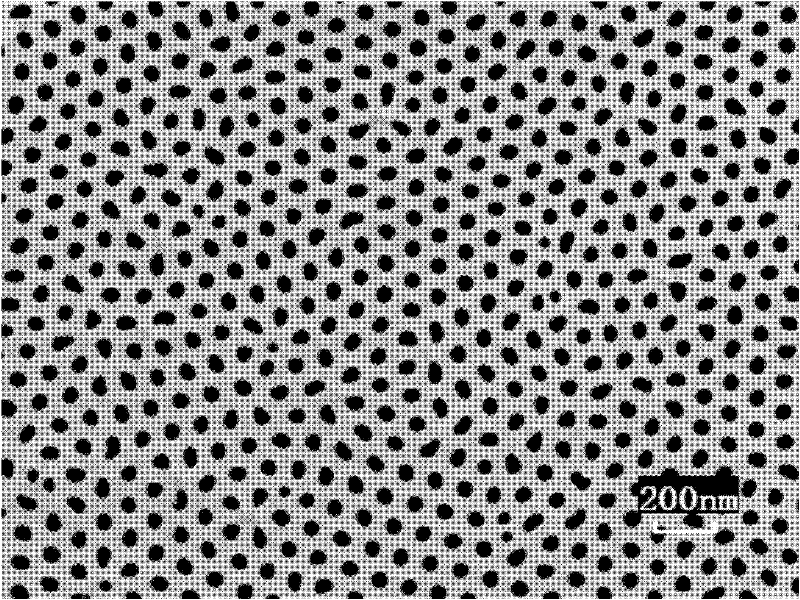
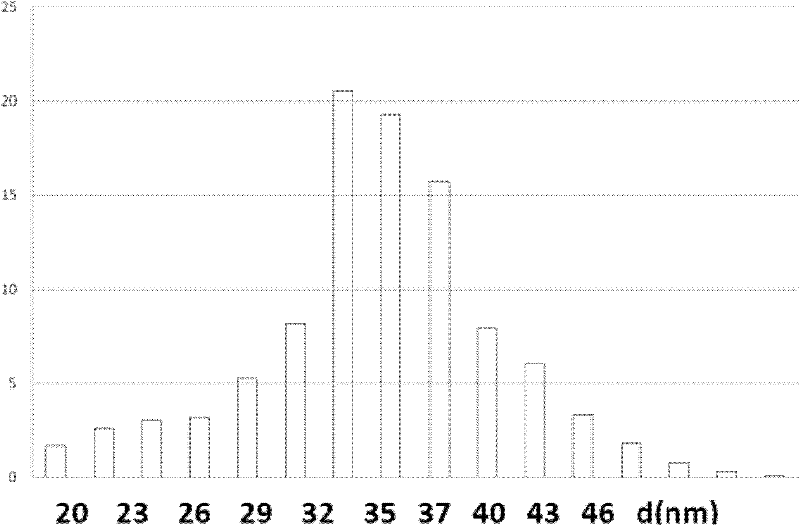
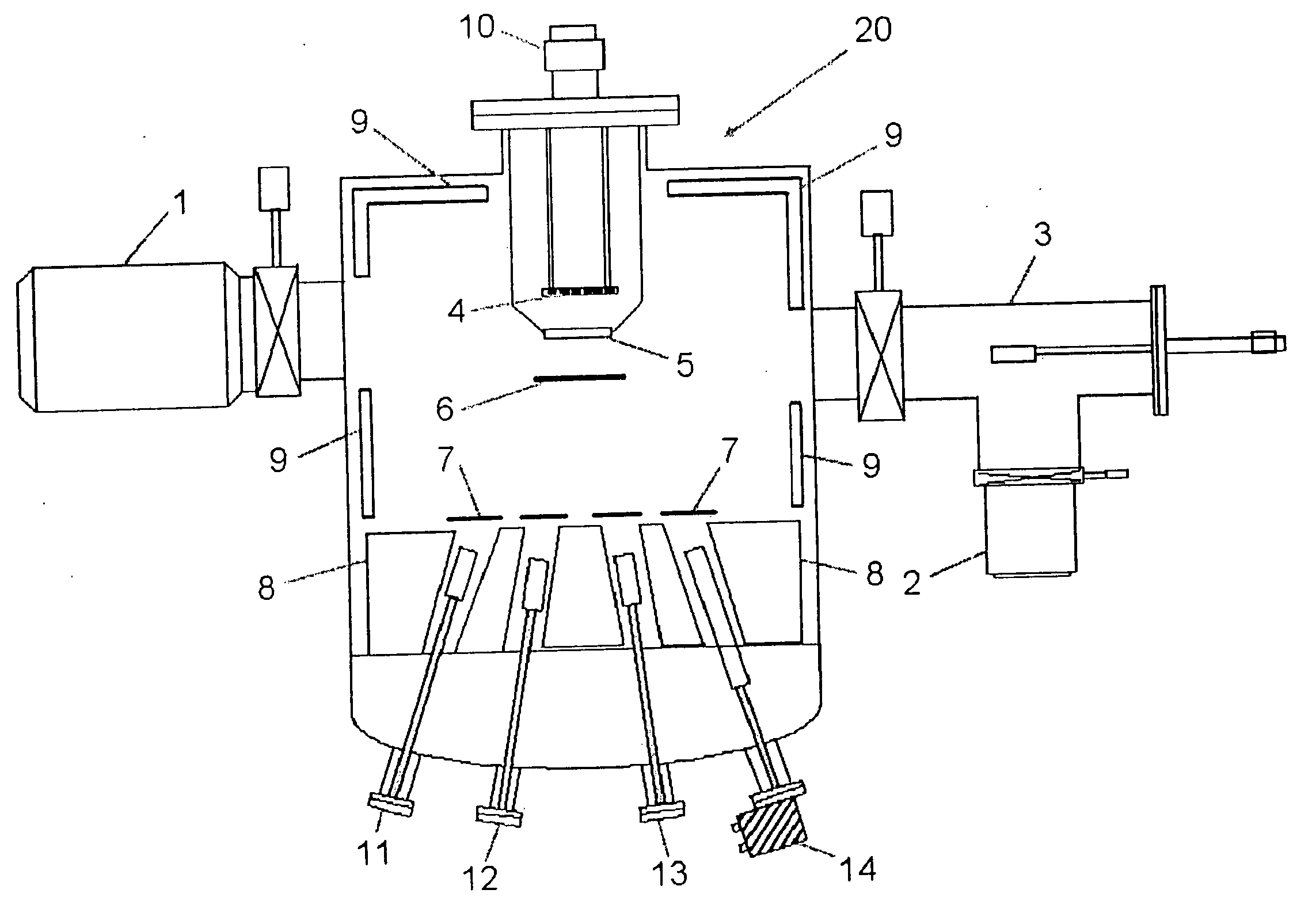
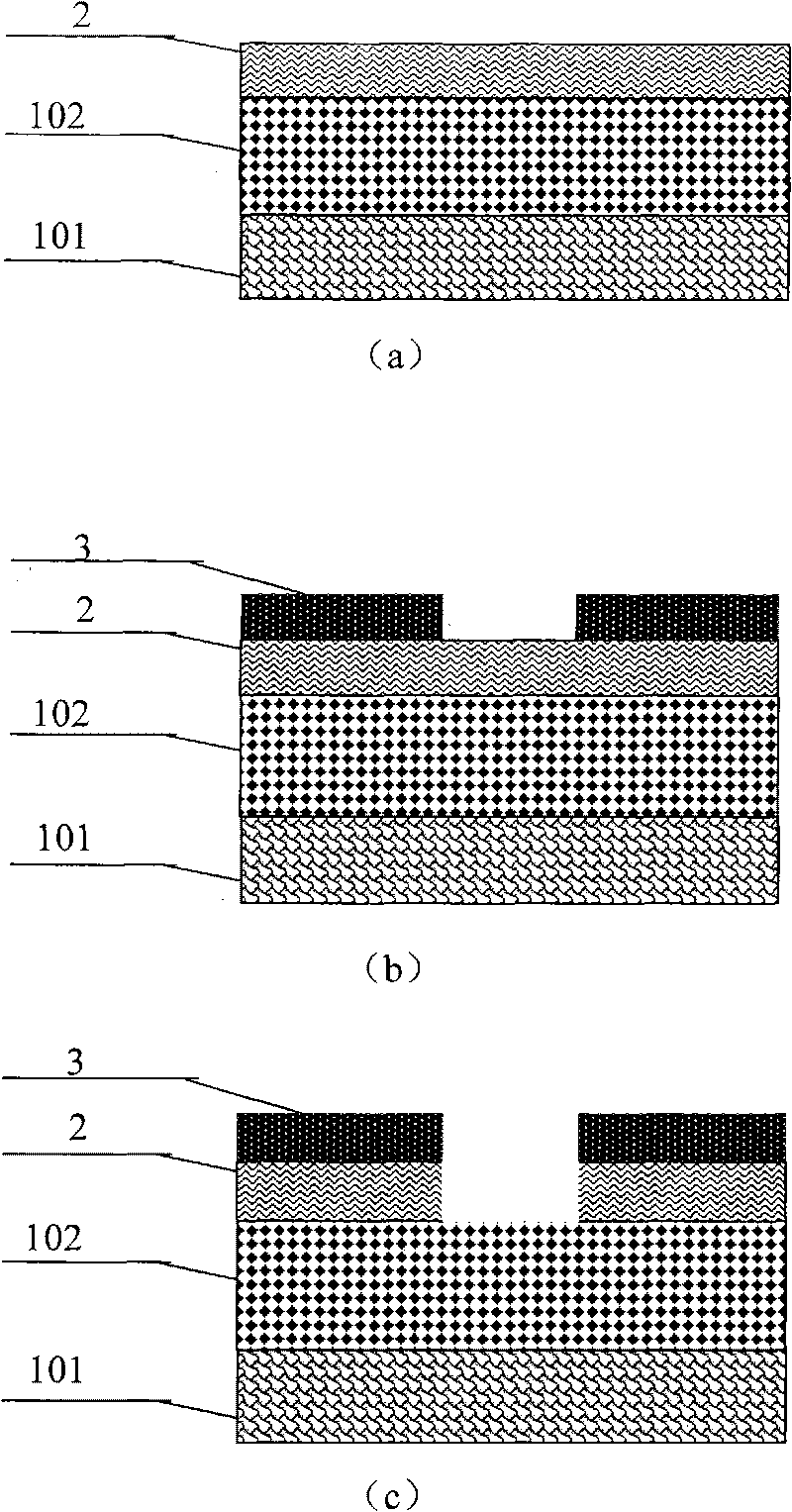
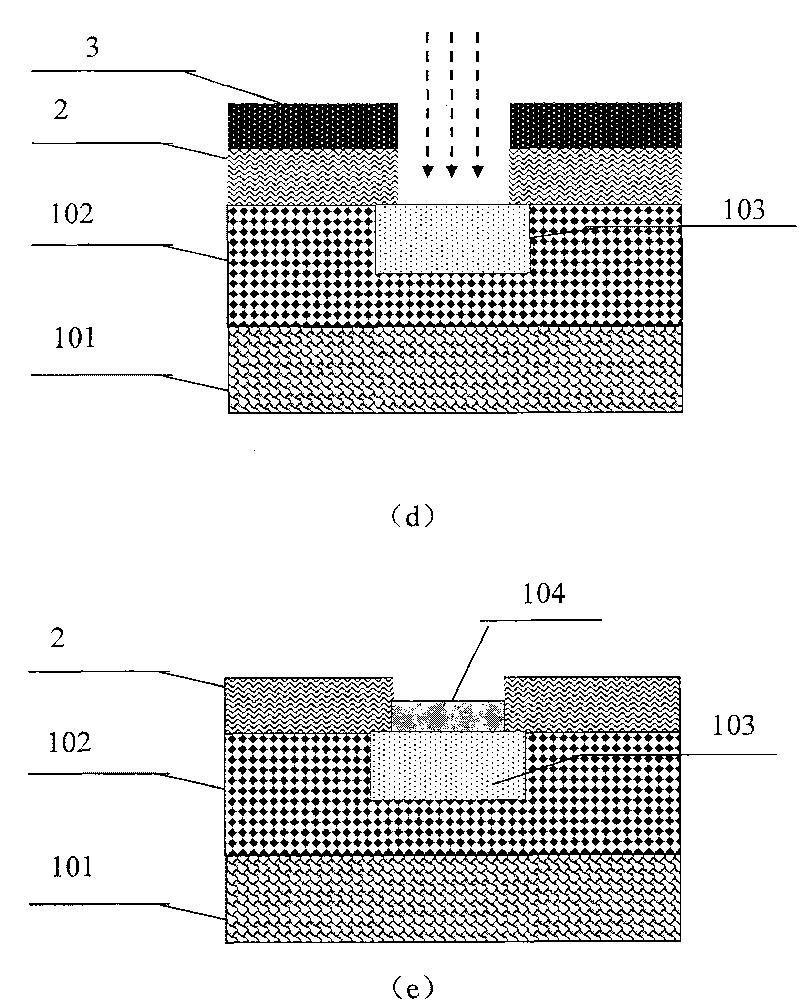
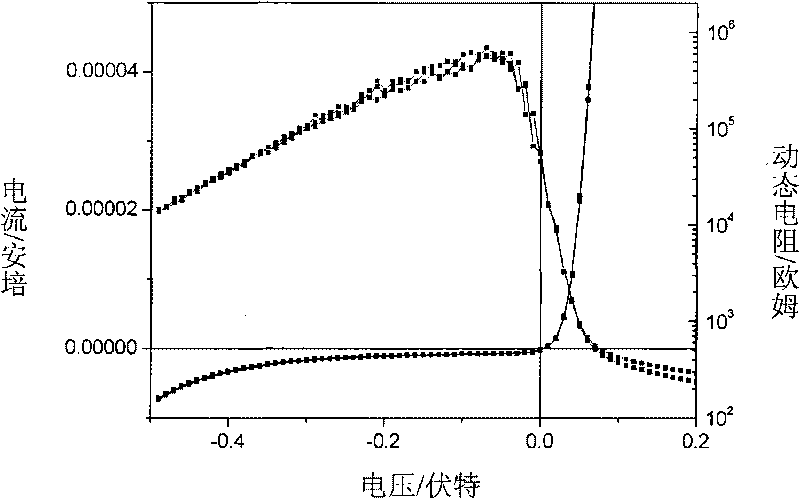
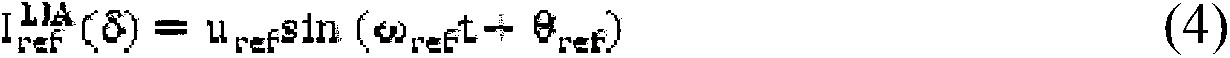Patents
Literature
164 results about "Molecular beam epitaxial growth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
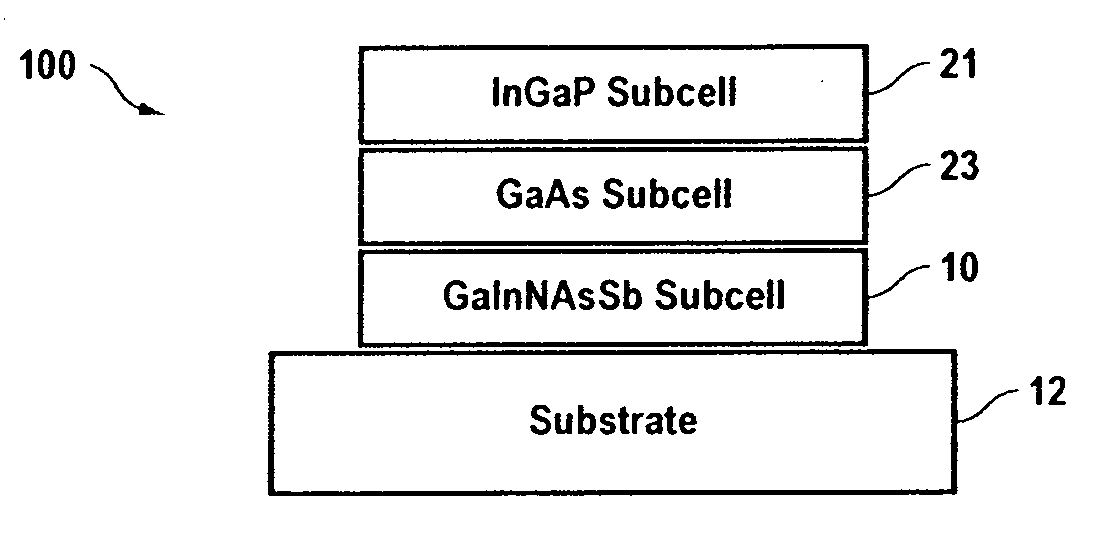
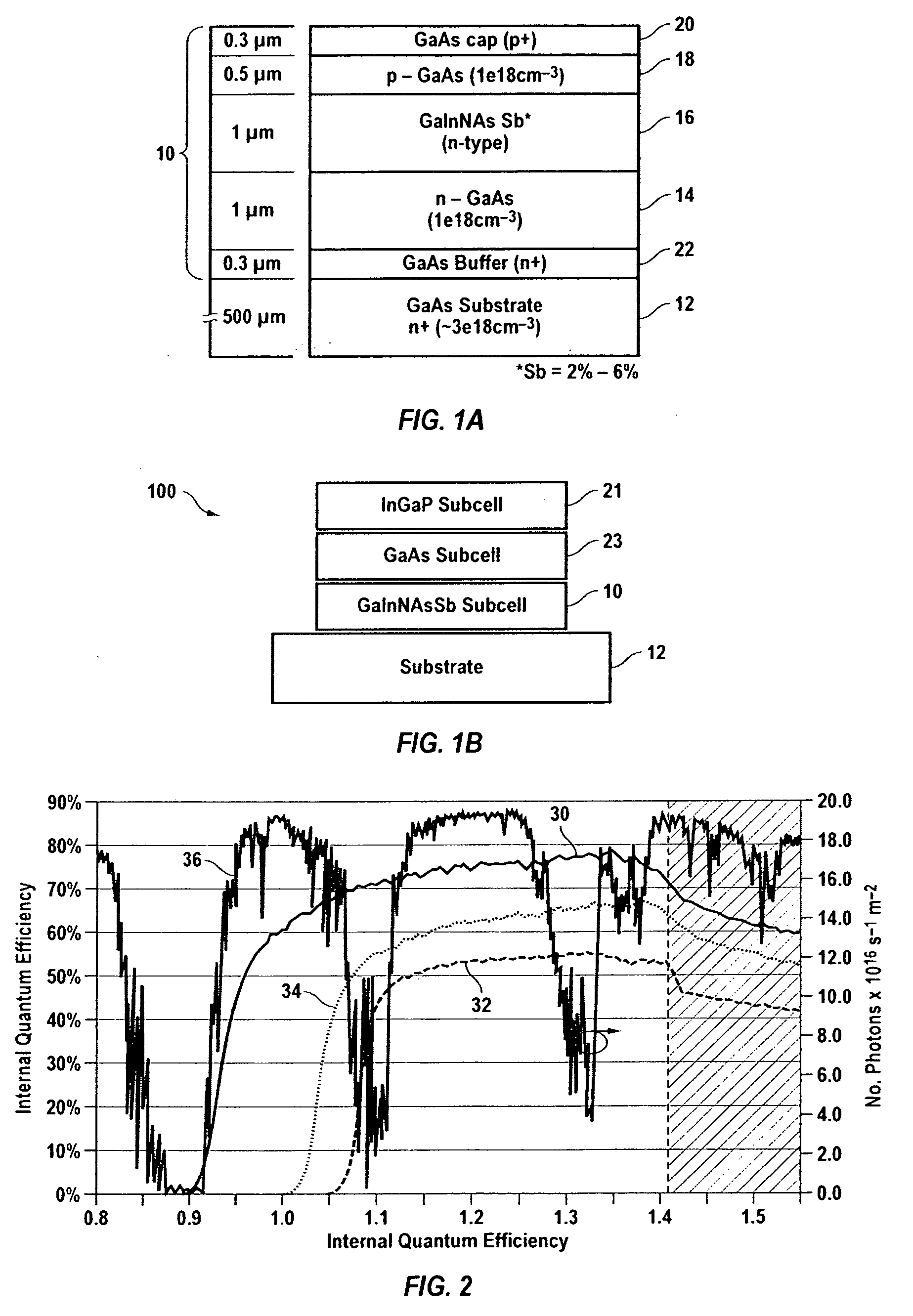
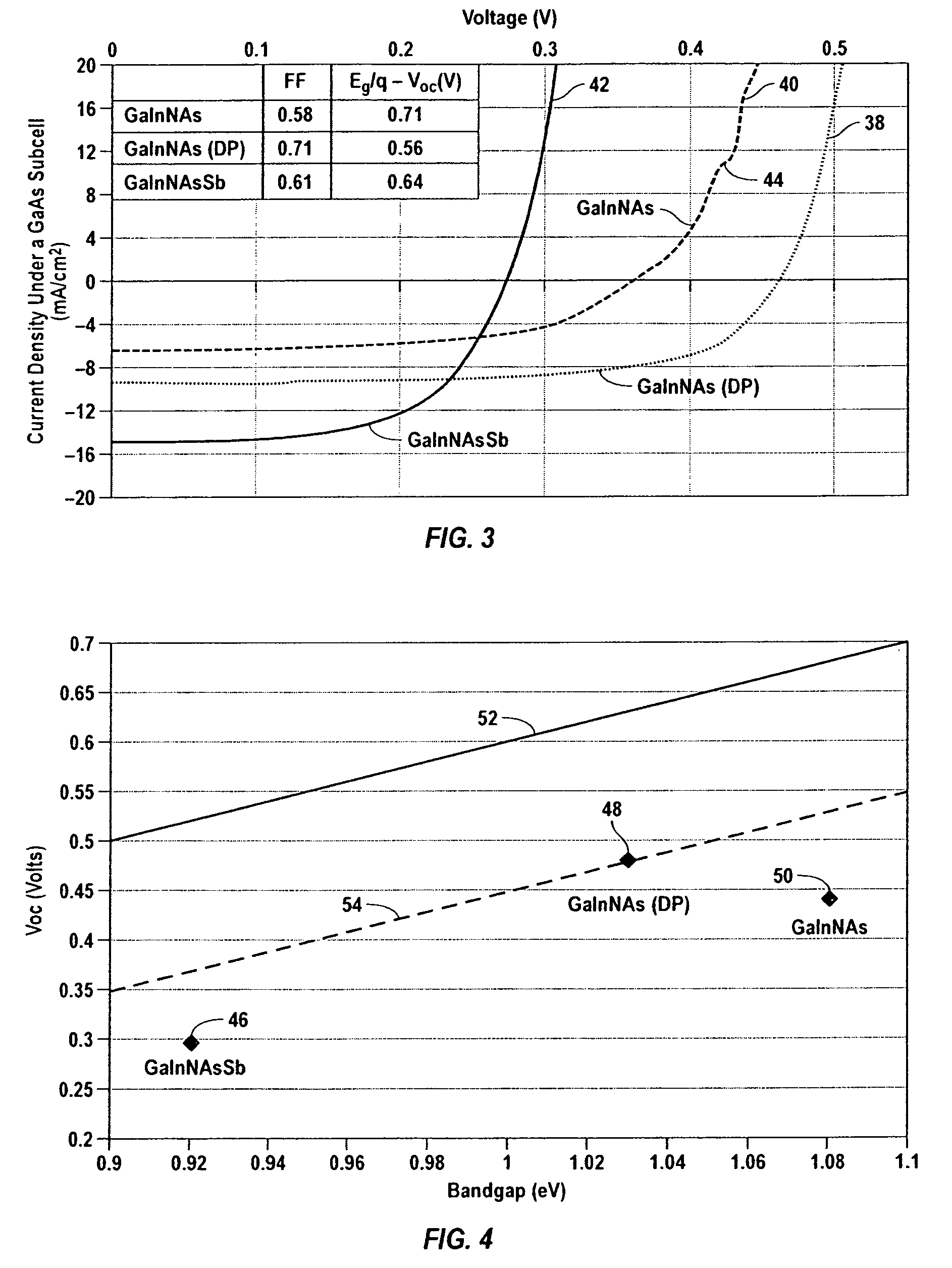
GaInNAsSb solar cells grown by molecular beam epitaxy
InactiveUS20090014061A1Improve featuresPromote efficient solar energy conversionFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationIndiumSemiconductor alloys
A high efficiency triple-junction solar cell and method of manufacture therefor is provided wherein junctions are formed between different types of III-V semiconductor alloy materials, one alloy of which contains a combination of an effective amount of antimony (Sb) with gallium (Ga), indium (In), nitrogen (N, the nitride component) and arsenic (As) to form the dilute nitride semiconductor layer GaInNAsSb which has particularly favorable characteristics in a solar cell. In particular, the bandgap and lattice matching promote efficient solar energy conversion.
