Patents
Literature
46 results about "Galactomyces candidum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
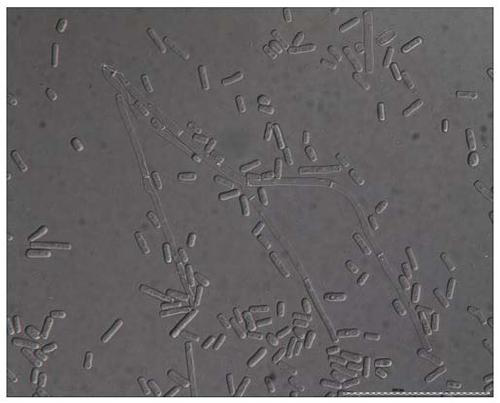
Galactomyces candidum is a plant pathogen. Geotrichum candidum is a filamentous yeast-like fungus commonly isolated from soil, air, water, milk, cheese, silage, plant tissues, digestive tract in humans and other mammals. G. candidum infections of plants and animals are very rare. In humans, fewer than 100 cases reported between 1842 and 2006 (and some were never confirmed). Dairy products have never been implicated in foodborne infection. Due to its technological interest in dairy products, it has been proposed to use G. candidum as a starter.
Plant lactobacillus strain and its application
InactiveCN1888051AImprove cleanlinessImprove adhesionBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsEscherichia coliStaphylococcus cohnii
The present invention discloses one plant lactobacillus strain and its application. The plant lactobacillus, Lactobacillus plantarum L323 CGMCC No. 1329, is separated from Chinese pregnant woman's vaginal secretion, and has relatively high bacteriotasis on common vaginal pathogens, such as staphylococcus aureus, candida albicans, colibacillus and vaginal Gardnar bacillus, and acid producing and H2O2 producing capacity higher than other lactobacillus. The plant lactobacillus, Lactobacillus plantarum L323 CGMCC No. 1329, may be used in preparing vaginal microbial preparation for preventing and / or treating vaginal infectious diseases.
Owner:TIANYOUDA BIO ENG SCI & TECH BEIJING +1
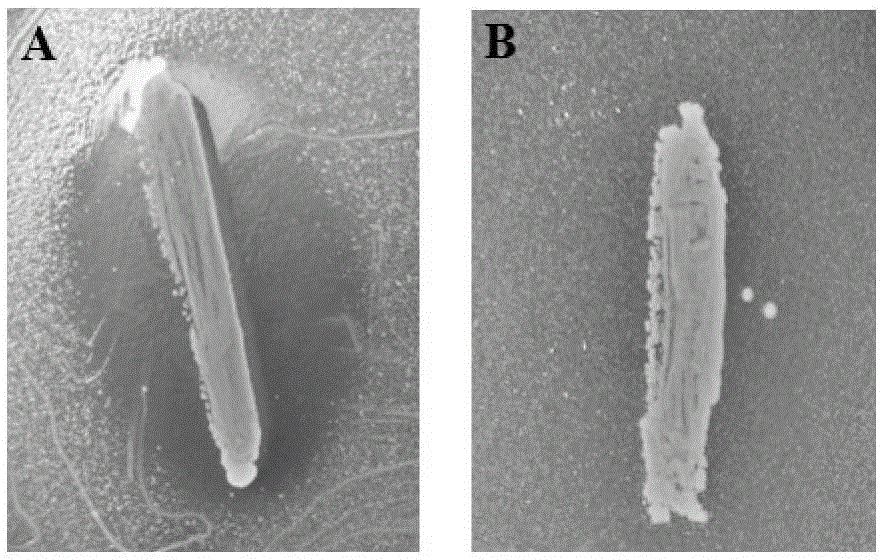
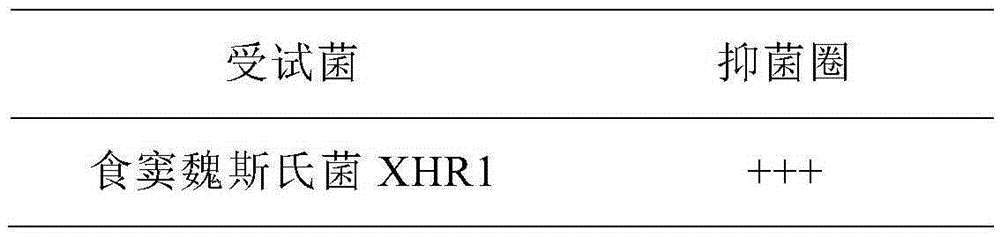
Weissella cibaria XHR1 and applications thereof and weissella cibaria XHR1 containing pickled vegetable
ActiveCN105255787AImprove micro-ecological levelExpansion of industrial productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesWeissella cibariaCandida famata
The invention provides a weissella cibaria XHR1 and applications thereof and a weissella cibaria XHR1 containing pickled vegetable. The preparation of the pickled vegetable is implemented through the steps of adding a culture solution of weissella cibaria XHR1 and bacterial powder of lactobacillus plantarum CICC 20764 into a pickled vegetable fermentation starting solution for pickling vegetables, so that the final concentration of weissella cibaria XHR1 is 10<6>-10<7> cfu / mL eventually, and then the final concentration of lactobacillus plantarum CICC 2076 is 10<5>-10<6> CFU / mL; and then, adding vegetables into the pickled vegetable fermentation starting solution, and carrying out vegetable pickling according to a traditional vegetable fermentation process, so that the pickled vegetable disclosed by the invention is obtained finally. According to the invention, prebiotic lactobacillus for inhibiting the growth of Candida albicans is applied to the fermentation of Sichuan pickled vegetables, so that the consumer group is wider, and the micro ecological level of alimentary canals of wide consumers can be improved, thereby inhibiting Candida albicans diseases from the perspective of public health.
Owner:XIHUA UNIV
LOCAL ADMINISTRATION OF CHICKEN YOLK IMMUNE GLOBULINS (IgY) TO TREAT AND PREVENT FUNGAL INFECTIONS
InactiveUS20100233162A1Easy to produceTreatment and prophylaxisEgg immunoglobulinsSenses disorderAntigenYolk
The present invention relates to a composition comprising IgY antibodies against at least two different fungi, the use of the composition for the preparation of a pharmaceutical especially for prophylaxis and / or therapy of all kinds of fungal infections, such as conditions caused by organisms belonging to the Candida genus or Aspergillus genus, especially of fungi that are less sensitive to antimycotica and a diagnotstic method using the IgY antibodies. Further it relates to immunisation of birds with a combination of at least two different species of fungi to the Candida genus or Aspergillus genus and a diagnostic method for fungi. It also relates to relates to a novel method for treatment and / or prophylaxis of fungal infections, especially infections by fungi which have lowered sensitivity or resistance to antimycotics. The method is both safe and effective. This is achieved by using IgY directed against fungi, in particular against Candida species, which have a lowered sensitivity or resistance against antimycotics. The specific IgY has been obtained by hyper immunising birds with one or several fungi as antigen in order to stimulate the production of immune globulins (IgY) against such fungi. The present invention also relates to a pharmaceutical product from eggs of birds containing immune globulin or a fragment thereof, which can be combined with other preparations, nutritients or pharmaceuticals for simultaneous, separate or sequential use in the prophylaxis or therapy of gastrointestinal infections in newborn infants.
Owner:BENGT AGERUP
Recombinant Bacillus subtilis for efficiently synthesizing acetylglucosamine
ActiveCN106479945AEasy to buildEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCandida famataGenetic engineering
