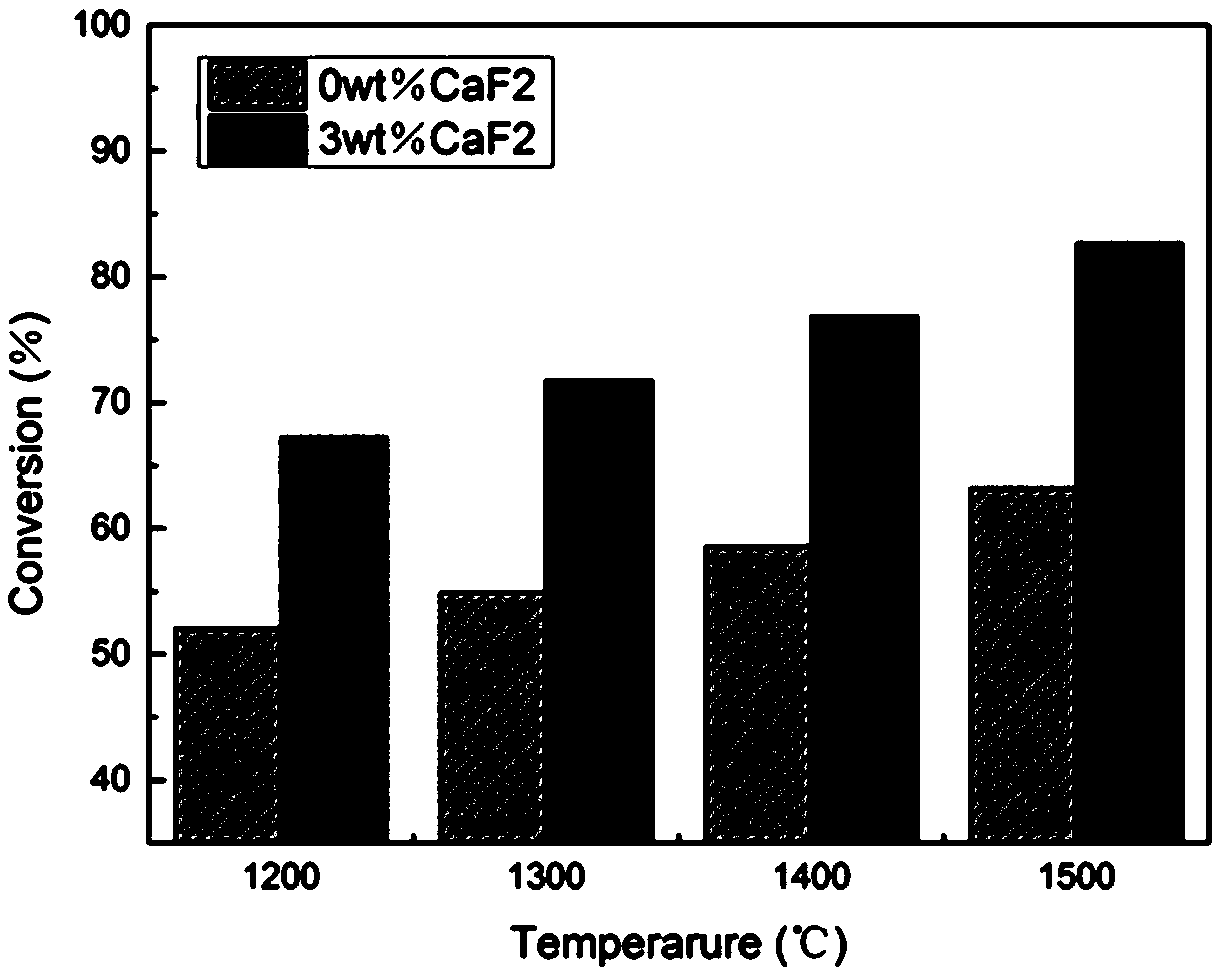
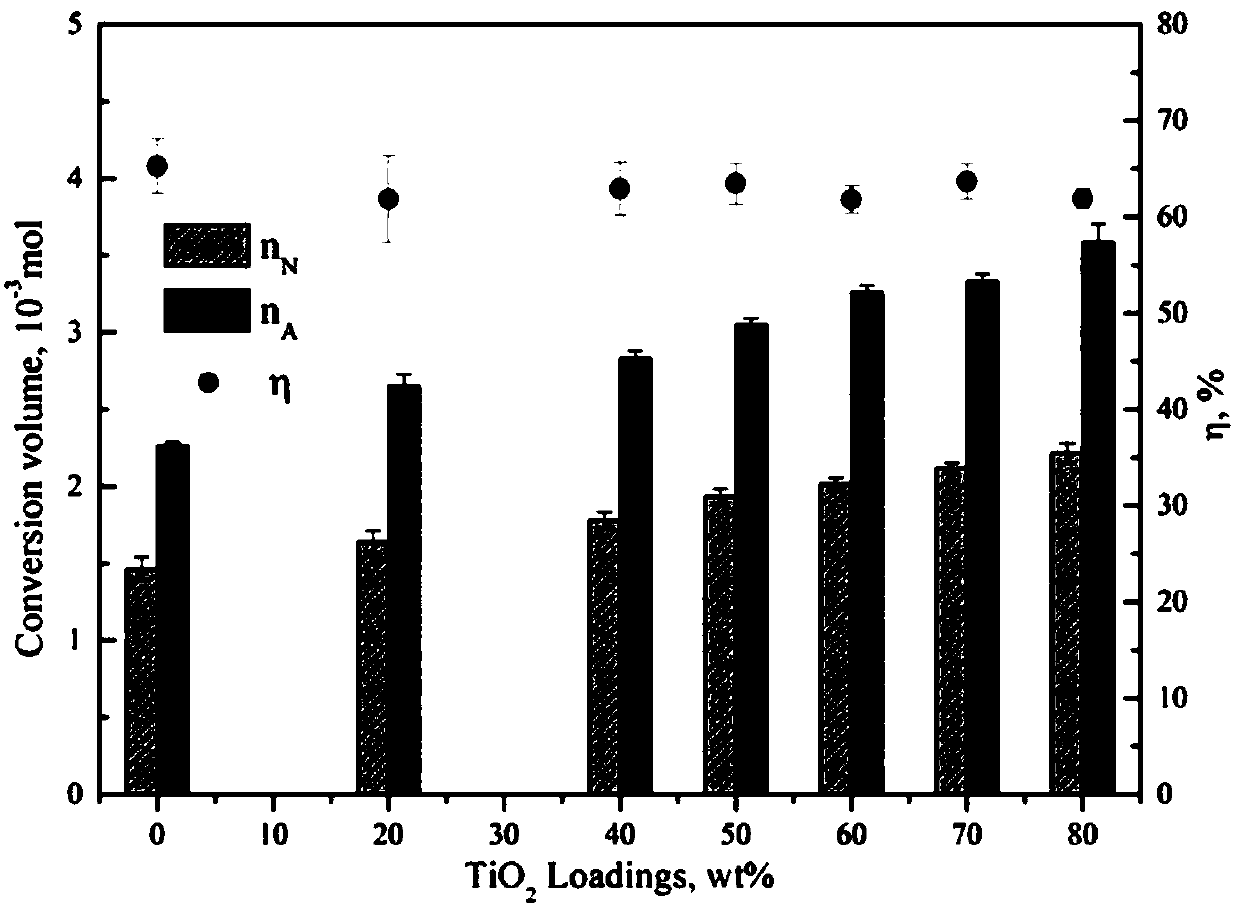
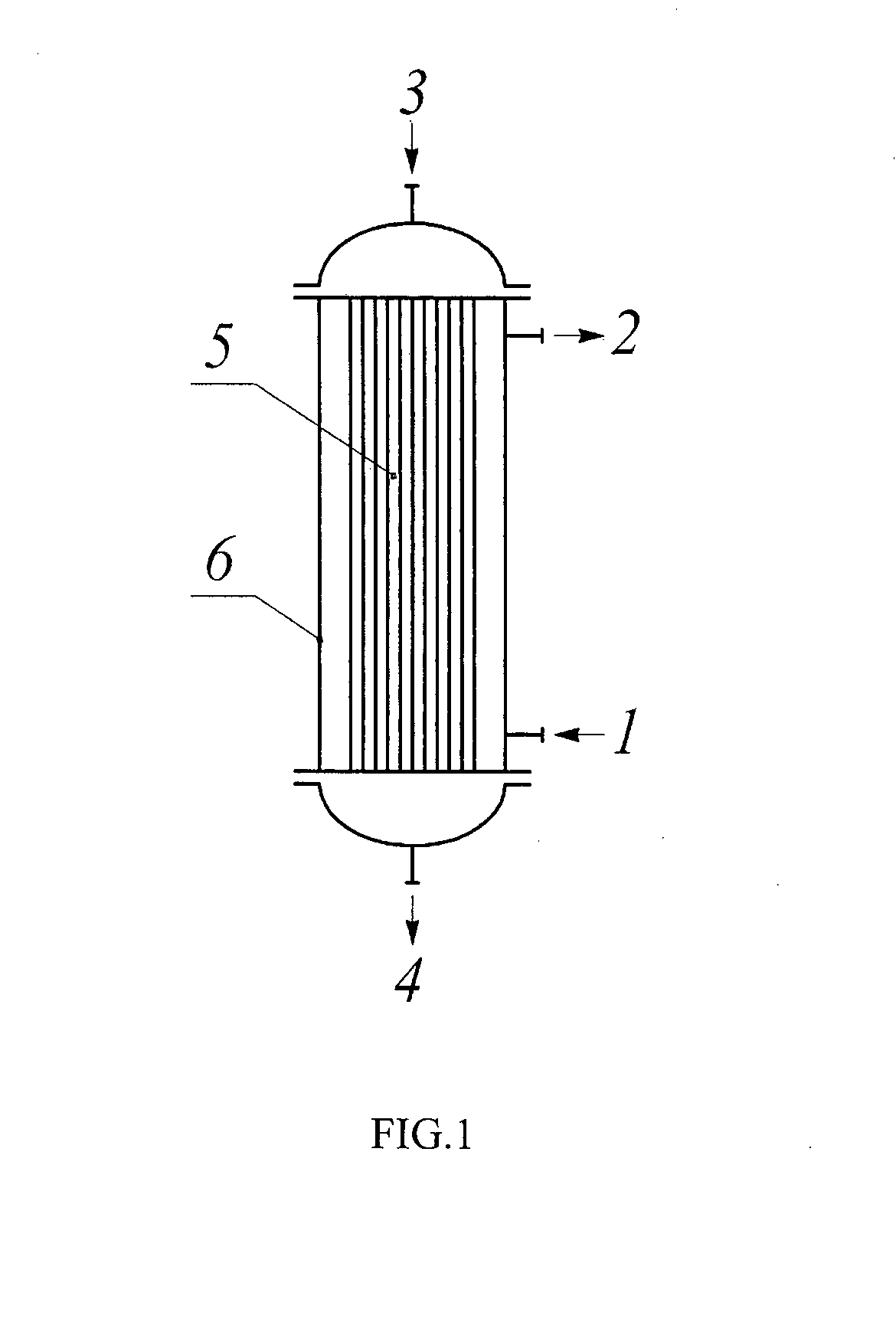
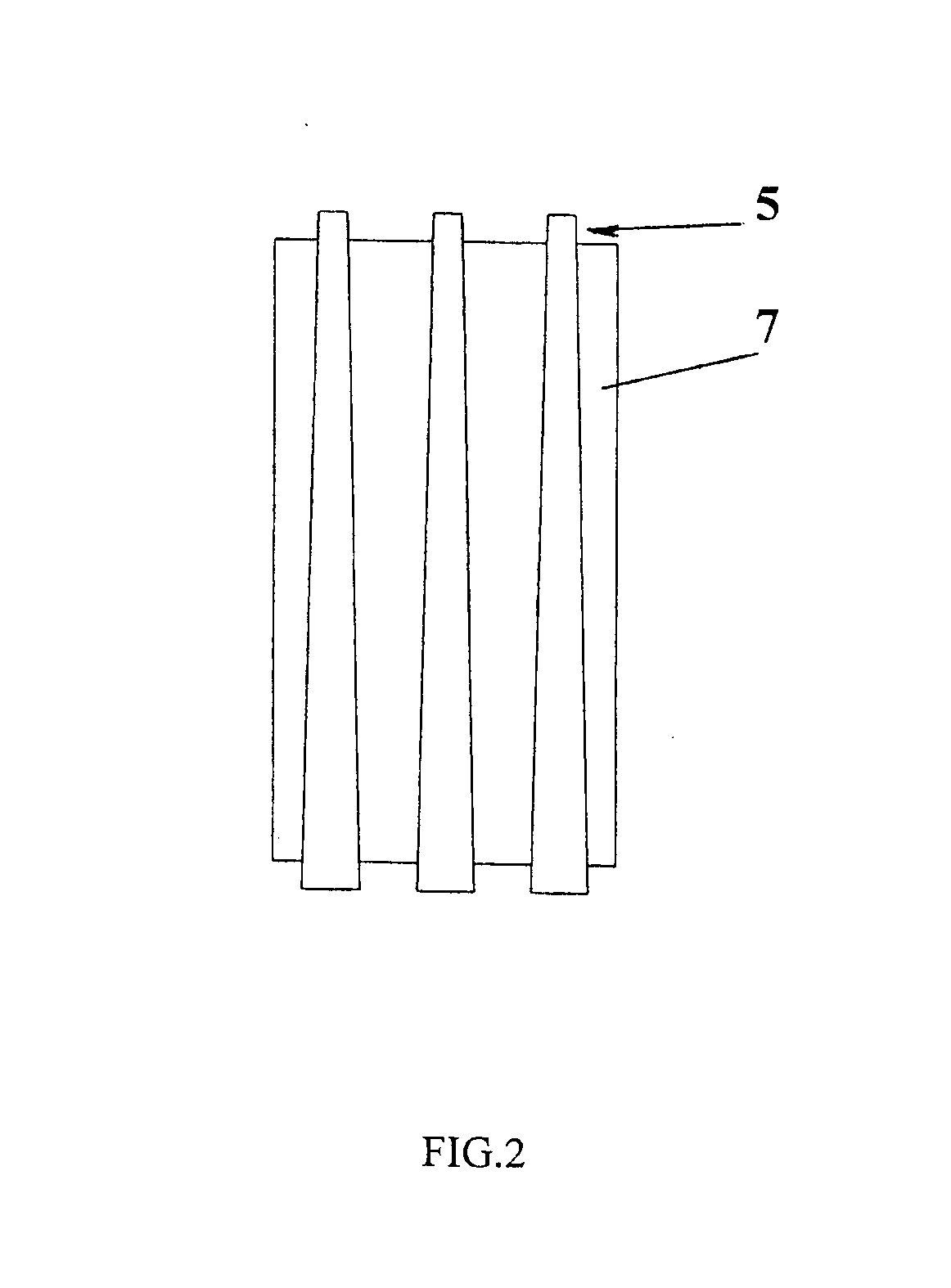
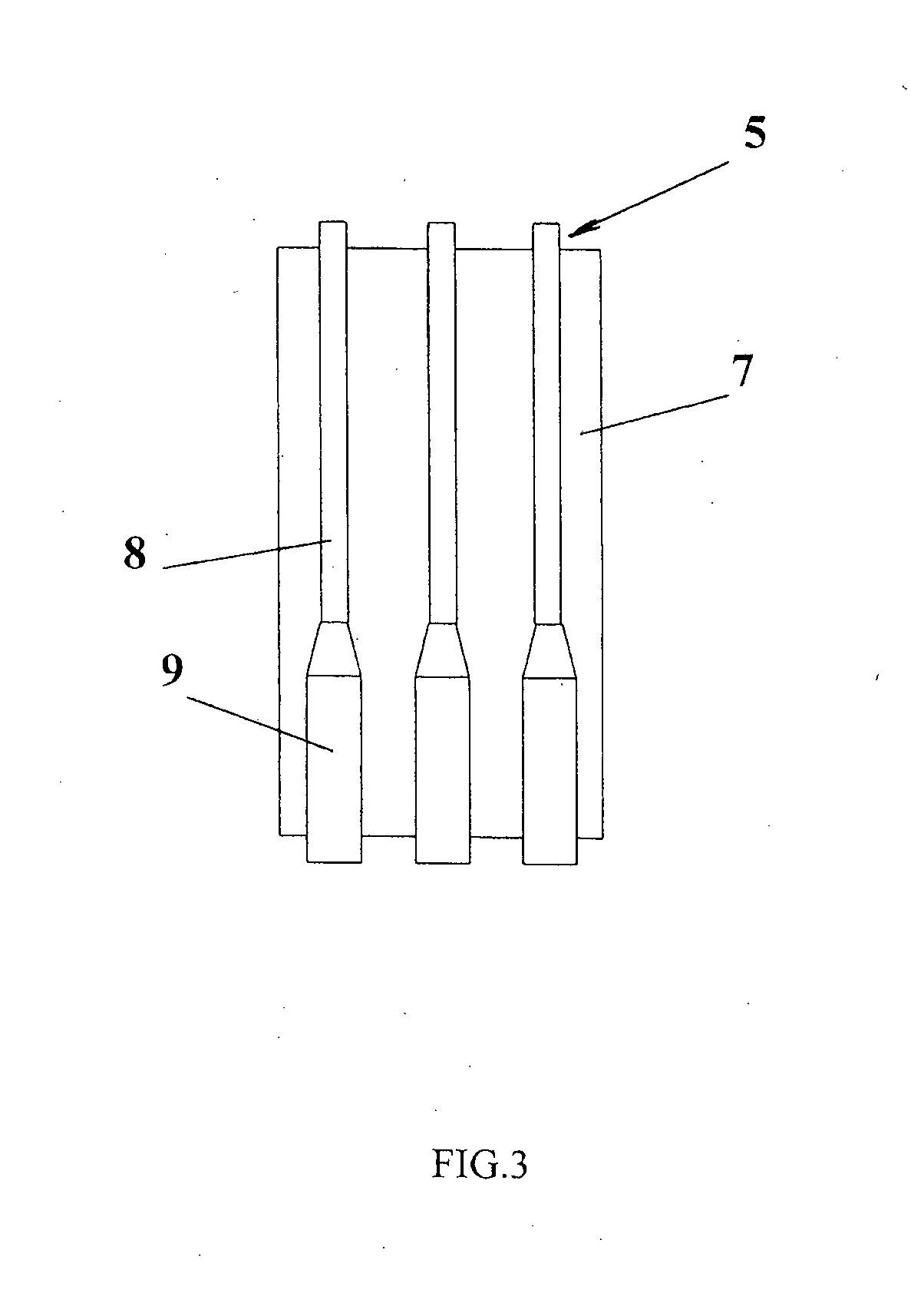
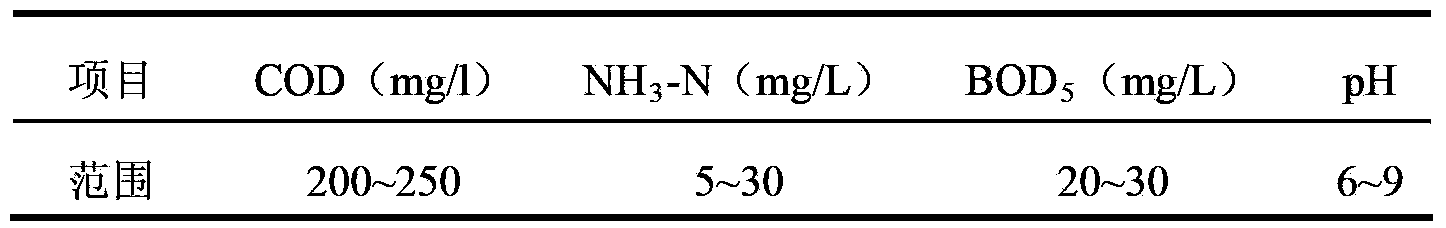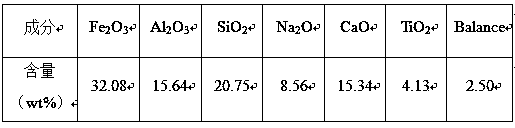Patents
Literature
50 results about "Coal chemistry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
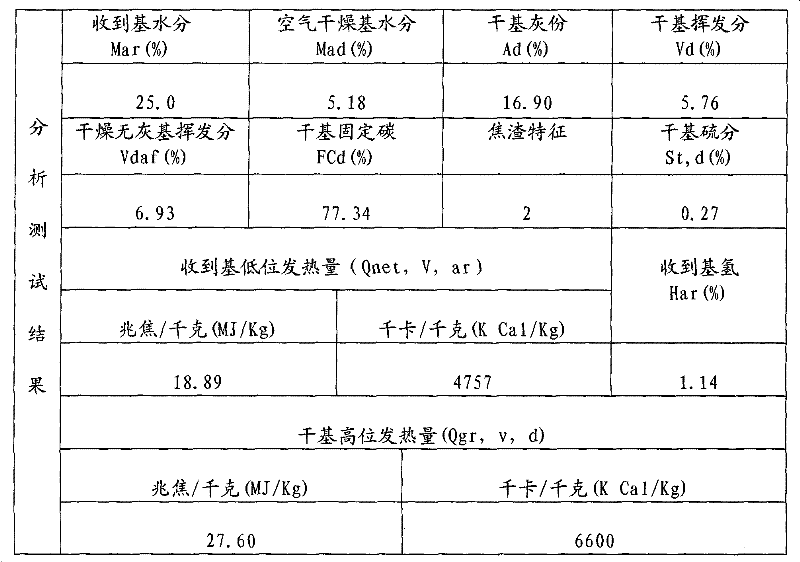
Coal is defined as a readily combustible rock containing more than 50% by weight of carbon. Coals other constituents include hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, ash, and sulfur. Some of the undesirable chemical constituents include chorine and sodium.
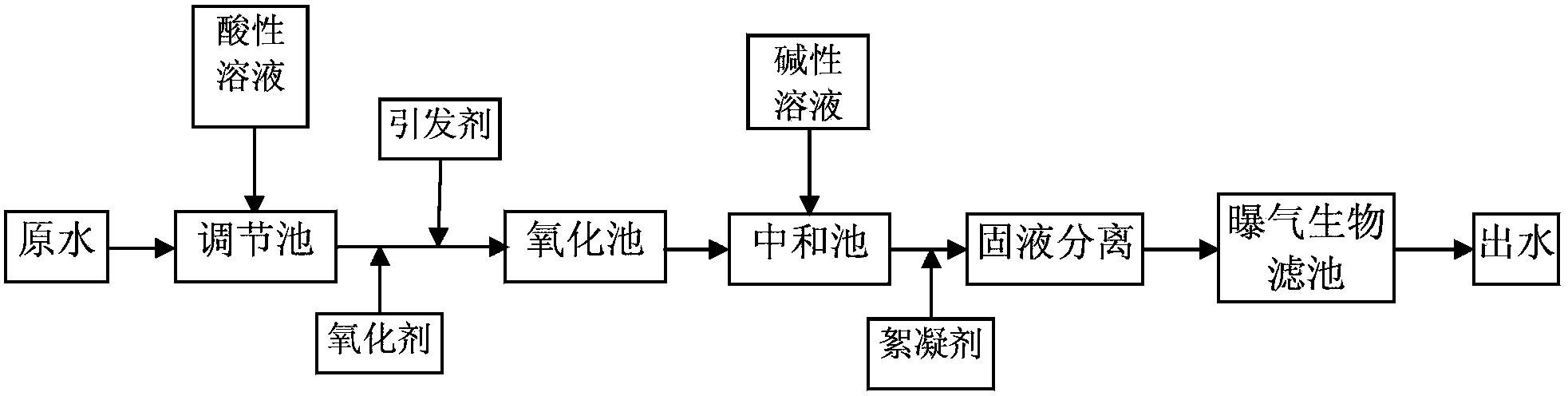
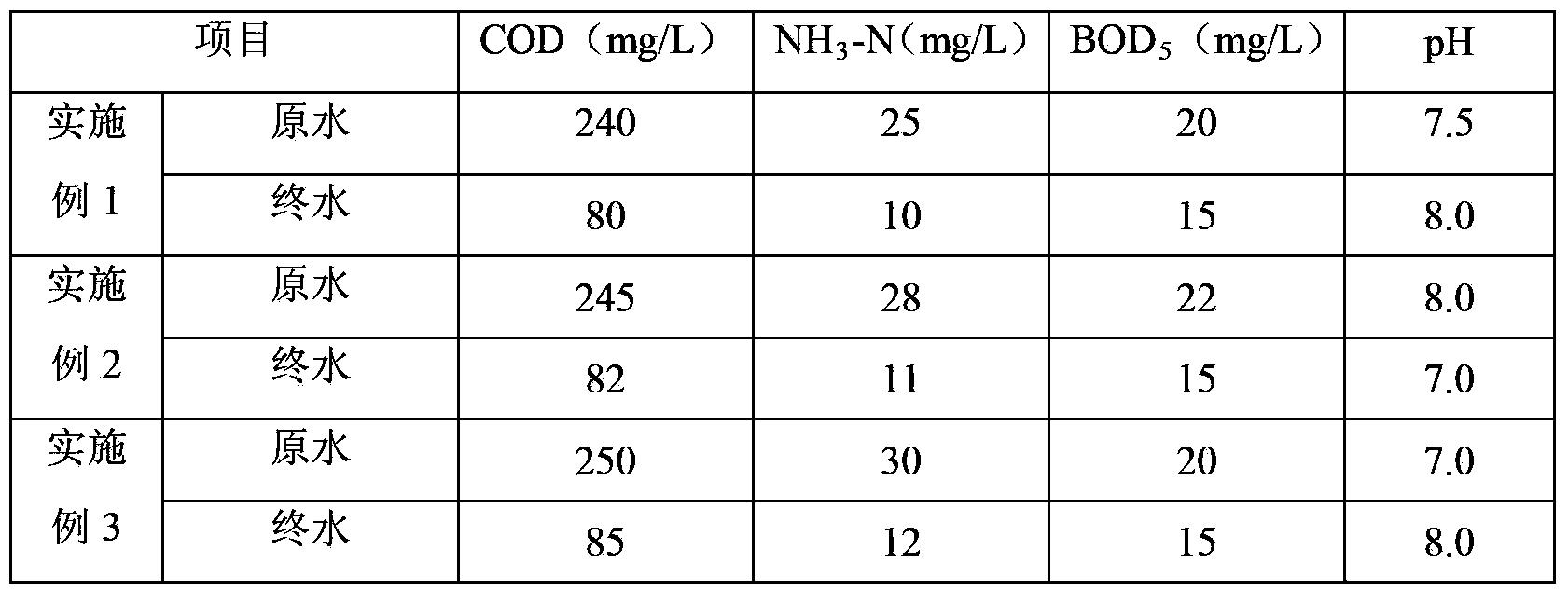
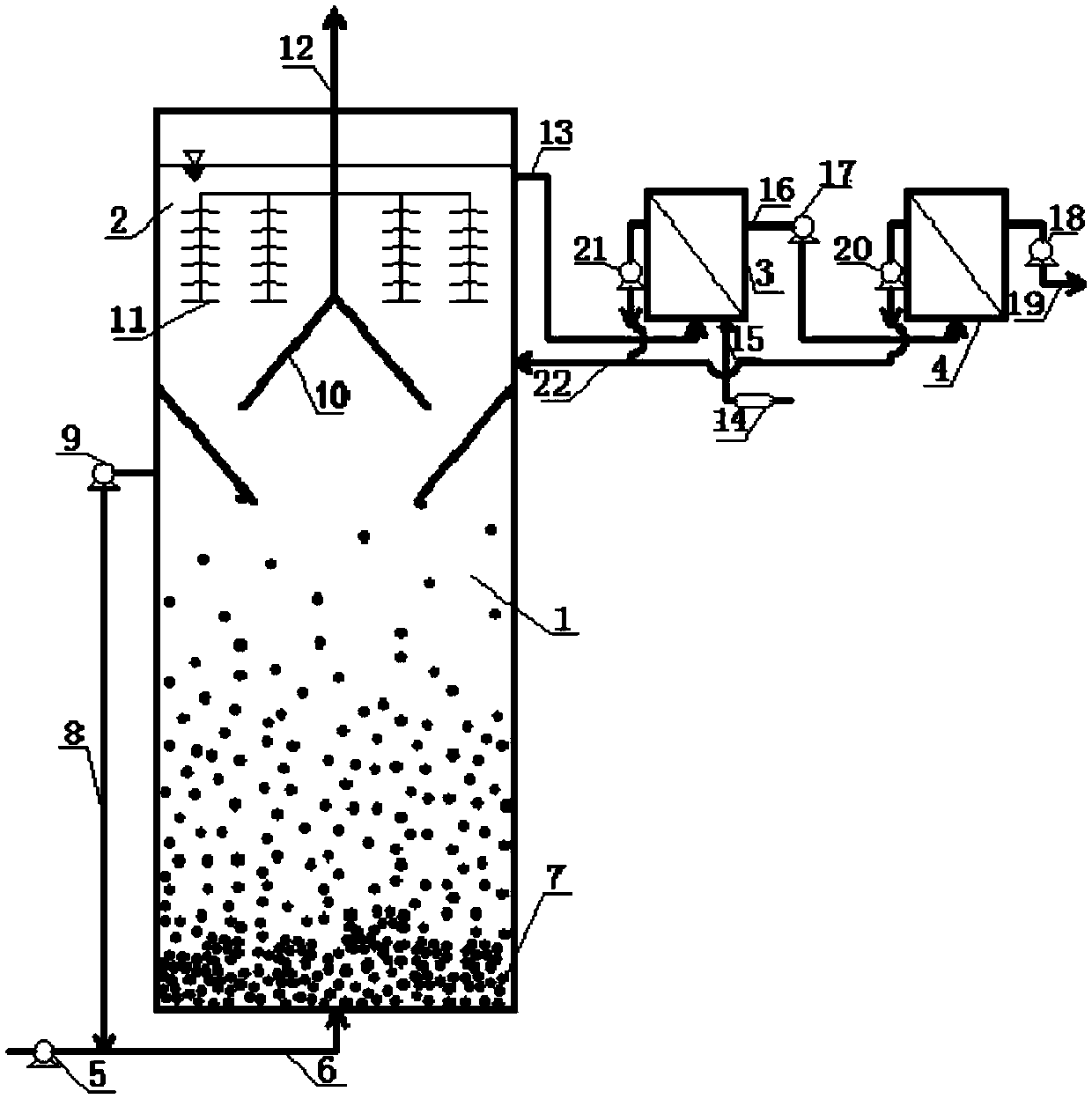
Processing method of wastewater in coal chemistry industry
ActiveCN104163539AReduce COD valueReduce CODMultistage water/sewage treatmentBiological oxidationCoal chemistry
The invention relates to a deep processing method of wastewater in the coal chemistry industry. The method comprises the following steps in sequence: subjecting the effluent, which has been processed by a secondary biochemical treatment for wastewater in coal chemistry industry, to a chemical oxidation treatment and a biological oxidation treatment in sequence. The processing method adopts a technology integrating the chemical oxidation and biochemical oxidation, thus overcomes the shortage of high operation cost of the chemical oxidation technology and the shortage of low COD elimination rate of the biochemical oxidation technology, and achieves the degradation of partial organic pollutants in wastewater. The processed wastewater reaches the discharge or recycle standard, and the pollution to the environment is reduced. The processing method has the advantages of high processing efficiency, low operation cost, and strong adaptability for wastewater in coal chemistry industry, the processed wastewater reaches the national environmental requirements, and thus the processing method can achieve good economic and social profits.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing synthetic natural gas