Owner:CACTUS MATERIALS INC +1
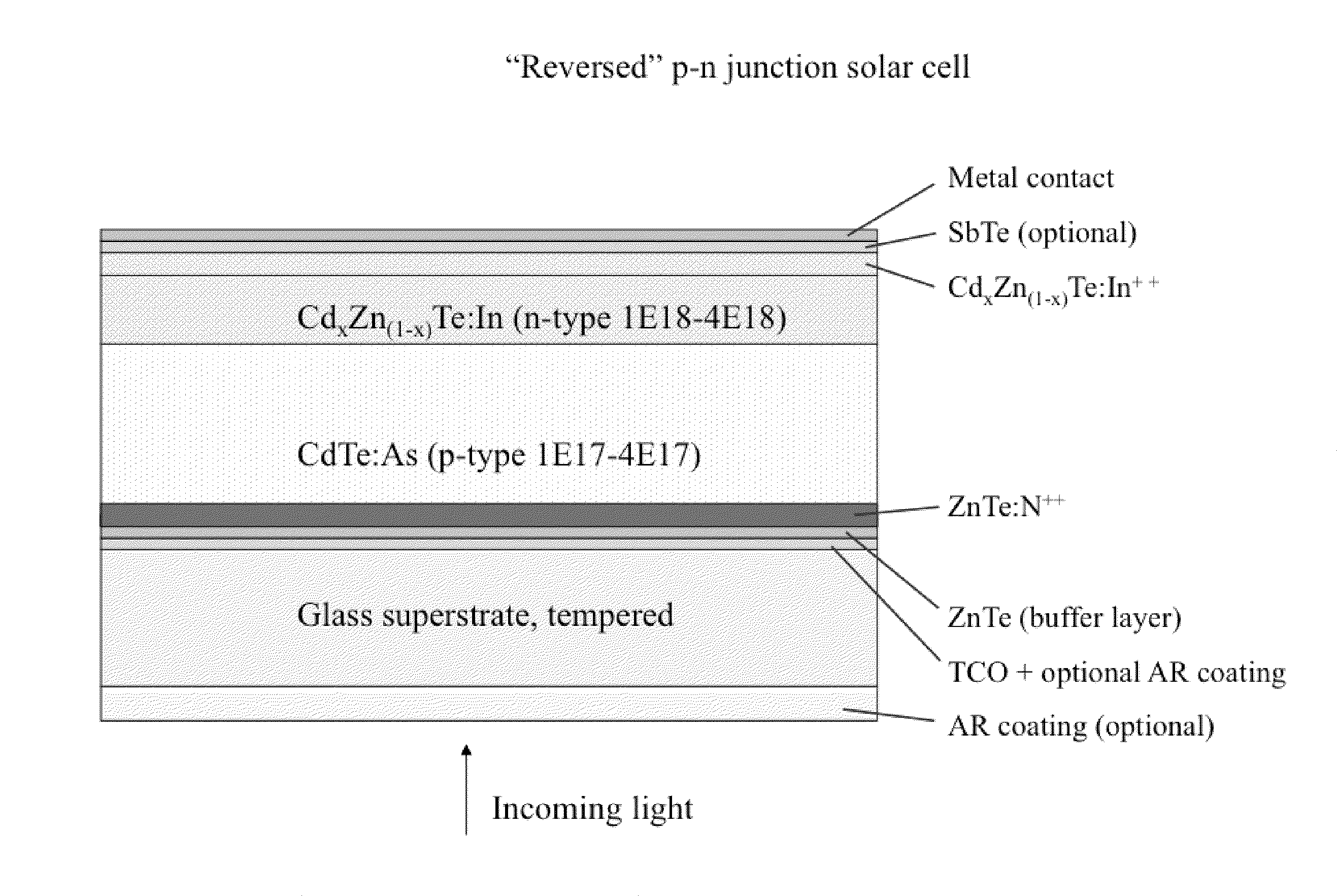
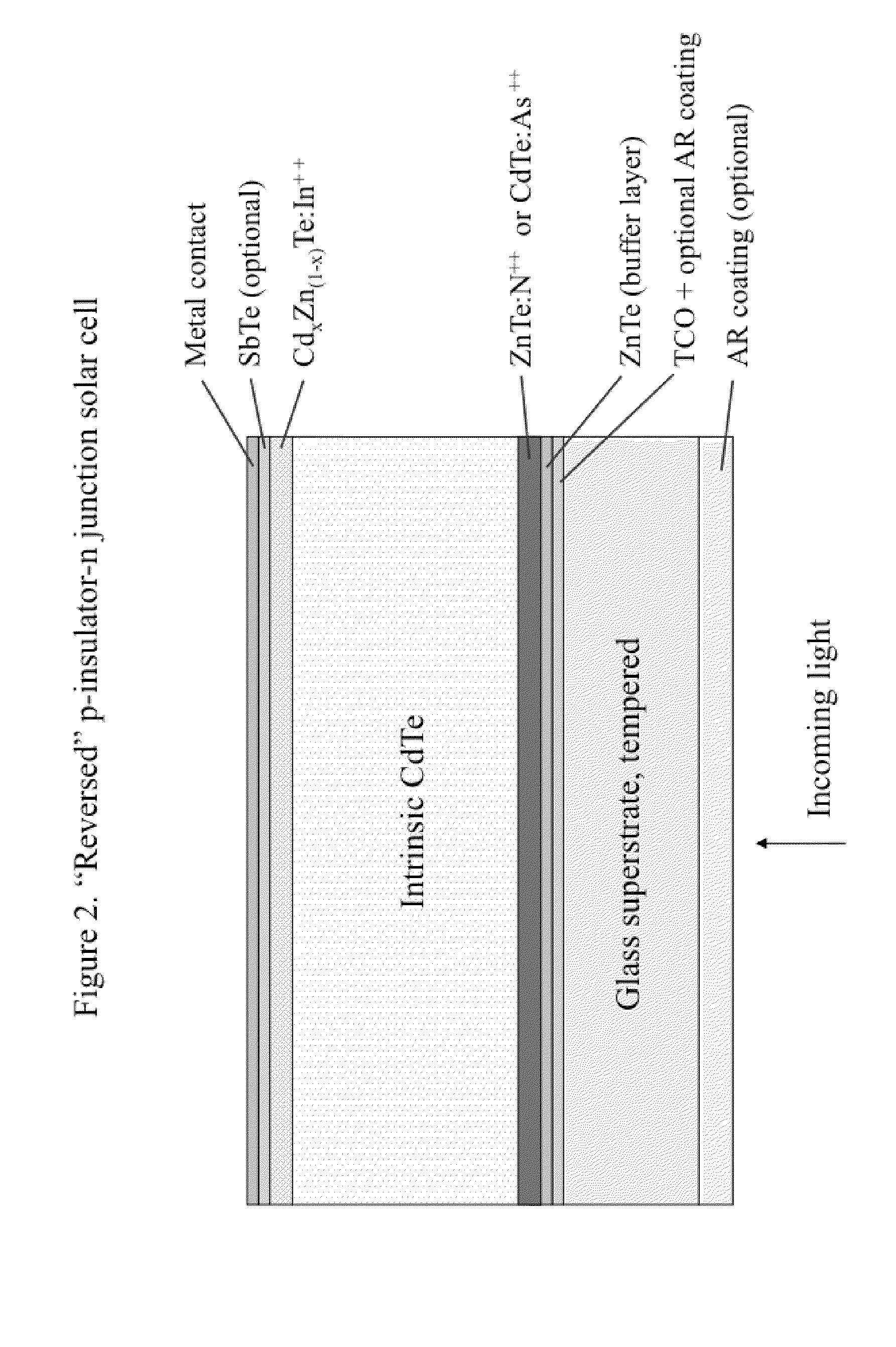
High Power Efficiency, Large Substrate, Polycrystalline CdTe Thin Film Semiconductor Photovoltaic Cell Structures Grown by Molecular Beam Epitaxy at High Deposition Rate for Use in Solar Electricity Generation
ActiveUS20100012188A1Improve performanceIncrease deposition rateFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationIntrinsicsEngineering
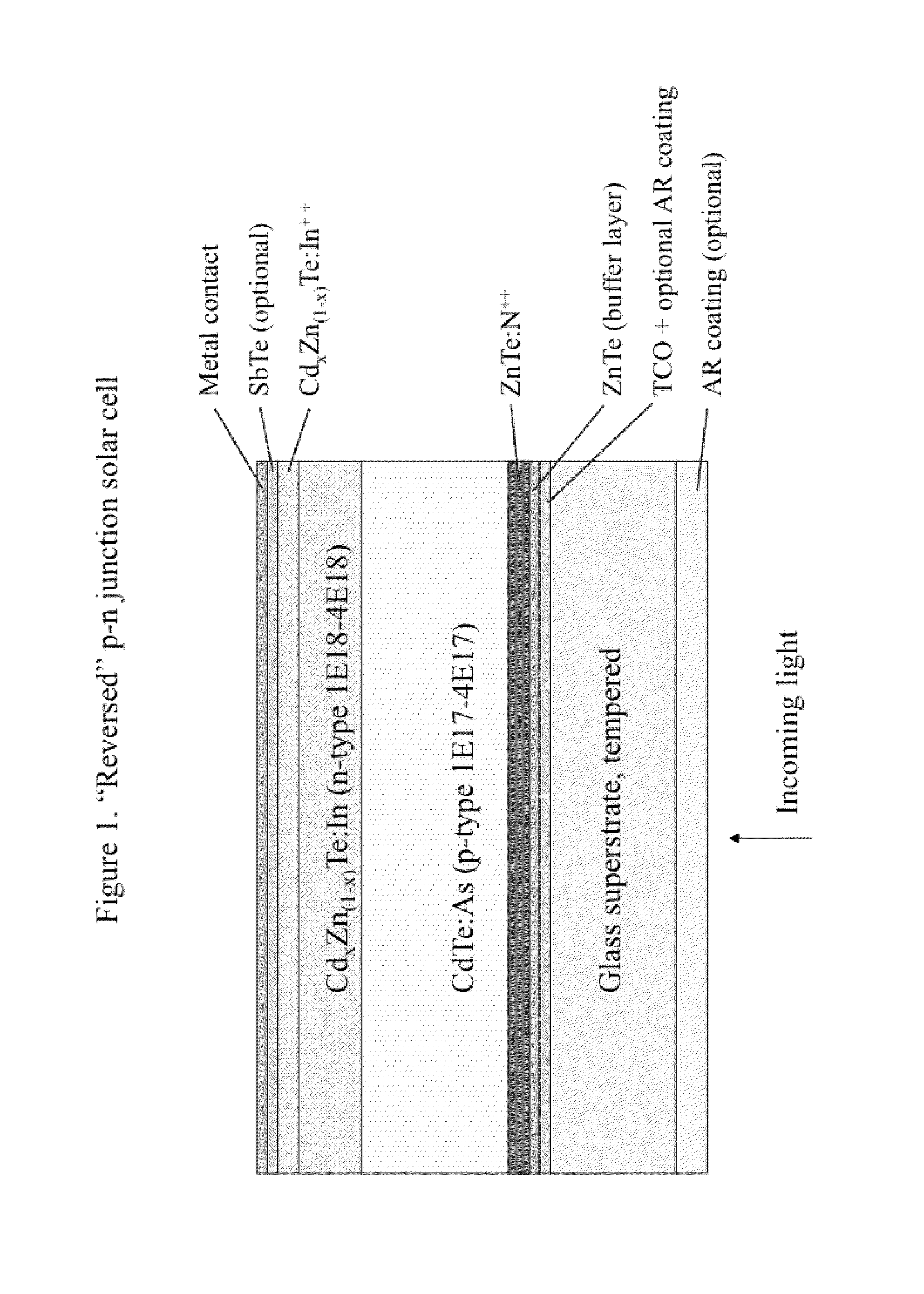
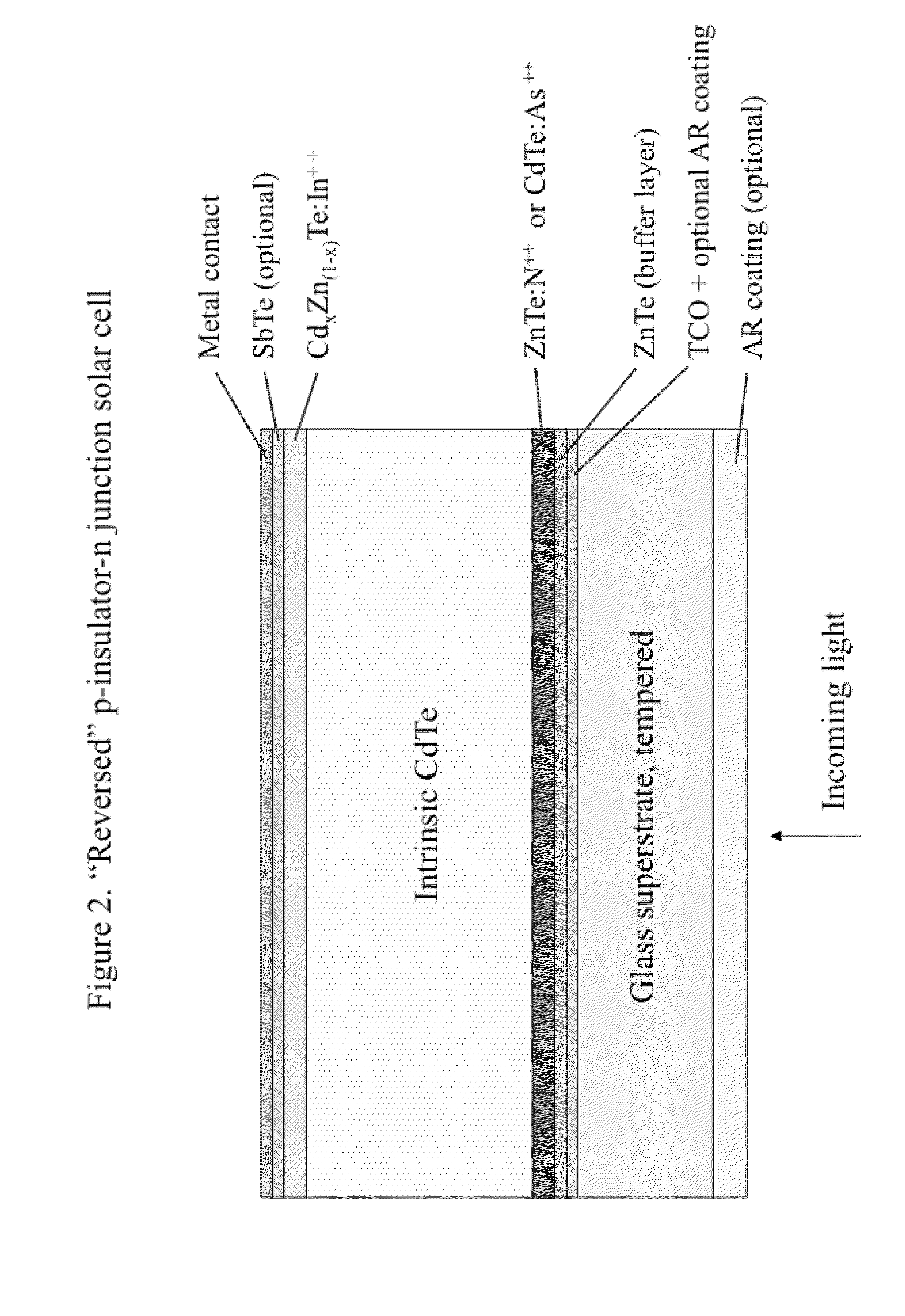
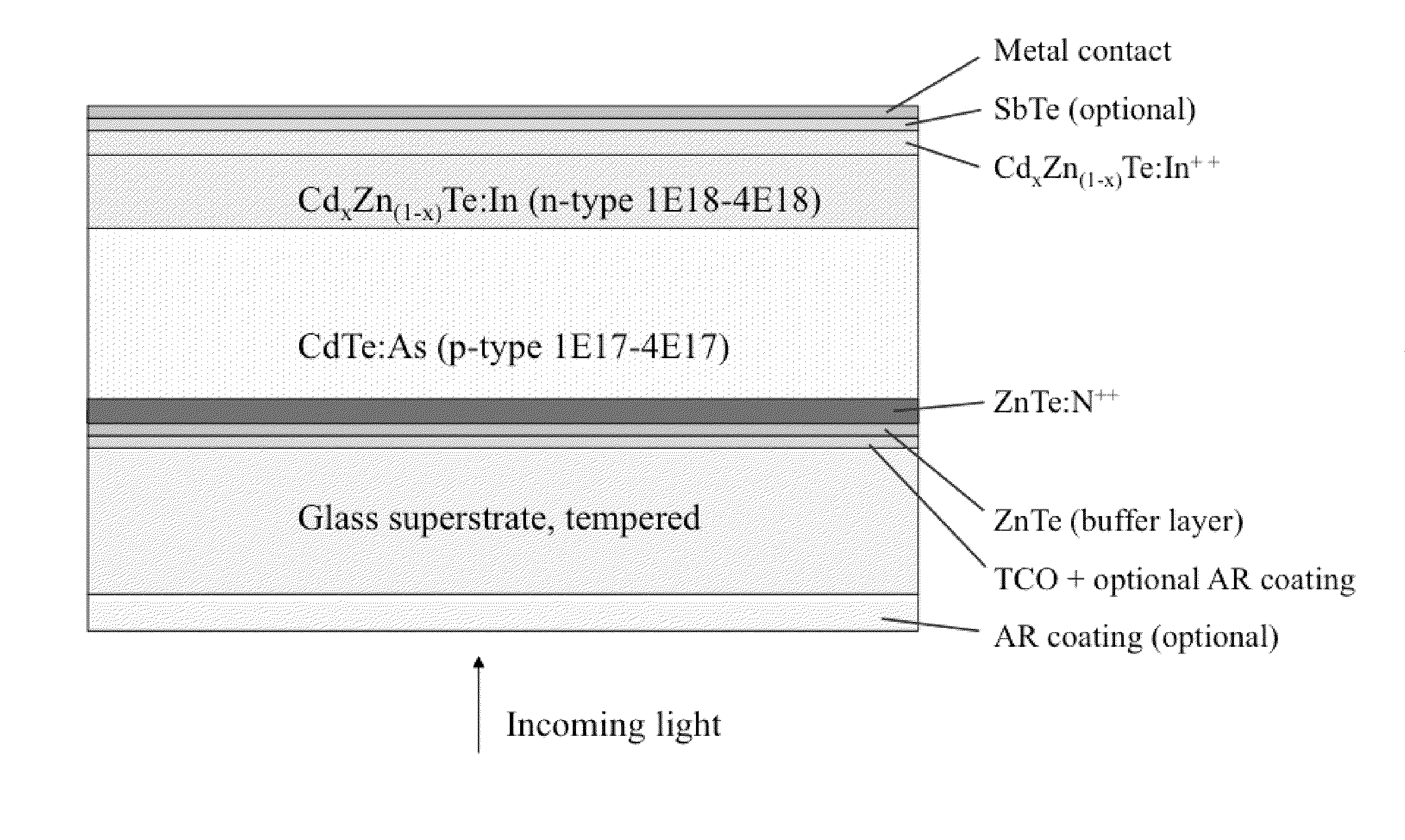
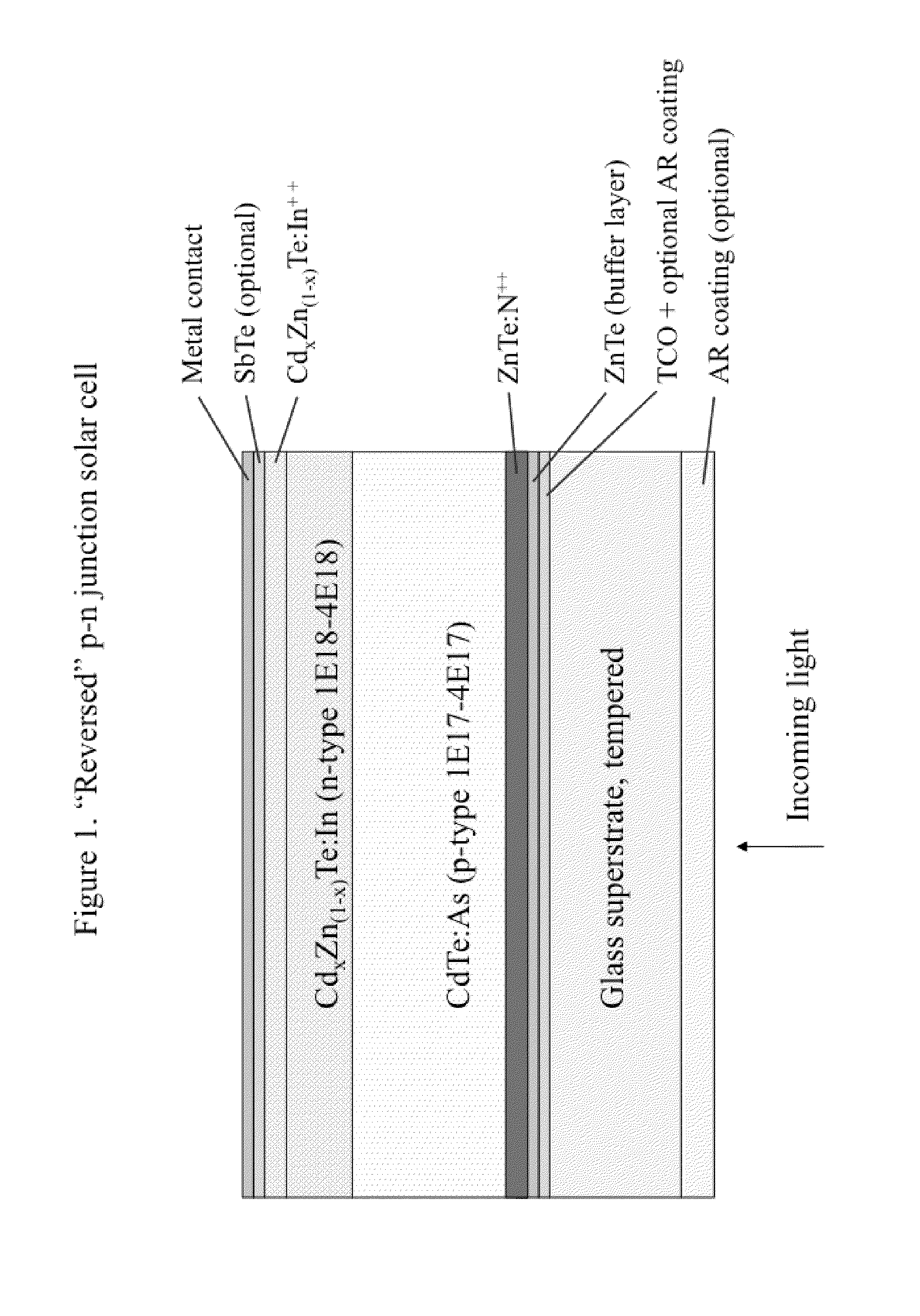
Solar cell structures formed using molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) that can achieve improved power efficiencies in relation to prior art thin film solar cell structures are provided. A reverse p-n junction solar cell device and methods for forming the reverse p-n junction solar cell device using MBE are described. A variety of n-p junction and reverse p-n junction solar cell devices and related methods of manufacturing are provided. N-intrinsic-p junction and reverse p-intrinsic-n junction solar cell devices are also described.
