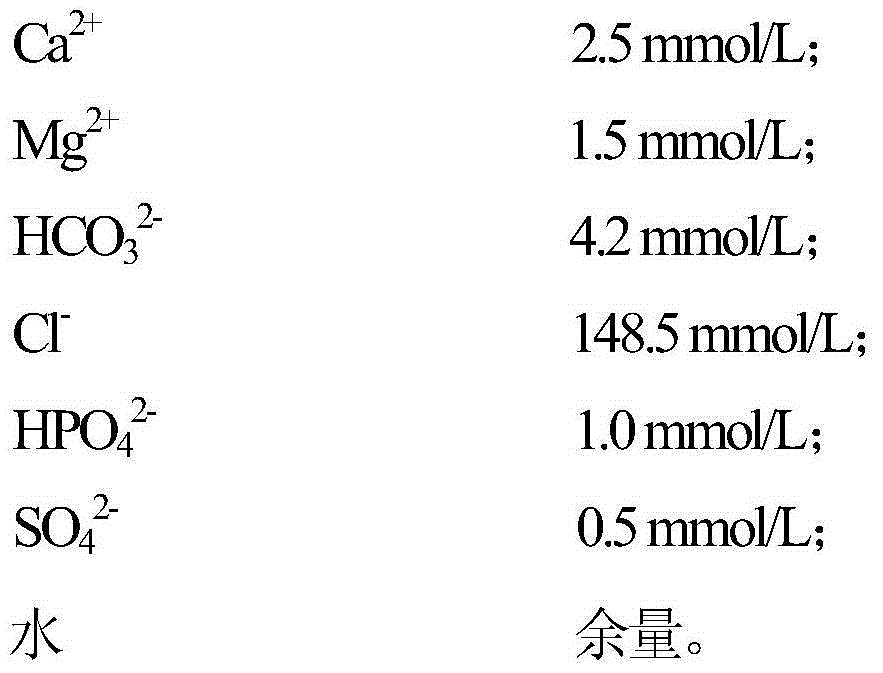Patents
Literature
217 results about "Bio ceramic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bio Ceramic. Bio Ceramic is made of ceramic and is a very fine filtering medium. It is to fine to use in a reverse osmosis system. If the water supply is not of high quality it would clog up in a few days.
Metal-ceramic composite articulation
InactiveUS6881229B2Minimal productionImprove flexural strengthBone implantJoint implantsHigh fractureIn vivo
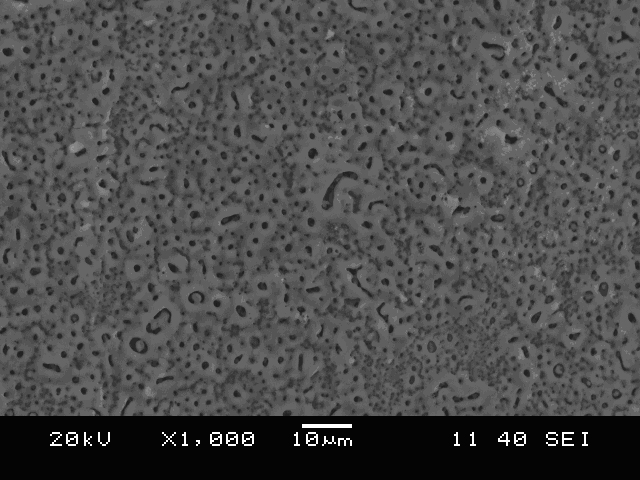
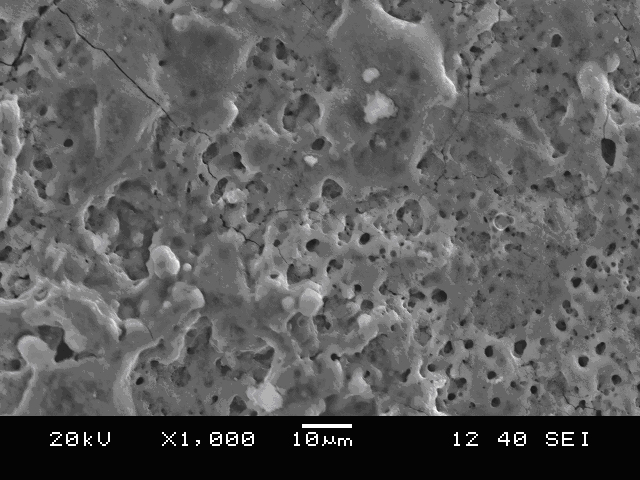
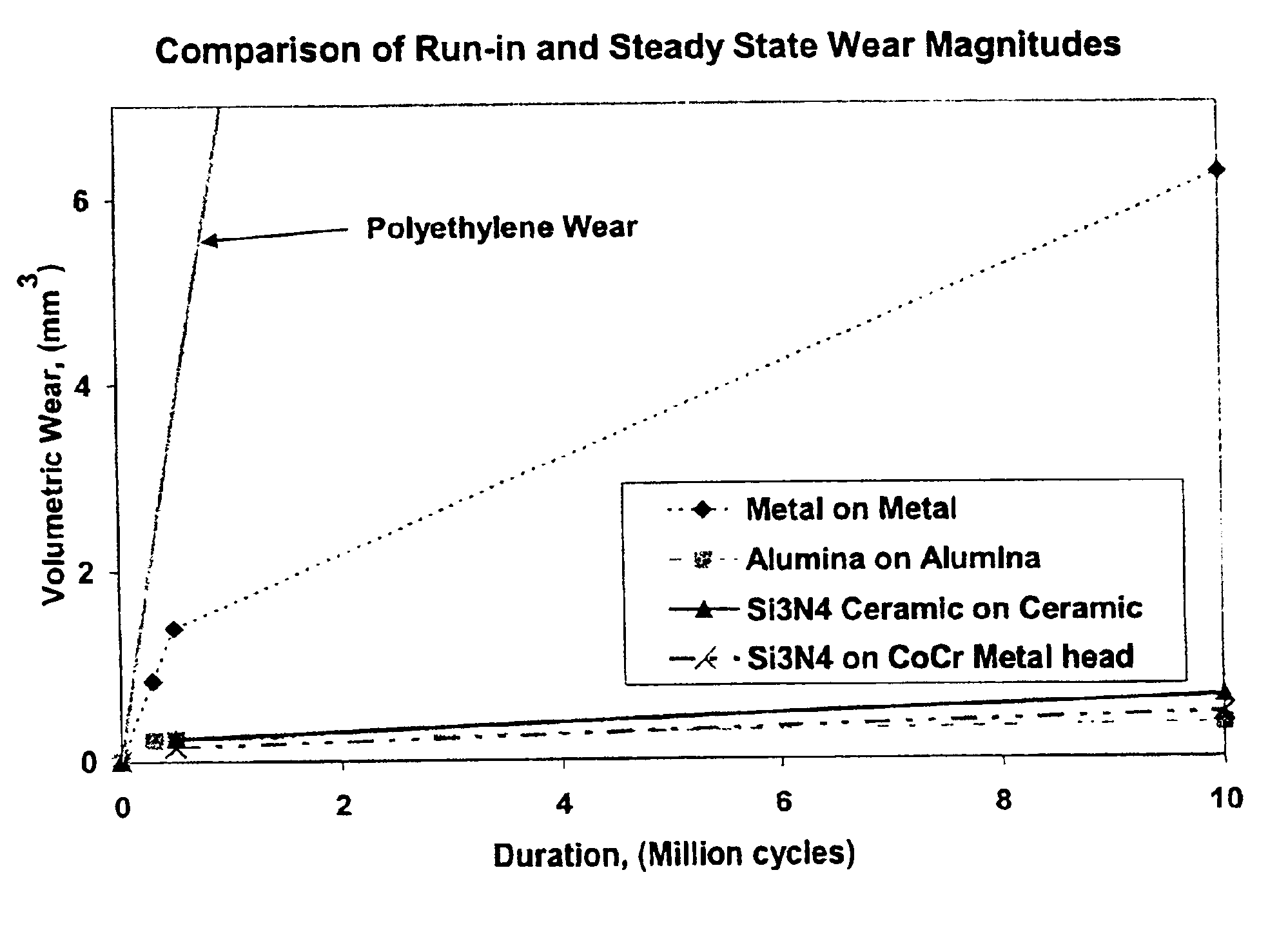
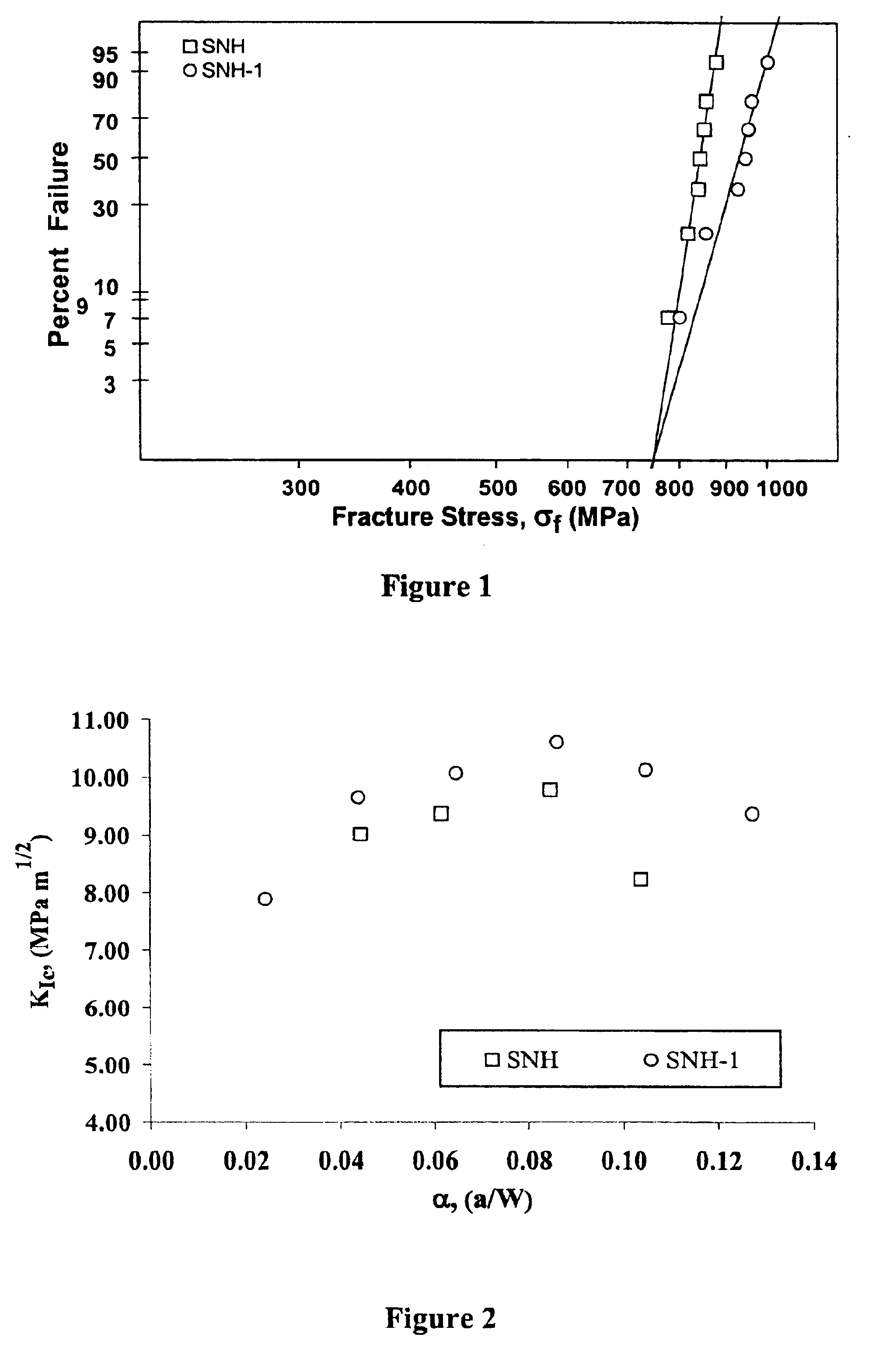
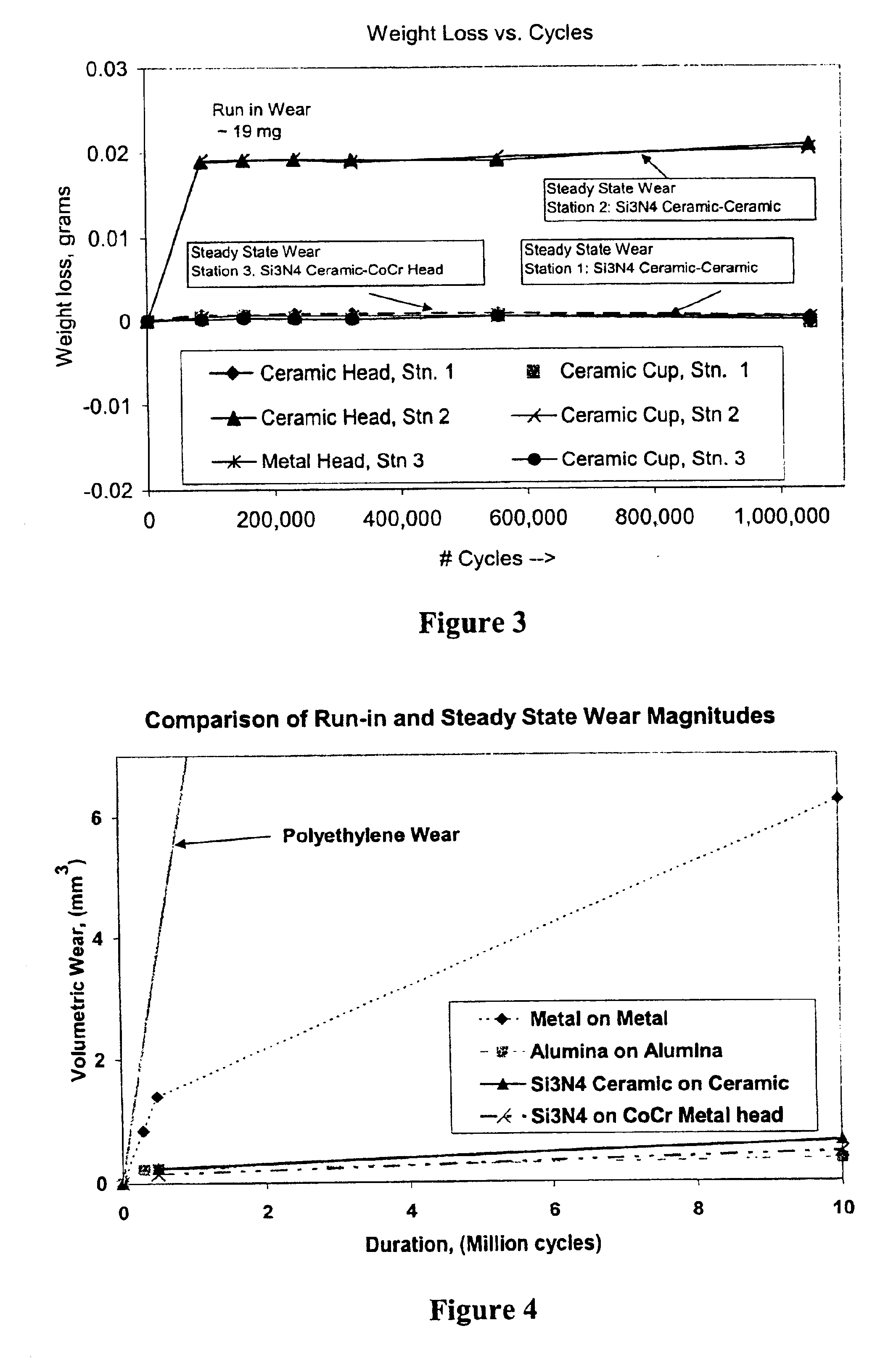
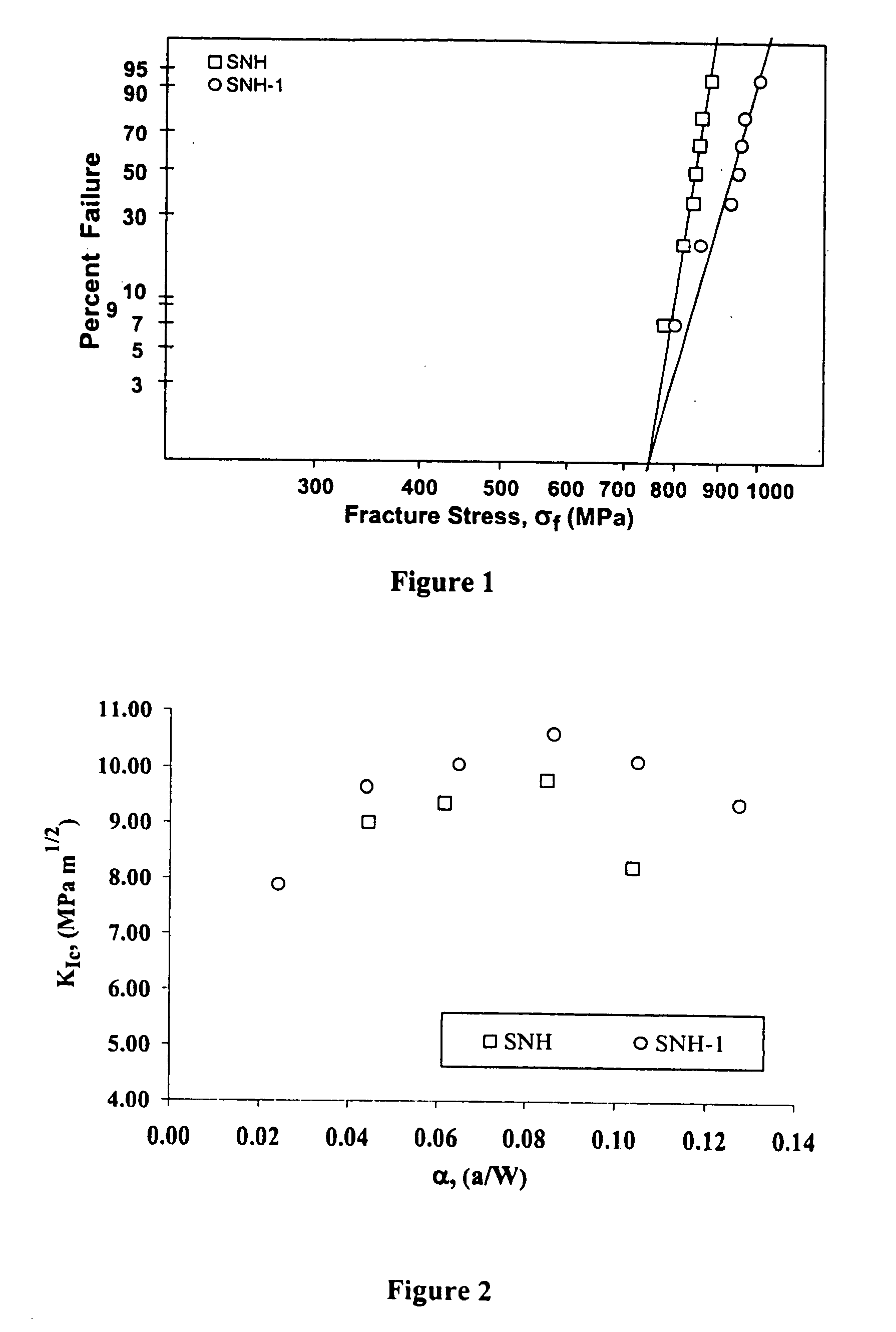
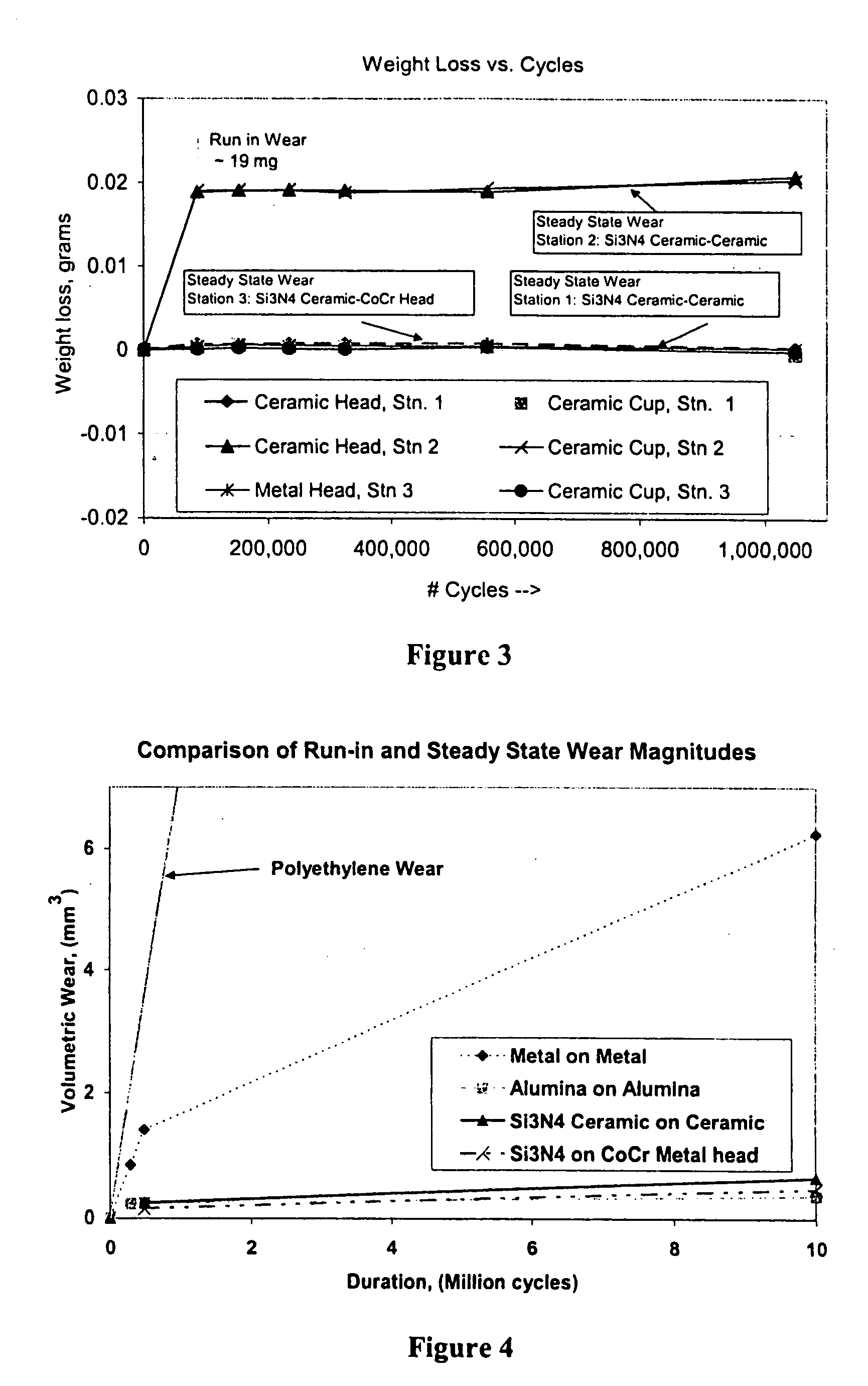
A ceramic-metal composite articulation is provided with substantial elimination of wear debris, wherein a ceramic material is provided with superior mechanical properties tailored for articulating with ceramic articulations having high flexural strength (greater than about 700 MPa), high fracture toughness (greater than about 7 MPa1 / 2) and a high Weibull modulus (greater than about 20), in comparison with presently available bio-ceramics such as alumina or zirconia. The mechanical property enhancement enables ceramic materials with greater reliability and significantly reduced in-vivo fracture risk to be obtained. Preliminary in-vitro wear performance, to several million cycles using established test protocols, of head / cup components in a prosthetic hip joint made from these ceramics also demonstrates the ultra low wear characteristics. These material properties substantially eliminate polyethylene (PE) wear debris mediated implant failures by offering an optimal combination of bio-mechanical safety and reliability with ultra low wear performance.
Owner:SINTX TECH INC
Bone restoration body with composite porous structure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102512267AGood mechanical compatibilityGood bone conductionBone implantFreeze-dryingReticular formation
A bone restoration body with a composite porous structure and a preparation method of the bone restoration body. The bone restoration body comprises a porous metal bracket and an infill body with a porous structure, wherein the porous metal bracket is of a three-dimensional net structure, a plurality of pores are arranged in the inner part of the porous metal bracket, and the infill body with the porous structure is fully filled in all the pores. The preparation method combines the direct metal rapid prototyping technology and the freeze drying technology and comprises the steps of preparing the porous metal bracket by a structural