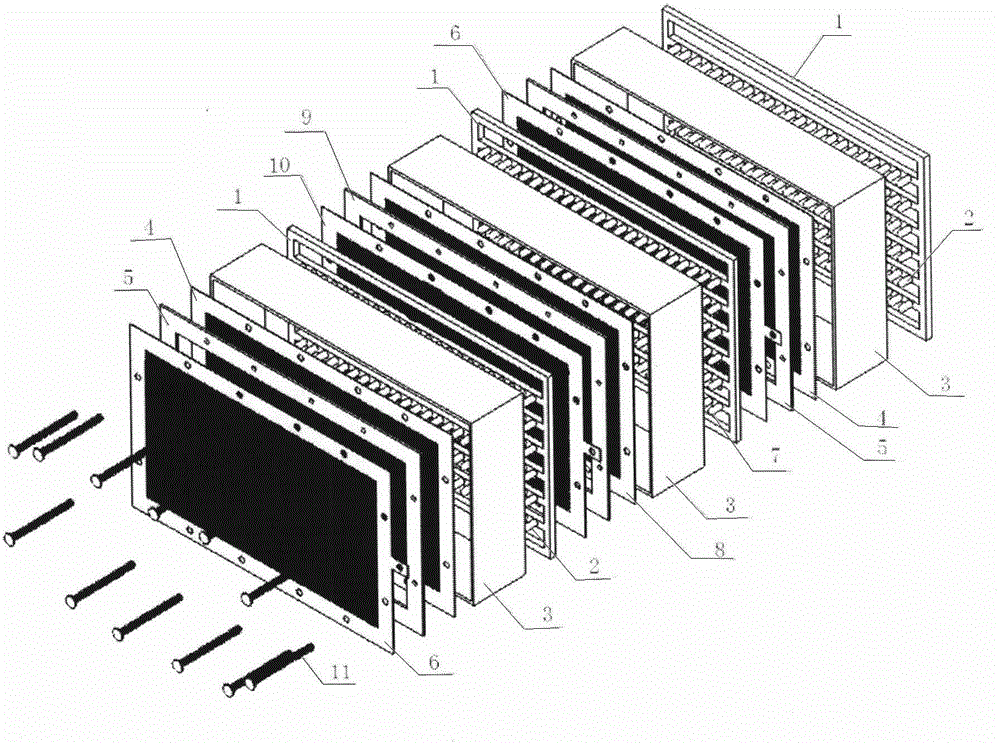
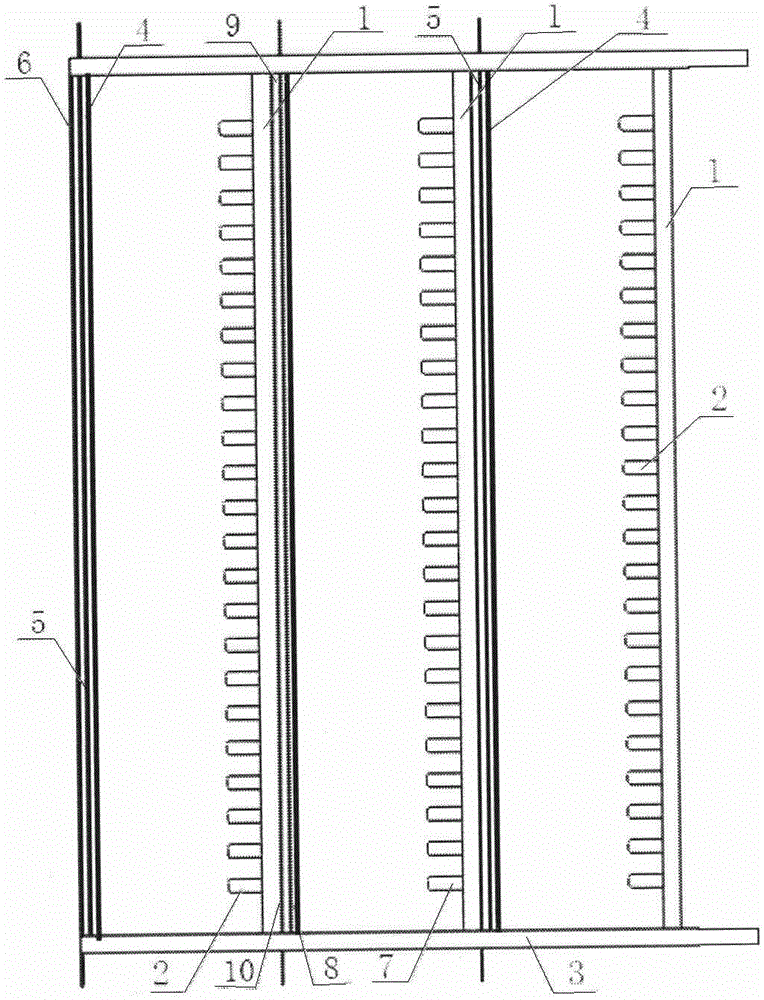
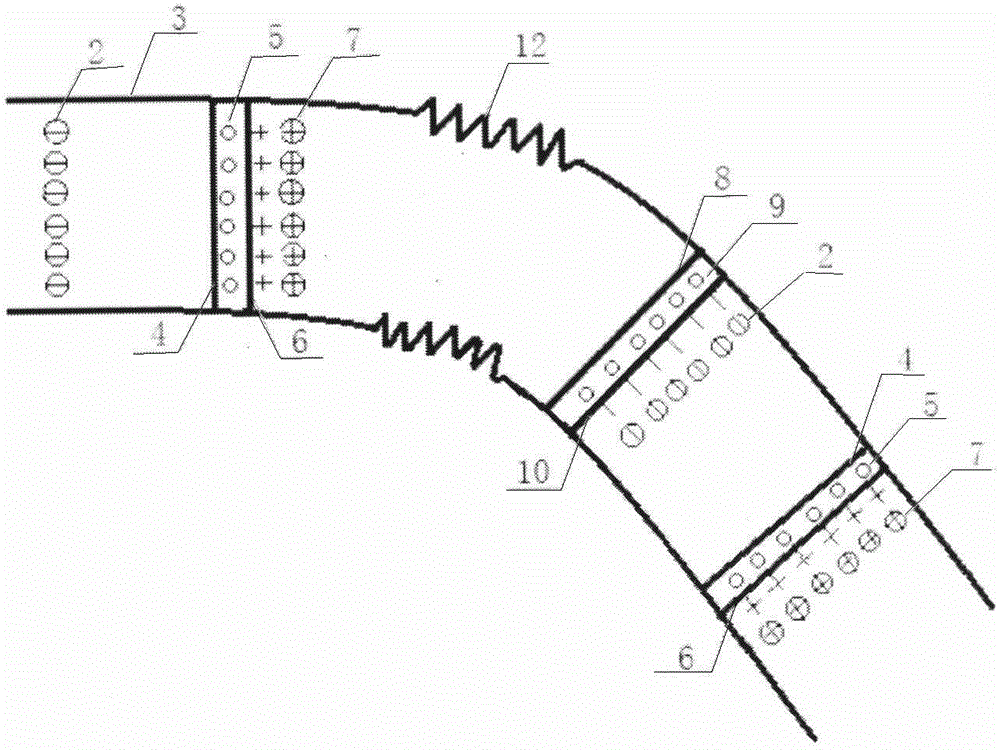
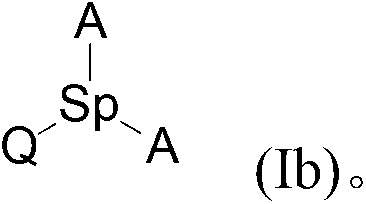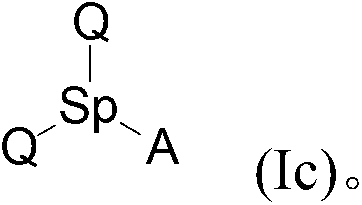Patents
Literature
89 results about "Nitrogen molecule" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A molecule of nitrogen gas is made up of two nitrogen atoms. There are other molecules in the atmosphere that have nitrogen atoms in them too, such as nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO 2 ).
Preparation method and use of carbon molecular sieve
InactiveCN101935032ASolve the problem of difficult and efficient separation of methane-nitrogenNitrogen purification/separationOther chemical processesHigh concentrationLoss rate
The invention relates to a preparation method and use of a carbon molecular sieve. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a conventional carbon molecular sieve; and expanding the pores in the conventional carbon molecular sieve by using a secondary activation technique and modifying the conventional carbon molecular sieve by adjusting the pores. The new carbon molecular sieve is prepared by using coal, coconut shell or phenolic resin, and the like as raw materials, by the conventional production steps of crushing, forming, carbonizing, steam activating, hydrocarbon settling and shrinking and the like and by secondary activation with KOH or CO2 as an activator. The activation temperature is between 550 and 850 DEG C; and the ignition loss rate of the product is kept be between 0.1 and 30 percent. In aspect of use, the carbon molecular sieve can be used for absorbing nitrogen molecules and can also be used for absorbing and separating methane and nitrogen in seam gas under a variable pressure while achieving an adsorption dynamic separation effect and allowing high-concentration methane gas to be collected at the exit of an adsorption tower directly; and thus, the methane in the seam gas can be used efficiently.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Adsorbing material for effectively adsorbing formaldehyde and other harmful substances in air
The invention relates to an adsorbing material for effectively adsorbing formaldehyde and other harmful substances in the air, belonging to the field of the adsorbing material for improving the air quality. The adsorbing material has the technical scheme that the material is characterized by comprising the raw materials based on the parts by weight: 10-20 parts of zeolite, 20-30 parts of sepiolite, 15-25 parts of diatomite, 10-15 parts of bentonite, 15-25% of active carbon and 6-12 parts of silicasol, wherein the silicasol is nanoscale silicon dioxide colloid water solution. The technical scheme also comprises the raw materials based on the parts by weight: 10-15 parts of higher molecular weight organic amine polymer with the molecular weight of 1800-50000, 5-10 parts of active carbon fiber and 10-20 parts of non-woven fabrics. The invention selects the substances with very strong adsorbing function and designs a set of formulation according to the different adsorption capacity and selectivity of the substances, so as to lead the substances to be matched with each other for adsorbing common indoor pollution gases such as formaldehyde, benzenes, hydrocarbons, other organic gas molecules larger than oxygen and nitrogen molecules in the air as well as virus bacterium and fine dust, thus purifying the indoor air, preventing decoration disease and improving the health level of residents.
Owner:傅桂云 +1
Plasma modified medical devices and methods
InactiveUS20130046375A1Increased apoptosisGood biocompatibilitySurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismActive agentThrombus
Coatings, devices and methods are provided, wherein the contacting surface of a medical device with at least one contacting surface for contacting a bodily fluid or tissue, wherein long-lasting and durable bioactive agents or functional groups are deposited on the contacting surface through a unique two-step plasma coating process with deposition of a thin layer of plasma coating using a silicon-containing monomer in the first step and plasma surface modification using a mixture of nitrogen-containing molecules and oxygen-containing molecules in the second step. The two-step plasma coating process enables the implantable medical device to prevent both restenosis and thrombosis under clinical conditions. The invention also relates to surface treatment of metallic and polymeric biomaterials used for making of medical devices with significantly improved clinical performance and durability.
