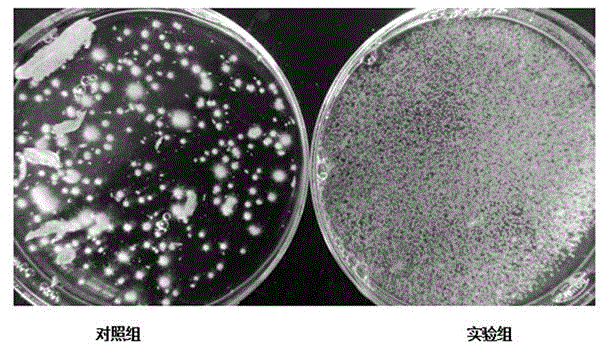
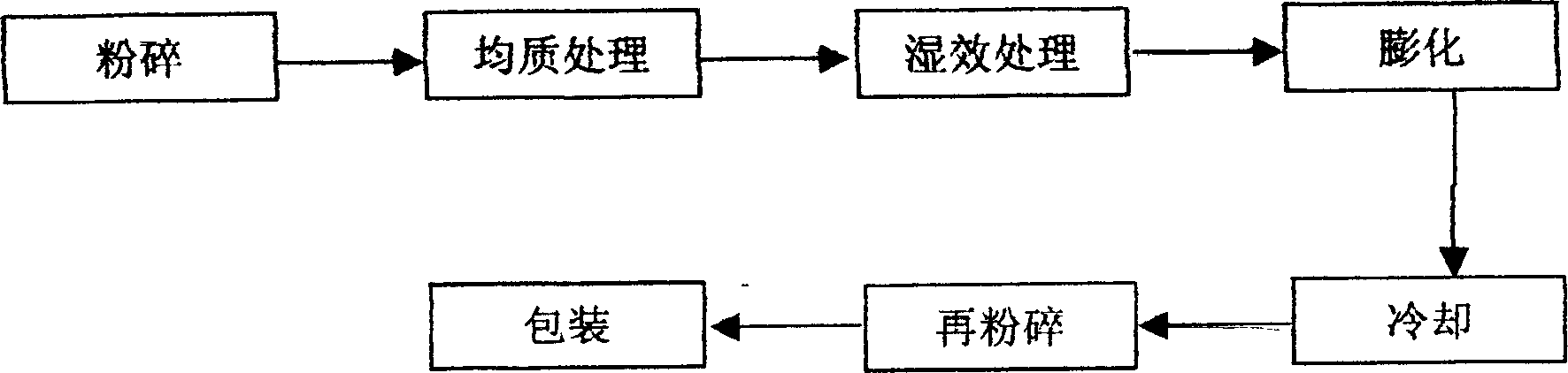
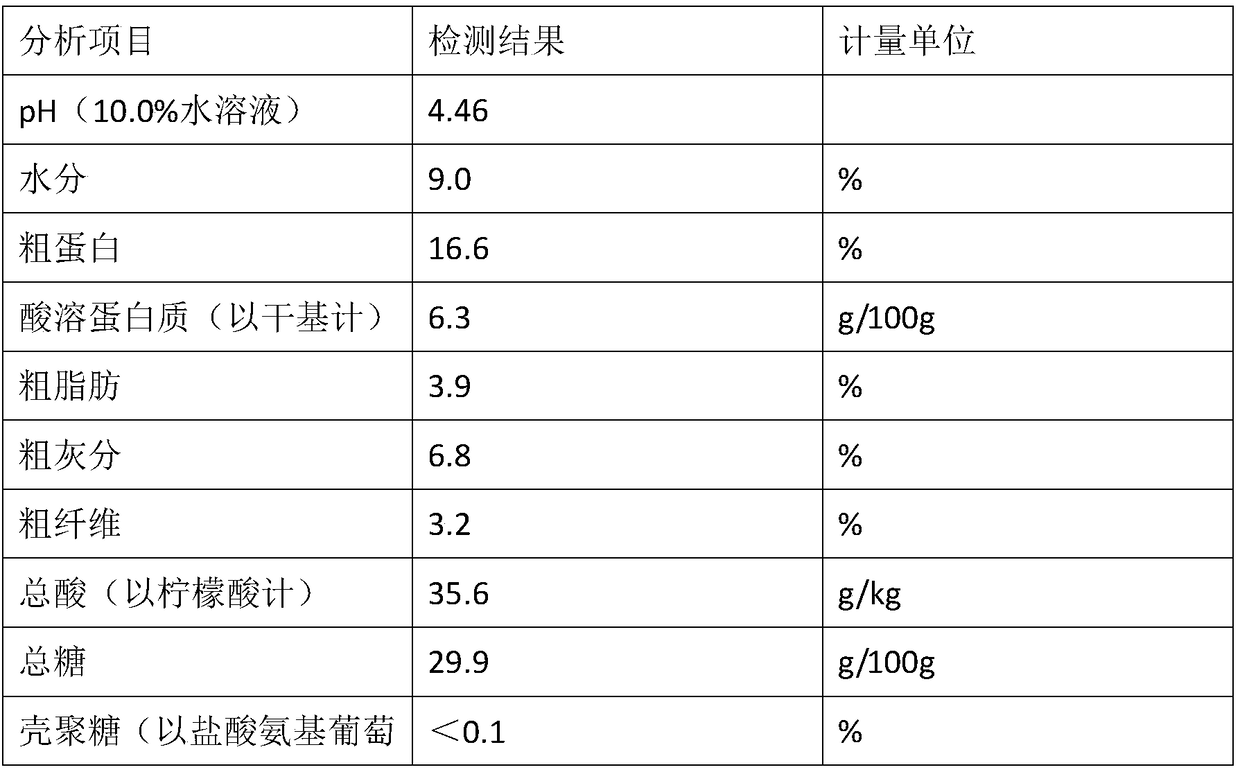
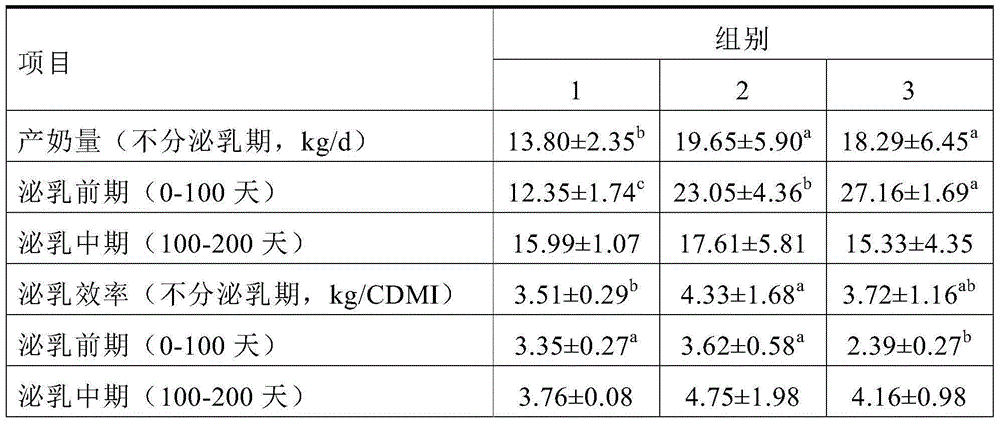
Patents
Literature
57 results about "Soy molasses" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Soy molasses is brown viscous syrup with a typical bittersweet flavor. A by-product of aqueous alcohol soy protein concentrate production, soy molasses is a concentrated, desolventized, aqueous alcohol extract of defatted soybean flakes.
Method for preparing high-purity soybean oligosaccharide from soybean whey wastewater
ActiveCN102702274AHigh purityImprove functionalitySugar derivativesOligosaccharidesWater bathsSaccharum
The invention relates to a method for preparing a high-purity soybean oligosaccharide from soybean whey wastewater, which comprises the following steps: (1) preprocessing of raw materials: heating soybean whey wastewater or soybean molasses diluent obtained from an industrial production in water bath to 10 to 80 DEG C, and pre-clarifying and filtering the heated product with a microfiltration membrane and / or an ultra-filtration membrane; (2) an enzymolysis process: adding enzyme into the filtrate of the soybean whey wastewater or the soybean molasses diluent obtained in step (1), stirring the obtained product at a speed of 50 rpm for 1 to 3 min, regulating the pH value to be 3 to 11, reacting the obtained product at the temperature of 0 to 60 DEG C for 10 min to 12 h, and then, inactivating the obtained product in boiling water bath for 10 to 15 min to obtain enzyme-inactivated solution; and (3),a nanofiltration and separation process: filtering the enzyme-inactivated solution with an ultra-filtration membrane again to remove enzyme, and then filtering and separating the obtained solution with a nanofiltration membrane to obtain nanofiltration concentrated solution, which is oligosaccharide solution. Compared with the prior art, the total amount of cane sugar, fructose, glucose and other monosaccharide in the prepared product does not exceed 5%, so that the technology is suitable for industrial mass production.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Ganoderma cultivation waste feed and preparation thereof
InactiveCN105795131AImprove immunitySmooth furFood processingAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyLean meat
The invention discloses ganoderma cultivation waste feed.The ganoderma cultivation waste feed is prepared from ganoderma cultivation waste, traditional Chinese medicine residues, soybean molasses, a texturizer, a complex enzyme and a complex microbial inoculant.A long animal experiment indicates that the prepared ganoderma cultivation waste feed contains a large quantity of beneficial ingredients including lactic acid bacteria, saccharomycetes, bacillus amyloliquefaciens, protein, peptide, amino acid, lactic acid, citric acid, ganoderan and the like, and has the effects of promoting livestock and poultry growth and improving animal immunity.When the ganoderma cultivation waste feed is used for feeding pigs and other livestock, the appetite is promoted, diseases are reduced, pig fur is smooth, and skin is red; the lean meat rate is obviously increased, and meat is bright red; the odor of feces is obviously relieved, the air environment around a pigsty is greatly improved, and the health of a breeder and the pigs is further benefited; glucose oxidase and catalase can quickly use up oxygen in gaps of fermentation materials, anaerobic fermentation of saccharomycetes and lactic acid bacteria is promoted, more lactic acid is accumulated, and long-term storage of the fermented feed is promoted.
