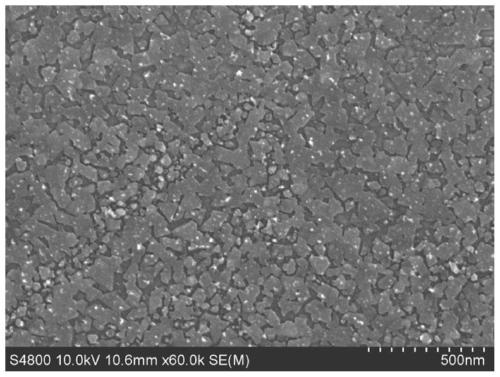
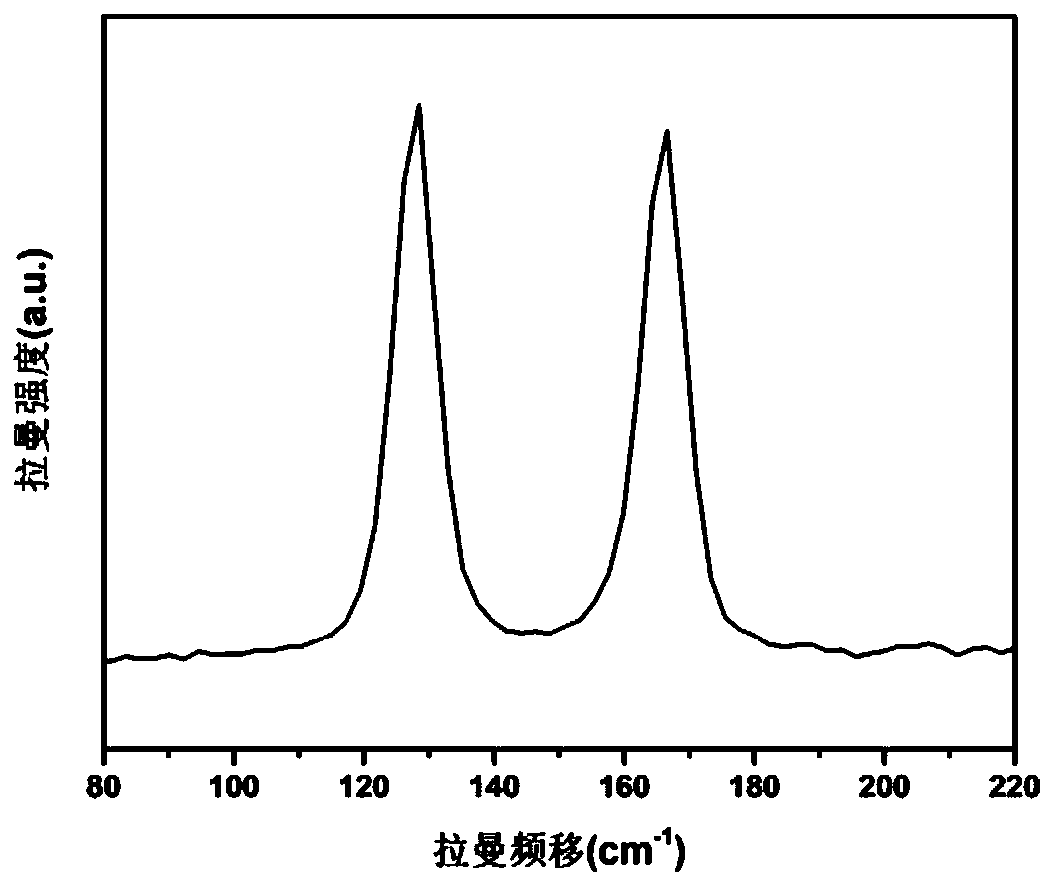
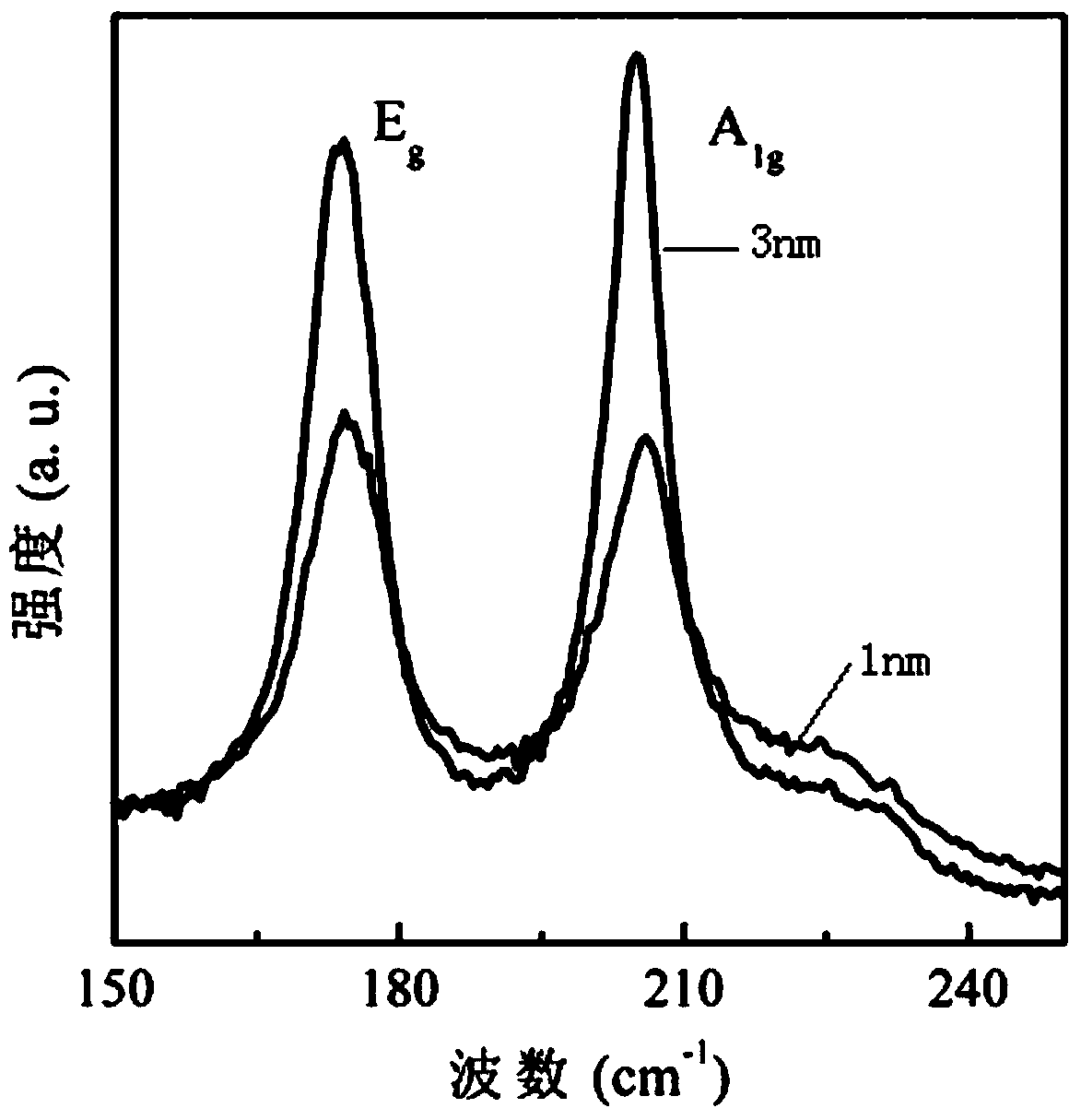
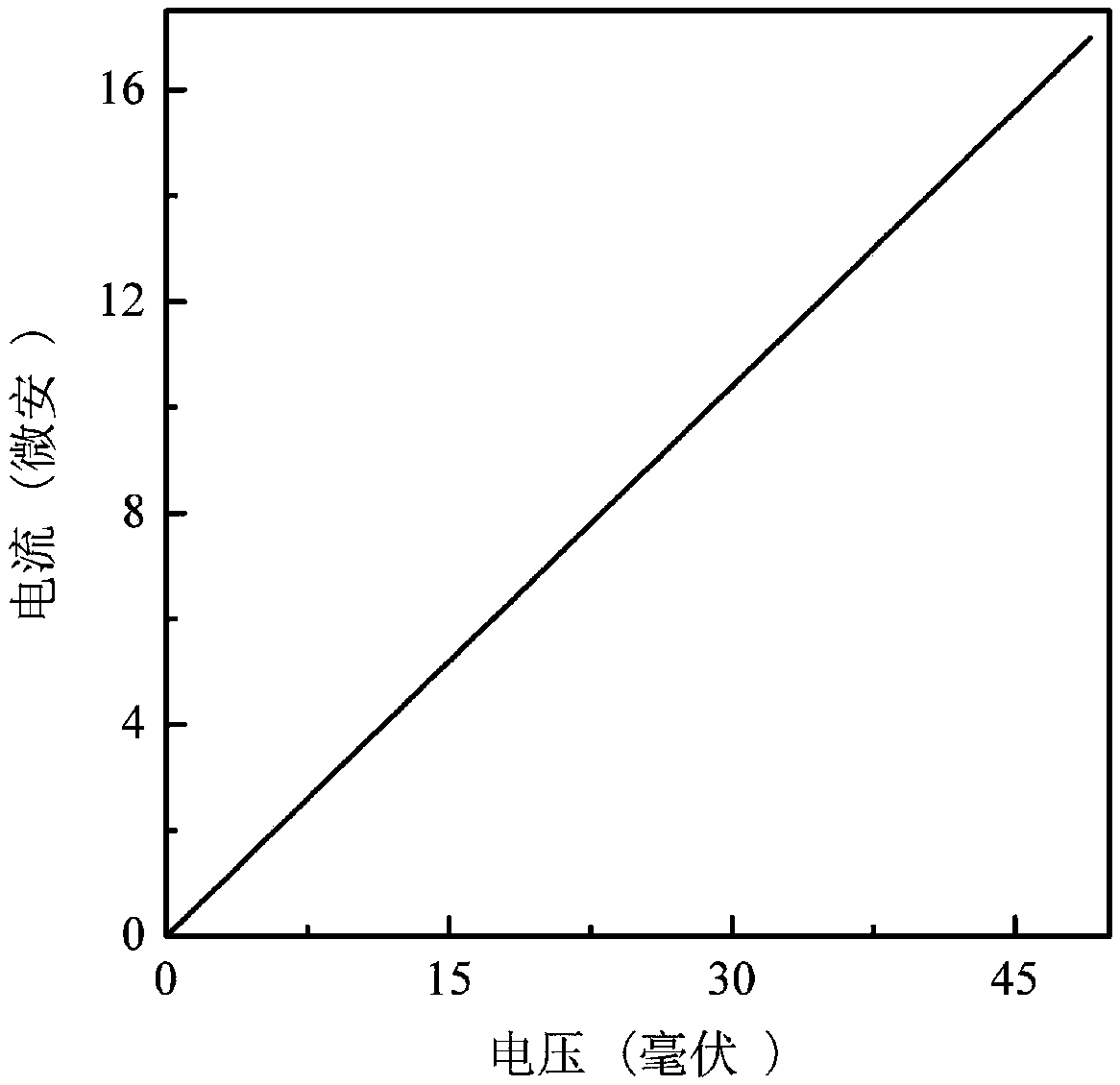
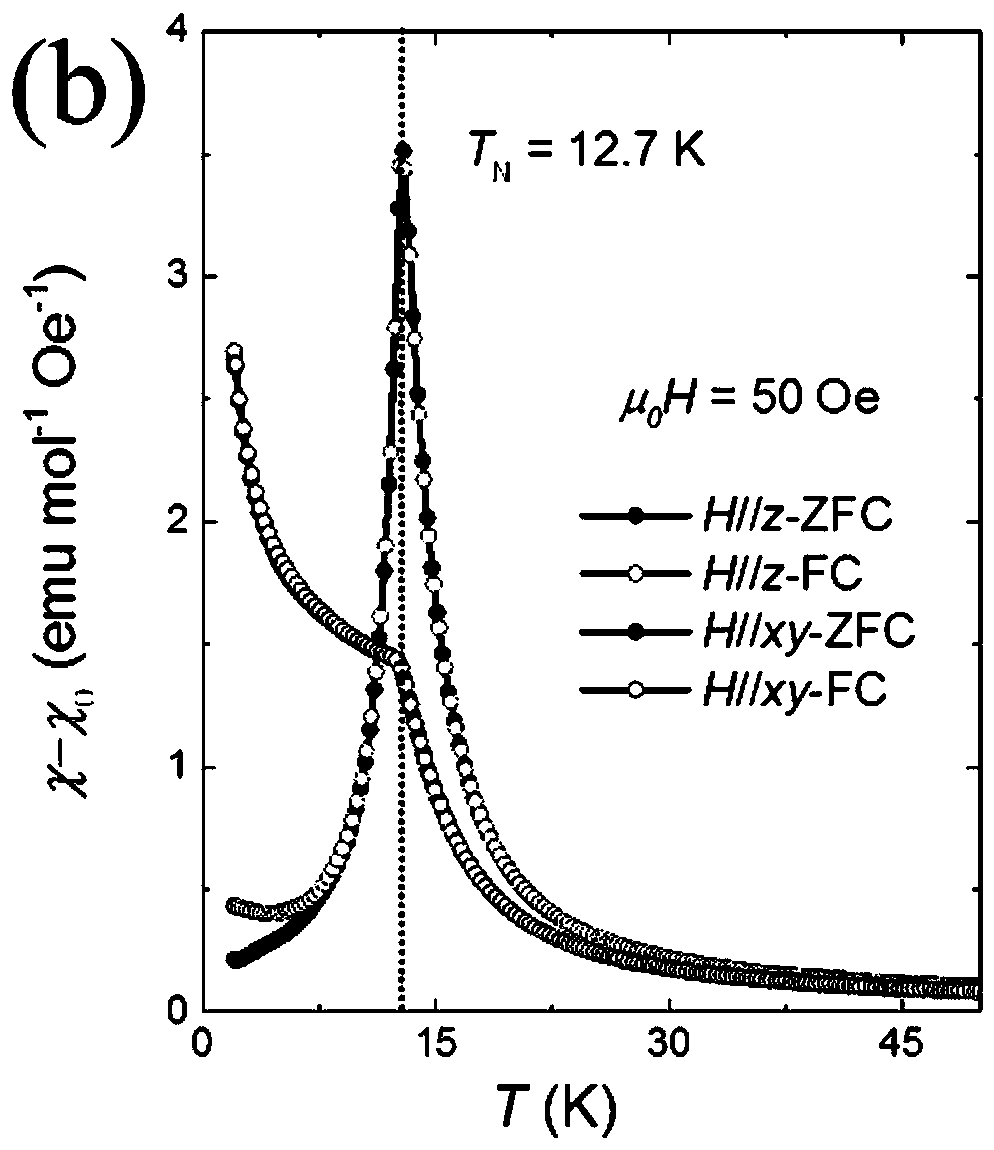
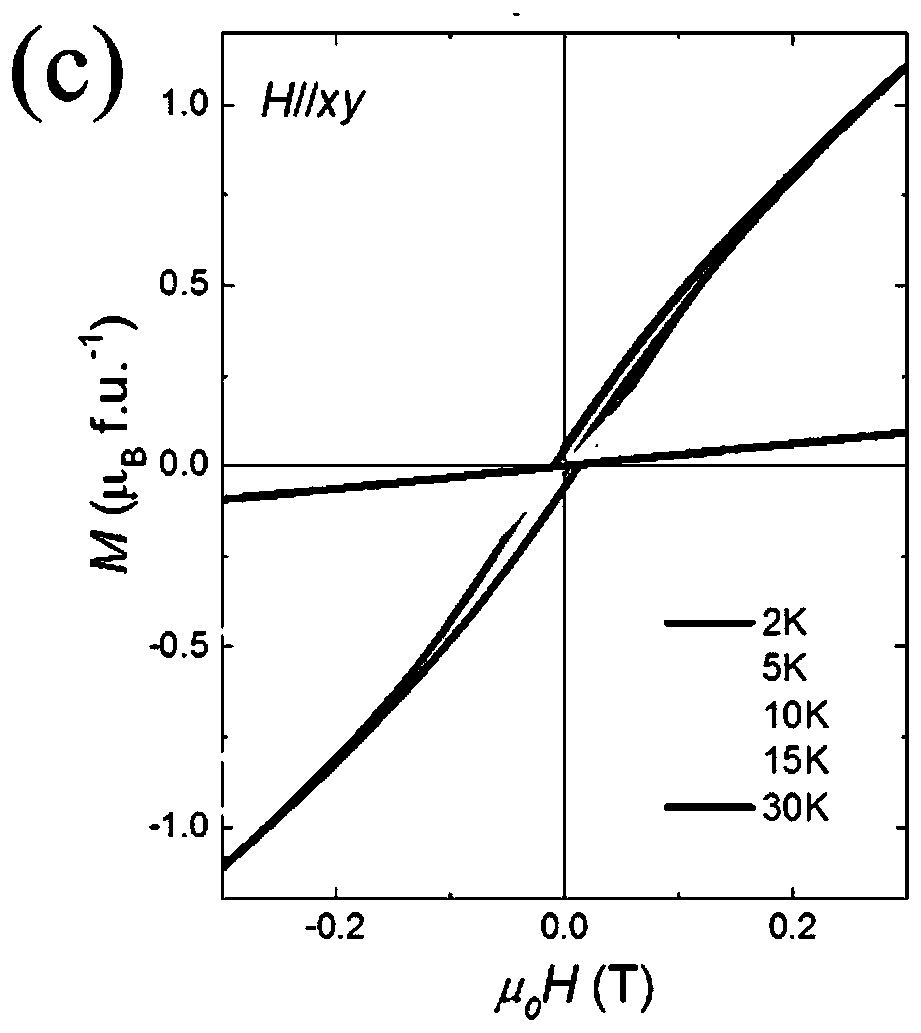
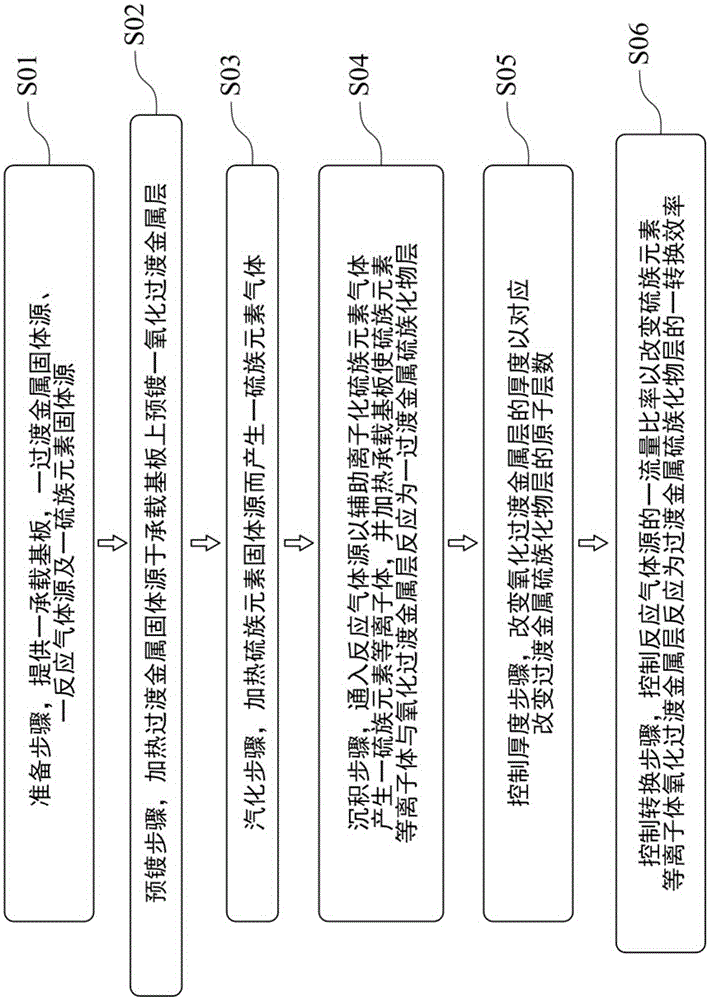
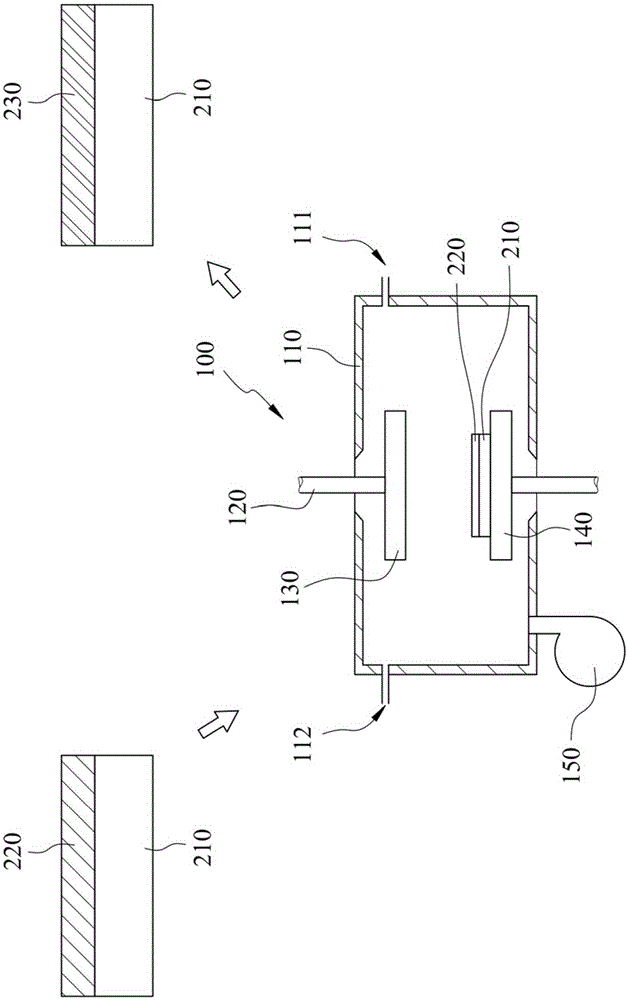
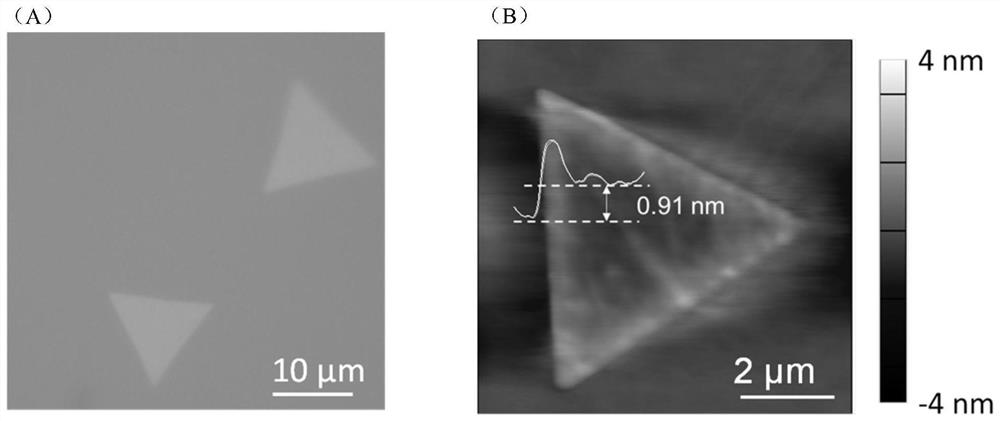
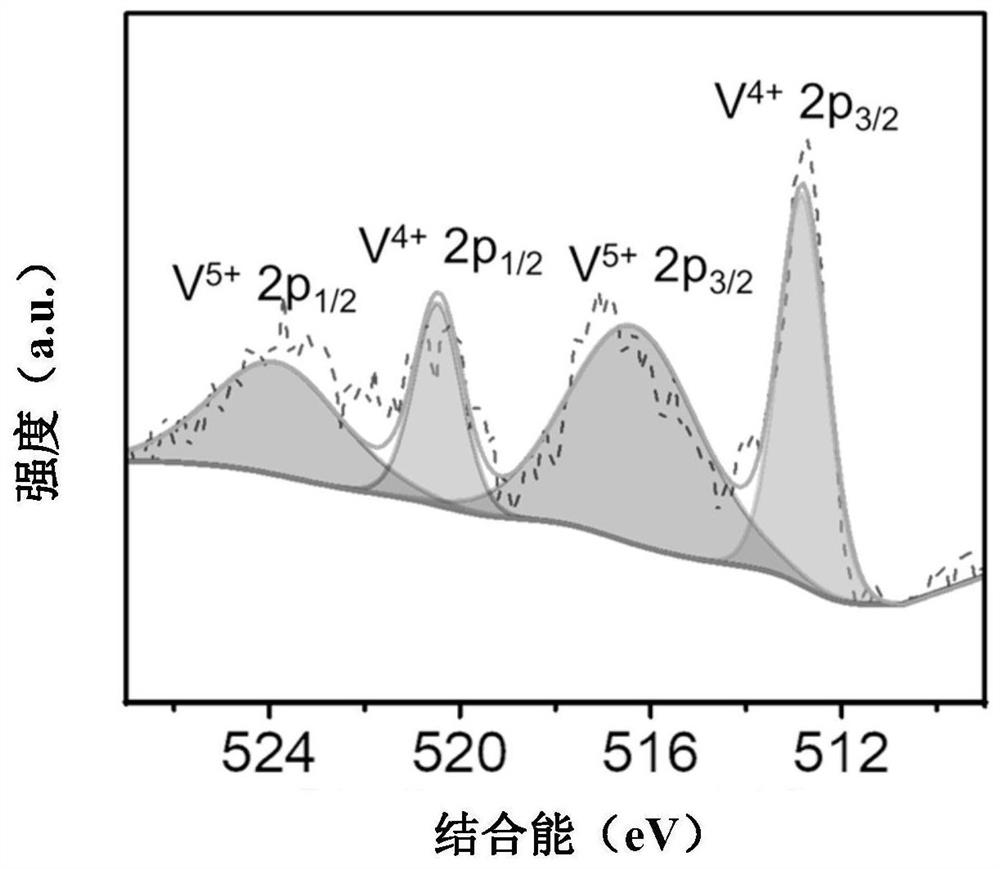
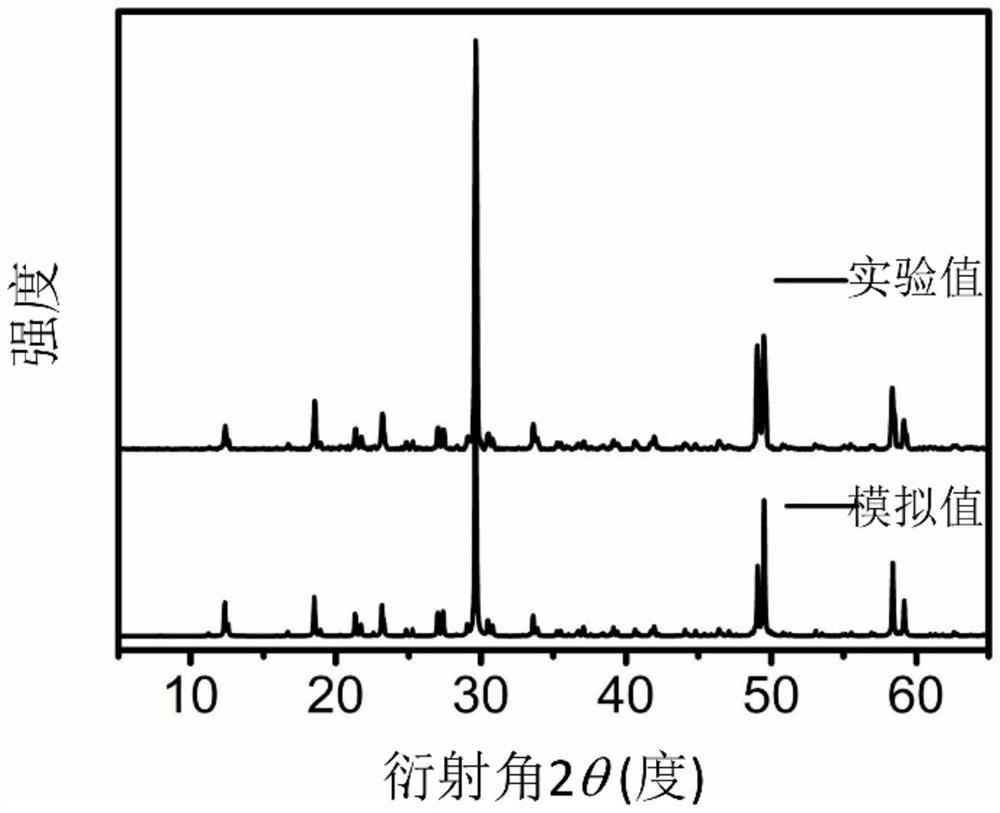
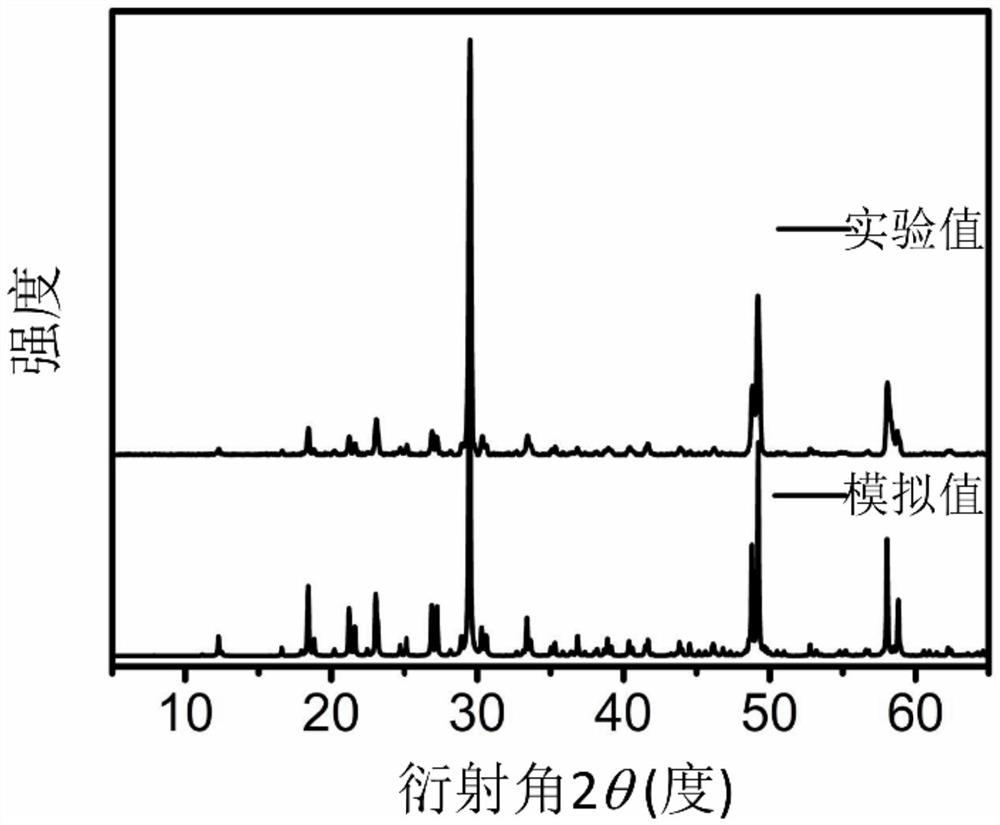
Patents
Literature
37 results about "Interchalcogen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The chalcogens react with each other to form interchalcogen compounds. Although no chalcogen is extremely electropositive, nor quite as electronegative as the halogen fluorine (the most electronegative element), there is a large difference in electronegativity between the top (oxygen = 3.44 — the second most electronegative element after fluorine) and bottom (polonium = 2.0) of the group. Combined with the fact that there is a significant trend towards increasing metallic behaviour while descending the group (oxygen is a gaseous nonmetal, while polonium is a silvery post-transition metal), this causes the interchalcogens to display many different kinds of bonding: covalent, ionic, metallic, and semimetallic.
