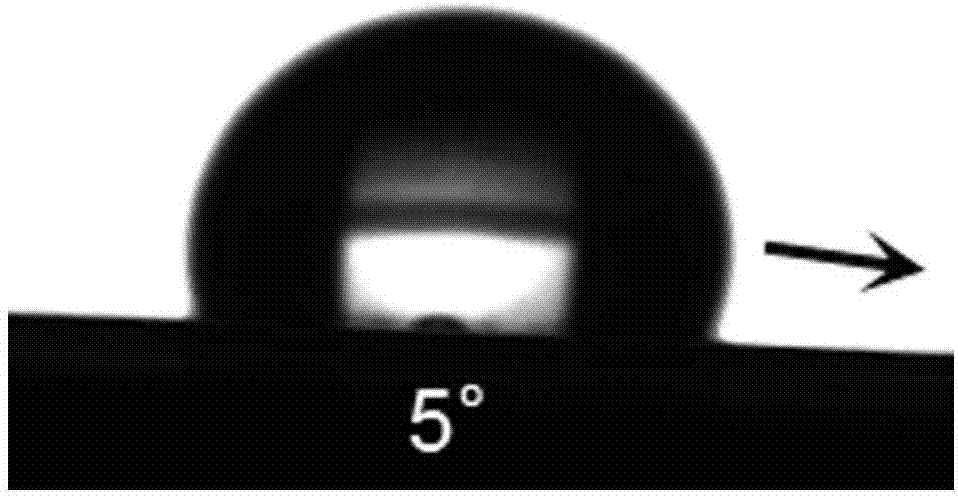
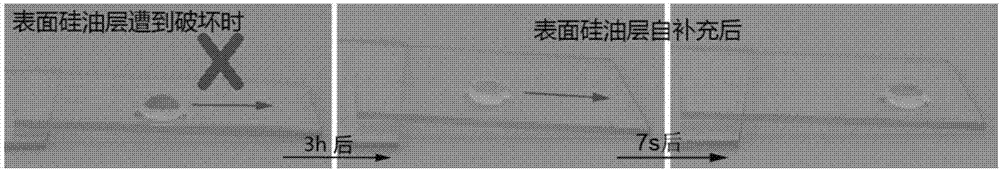
High-transparent and super-lubricating glass coating having self-supplement performance, and preparation method and application of same
The invention discloses a preparation method for forming a high-transparent and super-lubricating coating on a surface of a glass substrate. The method includes the following steps: 1) cleaning a glass slide with a solvent and drying the glass slide; 2) spin-coating the glass substrate with a toluene solution of a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) prepolymer and a curing agent, and curing the solution to form a PDMS coating; 3) soaking the glass substrate coated with the PDMS coating in dimethyl silicone oil so that silicone oil molecules penetrate through the internal skeleton network of the PDMS coating and the surface of the coating. The coating has excellent transparence and is higher than 90% in light transmittance in the wavelength range from ultraviolet to visible light. Contact angle of a water drop on the coating is 109 degrees and the water drop can slip off from the coating very easily, so that the coating has excellent super-lubricating performance. The preparation method is simple and is free of special devices and chemical reagents. The high-transparent and super-lubricating coated glass can be widely applied for manufacturing durable and anti-scratch glasses lens, window glass having self-cleaning function, etc.