Owner:URIEL SOLAR
High Power Efficiency, Large Substrate, Polycrystalline CdTe Thin Film Semiconductor Photovoltaic Cell Structures Grown by Molecular Beam Epitaxy at High Deposition Rate for Use in Solar Electricity Generation
ActiveUS20100015753A1Improve performanceIncrease deposition rateFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesIntrinsicsEngineering
Solar cell structures formed using molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) that can achieve improved power efficiencies in relation to prior art thin film solar cell structures are provided. A reverse p-n junction solar cell device and methods for forming the reverse p-n junction solar cell device using MBE are described. A variety of n-p junction and reverse p-n junction solar cell devices and related methods of manufacturing are provided. N-intrinsic-p junction and reverse p-intrinsic-n junction solar cell devices are also described.
Owner:URIEL SOLAR
Molecular beam epitaxy method
InactiveUS6146458ALocalReduce decreaseAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthGroup elementAmmonia
A method of growing a layer of Group III nitride material on a substrate by molecular beam epitaxy includes the steps of (i) disposing a substrate in a vacuum chamber, (ii) reducing the pressure in the vacuum chamber to a pressure suitable for epitaxial growth by molecular beam epitaxy, (iii) supplying ammonia through an outlet of a first supply conduit into the vacuum chamber so that the ammonia flows towards the substrate; and (iv) supplying a Group III element in elemental form through an outlet of a second supply conduit into the vacuum chamber so that said Group III element flows towards the substrate. The method causes a layer containing Group III nitride to be grown on the substrate by molecular beam epitaxy. In the method, the outlet of the first supply conduit is disposed nearer to the substrate than the outlet of the second supply conduit.
Owner:SHARP KK
Acoustic wave sensor apparatus, method and system using wide bandgap materials
InactiveUS20060032312A1Velocity increasesImprovement factorAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNanomagnetismAnalyteAcoustic wave
An acoustic wave sensor to detect an analyte, the sensor comprising a piezoelectric material including a wide bandgap semiconductor material grown using plasma source molecular beam epitaxy.
Owner:AUNER GREGORY W +4
Mbe growth of an algan layer or algan multilayer structure
InactiveUS20060237740A1Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAmmoniaSemiconductor
A method of growing an AlGaN semiconductor layer structure by Molecular Beam Epitaxy comprises supplying ammonia, gallium and aluminium to a growth chamber thereby to grow a first (Al,Ga)N layer by MBE over a substrate disposed in the growth chamber. The first (Al,Ga)N layer has a non-zero aluminium mole fraction. Ammonia is supplied at a beam equivalent pressure of at least 1 10−4 mbar, gallium is supplied at a beam equivalent pressure of at least 1 10−8 mbar and aluminium is supplied at a beam equivalent pressure of at least 1 10−8 mbar during the growth step. Once the first (Al,Ga)N layer has been grown, varying the supply rate of gallium and / or aluminium enables a second (Al,Ga)N layer, having a different aluminium mole fraction from the first (Al,Ga)N layer to be grown by MBE over the first (Al,Ga)N layer. This process may be repeated to grown an (Al,Ga)N multilayer structure.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method for preparing film bulk acoustic wave resonator on the basis of monocrystal AlN
InactiveCN105703732AHigh c-axis orientationAvoid lossImpedence networksThin-film bulk acoustic resonatorElectromechanical coupling coefficient
The invention discloses a method for preparing film bulk acoustic wave resonator on the basis of a monocrystal AlN. The method comprises the following steps of: growing (111) an oriented monocrystal Al film on a preparation substrate by using a molecular beam epitaxial growth method; growing (002) an oriented monocrystal AlN film on the oriented monocrystal Al film by using a pulse laser deposition growth method; and depositing a layer of metallic film on the AlN film to form a Al / AlN / metal sandwich piezoelectric stack structure. The piezoelectric stack structure based on monocrystal AlN prepared by the method can be used for preparing the film bulk acoustic wave resonator. The piezoelectric performance of the monocrystal AlN film is superior to that of a polycrystal AlN piezoelectric film applied to film bulk acoustic wave resonator so that the quality factor and a valid electromechanical coupling factor of a device are increased.
Owner:FOSHAN AIFO LIGHT FLUX TECH CO LTD
A method for making IV-VI sector semiconductor single crystal film on CdZnTe underlay
InactiveCN101236905AQuality improvementClear interfaceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFrom condensed vaporsBridgman methodGas phase
