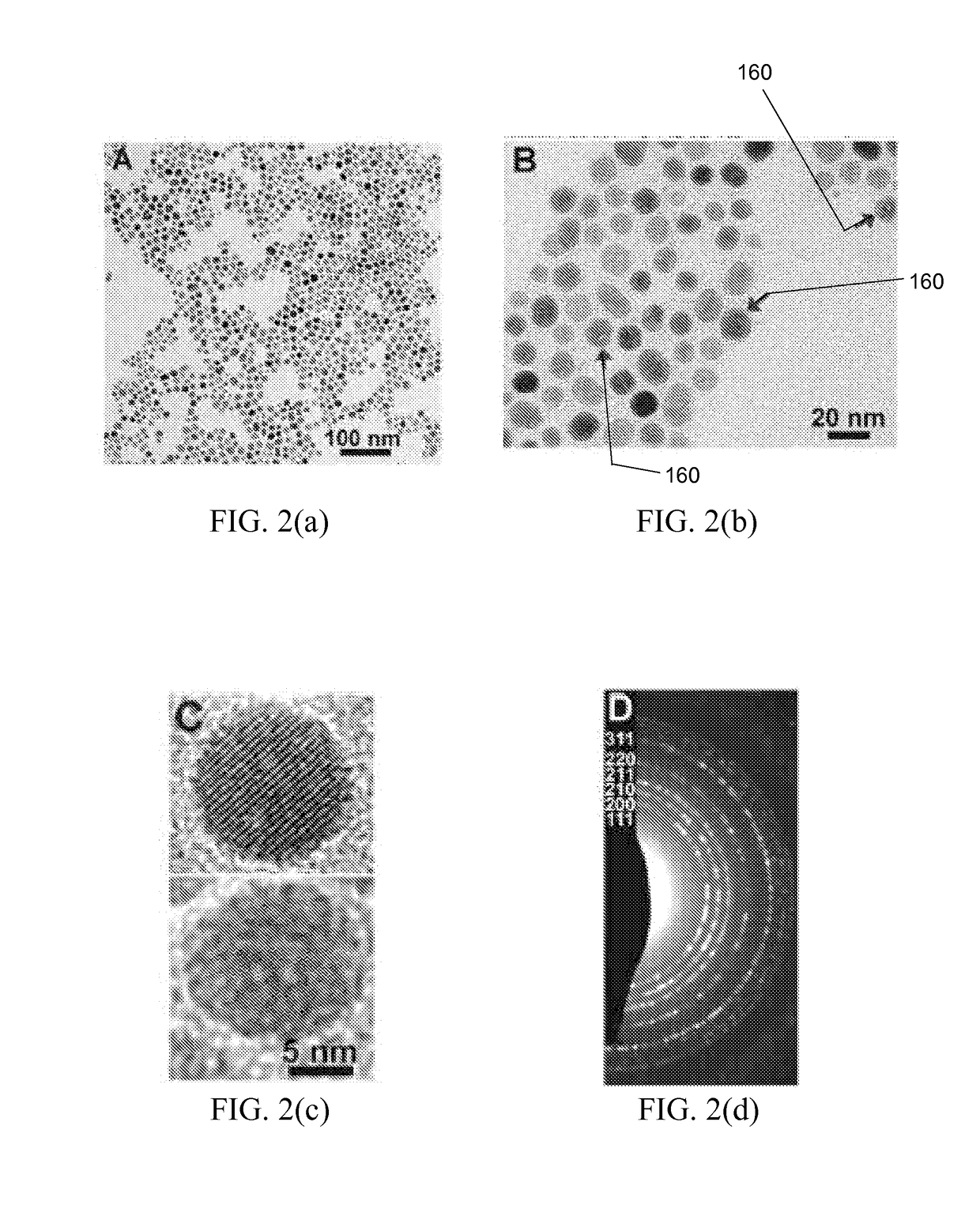
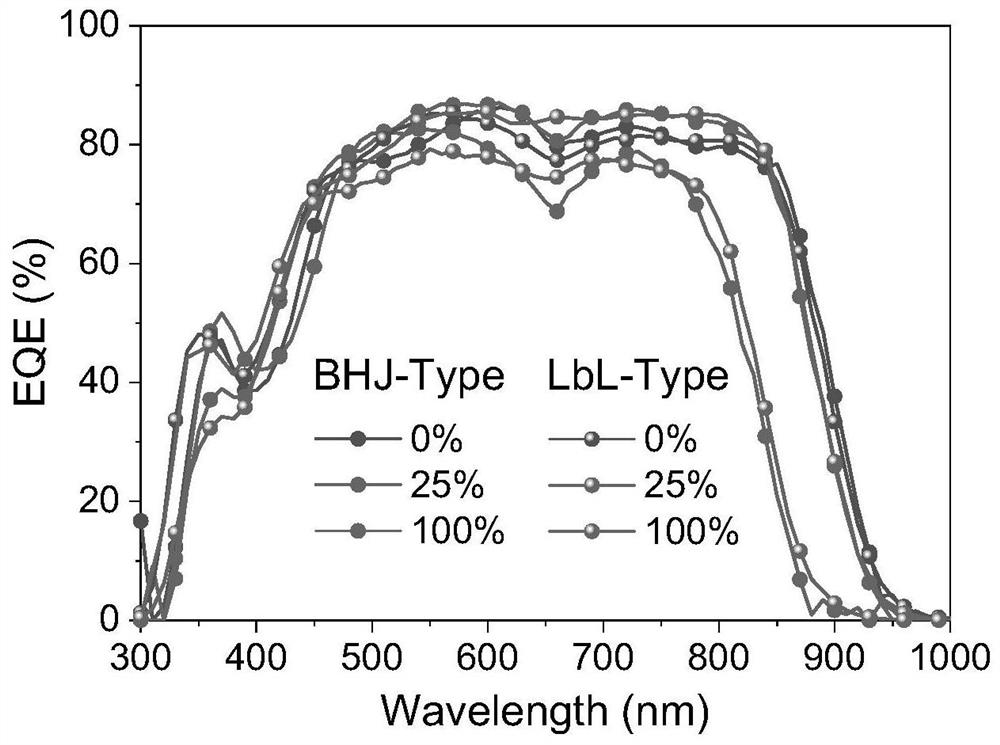
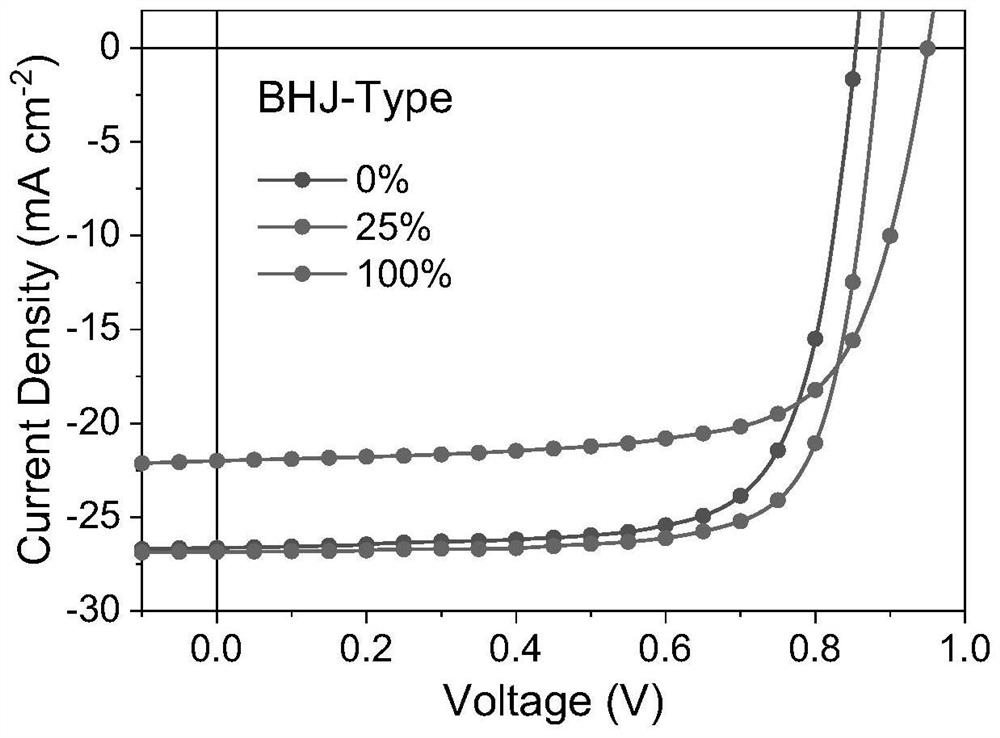
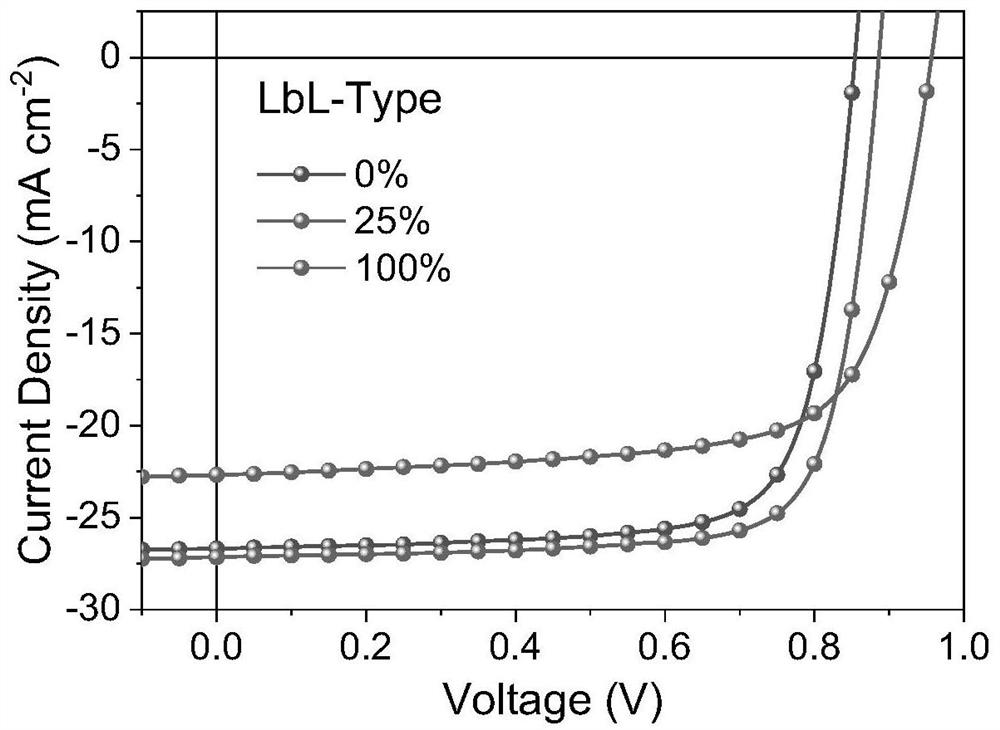
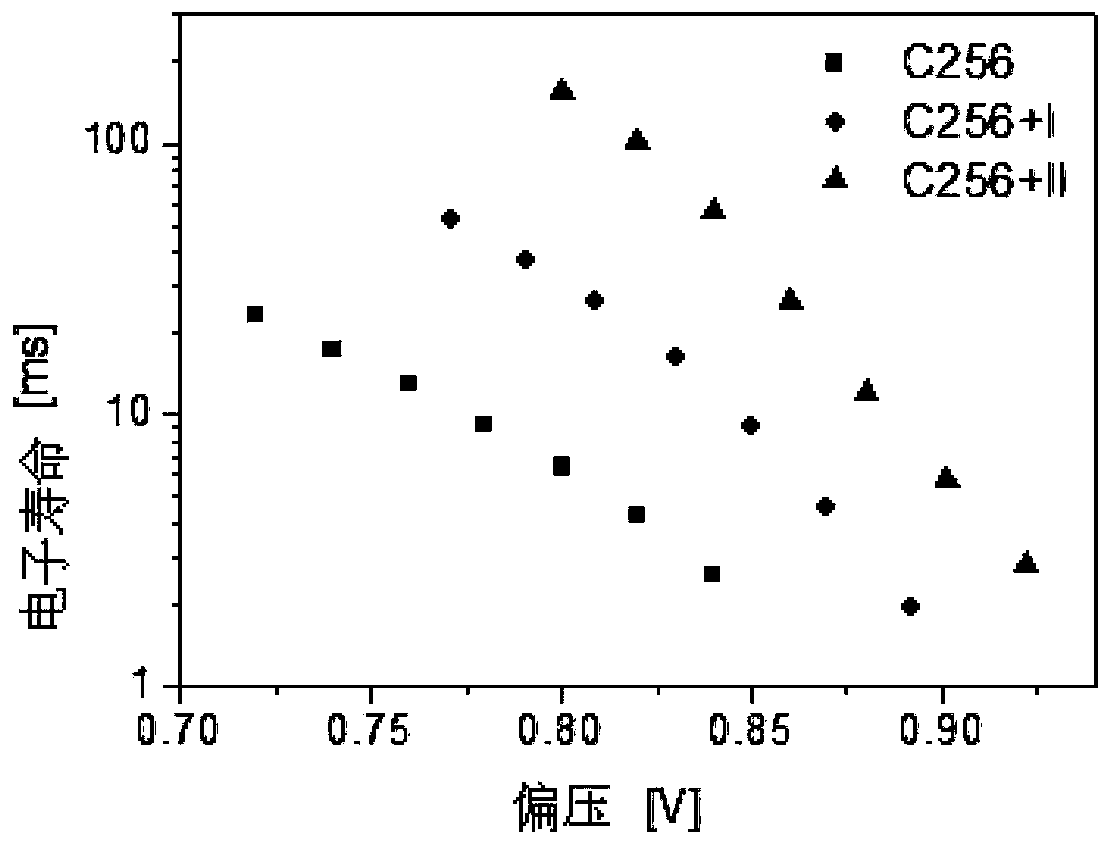
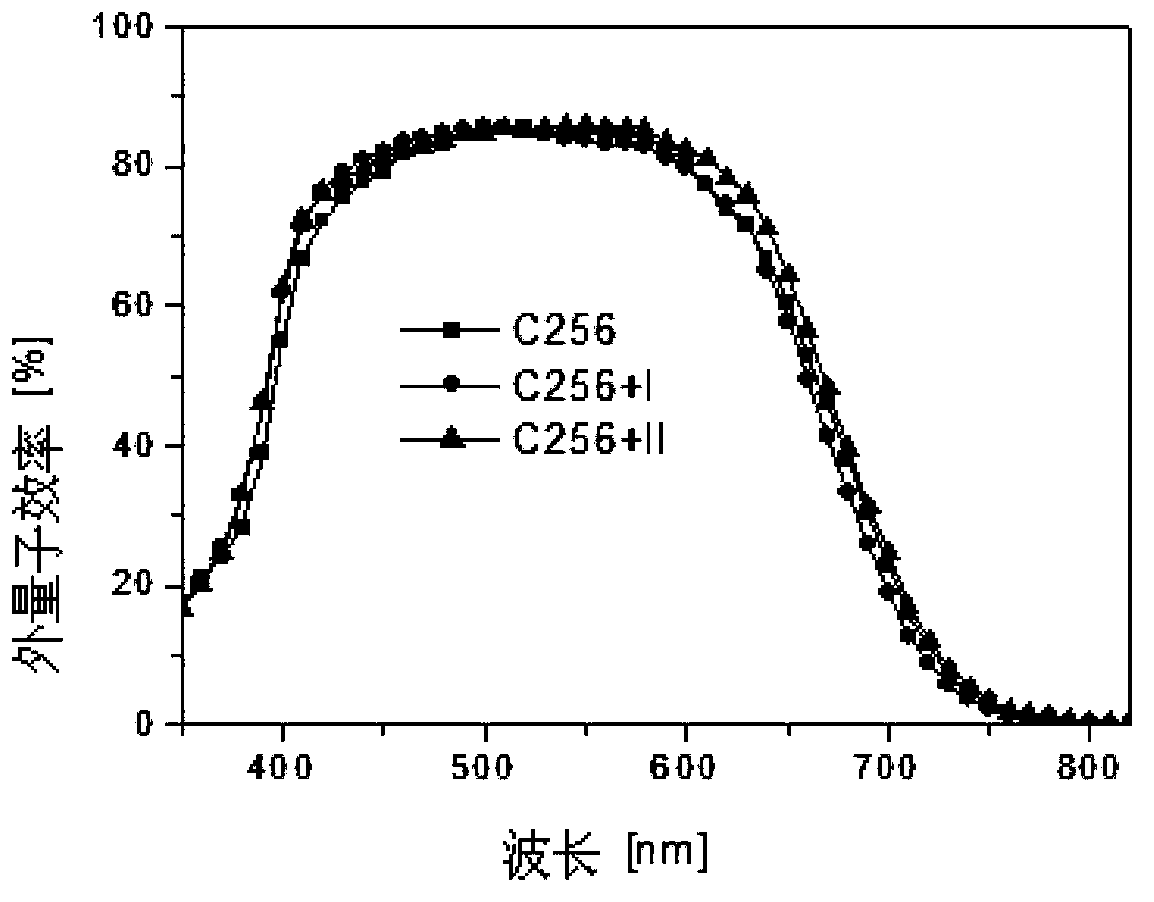
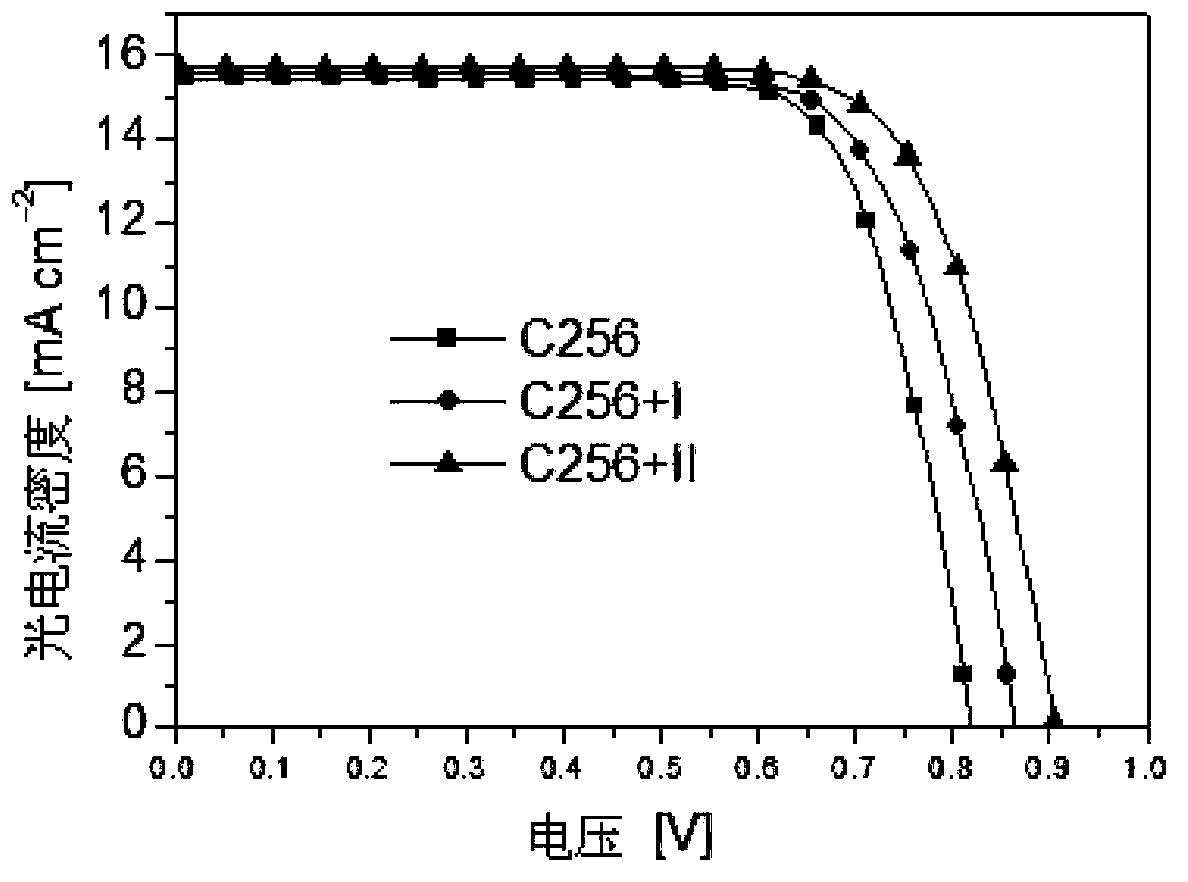
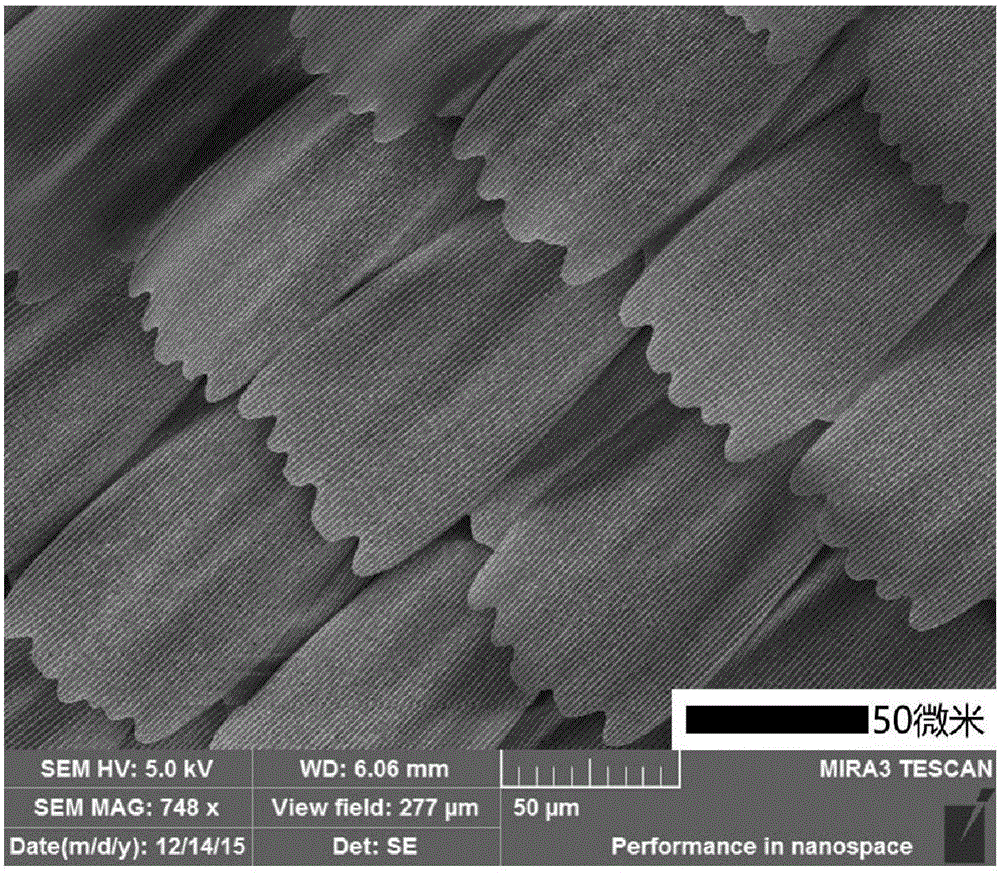
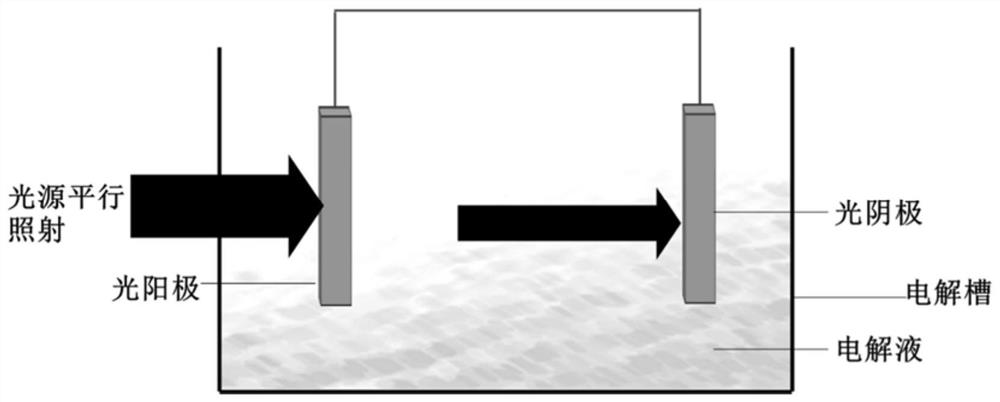
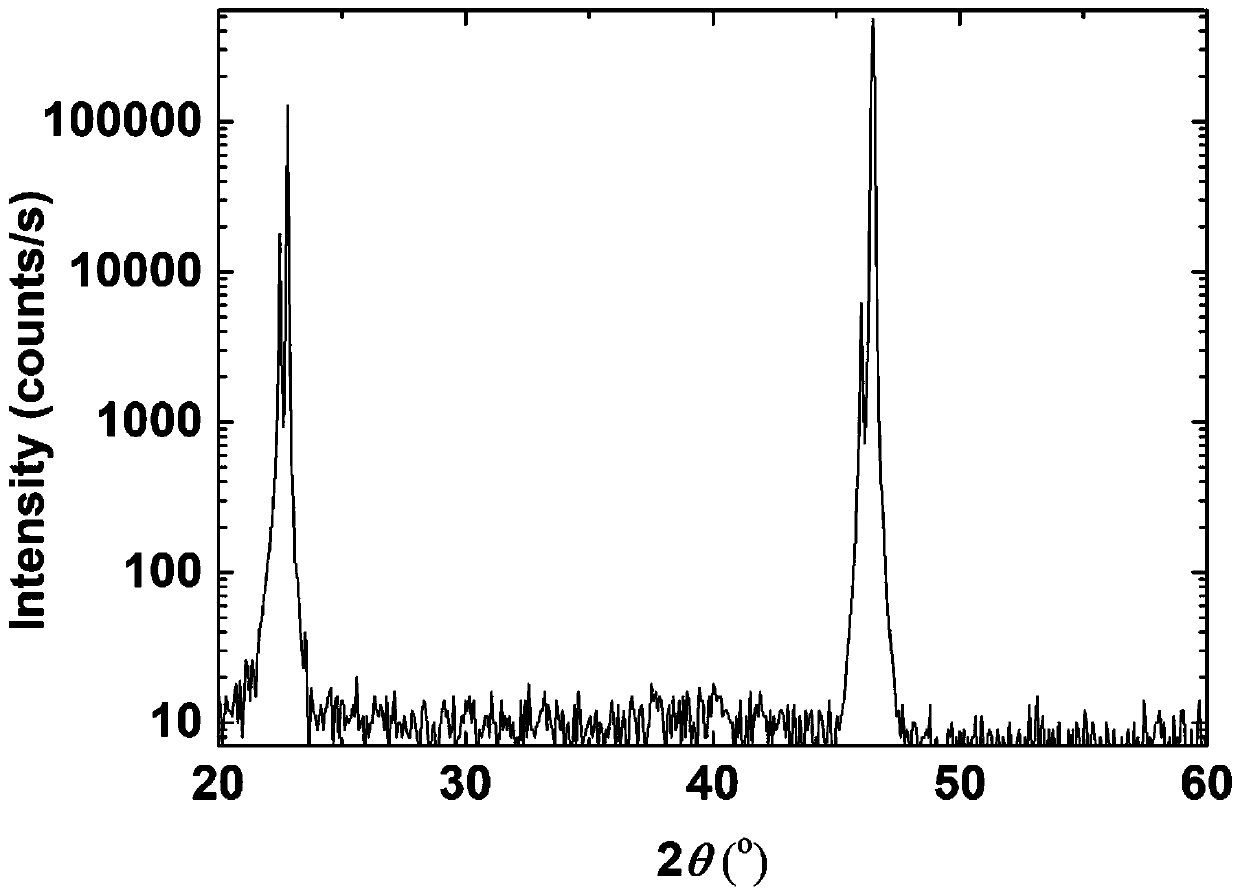
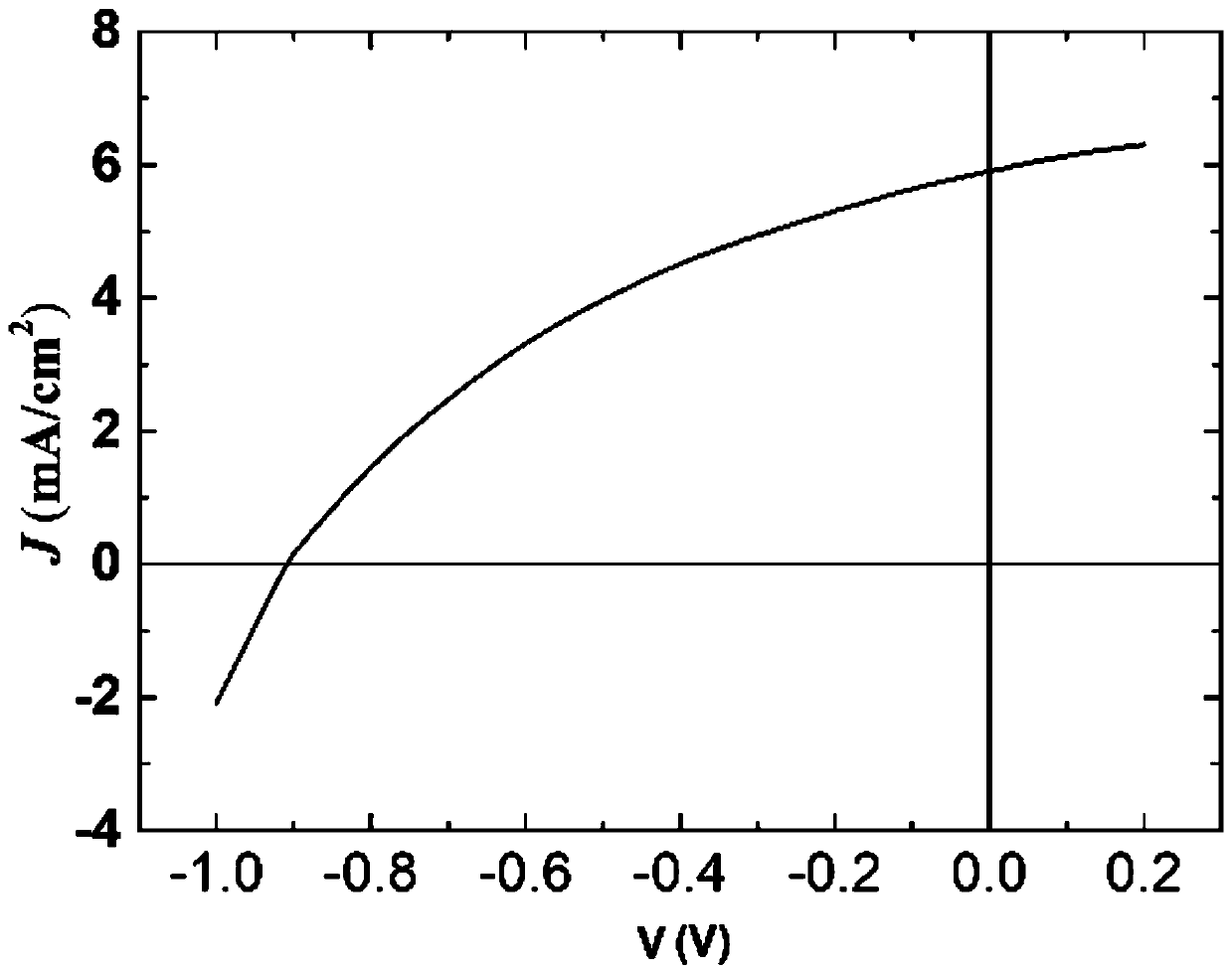
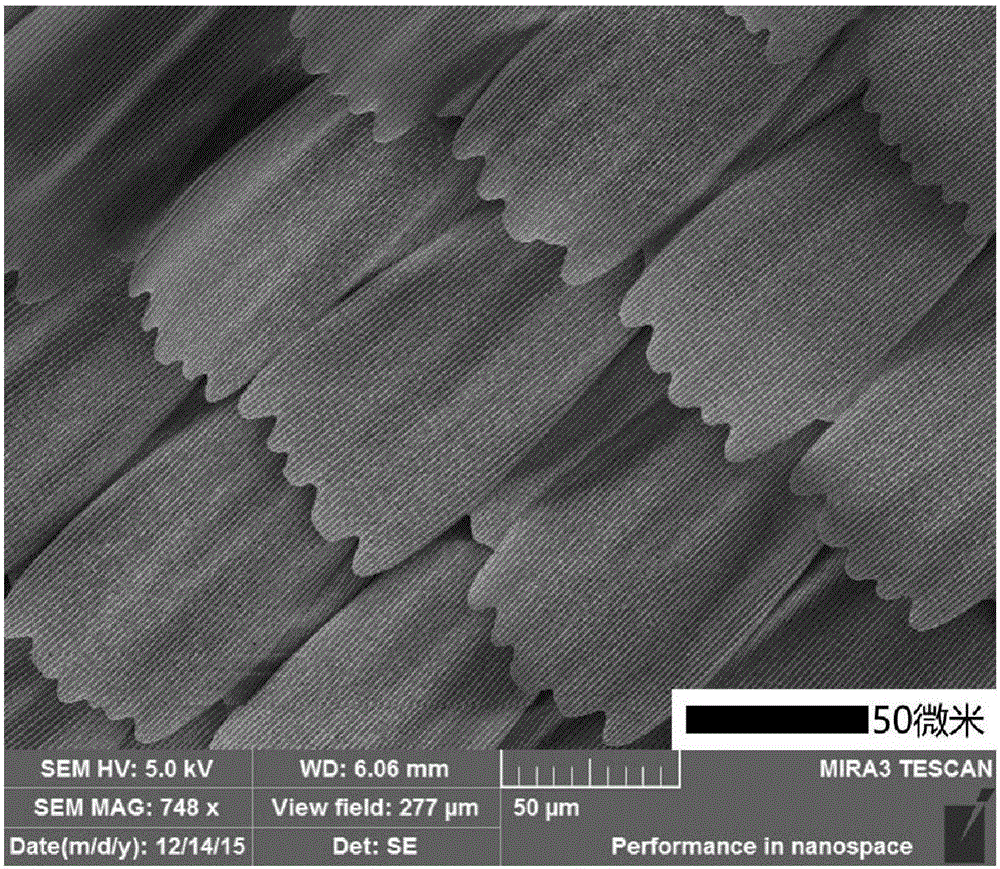
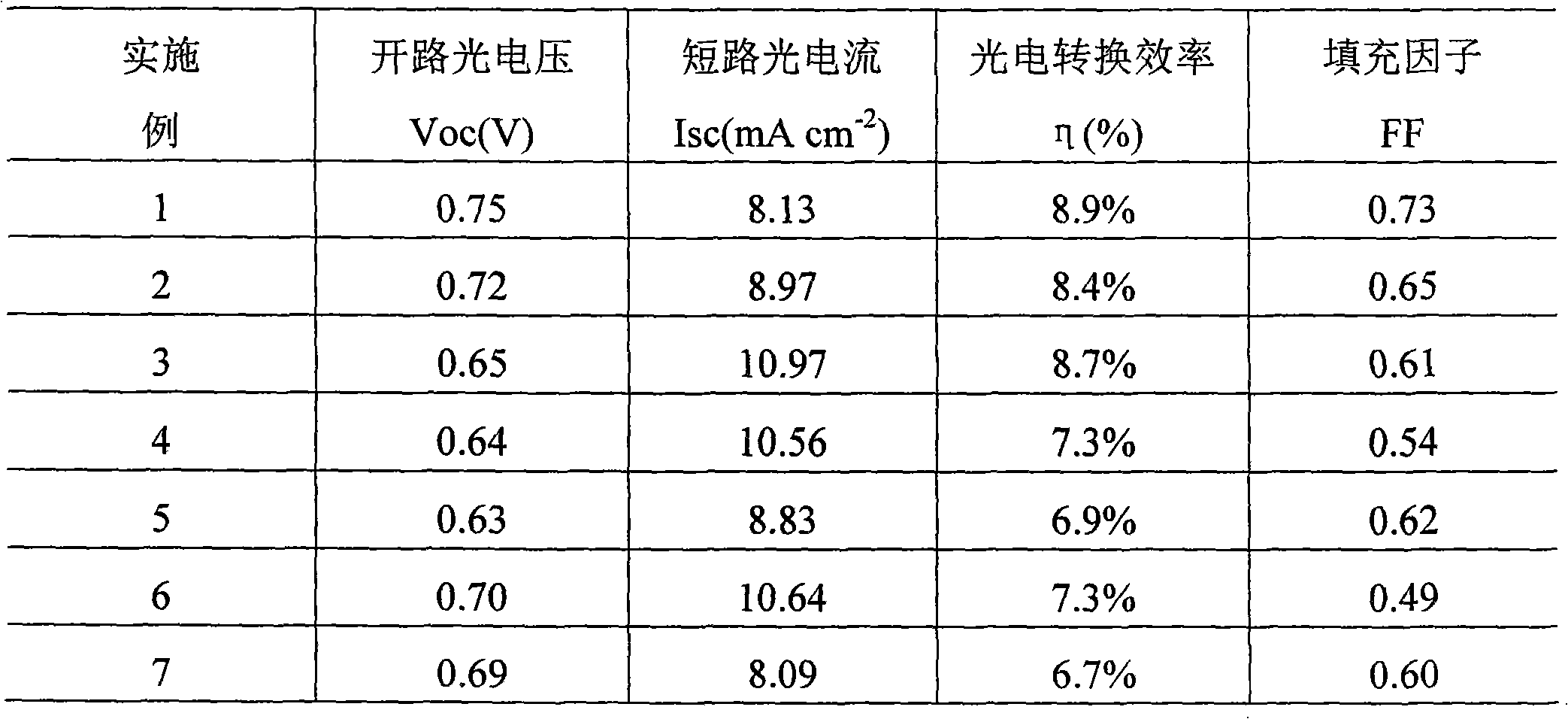
Patents
Literature
48results about How to "Increase photovoltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
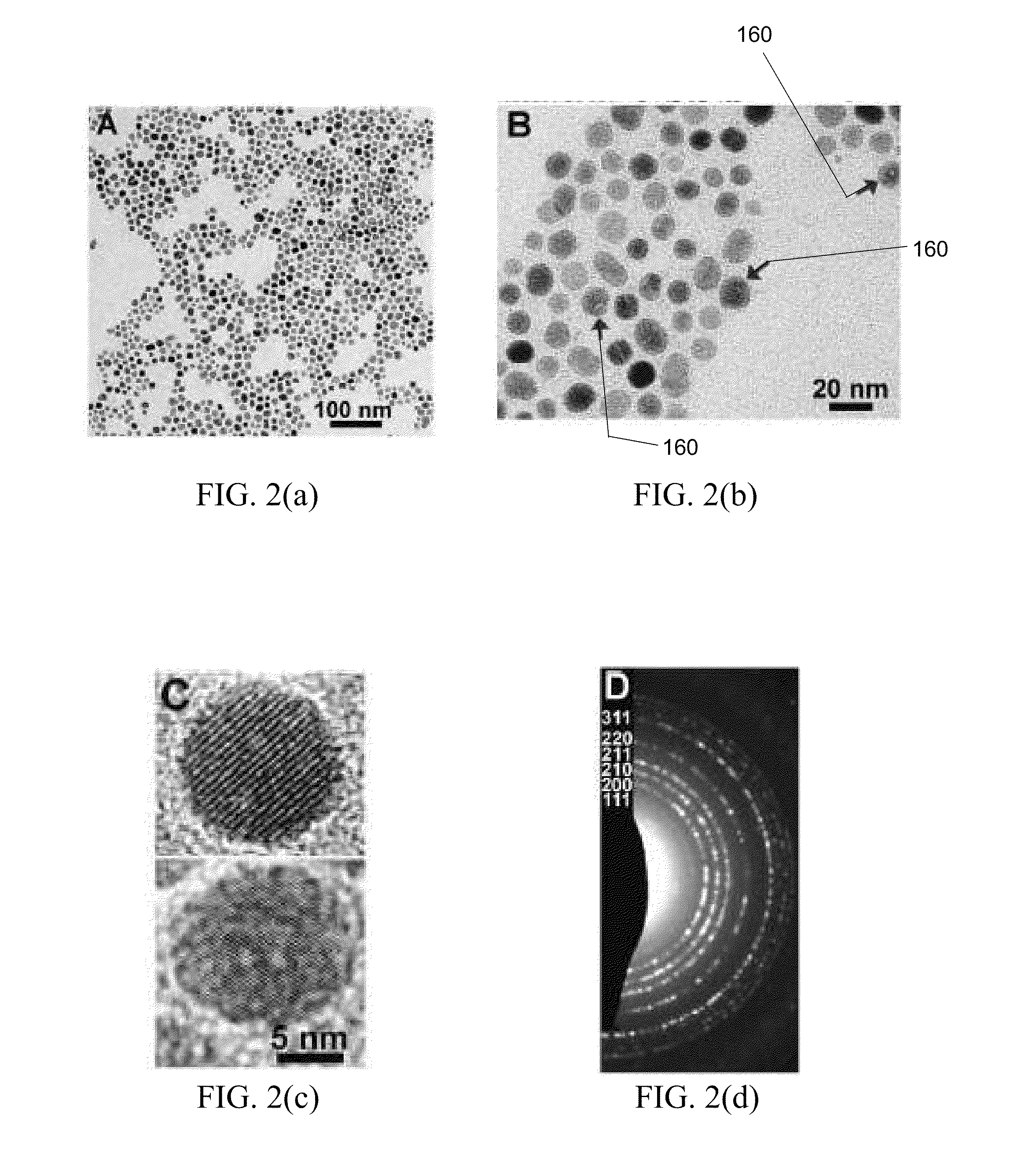
Method To Synthesize Colloidal Iron Pyrite (FeS2) Nanocrystals And Fabricate Iron Pyrite Thin Film Solar Cells
InactiveUS20110240108A1Excellent manufacturing scalabilityLow costMaterial nanotechnologySulfur compoundsHeterojunctionMetal foil
Systems and methods are provided for the fabrication and manufacture of efficient, low-cost p-n heterojunction pyrite solar cells. The p-n heterojunction pyrite solar cells can include a pyrite thin cell component, a window layer component, and a top surface contact component. The pyrite thin cell component can be fabricated from nanocrystal paint deposited onto metal foils or microcrystalline pyrite deposited onto foil by chemical vapor deposition. A method of synthesizing colloidal pyrite nanocrystals is provided. Methods of manufacturing the efficient, low-cost p-n heterojunction pyrite solar cells are also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Rare earth-doped titanium dioxide photo-anode for dye-sensitized solar cell and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101819885AIncrease photocurrentIncrease photovoltageLight-sensitive devicesSolid-state devicesRare earthHYDROSOL
The invention discloses a rare earth-doped titanium dioxide photo-anode for a dye-sensitized solar cell. The photo-anode is prepared from a rare earth compound and tetrabutyl titanate by the following steps of: preparing nano-crystalline titanium dioxide colloid with the tetrabutyl titanate by a hydrothermal method; dissolving the rare earth compound in solution of nitric acid to obtain solution of nitrate, hydrolyzing the tetrabutyl titanate to obtain titanium dioxide sol, adding the solution of nitrate into the sol and processing the mixture by the hydrothermal method and high temperature calcining to obtain the rare earth-doped titanium dioxide powder; and adding the rare earth-doped titanium dioxide powder into the titanium dioxide colloid, scattering, coating and calcining the