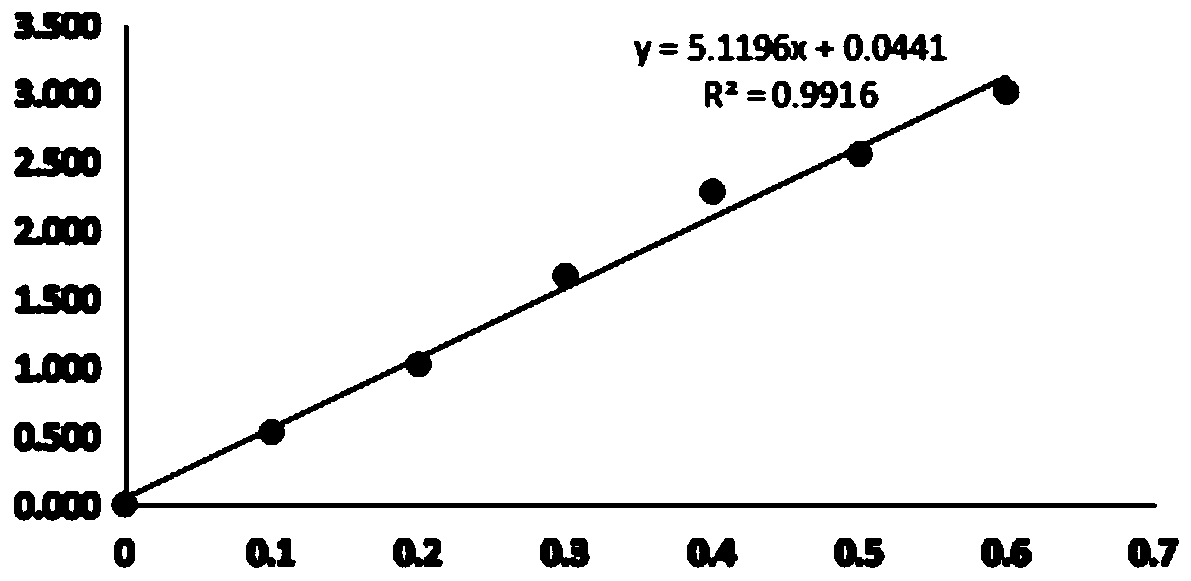
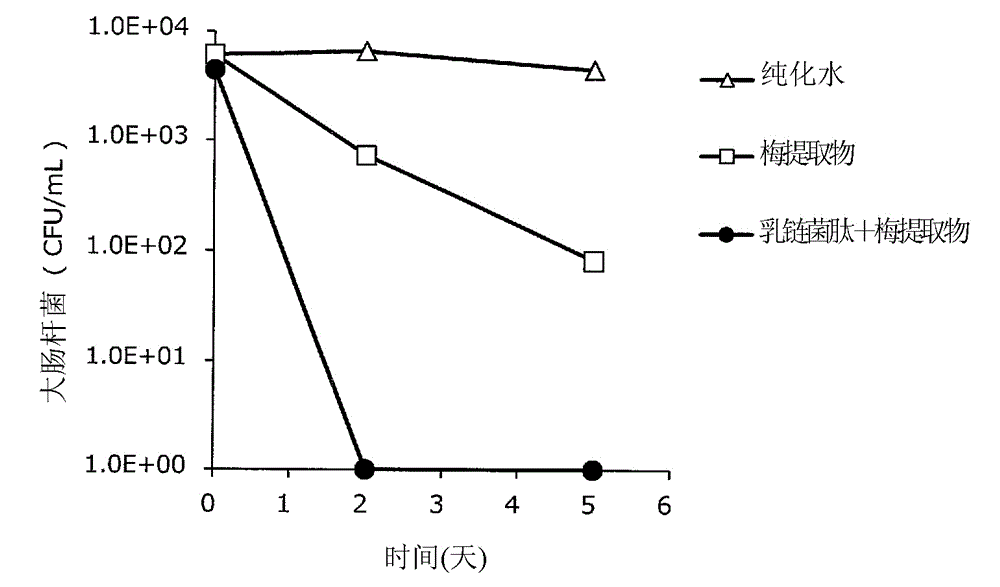
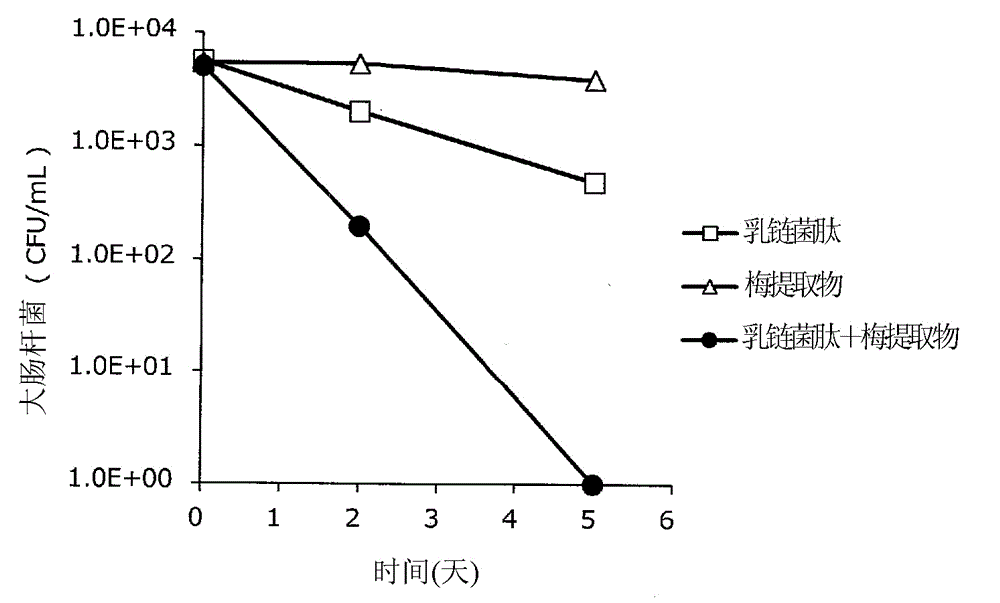
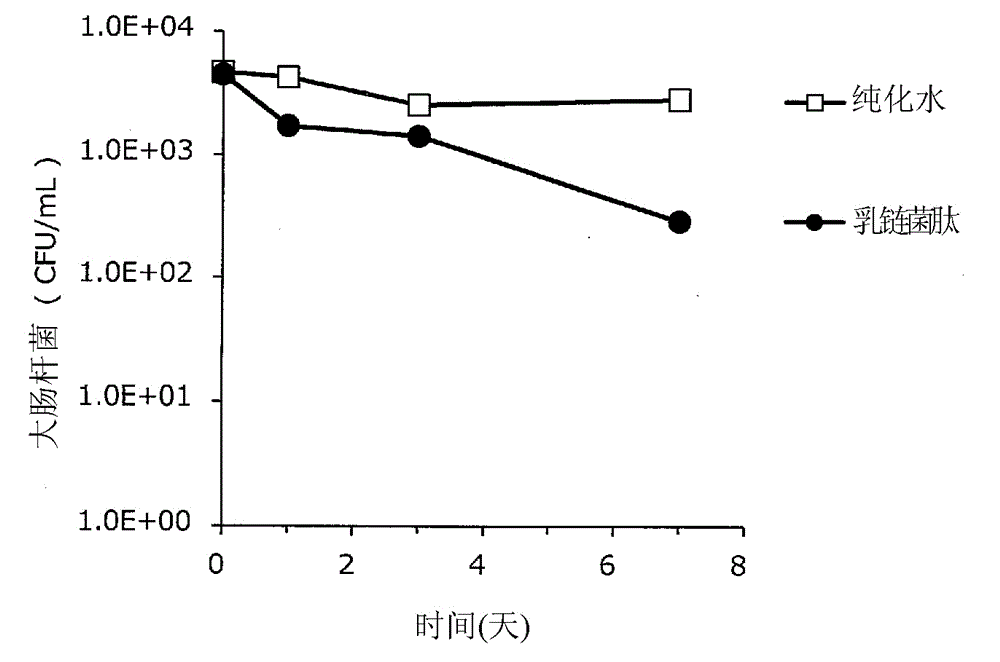
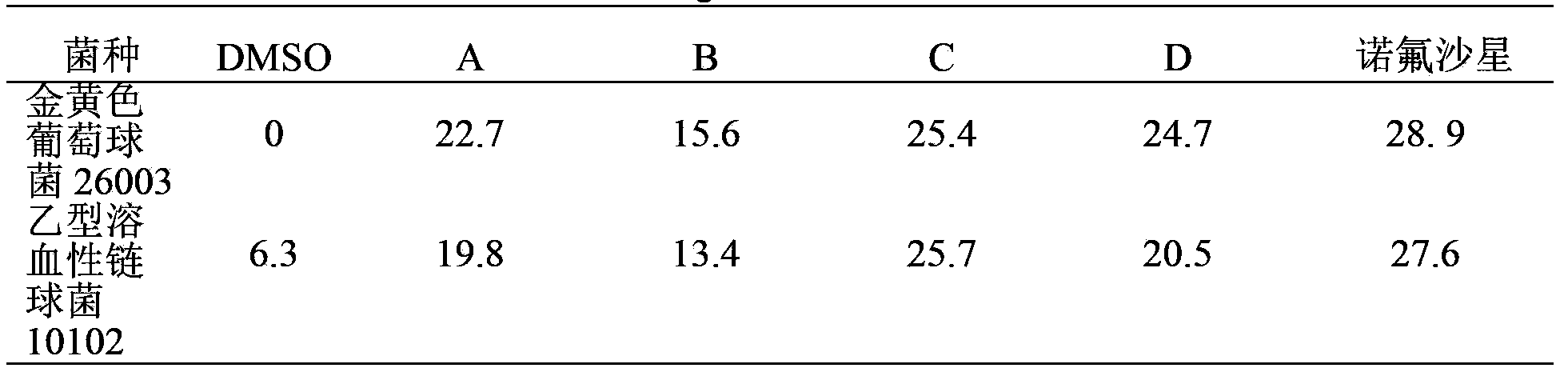
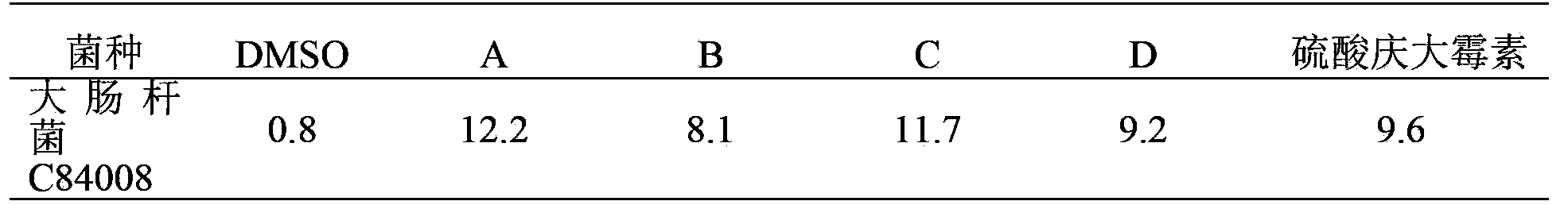
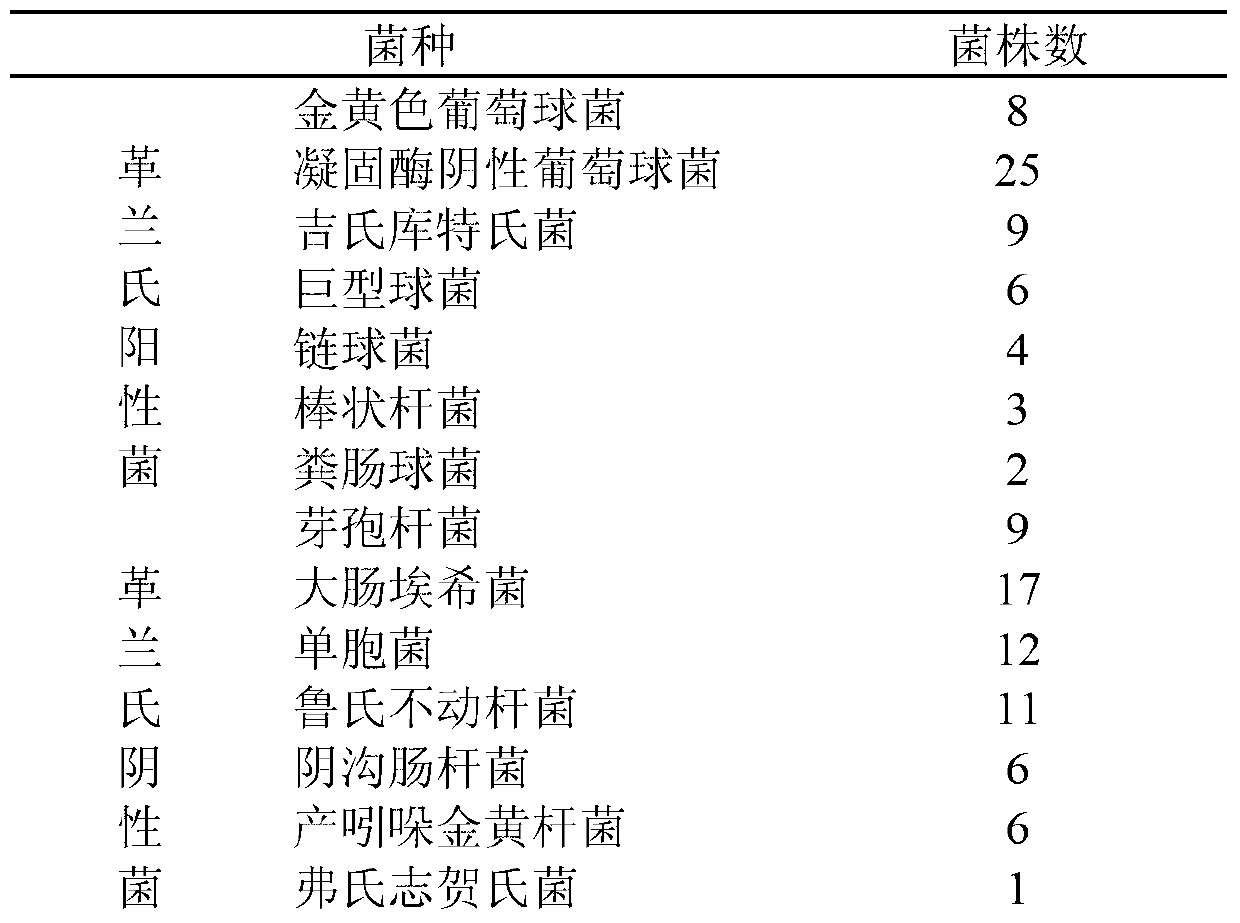
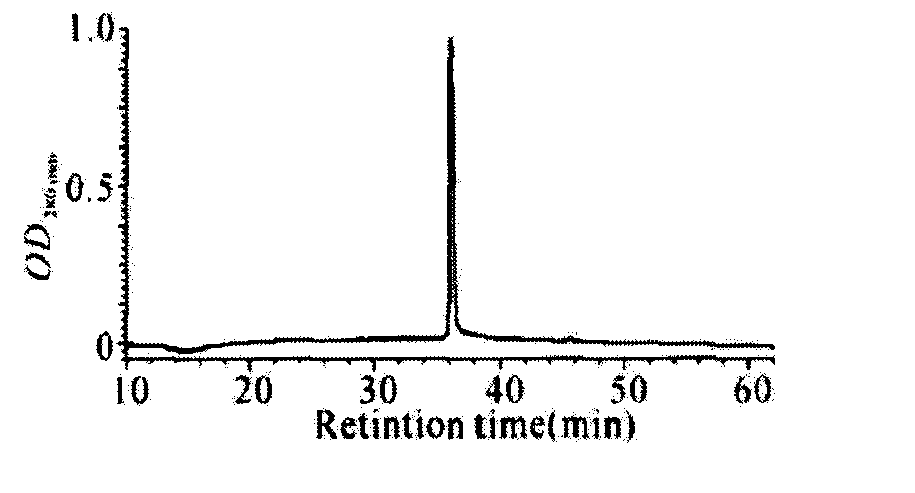
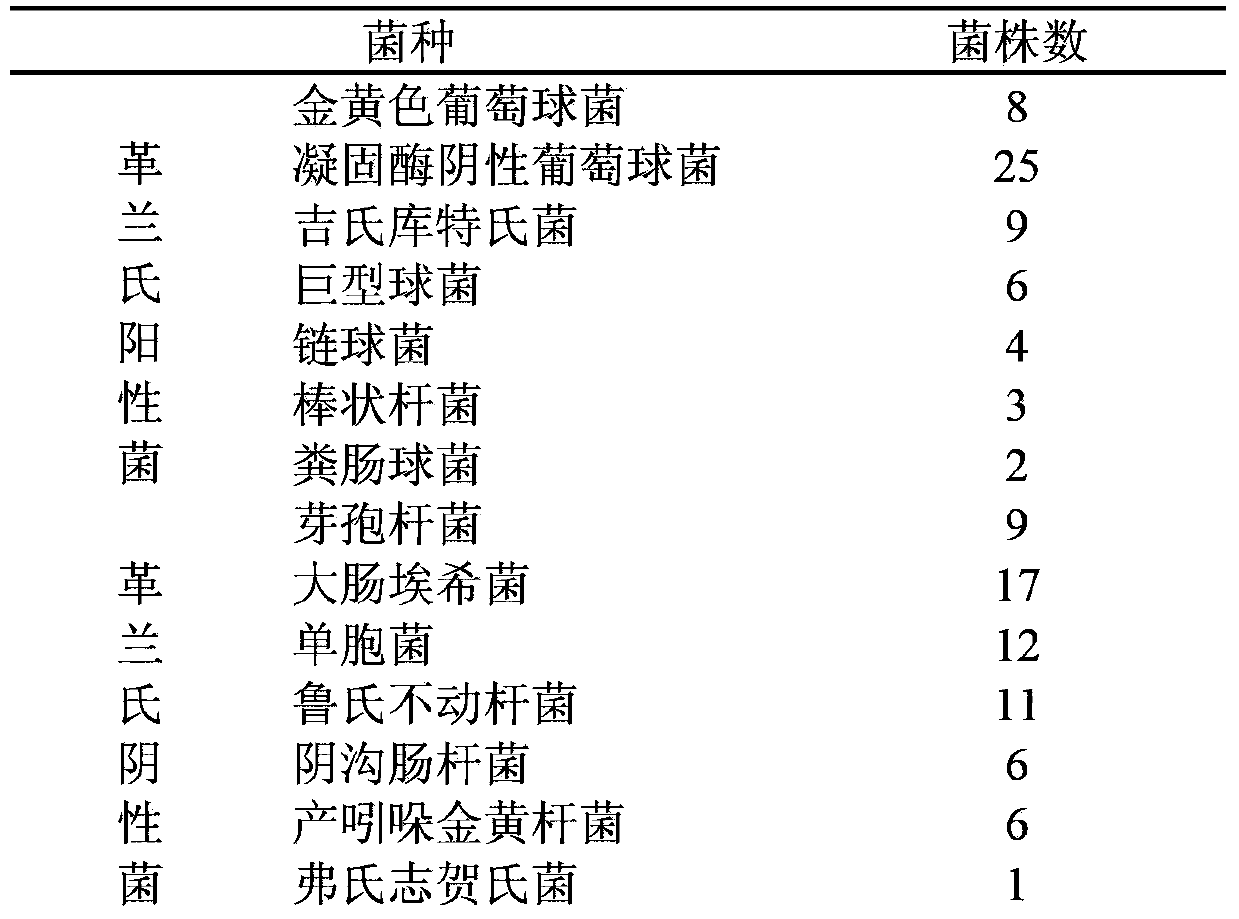
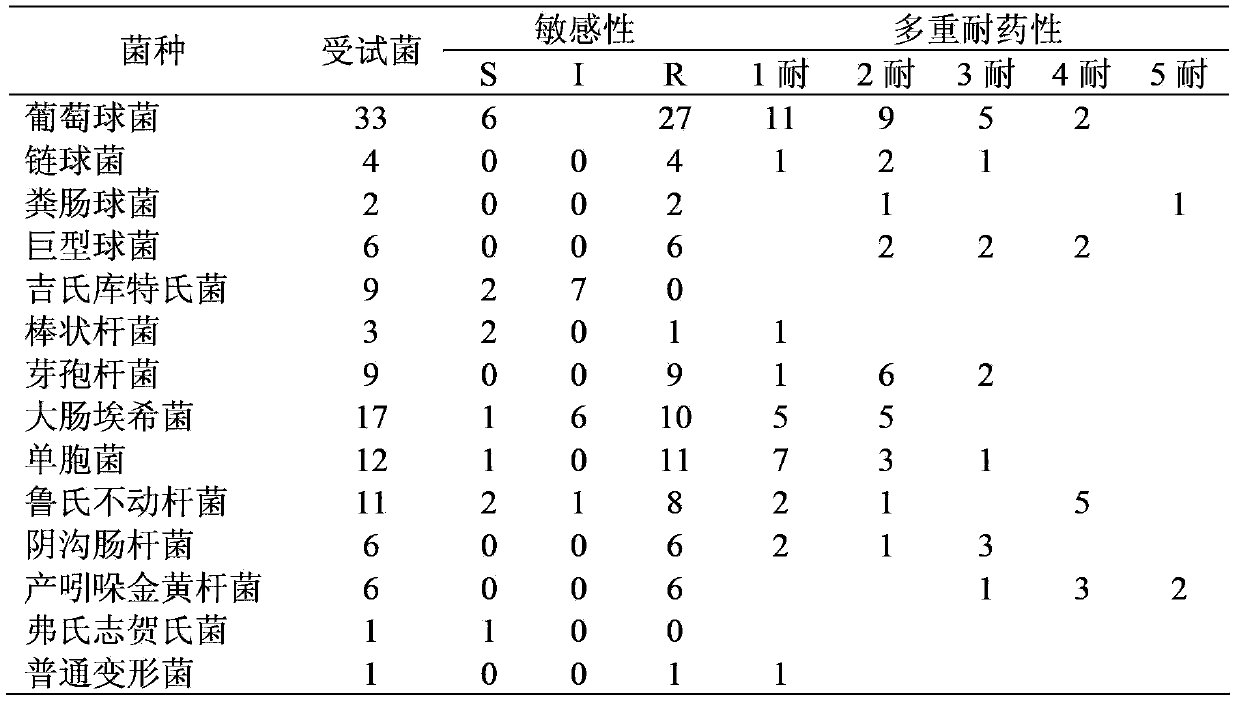
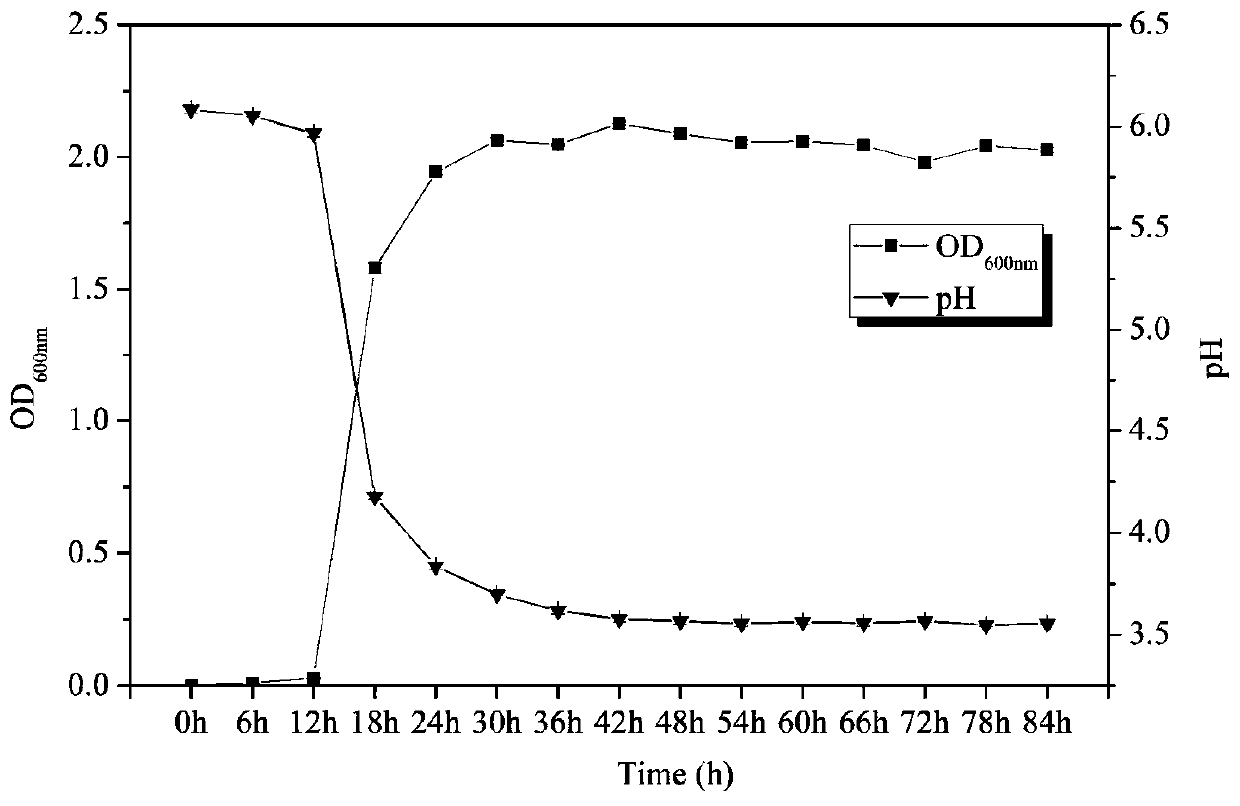
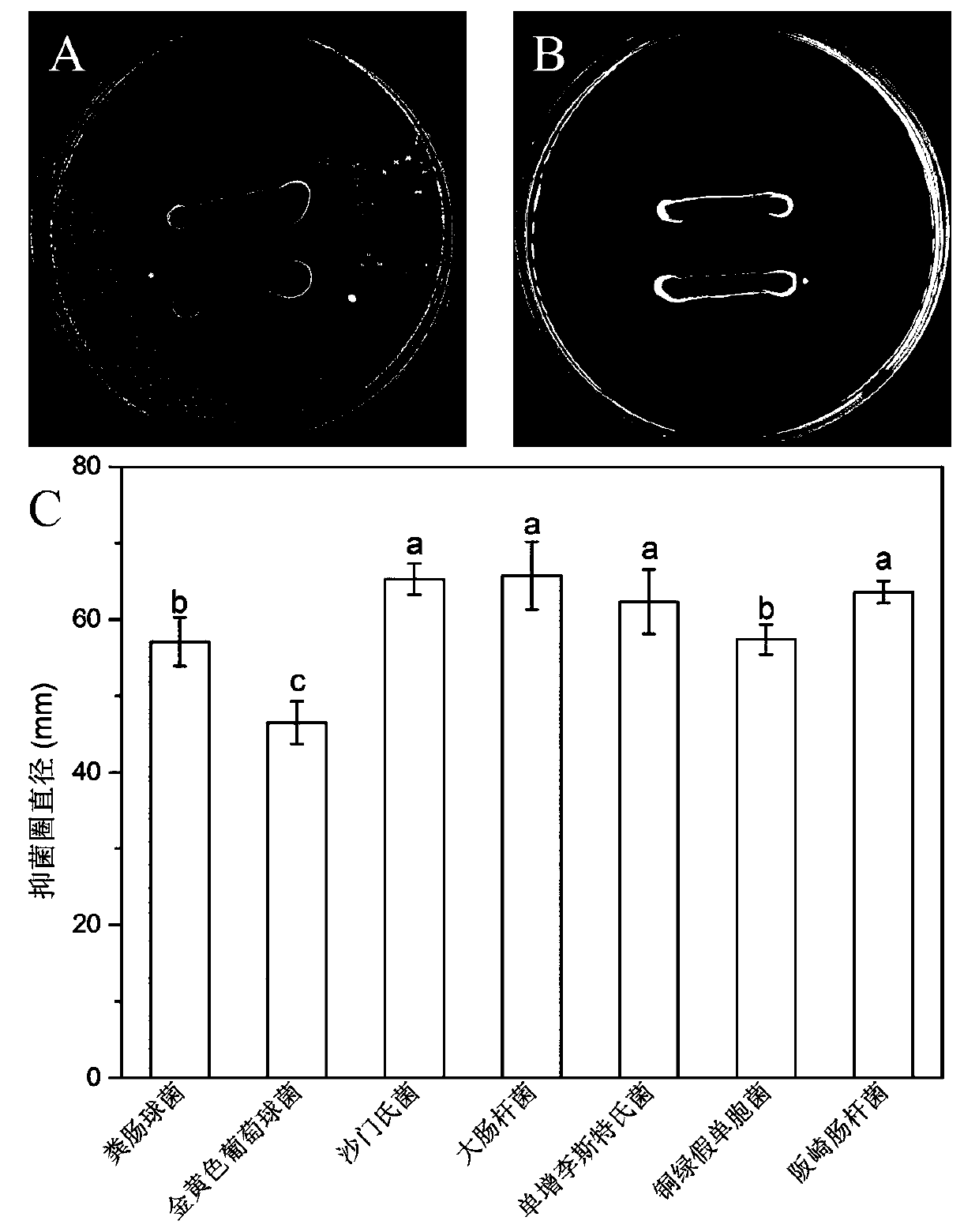