The invention discloses recombinant Bacillus subtilis for efficiently synthesizing acetylglucosamine and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. Recombinant Bacillus subtilis BSGN6-PxylA-glmS is used as a starting strain, glucosamine synthetic route is enhanced by overexpressing glucosamine acetylase coding gene (CaGNA1) from Candida albicans SC5314 or knocking out unnecessary area skin at the same time, and accumulated acetylglucosamine Bacillus subtilis genetically-engineered bacteria are obtained; the yield is 21% or 94% higher than that of CaGNA1 genetically-engineered bacteria from overexpressed Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and the basis is laid for the further metabolic engineering modification of Bacillus subtilis.
Owner:SHANDONG RUNDE BIOTECH CO LTD
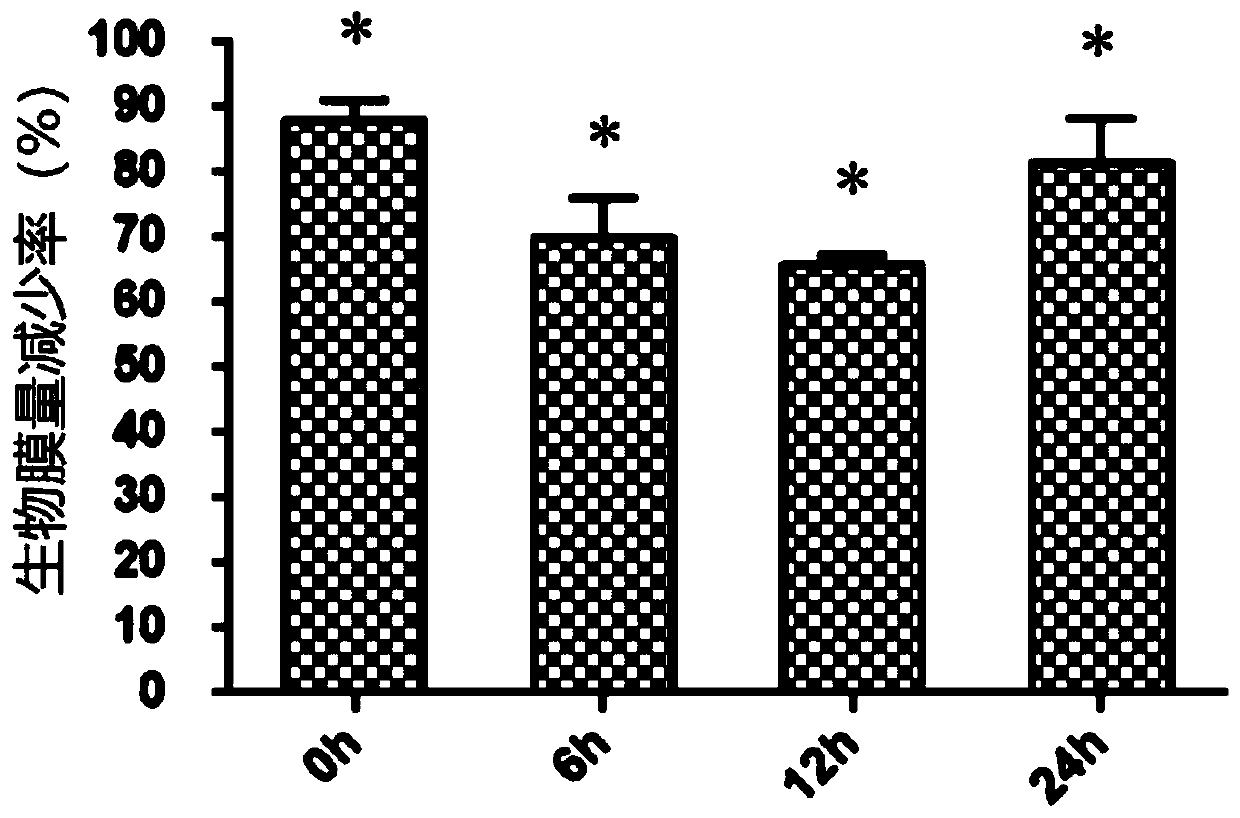
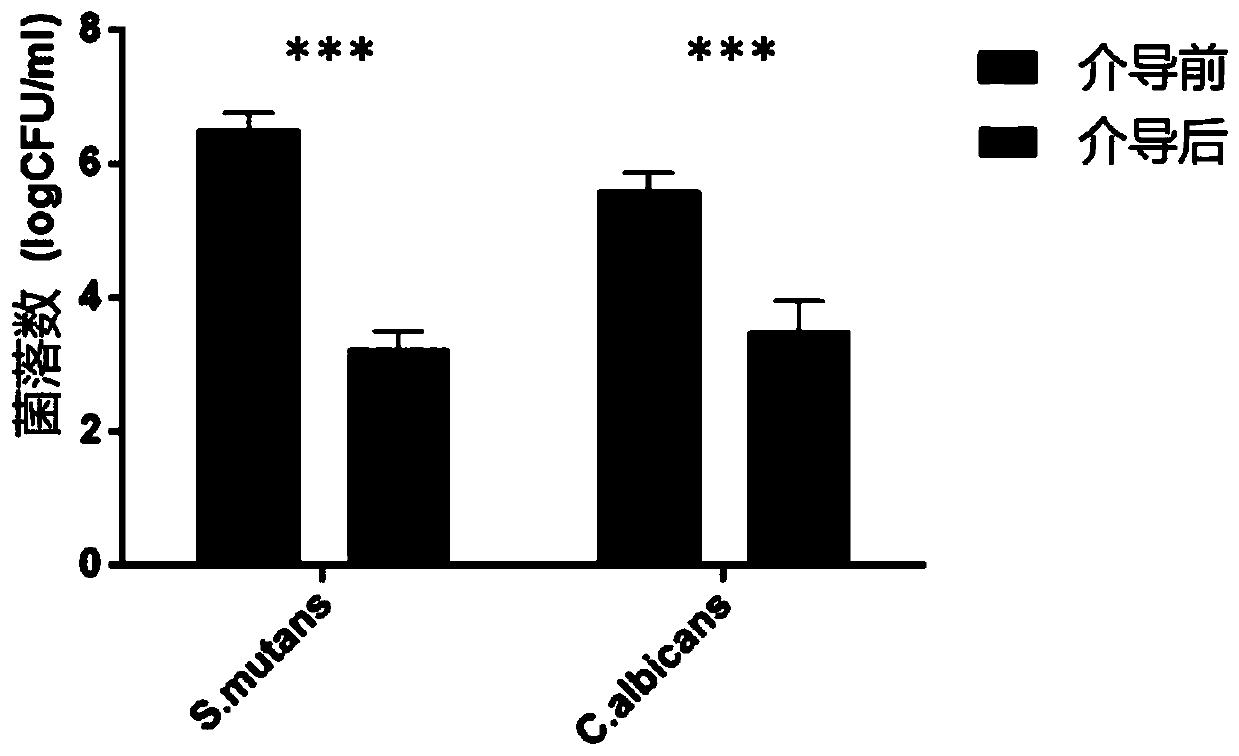
Method capable of inhibiting streptococcus mutans and candida albicans double-bacteria biofilm
ActiveCN109908185AInhibitor formationViable count reductionAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsSphaerotrichia divaricataSucrose
The invention discloses a method capable of inhibiting a streptococcus mutans and candida albicans double-bacteria biofilm and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. At different stages offorming the double-bacteria biofilm, lactobacillus plantarum CCFM8724 can inhibit the double-bacteria biofilm in vitro, exopolysaccharide amount and pathogenic bacteria number in the biofilm can be reduced remarkably when the double-bacteria biofilm is allowed to act at different times, 1.6mg / mL of lysozyme can be tolerated, film forming performance is poor at different sucrose concentrations andlower than below 0.80, and it shows that lactobacillus plantarum cannot replace cariogenic bacteria to form a cariogenic biofilm. The method has efficacy of reducing oral cariogenic bacterial plaque and preventing and treating decayed teeth and is expected to open a new functional market for preventing and treating decayed teeth through probiotics.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Compositions for controlling the psyllids trioza erytreae and diaphorina citri, vectors of bacteria of the genus candidatus liberibacter, which cause the most serious known disease of citrus, namely huanglongbing (HLB)
The present invention relates to the use of compositions that, when applied to citrus, are capable of controlling the psyllids Trioza erytreae and Diaphorina citri, vectors of bacteria of the genus Candidatus liberibacter, which cause the disease known as Huanglongbing (HLB), deemed to be the most destructive disease currently to affect citrus crops worldwide. These compositions may contain, without distinction, or jointly, as active components, vitamin K3, soluble derivatives thereof (preferably menadione sodium bisulphite [MSB]) or sparingly soluble derivatives thereof (preferably menadione nicotinamide bisulphite [MNB]), with respective concentrations of between 0.0001 and 200 ppm, 0.001 and 10 000 ppm, preferably vitamin K3 between 0.001 and 100 ppm, MSB between 0.01 and 5000 ppm, and MNB between 0.01 and 5000 ppm. Said compositions are applied preferably by spraying to the aerial part of the plant or via the irrigation system, and may be mixed with a variety of additives, such as organic and inorganic fertilizers, insecticides, nematocides, fungicides, bactericides, acaricides or herbicides.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC)
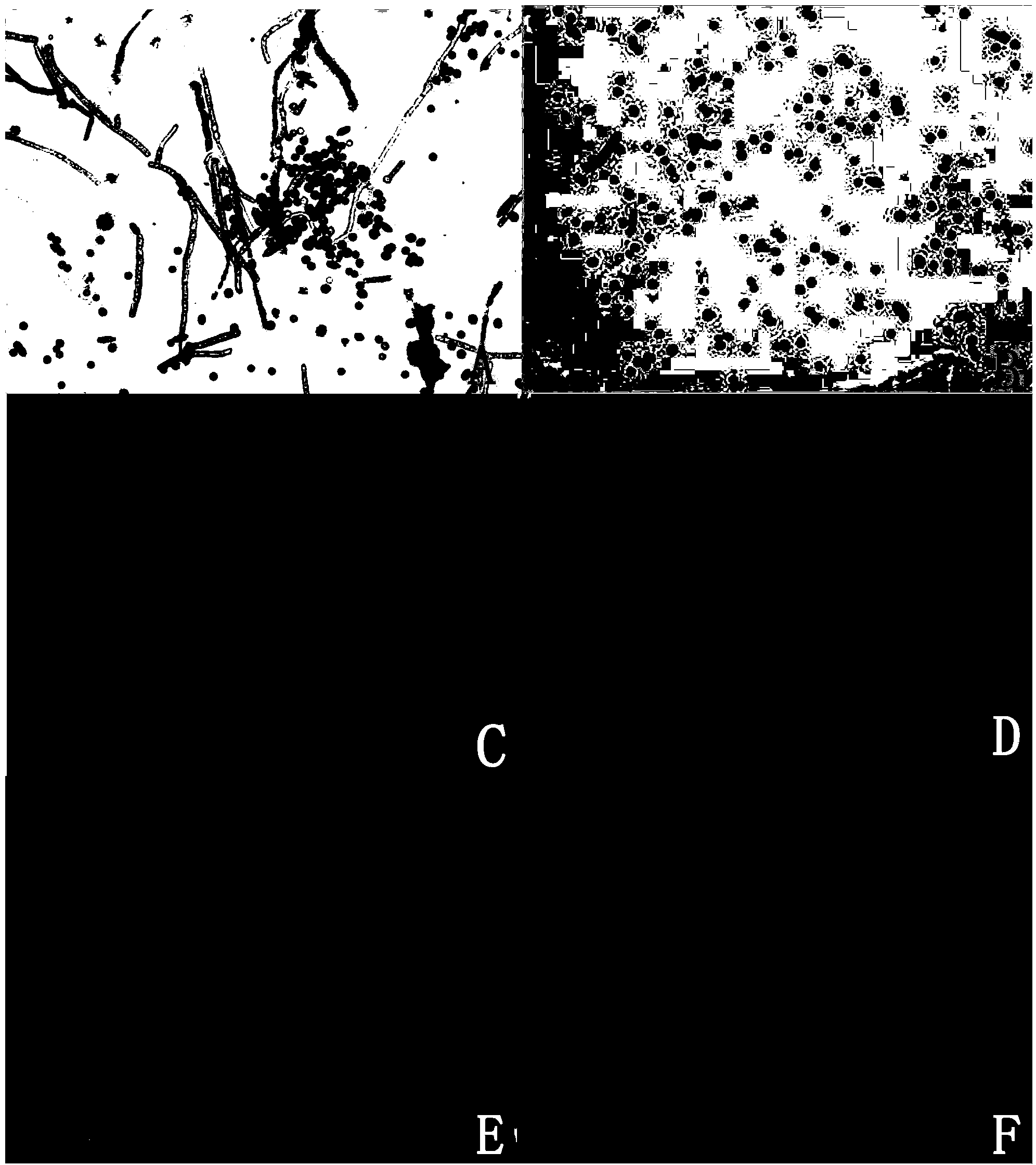
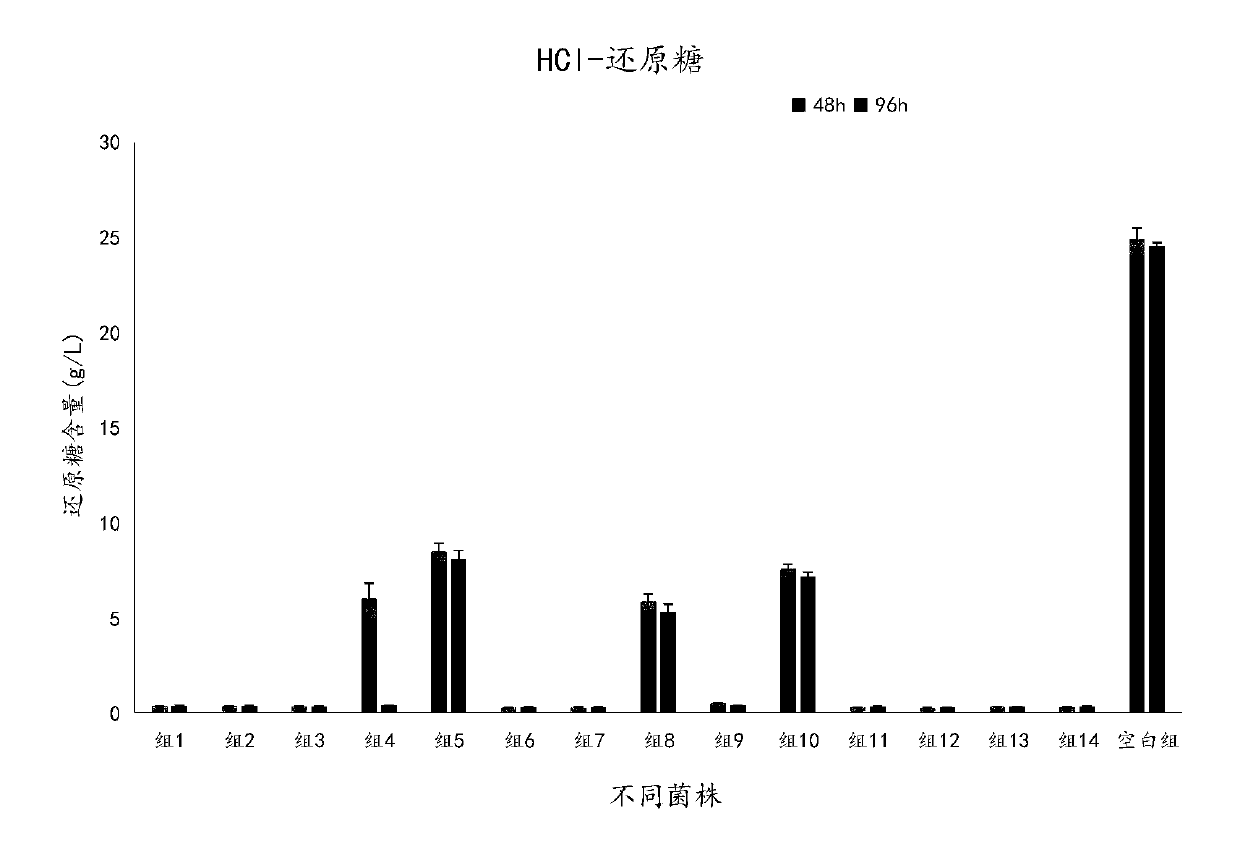
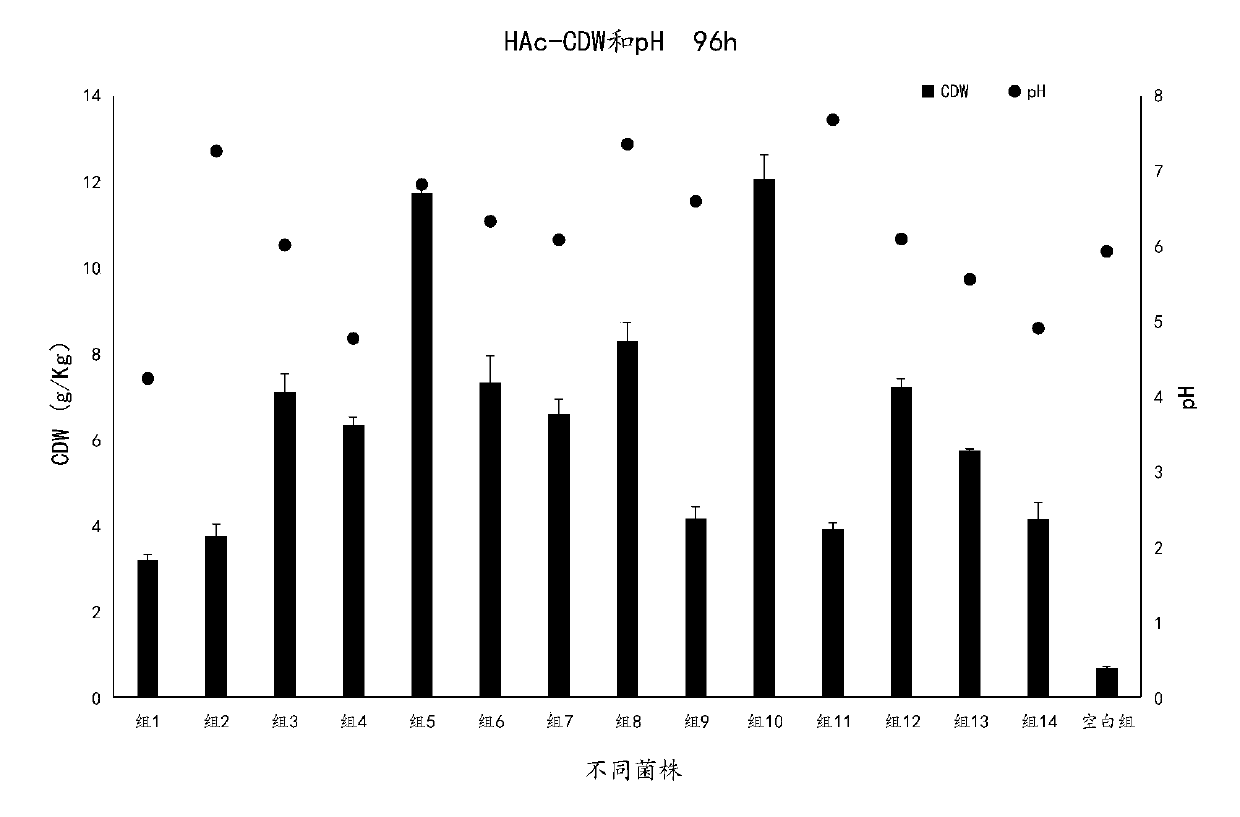
Galactomyces candidum and method for treating high-ammonia-nitrogen biogas slurry by using galactomyces candidum to produce single cell protein
ActiveCN110982706ARapid productionHigh DCW concentrationFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCentrifugation
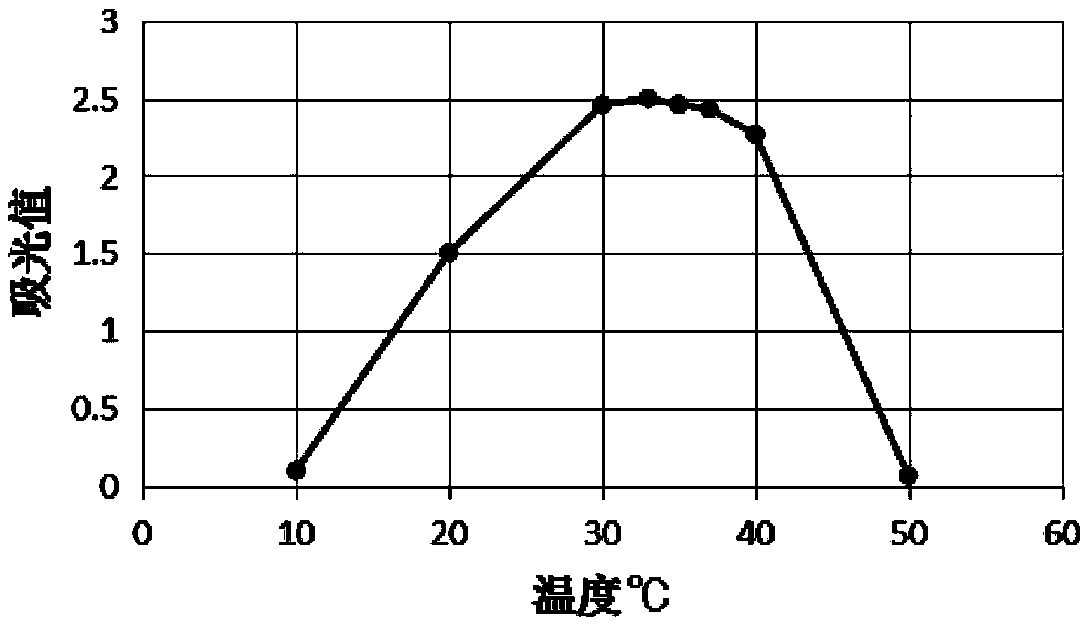
The invention belongs to the field of biological fermentation, and particularly relates to a galactomyces candidum and a method for treating high-ammonia-nitrogen biogas slurry by using the galactomyces candidum to produce single cell protein. The invention has the following specific technical scheme: the galactomyces candidum has a preservation number of CGMCC No.18570. The method of fermenting the biogas slurry comprises the following steps: taking the biogas slurry, performing filtration to remove large-particle impurities, adding a carbon source, adjusting a carbon-to-nitrogen ratio to 6:1to 10:1, and adjusting the pH to 5.5-7 to obtain a fermentation substrate; inoculating the fermentation substrate with the galactomyces candidum grown to a logarithmic stage, and performing fermentation at 20-30 DEG C; and after the fermentation is completed, performing centrifugation on the fermentation liquid, and drying the precipitate obtained after centrifugation at 50-60 DEG C to a constantweight to obtain the required single cell protein. The method only needs a period of biological reaction to treat the biogas slurry, has a low running cost and convenient operation, has an excellenttreatment effect on the biogas slurry, and can provide high economic value products, thereby providing an integrated and economic solution for biogas slurry treatment.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Novel wide-spectrum bacillus resisting clinical and plant pathogenic fungi and application thereof
InactiveCN103087939ABroad antifungal spectrumGood antibacterial effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesBacterial strain