The invention provides a method for preparing an IV-VI semiconductor single crystal thin film on a CdZnTe substrate, wherein, in a molecular beam epitaxy(MBE) device, by adopting an MBE growth method and utilizing molecular beam sources of different IV-VI compounds and under different growth temperatures(200 to 425DEG C), the single crystal thin film is epitaxially grown on the CdZnTe single crystal substrate materials; the CdZnTe substrate has a general formula of Cd1-xZnxTe, wherein X is equal to 0 to 0.3; the single crystal thin film grows by the vertical Bridgman method or vapor transport method, is cut along the (111) crystal orientation or (100) crystal orientation, is mechanically polished by Al2O3 powder and then is chemically polished by the bromine-methanol, the concentration of which is 1 percent. The method for preparing an IV-VI semiconductor single crystal thin film on a CdZnTe substrate has the advantages of being capable of realizing the controllable growth of device structures such as hetero junction, quantum well and superlattice, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
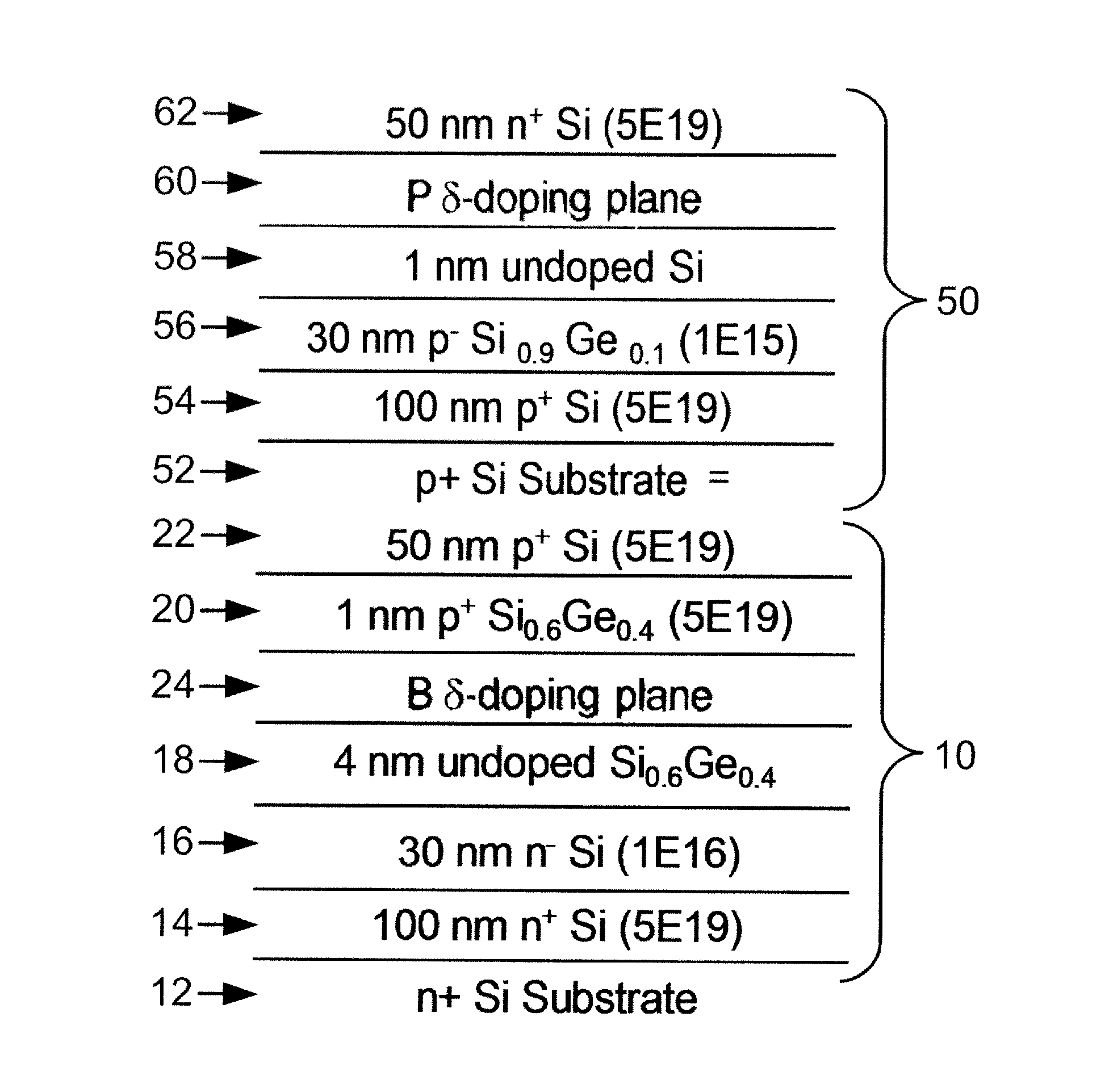
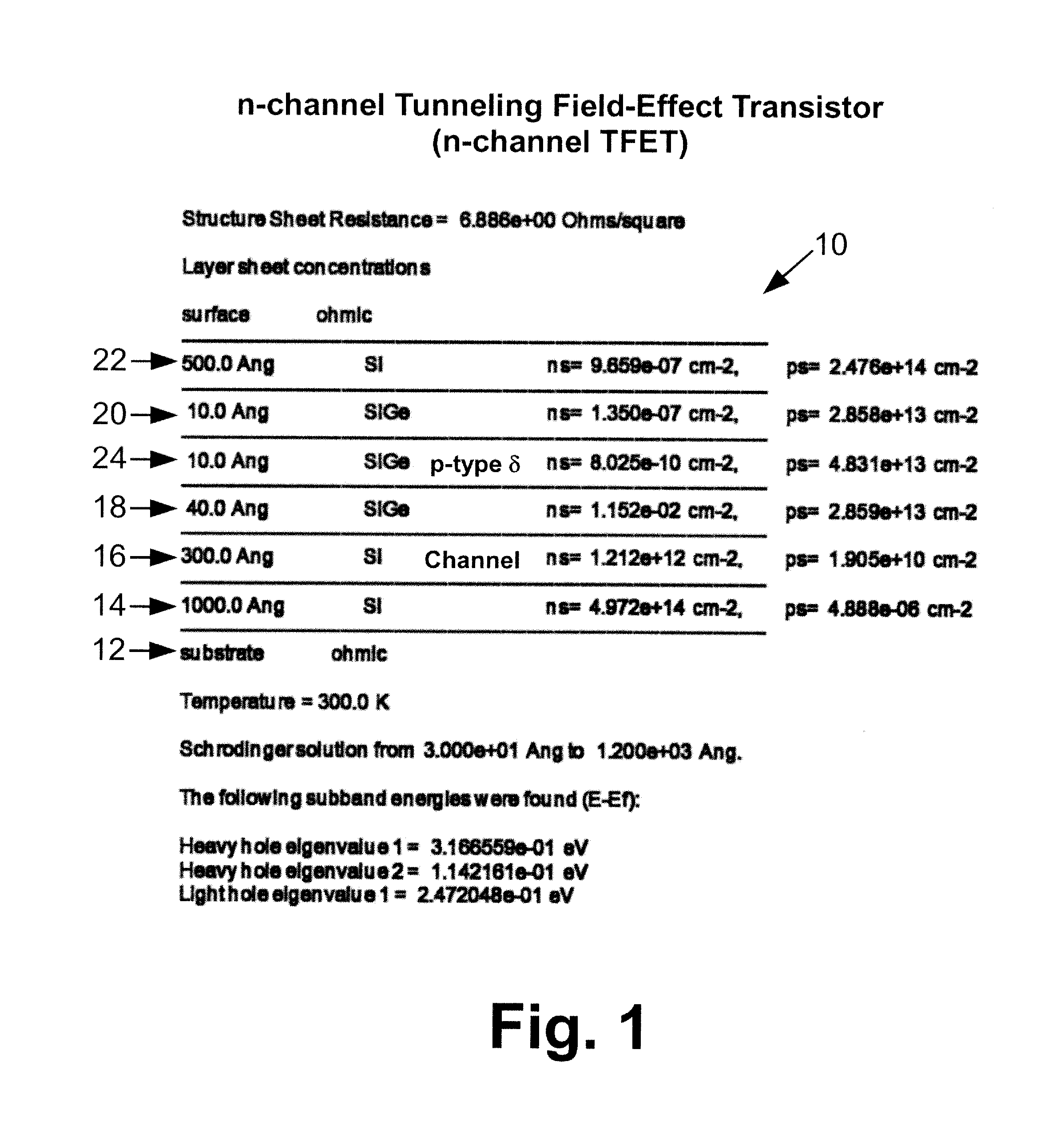
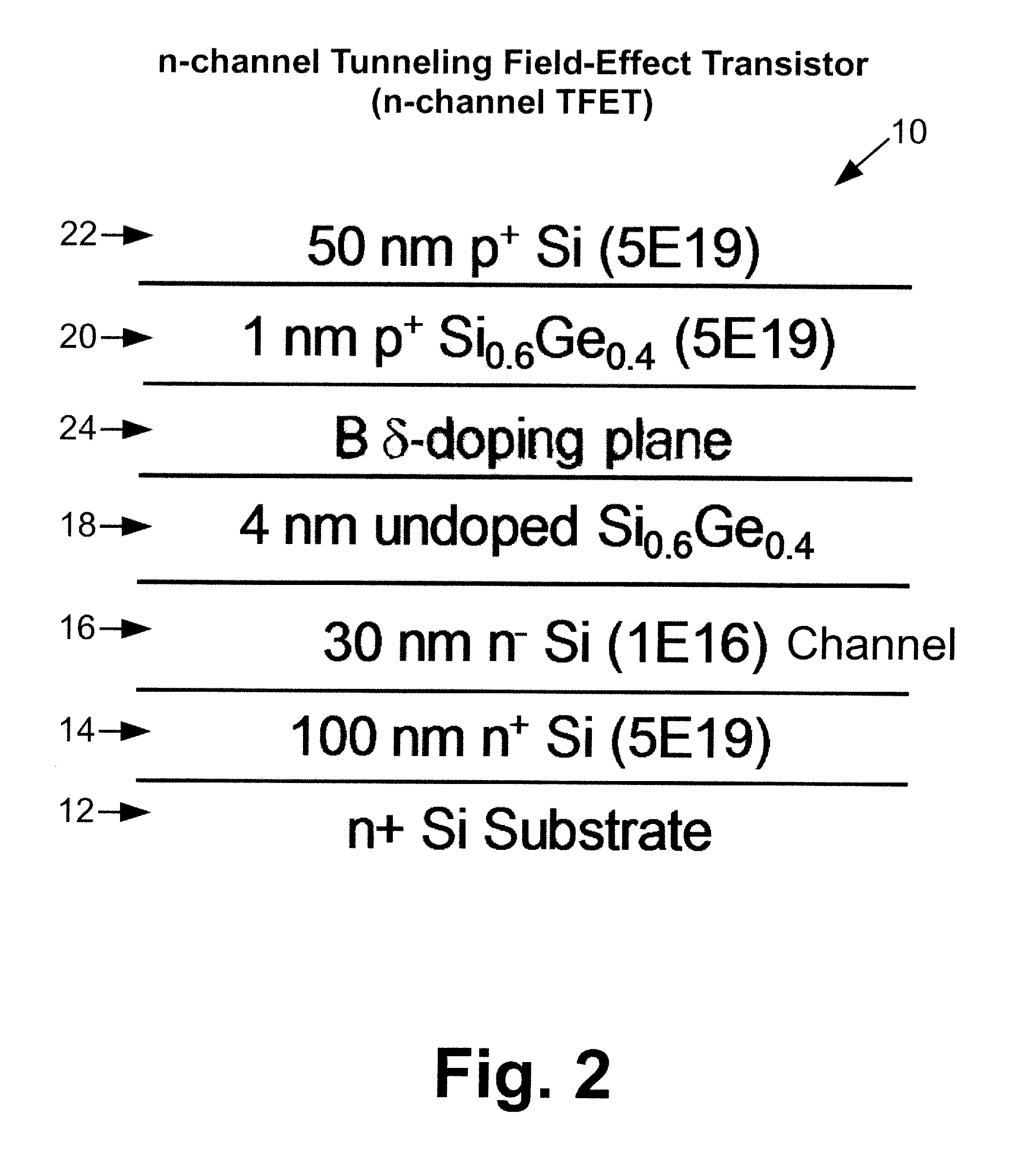
Silicon-based tunneling field effect transistors and transistor circuitry employing same
ActiveUS20120199814A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDelta dopingTransistor circuits
A p-channel tunneling field effect transistor (TFET) is selected from a group consisting of (i) a multi-layer structure of group IV layers and (u) a multi-layer structure of group III-V layers. The p-channel TFET includes a channel region comprising one of a silicon-germanium alloy with non-zero germanium content and a ternary III-V alloy. An n-channel TFET is selected from a group consisting of (i) a multi-layer structure of group IV layers and (u) a multi-layer structure of group III-V layers. The n-channel TFET includes an n-type region, a p-type region with a p-type delta doping, and a channel region disposed between and spacing apart the n-type region and the p-type region. The p-channel TFET and the n-channel TFET may be electrically connected to define a complementary field-effect transistor element. TFETs may be fabricated from a silicon-germanium TFET layer structure grown by low temperature (500 degrees Centigrade) molecular beam epitaxy.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV
GeSn-GeSi material based heterogeneous phototransistor and fabrication method thereof
InactiveCN105789347ANarrow detection wavelengthNarrow detection wavelength rangeFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesCMOSHeterojunction
The invention discloses a GeSn-GeSi material based heterogeneous phototransistor and a fabrication method thereof. A collector and an emitter of the transistor both adopt a GeSi material, a light absorption region and a base region both adopt a GeSn material, an emitter region, the base region, the light absorption region and a collector region are sequentially and vertically arranged, and a passivation layer encircles the peripheries of the emitter region, the base region, the light absorption region and the collector region. According to the fabrication method of the transistor, the GeSn material is grown by a low-temperature solid-source molecular beam epitaxial process, and the fabrication method is a standard complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) fabrication method. The GeSn material with a high light absorption coefficient forms heterojunctions in the light absorption region, the GeSi emitter region and the collector region, the light sensitivity and light current during detection of an infrared light signal by the transistor are improved, and the GeSn-GeSi material based heterogeneous phototransistor has high light absorption rate.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
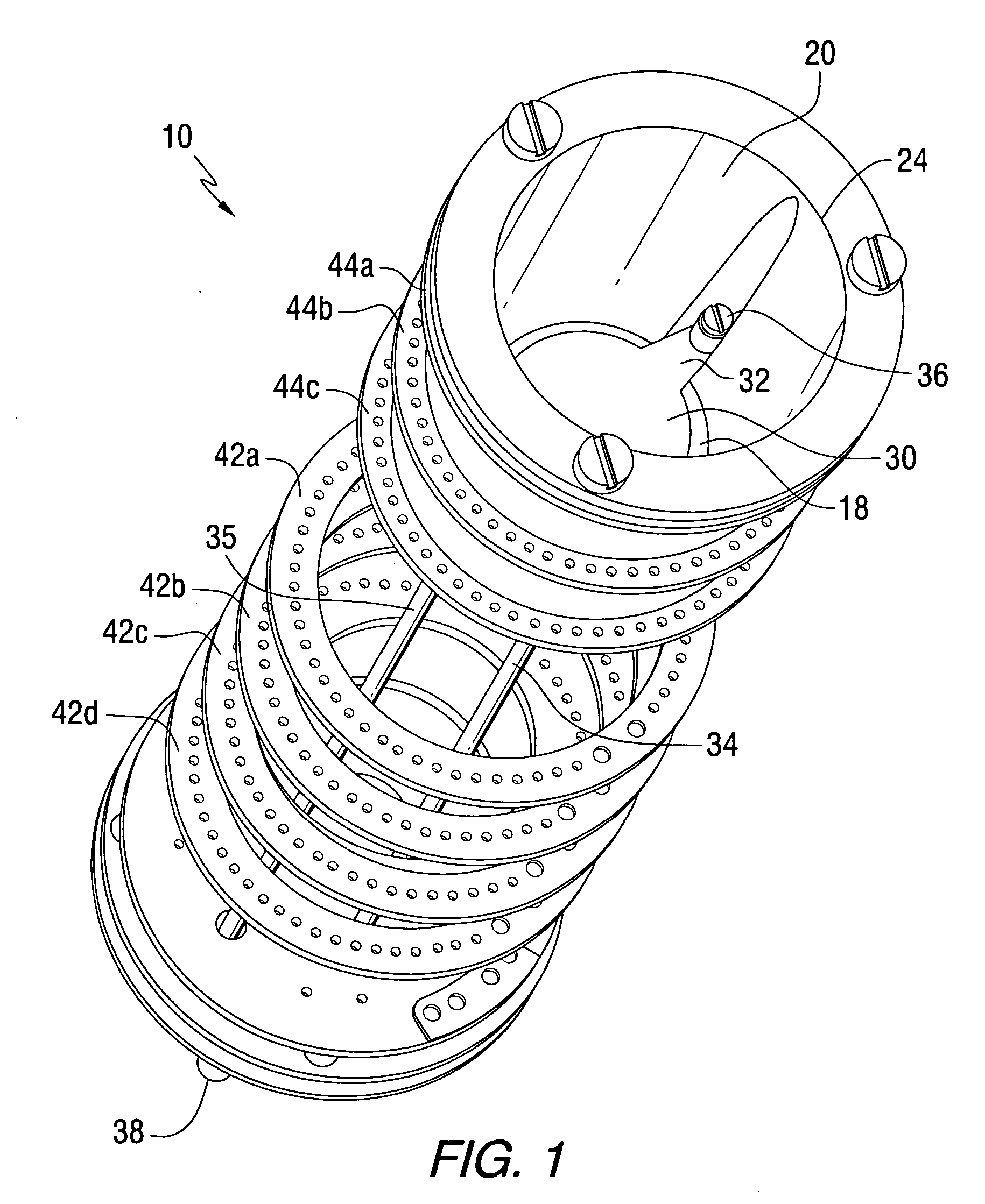
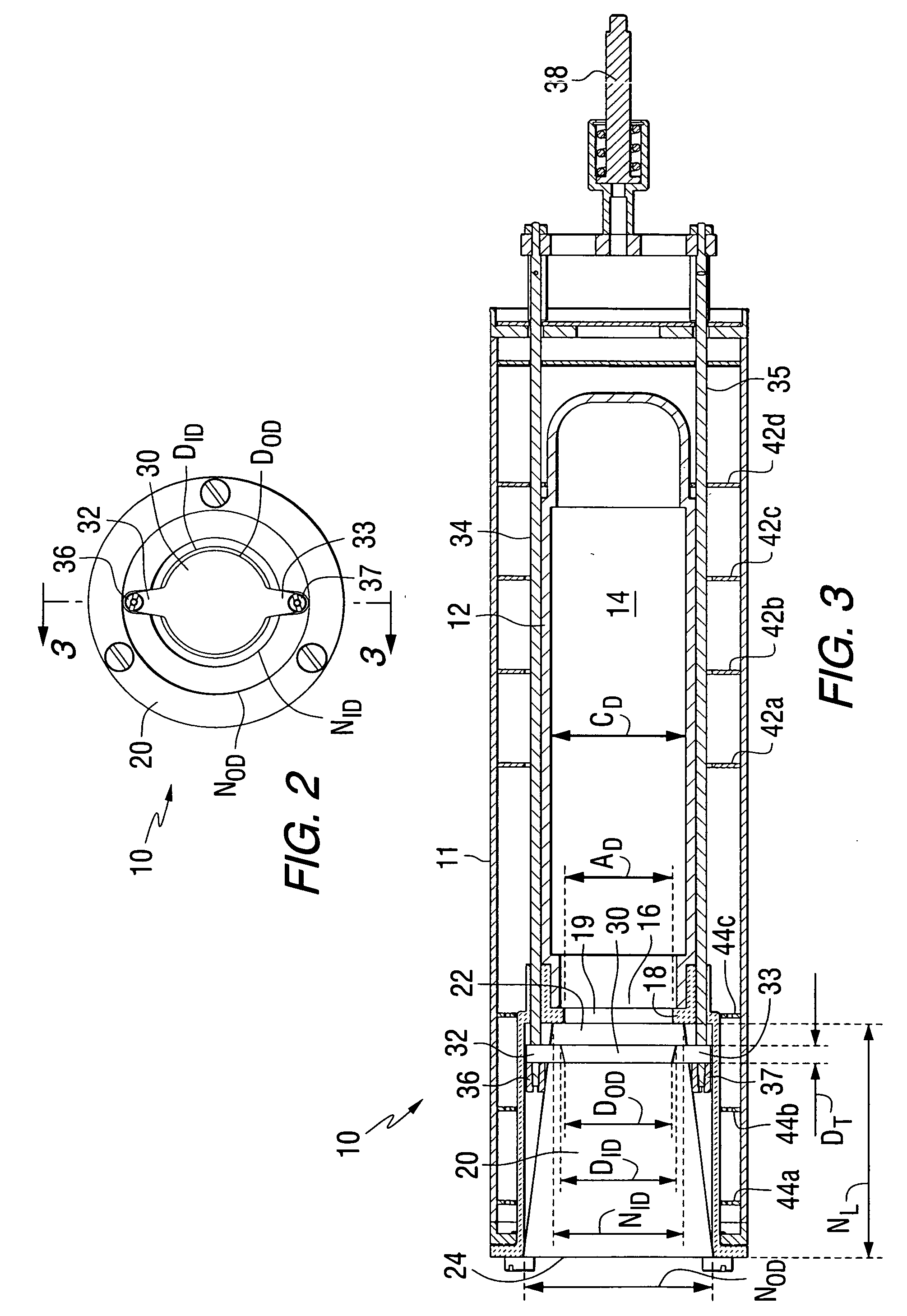
Effusion Cell Valve
A valve for an effusion cell is disclosed. The valve includes a valve seat having an opening in communication with an interior chamber of a heating crucible. A disk-shaped valve member is axially movable with respect to the valve seat in order to increase or decrease the effective size of the valve seat opening. An outlet nozzle may be provided downstream from the valve seat. The valve provides mechanical adjustment of the deposition rate of the evaporated material replacing thermal changes as the means to control the deposition rate or flux from the effusion cell. The nozzle, valve disk and valve seat may be made of machined graphite coated with a carbon-containing material such as pyrolytic graphite, silicon carbide, or the like. The effusion cell may be used for molecular beam epitaxial growth of various materials incorporating mechanical control of the flux without negatively impacting the state of the art qualities of the deposited films with respect to deposition uniformity, surface morphology and background doping.
Owner:ESCI
Preparation method of high-temperature superconducting thin film
ActiveCN103184513AGuaranteed 2D epitaxial growthAtomic level flatteningPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesCrystal structureCondensed matter physics