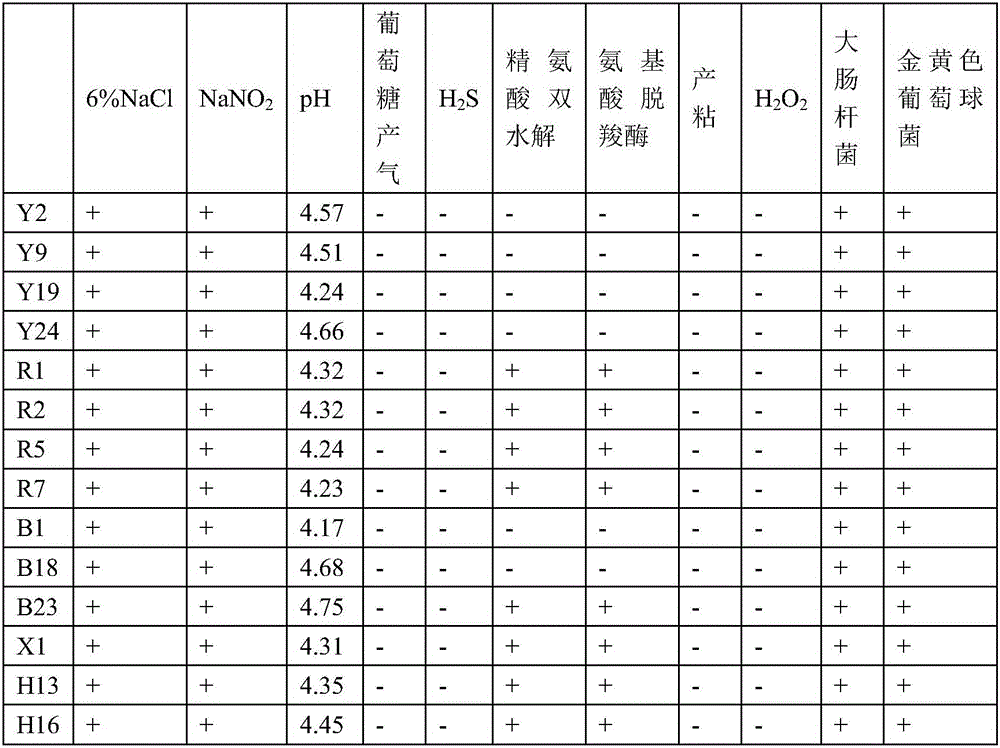
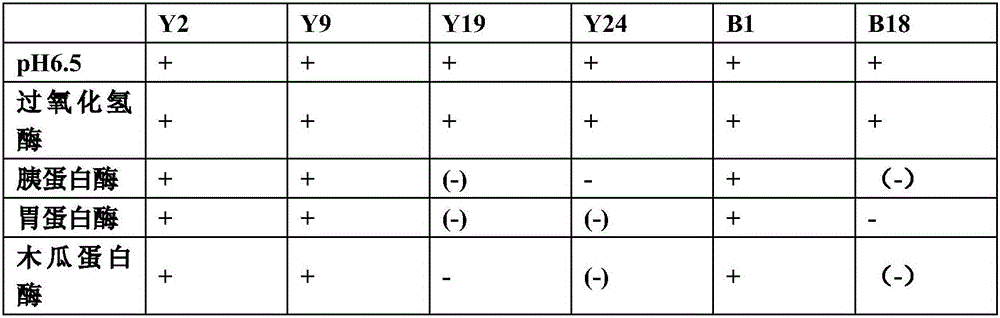
Patents
Literature
44 results about "Gram Positive Bacillus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gram-positive bacilli belong to a class of rod-shaped bacteria that acquire a violet color when subjected to the Gram staining method. Aside from its characteristic shape, this class of bacteria has a thick peptidoglycan layer, which lends itself to better absorption of antibiotics.