design and the direct metal rapid prototyping technology, pouring uniformly-mixed polymer solution or polymer / biological ceramics mixing solution into the porous metal bracket, carrying out freezing treatment, and then forming the infill body with the porous structure through freeze drying so as to obtain the bone restoration body with the composite porous structure, wherein the infill body with the porous structure has micropore characteristics. The bone restoration body has good mechanics compatibility, can obtain good bone conduction performance and bone induction performance, improves bone integration efficiency and can be used for clinical treatment of segmental bone defect of a bearing part.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Deep heating magnetic wrap for joints and tissue
InactiveUS6652446B1Convenient Application RequirementsEasy to useElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using permanent magnetsFiberEngineering
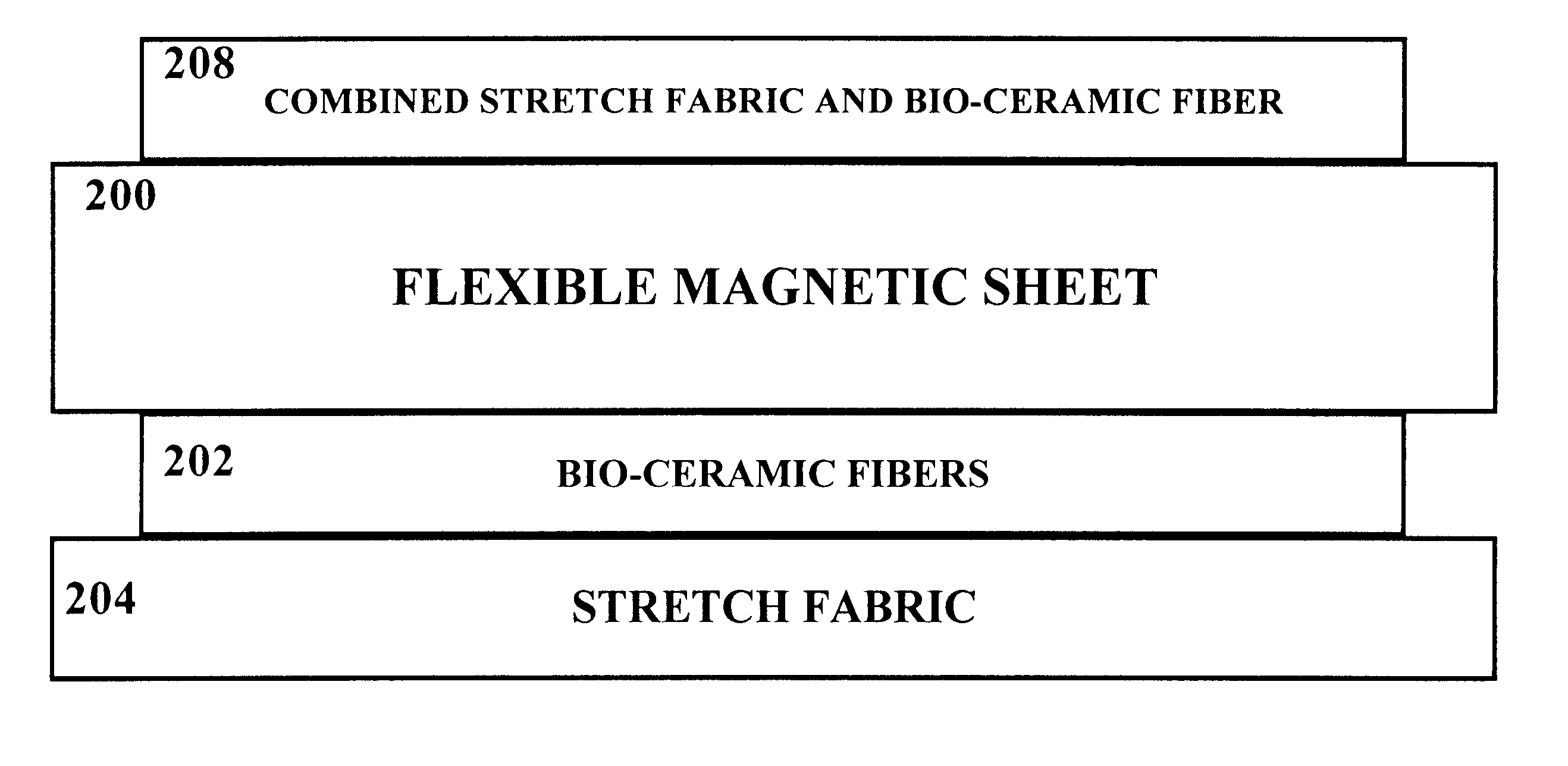
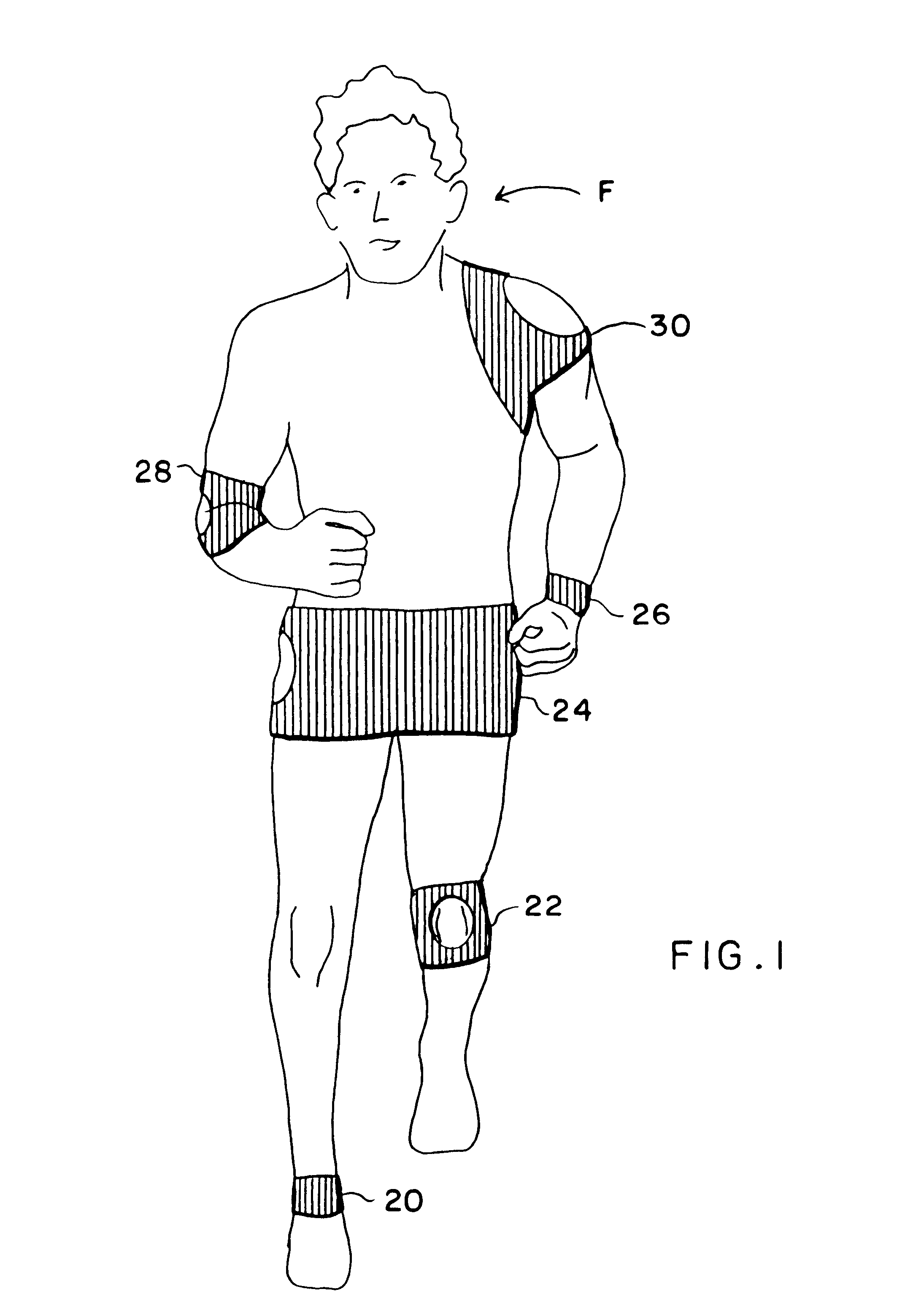
Flexible and elastic magnetic joint wraps incorporate superstrong magnets with alternating polarities and incorporate bio-ceramic fibers to provide enhanced magnetotherapeutic and far-infrared effects. Magnetotherapeutic joint wraps that are flexible and elastic incorporate superstrong magnets as well as far-infrared emitters in an attachably detachable manner so as to provide magnetotherapy and far-infrared therapy to joints and surrounding tissues. Neoprene or the like may incorporate superstrong magnets such as those based on iron (magnetic ferrite) or neodymium (particularly neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB)) in order to provide superstrong static magnetism by which magnetotherapy may be effected. Elements that are generally oppositely opposed serve to detachably attach portions of the magnetic wrap to one another so that the magnetic joint wrap may conform to the local shape and form of the area adjacent the joint. Such attachment elements may include VELCRO(R) hook and loop fasteners as well as buttons, snaps, and the like. The superstrong magnets are constructed such that they may be incorporated in flexible and elastic materials such as neoprene. This provides means by which a magnetic wrap may tautly wrap around the joint and adjacent area when attached by the attachment elements. A soft cover may incorporate or cover bio-ceramic fibers which provide far-infrared treatment for the adjacent tissues and / or joints. Additionally, eye and face masks may incorporate the superstrong magnets and bio-ceramic fibers as used in the deep heating magnetic joint wrap of the present invention to good advantage.