Owner:孙中涛 +1
Health Care Product containing Isoflavone Aglycones and Method of Producing the Same
InactiveUS20070207224A1Easy to storeRelieving menopausal symptomBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsDiseasePlant Sources
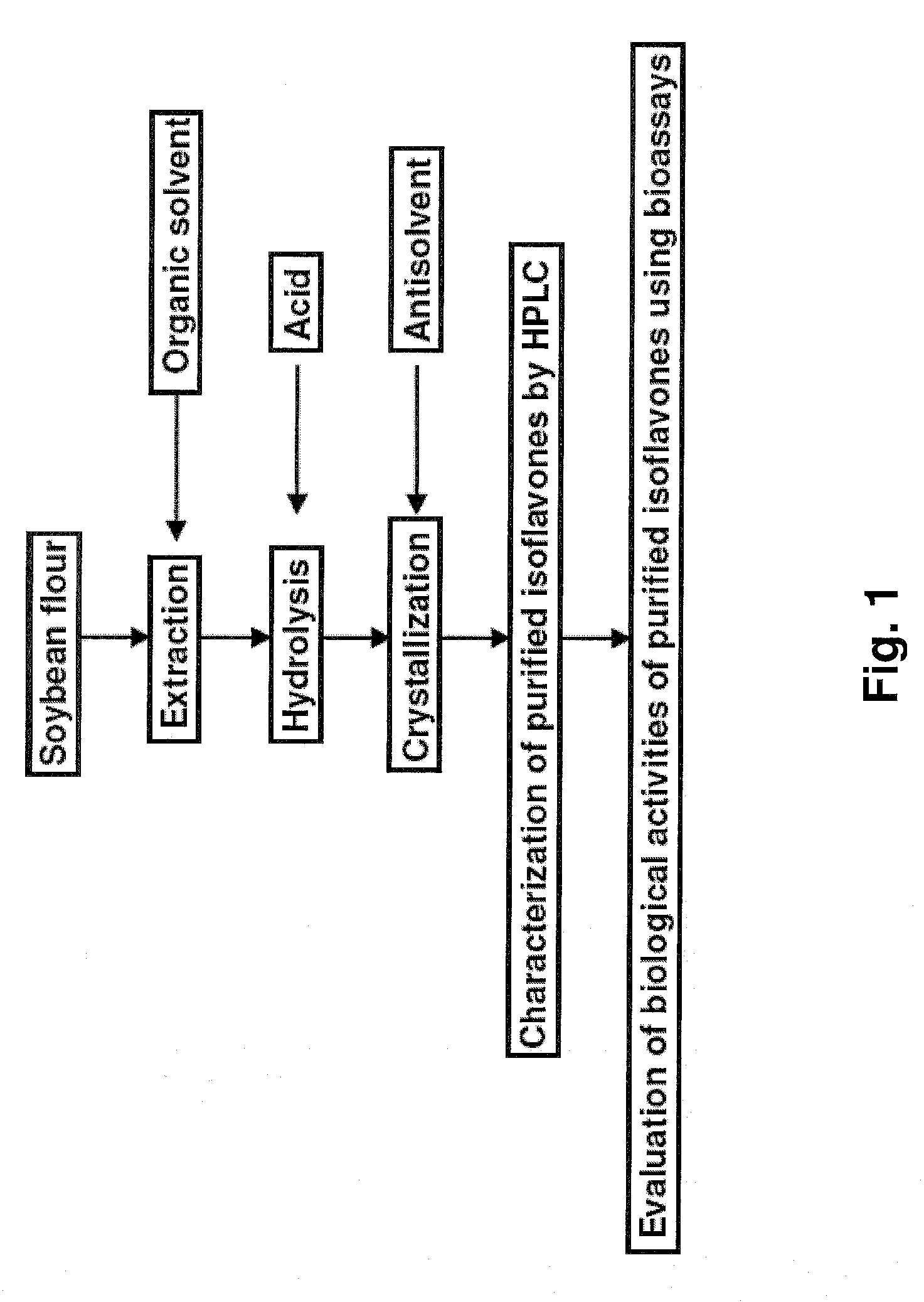
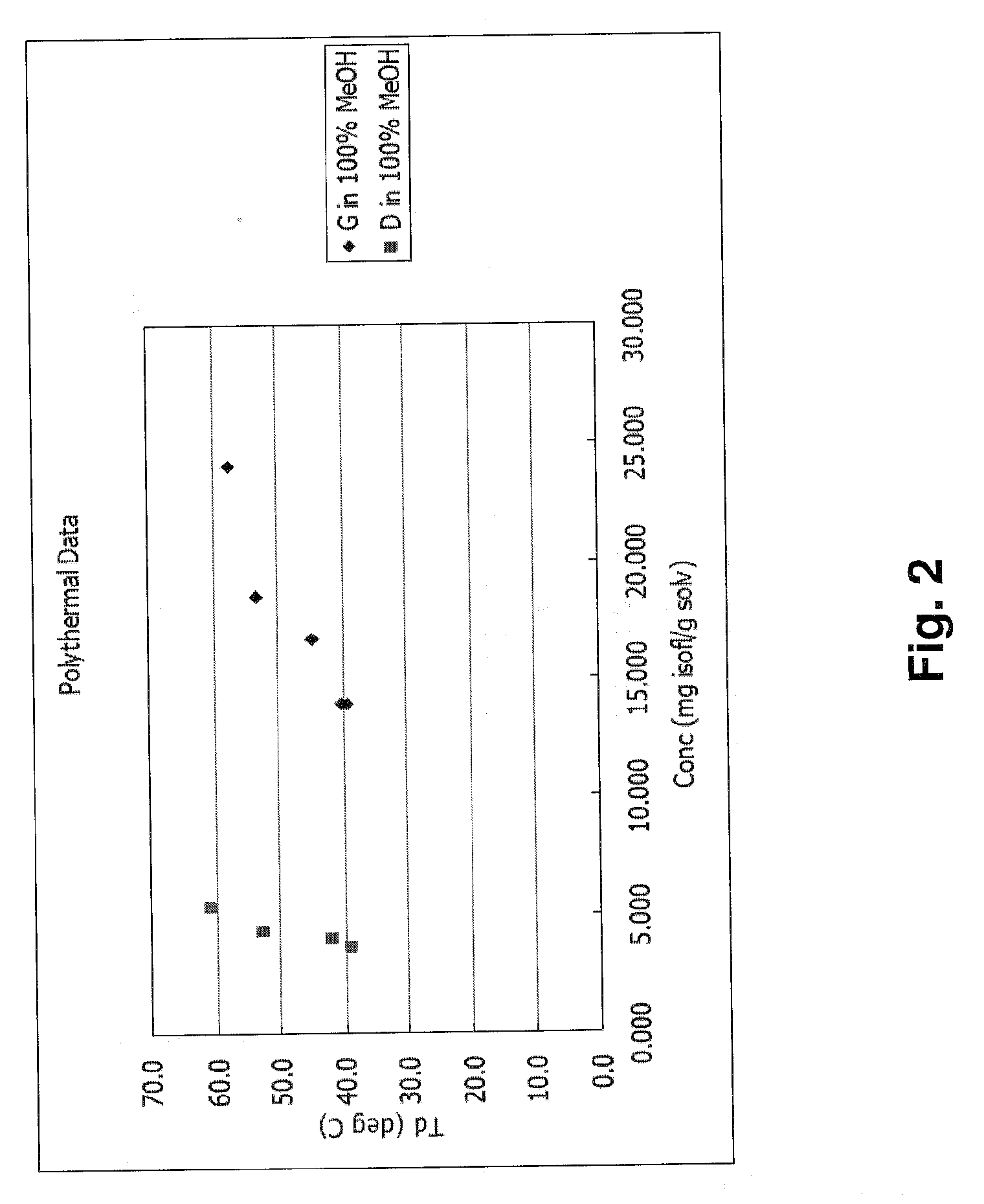
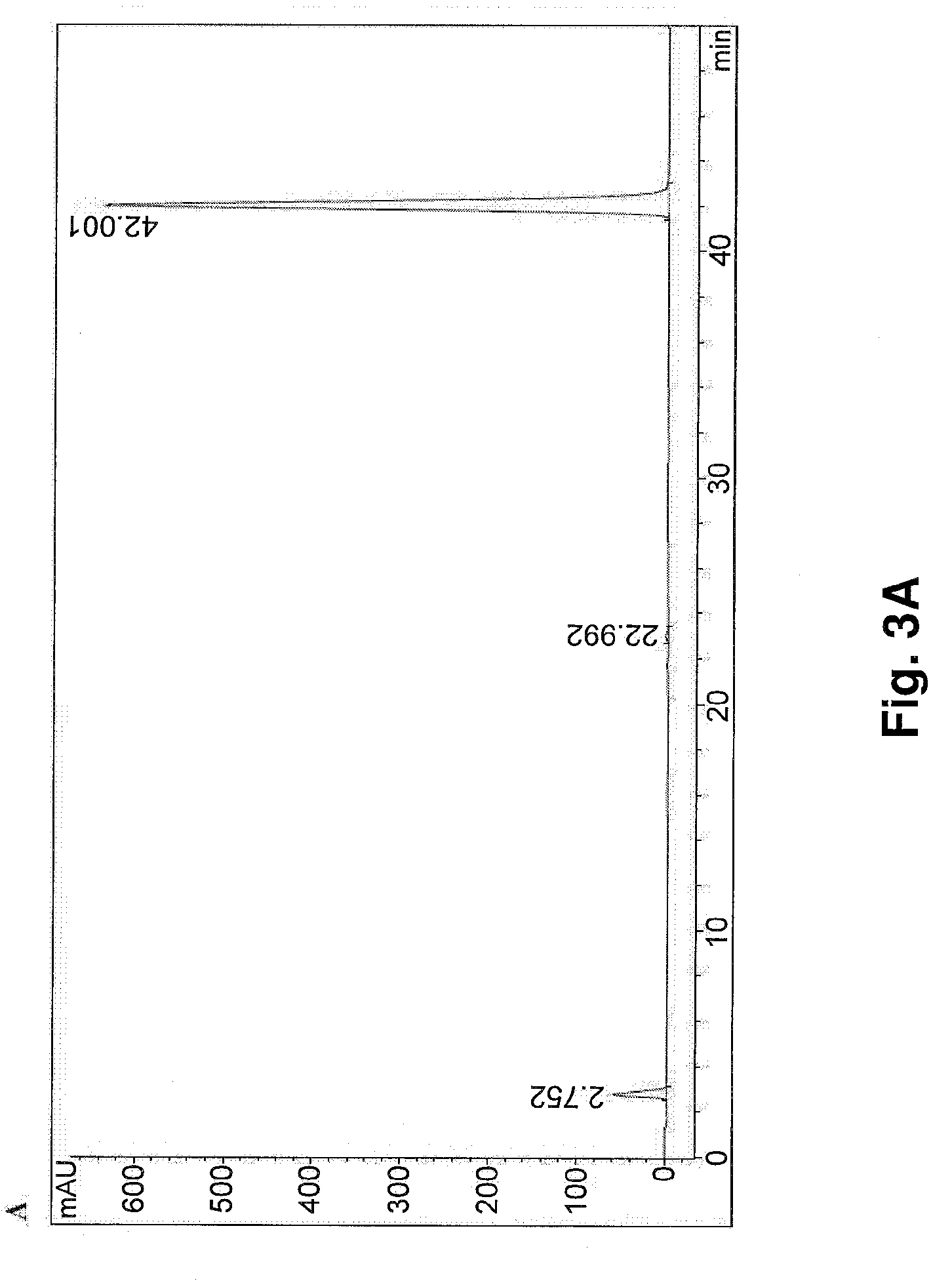
This invention relates to a novel soy isoflavone product with high purities and strong biological activities and the method of producing the same from natural soybeans, soybean materials (i.e. tofu dregs, soy molasses) and other plant sources. The method includes three steps consisting of extraction with an organic solvent, hydrolysis using an acid and crystallization using an antisolvent. The procedure is very simple and thus can be easily adapted for large-scale manufacturing. Moreover, the procedure is able to produce a high yield of total isoflavones at a lower cost. HPLC analysis and E-Screen bioassay reveal that the obtained product not only contains a high content of isoflavone aglycones by weight of dry matter but also exhibits strong estrogenic activity toward human cells. Therefore, the product should be efficacious for relieving menopausal symptoms and other estrogen-deficient diseases and can be used in health care supplements or as additives for foods, beverages or cosmetics.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Energy type mixed feed instead of corn and method for producing the same
InactiveCN101480218AImprove digestibilityLow costFood processingAnimal feeding stuffFiberAdditive ingredient
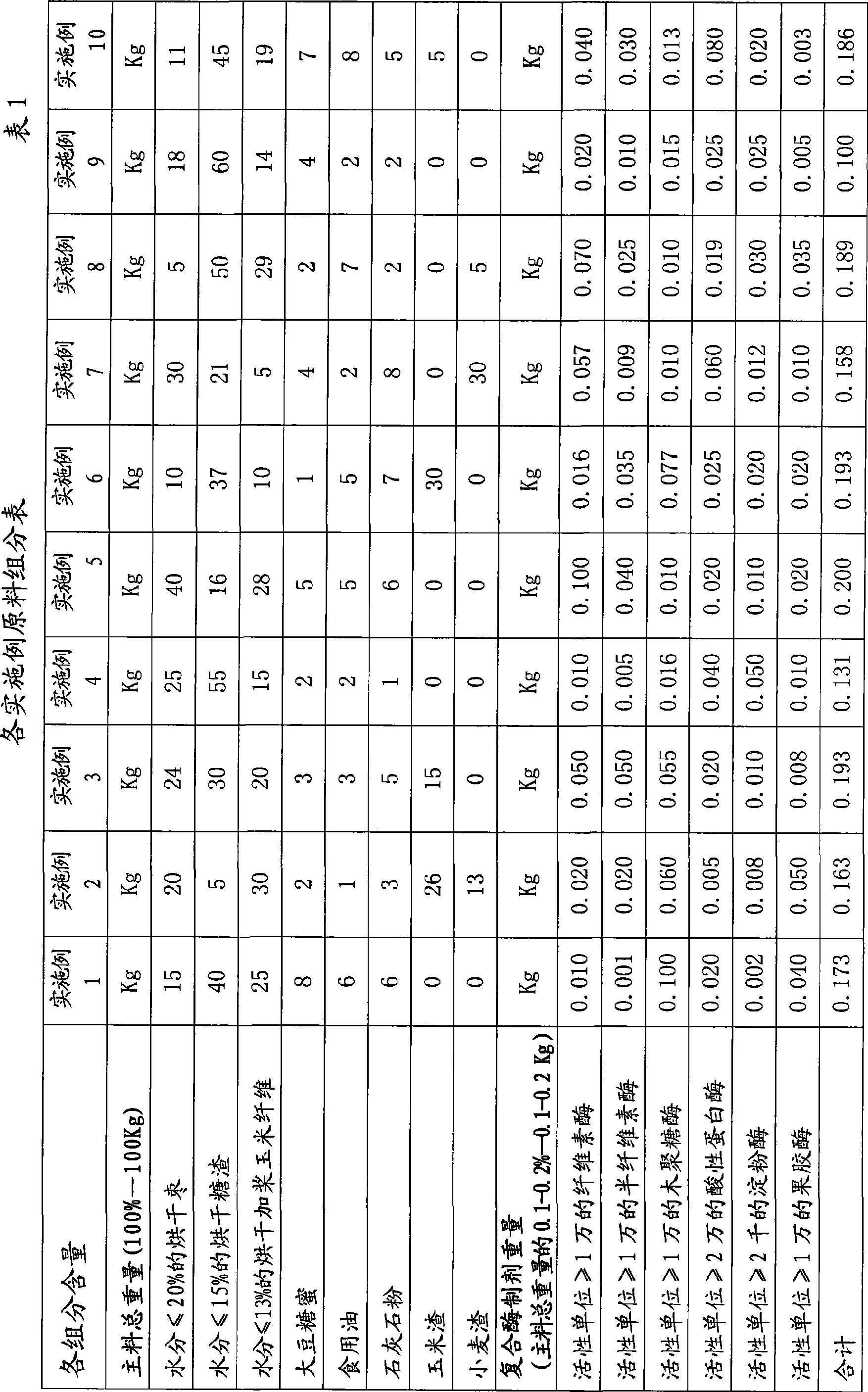
The invention relates to energy-type compound feed for replacing corn, which is characterized by comprising main material and compound enzyme preparation. Measured by 100 percent of weight, the main material comprises following ingredients by weight percentages: 5 to 40 of dried jujubes, 5 to 60 of dried candy pomace, 5 to 30 of dried corn fibers with syrup, 1 to 8 of bean molasses, 1 to 8 of edible oil, 1 to 8 of limestone powder, 0 to 30 of corn grit and 0 to 30 of wheat grit; the weight of the compound enzyme