Owner:CHEN MENG
Atmospheric pressure induced air dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) low temperature plasma generation device
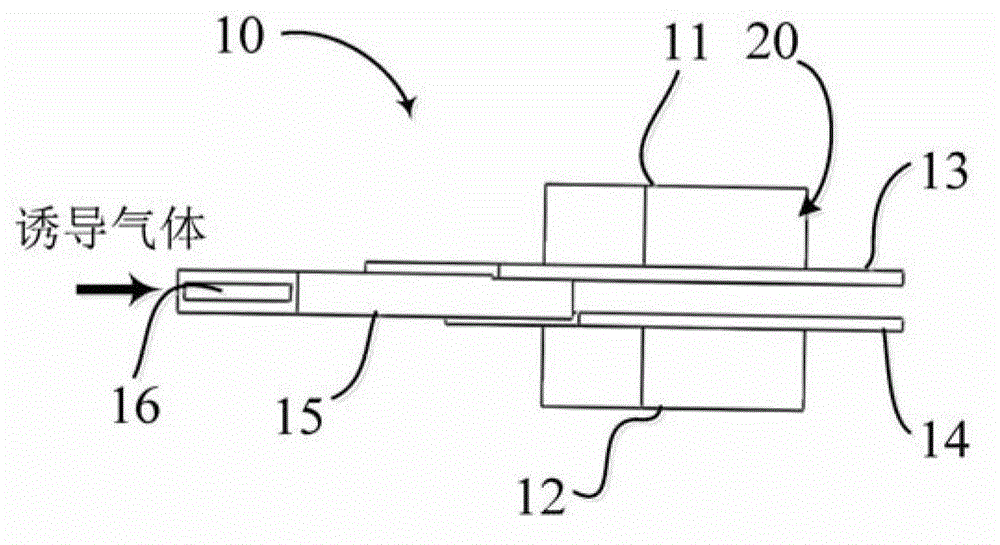
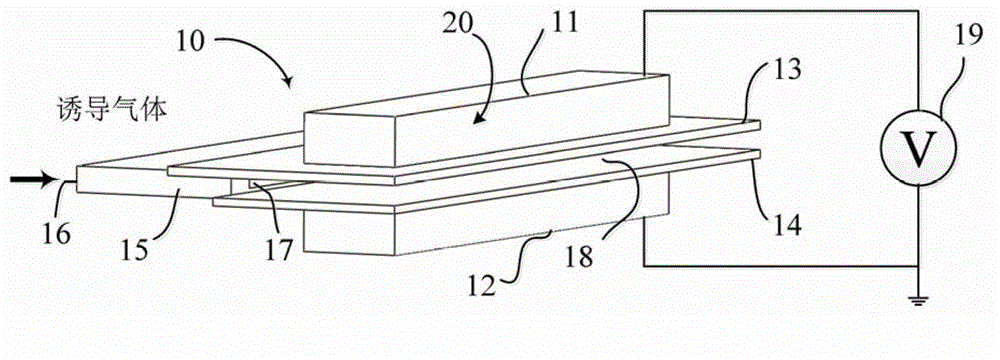
The invention aims to provide an atmospheric pressure induced air dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) low temperature plasma generation device. The device comprises a discharge unit provided with a DBD electrode structure and a narrow slit cavity body connected to the front end of the discharge unit, wherein the discharge unit comprises two oppositely-arranged plate electrodes; an insulation medium plate used for limiting a discharge current between the two plate electrodes is fixedly arranged on the plane of the inner side of a high voltage electrode; a sample to be processed, which is plate-shaped, is movably mounted on the plane of the inner side of a grounding electrode in a manner of being parallel and opposite to the insulation medium plate; the narrow slit cavity body is provided with a gas inlet port used for connecting induced gas into the narrow slit cavity body, and a narrow-slit-shaped gas outlet port; and the gas outlet port is embedded between the insulation medium plate and the sample to be processed. The plasma generation device provided by the invention can produce evenly-dispersed plasma; and the plasma is rich in active species such as metastable-state nitrogen molecules, hydroxyl radicals and oxygen atoms, and can be used for conducting material surface modification, sterilization, disinfection, and the like.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
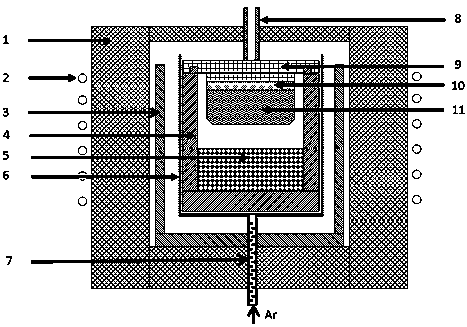
Growth device and growth method for preparing high-purity semi-insulating carbonized silicon single crystals efficiently
ActiveCN107723798AReduce nitrogen impurity contentImprove efficiencyPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsSingle crystalNitrogen gas
The invention discloses a growth device and a growth method for preparing high-purity semi-insulating carbonized silicon single crystals efficiently. The growth method is implemented by the carbonizedsilicon single crystal growth device with a structure of an inert gas graphite flow guide tube and a graphite current-limiting cover. Inertia gases generate forced convection under the action of thestructure, and a forced convection layer is formed on the outer wall of a graphite crucible. When speed and flow of the gas convection are high, influences of diffusion on concentration distribution can be inhibited. In the method, directional movement of the forced convection layer can prevent nitrogen molecules outside the graphite crucible from dispersing into the graphite crucible, so that theproblem that adsorption nitrogen serves as a pollution source in a heat insulating system is solved. According to the method, an inertia-gas atmosphere isolation room system is not needed, and a long-term nitrogen removal process based on furnace vacuumizing is also not needed. The growth device and the growth method have the advantages of high efficiency and equipment simplicity, and can be widely applied to multiple carbonized silicon single crystal furnace systems in the field.