Owner:BOVE ANTHONY +1
Magnetotherapeutic device with bio-ceramic fibers
InactiveUS6383129B1Convenient Application RequirementsEasy to useElectrotherapySurgeryFiberPolyester
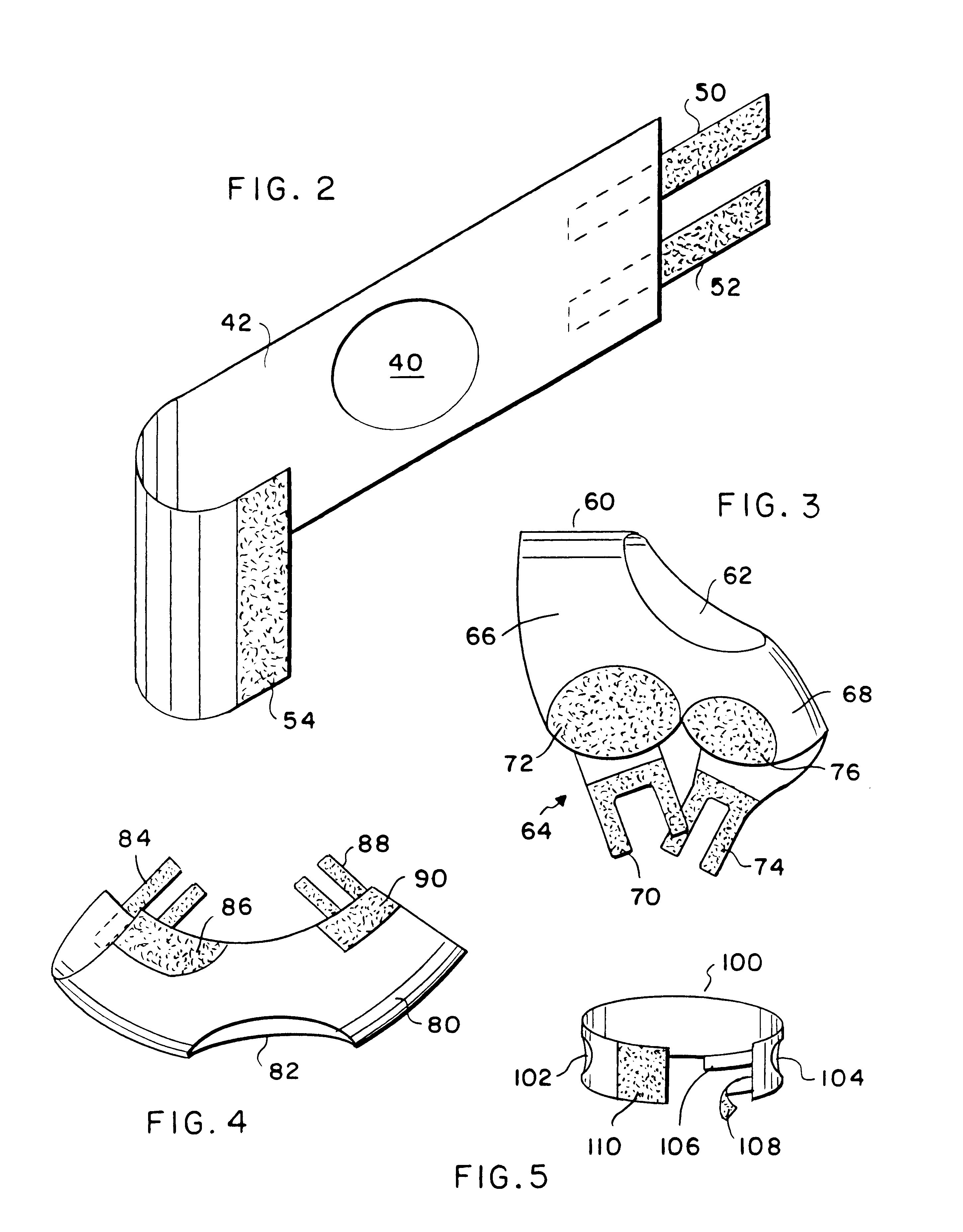
A magnetotherapeutic device incorporates bio-ceramic fibers so as to provide simultaneous magnetotherapy and far infra-red wave therapy. Generally encased in clear plastic or the like, the magnetotherapeutic device of the present invention may take the form of a transparent disk having a plastic rim. A stainless cap may provide an attractive top surface into which a logo or symbol may be embossed. It also enhances the magnetic affects on the side opposite the stainless steel cap, the side that is applied to the body. A strong magnet such as one incorporating neodymium may underlie the stainless steel cap to provide magnetotherapy in the present invention. Bio-ceramic fibers emitting the far infra-red wavelengths of 8-14 microns underlie the strong neodymium magnet. A mat of woven bio-ceramic fibers or the like may provide such a structure. In order to provide ventilation and communication between the environment outside of the magnetotherapeutic device of the present invention, perforated or foramenous mylar may serve as a bottom cover encasing the stainless steel cap, neodymium magnet, bio-ceramic fibers, and the plastic case. The perforated or foramenous mylar may then provide better communication between the thermal radiation of the adjacent body and emittance of far infra-red waves by the bio-ceramic fibers.
Owner:NYUU MAGUNETEIKUSU
3D printing bionic porous biological ceramic artificial bone and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111070376APrecise porosity controlGood molding propertiesAdditive manufacturing apparatusBone implantHuman bodyTissue fluid
The invention discloses a 3D printing bionic porous biological ceramic artificial bone and a preparation method thereof. A porous biological ceramic artificial bone model is designed through a TPMS and CSG combined method, slurry capable of being used for printing is prepared through biological ceramic powder and a binding agent, macropores and micropores are distributed in the porous biological ceramic artificial bone prepared through the combination with the 3D filament-free printing process, the pore diameter of the micropores is smaller than 100 micrometers, the pore diameter of the macropores is 200-800 micrometers, the total porosity is 20% to 80%, the communicating rate between the macropores is not lower than 99%, precise design of porosity, communication and homogeneity in the artificial bone is achieved, and meanwhile good pore communication is ensured. Adopted raw materials have good biocompatibility, entry passageways of cells and tissue fluid are provided by the macropores, the micropores can better adsorb tissue fluid nearby for cell growth, the cell growth speed and the new bone generation speed can be increased by combining the micropores with the marcropores, and application of the porous biological ceramic artificial bone in human body large bone defect repair clinic treatment is facilitated.
Owner:西安点云生物科技有限公司
Preparation methods of ceramic slurry for air pressure extrusion type three-dimensional printing and biological ceramic bracket
ActiveCN105196398AImprove liquidityHigh standardAdditive manufacturing apparatusCeramic shaping apparatusCeramic bracketsWater soluble
The invention discloses a preparation method of ceramic slurry for air pressure extrusion type three-dimensional printing. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (11) adding biological active ceramic powder into a solvent, performing ball grinding by a planetary ball grinder for 3 to 12 hours, and obtaining slurry, wherein the solid phase content of the slurry is 35 to 55 vol%; (12) adding a water-soluble rheological additive into the slurry obtained in the step (11), performing ball grinding by the planetary ball grinder for 0.5 to 3 hours, then transferring the slurry into a material feeding barrel, performing ultrasonic oscillation and low-temperature debubbling in sequence, and obtaining the ceramic slurry for air pressure extrusion type three-dimensional printing. The invention further discloses a preparation method of a biological active ceramic bracket by adopting an air pressure extrusion type three-dimensional printing forming technology. The ceramic slurry prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention is high in solid phase content and good in printing performance and coagulability; the prepared biological active ceramic bracket can be connected by 100 percent, and the appearance structure and the internal size of the biological active ceramic bracket can be controlled.
Owner:广州康睿医疗器械有限公司
Traction mouse pad
InactiveUS6383607B1Great tractionReduce manufacturing costDecorative surface effectsOrnamental structuresControl layerDust particles
A mouse pad with improved self-cleaning and traction features. The mouse pad is a planar structure with a parallel top control layer and a bottom anti-skid coating. Formed on the top layer is a top control layer with a plurality of alternating, equal height, prismatic and pyramidal shapes, which provide improved cleaning and traction properties. Small troughs are formed between the adjacent shapes, which collect fine dirt and dust particles that are swept from the surface of the mouse ball during use. In one embodiment, the top control surface is made of flexible material that allows the prismatic and pyramidal shapes to bend slightly when the ball of a mechanical mouse rolls over the top surface. This bending action provides improved self-cleaning and traction features. In another embodiment, the top layer is made of transparent material. An ink layer may be applied to the bottom surface of the top layer. After the ink coating has dried, a white pigment coating may be applied over the ink coating to enhance the colors. A bio-ceramic compound designed to release infrared radiation may be added to the white pigment coating. Also enclosed herein is a method of manufacturing a mouse pad with a top control layer comprised of alternating prismatic and pyramidal shapes.
Owner:SHIN KWANGSUP
Calcium silicate/hydroxylapatite composite biological ceramic material and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101700415AGood mechanical propertiesModulate biological activityProsthesisCalcium silicateApatite