InactiveCN102229827AHigh reaction space velocityThe ratio of hydrogen to carbon is easy to adjustGaseous fuelsNew energyMethanation
The invention discloses a method for producing synthetic natural gas, which belongs to the technical field of coal chemistry and new energy. The method for producing the synthetic natural gas comprises: dividing raw material gases from a general gas source into low-carbon synthetic gases with a hydrogen to carbon ratio, namely a (H2-CO2) to (H2+CO2) ratio, being 4.5 to 15.0 and high-carbon synthetic gases with a hydrogen to carbon ratio being 0 to 2.0; according to a reaction temperature requirement, mixing the low-carbon synthetic gases with steam at certain flow, allowing the mixed gases to enter a primary thermal-insulation reactor to undergo a methanation reaction, subjecting the gases from the primary thermal-insulation reactor to heat exchange, mixing the gases with the high-carbon synthetic gases at a certain flow, and allowing the newly mixed gases into a secondary thermal-insulation reactor to undergo a methanation reaction; repeating the previous process for several times; and finally, obtaining the synthetic natural gas by processes of heat exchange, cooling, drying, compression and the like. The method has the characteristics that: (1) circulating equipment is not used; (2) all reactions are performed in thermal-insulation reactors, multiple stages of reactors are connected in series, and the reaction space velocity is high; and (3) the hydrogen to carbon ratio of the whole reaction system can be regulated easily, and the methane content in the product gas may reach over 95 percent.