The invention relates to a preparation method of a high-temperature superconducting thin film. The method specifically comprises steps as follows: providing an SrTiO3 substrate and placing the SrTiO3 substrate in a super-high vacuum system, growing an FeSe monocrystal layer on the surface of the SrTiO3 substrate by adopting a molecular beam epitaxy growing technology, and growing a protective layer with a layered crystal structure by adopting the molecular beam epitaxy growing technology and covering the surface of the FeSe monocrystal layer with the protective layer. By means of the method, the high-quality and ultrathin high-temperature superconducting thin film can be prepared, the starting temperature of superconducting transition of the thin film is above 54K, and the critical current density is higher than 106A / cm<2> when the starting temperature of superconducting transition of the thin film is 12K.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Method for epitaxial growth of molecular beam of low-density InAs quantum dots
InactiveCN102034909AImprove luminous efficiencyImprove collection efficiencySemiconductor devicesDistributed Bragg reflectorLength wave
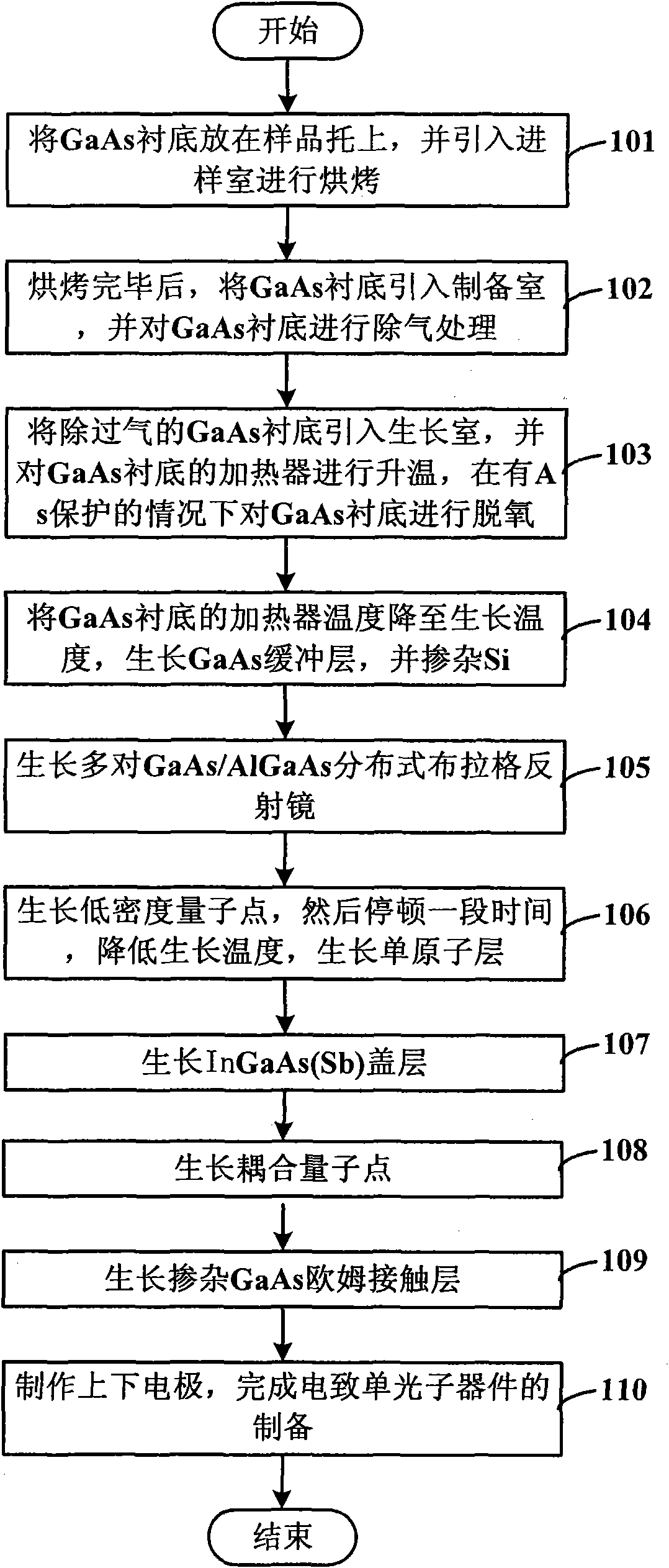
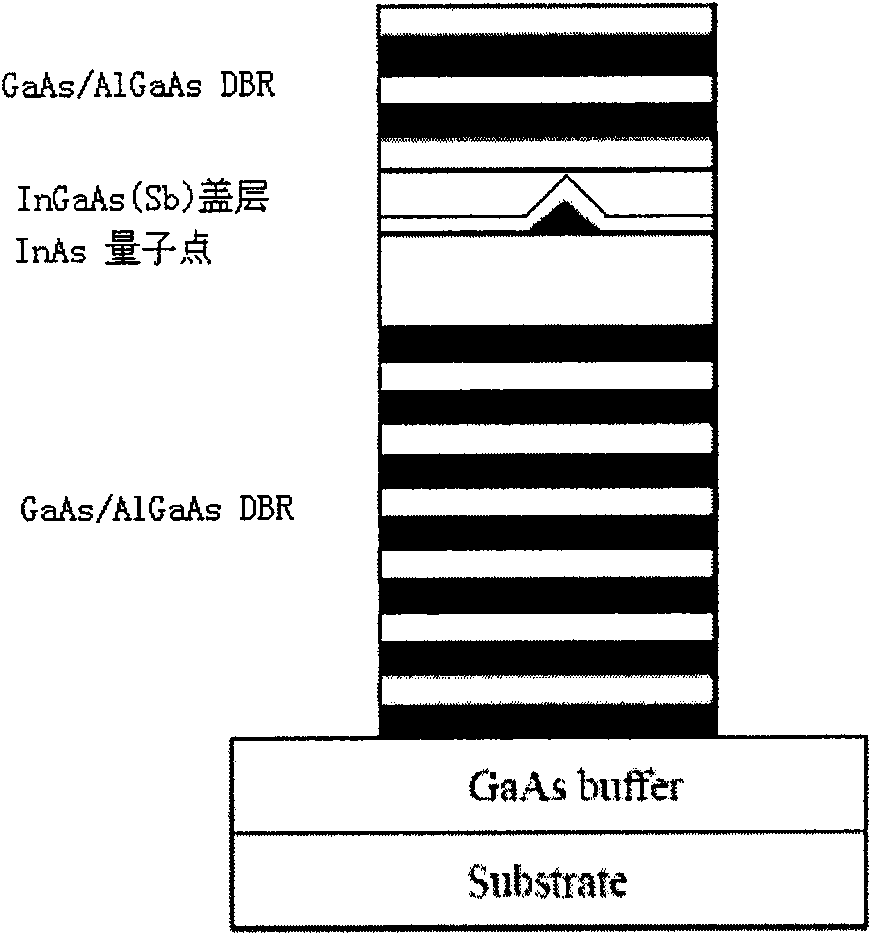
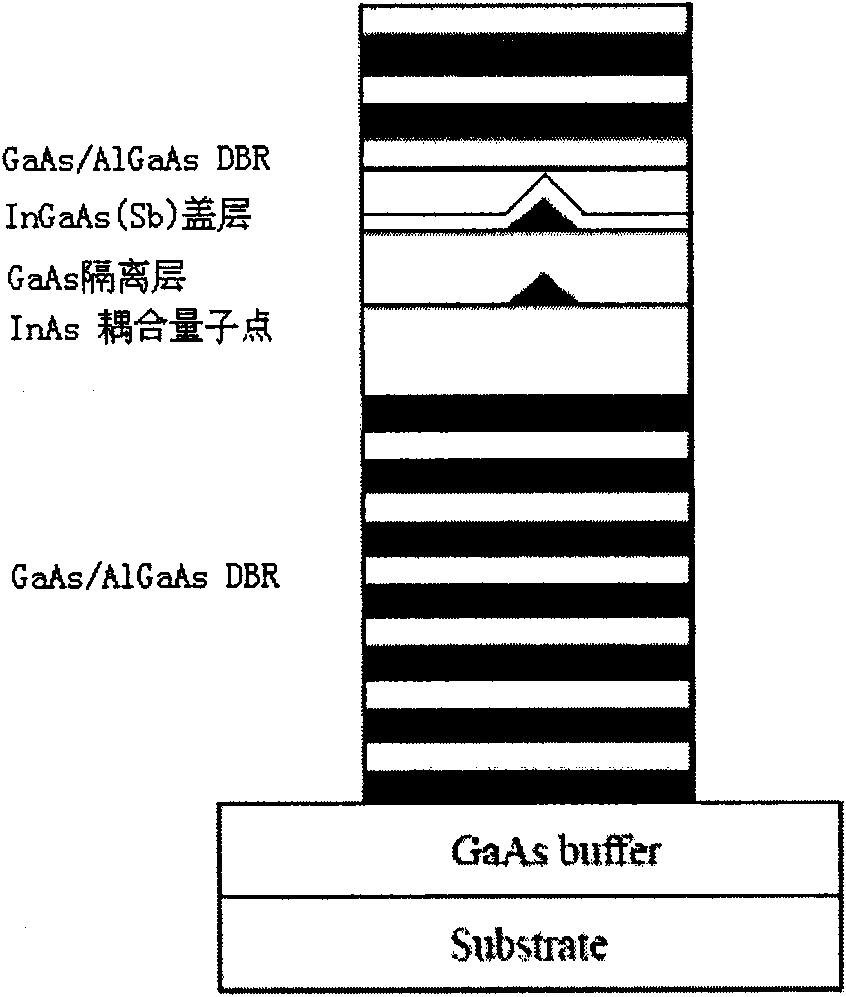
The invention discloses a method for epitaxial growth of a molecular beam of low-density InAs quantum dots, which comprises the following steps of: putting a GaAs substrate on a sample support, and introducing the GaAs substrate into a sample introduction room for baking; after baking, introducing the GaAs substrate into a preparation room, and degassing the GaAs substrate; introducing degassed GaAs substrate into a growth room, heating a heater of the GaAs substrate, and deoxidizing the GaAs substrate under the protection of As; cooling the heater of the GaAs substrate to the growth temperature, growing a GaAs buffer layer, and doping Si; growing a plurality of pairs of GaAs / AlGaAs distributed Bragg reflectors; reducing the growth temperature, and growing low-density quantum dots; growing an InGaAs(Sb) covering layer; growing coupled quantum dots to expand the wavelength; growing a doped GaAs layer; and manufacturing upper and lower electrodes. By using the method, the luminous efficiency of the quantum dots is effectively improved, the collection efficiency is improved, and the regulation and control of the wavelength are realized.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Molecular beam epitaxy growth of ternary and quaternary metal chalcogenide films
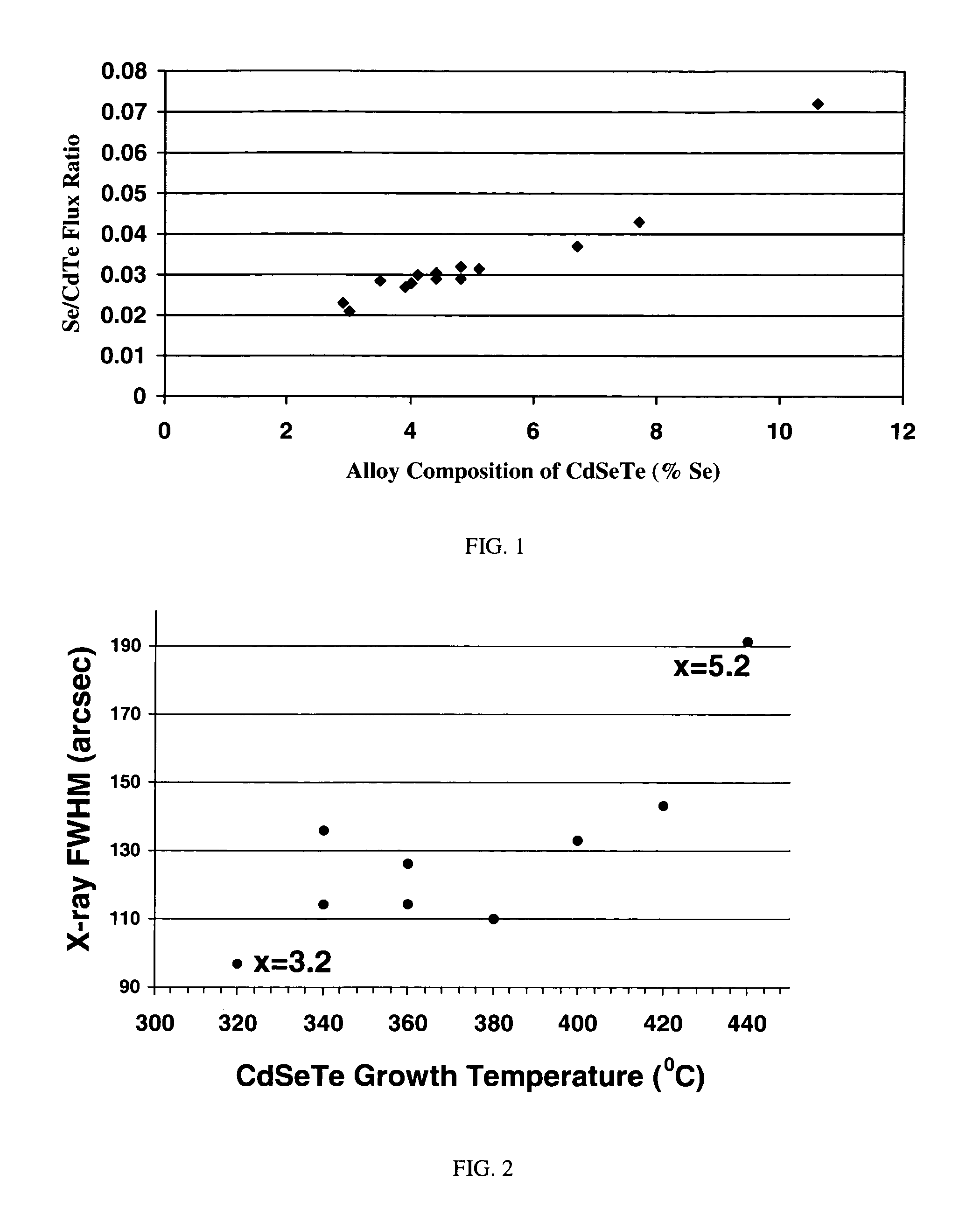
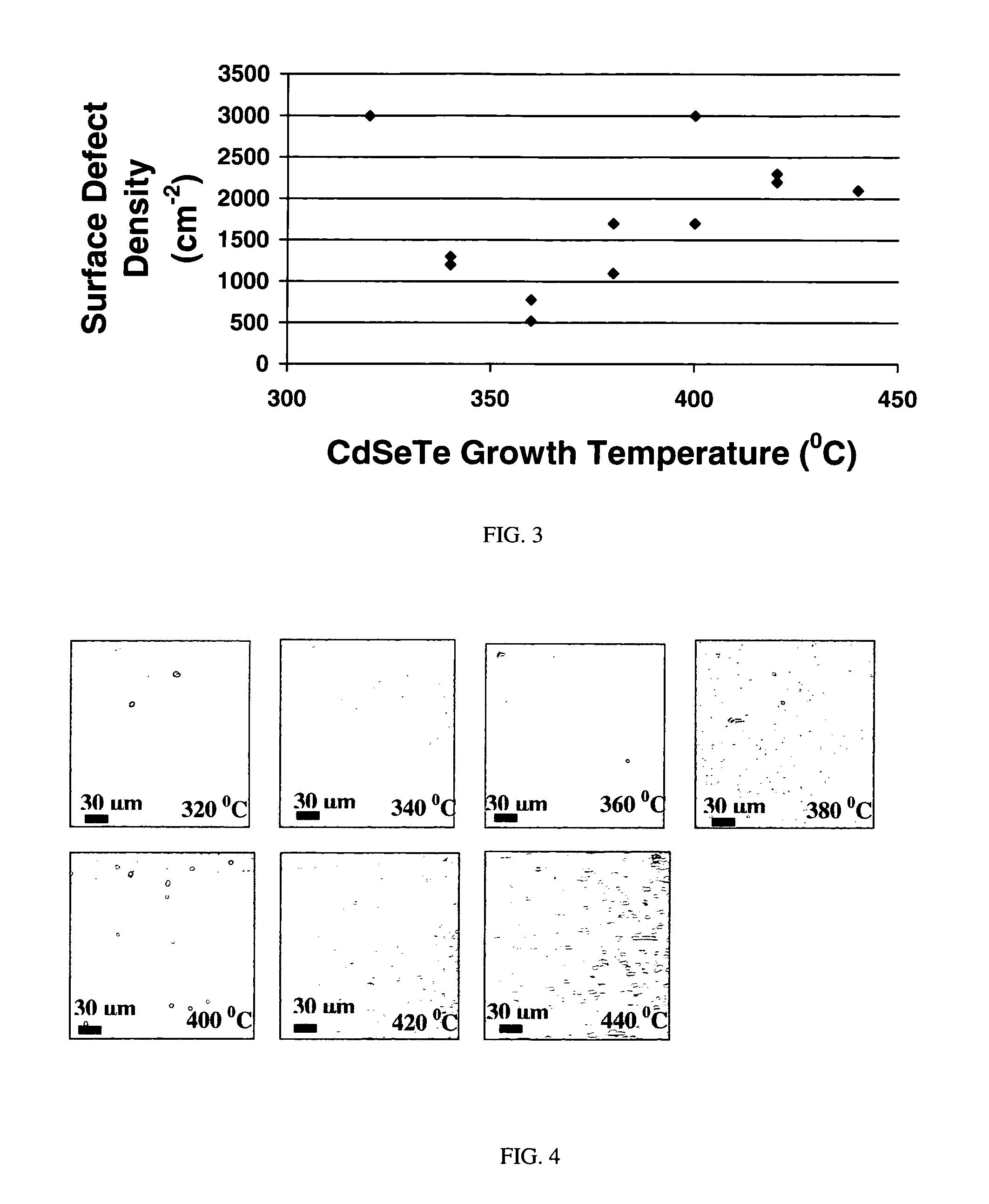
InactiveUS7518207B1Improve surface morphologyReduce surface defect densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationRocking curveSulfur
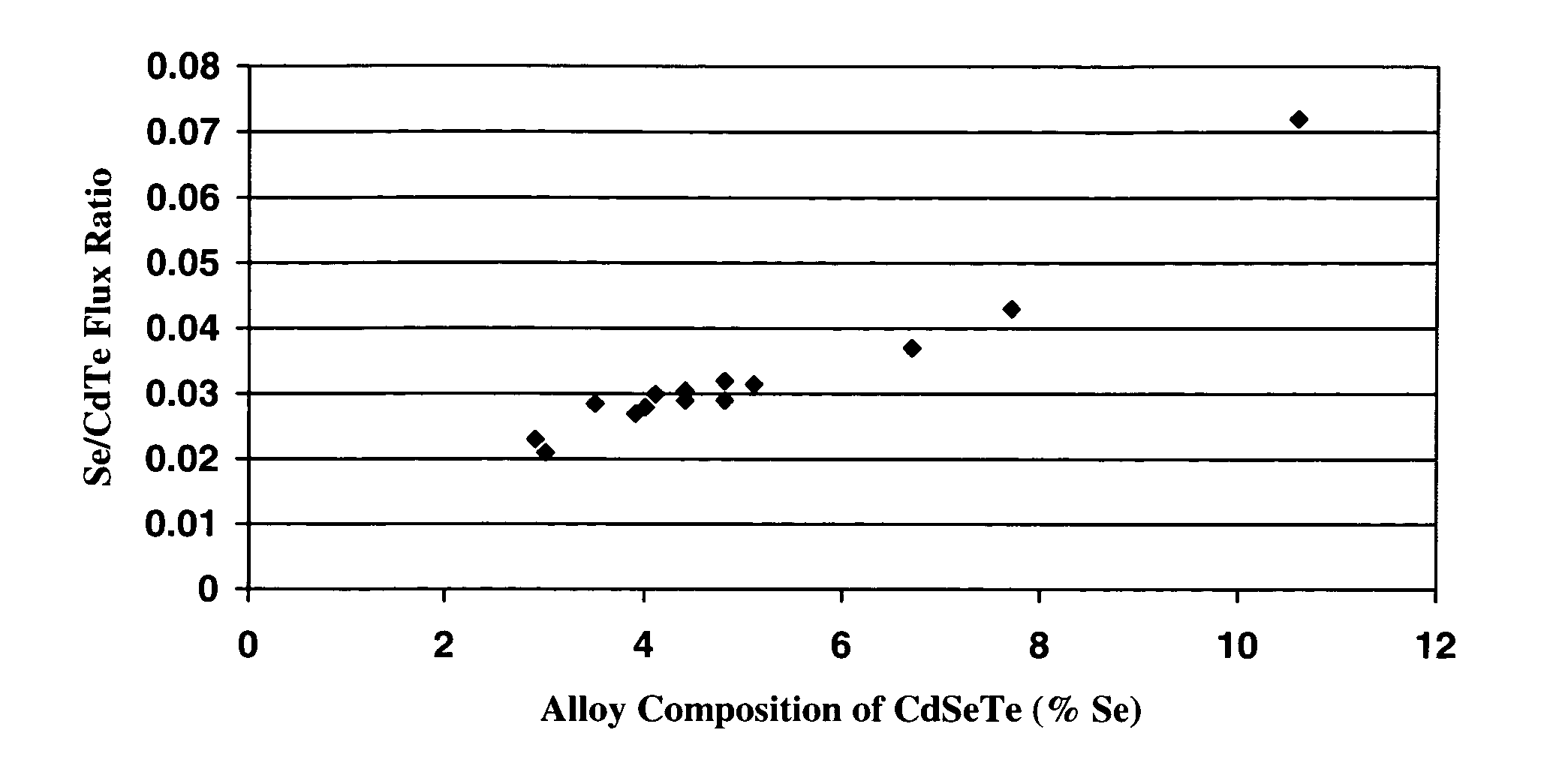
The ternary alloy CdSexTe1-x(2 1 1) and the quaternary alloy Cd1-zZnzSexTe1-x have been grown on Si(2 1 1) substrates using molecular beam epitaxy (MBE). The growth of CdSeTe is facilitated using a compound CdTe effusion source and a Se effusion source while the growth of CdZnSeTe is facilitated using a compound CdTe effusion source, a compound ZnTe effusion source, and an elemental Se source. The alloy compositions (x) and (z) of CdSexTe1-x ternary compound and Cd1-zZnzSexTe1-x are controlled through the Se / CdTe and ZnTe / CdTe flux ratios. The rate of Se incorporation is higher than the rate of Te incorporation as growth temperature increases. As-grown CdSeTe with 4% Se and CdZnSeTe with 4% Zn+Se, which is substantially lattice matched to long-wavelength infrared HgCdTe materials, exhibits excellent surface morphology, low surface defect density (less than 500 cm2), and a narrow X-ray rocking curve (a full-width at half maximum of 103 arcsec).
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
AlGaN-based solar-blinded ultraviolet avalanche heterojunction photoelectric transistor detector and fabrication method thereof
InactiveCN107863413AQuick responseAvoid the problem of high multiplication noiseFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationHeterojunctionPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention relates to the technical field of a semiconductor ultraviolet photoelectric detector, in particular to an AlGaN-based solar-blinded ultraviolet avalanche heterojunction photoelectric transistor detector and a fabrication method thereof. The AlGaN-based solar-blinded ultraviolet avalanche heterojunction photoelectric transistor detector comprises a substrate, wherein an unintentionally-doped low-temperature AlN buffer layer, an unintentionally-doped high-temperature AlN buffer layer, an unintentionally-doped Al<m>Ga<1-m>N window layer, an n-type Al<m>Ga<1-m> layer, an n-type Al<n>Ga<1-n>N constituent slowly-changing layer, an unintentionally-doped AlGa<1-a>N absorption multiplication layer, an unintentionally-doped AlGa<1-b>N absorption multiplication layer, an unintentionally-doped Al<c>Ga<1-c>N absorption multiplication layer, an Mg-doped p-type Al<x>Ga<1-x>N layer, an unintentionally-doped Al<x>Ga<1-x>N layer, an n-type Al<y>Ga<1-y>N constituent slowly-changing layer, an n-type Al<z>Ga<1-z>N layer and an n-type ohmic contact electrode are sequentially grown on the substrate by a metal organic chemical vapor deposition epitaxial growth method (or a molecular beam epitaxial growth method), and the n-type ohmic contact electrode is finally obtained by deposition of a device process.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Molecular beam epitaxy growing method of high-speed vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