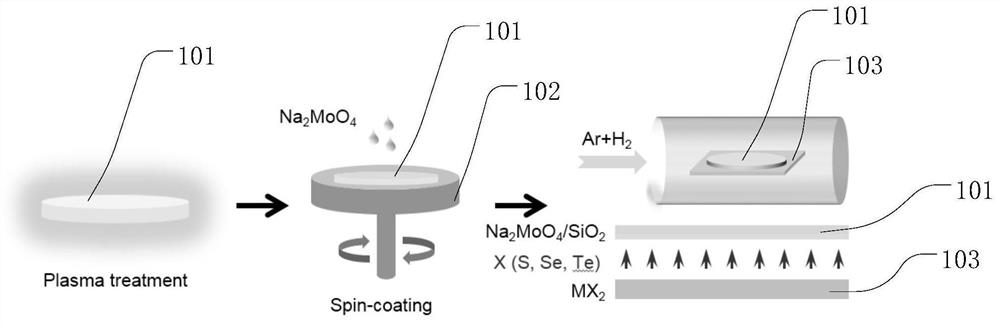
Transition metal chalcogenide film and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109824098AImprove scalabilityIncrease the areaRuthenium/rhodium/palladium/osmium/iridium/platinum compoundsNanotechnologyIridiumGas phase
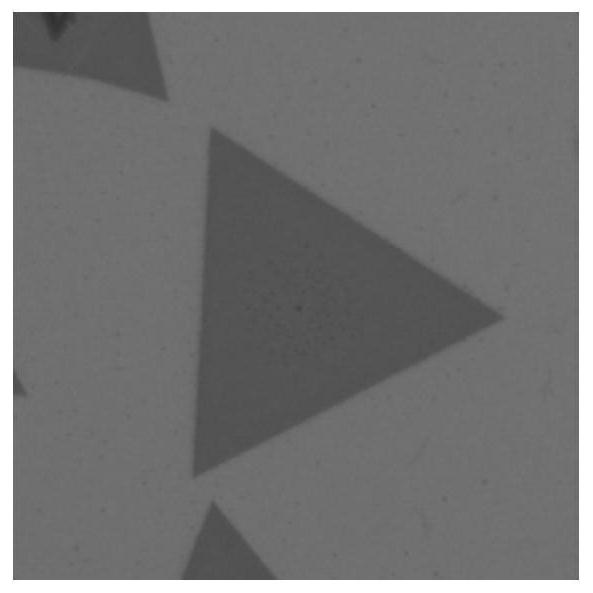
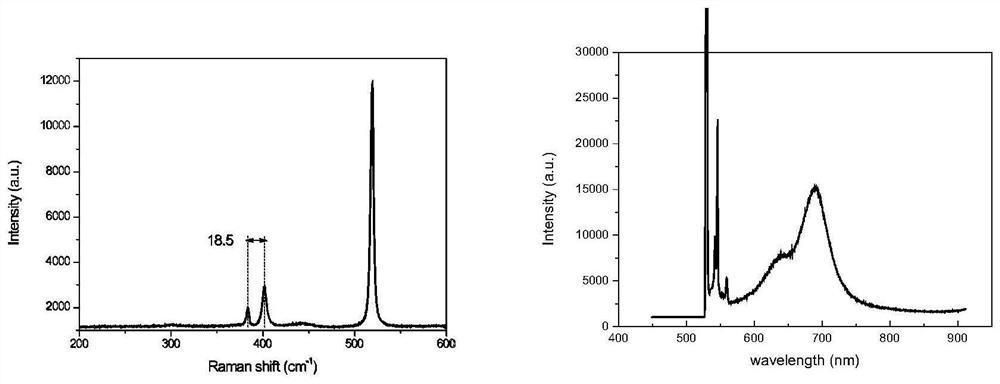
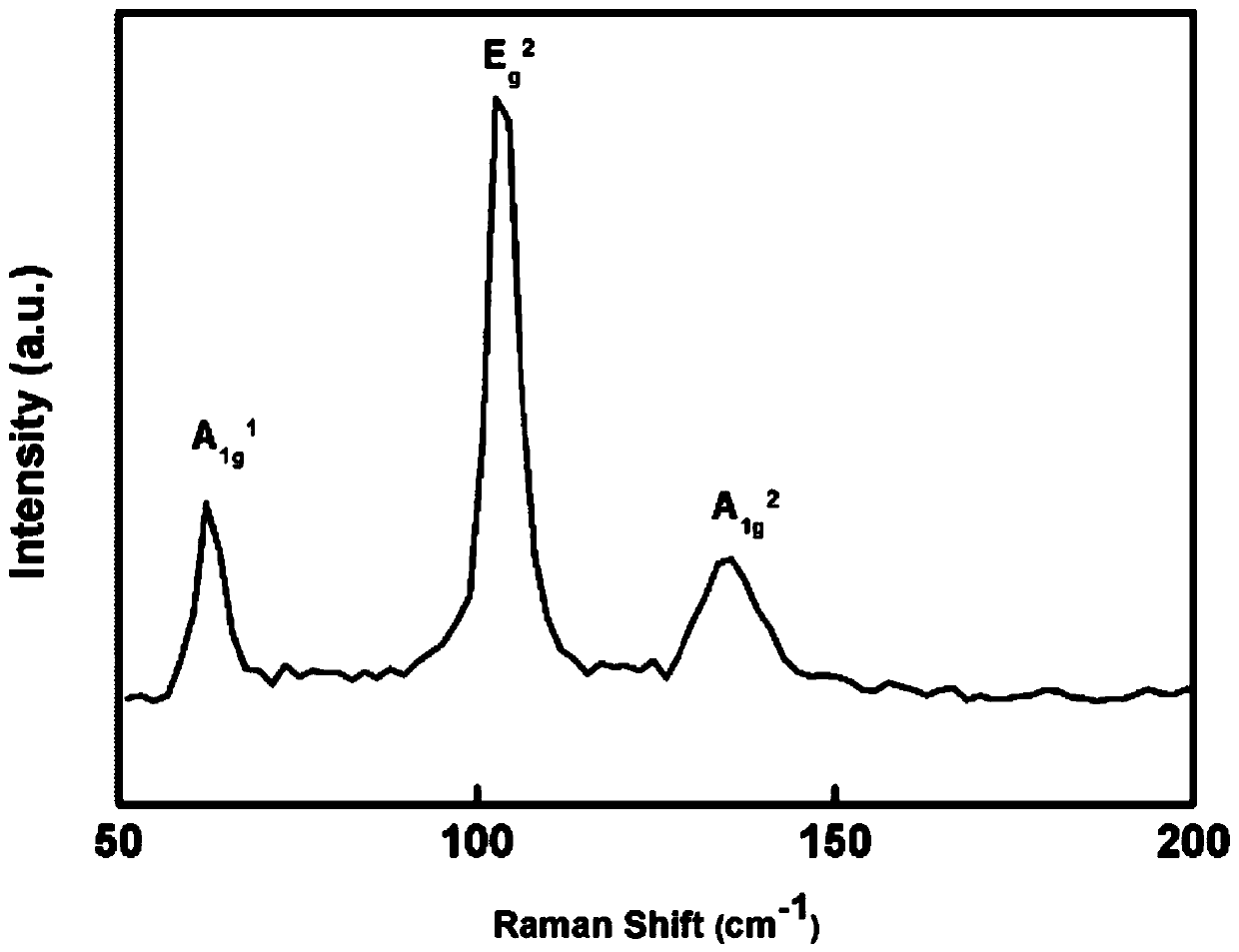
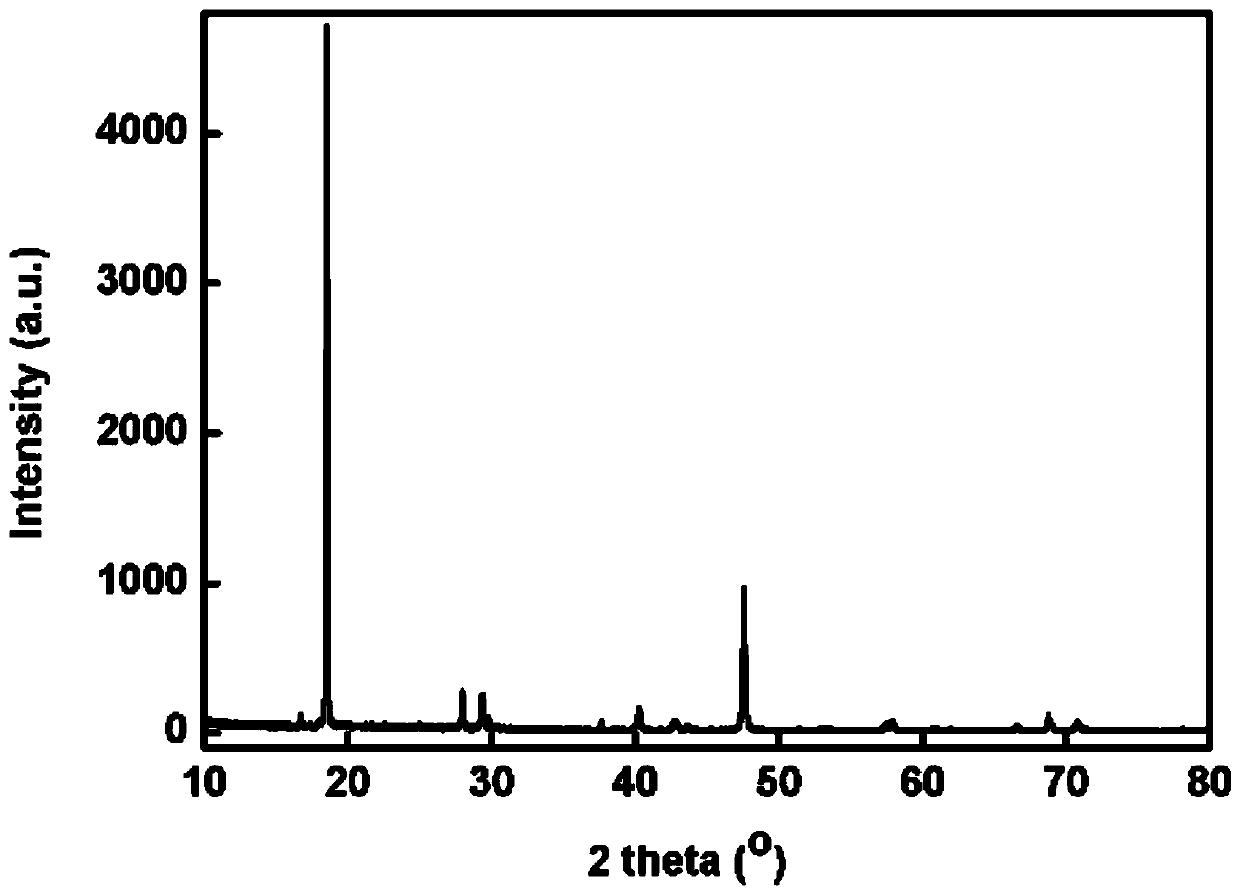
The invention provides a transition metal chalcogenide film and a preparation method and application thereof. Platinum group metal is adopted as the transition metal and comprises any one of ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, osmium and iridium or platinum, and chalcogen in a transition metal chalcogenide comprises any one of sulfur and selenium or tellurium. The method comprises the steps of separately heating a platinum group metal source and a chalcogen source in a protective gas atmosphere, carrying out a chemical vapor deposition reaction, and forming the transition metal chalcogenide film ona substrate. According to the method, a platinum group metal source is used as a raw material, a chemical vapor deposition method is adopted, continuous and controllable formation of the two-dimensional platinum group metal chalcogenide film in a large area is achieved, the surface of the obtained film material is flat, and the film material has excellent electrical and optical properties and hasa broad application prospect in the field of nano electronic devices.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Large-area and graphical transition metal sulfide thin film preparation methods
PendingCN108914062AAchieving size can be cutCut to sizeVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingInterchalcogenPhotocatalysis
The invention discloses large-area and graphical transition metal sulfide thin film preparation methods. The large-area preparation method comprises the following steps of 1, depositing transition metal onto a substrate through a coating technology, so that a transition group metal thin film is formed; and 2, conducting a sulfuration reaction on the transition group metal thin film, wherein the chemical formula of transition metal sulfide is AB2, A represents a transition group metal element, and B represents a sulfur group element. The invention further discloses the graphical transition metal sulfide thin film preparation method. The coating technology is adopted; the transition metal thin film of a certain thickness is deposited on the substrate, and then, selenium atoms evaporating inthe molten state react with metallic platinum at the certain temperature and pressure intensity, so that the large-area and graphical platinum diselenide thin film with the thickness being adjustableis finally obtained. The methods are simple and easy to implement; obtained platinum diselenide is high in electric conductivity; the technology is compatible with a modern semiconductor processing technology; and the wide prospects are achieved in the aspects of photoelectric devices, sensing devices and photocatalysis.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Transition metal sulfur-group compound thin-layer material as well as preparation method thereof and application thereof
ActiveCN110257800AGood lookingGood opticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingShielding gasReaction temperature
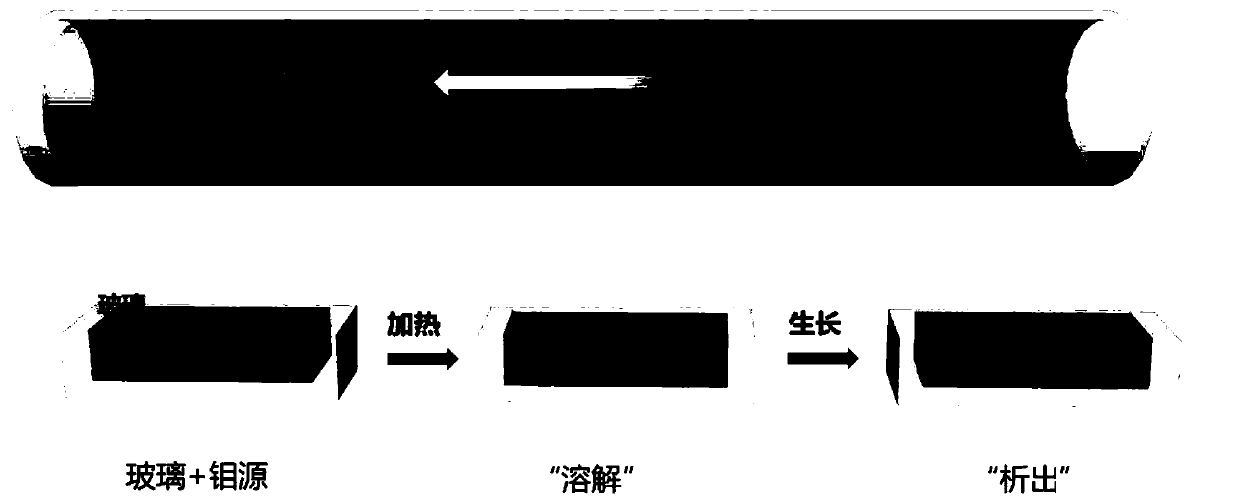
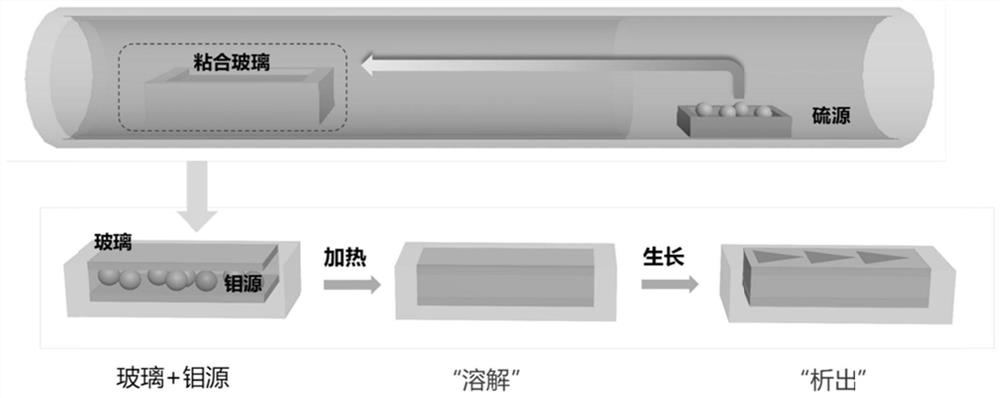
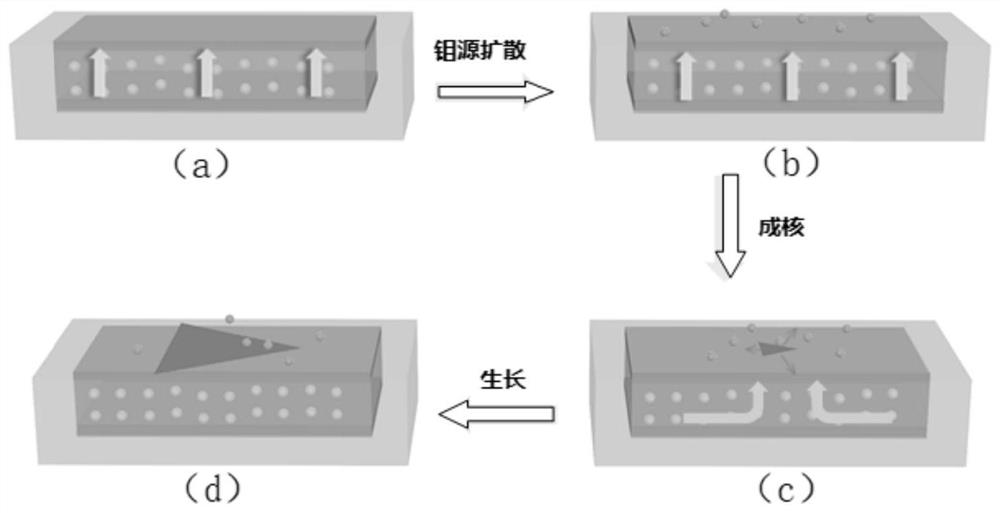
The invention discloses a transition metal sulfur-group compound thin-layer material as well as a preparation method thereof and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: uniformly spreading a transition metal source between two linings to prepare a sandwich structure; performing thermal treatment on the sandwich structure, fusing and bonding two substrates together, performing chemical vapor deposition reaction on a sulfur-group element source and the fused bonded sandwich structure under protection of protective gas, heating the transition metal source to dissolve and diffuse at a reaction temperature, separating out the transition metal source on the surfaces of the substrates, and enabling the transition metal source to react with the sulfur-group element source, wherein the sulfur-group element source comprises one or more of a sulfur source, a selenium source and a tellurium source. In this way, a dissolving-separating out principle is combined with the chemical vapor deposition reaction to prepare the transition metal sulfur-group compound thin-layer material, and a preparation process of the transition metal sulfur-group compound thin-layer material is simple and easy, and is controllable in process; and the obtained transition metal sulfur-group compound thin-layer material is uniformly distributed in a centimeter-level range, is good in morphology, is excellent in performances such as optical performances and electrical performances, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:TSINGHUA BERKELEY SHENZHEN INST