The invention relates to a calcium silicate / hydroxylapatite composite biological ceramic material and a preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the field of biological materials. Calcium silicate / hydroxylapatite nano composite powder prepared by a chemical method is used as a raw material and carried out the dry pressing and molding to obtain a material biscuit, and the biscuit is calcined at 1000-1200 DEG C for 1-10 hours to obtain a degradable calcium silicate / hydroxylapatite composite biological ceramic material which has good mechanical properties and is used for repairing the defects of hard tissues. The biological activity, the degradability and the mechanical strength of the biological ceramic material of the invention can be adjusted and controlled. The invention has simple and easy processes and convenient popularization.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Collidal forming process for preparing high strength light ceramic material
The present invention belongs to the field of ceramic material preparing technology, and is especially colloidal state forming process for preparing light high strength ceramic material. The process includes the following steps: preparing suspension with very low solid phase content with special organic monomer, solvent, initiator or chelating agent, and ceramic powder; in-situ solidification through gel polymerization of monomer or high molecular cross-linking to obtain ceramic biscuit; drying, removing binder and no-pressure high temperature sintering to obtain light high strength ceramic material. The present invention can control the porosity and pore size of the ultimate product through altering the solid phase content in the suspension, the sintering condition and the powder size. The present invention has simple technological process, low cost, environment friendship and other advantages, and the produced ceramic material has wide application range.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for strengthening and toughening biological ceramic material by use of graphene and preparing artificial bone prepared from material
InactiveCN103656752AHigh strengthImprove toughnessProsthesisCalcium silicateSelective laser sintering
Aiming at the problems of low strength and low toughness of bioactive ceramics, the invention provides a method for strengthening and toughening a bioactive ceramic material by use of graphene and preparing graphene / biological ceramic artificial bone by a selective laser sintering (SLS) technology. The method has the advantages that graphene is added into the bioactive ceramic (hydroxylapatite, calcium phosphate, bioglass, calcium silicate and the like) as a nano enhanced phase, and the strength and toughness of the ceramic can be remarkably improved by use of the excellent mechanical property of graphene; the SLS technology is applied to the preparation process of graphene / biological ceramic artificial bone, and the sintering time can be shortened to the second level and even millisecond level by use of the characteristic of quick heating and cooling of laser so as to avoid structural injury of graphene caused by long-time high-temperature effect. The method for strengthening and toughening the ceramic material by use of graphene provided by the invention is of great significance to the application of bioactive ceramic to the load bearing parts of the human body.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
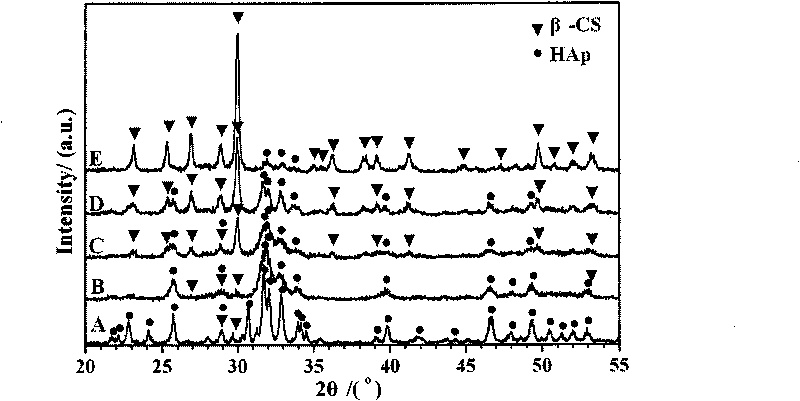
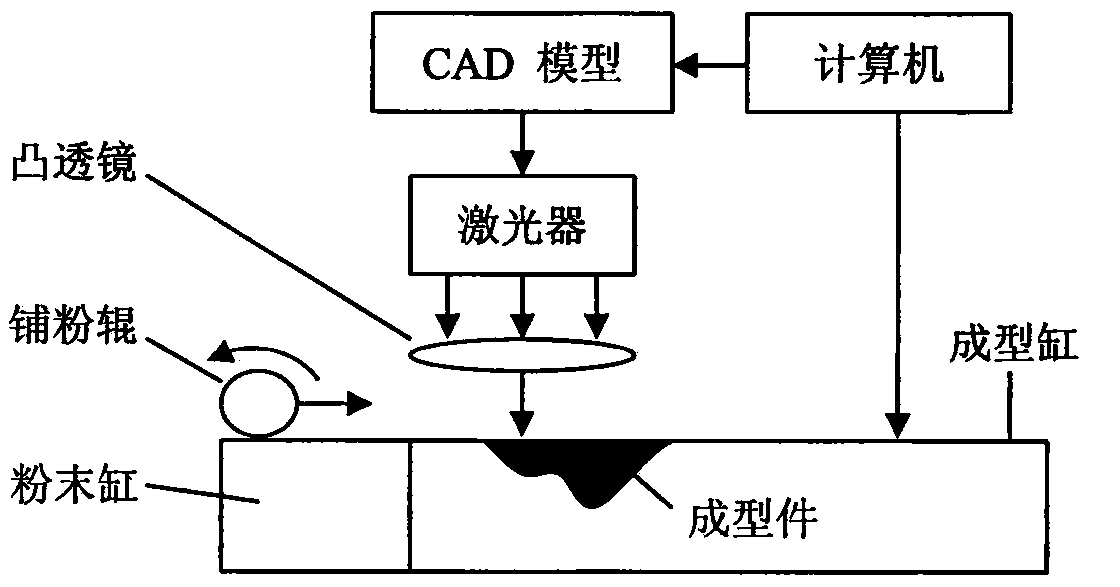
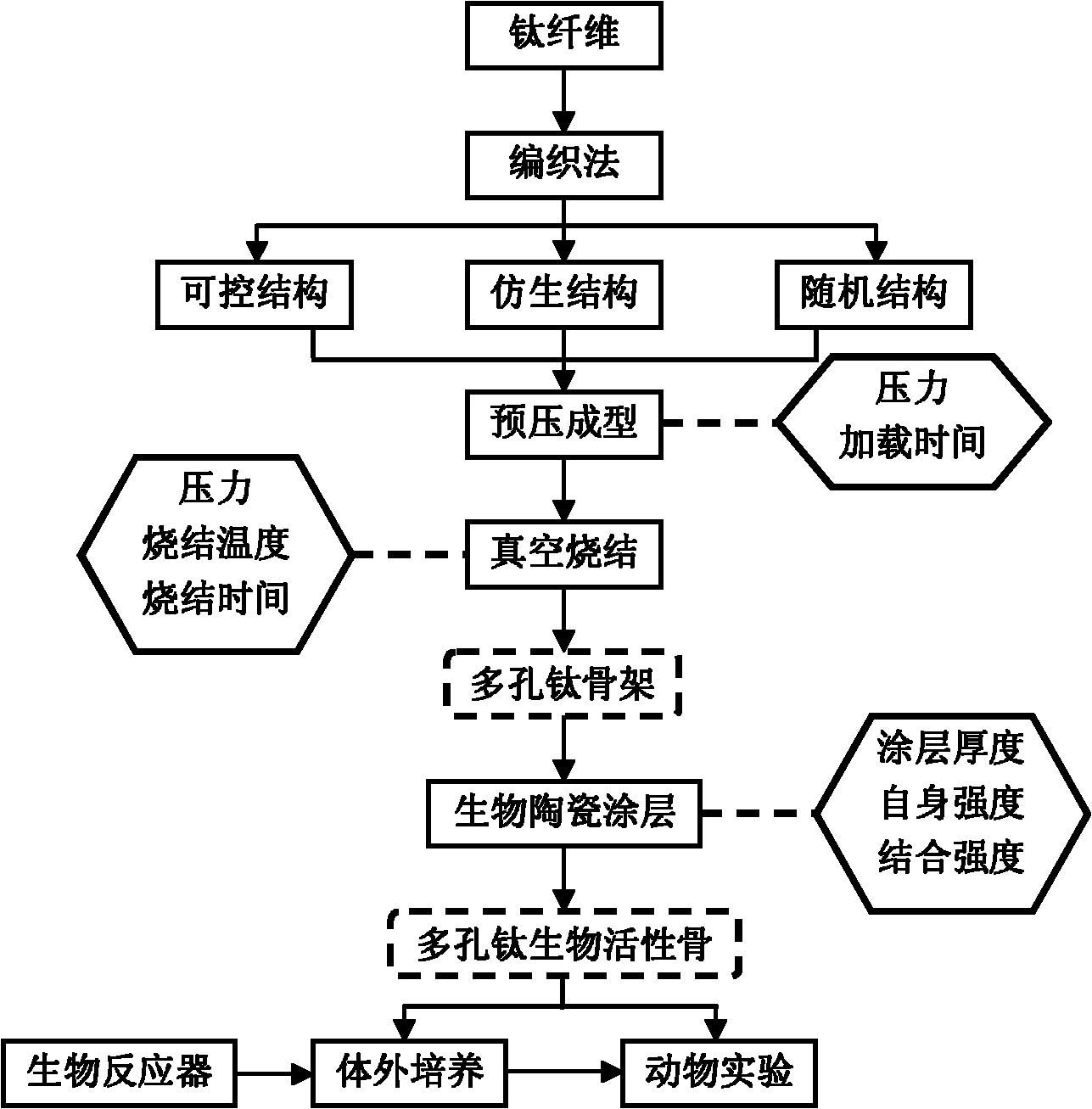
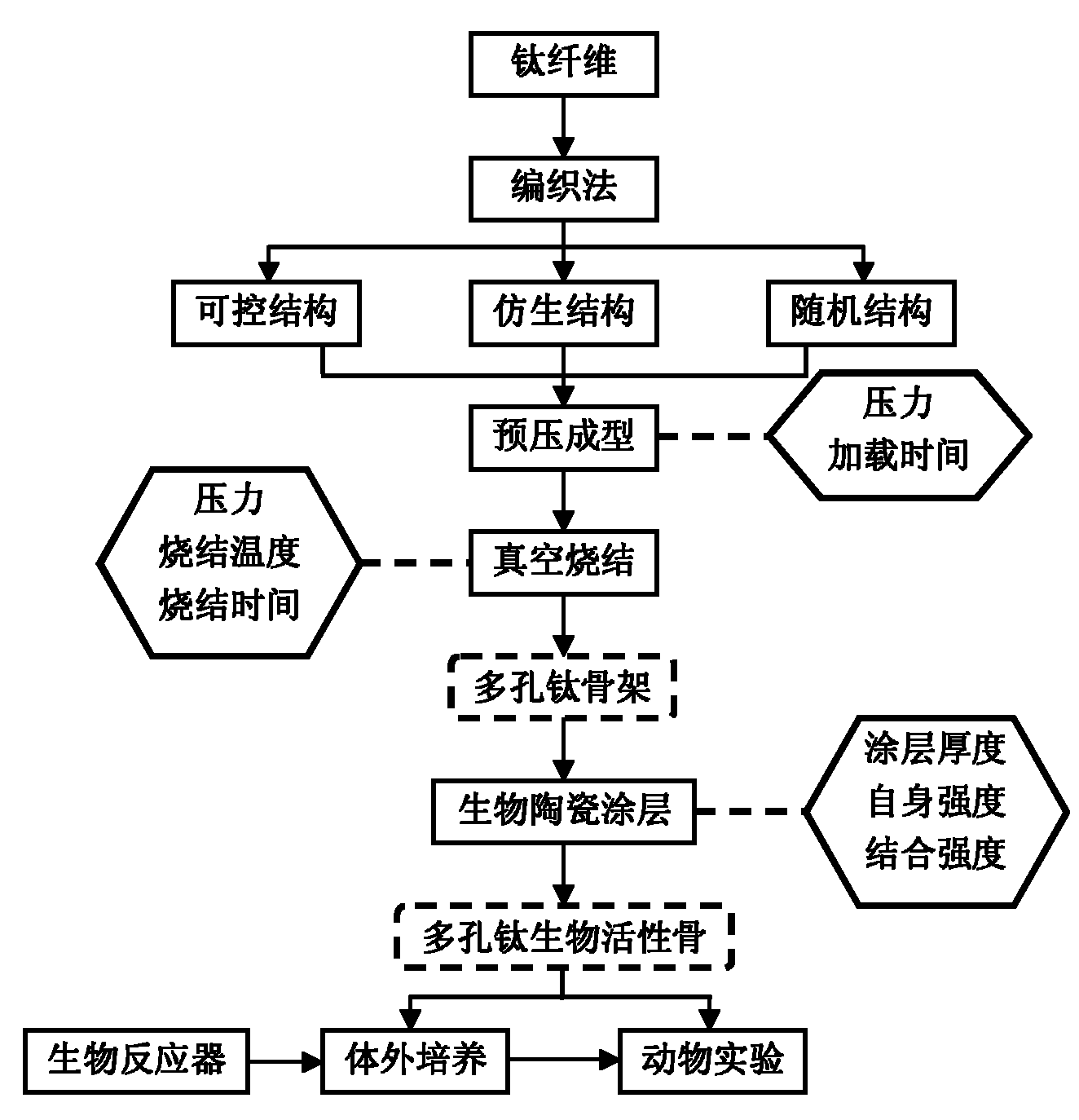
Preparation method of bio-ceramic coating titanium-wire sintering porous titanium artificial bone
InactiveCN101889912AHave biological propertiesBiologically activeBone implantCoatingsFiberPrincipal stress
The invention discloses a preparation method of a bio-ceramic coating titanium-wire sintering porous titanium artificial bone, belonging to the biomedical engineering field. In the invention, a three-dimensional weaving method is utilized, a titanium metal fiber wire is constructed into a controllable structure model, a random structure model and a bionic structure model which can stimulate the bone trabecula and principal stress line of a human bone, and then is prepared into the porous titanium artificial bone through prepressing molding and vacuum sintering, after that, a sol-gel method is utilized to manufacture a gradient coating or a complex coating on the surface of the porous titanium artificial bone, so that the gradient coating transiting from titanium dioxide to bio-ceramics or the bio-ceramics-titanium dioxide complex coating is formed on the surface of the porous titanium artificial bone to obtain the bio-ceramic coating titanium-wire sintering porous titanium artificial bone. The preparation method not only can protect the titanium metal skeleton and prevent titanium ions from dissociating to enter a human body, but also can ensure that the titanium metal skeleton the surface of which is coated with the bio-ceramics has the biological characteristics, therefore, the bio-ceramic coating titanium-wire sintering porous titanium artificial bone can be applied to repairing clinical segmental defect of long bones.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Preparation method and application of antibacterial bio-ceramic film with titanium or titanium alloy surface containing copper
ActiveCN104674321AAvoid corrosionIncrease growth rateSurgerySurface reaction electrolytic coatingPulse power supplyTitanium alloy
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of an antibacterial bio-ceramic film with the titanium or titanium alloy surface containing copper and belongs to the technical field of treating metal surfaces. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a Ca, P and Cu containing porous hard ceramic layer under a single square wave pulsed power supply mode; and carrying out hydrothermal treatment or alkali treatment to obtain the CuO / HA antibacterial bio-ceramic film. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the prepared ceramic layer and a matrix are in metallurgical bonding and are good in bioactivity and obvious in antibacterial effect; the prepared antibacterial bio-ceramic film is suitable for dental implant in the field of oral cavities as well as bone union plates, bone nails and the like of orthopaedics; and the ceramic layer is good in protein adsorbability and adhesion, increment and differentiation abilities of cells and is capable of greatly shortening the bonding time of the traditional medical implanting material and bones.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
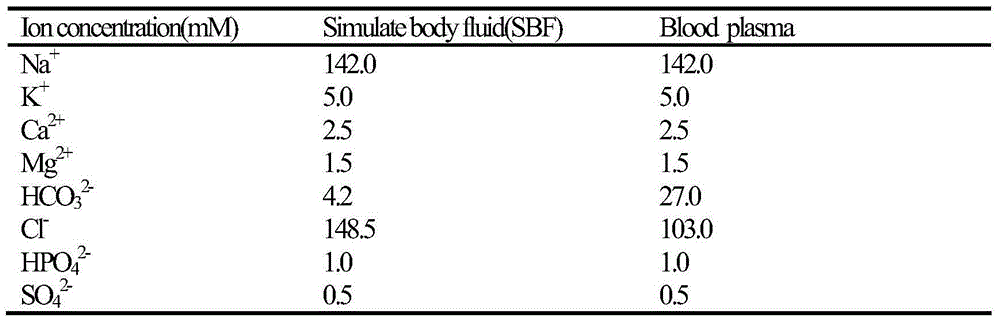
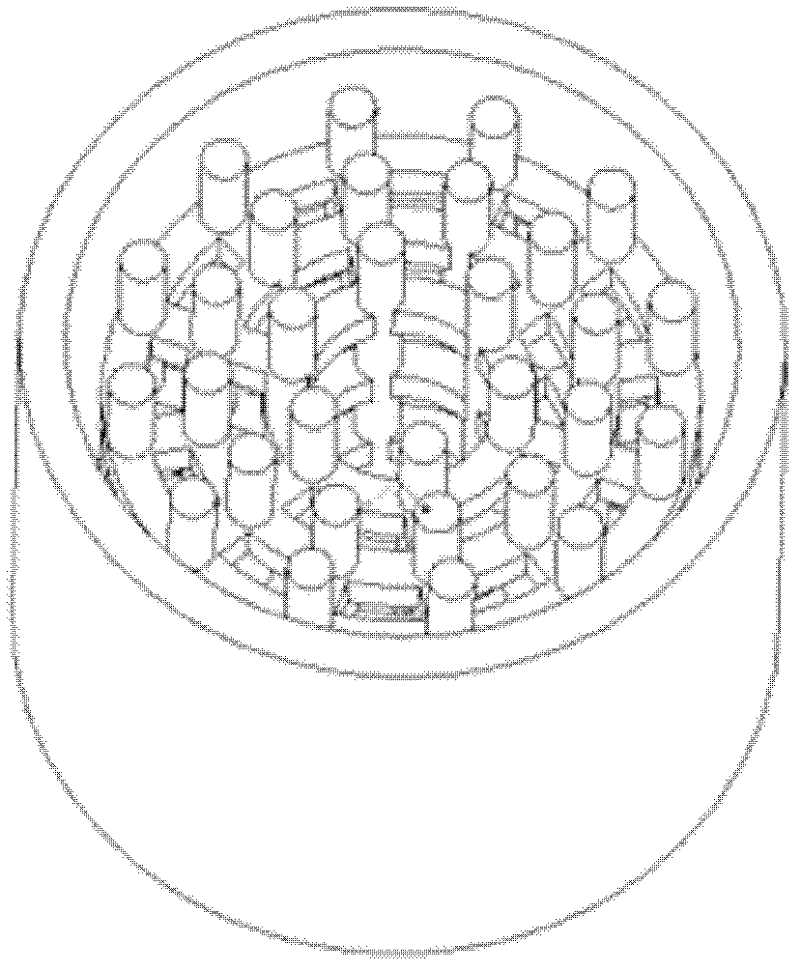
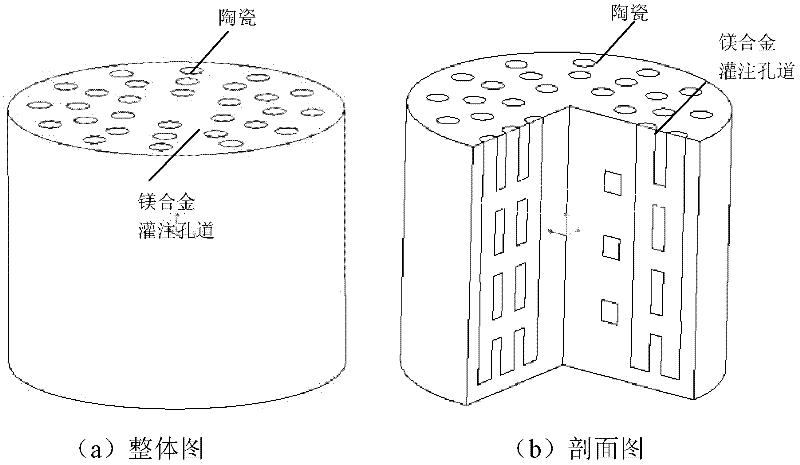
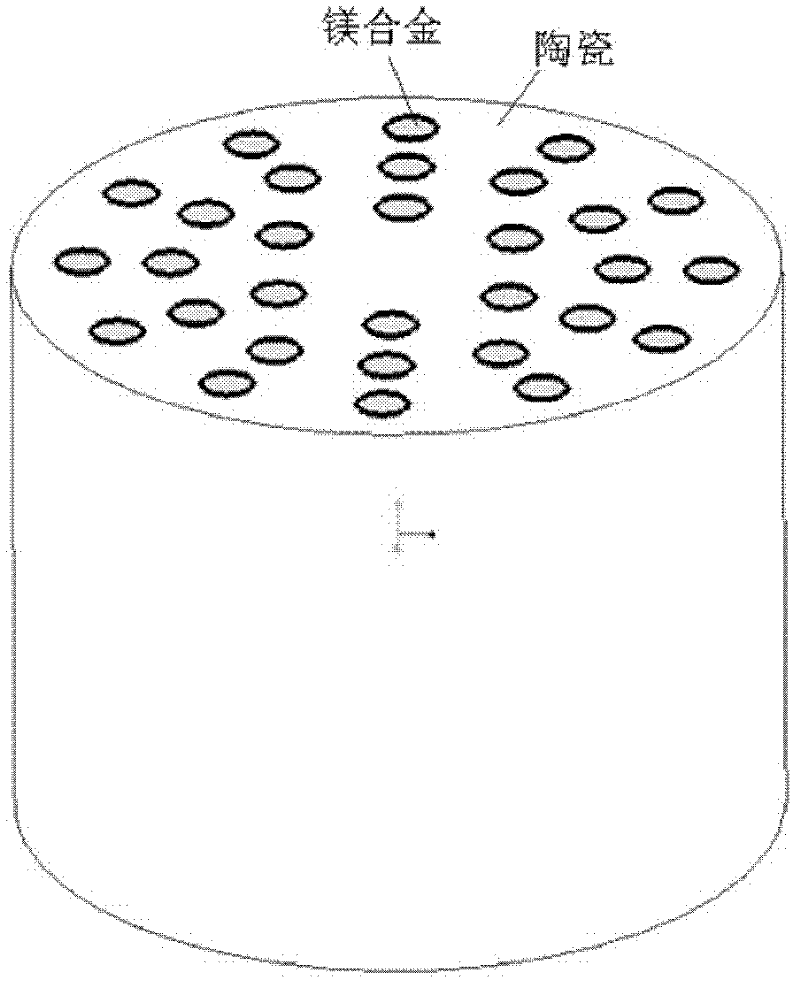
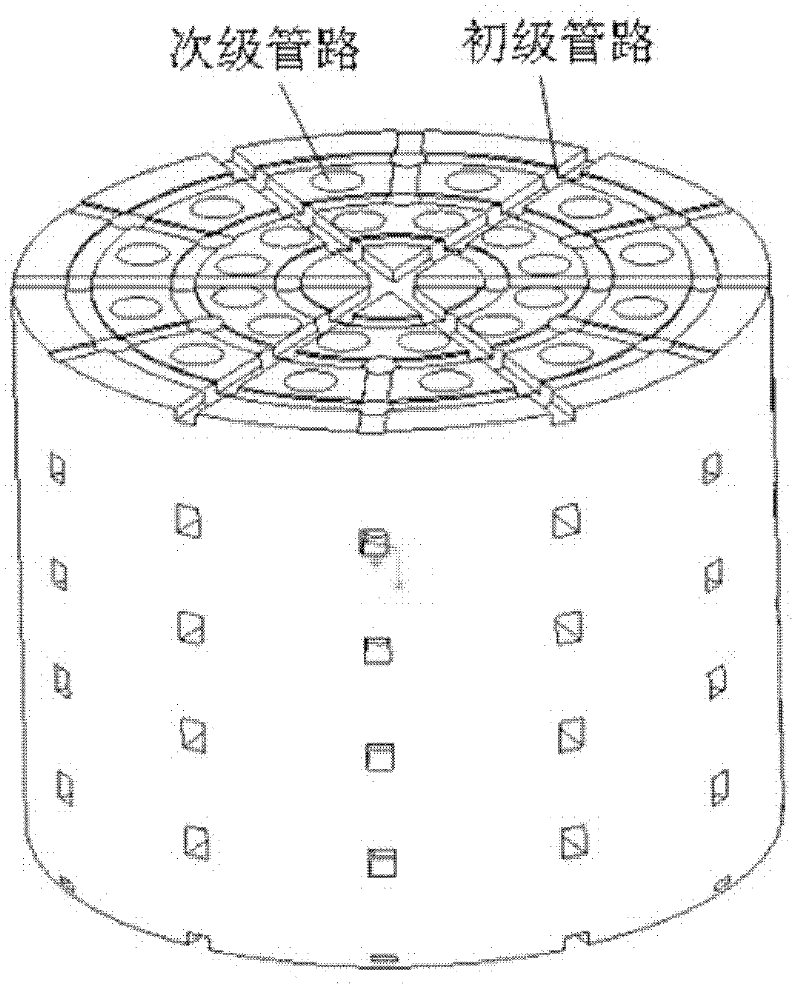
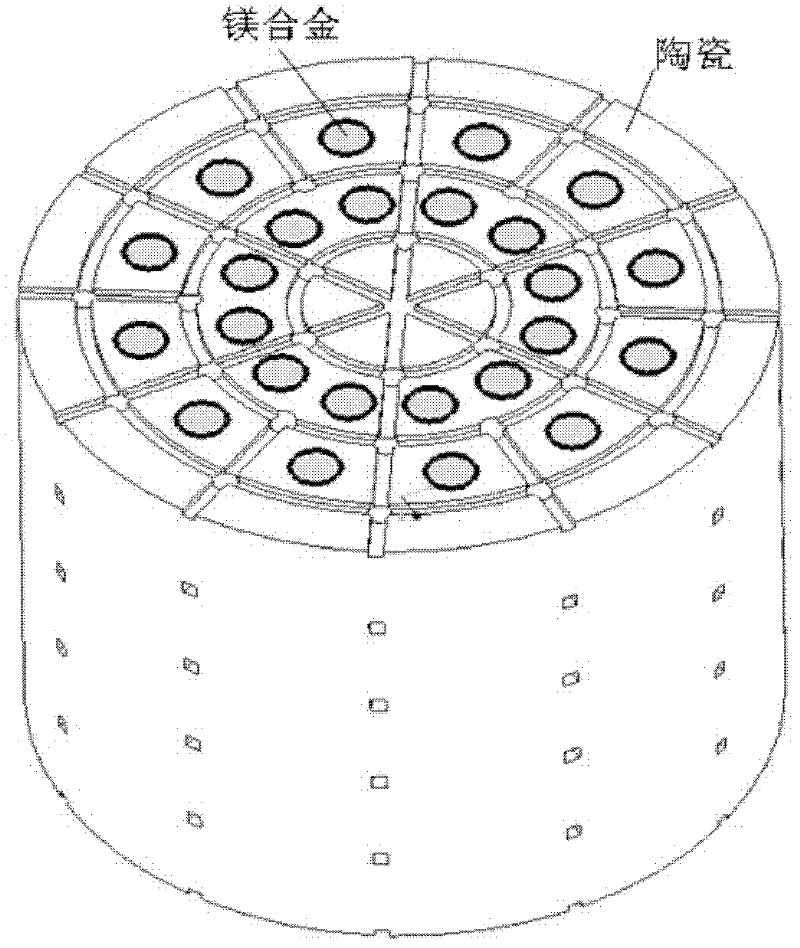
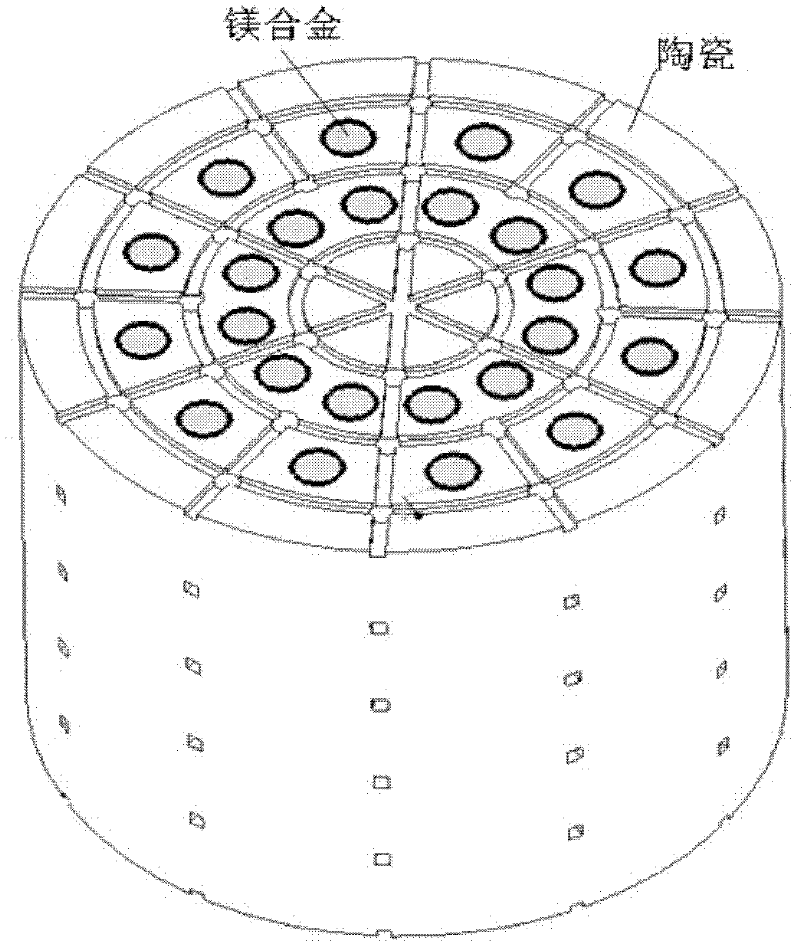
Magnesium alloy/biological ceramic bone bracket based on photocuring and gel casting and forming method of bone bracket
InactiveCN102335460AImprove early mechanical propertiesMeet growthBone implantBiomechanicsGel casting