ActiveCN105337166AReduce the impactReduce spreadLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserDelta doping
The invention provides a molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) growing method of a high-speed vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser. The method comprises the steps that deoxidation pretreatment is conducted on a GaAs substrate, and epitaxial growth of a GaAs buffer layer, a lower DBR, an active region, an oxidation confinement layer and an upper DBR is sequentially achieved; in the growth process, the active region is clamped between the upper DBR and the lower DBR, and a delta-doping method is adopted by the potential barrier middle position of the active region, wherein a doping source adopts carbon (C), and growth is stopped for a period of time under the protection of As after delta-doping is completed. By means of the method, the technical problems of reducing a threshold, increasing differential gain and reducing nonlinear gain compression are solved, and the good effects of reducing optical losses, decreasing line width and increasing output power and intrinsic bandwidth are achieved.
Owner:WUHAN TELECOMM DEVICES
Method for growing InGaAs film on GaAs substrate
InactiveCN102560634AEffectively filter dislocationsFacilitated releasePolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesPhysical chemistryThin membrane
The invention discloses a method for growing an InGaAs film on a GaAs substrate, which comprises the following steps of: (1) cleaning the GaAs substrate; (2) pre-processing the GaAs substrate; (3) deoxidizing; (4) growing a GaAs buffer layer; (5) growing a low-temperature single-layer In0.6Ga0.4As big-mismatch buffer layer; and (6) growing an In0.3Ga0.7As epitaxial film, wherein the In0.6Ga0.4As big-mismatch buffer layer and the In0.3Ga0.7As epitaxial film both can be prepared by using the molecular beam epitaxial growth or metal organic vapor deposition technology. Various defects caused by mismatch stress can be lowered by the big-mismatch buffer layer. The prepared In0.3Ga0.7As epitaxial layer has lower defect density. The method has the advantages of simple buffer layer structure, simple and convenient epitaxial growth process, low defect density of the In0.3Ga0.7As epitaxial film, high crystal quality and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
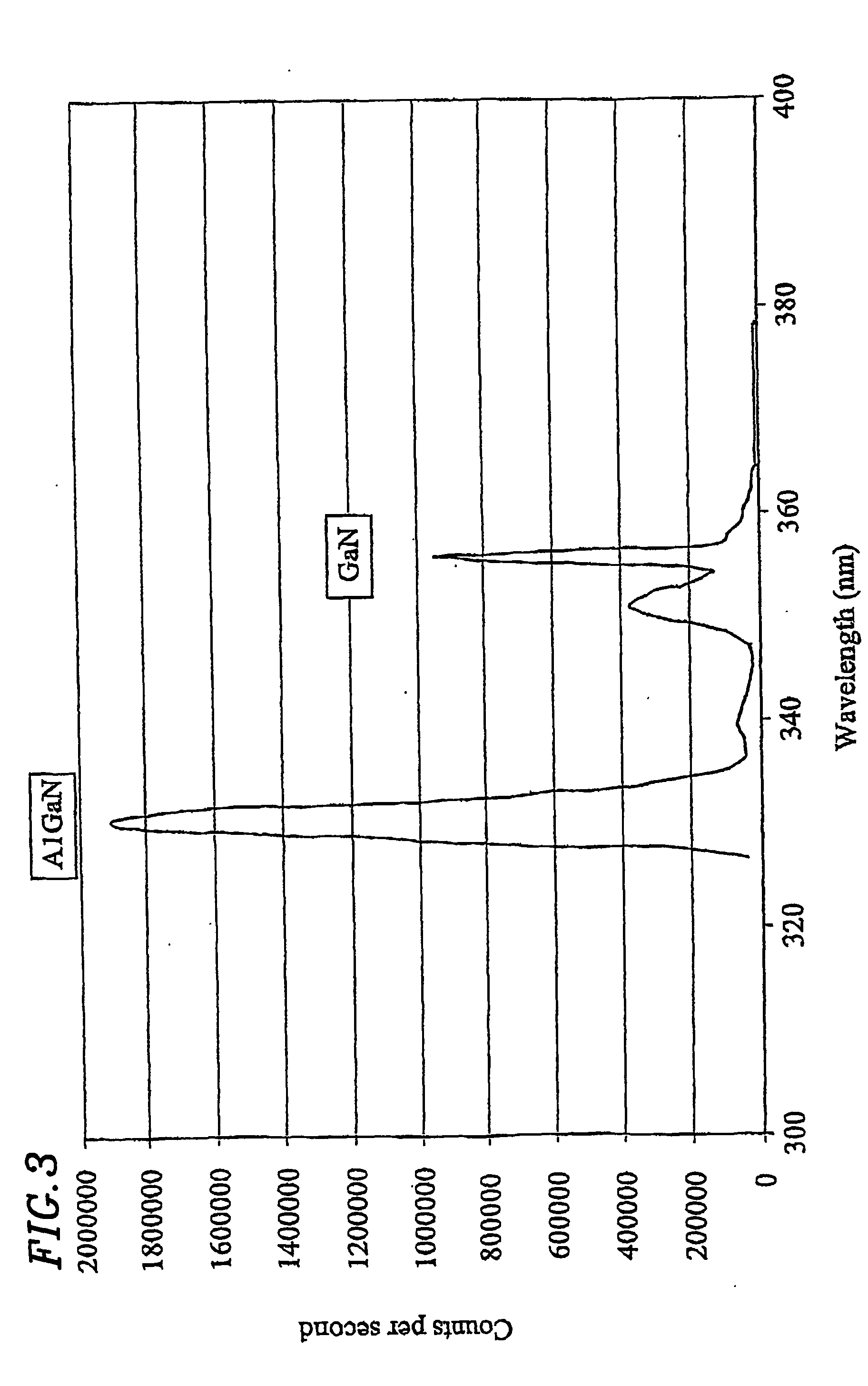
Modifying the optical properties of a nitride optoelectronic device
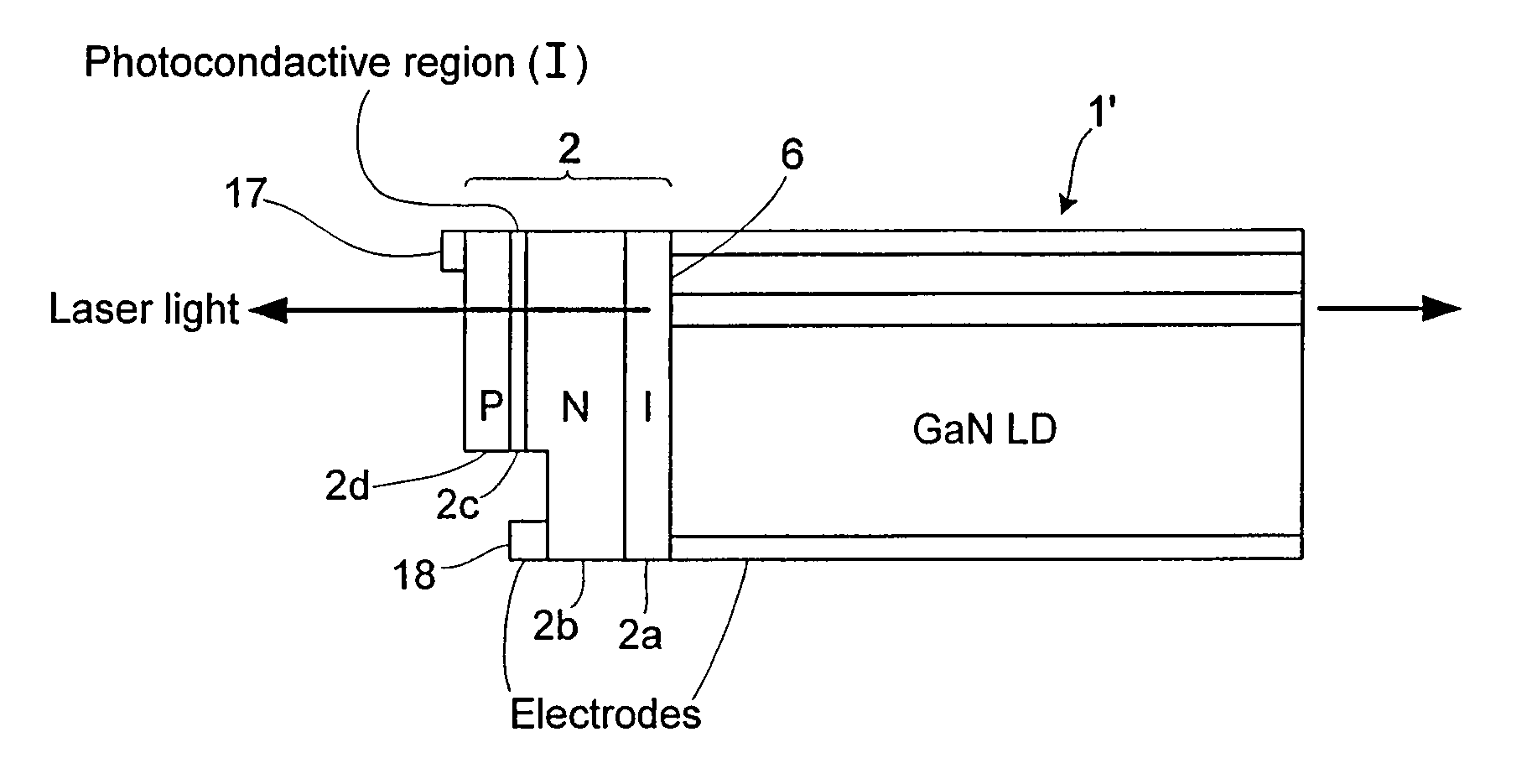
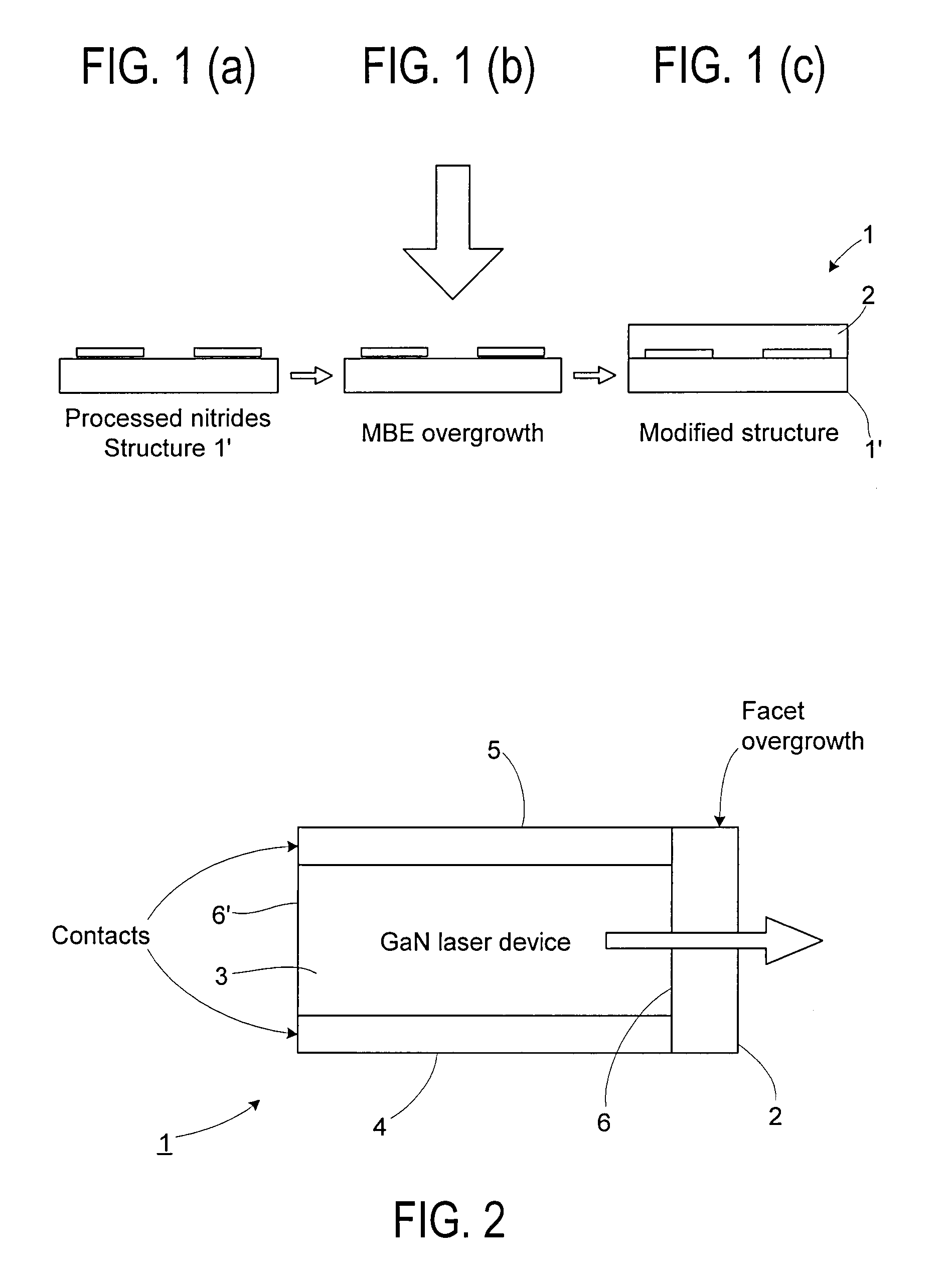
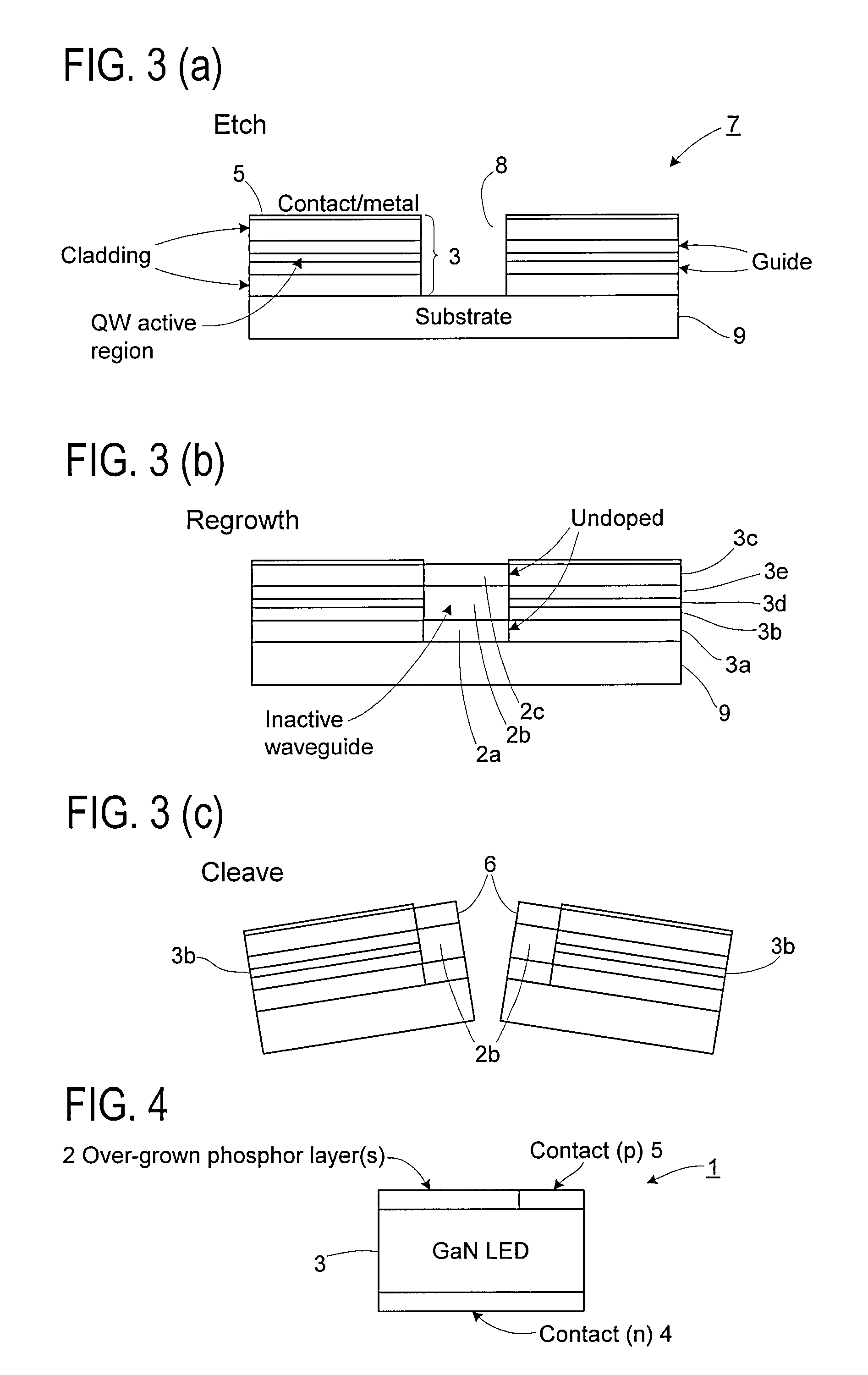
InactiveUS20080014667A1Short timeNovel and improved optical characteristicSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor laser optical deviceOptical propertyNitrogen
A method of modifying the optical properties of a processed nitride semiconductor light-emitting device initially comprises disposing the processed nitride semiconductor light-emitting device in a vacuum chamber. One or more nitride semiconductor layers are then grown by molecular beam epitaxy thereby to modify the optical properties of the processed light-emitting device. Activated nitrogen, for example from a plasma source, is supplied to the vacuum chamber during growth of the nitride semiconductor layer(s). The use of activated nitrogen reduces the growth temperature required for the growth of the nitride semiconductor layer(s), as the need for thermal activation of a nitrogen species is eliminated. Moreover, use of a growth method such as, for example, plasma-assisted MBE to grow the nitride semiconductor layer(s) allows much more precise control of their thickness and composition.
Owner:SHARP KK
Preparation method for laminated molybdenum disulfide film
ActiveCN104746137AFlat surfaceStructural rulesPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesSulfurBeam source
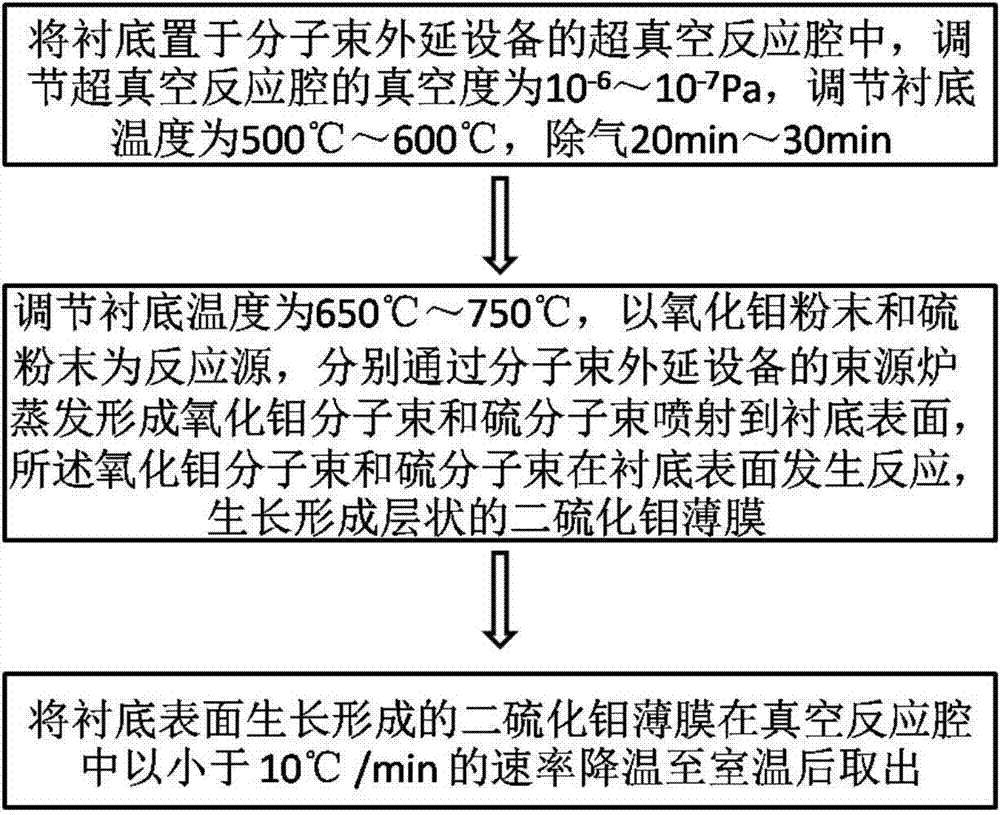
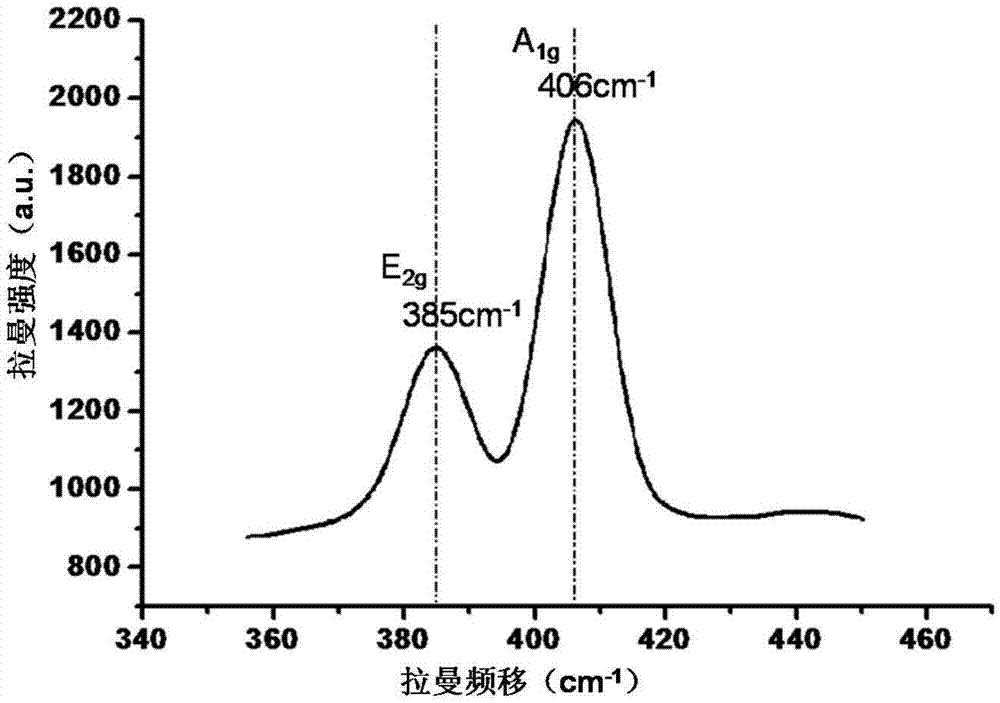
The invention discloses a preparation method for a laminated molybdenum disulfide film. An MBE (Molecular Beam Epitaxy) method is adopted. The preparation method comprises the following steps of 1) placing a substrate in an ultra-vacuum reaction cavity of an MBE instrument, adjusting the vacuum degree of the ultra-vacuum cavity to be (10<-6>)-(10<-7>)Pa, adjusting the temperature of the substrate to be 500-600 DEG C, and degassing for 20-30 minutes; 2) adjusting the temperature of the substrate to be 650-750 DEG C, taking molybdenum oxide powder and sulphur powder as reaction sources, evaporating the molybdenum oxide powder and sulphur powder respectively through a beam source furnace of the MBE instrument to form a molybdenum oxide molecular beam and a sulphur molecular beam, spraying the molybdenum oxide molecular beam and the sulphur molecular beam on the surface of the substrate, and reacting the molybdenum oxide molecular beam and the sulphur molecular beam on the surface of the substrate to form the laminated molybdenum disulfide film through growing. According to the preparation method, the laminated molybdenum disulfide film with controllable repetitive layers, regular growing structure and smooth surface is prepared through the MBE technology.