Owner:大连瑞克科技股份有限公司
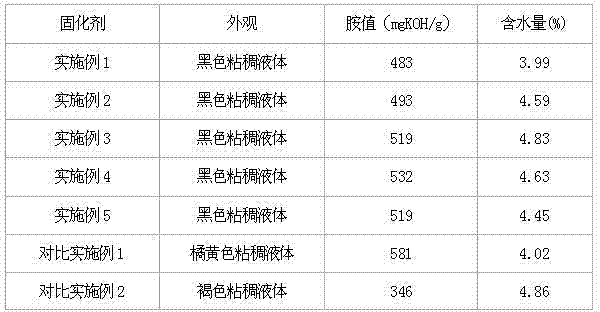
Solvent lignin-modified epoxy resin curing agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102134305ARetain chemical activityHigh purityEpoxy resin coatingsPtru catalystMannich reaction
The invention provides a solvent lignin-modified epoxy resin curing agent and a preparation method thereof. The epoxy resin curing agent is prepared from the following raw materials in part by weight: 10 to 30 parts of solvent lignin or derivative of the solvent lignin, 30 to 60 parts of phenol, 15 to 35 part of aldehyde, 20 to 45 part of ammine and 0.05 to 0.2 part of sulfuric acid catalyst. The phenol-aldehyde-ammine epoxy resin curing agent is prepared by the Mannickreaction of the solvent lignin or derivative of the solvent lignin and the phenol, aldehyde and ammine. When the solvent lignin-modified phenol-aldehyde-ammine epoxy resin curing agent provided by the invention is used, petrochemical and coal chemical products can be replaced, the consumption of the petrochemical and coal chemical products is reduced, the cost of the epoxy resin is reduced, the lignin renewable resource in the waste from biorefinery is fully utilized, and the development of low-carbon economy is promoted.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Anaerobic-micro-aerobic membrane bioreactor and operation method thereof
ActiveCN105366806AReduce pollutionReduce pollution loadWaste based fuelTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesFiltration membraneCollection system
The present invention relates to an anaerobic-micro-aerobic membrane bioreactor and an operation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of waste anaerobic biological treatment. The bioreactor combines an Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Bed body portion with a two stage membrane module, wherein the body portion comprises a granular sludge anaerobic reaction zone, a three-phase separator, a settling zone and a biogas collection system; and the two stage membrane module are an ultrafiltration membrane module and a nano filtration membrane module, respectively, and an aeration system is arranged at the bottom of the ultrafiltration membrane module. Concentrated water trapped by the ultrafiltration membrane module and the nano filtration membrane module flows back to the bottom of the settling zone, and in the micro-aerobic environment, hardly degradable organic matters are further degraded. The volume loading rate of the reactor in treating hardly degradable organic waste water of pharmacy and coal chemistry can reach about 15 kg COD / (m<3>.d). The anaerobic-micro-aerobic membrane bioreactor and the operation method of the present invention solve the problems that in the prior art when the efficient anaerobic reactors represented by UASB treat hardly degradable waste water, the hydraulic retention time is long, the effect is not ideal, the conventional anaerobic membrane bioreactors have significant membrane contamination, and the hardly degradable organics removal effect is poor.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
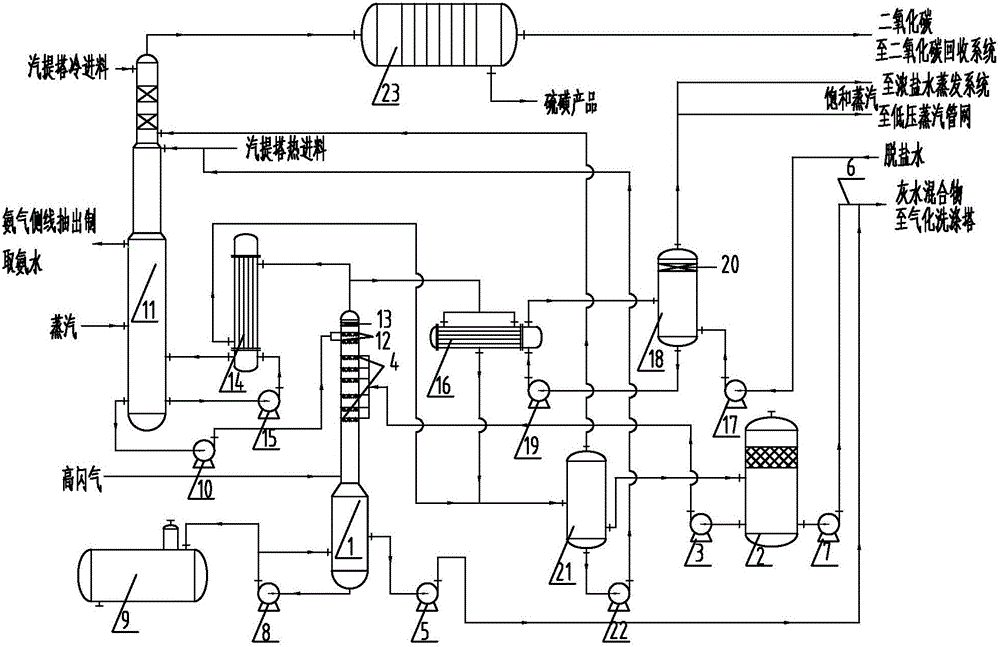
Comprehensive utilization method for coal chemical industry gasified black water high-temperature flashing steam
ActiveCN106587233AFlexible temperature controlAvoid badGas treatmentUsing liquid separation agentDeaeratorEngineering
The invention relates to a comprehensive utilization method for coal chemistry industry gasified washing black water high-temperature flashing steam. The high-temperature flashing steam first directly heats part of a grey water mixture to high temperature in a combined purifying tower, and then grey water and a low-temperature grey water mixture which is discharged through a deaerator are mixed and pumped into a vaporization washing tower to be recycled after set temperature is reached; the non-condensation high-temperature flashing steam is purified on the upper section of the tower, a first high-temperature flashing steam condenser and a second high-temperature flashing steam condenser are introduced to prepare secondary steam, the secondary steam is used for a raw ammonia recycling stripping tower and a strong brine evaporating system, and excessive secondary steam is introduced into a low-pressure steam pipeline net; part of high-temperature flashing steam condensate is introduced into the gasification deaerator, the remaining condensate and non-condensation high-temperature flashing steam enter the ammonia recycling stripping tower for separation, ammonia gas is pumped out along a lateral line to prepare ammonium hydroxide, carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide and other gas are introduced into a sulfur recycling system for sulfur recycling and then enter a carbon dioxide recycling system. Finally, the high-temperature flashing steam is sufficiently utilized.
Owner:中诚和易(北京)国际科技有限公司
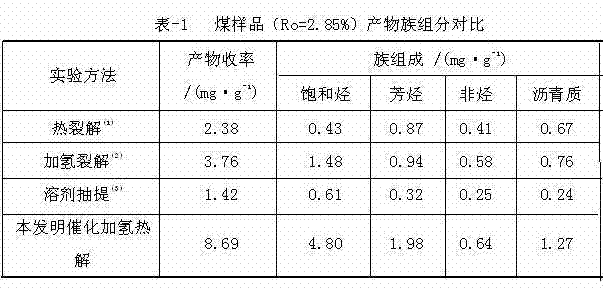
Method for treating biological marker by using kerabitumen hydrogenation pyrolysis catalyst
InactiveCN102191074AHigh yieldComplete structurePhysical/chemical process catalystsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionBiogeochemistryBiomarker (petroleum)
The invention discloses a method for treating a biological marker by using a kerabitumen hydrogenation pyrolysis catalyst and belongs to the field of geochemistry. The method comprises the following steps of: reacting ammonium molybdate with sulfide to prepare a catalyst precursor thioammonium molybdate; preparing water / methanol solution of thioammonium molybdate; dipping a sediment sample into the solution and performing vacuum drying, so that the mass percentage of the loaded molybdenum (Mo) is 1 percent; hydrogenating and pyrolyzing the sample by adopting temperature programming operation; and collecting the reaction product by using a dry ice cold trap. The method is applicable in the fields of oil gas geochemistry, biogeochemistry, coal chemistry and the like. By the method, typical biomarker compounds can be effectively extracted from high-evolution sedimentary organic matters in a geologic body; the problem that sufficient biomarker compounds are generated difficultly in the conventional test system is solved; and deficiency of the free biomarker compounds is overcome by organic micromolecules bonded by covalent bond in the kerabitumen and obtained by pyrolyzing. The method is simple and convenient and high in catalytic property, and has a wide application prospect in the field of geochemistry.