The invention relates to a novel wide-spectrum bacterial strain Bacillus sp. AH-E-1 inhibiting clinical and plant pathogenic fungi, and an application thereof. The main content comprises: (1) Bacillus sp. AH-E-1 is a newly-discovered bacillus strain or subspecies; (2) Bacillus sp. AH-E-1 can produce anti-fungus substances after fermentation under appropriate conditions; (3) Bacillus sp. AH-E-1 can significantly inhibit 20 clinical pathogenic fungi such as aspergillus flavus, aspergillus fumigates, trichophyton rubrum, trichophyton mentagrophyte, candida glabrata, cryptococcus neoformans, and the like; (4) Bacillus sp. AH-E-1 can significantly inhibit 13 plant pathogenic fungi such as staphylococcus, magnaporthe oryzae, rhizopusstolonife, and the like. The invention provides an excellent novel anti-fungus substance producing bacterial strain which has the advantages of wide fungus-inhibiting spectrum, obvious effect, and the like.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL
Preparation method of actinomycin D and application thereof
ActiveCN104450580ABroad-spectrum and highly potent antagonistic activityAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsVerticillium speciesMonilinia laxa
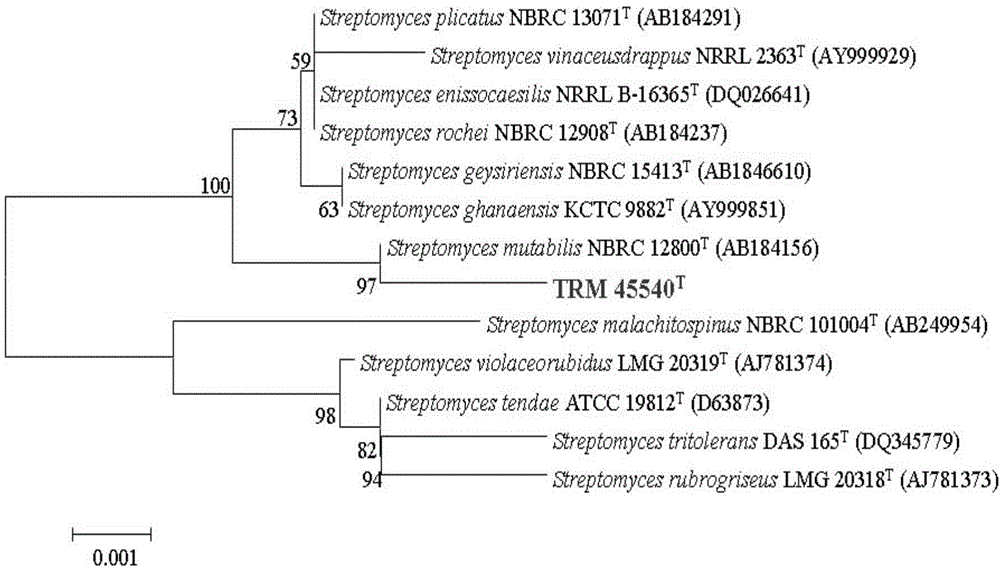
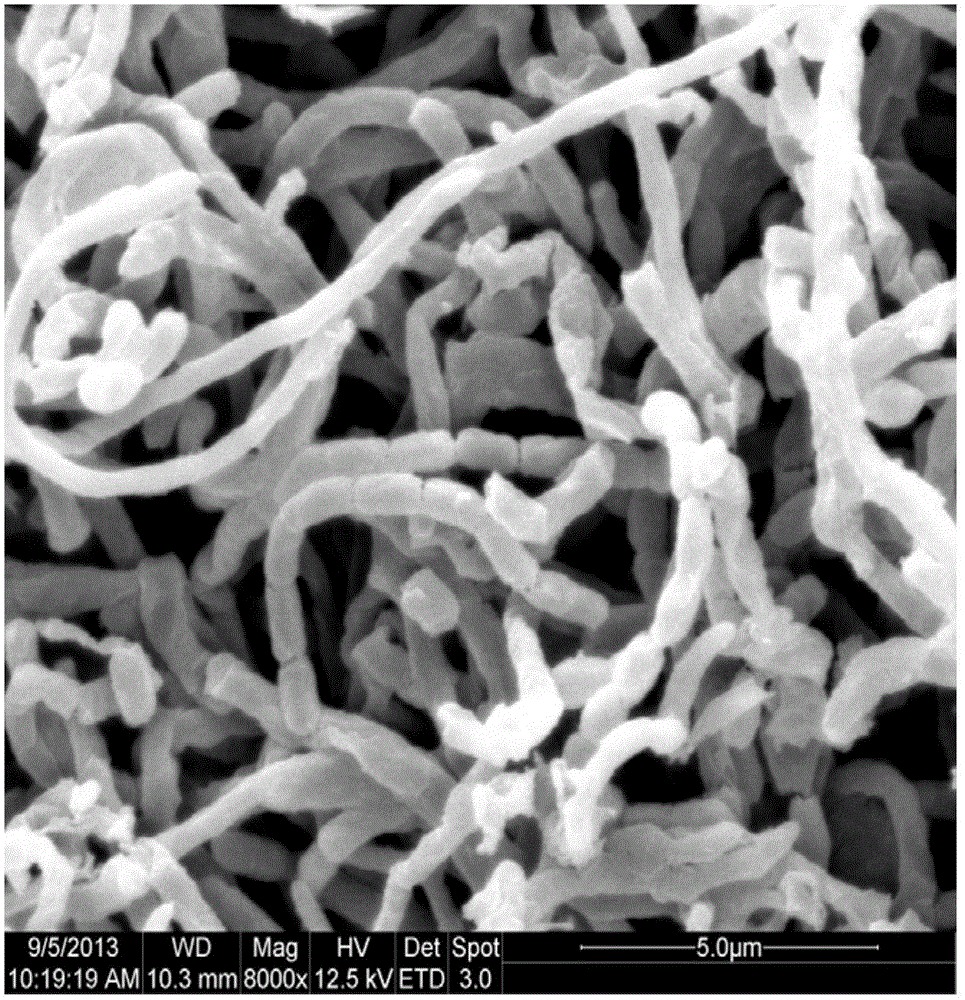
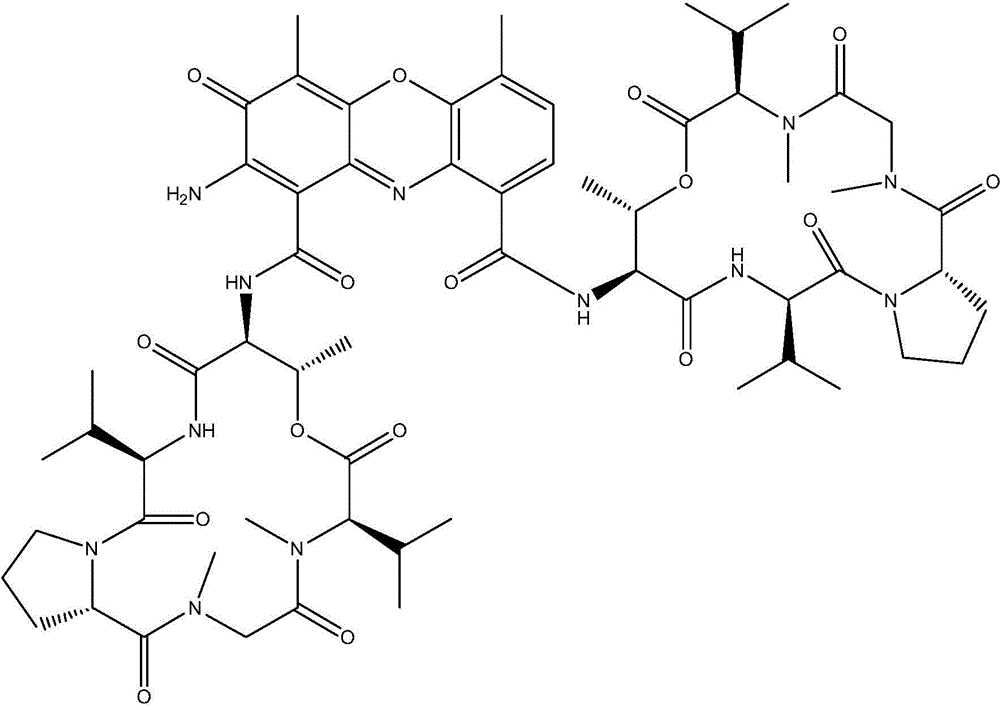
The invention discloses a novel actinomycin strain which generates actinomycin D: Streptomycesmutabilis TRM45540, preserved in U. S. Department of Agriculture Agricultural Research Service (ABS) Culture Collection on 14th, April, 2014 with the preservation number of NRRL B-59117. Meanwhile, the invention further discloses a seed medium which efficiently produces actinomycin D by using the strain, a fermentation medium and a preparation process of extracting and separating actinomycin D from fermentation liquor. An antibacterial activity test shows that the strain and the actinomycin D generated by fermentation of the strain have broad-spectrum and efficient antagonistic activity on pathogenic bacteria such as cotton verticillium and fusarium wilts, walnut pythium ultimum, staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus epidermidis, candida albicans and the like and have an important application value and a very good application and development prospect on safe production of crops such as cotton, walnuts and the like and in preventing and controlling diseases such as bovine mastitis, women's vaginitis and the like.
Owner:TARIM UNIV
Gene chip for detecting 15 clinical common pathogenic microorganisms
ActiveCN102080127AWith monitoring functionStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceCandida tropicalisRhizopus oryzae
The invention discloses a gene chip for detecting 15 clinical common pathogenic microorganisms. The gene chip comprises specific detection probes fixed on a solid phase vector, wherein the probes are designed for 16SrRNA gene and ITS gene sequences of staphylococcus aureus, klebsiella pneumoniae, pseudomonas aeruginosa, proteus mirabilis, Escherichia coli, shigella, enterobacter aerogenes, pseudomonas fluorescens, candida albicans, candida glabrata, candida tropicalis, candida parapsilosis, aspergillus terreus, aspergillus flavus and rhizopus oryzae, and screened and verified by repeated tests, and have high hybridization specificity and accuracy. The chip provided by the invention ensures simple detection operations and relatively lower cost, saves time, is applied to the screening of the clinical common pathogenic microorganisms, the early rapid diagnosis of critical patients and the diagnosis of suddenly occurring infection event pathogens and favorable for clinically rapidly diagnosing infection sources and functions in the early detection and early diagnosis of clinical diseases.
Owner:GUANGZHOU IMPROVE MEDICAL TECH CO LTD +1
Application of Antimicrobial and Glycemic Control Activities of Lo Han Kuo Fruit (Siraitia grosvenorii)
InactiveUS20120141386A1Prevention of dental cariesGreat market potentialAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsPorphyromonas gingivalisMonilinia laxa
The present invention discloses an application of the extract of Lo Han Kuo (LHK) fruit (Siraitia grosvenorii Swingle) for its dual related functions. Specifically, this is related to the use of LHK extract for its antimicrobial activities against pathogens Streptococcus mutans, Porphyromonas gingivalis, A. actinomycecomitan, F. nucleatum, and Candida albicans, and its low glycemic index for use by general population as well as the diabetics to improve oral health.
Owner:ORACEUTICALS
Lactobacillus sp. strain having ability to inhibit proliferation of virginal pathogenic microorganisms
InactiveUS20180117100A1Increase blockingImprove treatmentAntibacterial agentsMilk preparationHuman papillomavirusCandida famata
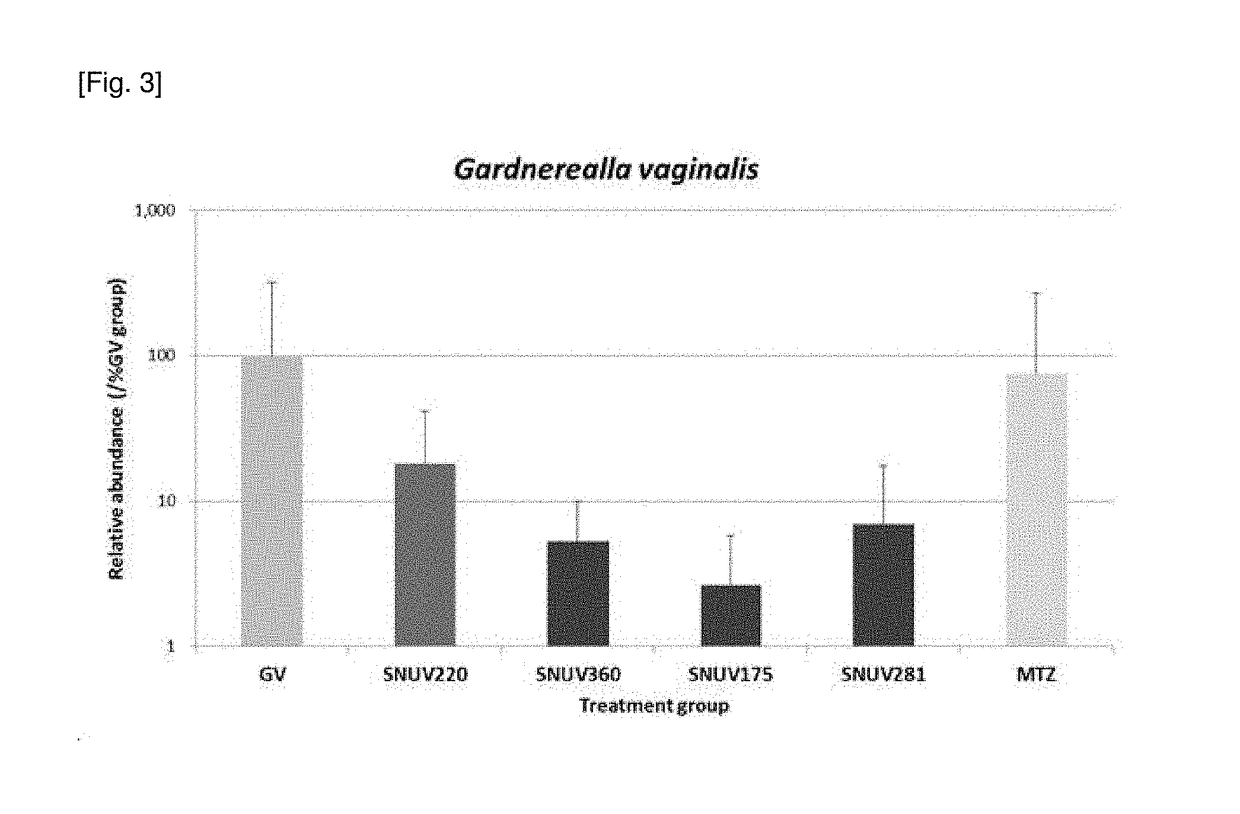
The present invention relates to a novel Lactobacillus sp. isolation strain having an activity to inhibit the growth of vaginitis pathogens, and a pharmaceutical composition, a health functional food, and a cleansing product, comprising the strain as an active ingredient. Therefore, the present invention exhibits an effect of inhibiting the growth of Sneathia spp. pathogens associated with the infection with human papillomavirus (HPV) and the incidence of bacterial vaginitis, Gardnerella vaginalis as a vaginitis pathogen, and Candida albicans as a causative bacteria of Candidal vaginitis, and an effect of recovering and maintaining the vaginal microflora, and thus can be used for the prevention and treatment of female vaginitis.
