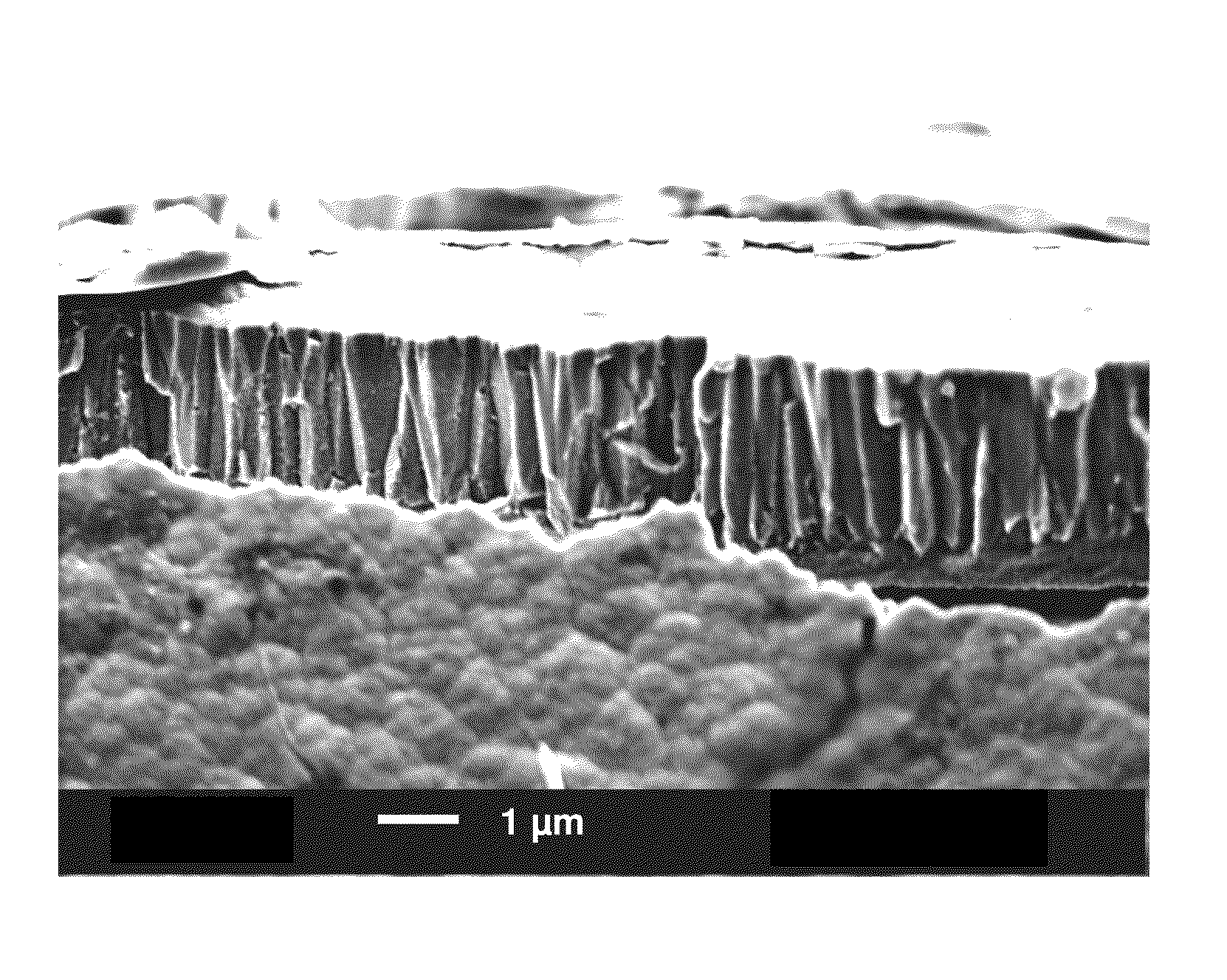
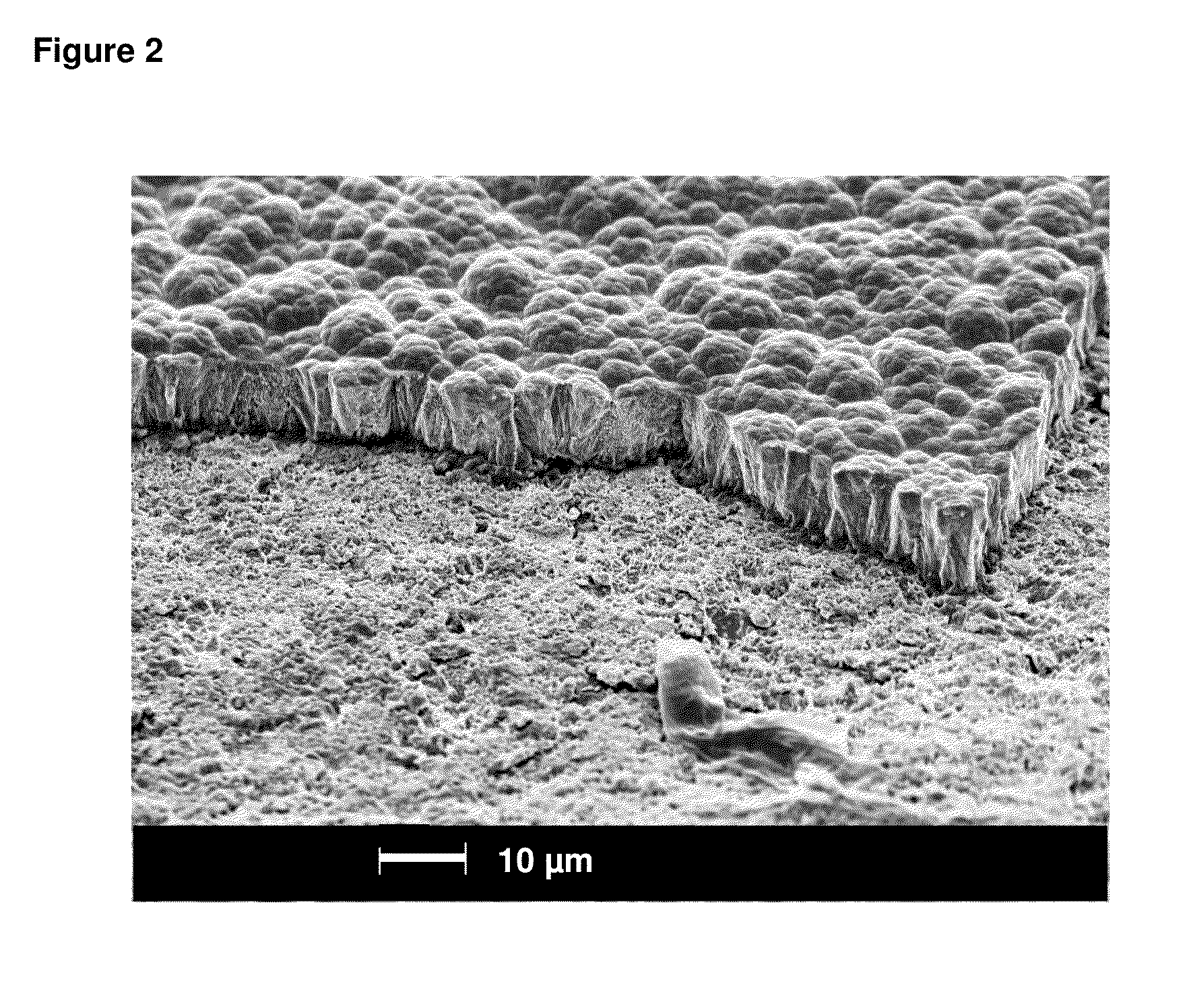
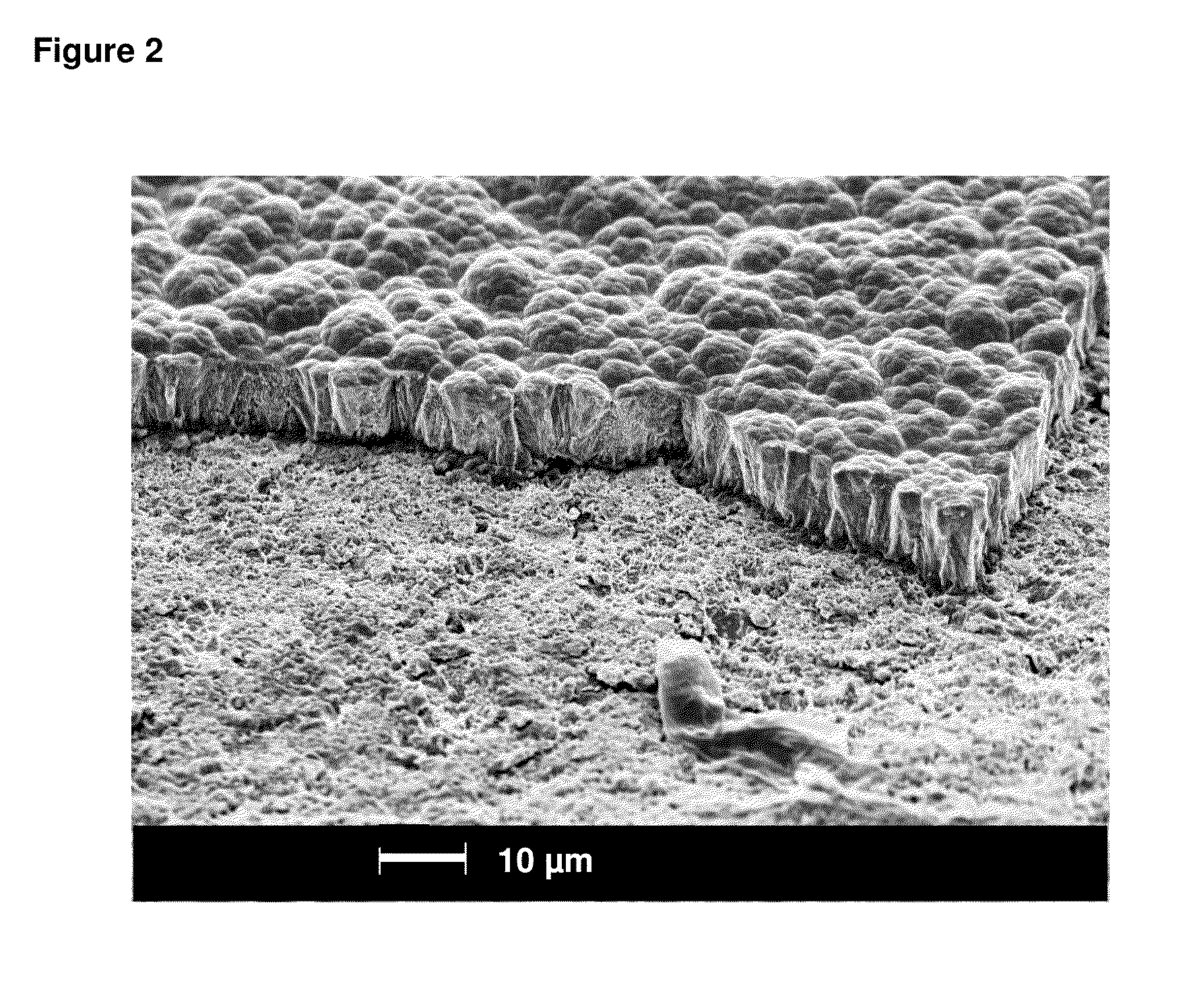
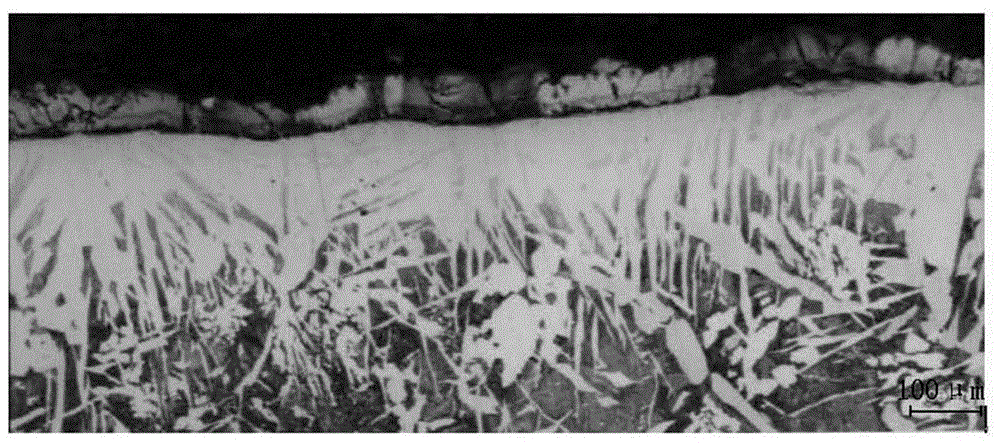
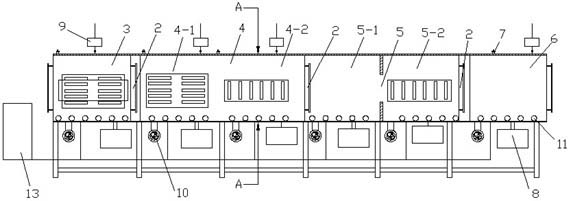
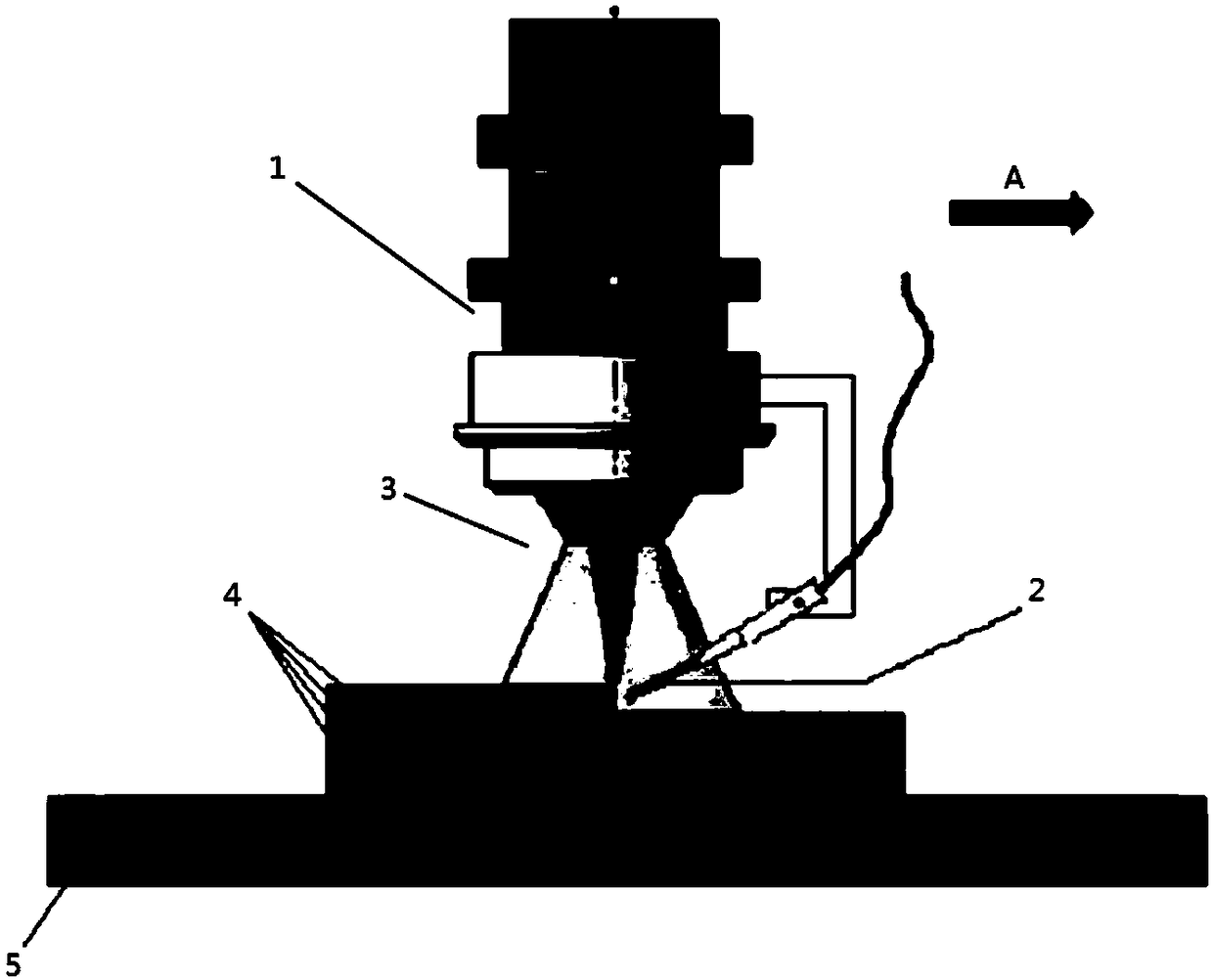
Patents
Literature
86 results about "Alloy deposition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tin-silver solder bumping in electronics manufacture
ActiveUS20070037377A1Improve stabilityReduced and entirely eliminated voidingCellsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrolysisThiourea
A process for forming a solder bump on an under bump metal structure in the manufacture of a microelectronic device comprising exposing the under bump metal structure to an electrolytic bath comprising a source of Sn2+ ions, a source of Ag+ ions, a thiourea compound and / or a quaternary ammonium surfactant; and supplying an external source of electrons to the electrolytic bath to deposit a Sn—Ag alloy onto the under bump metal structure.