mixture at a high temperature to prepare the rare earth-doped titanium dioxide photo-anode. The photo-anode and the preparation method have up-conversion luminescence function and p-type doping effect and improve the photocurrent and photovoltage of the cell, the Fermi level of the titanium dioxide and the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the cell. The method is used for improving the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the dye-sensitized solar cell with simple process and abundant raw materials and can also be used for the related fields of other solar cells and the like.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Water-soluble fast reaction kinetics couple-based photoelectrochemical energy storage battery
ActiveCN106329033AEasy in situ transformationAdjustable capacityPhotoelectrochemical storage cellsElectrochemical responseExternal bias
The invention provides a water-soluble fast reaction kinetics couple-based photoelectrochemical energy storage battery. When the battery is charged, in-situ transformation of light energy into chemical energy is achieved by using photoelectrochemical reaction driven by self-bias of narrow band gap photoelectrodes and the chemical energy is stored into an active material of a battery electrolyte; and when the battery is discharged, electrochemical reaction is carried out, thereby achieving transformation of the chemical energy into electric energy. The photoelectrochemical energy storage battery integrates a photoelectrochemical battery and a flow battery; the disadvantage that a solar cell cannot achieve electric energy storage is overcome; meanwhile, a single charging mode of the energy storage battery is also expanded; and solar energy in-situ transformation, storage and controllable utilization without assistance of external bias are achieved. Water-soluble fast reaction kinetics redox couples are adopted as the active material; the utilization rate of photo-induced carriers on the surfaces of photoelectrodes is close to 100%; meanwhile, the discharge power density of the battery can reach 0.5W / cm<2>; large-scale amplification can be achieved; and the photoelectrochemical energy storage battery is suitable for different scales of solar energy-energy storage-power generation processes.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Efficient and stable silicon-based photocatalytic hydrogen evolution electrode, preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN109267096ARaise the photovoltageThe operation process is simpleLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingChemical vapor deposition coatingChemistryTitanium oxide
