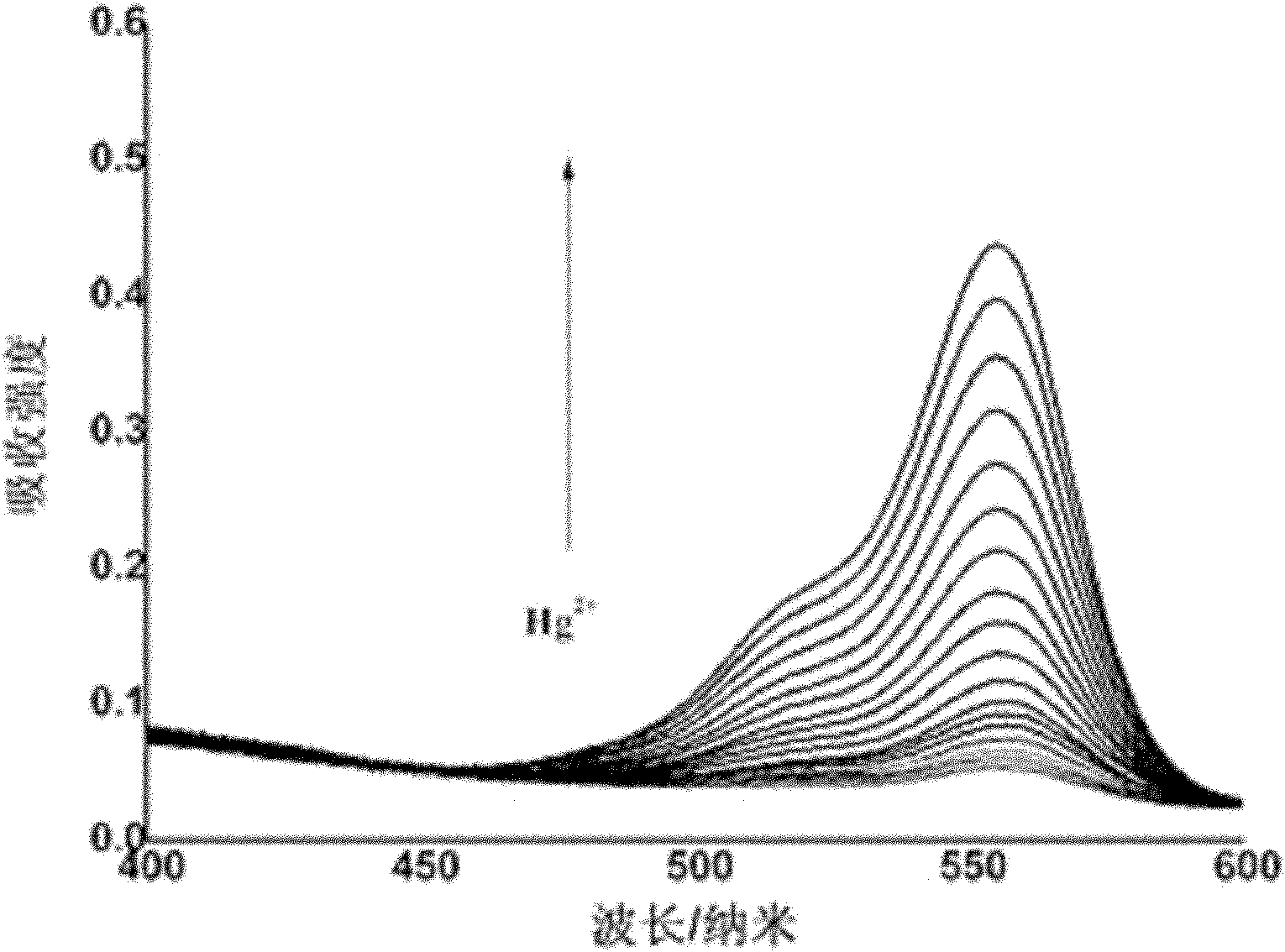
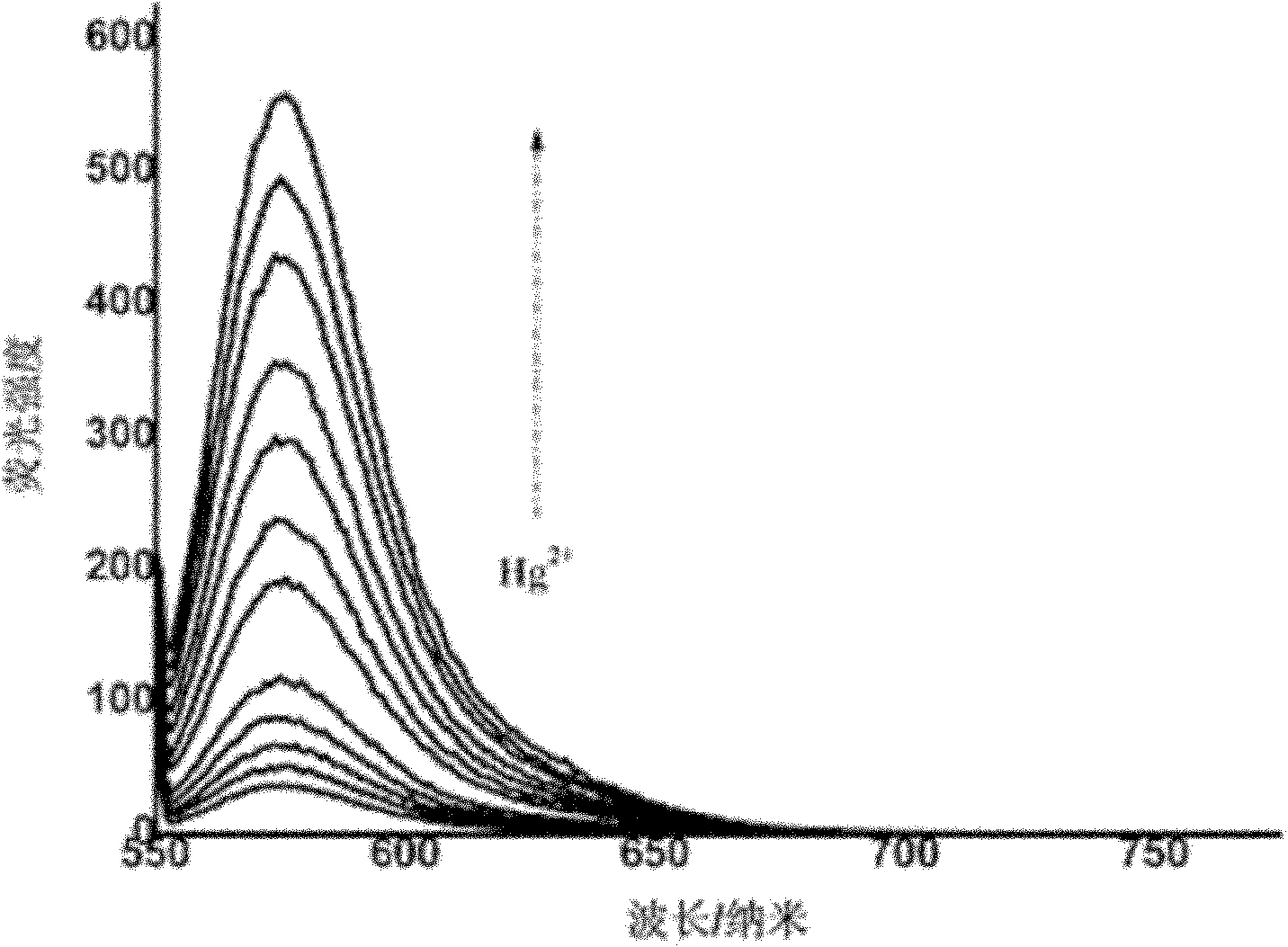
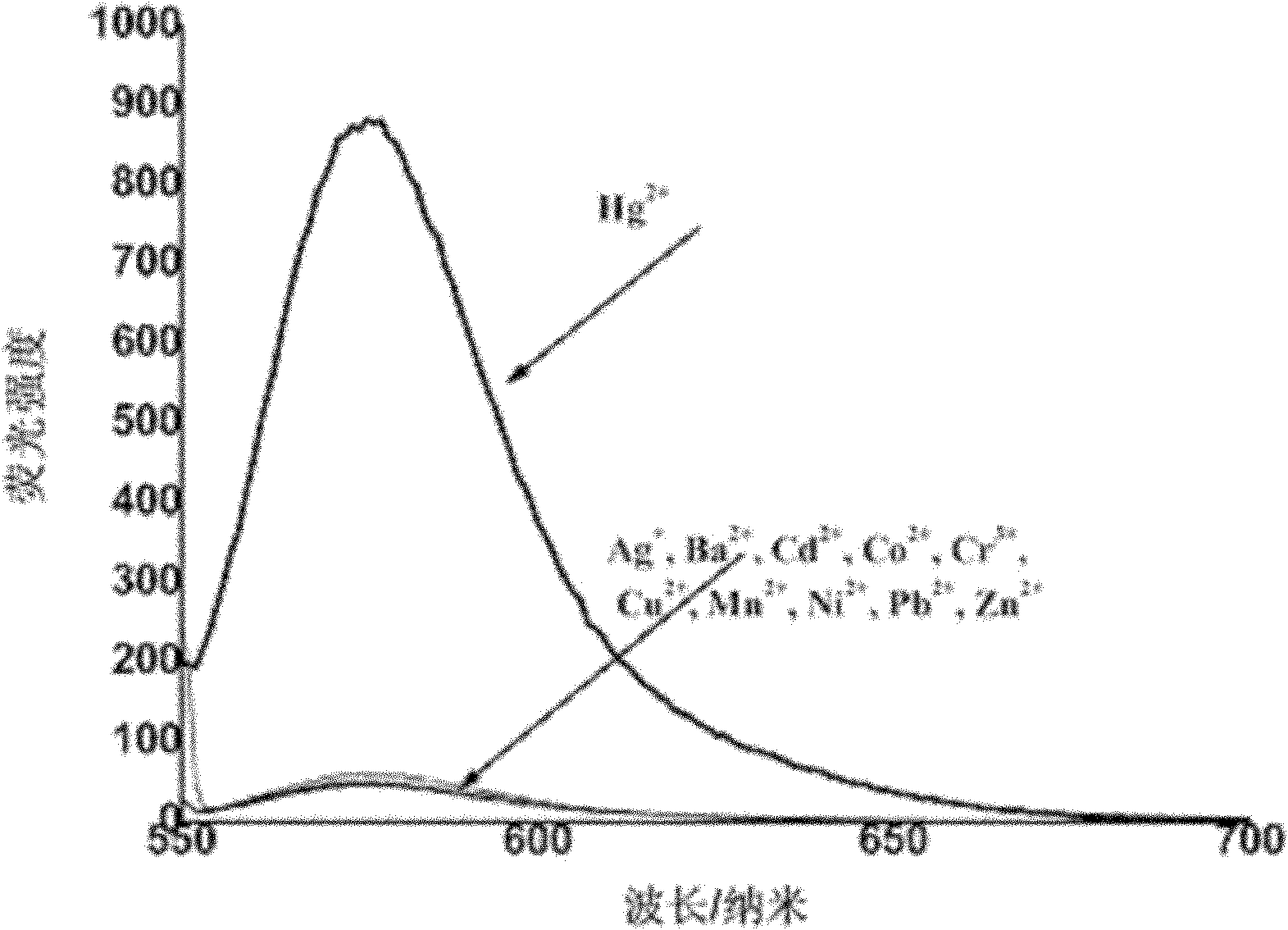
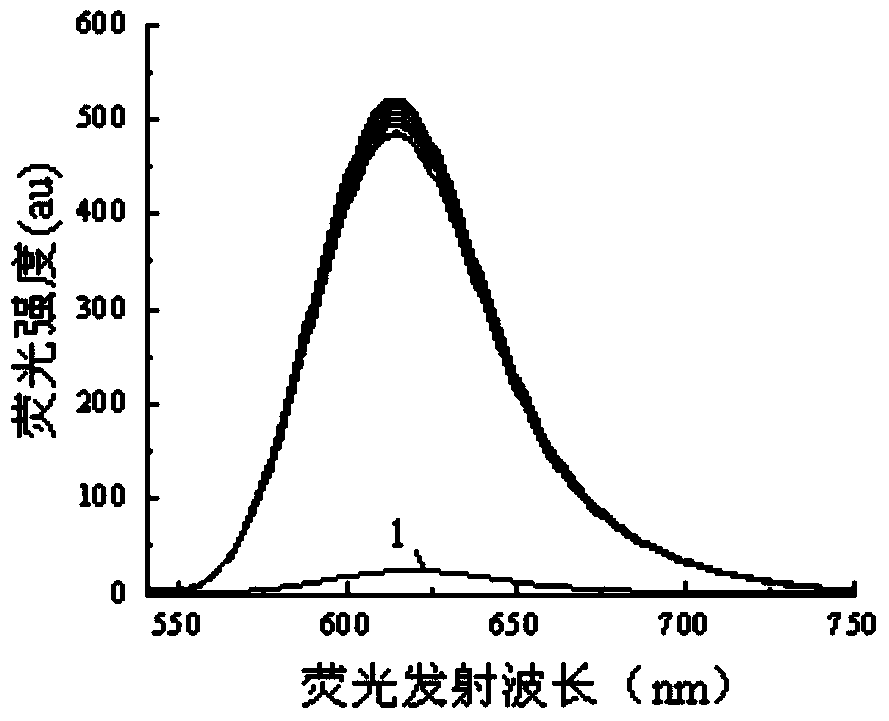
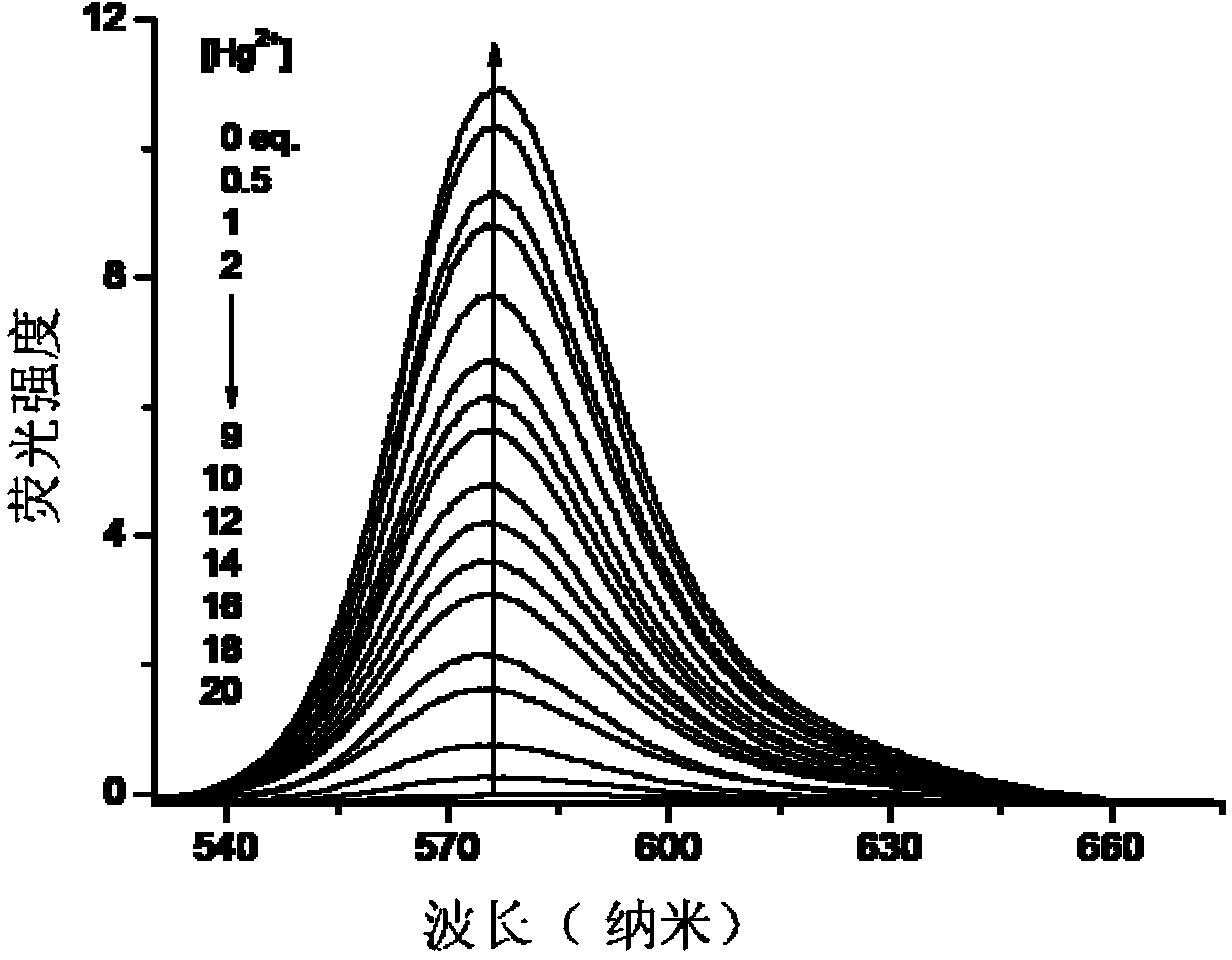
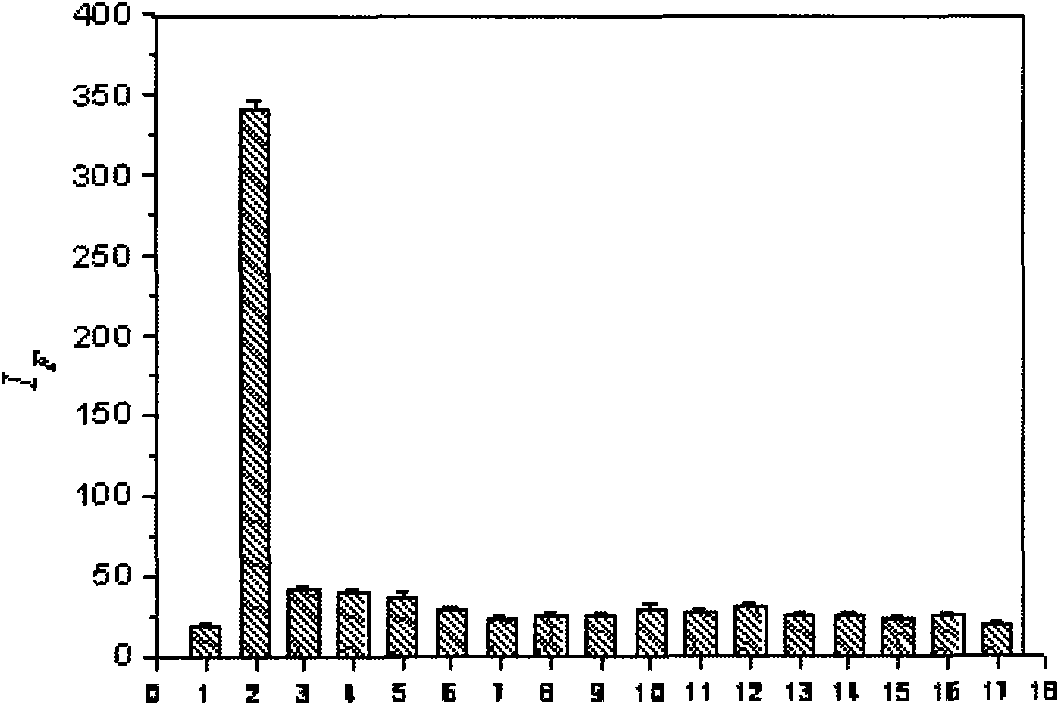
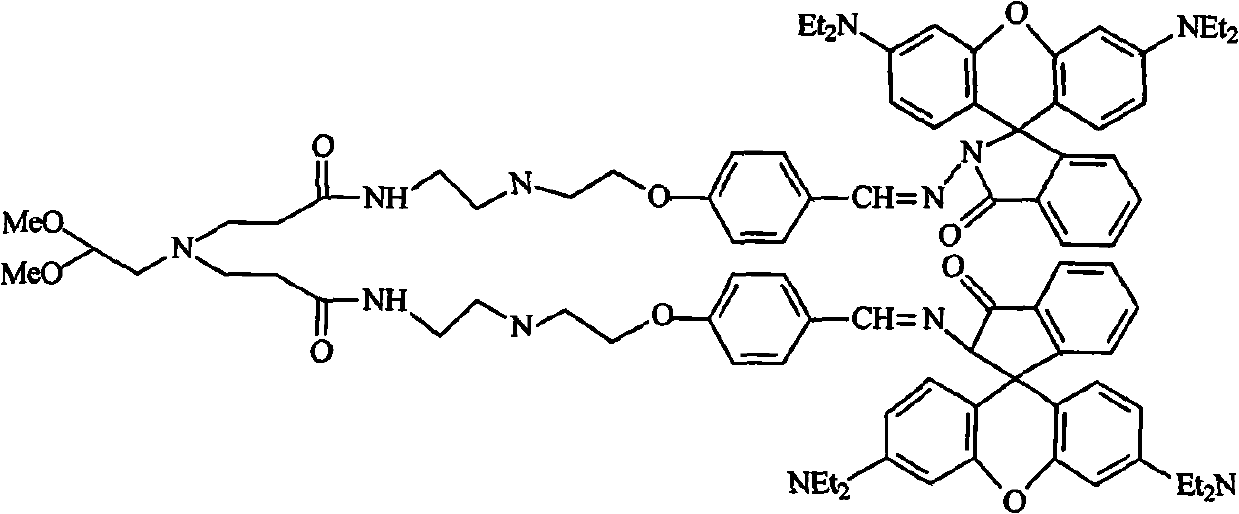
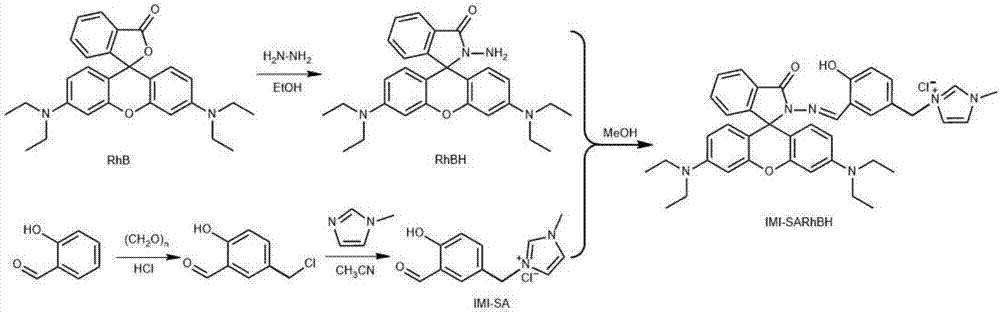
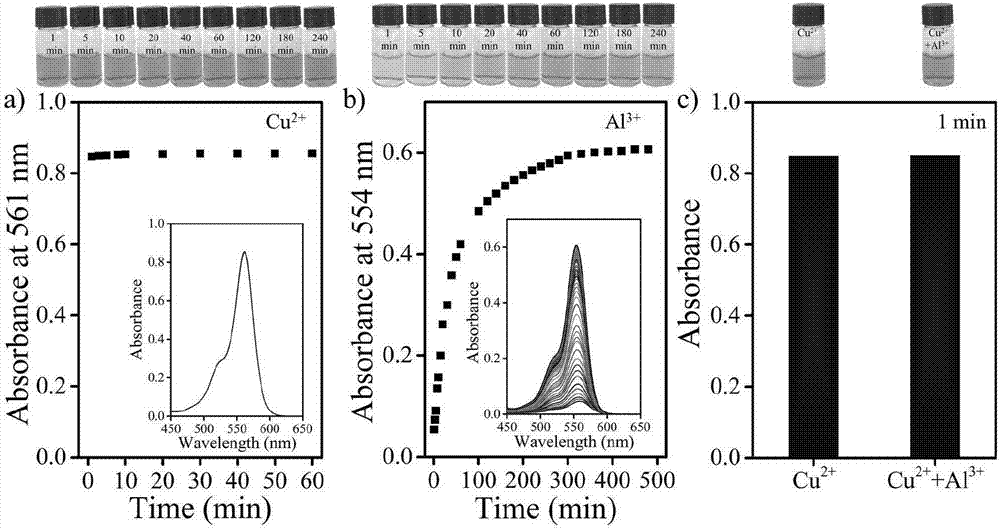
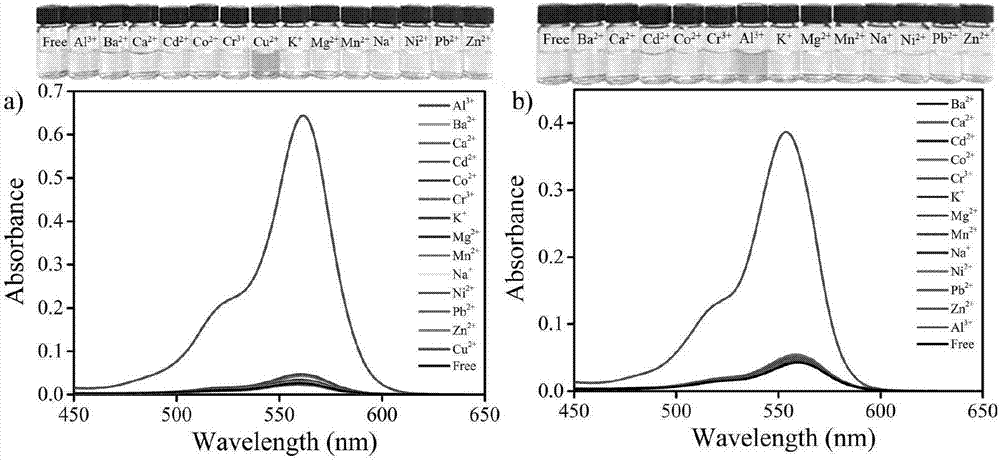
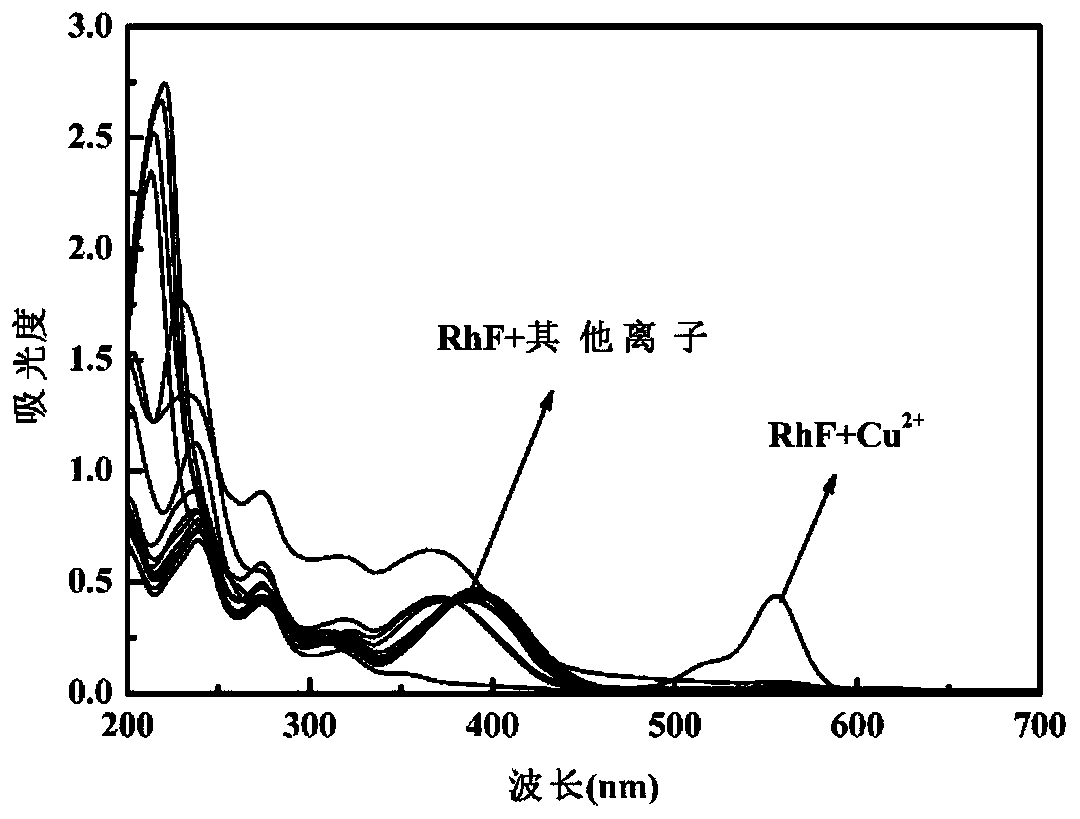
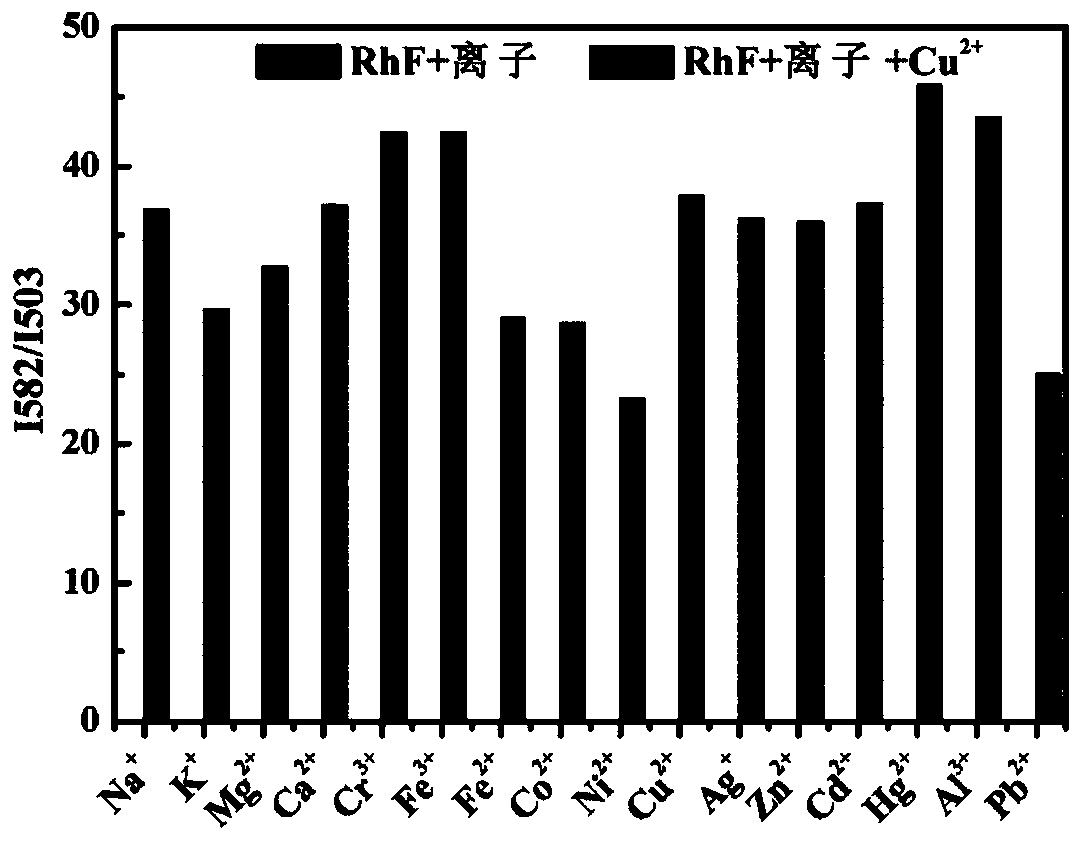
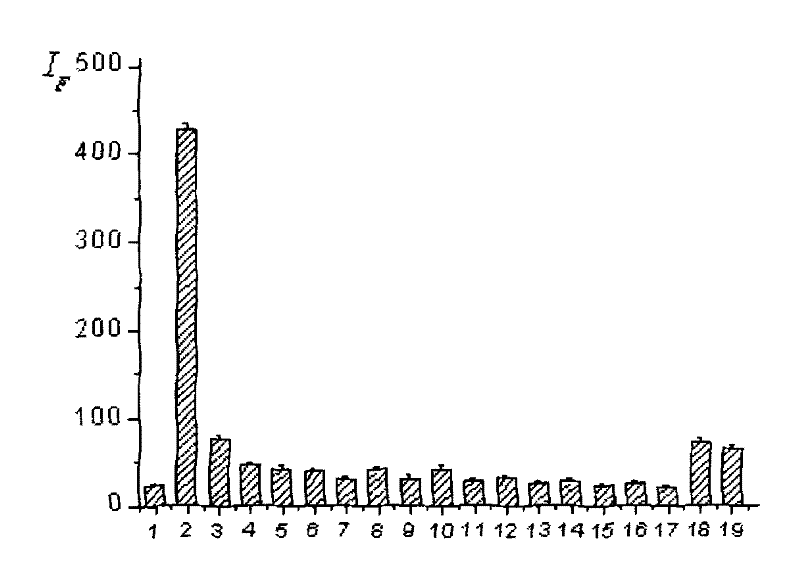
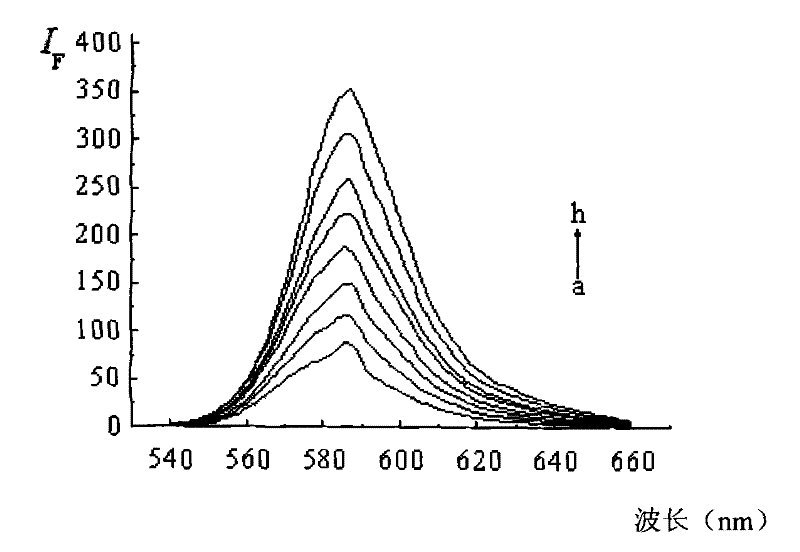
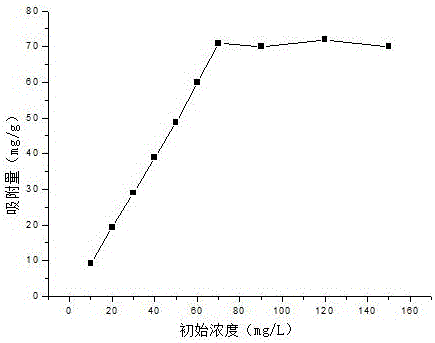
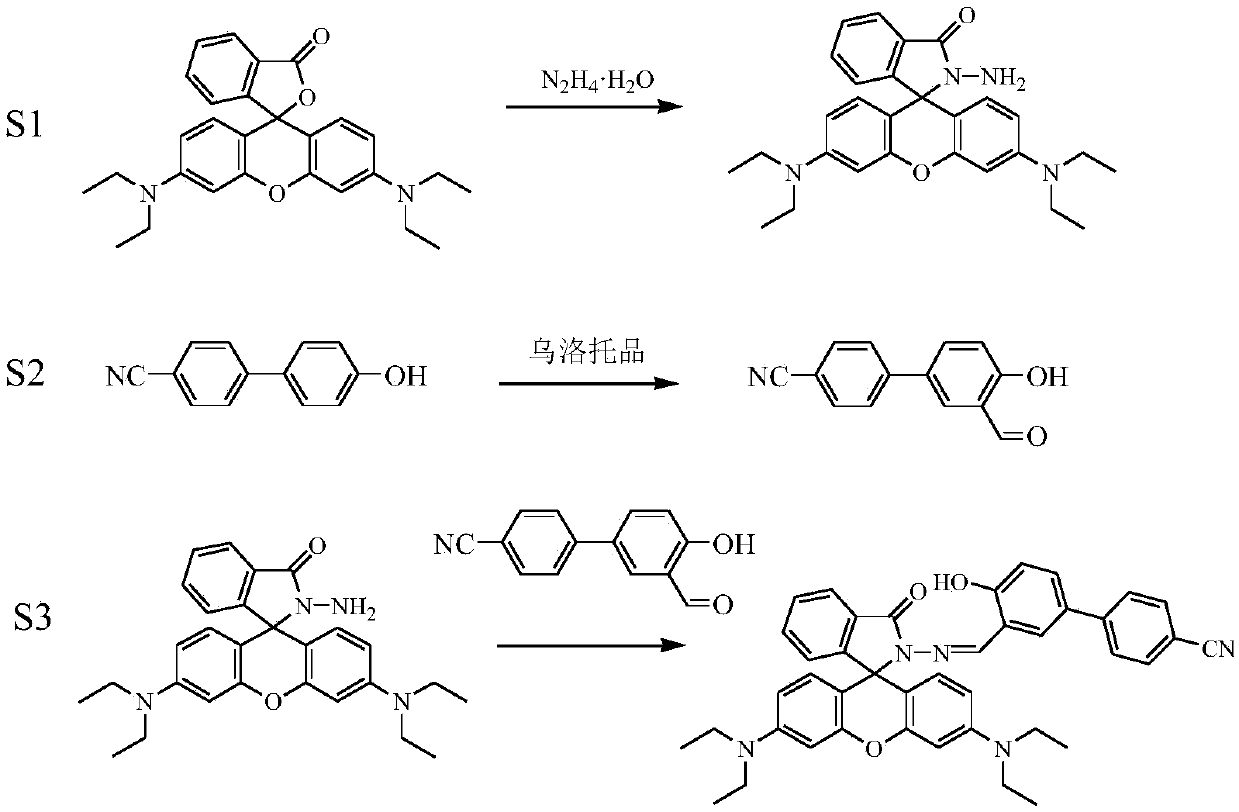
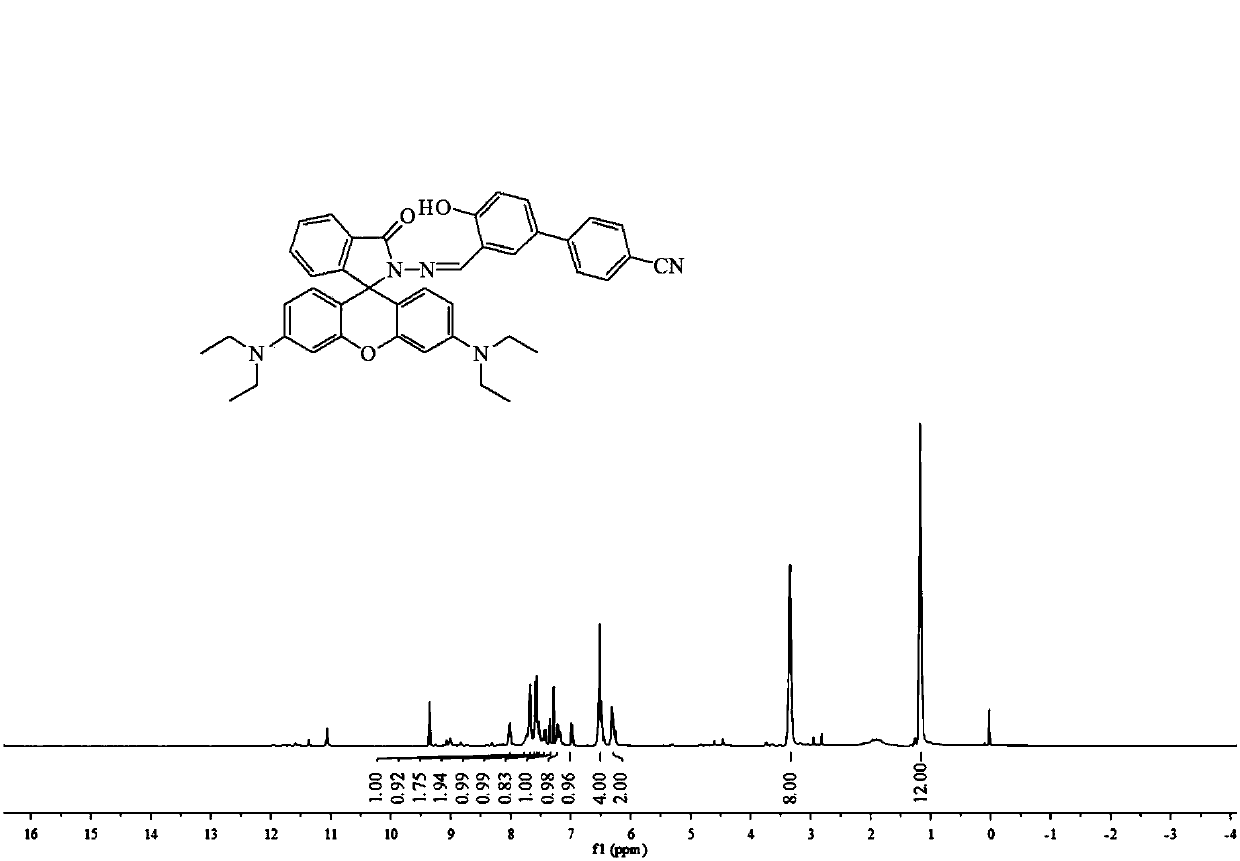
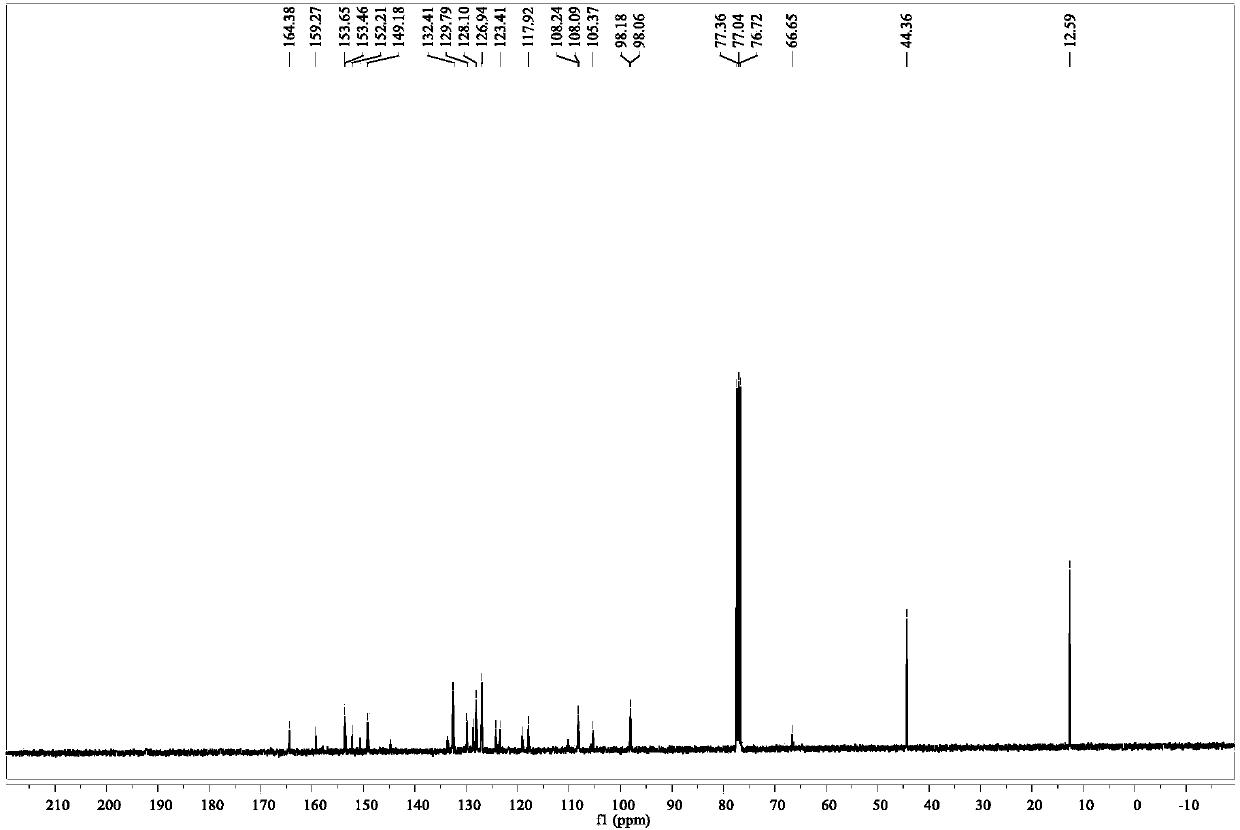
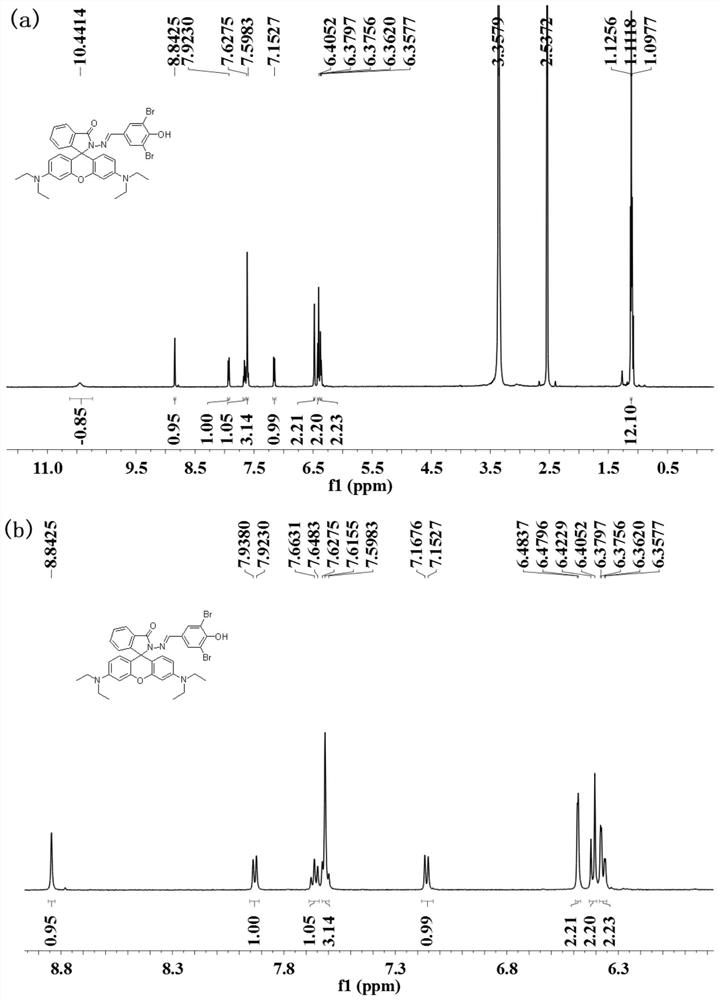
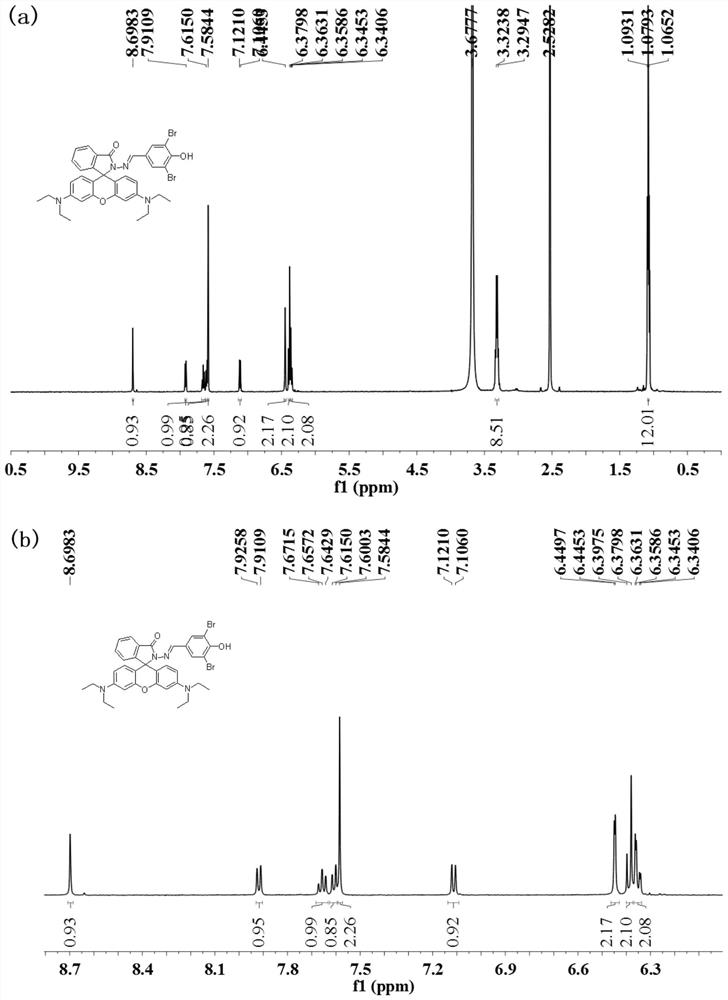
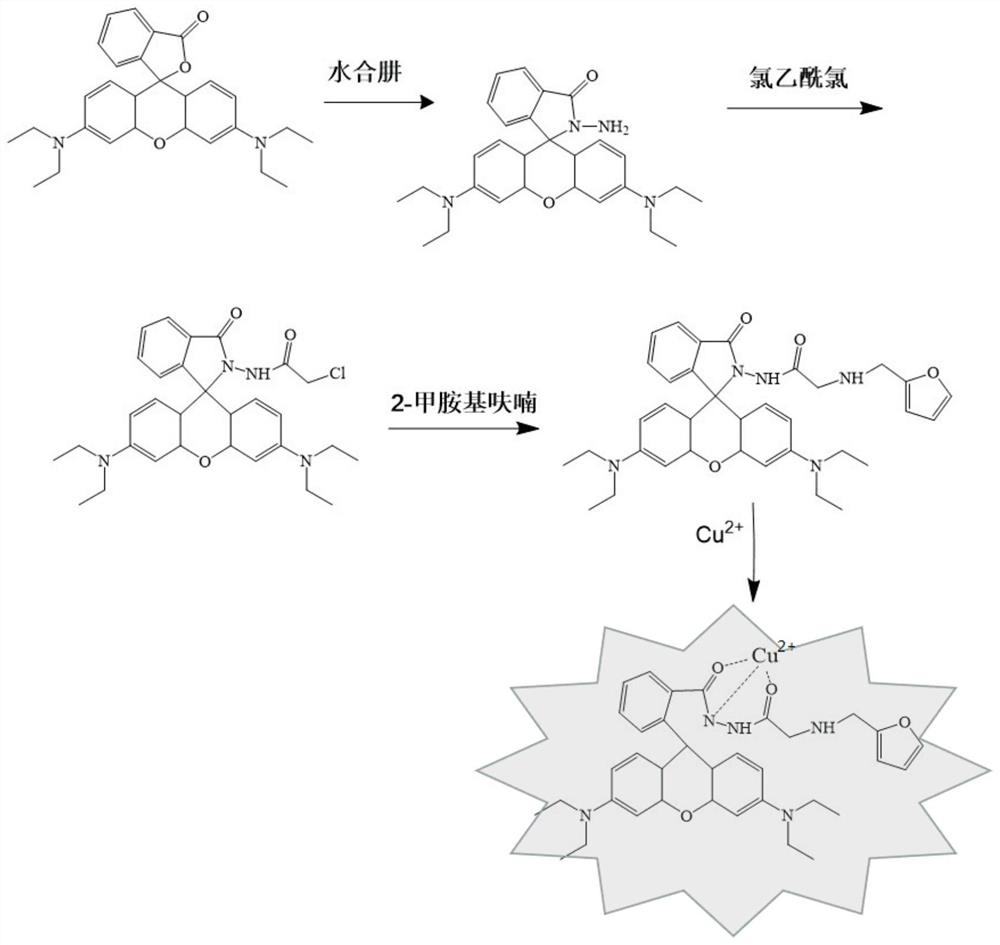
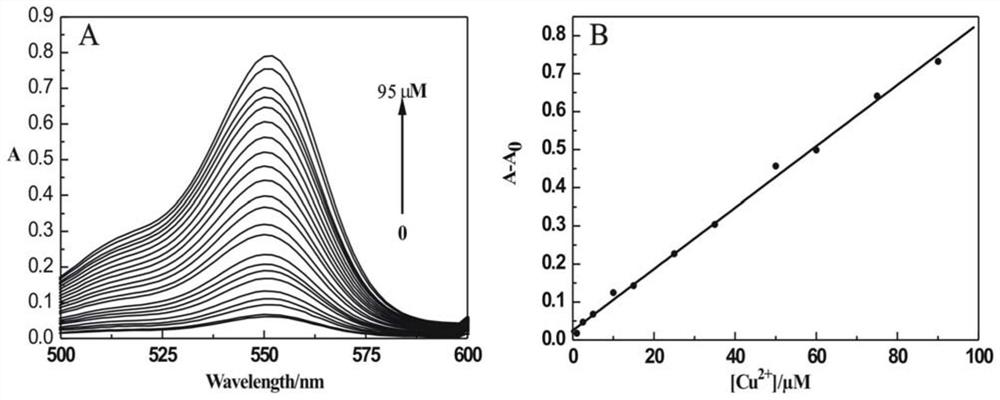
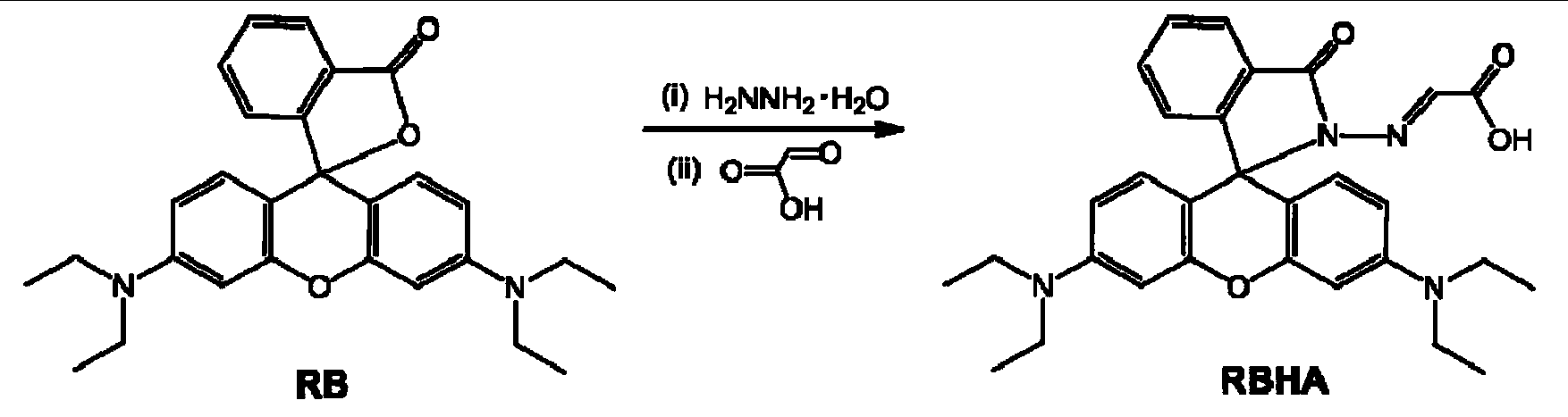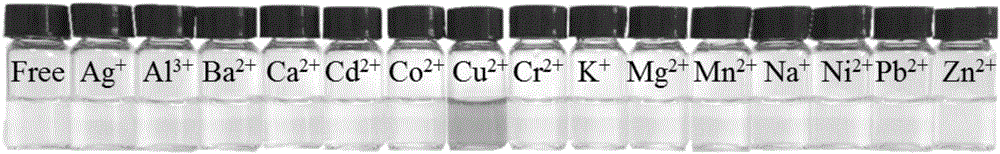Patents
Literature
45 results about "Rhodamine B hydrazide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Preparation of hydrophilic polymer and application thereof in detecting mercury ions based on change of fluorescence and color
InactiveCN102153700AIncrease contentQuick responseMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorOrganic dyesSolubilityGlycidyl methacrylate
The invention discloses preparation of hydrophilic polymer and application thereof in detecting mercury ions based on the change of fluorescence and color, particularly a rhodamine B hydrazide grafted hydrophilic polymer probe applied to the detection of mercury ions in aqueous medium based on the change of fluorescence and color and a kit and test paper applied to the detection of the mercury ions by using the probe, belonging to the technical field of material preparation and heavy metal ion detection. The polymer containing a rhodamine chromophore is prepared by subjecting rhodamine B hydrazide and propylene oxide on the side chain of polyvinylpyrrolidone-glycidyl methacrylate which is a water-soluble polymer to ring-opening reaction, has good water solubility and can be applied to selectively detecting the mercury ions by using visual colorimetry and fluorescence detection. The probe realizes the high-sensitivity and high-selectivity rapid quantitative or semi-quantitative detection of the trace mercury ions in the aqueous medium, has a simple synthetic route, low cost and convenience of use, is applicable to amplified synthesis and actual production and has great application prospects in the field of medicine, biology and environmental science and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