Owner:MACDERMID ENTHONE INC
Process for preparing invor alloy foil
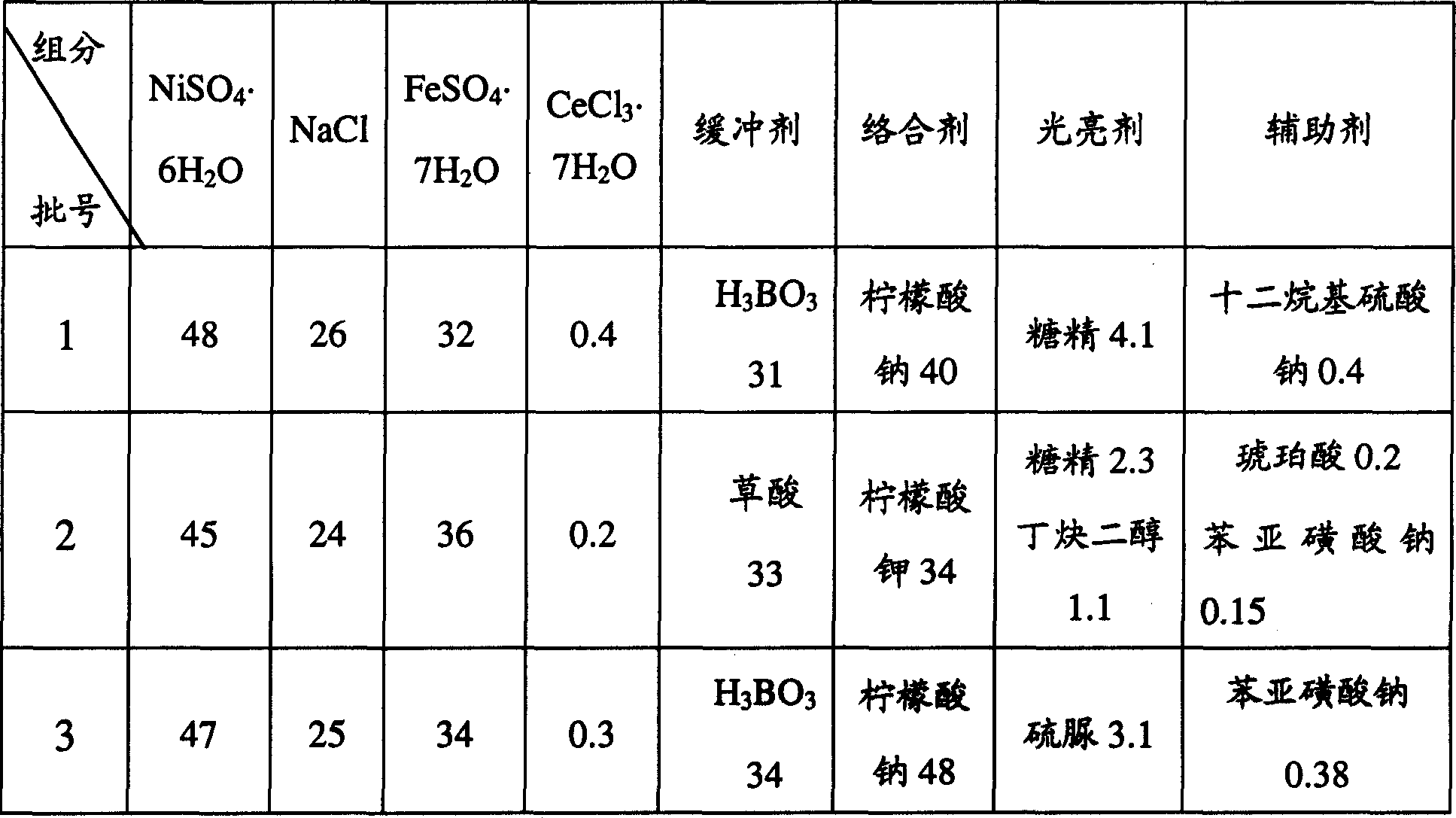
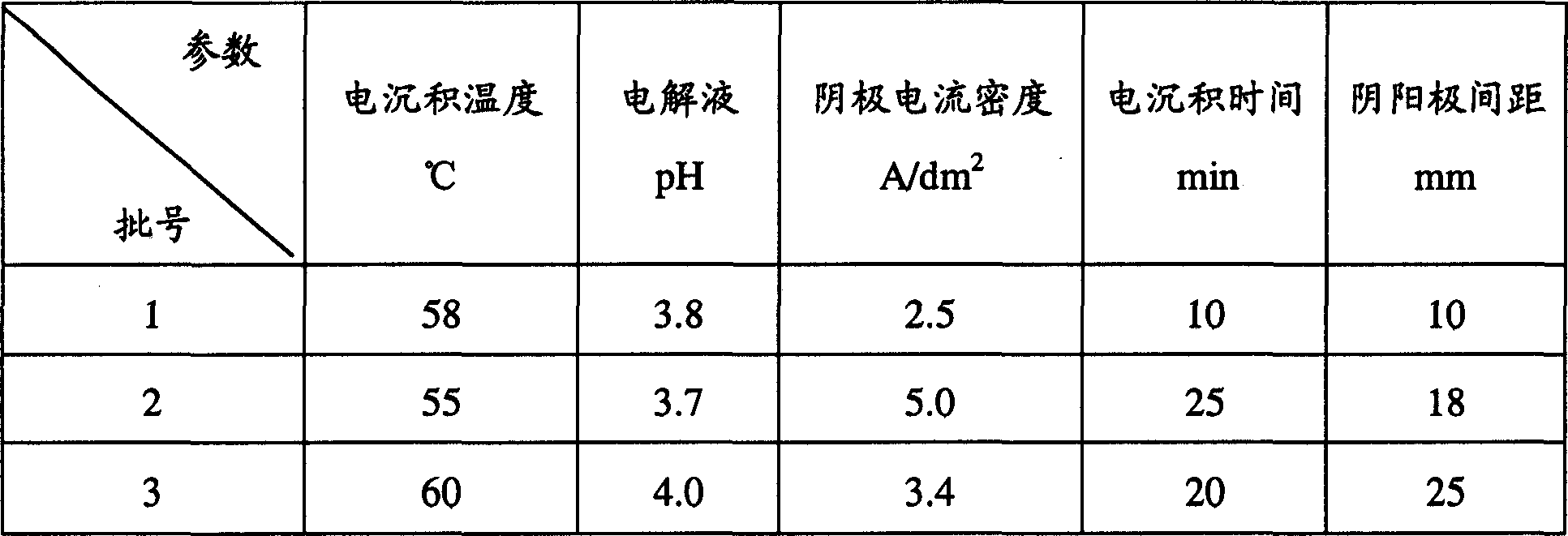
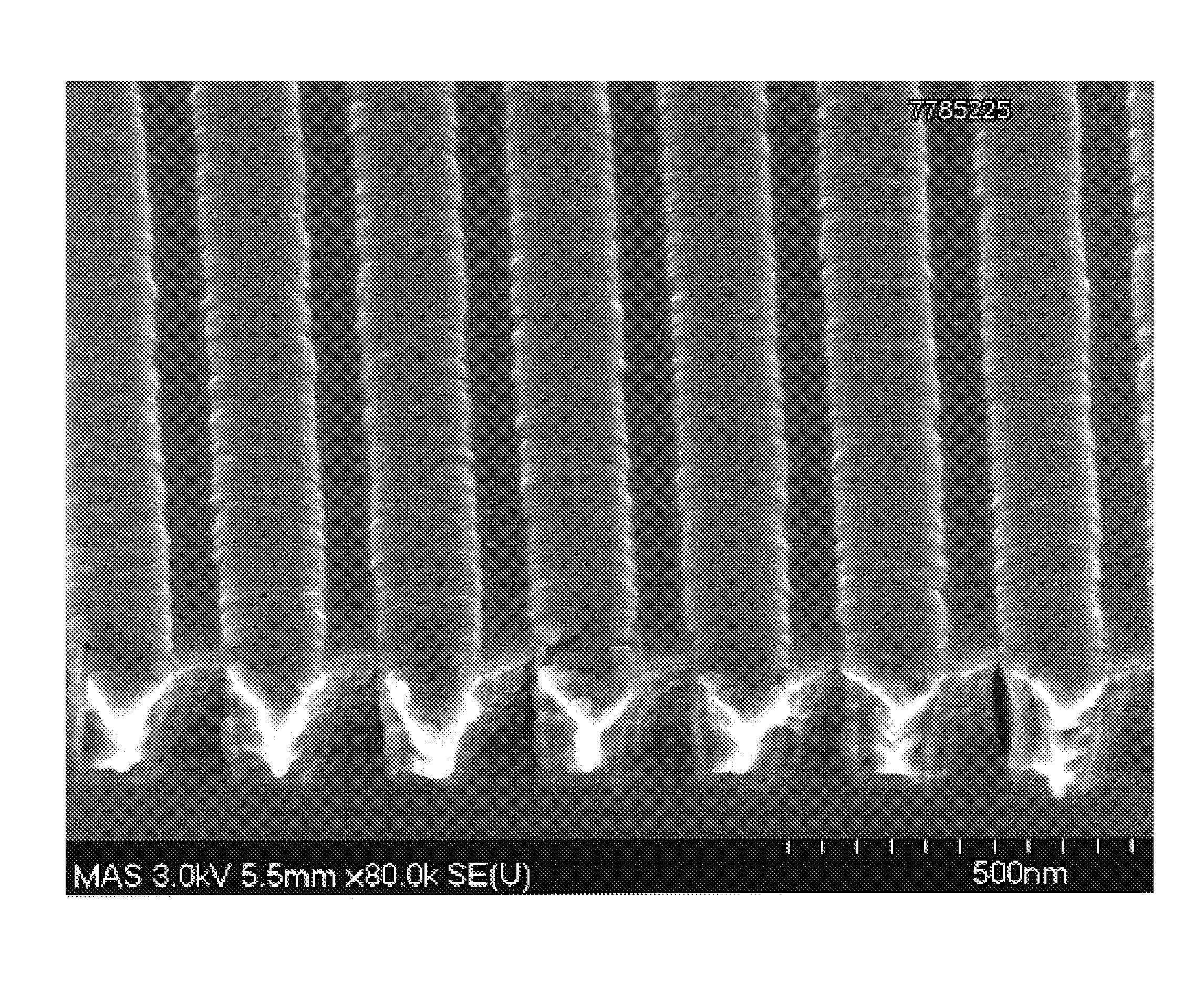
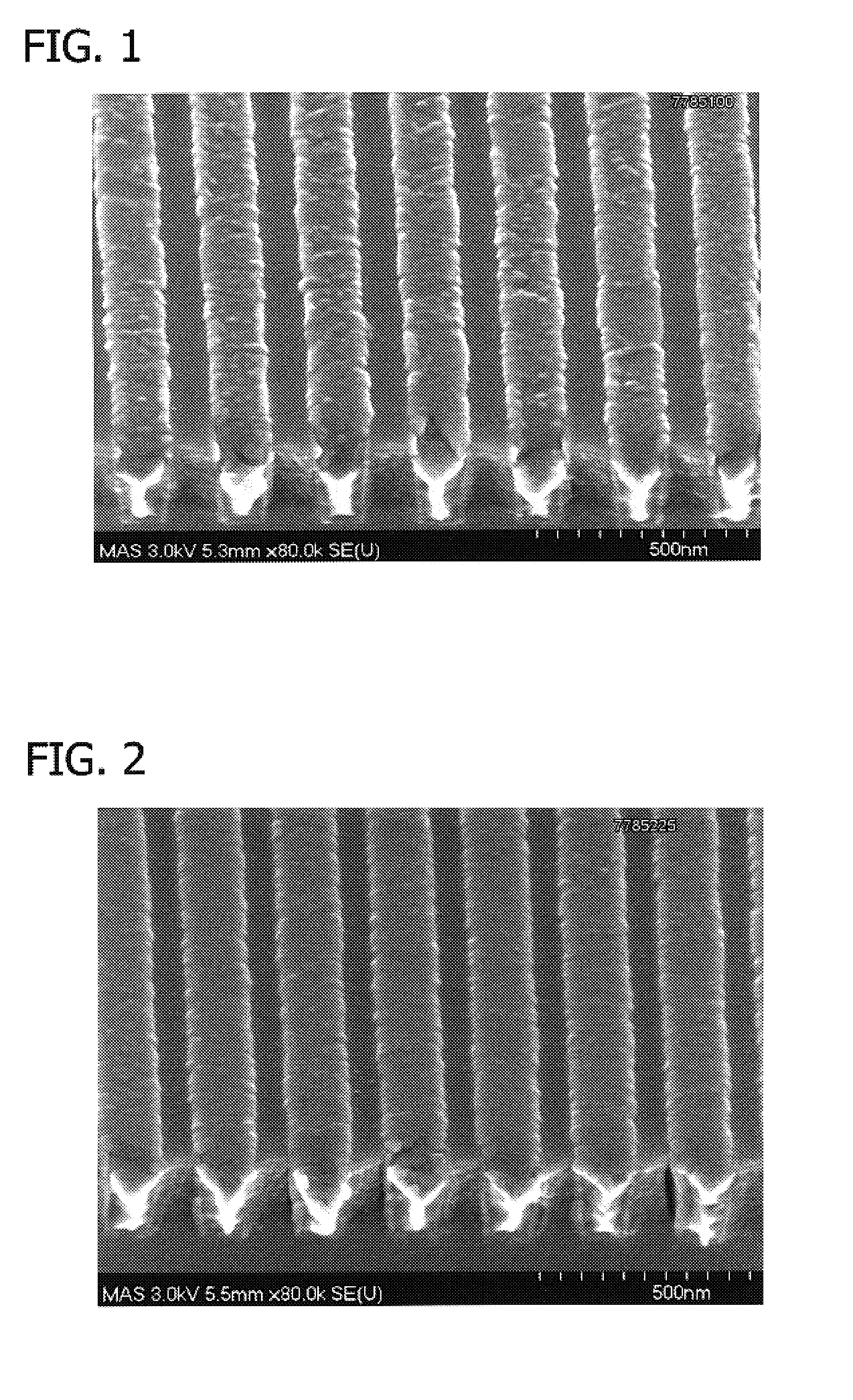
InactiveCN1793433AFlat and bright appearanceDense tissueElectroforming processesVolumetric Mass DensityAlloy
The invention relates to a Invar alloy foil manufacturing method. It belongs to precious alloy field. The Invar alloy is Fe-Ni alloy with 35-37% (wt%) nickel. The manufacturing method is electro deposition. Electrolyte is sulfate system with low metal salt density. Buffer, complexing agent, brightener, auxiliary, and 304 stainless steel, Ir2; the distance of cathode and anode is 10-30mm; the electro deposition time is 5-50min. and it includes the following steps: putting cathode in electroplating solution; electrifying direct current for curtain time; depositing Invar alloy on the cathode; taking it out; cleaning; drying; peeling off the formed Fe-Ni alloy layer to form Invar alloy foil.