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP NO 46 RES INST
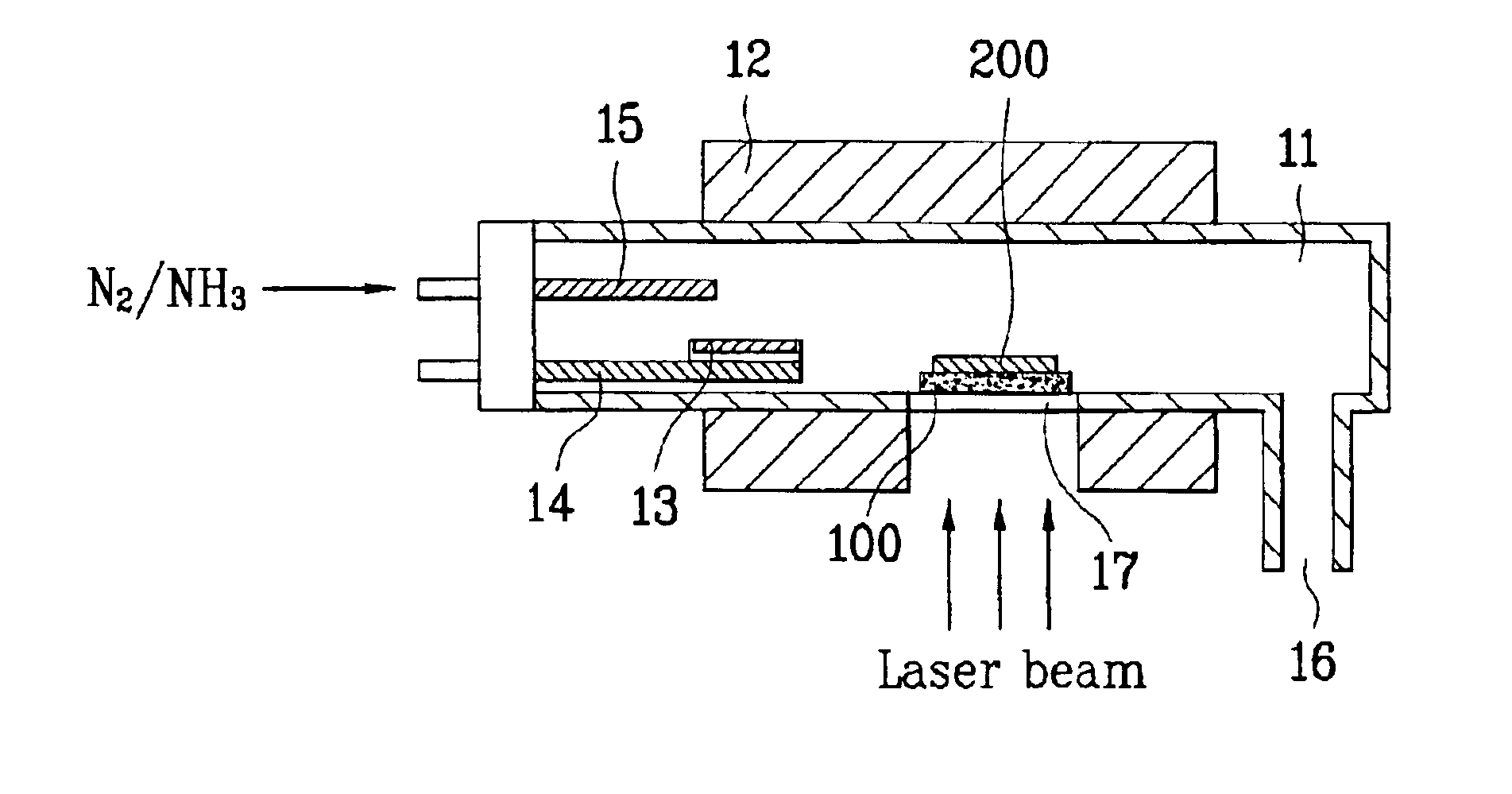
Apparatus for manufacturing GaN substrate and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS6923859B2Prevent micro-cracksAvoid bendingRadiation applicationsBy zone-melting liquidsChemical reactionOptoelectronics
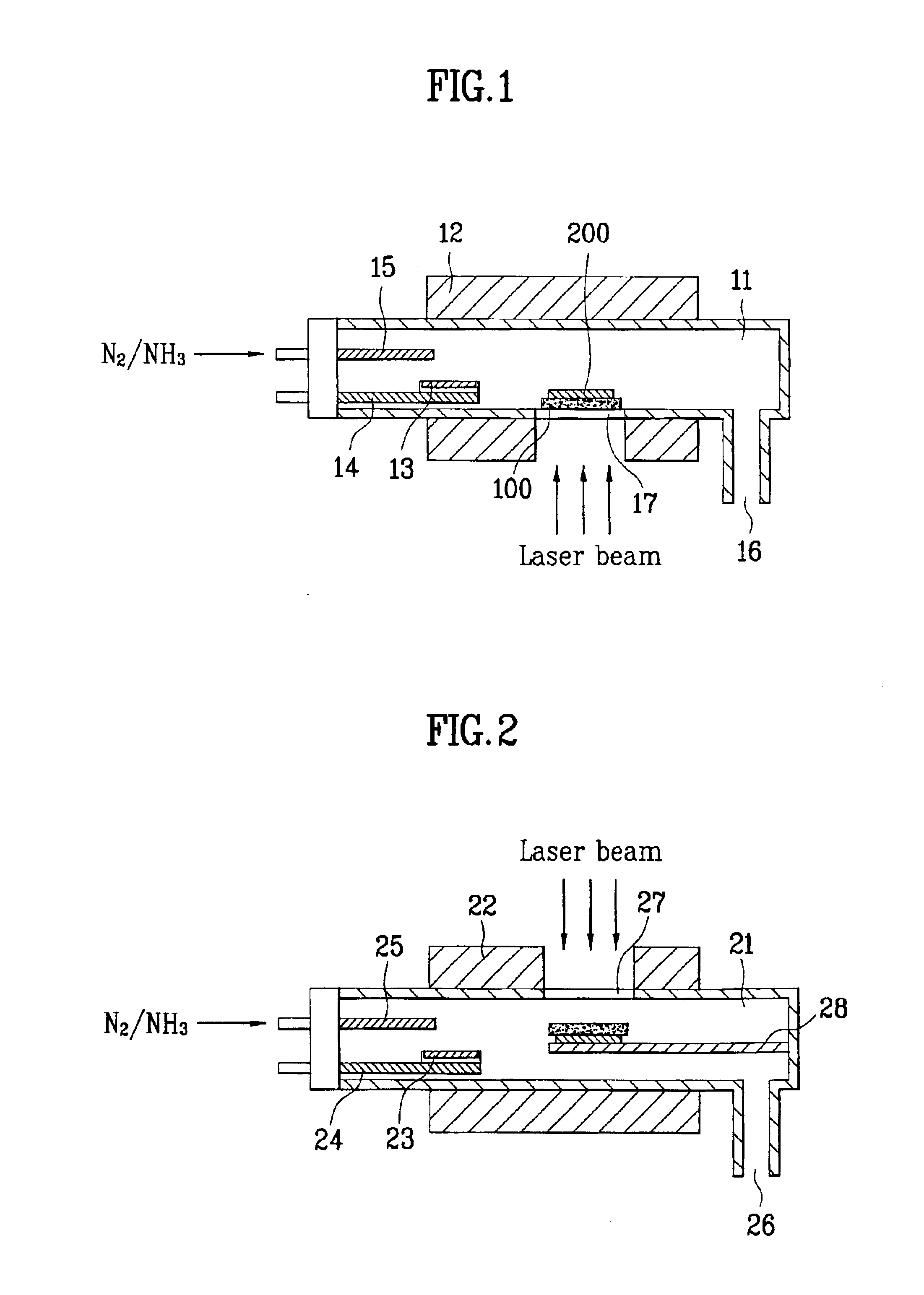
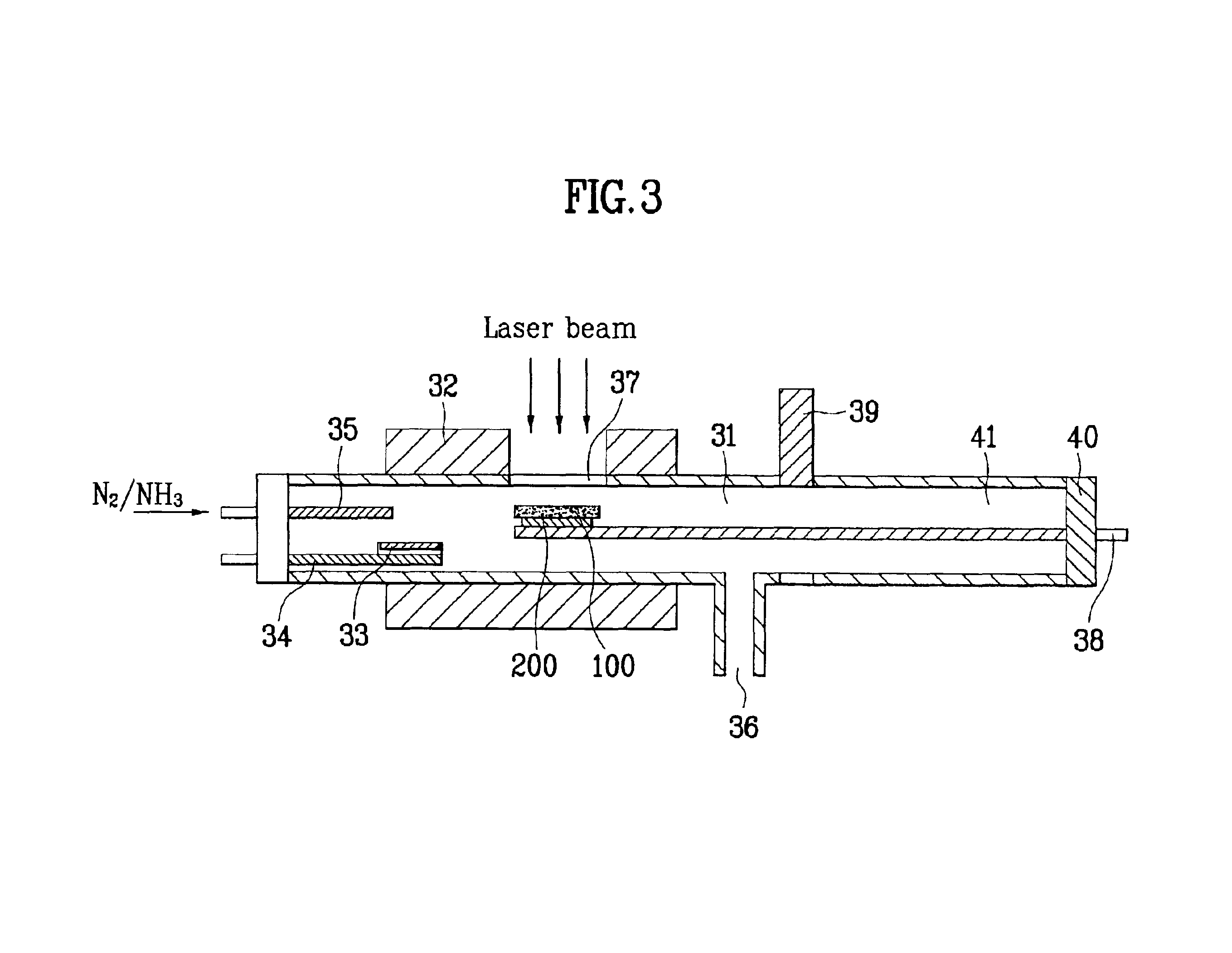
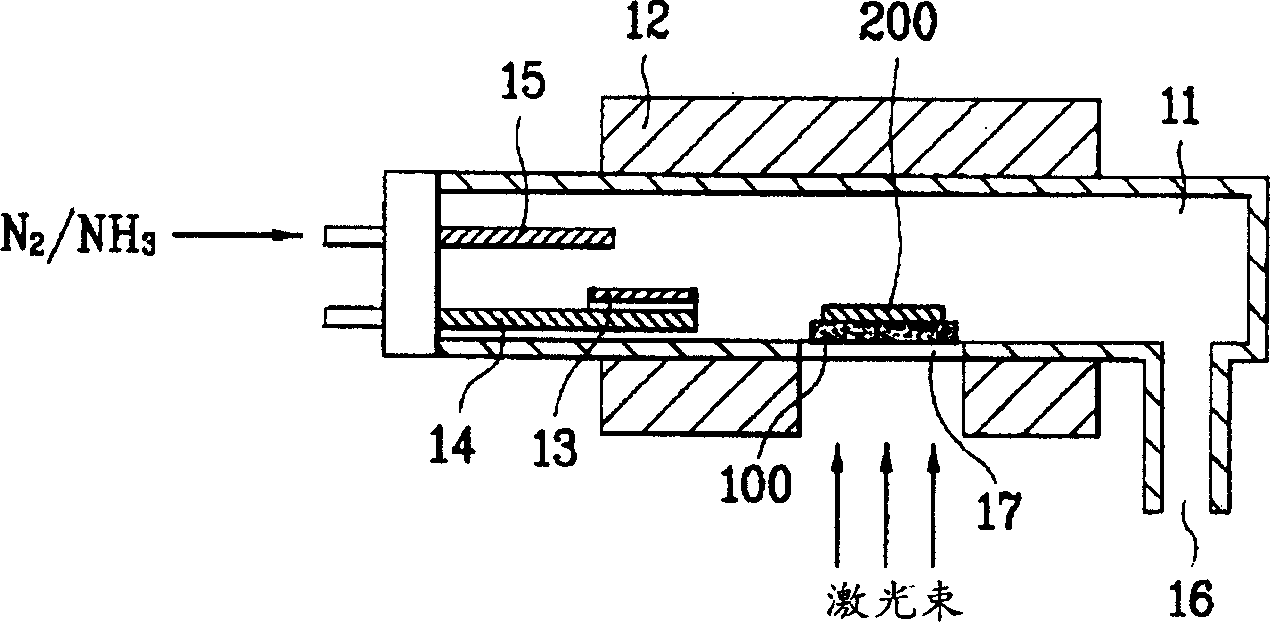
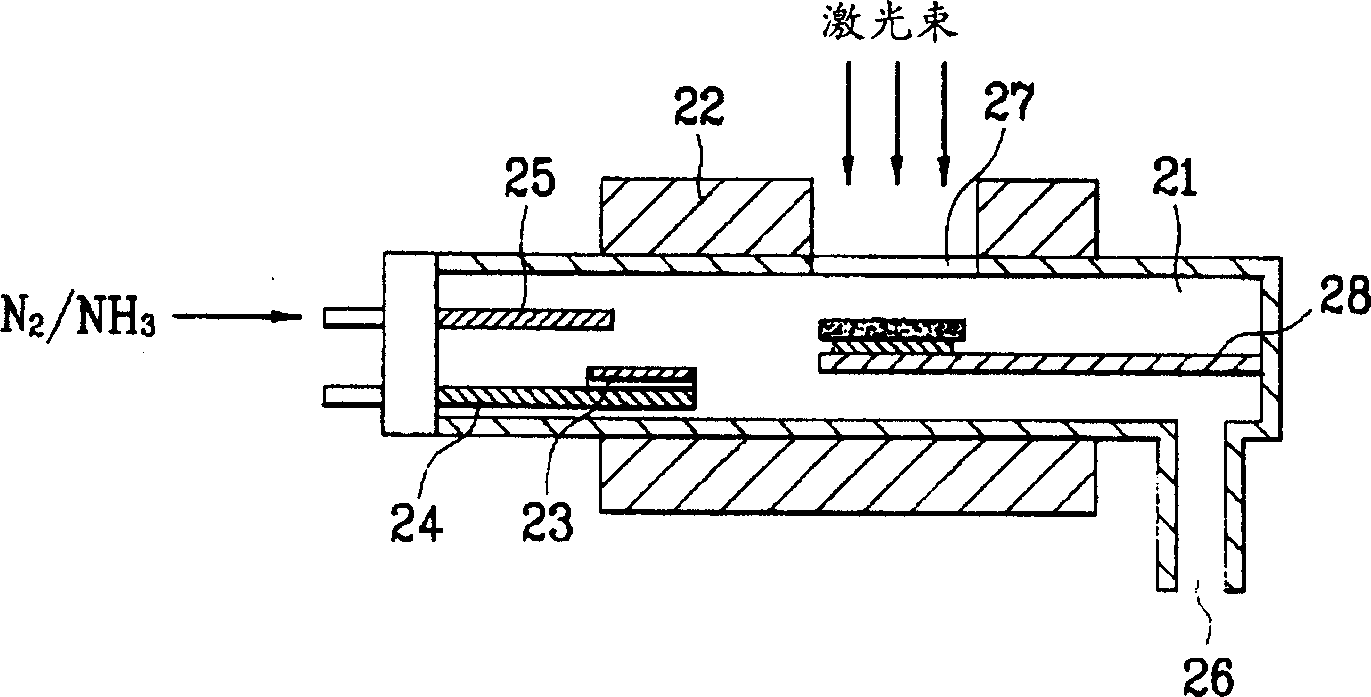
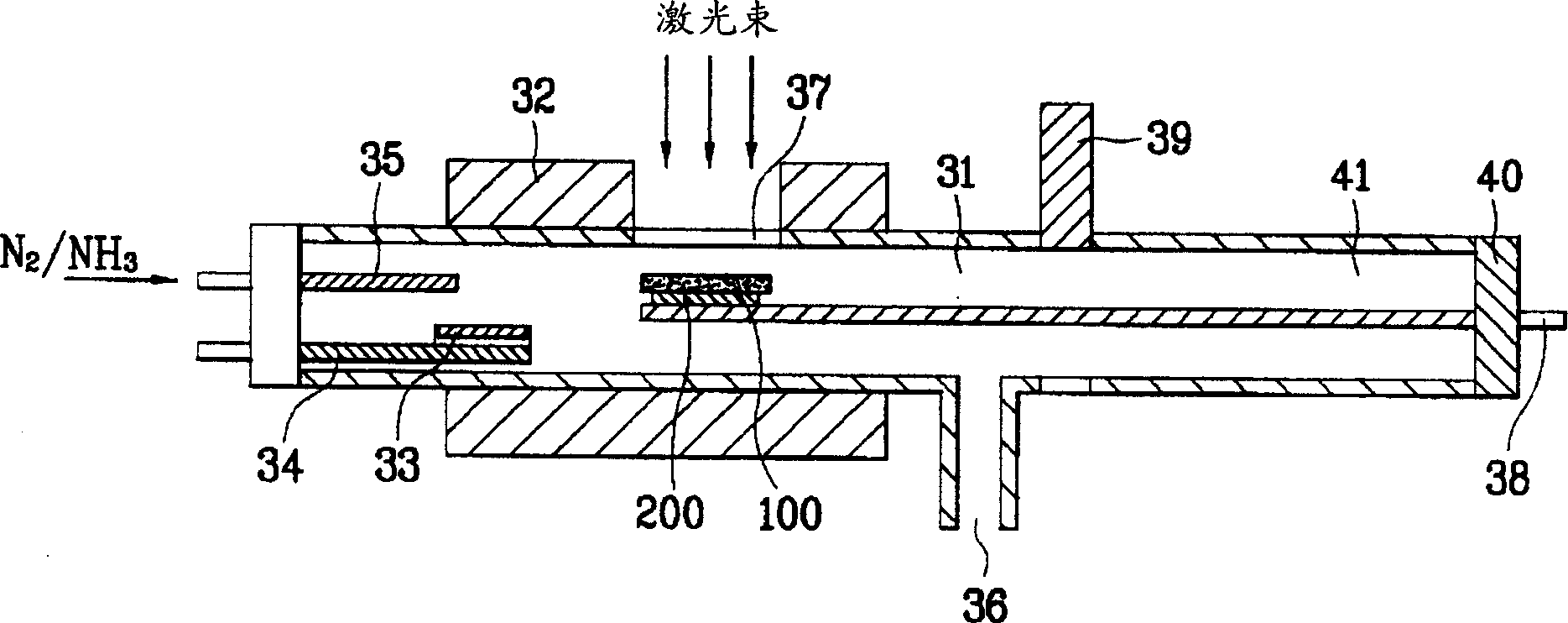
Disclosed are an apparatus for manufacturing GaN substrate and a manufacturing method thereof enabling to prevent micro-cracks or bending of a GaN substrate by separating a substrate and a GaN layer from each other after growing the GaN layer on the substrate in the same chamber. The present invention includes a chamber for loading a substrate therein, a heating means heating the chamber, a Ga boat installed inside the chamber to receive a Ga molecule producing material, an injection pipe injecting a nitrogen molecule producing gas in the chamber, the nitrogen molecule producing gas reacting chemically on the Ga molecule producing material to form a GaN layer on the substrate, and a transparent window at a circumference of the chamber to apply a laser beam to the substrate.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method for preparing thermoplastic elastomer foamed beads
The invention discloses a method for preparing thermoplastic elastomer foamed beads. According to the method, carbon dioxide and nitrogen mixed gas can be retained inside foamed bead bubbles, so that volume shrinkage of the foamed bead bubbles in the air exchange process is inhibited, and large expansion ratio is maintained. The method includes the steps: dipping thermoplastic elastomer beads in high-pressure nitrogen atmosphere at normal temperature; placing the thermoplastic elastomer beads sufficiently absorbing nitrogen in carbon dioxide in a super-critical state, performing swelling diffusion and inducing the thermoplastic elastomer beads dissolving the nitrogen and the carbon dioxide to expand in a foaming manner to prepare the thermoplastic elastomer foamed beads. The nitrogen and carbon dioxide mixed gas is retained inside the thermoplastic elastomer foamed beads, a bubble structure is supported by nitrogen molecules in the bubbles in the process of gas exchange with external air in a natural environment, and high product foaming ratio is maintained.