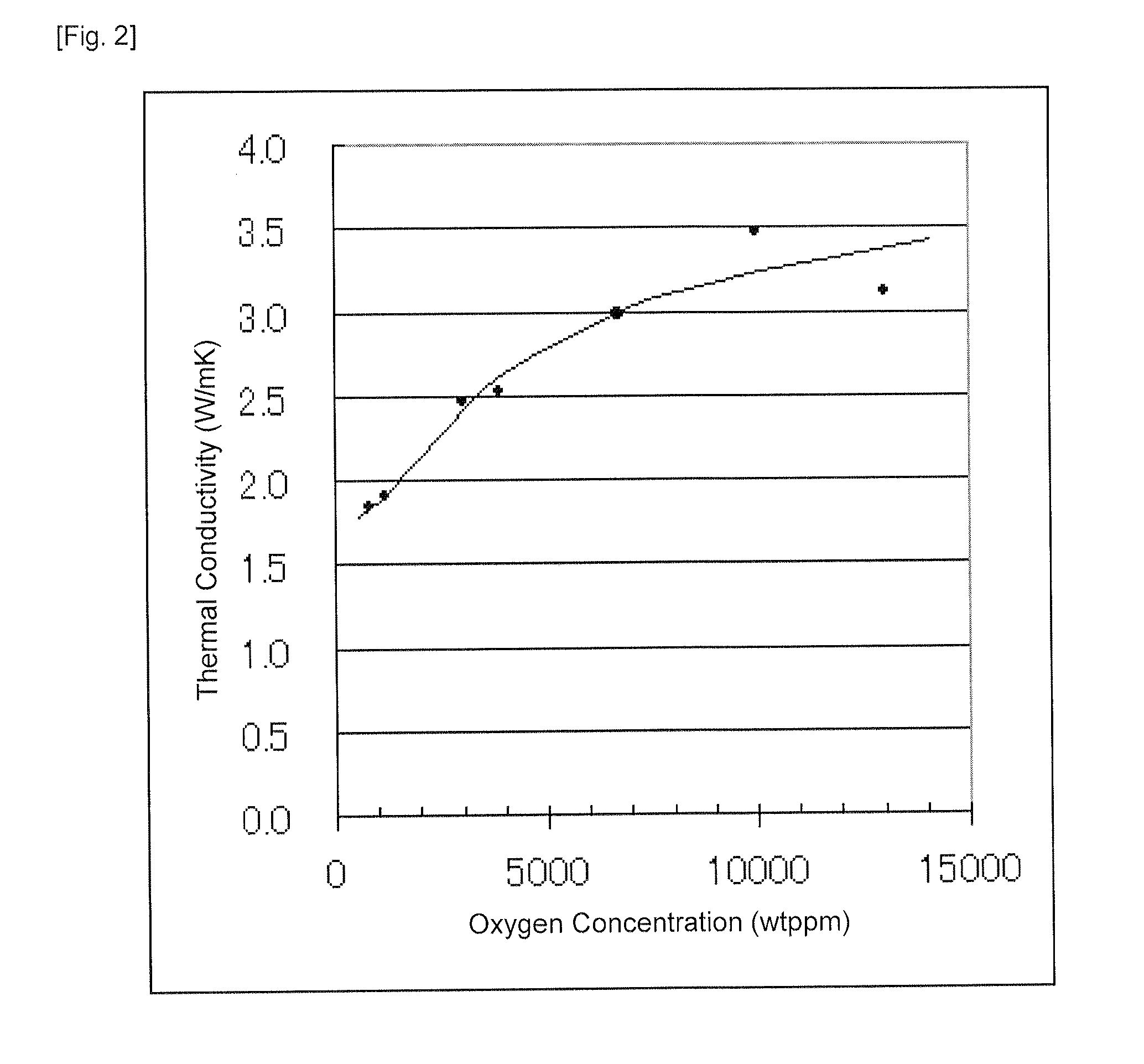
Target of Sintered Compact, and Method of Producing the Sintered Compact
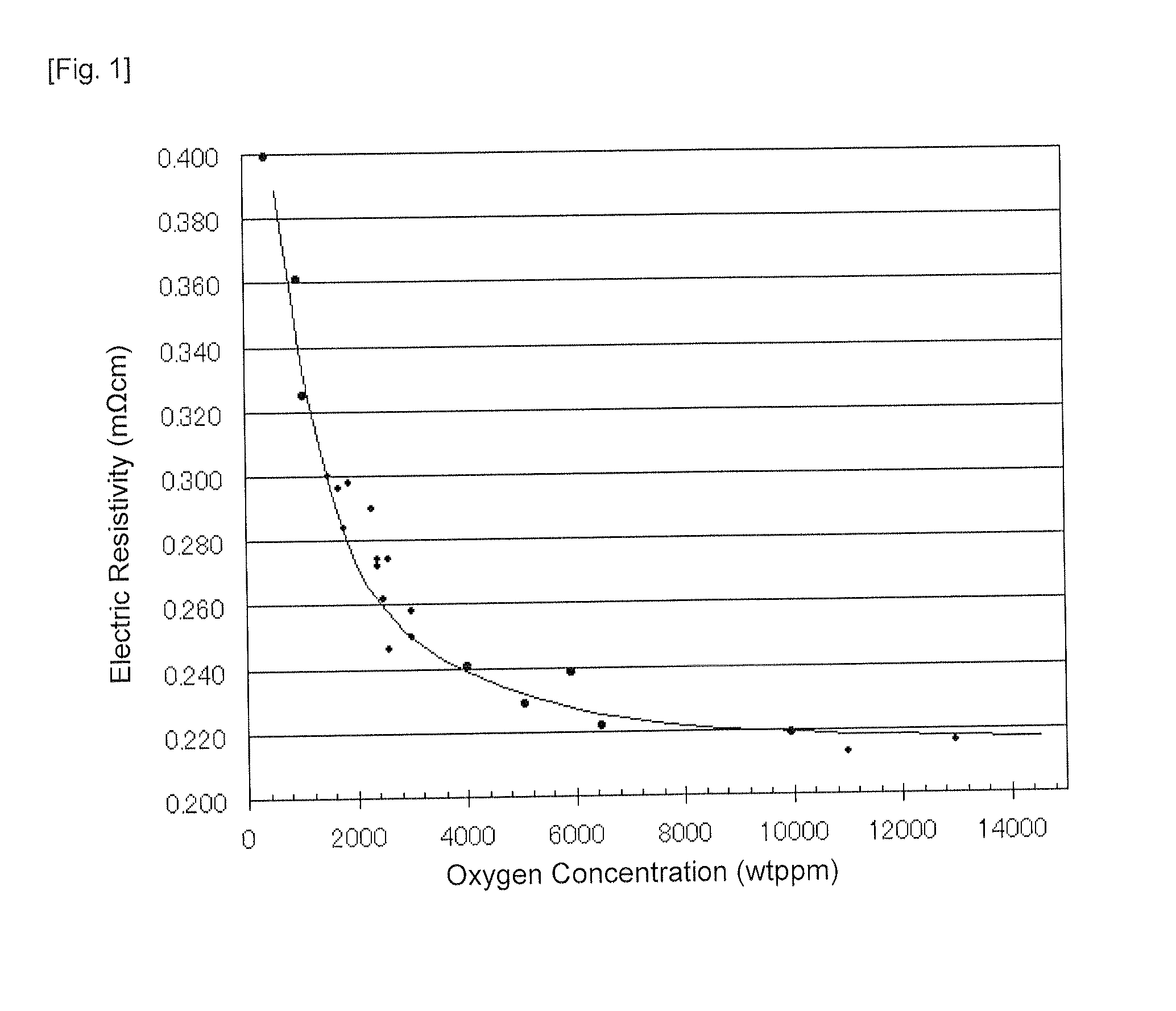
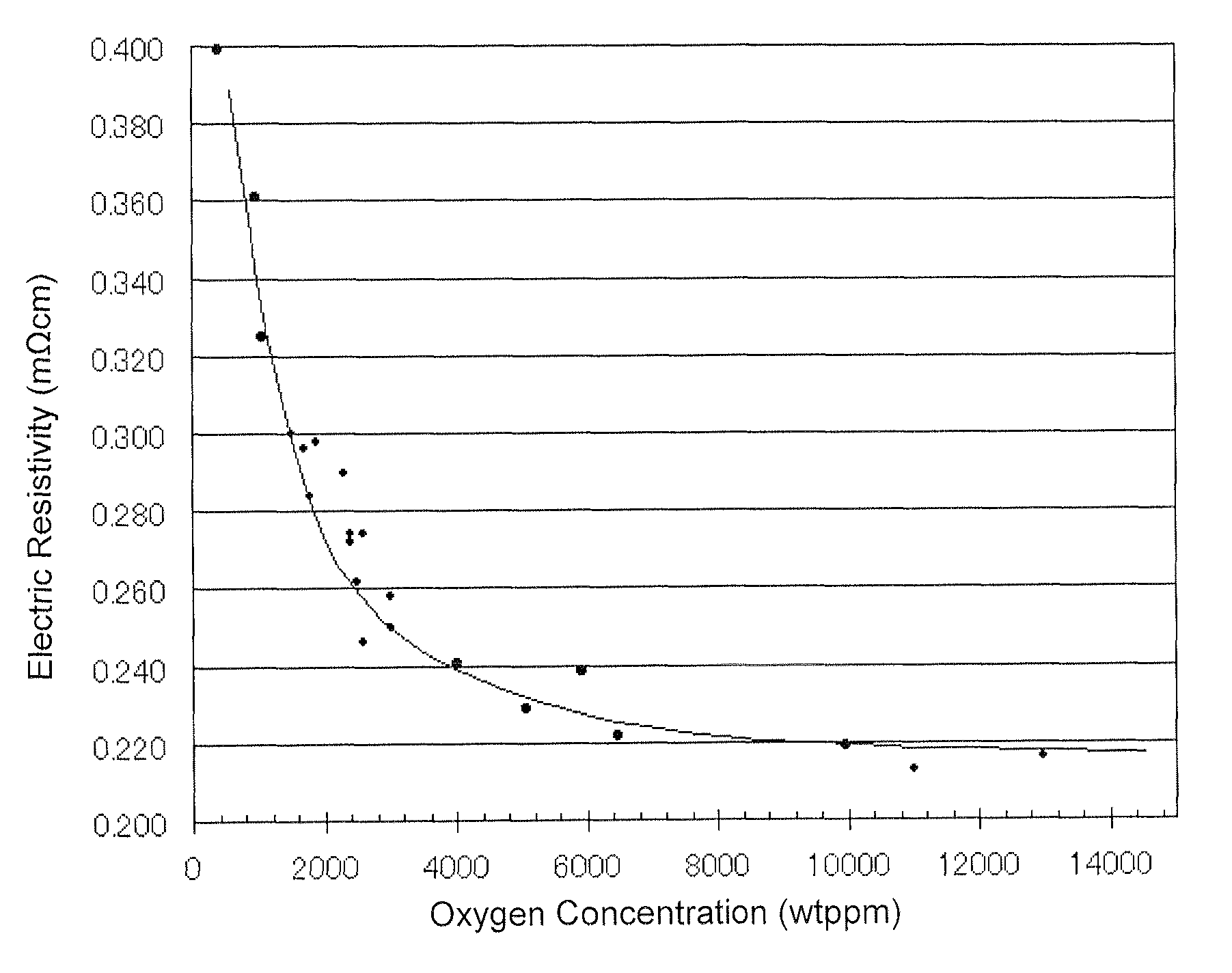
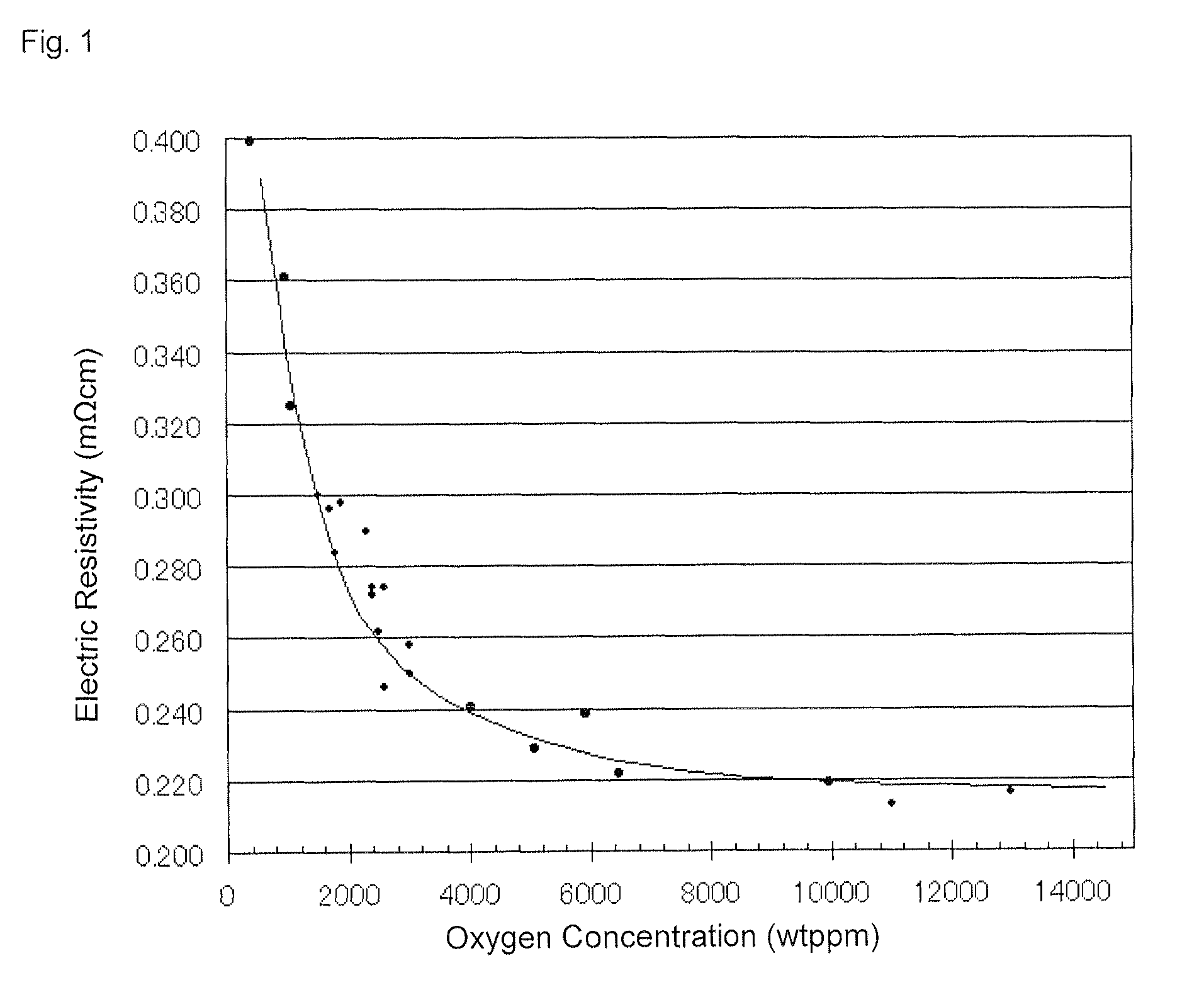
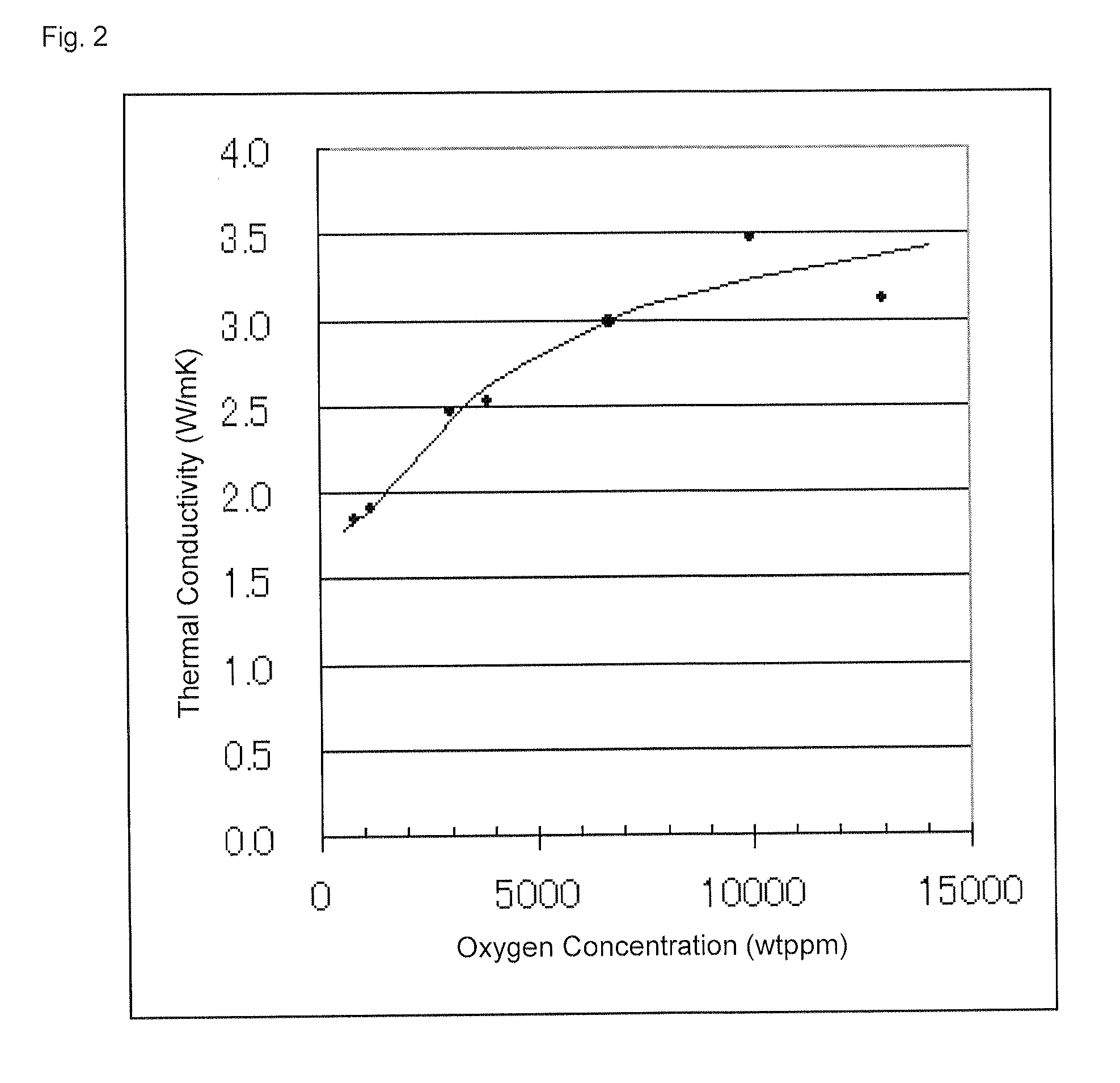
Provided is a target of sintered compact essentially consisting of an element of (A), an element of (B) and an element of (C) below, wherein the thermal conductivity is 2.5 W / mK or more and the oxygen concentration is 5000 ppm or more:(A) one or more chalcogenide elements selected from S, Se, and Te;(B) one or more Vb-group elements selected from Bi, Sb, As, P, and N; and(C) one or more IVb-group elements or IIIb-group elements selected from Ge, Si, C, Ga, and In. Also provided is a technology enabling stable DC sputtering, and stable and high-speed sputtering by applying high electric power, by improving heat accumulation and diffusion of volatile components due to the sputtering target having high thermal conductivity and low electric resistivity.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
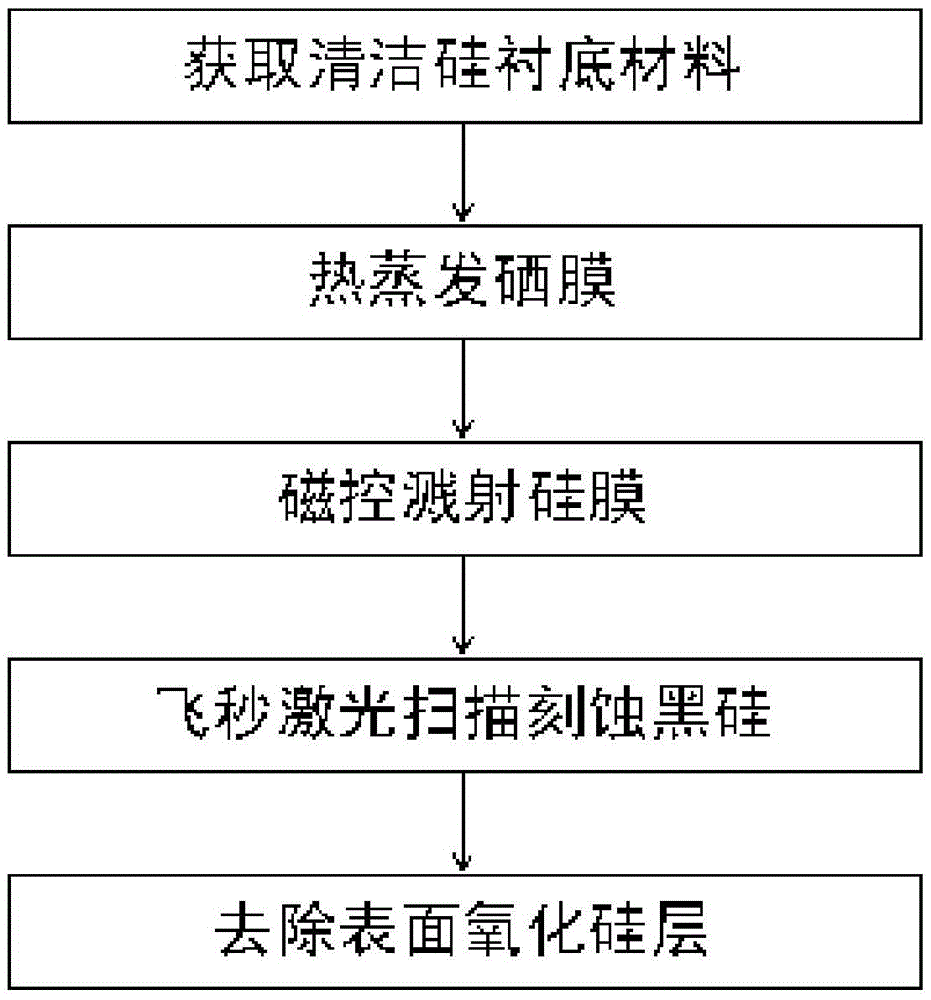
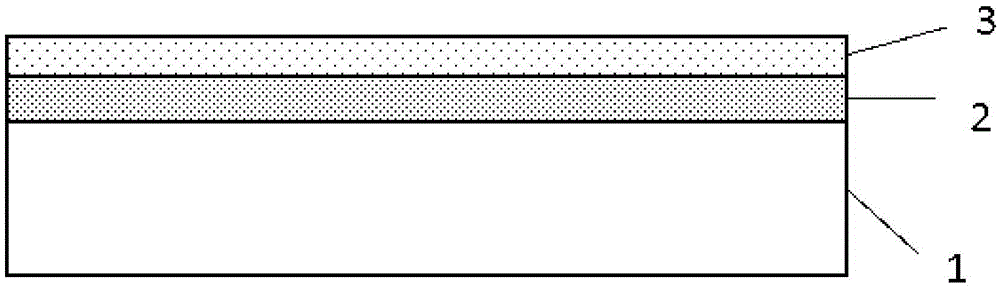
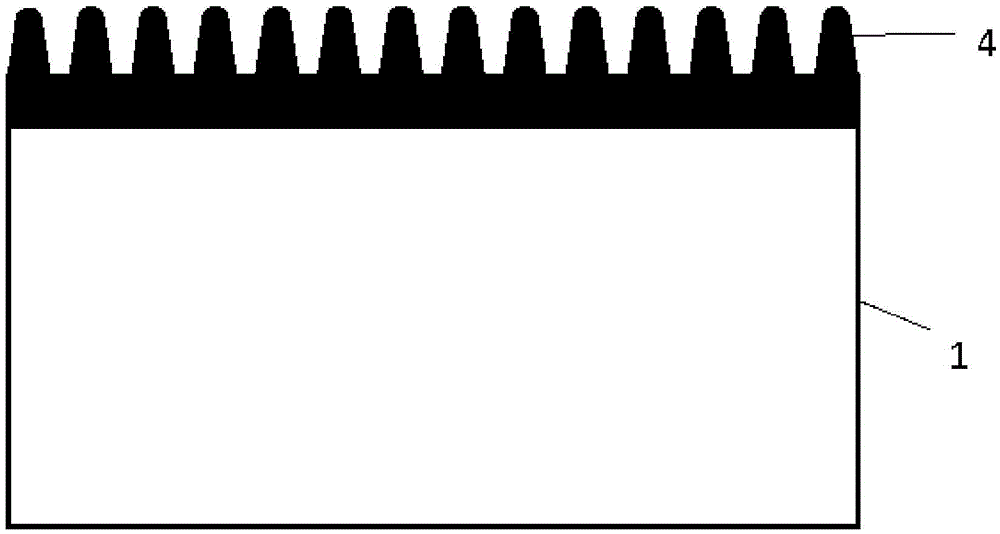
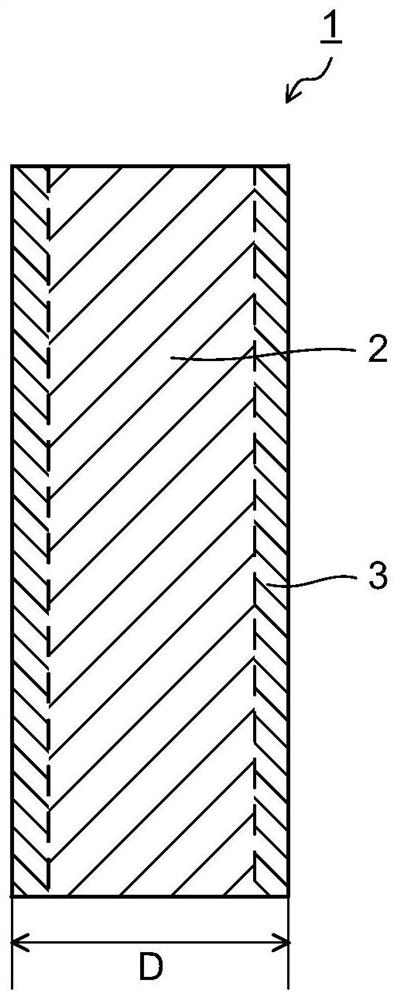
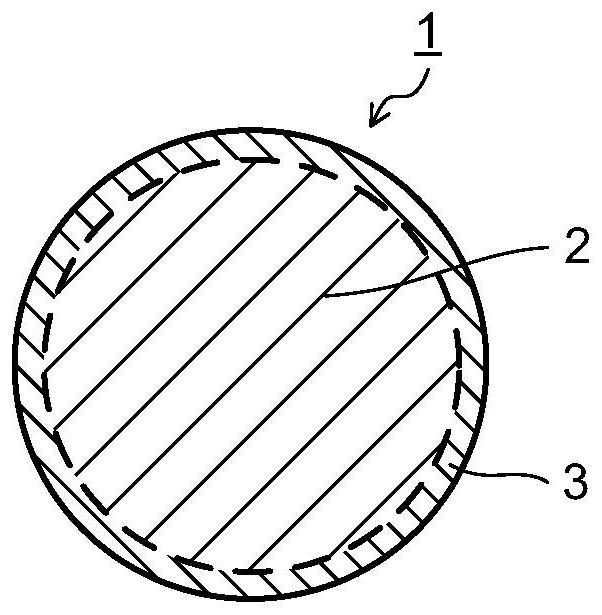
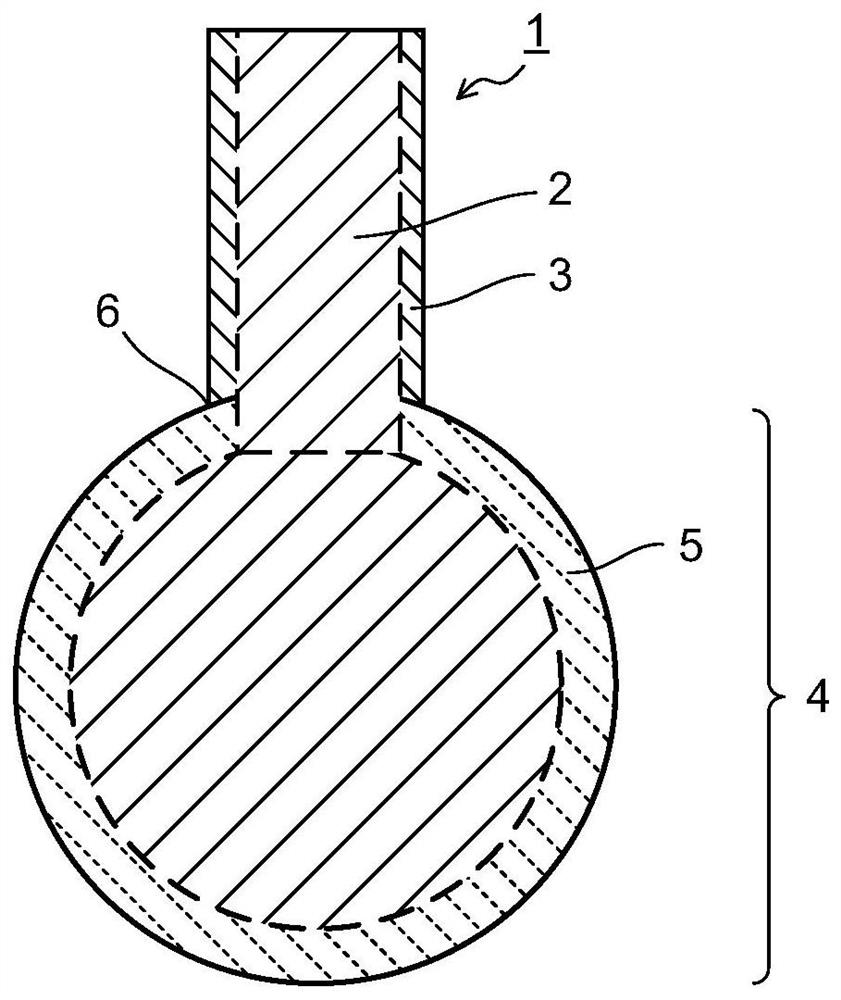
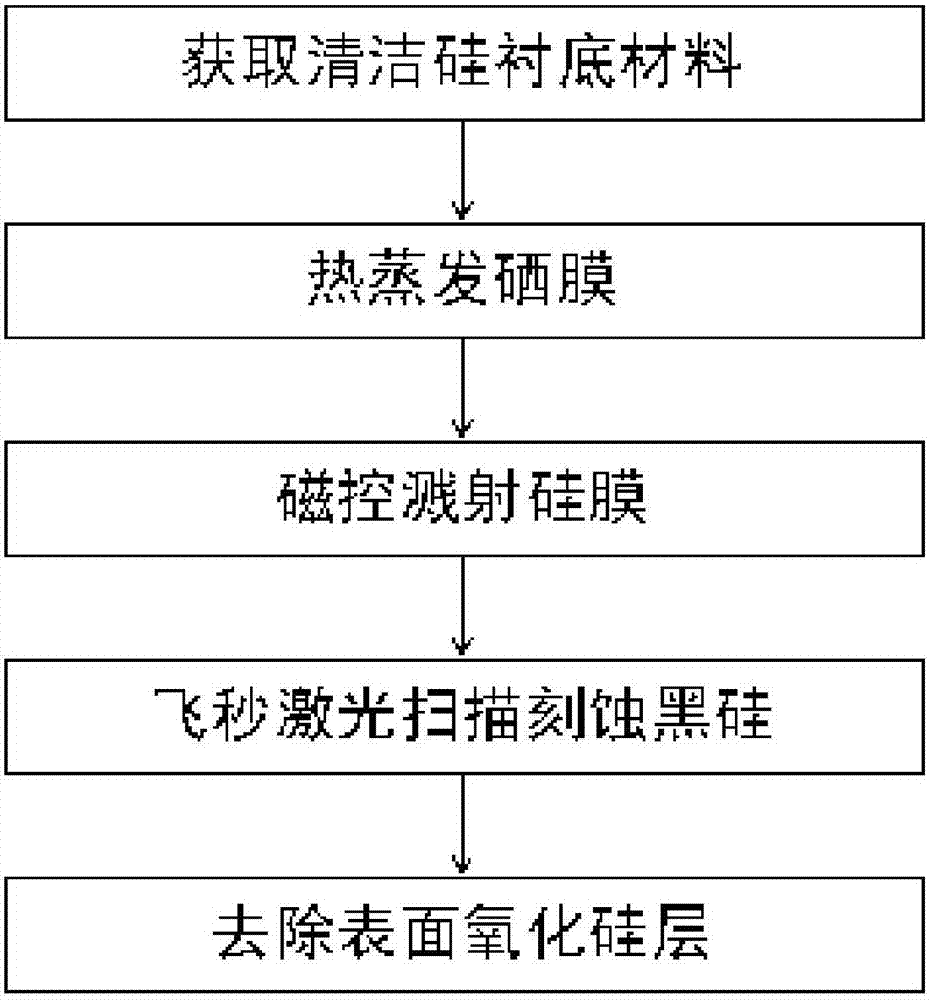
Method for preparing black silicon material
InactiveCN105655419AReduce volatilityImprove absorption rateFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesMaterials preparationLaser etching
The invention belongs to the field of black silicon material preparation, and particularly relates to a method for preparing a selenium-silicon composite film in a thermal evaporation and magnetron sputtering mode and preparing black silicon in a femtosecond laser etching mode. According to the method, as a silicon film formed on a selenium film in the existing technology in a sputtering mode serves as a protection layer, volatilization of chalcogens in the femtosecond laser etching process is reduced, the doping content is increased, impurities Se introduced by laser pulse irradiation can be prevented from dispersing to the grain boundary, and thus the doping concentration of impurities Se on the surface is guaranteed to improve the absorptivity of black silicon. The absorptivity of black silicon prepared through the method is higher than 95% at the 400-1100 nm band, and the absorptivity of black silicon is higher than 90% at the 1100-2200 nm band. Compared with a black silicon material prepared through a method that only a selenium film is formed in a thermal evaporation mode, but no silicon protection layer is formed for covering, the absorptivity of black silicon prepared through the method is obviously increased at the near-infrared band.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for controllably synthesizing near-infrared silver telluride quantum dots
ActiveCN112960655AReduce usageHigh preparation temperatureLuminescent compositionsMetal selenides/telluridesQuantum yieldQuantum dot
The invention discloses a silver precursor, a tellurium precursor and a preparation method for controllably synthesizing silver telluride quantum dots. The method comprises the following steps: mixing one or more silver mercaptide with organic phosphine to prepare an activity-adjustable silver precursor, and thermally injecting the tellurium precursor synthesized in air, thereby obtaining the silver telluride quantum dot. The method is easy to operate, good in repeatability and low in cost. The emission wavelength of the silver telluride quantum dot is adjustable in a range of 1150nm-2000nm by regulating and controlling the types and the proportion of thiol and phosphine, the proportion of a silver source to a tellurium precursor and the reaction time, the half-peak width of the emission wavelength is narrow, and the fluorescence quantum yield can reach more than 10%. The method can be used in the field of biomedical imaging, can also be used for preparing other nano materials containing silver or chalcogenide elements, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Magnetic topological insulator heterojunction single-crystal material and synthesis method thereof
InactiveCN110699754AControl shapeSimple preparation processPolycrystalline material growthFrom solid stateHeterojunctionSingle crystal
The invention provides a magnetic topological insulator heterojunction single-crystal material and a synthesis method thereof. The synthesis method comprises the following steps: grinding metal and chalcogen, then charging a quartz tube with the ground metal and chalcogen, and carrying vacuum tube sealing; heating the sealed quartz tube, maintain the sealed quartz tube at a certain temperature, and carrying out cooling treatment; subjecting the cooled quartz tube to cooling treatment again; and carrying out ice-bath quenching on the quartz tube which is cooled again so as to obtain the magnetic topological insulator heterojunction single-crystal material. The preparation method is simple to operate, does not involve any transfer method, uses no expensive special production equipment, has high production efficiency, and can be used for quickly preparing the single-crystal material with a natural magnetic topological insulator heterojunction.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method of preparing transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD)