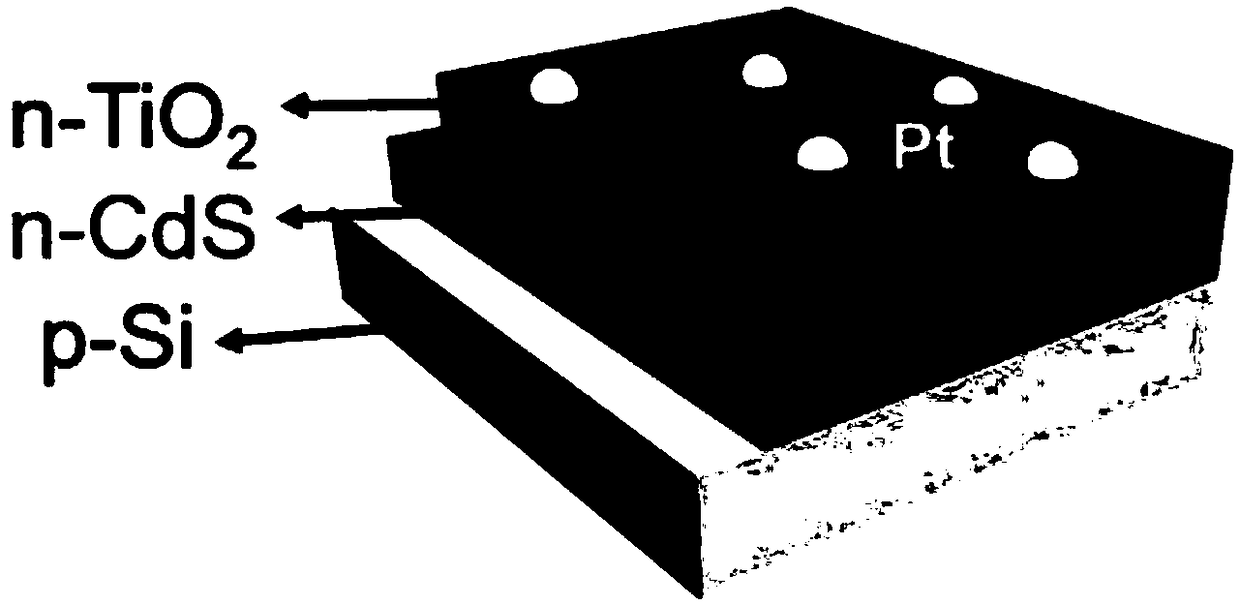
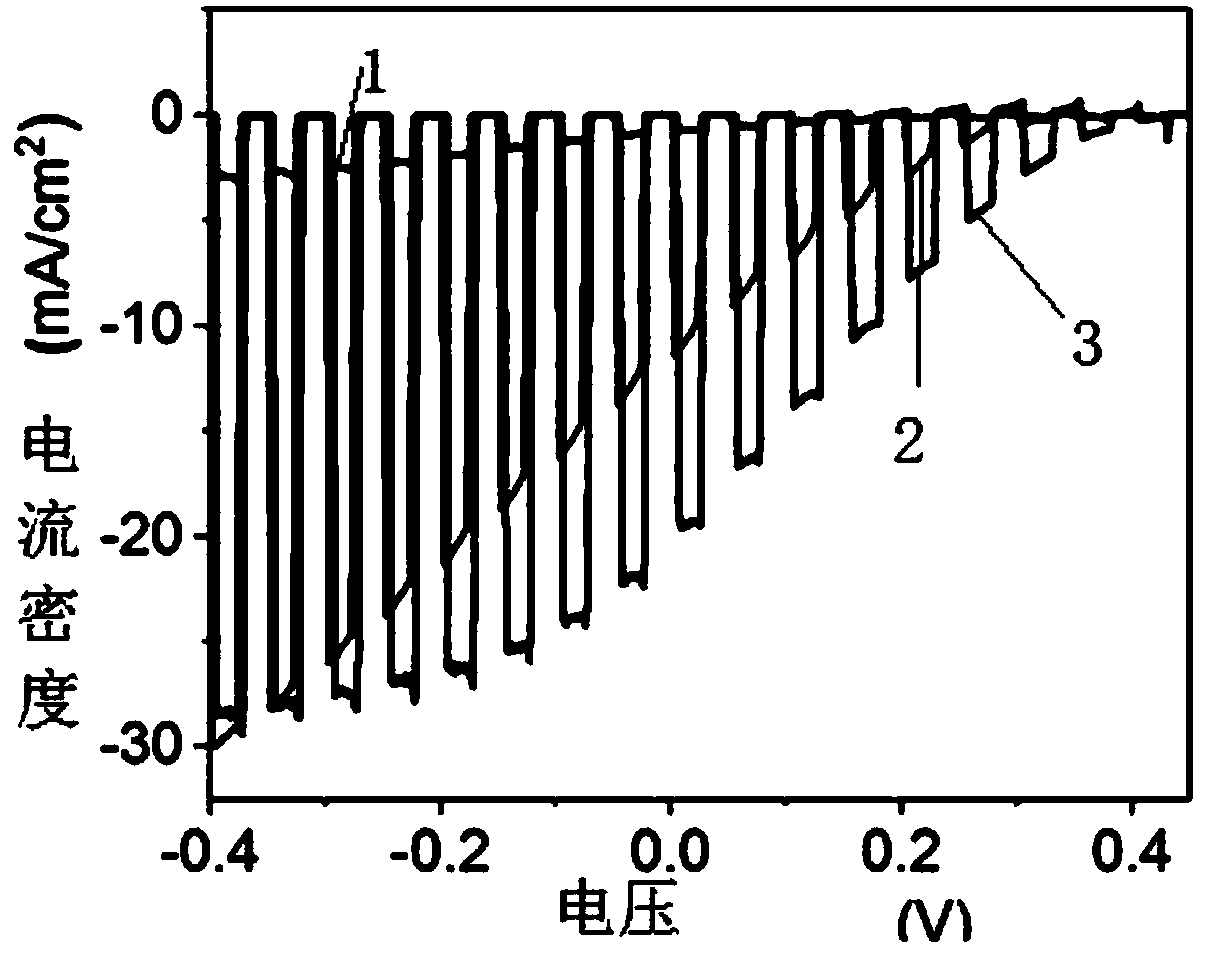
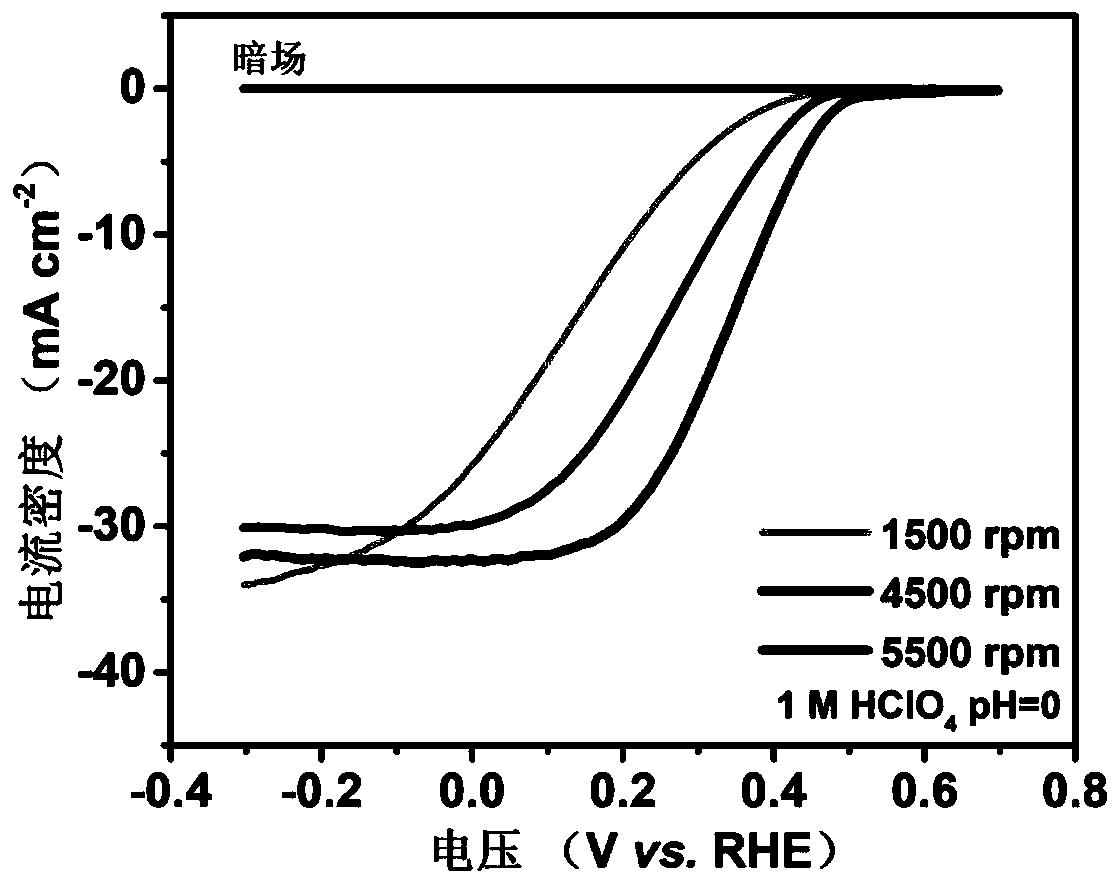
The invention discloses an efficient and stable silicon-based photocatalytic hydrogen evolution electrode, a preparation method and applications thereof, wherein the efficient and stable silicon-basedphotocatalytic hydrogen evolution electrode comprises a p-type silicon substrate, a cadmium sulfide heterojunction layer, a titanium oxide protection layer and a platinum co-catalyst. The preparationmethod mainly comprises four steps of silicon wafer substrate surface cleaning, cadmium sulfide layer deposition, titanium oxide layer deposition and platinum aid loading. According to the present invention, the preparation of silicon and cadmium sulfide heterojunction is effectively achieved, the photo-generated voltage is increased, the problem that the silicon-based photocathode is unstable inthe aqueous solution is solved, and the stability of the material is improved; and the preparation method has advantages of simple operation process, strong controllability, stable photoelectrocatalytic performance of the product, and good repeatability.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Novel 2,6-site-substituted BODIPY organic dye sensitizer and preparation method therefor
ActiveCN105238092ACommonly available raw materialsReduce manufacturing costMethine/polymethine dyesLight-sensitive devicesSynthesis methodsElectron donor
The present invention relates to a novel 2,6-site-substituted BODIPY organic dye sensitizer and a preparation method therefor. The organic dye sensitizer is organic photovoltaic materials with a D-pi-A structure. By taking a meso-site-substituted BODIPY core as a pi bridge framework, the sites 2 and 6 of the BODIPY core is respectively substituted by an electron donor and an electron acceptor. The present invention further discloses a preparation method for the above the dye sensitizer. The preparation method obtains a dye molecule having a general structural formula I by taking 2,4-dimethylpyrrole as an initial reaction raw material, performing a serials of simple synthesis reactions, and finally performing classical Suzuki coupling and Knoevenagel condensation reactions. The dye sensitizer synthesis method is simple, easy to control and high in yield, and has general applicability. When the method is applied to dye sensitized solar cell preparation, a dye sensitized solar cell material with a high fill factor and an ideal photoelectric conversion efficiency can be obtained. The formula I is shown in the description.