Owner:HANGZHOU BOSTE NEW MATERIALS TECH CO LTD
Conductive pattern formation ink, conductive pattern and wiring substrate
InactiveUS20090145638A1Improve reliabilityStably ejectedNanotechConductive layers on insulating-supportsWater basedGas analysis
A conductive pattern formation ink which can be stably ejected in the form of liquid droplets and form a conductive pattern having high reliability, a conductive pattern having high reliability, and a wiring substrate provided with the conductive pattern and having high reliability are provided. The conductive pattern formation ink is used for forming a conductive pattern by ejecting the ink in the form of liquid droplets on a surface of a ceramic molded body using a liquid droplet ejecting method, the ceramic molded body being made of a material containing ceramic particles and a binder. The ink contains a water-based dispersion medium, and metal particles dispersed in the water-based dispersion medium, wherein the water-based dispersion medium contains oxygen molecules and nitrogen molecules, and wherein when the water-based dispersion medium is analyzed using a gas chromatography method, a total amount of the oxygen and nitrogen molecules contained in the water-based dispersion medium is 12 ppm or less.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Diamond single crystal, method for producing the same, and single crystal diamond tool
ActiveUS20150176155A1High hardnessEasy to processPolycrystalline material growthLayered productsGas phaseTransmittance
A method for producing a diamond single crystal includes implanting an ion other than carbon into a surface of a diamond single crystal seed substrate and thereby decreasing the transmittance of light having a wavelength of 800 nm, the surface having an off-angle of 7 degrees or less with respect to a {100} plane, and homoepitaxially growing a diamond single crystal on the ion-implanted surface of the seed substrate using a chemical vapor synthesis under synthesis conditions where the ratio NC / NH of the number of carbon-containing molecules NC to the number of hydrogen molecules NH in a gas phase is 10% or more and 40% or less, the ratio NN / NC of the number of nitrogen molecules NN to the number of carbon-containing molecules NC in the gas phase is 0.1% or more and 10% or less, and the seed substrate temperature T is 850° C. or more and less than 1000° C.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording device
InactiveUS20060154113A1Improve recording effectImprove uniformityRecord information storageMagnetic recordingOxygenRecording layer
A perpendicular magnetic recording medium and a magnetic recording device with the medium are disclosed. Ferromagnetic crystal grains in a granular magnetic recording layer are grown with a constant grain diameter in a columnar shape, and the nonmagnetic grain boundaries comprise at least two types of oxides or nitrides, preferably of elements selected from Cr, Si, Al, Ti, Ta, Hf, Zr, Y, Ce, and B. The maximum G1 of absolute values of standard Gibbs free energy of formation for oxidation of ferromagnetic elements composing the ferromagnetic crystal grains, the minimum G2 and the second smallest G3 of absolute values of standard Gibbs free energy of formation per 1 mol of oxygen molecules for oxidation of elements composing the nonmagnetic grain boundaries satisfy inequalities G1<G2<G3 and (G2−G1)>(G3−G2) and G3−G2 is preferably smaller than 200 kJ / mol. The oxides can be replaced by nitrides, in which case the maximum G11 of absolute values of standard Gibbs free energy of formation per one mole of nitrogen molecules in nitridation of ferromagnetic elements composing the ferromagnetic crystal grain, and the minimum G12 and the second smallest G13 of absolute values of standard Gibbs free energy of formation per one mole of nitrogen molecules in nitridation of elements composing the nonmagnetic grain boundary satisfy the following inequalities G11<G12<G13 and (G12−G11)>(G13−G12), and G13−G12 is preferably smaller than 200 kJ / mol.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC DEVICE TECH CO
On-board oxygen production system for aircraft, in particular long-range aircraft
Method and system on board an aircraft for the production of an oxygen-enriched gas stream from an oxygen / nitrogen gas mixture, particularly air, comprising at least one adsorber containing at least one adsorbent for adsorbing at least some of the nitrogen molecules contained in the oxygen / nitrogen feed mixture, characterized in that the adsorbent comprises a faujasite-type zeolite, having a Si / Al ratio of 1 to 1.50, exchanged to at least 80% with lithium cations. Aircraft equipped with such a system, in particular an airliner, especially an airliner of the long-range, large-capacity type.
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE
Method of growing an active region in a semiconductor device using molecular beam epitaxy
InactiveUS20090256165A1NanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialNitrogen
A method of making an (Al, Ga, In)N semiconductor device having a substrate and an active region is provided. The method includes growing the active region using a combination of (i) plasma-assisted molecular beam epitaxy; and (ii) molecular beam epitaxy with a gas including nitrogen-containing molecules in which the nitrogen-containing molecules dissociate at a surface of the substrate at a temperature which the active region is grown.
Owner:SHARP KK
Graft polymer to which combined nitrogen molecules are grafted
The present invention relates to a modified polymer produced by grafting a compound thereto, said compound including at least one group Q and at least one group A bonded together by at least one, and preferably only one, spacer group Sp, where: Q includes a dipole containing at least one, and preferably only one, nitrogen atom capable of being grafted onto the polymer chain by [l,3]-dipolar cycloaddition; A includes a combined group that includes at least one nitrogen atom; and Sp is an atom or a group of atoms forming a bond between Q and A.
Owner:MICHELIN & CO CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN
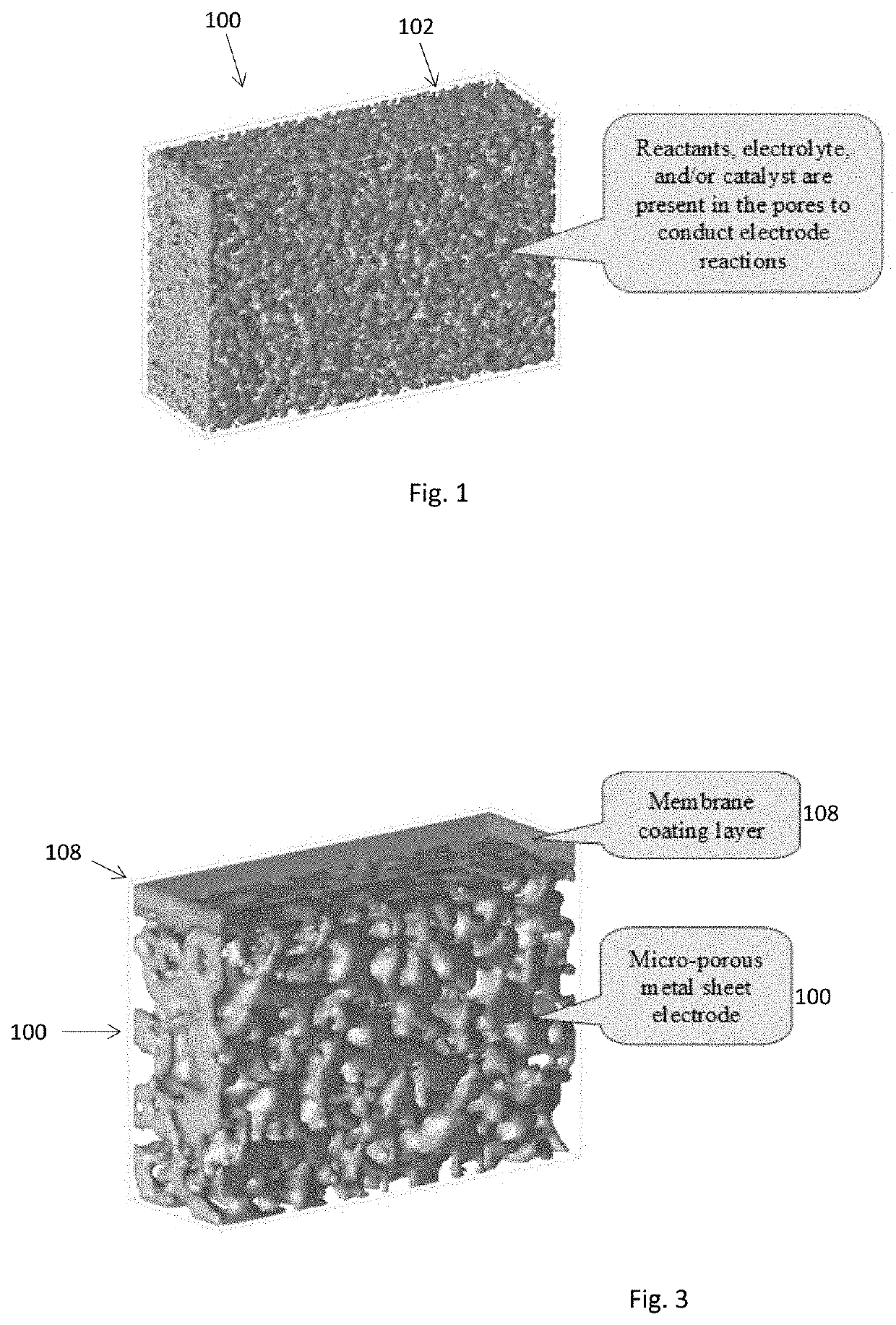
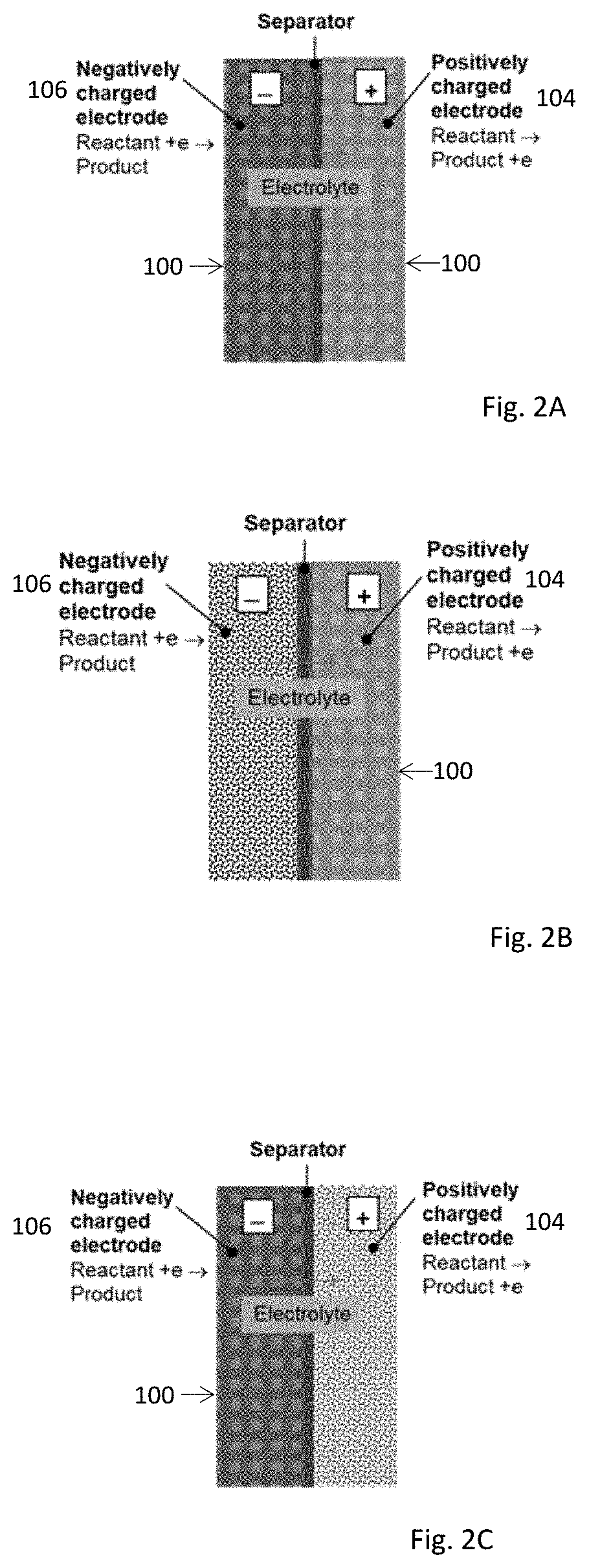
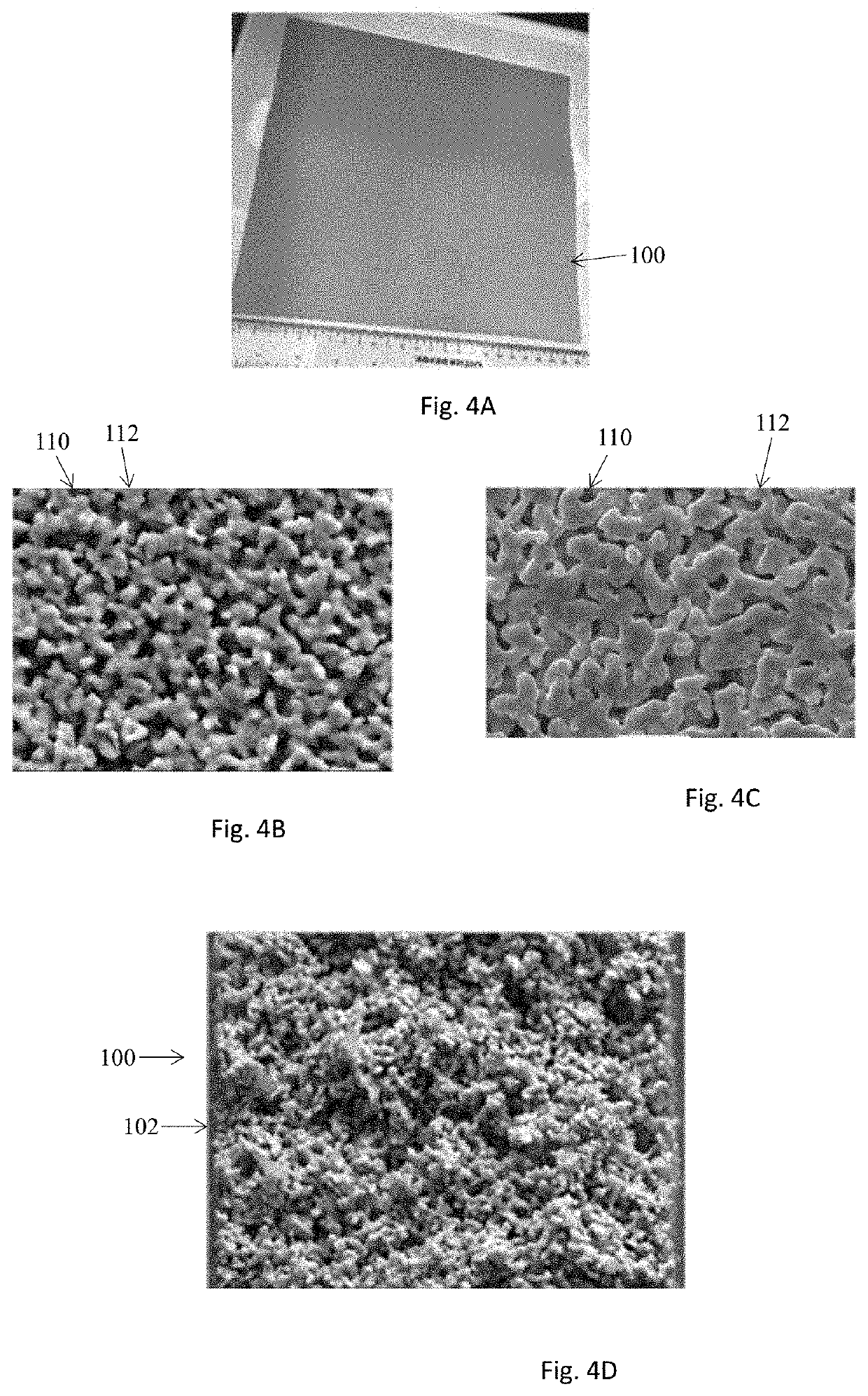
Electrochemical Device Comprising Thin Porous Metal Sheet
ActiveUS20190376193A1Improve electronic conductivityElectrolytic capacitorsCell electrodesCeramic coatingElectrochemistry
Electrochemical device using thin micro-porous metal sheets. The porous metal sheet may have a thickness less than 200 μm, provides three-dimensional networked pore structures of pore sizes in the range of 2.0 nm to 5.0 μm, and is electrically conductive. The micro-porous metal sheet is used for positively and / or negatively-charged electrodes by providing large specific contact surface area of reactants / electron. Nano-sized catalyst or features can be added inside pores of the porous metal sheet of pore sizes at sub- and micrometer scale to enhance the reaction activity and capacity. Micro-porous ceramic materials may be coated on the porous metal sheet at a thickness of less than 40 μm to enhance the functionality of the porous metal sheet. The ceramic coating layer of non-electrical conductivity can function as a membrane separator. The electrochemical device may be used for decomposing molecules and for synthesis of molecules such as synthesis of ammonia from water and nitrogen molecules.