Owner:XINXIANG UNIV
Catalyst for synthesis of hydrocarbons from CO and H2 and preparation method thereof
The disclosed technology relates to nanotechnology, petrochemistry, gas chemistry, coal chemistry, in particular to a catalyst based on carbon nanotubes for synthesis of hydrocarbons from CO and H2 and a preparation method thereof. The carbon nanotubes fixed in the catalyst pellet pores improve mass and heat transfer in the catalyst pellet and the catalyst bed.
Owner:INFRA XTL TECH
Compound additive for briquettes
The invention relates to a compound additive for briquettes, which comprises the following raw materials by weight: 5-15 parts of calcium lignosulphonate, 1-6 parts of sodium dihydrogen phosphate, 0-7 parts of electric lime, 5-15 parts of magnesium chloride, 0.5-5 parts of humic acidic ammonium, 5-15 parts of calcium hydrate, 2-6 parts of potassium nitrate, 0.5-3 parts of potassium permanganate, 0.2-2 parts of sodium nitrate, 0-3 parts of sodium chloride, 6-12 parts of kaoline, 3-7 parts of castor seed oil residue, 0.2-1 parts of polyvinyl alcohol and 8-12 parts of water. A preparation method thereof comprises the step of only uniformly mixing the raw materials by weight. The briquettes prepared by mixing the compound additive, coal washery sludge and middlings can be free of drying so as to lower the cost, has the smoke suppression effect of 70-90 percent and can also achieve the environmental protection requirements through detection by Shanxi Institute of Coal Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Taiyuan environmental detection center.
Owner:庄利斌
Method for preparing nanometer carbon fiber by coal
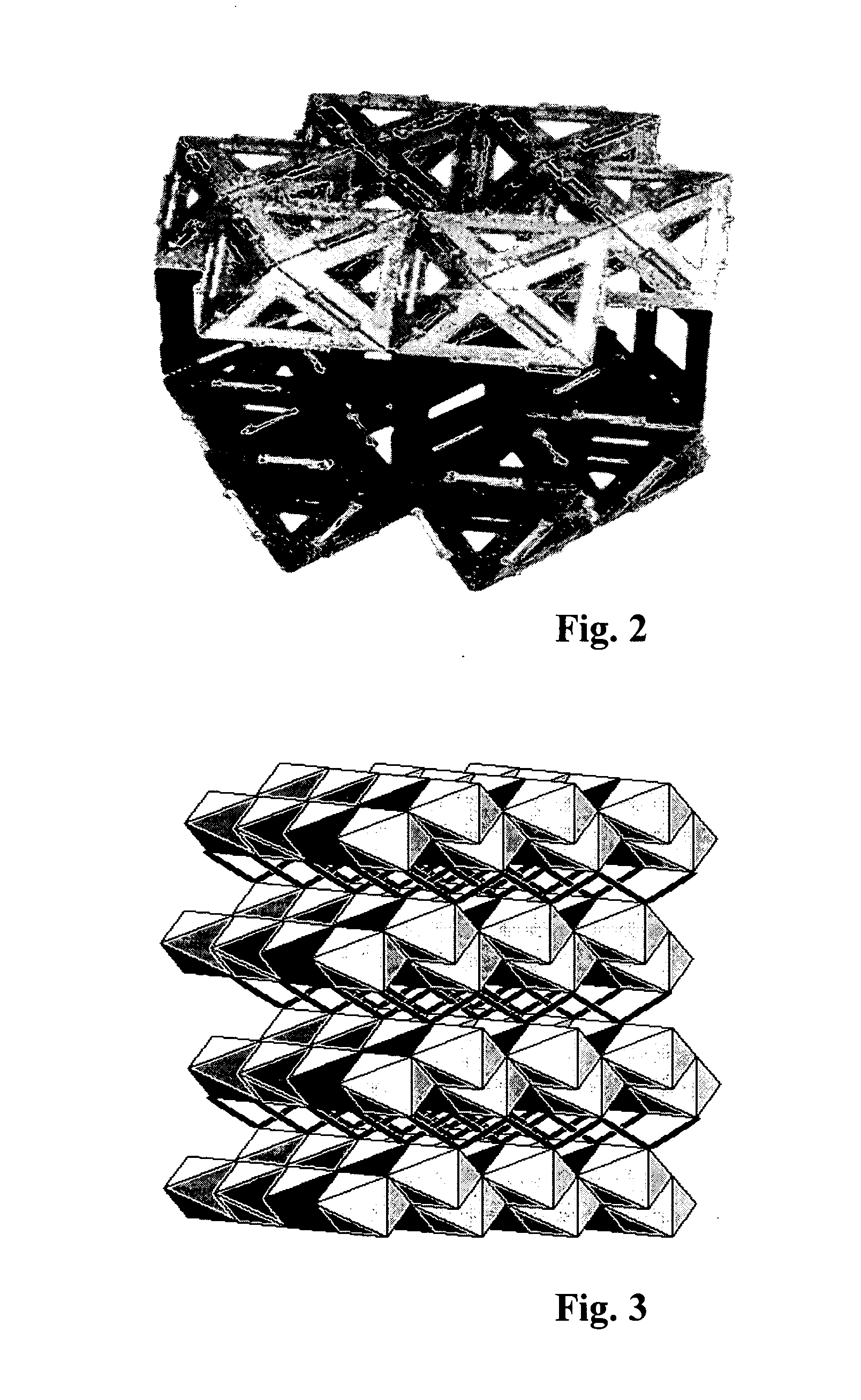
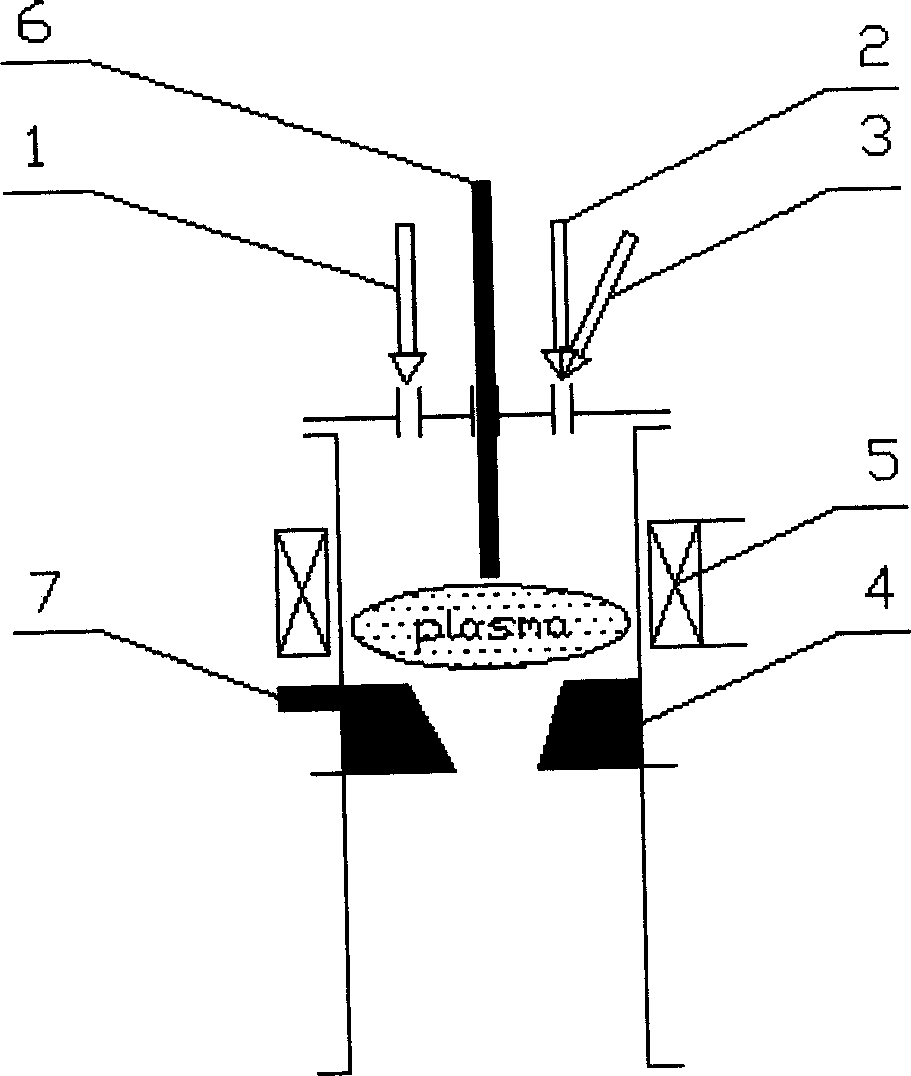
The invention is a method for using coal to produce nano carbon fiber, which belongs to new material synthesis and process technology field, which is the cross field of coal chemistry, carbon material and plasma science. The character lies in: the invention uses plasma direct current arc ejection technology to process coal ash, the water-vapor is used as accelerator, the transition metal is catalyst, the invention uses the fixed bed to control the stop time of high temperature arc area of coal ash, gets large quantity of nano grade hollow fiber product, the diameter is between the nano carbon pipe and the carbon fiber generated by the gas phase. The effect of the invention is the material is cheap, the process is simple.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
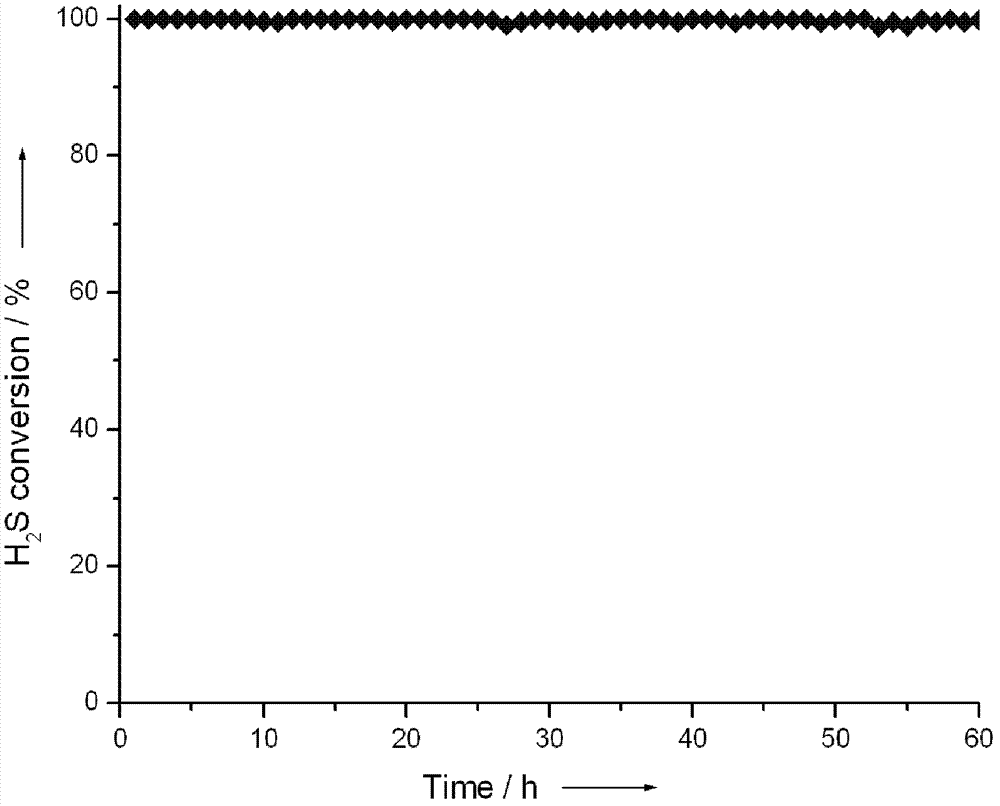
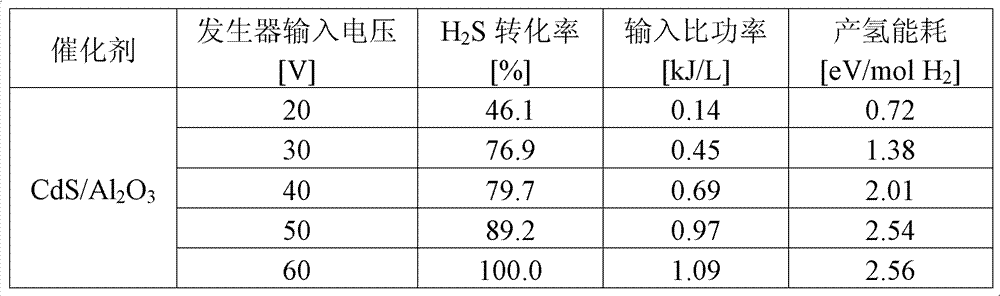
Method of decomposing hydrogen sulfide for preparation of hydrogen and elemental sulfur
ActiveCN102408095BIncrease added valueSulfur preparation/purificationHydrogen productionDecompositionCopper oxide
The invention discloses a method of decomposing hydrogen sulfide for preparation of hydrogen and elemental sulfur, which belongs to the technical field of hydrogen production and gas purification. The invention is characterized in that: hydrogen sulfide or gas containing hydrogen sulfide is subjected to ionization through blockage of discharge by using a medium so as to form uniformly distributednon-equilibrium plasma, and hydrogen sulfide spontaneously decomposes into hydrogen and elemental sulfur in the plasma; when there is a photocatalyst in the plasma, energy in the photons of the photocatalyst can be utilized to promote decomposition of hydrogen sulfide, and complete conversion can be realized under proper conditions. All the frequently used solid photocatalysts can be used in the above mentioned process, e.g., titanium oxide, cerium oxide, zirconia, zinc oxide, cadmium oxide, copper oxide, molybdena, tungsten oxide, zinc sulfide, cadmium sulfide, copper sulfide, molybdenum sulfide, tungsten sulfide and a mixture composed of two or more selected from the above-mentioned photocatalysts; the photocatalysts can also be loaded on a porous material to prepare load type catalysts. The method provided in the invention is especially applicable to treatment of gas containing hydrogen sulfide in the industries of natural gas, petroleum and coal chemistry and is also applicable topreparation of hydrogen and elemental sulfur through dissociation of gas containing hydrogen sulfide in the fields of metallurgy, sea and the like. The method has no special requirements for or restriction on the source and composition of gas; thus, the method has universality to preparation of hydrogen through decomposition of hydrogen sulfide.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Process for producing synthetic liquid hydrocarbons and reactor for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis
InactiveUS8524787B2Organic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionLiquid productSyngas
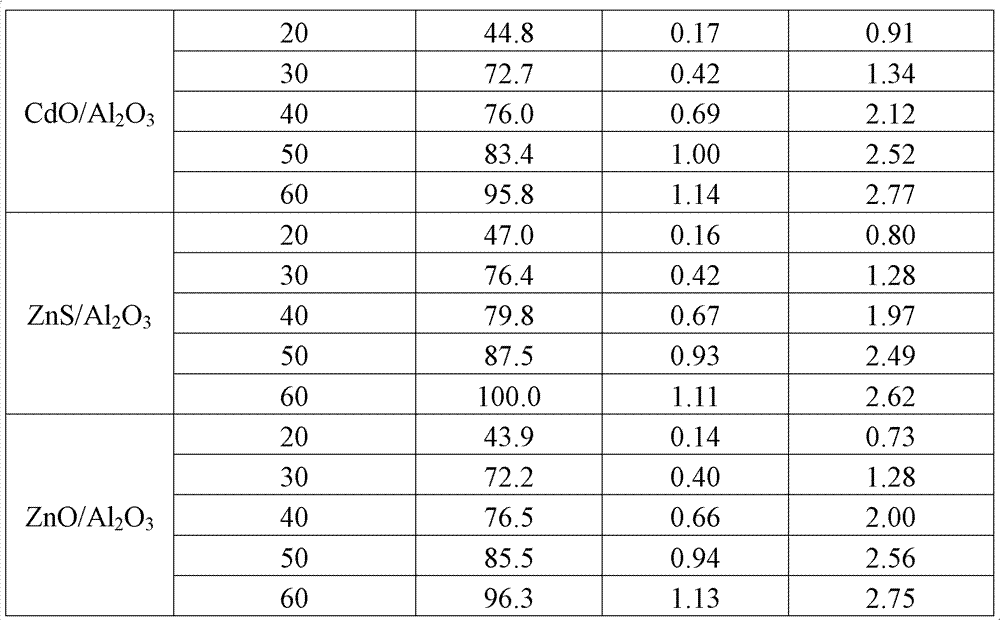
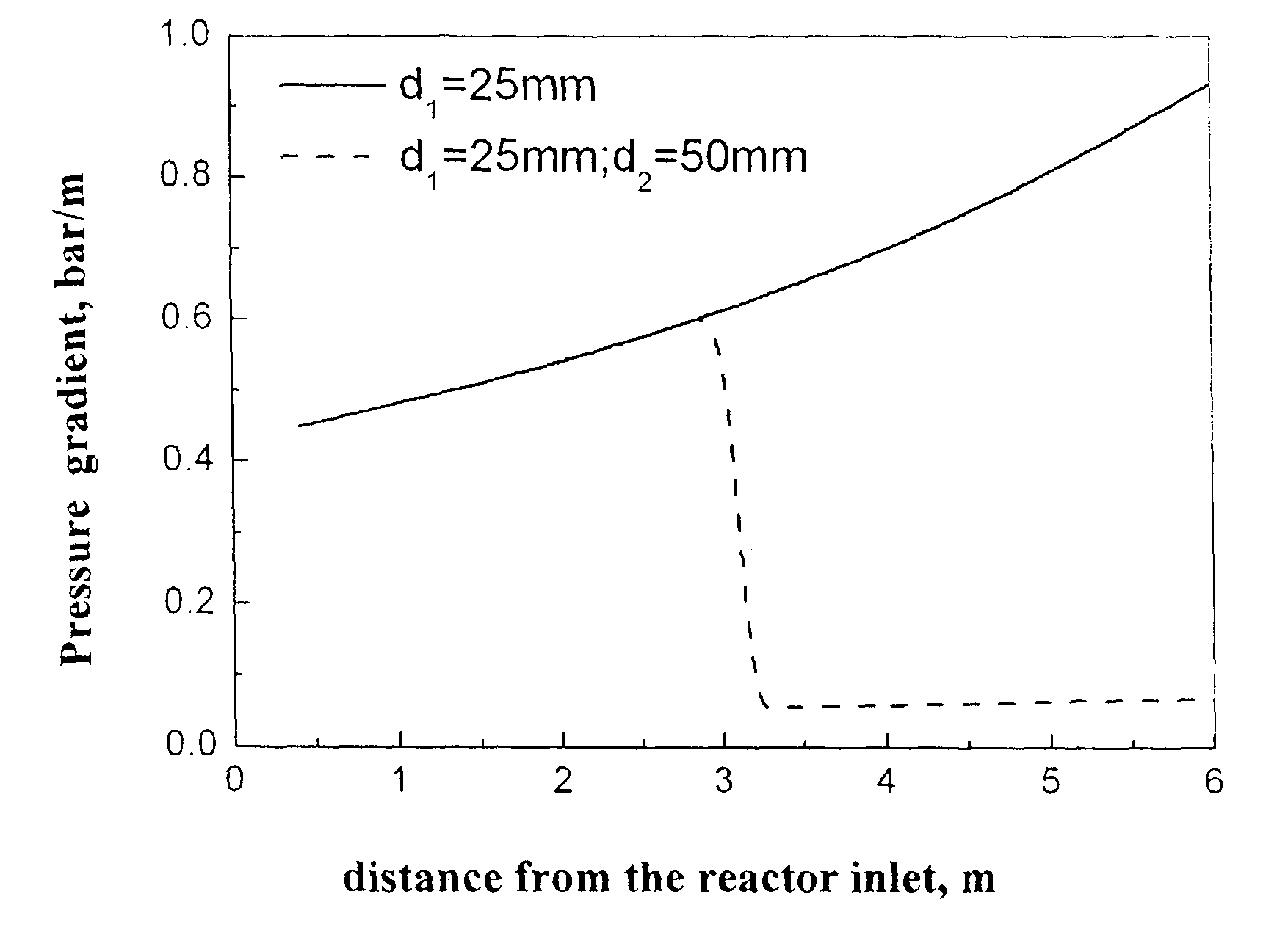
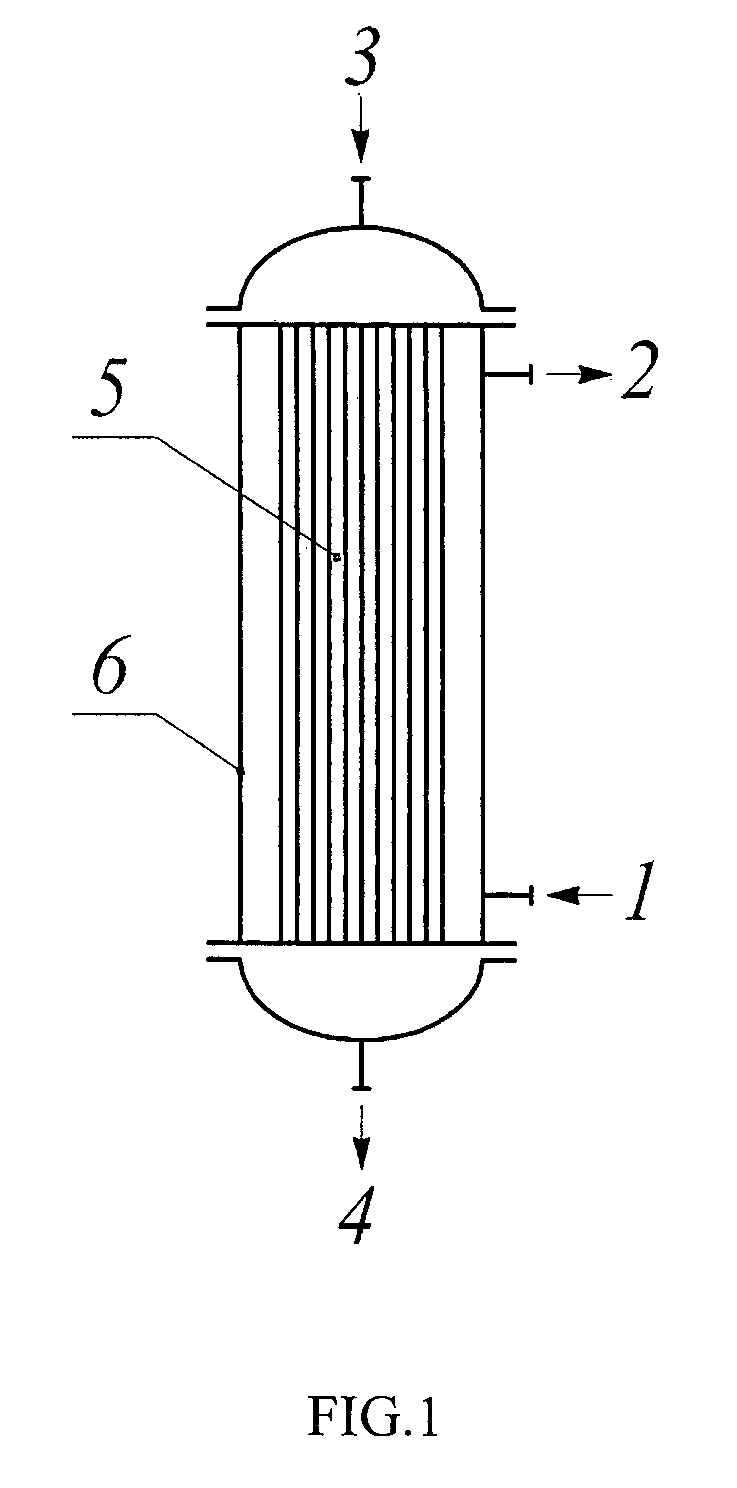
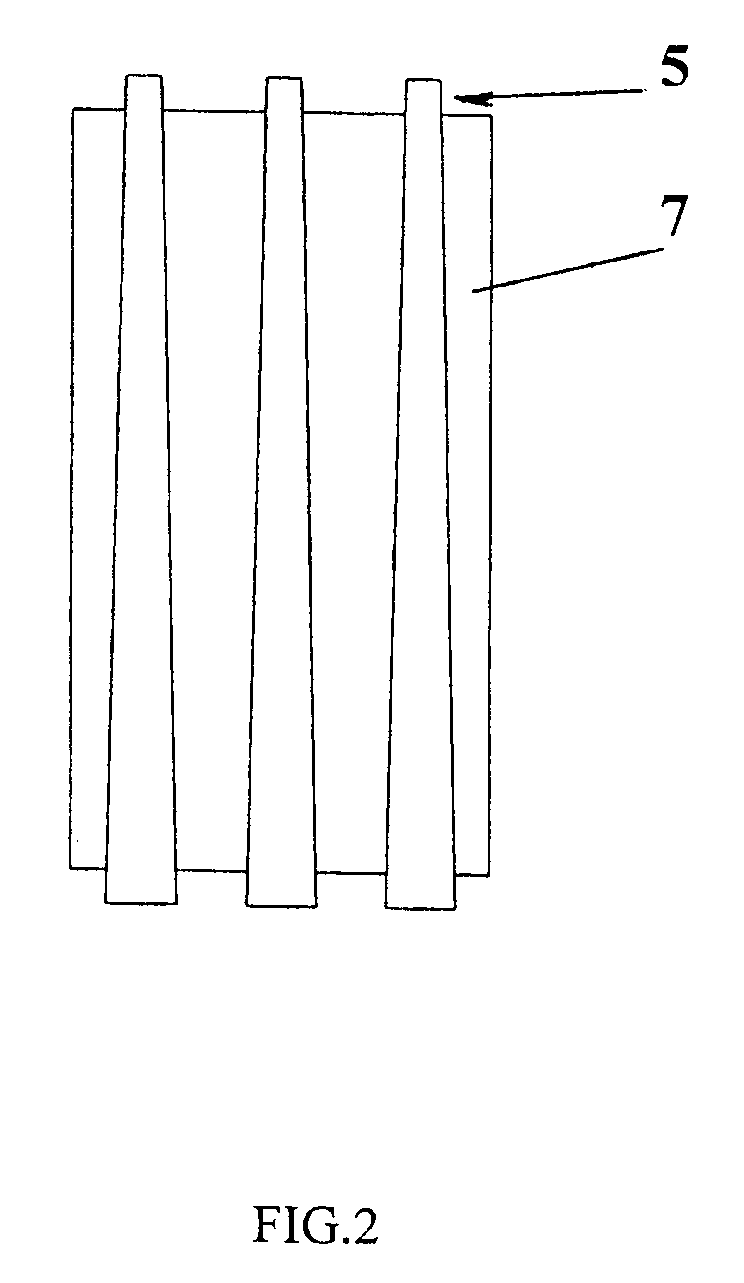
The disclosure relates to petrochemistry, gas chemistry, coal chemistry, particularly to a synthesis of hydrocarbons C5 and higher from CO and H2 under the Fischer-Tropsch reaction; the invention relates to a process and a system for producing synthetic liquid hydrocarbons. A process for producing synthetic liquid hydrocarbons is provided by catalytic converting syngas under the Fischer-Tropsch reaction on a fixed catalyst bed in a vertical shell and tube reactor with coolant supply into shell wherein as soon as the syngas conversion degree achieves 60-80%, a pressure gradient along the tubes is reduced below 0.1 bar / m and this value is maintained during the whole process. A reactor for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis is provided comprising tubes with catalyst in a shell, the ratio of the tube diameter at the tube outlet to the diameter at the inlet is from 1.5 / 1 to 2.5 / 1. The invention gives a possibility to achieve the optimum temperature range in the catalyst bed; it improves heat and mass-transfer and shut out an accumulation of the liquid products in the bottom of the tubes.