The invention provides a method of preparing transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs). The TMDs is produced in such a process environment that substrate temperature is 150-500 DEG C and pressure is 25-760 torr. In the method, the chalcogens are obtained in a manner of heating a solid chalcogen source and ionizing the solid chalcogen source to form chalcogen plasma, so that the method is free of using hydrogen sulfide gas, which is extremely poisonous, for producing the TMDs in the prior art.
Owner:阙郁伦
Silver-containing P-type semiconductor
InactiveCN101036240AImprove efficiencyHigh thermoelectric figure of meritThermoelectric device junction materialsPhysical chemistryLanthanide
A thermoelectric composition comprises a material represented by the general formula (AgaX1-a)1+-x (SnbPbl-b)m M'1-yQ2+m wherein X is Na, K, or a combination of Na and K in any proportion; M' is a trivalent element selected from the group consisting of Sb, Bi, lanthanide elements, and combinations thereof; Q is a chalcogenide element selected from the group consisting of S, Te, Se, and combinations thereof; a and b are independently > 0 and =1; x and y are independently > 0 and < 1; and 2 =m =30. The compositions exhibit a figure of merit ZT of up to about 1.4 or higher, and are useful as p-type semiconductors in thermoelectric devices.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Chalcogenide film, device including, and method of forming same
The invention relates to a chalcogenide film comprising a noble metal chalcogenide material having a formula MCx. M may represent a noble metal, C may represent a chalcogen, x may be any one positivevalue equal to or more than 1.4 and less than 2. The chalcogenide film may be configured to generate electrons and holes upon light incident on the chalcogenide film. A method of producing a chalcogenide fil m with increased vacancy or defect is provided, wherein increasing vacancies or defects may lead to decrease in bandgap and enhance absorption at wavelength range such as mid-infrared. The chalcogenide film is used in a device including photodetector or a solar cell.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
Target of sintered compact, and method of producing the sintered compact
ActiveUS9299543B2Good electrical and thermal conductivityReduce generationCellsElectric discharge tubesSputteringGroup element
Provided is a target of sintered compact essentially consisting of an element of (A), an element of (B) and an element of (C) below, wherein the thermal conductivity is 2.5 W / mK or more and the oxygen concentration is 5000 ppm or more:(A) one or more chalcogenide elements selected from S, Se, and Te;(B) one or more Vb-group elements selected from Bi, Sb, As, P, and N; and(C) one or more IVb-group elements or IIIb-group elements selected from Ge, Si, C, Ga, and In. Also provided is a technology enabling stable DC sputtering, and stable and high-speed sputtering by applying high electric power, by improving heat accumulation and diffusion of volatile components due to the sputtering target having high thermal conductivity and low electric resistivity.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CORP
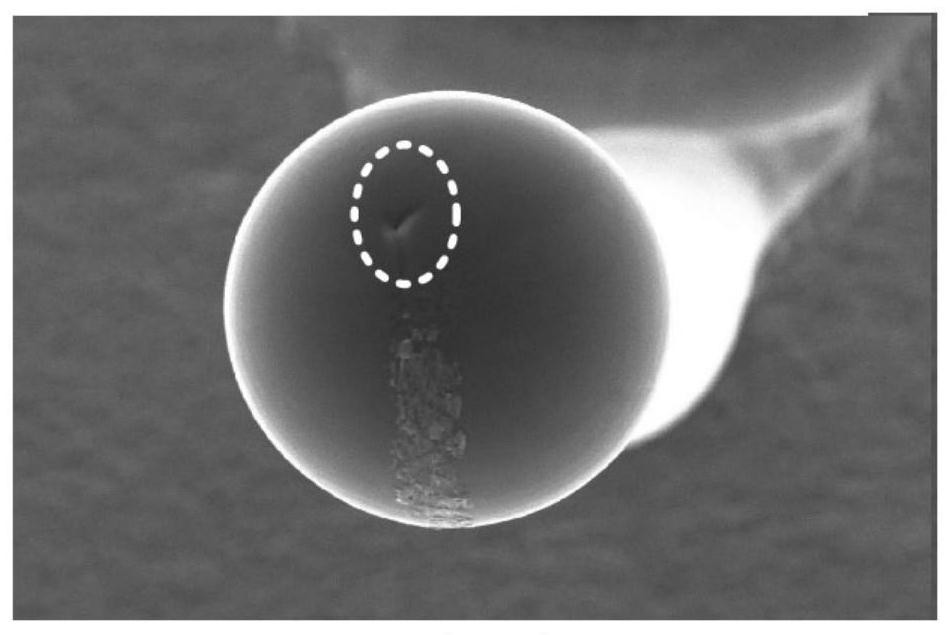
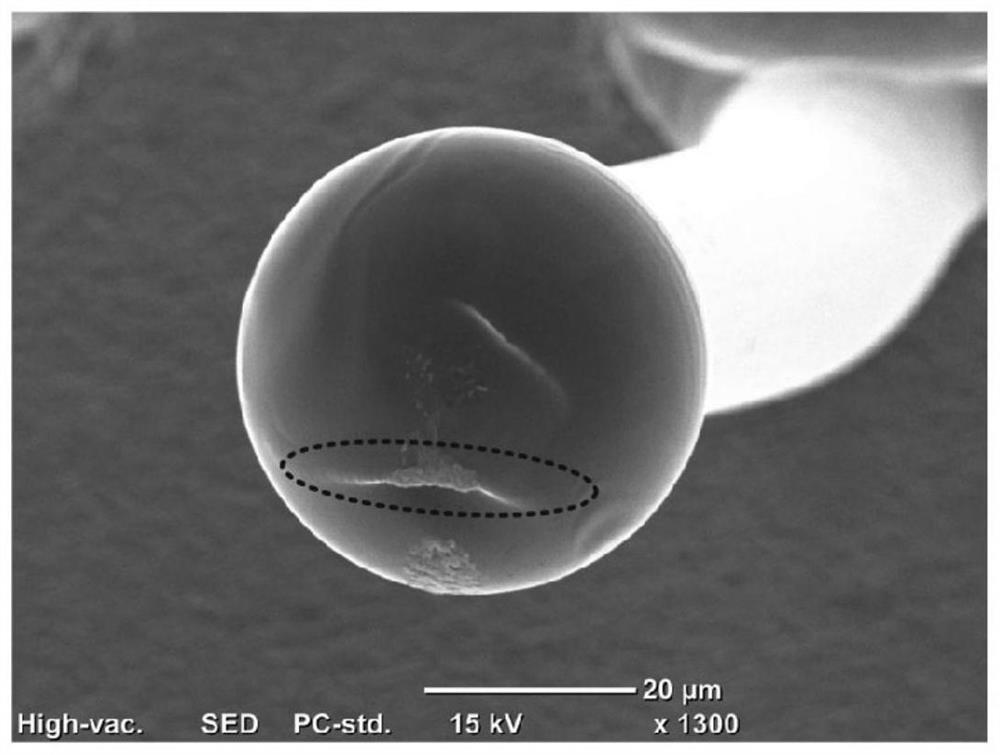
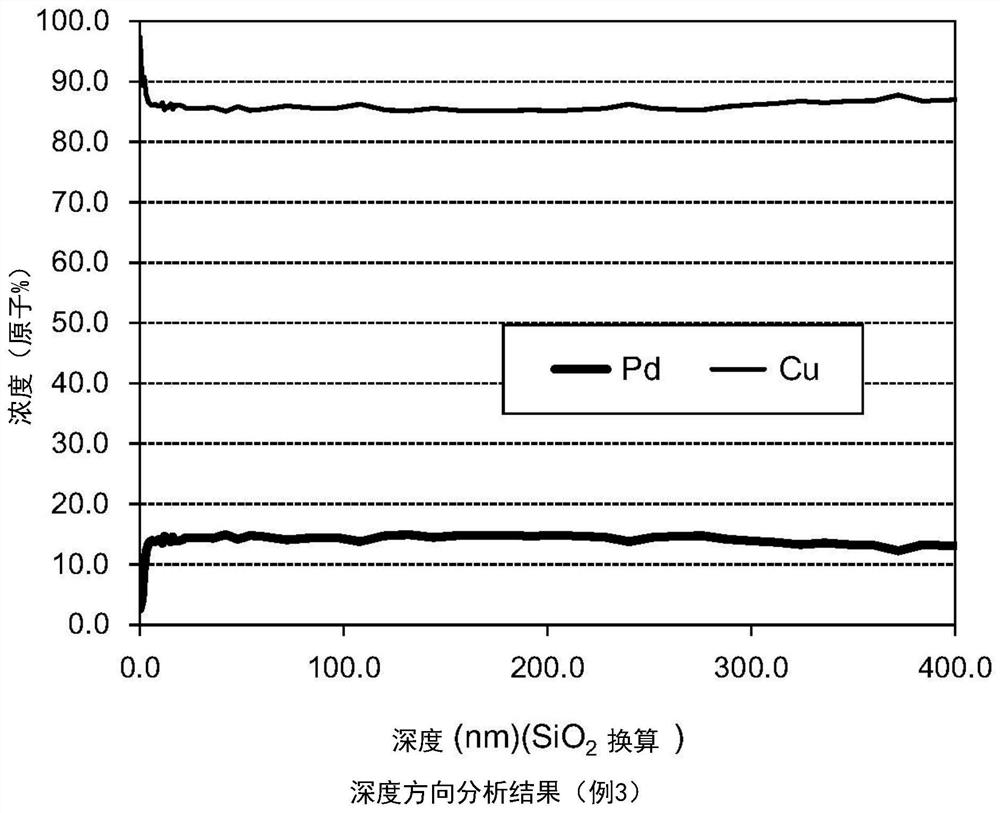
Palladium-coated copper bonding wire and method for manufacturing same
PendingCN113169077AImprove bond reliabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysical chemistryCopper
The present invention provides a palladium-coated copper bonding wire which does not undergo the formation of shrinkage cavities during a first bonding procedure, has high bonding reliability, and can keep the excellent bonding reliability thereof for a long period of time even in high-temperature / high-humidity environments. A palladium-coated copper bonding wire, in which the concentration of palladium is 1.0-4.0% by mass inclusive, the total concentration of sulfur-group elements is 50 ppm by mass or less, and the concentration of sulfur is 5-12 ppm by mass inclusive or the concentration of selenium is 5-20 ppm by mass inclusive or the concentration of tellurium is 15-50 ppm by mass inclusive all relative to the total amount of copper, palladium and sulfur-group elements, and a palladium-rich region having an average palladium concentration of 6.5-30.0 at.% relative to the total amount of copper and palladium exists in a region lying between the surface of a tip part of a free air ball formed at a tip of the wire to the depth of 5.0-100.0 nm inclusive from the surface of the tip part.