Owner:MOLECULE WORKS INC
Tandem electric field force aircraft propelling device
The invention provides a tandem electric field force aircraft propelling device which can be applied to various occasions inside and outside the atmosphere. The propelling device comprises positive and negative ion generator array layer frames, positive and negative ion generators, shells, positive and negative screen grids, positive and negative neutral layers, positive and negative accelerating grids and insulating fixing bolts. Air is ionized continuously through alternating current and the positive and negative ion generators to generate a large number of positive and negative ions, and the ions are immediately captured by oxygen molecules, nitrogen molecules, carbon dioxide molecules and the like in the air, so that weak positive ion wind and negative ion wind are generated. After multi-stage ionization and multi-stage acceleration, ion wind with a high speed and large flux is output from an accelerator; accordingly, the propelling device can provide large thrust force, and has the advantages of being stable in operation, free of noise, large in specific impulse and thrust force, wide in application occasion and the like.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV +1
Free-cutting steel part and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102732821AImprove surface propertiesLayered productsSolid state diffusion coatingNitrideCarbonitriding
The invention discloses a free-cutting steel part and a manufacturing method thereof. The free-cutting steel part comprises a matrix and a reinforcing layer, wherein the matrix contains more than one free-cutting elements, and the reinforcing layer contains carbon and nitrogen elements; and the method disclosed by the invention is implemented mainly by using a mode of carrying out carburization firstly and then carrying out carbonitriding, and optimized parameters and processes are adopted. The free-cutting steel part and manufacturing method thereof disclosed by the invention have the beneficial effects that the defect that nitrogen atoms are changed into nitrogen molecules so as to form holes and black tissues as nitrides are decomposed and removed caused by increment of the carbon concentration can be avoided, and the surface performance is good.
Owner:鑫光热处理工业(昆山)有限公司
Apparatus with nano-sized platinum black and oxygen-rich ceramic powder for filtering the incoming air into an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20060059876A1Large filter areaImprove filtering effectCombination devicesDispersed particle filtrationChemical reactionMetallurgy