Owner:INFRA XTL TECH
Catalyst for synthesis of hydrocarbons from co and h2 and preparation method thereof
InactiveUS20120214664A1Stable to overheatingIncrease heatMaterial nanotechnologyMolecular sieve catalystsCarbon nanotubeCoal chemistry
The disclosed technology relates to nanotechnology, petrochemistry, gas chemistry, coal chemistry, in particular to a catalyst based on carbon nanotubes for synthesis of hydrocarbons from CO and H2 and a preparation method thereof. The carbon nanotubes fixed in the catalyst pellet pores improve mass and heat transfer in the catalyst pellet and the catalyst bed.
Owner:INFRA XTL TECH
Method for mixing coal for solid-state deslagging coal chemistry industry device
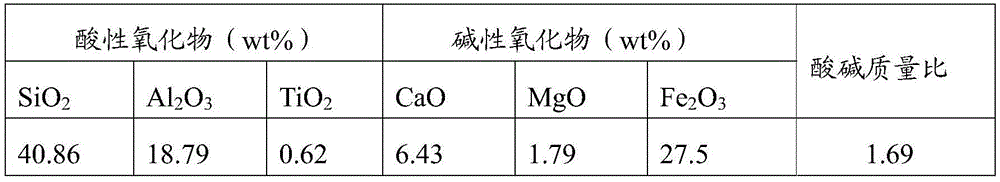
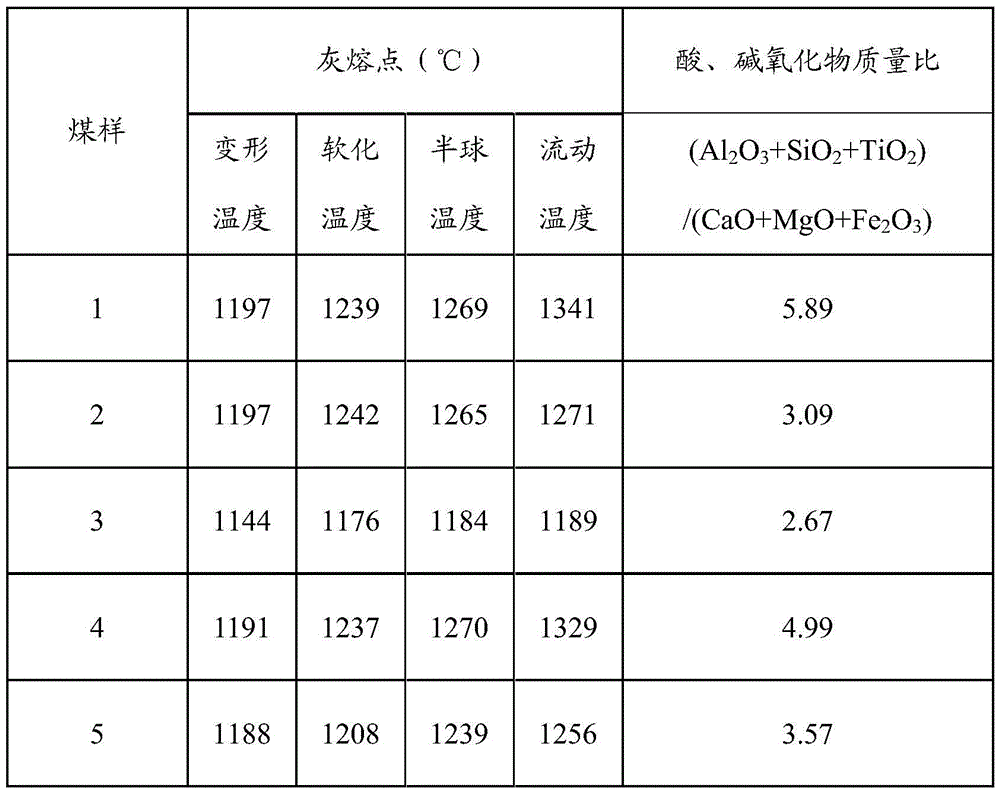
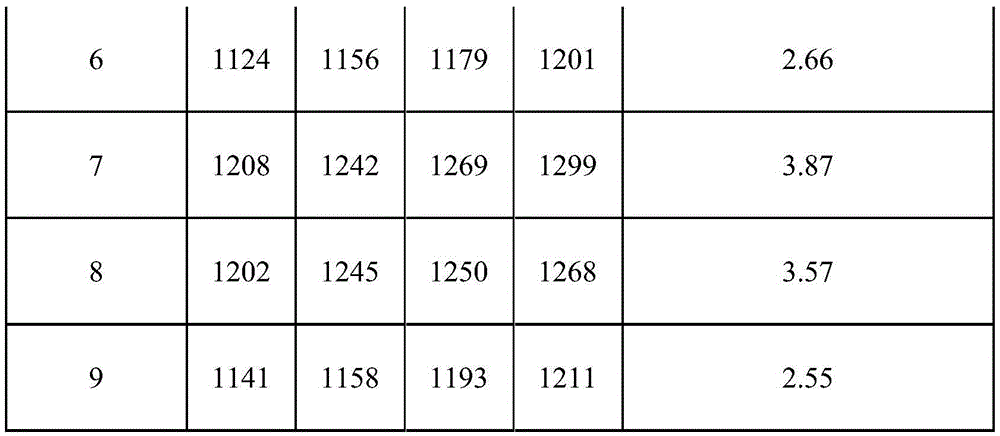
The invention discloses a method for mixing coal for a solid-state deslagging coal chemistry industry device. The method includes: adding an additive into raw coal, wherein through the additive, a ratio of total weight of acidic oxide to that of alkaline oxide in coal ash obtained after a mixture of the raw coal and the additive is burnt is not less than 2.5. Acidic-alkaline substance ratio is changed by controlling a mass ratio of acidic and alkaline oxide in coal ash and adding different additives according to different coal ash components, so that coal ash melting temperature is increased; not aiming at specific substances in specific raw coal and coal ash, the method is conducive to being widely applied.
Owner:CHNA ENERGY INVESTMENT CORP LTD +1
Trapping and pyrolysis method for carbon dioxide
The invention relates to the field of emission reduction and conversion of carbon dioxide, in particular to a trapping and pyrolysis method for carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide in smoke is converted into a sodium bicarbonate solution by a sodium carbonate solution in a carbonizer, and a pyrolyzer resolves high-purity carbon dioxide quickly. The pollution due to excessive carbon dioxide generated when fossil fuel is burnt is avoided, and energy conservation, environmental protection, energy crisis reduction and greenhouse effect reduction are realized. The method has the benefits that (1) the trapping rate of the carbon dioxide is significantly increased by the synergistic action of sodium carbonate, a catalyst and an activating agent; (2) the solution decomposes the carbon dioxide quickly, and the dissociation cost is lowered; and (3) the equipment investment is low, a large amount of carbon dioxide can be trapped and pyrolyzed, near zero release of the carbon dioxide can be realized, and the method is suitable for key coal-consumption industries of coal power, coal chemistry, steel, cement, papermaking, metallurgy, printing and dyeing, chemical engineering and the like to trap, recover and apply carbon dioxide resources on a large scale, and reduces the greenhouse effect.
Owner:浙江森井生物技术股份有限公司
Carbon nanometer tube arc discharge preparation method under vacuum condition
InactiveCN1544319ALow costThe preparation process conditions are simpleEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsEvaporationCarbon nanotube
The invention belongs to the field of coal chemistry and carbon material, in particular a process for preparing large amounts of carbon nano tubes using coal as raw material by arc discharge technology under vacuum condition, wherein coal based carbon rod or coal based composite charcoal rod prepared by mixing coal and catalyst is used as anode in the arc plasma apparatus for discharge evaporation under vacuum condition, the reactor is opened after the ending of discharge to obtain large size high purity single walled carbon nano tubes in film shape or gram magnitude pure multiple wall carbon nano tubes.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
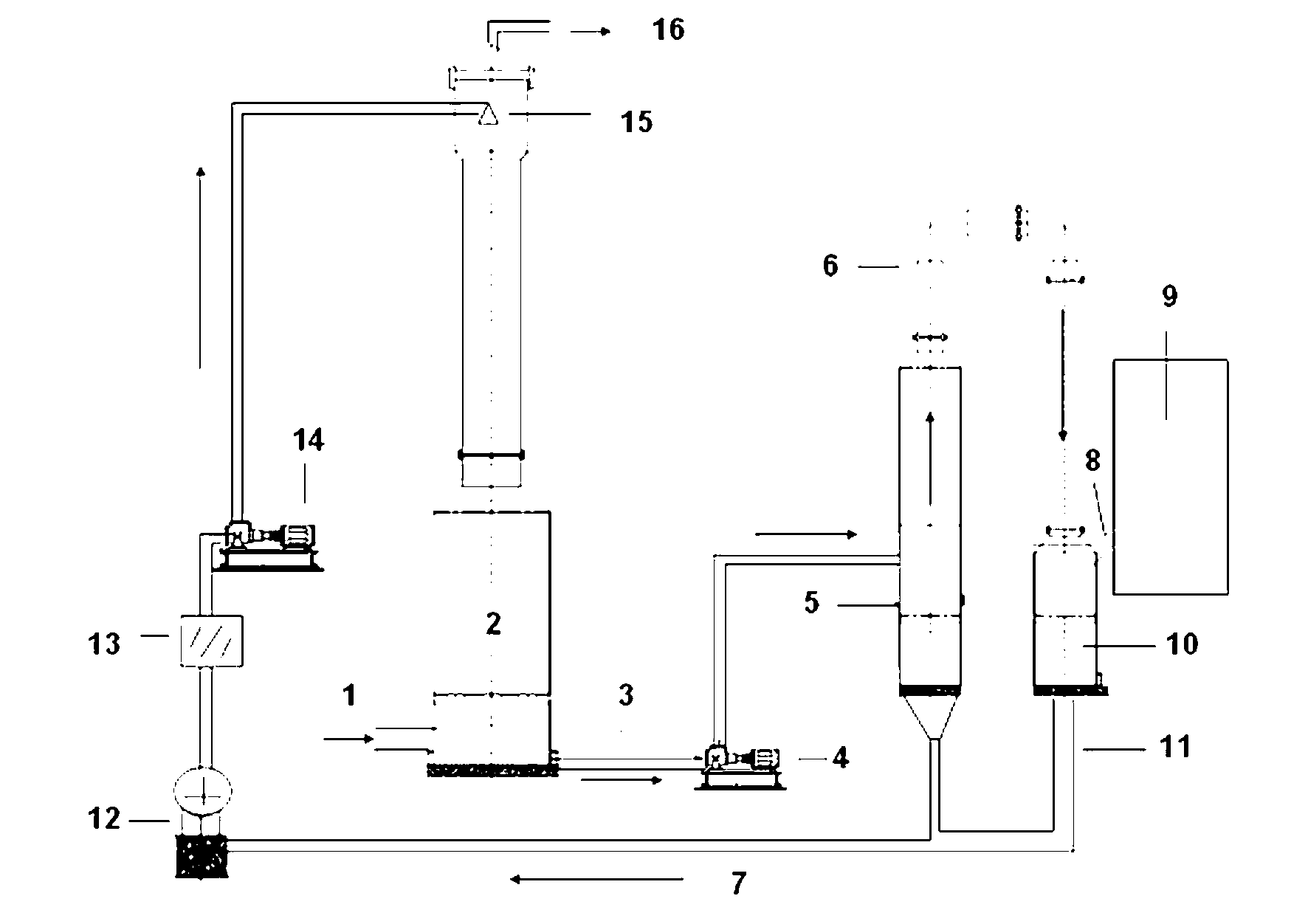
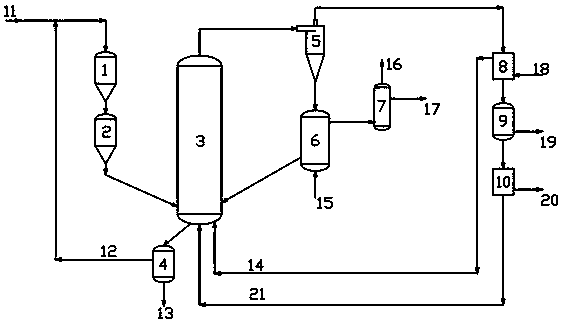
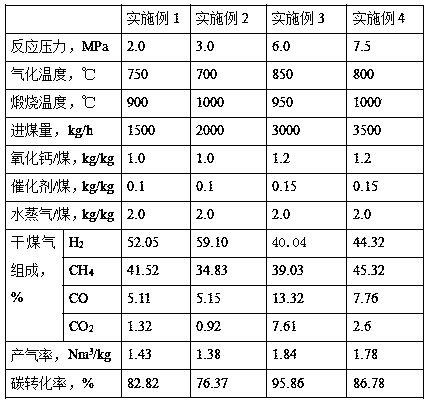
Device and process for preparing methane by coal chemical looping catalytic gasification based on calcium oxide
InactiveCN110951508AAchieving self-heating balanceEffective combinationGaseous fuelsEnergy inputChemical industryPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a device and process for preparing methane by coal chemical looping catalytic gasification based on calcium oxide, and belongs to the field of energy and chemical industry. Thedevice is composed of a feeding device, a fluidized bed gasification reactor, a calcination reactor and a gas purification and separation device. Coal, a catalyst and calcium oxide undergo a methanation reaction in a fluidized bed gasification reactor, calcium oxide and carbon dioxide react to generate calcium carbonate, balance is promoted to move to methane generation, and meanwhile heat neededby the gasification reaction is supplemented, calcium carbonate is decomposed into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide in a calcining reactor, calcium oxide is returned to the fluidized bed gasificationreactor for cyclic utilization, and coal gas generated in the fluidized bed gasification reactor is purified and separated so that high-purity methane is obtained. The process has the advantages of simple technological process, self-heating balance of the system, low carbon and high efficiency.