preparation is 0.1 percent to 0.2 percent of the weight of the main material, and the compound enzyme preparation comprises cellulase, hemicellulase, xylanase, acid protease, amylase and pectase. When the energy-type compound feed is prepared firstly, compound enzyme premix is prepared and then the compound enzyme premix is uniformly mixed with the limestone powder, the edible oil and other crushed main material. The invention has the advantages that corn waste, discarded jujubes and low-price grain dregs are utilized to make the energy-type compound feed which has the nutrition content up to or beyond the nutrition content of single corn energy feed, saves the grain, protects the environment and decreases the cost.
Owner:田志强
Soy phytochemical composition
Disclosed is a soy phytochemical composition obtained by removing soluble components out of acidified soy molasses by settling, decantation and / or centrifugation to obtain a precipitated residue sediment containing not less than 6% of isoflavones, not less than 18% of saponins and not less than 13% of crude low molecular weight protein material on a dry matter basis.
Owner:CHAJUSS DANIEL
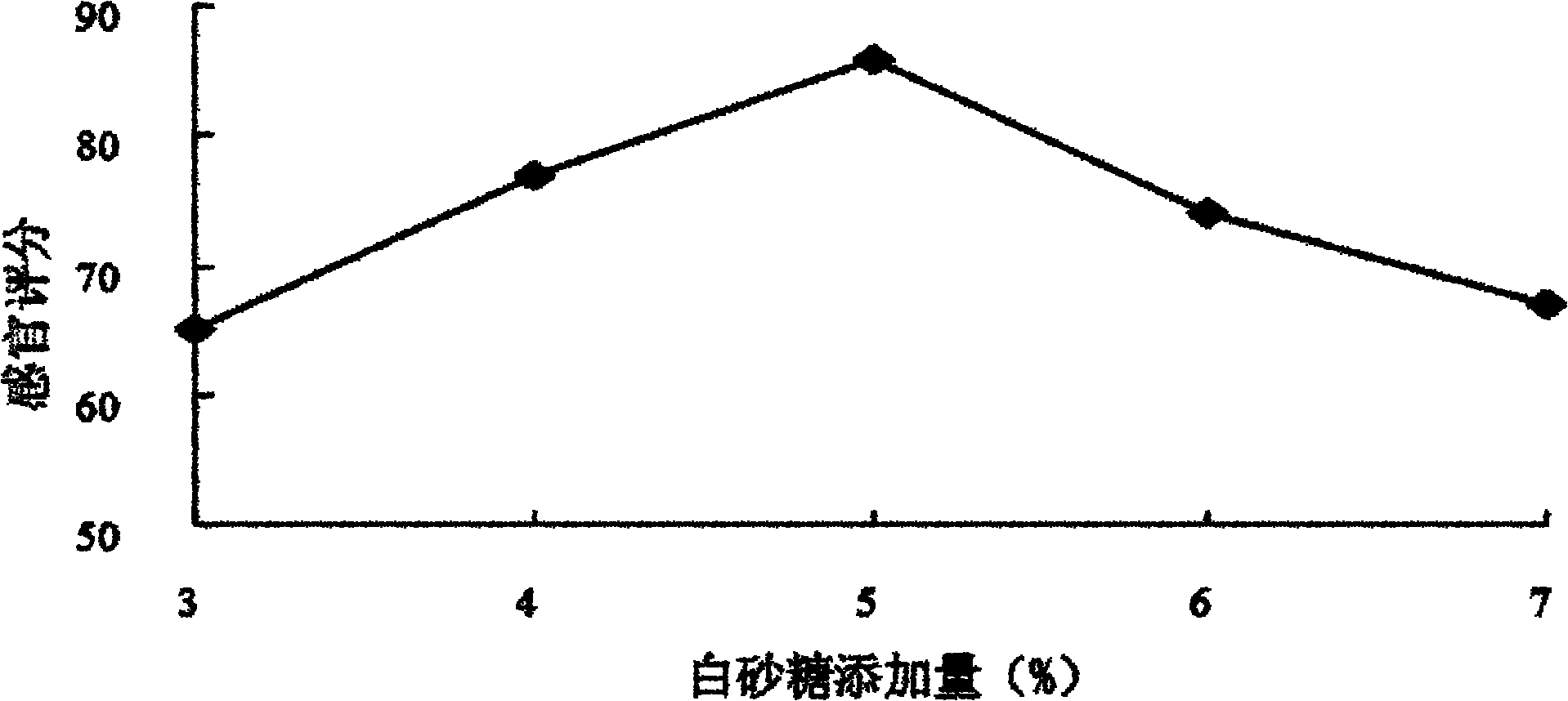
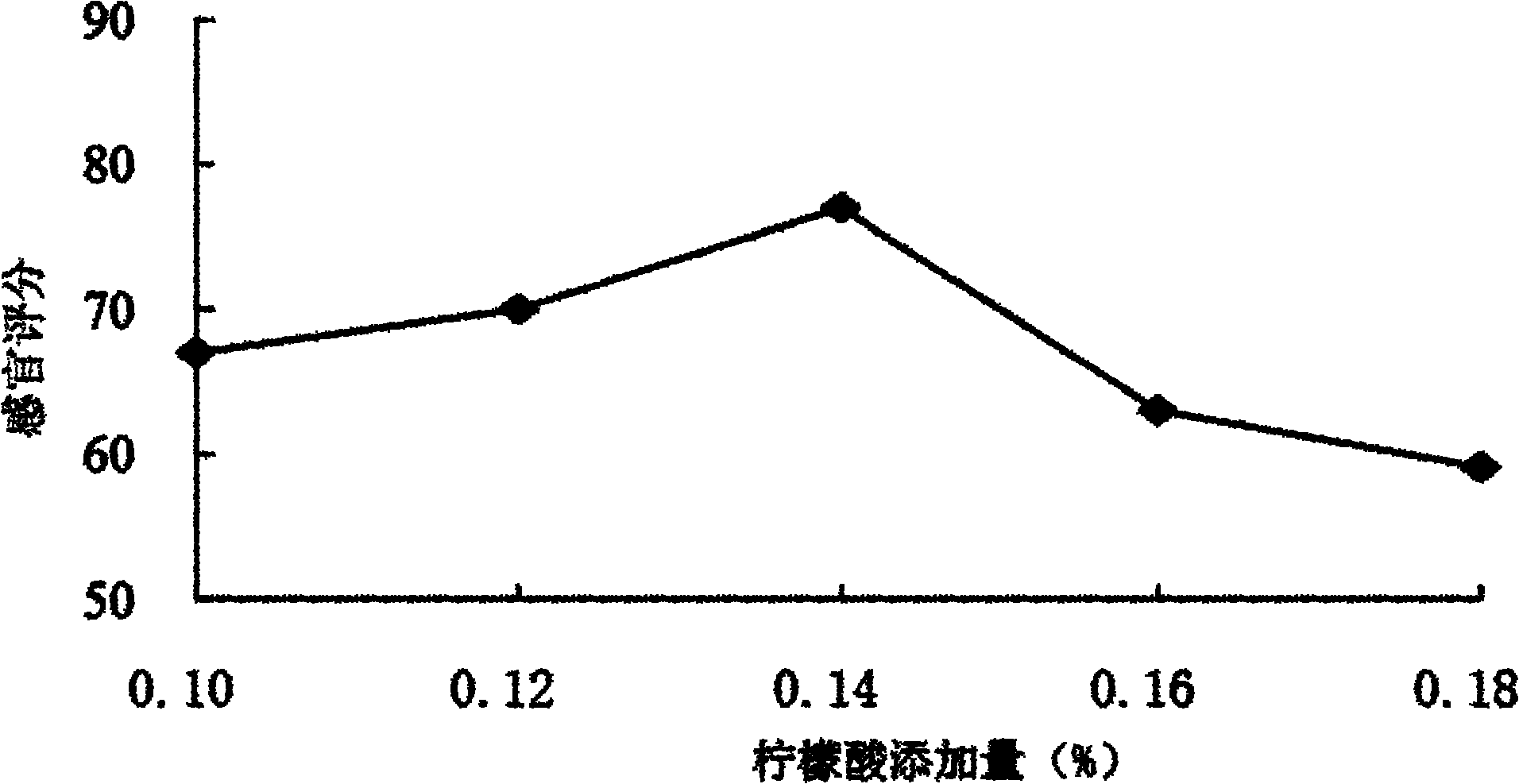
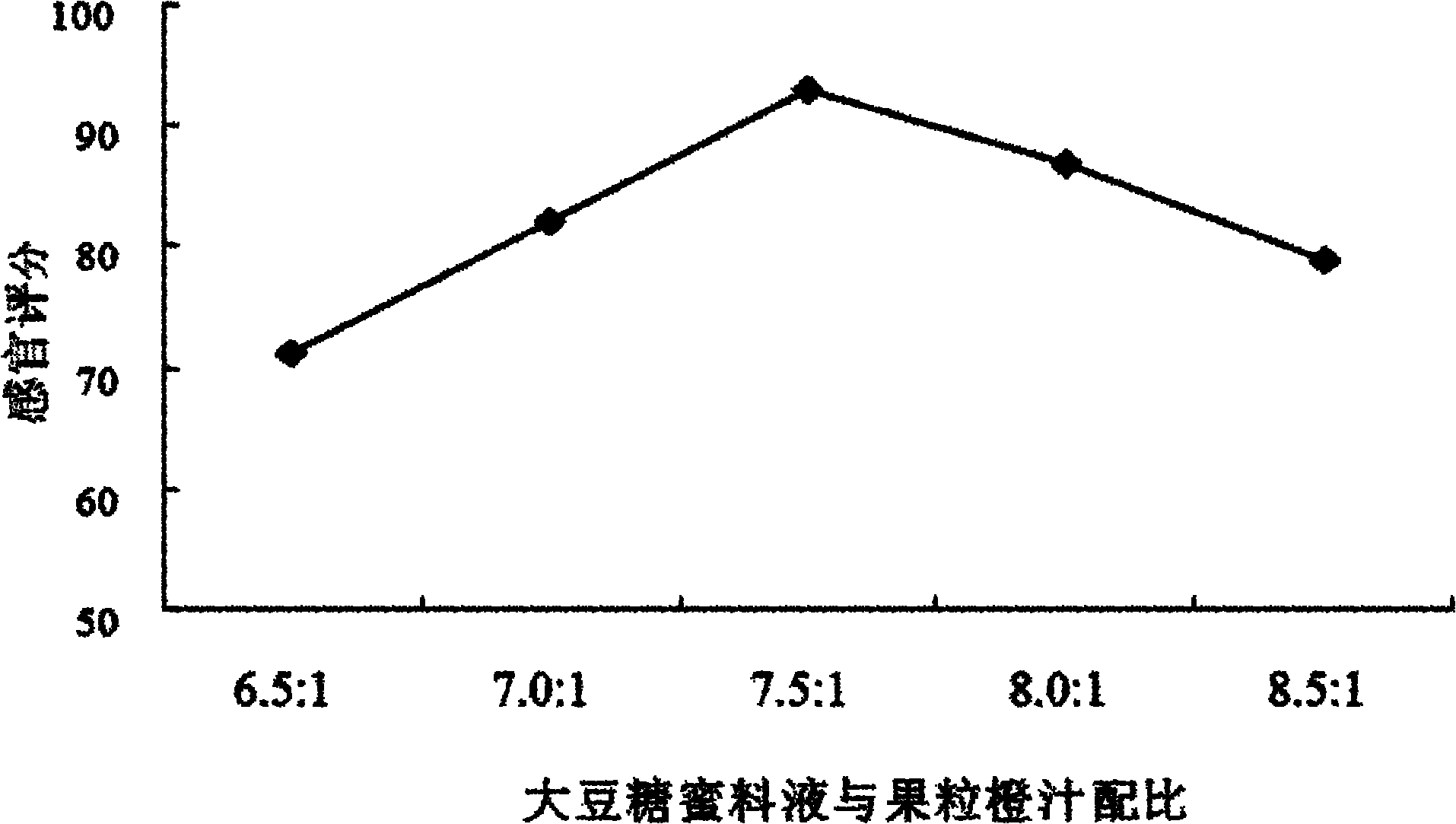
Soybean molasses fruit orange functional beverage and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a soybean molasses fruit orange functional beverage and a preparation method thereof, relating to a functional beverage and a preparation method thereof. The invention solves the problem that soybean molasses is wasted or used as feed currently. The soybean molasses fruit orange functional beverage is prepared from soybean molasses, water, fruit orange juice, white granulated sugar, citric acid, sodium carboxy methyl cellulose, xanthan gum and sodium alginate by the steps of pretreatment, acid treatment, alkali treatment, rinsing, fruit grain separating, gizzard hardening, fruit orange juice preparing, blending, homogenizing, sterilizing and canning. The soybean molasses fruit orange functional beverage provided by the invention has the main characteristics