An air filter for an internal combustion engine having a rigid type ceramic filter element made by foaming oxygen-rich ceramic powder for creating a plurality of pass-through holes. In this way, the incoming air obtains a thorough contact with the oxygen-rich powder. Meanwhile, the material of the oxygen-rich ceramic releases negative ions to activate the air entering into the internal combustion engine. Moreover, nano-sized platinum black is coated to the surface of the pass-through holes of the ceramic filter element. So, the incoming air passing through the pass-through holes of the ceramic filter element is catalyzed in chemical reactions to divide the water molecule cluster into smaller particles. Meanwhile, the freedom of water molecule is increased to permit an instant decomposition of oxygen and nitrogen molecules, a complete combination with the fuel injected into the internal combustion engine, and a thorough mixing and a better combustion efficiency.
Owner:YUAN ANDY +1
Method and apparatus to infuse water with nitrate (NO3) and nitrite (NO2) using electrical plasma for use in plant fertilization
ActiveUS20180071707A1Reduce energy lossNitrogen compoundsTransportation and packagingNitriteWater trap
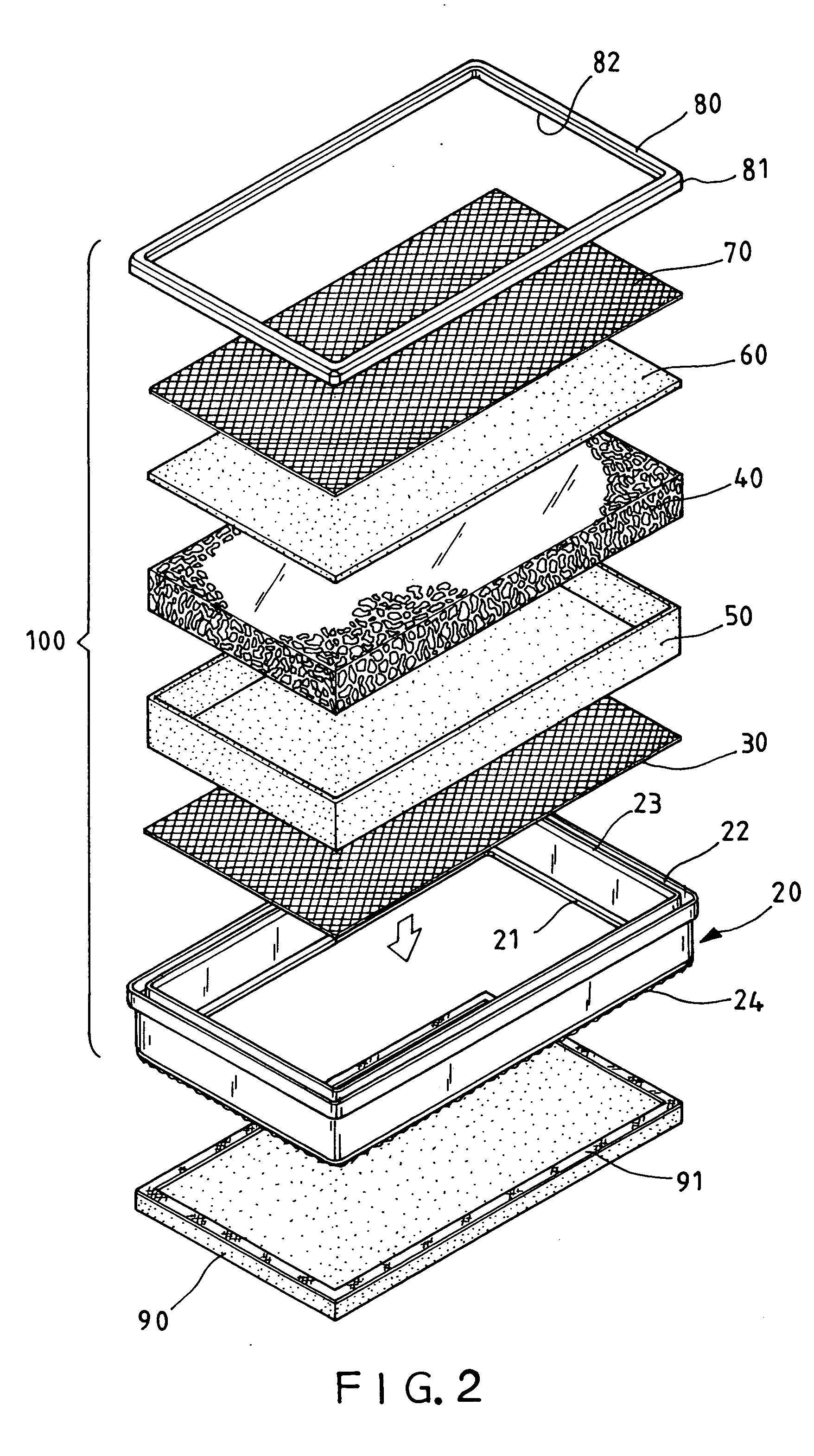
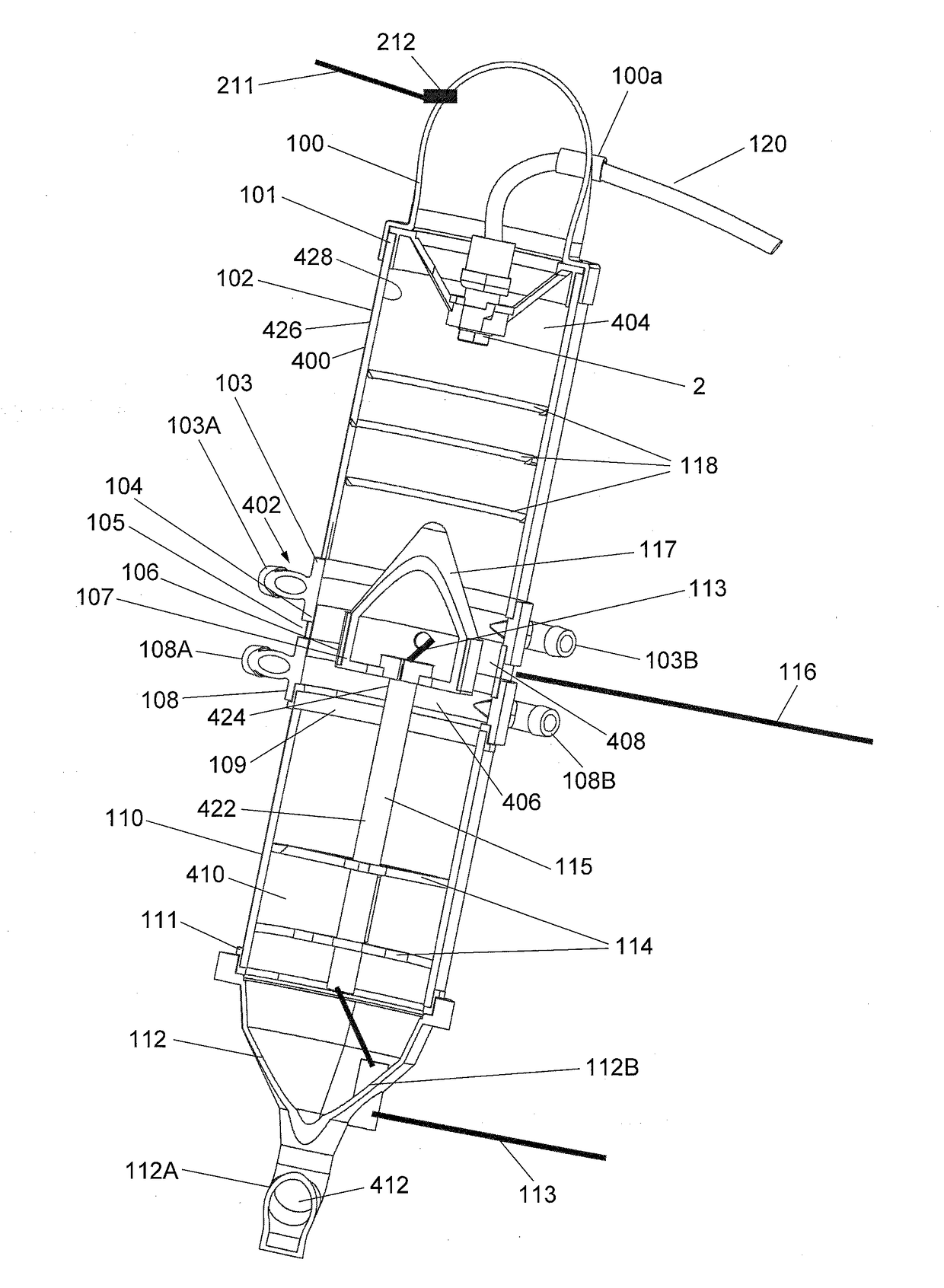
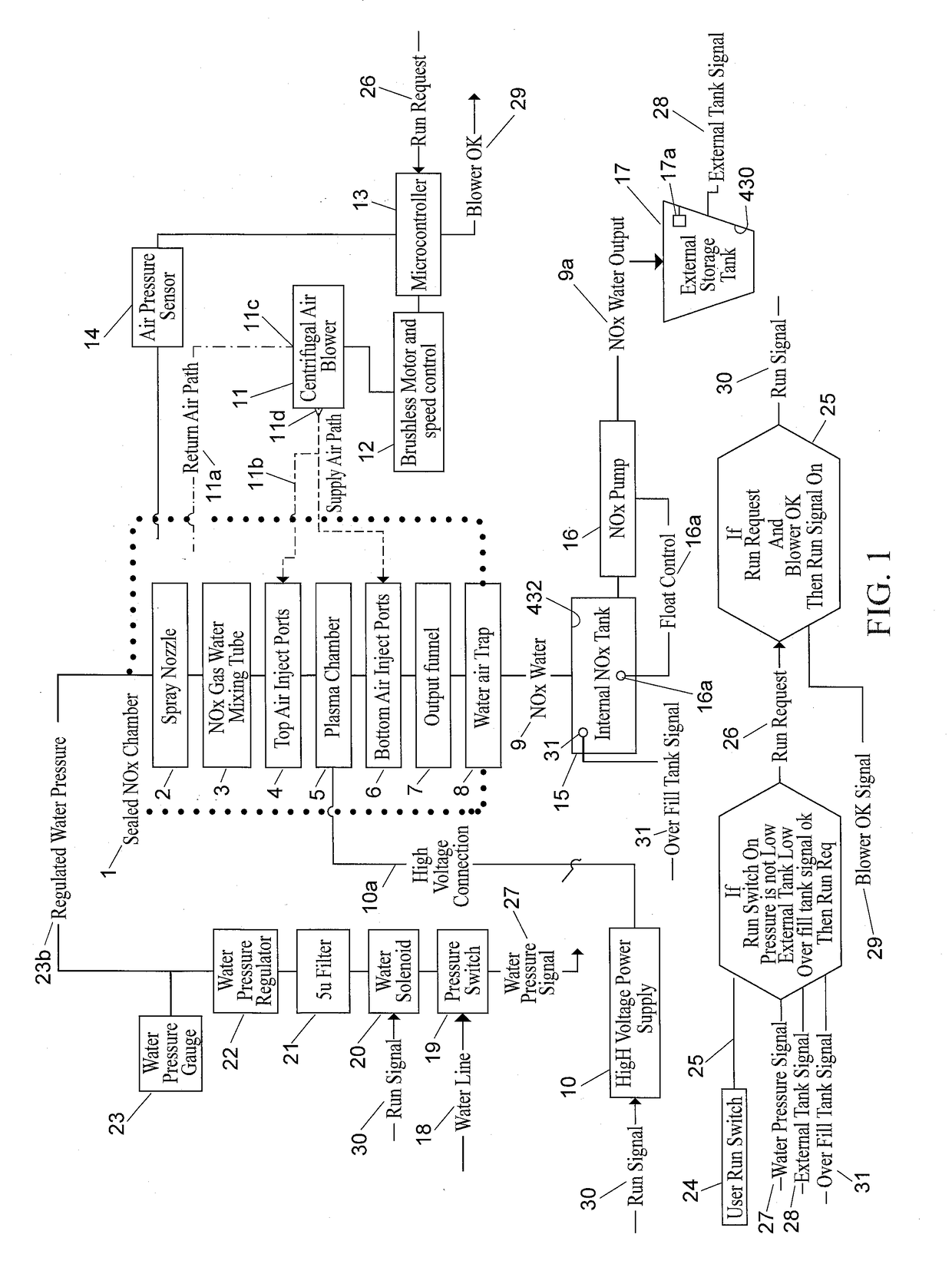
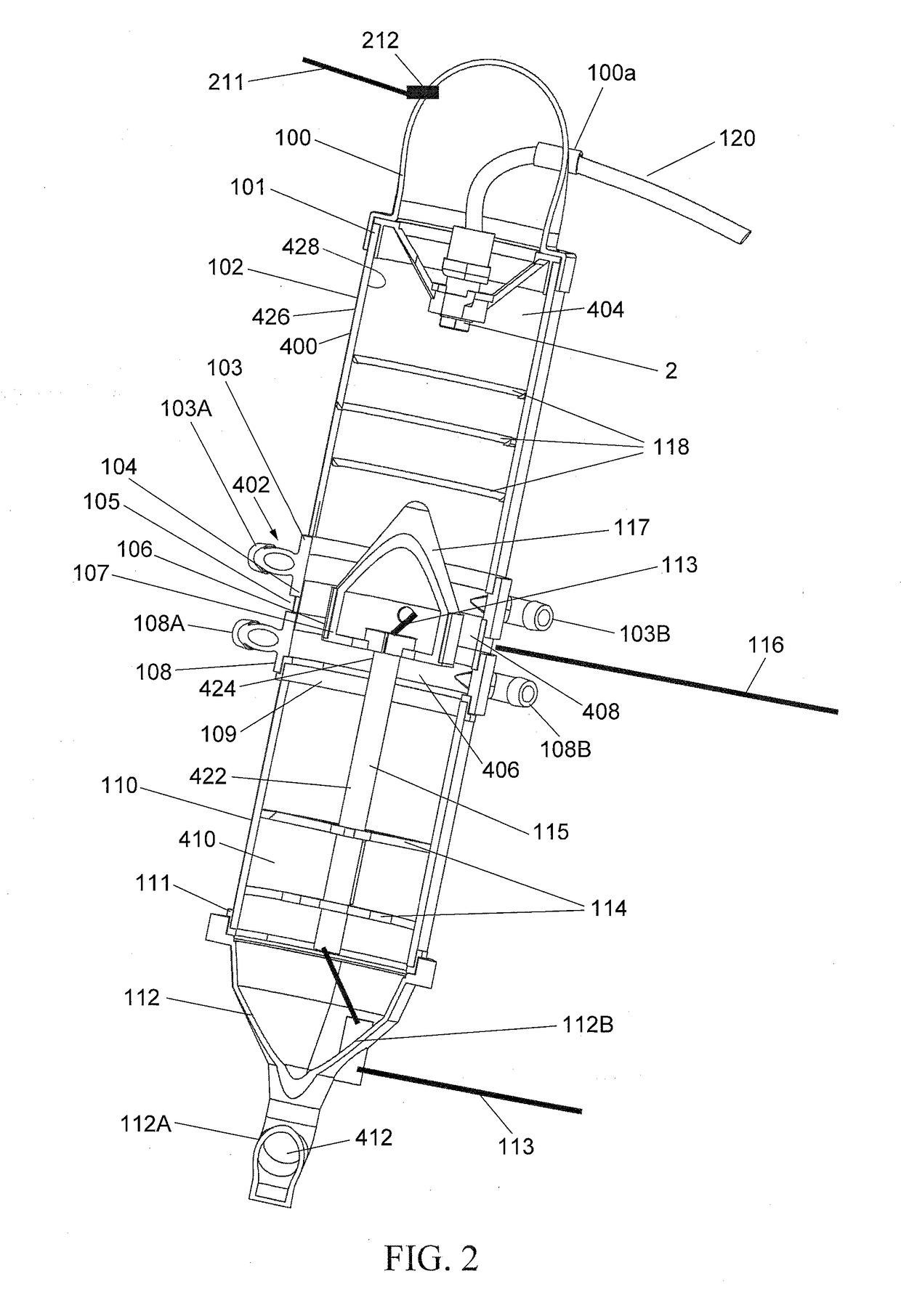
A nitrogen-enriched water generator includes an elongated housing defining a sealed nitrogen / oxygen chamber in which nitrogen molecules are combined with oxygen molecules to form a nitrate (NO3) or a nitrite (NO2) gas (NOx gas). The housing includes an NOx gas and water mixing tube, a plasma generator and a nitrogen-enriched water trap. A water spray nozzle sprays water into the chamber. At least one air injection port injects air into the chamber. A vacuum port removes a volume of NOx gas not absorbed by the water from the sealed nitrogen / oxygen chamber.
Owner:SALERNO MARK
Method for regenerating and extracting waste mineral oil by filling nitrogen extracting
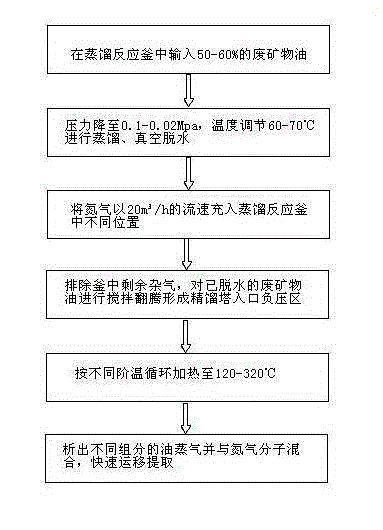
InactiveCN103146423ALower boiling temperatureBoiling temperature achievedTreatment with plural serial refining stagesLubricant compositionDistillationNitrogen gas
The invention discloses a method for regenerating and extracting waste mineral oil by filling nitrogen. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) delivering waste mineral oil into a distillation reactor, distilling at reduced pressure after reducing the pressure to -0.1MPa to -0.02Mpa, and dehydrating in vacuum; (2) filling nitrogen into different parts of the distillation reactor, removing other residual miscellaneous gases in the space of the distillation reactor, stirring the dehydrated waste mineral oil, and forming a negative-pressure zone at the inlet of a rectification tower; and (3) circularly heating the stirred waste mineral oil to 120-320 DEG C according to different thermophases, separating out oil steam with different components, mixing the oil steam with nitrogen molecules, transporting quickly, and extracting. The method effectively solves the problems of low regeneration yield of the waste mineral oil, low extraction efficiency and environment pollution.