Owner:邳州市润宏实业有限公司
Pyramid silicon-based photocathode with uniform pn homojunction layer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110923817AIncrease photovoltageSafe preparationPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsSemiconductor electrodeEtching
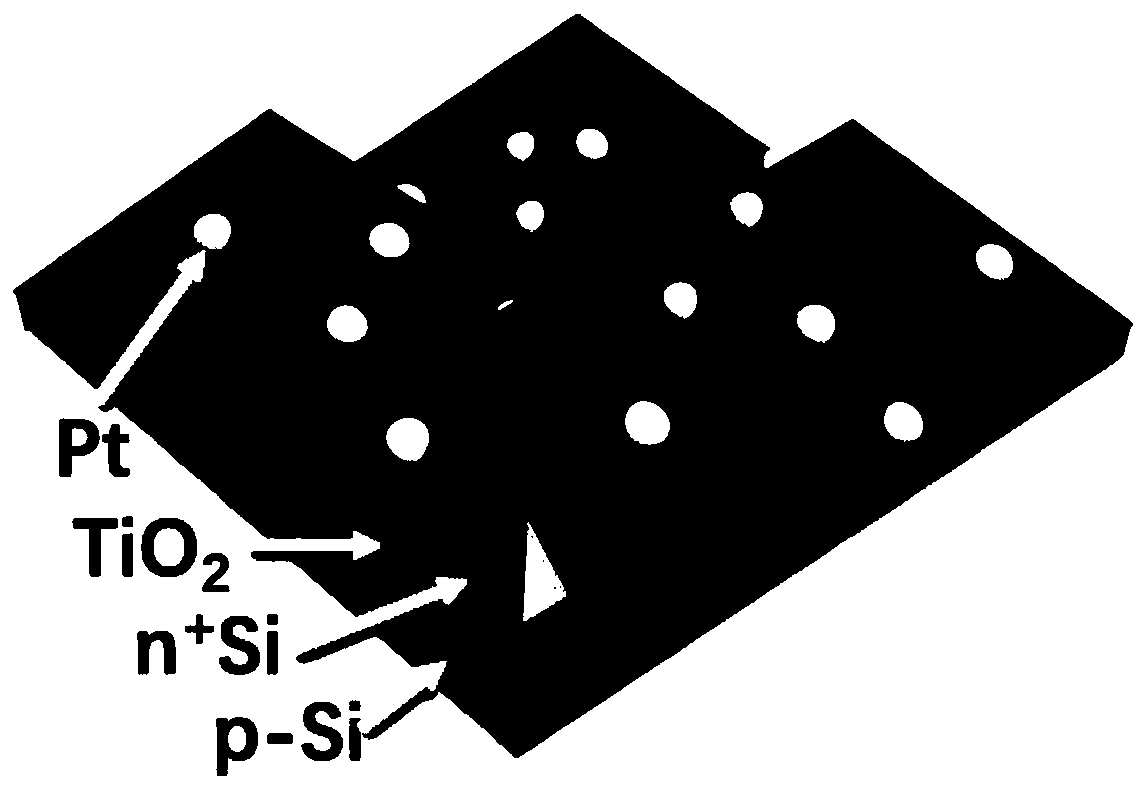
The invention belongs to the technical field of photoelectrochemical cell semiconductor electrodes, and discloses a pyramid silicon-based photocathode with a uniform pn homojunction layer and a preparation method thereof. The uniform pn homojunction layer is diffused on a pyramid morphology p-type silicon substrate, a titanium dioxide protective layer is deposited on an atomic layer on the pn homojunction layer, and platinum nanoparticles are photoelectrically deposited on the titanium dioxide protective layer to serve as a catalyst. The preparation method mainly comprises five steps of silicon wafer substrate pyramid morphology etching, surface cleaning, spin coating and high-temperature diffusion, titanium dioxide layer deposition and platinum catalyst loading. the uniform pn homojunction layer is effectively prepared on the pyramid-shaped silicon substrate, and the photo-generated voltage and the stability are improved; AND the preparation method has the advantages of safe and simple operation process, cheap and easily available raw materials, stable photoelectrocatalysis performance and good repeatability.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
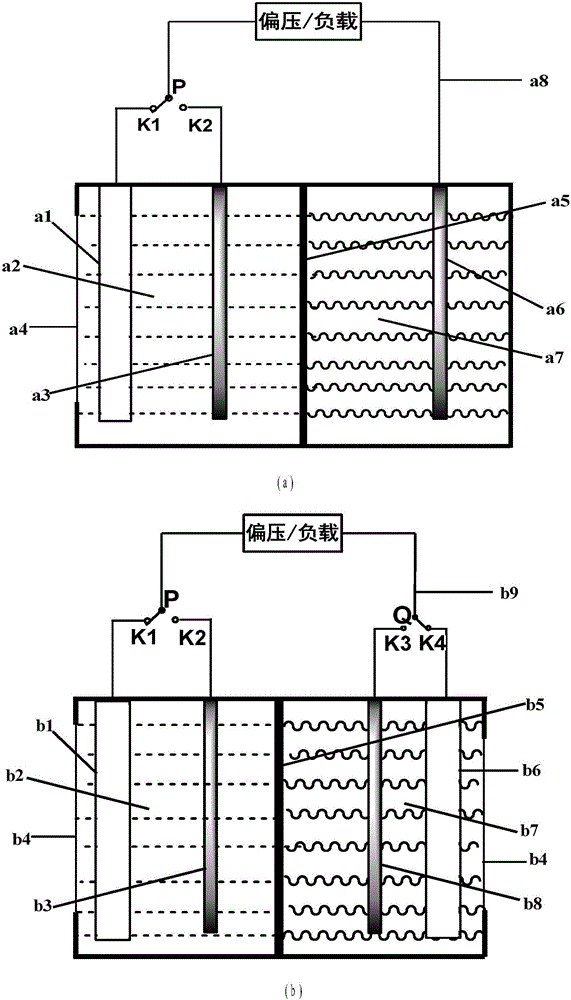
Photoelectrochemical cell, system and process for light-driven production of hydrogen and oxygen with a photoelectrochemical cell, and process for producing the photoelectrochemical cell
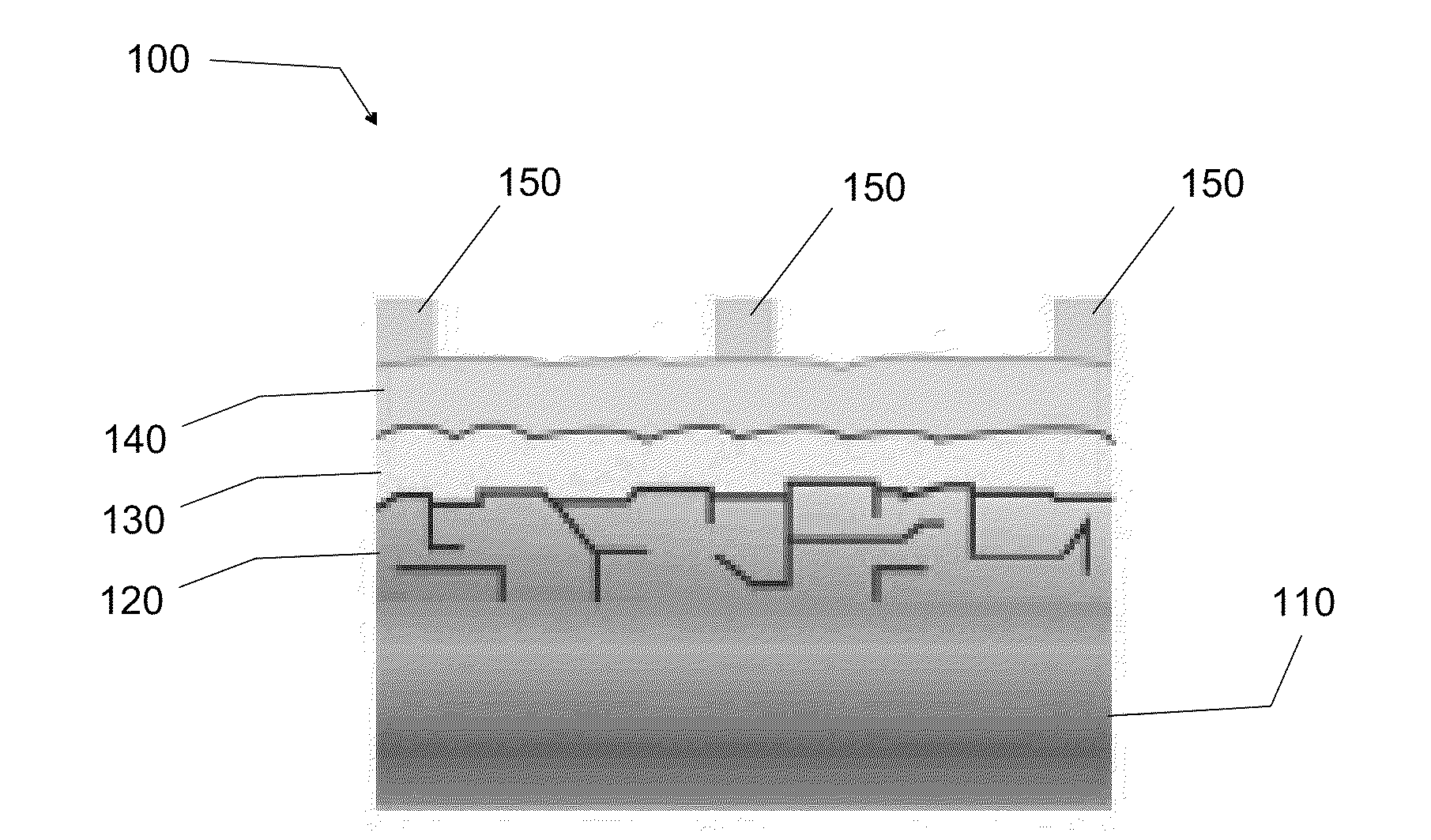
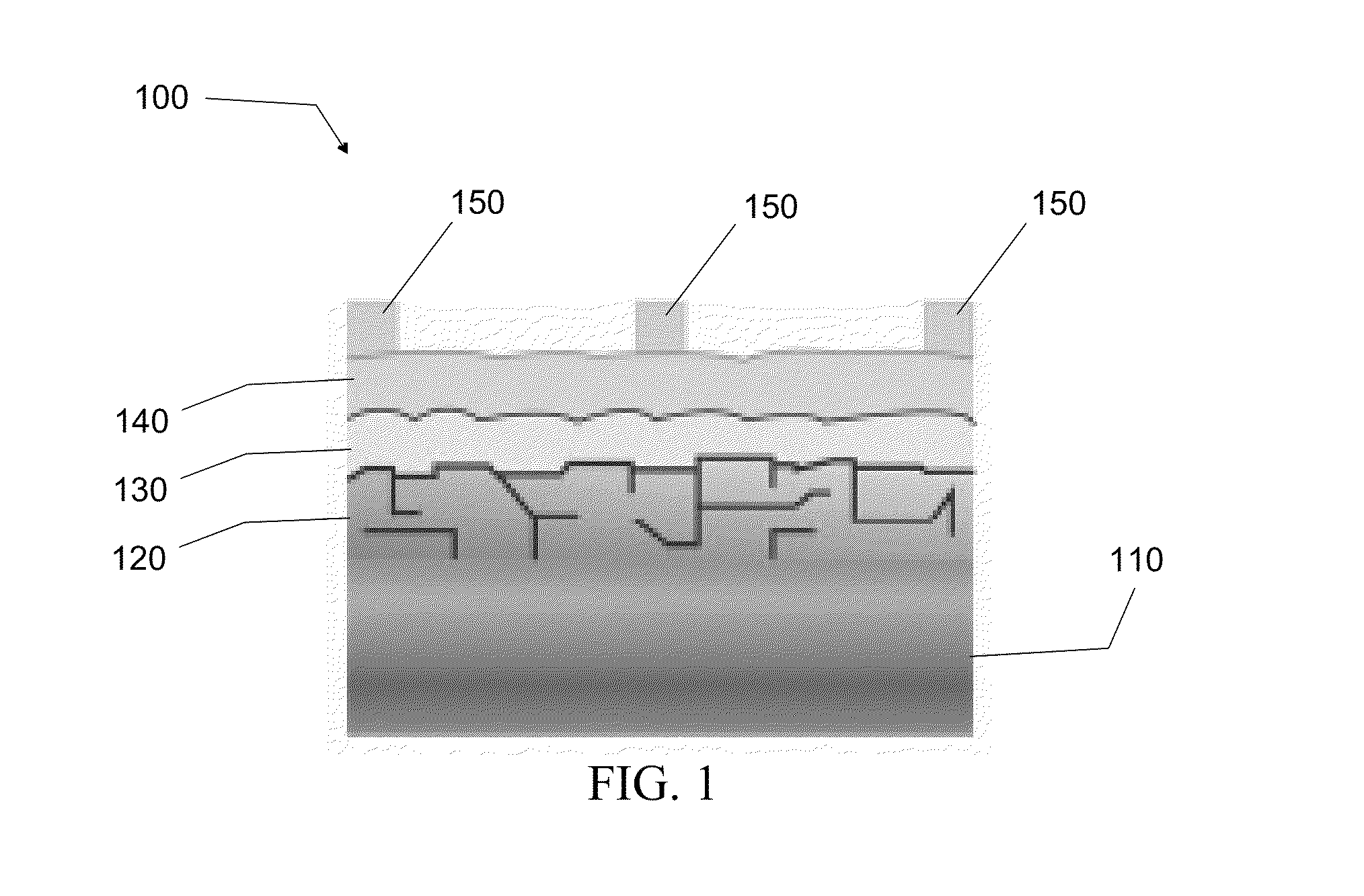
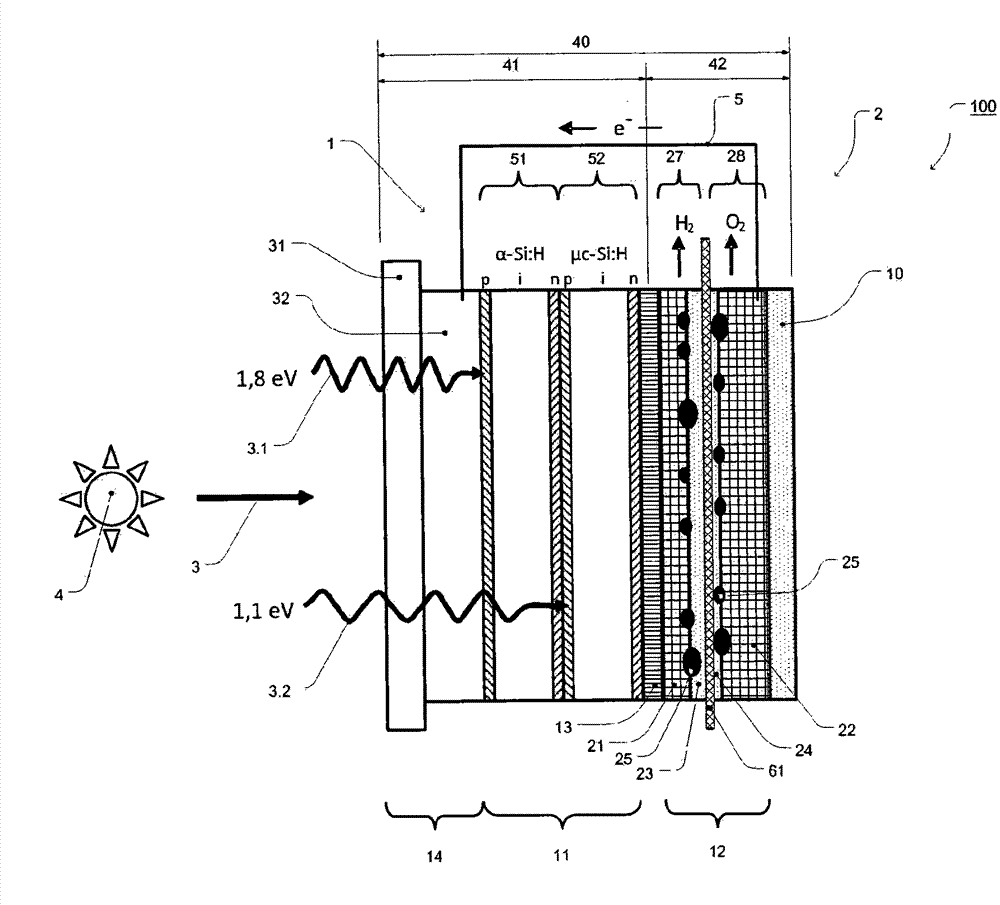
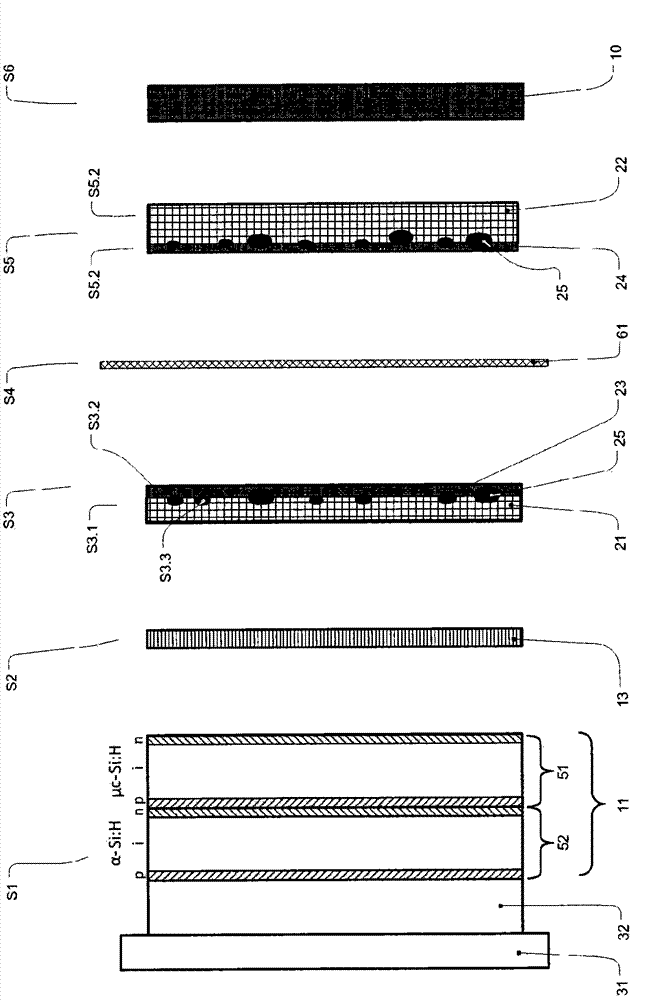
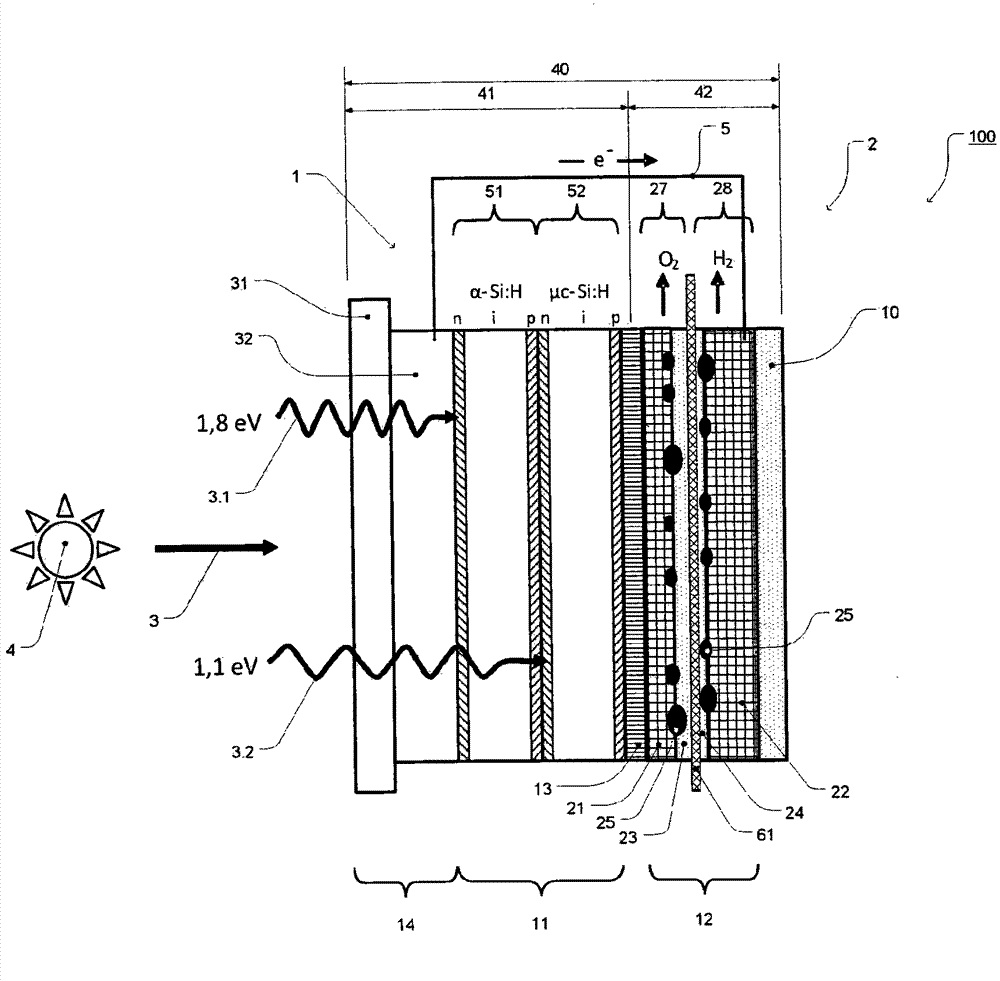
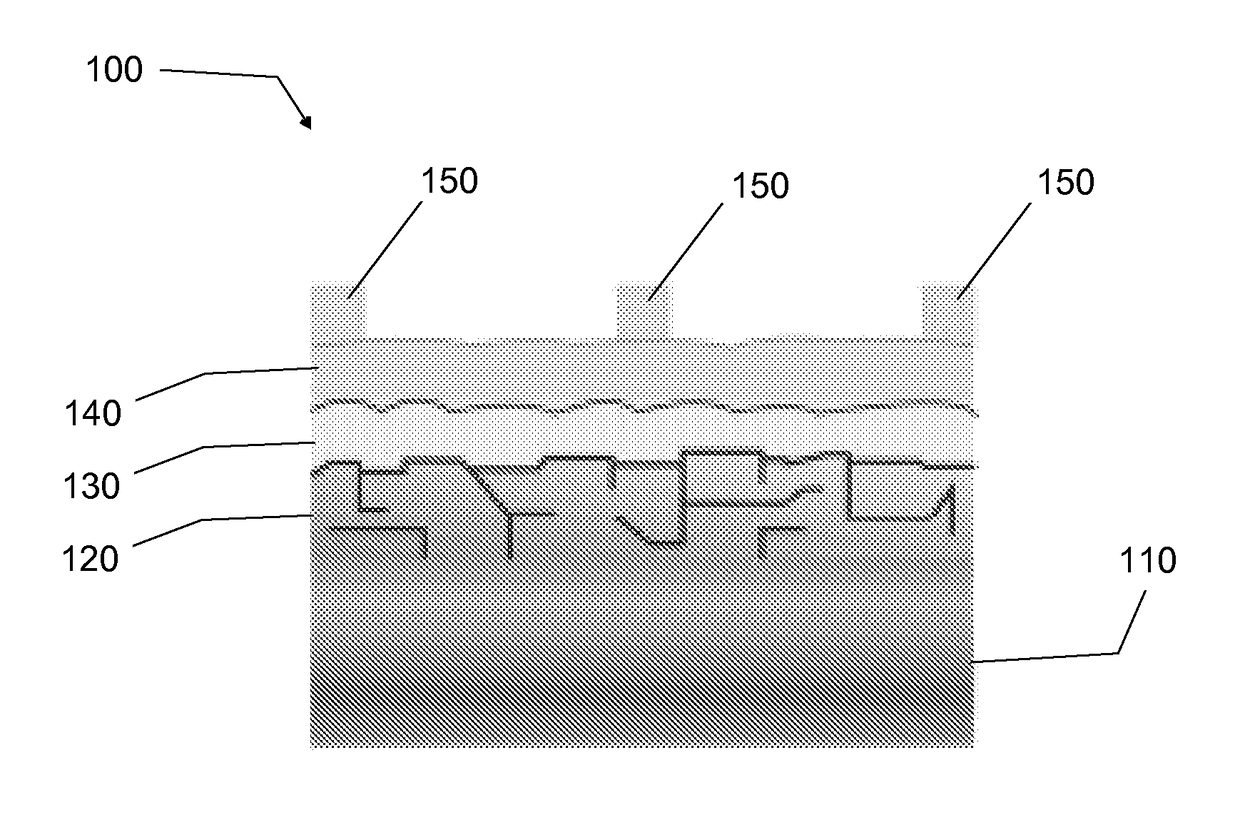
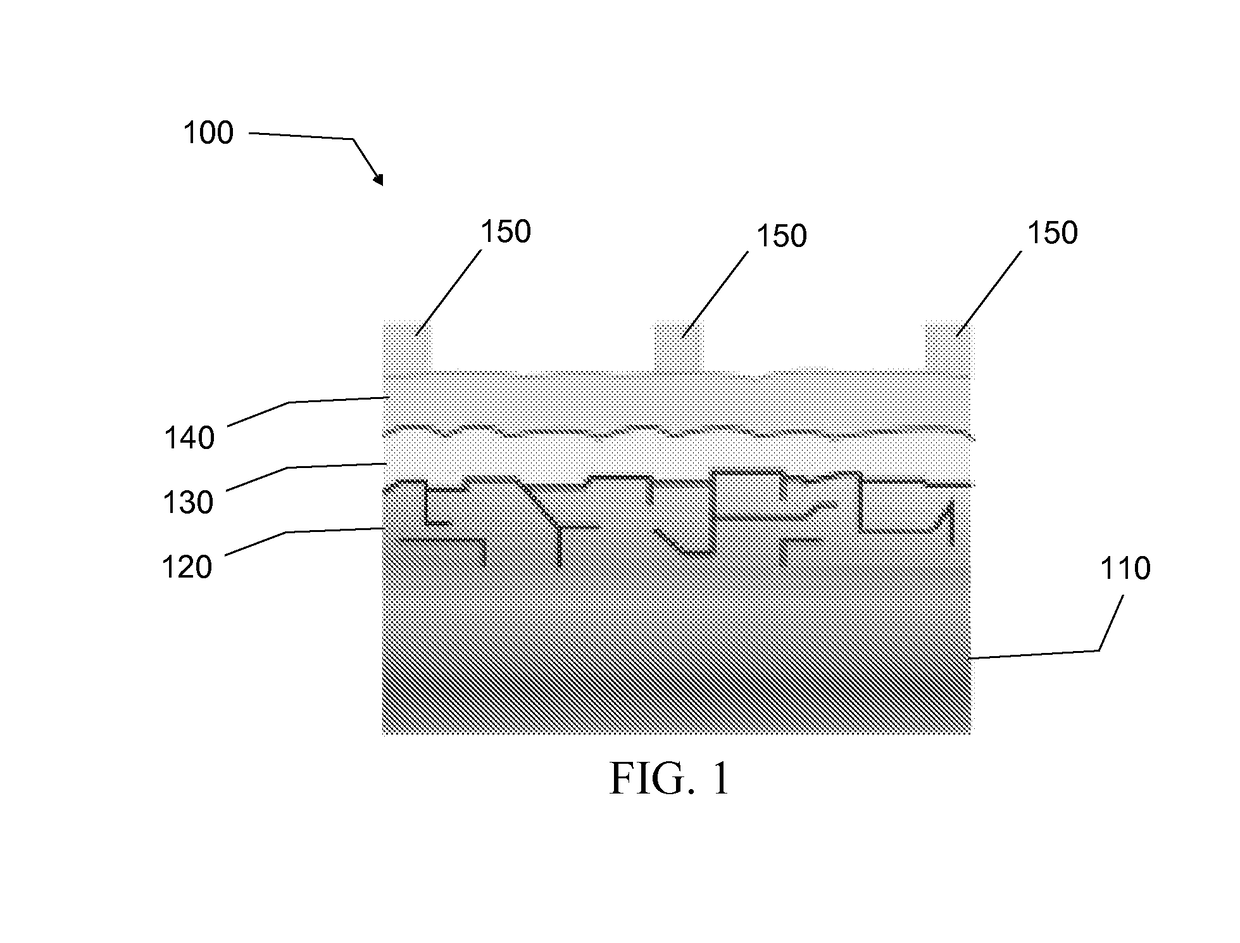
The invention relates to a photoelectrochemical cell 100 for light-driven production of hydrogen and oxygen, especially from water or another electrolyte based on aqueous solution, having a photoelectric layer structure 1 and an electrochemical layer structure 2 in a layer construction 40, where - the photoelectric layer structure 1 for absorption of light 3 uninfluenced by the electrolyte 10 forms a front side 41 of the layer structure 40, and - the electrochemical layer structure 2, for accommodation of the electrolyte 10, forms a reverse side 42 of the layer construction 40, and - a conductive and corrosion-inhibiting coupling layer 13 forms electrical contact between the photoelectric layer structure 1 and the electrochemical layer structure 2 in the layer construction 40, where - the electrochemical layer structure 2 has an electrode structure of a front electrode 21 and an electrode structure of a rear electrode 22, between which is arranged an ion exchange layer 61 such that an integrated layer construction 40 is formed with the ion exchange layer 61 in contact with the electrode structure of the front electrode 21 formed for conversion of the electrolyte 10 and / or with the electrode structure of the rear electrode 22.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Tantalum oxide protected P-type silicon photocatalytic hydrogen evolution electrode and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109267097AImprove stabilityFacilitate surface reactionEnergy inputElectrodesPtru catalystPhotocathode
The invention discloses a tantalum oxide protected P-type silicon photocatalytic hydrogen evolution electrode and a preparation method thereof, wherein the tantalum oxide protected P-type silicon photocatalytic hydrogen evolution electrode comprises a surface phosphorus heavily doped p-type silicon substrate, a tantalum pentoxide outer protection layer and a platinum co-catalyst. The preparation method mainly comprises three steps of silicon wafer substrate surface heavy doping treatment, tantalum pentoxide outer protection layer depositing and platinum co-catalyst loading. According to the present invention, with the preparation method, the surface heavy doping of the silicon substrate is achieved, the initial potential of the photoelectrochemical cell photocatalytic hydrogen evolution isincreased, the instability of the silicon-based photocathode in the aqueous solution is solved, and the stability of the material is improved; and the preparation method has advantages of simple operation process, strong controllability, stable photoelectrocatalytic performance of the product, and good repeatability.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Preparation method of dye-sensitized solar cell grapheme-doped composite electrode
ActiveCN103337368AEasy transferHigh densityLight-sensitive devicesFinal product manufactureDoped grapheneSlurry
The invention discloses a preparation method of a dye-sensitized solar cell grapheme-doped composite electrode. The preparation method comprises the following steps that: a hydrothermal method is adopted to prepare a TiO2 nano array on conductive glass, and as a result, direct electron channels are provided, and the diffusion length of electrons can be increased, and electron recombination can be reduced, and the lifetime of the electrons can be increased; the hydrothermal method is adopted to prepare TiO2-graphene nano particles, and as a result, doped graphene can not only reduce the recombination of photogenerated electrons and holes, but also can enhance the capture of light, and the number of the photogenerated electrons can be increased; the TiO2-graphene nano particles are printed on the TiO2 nano array through a screen printing method, and as a result, a larger specific surface area can be obtained, and dye adsorption quantity can be increased; an organic solvent can be removed from a slurry through sintering; and the dye is adsorbed, and the dye-sensitized solar cell grapheme-doped composite electrode can be obtained.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