Owner:SHANXI INST OF COAL CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Catalyst for synthesis of hydrocarbons from CO and H2 and preparation method thereof
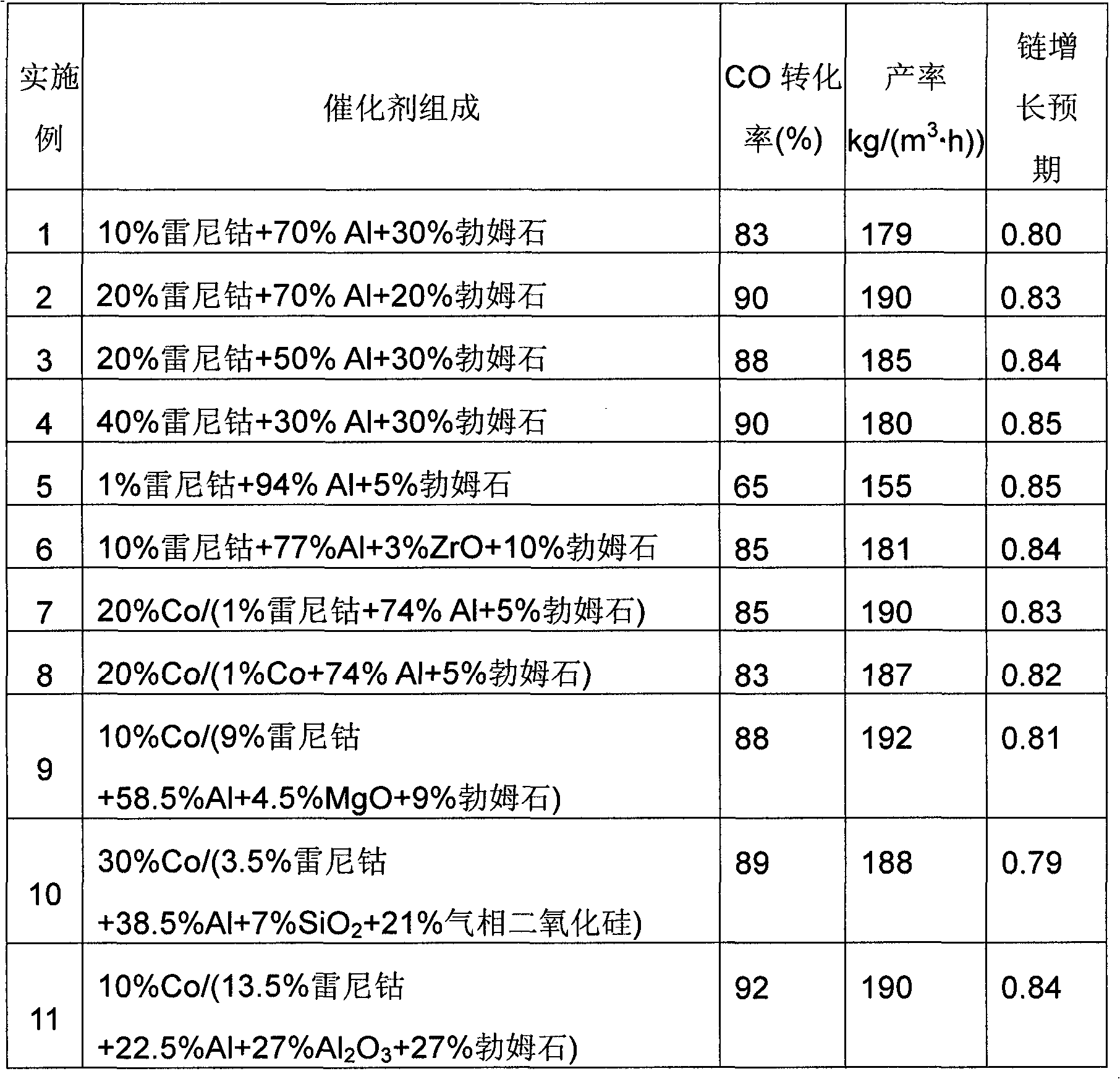
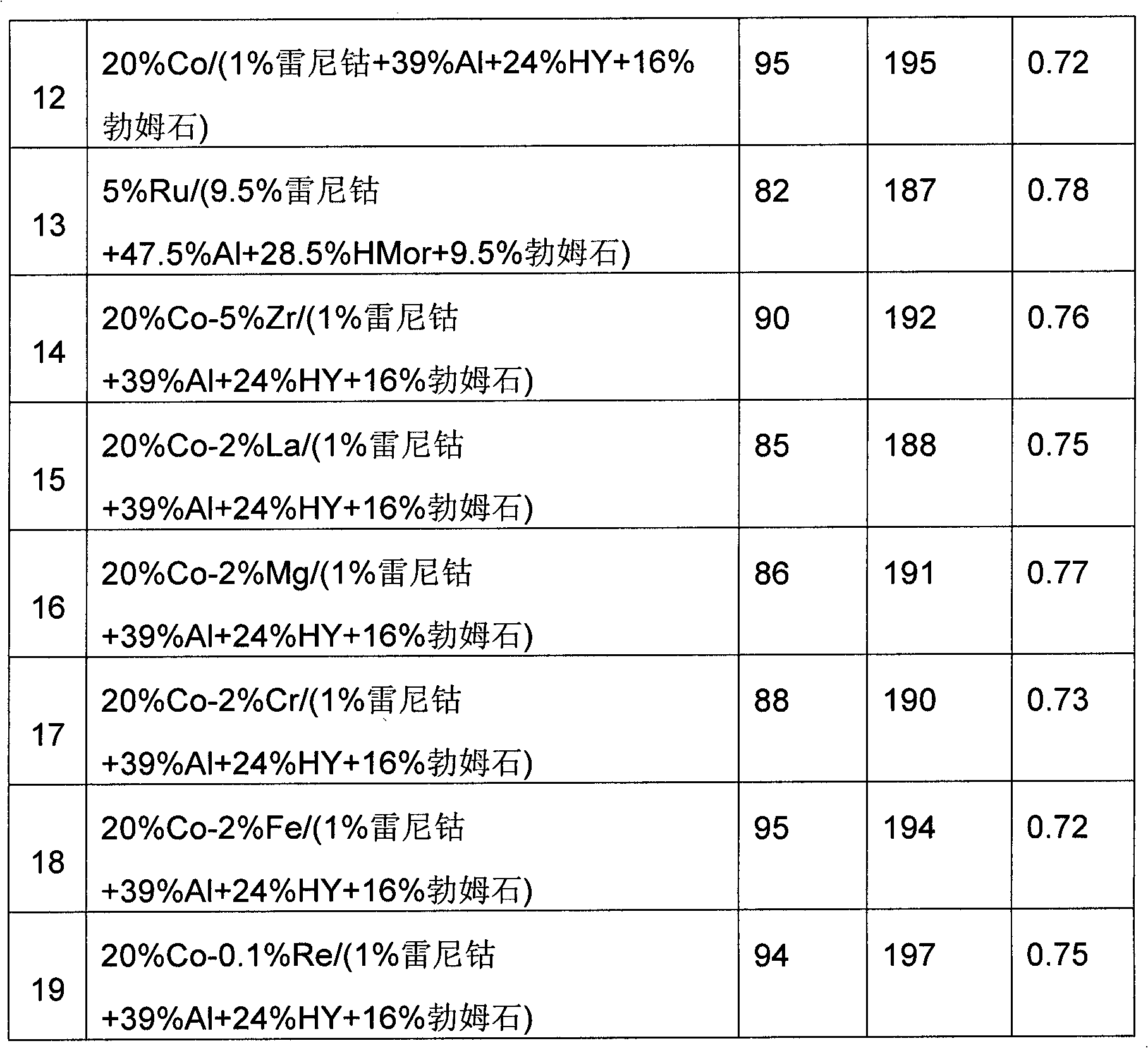
InactiveCN102711990AHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMolecular sieve catalystsActive componentCoal chemistry
The present invention relates to petrochemistry, gas chemistry, coal chemistry, particularly the invention relates to a catalyst for synthesis of hydrocarbons from CO and H2 and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst is pelletized and comprises at least Raney cobalt as active component in an amount of 1-40% by weight based on the total weight of the catalyst, metallic aluminium in an amount of 25-94% by weight based on the total weight of the catalyst and a binder in an amount of 5-30% by weight based on the total weight of the catalyst. The present invention provides the catalyst stability to overheating and high productivity of hydrocarbons C5-C100 for synthesis of hydrocarbons from CO and H2.
Owner:INFRA XTL TECH
Energy-saving blending diesel component agent
InactiveCN110835561AThe appearance is clear and brightNo smellLiquid carbonaceous fuelsOil and greaseSocial benefits
The invention relates to a multifunctional energy-saving component agent, which belongs to the field of vehicle diesel energy saving. The component agent can be used as an important component of a novel type of synthetic diesel, and is prepared by mixing transparent bright oil with various substances such as functional agents, wherein the transparent bright oil is obtained by subjecting a coal chemistry product that is low-naphthalene rectification wash oil as a mother liquid to deep modification. The component agent has a low production cost and good performance, can be mixed with diesel in any ratio, and is a good new component material for synthetic diesel oil. In addition to effects of saving energy and reducing the use cost of the vehicle, the component agent also has the functions ofsupporting combustion, clearing oil passages, preventing ice, increasing the cetane number, improving engine operating conditions, improving engine starting performance, purifying exhaust, and reducing emission of harmful gas. The component agent plays a positive role in saving the increasingly depleted petroleum resources and has good economic and social benefits.
Owner:王彤
Catalyst for synthesis of hydrocarbons from CO and H2 and preparation method thereof
InactiveUS8735317B2Molecular sieve catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationProduction rateActive component
The present invention relates to petrochemistry, gas chemistry, coal chemistry, particularly the invention relates to a catalyst for synthesis of hydrocarbons from CO and H2 and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst is pelletized and comprises at least Raney cobalt as active component in an amount of 1-40% by weight based on the total weight of the catalyst, metallic aluminium in an amount of 25-94% by weight based on the total weight of the catalyst and a binder in an amount of 5-30% by weight based on the total weight of the catalyst. The present invention provides the catalyst stability to overheating and high productivity of hydrocarbons C5-C100 for synthesis of hydrocarbons from CO and H2.
Owner:INFRA XTL TECH
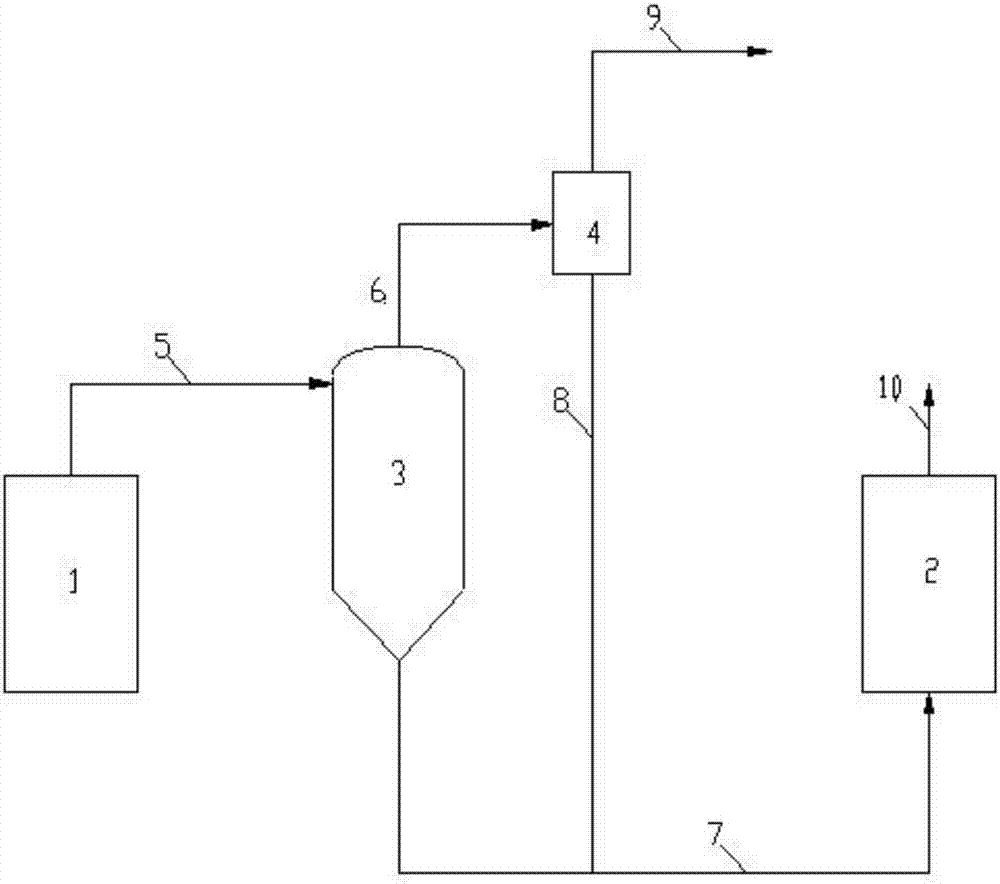
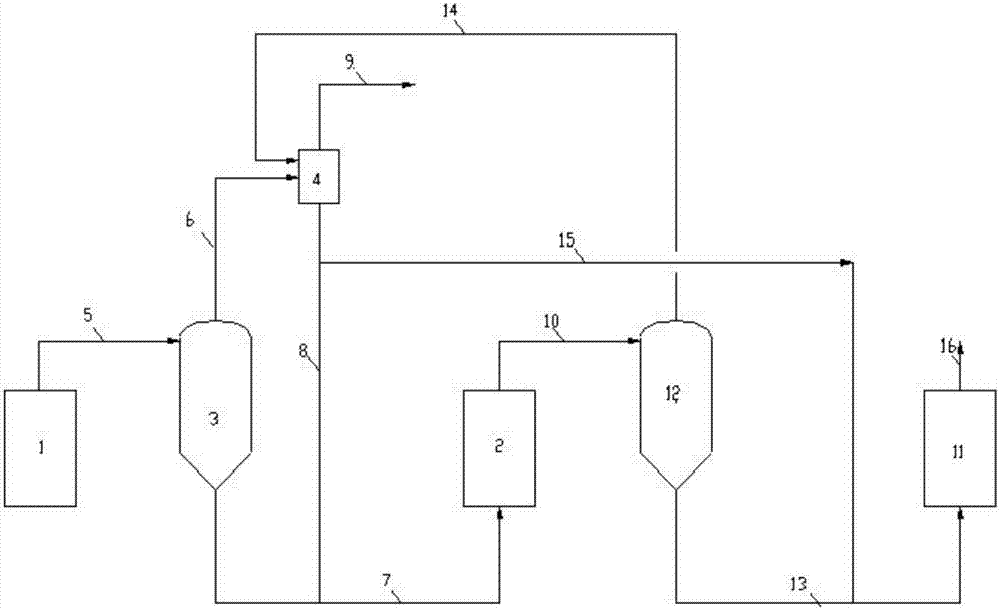
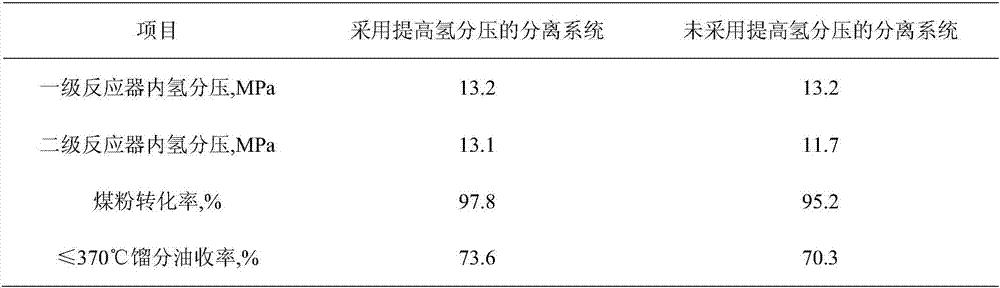
Method for increasing partial hydrogen pressure of hydrogenation reaction system, and design method and application thereof
InactiveCN106957681AImprove conversion rateHigh yieldTreatment with hydrotreatment processesGas phaseHydrogen pressure
The invention provides a method for increasing the partial hydrogen pressure of a hydrogenation reaction system, and a design method and an application thereof, which are used for increasing the partial hydrogen pressure of the hydrogenation reaction system and belong to the fields of petroleum chemistry and coal chemistry. The hydrogenation reaction system comprises at least two reactors. The method comprises the following steps that materials discharged from the former-stage reactor firstly enter a separating system for increasing the partial hydrogen pressure to conduct separation, then non-hydrogen components obtained are separated and discharged, and hydrogen components and liquid-solid phases enter the next-stage reactor. The materials from an outlet of the former-stage reactor are effectively separated by the separating system, the liquid-solid phase enters the next-stage reactor, and the gas phase is separated again, so that after the concentration of the hydrogen in the gas phase is increased, and the hydrogen enters the next-stage reactor. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the partial hydrogen pressure of the next-stage reactor can be increased, the reaction depth can be effectively increased, the material conversion ratio and the light-oil yield can be increased, the space speed of the next-stage reactor also can be increased and the energy consumption can be reduced.