Owner:佛山市和挚承环保科技有限公司
Low energy laser-induced ignition of an air-fuel mixture
ActiveUS8858222B1Eliminate needImprove directionPulsating combustionIncandescent ignitionUltravioletEngineering
A new approach for igniting an air-fuel mixture in a turbine or other engine is disclosed. Resonance-enhanced multiphoton ionization (REMPI) is used to generate volume ionization within an air-fuel flow and induce an ignition arc. The output of a relatively low energy single pulsed ultraviolet laser is aimed across an electric field inside a volume of air to create a pre-ionized channel so that a smaller voltage electric field is sufficient to create an electrical arc that follows the pre-ionized channel and will ignite an air-fuel mixture. Because the arc follows the pre-ionized channel, it can be directed to an optimal location inside an ignition volume for igniting the air-fuel mixture. A specific example embodiment is described using a 287.5 nm wavelength pulsed ultraviolet laser to excite ground state oxygen molecules to a specific excited state having a coincident term energy with a specific nitrogen molecule excited state.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETED BY THE SEC OF THE THE
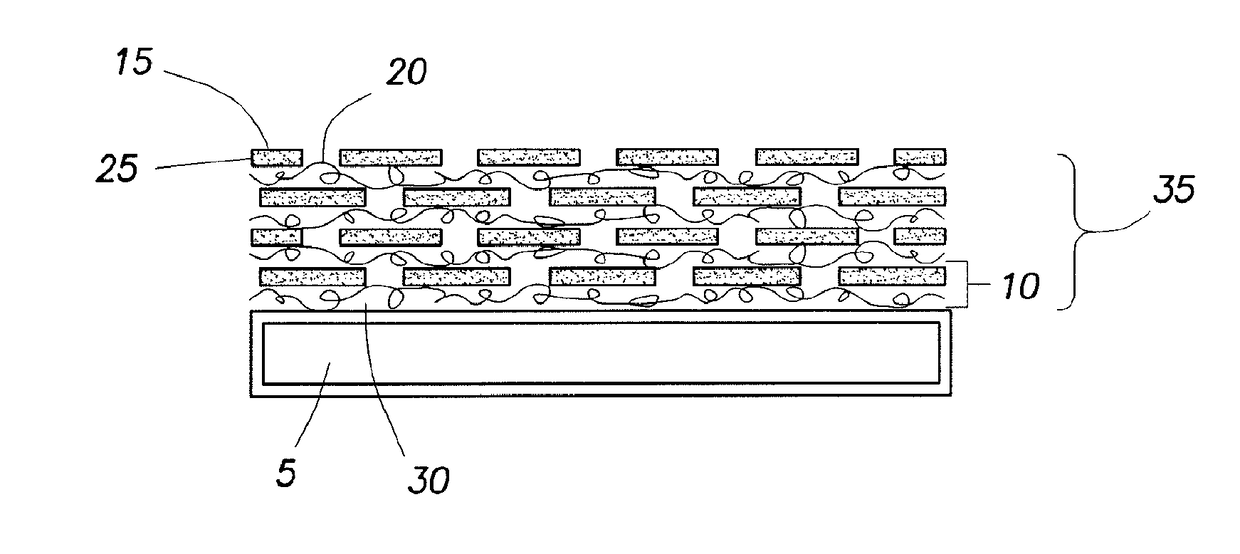
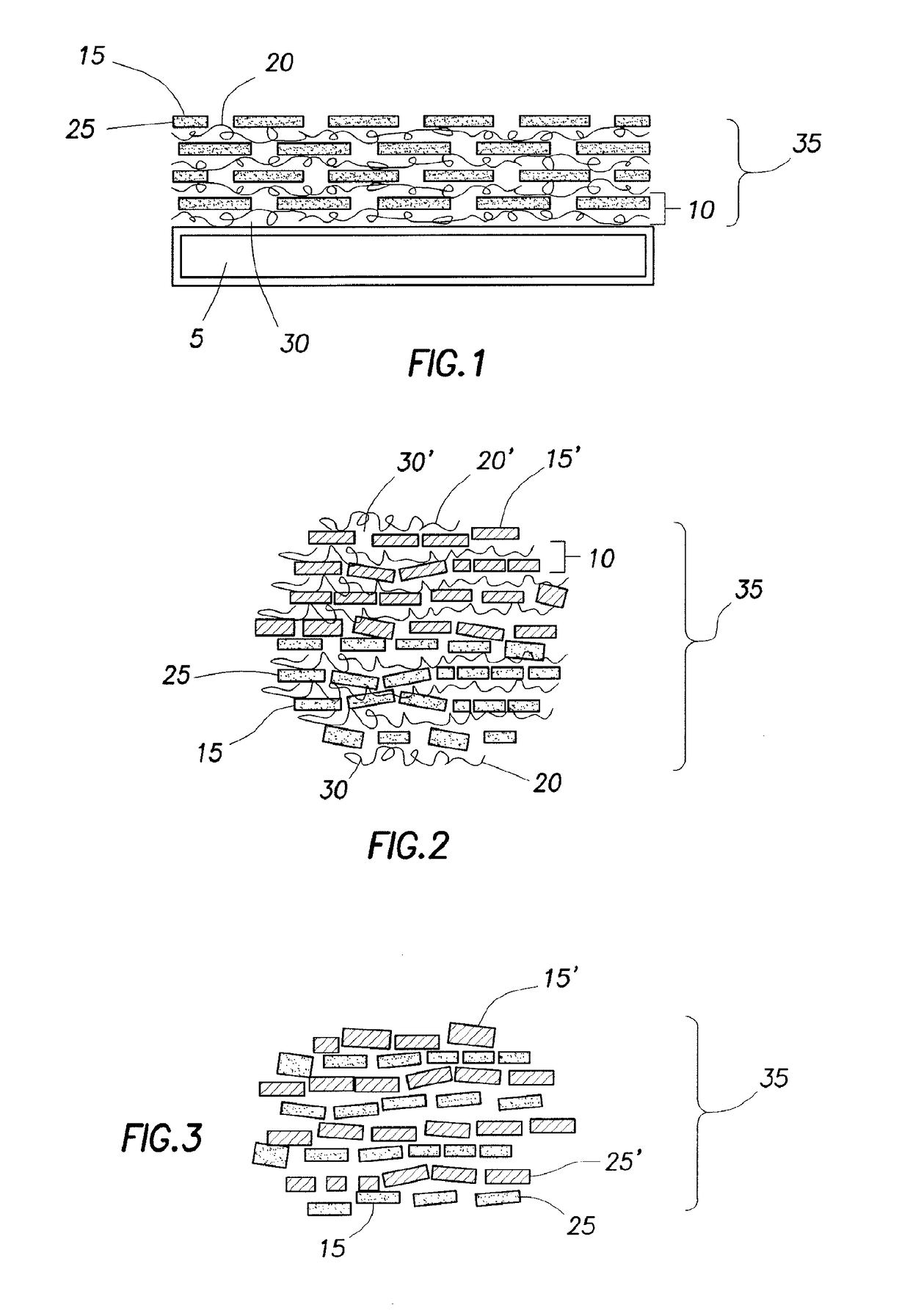
Hand for Nanocoated Fabric
A method includes coating a substrate to provide a flame resistant substrate. In an embodiment, the method includes exposing the substrate to a cationic solution to produce a cationic layer deposited on the substrate. The cationic solution comprises cationic materials. The cationic materials comprise a polymer, a colloidal particle, a nanoparticle, a nitrogen-rich molecule, a geopolymer, a carbon-based filler, or any combinations thereof. The method also includes agitating the substrate. The method further includes exposing the cationic layer to an anionic solution to produce an anionic layer deposited on the cationic layer to produce a layer comprising the anionic layer and the cationic layer. The anionic solution comprises a layerable material.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of carbon defect type carbon nitride material for photocatalytic nitrogen fixation
PendingCN113086955AImprove photocatalytic activityInhibit surface recombinationPhysical/chemical process catalystsNitrogen and non-metal compoundsCarbon nitrideThin layer
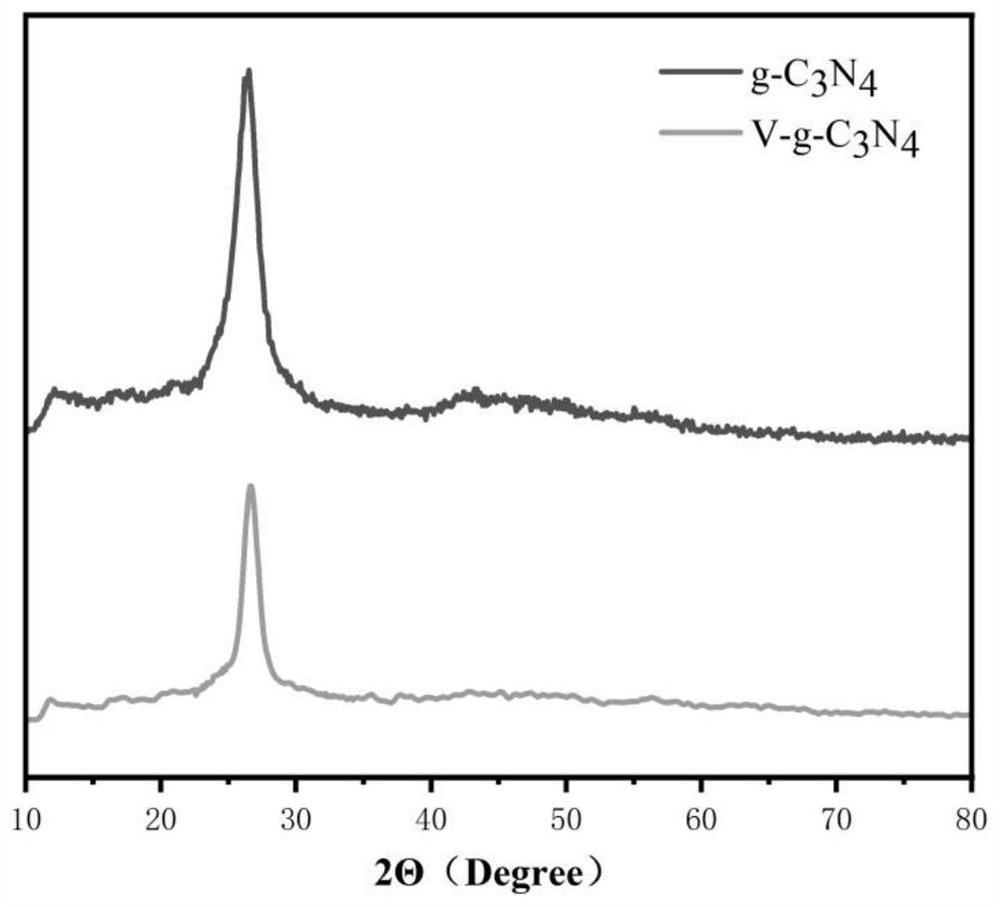
The invention discloses a preparation method of a carbon defect type carbon nitride material for photocatalytic nitrogen fixation. The mesoporous carbon nitride which is loose in structure and has more surface carbon defects is obtained by taking urea as a precursor through a high-temperature stripping method. Through control of an atomic scale structure and construction of surface defects, the photocatalytic activity of the prepared carbon defect type carbon nitride on ammonia conversion is greatly improved compared with that of bulk phase g-C3N4. By utilizing a thin layer structure, more surface carbon vacancies and a mesoporous structure, the light absorption capacity of a visible light region can be enhanced, and the photo-generated charge separation efficiency can be improved. What is worthy of noting is that the engineering carbon vacancies greatly promote adsorption and activation of nitrogen molecules, the nitrogen fixation activity of the defect ultrathin g-C3N4-V (carbon defect type carbon nitride) material is improved, and the preparation method is simple, easy to implement, rapid and convenient and has universality.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for measuring nitrogen in carbon series heating agent
InactiveCN109324081AEasy to operateReliable data supportMaterial heat developmentContent determinationHelium
The invention discloses a method for measuring nitrogen in a carbon series heating agent, and belongs to the technical field of nitrogen element measuring methods. The method for measuring nitrogen inthe carbon series heating agent is used for measuring the content of a nitrogen element in the carbon series heating agent. According to the technical scheme, the method includes the steps of samplepreparation, blank experiment, instrument calibration and content determination. First, a sample to be tested is loaded into a tin capsule and compacted, then placed in a graphite crucible and meltedin a helium atmosphere, nitrogen is released in a nitrogen molecule mode, quantitative detection is performed by a thermal conductivity detector, and finally a computer directly displays in the form of percentage nitrogen content. The method for measuring nitrogen in the carbon series heating agent is the first to determine the content of the nitrogen element in the carbon series heating agent inthe industrial production, in the absence of corresponding standard, the determination of the nitrogen element in the carbon series heating agent by an inert gas fusion-thermal conductivity method isrealized, and the blank of the determination of the nitrogen element in the carbon series heating agent by the inert gas fusion-thermal conductivity method is filled. The method for measuring nitrogenin the carbon series heating agent has the remarkable advantages of being simple and fast, low in price, high in sensitivity, environmentally friendly and suitable for industrial analysis, and provides reliable data support for production.