TiO2 nano-tube doped with cobalt element and preparation method thereof and applications
ActiveCN108206094AHigh activityGood tubular shapeLight-sensitive devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationPhotocatalytic degradationCobalt
The present invention discloses a TiO2 nano-tube doped with a cobalt element and a preparation method thereof and applications. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a TiO2 nano-scale powder doped with the cobalt element via a TiCl4 hydrolysis method; and preparing the TiO2 nano-tube doped with a cobalt element by using a hydrothermal synthesis method combined with a liquid-phase deposition treatment. The TiO2 nano-tube doped with the cobalt element can maintain good tubular morphology under 400 DEG C heat treatment, the crystal structure is an anatase / rutile mixed crystal structure, and the nano-tube has relatively high specific surface area. The recombination of photo-generated electron-hole pair is effectively inhibited via cobalt element doping combined withthe liquid-phase deposition process, so that the activity of photo-catalytic degradation of methyl orange is largely improved, and an assembled dye-sensitized solar cell taking the prepared TiO2 nano-tube doped with the cobalt element as an anode material shows excellent photoelectric conversion performance.
Owner:FOSHAN UNIVERSITY
Graphene/silicon photodetector with passivated interface and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104600131AIncrease photovoltageHigh on/off ratioFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
The invention discloses a graphene / silicon photodetector with a passivated interface and a preparation method thereof. The graphene / silicon photodetector with the passivated interface is provided with a back electrode, a silicon wafer, an aluminum oxide layer, a graphene layer and a front electrode in sequence from the bottom to top. The preparation method includes that growing the aluminum oxide layer with 0.2 to 10 nanometers in thickness on one surface of the clean silicon wafer, transferring the graphene to the aluminum oxide layer, and respectively manufacturing the front electrode and back electrode on the other surfaces of the graphene and the silicon wafer. According to the graphene / silicon photodetector with the passivated interface, an aluminum oxide interface passivation layer is added between the silicon wafer and the graphene, and the special structure is capable of improving the photovoltage of the photodetector and the switch ratio thereof; the preparation method is simple in technique, low in cost and convenient to popularize.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Quasi-solid nano-composite gel electrolyte, its production and use
InactiveCN100470685CImprove performanceSolve the sealing problemIndividual molecule manipulationCapacitor electrolytes/absorbentsFuel cellsLiquid state
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Carbon-based perovskite solar cell based on multifunctional interface modification layer
InactiveCN110676385AEasy to prepareLow costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical batteryEngineering
The invention discloses a carbon-based perovskite solar cell based on a multifunctional interface modification layer, which belongs to the field of photoelectric devices, and particularly relates to alkali metal hydroxide as an interface modification layer between an electron transport layer and a perovskite light absorption layer and used for a perovskite solar cell. The carbon-based perovskite solar cell based on the multifunctional interface modification layer structurally comprises a transparent conductive substrate, an electron transport layer, a perovskite layer and a carbon electrode. Alkali metal hydroxide is modified between the electron transport layer and the perovskite layer mainly by a coating method. The modification layer improves the film forming quality of the perovskite layer by reducing the interfacial tension and the work function of the electron transport layer so as to promote carrier transport between interfaces and weaken non-radiative recombination in the film.The photoelectric conversion efficiency and the open-circuit voltage of the all-inorganic carbon-based perovskite solar cell integrated by the method are remarkably improved, and the stability and the hysteresis effect are remarkably improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method to synthesize colloidal iron pyrite (FeS2) nanocrystals and fabricate iron pyrite thin film solar cells
ActiveUS9862617B2Excellent manufacturing scalabilityLow costMaterial nanotechnologySpecial surfacesHeterojunctionGas phase
Systems and methods are provided for the fabrication and manufacture of efficient, low-cost p-n heterojunction pyrite solar cells. The p-n heterojunction pyrite solar cells can include a pyrite thin cell component, a window layer component, and a top surface contact component. The pyrite thin cell component can be fabricated from nanocrystal paint deposited onto metal foils or microcrystalline pyrite deposited onto foil by chemical vapor deposition. A method of synthesizing colloidal pyrite nanocrystals is provided. Methods of manufacturing the efficient, low-cost p-n heterojunction pyrite solar cells are also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Efficient ternary organic solar cell prepared based on step-by-step deposition method
PendingCN111883659AOptimize energy level structureIncrease photovoltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic solar cellHeterojunction