Lactobacillus plantarum and bacteriocins produced by lactobacillus plantarum and capable of inhibiting Gram negative bacteria
InactiveCN101812414AHigh activityBroad antibacterial spectrumBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAlcohol sugarsFermentation
The invention relates to a strain of lactobacillus plantarum and bacteriocins produced by the lactobacillus plantarum and capable of inhibiting Gram negative bacteria. The bacteriocins have the advantages of broad antibacterial spectrum, thermal stability and stable pH, degradability by protease, no residue in a human body and high safety. A lactobacillus plantarum strain is preserved on June 29, 2009 with a preservation number of CGMCC No.3151. A production strain is obtained by separating 'Jiaoke', a conventional dairy product in Inner Mongolia; on a MRS culture medium, colonies are ivory and round with a protruded center and orderly edges; the strain has two blunt round ends and a short and straight stem; and the size of the strain is 0.4 to 0.7 mu m *2 to 3 mu m. The strain is a non-spore Gram positive bacillus, and is identified as the lactobacillus plantarum through an API50CHL sugar alcohol fermentation test, a 16S rRNA sequence homology analysis test and a recA gene multiplex PCR method. The lactobacillus plantarum KLDS1.0391 is used as the production strain and is fermented and purified by using the improved MRS culture medium to obtain the bacteriocins of the lactobacillus plantarum. The bacteriocins are used in food preservatives.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation of blattodea polypeptide, and uses of the same in anti-gram-positive bacteria and anti-gram-negative bacteria
InactiveCN102743741AHigh yieldBroad biological activityAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsChemical productsGram Positive Bacillus
The present invention relates to preparation of a blattodea polypeptide, and uses of the blattodea polypeptide in anti-gram-positive bacteria and anti-gram-negative bacteria. Specifically the present invention relates to a blattodea extract effective fraction having a function of prevention and treatment of bacterial infection diseases, a preparation method and a medical use thereof. The Periplaneta Americana extract effective fraction of the present invention is a polypeptide substance with a molecular weight less than 5000 dalton, and is prepared by the following steps: carrying out solvent extraction and membrane separation on fresh polypide or dried polypide of Periplaneta Americana to obtain the product of the present invention, wherein the polypeptide active substance of the effective fraction has significant anti-gram-positive bacteria activity and anti-gram-negative bacteria activity, can be prepared into forms of a hydrogel, a cataplasm, lyophilized powder, a water agent, an aerosol, a suppository, a film agent, an external application liniment, and an ointment, and can be used for preparations of drugs for prevention and treatment of diseases related to gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria and infections, daily chemical products or medical devices.
Owner:DALI UNIV
Marine Streptomyces strain and use thereof
InactiveCN102220271AHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsCandida famataHigh activity
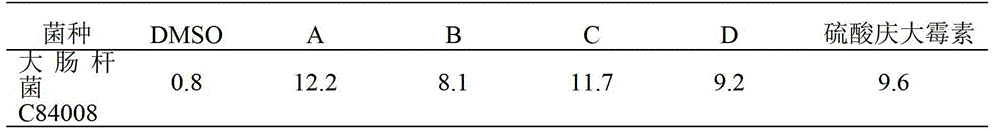
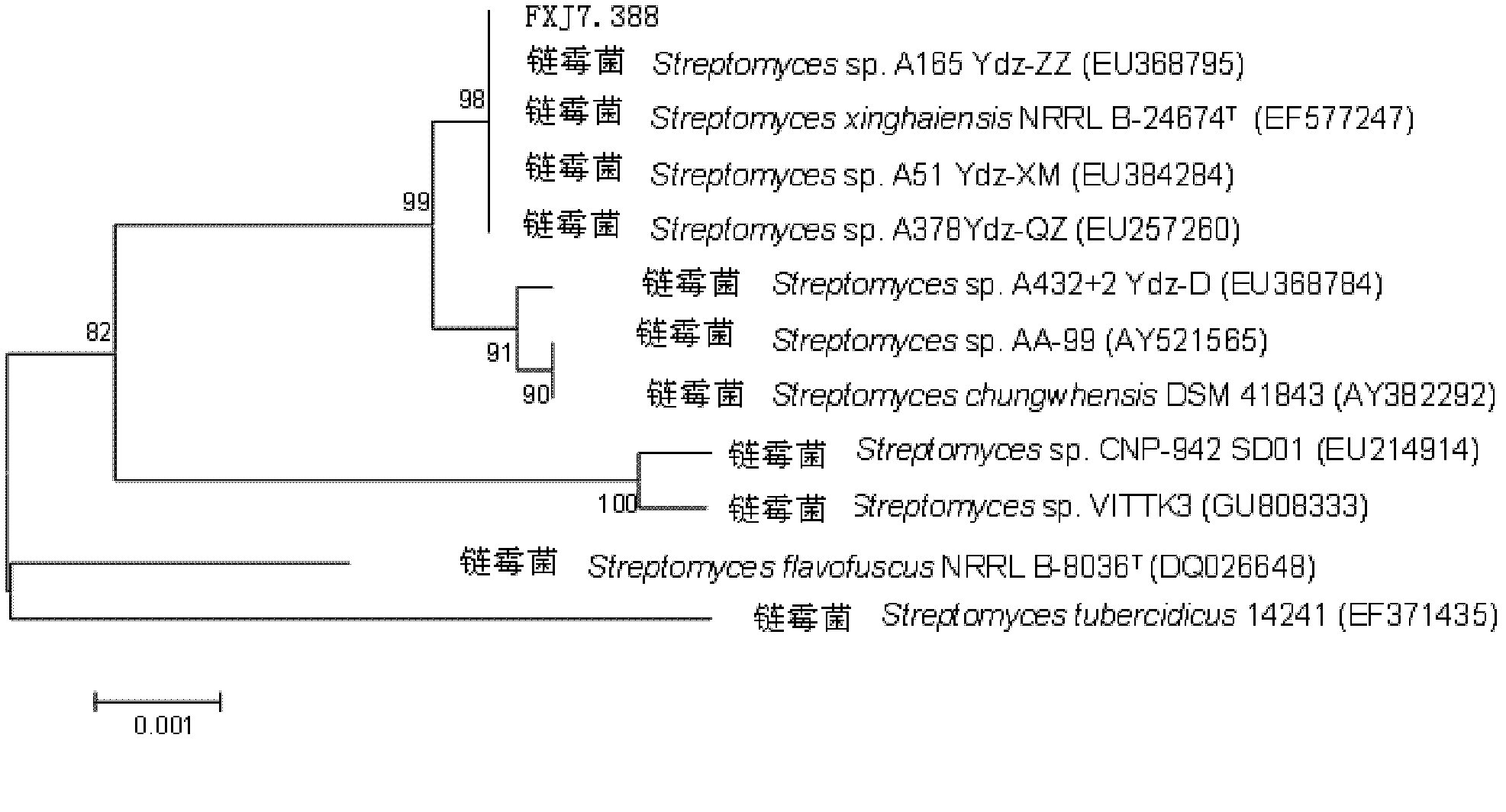
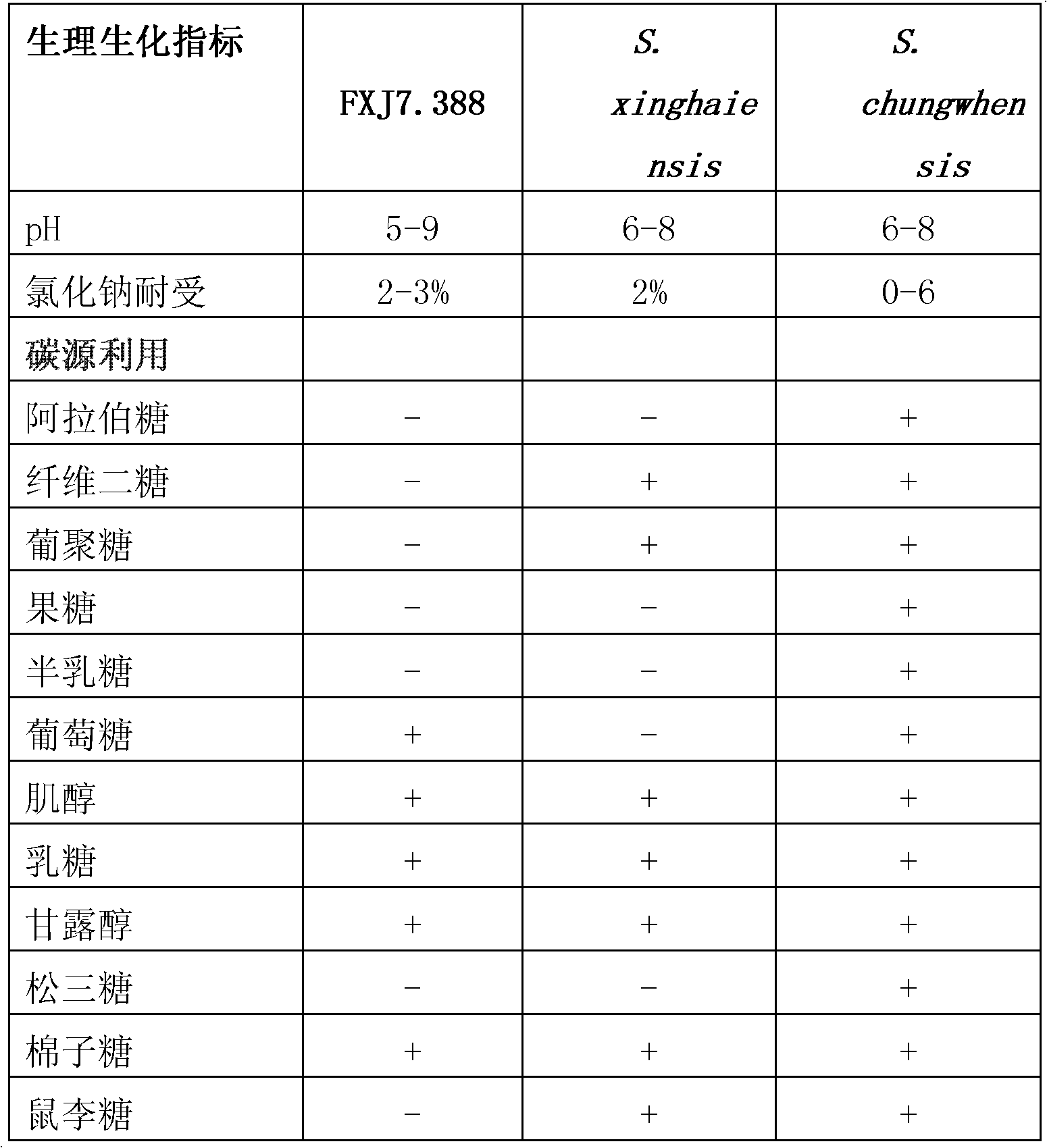
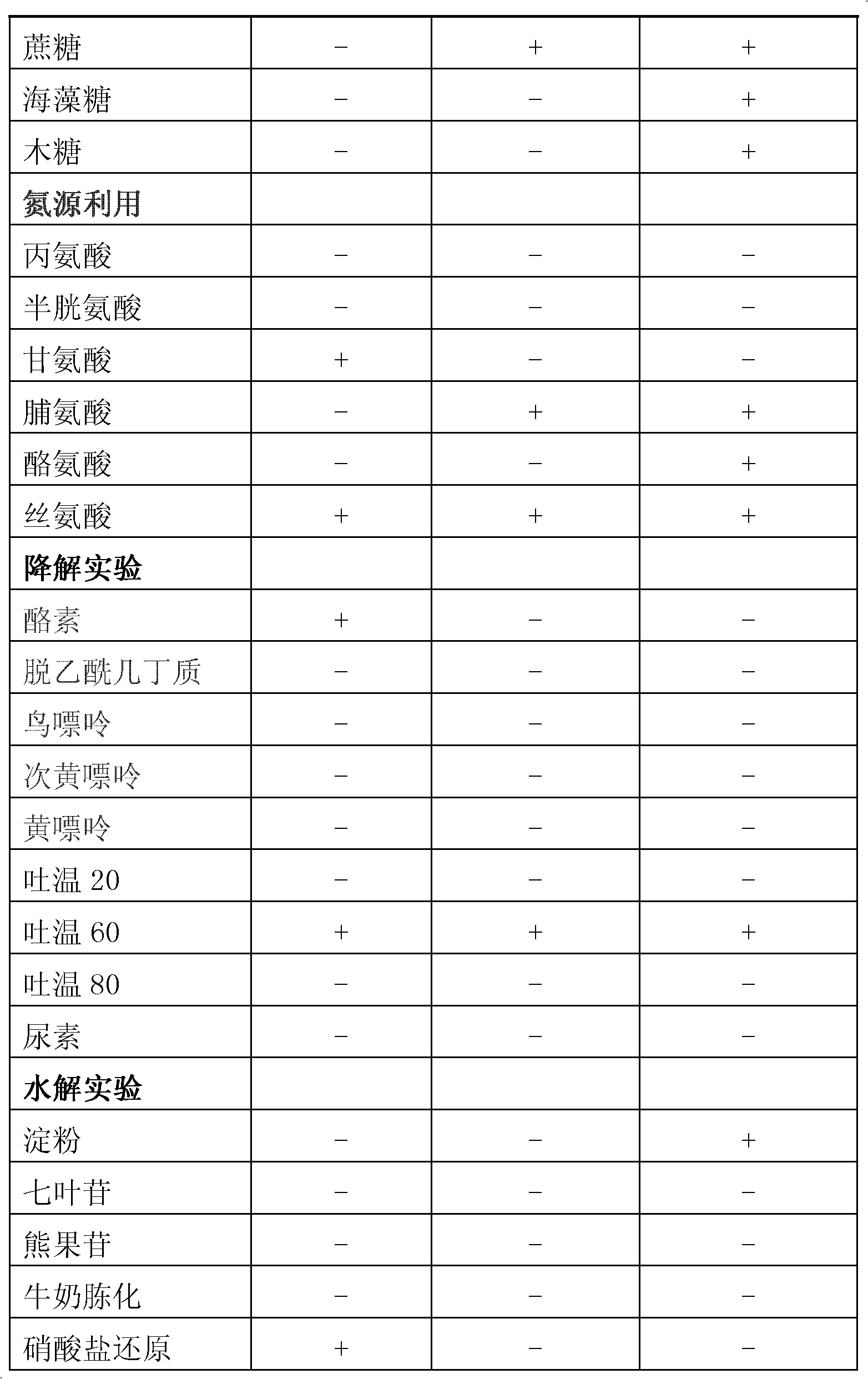