The invention discloses a magnesium alloy / biological ceramic bone bracket based on photocuring and gel casting and a forming method of the bone bracket. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing computer-aided design (CAD) models of the bracket and a bracket negative model through shape correlation and microstructure simulation by using reverse engineering and CAD according to the structures of different bone defect parts and the analysis results of biomechanics; making a resin bracket negative model by a photocuring technology; filling ceramic slurry into the bracket negative model by a gel casting process, curing and sintering at a high temperature to make a biological activity ceramic framework with mutually-communicated porous pipelines; and casting molten magnesium alloy into the porous pipelines of the biological activity ceramic framework by a vacuum suction casting method, cooling for solidification, and thus obtaining the magnesium alloy / biological ceramic simulation composite structure bone bracket. The internal microstructure of the made bracket consists of the mutually-communicated pipelines, the magnesium alloy is filled in the pipelines to increase the early mechanical property of the composite bracket, and the pipelines filled with the magnesium alloy become mutually-communicated pore passages as the magnesium alloy is corroded and degraded, so that the requirements of organization growth, nutrition and metabolism are met.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Apparatuses, devices, systems and methods employing far infrared radiation and negative ions
InactiveUS7021297B1Improve fuel efficiencyWater/sewage treatment by irradiationExhaust apparatusCombustionEngineering
Apparatuses, devices, systems and methods employing a material or combination of materials capable of emitting both far infared radiation and negative ions are provided. The material at least include a first part of, for example, a bio-ceramic, and a second part that includes an additional oxide material. The material can be used in a variety of different applications including, for example, internal engine combustion, natural gas combustion, water purification or the like.
Owner:SLINGO FRED M
Preparation method of hydroxyapatite/zirconium dioxide biological ceramic composite material and its products
The invention relates to a preparation method of hydroxyapatite / zirconium dioxide biological ceramic composite material which comprises preparing zirconium dioxide super fine, then preparing hydroxyapatite powder, and loading zirconium dioxide super fine and hydroxyapatite powder into die casting arrangement, pressurizing to obtain blanks, then placing into high temperature furnace for burning. The preparing material has good biocompatibility and high strength and tenacity.
Owner:HANGZHOU CITY XIAOSHAN DISTRICT TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICAL HOSPITAL
Metal-ceramic composite articulation
InactiveUS20050090903A1Minimal productionIncrease resistanceBone implantJoint implantsHigh fractureIn vivo
A ceramic-metal composite articulation is provided with substantial elimination of wear debris, wherein a ceramic material is provided with superior mechanical properties tailored for articulating with ceramic articulations having high flexural strength (greater than about 700 MPa), high fracture toughness (greater than about 7 MPam1 / 2) and a high Weibull modulus (greater than about 20), in comparison with presently available bio-ceramics such as alumina or zirconia. The mechanical property enhancement enables ceramic materials with greater reliability and significantly reduced in-vivo fracture risk to be obtained. Preliminary in-vitro wear performance, to several million cycles using established test protocols, of head / cup components in a prosthetic hip joint made from these ceramics also demonstrates the ultra low wear characteristics. These material properties substantially eliminate PE wear debris mediated implant failures by offering an optimal combination of bio-mechanical safety and reliability with ultra low wear performance.
Owner:SINTX TECH INC
Method for preparing calcium polyphosphate / tricalcium phosphate two-phase biological ceramic
The invention relates to a method for preparing calcium polyphosphate / tricalcium phosphate novel two-phrase biological ceramics in the technical field of biomedical materials, which comprises the following steps of: step one, using Ca(H2PO4)2 question mark H2O to prepare amorphous CPP powder; step two, mixing CPP and HAP according to the weight ratio of 0.12-0.30 to prepare mixed powder; step three, adding polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) aqueous solution to the powder sample, mixing and granulating; step four, conducting dry press forming; and step five, sintering the dried sample. By taking animal bone dust and monocalcium phosphate monohydrate as the raw material, the method optimizes the mixture ratio of the powder and the sintering temperature and obtains the calcium polyphosphate / tricalcium phosphate two-phrase biological ceramics with controllable two-phrase content and improved degradation performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Micropore ceramics and method for sustained-release of medicament or biological preparation and use thereof
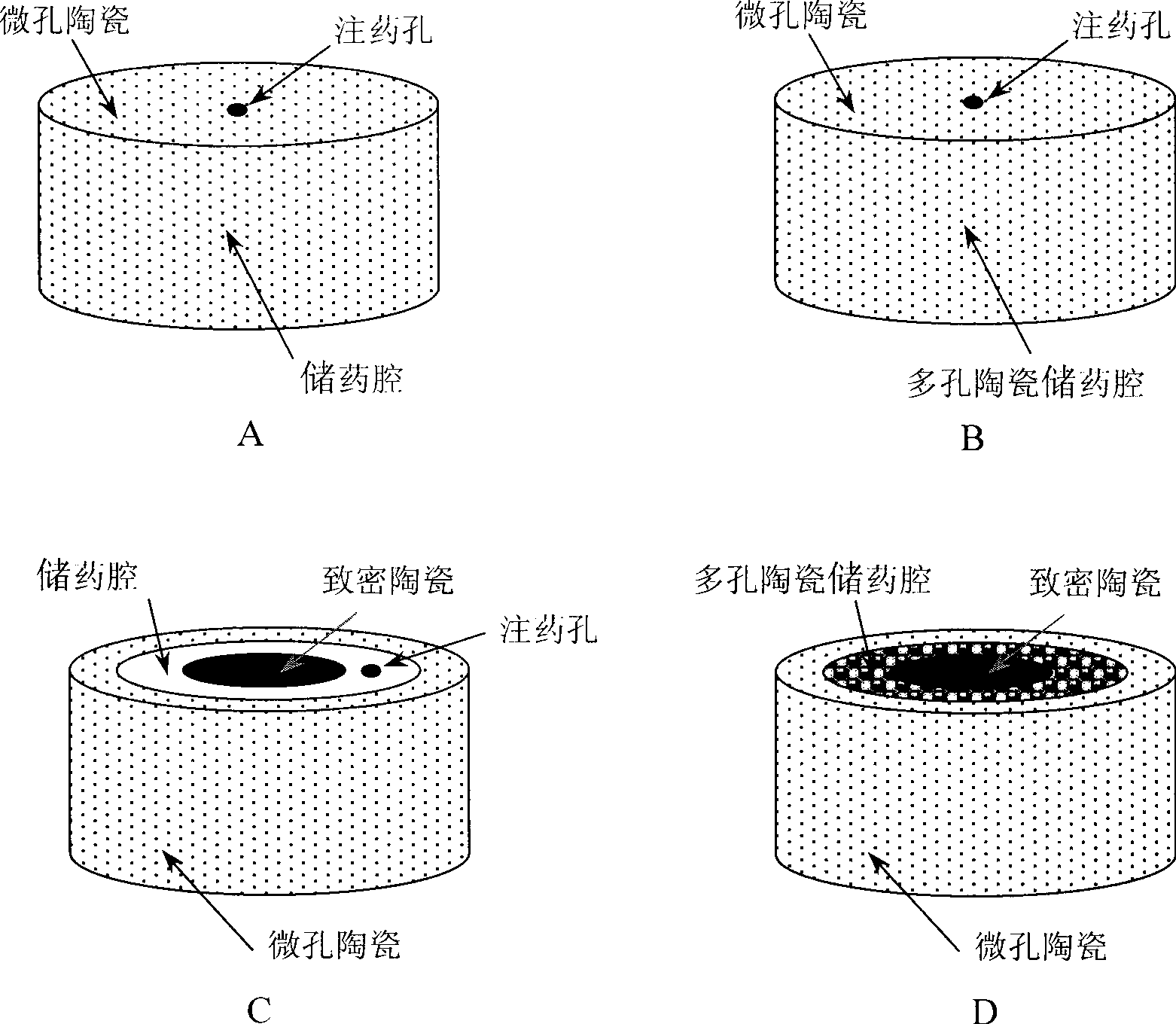
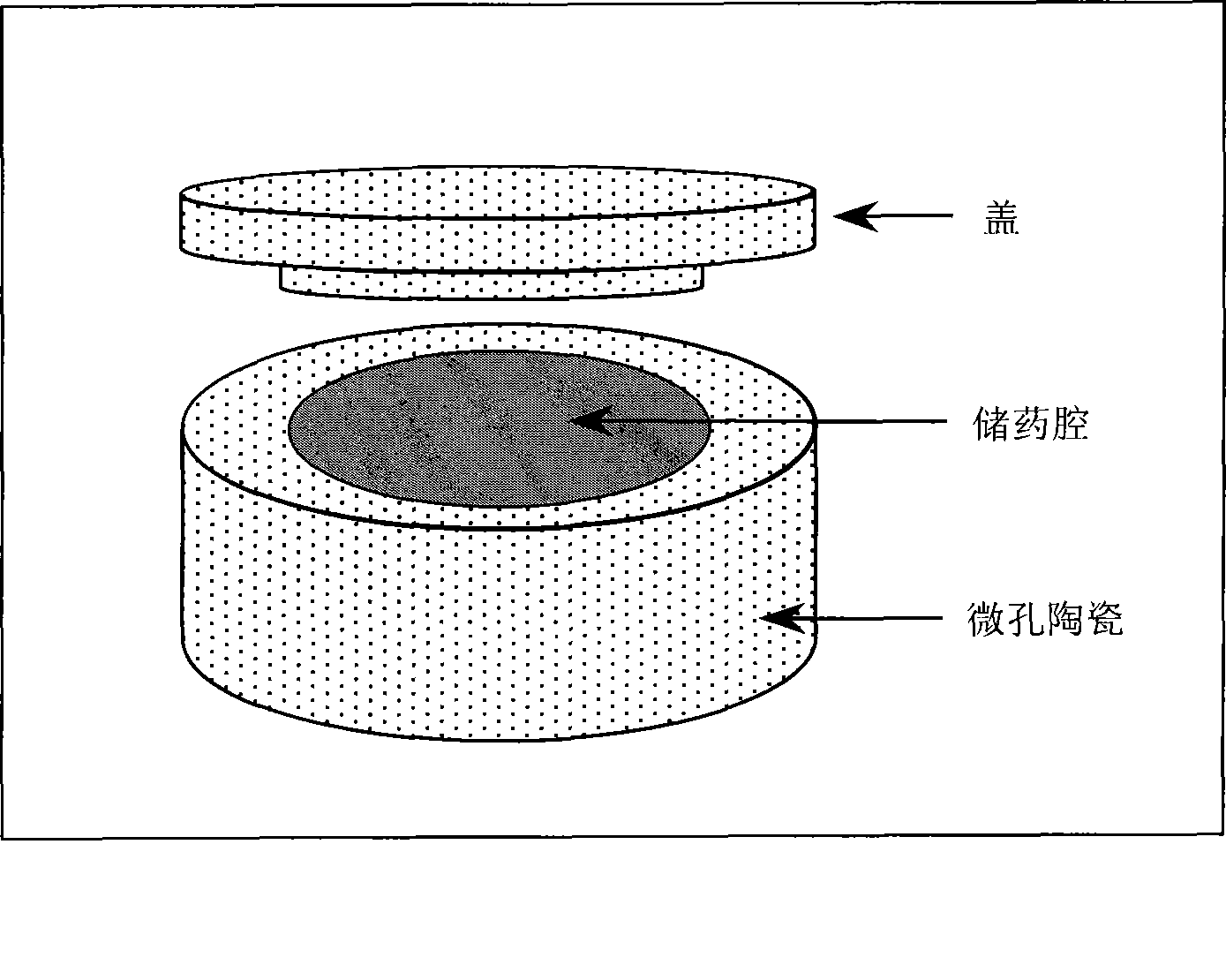
InactiveCN101461943AAchieve topicalAchieve repair and reconstructionPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCeramicwareComposite ceramicVolumetric Mass Density
The invention relates to microporous ceramics capable of slowly releasing medicines and biological agents, a method for preparing the same and application thereof. By utilizing the slow release effect of the microporous biological ceramics and accurately controlling the size and density of micropores, microporous biological ceramic products with different forms, structures and sizes are prepared; and the medicines and the biological agents are loaded in the microporous biological ceramic products. In the method, a ceramic blank is added with a soluble or volatile fine grain, or the size of ceramic power grains is controlled, or the sintering temperature is controlled, so that the size and density of the micropores, which are required in design, are formed in the biological ceramics. By the mold pressing method and the grouting method, products with different forms, structures and sizes can be prepared; furthermore, the single microporous ceramics, microporous / porous composite ceramics, microporous / compact substance composite ceramics, or microporous / porous / compact substance composite ceramics can be prepared; and the effects of medicine storage and slow release are achieved by the micropore, and the double biological reconstruction of bone defect and slow release of the medicine is completed.