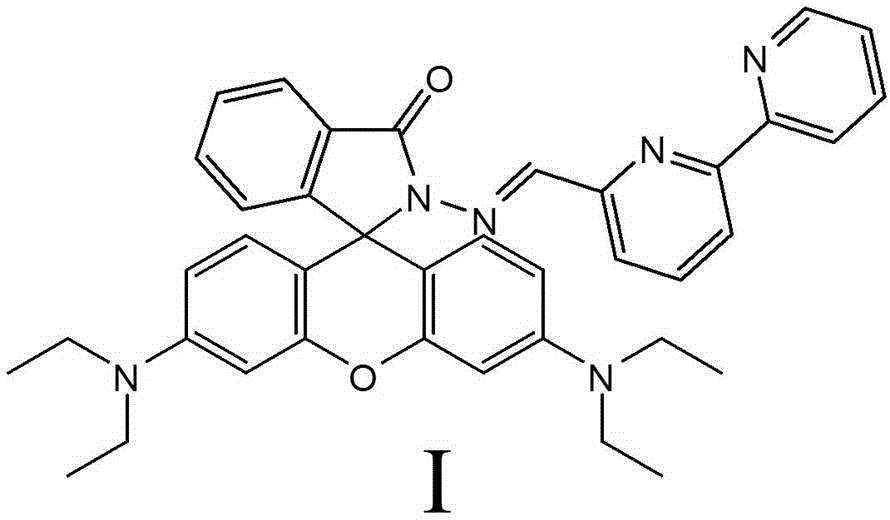
Rhodamine fluorescent molecular probe using quinoline derivative as identification group and synthesis method thereof
InactiveCN103409135AHigh selectivityHigh sensitivityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceChromatographic separationSynthesis methods
The invention provides a rhodamine fluorescent molecular probe using a quinoline derivative as an identification group and a synthesis method thereof, and relates to a rhodamine fluorescent molecular probe and a synthesis method thereof, solving the problem that the existing rhodamine fluorescent probe molecules based on the quinoline derivative identification group are few. A structural formula of a fluorescent molecular probe is as shown in specifications. A preparation method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing reaction liquid; and 2, adjusting the pH value of the reaction liquid, carrying out spin-drying and performing silica gel column chromatographic separation to obtain the rhodamine fluorescent molecular probe using the quinoline derivative as the identification group. A structural formula of another fluorescent molecular probe is as shown in specifications. A preparation method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing an intermediate rhodamine B hydrazide; and 2, dissolving the intermediate rhodamine B hydrazide and a quinoline-2-aldehyde derivative into absolute ethanol, refluxing under the protection of nitrogen, carrying out spin-drying and performing silica gel column chromatographic separation to obtain the rhodamine fluorescent molecular probe using the quinoline derivative as the identification group. The rhodamine fluorescent molecular probe disclosed by the invention is applied to the field of fluorescent imaging detection of metal ions in biological tissues and cell microenvironments.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY
Functional reactive dye for zinc ion probe, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105400233AWith zinc ion probe functionHas functional reactive dye propertiesReactive dyesDyeing processStructural formulaSolvent