Owner:TANAKA DENSHI KOGYO KK
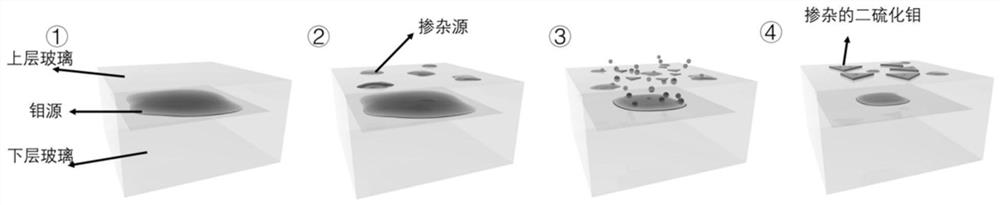
Doped transition metal chalcogenide film and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113201723AAvoid it happening againImprove control abilityFinal product manufactureChemical vapor deposition coatingPhysical chemistryThin membrane
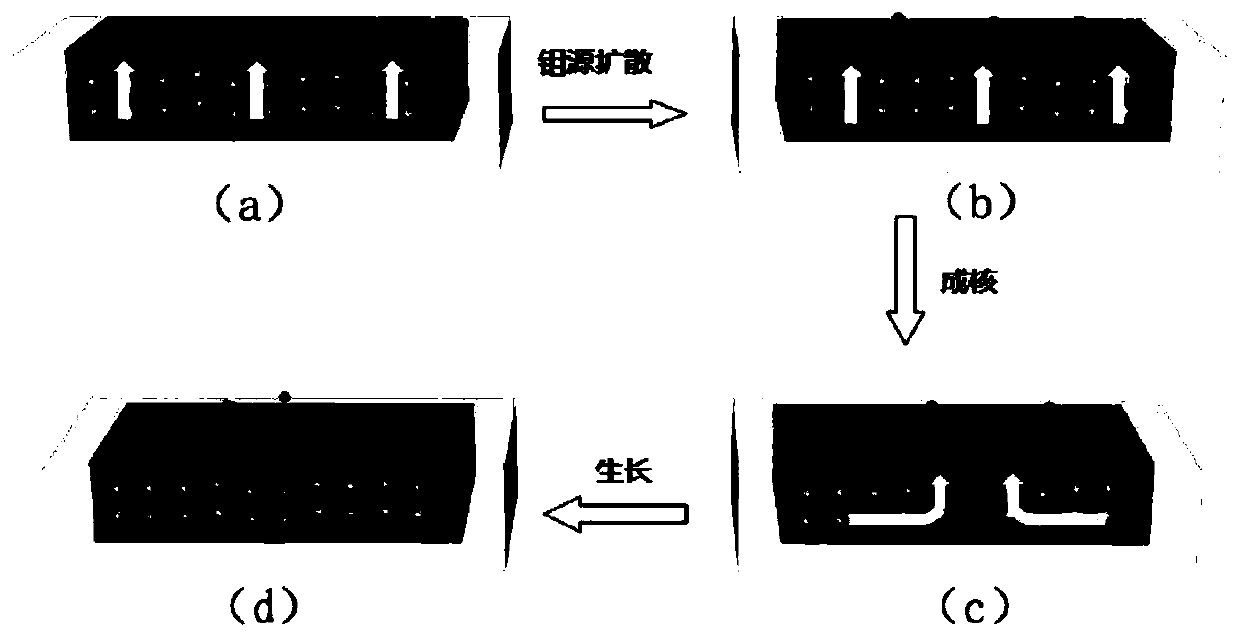
The invention discloses a doped transition metal chalcogenide film and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of providing a substrate, wherein a transition metal source is arranged in the substrate, and a heterogeneous metal source is arranged on the surface of the substrate; and enabling the chalcogens source to be in contact with the substrate, carrying out heating in a protective atmosphere, and carrying out a chemical vapor deposition reaction to obtain the doped transition metal chalcogenide film. In the heating treatment process, the transition metal source is continuously diffused from the substrate and separated out from the surface of the substrate. The separated transition metal source and the chalcogens source are subjected to the chemical vapor deposition reaction in the protective atmosphere, the heterogeneous metal source is embedded into a crystal lattice in the growth process of a transition metal chalcogenide, and a doped sample is obtained. According to the doped transition metal chalcogenide film and the preparation method and application thereof, the regulation and control capacity for the concentration of doped metal elements is improved through a double-face reaction source supply strategy adopted by the method, and the universality problem during doping of various metal elements in a single-face source mode is solved.
Owner:TSINGHUA BERKELEY SHENZHEN INST
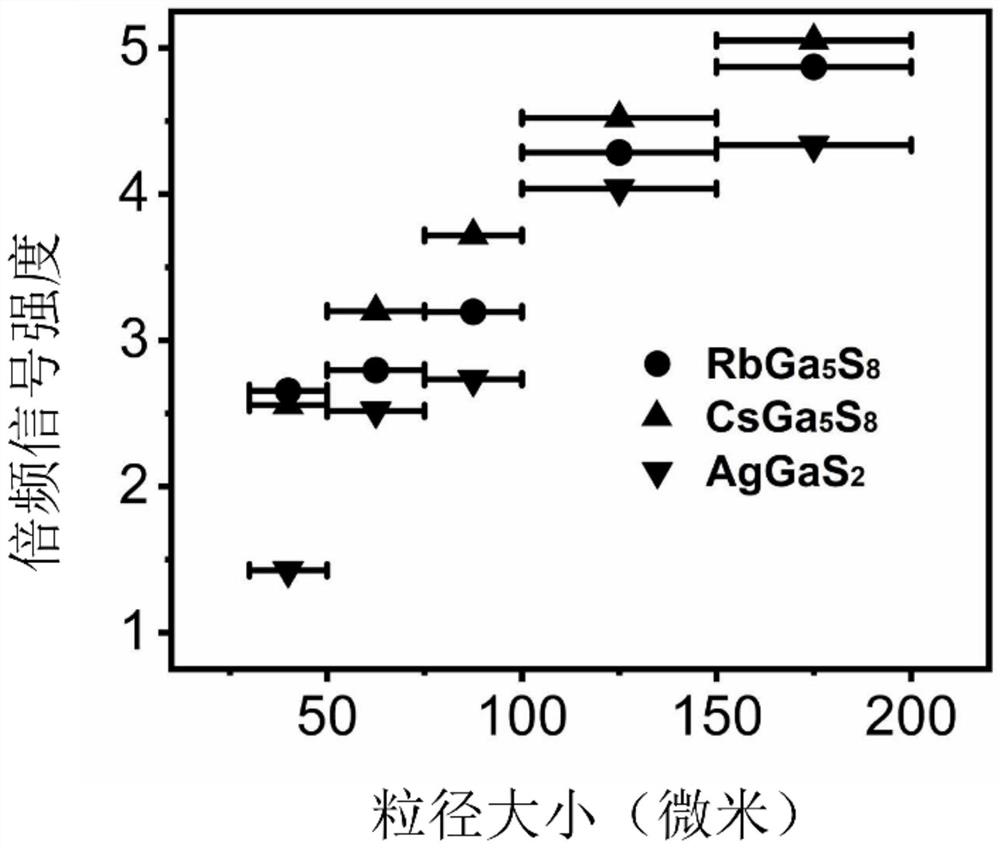
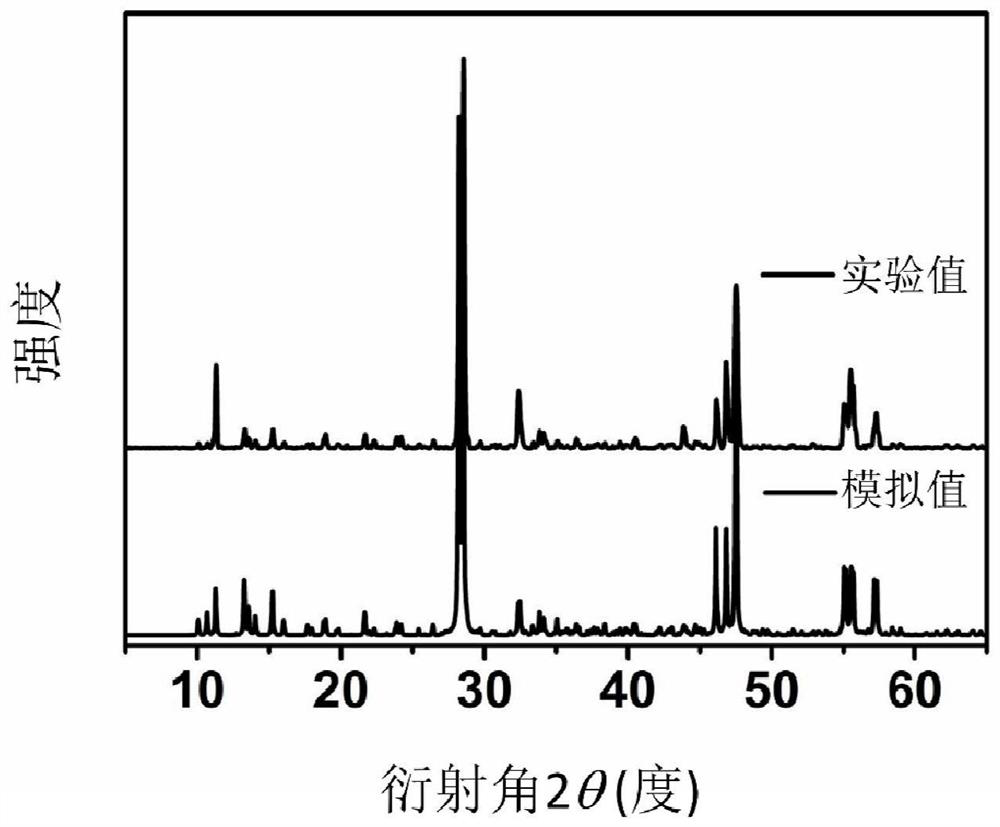
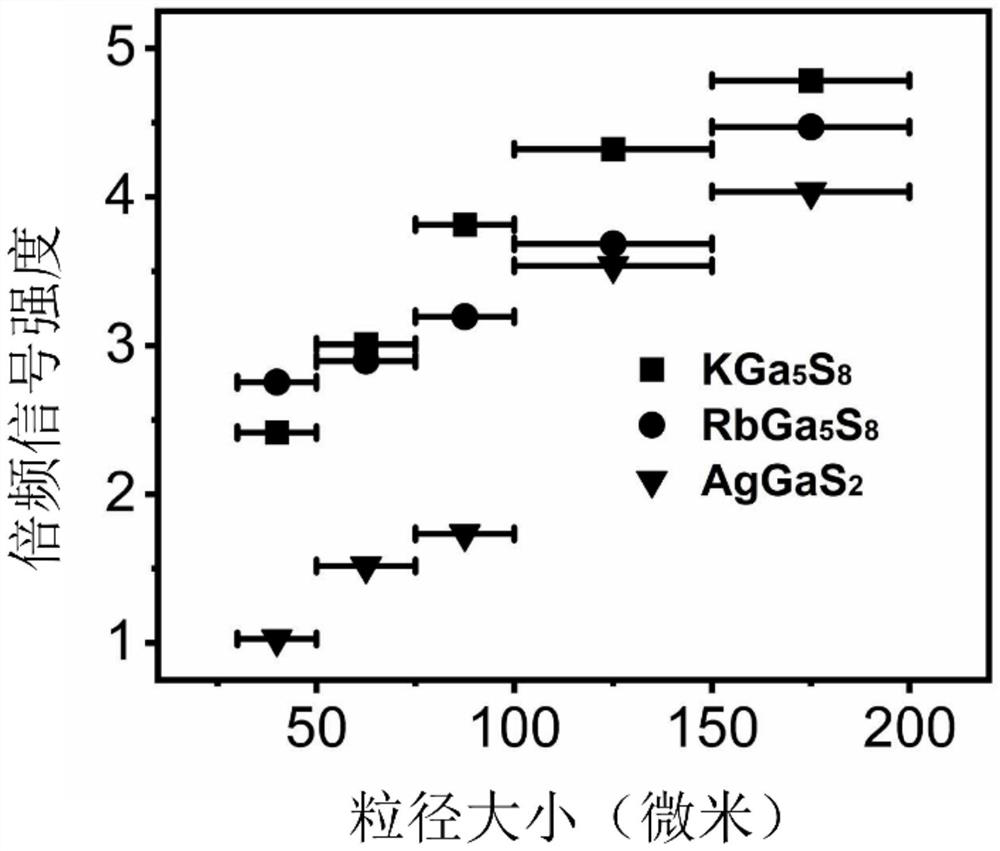
Gallium-containing orthogonal inorganic compound crystal, preparation method thereof and application of gallium-containing orthogonal inorganic compound crystal as infrared nonlinear optical crystal material
ActiveCN114574972AImprove performancePolycrystalline material growthFrom solid stateNonlinear optical crystalCrystal system
The invention discloses a gallium-containing orthogonal inorganic compound crystal. The compound has the following chemical formula: AGa5Q8. Q is selected from one of chalcogenide elements. The gallium-containing inorganic compound belongs to an orthorhombic crystal system and an Iba21 space group. The invention further discloses a method for preparing the gallium-containing orthogonal inorganic compound crystal. The invention further discloses application of the material as a nonlinear optical crystal. The gallium-containing inorganic compound provided by the invention has the excellent characteristics of high laser damage threshold, high frequency multiplication signal intensity and the like. The method for preparing the gallium-containing inorganic compound provided by the invention has the advantages of high yield and simple synthesis process.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Mid and far-infrared nanocrystals based photodetectors with enhanced performances
ActiveUS10944065B2Promote absorptionTotal current dropThermoelectric device with dielectric constant thermal changeArsenic sulfidesPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
Disclosed is a plurality of metal chalcogenide nanocrystals coated with multiple organic and inorganic ligands; wherein the metal is selected from Hg, Pb, Sn, Cd, Bi, Sb or a mixture thereof; and the chalcogen is selected from S, Se, Te or a mixture thereof; wherein the multiple inorganic ligands includes at least one inorganic ligands are selected from S2−, HS−, Se2−, Te2−, OH−, BF4−, PF6−, Cl−, Br−, I−, As2Se3, Sb2S3, Sb2Te3, Sb2Se3, As2S3 or a mixture thereof; and wherein the absorption of the C—H bonds of the organic ligands relative to the absorption of metal chalcogenide nanocrystals is lower than 50%, preferably lower than 20%.