Owner:厦门烯成石墨烯科技有限公司
Spectroscopic method and device for quickly testing type II infrared superlattice interface quality
ActiveCN103134779ASo as not to damageUnlimited integration time limitEmission spectroscopyAnalysis by material excitationSample MeasurePhotoluminescence
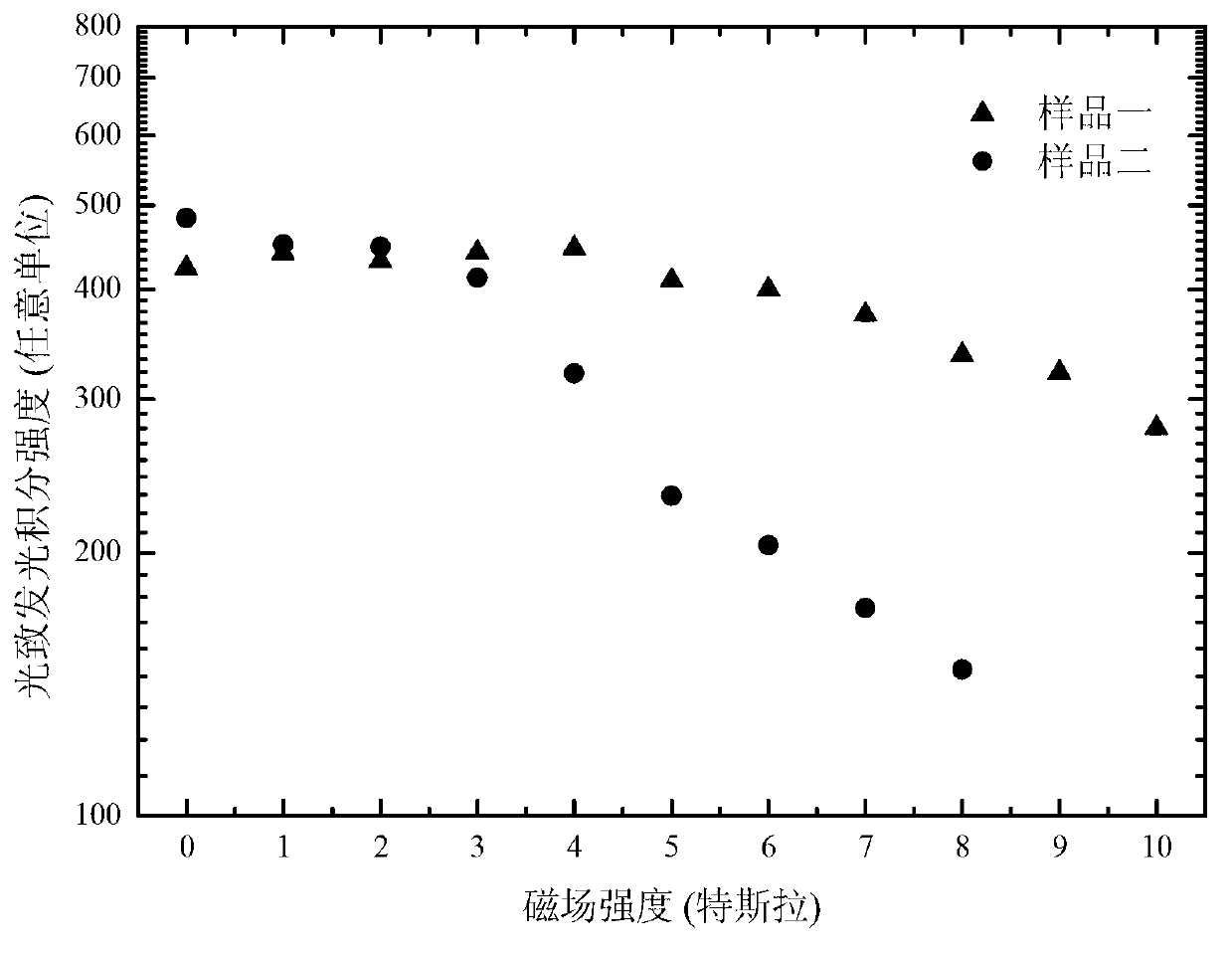
The invention discloses a spectroscopic method and a device for quickly testing type II infrared superlattice interface quality. The spectroscopic device comprises a Fourier transform infrared measuring system which has a function of step scan, a laser device which serves as a pump light source, a temperature-changing and magnetic-field-changing sample measuring system, a phrase lock amplifier which connects a detector and a circuit control panel in the Fourier transform infrared measuring system, and a wave chopper which is arranged between the temperature-changing and magnetic-field-changing sample measuring system and the laser device. With the spectroscopic device being used, the type II infrared superlattice interface quality is quickly tested through measuring the degree of attenuation of the photoluminescence intensity of type II infrared superlattices along a magnetic field. The test for infrared band In As / Ga Sb type II infrared superlattices of molecular beam epitaxy indicates that the spectroscopic method for quickly testing the type II infrared superlattice interface quality is an optical method capable of quickly and conveniently testing type II infrared superlattice interfaces. The spectroscopic method for quickly testing the type II infrared superlattice interface quality has the advantages of being lossless and sensitive, and is especially suitable for the detection of weak optical signals on the type II infrared superlattice interfaces.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for growing ordered silicon-based germanium quantum dots
ActiveCN102201491AHigh densityLimit positionFinal product manufactureNanotechnologyHigh densityQuantum dot
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-density and ordered germanium quantum dots on a silicon substrate, which comprises the following steps of: adhering porous anodic aluminum oxide on a surface of a silicon wafer cleaned by an RCA (Remote Control Adapter); putting the silicon wafer in molecular beam epitaxial growth equipment for growing the germanium quantum dots after through holes are arranged on the silicon wafer; and removing a template through a high-temperature annealing process to leave periodically arranged germanium quantum dot structures. When the method disclosed by the invention is adopted, the high-density and ordered germanium quantum dots can be obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
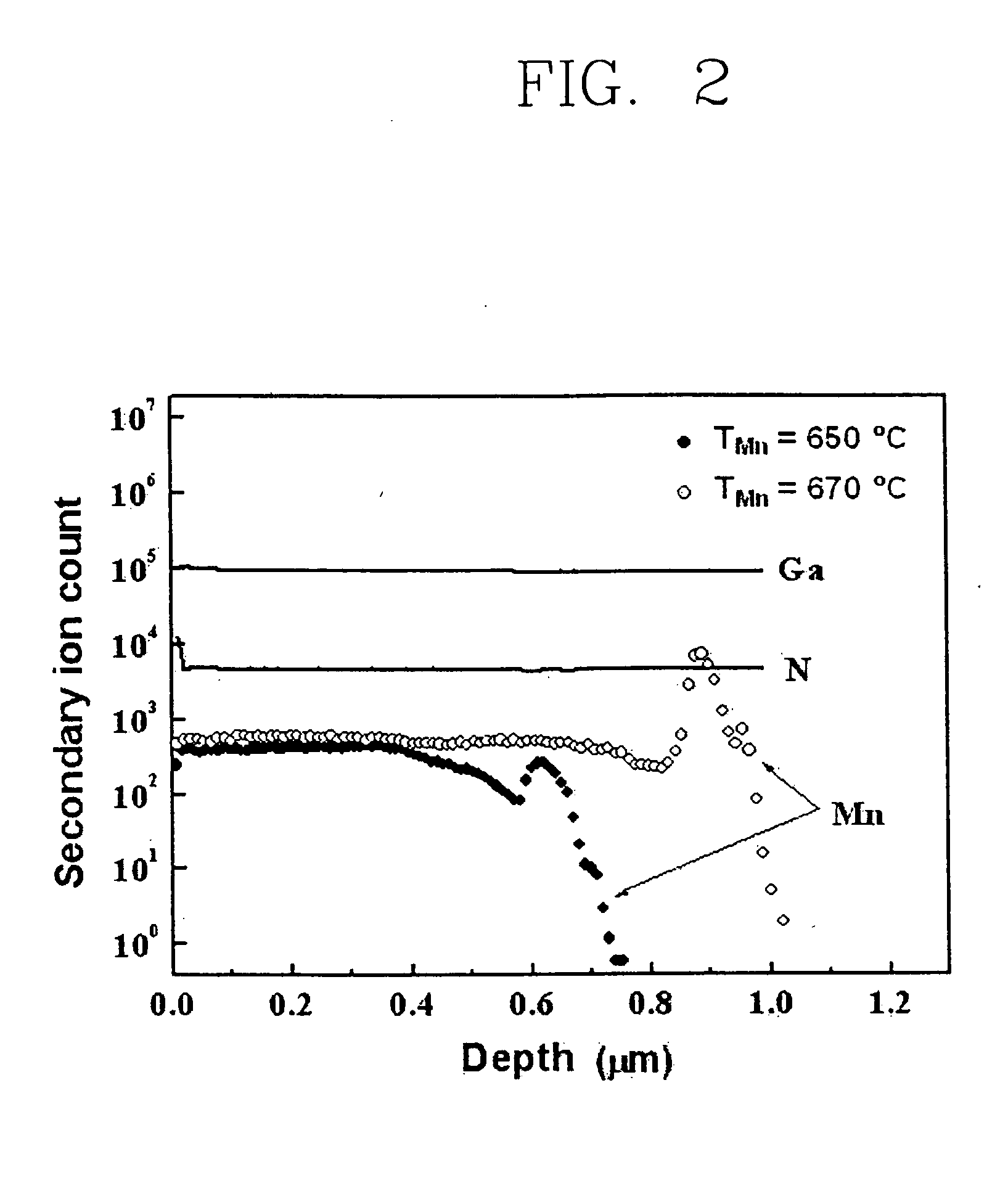
Room temperature ferromagnetic semiconductor grown by plasma enhanced molecular beam epitaxy and ferromagnetic semiconductor based device
InactiveUS20050045976A1Nanostructure applicationNanomagnetismRoom temperatureFerromagnetic semiconductor
A 3 group-5 group compound ferromagnetic semiconductor, comprising one material ‘A’ selected from the group of Ga, Al and In and one material ‘B’ selected from the group consisting of N and P, wherein one material ‘C’ selected from the group consisting of Mn, Mg, Co, Fe, Ni, Cr and V is doped as a material for substituting the material ‘A’, the compound semiconductor has a single phase as a whole. The ferromagnetic semiconductor can be fabricated by a plasma-enhance molecular beam epitaxy growing method and since it shows the ferromagnetic characteristics at a room temperature, it can be applied as various spin electron devices.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY CO LTD
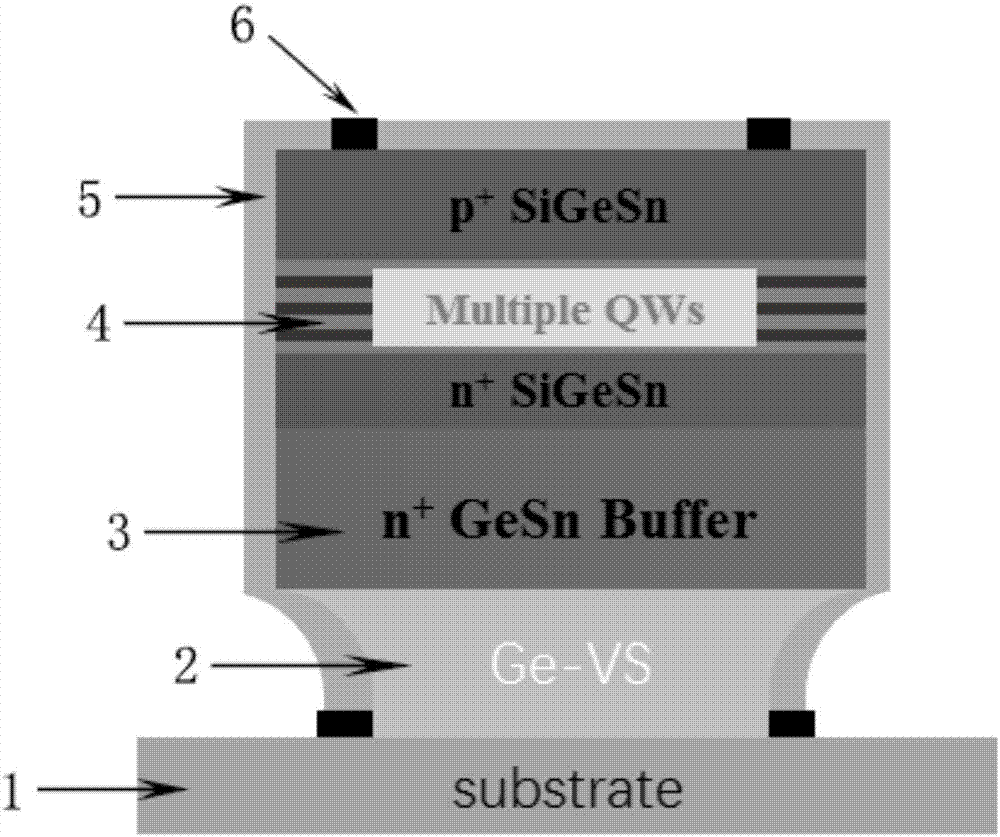
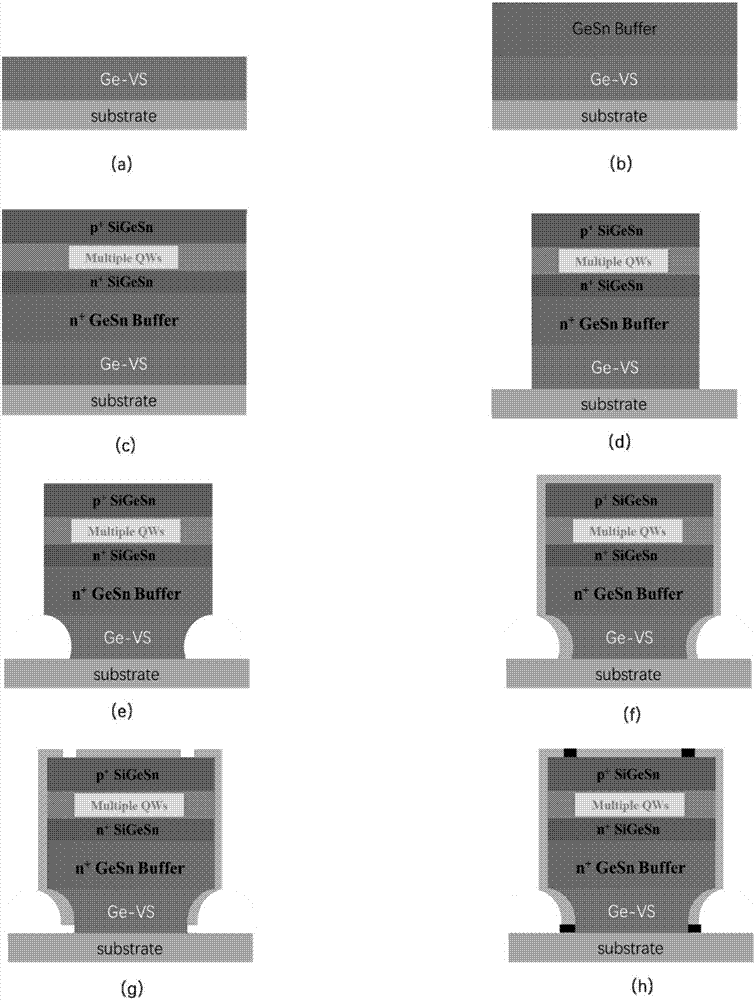
Strain multiple quantum well laser device based on GeSn/SiGeSn material and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN107342535ALower bandgapRedshift working wavelengthLaser active region structureManufacturing technologyPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a strain multiple quantum well laser device based on GeSn / SiGeSn material and a manufacturing method thereof. A barrier layer adopts a GeSiSn material; and the barrier layer adopts a GeSn material. A pseudo substrate (Ge), a buffer layer (GeSn) and an active area (GeSn / GeSiSn) are vertically distributed on a substrate (Si) from bottom to top in sequence, and an Si3N4 tensile stress film is wrapped around the pseudo substrate, the buffer layer and the active area. The manufacturing method of the laser device disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: (1) adopting a low-temperature solid-source molecular beam epitaxy growth technology to grow the GeSn and GeSiSn materials; and (2) adopting a standard laser device manufacturing technology to process the device. Through a multiple quantum well structure and the tensile strain introduced by the additionally added Si3N4 stress film, red shift occurs for the laser wavelength of the laser device, the optical gain of the laser device is obviously improved, and the threshold value is greatly reduced.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
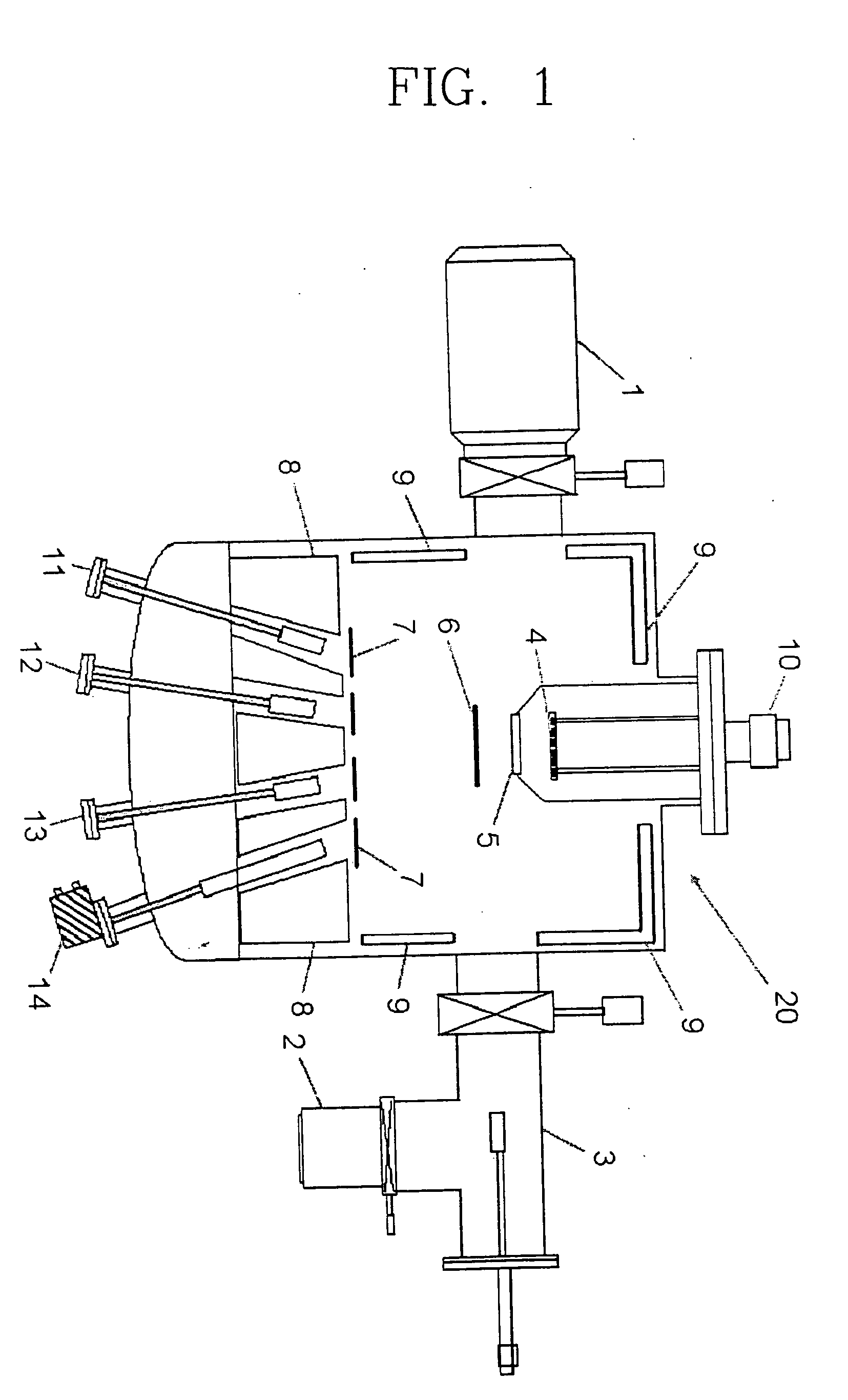
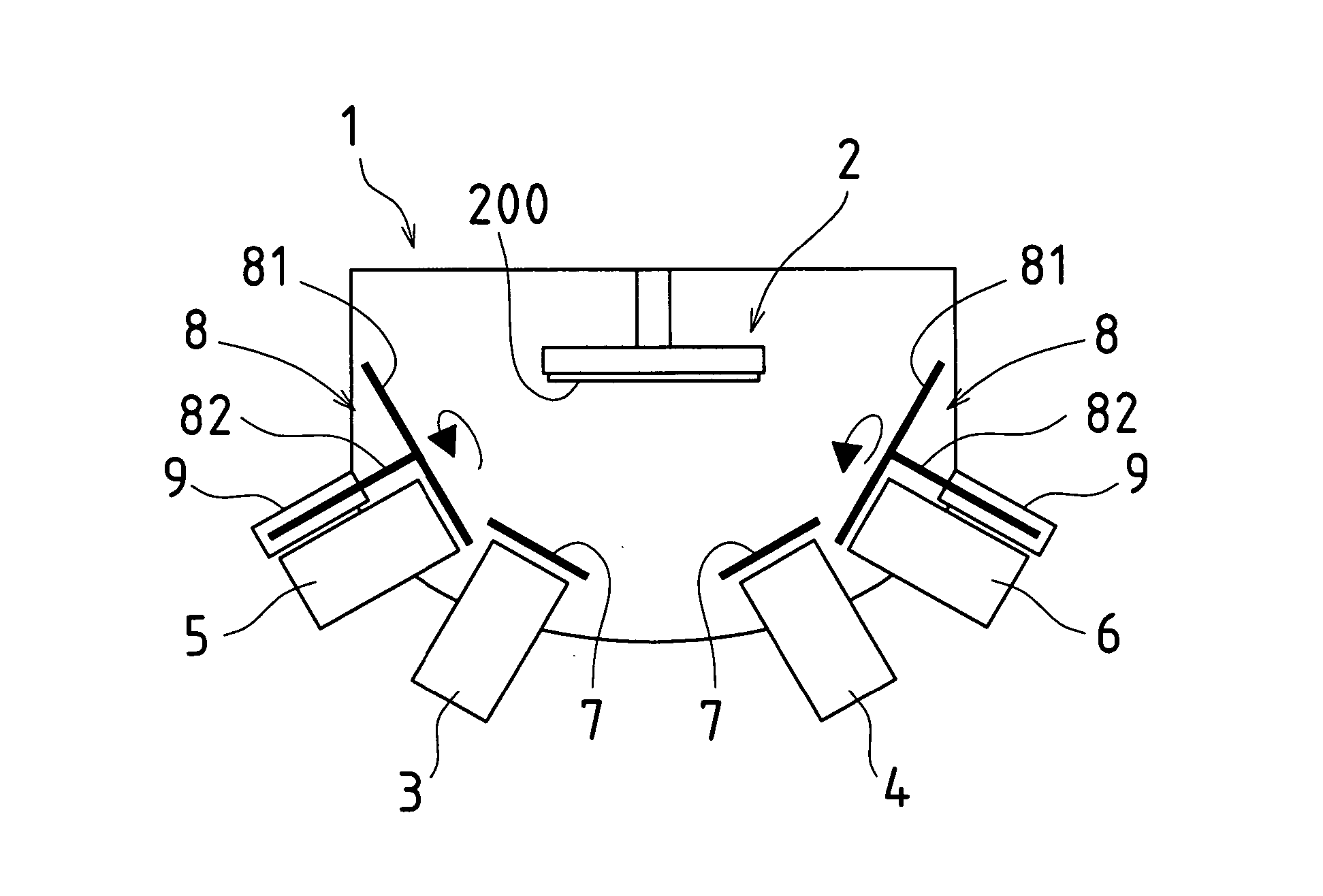
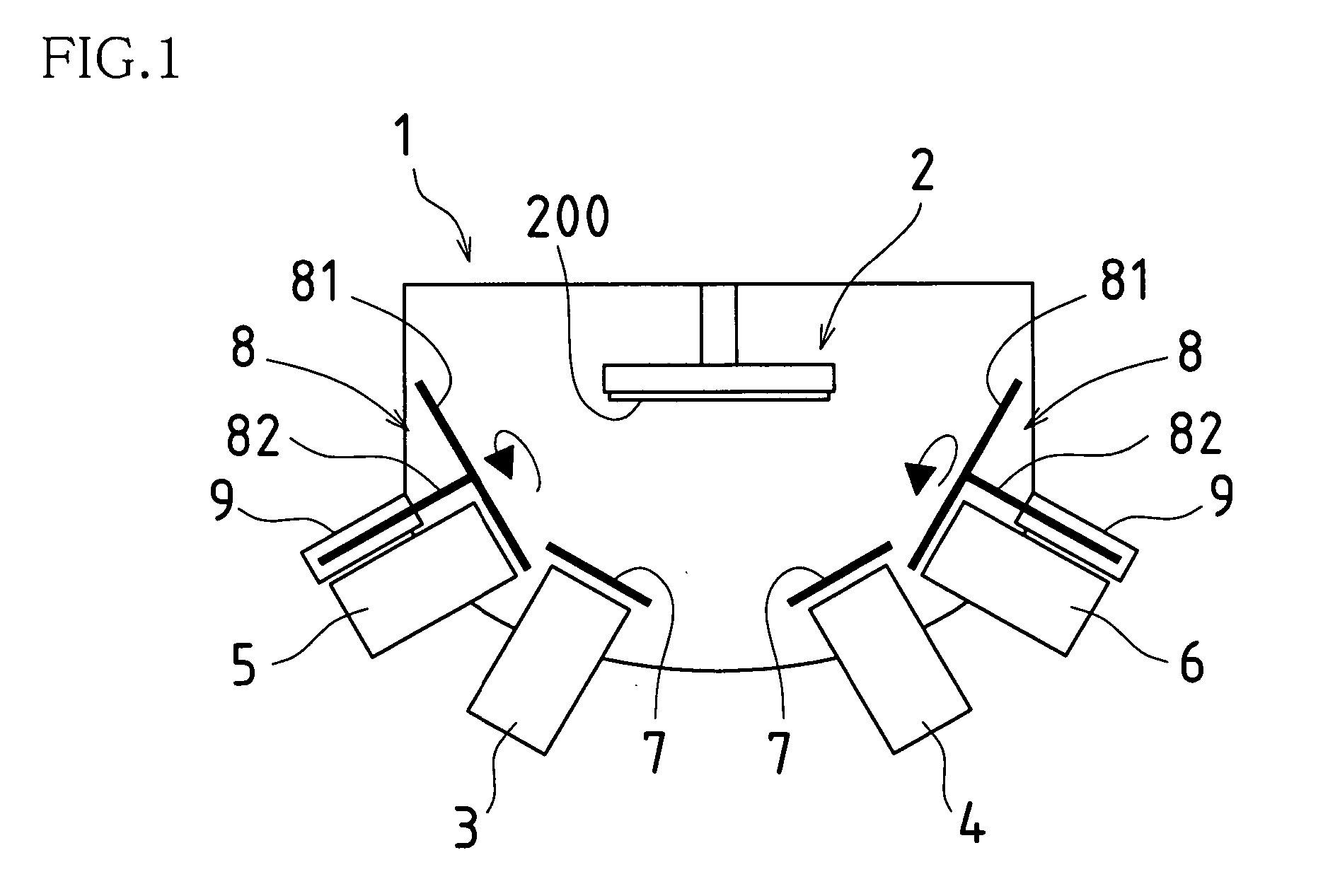
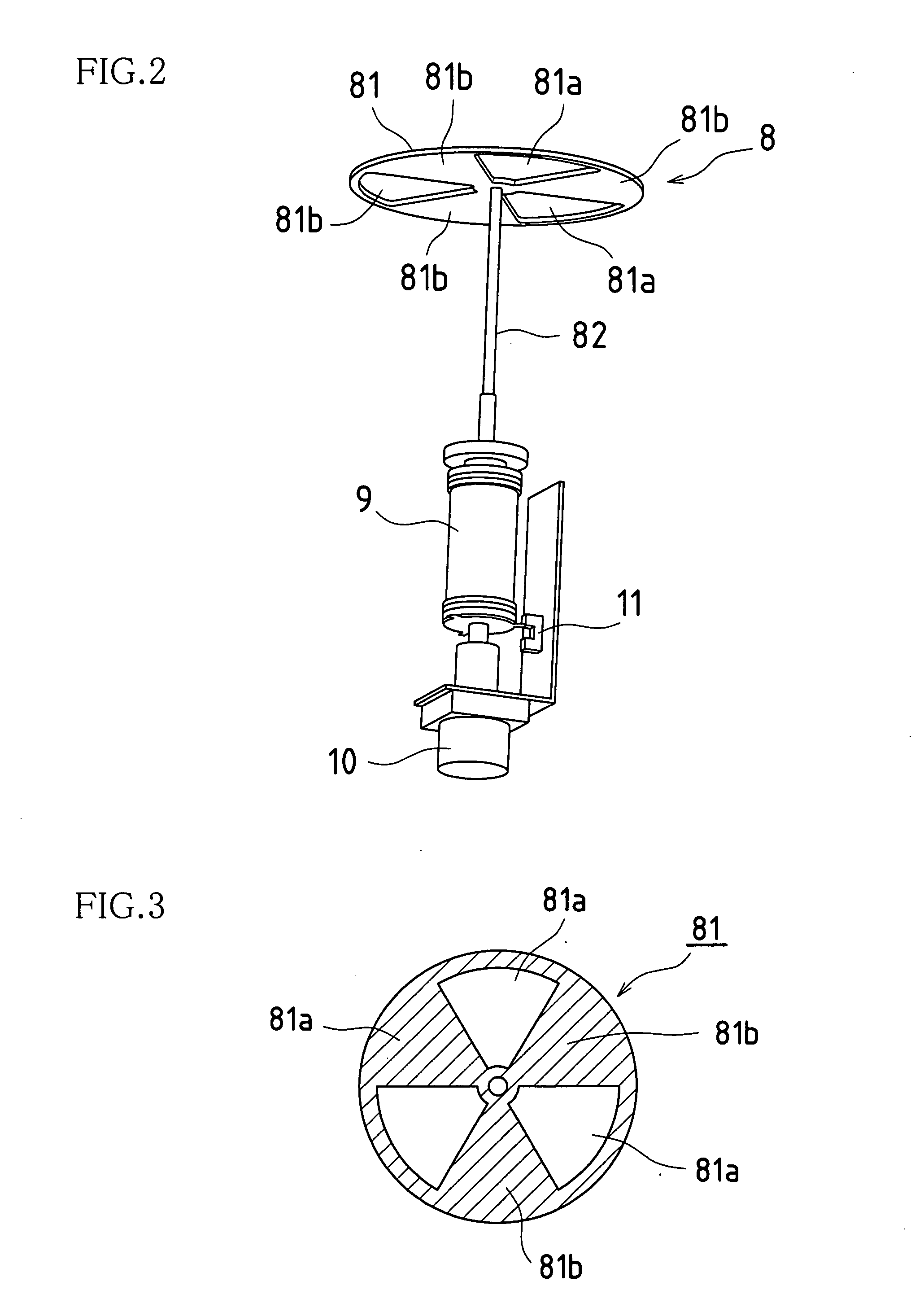
Molecular beam epitaxy growth apparatus and method of controlling same
InactiveUS20050045091A1Control is easy and effectiveRapid and stable and highly reliable intermittency controlAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthAlloyCrystal growth
In system(s) utilizing multiple molecular beams of Group V material(s) (and / or Group VI material(s)), rotary beam chopper(s)) 8 and so forth are installed in front of respective discharge port(s) of such plurality of Group V molecular beam source cell(s) 5, 6 (and / or Group VI molecular beam source cell(s)); intermittency control causing molecular beam(s)) discharged from respective molecular beam source cell(s) 5, 6 to be repeatedly blocked and discharged in periodic fashion is carried out; and mutual synchronization of such molecular beam(s)) subjected to intermittency control causes supply of respective molecular beam(s)) of multiple Group V materials (and / or Group VI materials) in sufficient quantity or quantities as necessary for crystal growth, with alloy ratio(s) within crystal(s) being efficiently controlled.