of pure, tasty and refreshing mouthfeel, bright orange-yellow color, uniformity, no sediment, sweet scent, high content of micromolecular active substances including soybean oligose, soybean isoflavone, soybean saponin, vitamin C and dietary fiber, rich nutriments, and easiness for absorption and utilization by human bodies, and is beneficial to the achievement of a certain societal and economic benefits.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF COMMERCE
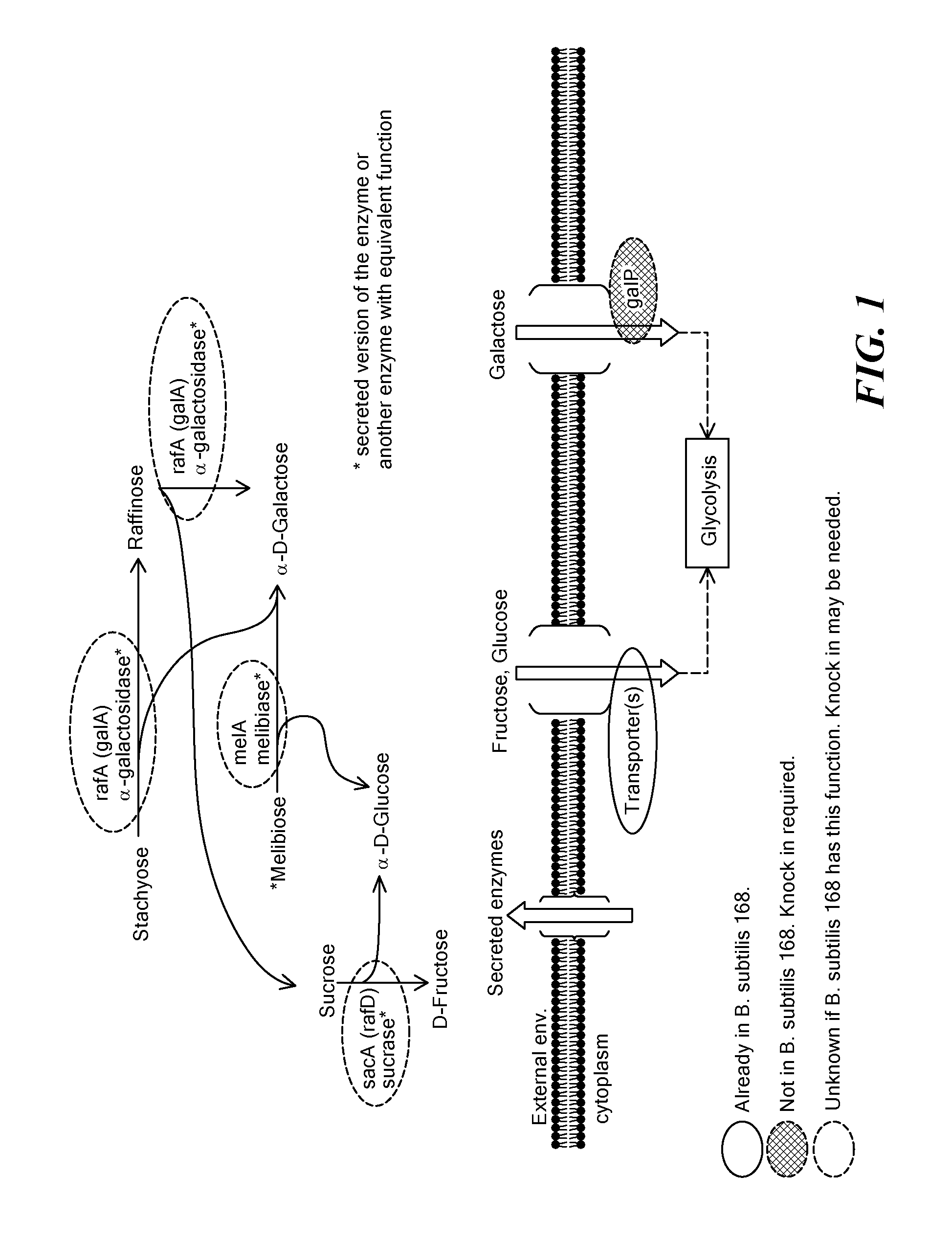
Engineered microorganisms and methods of use
InactiveUS20110059487A1Efficient use ofValid conversionBacteriaFermentationMicroorganismBiotechnology
Owner:MODULAR GENETICS
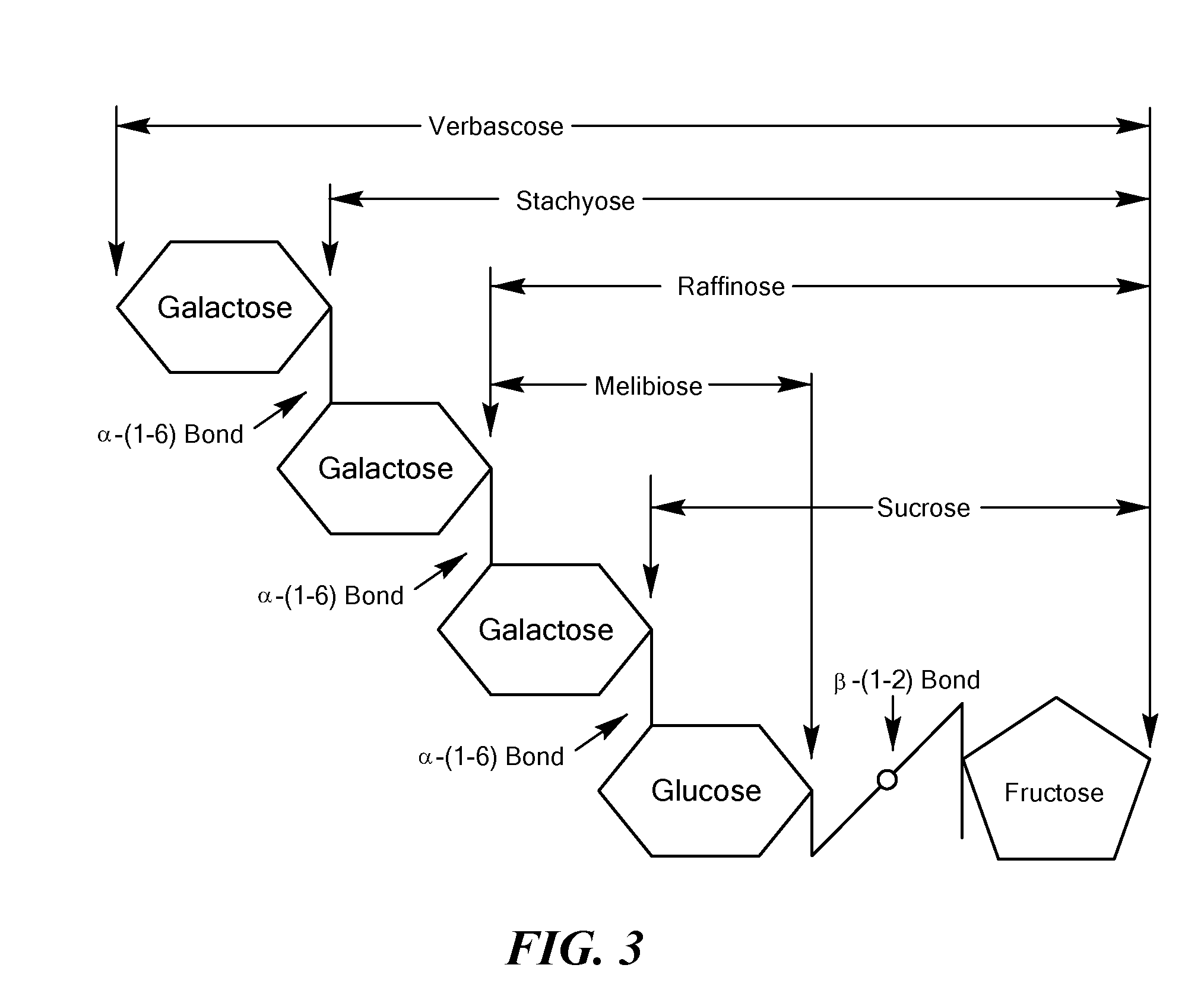
Method for producing manninotriose and melibiose by fermenting soy molasses
InactiveCN101974582APromote application developmentSolve the use problemMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyChromatographic separation
The invention relates to a method for producing manninotriose and melibiose by fermenting soy molasses, which comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a spore fungus suspension; (2) inoculating the spore fungus suspension into a sterilized liquid seed culture medium; (3) inoculating the primary liquid seed into a sterilized 5L seeding tank, and fermenting and culturing to obtain secondary liquid seed; (4) inoculating the secondary liquid seed into a sterilized fermentation tank, and fermenting and culturing by using soy molasses dilution as the culture medium; and (5) centrifugating the fermentation liquid to remove thalli, and carrying out chromatographic separation by using active carbon columns, thereby further obtaining manninotriose and melibiose crystals. The method is used for producing the manninotriose and the melibiose by fermenting the cheap material soy molasses, thereby effectively solving the problem of utilization of waste molasses; and the invention has the advantages of simple technique, high yield, good quality and low cost, does not need complicated equipment, and is beneficial to development and application of the manninotriose and the melibiose.