The invention relates to a functional reactive dye for a zinc ion probe, and a preparation method and application thereof. The dye has a structural formula as described in the specification. The preparation method comprises the following steps: subjecting rhodamine B and hydrazine hydrate to a heating reflux reaction so as to obtain rhodamine B hydrazide; subjecting methyl p-aminobenzoate and hydrazine hydrate to a heating reflux reaction, dissolving a product in a solvent, adding salicylaldehyde drop by drop and then carrying out a heating reflux reaction so as to obtain salicylaldehyde-4-aminobenzoyl hydrazone; and dissolving cyanuric chloride in a solvent, adding an acid binding agent, adding rhodamine B hydrazide drop by drop at a temperature in a range of -5 to 5 DEG C, carrying out a reaction under stirring so as to obtain a concentration product, dissolving the concentration product in a solvent, adding the acid binding agent, adding salicylaldehyde-4-aminobenzoyl hydrazone drop by drop and carrying out a reflux reaction with temperature controlled so as to obtain the functional reactive dye. The functional reactive dye has good selectivity on zinc ions, is convenient to use in sewage treatment and exerts good usage effect.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
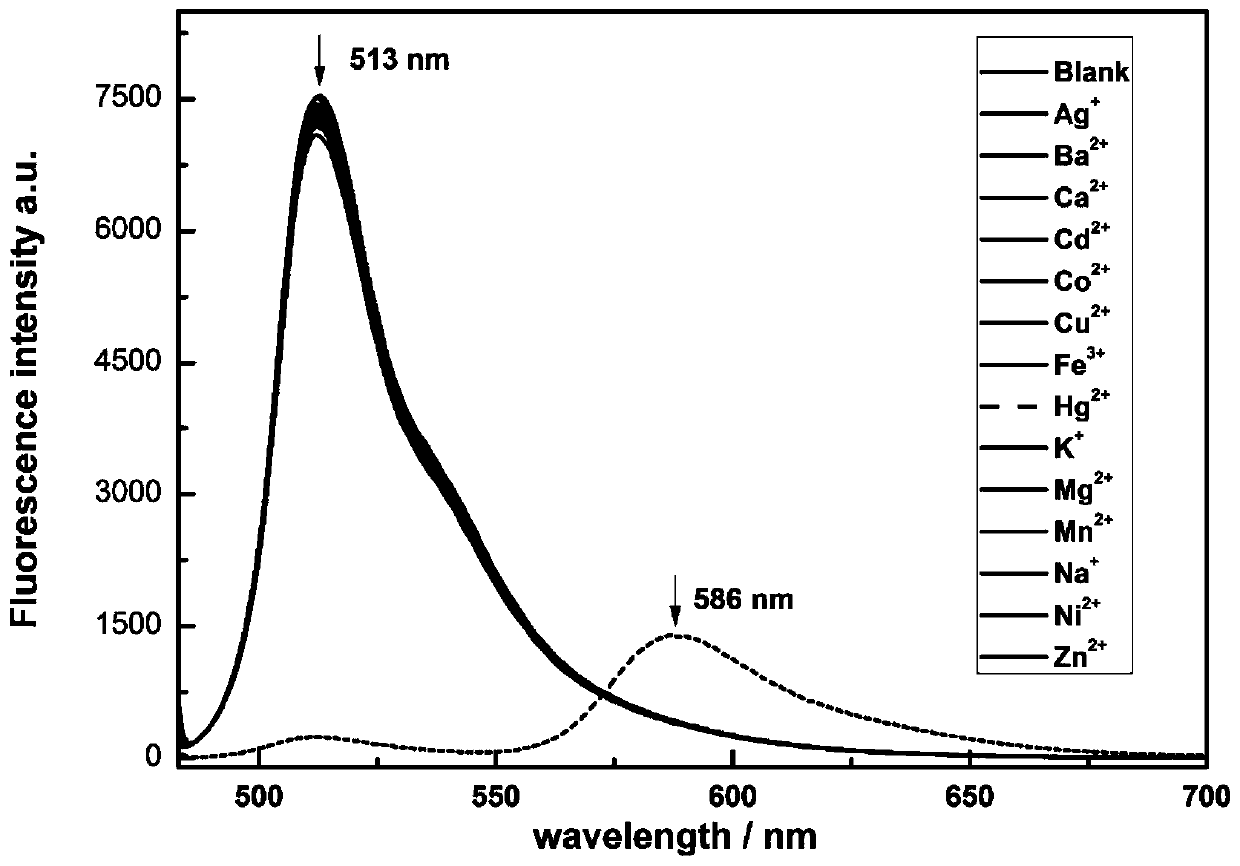
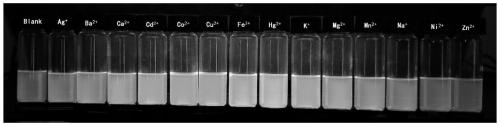
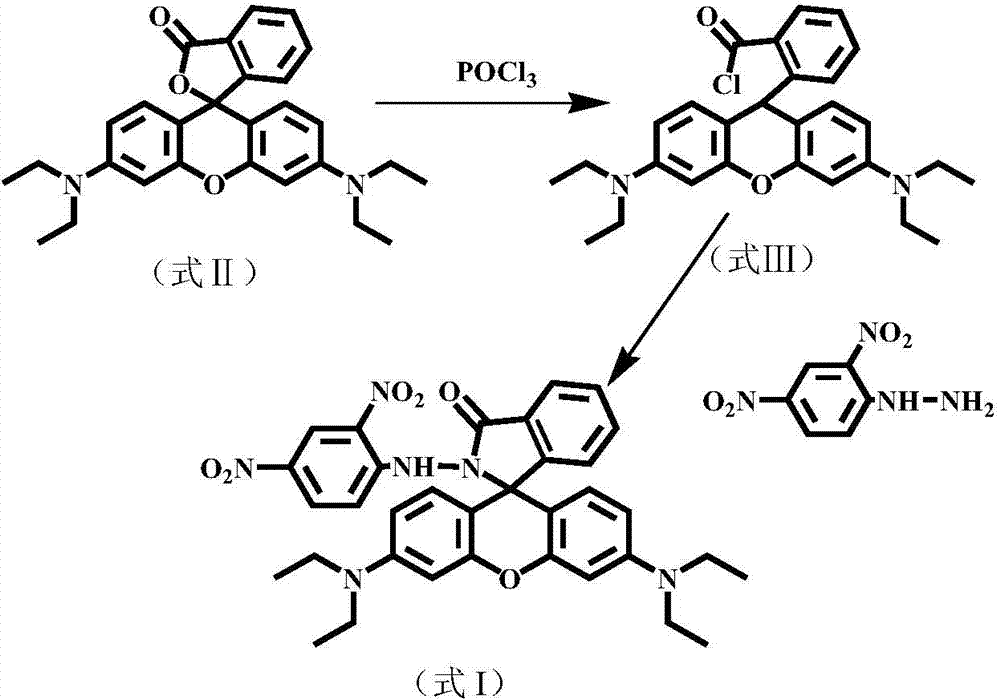
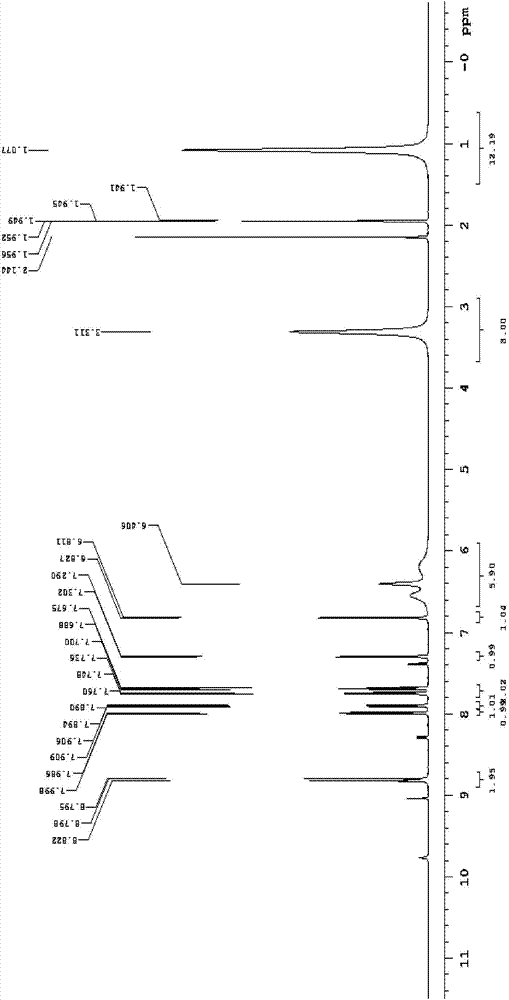
N-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)-rhodamine B hydrazide and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102827175ANo distractionEliminate distractionsOrganic chemistryColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescent spectraDinitrophenyl
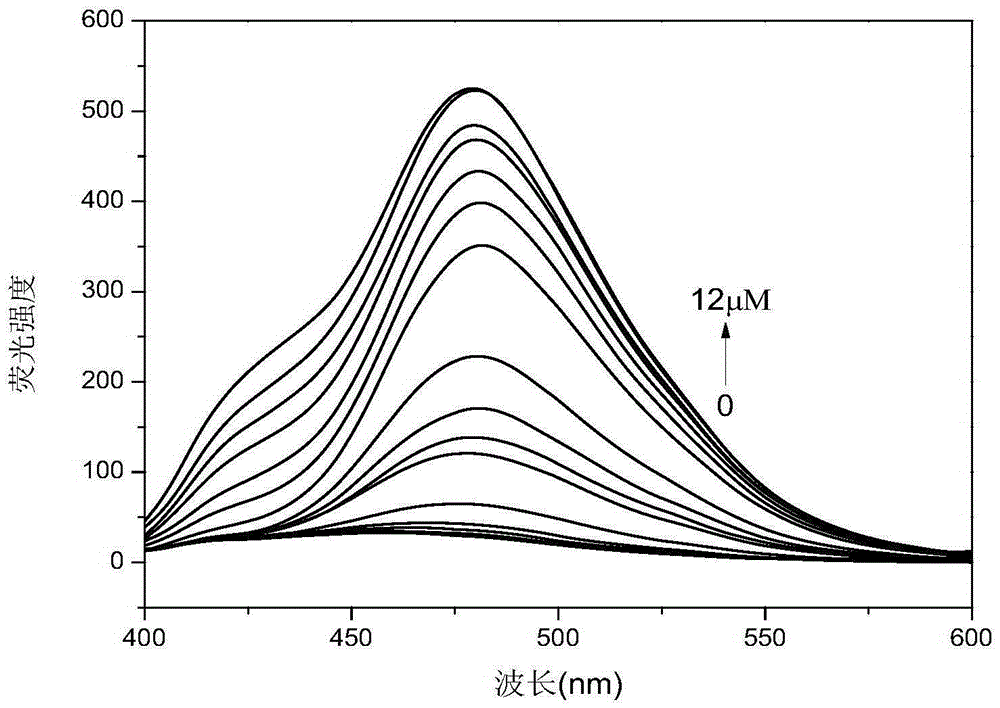
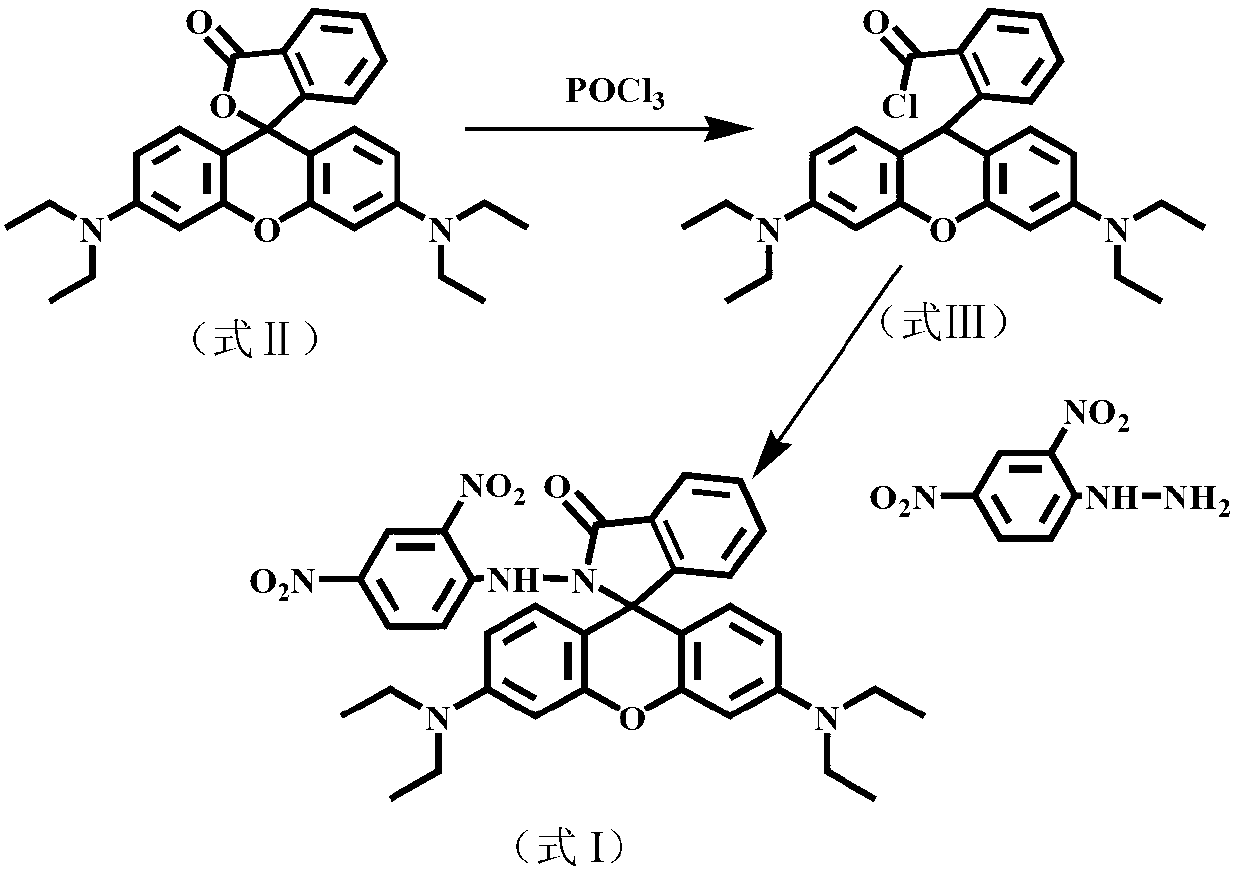
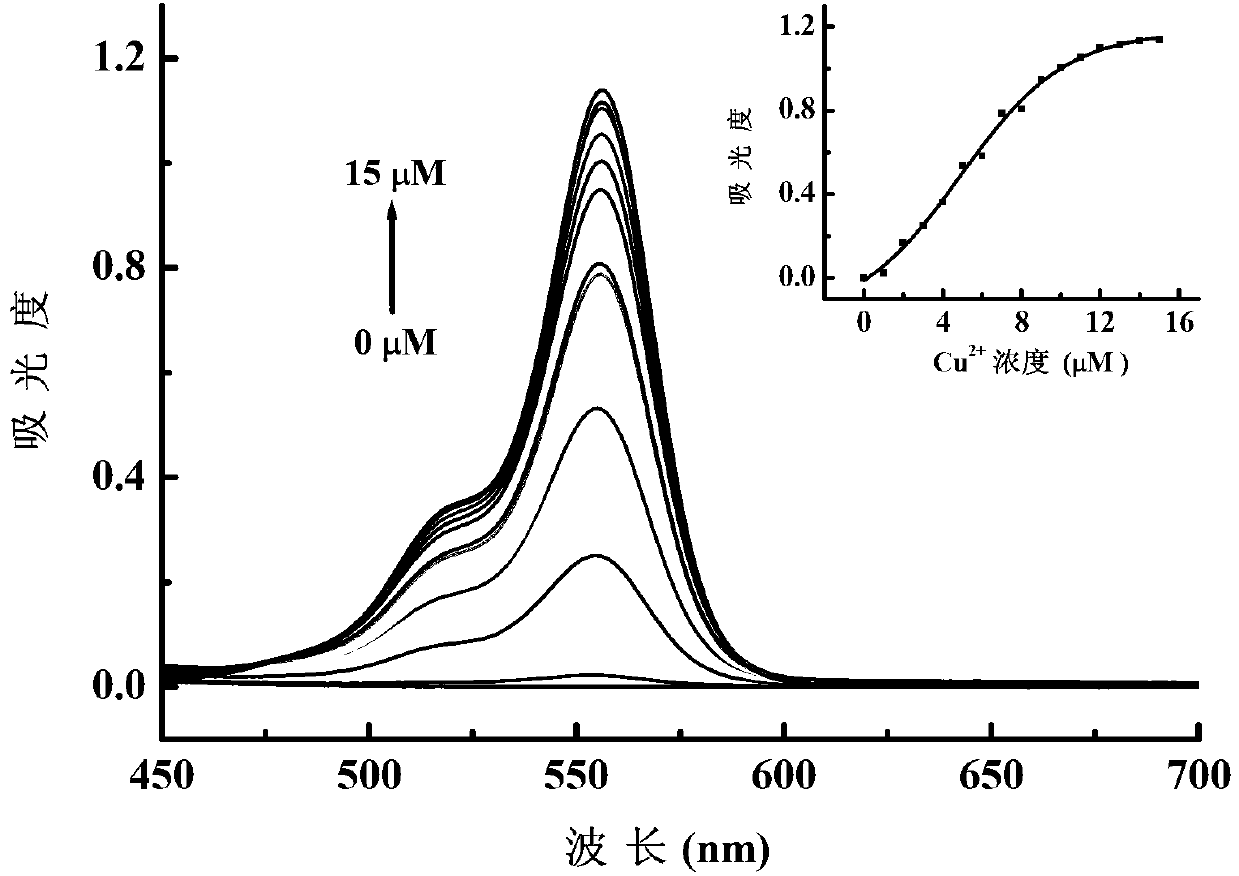
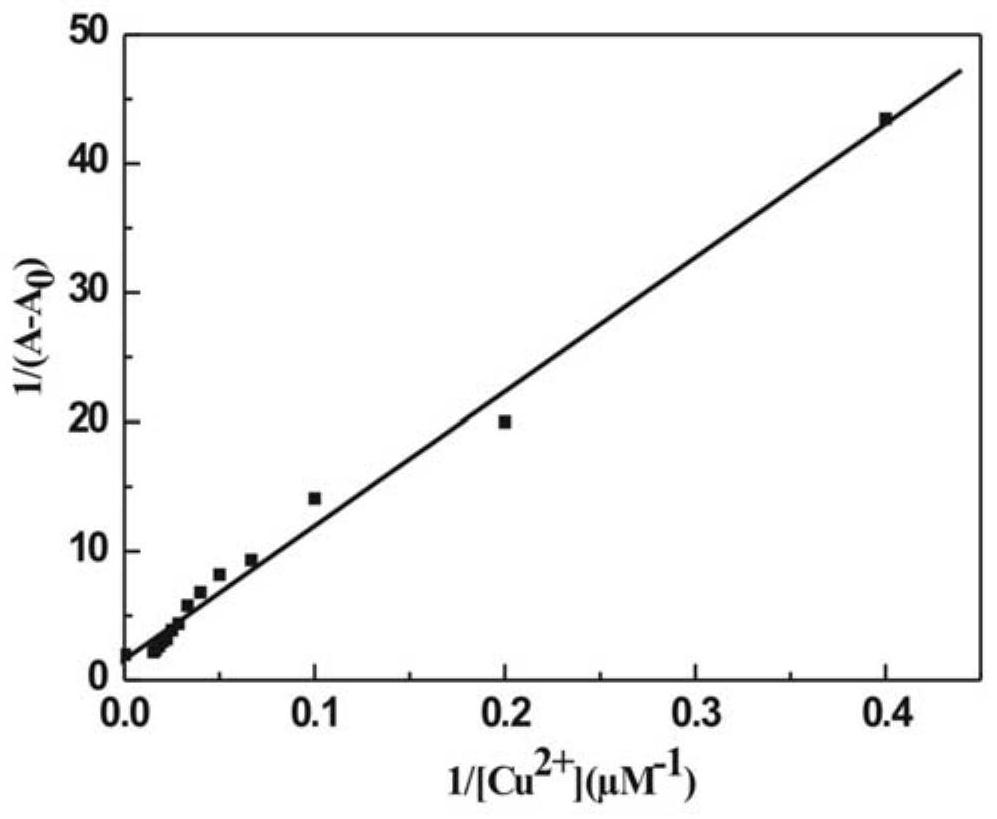
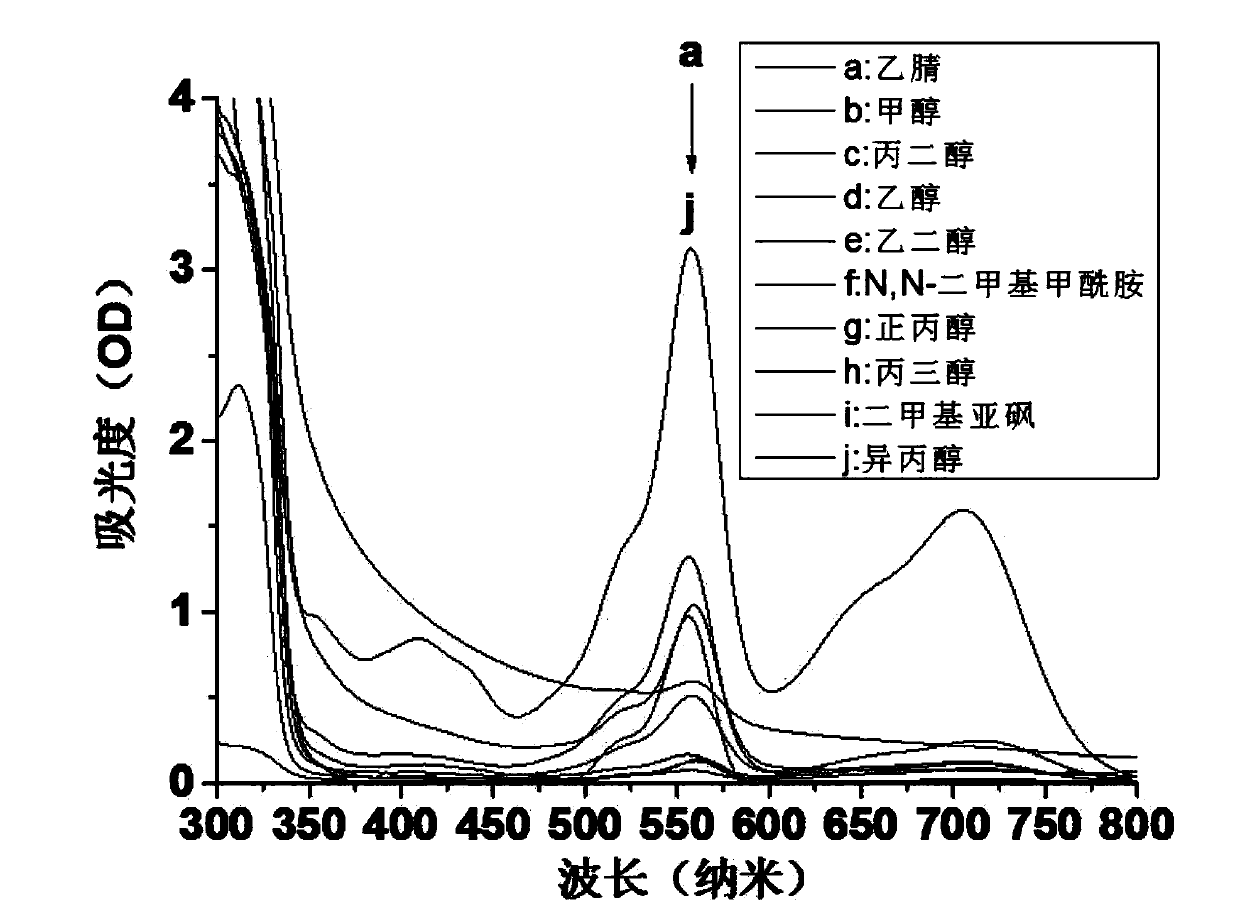
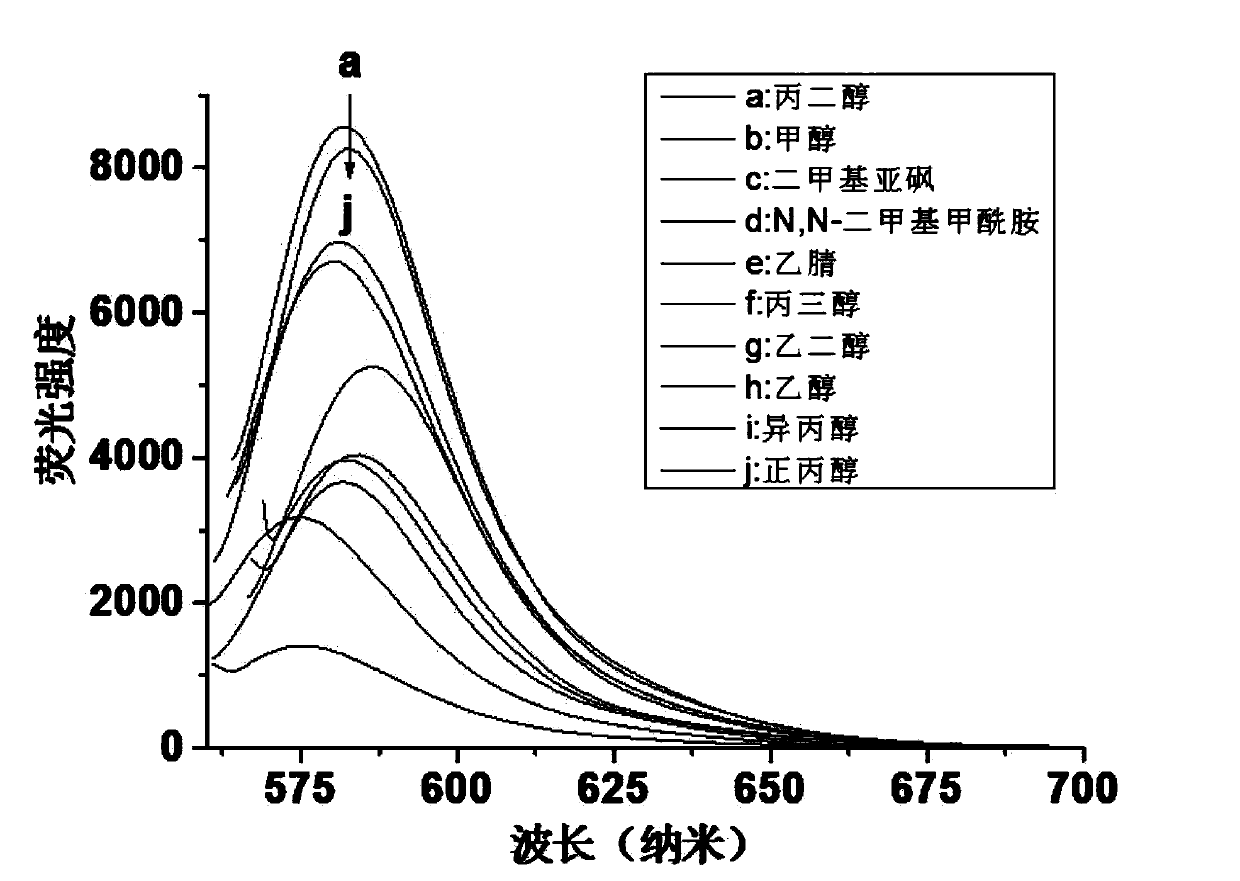
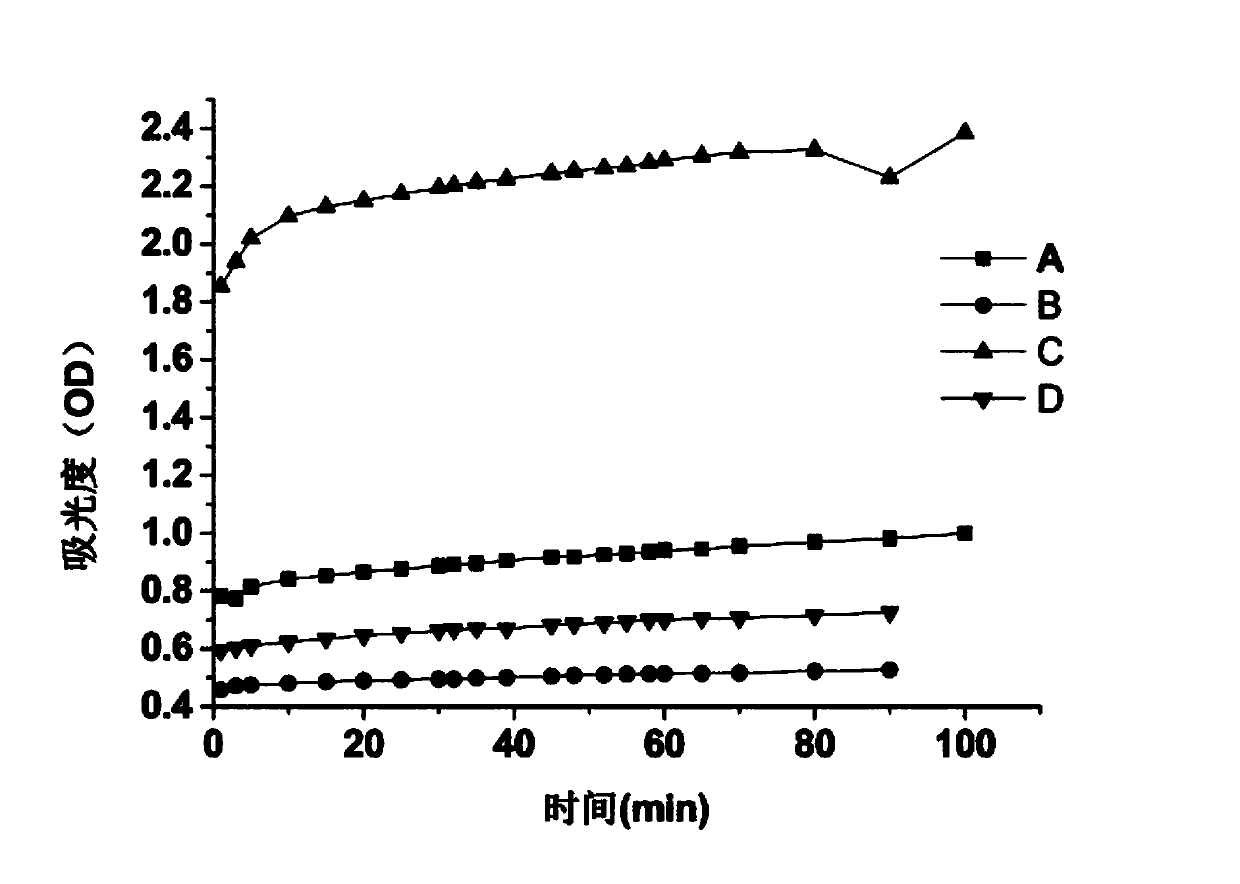