Owner:KO BIOLABS INC
Method for separating and screening out antagonistic bacterium from lycoris aurea bulb
PendingCN105524871AShorten the growth cycleLow environmental requirementsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesMeloidogyne oryzae
The invention relates to a method for separating and screening out an antagonistic endophytic bacterium from a lycoris aurea bulb. According to the method, by using an endophyte separation method, an endophytic bacterium is obtained by separating the endophytic bacterium from the lycoris aurea bulb; an improved confrontation culture method is adopted, test magnaporthe grisea is dripped in the center of a flat plate, and is cultured for 2-3 days; four crosswise corners around the magnaporthe grisea are inoculated with four bacterial strains respectively, and culture is carried out for 5-6 days; through observation, a bacterium having a bacteriostatic effect is the antagonistic bacterium obtained through screening. The antagonistic bacterium having an obvious inhibiting effect on magnaporthe grisea of rice is obtained; an antimicrobial spectrum experiment proves that the antagonistic bacterium also has an inhibiting effect on fusarium graminearum, aspergillus fumigatus and candida albicans. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the screening efficiency can be remarkably improved, and the antagonistic bacterium obtained by separation can be used as a biocontrol bacterium for being prepared into a microbial preparation, thus providing a basis for biological control over diseases.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Strain of lactobacillus pentosus as probiotic
ActiveUS20160193260A1High activityIncrease capacityAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsBacterial vaginosisCandida famata
Provided is the new strain Lactobacillus pentosus CECT 7504 and compositions and products comprising said strain and uses in the prevention and / or treatment of candidiasis (oral, intestinal and vaginal) and of bacterial vaginosis.
Owner:GYNEA LAB
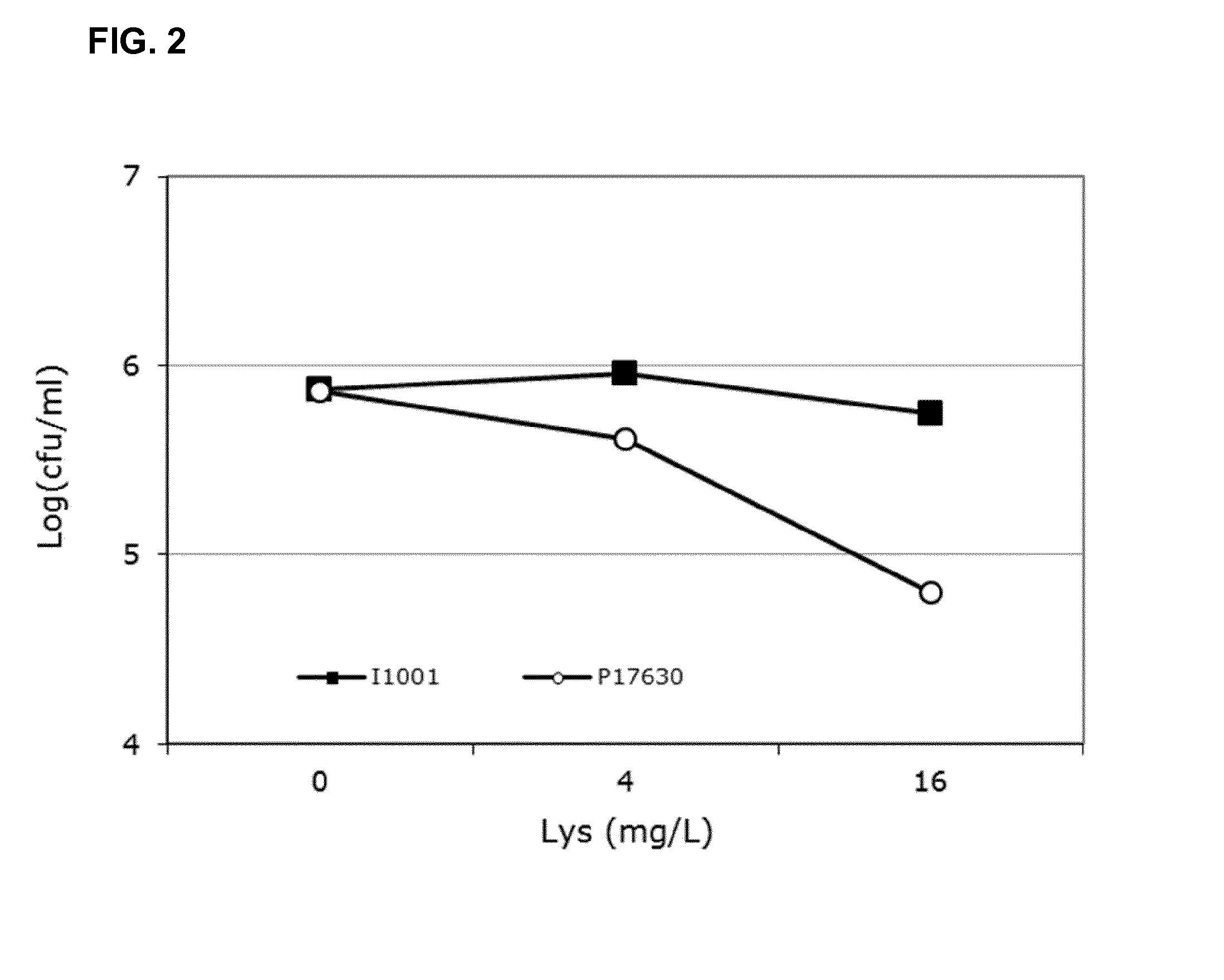
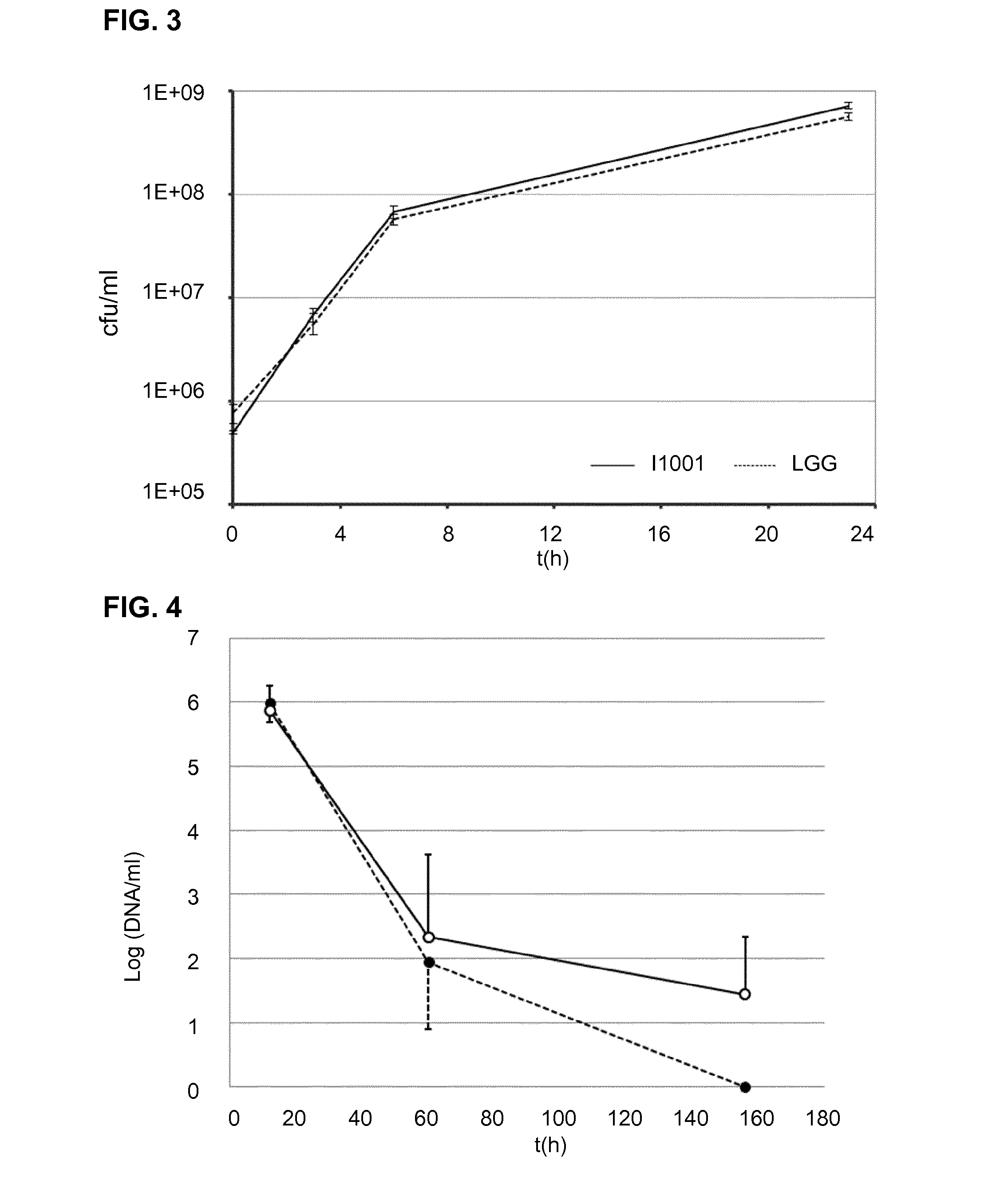
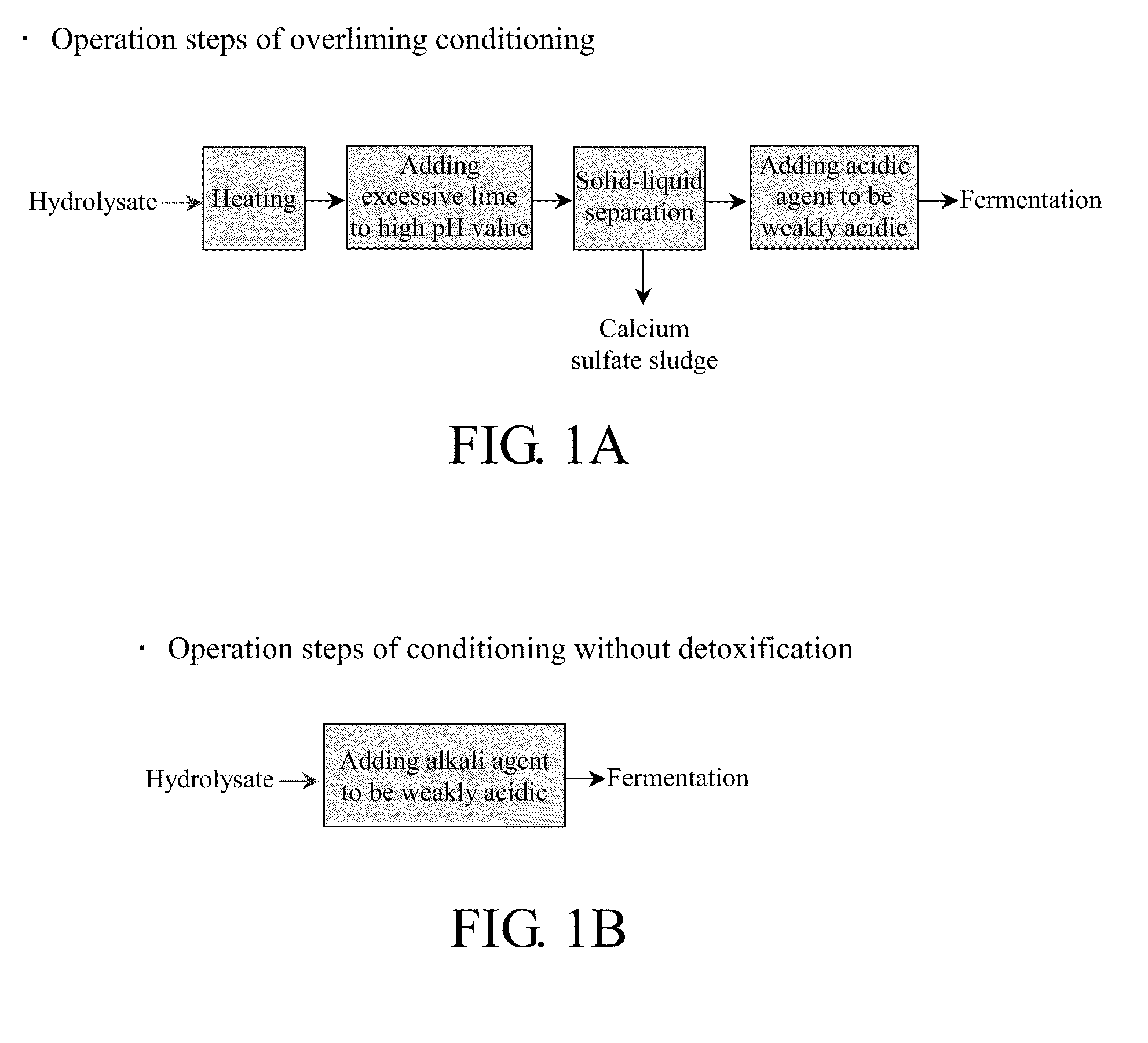
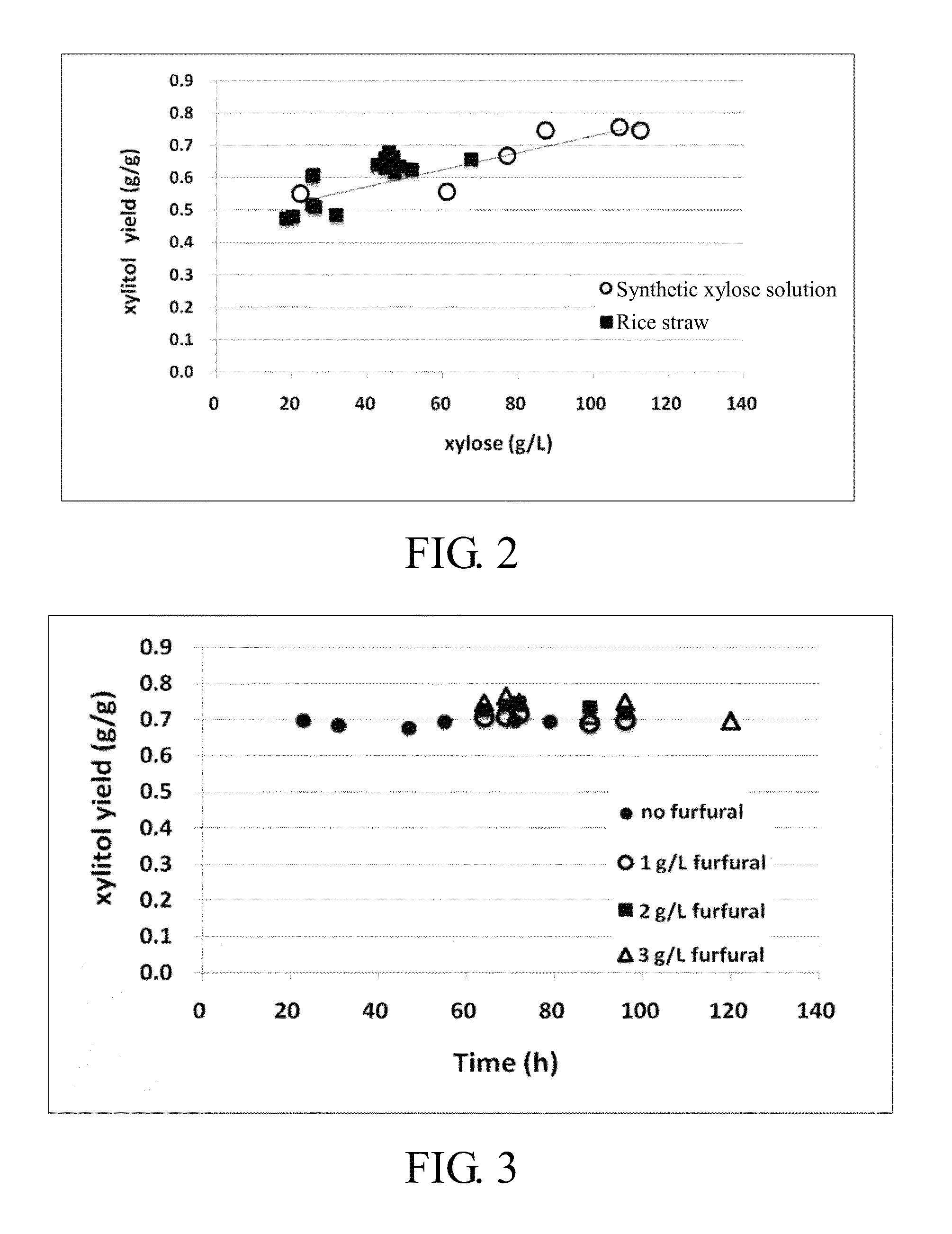
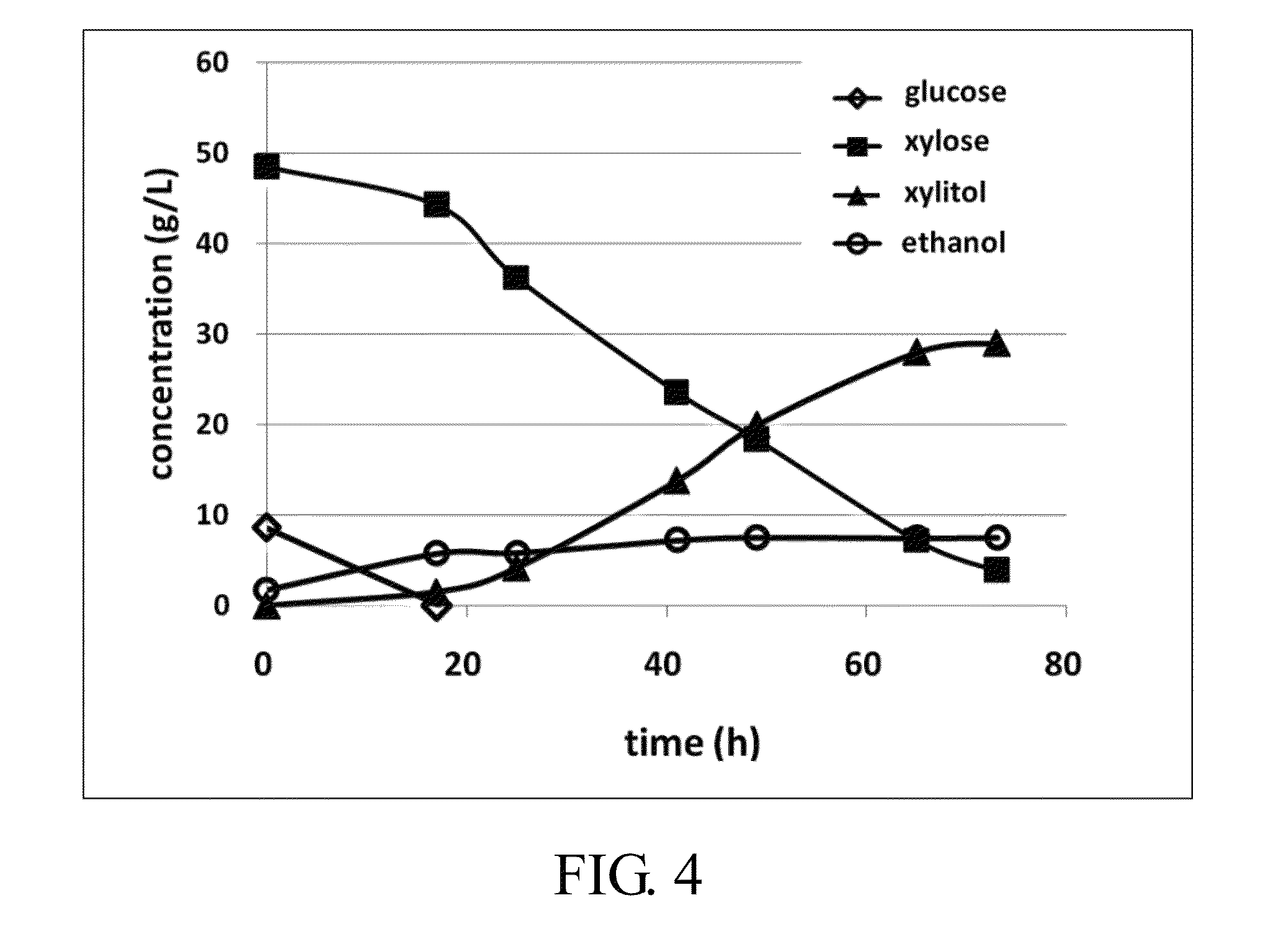
Method for producing xylitol from lignocellulosic hydrolysates without detoxification
InactiveUS8409835B2Improve toleranceValid conversionSugar derivativesMicroorganismsCelluloseHydrolysate
A method for producing xylitol by fermentation of lignocellulosic hydrolysates without detoxification is provided. By using the originally isolated yeast Candida sp., xylose can be effectively converted into xylitol. The invention also provides the Candida strain having high furfural tolerance, and is capable to produce xylitol from various types of non-detoxified lignocellulosic hydrolysates, in which the overall utilization of xylose in hydrolysate can reach over 95%.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