Owner:NEXDOT
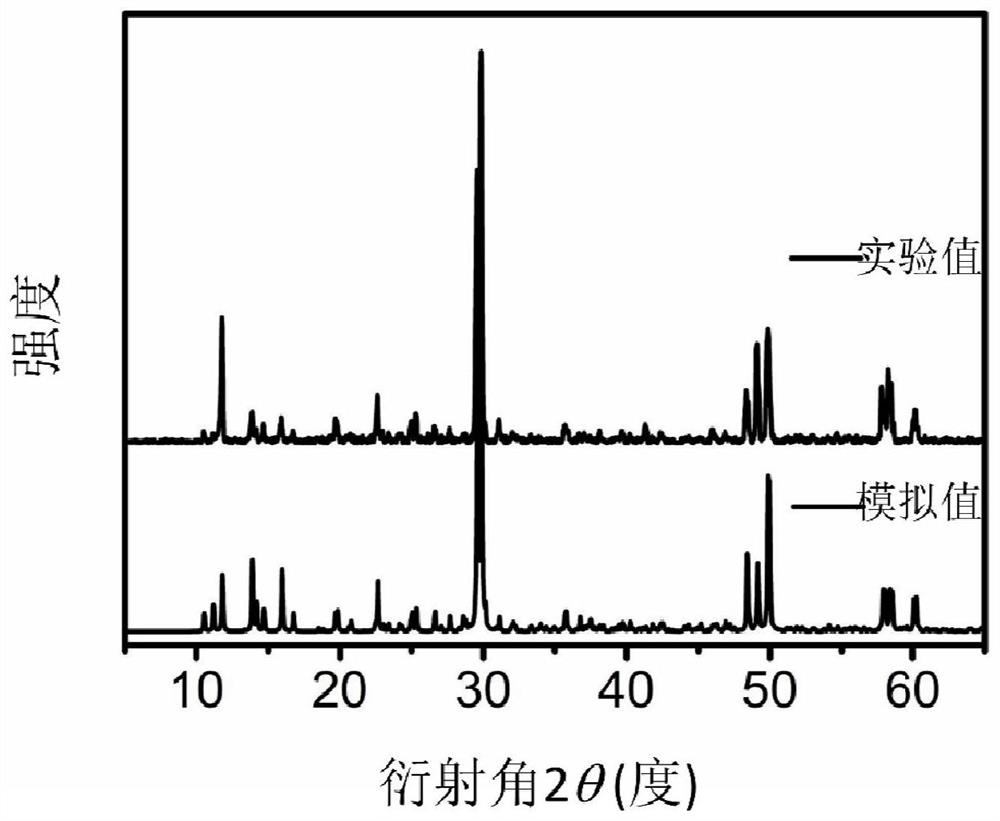
Gallium-containing monoclinic inorganic compound crystal, preparation method thereof and application of gallium-containing monoclinic inorganic compound crystal as infrared nonlinear optical crystal material
ActiveCN114574973AImprove performancePolycrystalline material growthFrom solid stateNonlinear optical crystalSpace group
The invention discloses a gallium-containing monoclinic inorganic compound crystal. The compound has the following chemical formula: AGa5Q8. Wherein A is selected from one of alkali metal elements; q is selected from one of chalcogenide elements; the gallium-containing monoclinic inorganic compound crystal belongs to a monoclinic system and a P21 space group. The invention further discloses a method for preparing the gallium-containing monoclinic inorganic compound crystal. The invention further discloses application of the material as a nonlinear optical crystal. The gallium-containing monoclinic inorganic compound crystal provided by the invention has the excellent characteristics of high laser damage threshold, high frequency multiplication signal intensity and the like. The method for preparing the gallium-containing monoclinic inorganic compound crystal provided by the invention has the advantages of high yield and simple synthesis process.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for growing single-layer telluride doping structure through impulse type injection of reactants
InactiveCN110863189APrecise and controllable growth conditionsEasy to operateChemical vapor deposition coatingMolybdenum tellurideReaction temperature
The invention discloses a method for growing a single-layer telluride doping structure through impulse type injection of reactants. According to the method, a plurality of transition metal organics and diethyl tellurium or molybdenum hexacarbonyl and a plurality of chalcogens are injected simultaneously to control the carrier gas flow to control the amount of telluride doping, the reaction temperature and the reaction time are controlled to control the area and the number of layers of telluride growth, and thus high-quality molybdenum ditelluride with the doping structure is obtained. The method has the advantages that growth conditions are precise and controllable, operation is easy and convenient, and the stable molybdenum ditelluride with the single-layer doping structure can be prepared. The prepared molybdenum ditelluride with the single-layer doping structure has broad application prospects in the fields of nano-electronical appliances, lubricating materials, photocatalysis and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
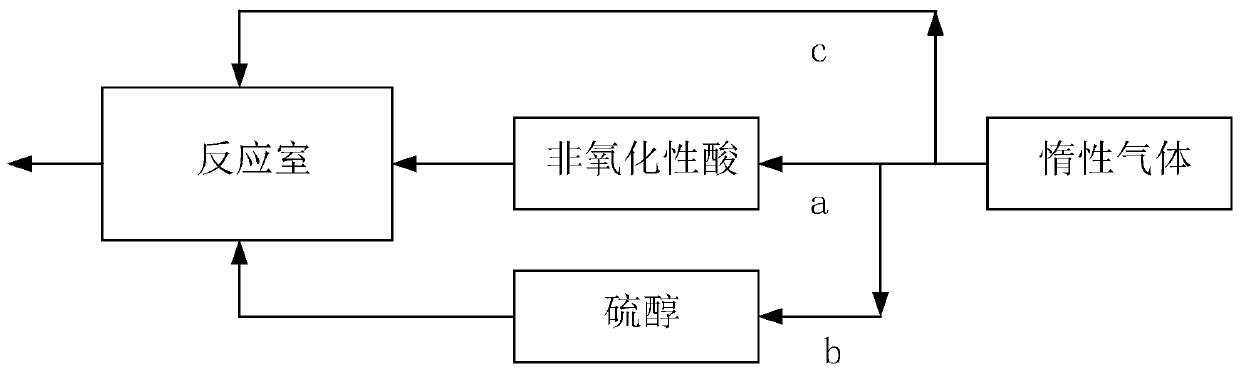
Preparation method and light-emitting device of modified metal chalcogenide
ActiveCN109599505BImprove charge transport efficiencyImprove luminous efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal chalcogenidesChemisorption
The invention belongs to the field of display devices and provides a preparation method of a modified metal chalcogen compound and a light emitting device. In the present invention, the metal chalcogen compound is provided, and the metal chalcogen compound is placed in a reaction chamber to perform the first modification treatment and the second modification treatment to obtain the modified metal chalcogen compound. In this preparation process, the first modification treatment reduces the defects of chalcogen elements through sufficient acid treatment, and releases the charges combined with the defect states of chalcogen elements, and at the same time removes the oxygen species (oxygen species) to obtain purer metal chalcogenides; the second modification treatment allows chalcogen defect states and thiols to chemically adsorb in the form of covalent bonds through thiol treatment, and eliminates the remaining defects on the surface of chalcogens to the minimum; thereby obtaining a modified metal chalcogenide with higher charge transport efficiency, which improves the luminous efficiency of the device. In addition, the preparation method has simple process and low cost, and can realize large-scale production.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
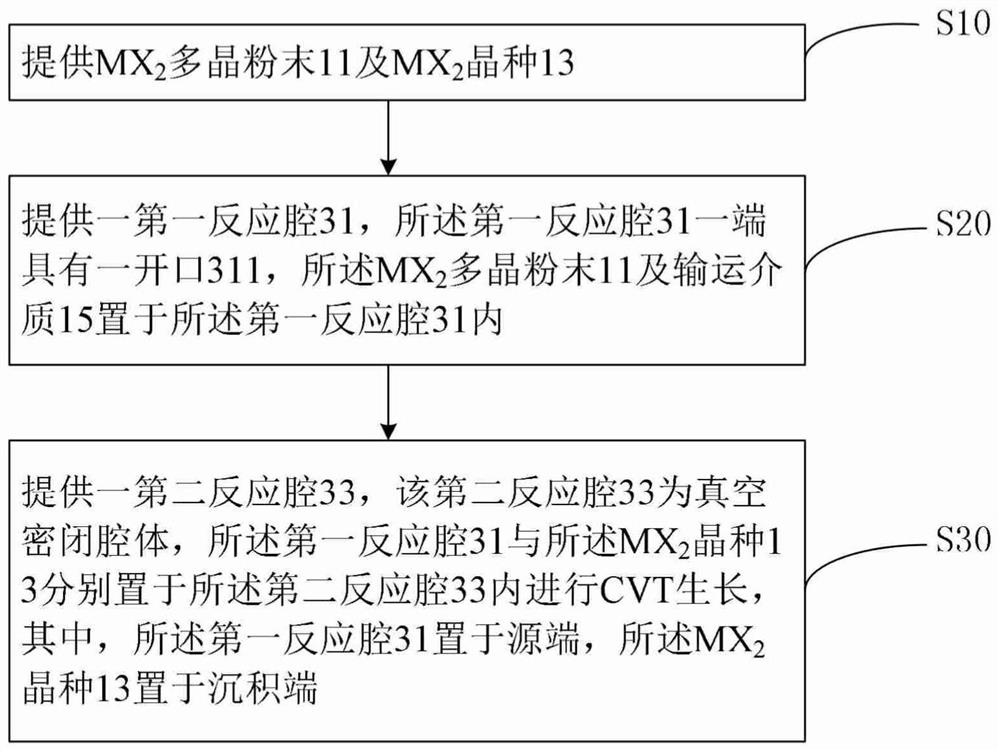
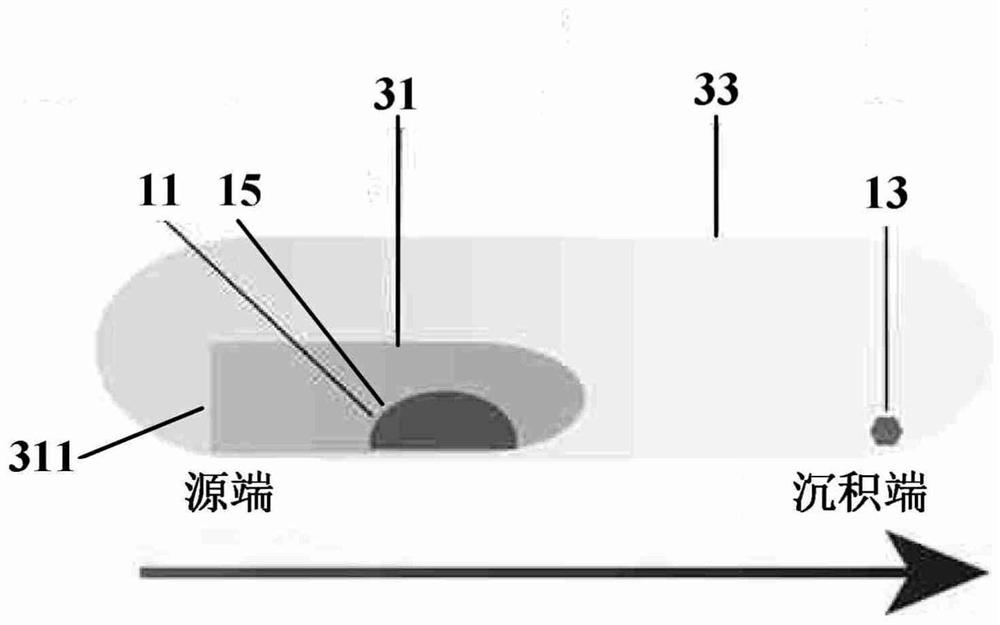
Preparation method of transition metal chalcogenide crystal
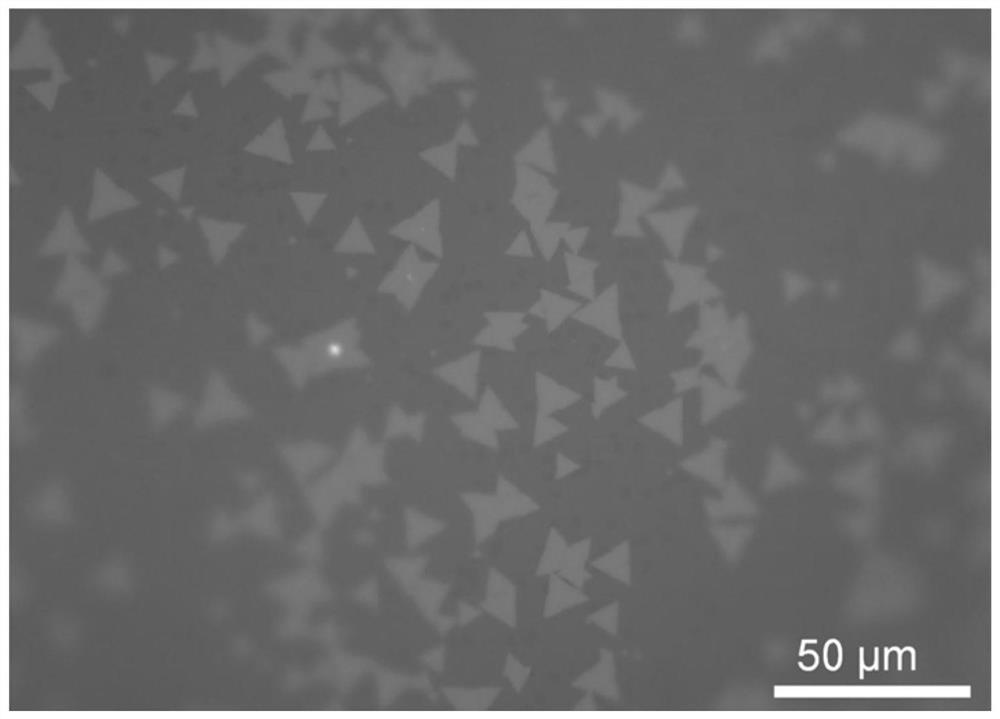
ActiveCN114059157ASmall sizeQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesPhysical chemistryChalcogen
The invention relates to a preparation method of a transition metal chalcogenide crystal, wherein the chemical formula of the transition metal chalcogenide can be expressed as MX2, and wherein M is a central transition metal element, and X is a chalcogen element. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing polycrystalline MX2 powder and an MX2 seed crystal; placing a transport medium and the polycrystalline MX2 powder in a first reaction chamber, and placing the MX2 seed crystal in a second reaction chamber, wherein one end of the first reaction cavity is provided with an opening, the second reaction cavity is vacuum-sealed and has a temperature gradient, the first reaction cavity is arranged in a high-temperature area in the second reaction cavity, and the MX2 seed crystal is arranged in a low-temperature area in the second reaction cavity.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
A core-shell structure type wave-absorbing material and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN110684507BImproved Impedance Matching CharacteristicsGood dispersionArmourOther chemical processesReflection lossSolvothermal reaction
The invention discloses a core-shell structure type wave-absorbing material and a preparation method thereof. The wave-absorbing material has a core-shell structure with two-dimensional transition metal-chalcogen compound nanosheets as the core and hollow carbon spheres as the shell. The preparation method comprises: dissolving hollow carbon spheres in a solvent, sequentially adding a transition metal source and a chalcogen source, stirring and dissolving, performing solvothermal reaction, and then obtaining the wave-absorbing material through post-treatment. The invention also discloses the application of the wave-absorbing material in military and civil high-frequency electromagnetic compatibility and protection fields. The density of the core-shell structure wave-absorbing material of the present invention is 0.3~1.5kg / cm 3 It can effectively improve the maximum reflection loss value and effective bandwidth of the material in the frequency range of 2-40GHz. It is an electromagnetic compatibility and protective material that can meet the needs of civilian high-frequency electronic devices and military airships, artillery shells and other weapons and equipment.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
A kind of transition metal chalcogenide thin layer material and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN110257800BGood lookingGood opticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingPhysical chemistryThin layer
The invention discloses a transition metal chalcogenide thin-layer material and its preparation method and application. The preparation method comprises: uniformly laying a transition metal source between two substrates to prepare a sandwich structure; heat-treating the sandwich structure , the two substrates are fused together, and then the chalcogen source and the fused-bonded sandwich structure are subjected to a chemical vapor deposition reaction under the protection of a protective gas, in which the transition metal source is heated to dissolve and diffuse at the reaction temperature , and precipitate on the surface of the substrate, and react with the chalcogen source; wherein, the chalcogen source includes one or more of sulfur source, selenium source and tellurium source. Through the above method, the present invention combines the principle of "dissolution-precipitation" with the chemical vapor deposition reaction to prepare transition metal chalcogenide thin-layer materials. The manufacturing process is simple and easy, and the process is controllable. The thin-layer material of the group compound is uniformly distributed in the range of centimeters, has good shape, excellent optical and electrical properties, and has broad application prospects.
Owner:TSINGHUA BERKELEY SHENZHEN INST
A chalcogen compound wafer-assisted localized growth method for transition metal chalcogenides
ActiveCN113511681BRaise supply temperatureSolve problemsFinal product manufactureZinc sulfidesWaferingTube furnace
The invention relates to a method for assisting localized growth of transition metal chalcogenides on a chalcogenide compound wafer. The preparation method comprises the following steps: uniformly coating a prepared substrate with a layer of transition metal source and then buckling it on the chalcogenide On the compound wafer, the two construct a localized space and place it in a tube furnace. At high temperature, the chalcogen released from the chalcogen wafer reacts directly with the transition metal source on the substrate to obtain the corresponding transition metal compound on the substrate. Compared with the conventional CVD method, this method perfectly solves the problem of insufficient and uneven supply of precursor source diffusion during the growth process. With the characteristics of simple process, fast growth rate and strong universality, it can be used to prepare different kinds of transition metal chalcogenide (TMDC) materials, which provides a new idea for the preparation of two-dimensional materials.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
A bismuth-based topological insulator material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109706525BQuality improvementLow costPolycrystalline material growthFrom melt solutionsBoron oxideGlass melting
The invention belongs to the technical field of insulator materials, and specifically relates to a bismuth-based topological insulator material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation methodcomprises the following steps: S1, uniformly mixing silicon dioxide powder, sodium hydroxide powder, boron oxide powder, bismuth-source compound powder and chalcogen element powder according to a molar ratio is 4: 4: 1: (0.05-0.5): (0.05-0.5) so as to obtain a mixture A; S2, melting the mixture A at a high temperature of 900 to 1100 DEG C, and carrying out cooling to a room temperature so as to obtain the bismuth-based topological insulator material; and S3, mixing the bismuth-based topological insulator material obtained in the step S2 with isopropyl alcohol, carrying out grinding so as to obtain bismuth-based topological insulator material powder, then dispersing the bismuth-based topological insulator material powder into isopropyl alcohol, and carrying out ultrasonic dispersion so asto obtain a bismuth-based topological insulator two-dimensional material. The method provided by the invention realizes natural growth of a crystal in a glass melt through a high-temperature glass melting method and utilization of low-cost raw materials, and realizes preparation of high-quality layered bismuth-based topological insulator binary and multiple system materials.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Gold-coated silver bonding wire and manufacturing method thereof, and semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
PendingCN112088425APromote formationInhibit migrationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialSemiconductor
A gold-coated silver bonding wire includes: a core material containing silver as a main component; and a coating layer provided on a surface of the core material and containing gold as a main component. The gold-coated silver bonding wire contains gold in a range of not less than 2 mass % nor more than 7 mass %, and at least one sulfur group element selected from the group consisting of sulfur, selenium, and tellurium in a range of not less than 1 mass ppm nor more than 80 mass ppm, with respect to a total content of the bonding wire.