The invention discloses N-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)-rhodamine B hydrazide and a preparation method and an application of the N-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)-rhodamine B hydrazide. The rhodamine B derivative provided by the invention is N-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)-rhodamine B hydrazide, the structural formula of which is I. The N-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)-rhodamine B hydrazide, is colorless and free from fluorescence, but can selectively react with Cu<2+> ions in chromogenic and fluorescent opening reaction. The colorless substance generates a system with excellent optical performance, so that the detection sensitivity and selectivity of Cu<2+> ions are greatly improved. Therefore, the N-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)-rhodamine B hydrazide is appropriate for high selectivity and high sensitivity detection for the Cu<2+> ions. Detection can be carried out by a light absorption spectrum and a fluorescence spectrum. (FORMULA I).
Owner:NAT RESERACH CENT OF GEOANALYSIS +1
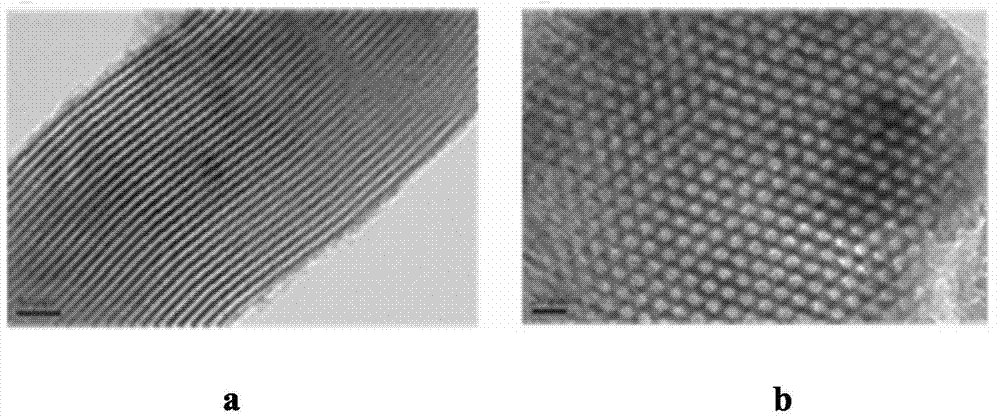
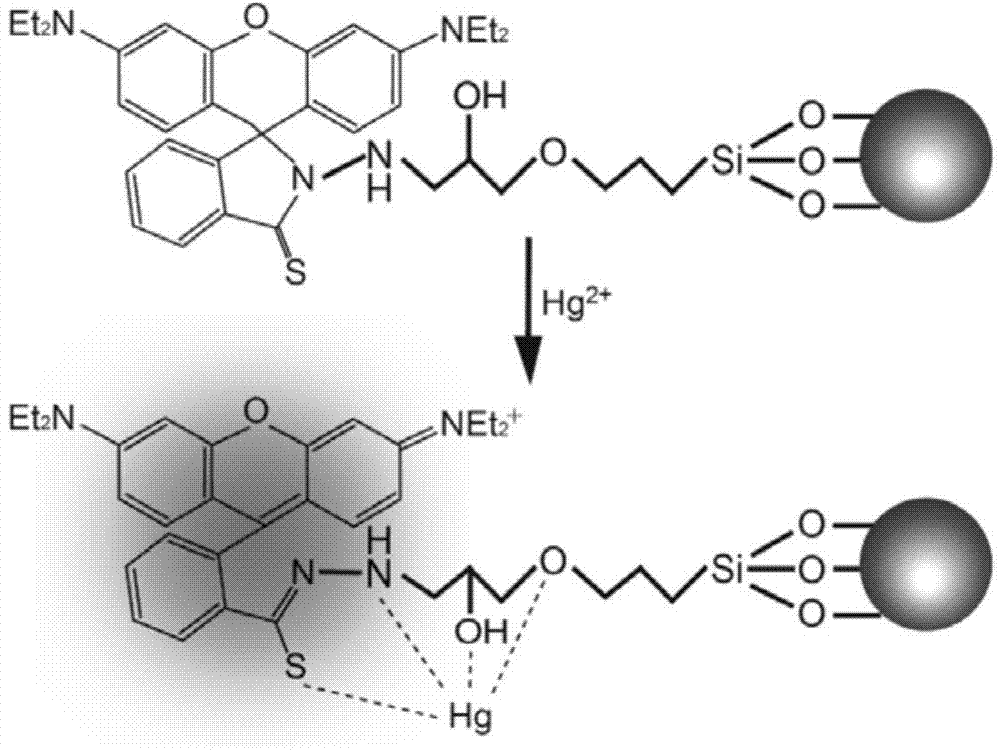
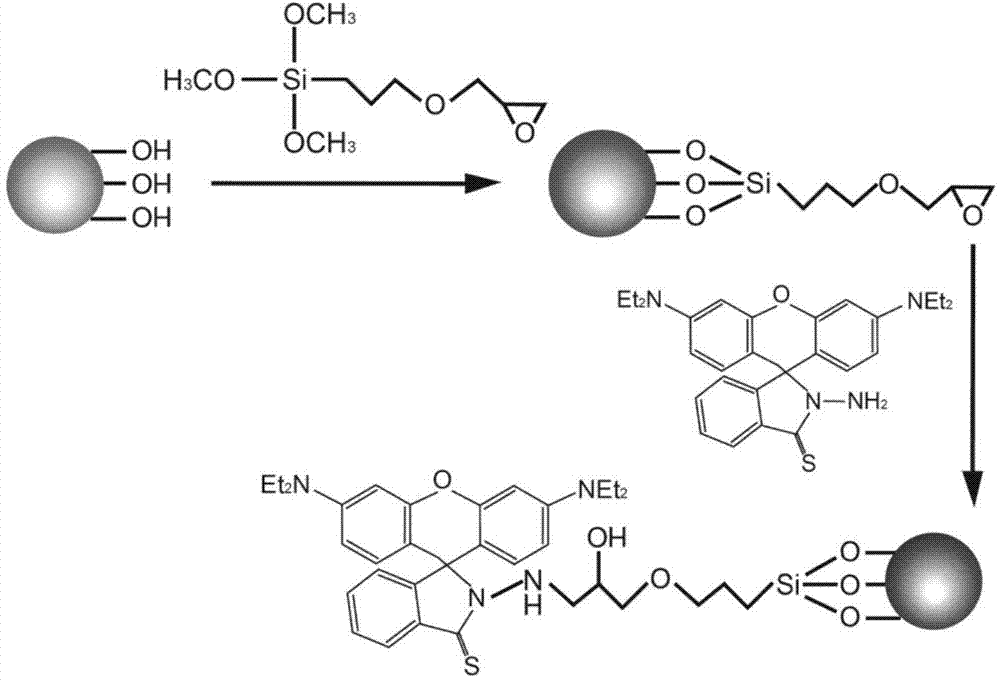
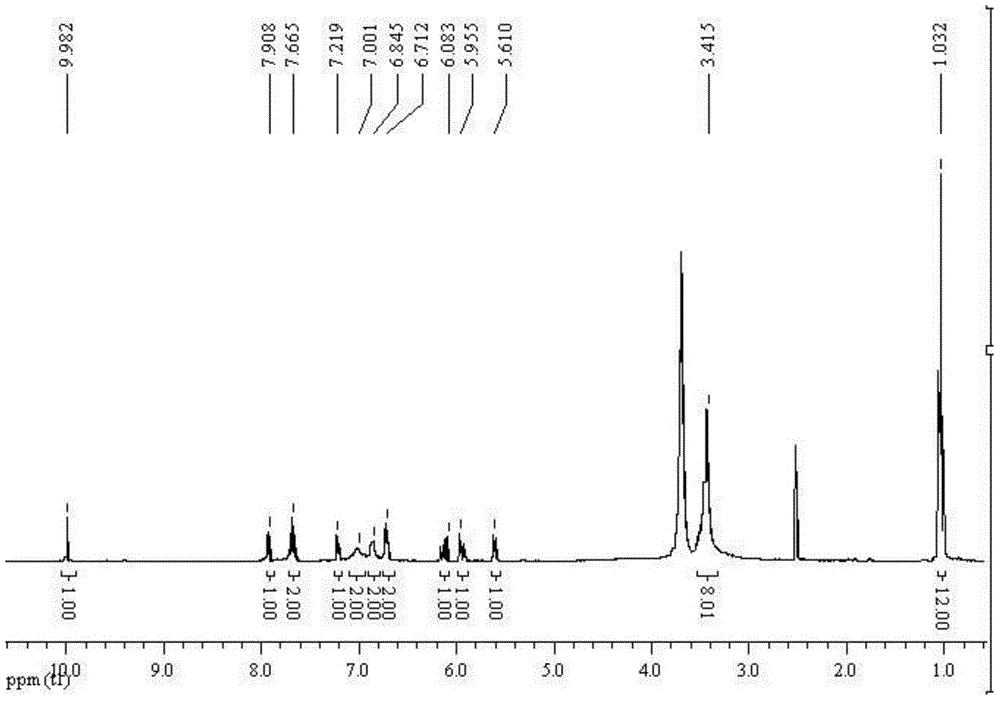
Modified SBA-15 mesoporous material as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104741085AHigh selectivityHigh sensitivityOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionChemical structureMercuric ion
The invention belongs to the technical field of a functional material, and in particular relates to a modified SBA-15 mesoporous material as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The mesoporous material is an SBA-15 mesoporous material modified by trimethoxy-[(3-ethylene oxide methox)yl propyl] silane and rhodamine B derivative, and the modified mesoporous material is prepared by the following steps: firstly, substituting silicon hydroxyl of an SBA-15 mesoporous material which is prepared in advance with a substitute (as shown in Specification), and then, carrying out a cycloaddition reaction with thio rhodamine B hydrazide (as shown in Specification), so as to obtain the modified SBA-15 mesoporous material with chemical structural formula as shown in Specification. The modified SBA-15 mesoporous material, as a hybridized mesoporous fluorescent adsorbent showing efficient detection and a capacity of removing mercury ions in a water body and integrating multiple functions, can simultaneously carry out detection and recovery processes on dangerous chemical substances in a water solution, an air system, and in particular in body blood or tissue.