The invention provides a marine Streptomyces strain and use thereof. The strain provided by the invention is Streptomyces sp. FXJ7.388, and the collection number of the strain is CGMCC No.4474. The invention also provides the use of the strain in the preparation of an antibacterial product. The antibacterial effect is to inhibit gram-positive bacteria, including Multi-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA 1-1), staphylococcus aureus CGMCC1.2386, bacillus subtilisGCMCC1.2428 and / or Candida albicans 2.538. Experiments prove that the Streptomyces sp. FXJ7.388 separated by the invention has the advantage of resisting gram-positive bacteria and Candida albicans, namely having high activity for resisting MRSA, staphylococcus aureus AND bacillus subtilis and certain inhibiting effect on Candida albicans.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Clostridium Daqing clostridium and application thereof
The present invention relates to clostridium 'daqing' clostridium and its uses. The present invention solves the problem it is difficult to remove or degrade polypropylene of oil field sewage. The clostridium 'daqing' clostridium -WL is preserved at CGMCC on January 10, 2007, preserving number being CGMCC No. 1911. The 'daqing' clostridium is Gram-positive bacilli, with endo-spore, facultative anaerobic, grows under pH 5.0-11.0,10-65 degree. The strain is variable in length, breadth being 0.4um-0.8um, length being 1.4um-4um, free of flagellum. The inventive 'daqing' clostridium -WL is a new strain, and can use polypropylene as unique carbon source which can be used in polypropylene biodegradation. 10ml 'daqing' clostridium -WL of concentration 6x10<6> per ml is added in oil field sewage with polypropylene concentration being 500mg / L and the polypropylene degradation rate is 35%-76% after 20 days.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Organic solvent resisting basified protease producing strain, gene and application thereof
InactiveCN101215534AHigh specific activityStrong solvent resistanceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus licheniformisNucleotide
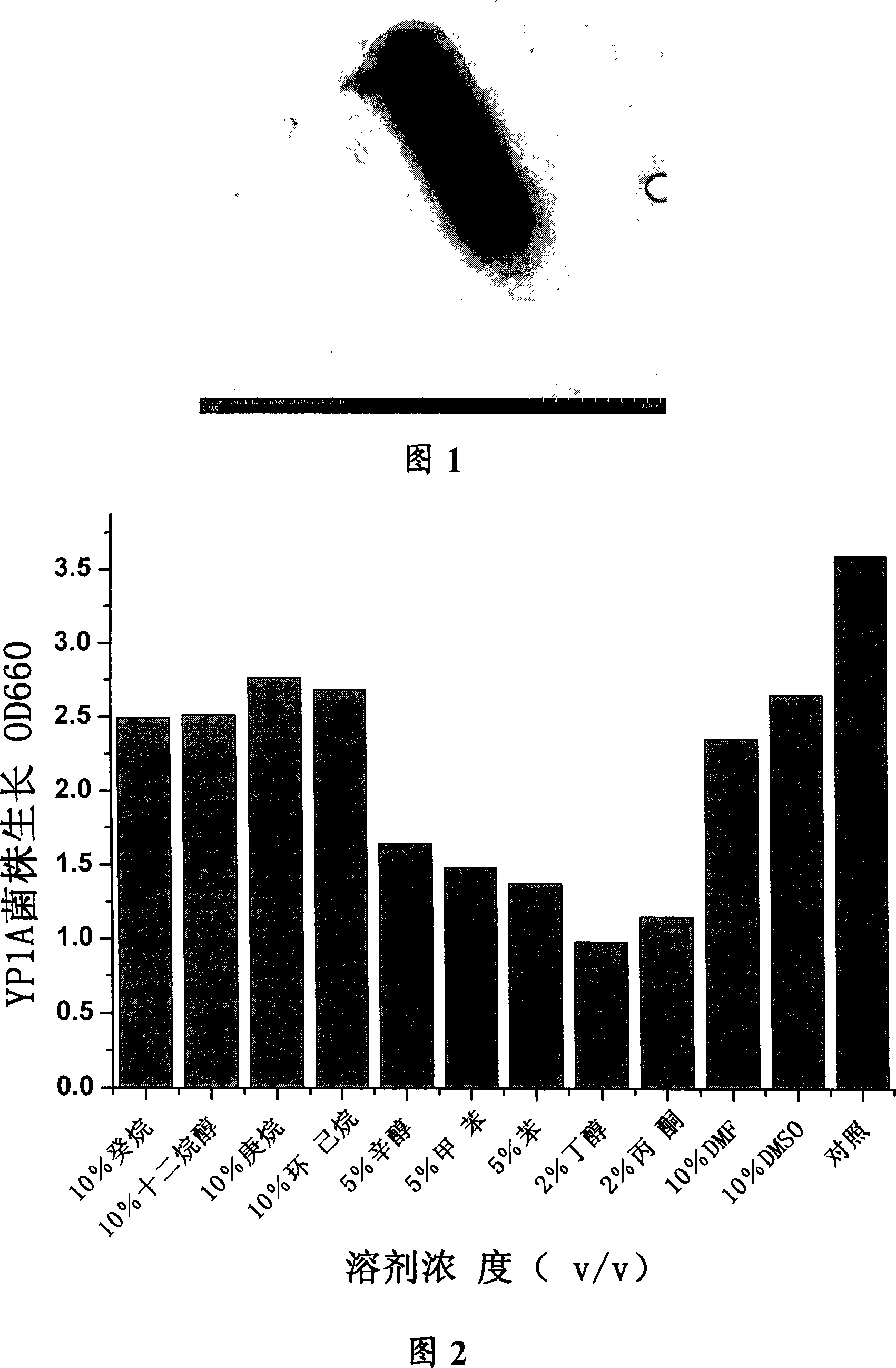
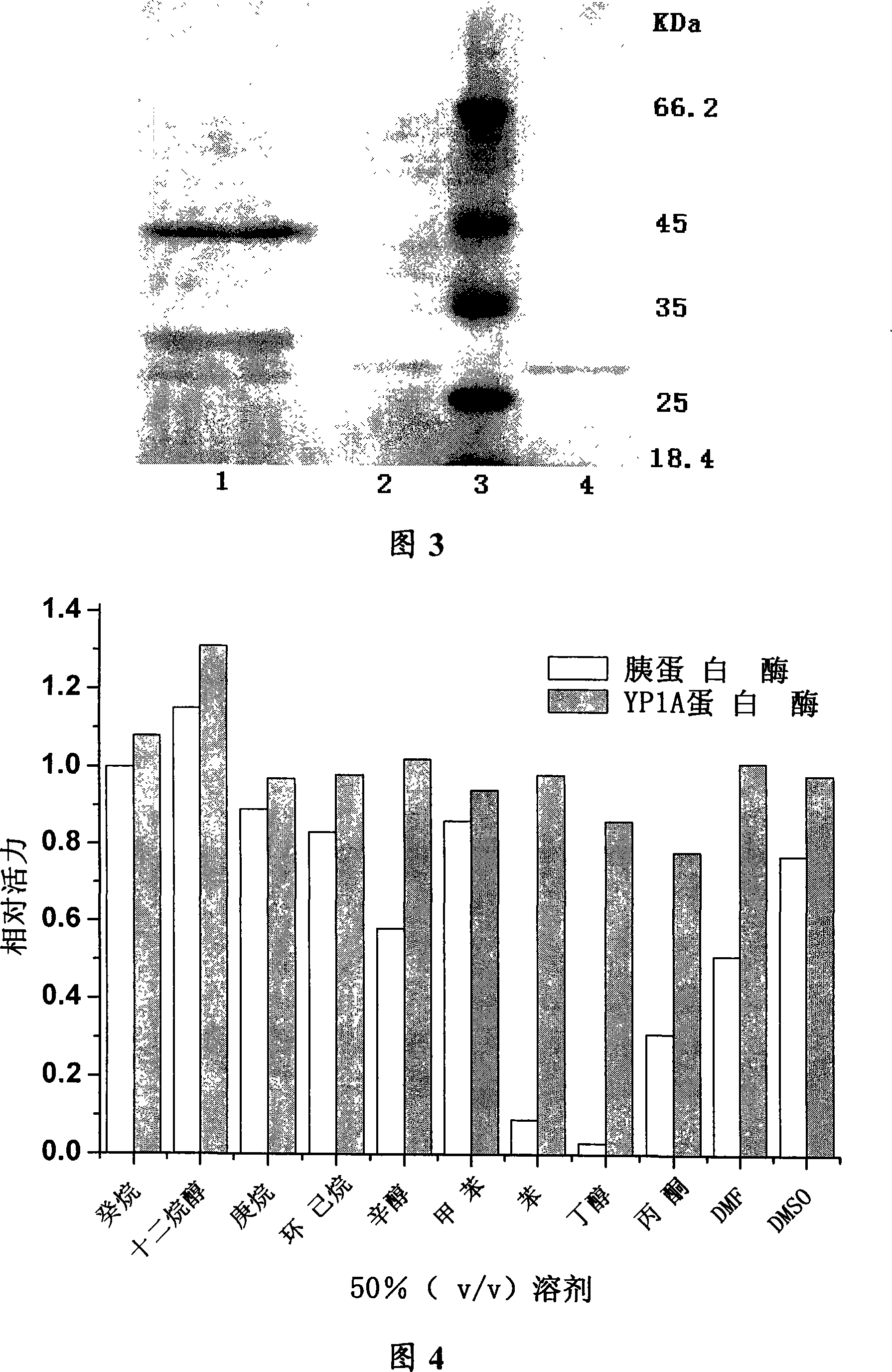
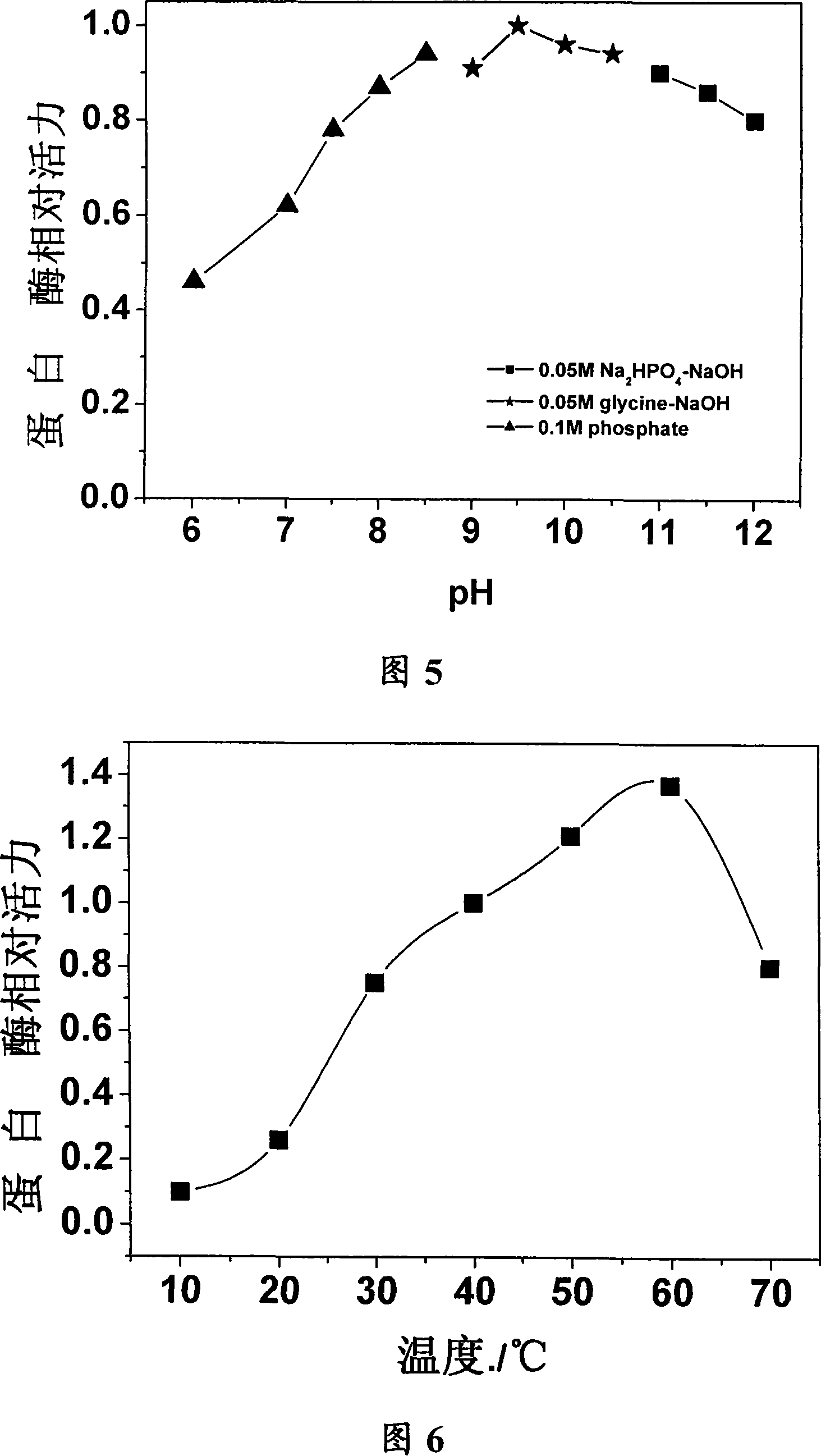
The invention discloses an organic solvent fastness alkaline proteinase generation strain and the gene and an application for catalyzing peptide to synthesize and resolve racemic amine and amino acid in the organic phase. The bacterial categorization naming is Bacillus licheniformis YP1A whose preservation register number is CCTCC No: M 207021 as Gram-positive bacillus and can tolerate certain density of a plurality of organic solvents. The invention separates and clones to obtain the coding gene of the proteinase generation strain, which is provided with nucleic acid sequence which is represented as SEQ ID NO: 1 and amino acid sequence as SEQ ID NO: 2. The organic solvent fastness alkaline proteinase is high in specific activity, strong in solvent tolerance, wide in action pH scale, strong in thermostable and strong alkalinity tolerance and the like. The proteinase can be applied in the application such as peptide synthesis in the organic phase, racemic amine and amino acid resolution and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Inhibition of gram positive bacteria
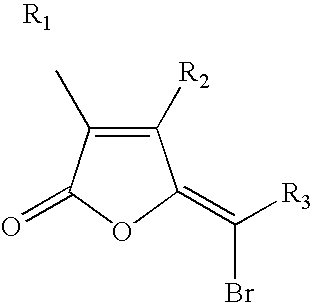
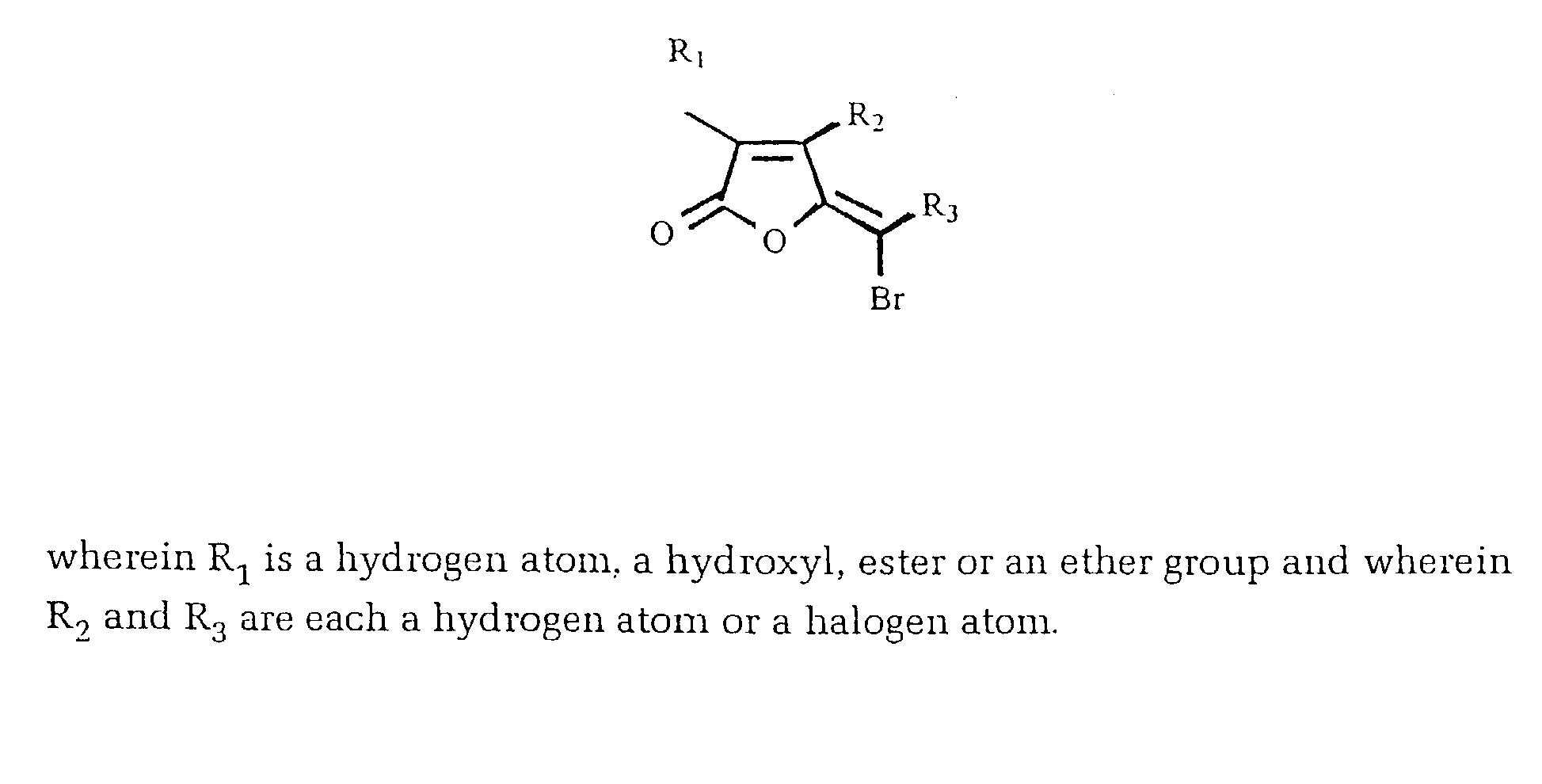
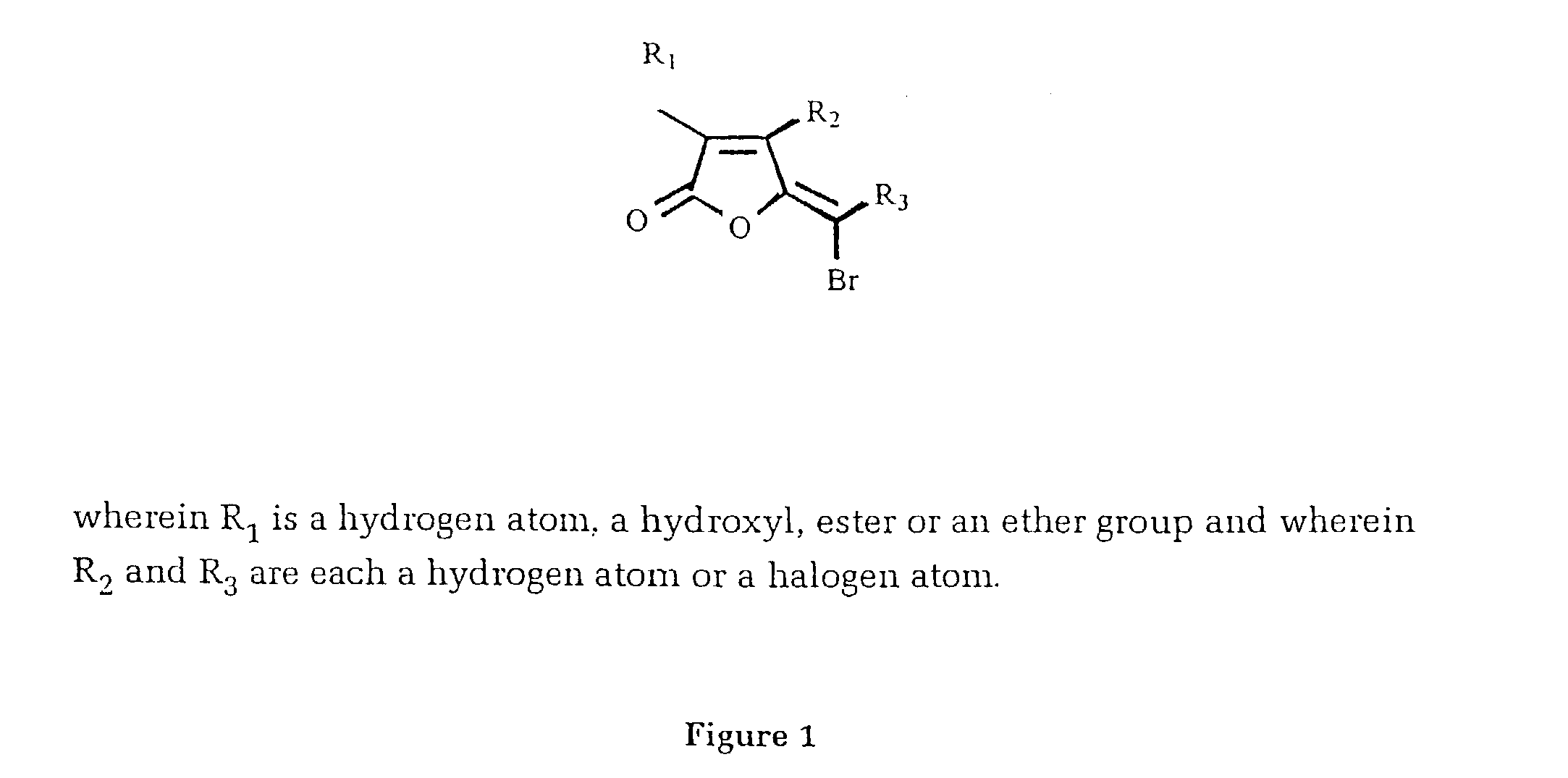
A method of inhibiting the growth R of a Gram positive bacterium, the method comprising treating the bacterium with an effective amount of one or more furanones having the Formula as set out in the Figure, wherein the effective amount of the one or more furanones does not substantially adversely effect the survival of an animal cell when exposed to the one or more furanones.