Owner:TANAKA DENSHI KOGYO KK
A kind of method for preparing black silicon material
InactiveCN105655419BReduce volatilityImprove absorption rateFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesProtection layerGrain boundary
The invention belongs to the field of black silicon material preparation, and in particular relates to a method for preparing a selenium-silicon composite film by means of thermal evaporation and magnetron sputtering, and using femtosecond laser etching to prepare black silicon. The invention uses a layer of silicon film sputtered on the selenium film as a protective layer in the existing process, which reduces the volatilization of chalcogen elements in the femtosecond etching process, increases the doping content, and can prevent the introduction of laser pulse irradiation. The impurity Se diffuses to the grain boundary, so as to maintain its doping concentration on the surface, so as to improve the absorption rate of black silicon. The absorption rate of the black silicon prepared by using the method is higher than 95% in the 400-1100nm wave band, and the absorption rate in the 1100-2200nm wave band is higher than 90%. Compared with the black silicon material prepared by thermally evaporating a layer of selenium film without covering the silicon protective layer, the absorption rate of the black silicon prepared by the method in the near-infrared band is significantly improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
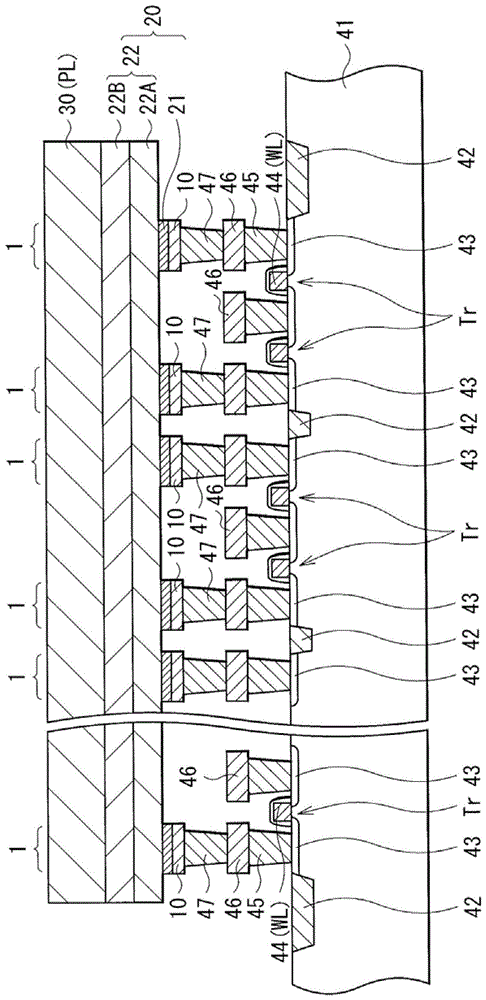
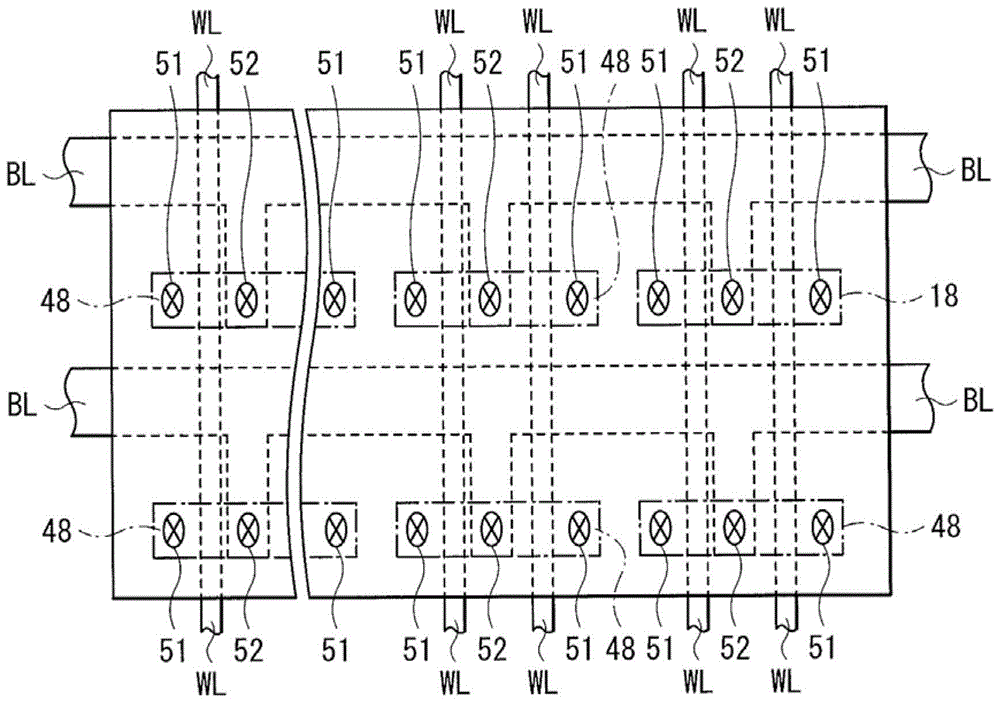
Storage Elements and Storage Devices
ActiveCN102820426BImprove featuresInhibit deteriorationElectrical apparatusDigital storageEngineeringChalcogen
A memory element including a memory layer disposed between a first electrode and a second electrode and a memory device including the memory element. The storage layer includes: an ion source layer containing one or more metal elements and one or more chalcogen elements among tellurium (Te), sulfur (S), and selenium (Se); Between the source layer and the first electrode, the resistance change layer includes a layer containing tellurium and nitrogen (N) and in contact with the ion source layer. The memory element and memory device of the present invention can provide good retention characteristics and improved repeated operation characteristics.
Owner:SONY CORP
Preparation method of chalcogenide tubular material
PendingCN113666341AComplete shapeImprove crystal qualityTin compoundsZinc sulfidesPhysical chemistryReaction zone
The invention relates to a preparation method of a chalcogenide tubular material, and belongs to the technical field of photoelectric material preparation. A solid chalcogenide raw material is placed in a low-temperature heating zone of a double-temperature-zone furnace reactor, a metal raw material is placed in a high-temperature vulcanization reaction zone of the double-temperature-zone furnace reactor, inert gas is adopted for gas washing, then the solid chalcogenide raw material in the low-temperature heating zone and the metal raw material in the high-temperature vulcanization reaction zone are heated, the solid chalcogenide raw material in the low-temperature heating zone releases gaseous chalcogenide to react with the metal raw material in the high-temperature vulcanization reaction zone to generate a gas-phase chalcogenide, and the gas-phase chalcogenide is condensed on the substrate to obtain the chalcogenide tubular material. The chalcogenide tubular material is simple in preparation process, large-scale production can be achieved, the specific surface area of the chalcogenide tubular material is large, photons can be better captured, the transmission rate of photon-generated carriers is increased, and the chalcogenide tubular material is suitable for being applied to the field of photoelectric semiconductors.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
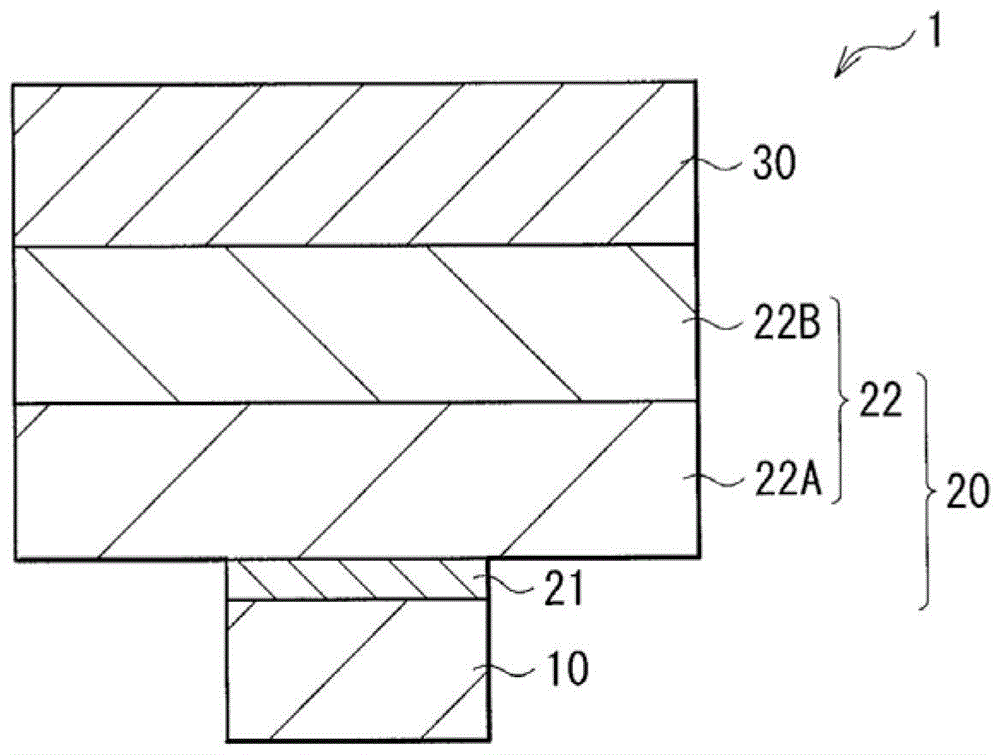
Laminate structure and method for manufacturing same, and semiconductor device
PendingCN112292758AImprove stabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialPhysical chemistry
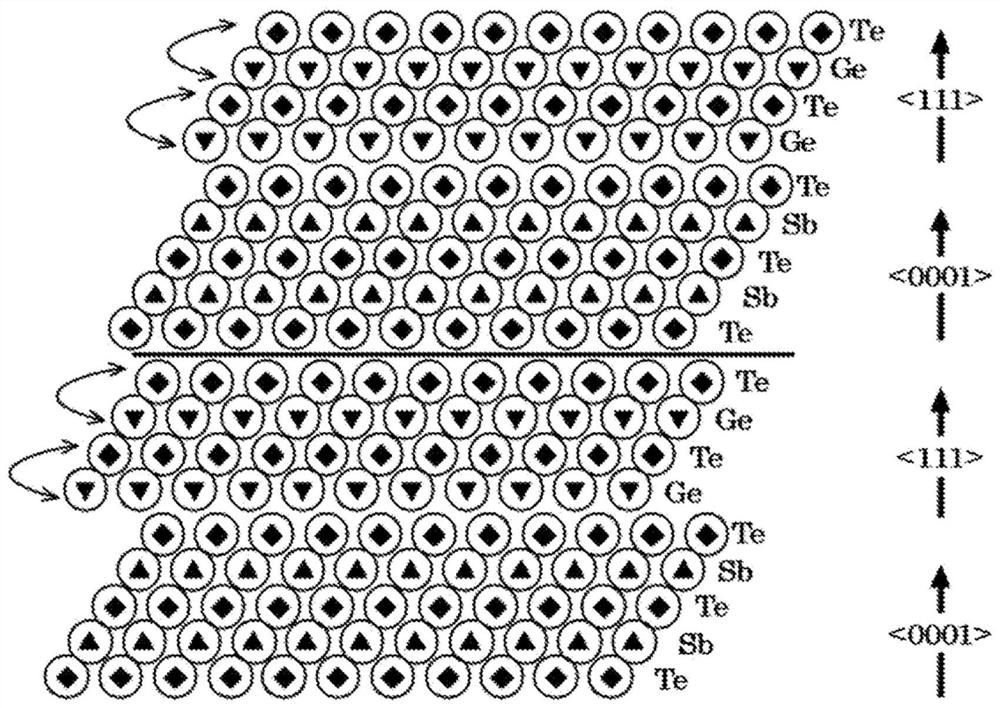
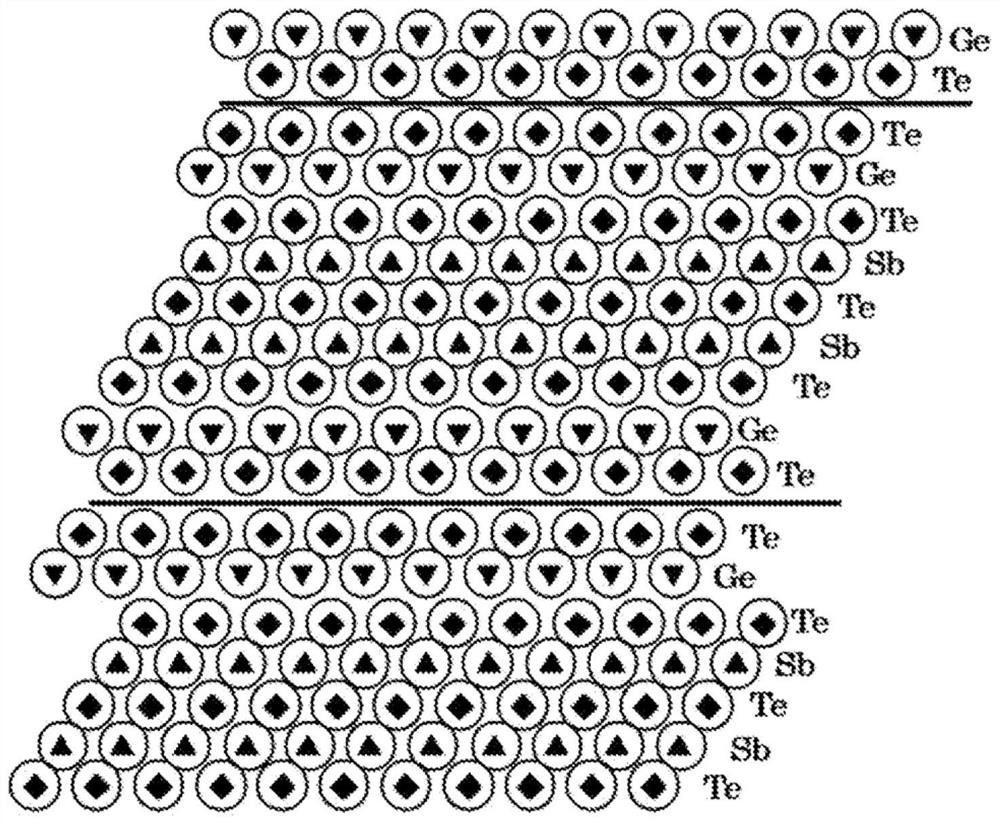
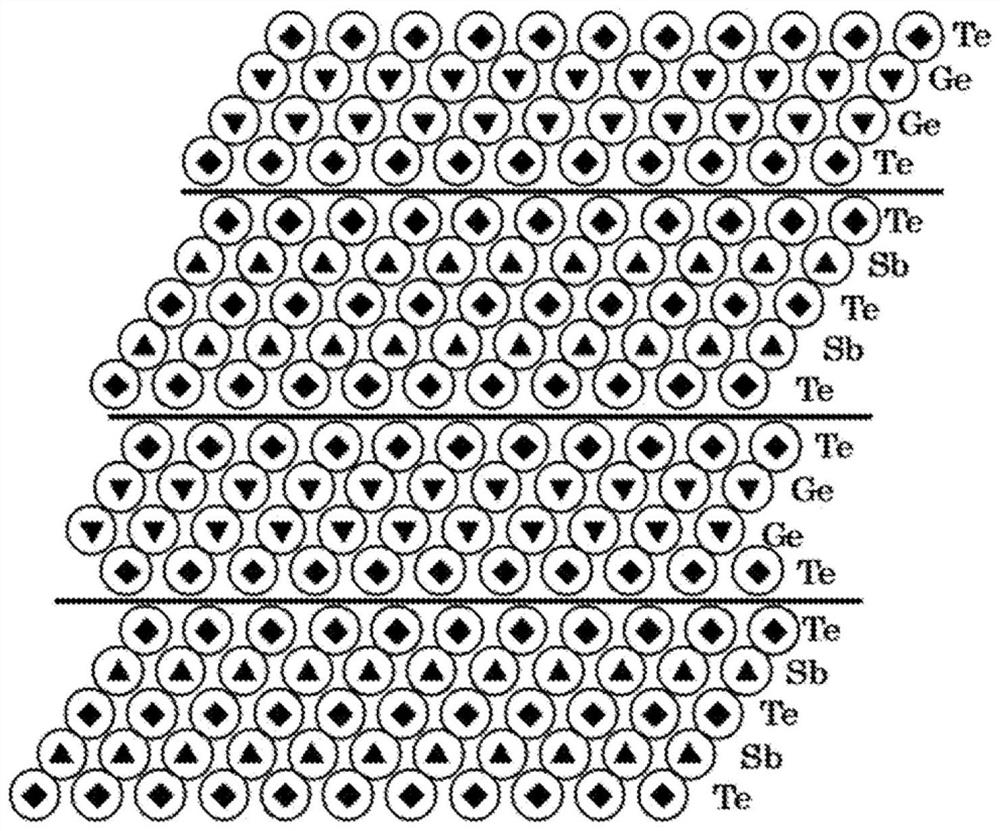
[Problem] The present invention addresses the problem of providing a laminate structure in which the atomic arrangement is highly stable, a method for manufacturing the laminate structure, and a semiconductor device in which the laminate structure is used. [Solution] This laminate structure is characterized in having an alloy layer A formed with germanium and tellurium being the main components, and an alloy layer B formed with tellurium and either antimony or bismuth being the main components, chalcogen atoms of sulfur and / or selenium being contained in the alloy layer A and / or the alloy layer B.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
Storage element, method of manufacturing storage element, and storage device
The present invention provides a storage element, a method for manufacturing the storage element, and a storage device, wherein the storage element sequentially includes a first electrode, a storage layer, and a second electrode. The storage layer includes: a resistance change layer disposed on the first electrode side; and an ion source layer containing one or more metal elements, and the ion source layer is disposed on the second electrode side. The ion source layer includes a first ion source layer and a second ion source layer, and the first ion source layer contains more than one of the chalcogen elements tellurium (Te), sulfur (S), and selenium (Se) and is set On the resistance change layer side, and the content of chalcogen elements in the second ion source layer is different from the content of chalcogen elements in the first ion source layer, and the second ion source layer is arranged on the second electrode side . According to the present invention, the ion source layer can be prevented from being deteriorated, and the heat resistance of the memory element is improved. In other words, the formed memory device has high reliability.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method for direct patterned growth of atomic layer transition metal dichalcogenides
A method of direct growth of a patterned transition metal dichalcogenide monolayer, the method comprising the steps of: providing a substrate covered by a mask having a pattern defined by one or more shaped holes; or a plurality of shaped holes thermally depositing the salt on the substrate so that the deposition salt is arranged on the substrate in a mask pattern; and thermally co-depositing the transition metal oxide and the chalcogen element onto the deposition salt to form Graphical patterning of transition metal dichalcogenide monolayers. Also provided are patterned transition metal dichalcogenide monolayers prepared according to the method.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com