Owner:ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY & MATERIALS CO LTD
Cobalt and nickel electroless plating in microelectronic devices
ActiveUS7332193B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnti-corrosive paintsAlloy depositionCobalt
An electroless plating method and composition for depositing Co, Ni, or alloys thereof onto a metal-based substrate in manufacture of microelectronic devices, involving a source of deposition ions selected from the group consisting of Co ions and Ni ions, a reducing agent for reducing the depositions ions to metal onto the substrate, and a hydrazine-based leveling agent.
Owner:MACDERMID ENTHONE INC
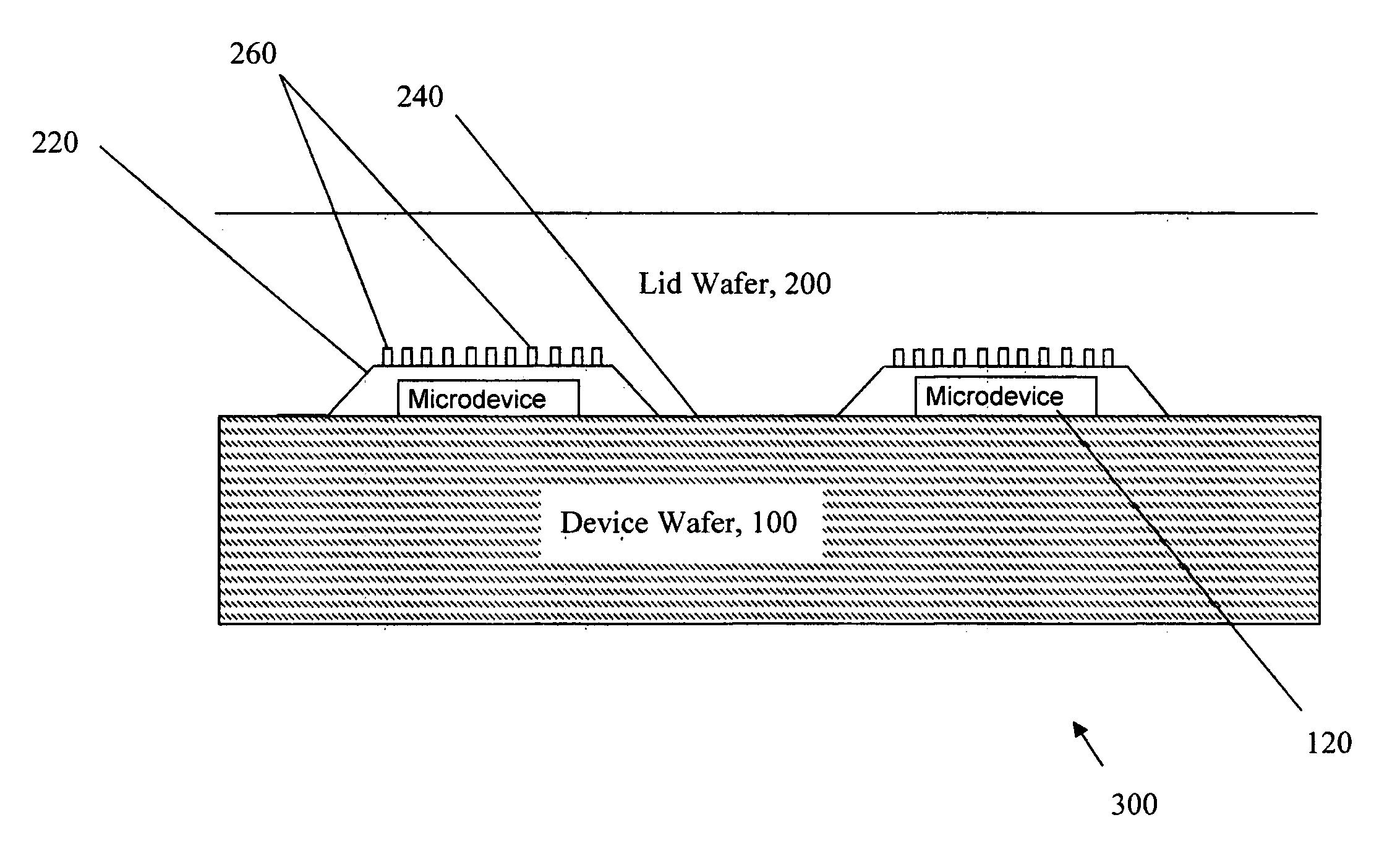
Gettering material for encapsulated microdevices and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20090001537A1Increase Zr compositionReduce Fe compositionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAlloy depositionThermal expansion
A method for providing improved gettering in a vacuum encapsulated microdevice is described. The method includes designing a getter alloy to more closely approximate the coefficient of thermal expansion of a substrate upon which the getter alloy is deposited. Such a getter alloy may have a weight percentage of less than about 8% iron (Fe) and greater than about 50% zirconium, with the balance being vanadium and titanium, which may better match the coefficient of thermal expansion of a silicon substrate. In one exemplary embodiment, the improved getter alloy is deposited on a silicon substrate prepared with a plurality of indentation features, which increase the surface area of the substrate exposed to the vacuum. Such a getter alloy is less likely to delaminate from the indented surface of the substrate material during heat-activated steps, such as activating the getter material and bonding a lid wafer to the device wafer supporting the microdevice.
Owner:INNOVATIVE MICRO TECH
External refining method for smelting ferrovanadium
The invention belongs to the field of metallurgy, and specifically relates to an external refining method for smelting a ferrovanadium alloy. The invention aims at providing an external refining method for smelting ferrovanadium, with regard to problems of a high vanadium content, high power consumption, serious electric furnace body erosion and the like in slag in a last smelting period of an existing ferrovanadium smelting method adopting a multi-period method. The method comprises two-period electric furnace smelting, a primarily-molten alloy after deslagging is cast in an ingot mould filled with a refining material and subjected to a mixing reaction after the smelting is completed, and external refining is carried out. The method is capable of greatly reducing a single-furnace power-on time, reducing furnace lining erosion of an electric smelting furnace, and prolonging an alloy deposition time, thus increase for an alloy yield is benefited, and remarkable social and economic benefits are achieved.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Ni-Co-P chemical plating solution and method thereof
InactiveCN103409736AReduce the temperatureImprove stabilityLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingChemical platingAlloy deposition
The invention relates to material surface chemical plating, and concretely relates to a solution for realizing the rapid plating of Ni-Co-P on the surface of a low carbon steel substrate under a low temperature condition, and a method thereof. Compared with the prior art, the solution and the method have the advantages of substantial chemical plating temperature reduction, solving of a problem that the plating speed of a low-temperature Ni-Co-P chemical plating process is low, and energy consumption reduction. The addition of earth elements improves the alloy deposition speed, increases the compactness of the finally obtained alloy plating layer and allows the alloy plating layer to have a high corrosion resistance.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
Method for preparing micro-nano-porous silver based on eutectic flux in-situ alloy deposition/alloy removing method
The invention relates to a method for preparing micro-nano-porous silver based on an eutectic flux in-situ alloy deposition / alloy removing method, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of nanometer materials. Under an open system, quaternary ammonium salt dried in vacuum at 80 DEG C is mixed with a hydrogen bond donor for reaction by 0.5-1 h to prepare eutectic ion liquid; metal induction salt is added in the eutectic ion liquid for uniform mixing to obtain eutectic ion liquid-metal salt compound electrolyte; a silver sheet serves as a cathode, and an inert anode serves as an anode to perform constant-current deposition in the obtained ion liquid-metal salt compound electrolyte to obtain an Ag base binary alloy plating layer on the surface of the cathode silver sheet; under an original electrolyte system, a three-electrode system is built to perform constant-potential dealloying; and the dealloyed cathode sheet is flushed by anhydrous ethanol and distilled water, and is dried to obtain the silver sheet with a micro-nano-porous structure. The method has such advantages as mild reaction conditions, controllability, low cost, no pollution and simple process.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
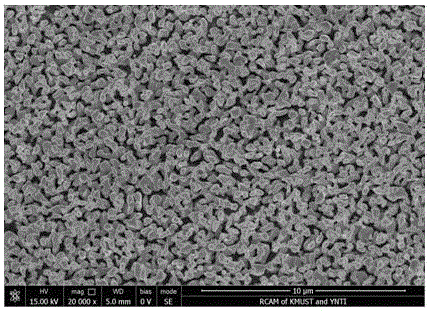
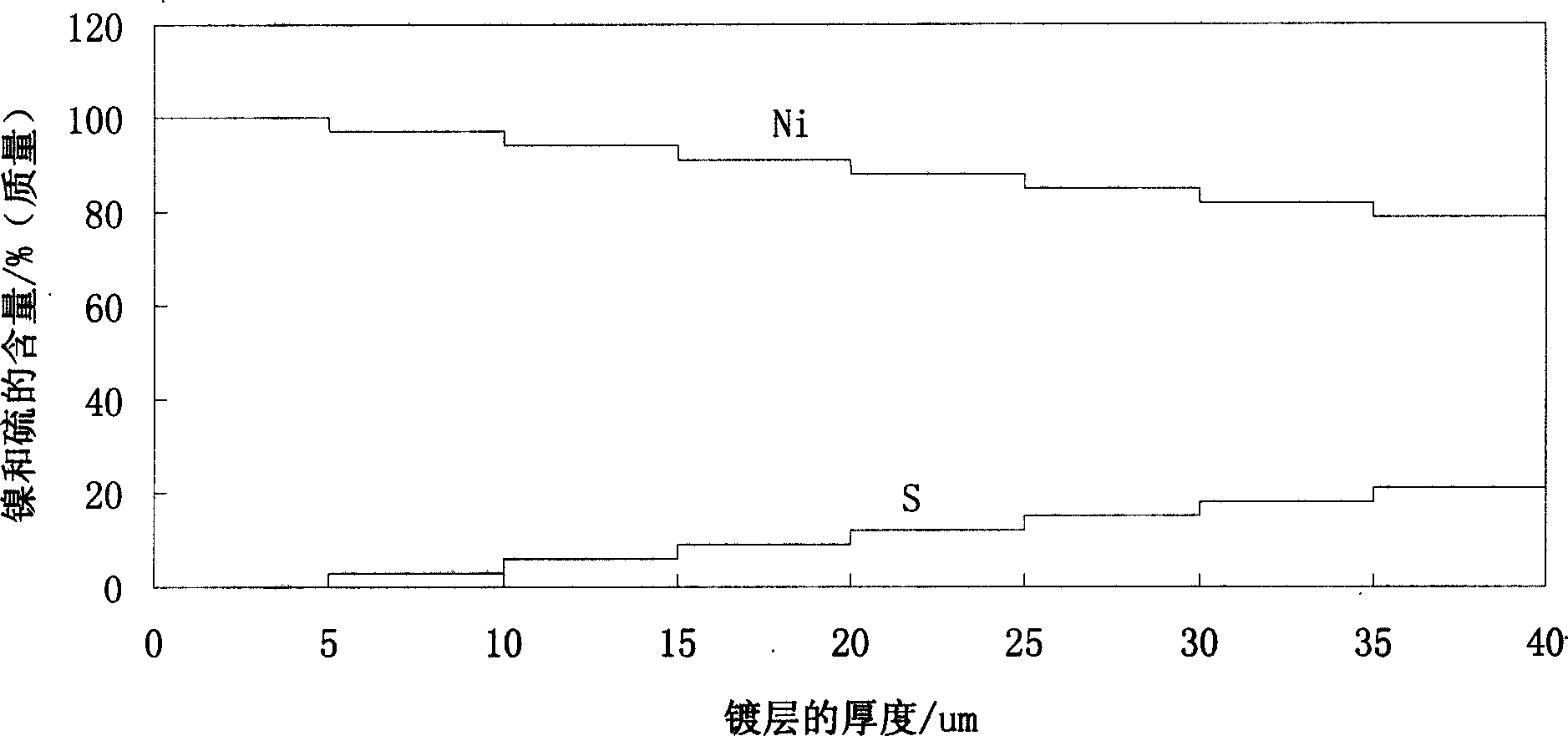
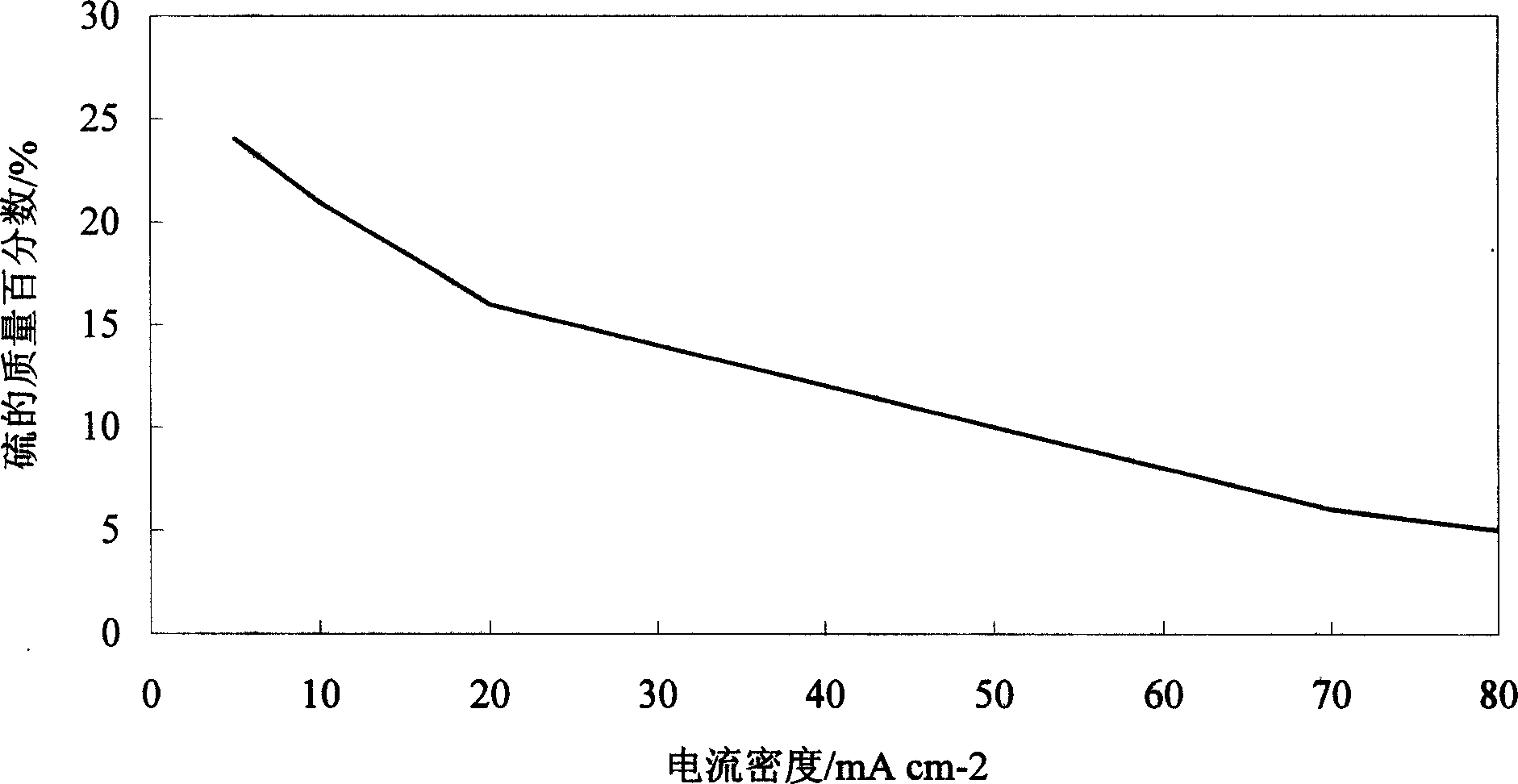
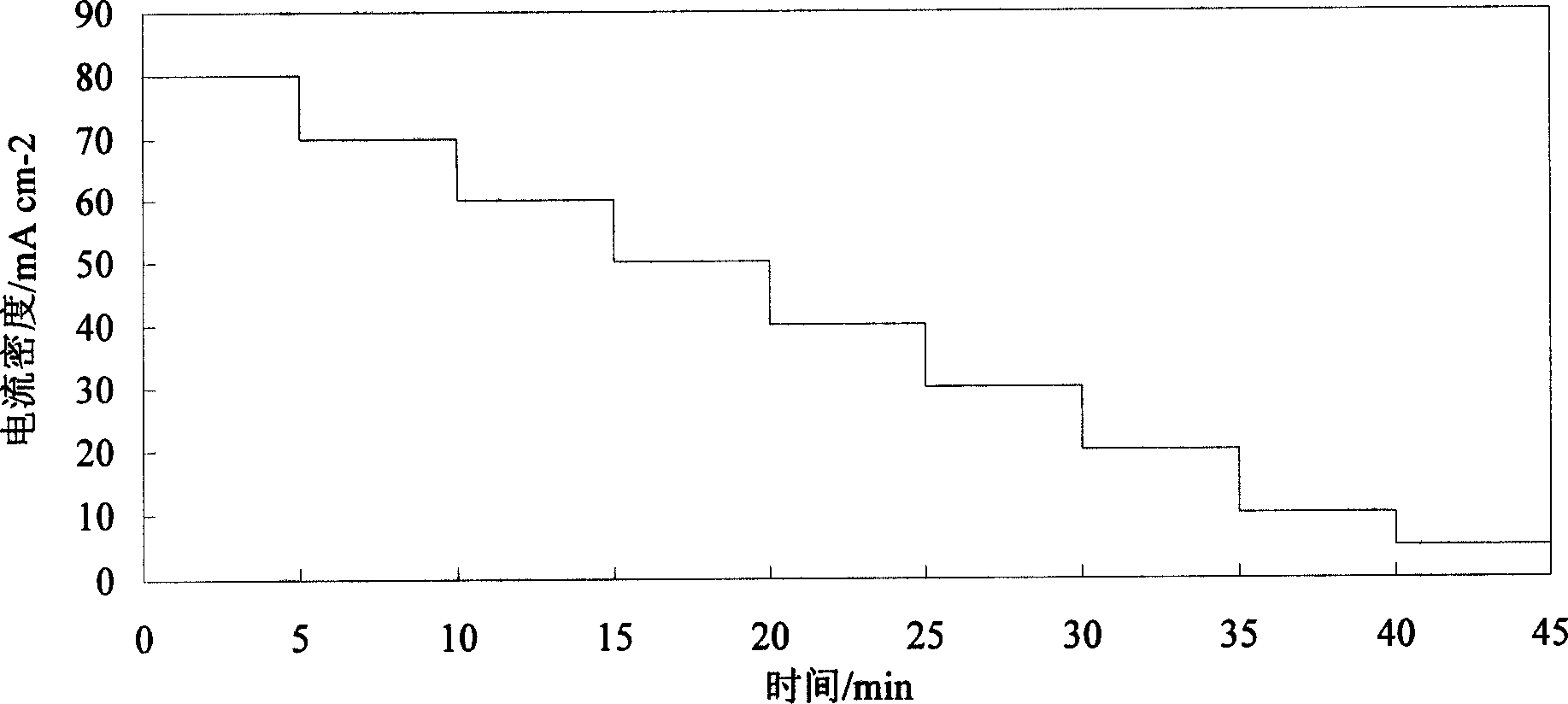
Ni-S active cathode for hydrogen evolution with gradient structure and method for preparing same
InactiveCN1844462AImprove corrosion resistanceExcellent hydrogen evolution activityElectrolytic inorganic material coatingElectrodesHydrogenAlloy deposition
This invention relates to the nickel-sulphur active hydrogen-separating cathode with grads structure and its making method, which is to deposit a thin layer of metal nickel on the base metal surface first, then control the current density change from high to low during deposition by current cascade-transition method in the solution containing nickel iron and sulphur compound, and then obtain nickel-sulphur alloy deposition layer on the ordinal iron cathode surface by electrochemical deposition, wherein the prepared electrochemical deposition layer has grads structure, that is the sulphur atom content increases gradually from base metal to deposition layer surface, but nickel atom content decreases. The advantage in this invention is that the active cathode has well hydrogen-separating active and active deposition layer and base metal have firm combining power, the capability is stable.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Cadmium telluride thin-film solar cell back contact layer production method and vertical coater
ActiveCN102628163AIncrease profitGuaranteed uniformityFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingAlloy depositionAlloy