Owner:UNISEARCH LTD
Pharmaceutical compositions for promoting the growth of gram-positive bacilli and increasing the acidity in the vagina and the use thereof
InactiveUS6964949B2Improve scalabilityIncrease acidityBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsGramPharmaceutical formulation
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical formulation for stimulating the growth of gram-positive bacilli and increasing the acidity in the vagina which comprises sucrose and / to maltose, to the use of certain sucrose and / or maltose, in preparing the pharmaceutical formulation for stimulating the growth of gram-positive bacilli and increasing the acidity in the vagina, in particular to a method of stimulating the growth of gram-positive bacilli and increasing the acidity in the vagina, treating the reduction of gram-positive bacilli and the lowness of acidity in vagina as well as the vaginitis and the disturbance of vaginal bacterioflora accompanying the reduction of gram-positive bacilli, especially bacterial vaginal disease.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO ONLLY
Screening method and application of lactobacillus plantarum
InactiveCN104877986AEnhanced inhibitory effectImprove thermal stabilityMutant preparationFood preservationFood additiveMononucleosis
The invention discloses a mutation breeding method of lactobacillus plantarum and application of a strain of the lactobacillus plantarum. The collection number of the lactobacillus plantarum in China general microbiological culture collection center is CGMCC No 5297. The lactobacillus plantarum can generate bacteriocin which has a better inhibiting effect on multiple gram-positive bacteria and especially has great a high inhibiting effect on listeria monocytogenes, and the bacteriocin has the advantages of better heat stability, acid stability and the like and can be applied as a food additive and a feed preservative agent which have wide application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Spirulina polypeptide P1 with bacteriostatic activity, and application thereof
ActiveCN104311645AEasy to synthesizeNo side effectsAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsSide effectAntibacterial agent
The invention provides a novel spirulina polypeptide P1 with bacteriostatic activity. An amino acid sequence of the spirulina polypeptide P1 is shown as Seq ID No.1. The spirulina polypeptide P1 with bacteriostatic activity is extracted from spirulina for the first time. Experiments demonstrate that the spirulina polypeptide P1 can effectively suppress gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria, has no toxic or side effect, can be used as a broad-spectrum antibacterial agent or a bacteria preservative, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
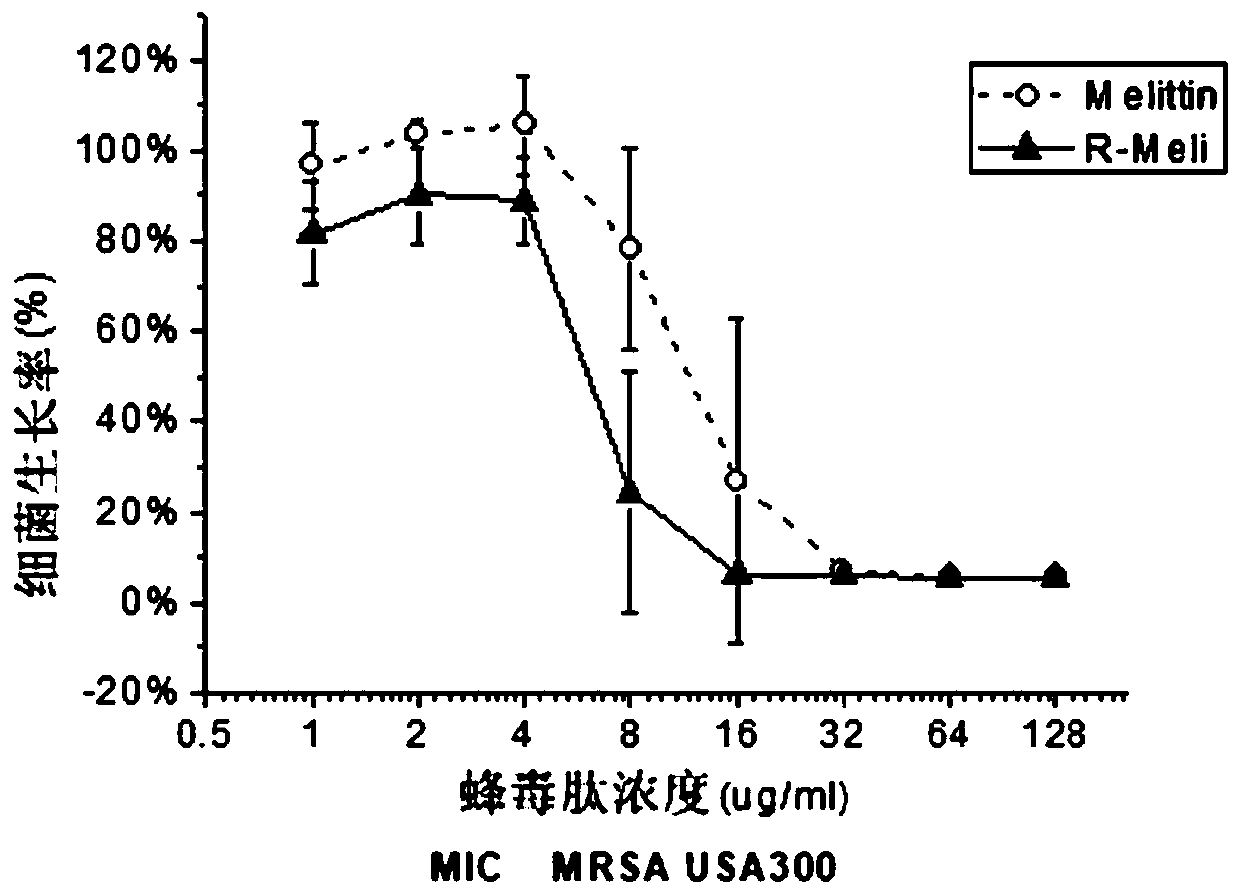
Novel melittin variant and application thereof
The invention relates to a novel melittin variant and an application thereof. At current, overuse of novel antibacterials and antibiotics is clinically to be developed, melittin as a good biology antibacterial agent is one of the best substitutes of the antibiotics. The inventor finds novel melittin based on the research. The melittin has good bacteriostasis and sterilizing capacity for Gram-negative bacteria, and through sequence improvement, the variant is obtained. Based on reservation of Gram-negative bacteria resistance of wild type melittin, good Gram-negative bacteria resistance is obtained. The novel melittin and the variant thereof provided by the invention have favorable clinical application prospects.