Owner:天津实发中科百奥工业生物技术有限公司
Method of treating kidney disease
The progression of kidney disease and especially polycystic kidney disease in humans may be retarded and the symptoms ameliorated by administration of an effective amount of soy molasses or isolated soyasaponins or mixtures thereof in conjunction with the essential amino acids. Restriction of protein to a moderate level of 0.8 g / kg / day or less is a preferable adjunct to this treatment.
Owner:CALTON GARY JIM
Method for preparing bacterial cellulose from soybean molasses
InactiveCN105349594AEfficient use ofHigh yieldMicroorganism based processesFermentationTwo stepFermentation
The invention relates to a method for producing bacterial cellulose from soybean molasses serving as a cheap raw material. The soybean molasses are pretreated and taken as a main carbon source, the bacterial cellulose is prepared with a two-step method, and the two-step method comprises shake cultivation and transferring to a shallow plate for standing fermentation. A new raw material is provided for production of the bacterial cellulose. Raw materials are widely sourced, the cost is low, the equipment method is simple, the cultivation time is short, the yield of the bacterial cellulose is high, and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method of extracting soybean oligosaccharides and soybean isoflavones by using soybean molasses
ActiveCN107188911ASimplify workloadReduce investmentSugar derivativesOligosaccharidesSoybean productEthyl acetate
The invention discloses a method for extracting soybean oligosaccharides and soybean isoflavones by using soybean molasses, and belongs to the field of soybean product production. The problems of low yield and low purity of soybean oligosaccharides and soy isoflavones extracted from the prior art are solved. The method comprises the following steps: diluting and fermenting the soybean molasses, boiling the soy molasses fermented broth, adding quicklime to stir evenly, standing, adjusting pH of the solution to be neutral, centrifuging to take supernatant, heating the supernatant, using AB-8 resins to conduct column chromatography, using acidic cationic resins and alkaline anion resins to conduct adsorption desalination treatment, and vacuum concentrating to get finished soy oligosaccharides; using an ethanol solution to elute AB-8 resins, distilling and recycling ethanol, using ethyl acetate to sink a soybean flavonoids concentrated solution, taking the supernatant to concentrate, getting soy isoflavone paste, drying and smashing to obtain the soybean isoflavones. The method of the invention can be used for simultaneously extracting the soybean oligosaccharides and the soybean isoflavones by using the soybean molasses.
Owner:山东中阳生物科技有限公司
Method and equipment for extracting isoflavone, saponin and oligosaccharide from soy molasses
ActiveCN103342691ARealize in-depth development and utilizationReduce wasteSugar derivativesSteroidsAlkaline proteaseSOY ISOFLAVONES
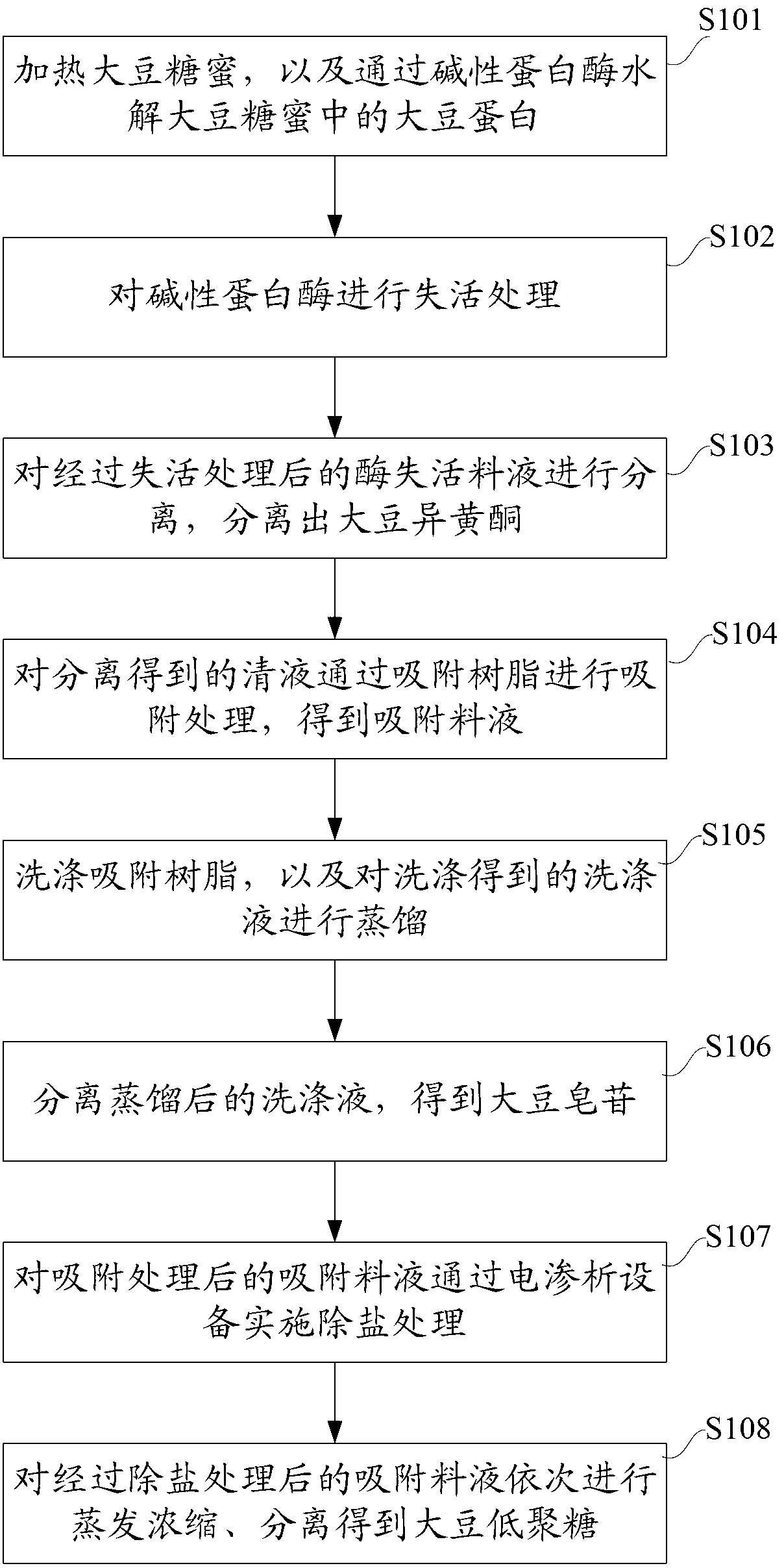
The invention provides a method and equipment for extracting isoflavone, saponin and oligosaccharide from soy molasses. The method comprises the following steps: a, heating the soy molasses, and hydrolyzing soy protein in the soy molasses through alkaline protease; b, carrying out inactivation treatment on the alkaline protease; c, separating enzyme deactivation liquid which is subjected to inactivation treatment, and separating out soy isoflavone; d, carrying out adsorption treatment on the separated clean liquid through adsorbent resin, so as to obtain adsorption liquid; e, washing the adsorbent resin, and distilling the washed washing liquid; f, separating the distilled washing liquid to obtain soy saponin; g, carrying out dechloridation treatment on the adsorption liquid which is subjected to adsorption treatment through an electrodialysis plant; and h, orderly evaporating, concentrating and separating the adsorption liquid which is subjected to dechloridation treatment, so as to obtain the soy oligosaccharide. By adopting the method provided by the invention, extraction of the soy isoflavone, the saponin and the oligosaccharide is achieved; deep development and utilization of the soy molasses are achieved; waste of resources is reduced.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA KERAN BIO TECH
Debittered soybean sirup and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101627815AThe preparation method is simple and efficientKeep active ingredientsFood preparationFlocculationSolid matter
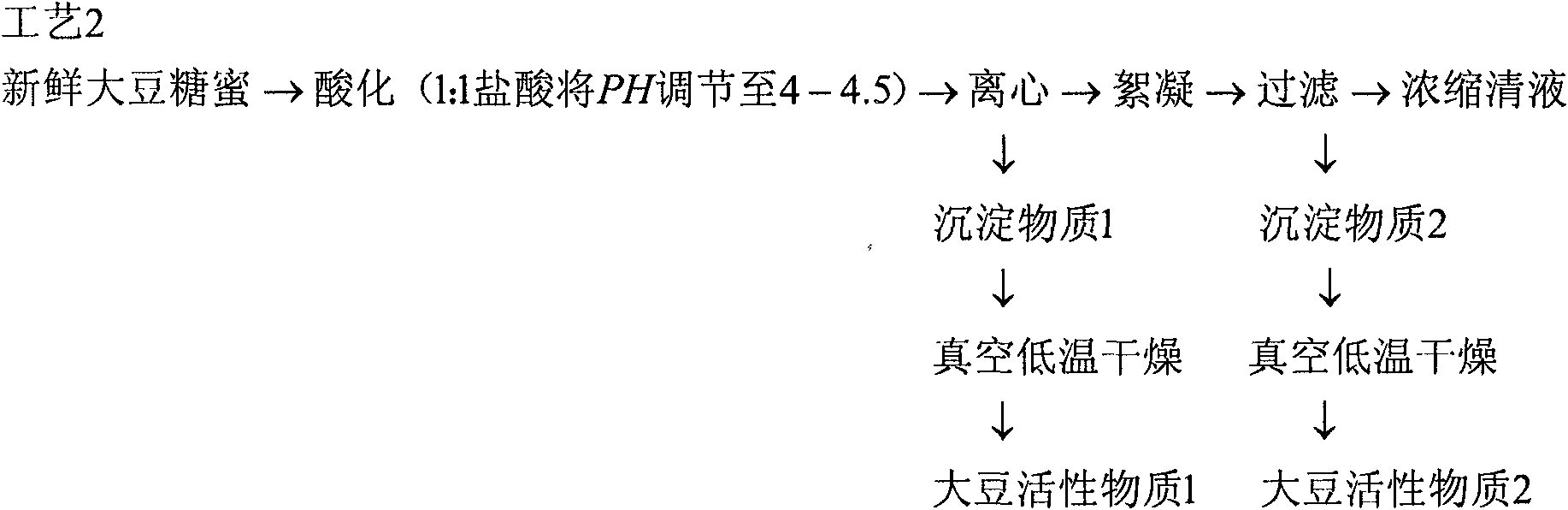
The invention discloses a method for preparing a debittered soybean sirup, which comprises the following steps: performing acid deposition by adding an acid for mixing so that the pH is between 3.5 and 5.0, preferably between 3.8 and 4.3; performing flocculation by adding a flocculating agent; and performing separation by separating solid matters and the liquid part, and connecting the solid matters and the liquid respectively, wherein the liquid part is the debittered soybean sirup. The invention also discloses the debittered soybean sirup prepared by the method and application thereof.