Owner:YANTAI UNIV
Method for preparing nano-titanium dioxide photocatalysis transparent glass coating by electrospinning technology
InactiveCN103819100ADemonstrate photocatalytic activityWith self-cleaning functionNanoparticleElectrospinning
The invention discloses a method for preparing a nano-titanium dioxide photocatalysis transparent glass coating by an electrospinning technology. The method comprises the specific steps as follows: (1) putting tetrabutyl titanate, acid and ethyl alcohol into a closed container, performing uniform stirring to obtain first sol, dissolving PVP (polyvinyl pyrrolidone) in DMF (dimethyl formamide), performing continuous stirring until the PVP is completely dissolved to obtain second sol, mixing the two types of sol, adding DEA (diethanol amine), and performing uniform stirring to obtain an electrospinning precursor solution; (2) putting a common glass slide serving as a glass substrate placed in a position right below an electrospinning spraying head, fixing the distance between the electrospinning spraying head and the glass substrate, and changing the flowing speed of the electrospinning precursor solution for spraying; (3) after electrospinning spraying is complete, calcining a product to obtain the nano-titanium dioxide photocatalysis transparent glass coating. The equipment is simple, and the process is simplified; the investment cost is low; the nano-titanium dioxide photocatalysis transparent glass coating can be widely applied to manufacturing of inorganic TiO2 nano particles.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Optically encoded glass-coated microwire
InactiveUS7071417B2Eliminate needCheap constructionInsulated cablesRecord carriers used with machinesOptical propertyOptoelectronics
Owner:DEMODULATION
Engineered glasses for metallic glass-coated wire
InactiveUS20050158545A1Good magnetic responseIncrease signal amplitudeGlass making apparatusQuartz/glass/vitreous enamelsAlloy compositeMaterials science
A metallic glass-coated wire is formed by drawing a hollow glass fiber from a container in which molten alloy is entrained and solidified. Interference stresses extant between the glass coating and the alloy core of the wire are produced by systematically controlling thickness and mechanical elastic properties of the glass. The interference stress is tailored by selection of glass thickness and chemistry to optimize wire drawing process conditions, such as drawing temperature and strain rate. In addition, the interference stress is especially tailored to assure physical integrity of the glass-alloy composite wire product. Local property variations along the wire length are minimized, facilitating production of discrete wire segments especially suited for use in EAS applications.
Owner:DEMODULATION
Method and etchant for removing glass-coating from metal wires