The invention discloses a cadmium telluride thin-film solar cell back contact layer production method, and the production process is carried out in the vacuum environment. The steps are as follows: a substrate is preheated to 160 DEG C to 220 DEG C; after the substrate is heated to 230 DEG C to 320 DEG C, the magnetron sputtering of antimony telluride is carried out; after the substrate is cooled to 80 DEG C to 120 DEG C, the sputtering of nickel-vanadium alloy is carried out; and the substrate is cooled to less than 70 DEG C and then discharged. The coating of a cadmium telluride thin-film solar cell back contact layer produced by the method is uniform, and the number of pinholes is less. The invention also discloses a vertical coater which adopts the method to produce cadmium telluride thin-film solar cell back contact layers, the vertical coater comprises but is not limited to a preheating chamber, a temperature-keeping antimony telluride deposition chamber, a nickel-vanadium alloy deposition chamber, a temperature-decreasing discharge chamber, a vacuum system and the like which are connected in series through vacuum valves, and the vertical coater can simultaneously coat both sides of the substrate, enlarge the effective region of the coating and increase the production efficiency, and is easy to overhaul.
Owner:CNBM CHENGDU OPTOELECTRONICS MATERIAL
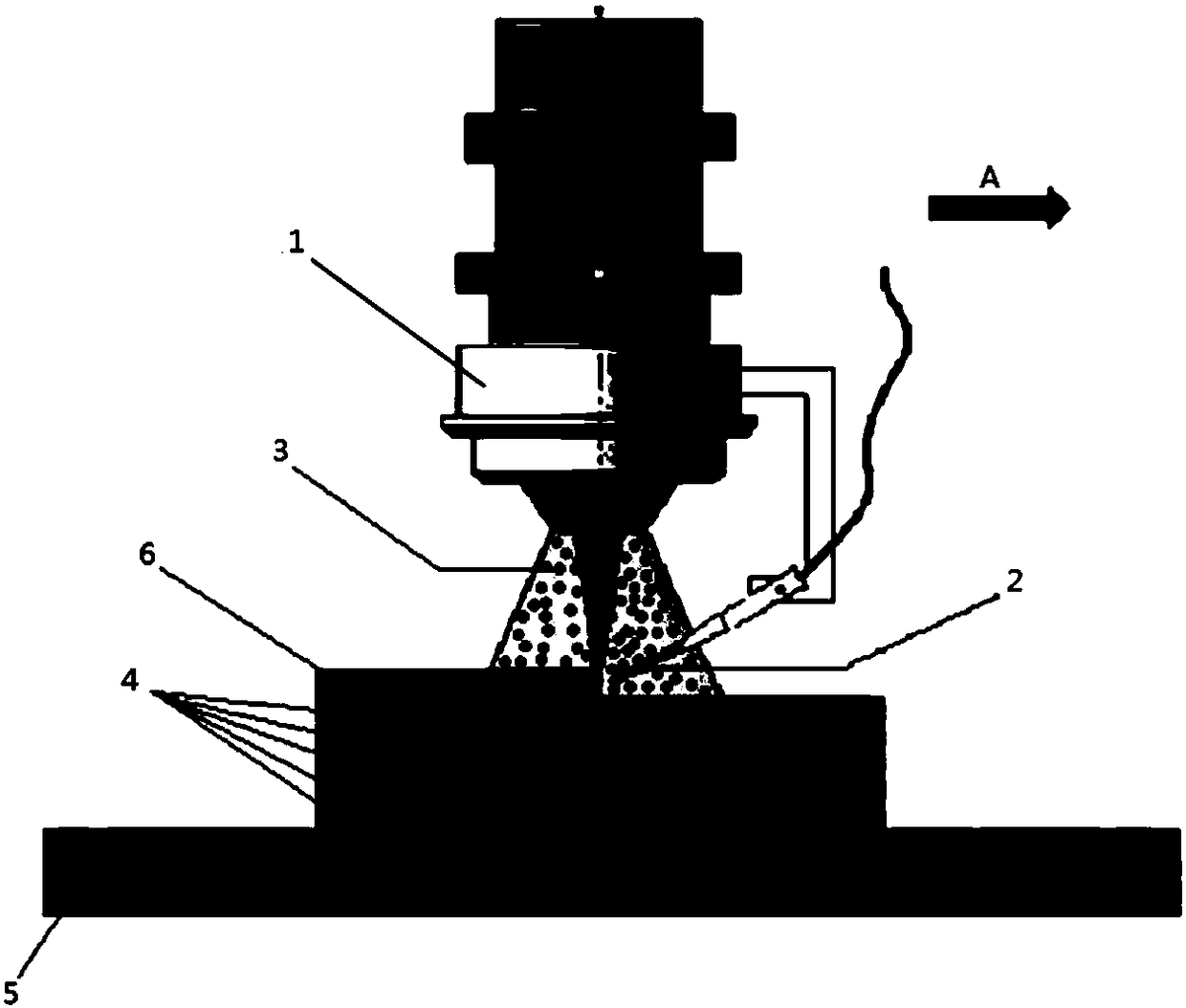
Method for preparing titanium alloy bone implant with surface bioactivity through synchronous wire-powder laser deposition
ActiveCN108452372ASurface bioactivity achievedRealize direct manufacturingAdditive manufacturing apparatusPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAlloy substrateAlloy deposition
The invention discloses a method for preparing a titanium alloy bone implant with surface bioactivity through synchronous wire-powder laser deposition, relates to a preparation method of a titanium alloy bone implant with surface bioactivity, and aims to solve the problems that a bio-coating for preparing a titanium alloy bone implant is liable to drop off and individual customization cannot be achieved. The method comprises the following steps: I, paraxially feeding a titanium alloy wire into a laser melting pool region by using a wire feeding machine, gradually melting the titanium alloy wire along with movement of the melting pool, re-solidifying the titanium alloy wire into a titanium alloy deposition layer, preparing another titanium alloy deposition layer on the first titanium alloydeposition layer, repeating the operation, and preparing titanium alloy deposition layers layer by layer so as to obtain a titanium alloy substrate; II, continuously paraxially feeding the titanium alloy wire, at the same time coaxially feeding a hydroxyapatite powder, performing overlapped laser deposition on the surface of the titanium alloy substrate so as to obtain a hydroxyapatite-titanium composite material layer, so as to obtain the titanium alloy bone implant with surface bioactivity. The method is adopted to prepare the titanium alloy bone implant with surface bioactivity.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH +1
Method for electroless nickel-phosphorous alloy deposition onto flexible substrates
ActiveUS9089062B2Printed circuit aspectsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingElectroless nickelAlloy deposition
The present invention relates to a method for electroless deposition of a bendable nickel-phosphorous alloy layer onto flexible substrates such as flexible printed circuit boards and the like. The nickel-phosphorous alloy layer is deposited from an aqueous plating bath comprising nickel ions, hypophosphite ions, at least one complexing agent and a grain refining additive selected from the group consisting of formaldehyde and formaldehyde precursors. The nickel-phosphorous alloy layers obtained have a columnar microstructure oriented perpendicular to the flexible substrate and are sufficiently bendable.
Owner:ATOTECH DEUT GMBH
Process of closing an opening in a component
A process for closing an opening in a surface of a component, and components formed thereby. The process entails forming a channel in the component surface so that the channel at least partially surrounds an opening at the component surface. An alloy is then deposited in the channel to form a crack-free deposit in the channel. A step is then machined that intersects the opening and is at least partially formed in the deposit. The step defines a recess that is at least partially surrounded by a peripheral portion of the deposit and has a surface recessed into the component surface. A cap is placed in the recess and welded to the peripheral portion of the deposit to define a weld joint that completely closes the opening. The surface of the weld joint is then machined to form a machined surface that is substantially flush with the component surface.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Submicron contact fill using a CVD TiN barrier and high temperature PVD aluminum alloy deposition
ActiveUS20060076680A1Increased electro-migration resistanceImprove electrical characteristicsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAlloy depositionChemical vapor deposition
A submicron contact opening fill using a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) TiN liner / barrier and a high temperature, e.g., greater than about 385° C., physical vapor deposition (PVD) aluminum alloy layer that substantially fills the submicron contact.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Chemical nickel-phosphorus-plated alloy solution and method for applying the same to printed wiring board to deposit nickel-phosphorus alloy
InactiveCN105828533AStabilized phosphorus contentStable crystalline formLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingConductive pattern reinforcementBisulfideThiazole
The invention relates to the technical field of printed wiring board chemical nickel-phosphorus-plated alloys, particularly to a chemical nickel-phosphorus-plated alloy solution and a method for applying the same to a printed wiring board to deposit a nickel-phosphorus alloy. The chemical nickel-phosphorus-plated alloy solution includes organic disulphides and polysulfides and inorganic polysulfides, and specifically contains but is not limited alkyl disulphides and derivatives thereof, thiuram and derivatives thereof, thiazole and derivatives thereof, and thiourea and derivatives thereof. The content of a sulfide accelerator in a chemical nickel plating solution is 0.05 to 50 ppm, can satisfy an actual production nickel depositing rate requirement, can prevent the nickel-phosphorus alloy deposited on a copper-based circuit from diffusion plating or skip plating, and can still keep nickel-phosphorus alloy deposition activity after aging of a bath solution.
Owner:GUANGDONG LEAR ELECTROCHEM LTD
Method for electroless nickel-phosphorous alloy deposition onto flexible substrates
ActiveUS20150009638A1Printed circuit aspectsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingElectroless nickelAlloy deposition
The present invention relates to a method for electroless deposition of a bendable nickel-phosphorous alloy layer onto flexible substrates such as flexible printed circuit boards and the like. The nickel-phosphorous alloy layer is deposited from an aqueous plating bath comprising nickel ions, hypophosphite ions, at least one complexing agent and a grain refining additive selected from the group consisting of formaldehyde and formaldehyde precursors. The nickel-phosphorous alloy layers obtained have a columnar microstructure oriented perpendicular to the flexible substrate and are sufficiently bendable.