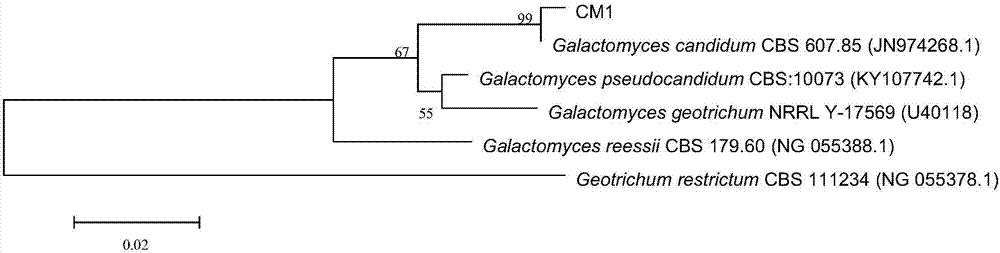
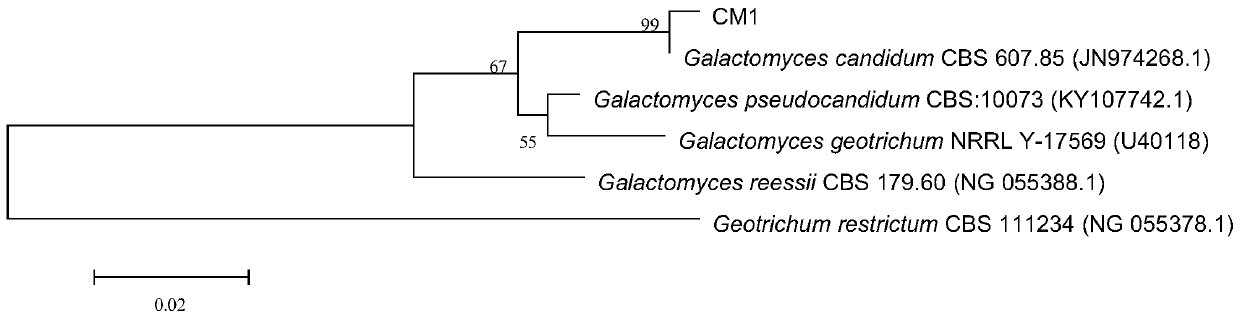
CM1 (Galactomyces candidum) capable of degrading cephalosporin antibiotics and application thereof
ActiveCN107955795AReduce the cost of trainingEasy to useFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismAntibiotic Y
The invention relates to CM1 (Galactomyces candidum) capable of degrading cephalosporin antibiotics and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The bacterial strain is preserved in the common microorganism center of the Chinese microorganism bacterial strain preservation management committee on November 10, 2017, and the preservation number is CGMCC NO.14633. The bacterial strain is easyto culture, grows quickly, and has the function of degrading cephalosporin antibiotics, and meanwhile the toxicity and inhibition effects of cephalosporin antibiotics on gram-positive bacteria can bedegraded and removed. The CM1 can be applied to fungicide production and treatment of waste of cephalosporin antibiotics production enterprises and residual cephalosporin antibiotics in the environment, and the harm of cephalosporin antibiotics to the environment and people is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Lactobacillus rhamnosus and application thereof
ActiveCN110172420AEnhanced inhibitory effectImprove survival rateAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsLactobacillus rhamnosusCandida famata
The invention discloses a strain of Lactobacillus rhamnosus. The strain with the preservation name of Lactobacillus rhamnosus B156, was preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on September 10, 2018, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.16453. The invention further discloses application of the Lactobacillus rhamnosus in preparing medicines inhibiting Candida albicansand Vibrio vulnificus, health care products or common food, and in preparing a preparation prolonging survival time of bagging planting of Anoectochilus roxburghii tissue culture seedlings. The Lactobacillus rhamnosus B156 provided by the invention and fermented yoghurt prepared by the strain can remarkably inhibit the growth of the Candida albicans; the strain can remarkably improve the survivalrate of zebra fish attacked by the Vibrio vulnificus, and remarkably prolong the survival time of the bagging planting of the Anoectochilus roxburghii tissue culture seedlings. Therefore, the Lactobacillus rhamnosus B156 provided by the invention has relatively high social application value.