Owner:THE INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
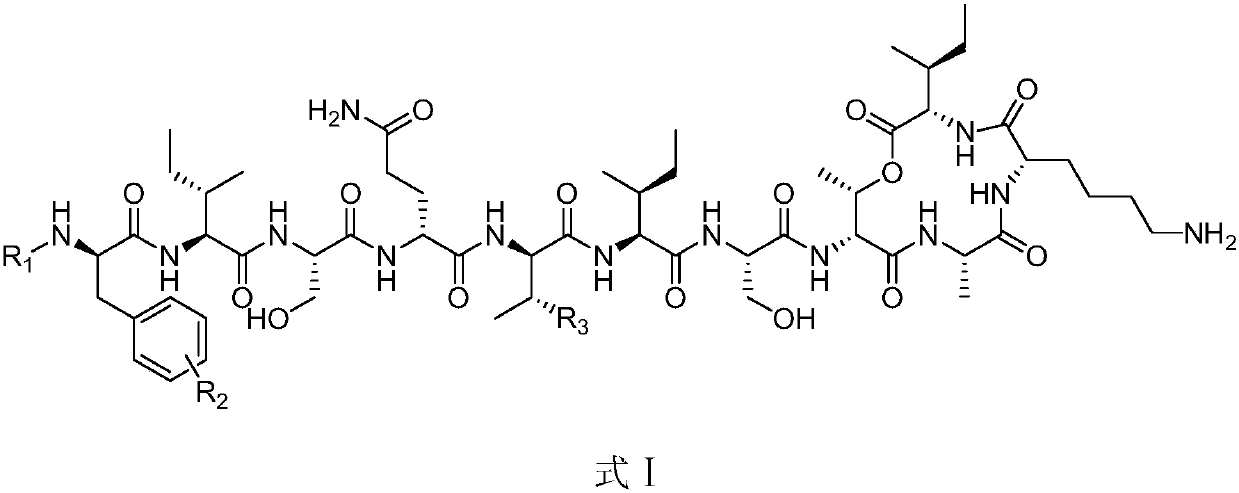
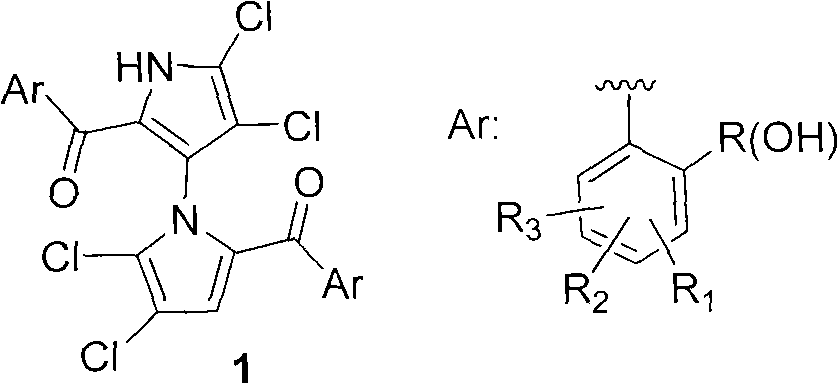
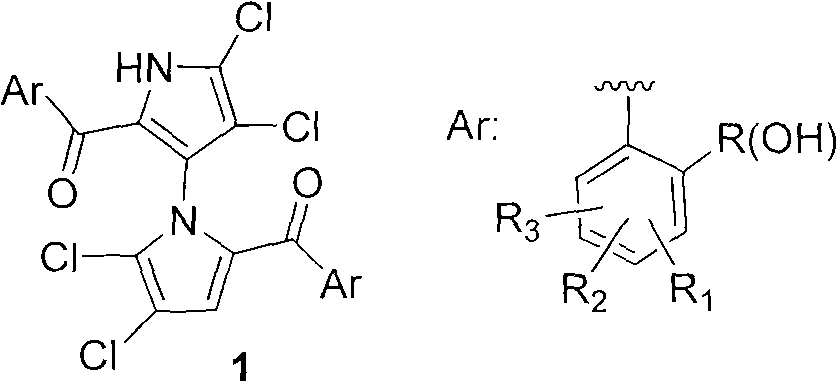
Novel antibiotic for treating drug-fast gram positive microbes and tuberculosis
ActiveCN107778352ASynthesis helpsAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibiotic YStructural formula
The invention discloses a novel antibiotic for treating drug-fast gram positive microbes and tuberculosis. The structural formula of the novel antibiotic of the invention is as shown in formula I, inthe formula I, the group R1 is hydrogen, alkyl with a carbon atom number of 1 to 15, alkenyl with a carbon atom number of 2 to 15, and alkynyl, aryl or acyl with a carbon atom number of 2 to 15; and the group R3 is alkyl with the carbon atom number of 1 to 15. A compound as shown in formula I can be used for inhibiting the growth and / or reproduction of the gram positive microbes. Since the gram positive microbes have severe drug fastness at present, the invention provides the novel antibacterial compound. A series of teixobacterin analogs are synthesized firstly by virtue of a solid-phase andliquid-phase combination way, and by adopting the convergence synthetic strategy, various kinds of compounds can be synthesized. The invention prepares a compound having an activity equivalent to thatof teixobactin.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Lactobacillus casei controlling bacterial soft rot of vegetables and its application
ActiveCN110408577AAddressing Agricultural ResiduesSolve environmental pollutionBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyMetabolite
The invention discloses Lactobacillus casei WX322 with a preservation number of CGMCC No.17710, a strain and its metabolites have broad-spectrum antibacterial activity, which can exhibit strong antibacterial ability against a variety of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria (including pathogenic and spoilage bacteria), can be used to prepare antibacterial or / and antiseptic products, and can beused in the fields of medical, food and other industry to control bacterial pathogens or spoilage bacteria, can also effectively inhibit the growth of the soft rot pathogen Pectobacterium carotovorum,and can be used to prepare products for controlling bacterial soft rot of vegetables, can control the decay of vegetables caused by Pectobacterium carotovorum before and after harvest, can effectively solve the problem of agricultural residues and environmental pollution caused by pesticide control, has good application potential in the biological control of vegetable bacterial soft rot, and alsoprovides an excellent basic strain for the development of microbial pesticides.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
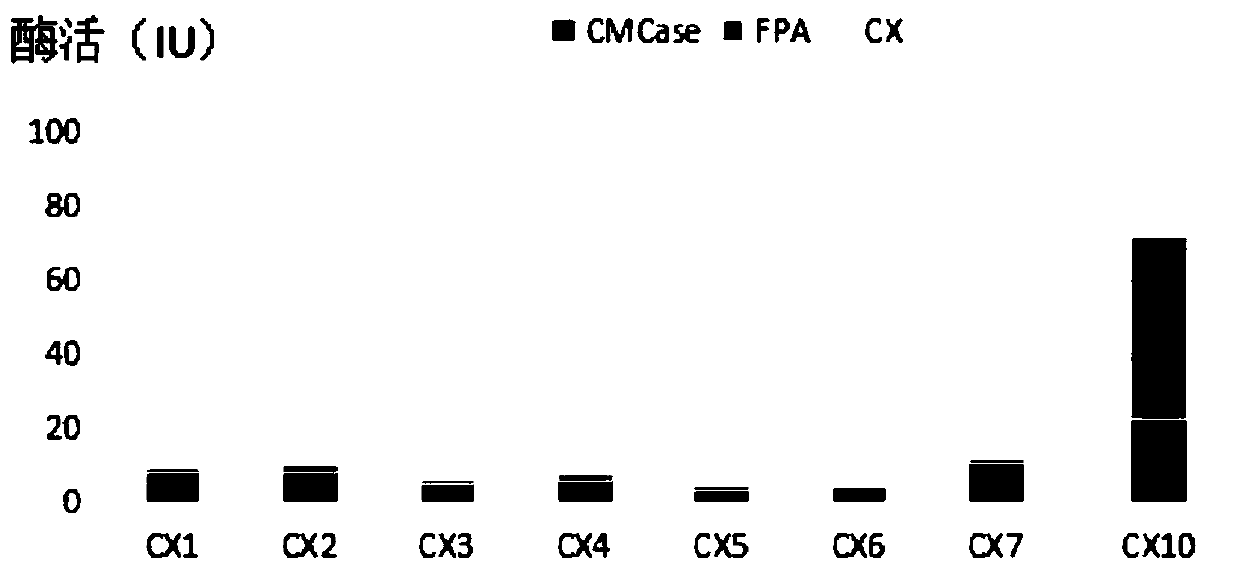
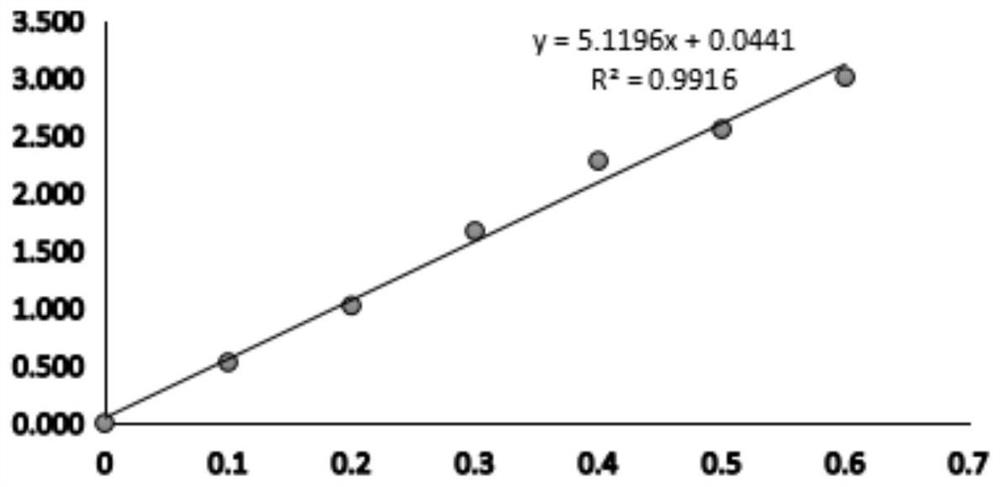
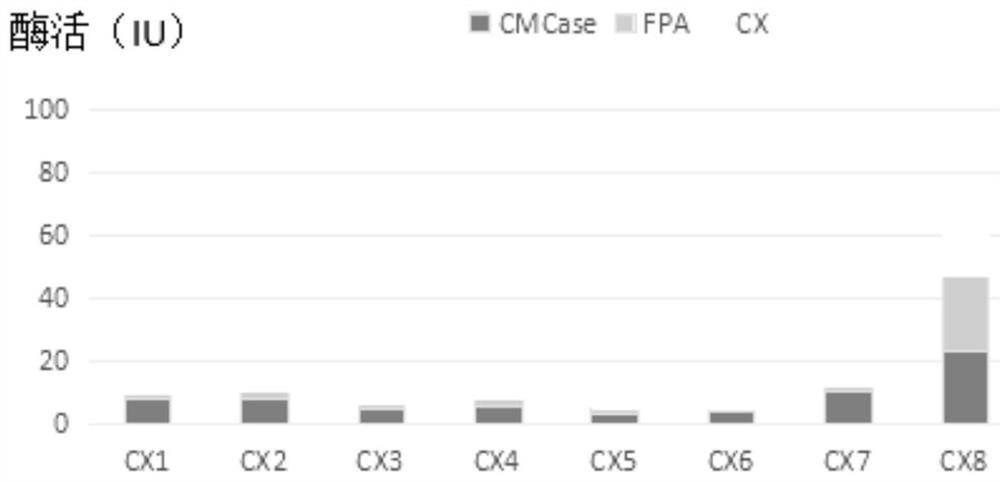
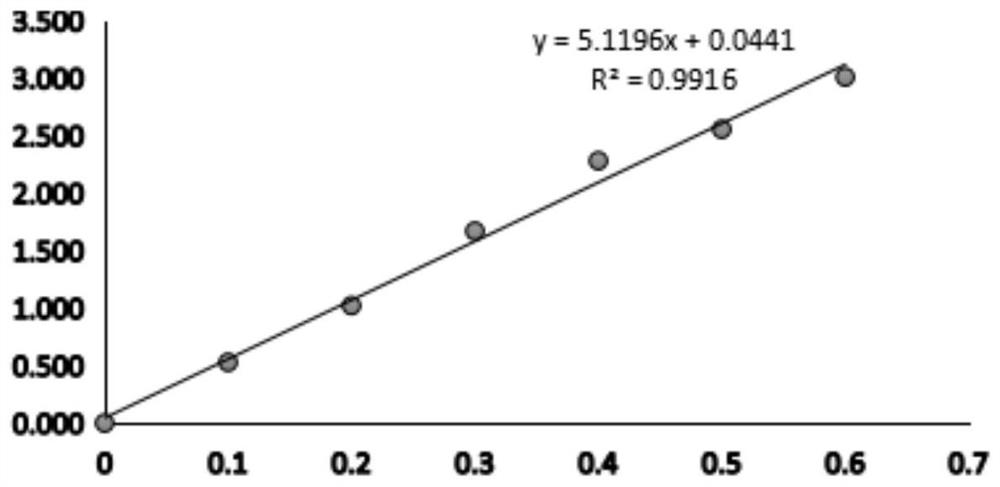
Cellulose decomposing strain CX10 from termite gut and application thereof
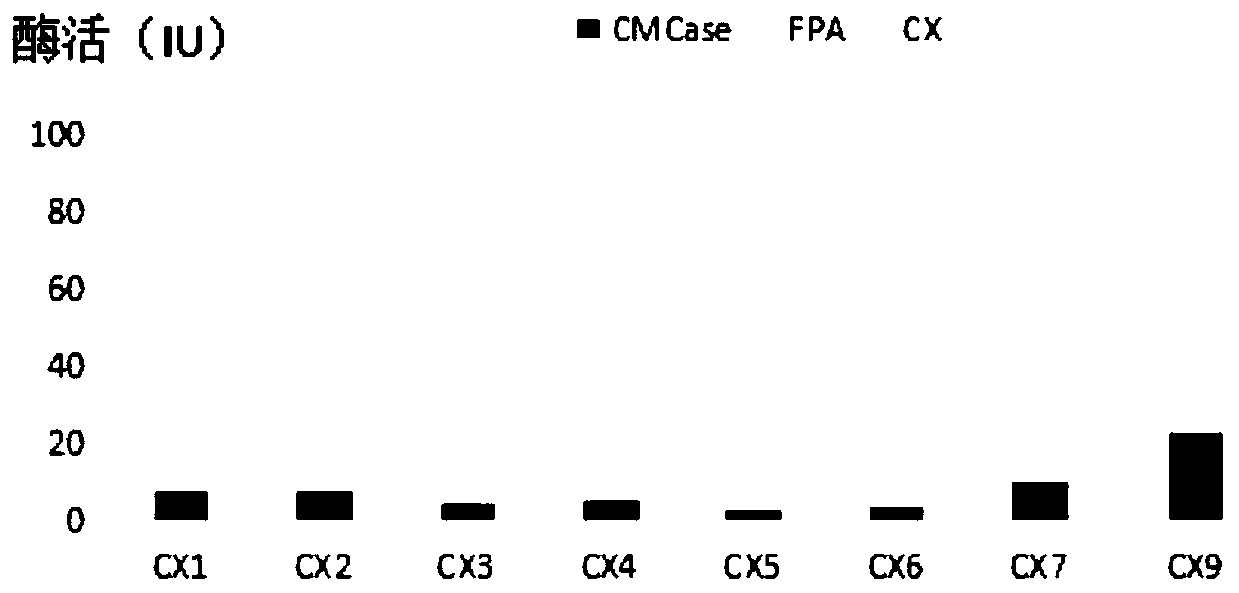
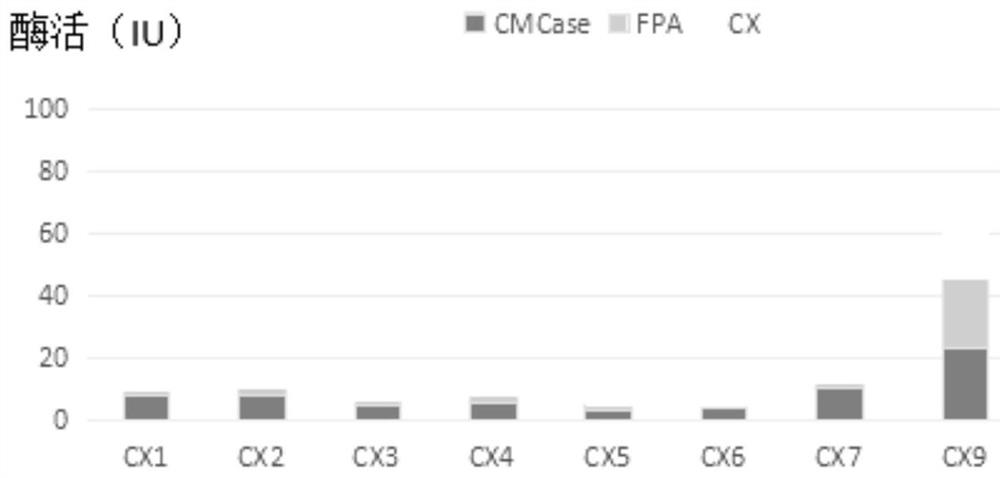
The invention discloses a cellulose decomposing strain CX10 from a termite gut and application thereof. The strain is preserved in the General Microbiological Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms at the No.3, first yard, Beichen west road, Chaoyang district, Beijing, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.16344. The strain is a gram-positive bacillus and free of capsules, endogenous spores can be seen after spore staining, the bacterial colony is a single one and in a cracked shape, the bacterial colony is white, and the edge of the bacterial colony is complete.The strain is a facultative anaerobic strain for producing cellulase; within 48 hours, the FPA enzyme activity of the strain is 49.5 U / mL, the CMCase enzyme activity is 95.0 IU / mL, and the CX enzyme activity is 23.26 IU / mL. The strain is very high in biodiversity value, and has a scientific value of further research on cellulose-enriched crops and development and application of a traditional Chinese medicine fermentation recycling.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY PHARMA OF CAAS
Antimicrobial composition
InactiveCN104918494AHas antibacterial activityImprove securityAntibacterial agentsBiocideFruit juiceRosaceae
The present invention provides a highly safe antibacterial composition showing antibacterial activity against both Gram-positive bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria, of which flavor is not impaired. The antibacterial composition of the present invention contains nisin, and one or two or more kinds of plant-derived ingredients selected from the group consisting of juice, extract, and distillate of a Rosaceae plant, and a mixture of these. It is preferred that the Rosaceae plant is a plant belonging to the genus Prunus , it is more preferred that the plant belonging to the genus Prunus is Prunus mume , and it is particularly preferred that the plant-derived ingredient is Prunus mume fruit juice. The antibacterial composition of the present invention is useful especially as a composition for oral cavity.
Owner:ECO FRIENDLY INST +1
Preparation of blattodea polypeptide, and uses of the same in anti-gram-positive bacteria and anti-gram-negative bacteria
InactiveCN102743741BHigh yieldBroad biological activityAntibacterial agentsBiocideChemical productsGram Positive Bacillus
The present invention relates to preparation of a blattodea polypeptide, and uses of the blattodea polypeptide in anti-gram-positive bacteria and anti-gram-negative bacteria. Specifically the present invention relates to a blattodea extract effective fraction having a function of prevention and treatment of bacterial infection diseases, a preparation method and a medical use thereof. The Periplaneta Americana extract effective fraction of the present invention is a polypeptide substance with a molecular weight less than 5000 dalton, and is prepared by the following steps: carrying out solvent extraction and membrane separation on fresh polypide or dried polypide of Periplaneta Americana to obtain the product of the present invention, wherein the polypeptide active substance of the effective fraction has significant anti-gram-positive bacteria activity and anti-gram-negative bacteria activity, can be prepared into forms of a hydrogel, a cataplasm, lyophilized powder, a water agent, an aerosol, a suppository, a film agent, an external application liniment, and an ointment, and can be used for preparations of drugs for prevention and treatment of diseases related to gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria and infections, daily chemical products or medical devices.