An etchant for and method of removing a glass coating on a metallic wire is provided. The etchant comprises an acid solution having metal ions contained therein. The metal ions prevent the acid solution from pitting or damaging the metallic wire, while allowing the acid solution to effectively etch and remove the glass coating. In one embodiment, a fluorine-based acid solution can be used. In another embodiment, a glass coated, metal alloy microwire is etched and the metal ions added to the etchant are chosen to be the same as the majority constituent element in the metal alloy. The glass coating can be either removed in full or only partially removed.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Titanium alloy casting ingot surface glass coating and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN110743765AHigh viscosityHigh softening temperatureLiquid surface applicatorsCoatingsIngotTitanium alloy
The invention discloses a titanium alloy casting ingot surface glass coating. The glass coating is manufactured through the following raw materials including, by mass, 65%-95% of a glass matrix, 5%-35% of a bonding agent and 0%-30% of an additive. The glass matrix is manufactured through the following raw materials including, by mass, 5%-12% of B2O3, 4%-20% of Al2O3, 3%-8% of ZrO2, 3%-9% of NiO and / or Cr2O3, 3%-11% of CaO and / or BaO, 5%-15% of a compound N and the balance SiO2. The invention further discloses a preparing method of the titanium alloy casting ingot surface glass coating, the rawmaterials are evenly mixed and put on the surface of a titanium alloy casting ingot in advance, and the glass coating is formed through heat treatment. The composition of the glass matrix is regulated, and the glass coating can have good high-temperature protection performance; and the technology is simple and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
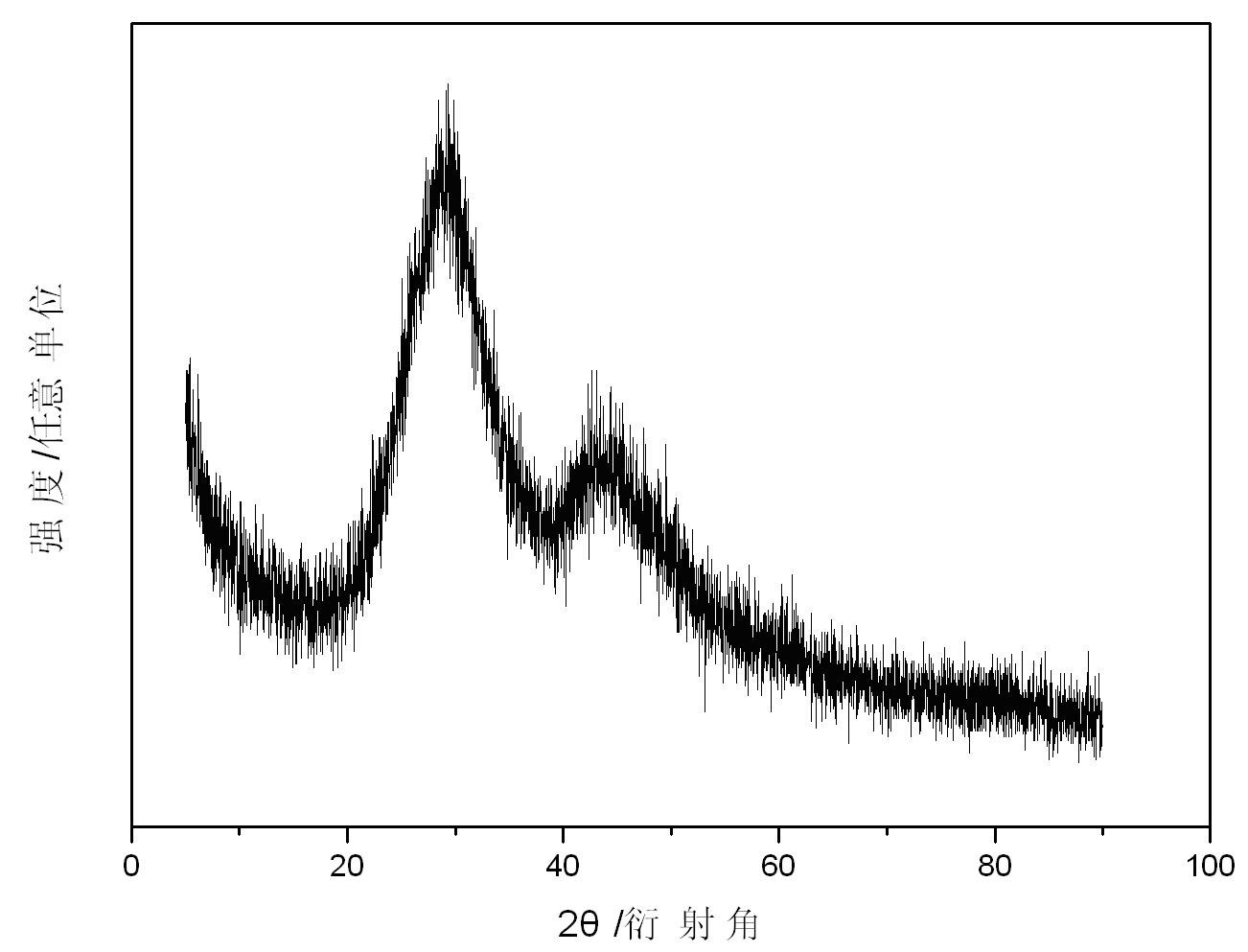
Aerogel surface high-temperature-resistant composite coating and preparation method thereof
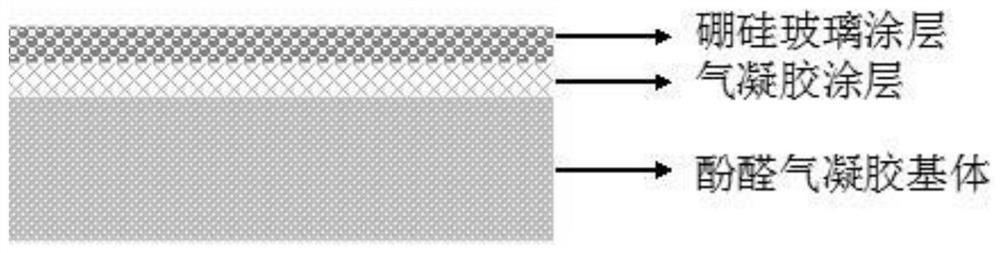
ActiveCN113929962AImprove antioxidant capacityImprove anti-scourabilityFireproof paintsGlass shaping apparatusOxidation resistantBorosilicate glass
The invention provides an aerogel surface high-temperature-resistant composite coating and a preparation method thereof, and the preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing aerogel and inorganic oxide sol to obtain an aerogel coating; (2) mixing and sintering B2O3 powder, Al2O3 powder and SiO2 powder, and then adding a solvent for ball milling and mixing to obtain a borosilicate glass coating; (3) coating the surface of a substrate with the aerogel coating, and drying to obtain an aerogel coating; and (4) coating the surface of the aerogel coating with the borosilicate glass coating, and drying to obtain the aerogel surface high-temperature-resistant composite coating containing the borosilicate glass coating. The high-temperature-resistant composite coating prepared by the method is not easy to fall off on the surface of a matrix, and has excellent oxidation resistance and scouring resistance.