Owner:CATECH TECH
Catalytic nitrogen carrier suitable for coal chemical looping ammonia production and preparation method thereof
PendingCN110711593AIncrease speedImprove conversion rateHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystAmmonia production
The invention discloses a catalytic nitrogen carrier suitable for a coal chemical-looping ammonia production process and a preparation method thereof; wherein the catalytic nitrogen carrier comprisesthe following components in percentage by mass: 20-30% of aluminum-based nitrogen carrier gamma-aluminum oxide, 3% of a nitrogen absorption reaction catalyst and 67-77% of a nitrogen release reactioncatalytic carrier titanium oxide. The catalytic nitrogen carrier can be prepared by a mechanical mixing method or an excessive impregnation method. The nitrogen absorption temperature of the catalyticnitrogen carrier is 800-1000 DEG C, the nitrogen release temperature is 1200-1500 DEG C, the nitrogen migration capacity is high, the cycling stability is good, the ammonia gas yield is high, and theconversion rate can reach 60% within 60-70 min.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Process for producing synthetic liquid hydrocarbons and reactor for fischer-tropsch synthesis
InactiveUS20120322898A1Organic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionLiquid productSyngas
The disclosure relates to petrochemistry, gas chemistry, coal chemistry, particularly to a synthesis of hydrocarbons C5 and higher from CO and H2 under the Fischer-Tropsch reaction; the invention relates to a process and a system for producing synthetic liquid hydrocarbons. A process for producing synthetic liquid hydrocarbons is provided by catalytic converting syngas under the Fischer-Tropsch reaction on a fixed catalyst bed in a vertical shell and tube reactor with coolant supply into shell wherein as soon as the syngas conversion degree achieves 60-80%, a pressure gradient along the tubes is reduced below 0.1 bar / m and this value is maintained during the whole process. A reactor for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis is provided comprising tubes with catalyst in a shell, the ratio of the tube diameter at the tube outlet to the diameter at the inlet is from 1.5 / 1 to 2.5 / 1. The invention gives a possibility to achieve the optimum temperature range in the catalyst bed; it improves heat and mass-transfer and shut out an accumulation of the liquid products in the bottom of the tubes.
Owner:INFRA XTL TECH
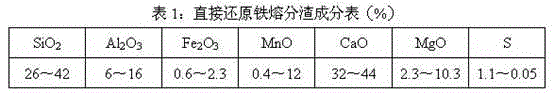
Method of using coal chemical industry waste water to treat directly-reduced iron melt separation slag to produce water-quenched slag
InactiveCN104928419AQuality improvementSolve the problem of more impurities in waste heat smelting direct reduced ironSlagProduced water
The invention discloses a method of using coal chemical industry waste water to treat directly-reduced iron melt separation slag to produce water-quenched slag. The method includes: feeding directly-reduced iron generated by a direct-reduction vertical furnace into a melt-separation electric furnace; obtaining melt separation slag through slag-iron separation; utilizing high-temperature sensible heat of the melt separation slag; using concentrated coal chemical industry waste water to perform water-quenching treatment on the melt separation slag to obtain the water-quenched slag serving as a raw material for cement production. By the method, impurity content of waste heat smelting directly-reduced iron is lowered, and purity of directly-reduced iron melt is improved; the coal chemical industry waste water is utilized for water-quenching treatment of the directly-reduced iron melt separation slag to generate the water-quenched slag used for producing cement, so that harmful waste water is changed into a useful resource, and near-zero emission and waste heat utilization of industrial production waste water of coal chemistry industry, metallurgy and power generation.
Owner:苏亚杰
Catalyst for Synthesizing Hydrocarbons C5-C100 and Method of Preparation Thereof
InactiveUS20090005242A1High catalytic activityHigh selectivityCatalyst activation/preparationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionAluminium hydroxidePetroleum
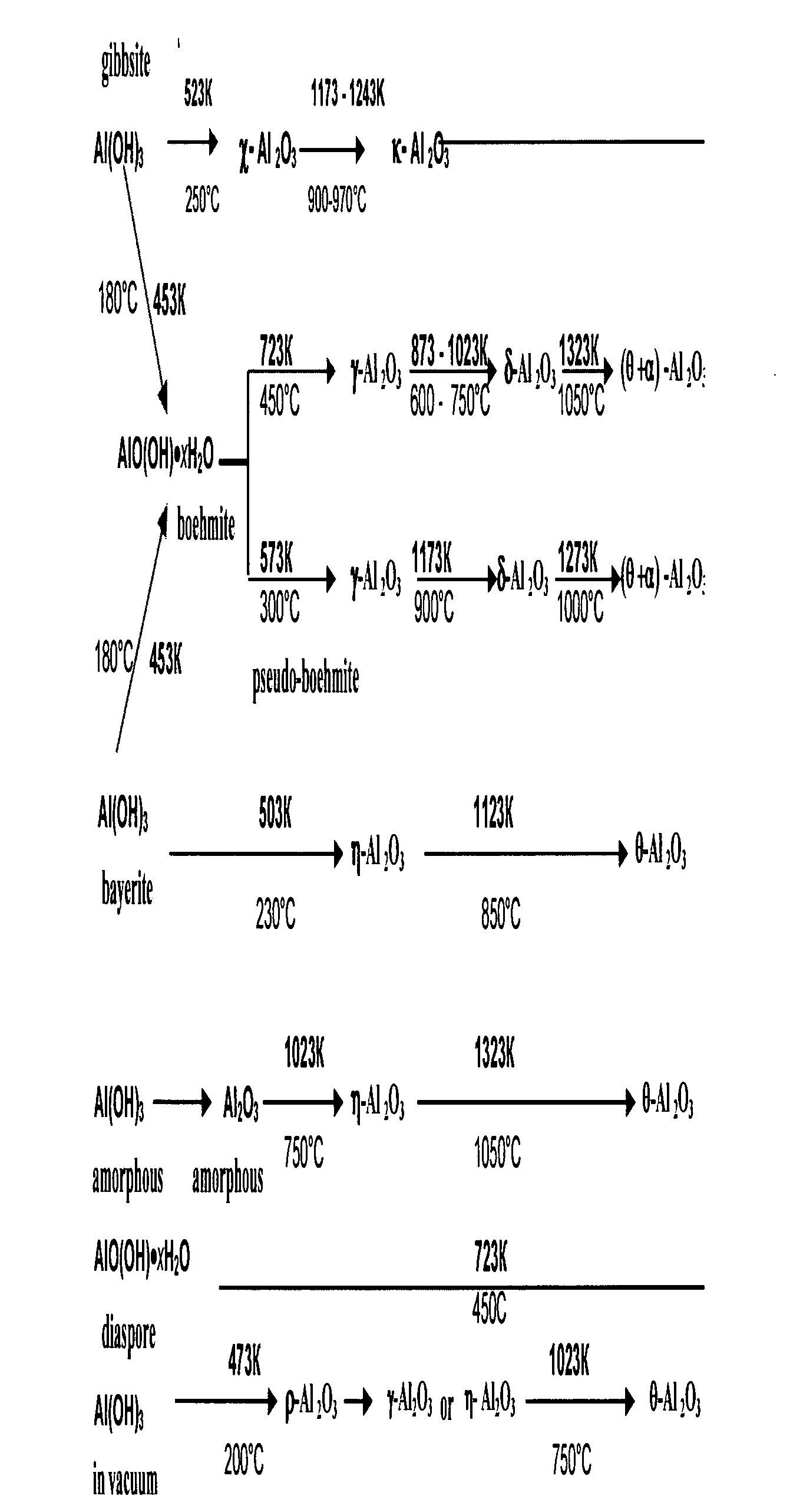
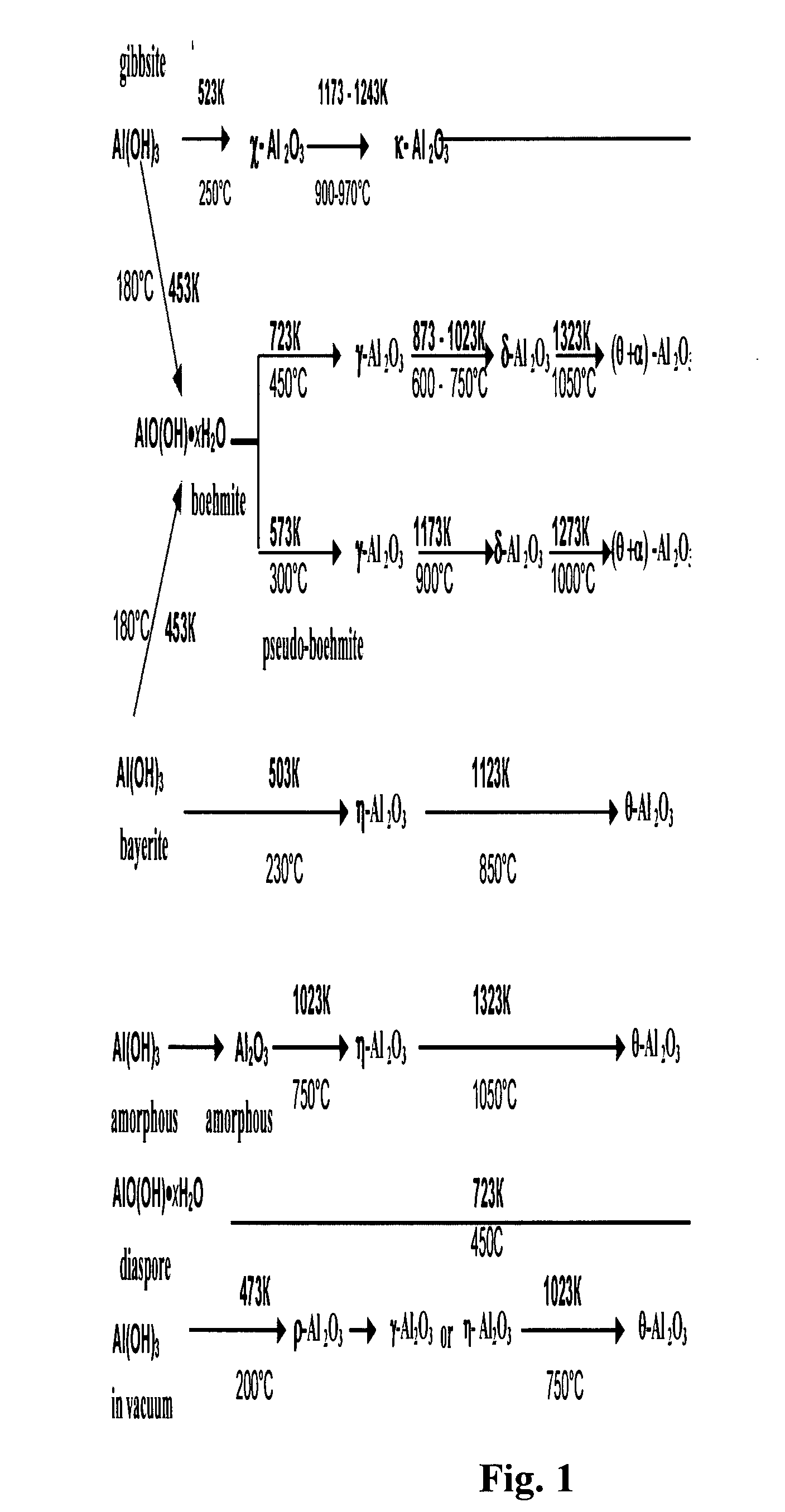
The invention relates to petroleum, gas, and coal chemistry, especially to catalysts for C5-C100 hydrocarbons synthesis in particular from CO and H2 and a method for producing such catalyst. The proposed catalyst comprises an aluminum-oxide-based support obtainable from a gibbsite structure of aluminum hydroxide and cobalt, which content ranges from 15 to 50 wt %. The method comprises preparation of an alumina based support by mixing cobalt compounds with aluminum hydroxide and calcination, wherein the aluminum hydroxide having a structure of gibbsite, the mixing provided in the dry form with a mole ratio of cobalt and aluminum in the range of from 1:1 to 1:30; impregnation of the support in two or more stages with a water solution of cobalt salt; and thermal treatment. Embodiments include providing the thermal treatment by drying and / or calcination, additional introduction of substances-promoters into the support through impregnation with salts solution of the promoters.