Owner:秦皇岛金海食品工业有限公司
Method for extracting isoflavone from soyabean molasses
The invention relates to a method for extracting isoflavone from soyabean molasses. Firstly, a by-product-soyabean molasses which is obtained when concentrated protein is produced by using low-temperature soyabean meals is selected as a raw material, the isoflavone content of the soyabean molasses is not less than 0.22 percent, and sugar degree is 45-55. The method comprises the following process steps of: placing the soyabean molasses as the raw material into a crystallizing tank with stirring, adding water to dilute until the sugar degree is 26-33, and heating the crystallizing tank to increase the temperature till boiling, wherein boiling time is 3-8 minutes; (2) adding gluconic acid delta lactone when the temperature of the molasses is reduced to 70-85 DEG C, continuously reducing the temperature of the molasses to 25-35 DEG C, and then stopping reducing the temperature, wherein the adding amount of the gluconic acid delta lactone is 1-2 per thousand of the weight of the molasses; (3) stopping the stirring, naturally subsiding for 35-45 minutes, and then introducing to a centrifugal machine to separate for 10-15 minutes; and (4) leading out separated mother liquor so as to separate crystalline isoflavone. The invention has the raw material which is the by-product, small equipment investment and high cost performance of the extracted isoflavone.
Owner:山东万得福生物科技有限公司
Method for producing citric acid by fermenting soybean molasses
InactiveCN103614421ALow priceImprove use valueMicroorganism based processesFermentationAspergillus nigerCulture mediums
The invention relates to a method for producing citric acid by fermenting soybean molasses. According to the method, soybean molasses is used as the unique carbon source, a required culture medium is added, and Aspergillus niger is adopted for fermentation to produce citric acid. The total acidity of the citric acid prepared by fermenting the soybean molasses is 9.02% under the following conditions: the mass concentration of the soybean molasses is 26%, the fermentation temperature is 35 DEG C, the initial pH value is 4.5, the fermentation time is 96 hours, and the inoculum size is 5%. The soybean molasses is fermented to produce the citric acid, thereby fully utilizing the precious resource soybean molasses; the development and utilization of the soybean molasses can reduce the environmental pressure, and can also greatly enhance the utilization value of the soybean molasses and change wastes into valuable substances. Besides, the price of the soybean molasses is low, so the production cost can be obviously lowered by using the soybean molasses as the fermentation substrate.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
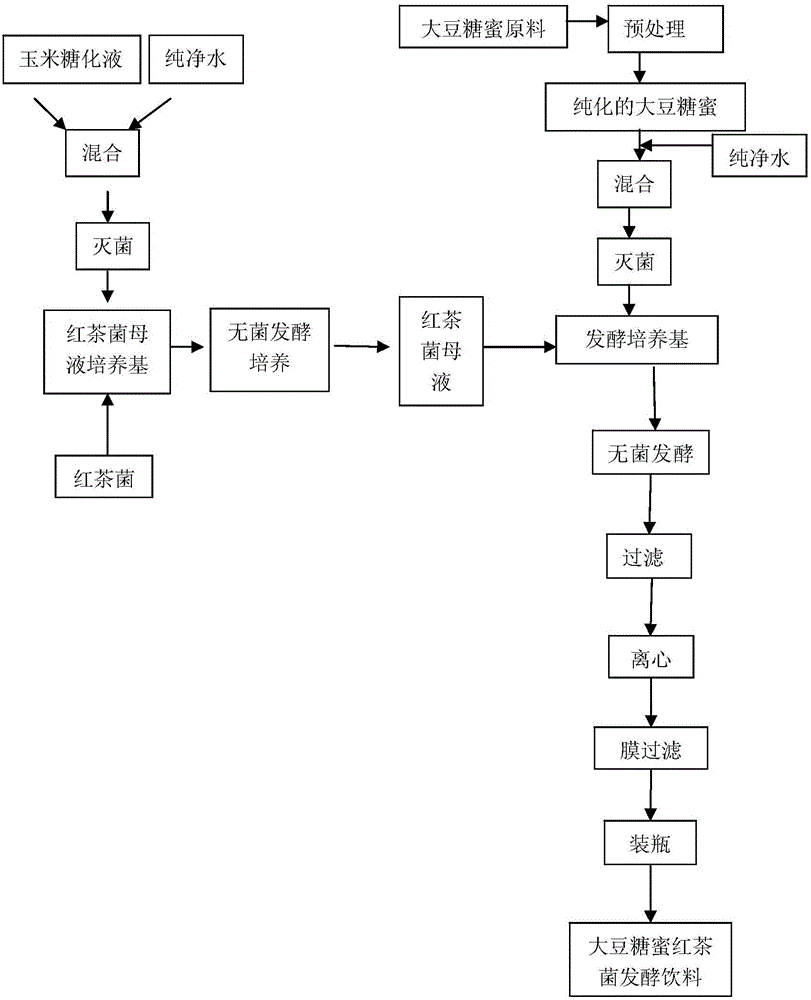
Soybean molasses-based kombucha-fermented beverage and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106173721AIncrease added valueReduce pollutionFood ingredient functionsEcological healthKombucha
The invention provides a biological beverage prepared from soybean molasses as a main raw material and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of beverages. The preparation method utilizes a corn saccharification liquid as a kombucha culture mother liquor, soybean molasses as a medium and kombucha as a fungus source to prepare the novel special soybean molasses-based kombucha-fermented beverage. Through the preparation method, the purified soybean molasses, corn saccharification liquid and kombucha are combined and produce synergism so that the tea beverage has obvious health care effects and comprehensive effects far higher than those of a food prepared only from soybeans and corn and the traditional kombucha beverage. The prepared soybean molasses-based kombucha-fermented beverage has short fermentation time and an ideal form, well retains original nutrition and function components of soybeans and corn, can be easily digested and absorbed, has a sour-sweet taste and good palatability, has a wide application range and is an ecological health beverage with beverage and medicine effects.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation of soybean molasses biological cellulose moisture mask
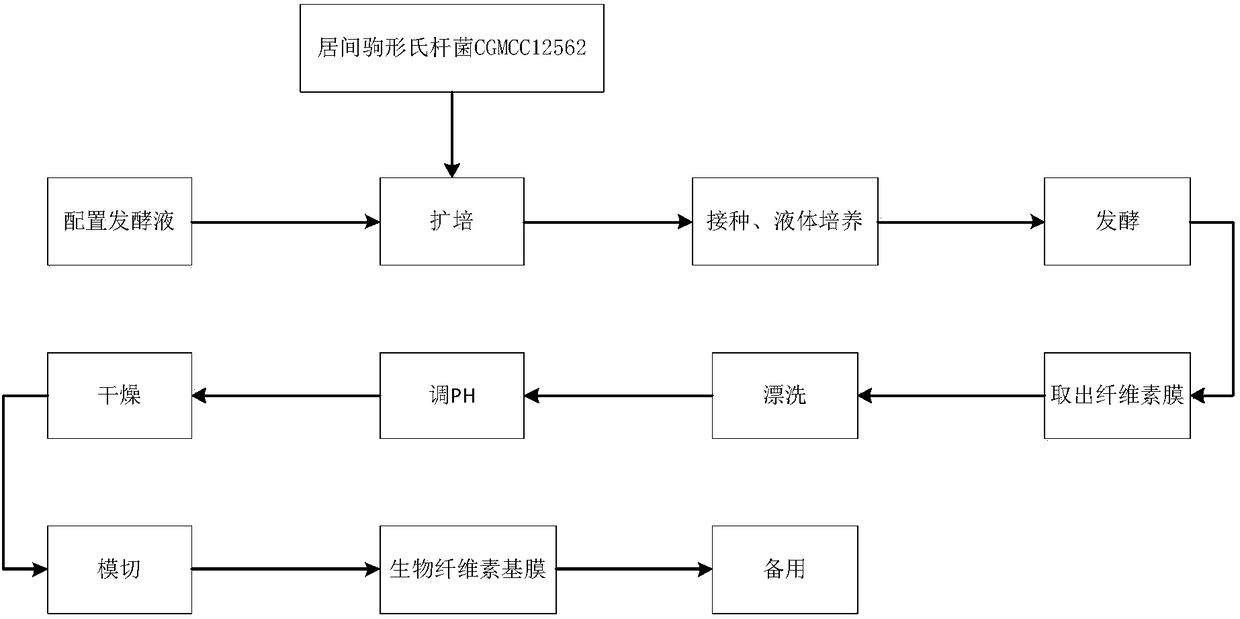
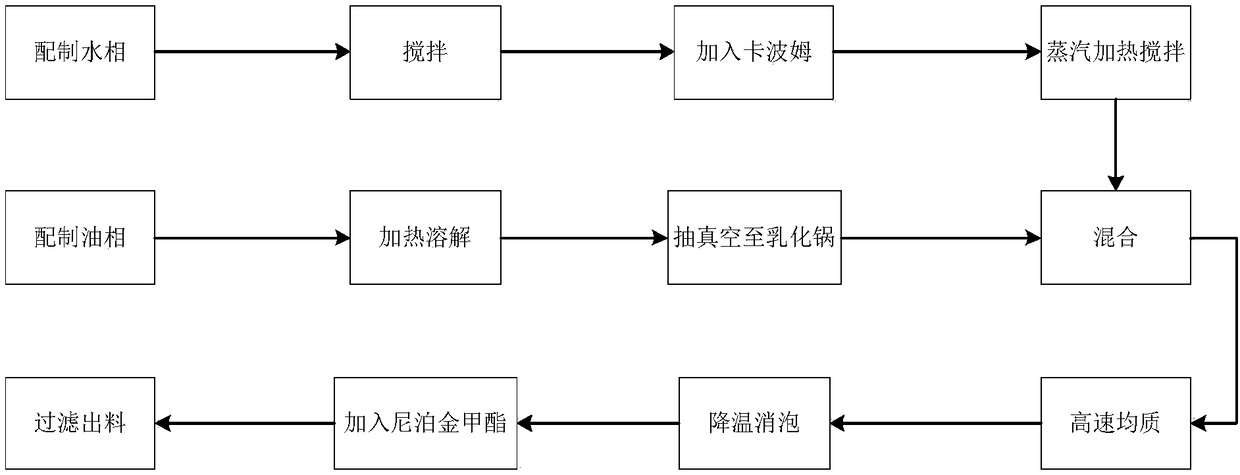
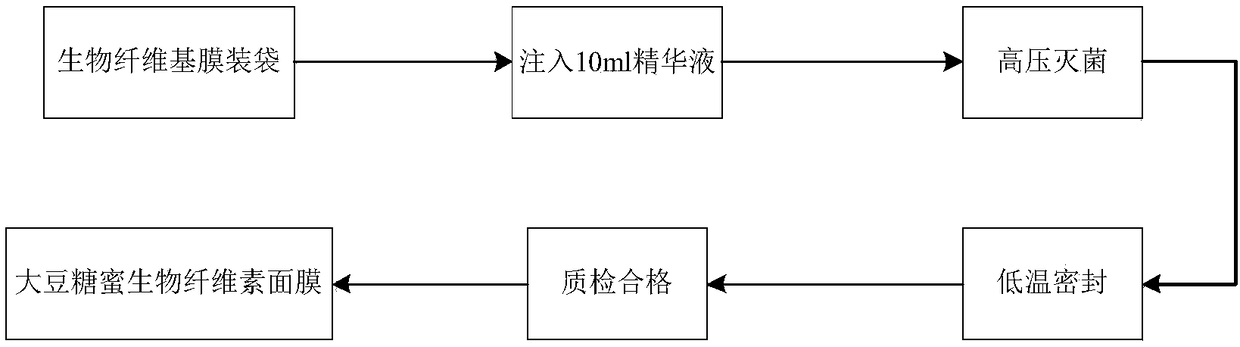
InactiveCN108403474AImprove tensile propertiesNo side effectsCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsCelluloseSide effect
The invention relates to preparation of a soybean molasses biological cellulose moisture mask. The biological cellulose moisture mask is prepared by the steps of inoculating a soybean molasses mediumwith Komagataeibacter intermedius CGMCC12562, which is amplified by a seed medium, so as to generate a biological cellulose base membrane, then matching with essence to prepare the biological cellulose mask, wherein the essence is prepared from a water phase and an oil phase, the water phase is prepared from 72 to 90% of deionized water, 2 to 6% of propylene glycol, 0.03 to 0.07% of EDTA-2Na, 0.02to 0.06% of PVP, and 0.1 to 0.5% of carbomer, the oil phase is prepared from 4 to 8% of glycerinum, 3 to 7% of polydimethyl siloxane, 1 to 5% of vitamin E, and 0.1 to 0.5% of methylparaben, testing the pH, water-retention rate, moisturizing rate, heat-resisting and cold-resisting stability of the mask. According to the soybean molasses biological cellulose moisture mask provided by the invention,the soybean molasses is taken as a fermentation substrate to prepare the biological cellulose mask, so that the mask has higher water holding capacity and anti-pulling capacity, and by matching withthe essence which is prepared by taking glycerinum, propylene glycol, carbomer and the like as raw materials, no side effects will generate; by taking the soybean molasses as the fermentation substrate, the cost of producing the mask can be reduced, meanwhile, the biological cellulose mask is degradable, so that no environmental pollution will be caused.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
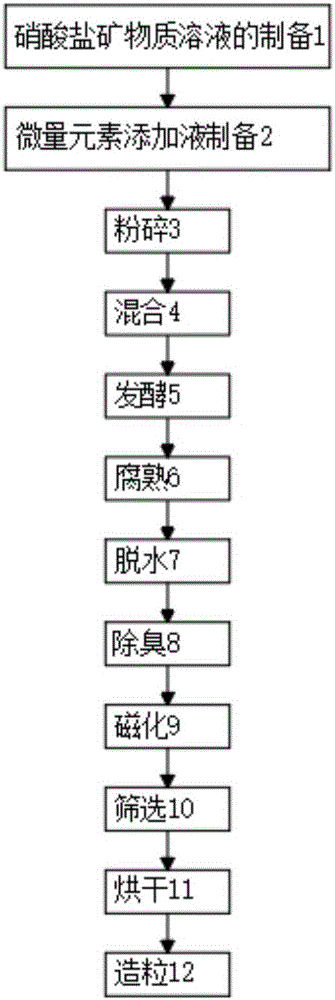
Magnetic biological fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106187609ASimple structureImprove ventilation and water permeabilityCalcareous fertilisersMagnesium fertilisersPotassiumPulverized fuel ash
The invention provides a magnetic biological fertilizer. The magnetic biological fertilizer comprises the following raw materials in parts by mass: 200-400 parts of nitrate mineral, 200-400 parts of plant stalk, 150-250 parts of soybean molasses, 100 parts of plant ash, 100 parts of pulverized fuel ash, 20 parts of composite strain and 10 parts of trace element addition solution. The nitrate mineral comprises the following nutrient components: greater than 30% of silicon dioxide, greater than 20% of calcium carbonate, greater than 12% of iron element, greater than 3% of magnesium element and greater than 5% of potassium element. The trace element addition solution comprises boron element, zinc element, molybdenum element, selenium element and the like. The composite strain comprises trichoderma pseudokoningii and bacillus subtilis. Through the magnetic biological fertilizer, the soil structure can be effectively improved; breathability and water permeability of the soil can be enhanced; nutrients in the soil are increased; adsorption quantity of organic matters is large; the nutrients are not liable to loss, easy to decompose and easy to absorb; the nitrate mineral, the biological fertilizer technique and the magnetic technology are effectively integrated; the magnetic biological fertilizer is complete in nutrients, strong in functionality, stable in physical and chemical indexes and excellent in mutual promotion effect.
Owner:辽宁东北丰专用肥有限公司
Physical method for extracting soybean isoflavone from soybean molasses