Owner:AEROSPACE INST OF ADVANCED MATERIALS & PROCESSING TECH
Cast glass-coated microwire for X-ray protection
InactiveUS20070141332A1Superior protection against X-ray radiationEffective absorptionGlass making apparatusYarnX-rayMaterials science
A glass-coated microwire includes a metal wire coated with a glass. The metal wire can contain, in weight %, 20-25% Bi, 6-12% Sn, 4-8% In, 3-5% Cu, 0.6-1.5% Si, 0.05-1.2% Ce, and a balance of Pb. The glass coating can contain, in mol. %, 12-15% SrO, 10-12% B2O3, 1-3% Al2O3, 5-15% SiO2, 1-3% ZnO, 0.5-1.5% Li2O, 2-5% SnO, 2-8% K2O, and a balance of PbO. The glass-coated microwire provides improved shielding against X-ray radiation.
Owner:GLOBAL MICRO WIRE TECH
Building up diffractive optics by structured glass coating
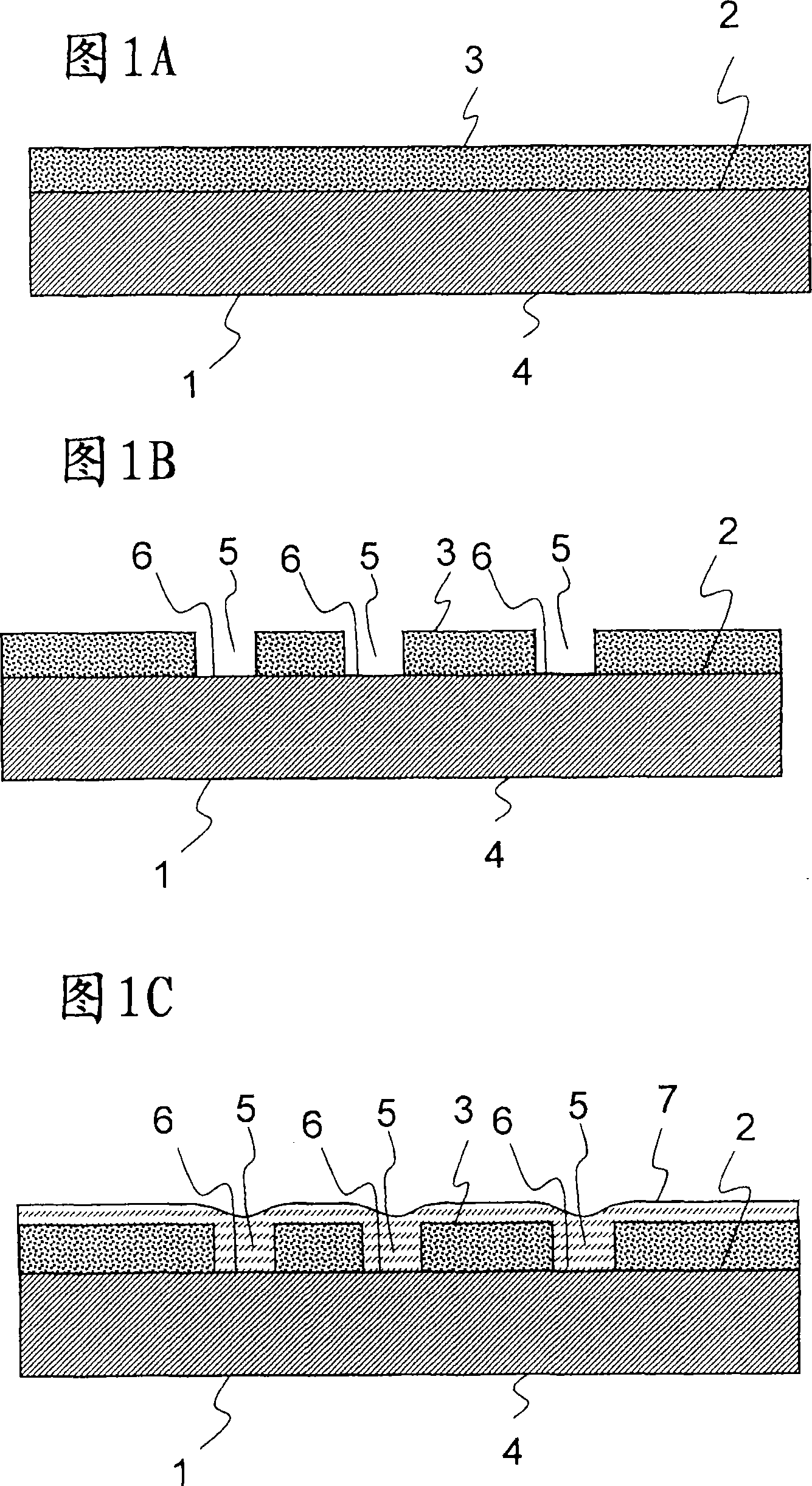
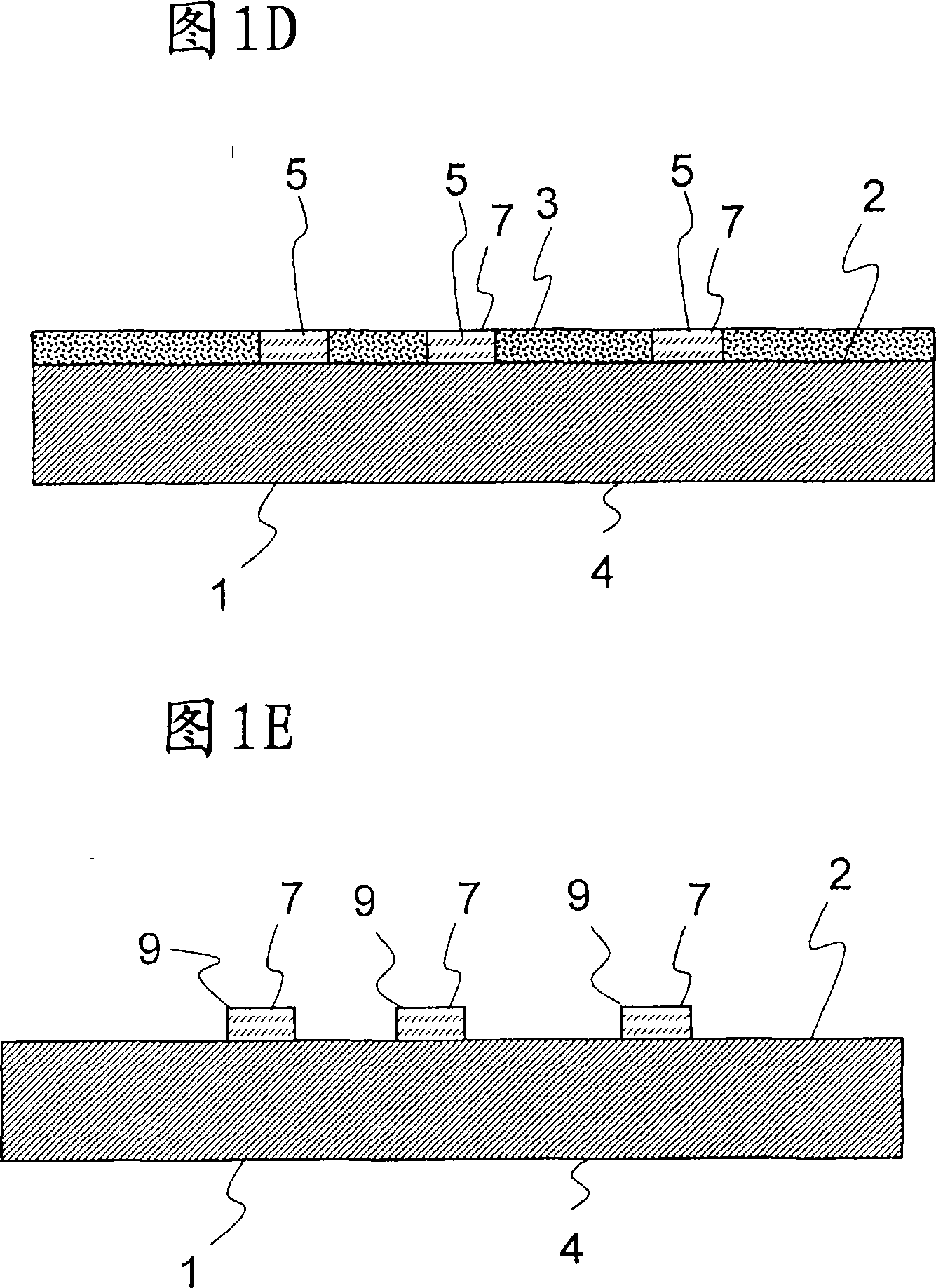
The invention relates to optical parts, and in particular to a process for applying an optically active structuring (7) to a substrate (1), and also to a component produce using a process of this type. The process for applying an optically active