Owner:SHARP KK
Molecular beam epitaxial (MBE) growth method of Bi element regulated and controlled GaAs-based nanowire crystal structure
InactiveCN103320866AGrowth Made EasyAchieve controlled growthPolycrystalline material growthFrom condensed vaporsNanowireCrystal structure
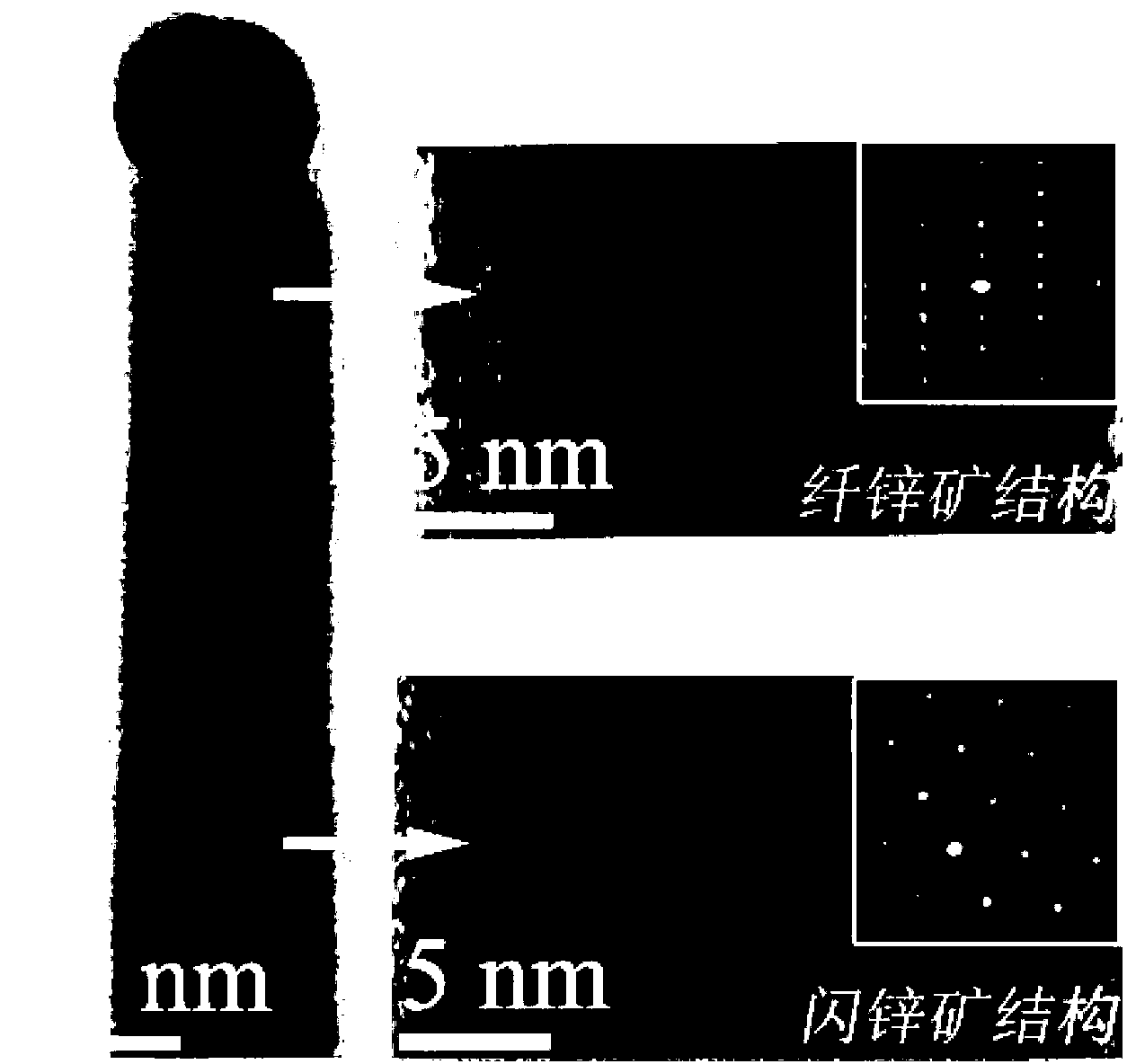
The invention discloses a molecular beam epitaxial (MBE) growth method of a Bi element regulated and controlled GaAs-based nanowire crystal structure. A Bi element is introduced as an activating agent during the growing process of nanowires in an MBE growth chamber, the ionicity of GaAs is reduced, and the formation of a nanowire zinc blende structure is promoted. The method is characterized in that the Bi evaporator source temperature is regulated during the process of nanowire growth according to the beam equivalent partial pressure of a Ga element so as to control the beam equivalent partial pressure of the Bi element and to ensure that the ratio of the beam equivalent partial pressure of the Bi element to that of the Ga element is x, and the value of x can influence the regulating and controlling ability of the Bi element to the nanowire crystal structure and influence the feature and the phase structure purity of the nanowires. The method has the benefits that the growth of the GaAs-bases nanowires with the zinc blende crystal structure can be easily realized without changing the growth process conditions of MBE, and thus the method is beneficial to the controlled growth of the GaAs-based nanowires with the wurtzite and zinc blende structure and the formation of a homogeneous heterophase heterogeneous structure of the nanowires, and provides an excellent material for preparing nanoscale photoelectronic devices.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
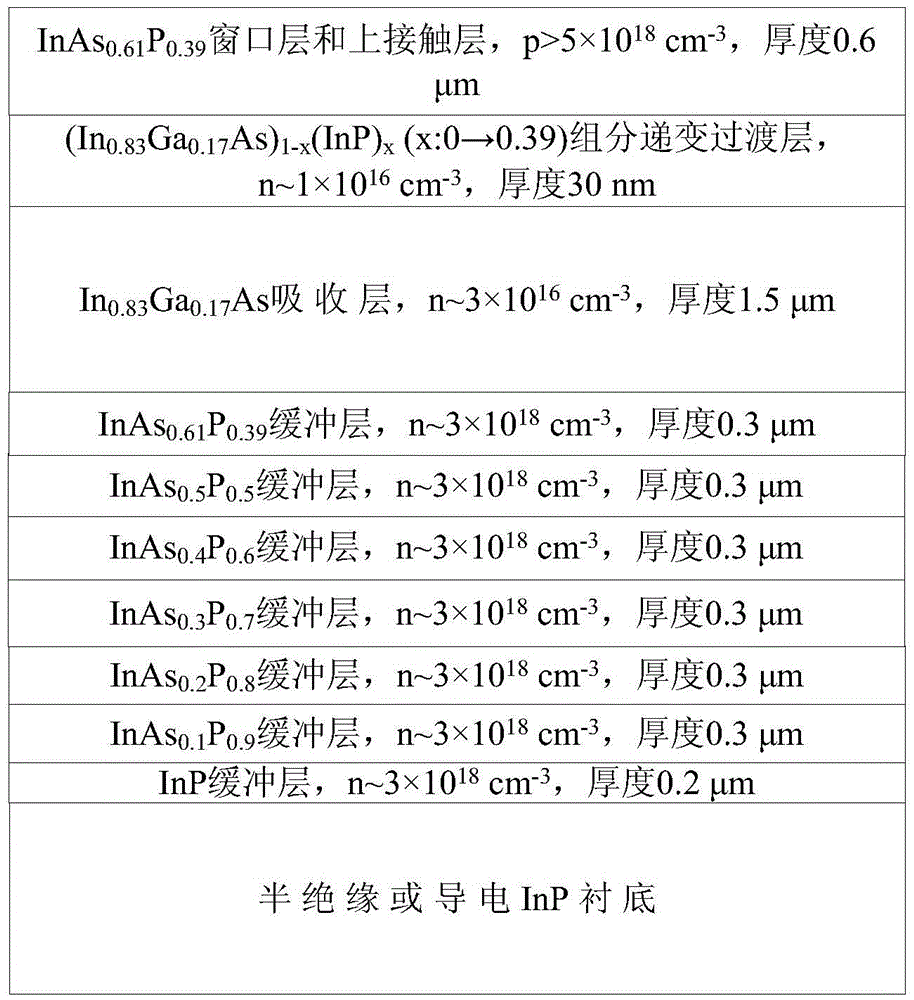
Gas source molecular beam epitaxy material growth method for component progressive transition layer
ActiveCN105609585AReduce blocking effectReduced transit timeFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMaterial growthHeterojunction
The invention relates to a gas source molecular beam epitaxy material growth method for a component progressive transition layer, and the method comprises the steps: growing the component progressive transition layer with one-side or two-side materials of a heterojunction containing two or more types of group-V elements through employing a gas source molecular beam epitaxy growth method, employing two or more gas sources for growth, wherein a group-III beam source is solid, a beam flow is controlled through shutter switching, a group-V beam source is gaseous, and the group-V beam flow intensity or V-III ratio is adjusted through pressure or flow; and obtaining the component progressive transition layer. The component progressive transition layer obtained through the method can effectively alleviate negative effects, caused by energy band peak of a heterogeneous interface or crystal lattice and component abrupt changes in a heterojunction device, on the performance of a device, thereby facilitating the improvement of the performance of the device or the development of a novel device.
Owner:湖南汇思光电科技有限公司
Indium nitride nano column epitaxial wafer grown on aluminum foil substrate and preparation method thereof
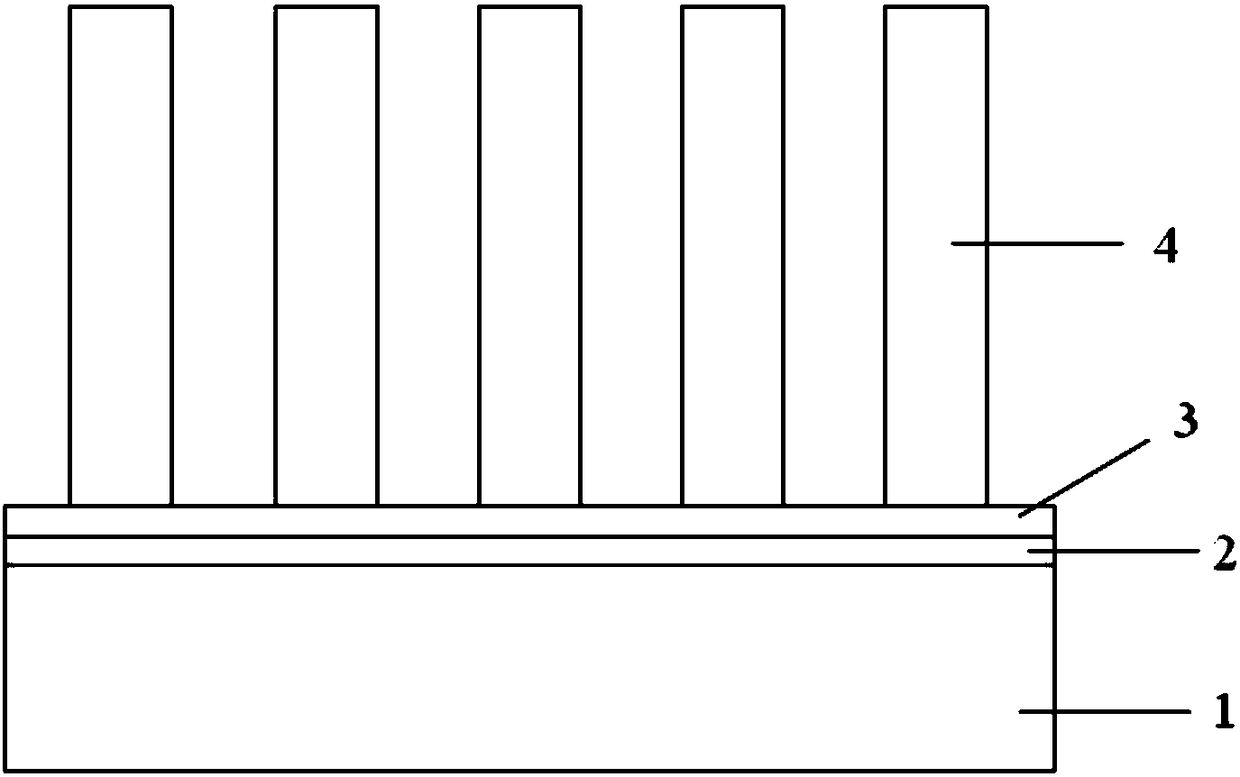
ActiveCN108206130AHelps growReduce defect densityMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureNanopillarSurface oxidation
The invention belongs to the technical field of nitride semiconductor devices and discloses an indium nitride nano column epitaxial wafer grown on an aluminum foil substrate and a preparation method thereof. An InN nano column epitaxial wafer grown on the aluminum foil substrate comprises an aluminum foil substrate, an amorphous aluminum oxide layer, an AlN layer and an InN nano column layer in sequence from bottom to top. The method comprises: 1, pretreating the surface-oxidized aluminum foil, and annealing in situ; 2, adopting a molecular beam epitaxial growth process, wherein the temperature of the substrate is from 400 to 700 DEG C, the pressure of the reaction chamber is from 4.0 to 10.0*10<-5> Torr, and the V / III beam ratio is from 20 to 40, growing the AlN nucleation points on the annealed aluminum foil substrate, and carrying out nucleation and growth of InN nano columns on the AlN. The nano columns of the invention are uniform in diameter and have high crystal quality. The defect density of an InN nano column epitaxial layer is greatly reduced, the radiation composite efficiency of carriers is improved, and the luminous efficiency of the nitride device is greatly improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Cadmium telluride in-situ passivation method of mercury cadmium telluride infrared focal plane chip
ActiveCN101740662ASimple processEasy to operateFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesMercury cadmium tellurideTe element
The invention discloses a cadmium telluride in-situ passivation method of a mercury cadmium telluride (HgCdTe) infrared focal plane chip, which relates to a manufacturing process technology of a photoelectric detector. The invention adopts the technical scheme that the cadmium telluride in-situ passivation method comprises the following steps of: at the end point of a mercury cadmium telluride infrared detection material grown by molecular beam epitaxy, firstly in situ growing a layer of cadmium telluride film on the surface of an HgCdTe film and carrying out nondestructive cadmium telluride in-situ passivation for the cadmium telluride film at a region to be passivated in the preparation process of an HgCdTe infrared detection chip, thereby effectively solving the problems of detection performance loss and low process stability of a mercury cadmium telluride (HgCdTe) infrared focal plane detection chip caused by a conventional cadmium telluride passivation method. The method has the characteristics of simple process, convenient operation, high stability and good passivation effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Two-dimensional ultrafast accurate nonvolatile memory based on self-rectification characteristic material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108649031AAchieve quasi-nonvolatile performanceIncrease write speedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesChemical vapor depositionComputer science
The invention belongs to the technical field of memories, and specifically discloses a two-dimensional ultrafast accurate nonvolatile memory based on a self-rectification characteristic material and apreparation method thereof. The material with a self-rectification characteristic is used for replacing the channel and tunneling layers of a traditional flash memory (Flash), and through a switchingcharacteristic of the material, a tunneling mechanism of traditional charges is replaced to realize ultrafast write-in and accurate nonvolatile memory. The preparation method comprises the followingsteps: firstly using mechanical stripping or chemical vapor deposition to obtain a two-dimensional material as a charge storage layer on a substrate, and then using molecular beam epitaxy to grow theself-rectification characteristic material CrX3 as device channels and switches. The novel memory with ultrafast write-in capacity and accurate nonvolatile characteristic can be prepared, the data storage time span between a dynamic random access memory and a flash memory is remedied, and the novel memory has great application prospects in the field of future memories.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Molecular beam epitaxial growth method of InAs/GaAsSb quantum dots
InactiveCN102509700AStrong electron confinement effectQuantum effect is obviousSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPhotovoltaic detectorsQuantum dot
The invention discloses a molecular beam epitaxial growth method of InAs / GaAsSb quantum dots, belonging to the field of the preparation technology of photoelectric devices. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly preparing a GaAsSb alloy thin layer with low antimony content; and then preparing stress self-assembly GaAs-based InAs / GaAsSb quantum dots by use of the molecular beam epitaxial growth technology for growing InAs quantum dots. In the method, the growth process is determined by thermodynamic parameters, the prepared GaAsSb alloy suffers little influence of technological conditions, the components are easy to control, controllable-density InAs / GaAsSb quantum dots are obtained, and a foundation is laid for the application of antimonide alloy-based InAs quantum dots in the fields of solar cells, photoelectric detectors and the like.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com