Owner:INST OF AGRI ENG TECH FUJIAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cladosporium sp. strain, and extract and application thereof
The invention discloses a Cladosporium sp. strain, and an extract and application thereof. The Cladosporium sp. FS86 is collected to China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on March 27th, 2014, wherein the address is Wuhan University, Wuhan City, PRC, and the collection number is CCTCC NO: M2014108. The fermentation extract has obvious inhibitory effects on Candida albicans, Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus flavus, Trichoderma viride, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, Cylindrocladium scoparium or Curvularia lunata. Therefore, the invention provides scientific references for developing new anti-pathogenic fungus drugs and exploring deep-sea-fungus-derived natural active substances.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM
Novel leuconostoc citreum and fermented foods using the same as a starter, and compositions thereof
ActiveUS20170006905A1Induce fermentation flavor and taste qualityInhibit deteriorationCosmetic preparationsBacteriaMonilinia laxaCosmetic ingredient
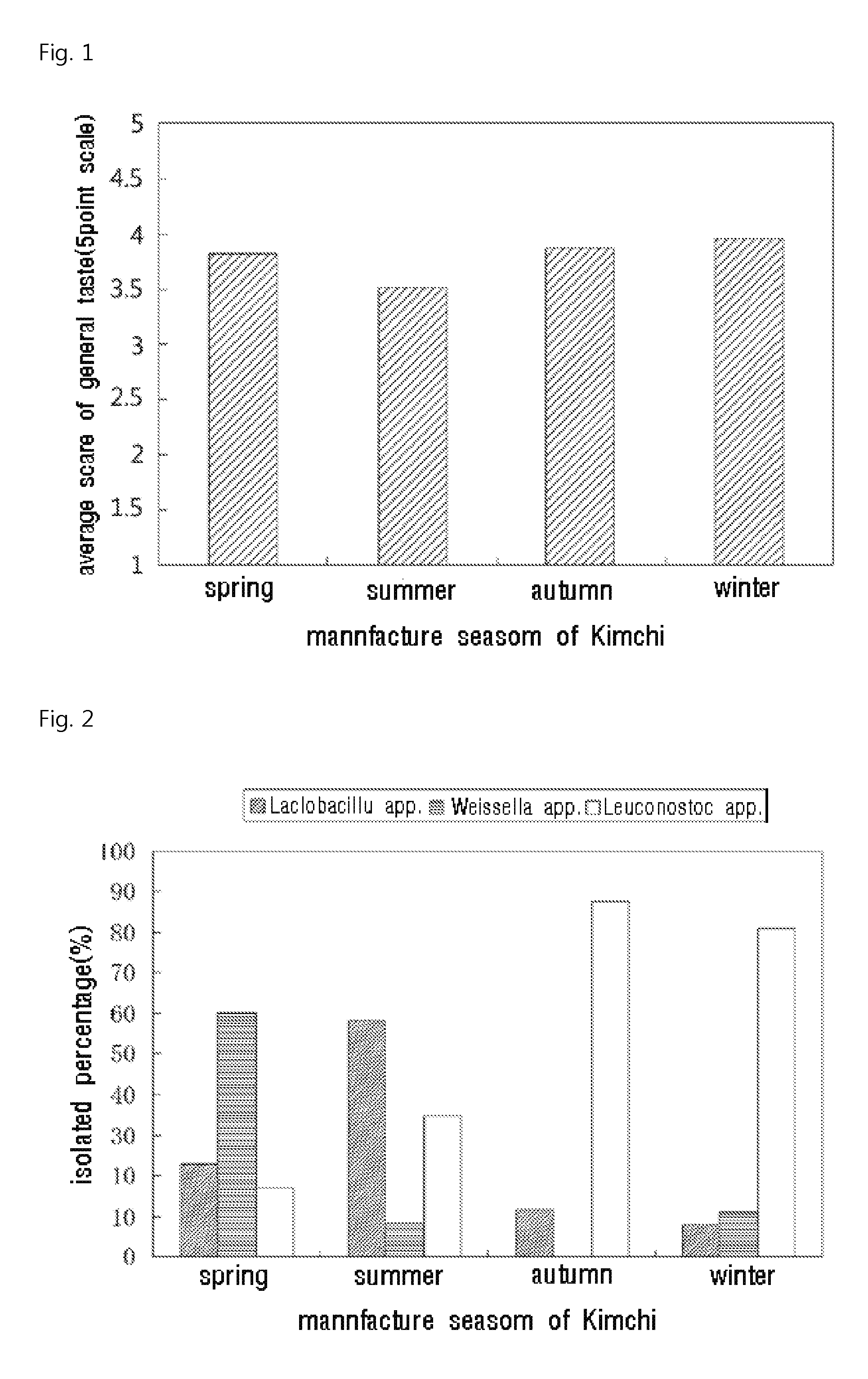
The present invention relates to Leuconostoc citreum CJGN34 KCTC 10974BP lactic acid bacteria, fermented foods including kimchi manufactured using the lactic acid bacteria as a starter, and lactic acid bacteria composition comprising of the lactic acid bacteria. The novel Leuconostoc citreum CJGN34 of the present invention enhances the general taste quality of kimchi; increases the intrinsic complex sour taste and carbonated taste of kimchi manufactured by traditional manufacturing method in wintertime; and regularly sustains the fermentation quality during the year; particularly, has an effect for controlling the deterioration of fermentation quality in the summer in which the taste quality deteriorates. Thus, the lactic acid bacteria of the present invention can be used as a starter in fermented foods including kimchi, or as a drug medicine in the form of a tablet or capsule mixed with carriers or additives, or a s probiotics for foods; or applied in cosmetic ingredients by mixing in a certain amount. Therefore, the lactic acid bacteria of the present invention can be used in a manner commonly applied in various fields of technology such as medicine, food, feed, cosmetics or the like.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Solid culture medium suitable for co-growing Candida albicans and staphylococcus
InactiveCN102517240AImprove the nutritional environmentGood growthFungiBacteriaStaphylococcus cohniiCandida famata
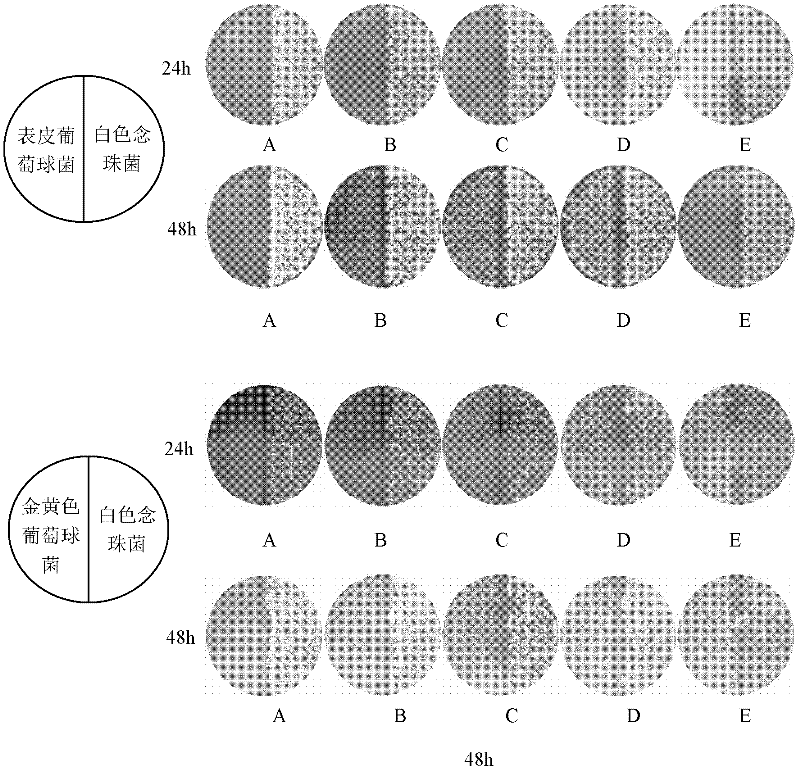
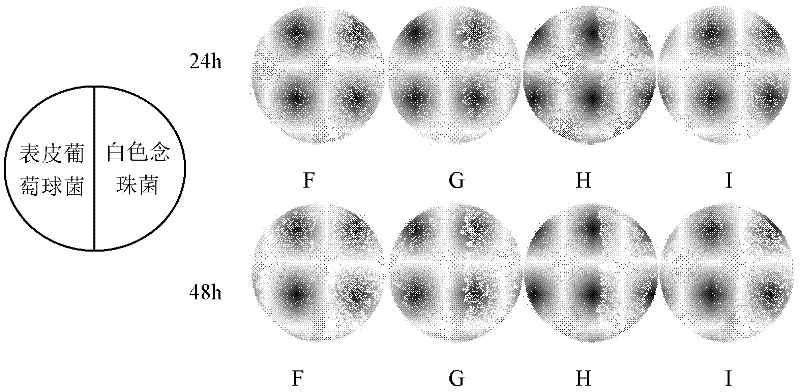
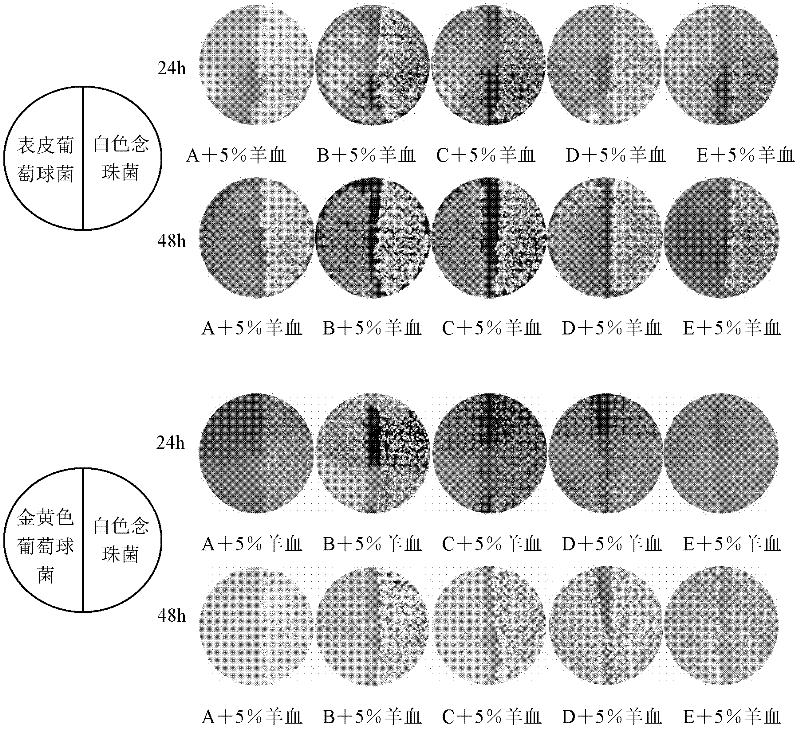
The invention discloses a culture medium for co-culturing Candida albicans and staphylococcus, and in particular relates to the influence of different nutritional components, calcium ions and blood on the growth of the Candida albicans and the staphylococcus and discussion on the proportion of a culture medium which is the most suitable for growing the Candida albicans and the staphylococcus. The culture medium comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 0.15 to 0.25 percent of yeast extract, 1.15 to 1.25 percent of peptone, 0.3 to 0.5 percent of glucose, 0.375 to 0.425 percent of NaCl, 0.25 to 0.255 percent of beef powder and 1.575 to 1.625 percent of agar powder. The Candida albicans and staphylococcus aureus / staphylococcus epidermidis are researched, and the influence of the culture medium on the size and shape of bacterial colonies of the Candida albicans and the staphylococcus aureus / staphylococcus epidermidis is directly evaluated by a streak plate method. Results show that the Candida albicans and the staphylococcus aureus / staphylococcus epidermidis can be well grown when the culture medium is adopted.
Owner:QIANFOSHAN HOSPITAL OF SHANDONG
Gene chip for detecting 15 clinical common pathogenic microorganisms
ActiveCN102080127BWith monitoring functionStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceCandida tropicalisRhizopus oryzae
The invention discloses a gene chip for detecting 15 clinical common pathogenic microorganisms. The gene chip comprises specific detection probes fixed on a solid phase vector, wherein the probes are designed for 16SrRNA gene and ITS gene sequences of staphylococcus aureus, klebsiella pneumoniae, pseudomonas aeruginosa, proteus mirabilis, Escherichia coli, shigella, enterobacter aerogenes, pseudomonas fluorescens, candida albicans, candida glabrata, candida tropicalis, candida parapsilosis, aspergillus terreus, aspergillus flavus and rhizopus oryzae, and screened and verified by repeated tests, and have high hybridization specificity and accuracy. The chip provided by the invention ensures simple detection operations and relatively lower cost, saves time, is applied to the screening of the clinical common pathogenic microorganisms, the early rapid diagnosis of critical patients and the diagnosis of suddenly occurring infection event pathogens and favorable for clinically rapidly diagnosing infection sources and functions in the early detection and early diagnosis of clinical diseases.
Owner:GUANGZHOU IMPROVE MEDICAL TECH CO LTD +1
Herbal care solution with antibacterial function
InactiveCN108578646AProtect healthRaw materials are easy to getAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsEscherichia coliMonilinia laxa
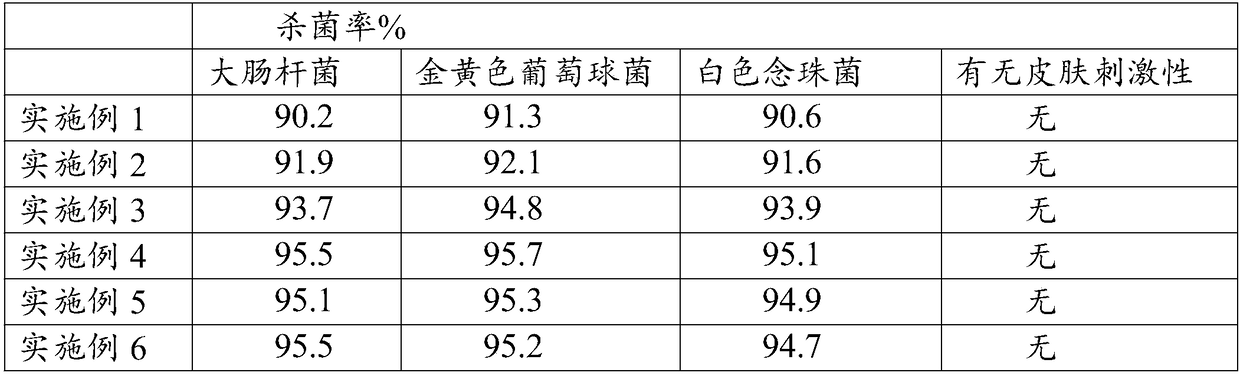
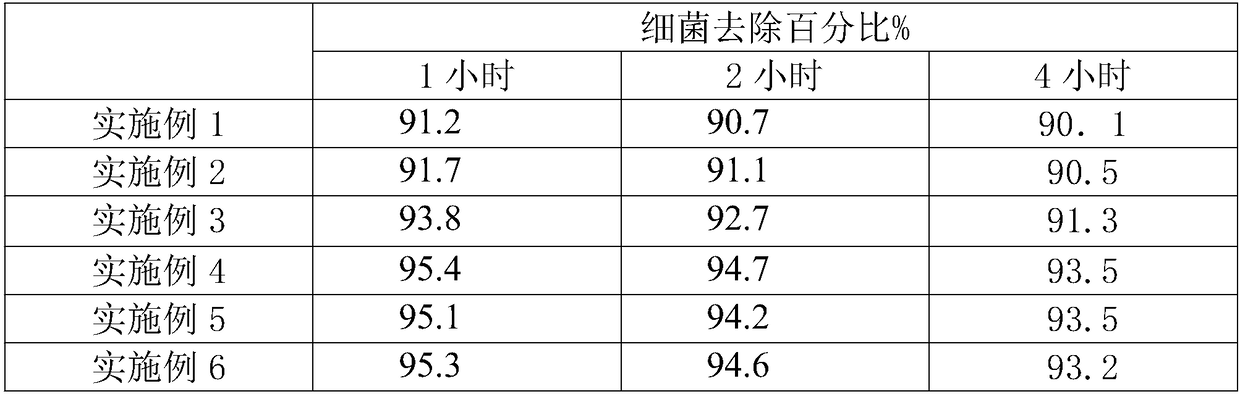
The invention discloses herbal care solution with an antibacterial function. The herbal care solution comprises, by weight, 30-40 parts of camellia meal, 28-38 parts of oriental latrine fly larvina, 25-35 parts of blueberry leaves, 25-35 parts of Mongolian dandelion herbs, 20-30 parts of euglena gracilis, 19-29 parts of common ducksmeat herbs, 19-29 parts of turmeric rhizomes, 17-27 parts of wormwoodlike motherwort herbs, 15-25 parts of Mongolian snakegourd fruits, 10-20 parts of sappan caesalpinia wood, 1-3 parts of cationic surface active agents and 35-45 parts of butylene glycol. The herbalcare solution with the antibacterial function can clear heat, remove toxicity, resist bacteria, inflammation and viruses, relieve itching, remove slough, facilitate growth of tissue regeneration andinhibit colibacillus, staphylococcus aureus and candida albicans in a long term, the antibacterial rate is 95.5%, 95.7% and 95.1%, and the herbal care solution is non-irritating to human bodies.