Owner:卢建熙
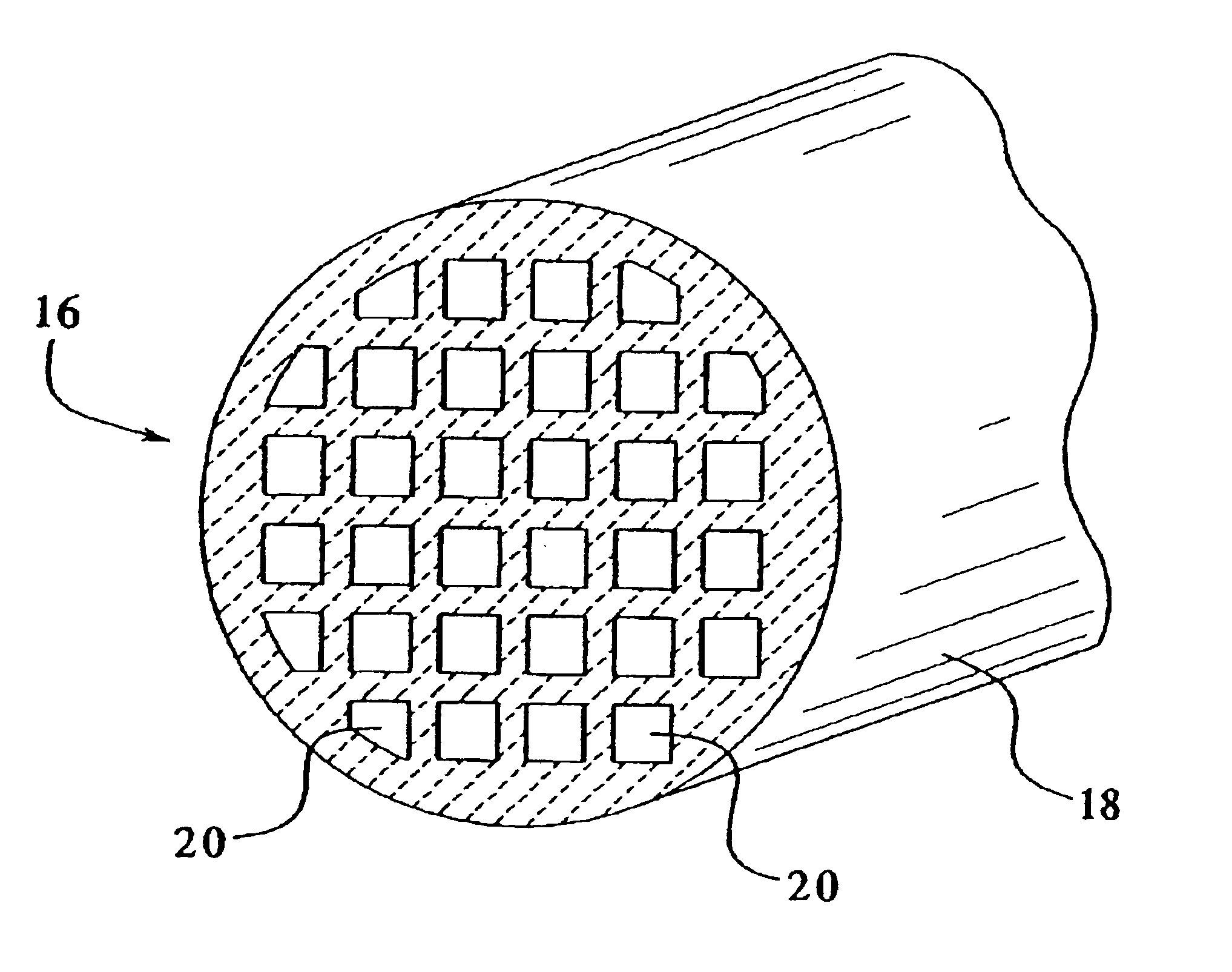
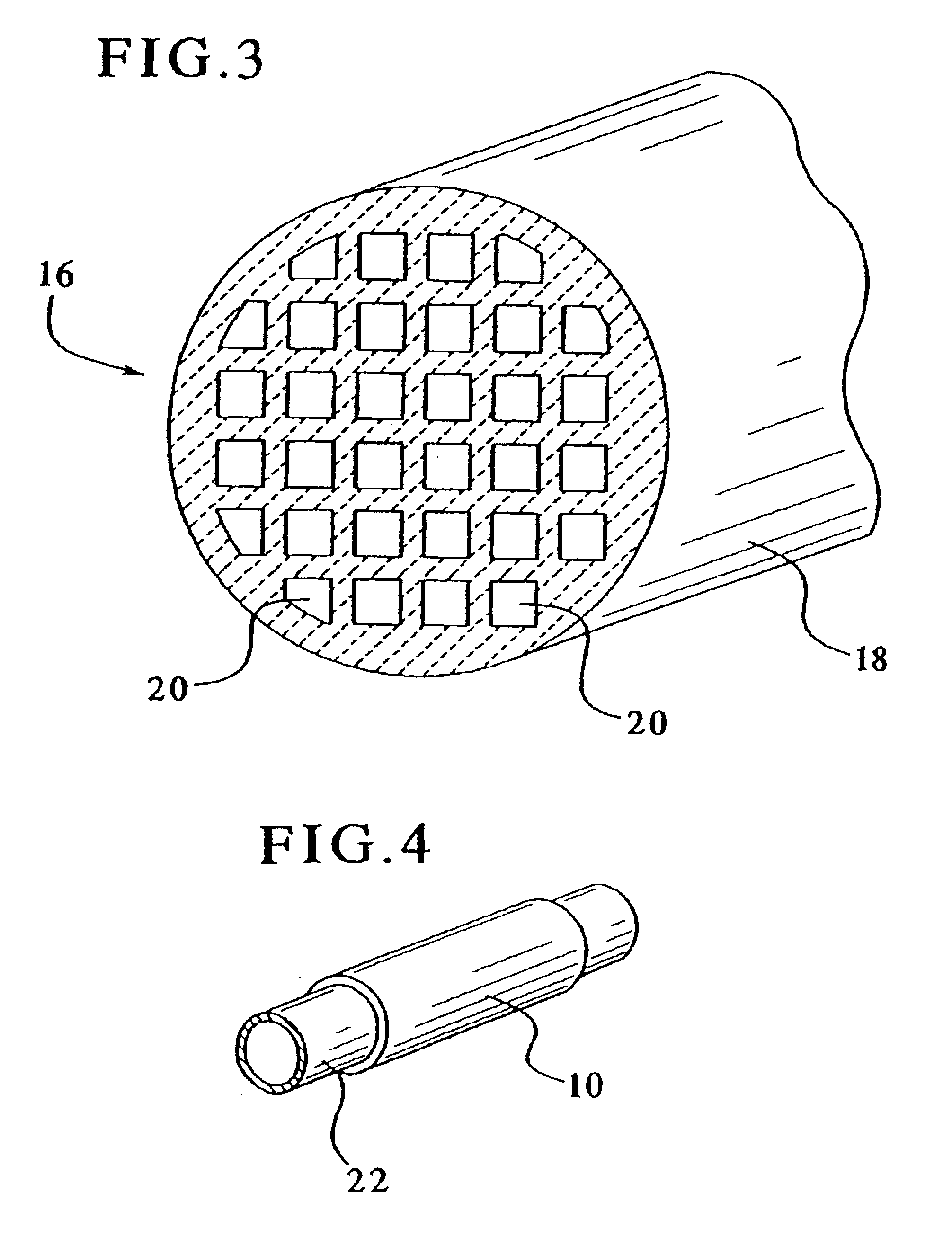
Porous magnesium alloy/biological ceramic bionic composite support and quick forming method thereof
ActiveCN102327648AImprove mechanical propertiesContinuous mechanical strengthBone implantBiomechanicsRapid prototyping
The invention relates to a porous magnesium alloy / biological ceramic bionic composite support and a quick forming method thereof. The quick forming method comprises the following steps of: performing appearance relativity, microstructural bionic design and structural optimization by means of reverse engineering and a computer-aided design (CAD) technology on the basis of analytical results of structures and biomechanics of different bone coloboma parts to establish a CAD model of the support; manufacturing a porous bioactive ceramic frame with two stages of pipelines which are not communicated mutually by a method for forming ceramics directly by photocuring; and casting molten magnesium alloy into a secondary pipeline of the biological ceramic frame by a vacuum suction casting method, cooling and solidifying to obtain the porous magnesium alloy / biological ceramic bionic composite support, wherein a primary pipeline is used for meeting the requirements of tissue growth and nutritionalmetabolism, and the magnesium alloy is filled into the secondary pipeline to enhance the mechanical property of the composite support and reduce a contact area of the magnesium alloy and body fluid, so that mass exchange of the magnesium alloy and a human body environment is avoided within a period of time of degrading ceramics to ensure the filled magnesium alloy provides continuous mechanical strength in the process of bone healing.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Preparation method of titanium alloy/biological ceramic layer composite material
InactiveCN101994143AGood biological propertiesGood mechanical compatibilitySurface reaction electrolytic coatingPlasma electrolytic oxidationElectrolysis
The invention discloses a preparation method of a titanium alloy / biological ceramic layer composite material. The method comprises the following steps of: fixing a metal connecting lead on a clean titanium substrate, and then dipping the titanium substrate into an electrolyte solution; and carrying out plasma electrolytic oxidation by adopting a heteropolar pulse current power supply to prepare a titanium oxide porous ceramic membrane composite material rich in Ca, P, Si and compounds thereof, wherein the solute in the electrolyte solution is rich in Ca, P and Si; the heteropolar pulse current power supply is characterized in that the forward / inverse current is 0-30A, the forward voltage is 0-750V, and the inverse voltage is 0-250; the pulse frequency is 50-1,500 Hz; the positive / negative duty cycle is 5-95 percent; the dead time is 0-60muS; the pulse number is 1-30; and the forward / inverse current and the forward / inverse voltage are not zero at the same time. The oxidation ceramic membrane and the titanium alloy substrate of the material have high interface bonding strength and excellent mechanical compatibility with bone tissues, and the porous structure and components of the oxidation membrane have excellent capacity of inducing and depositing apatite.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for carrying out surface modification on ceramic material through liquid permeation
The invention relates to a method for carrying out surface medication on a ceramic material through liquid permeation, belonging to the technical field of surface modification of biological ceramic materials. The method comprises the following steps of selecting one or more of zirconium oxide, aluminum oxide, silicon dioxide, calcium oxide, silicon carbide and other metal oxides or carbides as a ceramic material blank before dense sintering; preparing a penetrating fluid with certain concentration from Ca, P, Si, Ti, Ag or the like which need to be added to the surface of the ceramic material, and soaking the ceramic material with one or combination of more of penetrating fluids respectively or simultaneously, wherein the penetrating fluid penetrates the surface of the ceramic material by using the characteristic that a ceramic blank has relatively high porosity before dense sintering, and after dense sintering, components in the solution are left on the surface layer of the ceramic material to form a gradient composite layer, so that the purpose of carrying out surface modification on the ceramic material is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING STOMATOLOGY HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Bionic bone/cartilage composite scaffold and preparation technology and fixing method thereof
InactiveCN103463676ASimple preparation processConvenient for clinical operationProsthesisBioceramicPolylactic acid