The invention discloses an efficient ternary organic solar cell prepared based on a step-by-step deposition method, and the solar cell comprises a substrate, an anode, an anode modification layer, anactive layer, a cathode modification layer and a cathode from bottom to top, wherein the active layer is a wide-band-gap polymer donor (PM6) film and a non-fullerene receptor compound (a mixture of BO-4Cl and BTP-S2) film which are sequentially deposited on the anode modification layer by adopting a spin-coating process. By utilizing poor compatibility between BTP-S2 and PM6 and large shearing force during film formation of a spin-coating process, the active layer can have an ideal PiN morphology structure, namely, a donor rich phase is formed at the interface of the anode modification layer,a receptor rich phase is formed at the interface of the cathode modification layer, and a bulk heterojunction thick film in which a donor and a receptor are uniformly mixed is formed in the middle. Therefore, according to the ternary organic solar cell obtained by the invention, efficient generation and efficient collection of photocurrent are realized at the same time, the PCE is not only higherthan that of a corresponding bulk heterojunction ternary cell, but also the highest efficiency (18.50%) of the organic solar cell so far is obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
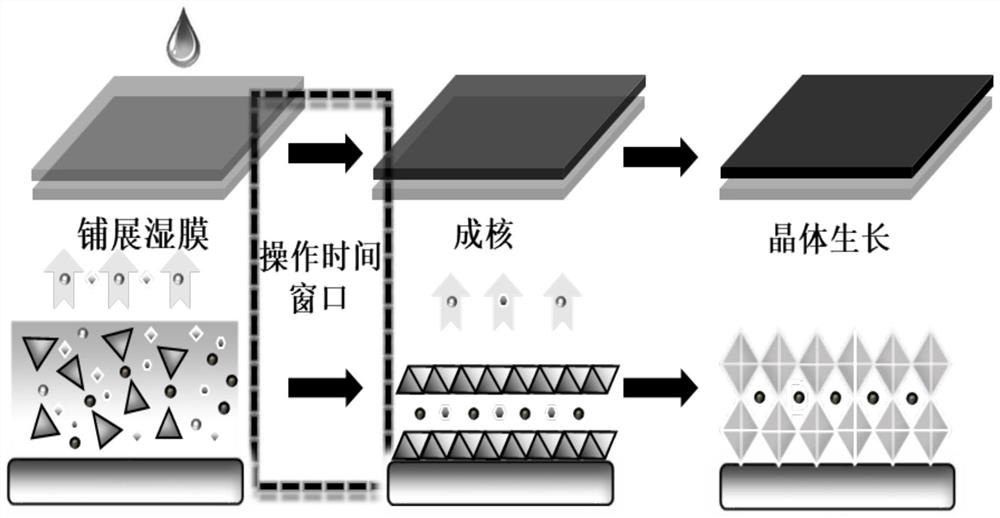
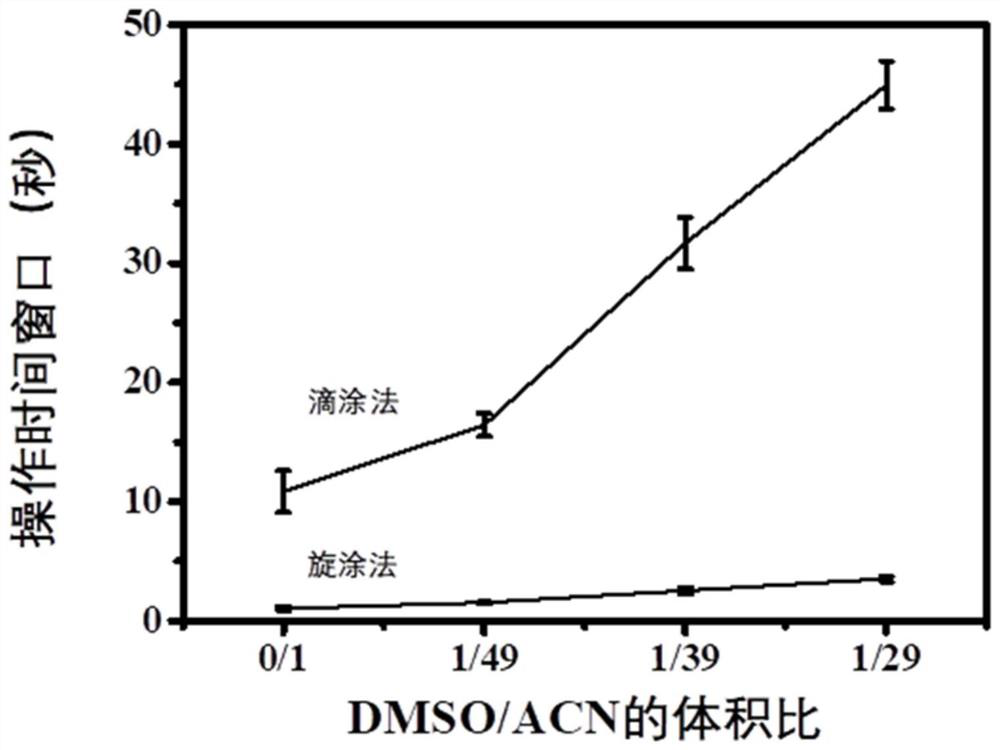
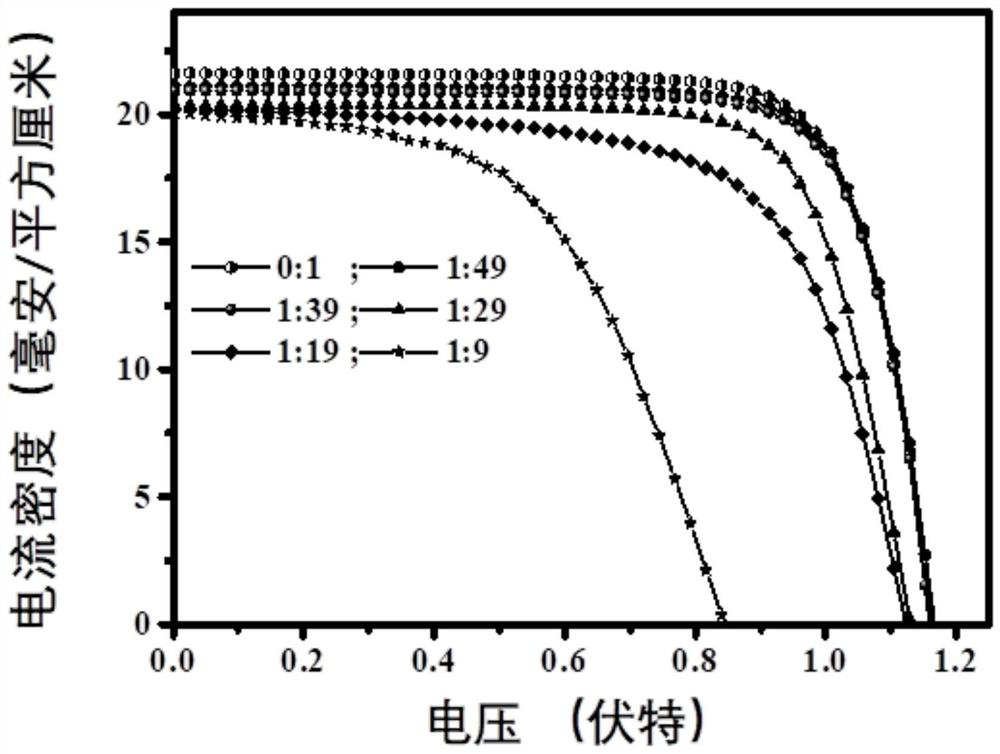
Perovskite solution with controllable and adjustable operation time window, cell, preparation method and application
ActiveCN113637355ANovel preparation methodStable outputSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPerovskite solar cellPyrrolidinones
The invention discloses a perovskite solution with a controllable and adjustable operation time window, a cell, a preparation method and application, and belongs to the field of perovskite solar cells. The perovskite solution comprises perovskite ABX3, an acetonitrile solvent and a coordination type solvent, A site is a methylamine ion, B site is a lead ion, X site is a halide ion, and the coordination type solvent is selected from dimethyl sulfoxide, N-methyl pyrrolidone and 4-tert-butylpyridine. The preparation method comprises the following steps: placing perovskite single crystals or iodine methylamine and lead iodide powder prepared by stoichiometric ratio in a methylamine atmosphere to obtain a yellow perovskite precursor solution, or dissolving the perovskite single crystals or iodine methylamine and lead iodide powder prepared by stoichiometric ratio in a methylamine ethanol solution to obtain a viscous yellow perovskite precursor solution, and then, uniformly mixing the coordination solvent and acetonitrile to obtain the perovskite ink. The invention also provides the perovskite cell, the preparation method and the application. The ink disclosed by the invention can realize adjustment of a processing time window and is extremely high in industrial applicability.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
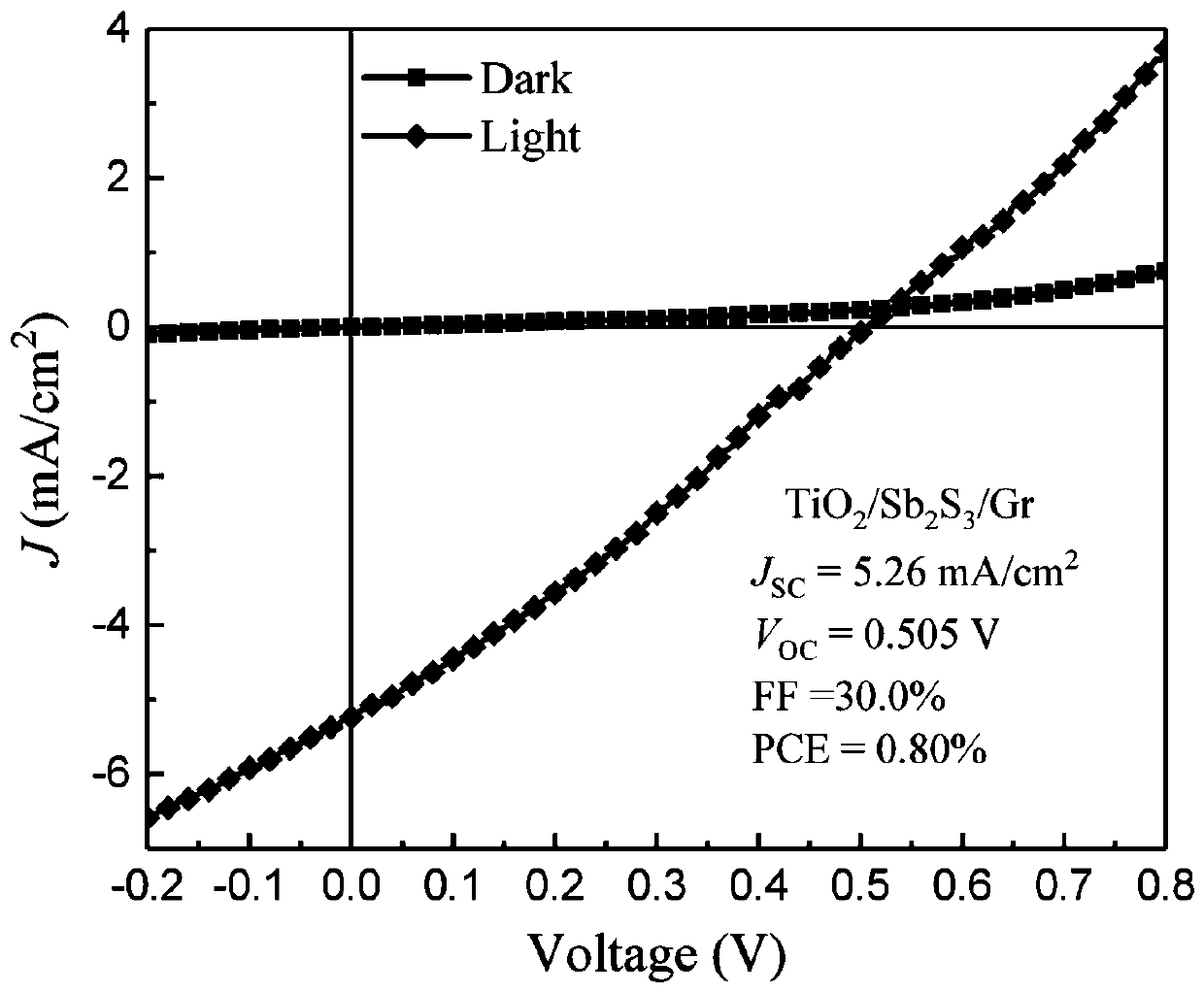
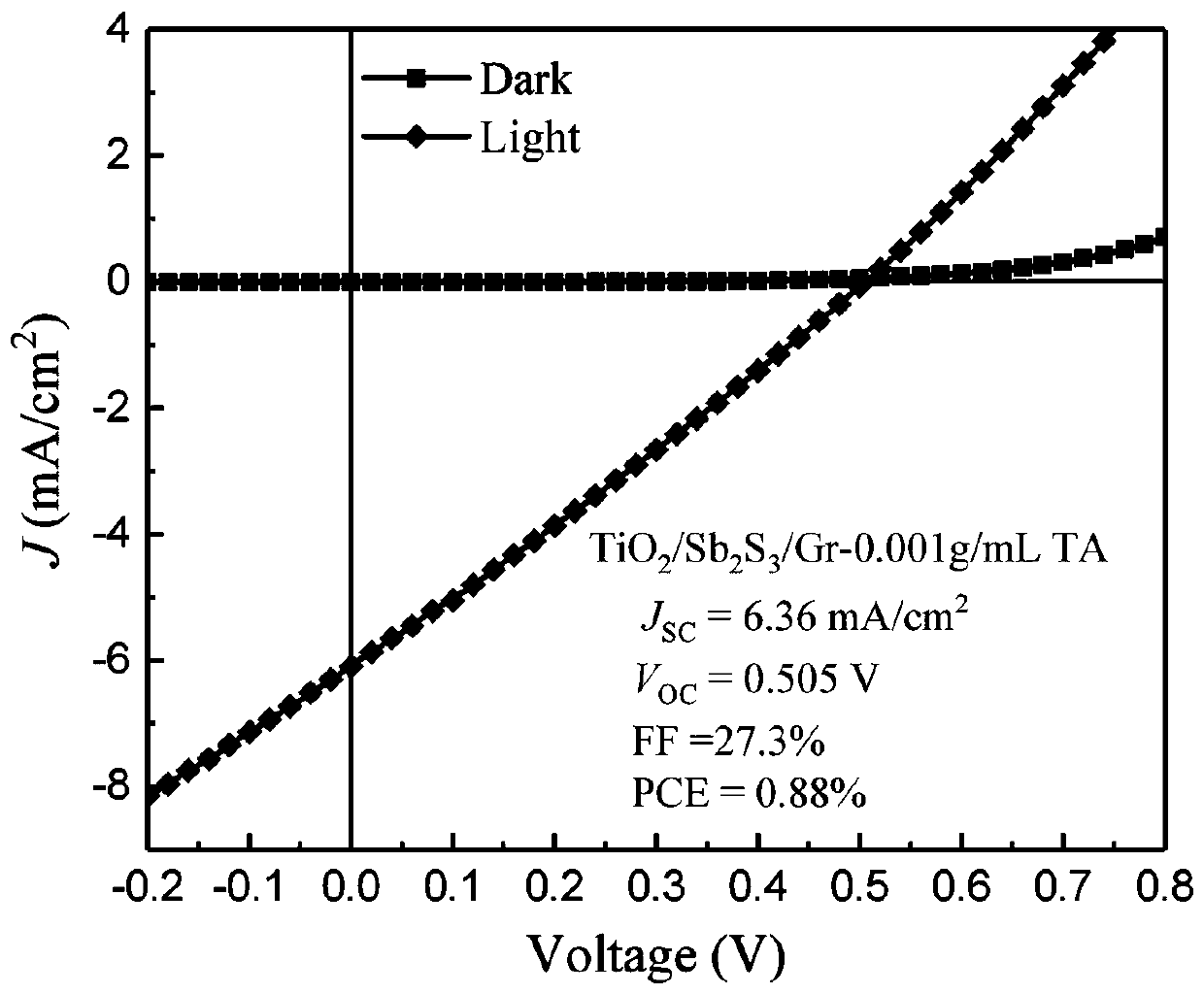
Fabrication method of Sb2S3-based full-inorganic thin film solar cell
ActiveCN107863401AImprove matchLarge open circuit photovoltageFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationVulcanizationEvaporation
The invention discloses a fabrication method of a Sb2S3-based full-inorganic thin film solar cell. The fabrication method comprises the steps of firstly, fabricating a layer of compact TiO2 thin filmon an FTO by employing a sol-gel method; secondly, depositing a Sb2S3 thin film by thermal evaporation after annealing of the TiO2 thin film, and performing surface vulcanization and simultaneously performing annealing on the Sb2S3 thin film by employing thioacetamide; and finally, transferring a graphene thin film grown by a chemical vapor deposition method to the Sb2S3 thin film to form a TiO2 / Sb2S3 / Gr thin film structure. The device obtains an open-circuit light voltage being 560mV, a short-circuit light current being 6.8 mA / cm<2> and photoelectric conversion efficiency being 1.17% under simulation sunlight source irradiation of 100 mW / cm<2> in a room temperature. Graphene is used as a hole transmission layer and a transparent conductive electrode of the Sb2S3-based solar cell, thus, the Sb2S3-based solar cell is low in cost and is simple to fabricate; and compared with the Sb2S3-based solar cells mostly employing organic hole transmission holes, the Sb2S3-based full-inorganic thinfilm solar cell has more stable device performance.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Organic Solar Cell or Photodetector Having Improved Absorption
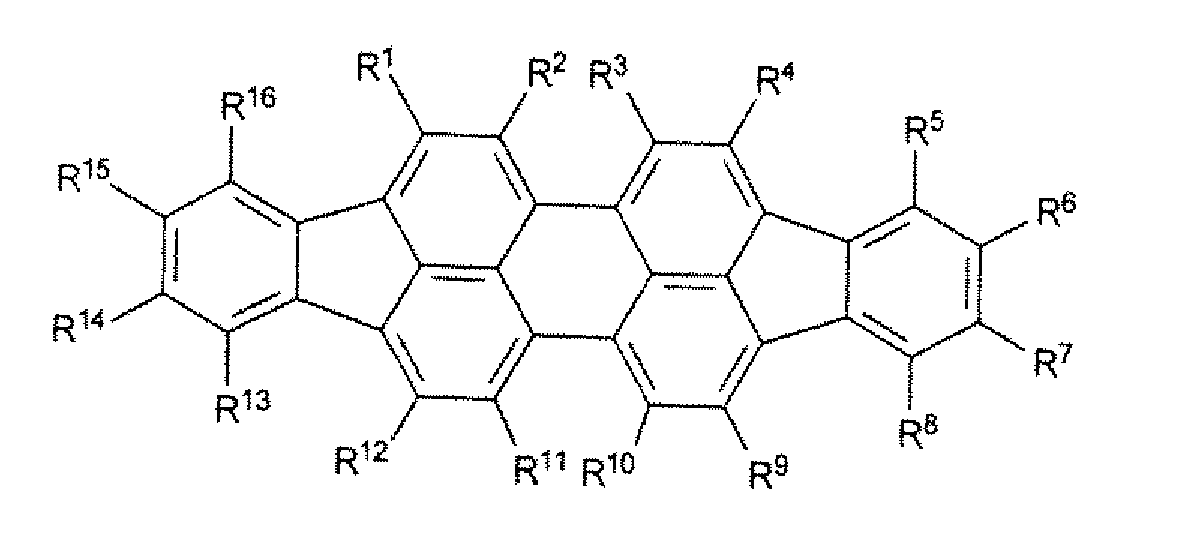
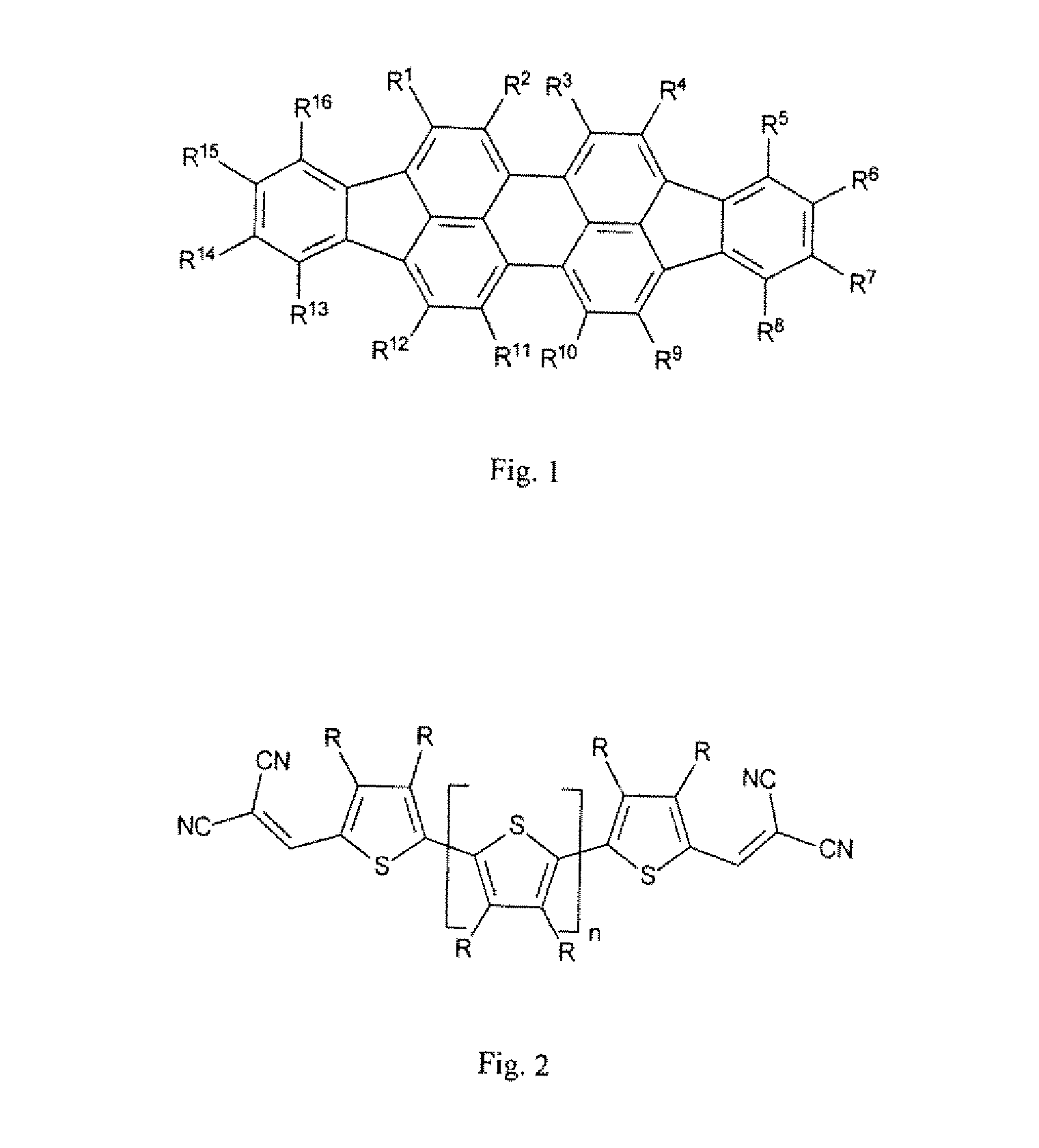
InactiveUS20120152303A1Improve concentrationEasy to manufactureMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic chemistryArylOrganic solar cell
The invention relates to an organic photoactive component, especially a solar cell or a photodetector, built up from a plurality of layers, wherein at least one of the layers comprises at least one di-indeno[1,2,3-cd:1′,2′,3′-lm]perylene compound of the general formula in Illustration 1, wherein each R1-R16 is independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, unsubstituted or substituted, saturated or unsaturated C1-C20-alkyl, C1-C20-heteroalkyl, C6-C20-aryl, C6-C20-heteroaryl, saturated or unsaturated carbocycle or heterocycle, which may be the same or different, wherein two adjacent radicals R1-R16 may also be part of a further saturated or unsaturated, carbocyclic or heterocyclic ring, wherein the ring may comprise C, N, O, S, Si and Se, and the use of the said component.