Owner:HEFEI XIAKANG ELECTRONICS COMMERCE CO LTD
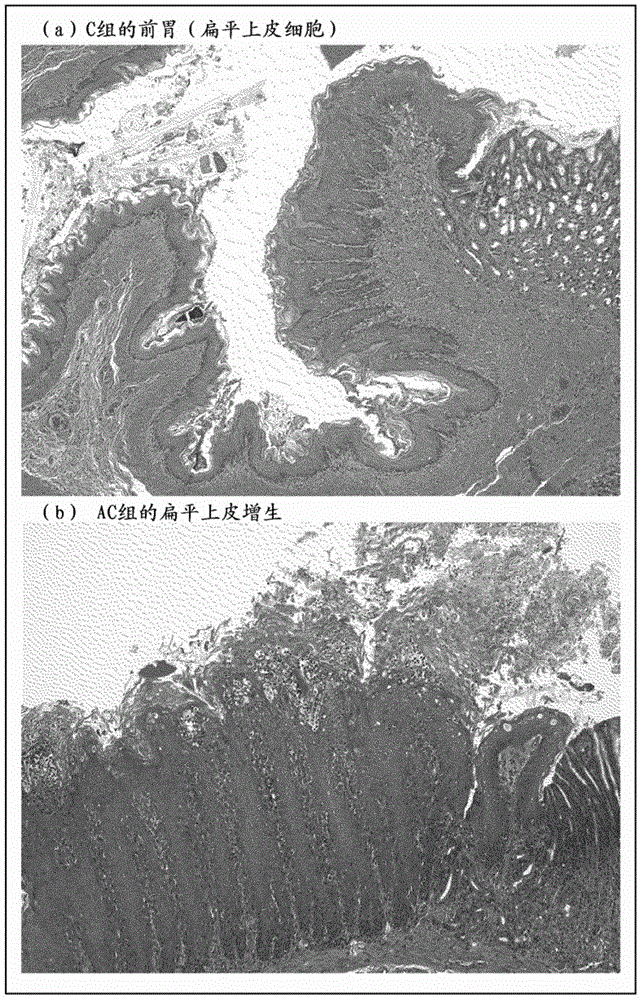
Prophylactic agent for squamous carcinoma, squamous carcinoma model anima, and method for producing said model animal
Provided are: a fermented material which is effective for the prevention of squamous carcinoma that is developed by Candida infection; a model animal for squamous carcinoma that is developed by Candida infection, in which the difference among individuals is smaller than those in conventional model animals and pharmacological efficacy can be evaluated more properly; and a method for producing the model animal. A prophylactic agent for squamous carcinoma that is developed by Candida infection, which comprises a fermented material produced by fermenting milk with L. bulgaricus, S. thermophilus and L. gasseri as an active ingredient.
Owner:MEIJI CO LTD +1
Candida albicans infection mould and construction method thereof
InactiveCN101078011AEasy to operateEasy to observeGenetic engineeringFermentationWhole bodyCandida famata
An animal model infected by candida albicans where the primary infection is the local abscess in the ear and is accompanied by the infection of candida albicans in all organs. The method is to inject the candida albicans into the subcutaneous of the ear of a rabbit and the concentration of the candida albicans is 1X105 / ml-1X1010 / ml. By doing so, not only the local abscess in the ear is formed, but all organs are infected through blood circulation. In this invention, the model is easy to obtain; the local abscess in the ear can be observed conveniently; the two ears can be compared and the infection of all the organs can be detected at the same time. Thus, the present invention provides a simple and convenient animal model for developing new methods and medicines for the treatment of candida albicans.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Microbial agent for decomposing TVOC (total volatile organic compound) and preparation method of microbial agent
PendingCN109082392AQuality improvementProtect your healthFungiGas treatmentESCHERICHIA COLI ANTIGENMicrobial agent
The invention relates to a microbial agent for decomposing TVOC (total volatile organic compound). Strains are added into fermentation liquid base solution and fermented to obtain the microbial agentand include rhodopseudomonas, rhodospirillum, lactobacillus, candida, nitrate bacteria, streptomyces and chromatium, and the total bacteria density of the microbial agent is (1-10)*10<8> bacteria / L. The microbial agent can be directly sprayed into air to treat the TVOC after dilution. Harmful substances in the TVOC can be purified, decomposed and transferred into harmless and odorless substances.Pathogenic bacteria such as pathogenic escherichia coli, mycetes, staphylococcus aureus and candida albicans can be removed, air quality is thoroughly improved, and fitness is protected.
Owner:侯希波 +1
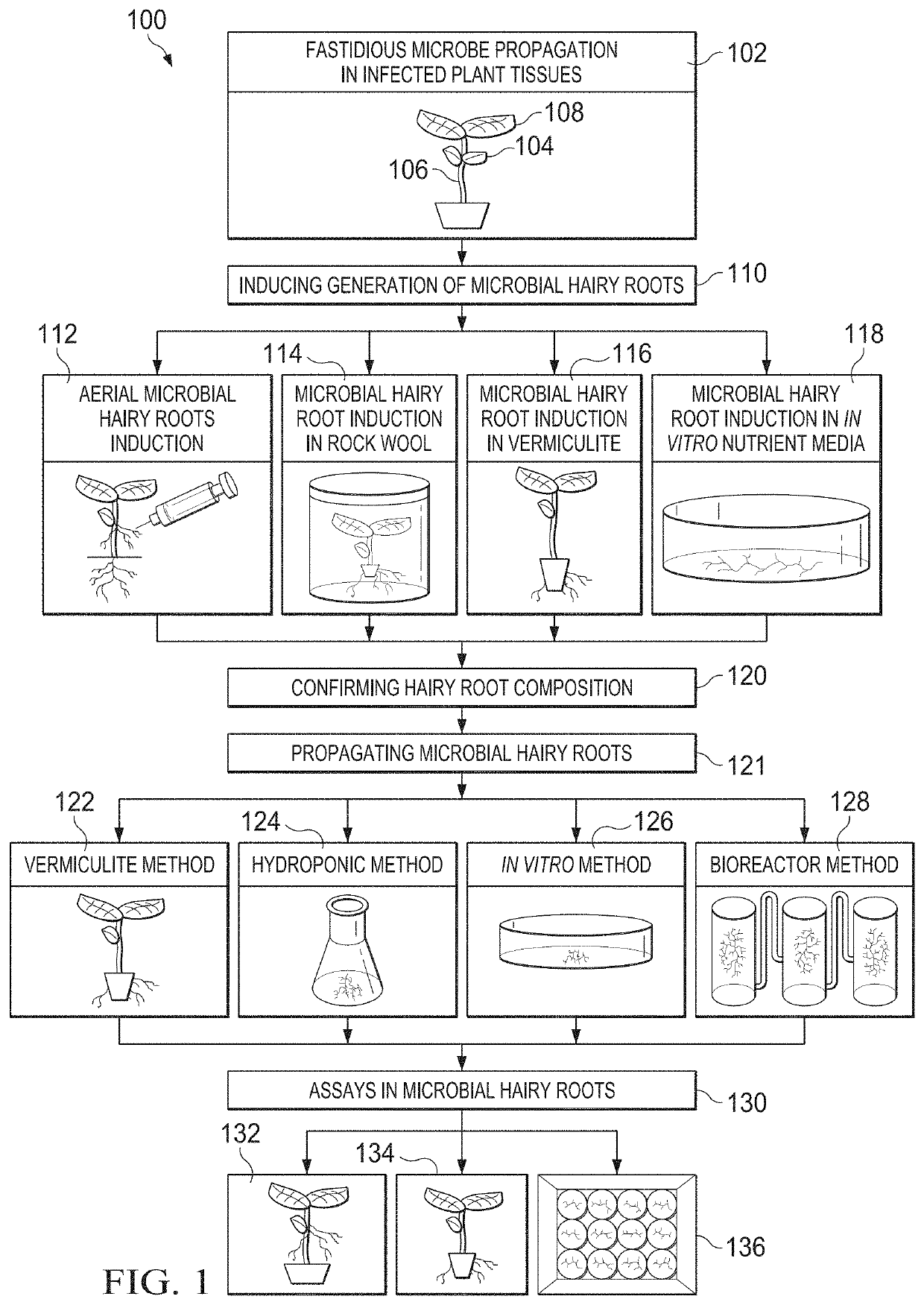
Methods, compositions, and systems for culturing and characterizing fastidious plant microbes
ActiveUS20190367962A1Easy, rapid and scalable platform to cultureMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant cellsDiseaseCandida famata
Numerous plant microbes, including the vascular-limited Candidatus spp.—causal agents of citrus greening and potato zebra chip diseases—are non-culturable. The present disclosure relates, according to some embodiments, to compositions, methods and systems for culturing such organisms. For example, the present disclosure relates to methods for culturing, propagating, and characterizing fastidious vascular-colonizing microbes using a hairy root system (e.g., in vitro, in planta). The present disclosure relates, in some embodiments, to methods for cultivating a fastidious plant microbe including: contacting a plant (e.g., a tomato plant, a potato plant, a citrus plant) colonized by a fastidious plant microbe (e.g., Xylella fastidiosa, Candidatus Liberibacter spp.) with a suspension of R. rhizogenes under conditions that permit induction of hairy roots colonized with the fastidious plant microbe, and propagating the colonized microbial hairy roots.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
A method for preventing and eliminating Candida albicans pollution in vitro cell culture of elite ice and snow athletes
InactiveCN103233059APrevent and Eliminate PollutionStrong broad-spectrum antibacterialMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesProtozoaMonilinia laxa
Owner:HARBIN INST OF PHYSICAL EDUCATION
A strain of Geotrichum candidum cm1 degrading cephalosporin antibiotics and its application
ActiveCN107955795BReduce the cost of trainingEasy to useFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAntibiotic drug
The invention relates to a strain of Galactomyces candidum CM1 capable of degrading cephalosporin antibiotics, belonging to the technical field of microorganisms. The strain was deposited in the General Microorganism Center of China Committee for Microorganism Culture Collection on November 10, 2017, with the preservation number CGMCC NO.14633. The strain is easy to cultivate, grows fast, has the function of degrading cephalosporin antibiotics, and can degrade and eliminate the toxicity and inhibitory effect of cephalosporin antibiotics on Gram-positive bacteria. It can be applied to the production of bacterial agents, to deal with the waste of cephalosporin antibiotic production enterprises and the residual cephalosporin antibiotics in the environment, and to reduce the harm of cephalosporin antibiotics to the environment and human beings.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Application of kalopanax saponin A in preparation of anti-candida albicans drugs, drug preparation of kalopanax saponin A, and drug preparation for diseases caused by candida albicans
InactiveCN110403950AReduce adhesionReduce virulenceOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsDiseaseVirulent characteristics
The invention discloses an application of kalopanax saponin A in preparation of anti-candida albicans drugs, a drug preparation of kalopanax saponin A, and a drug preparation for diseases caused by candida albicans. The inhibition of the virulence of candida albicans is used as a breakthrough point, and the effect of low-toxic kalopanax saponin A not easily producing drug resistance on the adhesion, mycelium formation and envelope formation of candida albicans are targetedly evaluated and screened. The results indicate that the toxicity of the kalopanax saponin A to caenorhabditis elegans growth is relatively small, and the kalopanax saponin A itself is indicated to have low toxicity and do not affect the growth of human cells; the kalopanax saponin A can effectively reduce the adhesion ability, yeast-mycelium morphological transformation ability and envelope formation ability of candida albicans at a sub dose lower than the minimum bacteriostasis concentration, has a good effect of reducing pathogenicity of candida albicans and achieves the purpose of the invention not mainly by killing candida albicans, so the kalopanax saponin A does not easily produce drug resistance. The kalopanax saponin A has a good application prospect in the research and development of antifungal drugs, especially in the research and development of the anti-candida albicans drugs.