The invention provides a bionic bone cartilage composite scaffold and preparation technology and fixing method thereof. According to the structure of the coloboma position of the cartilage of patient, reverse engineering and CAD technology are used for designing the composite scaffold which is matched with the coloboma position; the composite scaffold comprises a biological ceramic bone scaffold, a polylactic acid fixing pile and a hydrogel cartilage scaffold; the light-cured biological ceramic bone scaffold is manufactured by indirect moulding; polylactic acid is perfused in the biological ceramic bone scaffold, and the biological ceramic bone scaffold is cured and polished in a vacuum mold casing machine, and then a biological ceramic / polylactic acid composite scaffold is obtained; the bionic bone cartilage composite scaffold is prepared by light-cured rapid moulding and hydrogel solution; the bionic bone cartilage composite scaffold is placed in the defect position by operation, and is drilled with a support for fixing; bone cement is poured into the support fixing hole, a polylactic acid fixing pile is hit into the fixing hole immediately, after solidification, the implantation of the bone cartilage composite scaffold is completed. The invention is used for repairing large-area bone / cartilage defect with good effect.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Two-phase calcium phosphate material, preparation method thereof, and two-phase calcium phosphate artificial bone ceramic
The invention discloses a two-phase calcium phosphate material, a preparation method thereof, and a two-phase calcium phosphate artificial bone ceramic, and belongs to the field of biological ceramic materials. The two-phase calcium phosphate artificial bone ceramic is prepared through preparing a beta phase tricalcium phosphate (beta-TCP) and hydroxy apatite (HA) mixture (the two-phase calcium phosphate material) from egg shells and carrying out a sintering process. The beta-TCP and the HA are prepared from the egg shells with abundant sources through a one-step chemical synthesis process, the mass proportions of the beta-TCP and the HA in the two-phase calcium phosphate are controlled through changing the particle dimensions of the egg shells in the hydrothermal synthesis process, and the preparation cost of the two-phase calcium phosphate material is low. The two-phase calcium phosphate ceramic is prepared through a template process under pressureless sintering conditions, and the two-phase calcium phosphate ceramic with different degradation speeds can be prepared through controlling the mass proportions of the beta-TCP and the HA, so different demands of bone defect patients on the degradation period of artificial bone scaffold materials due to individual difference are met.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
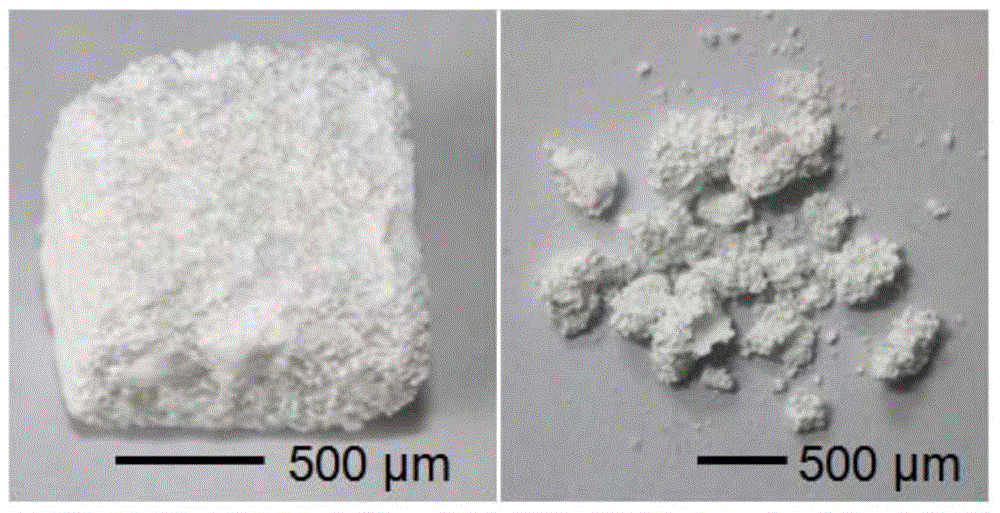
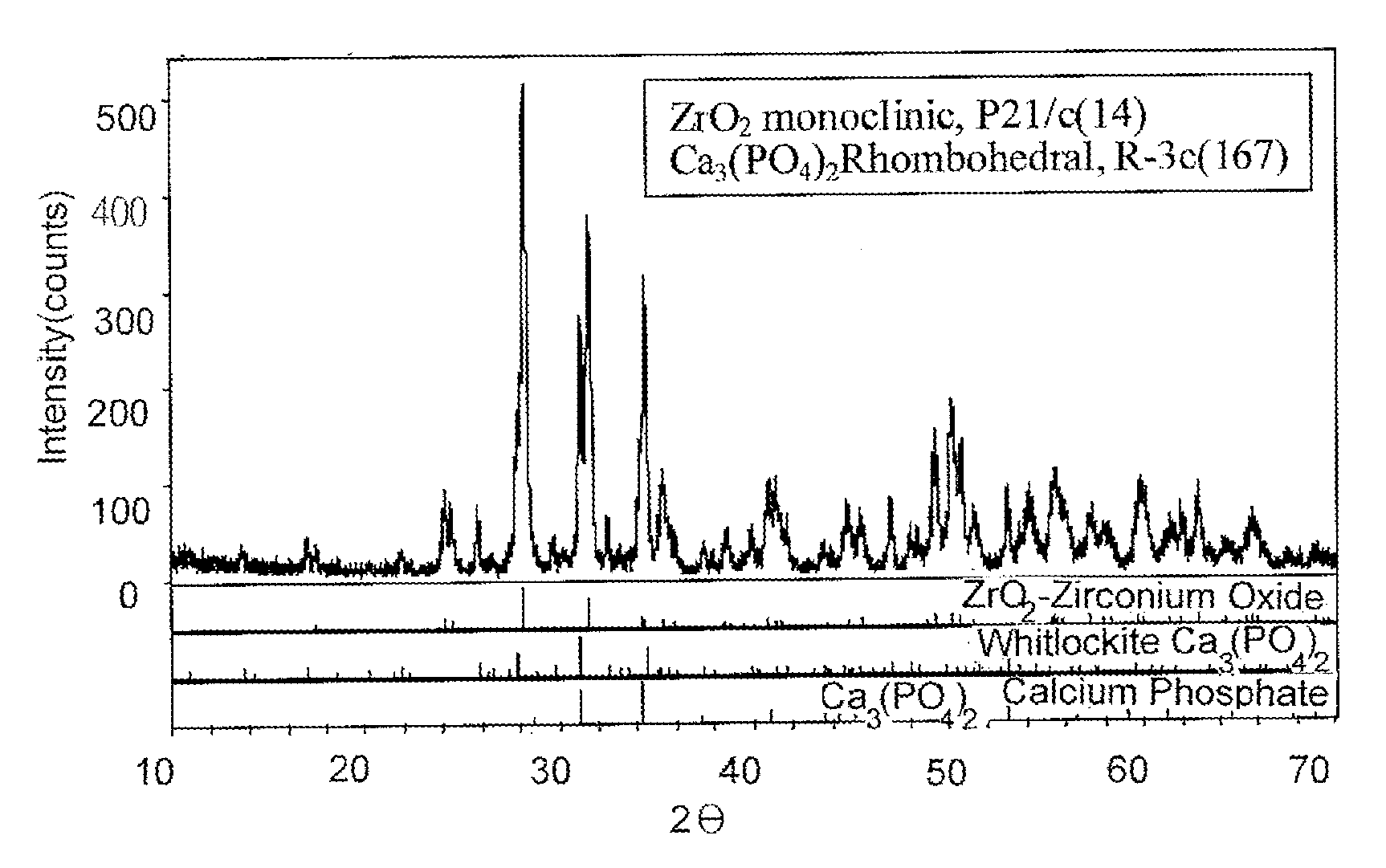
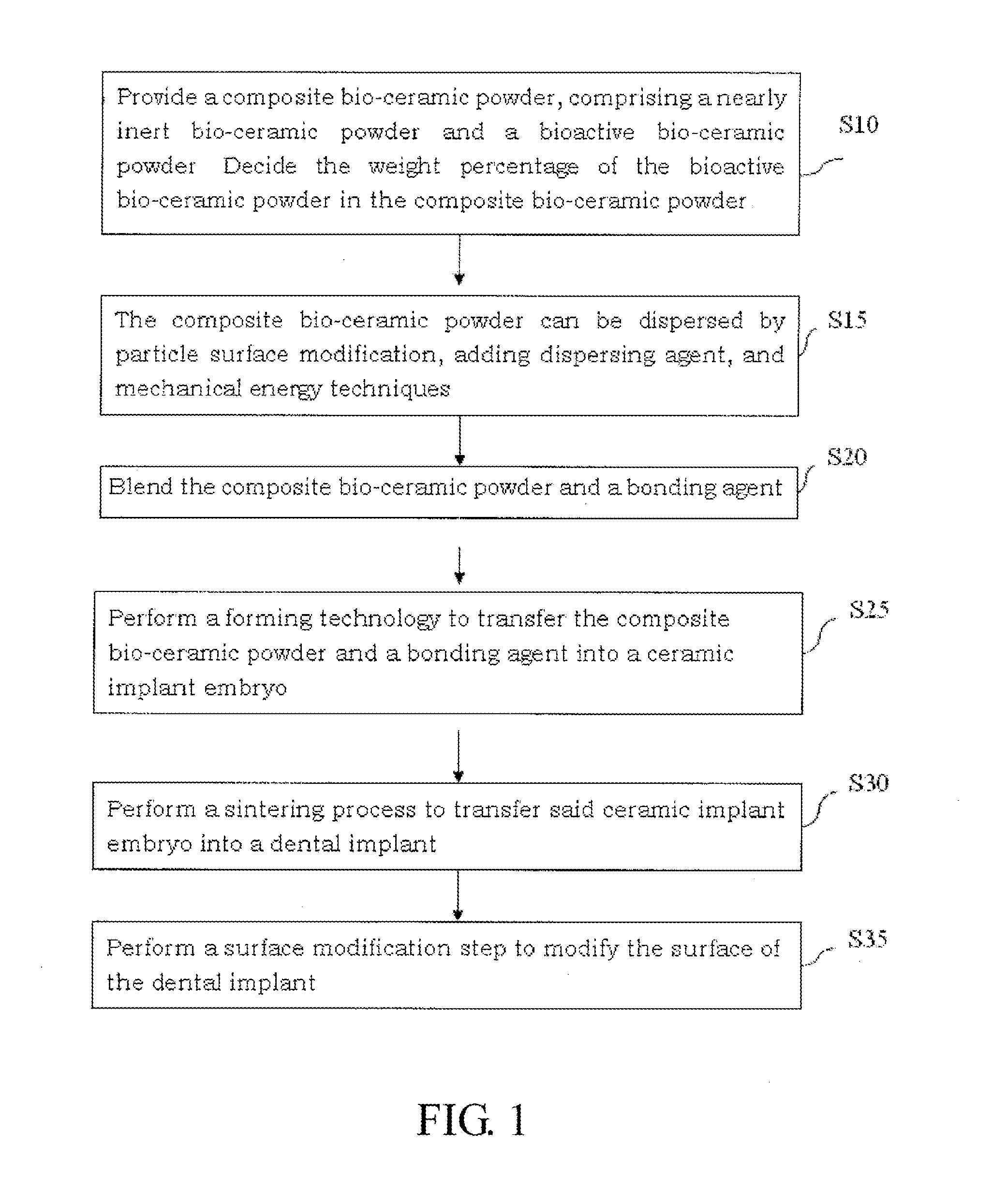
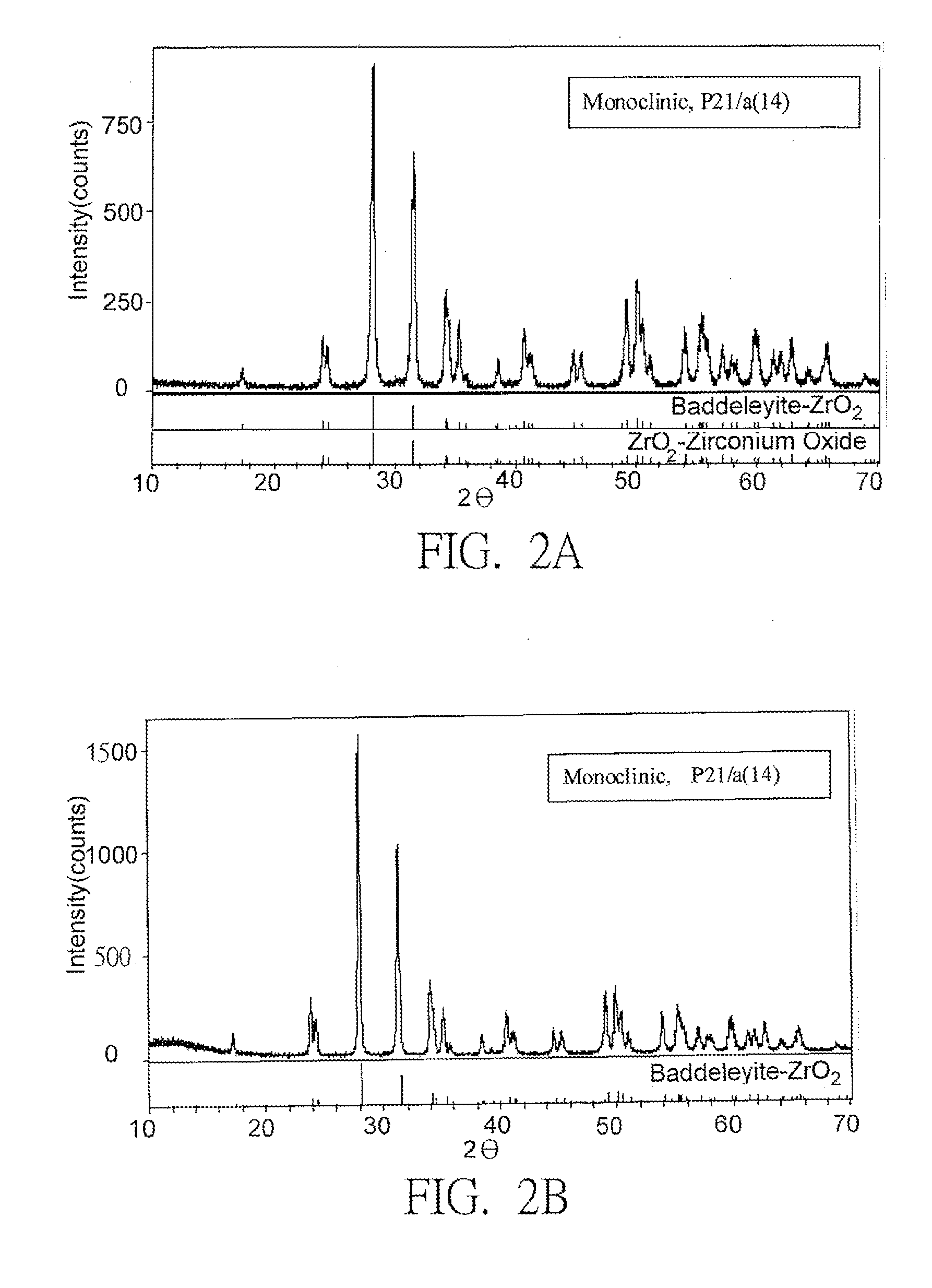
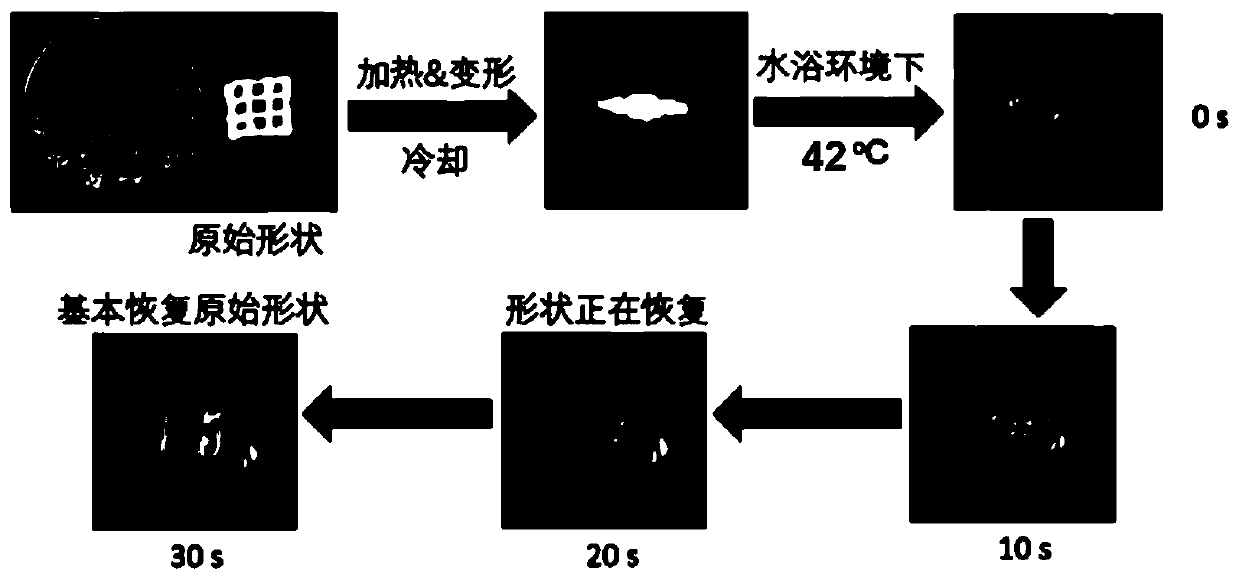
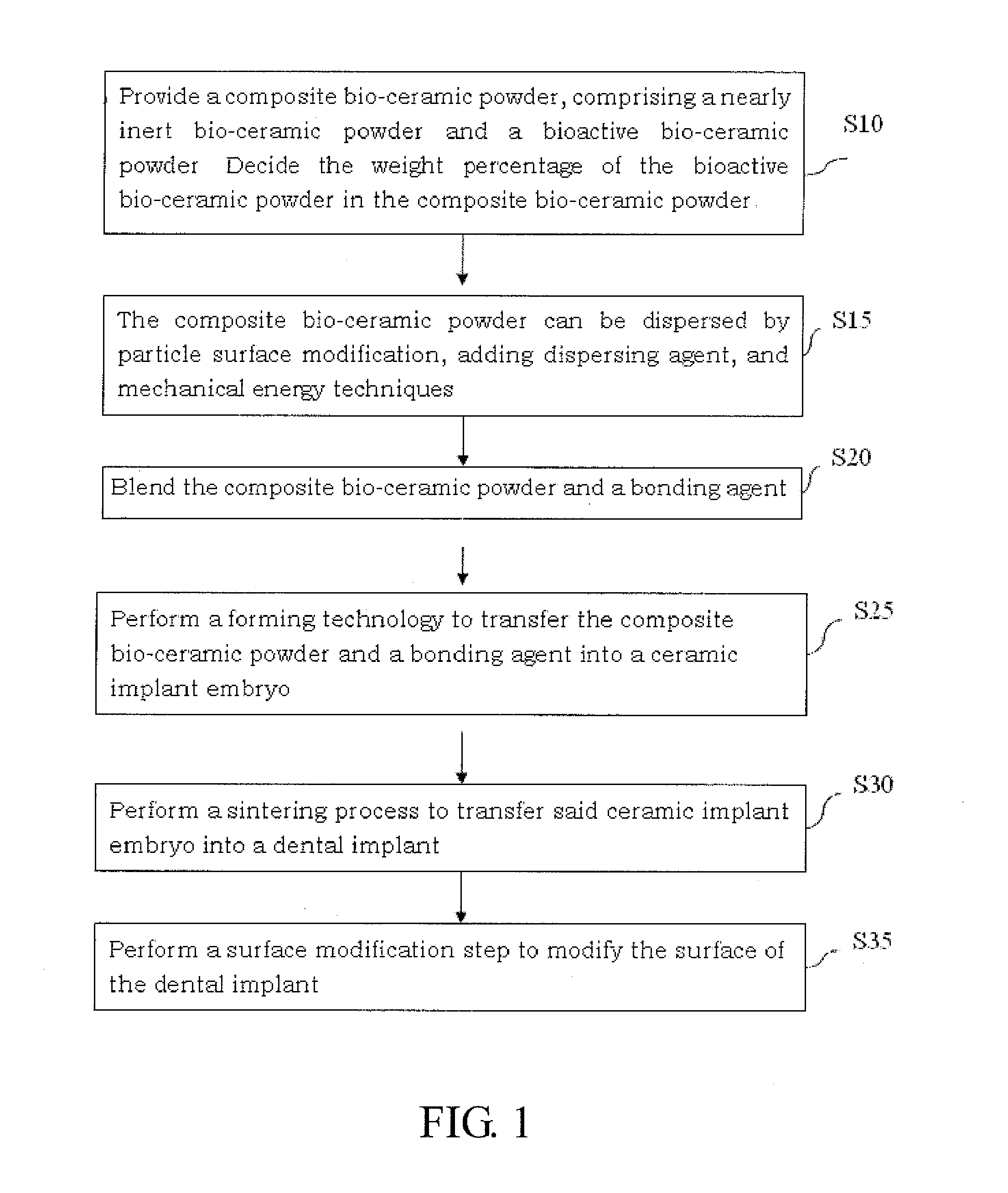
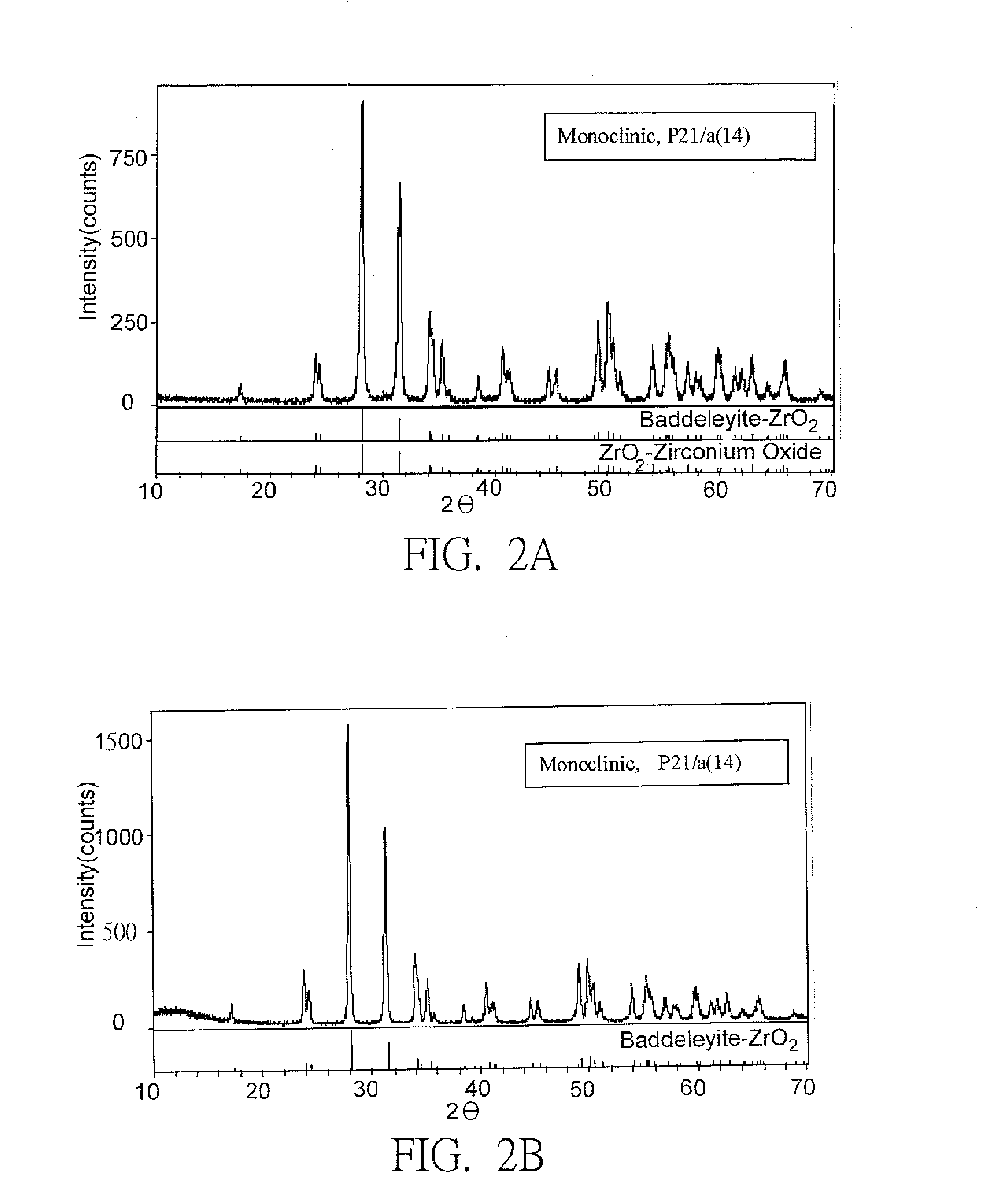
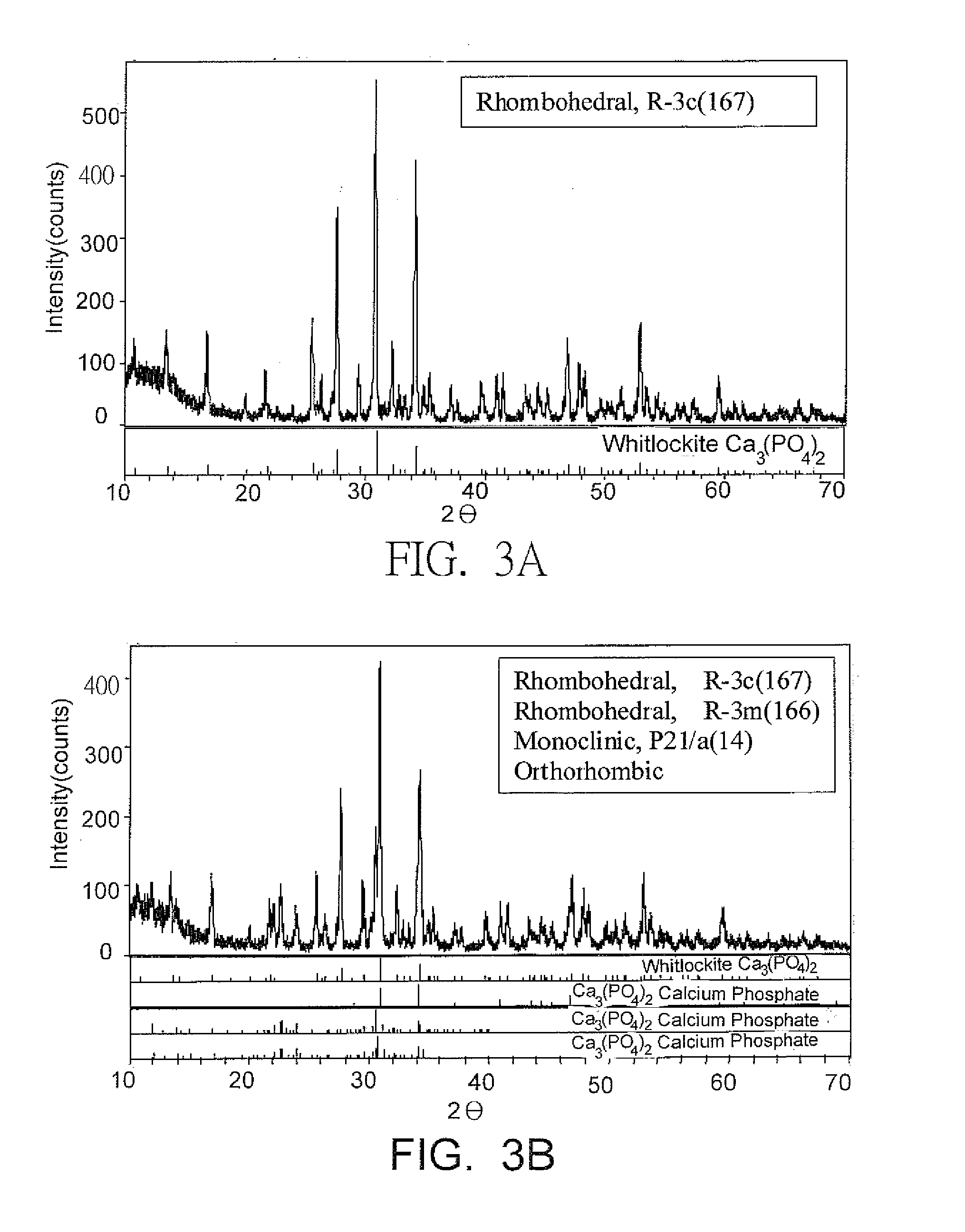
Composite Bio-Ceramic Dental Implant and Fabricating Method Thereof
InactiveUS20110195378A1Low mechanical strengthHigh mechanical strengthDental implantsBiocideUltimate tensile strengthDental implant
A composite bio-ceramic dental implant and fabricating method thereof are disclosed. The composite bio-ceramic is sintered at a temperature between 1000 and 1800° C. using the nearly inert bio-ceramic powder and the active bio-ceramic powder or the completely resorbable bio-ceramic powder. The bioactive bio-ceramic material is dispersed in the inert bio-ceramic material. Therefore, the composite bio-ceramic has enough mechanical strength and good bioactivity for dental implant.
Owner:NAT TAIPEI UNIV OF TECH
Zirconia biological ceramic and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses zirconia biological ceramic and a preparation method thereof, relating to the field of biological materials. The average particle size of the ceramic is 0.2-0.5mm, and the ceramic comprises the following components in parts by weight: 60-80 parts of zirconia, 2-6 parts of nanometer titania, 3-7 parts of nanometer aluminum oxide, 0.2-0.5 part of rare-earth chloride and 3-8 parts of alginate fibers. The method for preparing the zirconia biological ceramic comprises the following preparation steps: (1) weighing; (2) performing ball milling; (3) performing cold press molding; (4) performing high-temperature and high-pressure calcining; and (5) cooling and taking out the ceramic. The zirconia biological ceramic provided by the invention has the characteristics of good wear-resisting property, high toughness and high biocompatibility and can serve as general medical implants or substitute materials of oral teeth.
Owner:SUZHOU VIVOTIDE BIOTECH
Photo-thermal chemotherapy bone repair material and preparation method of tissue engineering scaffold
InactiveCN109010925APromote repairExcellent mechanical propertiesTissue regenerationProsthesisPrinting inkBone conduction hearing