structuring to a substrate comprises in particular photolithographic techniques and the deposition of material via physical vapor deposition processes.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
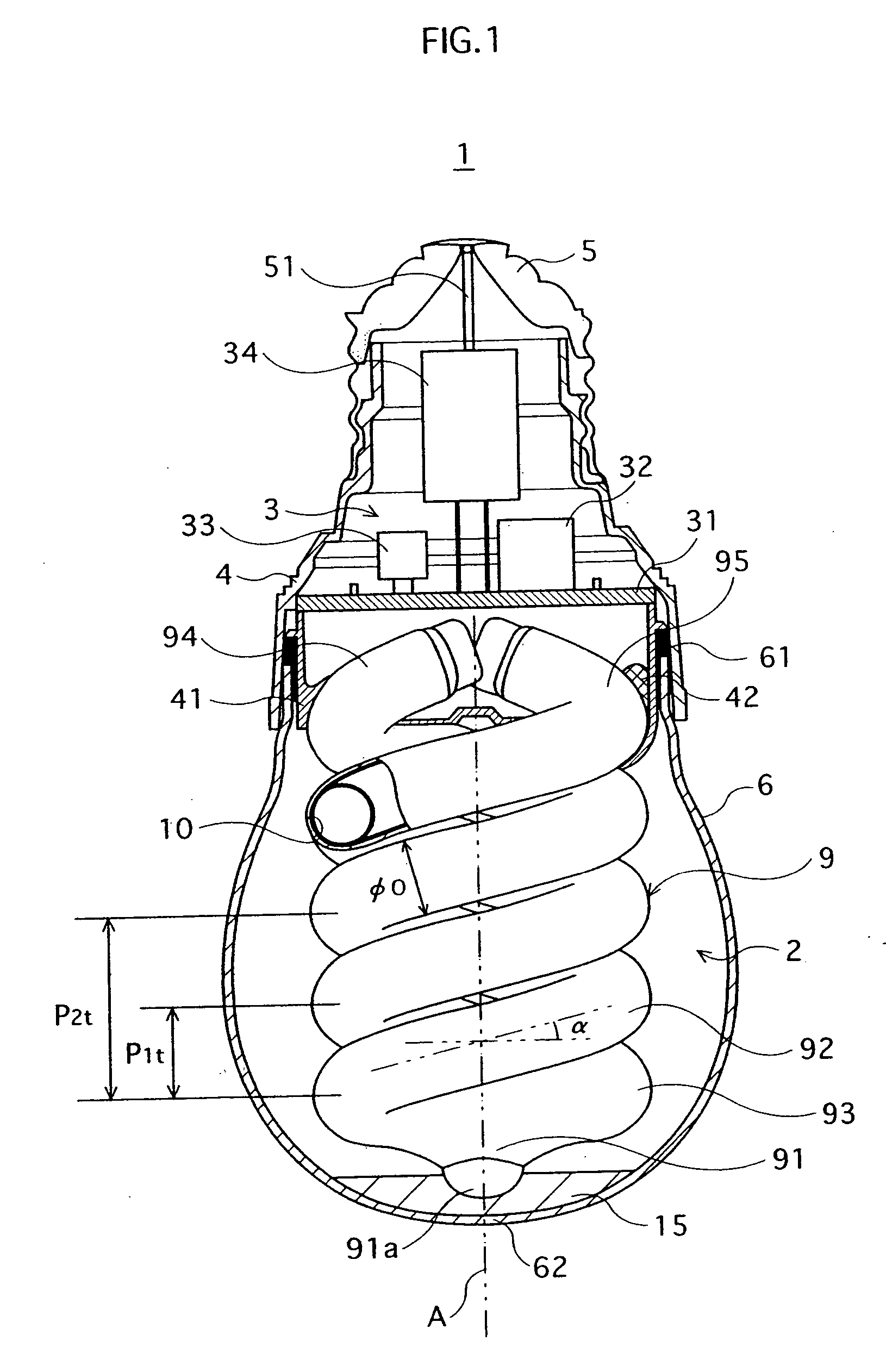
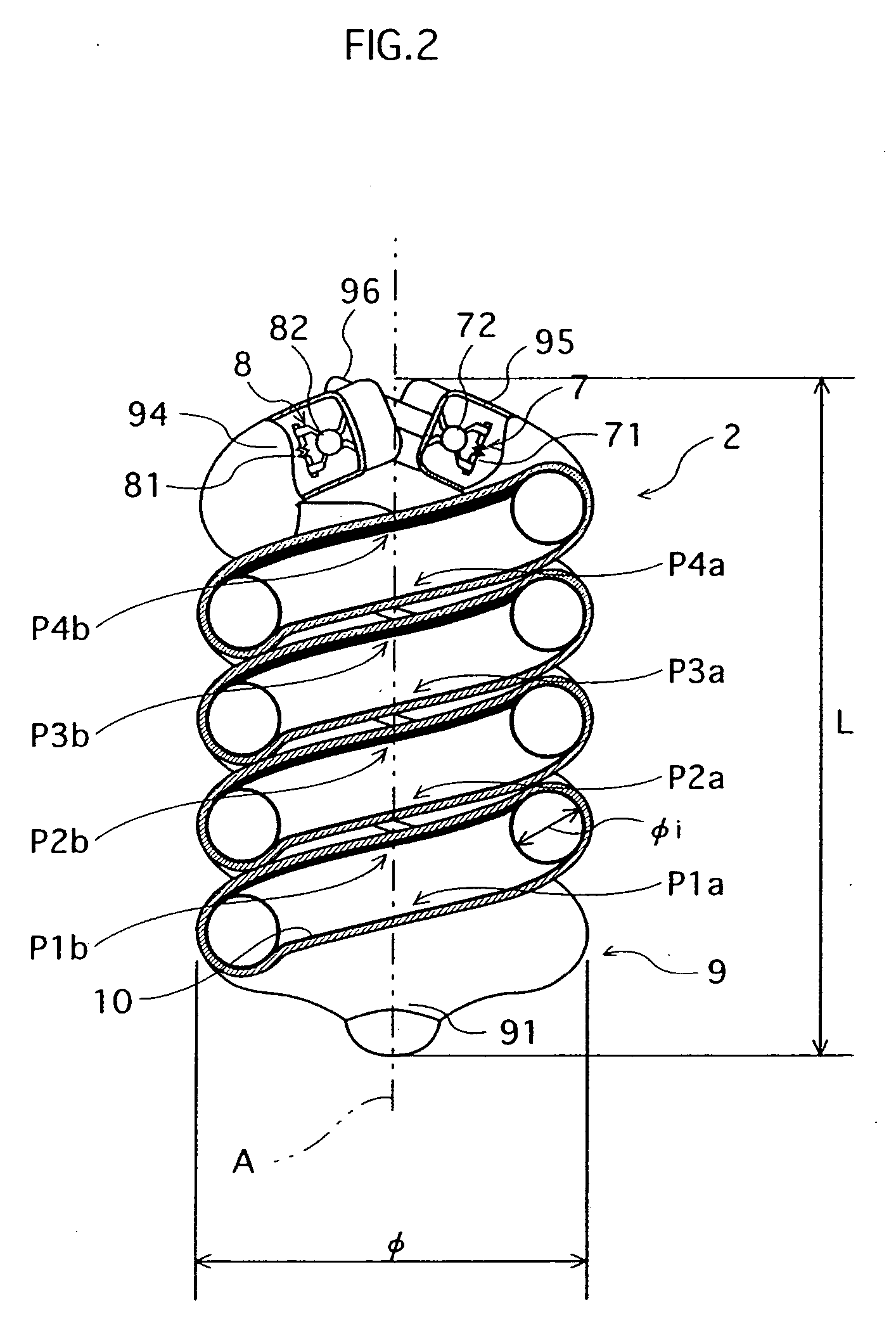
Arc tube, discharge lamp, and production method of such arc tube, which enables brighter illuminance
InactiveUS20060030232A1Convenient lightingEasy to useElectroluminescent light sourcesVessels or leading-in conductors manufactureIlluminancePhosphor
Disclosed is a compact self-ballasted fluorescent lamp that includes a phosphor coating provided inside a glass tube bent to have a double-spiral configuration. The arc tube has two spiral parts that are wound around an axis “A”, and a turning part joining the two spiral parts. At any cross section of the glass tube, the applied phosphor coating is thicker in the inner surface of the glass tube near the ends of the glass tube in the axis “A” direction, than in the inner surface near the turning part.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com