Owner:ATOTECH DEUT GMBH
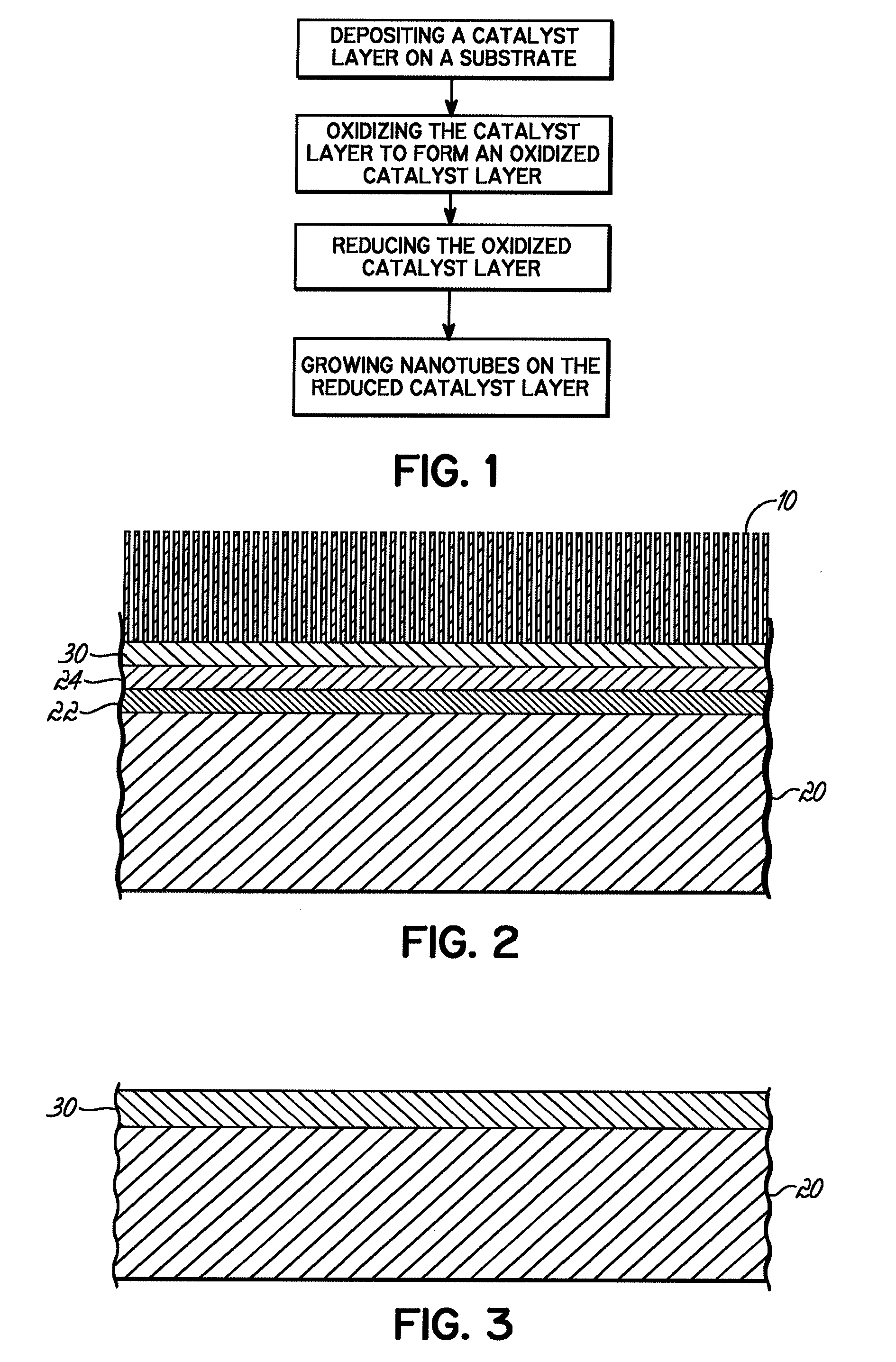
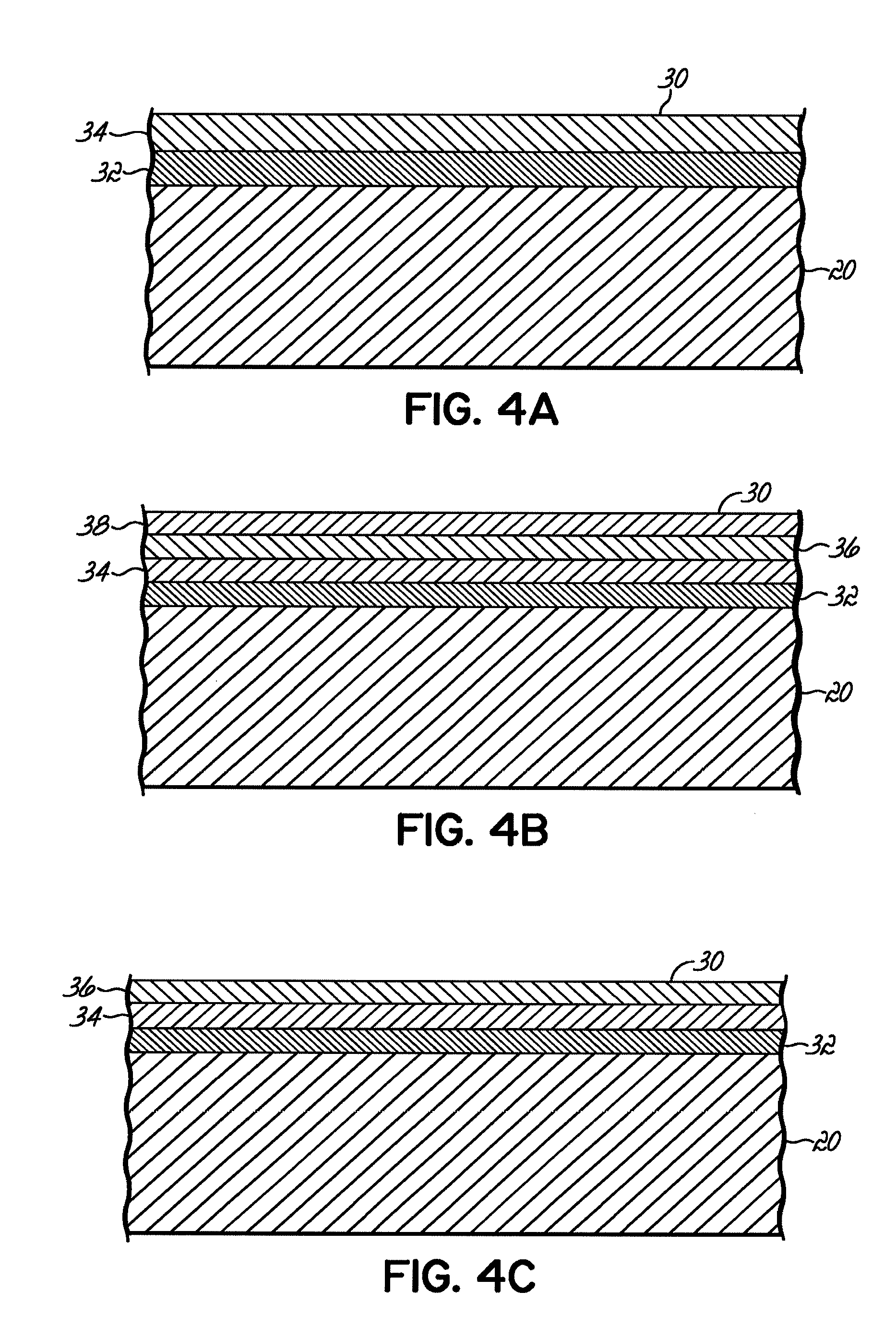
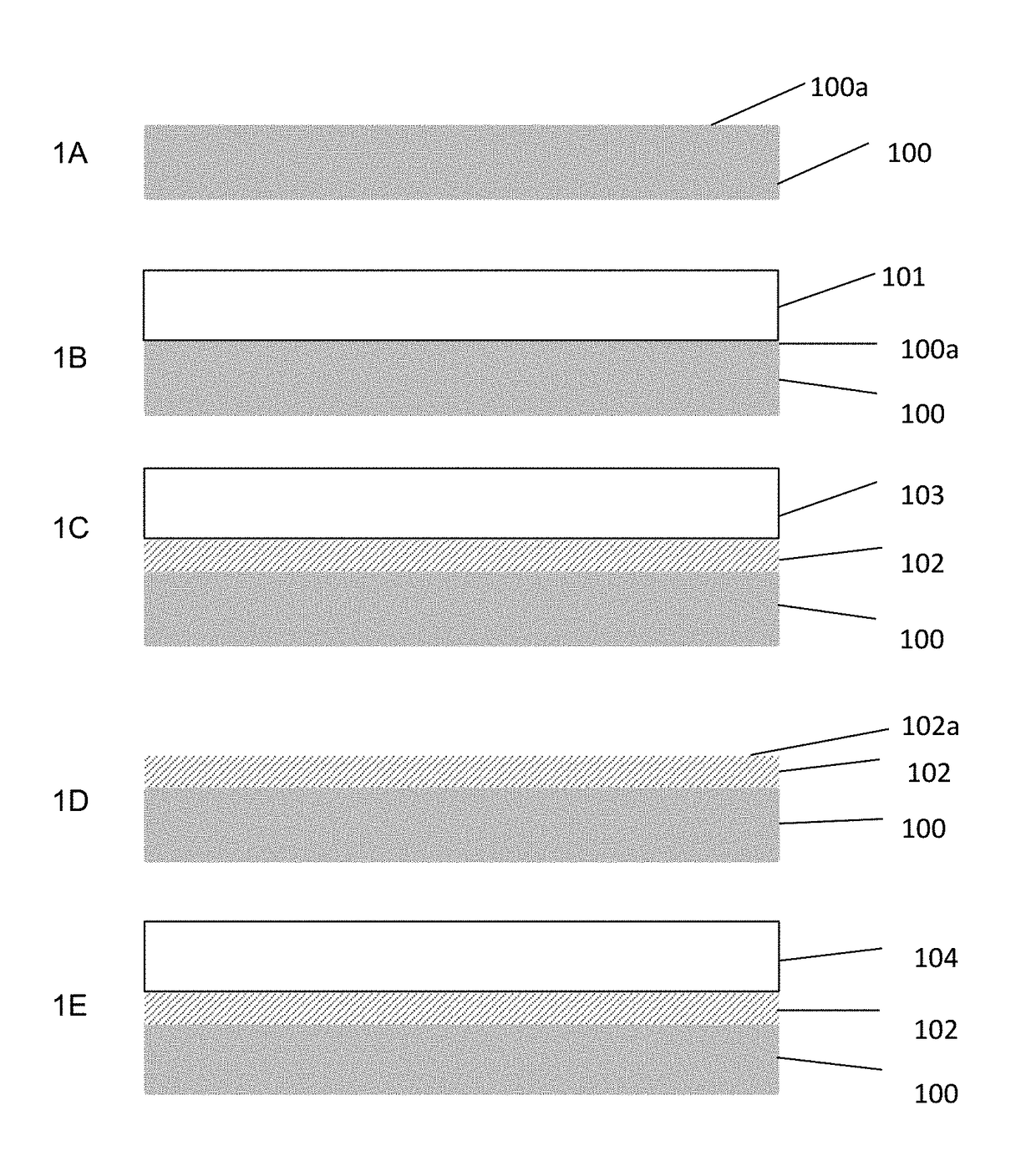
Composite catalyst and method for manufacturing carbon nanostructured materials
A method of forming a carbon nanotube array substrate is disclosed. One embodiment comprises depositing a composite catalyst layer on the substrate, oxidizing the composite catalyst layer, reducing the oxidized composite catalyst layer, and growing the array on the composite catalyst layer. The composite catalyst layer may comprise a group VIII element and a non-catalytic element deposited onto the substrate from an alloy. In another embodiment, the composite catalyst layer comprises alternating layers of iron and a lanthanide, preferably gadolinium or lanthanum. The composite catalyst layer may be reused to grow multiple carbon nanotube arrays without additional processing of the substrate. The method may comprise bulk synthesis by forming carbon nanotubes on a plurality of particulate substrates having a composite catalyst layer comprising the group VIII element and the non-catalytic element. In another embodiment, the composite catalyst layer is deposited on both sides of the substrate.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
Process for indium or indium alloy deposition and article
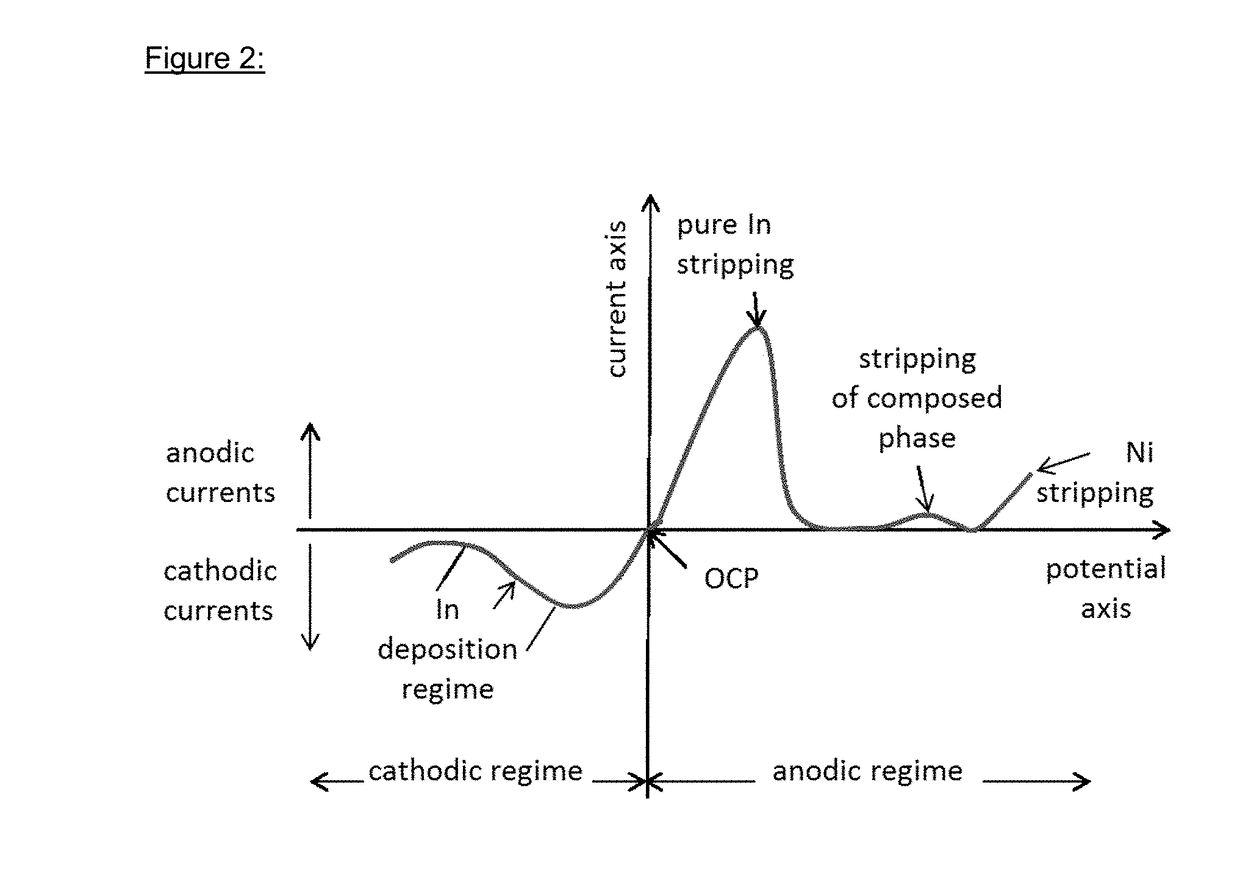
ActiveUS20180298511A1Liquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingSuperimposed coating processIndiumMetal alloy
The present invention deals with a process for deposition of indium or indium alloys and an article obtained by the process, wherein the process includes the stepsi. providing a substrate having at least one metal or metal alloy surface;ii. depositing a first indium or indium alloy layer on at least one portion of said surface whereby a composed phase layer is formed of a part of the metal or metal alloy surface and a part of the first indium or indium alloy layer;iii. removing partially or wholly the part of the first indium or indium alloy layer which has not been formed into the composed phase layer;iv. depositing a second indium or indium alloy layer on the at least one portion of the surface obtained in step iii.v.