Owner:DALI UNIV
Application of amomum tsao-ko oil in preparation of drugs for treating bacterial infectious diseases
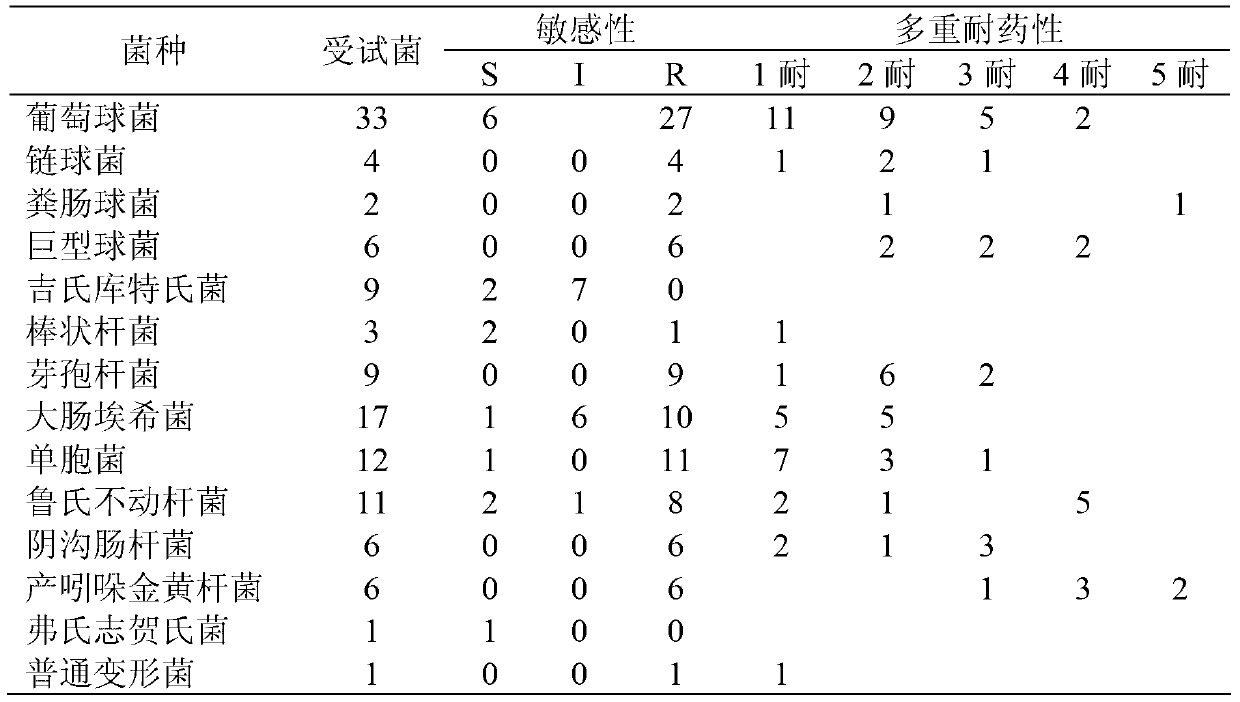
InactiveCN103341114AHas antibacterial activityGood antibacterial effectAntibacterial agentsPlant ingredientsBacteroidesShigella flexneri
The invention provides an application of amomum tsao-ko oil in preparation of drugs for treating bacterial infectious diseases. The bacteria may be coagulase negative staphylococci, kurthia gibsonii, megacoccus, corynebacterium, enterococcus faecalis, bacillus, escherichia coli, monad, acinetobacter lwoffii, flavobacterium indologenes, enterobacter cloacae, flexneri or common mycetozoan. The drugs mentioned in the invention have antimicrobial activity to gram-positive bacterium and gram-negative bacterium, also have high bacteriostatic action to persister therein and simultaneously have good antibacterial action in body, so the drugs can effectively treat infectious diseases caused by various strains in gram-positive bacterium and gram-negative bacterium, therefore the invention provides a new drug use option for clinic.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Cellulose degradation bacterium CX9 from termite gut and application thereof
The invention discloses a cellulose degradation bacterium CX9 from termite gut and application thereof. The strain is preserved in the China Center For Type Culture Collection in No.3, No.1 yard on Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing on August 27th, 2018 and has the preservation number of CGMCC No.16343. The strain is gram-positive bacilli without capsules, endogenous spores can be seenafter spores are dyed, bacterial colonies are each in a crack shape and are independent of one other or connected to form a piece, and the bacterial colonies have the white color and complete edges. The strain is a facultative anaerobic strain capable of generating cellulase; the strain has the CMCase enzyme activity of 70.4 IU / mL and CX enzyme activity of 25.23 IU / mL within 48 hours. The strain has quite high biodiversity value and also has further research scientific value in the development and application of the fermentation and reutilization technology of cellulose-enriched crops and traditional Chinese medicines.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY PHARMA OF CAAS
Polypeptide with resistance to gram-positive bacteria
The invention provides polypeptide with resistance to gram-positive bacteria, and a gene for coding the polypeptide. The sequence of the polypeptide is as show in SEQ ID NO:1, and the nucleotide sequence of the gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO:2. Pomfret is infected by gram positive microorganisms frequently used in the field of aquatic products, the polypeptide with resistance to gram-positive bacteria is obtained by using a subtractive hybridization method, and the polypeptide can be used as a feed additive for the pomfret.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV +1
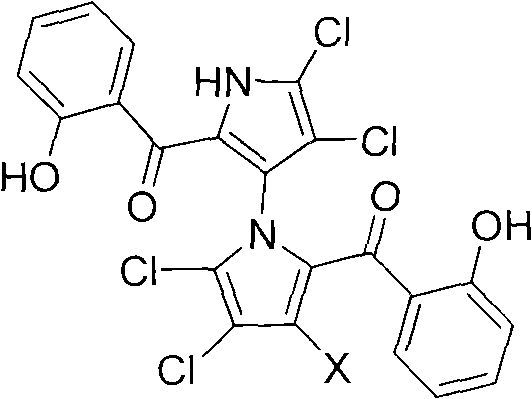
(+/-)-marinopyrrole A for resisting methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and synthesized derivative thereof
ActiveCN101786979BSmooth preparation processShort synthetic routeAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMethicillin sensitiveMethicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
Purification, gene cloning, and enzymatic characteristic identification of chitosanase
The invention relates to purification, gene cloning, and enzymatic characteristic identification of chitosanase. A strain is separated from a contaminated yeast culture solution, and is identified to be a gram-positive bacillus; a main protein product secreted by the strain is purified, and subjected to N-end amino acid sequence determination, and the result shows that the protein product is quite similar to some known endo-chitosanases. Based on the homologous DNA sequence, a full-length gene is cloned by a PCR method. The strain grows quite rapidly, and the constitutive secretion product is mainly endo-chitosanase. The enzyme can be purified by two steps of hydrophobic chromatography and molecular sieve. The enzymatic characteristics of the enzyme and the conditions for catalyzing the degradation of chitosan into chitosan oligosaccharide by the enzyme are further studied. When the yield of the chitosanase is increased, the chitosanase is expected to be used for chitosan oligosaccharide production, and the chitosanase has actual application value.
Owner:SUZHOU ZHONGTONG BIOTECH
Application of Amomum tsao-ko oil to preparation of medicament for treating bacterial infectious disease
InactiveCN103394016AHas antibacterial activityGood antibacterial effectAntibacterial agentsAgainst vector-borne diseasesBacteroidesPseudomonas
The invention provides application of Amomum tsao-ko oil to preparation of medicaments for treating bacterial infectious diseases. The bacteria is coagulase negative staphylococcus, Kurthia gibsonii, megacoccus, corynebacterium, enterococcus faecalis, bacillus, escherichia coli, Pseudomonas, Acinetobacter lwoffii, Chryseobacterium indologenes, Enterobacter cloacae, S.flexneri or proteus vulgaris. The medicine provided by the invention has antibacterial activity against gram positive bacteria and gram negative bacteria, as well as strong inhibitory effect on the resistant strains, and also has good antibacterial effect in vivo; in addition; and the medicament can effectively treat clinical infectious diseases caused by gram positive and gram negative bacteria of various types, and provides a novel clinical medicine choice.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Lactobacillus plantarum capable of producing various broad-spectrum antibacterial metabolites and application thereof
ActiveCN110527651AGrowth inhibitionEnhanced inhibitory effectFruit and vegetables preservationBacteriaEscherichia coliFood borne
The invention discloses Lactobacillus plantarum MS031 with a deposit number of CGMCC No. 17711. The bacterium has broad-spectrum antibacterial activity and can further produce various antibacterial active metabolites, including bacteriocins capable of inhibiting Gram-positive bacteria and broad-spectrum antibacterial metabolites capable of inhibiting both Gram-positive bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria, and can be used for preparing antibacterial or / and antiseptic products. The broad-spectrum antibacterial metabolites are respectively adsorbed on surface of the bacteria and secreted into fermentation liquor, can effectively inhibit growth of various food-borne pathogenic bacteria such as Listeria monocytogenes, salmonella, escherichia coli and the like in fresh-cut fruits and vegetables,can make up for shortcomings that most existing antibacterial agents have no effect on Gram-negative bacteria, and have good application prospects.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Separating, screening and identifying method of lactobacillus sake
InactiveCN106282054AThe operation process is reasonable and simpleReduce consumptionBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementLactobacillus sakeFeed additive
Lactobacillus sake is a natural food preservative and feed additive with potential development capacity; the lactobacillus sake is simplex in obtaining method and small in yield, so use and popularization of the lactobacillus sake are seriously influenced; meanwhile the lactobacillus sake is complex in preparation step and high in expenditure. A method for obtaining the lactobacillus sake by separating, screening and identifying bacteriocin producing lactic acid bacteria includes the steps of firstly, primary screening work of strains; secondly, secondary screening work of the strains, wherein in the secondary screening of the strains, an antibacterial test is conducted on a plurality of lactic acid bacteria strains obtained in the first step with gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria as indicator bacteria, and the strains which can inhibit gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria and have the dual inhibition characteristic are selected; thirdly, fermentation characteristic test work; fourthly, inspection of influences of other factors on the strains; fifthly, inspection of influences of pH and temperature on bacteriocin crude extracts; sixthly, physiology and biochemistry identification work and molecule identification work.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Method and reagent kit for establishing experimental model of diabetic foot ulcer rat with mixed infection of Gram positive bacteria and negative bacteria
InactiveCN103463135AEase of evaluationGood repeatabilityOrganic active ingredientsBacteria material medical ingredientsDiabetes modelHigh fat
The invention discloses a method and a reagent kit for establishing an experimental model of a diabetic foot ulcer rat with mixed infection of Gram positive bacteria and Gram negative bacteria. The method comprises the following steps: after the rat is fed by a high fat feed for eight weeks, injecting streptozotocin to generate a diabetic model, after the diabetic model is stable, generating a scald with the depth of II degrees in the skin of the diabetic rat, and three days later, injecting mixed suspension of the Gram positive bacteria and the Gram negative bacteria at the scald. In addition, the invention also discloses the reagent kit for establishing the experimental model of the diabetic foot ulcer rat with the mixed infection of the Gram positive bacteria and the Gram negative bacteria. The reagent kit comprises the mixed suspension of the Gram positive bacteria and the Gram negative bacteria. According to the diabetic ulcer experimental animal model disclosed by the invention, by detecting the changes of biochemical indicators after drug intervention, results show that the model has the characteristic of being capable of generating the diabetic foot ulcer with various bacteria colony infections, and the characteristics of long healing time of an ulcer wound surface, sensitivity to drug reaction and the like.
Owner:SHUGUANG HOSPITAL AFFILIATED WITH SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
Antibacterial preservative and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108719740AInhibitory activityHigh antibacterial activityFood preservationEscherichia coliGram Positive Bacillus
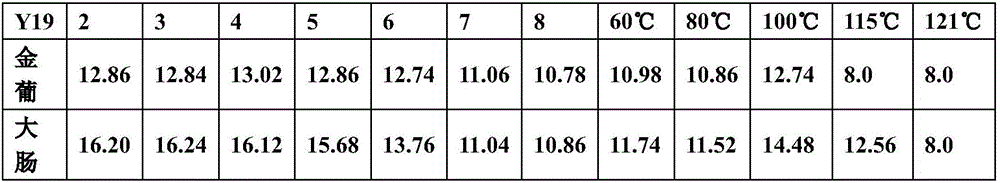
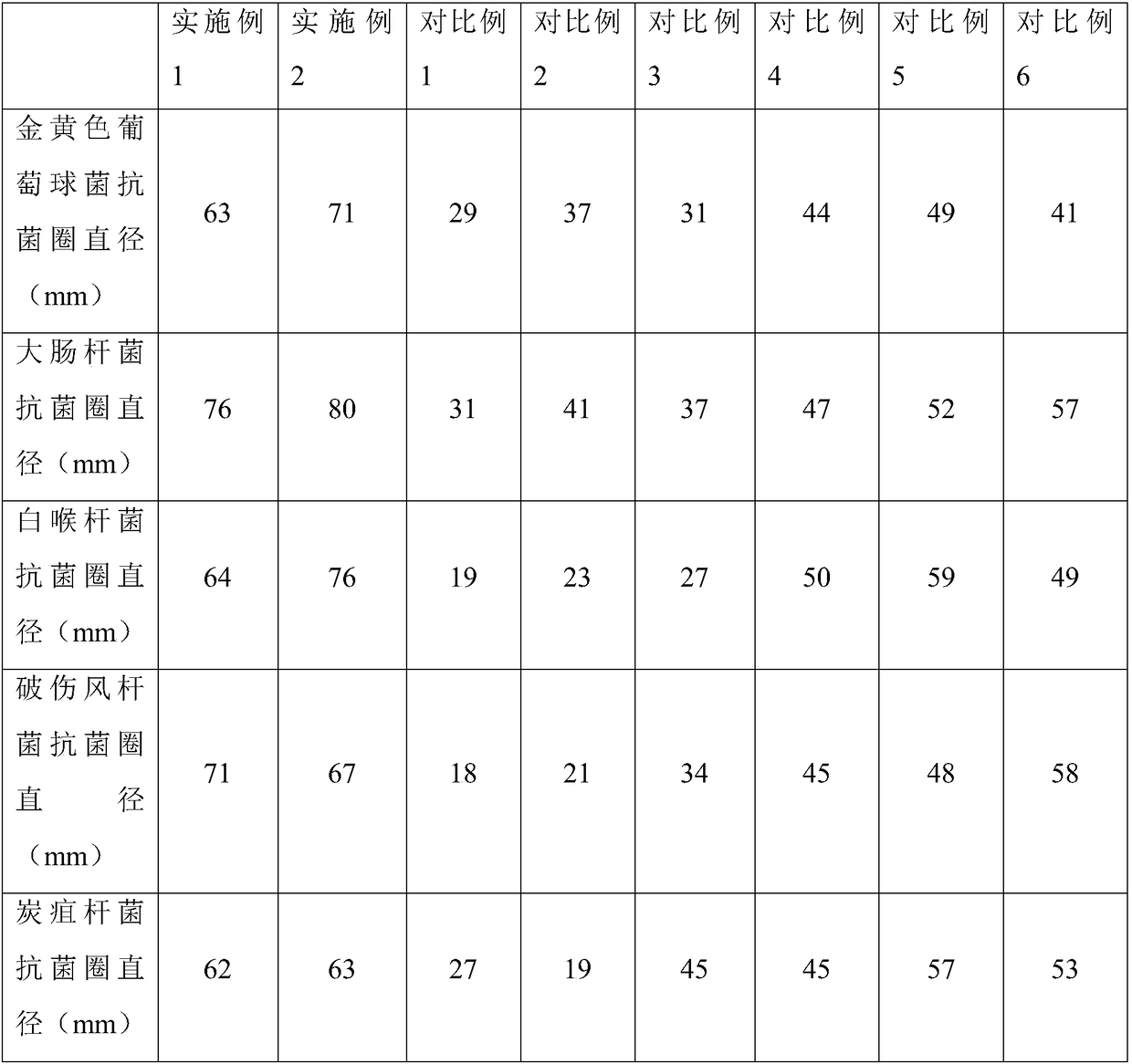
The present invention discloses an antibacterial preservative and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of food processing. The antibacterial preservative is prepared by grafting gellan gum oxide with lactic streptococci, has advantages of wide application environment, strong antibacterial activity and strong heat resistance, can effectively inhibit activities of Gram-positive bacteria of staphylococcus, escherichia coli, etc., and is applied in the staphylococcus aureus and escherichia coli; antibacterial circles can reach 70 mm and 80 mm, respectively; and besides,the antibacterial preservative has strong preservation ability, can very well increase shelf life and stability of food, and can be applied on surfaces and cutting sections of fruits and vegetables,and dissolved in fruit and vegetable juice; and the fruits, vegetables and fruit and vegetable juice can be kept at 25 DEG C for 5 days without deterioration.