Owner:HANDAN IRON & STEEL GROUP +1
Hollow glass desiccant and production method thereof
InactiveCN101829479AEnhanced adsorption functionEasy to controlOther chemical processesDispersed particle separationDesiccantVolumetric Mass Density
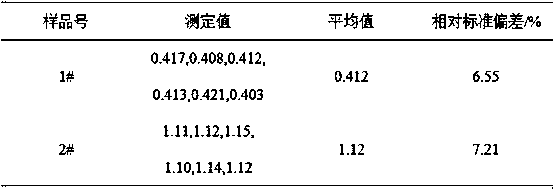
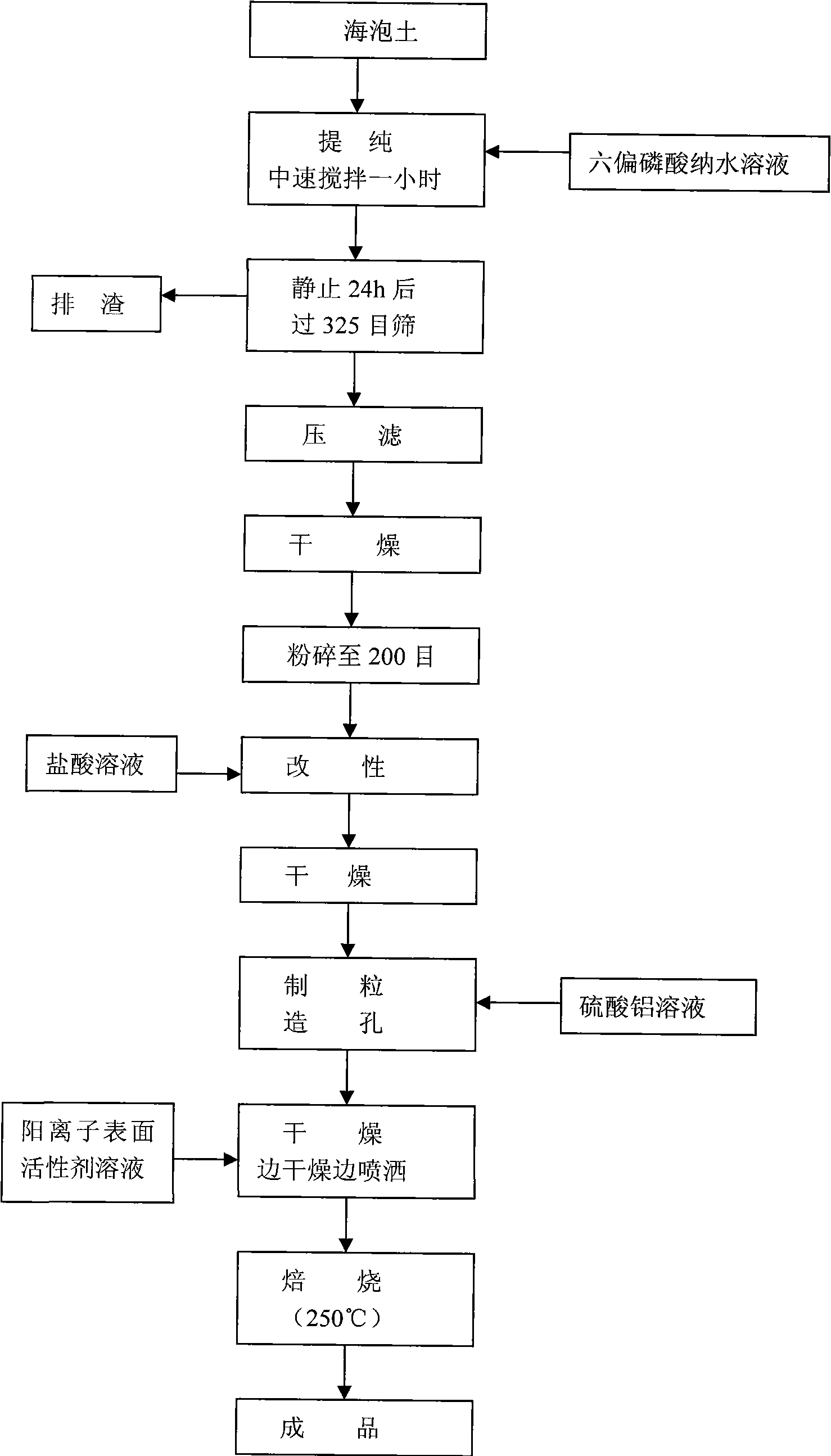
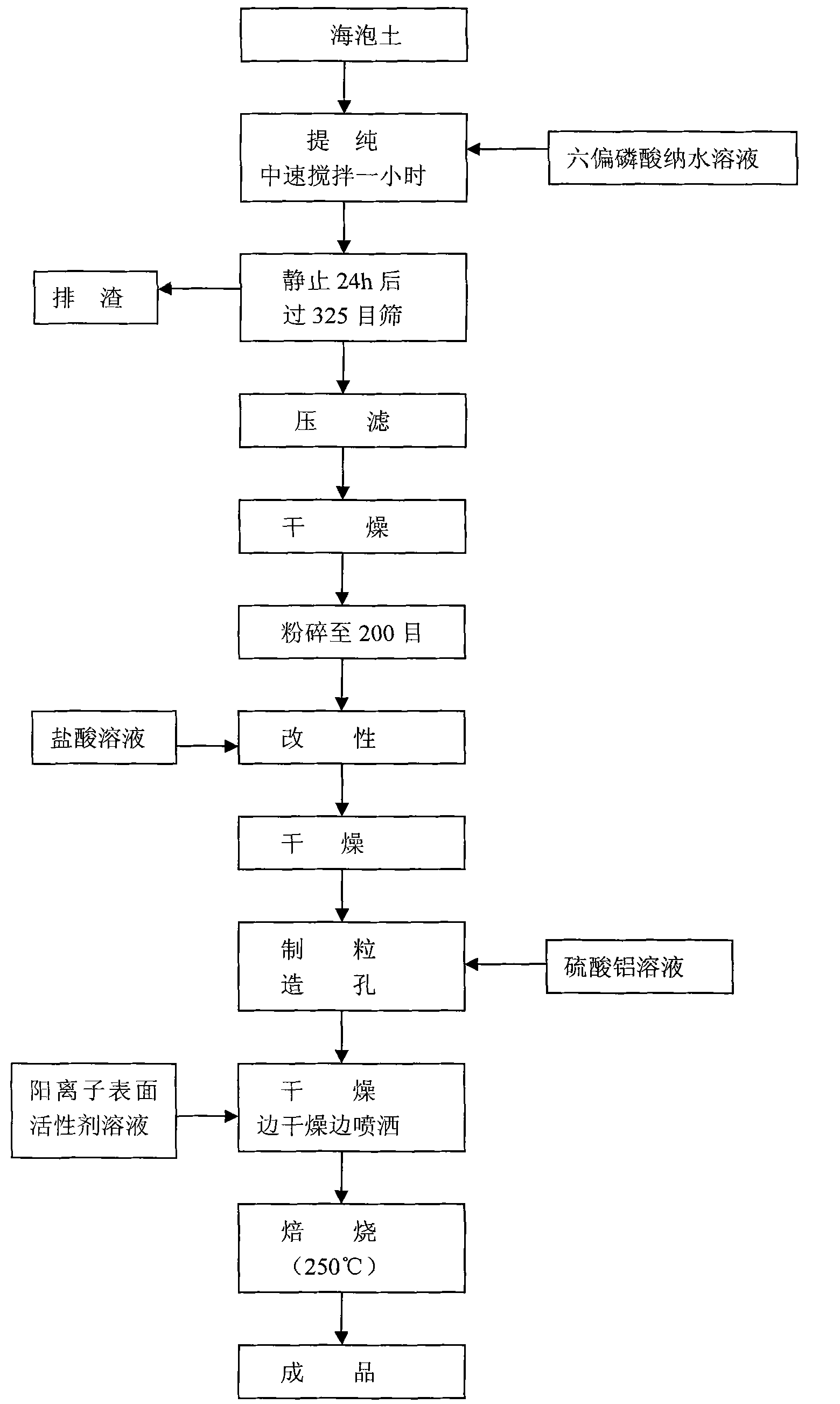
The invention discloses a hollow glass desiccant comprising the following raw materials in parts by weight: 100 parts of sepiolite, 1-4 parts of hydrochloric acid, 2-15 parts of aluminum sulfate, 0.1-0.5 part of cation surfactants and 1-5 parts of sodium hexametaphosphate. The grain size of a finished product is 0.5-5 mm, the stacking density is 0.65-0.8 g / ml, the temperature rise is not less than 30 DEG C, the static water adsorbance is not less than 20%, the static nitrogen adsorbance is not greater than 0.2%, the abrasion rate is not greater than 0.2%, and the water content is not greater than 2%. The performance of the product in the invention is obviously higher than that of the hollow glass desiccant in the prior art, the product has higher adsorption capacity on water and also effectively reduces the adsorption capacity on oxygen molecules and nitrogen molecules, and the manufacturing cost is greatly reduced. The invention also discloses a production method of the hollow glass desiccant.
Owner:宁波市沧海新材料开发有限公司
Welding method based on quartz tuning fork crystal three-temperature-area nitrogen blowing
InactiveCN103560765ANo pollution in the processNot easy to chemical reactionImpedence networksChemical reactionEngineering
The invention relates to the field of welding, in particular to a welding method based on quartz tuning fork crystal three-temperature-area nitrogen blowing. The welding method is characterized in that a nitrogen making machine is connected with one end of a drying machine through a pipeline, and the other end of the drying machine is respectively connected with a flow-limiting valve A, a flow-limiting valve B and a flow-limiting valve C through pipelines; the flow-limiting valve A is connected with a drying temperature area through a filter A, a heating wire A and a drying temperature area pipeline, and the other end of the heating wire A is connected with an adjustable converter A; the flow-limiting valve B is connected with a preheating temperature area through a filter B, a heating wire B and a preheating temperature area pipeline, and the other end of the heating wire B is connected with an adjustable converter B; the flow-limiting valve C is connected with a high temperature area through a filter C, a heating wire C and a high temperature pipeline, and the other end of the heating wire C is connected with an adjustable converter C; the drying temperature area, the preheating temperature area and the high temperature are provided with product track grooves. By the adoption of the technical scheme, due to the fact that chemical reactions among nitrogen molecules, tuning fork pieces and tuning fork base metal components do not easily occur at a high temperature, an oxidation process and dust pollution do not exist, and quality of products can be stable.
Owner:HUBEI TKD ELECTRONICS TECH
All-optical-fiber filtering device based on optical fiber F-P filter
ActiveCN106443888AReduce volumeReduce weightElectromagnetic wave reradiationOptical light guidesRayleigh scatteringShunt Device
The invention discloses an all-optical-fiber filtering device based on an optical fiber F-P filter. The all-optical-fiber filtering device comprises an optical fiber coupling and shunting device and a two-stage-cascaded all-optical-fiber filtering device which are connected with each other. The all-optical-fiber filtering device is composed of an optical fiber coupler, an optical fiber band-pass filter and the optical fiber F-P filter, an optical fiber structure is adopted in the whole light splitting technology, atmosphere echo signals received by a telescope are coupled to an all-optical-fiber light splitting system through optical fibers, all-optical-fiber input and filtering output are achieved through connection between the optical fibers, the size and the weight of the light splitting system are greatly decreased, and the device has the structural advantages of being stable in system and high in reliability and anti-jamming property. Meanwhile, vibration raman scattering signals of water vapor molecules in an atmosphere and vibration raman scattering signals and mie-rayleigh scattering signals of nitrogen molecules in the atmosphere can be extracted from the spectral characteristics respectively, and the mie-rayleigh scattering signals and other stray light signals are highly inhibited in a raman channel.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for synthesizing nitric acid
ActiveCN108313993AHigh catalytic activityImprove adsorption capacityTungsten oxides/hydroxidesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPhotocatalytic reactionGram
The invention provides a method for synthesizing nitric acid, and the method is as follows: mixing a pit-rich WO3 nanosheet material with water, introducing a mixed gas of nitrogen and oxygen into anobtained water phase, and performing a photocatalytic reaction under illumination conditions to obtain the nitric acid. The pit-rich WO3 nanosheet material is used as a catalyst for synthesizing of the nitric acid by photocatalytic conversion with nitrogen molecules as a nitrogen source. Due to the unique rich pit structure of the pit-rich WO3 nanosheet material, the pit-rich WO3 nanosheet material has high catalytic activity as the catalyst, and finally makes N2 reaction activity high. Experimental results show that the average rate of the catalyst per gram for catalytic synthesis of the nitric acid is 1.22 mg.g<-1>.h<-1>.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Apparatus with nano-sized platinum black and oxygen-rich ceramic powder for filtering the incoming air into an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7255838B2Large filter areaImprove filtering effectCombination devicesDispersed particle filtrationChemical reactionMetallurgy
An air filter for an internal combustion engine having a rigid type ceramic filter element made by foaming oxygen-rich ceramic powder for creating a plurality of pass-through holes. In this way, the incoming air obtains a thorough contact with the oxygen-rich powder. Meanwhile, the material of the oxygen-rich ceramic releases negative ions to activate the air entering into the internal combustion engine. Moreover, nano-sized platinum black is coated to the surface of the pass-through holes of the ceramic filter element. So, the incoming air passing through the pass-through holes of the ceramic filter element is catalyzed in chemical reactions to divide the water molecule cluster into smaller particles. Meanwhile, the freedom of water molecule is increased to permit an instant decomposition of oxygen and nitrogen molecules, a complete combination with the fuel injected into the internal combustion engine, and a thorough mixing and a better combustion efficiency.
Owner:YUAN ANDY +1
Device and method for mfg. GaN base
InactiveCN1444295APolycrystalline material growthVacuum evaporation coatingChemical reactionEngineering
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Air intake control method of combustion chamber
PendingCN110671240AInternal combustion piston enginesAir intakes for fuelCombustion chamberEmission standard
The invention discloses an air intake control method of a combustion chamber. The air intake control method is characterized in that air is treated before entering the combustion chamber of an engineby means of the physical separation means, before air enters the engine, enrichment of combustion unfavorable components represented by nitrogen molecules and combustion favorable components represented by oxygen molecules are completed, and the two parts of components enter the combustion chamber of the engine in respective enriched states to be combusted. The air intake control method has the advantages that front-end treatment can be carried out on intake air of the combustion chamber, the air intake control method is beneficial to sufficient combustion of the combustion chamber, the effects of energy saving and emission reduction are generated, emission pollution is reduced, and the emission standard is improved.
Owner:重庆创世纪环保科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com