Owner:HUAIYIN TEACHERS COLLEGE +1
Rhodamine structure based Cu<2+> fluorescent probe and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104087285AOpen loop easyImprove anti-interference abilityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceSurface cleaningSolvent
The invention discloses a rhodamine structure based Cu<2+> fluorescent probe and a preparation method thereof. A structural formula of the rhodamine structure based Cu<2+> fluorescent probe is shown in the description. The preparation method of the rhodamine structure based Cu<2+> fluorescent probe comprises the steps of preparing rhodamine B hydrazide, preparing a rhodamine B hydrazide suspension, preparing an acryloyl chloride suspension, preparing a Cu<2+> fluorescent probe, and carrying out surface cleaning on Cu<2+> fluorescent probe Mrh. According to the rhodamine structure based Cu<2+> fluorescent probe and the preparation method thereof, the Cu<2+> fluorescent probe has good solvent applicability and high anti-interference property.
Owner:KUNSHAN DONGDA ZHIHUI TECH CONSULTANT
Reactive rhodamine fluorescent probe for detecting mercury ions, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103820103AFluorescent signal enhancementHighly selective detectionOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceGlyoxylic acidEvaporation
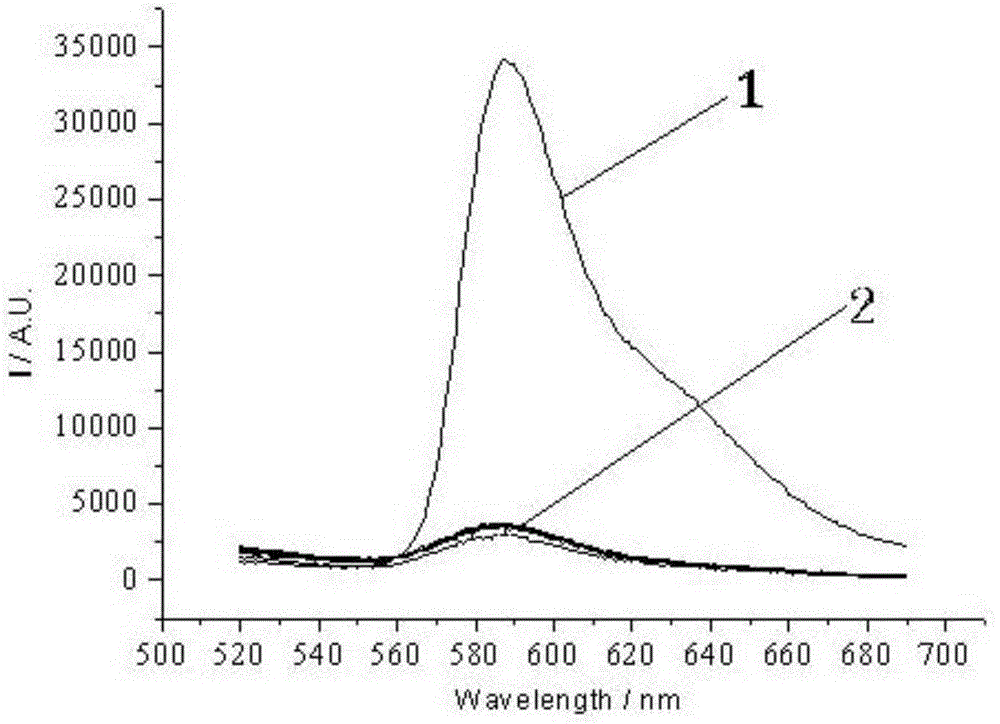
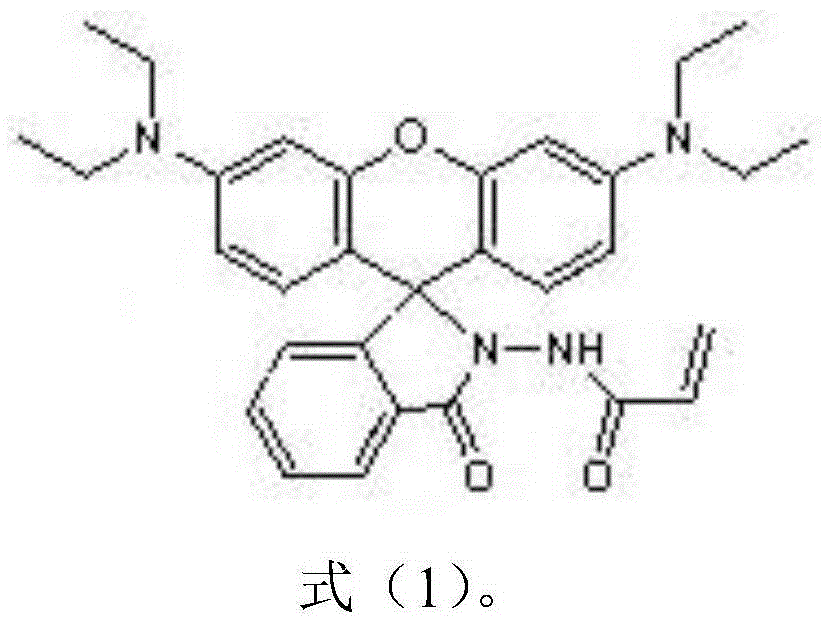
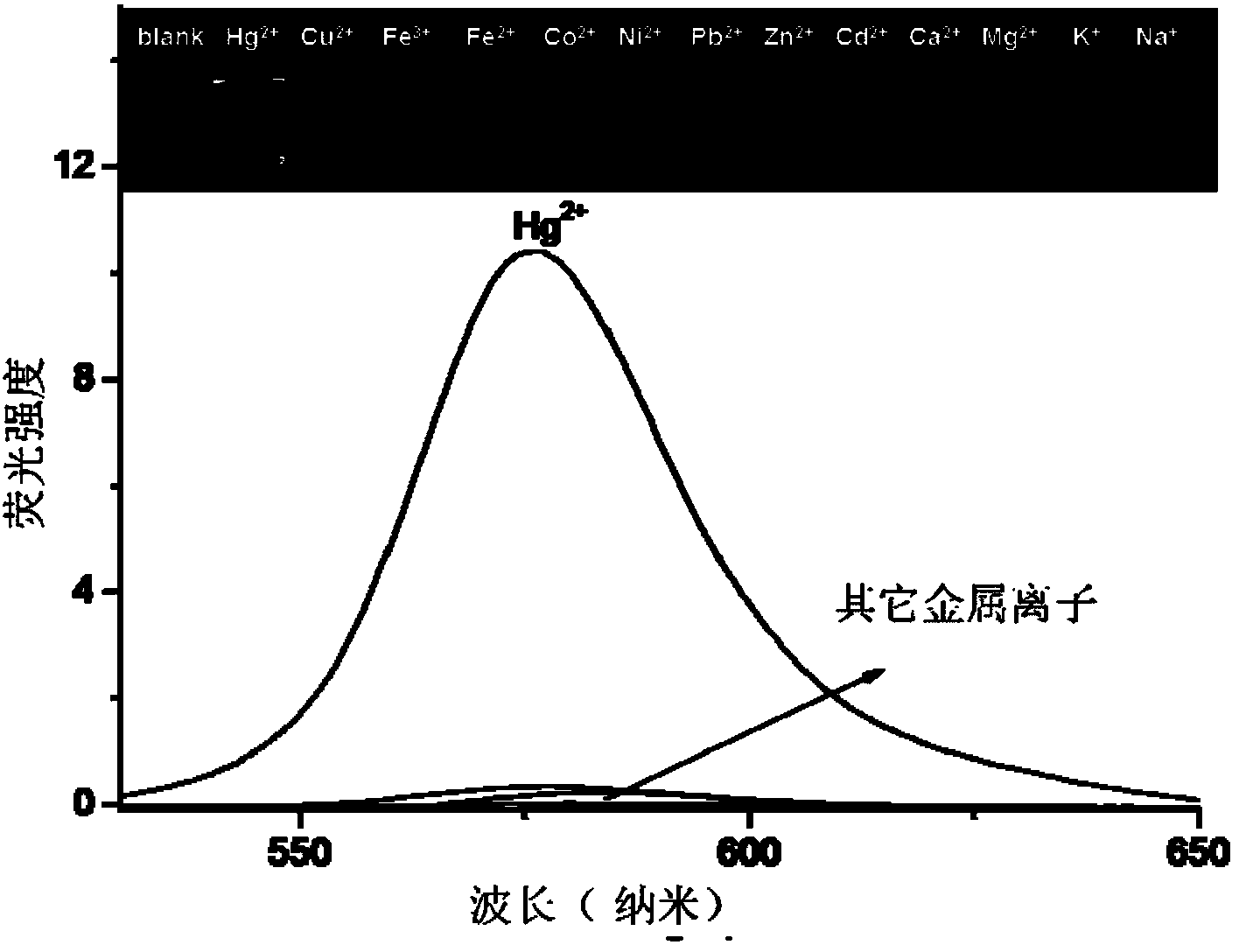
The invention relates to a reactive rhodamine fluorescent probe for detecting mercury ions, and a preparation method thereof. A structural formula of the reactive rhodamine fluorescent probe RBHA is shown in the description. The preparation method comprises the steps of adding rhodamine B and hydrazine hydrate into a solvent, reacting for 1-2 h under refluxing at a temperature of 80-90 DEG C; carrying out rotary evaporation; adding water and adjusting pH; filtering; and purifying to obtain rhodamine B hydrazide; dissolving the rhodamine B hydrazide and glyoxylic acid in a solvent; reacting overnight with stirring at a room temperature; filtering; and purifying to obtain the reactive rhodamine fluorescent probe. The reactive rhodamine fluorescent probe has high selectivity for the mercury ions, has no obvious interference with other common ions, can work in an environment with a wide pH scope ranging from 5 to 10, and has application prospects in bioluminescent imaging and analysis of environmental water samples.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
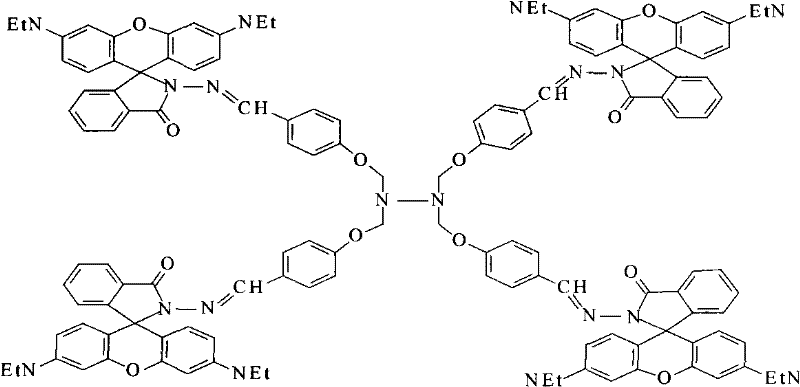
Method for manufacturing novel dendritic fluorescent chemosensor and application
InactiveCN102020985ASensing shortcutSensitiveOrganic chemistryChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceEthylenediamineFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a dendritic fluorescent chemosensor and the method for detecting Fe<3+> in a sample. The method for manufacturing the dendritic fluorescent chemosensor is mainly technically characterized by comprising the following steps of: performing reaction on aminoacetaldehyde dimethyl acetal, methyl acrylate and ethylenediamine in a methanol medium under the protection of argon at the temperature of 55 to 65 DEG C for 24 to 30 h to obtain a dendritic compound; and reacting in darkness the dendritic compound with rhodamine B hydrazide in the methanol medium under the protection of the argon at room temperature for 48 to 58 h by taking 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde as a crosslinker, and performing filtration and washing to obtain the dendritic fluorescent chemosensor. In the detection method, the mixed solution of ethanol and water serves as the medium, and the Fe<3+> content of various samples is determined by utilizing a fluorophotometer in Tris-HCl buffer solution with the pH value of 6.8 to 7.5. The dendritic fluorescent chemosensor has the linear range of 0 to 10.0 mu g.mL<-1>, the detection limit of 0.026 mu g.mL<-1>, and sensitivity and selectivity which are valuable in analytical chemistry.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Fluorescent probe for detecting mercury ions and preparation method and application of fluorescent probe
ActiveCN110117295AHigh sensitivityGood choiceGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceBenzoic acidPhotochemistry
The invention provides a fluorescent probe for detecting mercury ions and a preparation method and application of the fluorescent probe. The chemical name of the fluorescent probe is 3-(4-(1,3,5,7-tetramethyl-8 propyl)boron fluoride dipyrrol-4-carbonyl)piperazine)-rhodamine B hydrazide. The fluorescent probe takes a boron fluoride dipyrrol fluorescent dye BODIPY unit as an energy donor, a rhodamine unit serves as an energy receptor, by means of bivalent mercury ions, 'on-off' of a spiramide ring is promoted, the purpose that the BODIPY unit and the rhodamine unit are subjected to fluorescenceresonance energy transfer to cause fluorescent red shift is achieved, and then a fluorescence ratio type probe can be used for detecting Hg<2+>; the fluorescent probe takes n-(3-hydroxyphenyl)piperazine and 2-(4-diethylamino)-2-hydroxyl)-benzoic acid as the raw materials, after a reaction is conducted, the raw materials and (1,3,5,7-tetramethyl-8-propoxycarbonyl succinimide)boron fluoride dipyrrolare subjected to a condensation reaction, and the fluorescent probe is obtained. The probe is an FRET-based ratio type fluorescent probe which is high in sensitivity, good in selectivity and capableof detecting the mercury ions in an aqueous phase.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
A preparing method of N-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)rhodamine B-hydrazide and an application of the N-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)rhodamine B-hydrazide for detection of Cu(II)
InactiveCN104262351ANo distractionEliminate distractionsOrganic chemistryColor/spectral properties measurementsOptical propertyDinitrophenyl
A preparing method of N-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)rhodamine B-hydrazide and an application of the N-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)rhodamine B-hydrazide for detection of Cu(II) are disclosed. The preparing method includes a step of reacting rhodamine B acid chloride and 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine to generate the N-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)rhodamine B-hydrazide. The N-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)rhodamine B-hydrazide itself is free of color and fluorescence, but can generate coloring and fluorescence generating reactions selectively with Cu<2+>, so that a colorless substance is turned into a system with excellent optical properties, and detection sensitivity and selectivity for the Cu<2+> are largely enhanced. Accordingly, the N-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)rhodamine B-hydrazide is suitable for high-selectivity and high-sensitivity detection of the Cu<2+>. The detection can be performed by a light absorption spectrum method and a fluorescence spectrum method.
Owner:NAT RESERACH CENT OF GEOANALYSIS +1
Organic complex mercury ion probe and preparation method and application thereof
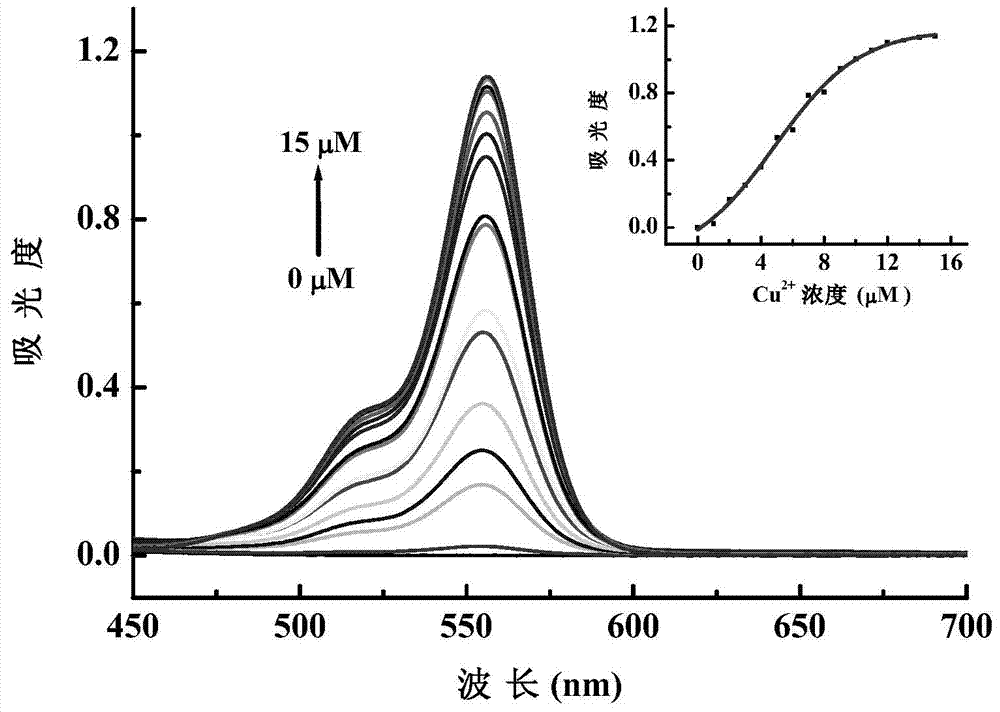
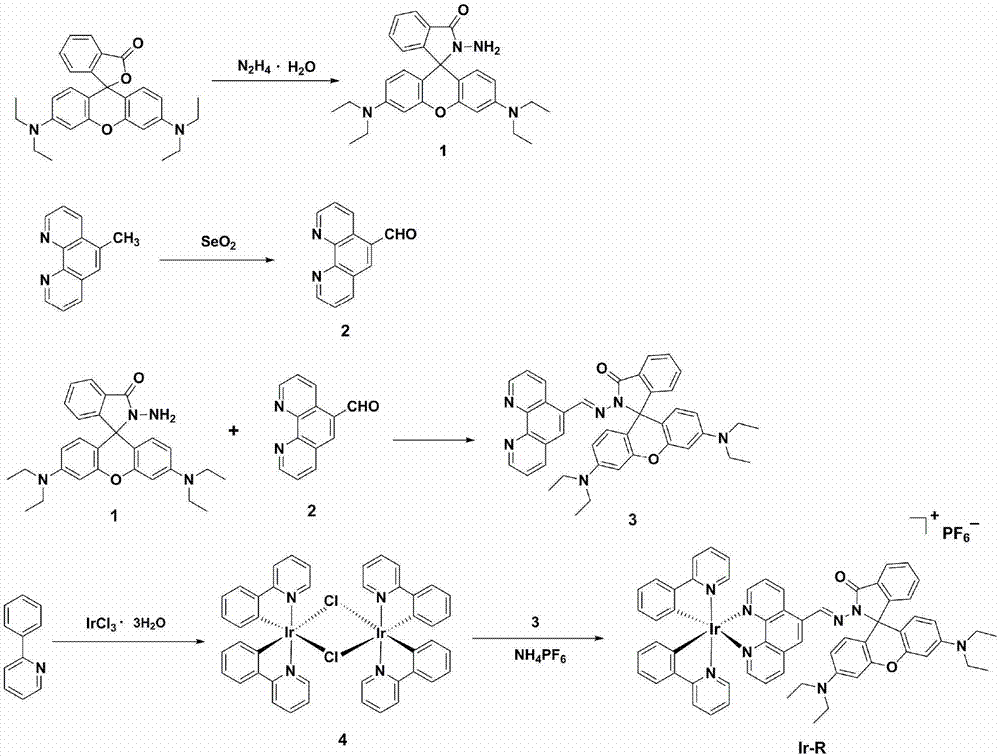
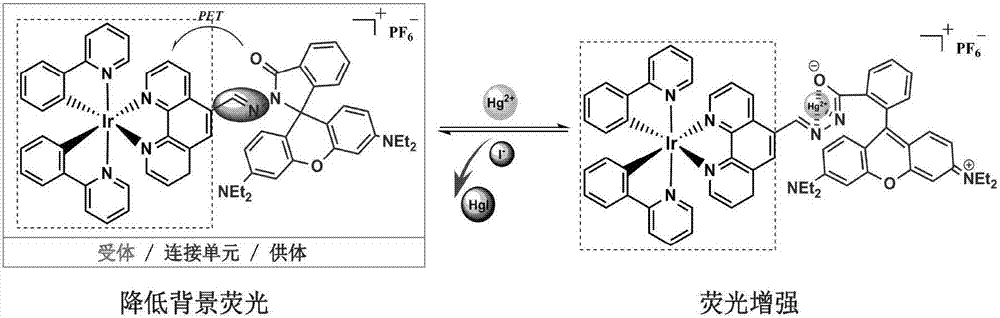
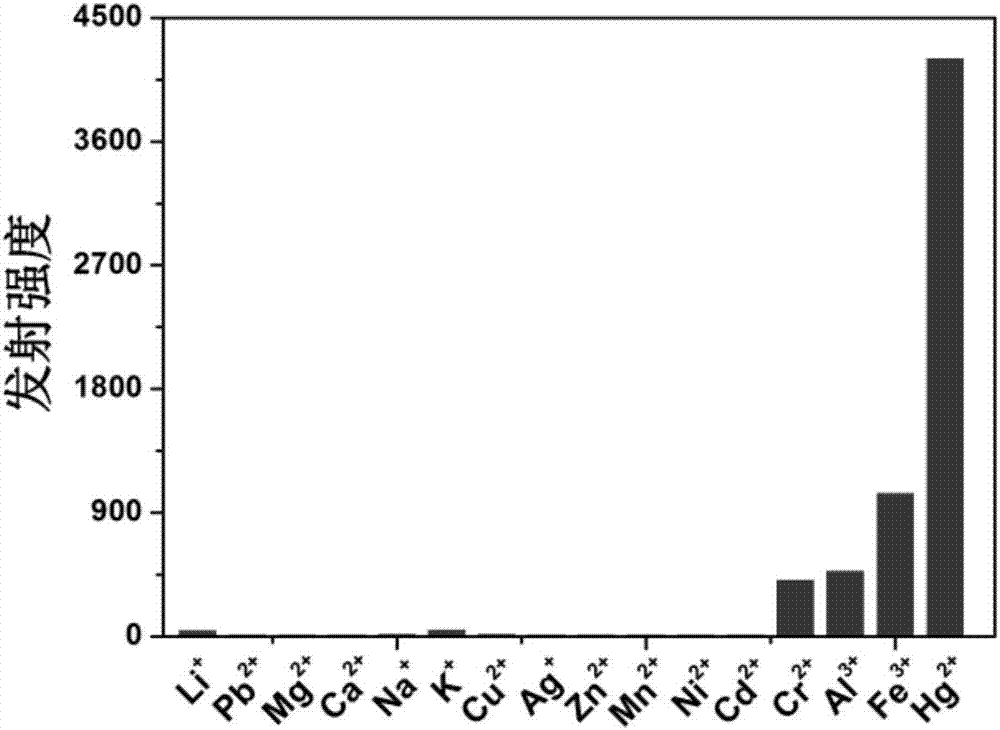
InactiveCN107417732AQuick checkGood choiceIndium organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceBiological cellPhenanthroline
The invention discloses an organic complex mercury ion probe and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of enabling rhodamine B to react with hydrazine hydrate to obtain pink solid rhodamine B hydrazide, and enabling 5-methyl phenanthroline to react with selenium dioxide to obtain 5-formyl phenanthroline; enabling a reaction product obtained by reacting the rhodamine B hydrazide and the 5-formyl phenanthroline to react with Ir2(ppy)4Cl2, and then reacting with NH4PF6, thus finally obtain the organic complex mercury ion probe. The preparation method of the probe is simple, and has the advantages of stable light emission, convenient and efficient operation and suitability for qualitatively, quantitatively and quickly detecting mercury ions in a solution, soil, biological cells and the like, and can be widely applied to the fields such as environment detection and biological cell imaging.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Water-soluble Rhodamine-based ion liquid probe for selectively distinguishing and identifying bimetallic ions and preparation method and application
InactiveCN107501285AGood water solubilityRealize detectionOrganic chemistryColor/spectral properties measurementsAluminum IonSolubility