The invention discloses a physical method for extracting soybean isoflavone from soybean molasses, and belongs to the technical field of soybean products. The problems of complex process, time consumption, energy consumption, relatively high cost, uncleanness and environment unfriendliness of the prior art are solved. The method comprises the following steps: (1) diluting the soybean molasses into diluted molasses; (2) heating and stirring the diluted molasses, and preserving heat; (3) performing centrifugal solid-liquid separation on the diluted molasses, and reserving precipitates; (4) dissolving precipitates in an ethanol solution, performing stirring and centrifugal separation, and extracting supernatant; (5) performing negative pressure distillation on the supernatant to recover ethanol and obtain pasty soybean isoflavone; (6) dissolving the soybean isoflavone again with the ethanol solution, performing centrifugal separation, and extracting supernatant; (7) performing negative pressure concentration on the supernatant in (6) to obtain a concentrated solution of the soybean isoflavone, and simultaneously recovering the ethanol; (8) performing vacuum drying on the concentrated solution of the soybean isoflavone, and performing crushing to obtain the soybean isoflavone. The method can be used for extracting the soybean isoflavone from the soybean molasses.
Owner:山东中阳生物科技有限公司
Material used for purifying wastewater from chemical industry
InactiveCN104986868AReduce eutrophicationImprove water qualityWater/sewage treatment by sorptionBiological water/sewage treatmentChemical industryEutrophication
The invention discloses a material used for purifying wastewater from chemical industry. The material comprises, by weight, 9 parts to 17 parts of concentrated hydrochloric acid, 3 parts to 10 parts of kieselguhr, 7 parts to 9 parts of conch shell powder, 2 parts to 7 parts of soybean molasses, 3 parts to 11 parts of sodium humate, 2.4 parts to 8 parts of actinomyces, 2 parts to 6 parts of rare earth, 6 parts to 14 parts of nanometer titania, 3 parts to 9 parts of polyethylene glycol serving as slow-release agents, 1.2 parts to 5 parts of activated aluminum oxide, 2 parts to 5 parts of golden cypress wood, 6 parts to 13 parts of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate, 4 parts to 9 parts of ethyl alcohol, 6.5 parts to 11 parts of chlorine dioxide, 9 parts to 16 parts of pine wood and 5 parts to 8 parts of surface active agents. The material used for purifying the wastewater from the chemical industry has the advantages that eutrophication of the water can be reduced, toxic and harmful substances in the water can be adsorbed, particles suspended in the water can be flocculated, and the water quality can be improved.
Owner:QINGDAO MAIKE 3D HI TECH CO LTD
Fertilizer for plantation of towel gourd
InactiveCN106518308AFree from destructionFull of nutritionCalcareous fertilisersAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserGlycerolCalcium borogluconate
A fertilizer for plantation of towel gourd relates to the technical field of crop plantation and is characterized by being prepared from the following materials (by weight): 30 parts of pig dung or urine, 5 parts of corn flour, 10 parts of red bean powder, 2 parts of sodium humate, 12 parts of diammonium phosphate, 12 parts of plant ash, 1 part of 1, 2, 3-glycerol, 2 parts of amino acid tablet powder, 5 parts of bamboo sawdust, 1 part of JT compound bacteria, 5 parts of banana peel, 6 parts of cut tobacco, 6 parts of onion powder, 5 parts of EM inocula, 20 parts of calcium gluconate, 4 parts of soy molasses, 20 parts of an auxiliary agent and 70 parts of purified water. The method is reasonable. The fertilizer is convenient to prepare, has rich nutrients and has good effects.
Owner:李士光
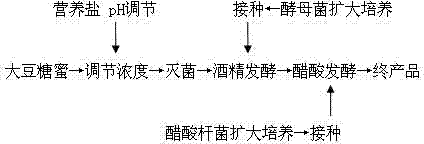
Method for producing acetic acid by fermenting soybean molasses
The invention relates to a method for producing acetic acid by fermenting soybean molasses. According to the method, soybean molasses is used as the carbon source, a required culture medium is added, and microzyme and Bacillus aceticus are adopted for fermentation to produce acetic acid. The method comprises the following steps: fermenting at 28 DEG C for 96 hours when the concentration of the soybean molasses is 35%, the pH value is 5.5 and the microzyme inoculum size is 10%; and fermenting at 30 DEG C for 120 hours when the pH value is regulated to 5.0 and the Bacillus aceticus inoculum size is 10%. By fermenting the soybean molasses to produce the acetic acid, the method fully utilizes the effective components in the soybean molasses, greatly enhances the utilization value, changes wastes into valuable substances, and alleviates the environmental pressure of the soybean molasses. Besides, the price of the soybean molasses is low, so the production cost can be obviously lowered by using the soybean molasses as the fermentation substrate.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for producing soybean isoflavone by utilizing soybean molasses
InactiveCN103965154AShort process routeReduce manufacturing costOrganic chemistryAlcoholColumn chromatography
The invention relates to a method for producing soybean isoflavone by utilizing soybean molasses. The method comprises the following step of extracting the soybean molasses through dilution, acid treatment, heat treatment, column chromatography, crystallization, drying and other processes, wherein the content of the obtained soybean isoflavone is more than 40 percent. The method has the benefits that as the soybean isoflavone is extracted by utilizing the soybean molasses as a by-product of an alcohol leaching soy protein concentrate, the added value of the soybean molasses is greatly increased; the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:荆门市德爱生物工程股份有限公司
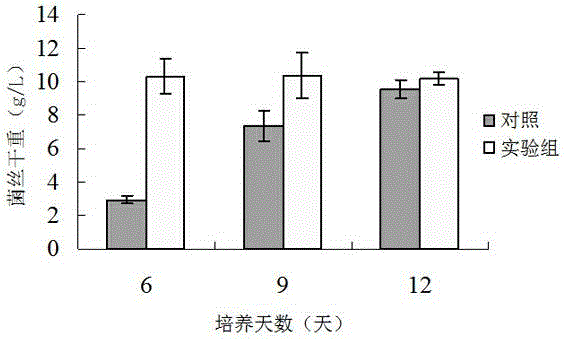
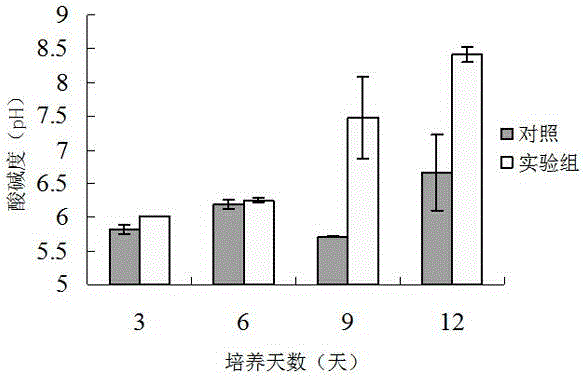
Soybean molasses hypsizigus marmoreus liquid nutrient medium and application thereof
InactiveCN104877918AQuality improvementIncrease market scopeFungiMicroorganism based processesFodderCulture mediums
The invention relates to a soybean molasses hypsizigus marmoreus liquid nutrient medium and application thereof and provides the recipe of the liquid nutrient medium which can promote hypsizigus marmoreus mycelial growth and increase pellet number. The soybean molasses hypsizigus marmoreus liquid nutrient medium has the advantages that when the liquid nutrient medium is used to cultivate hypsizigus marmoreus, the mycelial concentration of the hypsizigus marmoreus can reach the maximum value of about 10g / L on the sixth day, pellet diameter can reach 0.1-0.5mm, the mycelial concentration is 3-4 times of that of a control group, and the pellet diameter of the control group is 1-3mm; the hypsizigus marmoreus metabolic capability is increased evidently; soybean molasses serving as cheap materials are widely applied to animal feed, but no reports indicate that the soybean molasses are used as additives during fungus liquid spawn production.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Diastatic fiber feedstuff and method for preparing same
InactiveCN1864515ASuitable for needsChange network structureFood processingAnimal feeding stuffFiberFibers tissue
The present invention discloses one kind of saccharified fiber feed used widely in raising farm animal. The saccharified fiber feed is prepared with corn peel as the waste from corn processing and soybean molasses as main material and through a special preparation process, which alters the netted structure of fiber tissue for easy absorption of animal. The saccharified fiber feed contains oligosaccharide, soybean isoflavone, saponin and other special nutritious components from soybean molasses and thus possesses special nourishing function. Especially, the soybean isoflavone can provide sow with natural estrogen to raise the propagation capacity greatly.