Owner:XUZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
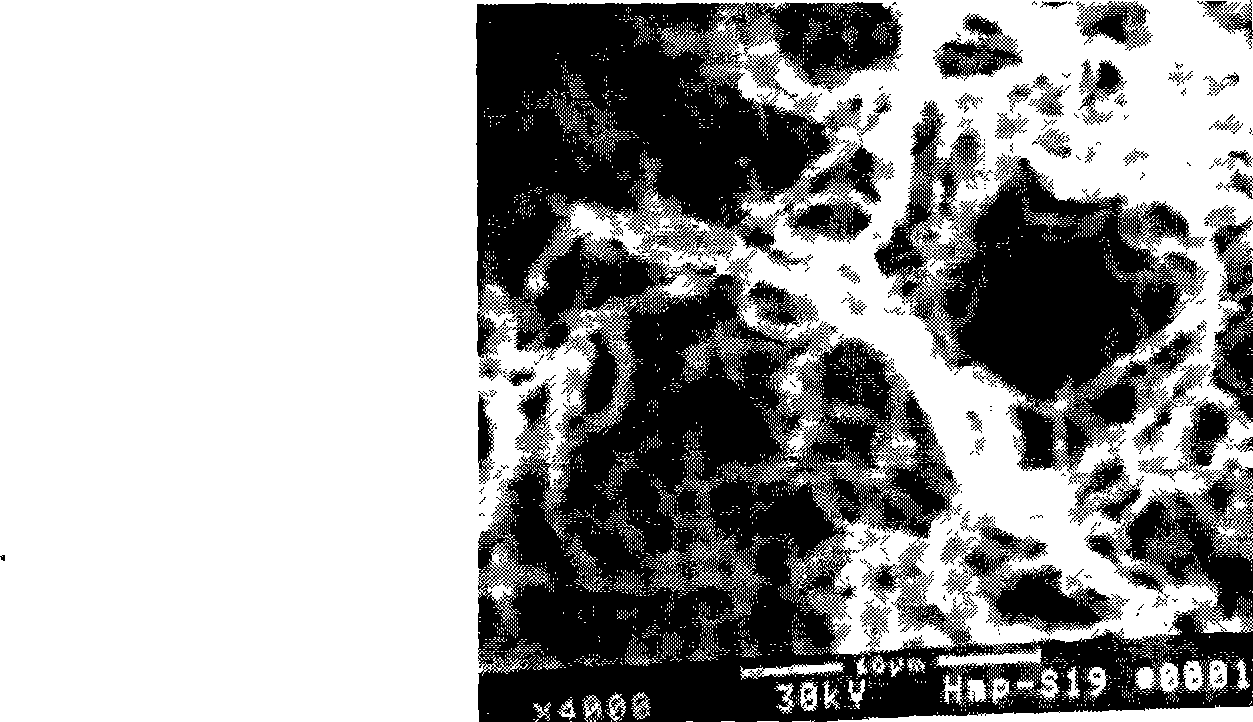
Sea actinomycete with antifungal activity and use thereof
InactiveCN101423805AGood antifungal activityIncrease resistanceBiocideBacteriaCandida famataMonilinia
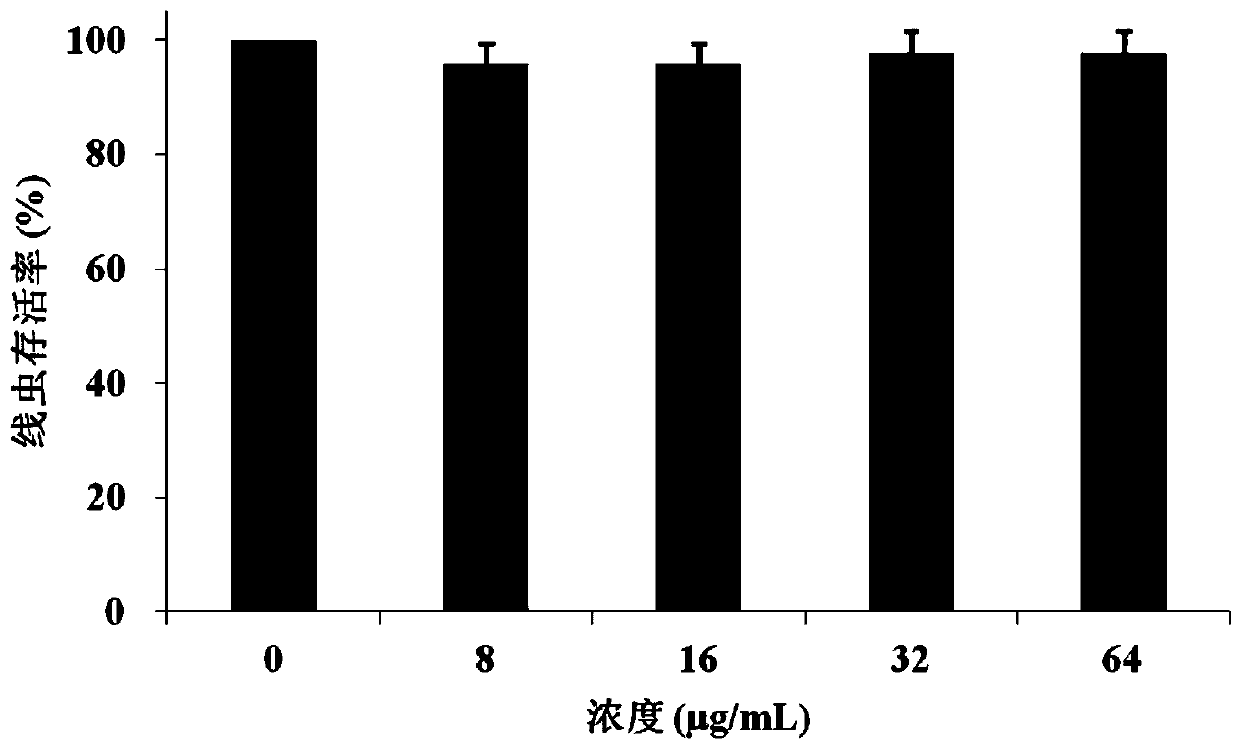
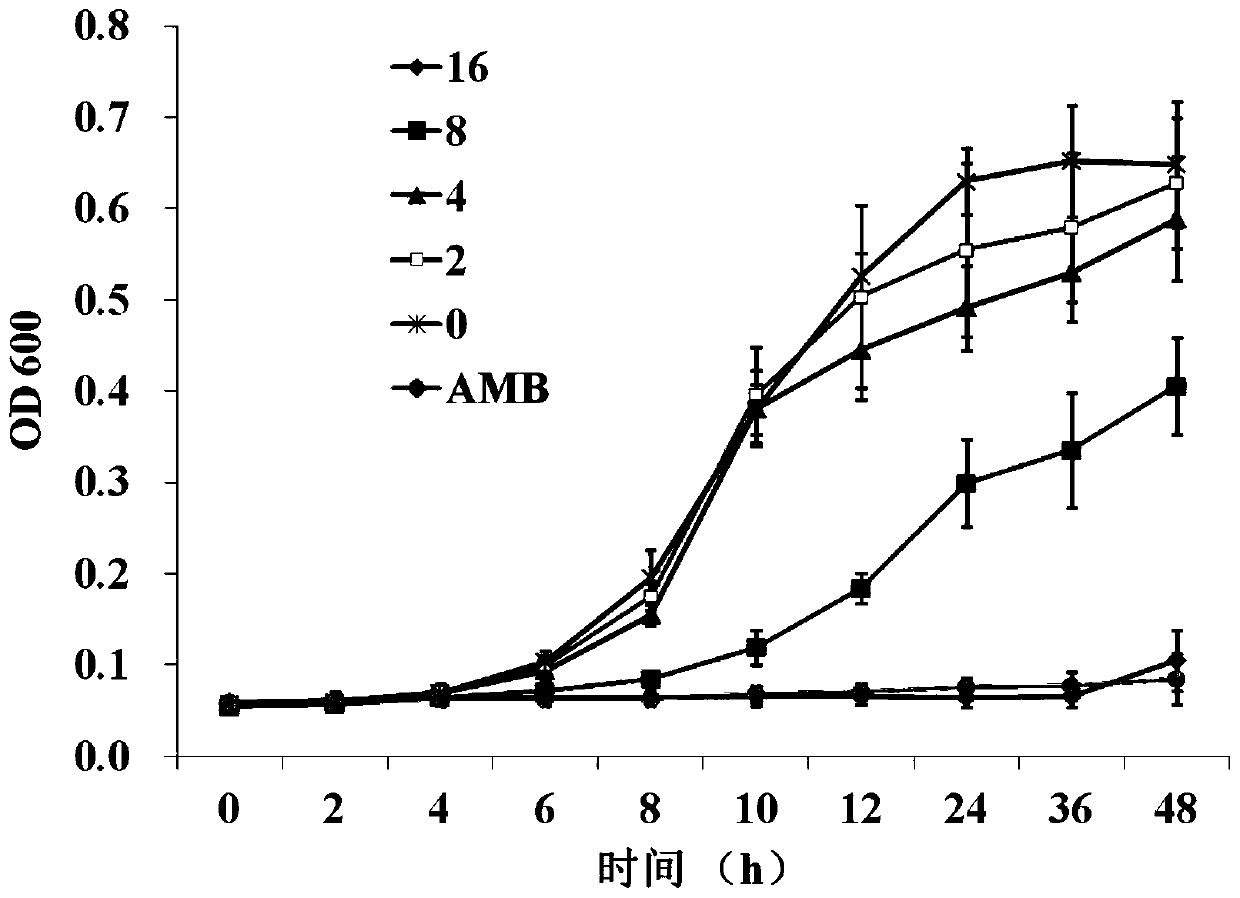
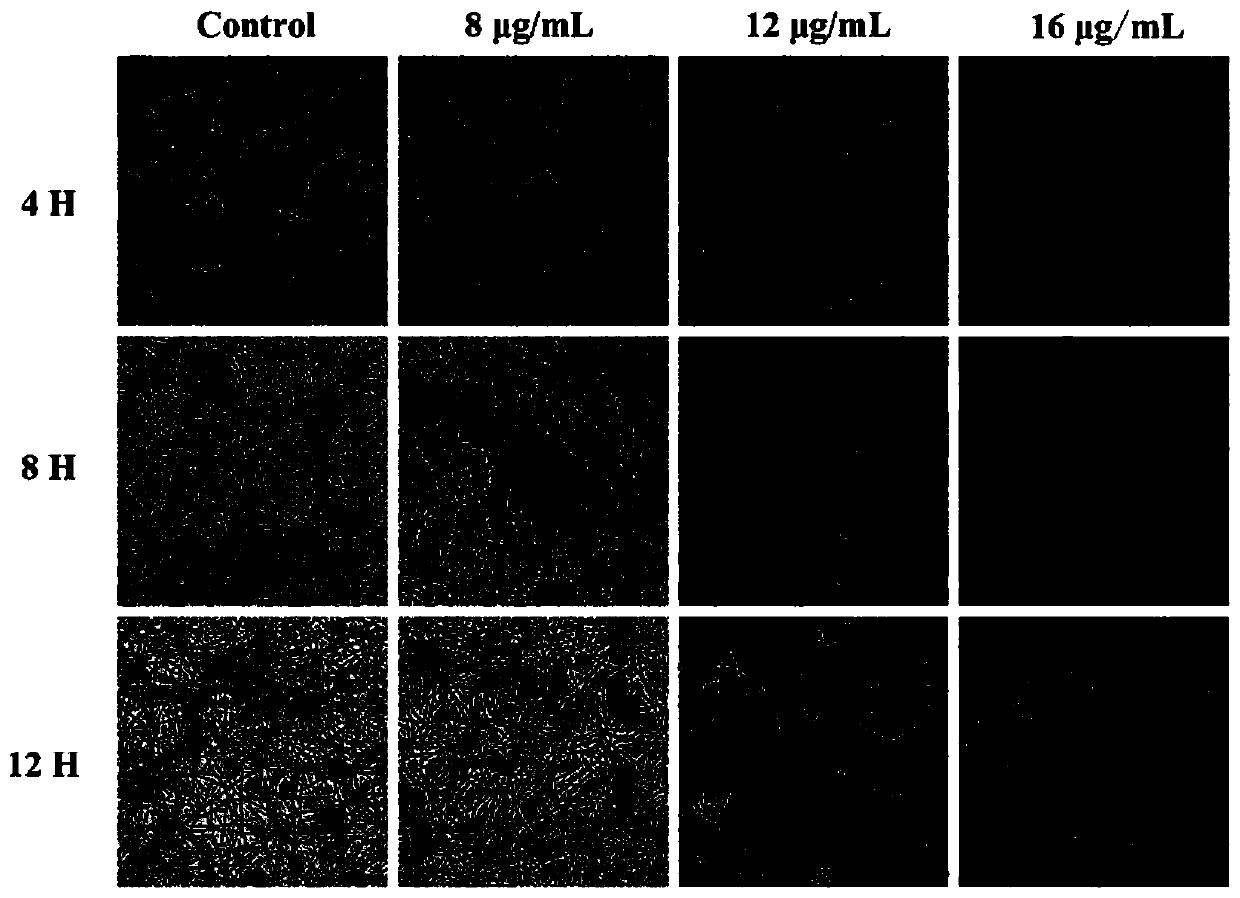
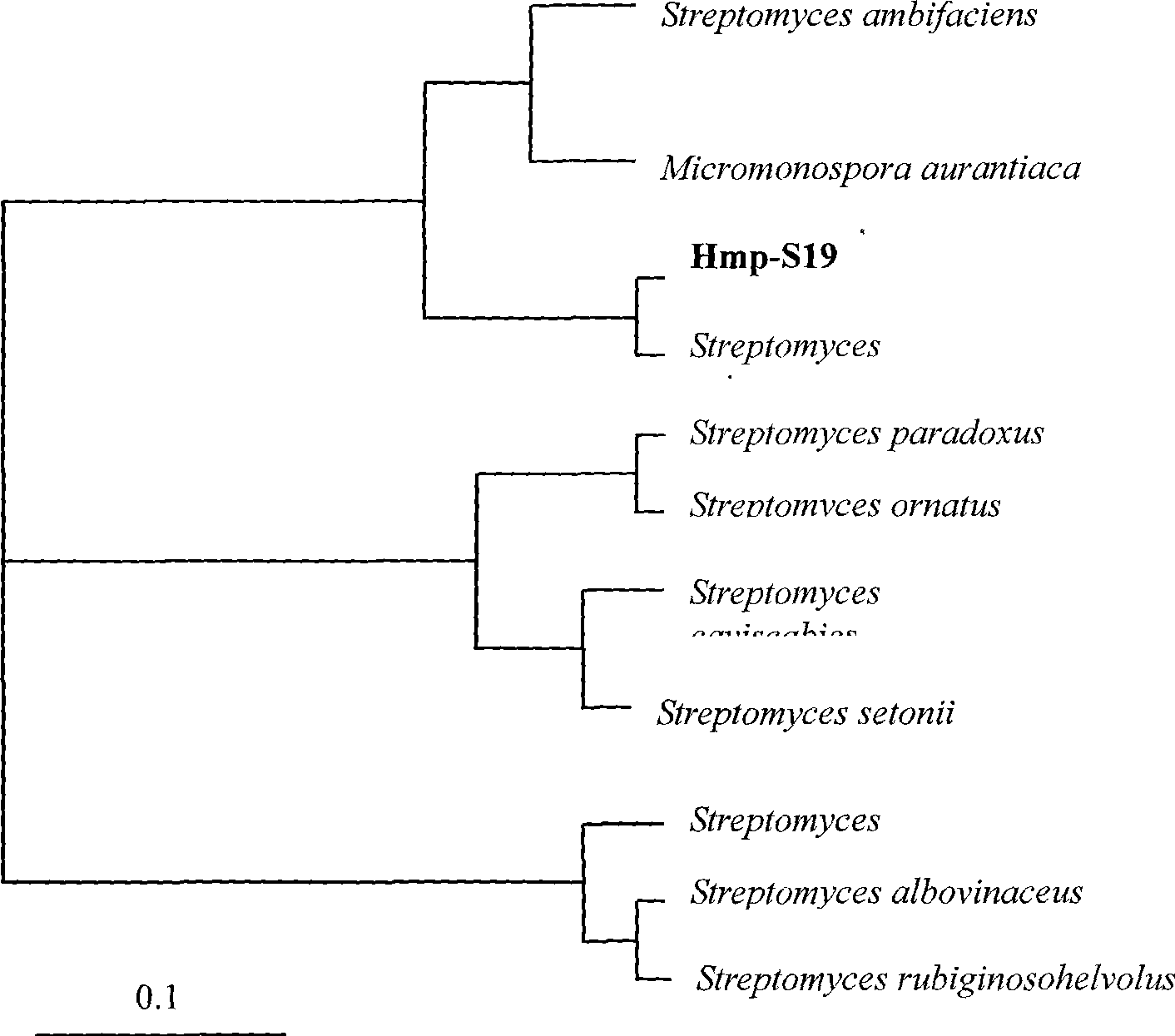
The invention relates to application of marine microorganism as well as prevention and treatment of fungal disease of animals and plants, in particular to marine actinomycete with antifungal activity and application thereof, The marine actinomycete is a strain of a Streptomyces griseus genus and is preserved in China center for type culture collection in April 13, 2007; the CCTCC NO is M 207046; and the diagnostic characteristic is named Streptomyces griseus Hmp-S19. The zymotic fluid of the strain has the functions of resisting Candida albicans, Pyricularia o ryzae, Fuarium oxysporum and other pathogenic fungi, and has stable and lasting effect and huge potential for developing a novel, high-efficient, nontoxic, natural, agricultural and medical drug.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com