The invention discloses a photo-thermal chemotherapy bone repair material and a preparation method of a tissue engineering scaffold. The bone repair material includes an oil-soluble high-molecular material, bio-ceramic powder, an oily solvent, a water-soluble bioactive material, water, an emulsifier, a chemotherapy medicine, and a photo-thermal agent. The preparation method includes: according tothe bone repair material, preparing a W / O emulsion, and sending the W / O emulsion to an ink cartridge of a printer as printing ink; establishing a tissue engineering scaffold three-dimensional model onCAD software, setting printing parameters, regulating the temperature of a shaping chamber in the printer, and printing a tissue engineering scaffold prefabricated member, so that when solvent in theprefabricated member is volatilized naturally, a finish product of the tissue engineering scaffold is formed. The tissue engineering scaffold has good mechanical character, can simulate bone tissue structure, has excellent bone guidance and bone conduction and excellent photo-thermal effect and is toxic-free, and can promote recovery of massive bone defects caused by bone tumor resection.
Owner:王翀
Composite Bio-Ceramic Dental Implant and Fabricating Method Thereof
InactiveUS20130150227A1Low mechanical strengthHigh mechanical strengthDental implantsTissue regenerationUltimate tensile strengthDental implant
A composite bio-ceramic dental implant and fabricating method thereof are disclosed. The composite bio-ceramic is sintered at a temperature between 1000 and 1800° C. using the nearly inert bio-ceramic powder and the active bio-ceramic powder or the completely resorbable bio-ceramic powder. The bioactive bio-ceramic material is dispersed in the inert bio-ceramic material. Therefore, the composite bio-ceramic has enough mechanical strength and good bioactivity for dental implant.
Owner:NAT TAIPEI UNIV OF TECH
Nano composite active biological ceramic powder and processing process thereof
The invention relates to the field of domestic ceramics, in particular to nanometer composite activity biological ceramic powder, which comprises 5-10 percent of nanometer yttrium, 1-5 percent of nanometer silver, 5-15 percent of nanometer zinc, 10-20 percent of iron titanium oxide, 20-35 percent of nanometer tourmaline and 25-35 percent of micron zeolite. By adding the ceramic material to all of the ceramic glazes, the produced ceramic products have the performances of air purification, rot resistance, deodorization, self-cleaning and antifouling and antibacterium; and colon bacillus and staphylococcus aureus reach larger than 99 percent. The ceramic powder can emit far infrared rays, release negative ions and play the roles of resisting bacteria, purifying, activating, keeping the pH value alkalescent, holding microcluster water and dissolving out the microelements needed by human body in improving water quality.
Owner:郑开明
Method for preparing bio-ceramic film on surface of magnesium/magnesium alloy through micro-arc oxidation
InactiveCN102304745AExtended service lifeLong-actingAnodisationMicro arc oxidationPlasma electrolytic oxidation
The invention discloses a method for preparing a bio-ceramic film on the surface of magnesium / magnesium alloy through micro-arc oxidation. The composite system solution of phosphate and silicate is used as electrolyte, magnesium or magnesium alloy is placed in the electrolyte to be used as an anode, a stainless steel plate is used as a cathode, the temperature of the electrolyte is controlled at 10-45 DEG C, the pulse frequency is adjusted to 100-2000 Hz, the duty cycle is 10-55%, and constant pressure treatment is performed for 3-120 min under voltage of 250-500V to grow a uniform and dense bio-ceramic film on the surface of magnesium or magnesium alloy in situ. By adopting the method, the uniform and dense bio-ceramic film can be fast obtained on the surface of magnesium or magnesium alloy; and the method does not have special demands on the material, shape, size and the like of magnesium or magnesium alloy, and has good generality.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
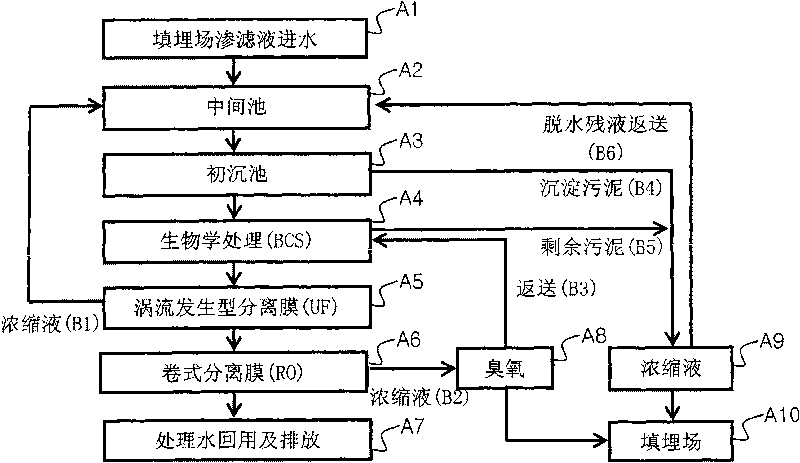
Treatment process of garbage percolate
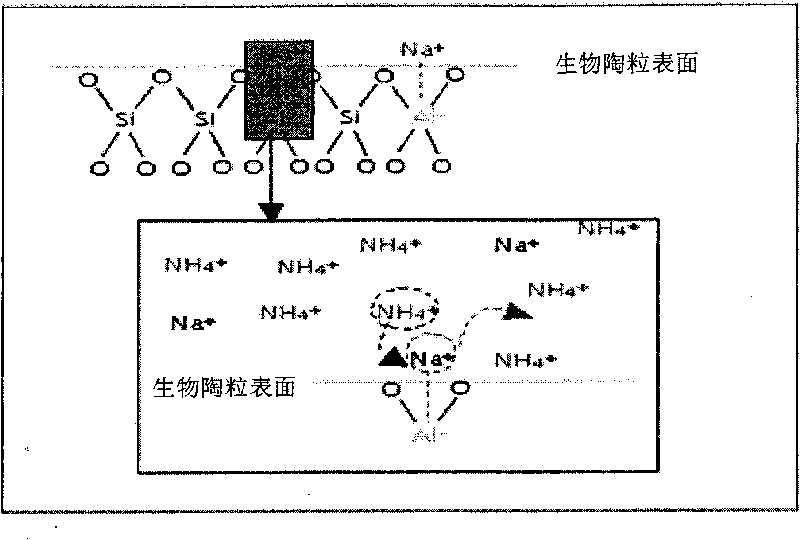
The invention discloses a treatment process of garbage percolate, comprising: 1), a pre-treatment procedure, the garbage percolate is led into a middle tank and a primary settling tank for adjusting the water quality and the water quantity; 2) a biological treatment procedure, the treatment fluid which passes through the pretreatment procedure is treated through a SBR (Sequencing Batch Reactor Activated Sludge Process) biological treatment method; 3) an advanced treatment procedure, after the treated fluid passes through the biotical treatment procedure, the treated fluid enters a vortex-generating type separation membrane device for treating, and then enters a roll type separation membrane device for treating. Another aspect of the invention comprises adding bio-ceramic to the biological treatment procedure and the bio-ceramic is used as carrier. In the invention, the process combining the biological treatment and the physical treatment which utilizes the separation membrane is more stable, efficient; the input cost and the using and maintenance cost for the facility construction is further reduced.
Owner:富康技术股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com