Owner:ATOTECH DEUT GMBH
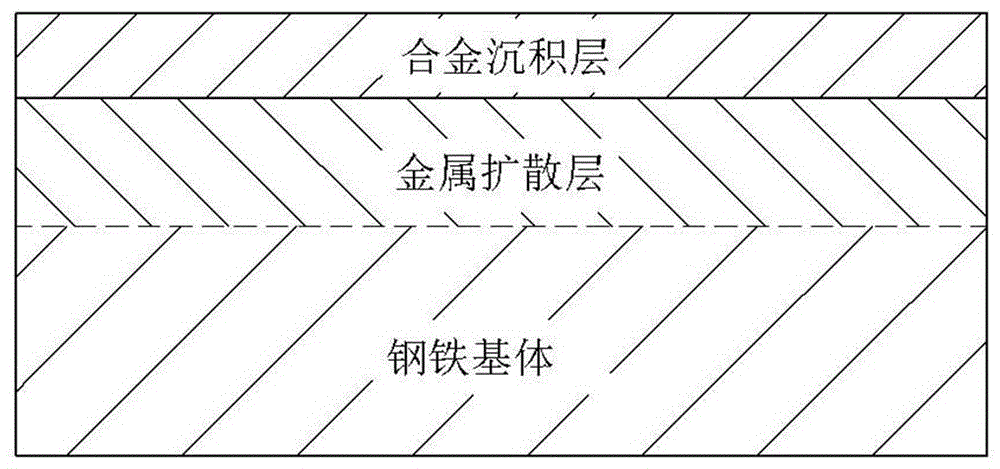
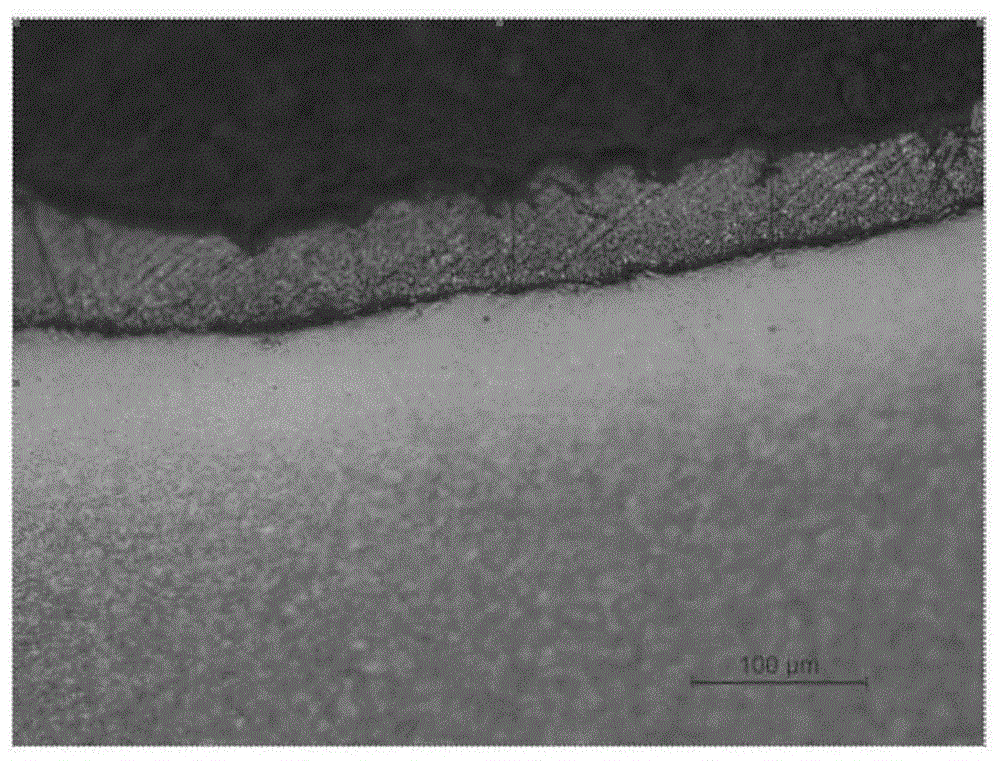
Steel surface modification structure formed through zinc-nickel infiltrated layer and preparation method for steel surface modification structure
ActiveCN106399925ASolid state diffusion coatingSuperimposed coating processAlloy depositionQuenching
The invention discloses a steel surface modification structure which is formed through a zinc-nickel infiltrated layer and has high corrosion resistance. The steel surface modification structure is a corrosion-resistant alloy structure formed on the surface of a steel substrate. The steel surface modification structure with the high corrosion resistance comprises an alloy deposition layer and a metal diffusion layer sequentially from the surface to the inside. The steel substrate is medium carbon steel or medium carbon low alloy steel. The alloy deposition layer is a zinc-iron compound. The diffusion layer comprises ferrite, pearlite and a quenching and tempering structure. The carbon content of the steel substrate is between 0.30% and 0.65%. The micro vickers hardness of the steel surface modification structure with the high corrosion resistance is between 240 and 500. The steel surface modification material provided by the invention has a very good corrosion resistant effect, and loss caused by steel corrosion can be reduced. Meanwhile, the invention further provides a preparation method for the steel surface modification structure formed through the zinc-nickel infiltrated layer.
Owner:CHONGQING DAYOU SURFACE TECH
A metal mask for vapor plating and a production method thereof
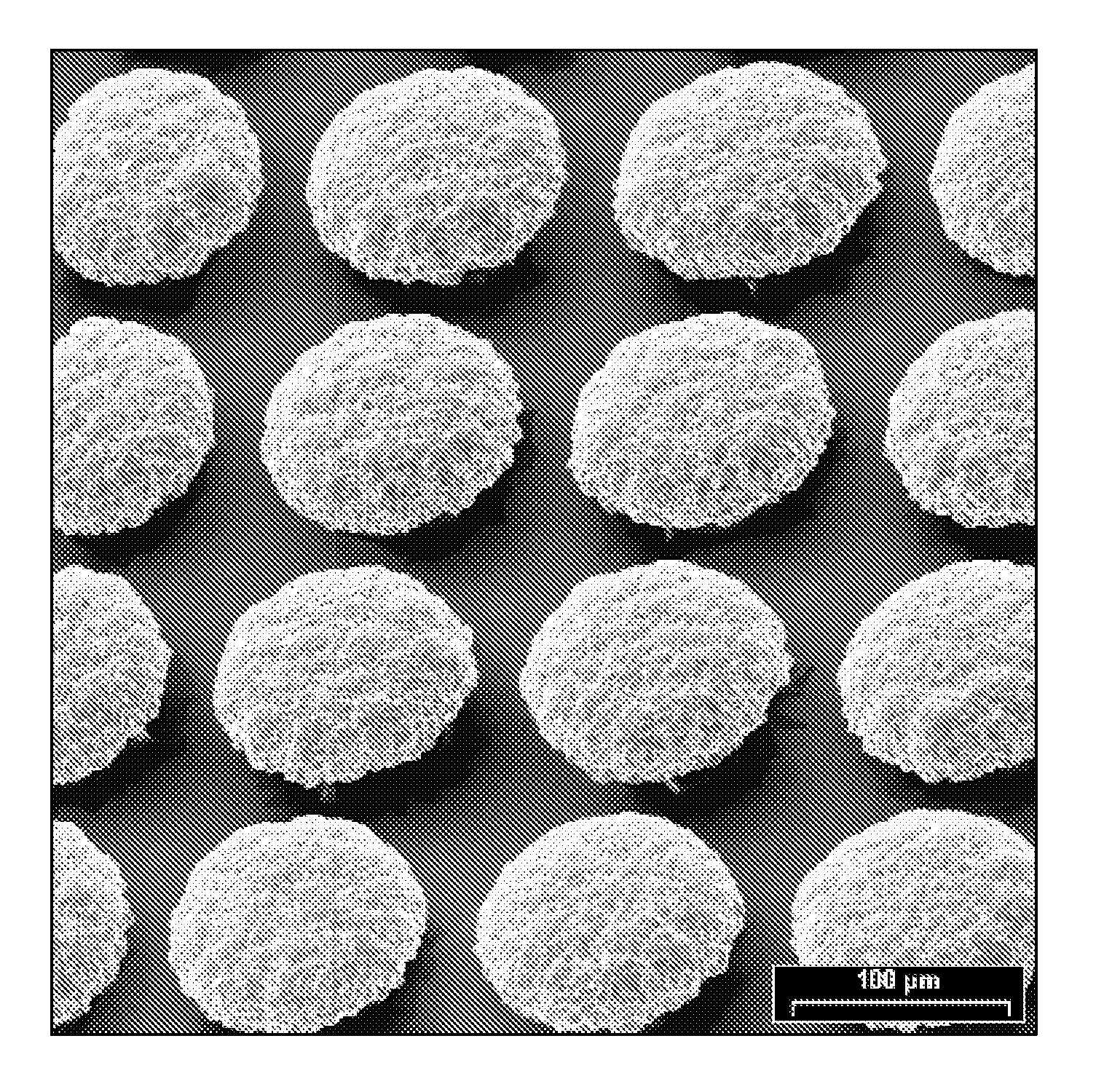
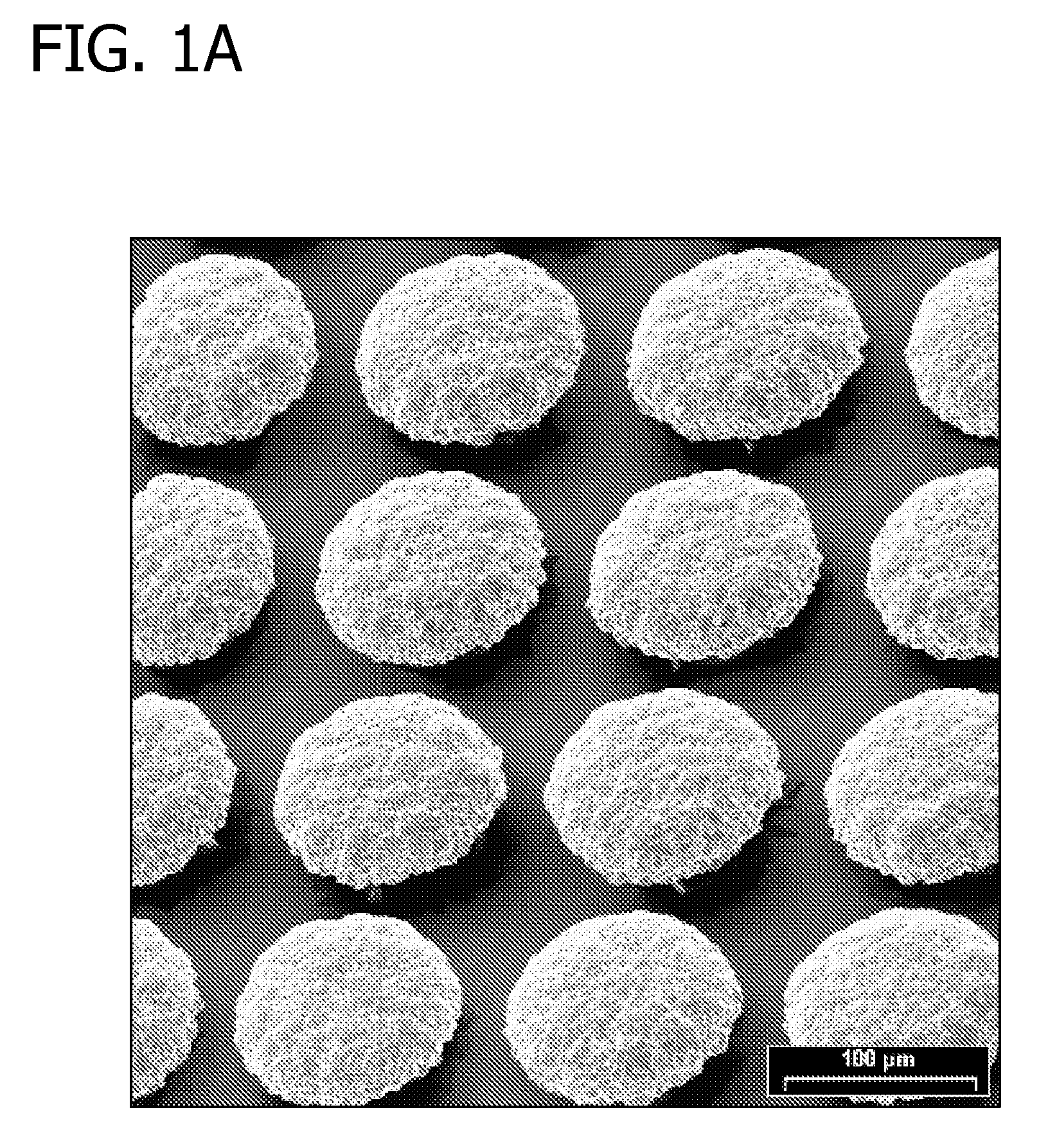
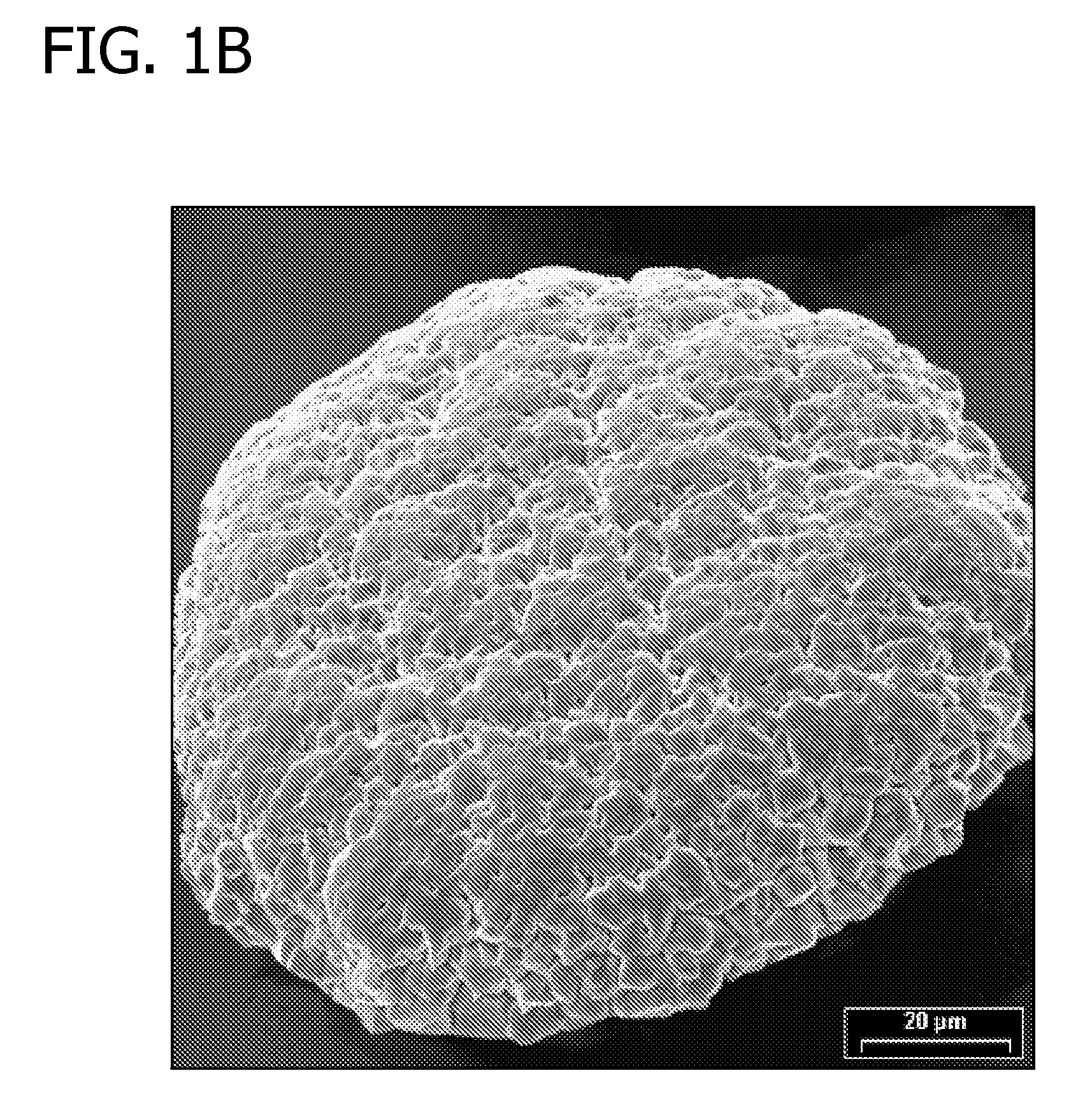
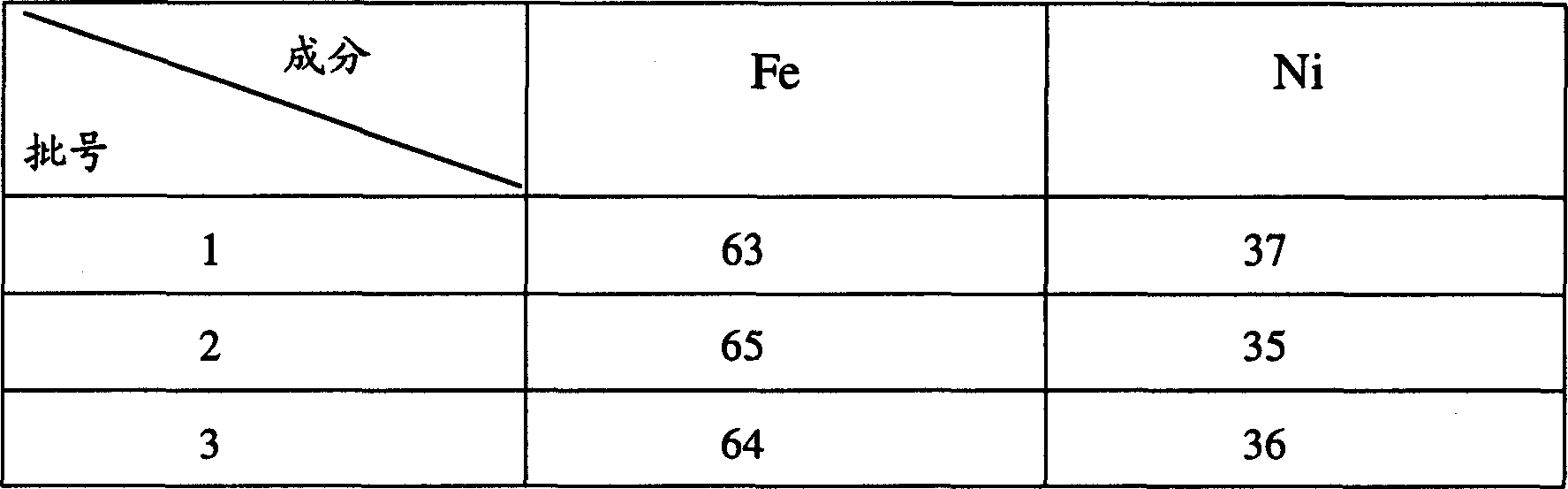
InactiveCN103205714AHigh precisionIncrease brightnessVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingInvar alloyAlloy deposition
The present invention relates to the technical filed of electroformed alloy deposition, and discloses a metal mask for vapor plating. Materials for the metal mask for vapor plating include iron and nickel, wherein the iron content is 63%-65%. The metal mask for vapor plating has good surface brightness, and a coating surface is good in quality; and compared with an etched invar alloy, the metal mask for vapor plating is low in the cost, simple in the process and energy-saving, and has a high opening precision, and openings with good quality. Meanwhile, the present invention also provides a production method for the metal mask for vapor plating.