Owner:DRESDEN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for filling surface molecular layer defects of wide bandgap semiconductor adopting nano structure
ActiveCN103390504ABlock approachExtended tunneling distanceLight-sensitive devicesCapacitor electrodesSemiconductor electrodeSolubility
The invention provides a method for filling surface molecular layer defects of a wide bandgap semiconductor adopting a nano structure, and effectively solves the problems that the interface charge composition is fast and the charge collecting efficiency is reduced during short-circuit due to the use of a cobalt-based single electron mediator with characteristics of low charge transfer reorganization energy and the like. The method comprises the steps as follows: an electrode of the wide bandgap semiconductor adopting the nano structure is soaked in a dye solution for dyeing; then a dyed semiconductor film is soaked in a solution containing a filling agent for filling the dye molecular layer defects; and the solubility of the dye in the solution containing the filling agent is smaller than 10 micromoles per litre. The invention further provides an application of the semiconductor electrode obtained with the method for filling the molecular layer defects of the wide bandgap semiconductor in dye-sensitized solar cells. According to the method for filling the surface molecular layer defects of the wide bandgap semiconductor adopting the nano structure, an electron tunneling distance of an interface composite reaction can be effectively controlled, so that the interface charge composition of the dye-sensitized solar cells is slowed down, and photovoltage, photocurrent and power conversion efficiency of a device can be improved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of TiO2 nanoparticles with photonic crystal characteristics
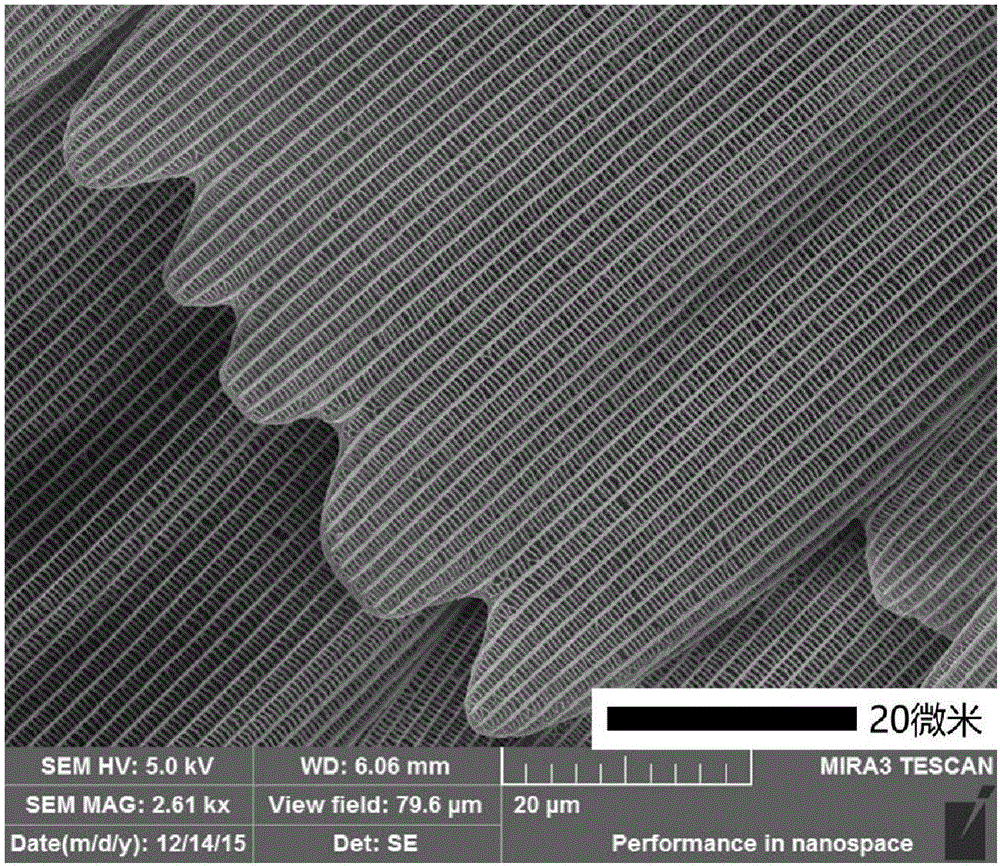
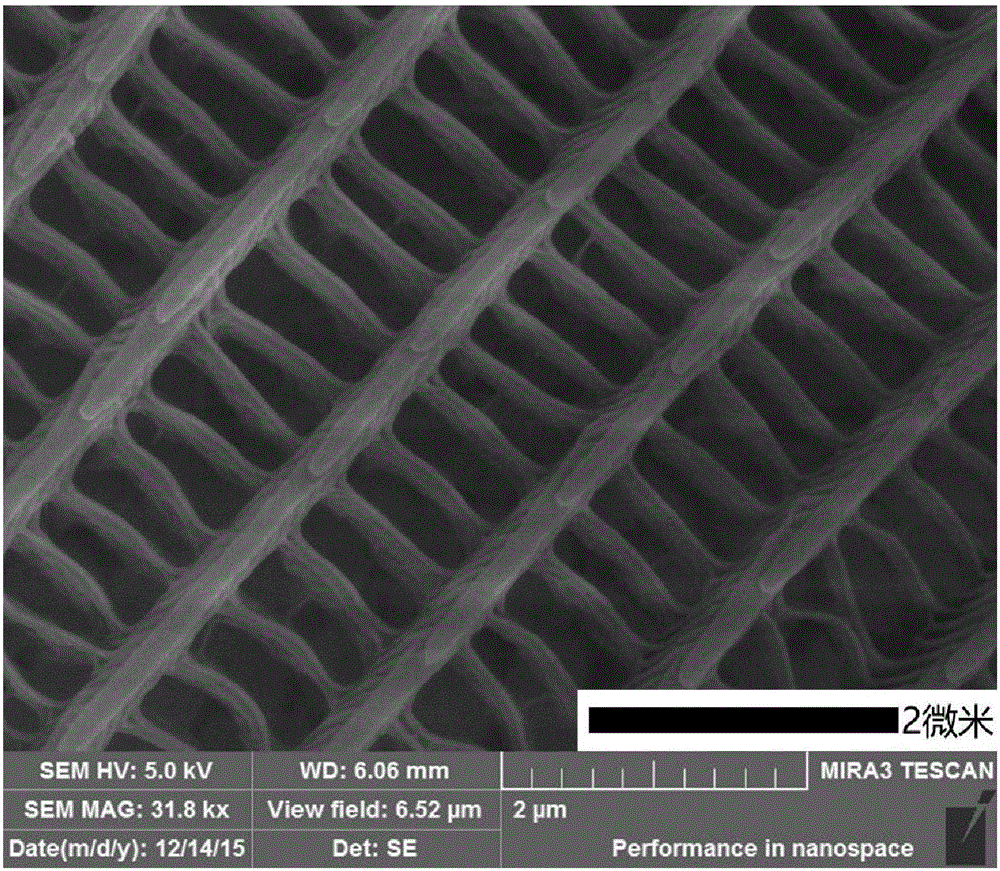
The invention discloses a preparation method of TiO2 nanoparticles with photonic crystal characteristics. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a precursor solution by mixing TiCl4 solution, absolute ethyl alcohol and deionized water; and with butterfly wings as a bio-template, treating the template by a solution impregnation method and removing the template at a high temperature to obtain the TiO2 nanoparticles. The preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple technology, easily available raw materials, good product structure and performance and the like; and the prepared TiO2 nanoparticles with photonic crystal characteristics have a good application prospect in the field of thin-film solar cell study.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
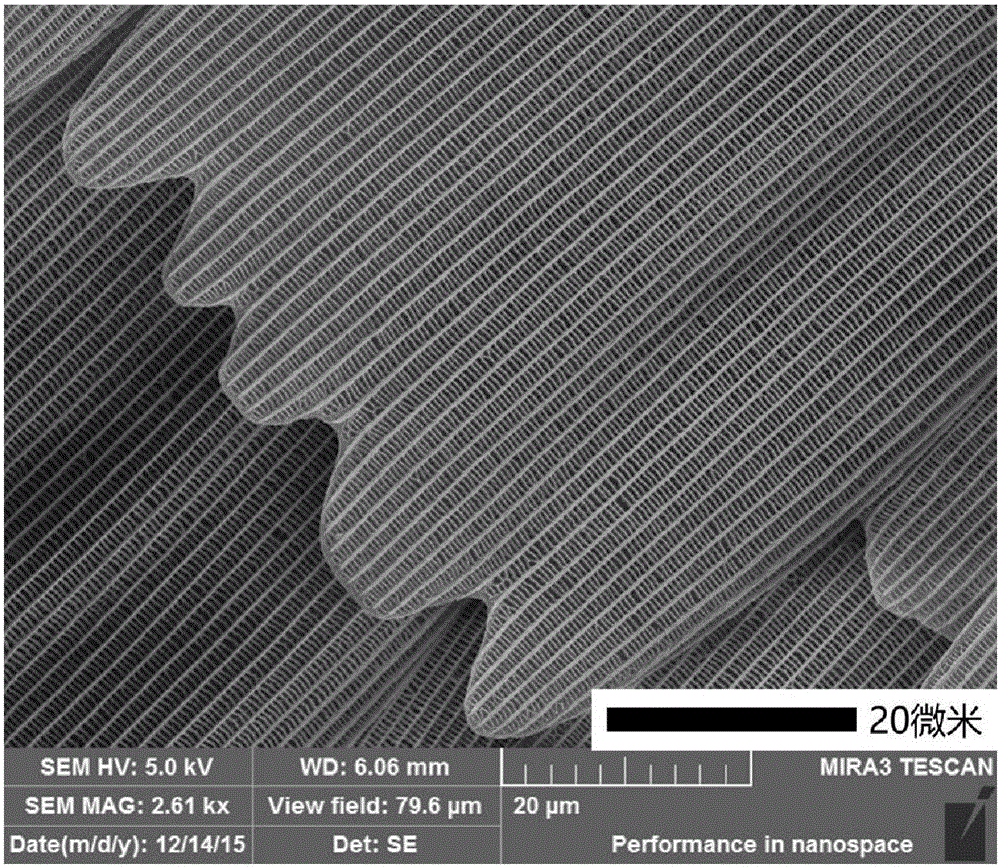
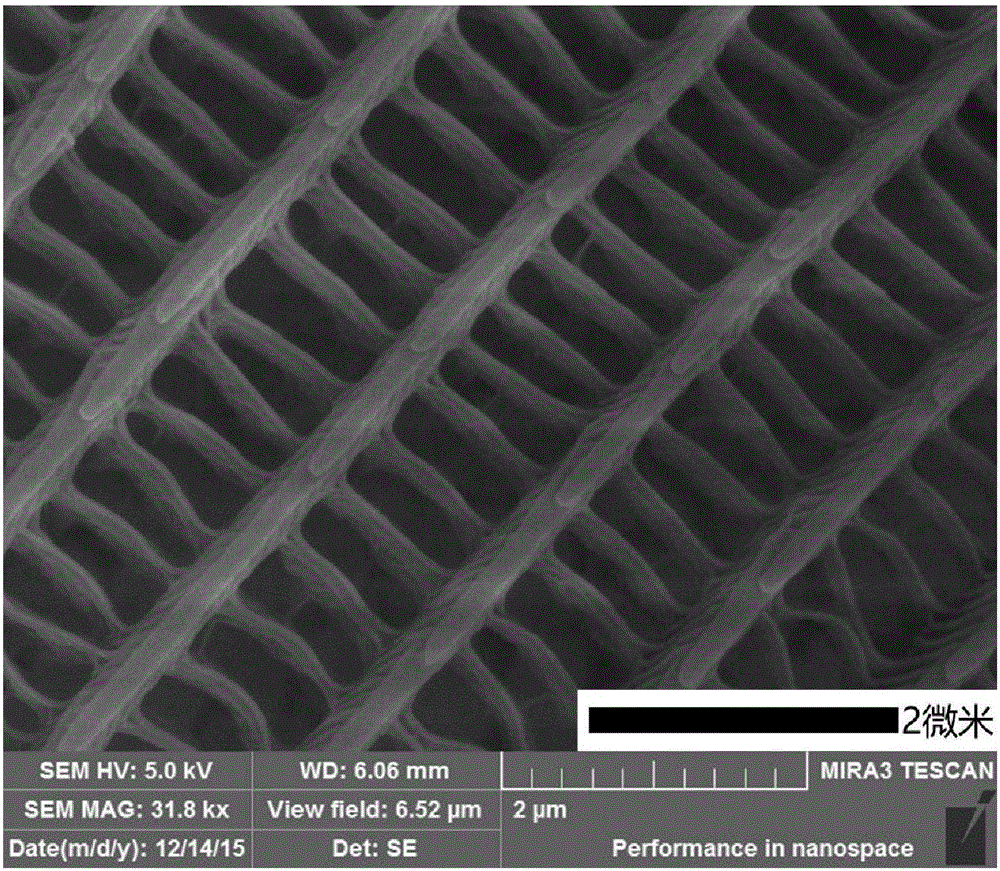
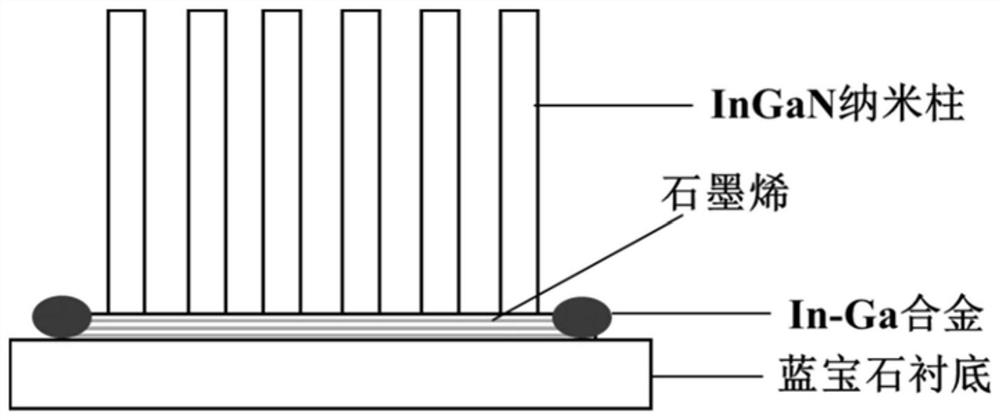
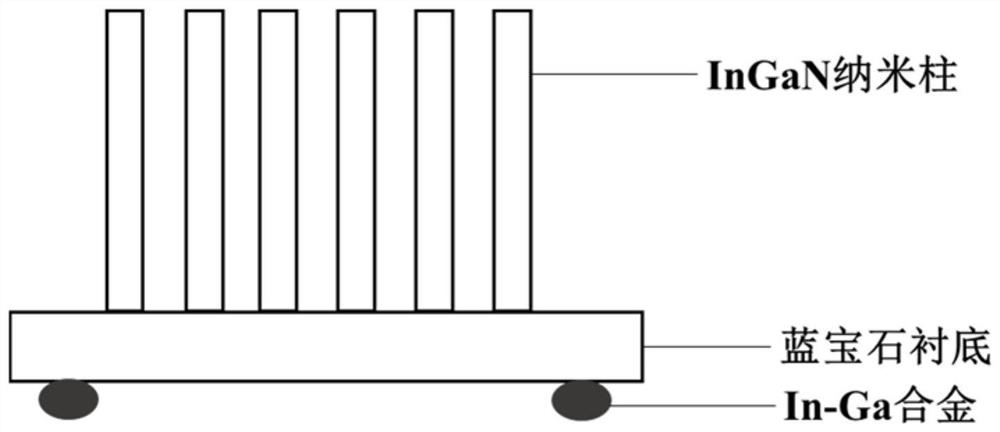
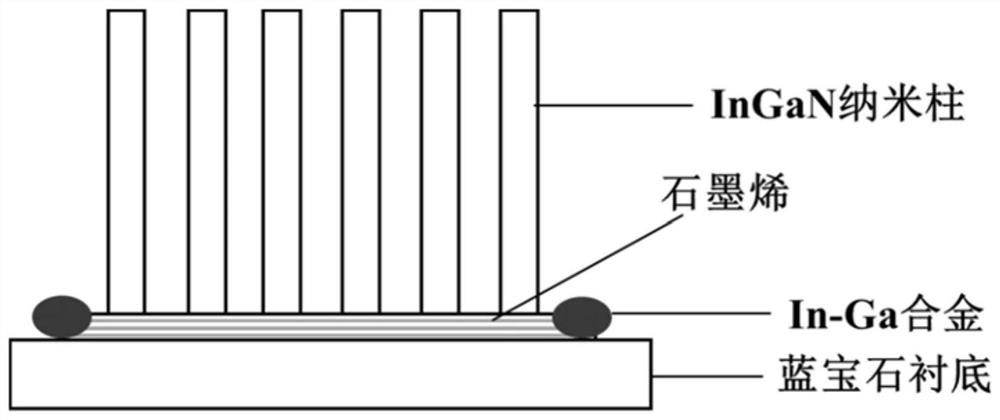
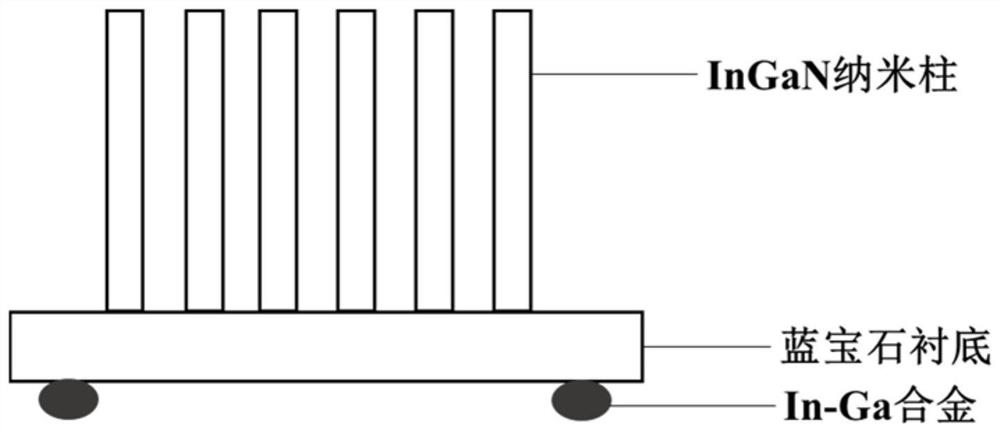
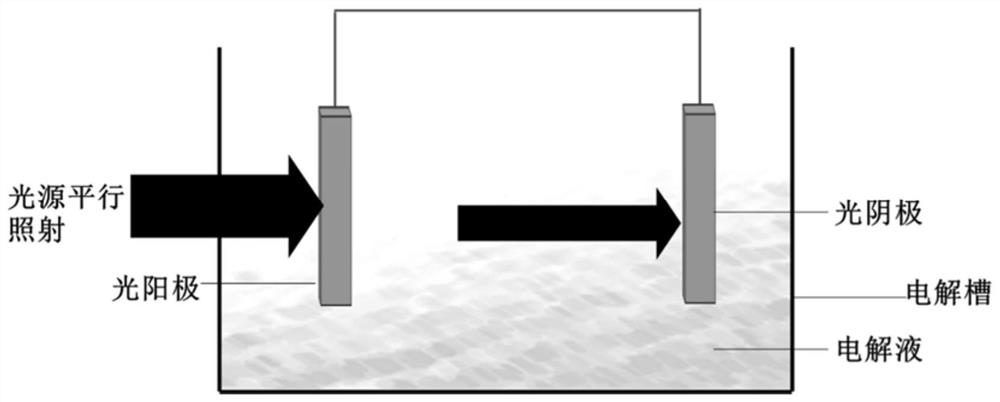
Unbiased photoelectrochemical hydrogen production system based on InGaN nanorod photoelectrode on graphene and application thereof
ActiveCN112760668AIncrease choiceCause poor qualityEnergy inputNanotechnologyElectrolytic agentSchottky barrier
The invention discloses an unbiased photoelectrochemical hydrogen production system based on an InGaN nanorod photoelectrode on graphene and application thereof. The system comprises a photo-anode, a photo-cathode, an electrolyte, a light source and an electrolytic tank, the photo-anode structure sequentially comprises a substrate, graphene on the substrate and an InGaN nano column growing on the graphene from bottom to top, and the photo-cathode structure sequentially comprises a substrate and an InGaN nano column growing on the substrate from top to bottom; graphene is used so that the selection range of the substrate is widened, the graphene can be used as a conductive electrode, and the cost is reduced; a Schottky barrier can be formed between the graphene and the nanorod so that photon-generated carriers can be separated, the carrier transport performance can be enhanced, and the photoelectric property of the nanorod can be greatly improved; meanwhile, due to the light transmission of the graphene, the InGaN nanorod integrated photoelectrode can be prepared, spectral absorption can be widened, the photovoltage needed by water decomposition can be improved, and unbiased photoelectric water decomposition hydrogen production is achieved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Full-oxide lead-free ferroelectric photovoltaic device with sandwich structure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110634974AImprove light absorption efficiencyEasy to separateFinal product manufactureIron compoundsElectron holeOxygen vacancy
The invention discloses a full-oxide lead-free ferroelectric photovoltaic device with a sandwich structure and a preparation method thereof. The photovoltaic device comprises a substrate, wherein thesubstrate is covered with a BFO layer, the BFO layer is covered with an ITO layer, and the BFO layer is a BiFeO3-delta film which grows in an epitaxial mode. The photovoltaic device is advantaged in that oxygen vacancy doping is ingeniously utilized to increase light absorption efficiency of a ferroelectric layer, and the built-in potential caused by the work function difference between the upperelectrode and the lower electrode is utilized to cooperate with the ferroelectric depolarization field, and thereby separation of photo-induced electron hole pairs is effectively promoted, and photoelectric conversion performance of the device is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
A tio with photonic crystal properties 2 Preparation method of nanoparticles
The invention discloses a preparation method of TiO2 nanoparticles with photonic crystal characteristics. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a precursor solution by mixing TiCl4 solution, absolute ethyl alcohol and deionized water; and with butterfly wings as a bio-template, treating the template by a solution impregnation method and removing the template at a high temperature to obtain the TiO2 nanoparticles. The preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple technology, easily available raw materials, good product structure and performance and the like; and the prepared TiO2 nanoparticles with photonic crystal characteristics have a good application prospect in the field of thin-film solar cell study.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
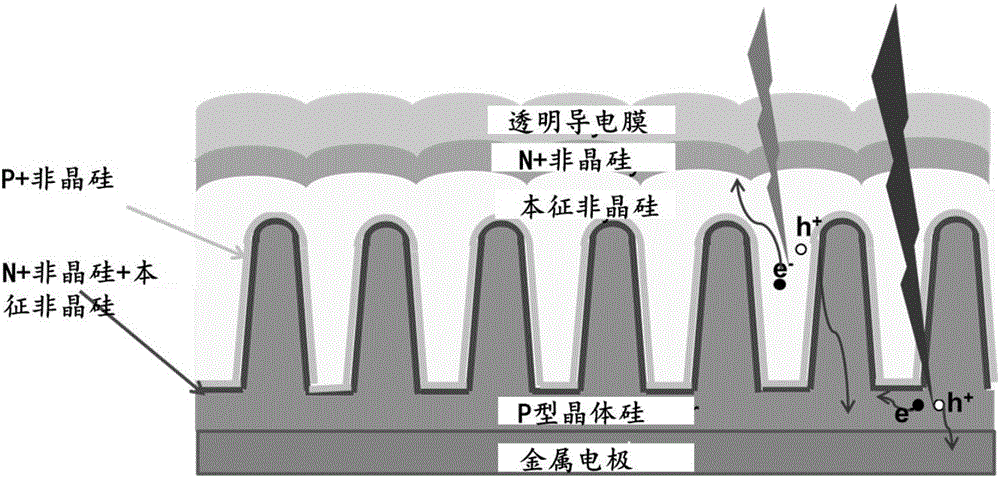
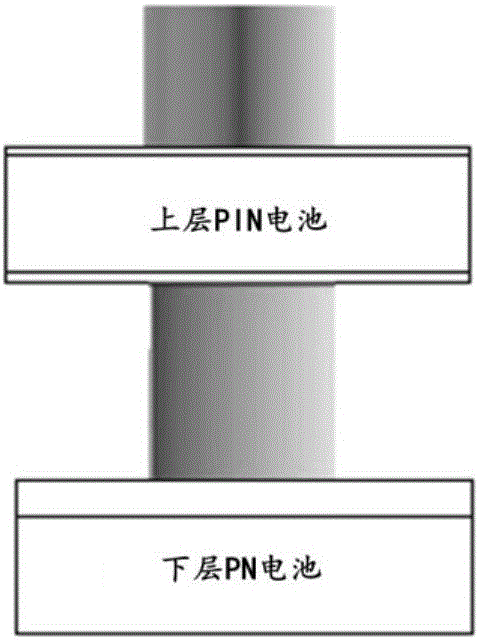
Silicon nanowire-based thin-film silicon crystalline silicon laminated solar photovoltaic cell
InactiveCN106784114ALow deposition temperatureAvoid negative effectsPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionSilicon nanowires
The invention discloses a silicon nanowire-based thin-film silicon crystalline silicon laminated solar photovoltaic cell, which comprises an NIP amorphous silicon laminated cell located on an upper layer and a PIN heterojunction silicon cell located on a lower layer, wherein the NIP amorphous silicon laminated cell and the PIN heterojunction silicon cell are connected in series through an amorphous silicon tunnel junction; and a silicon nanowire array is arranged on the upper surface of crystalline silicon of an absorption layer of the PIN heterojunction silicon cell. The silicon nanowire array is introduced into the laminated cell, so that the cell has a light trapping advantage of the nanowire array, and relatively high open-circuit voltage and short-circuit current of the laminated cell at the same time.