The invention discloses a water-soluble Rhodamine-based ion liquid probe for selectively distinguishing and identifying bimetallic ions and a preparation method thereof, which are applied into pure water phase to singly and selectively distinguish and identify copper ions and aluminum ions. The water-soluble Rhodamine-based ion liquid probe is prepared by dehydrating and condensing salicylaldehyde imidazole chlorate ion liquid and Rhodamine B hydrazide, and has the advantages that the cost of raw materials is low, the obtaining is easy, the preparation is simple and convenient, the water solubility is good, and the like; the trace copper and alumnum can be detected at high efficiency in pure water environment; by utilizing the obvious difference of response times of copper ions and aluminum ions, the selective distinguishing and identifying under the copper and aluminum co-existence environment is realized.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Copper ion ratio type fluorescent probe based on rhodamine derivative and preparation method and application
ActiveCN110156806AImprove anti-interference abilityLow detection limitOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceDistillation
The invention discloses a copper ion ratio type fluorescent probe based on a rhodamine derivative and a preparation method and application. The chemical formula of the fluorescent probe is C41H45N5O2.A rhodamine B hydrazide intermediate is firstly prepared, then an ethanol solution of the rhodamine B hydrazide intermediate and an ethanol solution of 1,3,3-trimethyl-2-(formylmethylene)indoline arerespectively prepared, the ethanol solution of 1,3,3-trimethyl-2-(formylmethylene)indoline is dropwise added into the ethanol solution of the rhodamine B hydrazide intermediate for carrying out a reaction, and the distillation and purification is performed to obtain the fluorescent probe. The fluorescent probe is applied to detect Cu<2+>. The fluorescent probe can specifically recognize Cu<2+>, the anti-interference ability is strong, the detection limit is low, the sensitivity is high, the fluorescent probe can be well applied to the Cu<2+> detection in the environment or organisms, and thefluorescent probe has important application values; and the preparation method of the fluorescent probe is simple, and the operability is strong.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Dendritic fluorescent chemical sensor, and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN102226082AThe synthesis method is simpleReaction conditions are easy to controlOrganic chemistryChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceArgon atmosphereOrganic synthesis
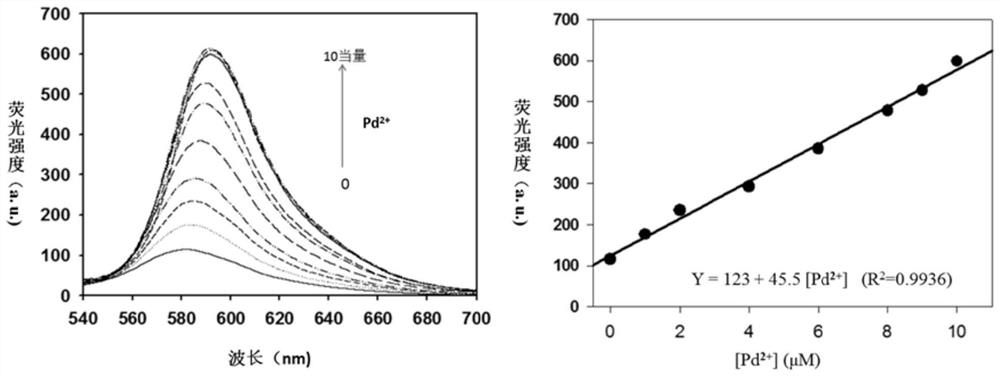
The invention discloses a dendritic fluorescent chemical sensor, and its preparation method and application, and also discloses a method for identifying and detecting Pd <2+> through the dendritic fluorescent chemical sensor. The invention belongs to the field of organic synthesis and analytical chemistry. The dendritic fluorescent chemical sensor is characterized in that rhodamine B hydrazide as a fluorescent active site is introduced into a dendritic compound to form a novel compound, wherein a structural formula of the novel compound is shown in the patent specification. The preparation method of the dendritic fluorescent chemical sensor comprises the following steps of in an argon atmosphere, putting an aldehyde compound with a quadrilateral molecular configuration into a reactor, adding ethanol into the aldehyde compound to make the compound dissolve, adding dropwisely rhodamine B hydrazide-ethanol solution into the aldehyde compound-ethanol solution with stirring under a constant pressure, wherein a mol ratio of the added aldehyde compound to the added rhodamine B hydrazide is 1: (4.2 to 4.5), when a adding process of the rhodamine B hydrazide-ethanol solution is finished, adding 1.0 to 2.0% by volume of glacial acetic acid into the mixed solution in the reactor, stirring well, carrying out a reflux reaction at a temperature of 100 DEG C for 18 to 22 hours, evaporating the resulting products to remove a solvent and collect residue, washing the residue 3 to 5 times by ethanol, and drying in a vacuum to obtain a dendritic fluorescent chemical sensor product which is a pale pink solid. The dendritic fluorescent chemical sensor prepared by the preparation method has four fluorescent active groups thus a sensing speed and a sensing sensitivity of the dendritic fluorescent chemical sensor is 4 times as high as a sensing speed and a sensing sensitivity of a small molecule. The dendritic fluorescent chemical sensor does not contain toxic solvents.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Preparation and application of mercury ion fluorescent probe compound based on rhodamine B
InactiveCN105669689AInnovative designGood choiceOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceLithiumFluorescence
Provided are preparation and application of a mercury ion fluorescent probe compound based on rhodamine B. The invention relates to the mercury ion fluorescent probe compound and the preparation and the application thereof, wherein the mercury ion fluorescent probe compound has the structure represented by the formula I. The preparation method comprises the steps: carrying out a reaction of 2,2'-bipyridine with methyl lithium under the protection of nitrogen gas to obtain 6-methyl-2,2'-bipyridine, then oxidizing methyl by selenium dioxide to obtain 6-aldehyde-2,2'-bipyridine; and carrying out a reaction of 6-aldehyde-2,2'-bipyridine and rhodamine B hydrazide to obtain the final product probe molecule. The probe molecule has good selectivity and sensitivity to mercury ions, has no toxicity to cells, and not only can be used for detection of mercury ions in water bodies but also can be used for detection and imaging of mercury ions in cells.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Preparation and application of aminoacylmethyl-(2-methylaminofuran)rhodamine amide derivative
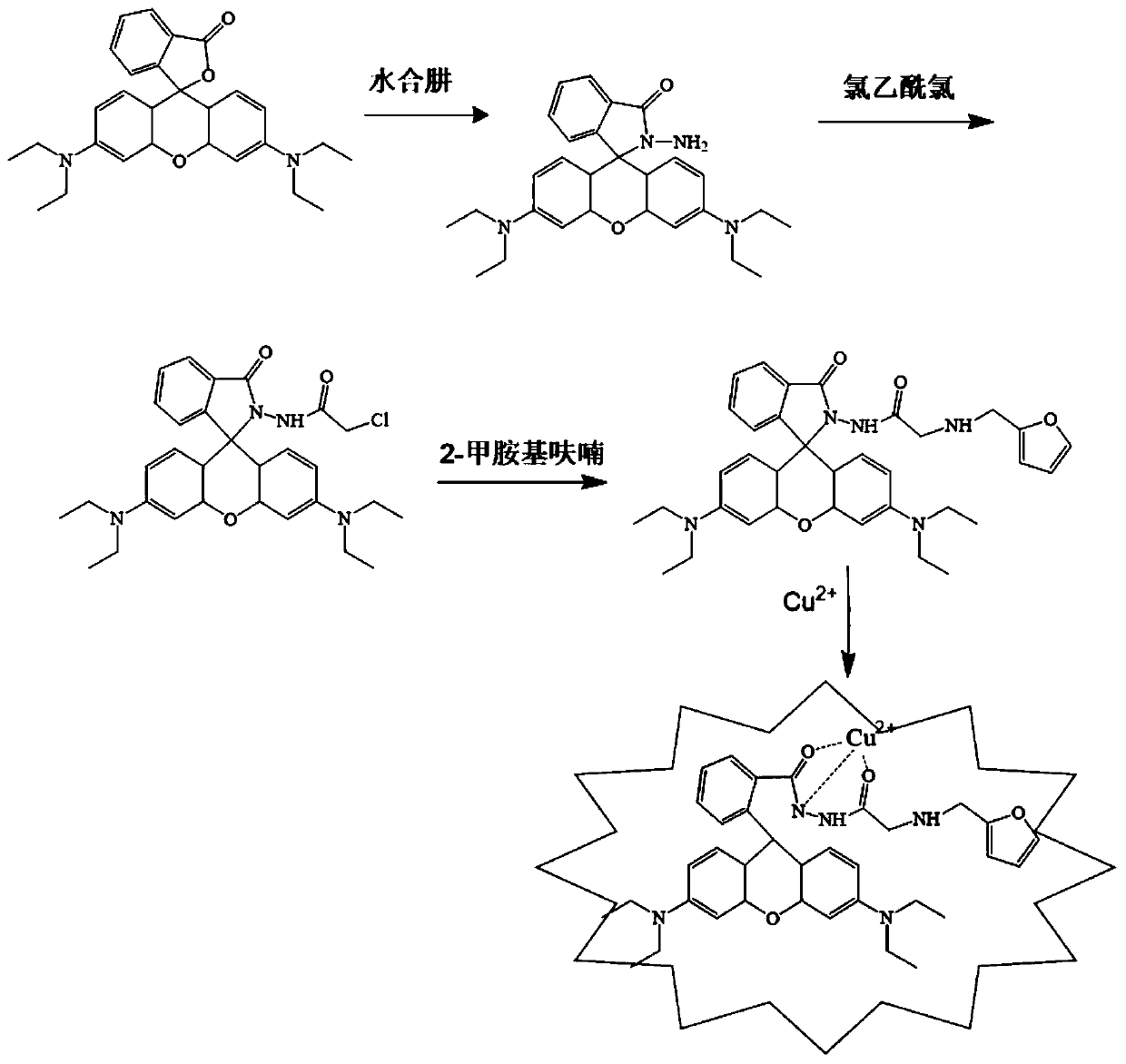
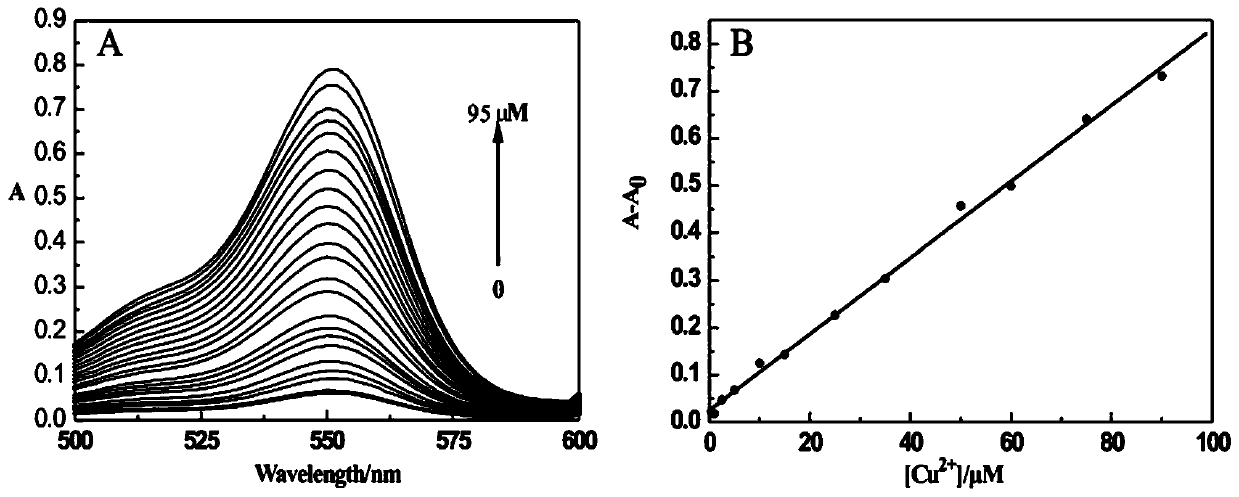
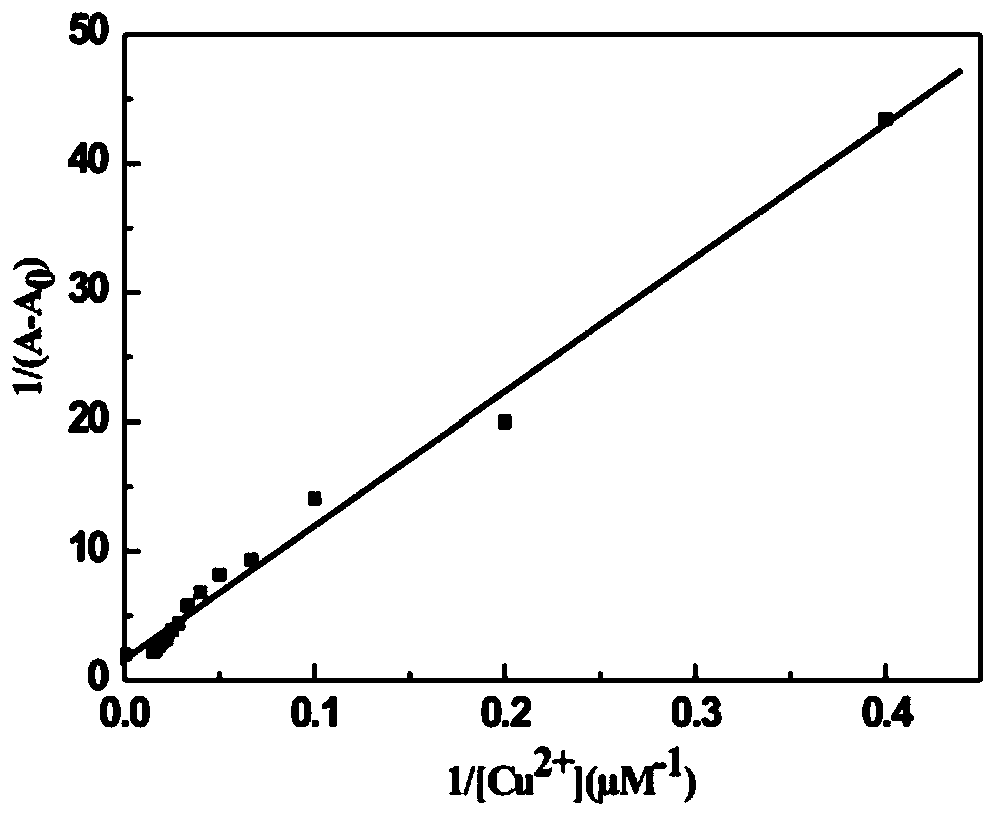
ActiveCN110028515AStrong penetrating powerLow biological toxicityOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorQuantum yieldExtinction
The invention discloses preparation and application of an aminoacylmethyl-(2-methylaminofuran)rhodamine amide derivative, and belongs to the technical field of synthesis and application of inorganic materials. The aminoacylmethyl-(2-methylaminofuran) rhodamine amide derivative is prepared by performing a reaction between rhodamine B and hydrazine hydrate to produce rhodamine B hydrazide first andthen respectively performing a condensation reaction with chloroacetyl chloride and 2-furanmethylamine. A aminoacylmethyl-(2-methylaminofuran)rhodamine amide compound synthesized according to a preparation method provided by the invention is a rhodamine derivative containing a lactone ring structure, and has the characteristics of excitation and emission wavelengths in a visible region, high fluorescence quantum yield, a molar extinction coefficient, good biocompatibility and the like; the preparation method thereof is simple, a reaction condition is mild, and the yield is relatively high; after combination with copper ions, the naked-eye recognition effect is good, the response is rapid, and the specific selectivity is high; even, the aminoacylmethyl-(2-methylaminofuran)rhodamine amide derivative can be applied to real-time online microdetection of the copper ions and can be developed into an optical sensing material with an important research significance.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Rhodamine B-grafted chitosan adsorbent and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN105817208AImprove stabilityImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesPreparing sample for investigationMercuric ionEnvironment water
The invention discloses a rhodamine B-grafted chitosan adsorbent and preparation and application thereof, and belongs to the field of adsorbing material preparation technologies. Preparation of the adsorbent comprises the steps that rhodamine B reacts with hydrazine hydrate to prepare rhodamine B hydrazide; rhodamine B hydrazide is grafted to chitosan by taking glyoxal as a cross-linking agent to obtain the adsorbent. According to the rhodamine B-grafted chitosan adsorbent, through the adsorptivity of chitosan and rhodamine B, bonding is firm, the property is stable, the selectivity is good, and the enrichment factor is large. The adsorbent can be used for adsorption and detection of mercury ions in an environmental water sample.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
pH-responsive fluorescence sensing material based on rhodamine B and cyanobiphenol, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN107698600AExcellent optical propertiesProne to isomerizationOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological cellHydrazine compound