Owner:KUN SHAN POWER STENCIL
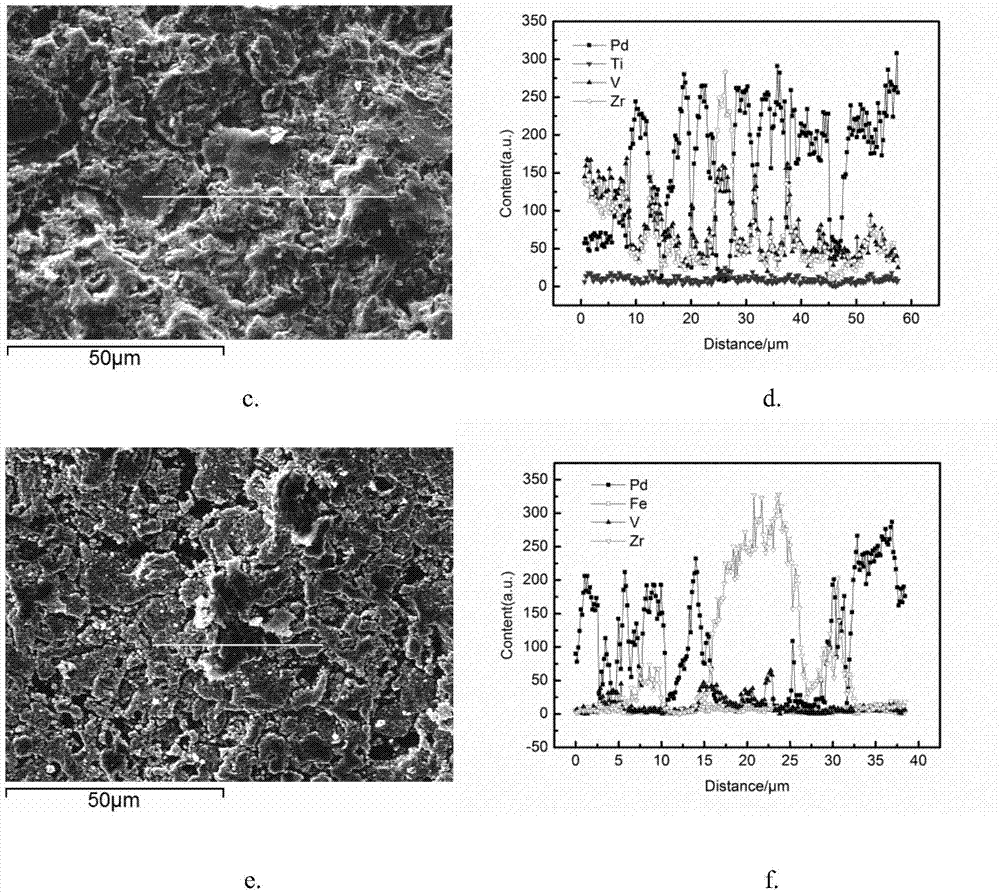
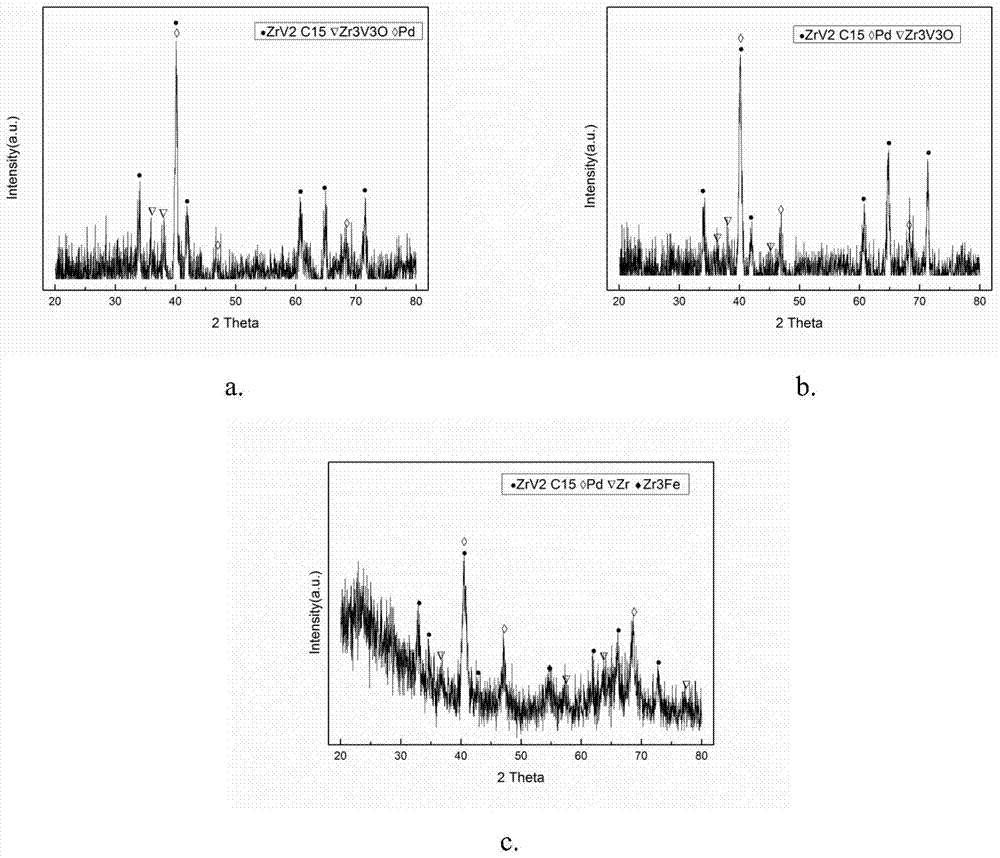
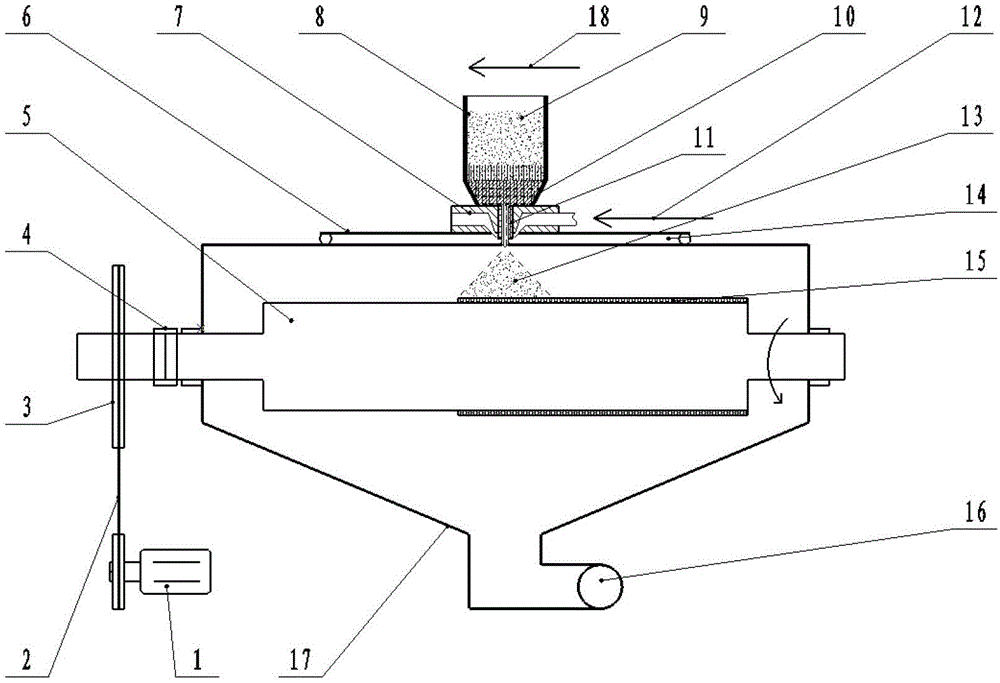
Method for Zr-based hydrogen storage alloy deposition of Pd film and plating solution for chemical plating
InactiveCN103668133ASolve the problem of pollution instabilityExtend your lifeLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingChemical platingAlloy deposition
The invention discloses a method for Zr-based hydrogen storage alloy deposition of a Pd film and a plating solution for chemical plating. The plating solution for chemical plating is obtained by mixing NH3.H2O, NH4Cl, palladium salt Pd(NH3)4Cl2, Na2EDTA and N2H4.H2O and then adding deionized water; through surface pretreatment, the chemical plating is performed on Zr-based alloy particles, so that the service life of the plating solution can be prolonged, the stability of the plating solution can be improved, the deposition speed is high, the cost is low, the obtained palladium film has no impurities, and a prepared plated layer has high purity and obtains good effects.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Technology for repairing roll by high-temperature molten-steel spray deposition based on thermit reaction
The invention discloses a technology for repairing a roll by high-temperature molten-steel spray deposition based on thermit reaction. The technology is characterized in that the thermit reaction and the spray deposition technology are combined, alloy liquid produced by the thermit reaction is directly deposited on the surface of the roll to be repaired by adopting a spray-deposition process, the initial deposition layer is remolten on the surface of the roll by adjusting the gas liquid ratio and the deposition height, so that a high-alloy deposition layer metallurgically bonded with the roll is formed. The roll repaired by utilizing the technology has the advantages that the wear resistance of the roll is improved, the service life of the roll is prolonged and the production cost of the steel rolling industry is greatly reduced.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Chemical nickel-plating method of metal surface
InactiveCN102002690AAvoid cavitationLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingAlloy depositionAlloy
The invention relates to a treatment technology of a metal surface, in particular to a chemical nickel-plating method of a metal surface, comprising three steps of: pretreatment of a metal work piece, pretreatment of chemical nickel-plating solution, and chemical nickel-plating. The method ensures that the thickness of the plating on the surface of the metal work piece, especially the metal with a deep hole / groove can amount to more than 130 microns; meanwhile, the method can prevent cavitation on the surface of the metal work piece due to the deposition of the nickel-phosphorus alloy on the surface of complex metal, and has the advantages of even plating, smooth surface, and no burr and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING YUANDA CATALYST MFG
Material for high-mechanical-strength parts
InactiveCN105779999AWorks well in combinationImprove impact resistanceElectrolytic coatingsVacuum evaporation coatingGas phaseAlloy deposition
The invention discloses a material for high-mechanical-strength parts. A titanium alloy steel plate and an aluminum alloy coating are matched and experimented again, a large number of experiments prove that by means of matching, the mechanical strength, the anti-fatigue strength and the shock resistance of the prepared metal material can reach the optimal state, the using performance of the metal material is improved greatly, and texture demands for manufacturing the parts of automobiles, the aerospace parts and the like are met. By arranging a curved groove with the V-shaped cross section, an aluminum alloy electro-deposition coating and the titanium alloy steel plate can be combined into one more firmly, and the shock resistance and the anti-fatigue strength can be improved more superiorly. In addition, by sequentially arranging the aluminum alloy electro-deposition coating and an aluminum alloy PVD gas phase physical deposition coating, the effect of coating combination can be better; and finally pyrolysis is set, an oxidation film can be formed on the surface of the aluminum alloy deposition coating better, and the comprehensive performance of the metal material is enhanced.
Owner:中原工学院信息商务学院
Machining method for electromagnetic shielding woven fabric with core-shell alloy structure
ActiveCN104746331AExcellent electromagnetic wave shielding performanceImprove shielding effectVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingPlasma technologyPlasma deposition
The invention provides a machining method for an electromagnetic shielding woven fabric with a core-shell alloy structure and relates to the technical fields of pre-treating cotton plain weave fabrics by using a plasma technology, carrying out double-metal core-shell alloy deposition on the surface of the fabric by adopting a plasma deposition technology, and preventing an alloy from oxidization by copper oxide and cuprous oxide and the like. According to the machining method, copper and the copper oxide react with oxygen at high temperature, and the binding strength of a metal layer and the fabric is improved by depositing cuprous oxide particles on the surface of the cotton fabric; under certain temperature, a silver-copper core-shell alloy structure is formed in helium gas by using a copper target and a silver target so that the shielding performance of the fabric is improved; and the cuprous oxide particles are formed on the surface of the alloy so that the alloy layer is prevented from being oxidized. By virtue of the machining method, the disadvantages that a conventional electromagnetic shielding frequency spectrum is relatively narrow and the shielding efficiency is low are overcome and the electromagnetic shielding performance of the cotton plain weave fabrics is improved. The electromagnetic shielding cotton fabric prepared by the machining method can be widely applied to the fields of anti-radiation clothes, high-electromagnetic-field protection and the like.