Owner:SHANGHAI DIANJI UNIV
Rare earth-doped titanium dioxide photo-anode for dye-sensitized solar cell and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101819885BIncrease photocurrentIncrease photovoltageLight-sensitive devicesSolid-state devicesElectrical batteryPhotocurrent
The invention discloses a rare earth-doped titanium dioxide photo-anode for a dye-sensitized solar cell. The photo-anode is prepared from a rare earth compound and tetrabutyl titanate by the following steps of: preparing nano-crystalline titanium dioxide colloid with the tetrabutyl titanate by a hydrothermal method; dissolving the rare earth compound in solution of nitric acid to obtain solution of nitrate, hydrolyzing the tetrabutyl titanate to obtain titanium dioxide sol, adding the solution of nitrate into the sol and processing the mixture by the hydrothermal method and high temperature calcining to obtain the rare earth-doped titanium dioxide powder; and adding the rare earth-doped titanium dioxide powder into the titanium dioxide colloid, scattering, coating and calcining the mixture at a high temperature to prepare the rare earth-doped titanium dioxide photo-anode. The photo-anode and the preparation method have up-conversion luminescence function and p-type doping effect and improve the photocurrent and photovoltage of the cell, the Fermi level of the titanium dioxide and the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the cell. The method is used for improving the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the dye-sensitized solar cell with simple process and abundant raw materials and can also be used for the related fields of other solar cells and the like.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Preparing method of non-metal doped dye sensitization TiO2 nano-crystal thin film photoelectrode
InactiveCN101587779BLarge poresImprove light absorption efficiencyElectrolytic capacitorsFinal product manufactureSlurrySolar cell
The invention belongs to the preparing field of TiO2 nano-crystal thin film photoelectrode of dye sensitization solar cell, especially relates to a preparing method of non-metal doped dye sensitization TiO2 nano-crystal thin film photoelectrode which is prepared by colloids containing non-metal doped large granule TiO2 nano-crystal and non-metal doped TiO2 nano-crystal granule. The photoelectrodeprepared by the invention is prepared by rotary coating the non-metal doped TiO2 colloidal sols and non-metal doped TiO2 power body slurry in order on a conductive substrate; after naturally drying, performing heat-treatment to obtain a nano-crystal thin film photoelectrode with porous structure. On one hand, the non-metal doped TiO2 nano-crystal granule changes the performance of the semiconductor, and is used as almsgiver to provide more carriers to improve the electric conductivity; on the other hand, the non-metal doped TiO2 nano-crystal granule changes the position of TiO2 energy band toimprove the photovoltage and the photo absorption efficiencies. The preparing method of the invention is simple and is easy to operate, is suitable for the industrial production preparation of the dyesensitization TiO2 nano-crystal thin film photoelectrode, and also is suitable for the fields of photochemical catalysis electrode and self-cleaning glass and so on.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH +1
A kind of 2,6-position substituted bodipy organic dye sensitizer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105238092BCommonly available raw materialsReduce manufacturing costLight-sensitive devicesMethine/polymethine dyesSynthesis methodsOrganic dye
The present invention relates to a novel 2,6-site-substituted BODIPY organic dye sensitizer and a preparation method therefor. The organic dye sensitizer is organic photovoltaic materials with a D-pi-A structure. By taking a meso-site-substituted BODIPY core as a pi bridge framework, the sites 2 and 6 of the BODIPY core is respectively substituted by an electron donor and an electron acceptor. The present invention further discloses a preparation method for the above the dye sensitizer. The preparation method obtains a dye molecule having a general structural formula I by taking 2,4-dimethylpyrrole as an initial reaction raw material, performing a serials of simple synthesis reactions, and finally performing classical Suzuki coupling and Knoevenagel condensation reactions. The dye sensitizer synthesis method is simple, easy to control and high in yield, and has general applicability. When the method is applied to dye sensitized solar cell preparation, a dye sensitized solar cell material with a high fill factor and an ideal photoelectric conversion efficiency can be obtained. The formula I is shown in the description.
Owner:邳州市润宏实业有限公司
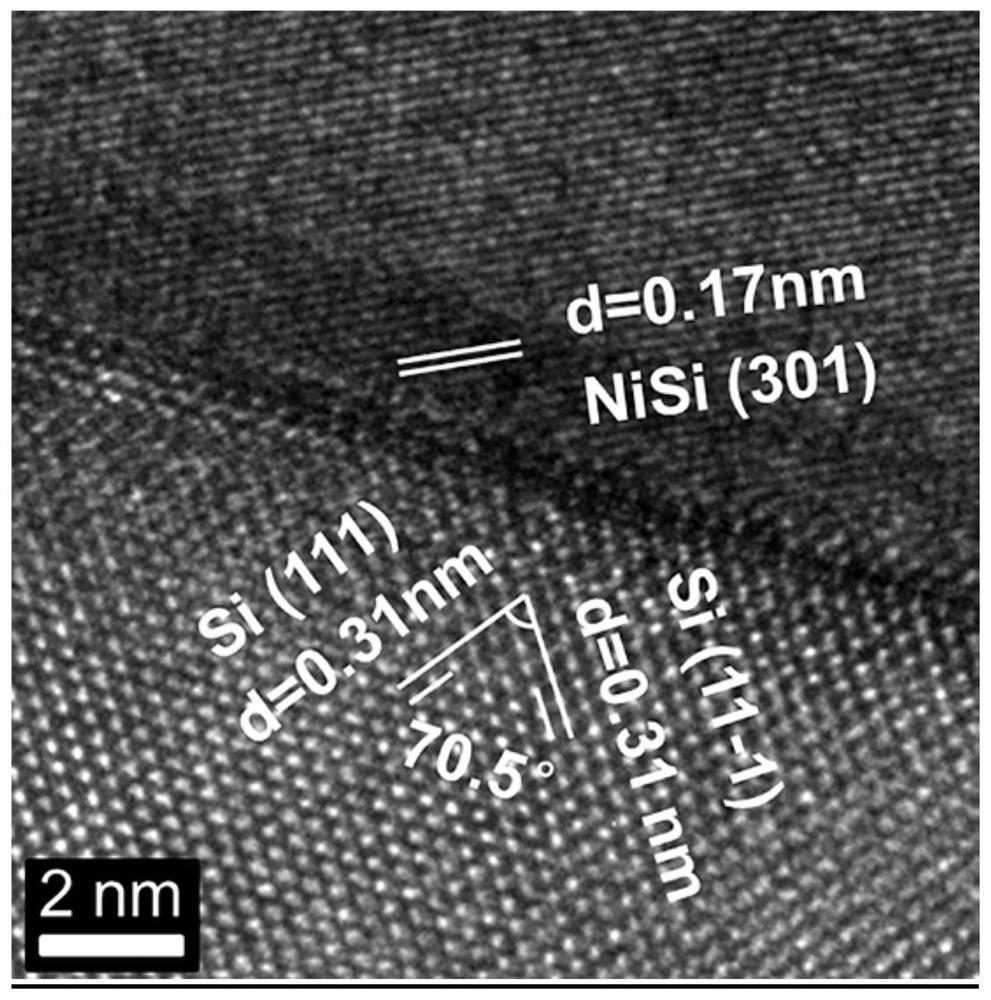
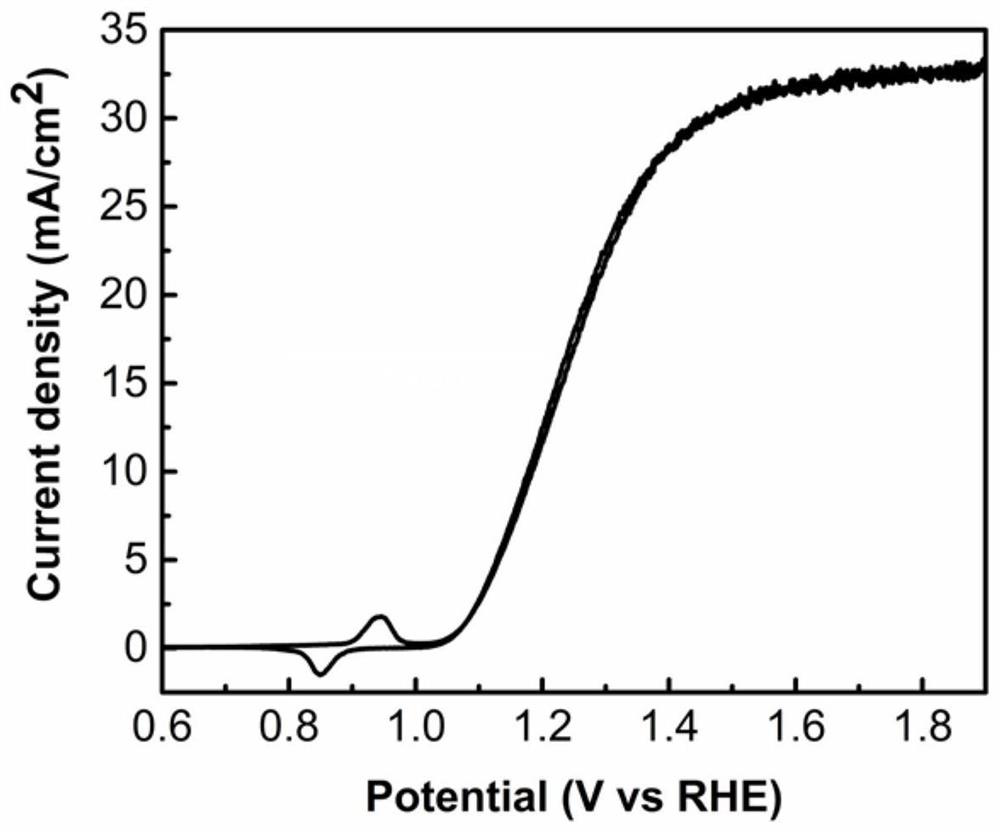
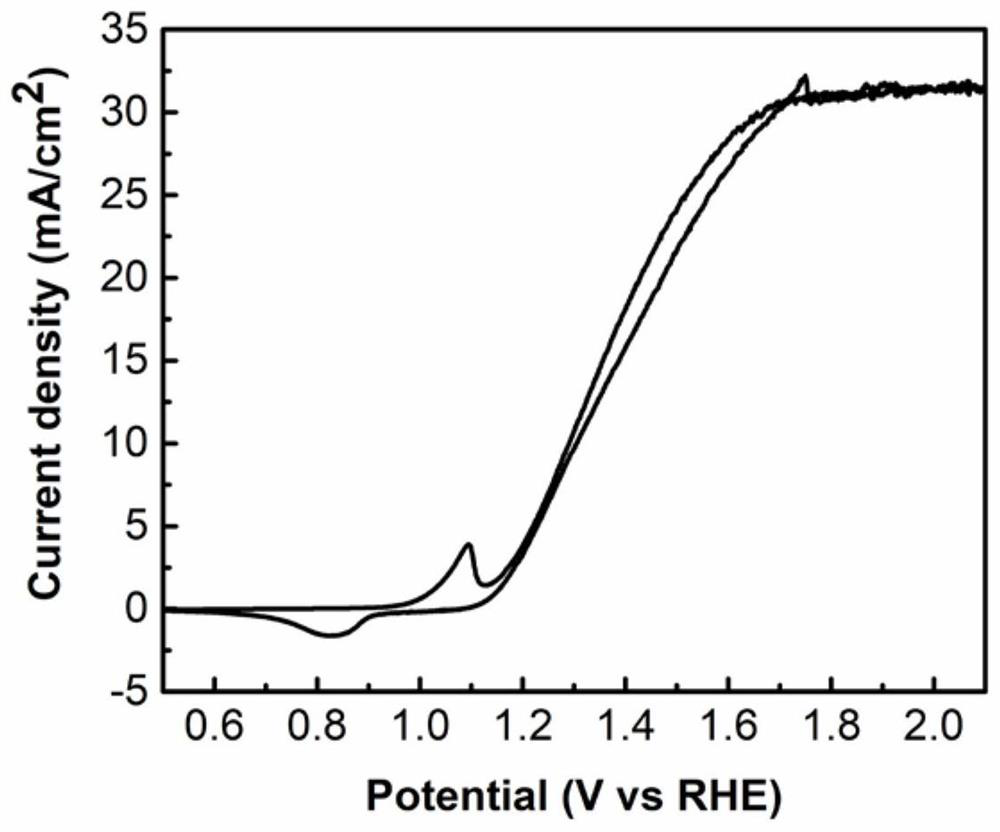
A b-doped nisi/n-si photoanode and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN109904251BHigh Schottky BarrierIncrease photovoltageFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesSchottky barrierPhotocurrent
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
An unbiased photoelectrochemical hydrogen production system and application based on ingan nanopillar photoelectrodes on graphene
ActiveCN112760668BIncrease choiceCause poor qualityEnergy inputNanotechnologyElectrolytic agentSchottky barrier
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
A kind of preparation method of dye-sensitized solar cell doped graphene composite electrode
ActiveCN103337368BEasy transferHigh densityLight-sensitive devicesFinal product manufactureDoped grapheneSlurry
The invention discloses a preparation method of a dye-sensitized solar cell grapheme-doped composite electrode. The preparation method comprises the following steps that: a hydrothermal method is adopted to prepare a TiO2 nano array on conductive glass, and as a result, direct electron channels are provided, and the diffusion length of electrons can be increased, and electron recombination can be reduced, and the lifetime of the electrons can be increased; the hydrothermal method is adopted to prepare TiO2-graphene nano particles, and as a result, doped graphene can not only reduce the recombination of photogenerated electrons and holes, but also can enhance the capture of light, and the number of the photogenerated electrons can be increased; the TiO2-graphene nano particles are printed on the TiO2 nano array through a screen printing method, and as a result, a larger specific surface area can be obtained, and dye adsorption quantity can be increased; an organic solvent can be removed from a slurry through sintering; and the dye is adsorbed, and the dye-sensitized solar cell grapheme-doped composite electrode can be obtained.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com