Owner:石晓岭
Beta-glucan-enriched fermented feed and preparation method thereof,
PendingCN108902452AGuaranteed contentLow costFood processingAnimal feeding stuffFiberHigh concentration
The present invention discloses a beta-glucan-enriched fermented feed and a preparation method thereof. The beta-glucan-enriched fermented feed comprises the following steps: (1) after soybean molasses are fermented, the fermented soybean molasses with water content of 40-70 wt% are obtained; (2) plant fiber feed raw materials with protein content of less than 20% are prepared; and 300-1,000 kg ofthe fermented soybean molasses obtained in the step (1) are added into per ton of the feed raw materials; and the materials are mixed and stirred; and (3) the mixture fermenting, drying and crushingare conducted to obtain the dry fermented feed. The preparation method is a step-by-step-method solid open-type fermentation technology; the soybean molasses and high-fiber feed raw materials are applied for production; due to the fact that the high-concentration molasses with solid content of 30%-60% are used for the fermenting, beta-glucan content in the fermentation product is ensured; and thefinished product achieves the high beta-glucan content and greatly reduces the cost of applying the beta-glucan for animal breeding.
Owner:PEARL RIVER FISHERY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI +1
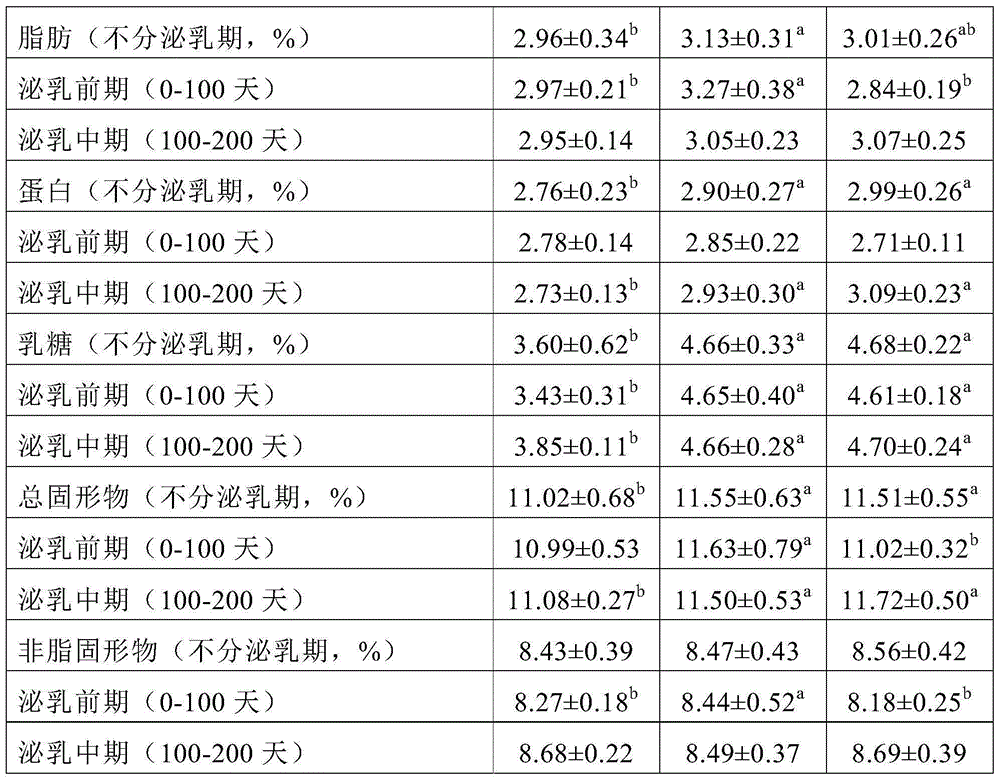
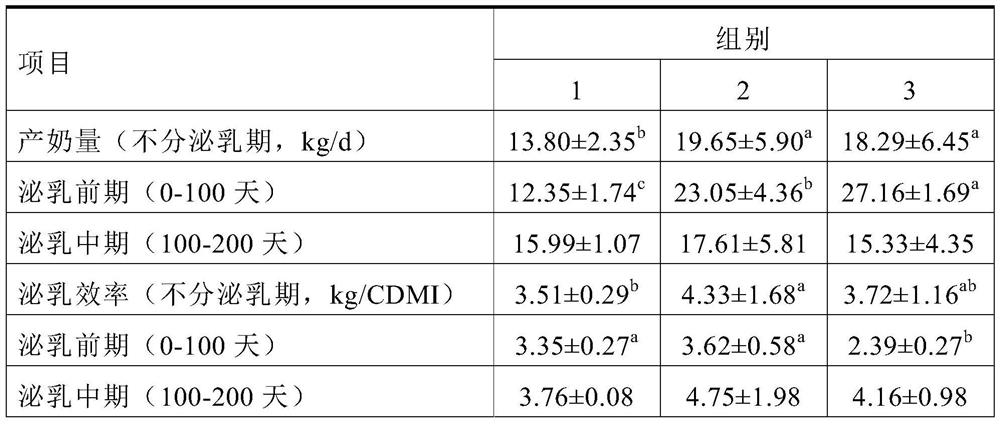
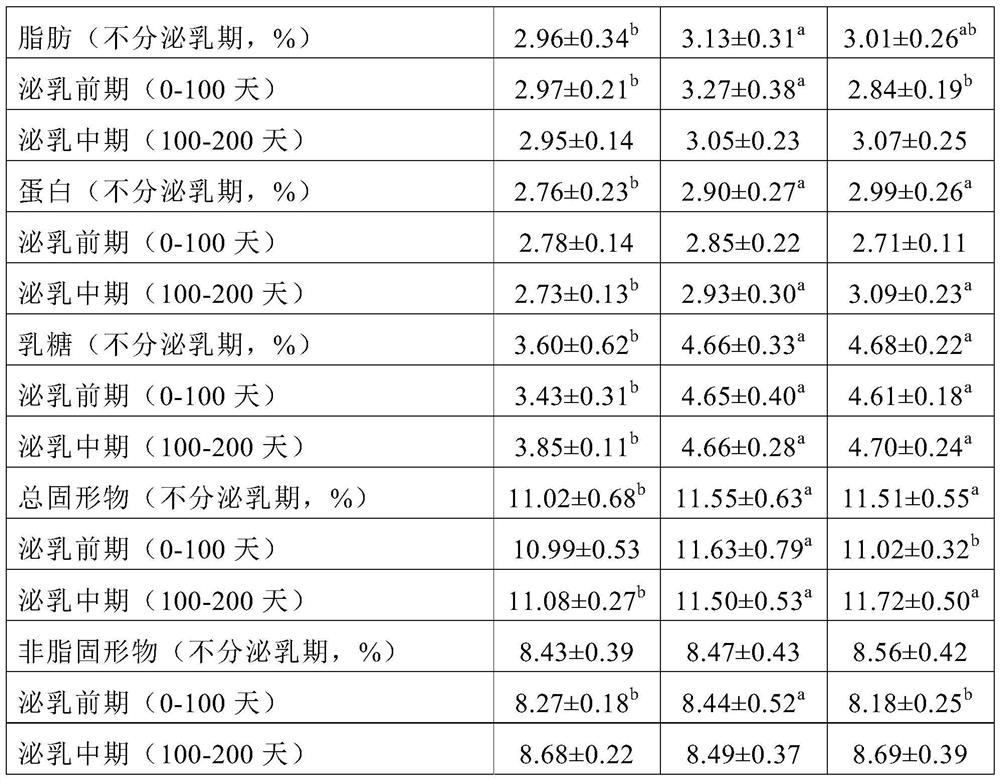
Raw materials of functional feed for improving milk yield and milk quality and application thereof
ActiveCN106615718AIncrease milk productionLow costFood processingAnimal feeding stuffAnimal scienceAdditive ingredient
The present invention relates to raw materials of a functional feed for improving milk yield and milk quality and an application thereof. In particular, the present invention provides a soybean molasses product. The product comprises a feed carrier and soybean molasses adsorbed on the feed carrier. The present invention also provides corn substitute materials and a feed, the corn substitute materials contain the soybean molasses product, and the feed contains the soybean molasses product or the corn substitute materials. The corn substitute materials can substitute parts of the corns in dairy cow feeds, which reduces the corn ingredients in the feed, significantly increases the milk yield of dairy cows, and enables parts of nutrition indexes in the milk to be significantly increased.
Owner:WILMAR SHANGHAI BIOTECH RES & DEV CENT
Lactic acid bacteria fermentation liquid rich in natural bromelain, and preparation method thereof
PendingCN109315587AIncrease the number of live bacteriaImprove product valueAnimal feeding stuffLactobacillusOrganic acid
The invention discloses lactic acid bacteria fermentation liquid rich in natural bromelain, and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method includes the steps of evenly mixing soybean molasses with water while sterilizing, and adding squeezed pineapple juice and lactic acid bacteria seed culture liquid, wherein the adding amount of the squeezed pineapple juice accounts for 3-10 per cent of the mixed solution, and the adding amount of the lactic acid bacteria seed culture liquid accounts for 0.3-0.5 per mill of the soy molasses mixed solution; performing constant-temperature anaerobicfermentation to obtain the lactic acid bacteria fermentation liquid rich in natural bromelain. The lactic acid bacteria fermentation liquid has the advantages that the pineapple juice is applied to lactic acid bacteria fermentation, so that the number of living bacteria of the lactic acid bacteria fermentation liquid can be improved remarkably; the product value of the lactic acid bacteria fermentation liquid can be increased, and the lactic acid bacteria fermentation liquid has high enzyme activity and organic acids, can allow the bromelain to play a role when being added into animal feed inthe subsequent stages and has the effects of stimulating appetite, repairing intestinal tracts, enhancing the immunity and promoting the growth of the farmed animals.
Owner:湛江市粤凯生物科技有限公司 +1
Feed produced utilizing traditional Chinese medicine dregs and preparation method thereof
PendingCN109418536AEnhance physical fitnessBoost immunityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffFeed processingAnimal science
The invention relates to traditional Chinese medicine dreg feed, and particularly discloses feed produced utilizing traditional Chinese medicine dregs and a preparation method thereof, belonging the field of feed processing. The feed is characterized in that the feed is prepared from, by weight, 300-600 parts of 'Tianmeng' medicine dreg powder, 50-150 parts of corn flour, 100-400 parts of mushroomresidue powder, 30-80 parts of soybean meal powder, 30-80 parts of soybean molasses, 2-4 parts of a premix of trace elements and 0.2-0.4 part of an inorganic salt. The feed is free of side and toxiceffects, free of generation of drug resistance, free of pollution to the environment and low in cost, can be adopted as a diet to feed animals in place of commercially available feed, and has fattening and healthcare effects superior to those of the commercially available feed.
Owner:RONGCHANG PHARM ZIBO CO LTD
A functional feed material for improving milk production and milk quality and its application
ActiveCN106615718BIncrease milk productionLow costFood processingAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyNutritional Indices
The present invention relates to raw materials of a functional feed for improving milk yield and milk quality and an application thereof. In particular, the present invention provides a soybean molasses product. The product comprises a feed carrier and soybean molasses adsorbed on the feed carrier. The present invention also provides corn substitute materials and a feed, the corn substitute materials contain the soybean molasses product, and the feed contains the soybean molasses product or the corn substitute materials. The corn substitute materials can substitute parts of the corns in dairy cow feeds, which reduces the corn ingredients in the feed, significantly increases the milk yield of dairy cows, and enables parts of nutrition indexes in the milk to be significantly increased.
Owner:WILMAR SHANGHAI BIOTECH RES & DEV CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com