The present invention relates to a pH-responsive fluorescence sensing material based on rhodamine B and cyanobiphenol, a preparation method and applications thereof, and belongs to the technical fieldof biochemical fluorescent sensing materials. According to the present invention, two pH-sensitive optical groups such as rhodamine B and cyanobiphenol are used base raw materials, wherein rhodamineB and hydrazine hydrate are subjected to a reaction to prepare rhodamine B hydrazide, and then the rhodamine B hydrazide and aldehyde-modified cyanobiphenol are combined through a Schiff base reactionto prepare the fluorescence sensing material; the method has advantages of mild preparation conditions and low raw material cost; the prepared material has good chemical stability, and has unique response properties to different pH values, wherein the responses can be presented through visible fluorescence and appearance color; and the prepared pH-responsive fluorescence sensing material can be used for the determination of the pH value in water and biological cells.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
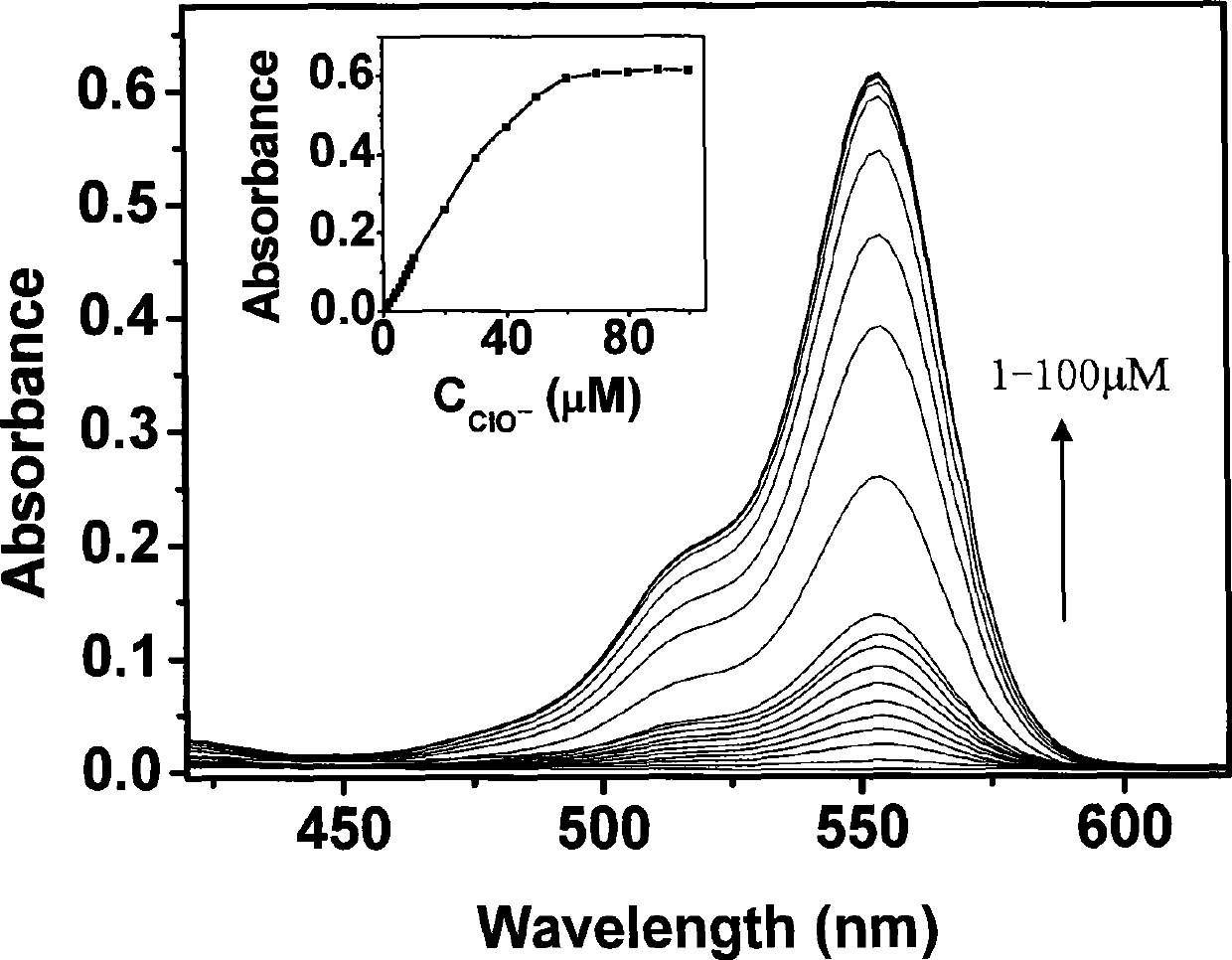
Colorimetric/fluorescent probe for detecting hypochlorite ions as well as preparation method and application of colorimetric/fluorescent probe
ActiveCN113603701AHigh sensitivityImprove interferenceOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluoProbesChemical structure
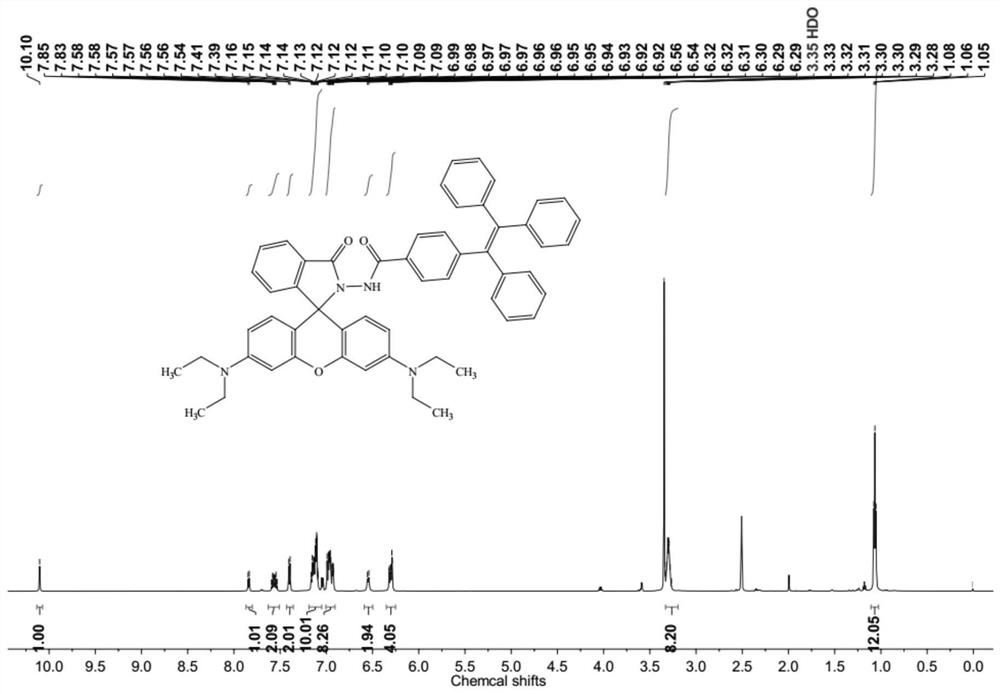
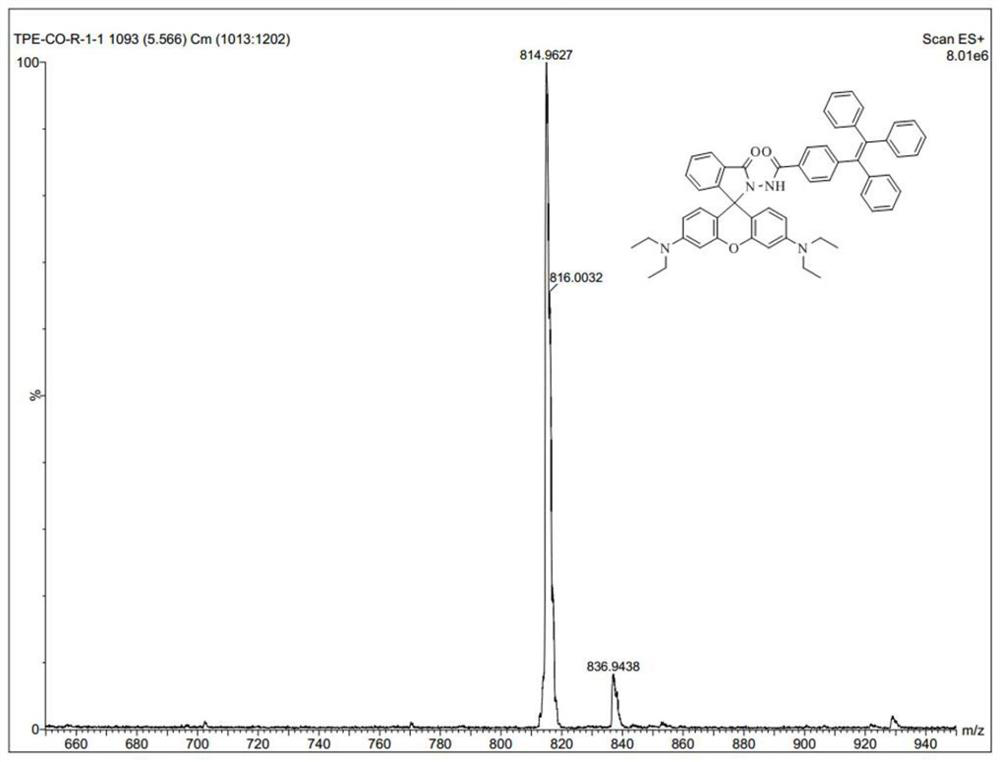
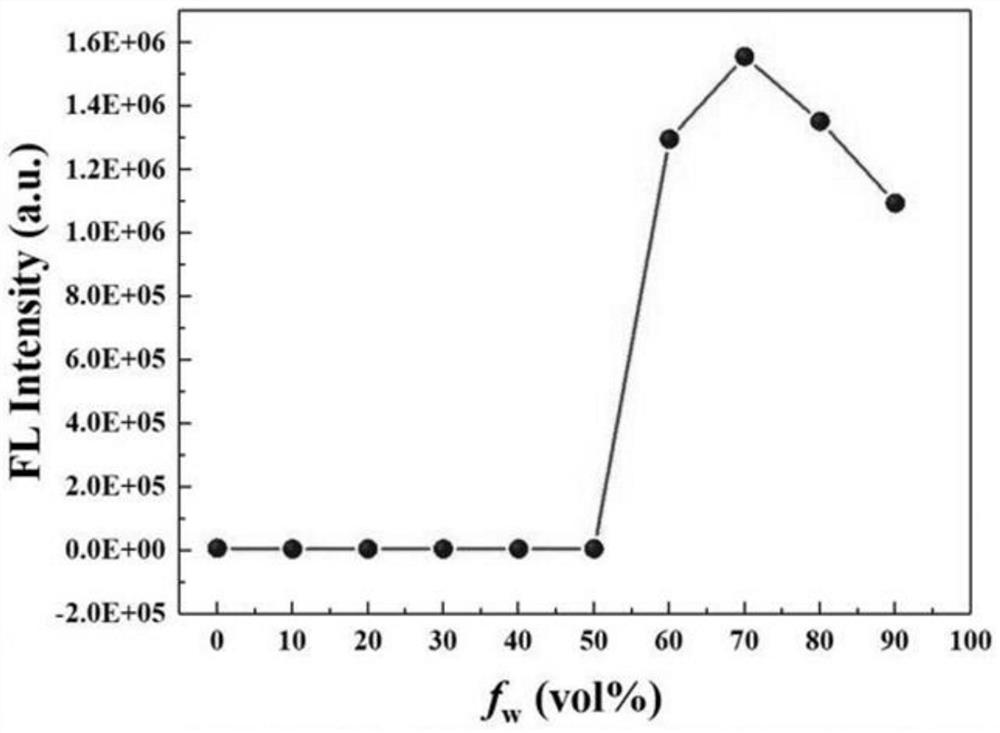
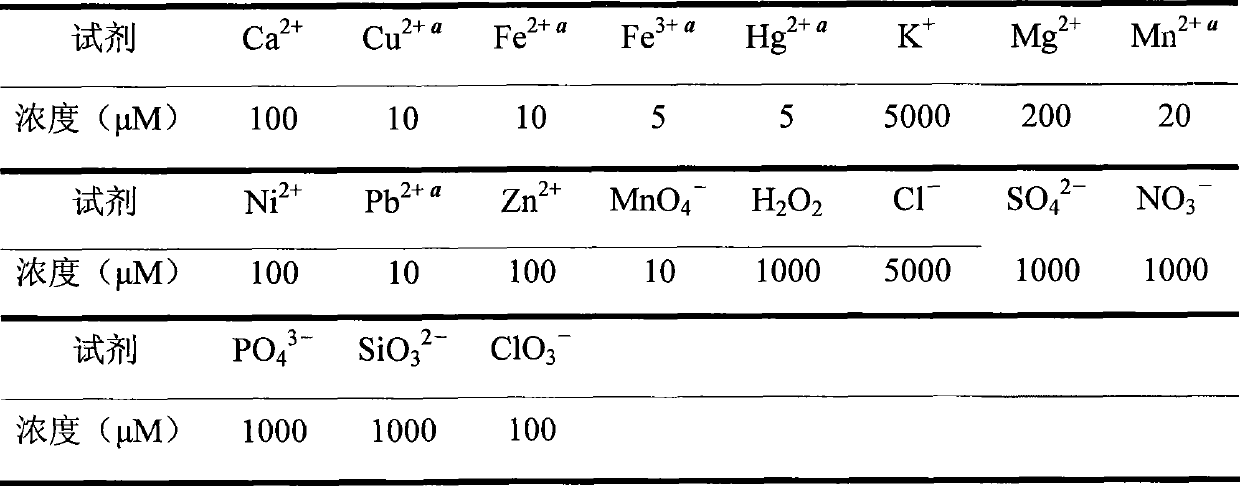
The invention relates to a colorimetric / fluorescent probe for detecting hypochlorite ions as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The fluorescent probe is named as TPE-acylamide-Rh, and the chemical structural formula of the fluorescent probe is as shown in a formula I. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving 1-(4-phenylformate)-1,2,2-triphenylethylene in thionyl chloride, conducting heating for a reaction, performing reacting with rhodamine B hydrazide under inert atmosphere and catalytic action, and carrying out purifying to obtain the fluorescent probe. The probe shows excellent selectivity, ion interference resistance and sensitivity on ClO<-> recognition performance in a solution state and an aggregation state. In addition, the probe forms nanoparticles in the aggregation state, so cell staining is easy, and cell imaging application is facilitated. Hela cell imaging research shows that the TPE-acylamide-Rh shows an excellent characteristic of identifying ClO<-> in cells. The preparation method for the probe is simple in process and short in synthesis route. The probe is applied to detection of hypochlorite ions, and the application range of the probe is widened.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
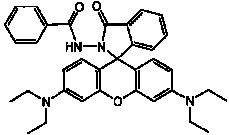
N-benzoyl rhodamine B hydrazine, preparation and use thereof
InactiveCN101302220BHigh detection sensitivityHigh selectivityOrganic chemistryColor/spectral properties measurementsQuantum yieldHypochlorite
The invention discloses N-benzoyl rhodamine B hydrazide, a method for making the same and an application of the same. The structure of the N-benzoyl rhodamine B hydrazine is shown in formula I. Due to having great molar absorptivity and high fluorescence quantum yield, xanthene dye is an excellent matrix of an optical probe. The xanthene dye derivative-N-benzoyl rhodamine B hydrazide can be selectively reacted with hypochlorite to carry out chromogenic and fluorescence opening reaction; therefore, a system with excellent optical performance can be generated by colorless matter; moreover, detection can be carried out through both a light absorption method and a fluorescence method. In addition, when the N-benzoyl rhodamine B hydrazide is used to detect hypochlorite, high detection sensitivity can be obtained and the detection can be completed just through adopting a small amount of samples, thereby broadening the application range of the method.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
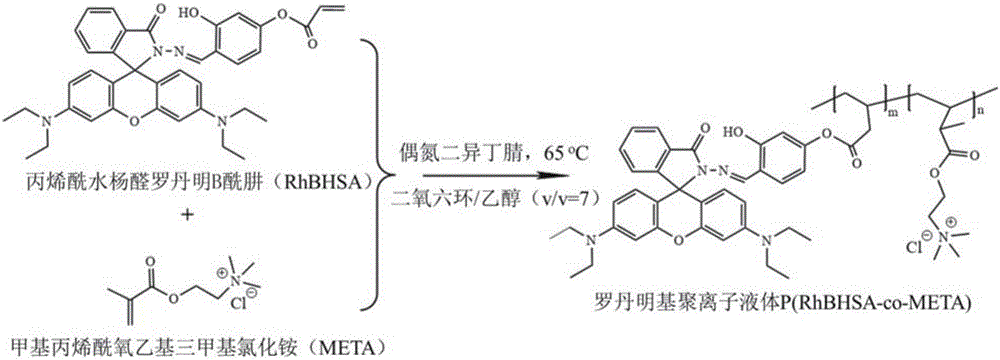
High-water-solubility rhodamine-based polyion liquid and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106519112ASensitive detectionGood water solubilityOrganic chemistryColor/spectral properties measurementsSolubilityBinding site
The invention belongs to the field of detection of heavy metal ions and particularly relates to high-water-solubility rhodamine-based polyion liquid and a preparation method thereof. The high-water-solubility rhodamine-based polyion liquid is applied to quick visual colorimetric detection of pure-water-phase copper ions. The rhodamine-based polyion liquid is formed by copolymerization of ion liquid monomers and salicylide-like rhodamine B hydrazide monomers, and has the advantages that the raw materials are low in cost and easy to obtain, preparation is easy and convenient, the rhodamine content is high, water solubility is excellent, and no nonspecific binding site exists; and efficient colorimetric detection of trace copper can be achieved in the environment of pure water, the detection limit of naked eyes and the detection limit of an ultraviolet-visible light spectrophotometric method are 0.5 micron and 0.15 micron correspondingly and are both far lower than 31 microns specified by the World Health Organization (WHO). In addition, the detection response time of detection of the rhodamine-based polyion liquid to copper ions is short, developing can be completed within 5s, and moreover, the rhodamine-based polyion liquid has excellent selectivity and is hardly influenced by other concomitant metal ions.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Preparation and application of N-(2-hydroxy-5-chlorobenzene)ylrhodamine B hydrazide
ActiveCN108610349AReduce dosageEasy to synthesizeOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceChlorobenzeneFluorescence
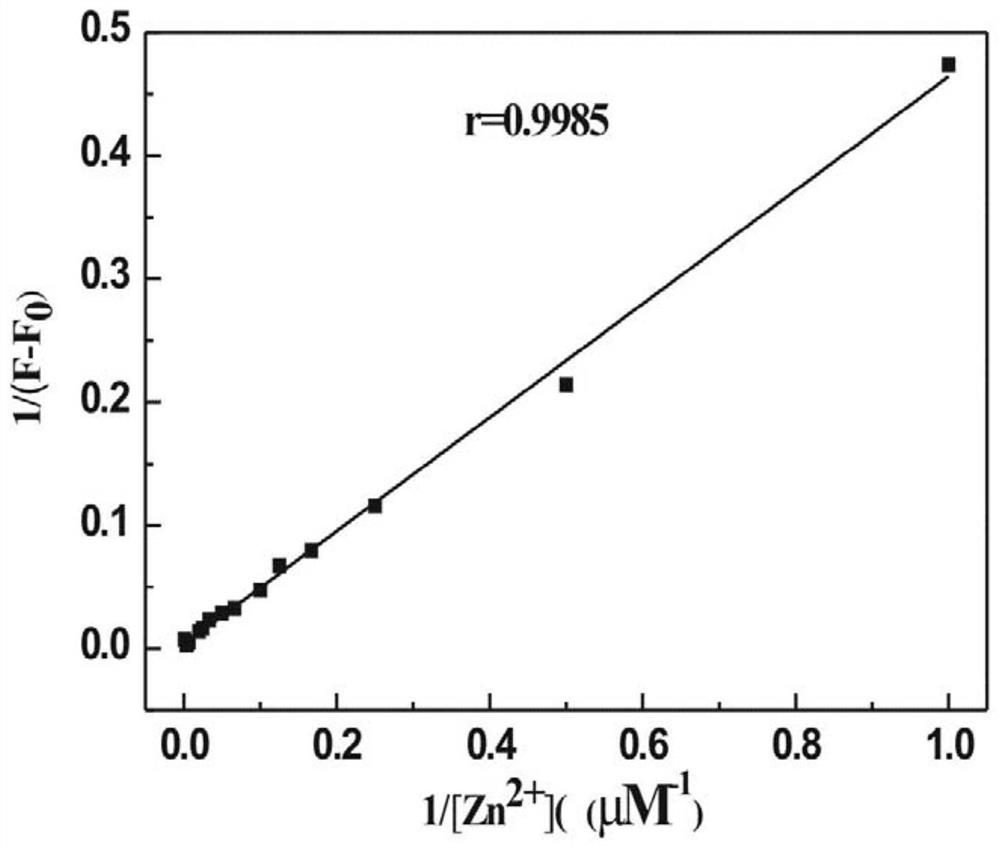
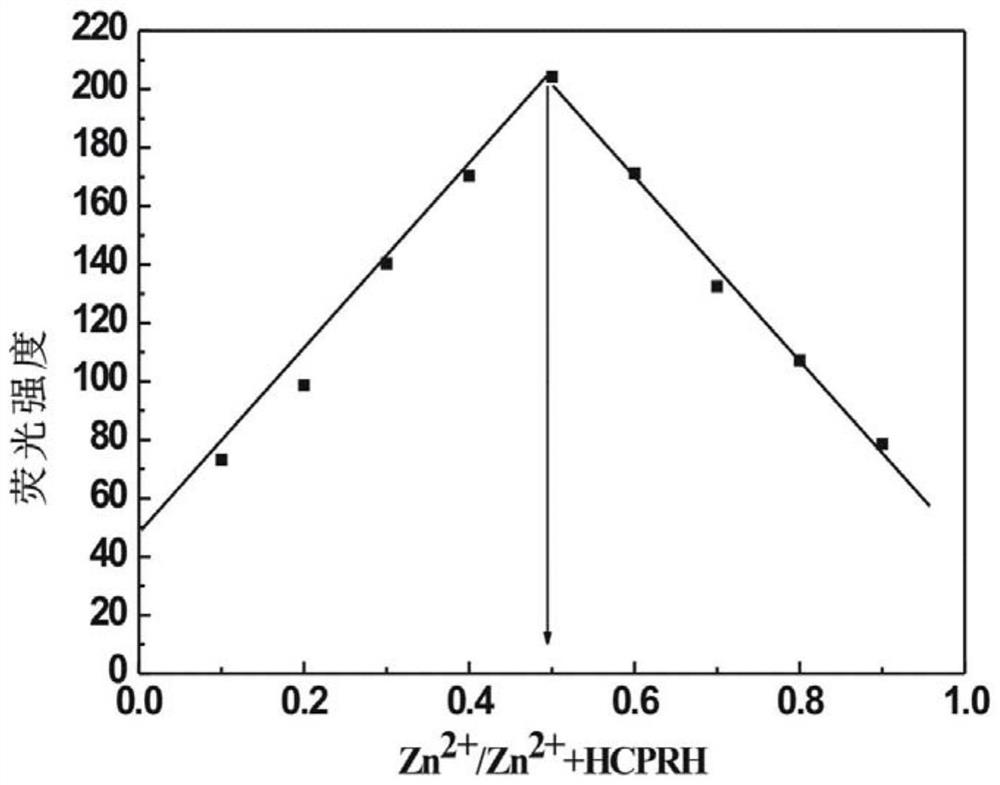
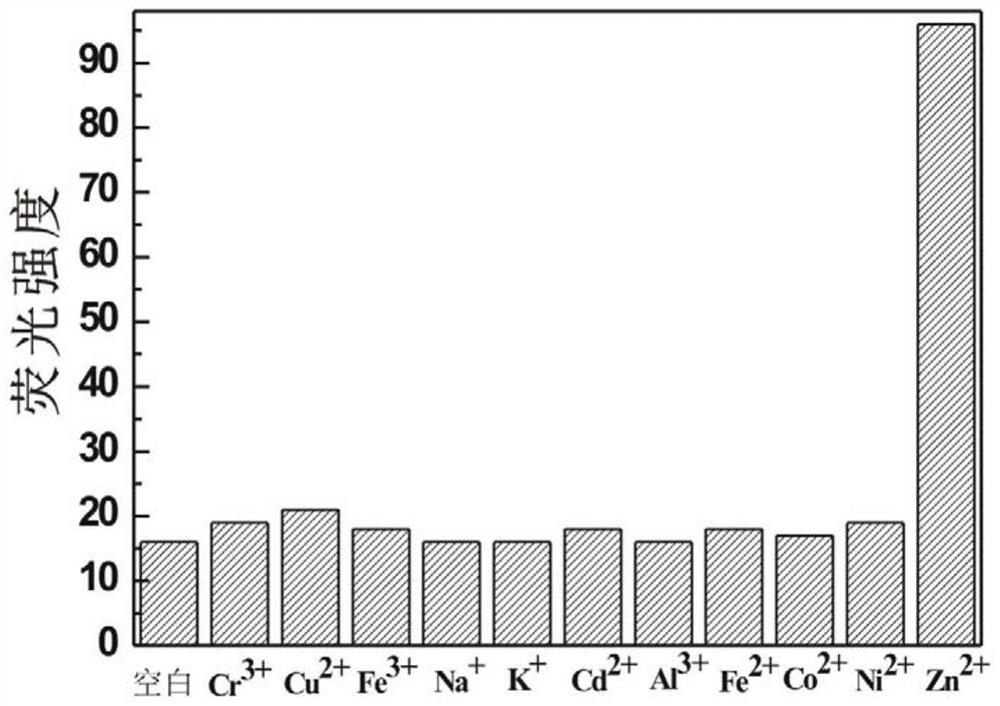
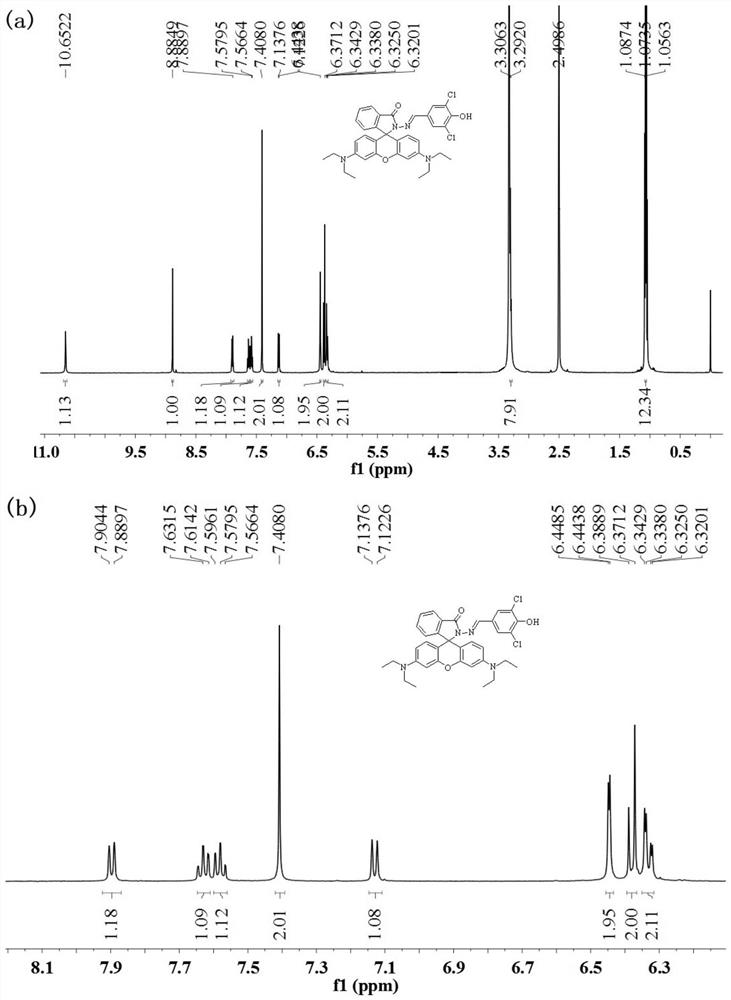
Belonging to the technical field of inorganic material synthesis and application, the invention provides preparation and application of N-(2-hydroxy-5-chlorobenzene)ylrhodamine B hydrazide. The invention adopts liquid-phase synthesis method. The method includes: firstly adding excess hydrazine hydrate into a rhodamine B ethanol solution, carrying out heating reflux reaction to obtain an initial product, then employing concentrated hydrochloric acid and a sodium hydroxide solution respectively to adjust the reaction system to neutral, thus obtaining a reduced intermediate product rhodamine B hydrazine; then further reacting the rhodamine B hydrazine with 5-chlorosalicylaldehyde in methanol, and conducting recrystallization to obtain N-(2-hydroxy-5-chlorobenzene)ylrhodamine B hydrazide for rapid, sensitive and highly selective recognition or even trace detection of zinc ions. The compound has the advantages of simple synthesis process, mild reaction conditions, small reagent dosage, lowmaking cost, little environmental pollution, and good optical properties and biocompatibility, and can be developed as a brand new fluorescent probe for zinc ion recognition in organisms.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Preparation method and application of 1-methylpiperazine rhodamine amide
InactiveCN110256452AEasy to synthesizeMild reaction conditionsOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceSolubilityPotassium carbonate
The invention provides a preparation method and an application of 1-methylpiperazine rhodamine amide, and belongs to the technical fields of synthesis and applications of organic materials. The preparation method concretely comprises the following steps: adding an excess amount of hydrazine hydrate to an ethanol solution of rhodamine B, heating for refluxing and reacting to obtain an initial product, and adjusting the reaction system to be neutral by using concentrated hydrochloric acid and a sodium hydroxide solution respectively to obtain a reduced pale pink intermediate rhodamine B hydrazide; dissolving the rhodamine B hydrazide in dichloromethane, and reacting the obtained dichloromethane solution of the rhodamine B hydrazide with chloroacetyl chloride under the action of an acid binding agent triethylamine to obtain a white solid; and finally dissolving the white solid in acetonitrile, and reacting the obtained solution with 1-methylpiperazine under the catalysis of potassium carbonate to prepare the 1-methylpiperazine rhodamine amide molecular probe. The synthesis method has the advantages of simplicity, low dosages of reagents, mild reaction conditions, and good water solubility of the product, and the synthesized probe has excellent selectivity, reversibility and stability in identification of hydrogen ions, and can be developed as an environmental pH optical sensor. .