Owner:YIXING ZHONGDA TEXTILE
Method for preparing metal glass coating by utilizing electrical sparkle deposition process
ActiveCN105297010AAvoid WeldingHigh content of amorphous phaseMetallic material coating processesCapacitanceAlloy
The invention relates to a method for preparing a metal glass coating by utilizing an electrical sparkle deposition process and belongs to the technical field of metal glass coating preparation. A metal A serves as an anode, an electric conductor where a metal A glass coating is pre-deposited serves as a cathode; in the preparation process, when the voltage is 50-60 V, the control capacitance is 40-200 [mu] F, the discharge frequency is 1000-2000 Hz, and the cooling velocity of an anode nickel base alloy deposited on the cathode is controlled to be 105-106 K / s; when the voltage is 61-99 V, the control capacitance is 20-39.9 [mu] F, the discharge frequency is 1000-2000 Hz, and the cooling velocity of a cathode nickel base alloy deposited on the cathode is controlled to be 105-106 K / s; when the voltage is 100-150 V, the control capacitance is 5-15 [mu] F, the discharge frequency is 1000-2000 Hz, and the cooling velocity of an anode nickel base alloy deposited on the cathode is controlled to be 105-106 K / s.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
GH742y alloy turbine disk blank preparation method
The invention discloses a GH742y alloy turbine disk blank preparation method, and belongs to the field of advanced engine material preparation, the preparation method combines the technical advantages of high purity, fine grain tissue and no macrosegregation ingot billet of high temperature alloy vacuum induction melting and spray forming rapid solidification process, and a final size turbine disk blank piece is obtained by subsequent hot isostatic pressing and forging and machining, so that a produced GH742y alloy deposition billet has the characteristics of high strength, good plasticity and easily forging processing and the like; the thermal processing difficult problem caused by macrosegregation of GH742y alloy which is conventionally hard to deform is solved, the comprehensive properties of the alloy is further enhanced, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Copper precursors for thin film deposition
Non-fluorinated copper precursors and methods for making and using same are described herein. In certain embodiments, the copper precursors described herein may be used as precursors to deposit copper films and alloys thereof on a substrate through, for example, atomic layer deposition or chemical vapor deposition conditions.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
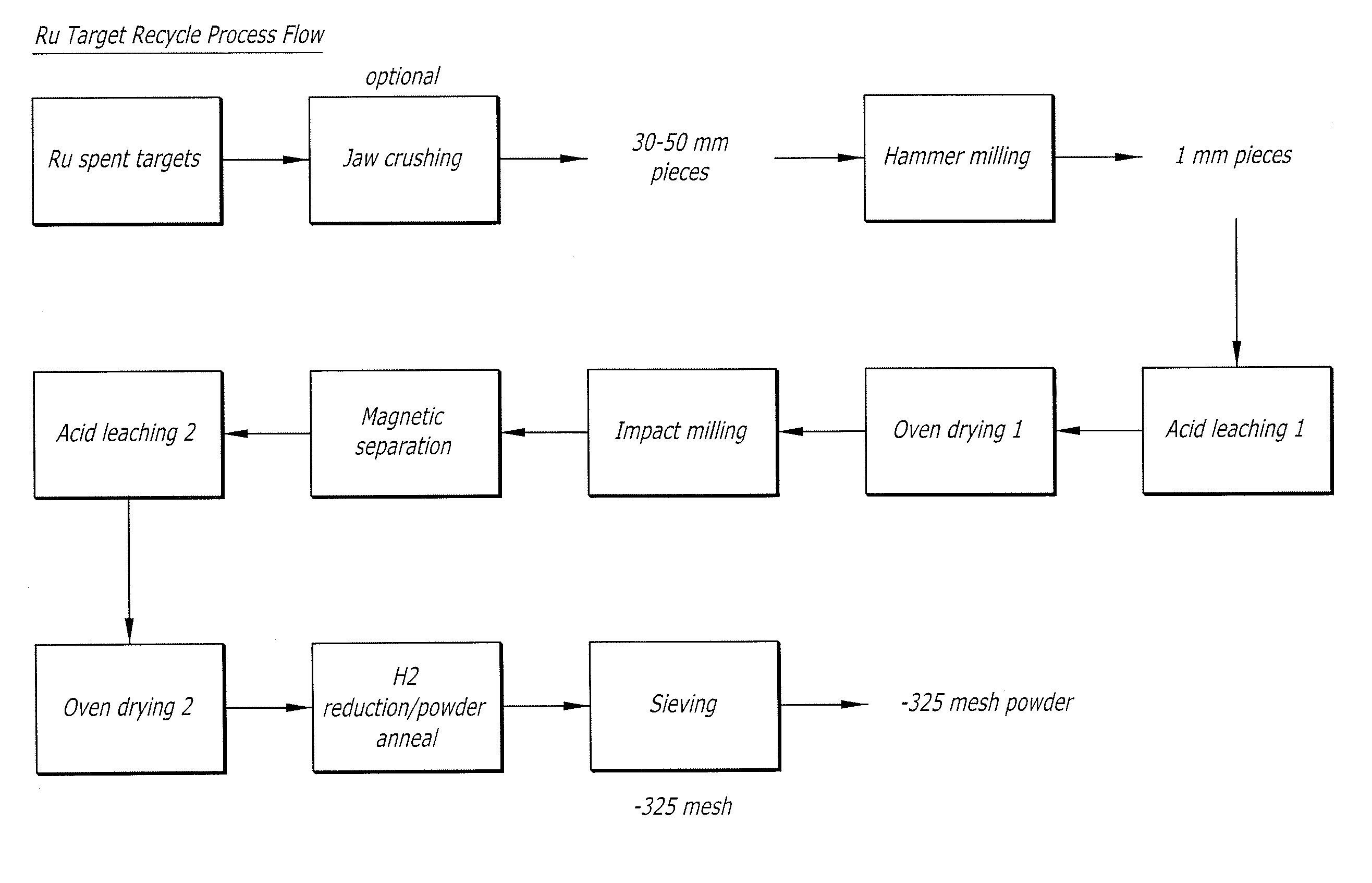
Methodology for recycling ru and ru-alloy deposition targets & targets made of recycled ru and ru-based alloy powders
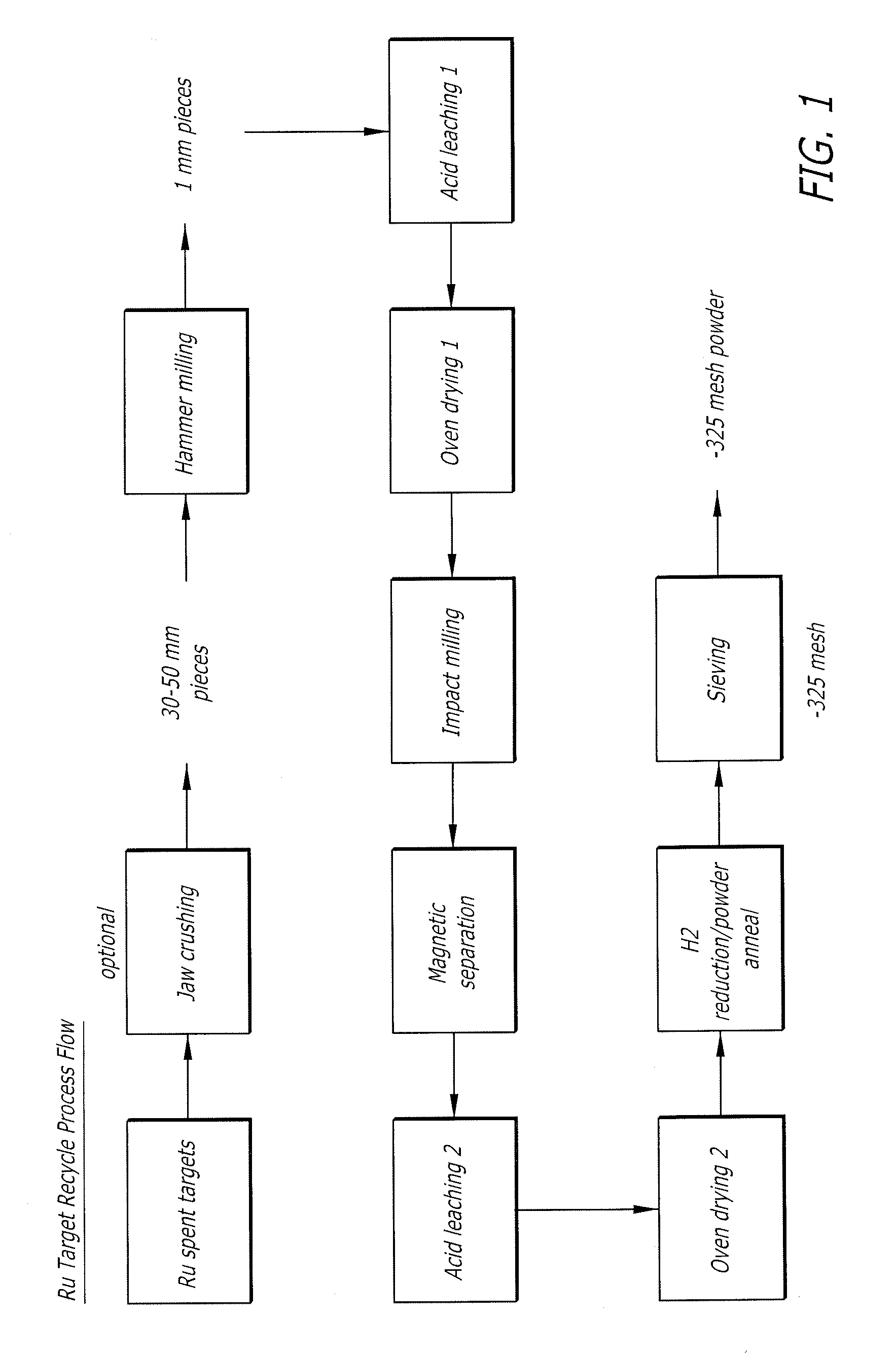
InactiveUS20090107837A1Simple methodIncrease depositionCellsVacuum evaporation coatingRutheniumAlloy deposition
A method of recycling ruthenium (Ru) and Ru-based alloys comprises steps of: providing a solid body of Ru or a Ru-based alloy; segmenting the body to form a particulate material; removing contaminants, including Fe, from the particulate material; reducing the sizes of the particulate material to form a powder material; removing contaminants, including Fe, from the powder material; reducing oxygen content of the powder material to below a predetermined level to form a purified powder material; and removing particles greater than a predetermined size from the purified powder material. The purified powder material may be utilized for forming deposition sources, e.g., sputtering targets.
Owner:HERAEUS INC
Method for preparing aluminum oxide nanostructure on surface of titanium alloy and improving antifouling property of titanium alloy
ActiveCN112663010AIncrease the surface contact angleDoes not change original surface propertiesVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingNano al2o3Alloy deposition
The invention relates to the field of metal surface modification, in particular to a method for preparing an aluminum oxide nanostructure on the surface of a titanium alloy and improving the antifouling property of the titanium alloy. The method comprises the steps that firstly, after the surface of the titanium alloy is cleaned, a nanometer aluminum coating is arranged on the surface of the titanium alloy in a magnetron sputtering manner, through heat treatment in air, an unoxidized Al and Ti substrate forms an alloy layer through atom diffusion, a magnesium powder solid phase method is used for dealloying, and the titanium alloy with nanometer aluminum oxide particles dispersed on the surface is obtained through cleaning and drying; and then, the titanium alloy surface with the nanometer aluminum oxide particles deposited on the surface is subjected to chemical modification through an ethanol solution of (3, 3, 3-trifluoropropyl) methyldimethoxysilane, and the hydrophobic performance of the titanium alloy surface is further improved. The method is simple and feasible, an atomic diffusion alloy deposition layer and a stable aluminum oxide coating are obtained through heat treatment in air, and a dispersed aluminum oxide structure can be prepared on the titanium alloy surface.
Owner:SOUTHERN MARINE SCI & ENG GUANGDONG LAB (ZHUHAI) +1
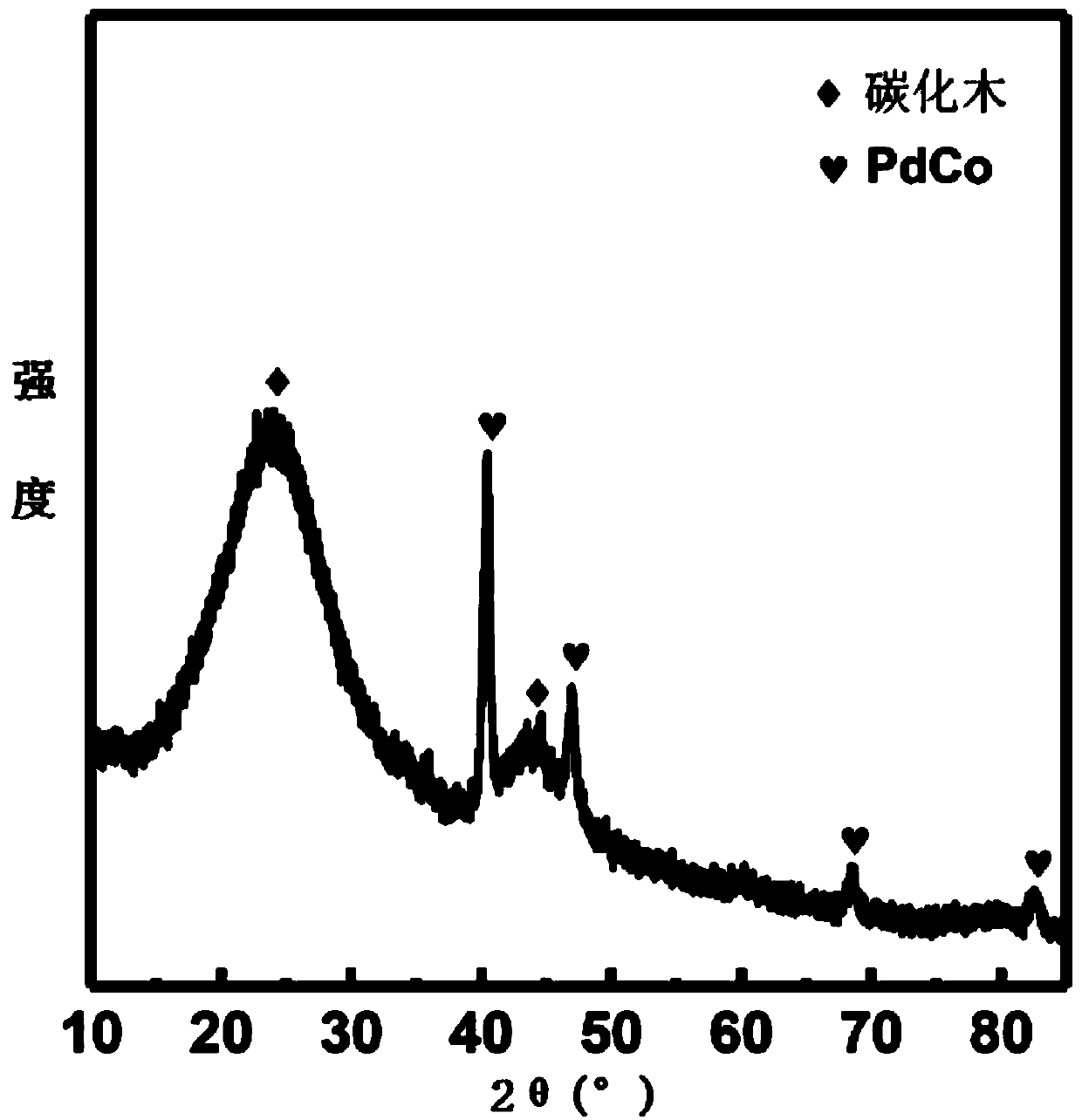
Preparation method of carbonized wood loaded PdCo alloy composite electrocatalyst
ActiveCN110890559AImprove conductivityLarge electrochemically active areaCell electrodesElectrolytic agentPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a preparation method of a carbonized wood loaded PdCo alloy composite electrocatalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: immersing wood chips into a zinc chloride solution for pretreatment, drying, pyrolyzing and carbonizing to obtain carbonized wood with a three-dimensional porous structure; taking the carbonized wood as a working electrode, taking a spectroscopically pure graphite rod as an auxiliary electrode, taking a mixed solution of palladium chloride, cobalt sulfate and sodium citrate as an electrolyte, carrying out constant-current deposition, and depositing a PdCo alloy on the surface of the carbonized wood, so as to obtain the composite electrocatalyst. The carbonized wood with the three-dimensional porous network structure is used asthe carrier of the electrocatalyst, and compared with a carbon carrier commonly used by an existing electrocatalyst, the network structure can provide a more efficient and stable electron transport network, and the conductivity of the composite electrocatalyst is improved; the three-dimensional porous structure is beneficial to exposing more active sites, increasing the electrochemical active areaof the electrocatalyst and being beneficial to quick permeation and diffusion of electrolyte, thereby being beneficial to improving the activity and stability of the composite electrocatalyst.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com