Owner:江苏惠田科技开发有限公司 +1
Bacillus firmus CX8 from termite gut and application of bacillus firmus CX8
ActiveCN111705008AHigh biodiversity valueBacteriaBiofuelsBiotechnologyFacultative anaerobic organism
The invention discloses bacillus firmus CX8 from a termite gut. The strain is collected in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) with the address of No.3, No.1 Yard, Beichen West Road, Beijing 3 Chaoyang District on August 27th, 2018, and has a collection number of CGMCC No. 16342. The strain is gram-positive bacillus and is free of capsule, endogenous spores can be seen through spore staining, a bacterial colony is round and single, the color of the bacterial colony is white, and the edge of the bacterial colony is complete. The strain is a facultative anaerobicstrain for producing cellulase; and within 48 hours, the CMCase enzyme activity of the strain is 67.8 IU / mL, and the CX enzyme activity of the strain is 20.96 IU / mL. The strain not only has very highbiodiversity value, but also has scientific value for further research in development and application of cellulose-enriched crop and traditional Chinese medicine fermentation recycling technologies.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY PHARMA OF CAAS
A cellulose-degrading bacterium cx9 from termite gut and its application
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY PHARMA OF CAAS
Method for constructing negative bacteria capable of expressing polysaccharides of positive bacteria and mutants thereof
ActiveCN106191091BPromote research and developmentPromote Applied ResearchBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSalmonella entericaBacterial polysaccharide
The invention provides a method for constructing a gram-negative bacterium capable of expressing a gram-positive bacterium polysaccharide. The method comprises the following steps: transforming a low-copy expression plasmid of the gram-positive bacterium polysaccharide into an asd and rfbP gene-deletion gram-negative bacterium, screening by a balanced lethal system to obtain the gram-negative bacterium capable of producing the gram-positive bacterium polysaccharide. The invention also provides the gram-negative bacterium capable of producing the gram-positive bacterium polysaccharide prepared by the method. The invention also provides a mutant of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium P0005, which is named as Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium P0005, and has the CCTCC NO: M 2016344. The gram-negative bacterium can express the gram-positive bacterium polysaccharide, and the method provided by the invention does not contain any resistance marker and meets the biosafety requirements of subsequent vaccines and other application.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Method for separating and identifying pathogenic bacteria of insects
InactiveCN108642193AOptimize usage orderIncrease concentrationMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesHemolymph
The invention discloses a method for separating and identifying pathogenic bacteria of insects, relating to the field of research for bacterial diseases of insects. The method comprises the followingsteps: S1, disinfecting the body surfaces of the insects carrying pathogenic bacteria, extracting hemolymph, carrying out diluting till the suitable concentration is achieved, coating an LB plate withthe diluent, carrying out culturing, picking out single colonies, thus obtaining pathogenic bacteria, carrying out pure culturing, transferring to liquid LB culture medium, and observing the morphological features of isolated strains under an oil immersion lens; S2, treating the thallus obtained by culturing in S1 by using lysozyme and SDS in sequence, and after the thallus is crushed, purifyingthe total DNA of the isolated strains through phenol extraction; and S3, amplifying the 16S rDNA with overall length of the isolated strains, after sequencing, carrying out clustering analysis, and determining the species of the isolated strain in combination with the morphological features of an isolated strain. The method for separating and identifying pathogenic bacteria of insects is universalfor gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria, and is suitable for separating and identifying pathogenic bacteria of the insects including bees, cotton bollworms, inchworms, Bombyx mori and the like, and the screened 16S rDNA amplification and sequencing primers are good in universality and high in stability.
Owner:INST OF ECONOMIC CROP HUBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Modified gram positive bacteria and uses thereof
ActiveUS9458467B2Improve the immunityImprove survivalBiocideBacteriaHigh GC gram-positive bacteriaLactic acid bacterium
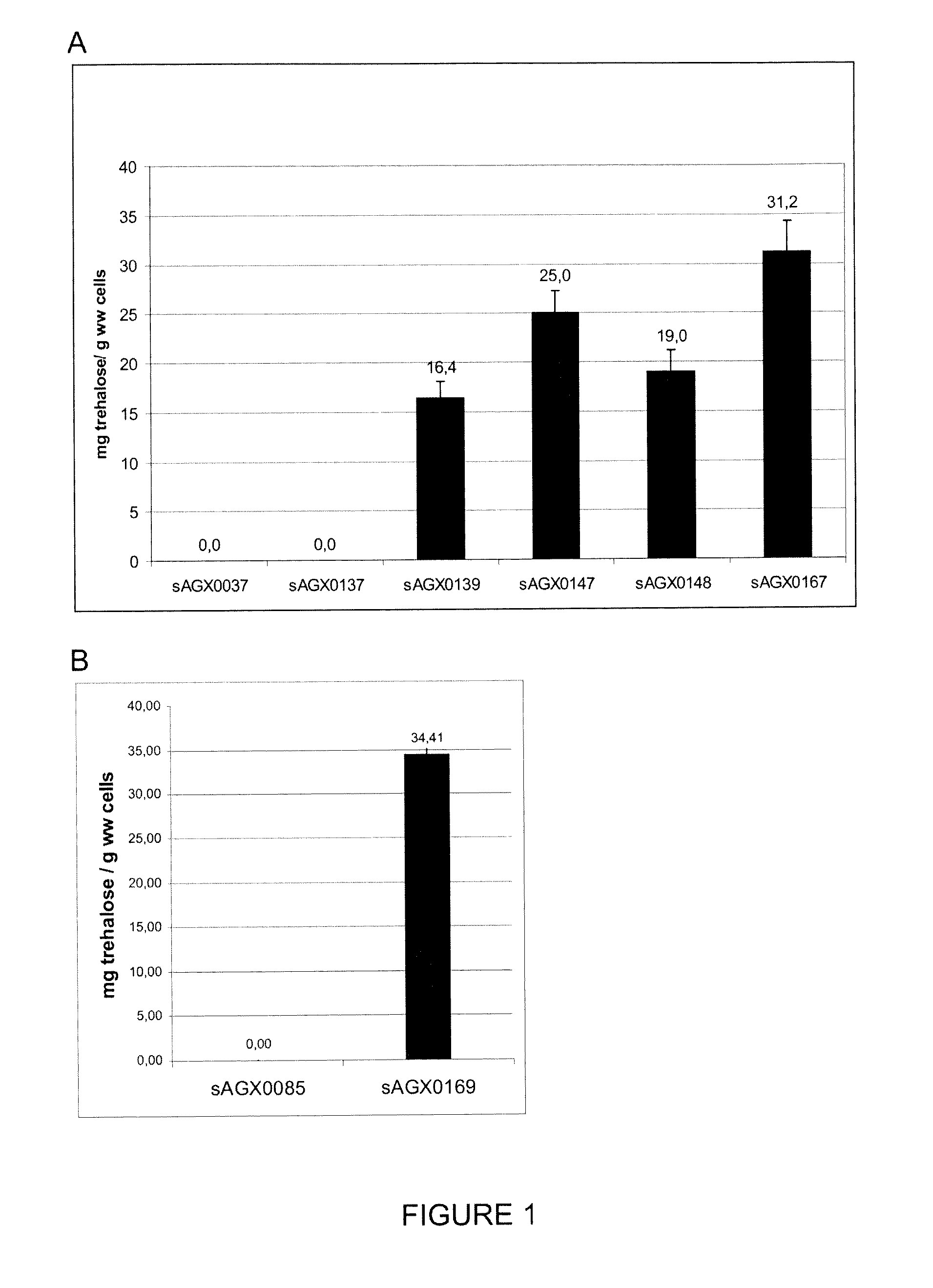
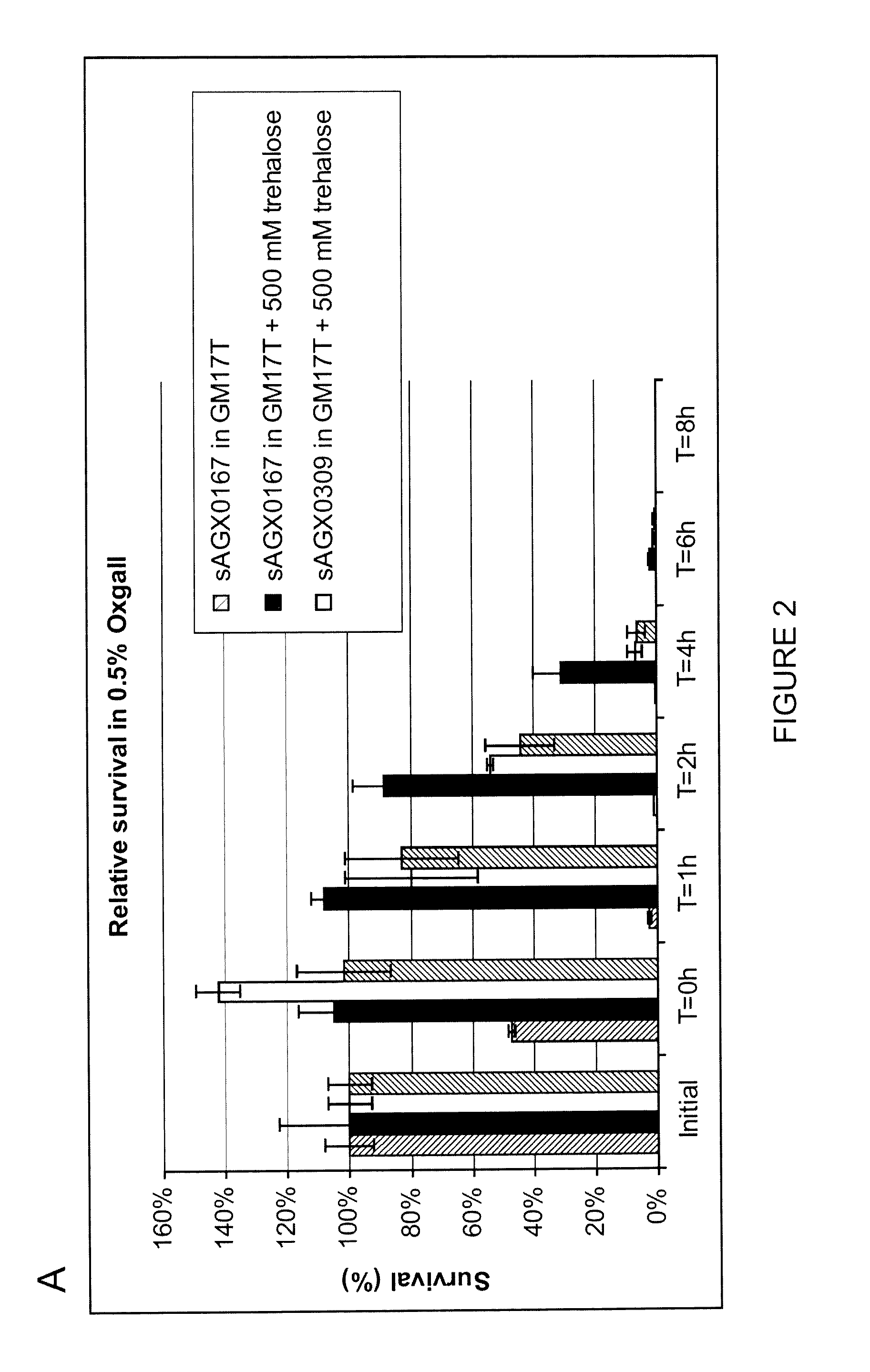
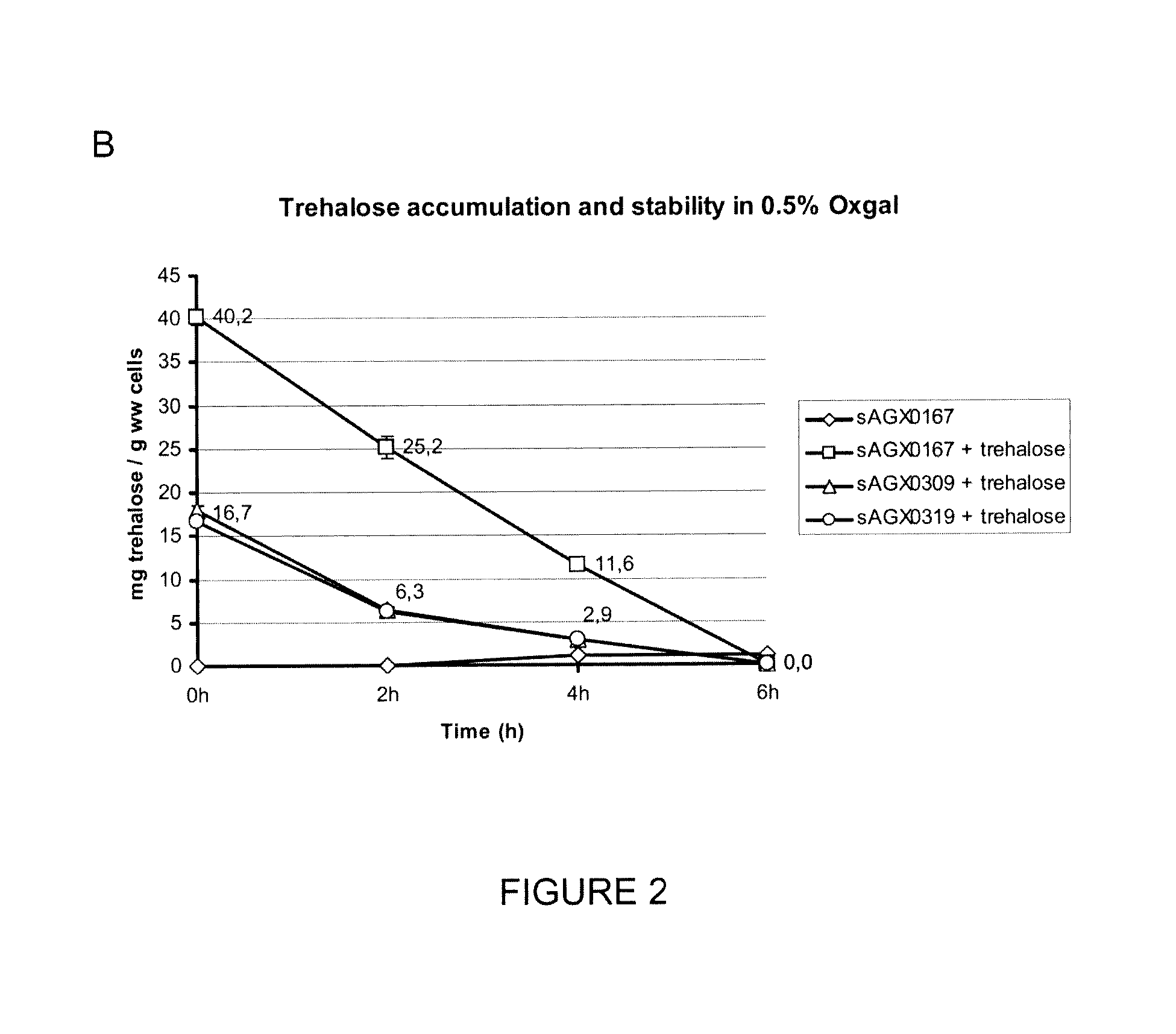
The present invention relates to a gram positive bacterium, preferably a lactic acid bacterium (LAB) or Bifidobacterium, with increased stress resistance and / or improved manufacturing, processing and / or storage characteristics. In particular, the invention relates to a gram positive bacterium which accumulate intracellular trehalose. The gram positive bacterium according to the invention lack trehalose 6-phosphate phosphorylase (TrePP) activity. The gram positive bacterium may further lack cellobiose-specific PTS system IIC component (ptcC) activity. The gram positive bacterium may further overexpress trehalose transporters. The invention further relates to compositions comprising such gram positive bacterium as well as methods and uses thereof.
Owner:INTREXON ACTOBIOTICS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com