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Calcium ion and zinc ion double-channel rhodamine fluorescent probe as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108276423AGood selective detectionEasy to useOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceHydrazine compoundNitrogen gas
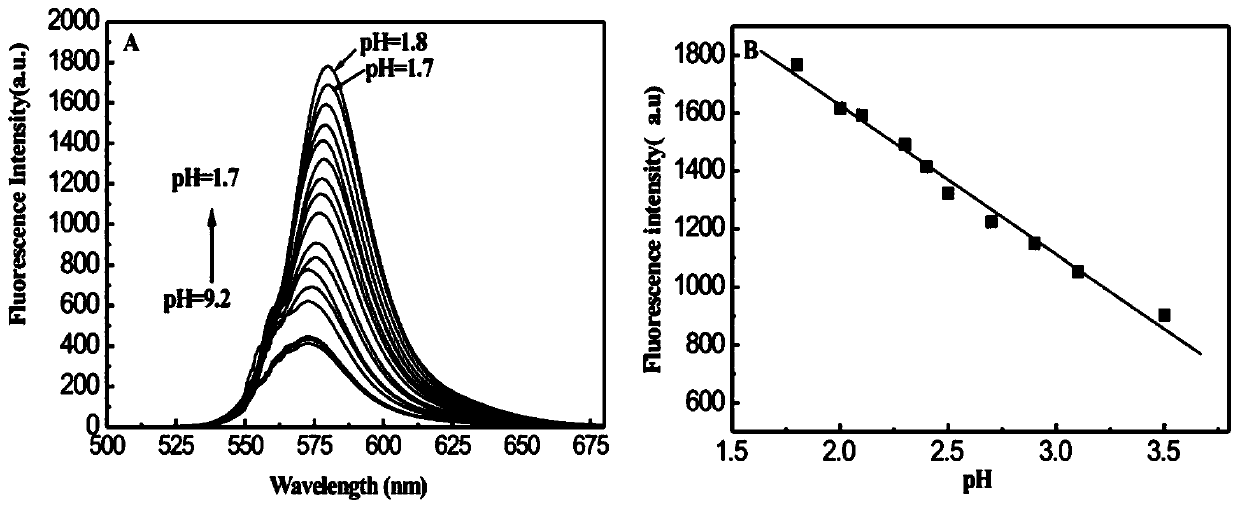
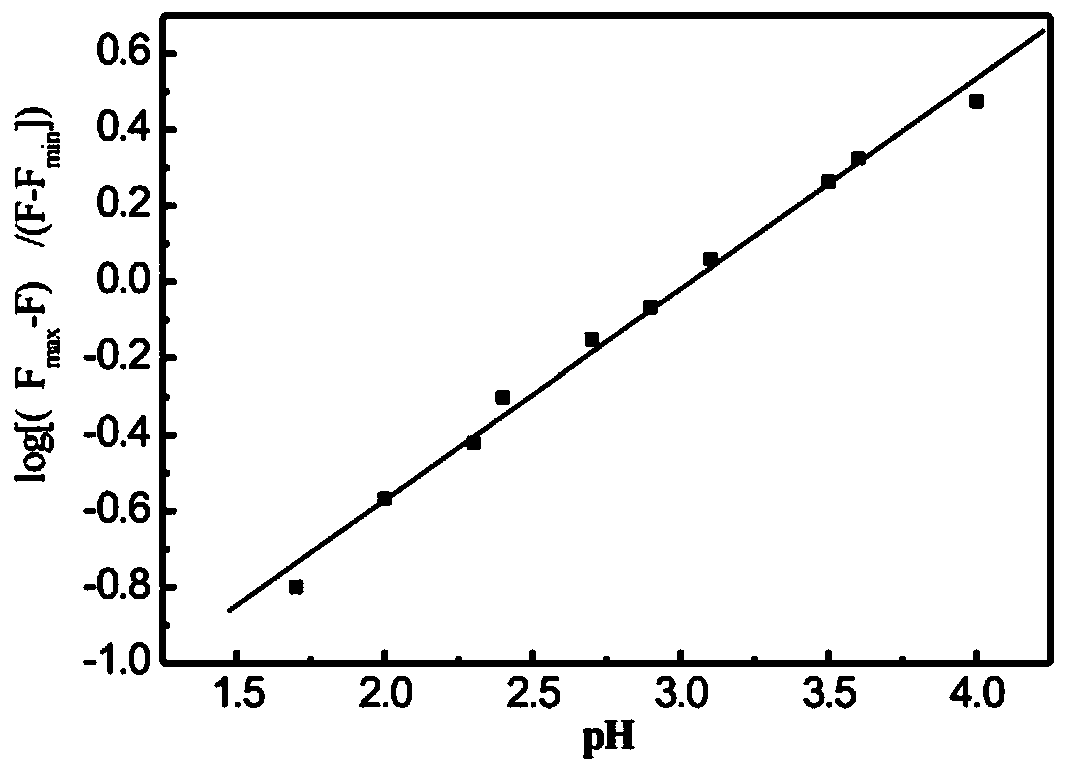
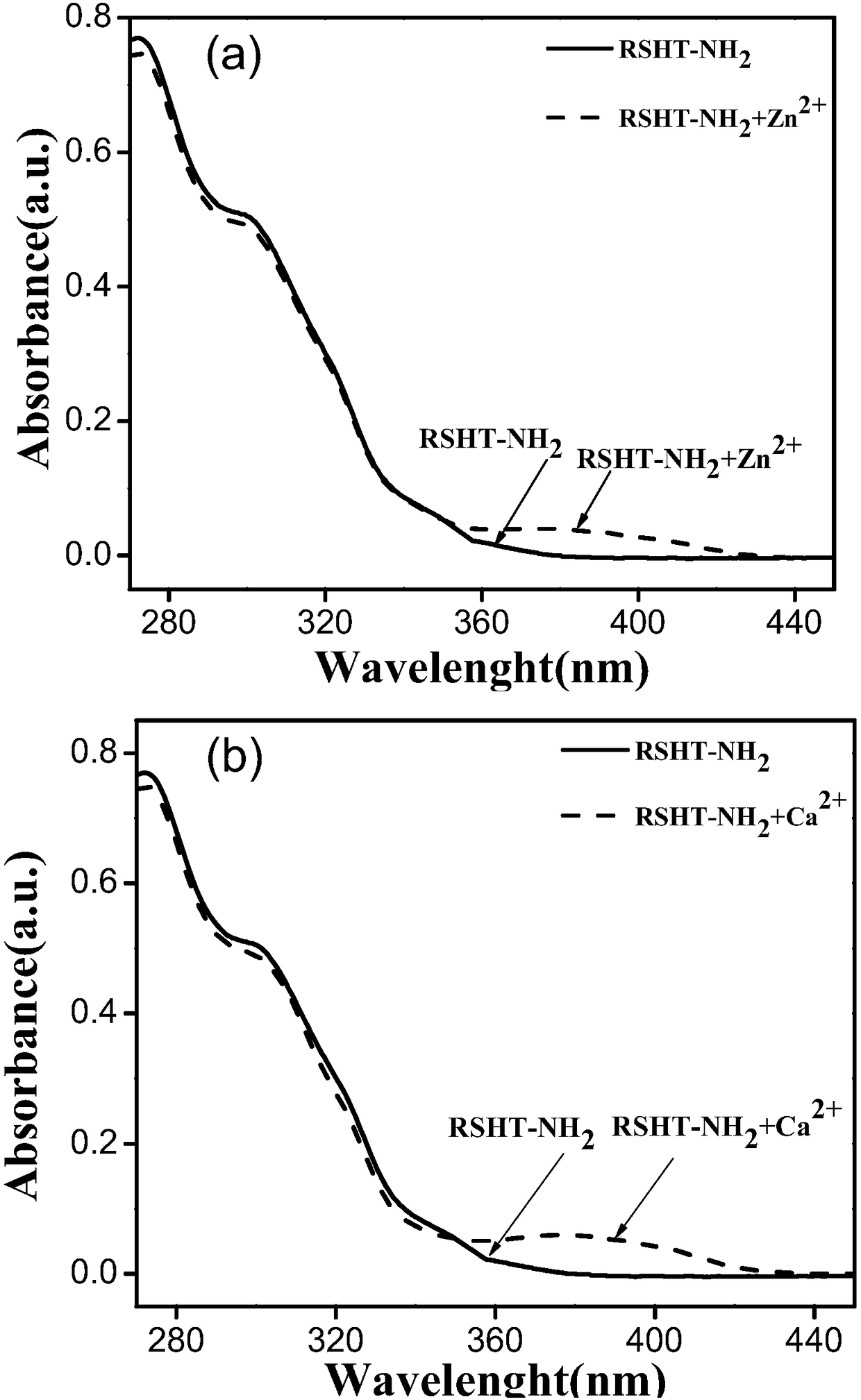
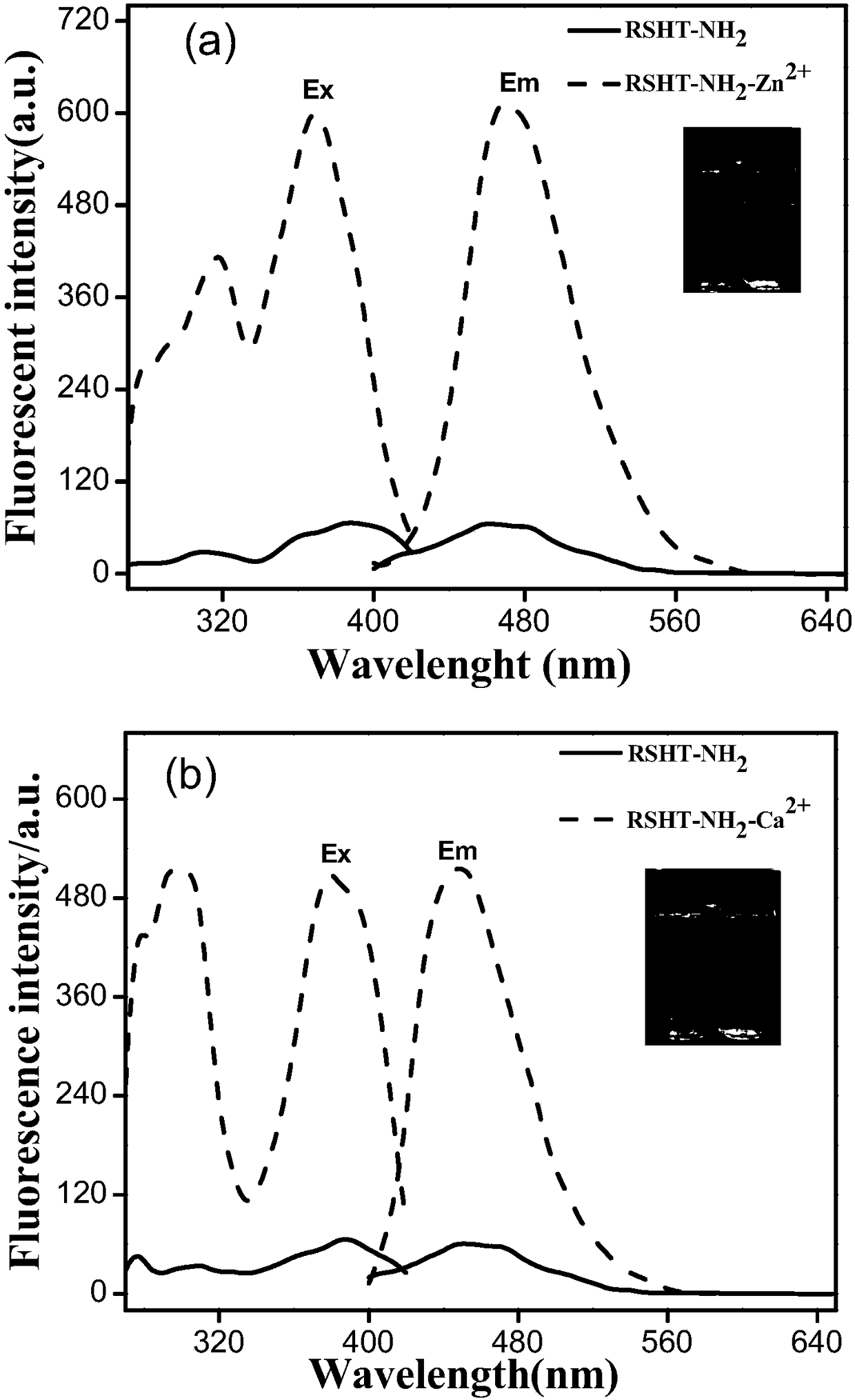
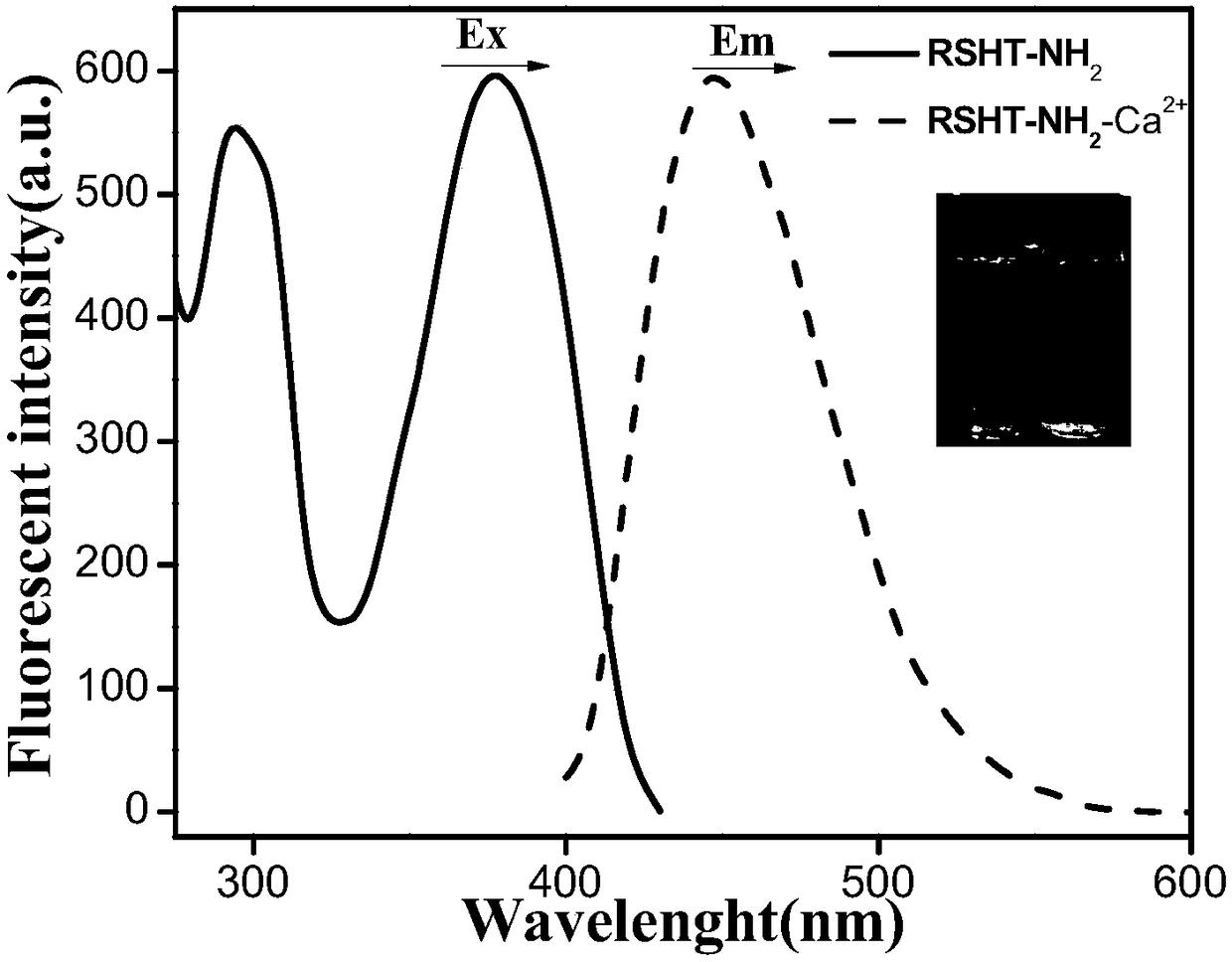
The invention relates to a calcium ion and zinc ion double-channel rhodamine fluorescent probe as well as a preparation method and application thereof. A structural formula of the calcium ion and zincion double-channel rhodamine fluorescent probe is as follows: the formula is shown in the description; the preparation method comprises the following steps: taking rhodamine B and hydrazine hydrate to react, so as to obtain rhodamine B hydrazide; carrying out reaction on p-aminobenzoate and the hydrazine hydrate; dissolving an obtained product into a solvent and dropwise adding salicylic aldehyde; reacting to obtain salicylic aldehyde-4-aminobenzoyl hydrazide hydrazone; dissolving cyanuric trichloride into the solvent and adding an acid binding agent; dropwise adding a THF (Tetrahydrofuran) solution of the rhodamine B hydrazide into an ice water bath under the protection of nitrogen gas; stirring to obtain RSH; dissolving the RSH and adding the acid binding agent; under the protection ofnitrogen gas, dropwise adding the salicylic aldehyde-4-aminobenzoyl hydrazide hydrazone and reacting to obtain RSHT; dissolving the RSHT and adding the acid binding agent; dropwise adding the hydrazine hydrate under the protection of N2 and reacting to obtain the probe. The fluorescent probe compound provided by the invention has very good selectivity on zinc ions and calcium ions, is convenientlyapplied to environmental applications and has a relatively good utilization effect.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Near-infrared fluorescent probe compound taking N-pyridine oxide derivative as recognition group as well as preparation and application of near-infrared fluorescent probe compound
ActiveCN112939996AImprove the coordination effectWith spatial apertureOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescencePhotochemistryHigh selectivity
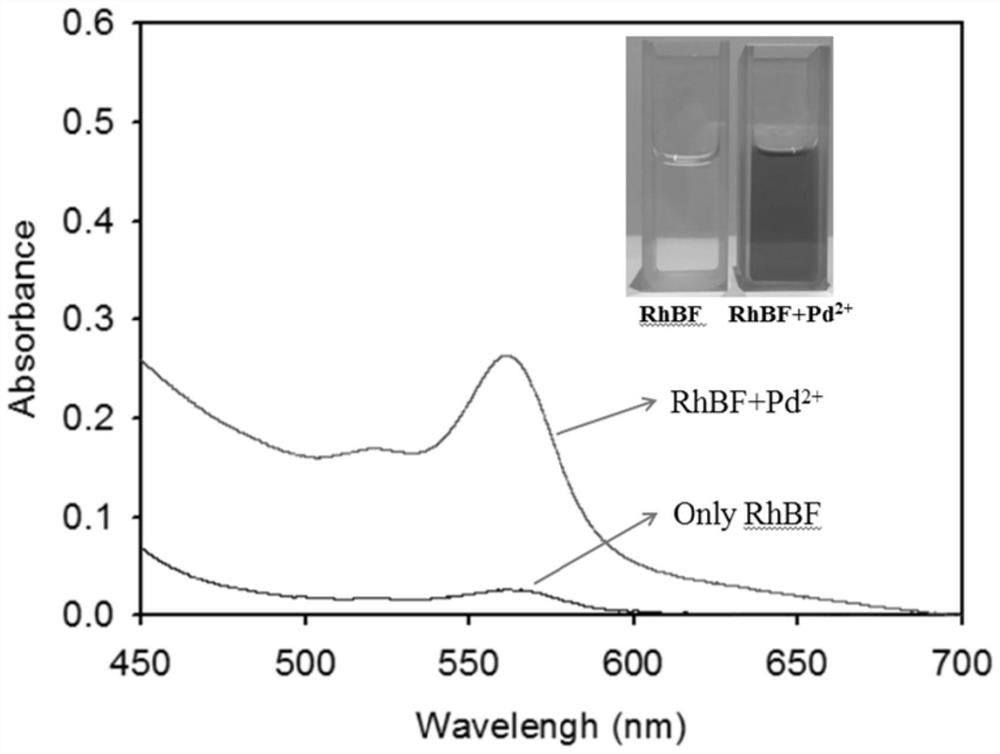
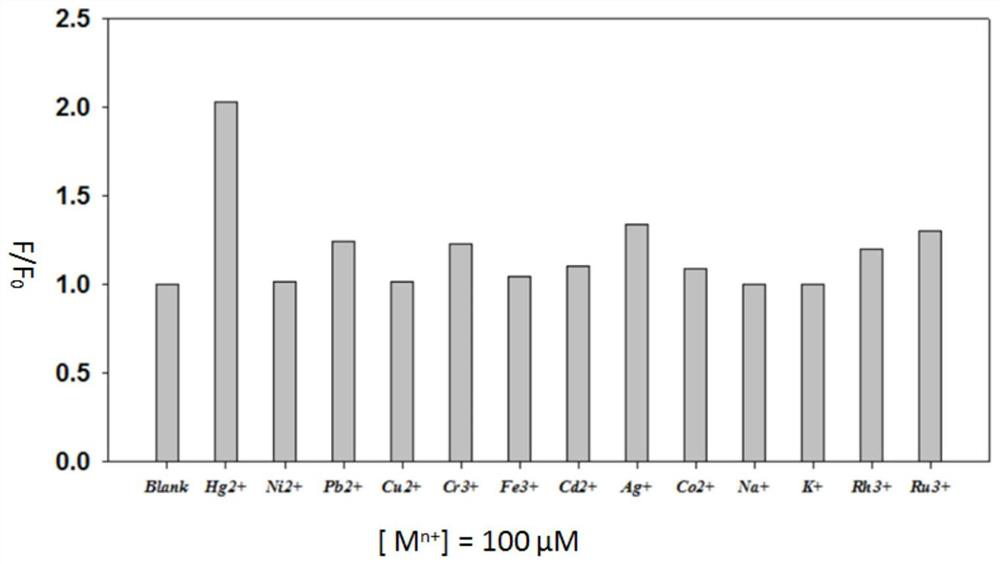
The invention discloses a near-infrared fluorescent probe compound taking an N-pyridine oxide derivative as a recognition group as well as preparation and application of the near-infrared fluorescent probe compound. The preparation method specifically comprises the following steps: firstly, oxidizing a pyridine heterocyclic compound into an N-pyridine-2-formaldehyde oxide derivative, and taking the N-pyridine-2-formaldehyde oxide derivative as a recognition group; finally, enabling rhodamine B hydrazide to react with the N-pyridine oxide derivative in an organic solvent, so as to obtain the N-pyridine oxide-rhodamine B near-infrared fluorescent probe. The N-pyridine oxide-rhodamine B type near-infrared fluorescent probe can detect divalent palladium ions with high sensitivity and high selectivity, can realize colorimetric and fluorescent dual-mode detection of the divalent palladium ions in the environment, and can also be used for rapid detection of the divalent palladium ions in cells. Besides, the applied N-pyridine oxide derivative is a new recognition group which is easily available in initial raw material and easy to prepare, and has a wide application prospect in the aspect of detecting other heavy metal ions after being combined with other common dyes.
Owner:GUANGZHOU YUEWANG AGRI CO LTD
Preparation and application of a kind of n-(2-hydroxyl-5-chlorophenyl)ylrhodamine b hydrazide
ActiveCN108610349BReduce dosageEasy to synthesizeOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluoProbesChlorobenzene
Belonging to the technical field of inorganic material synthesis and application, the invention provides preparation and application of N-(2-hydroxy-5-chlorobenzene)ylrhodamine B hydrazide. The invention adopts liquid-phase synthesis method. The method includes: firstly adding excess hydrazine hydrate into a rhodamine B ethanol solution, carrying out heating reflux reaction to obtain an initial product, then employing concentrated hydrochloric acid and a sodium hydroxide solution respectively to adjust the reaction system to neutral, thus obtaining a reduced intermediate product rhodamine B hydrazine; then further reacting the rhodamine B hydrazine with 5-chlorosalicylaldehyde in methanol, and conducting recrystallization to obtain N-(2-hydroxy-5-chlorobenzene)ylrhodamine B hydrazide for rapid, sensitive and highly selective recognition or even trace detection of zinc ions. The compound has the advantages of simple synthesis process, mild reaction conditions, small reagent dosage, lowmaking cost, little environmental pollution, and good optical properties and biocompatibility, and can be developed as a brand new fluorescent probe for zinc ion recognition in organisms.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Single-factor-initiated photochromic sensing material as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN114539274AHigh sensitivityQuick responseOrganic chemistryInksSalicylaldehydeStructural formula
The invention discloses a single factor initiated photochromic sensing material and a preparation method and application thereof, the structural formula of the sensing material is shown as follows: in the structural formula, substituent groups R1 and R3 are any one of Cl, Br and I elements, and a substituent group R2 is hydroxyl. Aiming at the problem that a photochromic material constructed on the basis of rhodamine B hydrazide and salicylaldehyde is poor in initiation ion selectivity at present, the invention provides a single-factor-initiated photochromic sensing material only initiated by Cu < 2 + >, and the sensing material realizes single-factor-initiated photochromism on the basis of a group capable of generating specific complexation with Cu < 2 + > contained in the sensing material. The photochromic sensing material has the advantages of high sensitivity, high response speed, good stability, capability of repeatedly writing and erasing information and the like.
Owner:QUFU NORMAL UNIV
Preparation and application of aminoacylmethyl-(2-methylaminofuran)rhodamine amide derivative
ActiveCN110028515BHigh fluorescence quantum yieldHigh molar extinction coefficientOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorQuantum yieldFuran
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for determining complexing capacity of medicine and copper ions
InactiveCN110470662AReflect complexation abilityReduce absorptionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsPink colorHydrazine compound
The invention provides a method for determining the complexing capacity of a medicine and copper ions. The method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing and stirring 100 [mu]l of the to-be-determined medicine and 100 [mu]l of a copper ion solution with the concentration of 0.1-10mmol / L; carrying out standing for 1-5 minutes; adding a mixture into 2ml of a rhodamine B hydrazine solution with the concentration of 0.1-5mmol / L; and carrying out a reaction for 3-10 minutes to obtain a to-be-determined solution. According to the technical scheme, the copper ions and the to-be-determined medicine are mixed in advance and then added into the rhodamine B hydrazide solution. If the to-be-determined medicine and the copper ions can be complexed, copper ion competition is formed between the to-be-determined medicine and rhodamine B hydrazides, so that the number of the open-loop rhodamine B hydrazides is reduced, finally the generated pink color becomes shallow, the ultraviolet absorptionand fluorescence emission intensities are reduced, and the changes of signals reflect the complexing capacity of the medicine and the copper ions.
Owner:PUTIAN UNIV
A fluorescent probe for detecting mercury ions and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN110117295BHigh sensitivityGood choiceGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceBenzoic acidFluoProbes
The invention provides a fluorescent probe for detecting mercury ions and its preparation method and application. Its chemical name is 3-(4-(1,3,5,7-tetramethyl-8 propyl) boron difluoride Pyrrole-4-carbonyl)piperazine)-rhodamine B hydrazide, the fluorescent probe of the present invention uses the boron fluoride dipyrrole fluorescent dye BODIPY unit as an energy donor, and the rhodamine unit is an energy acceptor. Mercury ions promote the "open-close" of the spiroamide ring to realize the fluorescence energy resonance transfer of BODIPY and rhodamine units, resulting in a red shift of fluorescence, which can be used to detect Hg 2+ The fluorescent ratio probe; the fluorescent probe is based on m-hydroxyphenylpiperazine and 2-(4-diethylamino)-2-hydroxyl)-benzoic acid as raw materials, and then reacted with 1,3,5 , 7‑Tetramethyl‑8‑propoxycarbonyl succinimide) obtained by condensation reaction of boron fluoride dipyrrole. The probe of the invention is a FRET-based ratiometric fluorescent probe with high sensitivity and good selectivity, which can detect mercury ions in water phase.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com