Owner:SYNTOP
Method and apparatus for continuously preparing foam carbon material from coal
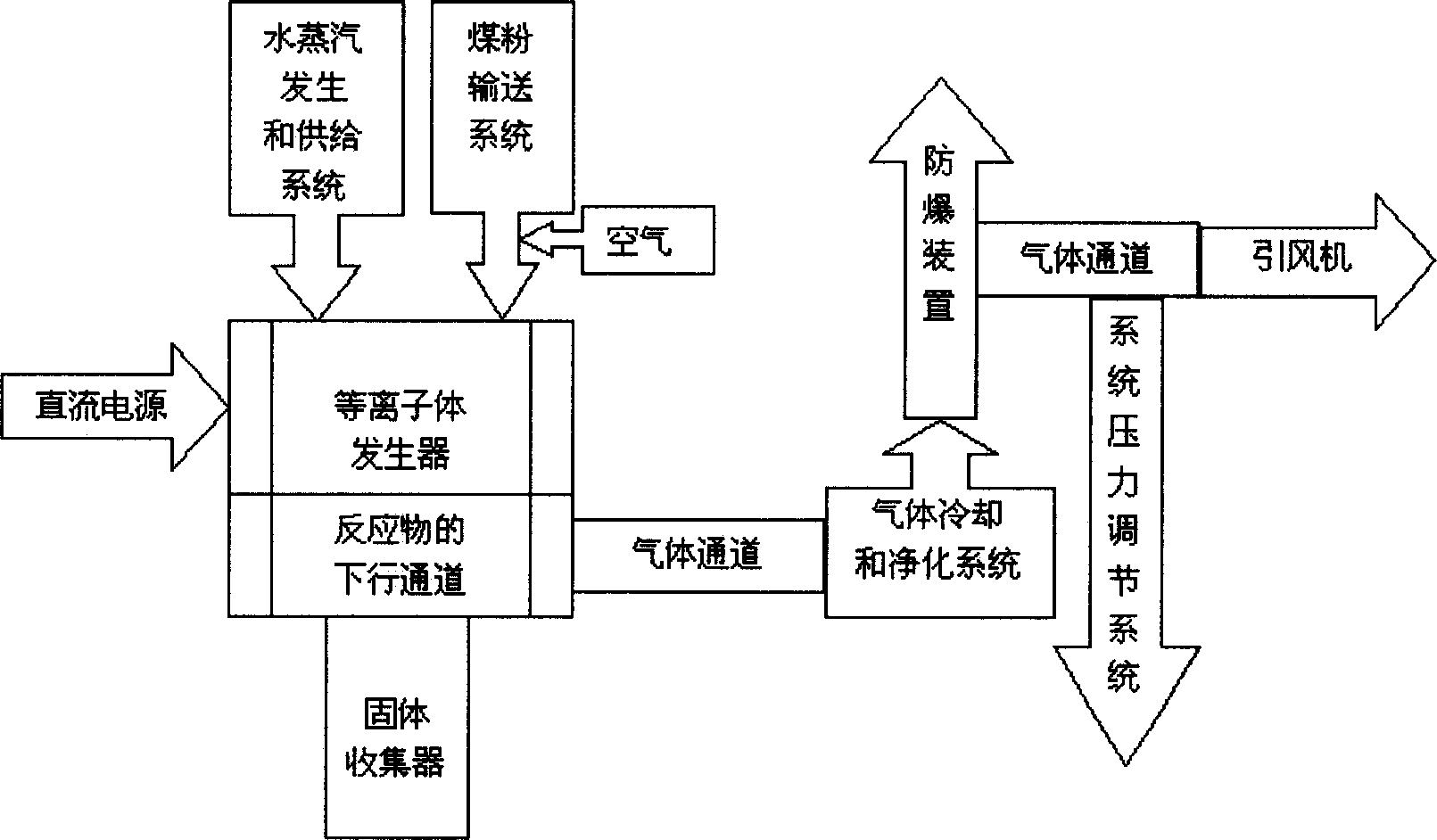
InactiveCN1528861AHigh degree of graphitizationIncrease profitIndirect heating destructive distillationChemical reactionExplosion protection
The invention belongs to a cross technology field of coal chemistry, chemical reaction project, plasma science and charcoal material science. It refers to a method and device for using coal and water steam as materials to produce foam charcoal material continuously. The method sprays powder coal and high temperature steam into direct current arc plasma and produce foam charcoal material continuously, the mixing, foaming, synthesizing charring and graphitizing are all completed in one step. The device is made up of steam generating and supplying system, coal powder transmitting system, plasma generator, solid collector, gas cooling and purifying system, explosion protection device, system pressure adjusting system and draught fan. The invention can be operated conveniently; it can be controlled, and can be operated continuously with low cost.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Solvent lignin-modified epoxy resin curing agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102134305BRetain chemical activityHigh purityEpoxy resin coatingsPtru catalystMannich reaction
The invention provides a solvent lignin-modified epoxy resin curing agent and a preparation method thereof. The epoxy resin curing agent is prepared from the following raw materials in part by weight: 10 to 30 parts of solvent lignin or derivative of the solvent lignin, 30 to 60 parts of phenol, 15 to 35 part of aldehyde, 20 to 45 part of ammine and 0.05 to 0.2 part of sulfuric acid catalyst. Thephenol-aldehyde-ammine epoxy resin curing agent is prepared by the Mannickreaction of the solvent lignin or derivative of the solvent lignin and the phenol, aldehyde and ammine. When the solvent lignin-modified phenol-aldehyde-ammine epoxy resin curing agent provided by the invention is used, petrochemical and coal chemical products can be replaced, the consumption of the petrochemical and coal chemical products is reduced, the cost of the epoxy resin is reduced, the lignin renewable resource in the waste from biorefinery is fully utilized, and the development of low-carbon economy is promoted.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
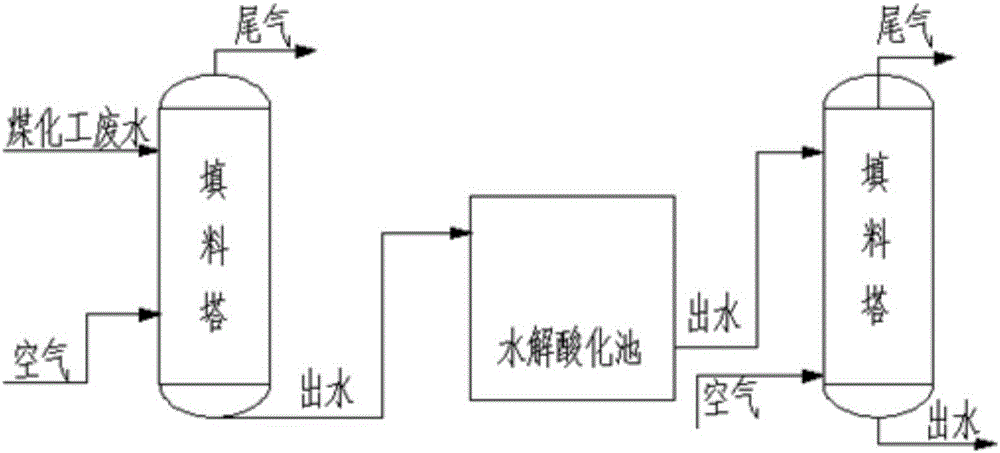
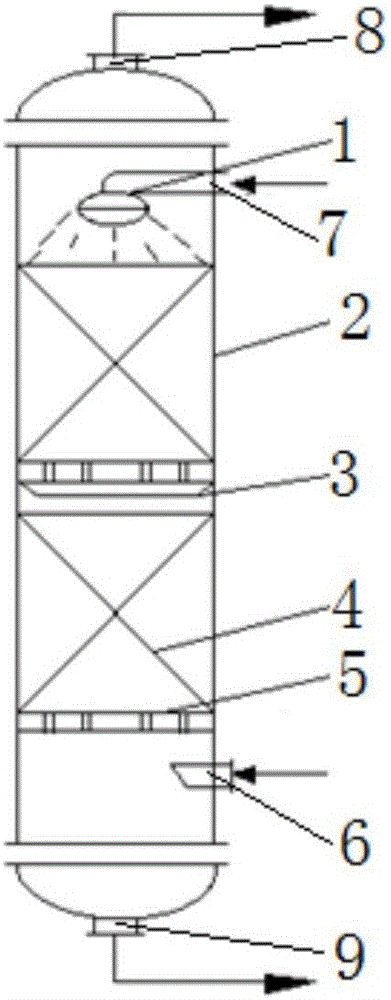
Coal chemical industry wastewater pretreatment method with combination of hydrolytic acidification and ammonia-nitrogen desorption
ActiveCN105906158AImprove biodegradabilityEnhance biological denitrification performanceWaste water treatment from quariesWater contaminantsPretreatment methodDesorption
The invention relates to a coal chemical industry wastewater pretreatment method with the combination of hydrolytic acidification and ammonia-nitrogen desorption. The coal chemical industry wastewater pretreatment method specifically comprises the following steps of 1, first-level ammonia-nitrogen desorption, wherein air is introduced into coal chemical industry wastewater with the high ammonia nitrogen concentration, normal-temperature aeration desorption is performed and stopped till the ammonia nitrogen concentration in the coal chemical industry wastewater is smaller than 300 mg / L; 2, hydrolytic acidification, wherein the coal chemistry wastewater treated after ammonia-nitrogen desorption is subjected to hydrolytic acidification, so that the B / C is improved to 0.3 or more; 3, second-level ammonia-nitrogen desorption, wherein air is introduced into outlet water obtained after hydrolytic acidification again, normal-temperature aeration desorption is performed, and the ammonia-nitrogen concentration generated in wastewater through hydrolytic acidification is decreased, so that the C / N is improved to 4.0-5.0, and the ammonia nitrogen density is smaller than 80-100 mg / L. Compared with the prior art, the coal chemical industry wastewater pretreatment method has the advantages that the wastewater biodegradability can be remarkably improved, the total nitrogen removal rate can reach 60-65%, and the C / N is improved to about 4.0-5.0 so as to reinforce the follow-up biological denitrification effect.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
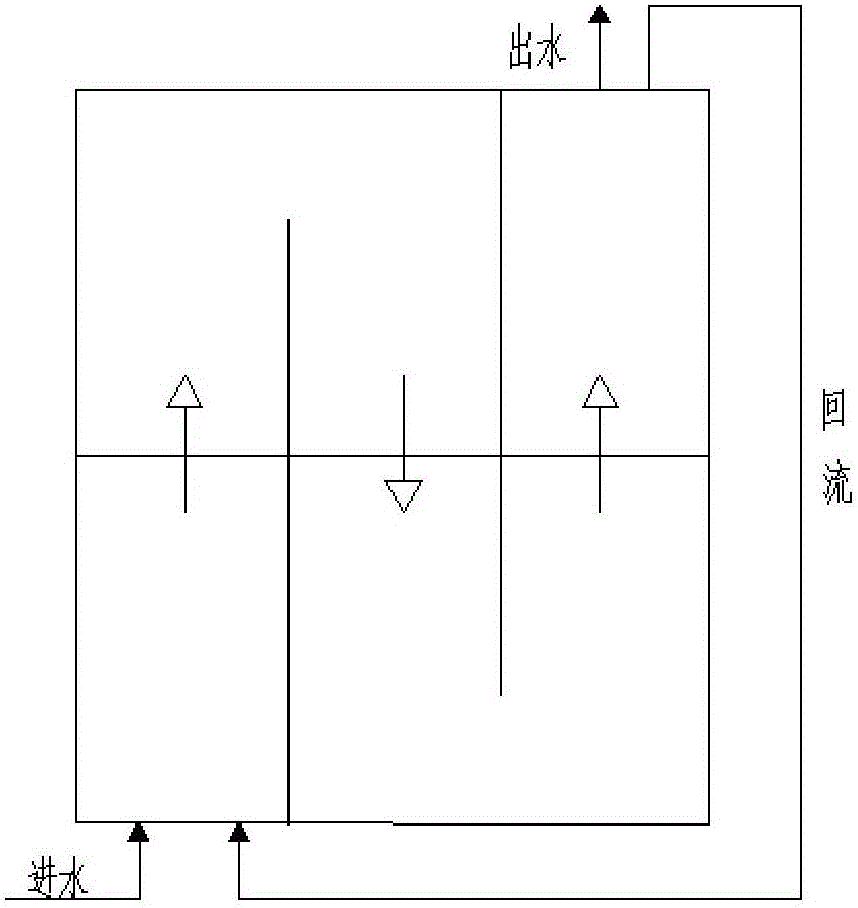
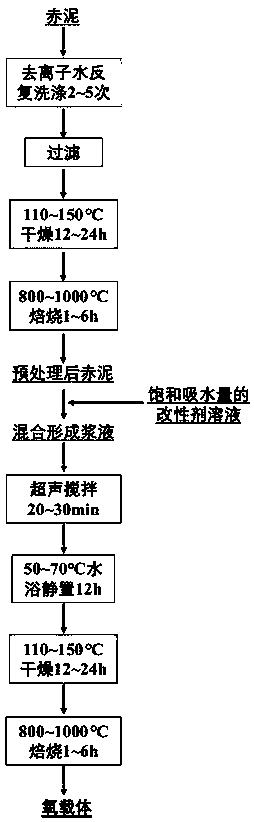
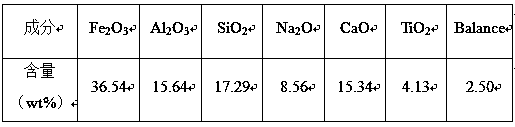
Method for preparing oxygen carrier of fuel coal chemical-looping combustion by using equal volume impregnation process
The invention relates to a method for preparing an oxygen carrier of fuel coal chemical-looping combustion by using an equal volume impregnation process, and belongs to the technical field of energy environment. The method comprises the following steps: repeatedly washing red mud until the pH is 7, performing drying at 110-150 DEG C for 12-24 h, performing roasting at 800-1000 DEG C for 2-6 h, after roasting is completed, performing grinding to form red mud powder, taking a small amount of the red mud powder, and measuring a saturation water absorption amount of the red mud; adding water intoa carrier, an auxiliary agent and an active ingredient to prepare a solution, wherein the volume of the solution is a volume corresponding to the saturation water absorption amount of the added red mud, slowly adding the red mud powder in the step 1 dropwise into the solution to form slurry, performing ultrasonic stirring for 20-30 min, placing the stirred material in a constant-temperature waterbath at 50-70 DEG C for 12 h, performing drying at 110-150 DEG C for 12-24 h, and performing conventional molding to obtain a molded mixture; and roasting the molded mixture at 800-1000 DEG C for 2-6h to obtain the oxygen carrier of the fuel coal chemical-looping combustion. According to the method, a modifier can be in full contact with the red mud base to form the material having fine particles, more internal pores and a large specific surface area, and the carrier has better reactivity with coal.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Process for producing synthetic liquid hydrocarbons and reactor for fischer-tropsch synthesis
InactiveCN102741379ALiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionChemical/physical processesLiquid productPetroleum
The present invention relates to petrochemistry, gas chemistry, coal chemistry, particularly to a synthesis of hydrocarbons C5 and higher from CO and H2 under the Fischer- Tropsch reaction; the invention relates to a process and a system for producing synthetic liquid hydrocarbons. A process for producing synthetic liquid hydrocarbons is provided by catalytic converting syngas under the Fischer-Tropsch reaction on a fixed catalyst bed in a vertical shell and tube reactor with coolant supply into shell wherein as soon as the syngas conversion degree achieves 60-80%, a pressure gradient along the tubes is reduced below 0.1 bar / m and this value is maintained during the whole process. A reactor for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis is provided comprising tubes with catalyst in a shell, the ratio of the tube diameter at the tube outlet to the diameter at the inlet is from 1.5 / 1 to 2.5 / 1. The invention gives a possibility to achieve the optimum temperature range in the catalyst bed; and it improves heat and mass-transfer and shut out an accumulation of the liquid products in the bottom of the tubes.
Owner:INFRA XTL TECH
Novel nozzle rotational flow structure and nozzle structure
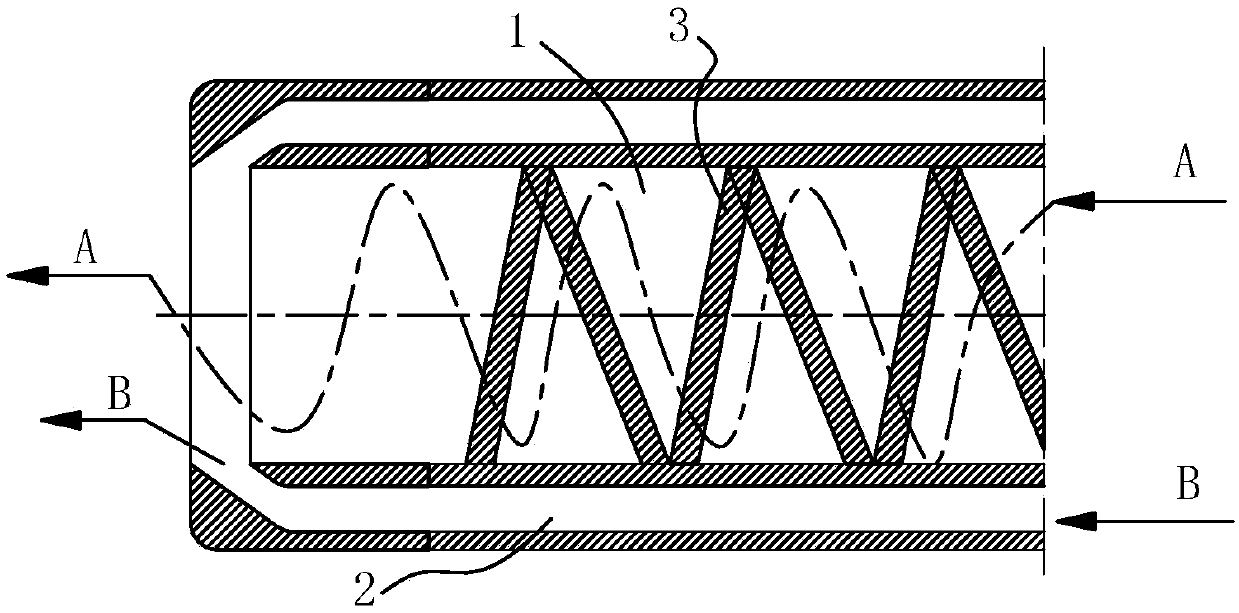
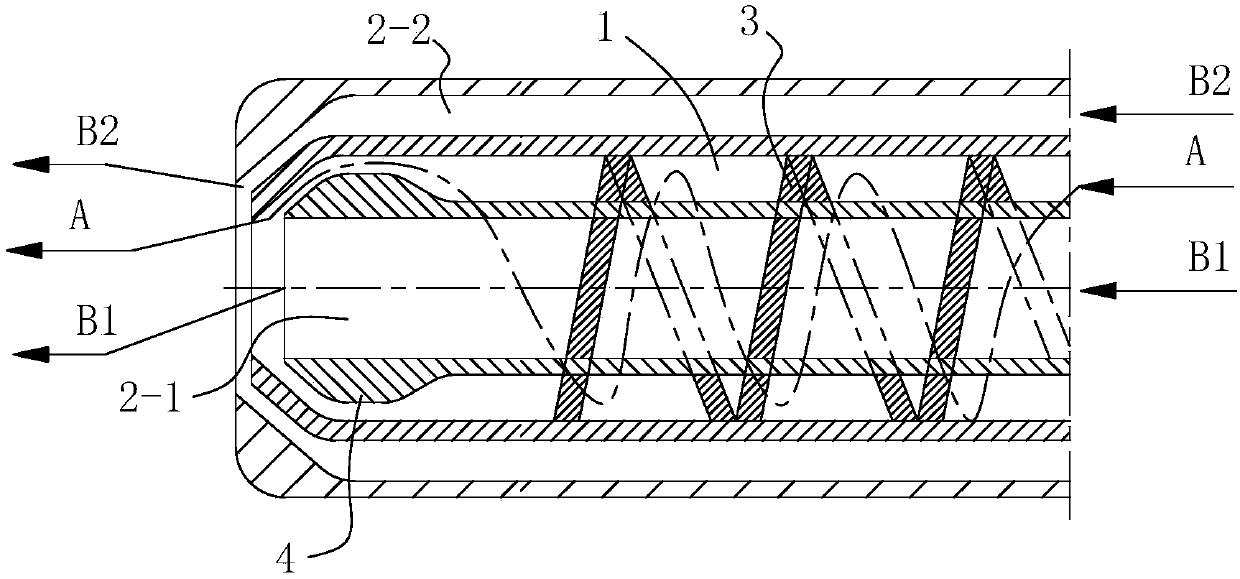
InactiveCN107723029AImprove atomization effectMeet the process requirementsGasification processes detailsGasification apparatus detailsEconomic benefitsCoal chemical industry
The invention discloses a novel nozzle rotational flow structure and a nozzle structure. The novel nozzle rotational flow structure is characterized in that a spiral baffle plate which is capable of enabling combustible medium to rotationally flow is arranged on the inner wall of a combustible medium passage formed in a nozzle, and the spiral baffle plate is an anti-wear and anti-corrosion spiralstripped plate; the spiral baffle plate stretches towards a direction of a spray head of the nozzle. Compared with a direct flow impact type structure in the prior art, a spiral linear structure of the invention has the advantages that the atomization effect is better, the technological requirements of various coal chemistry industry technologies can be met, and the economic benefit of a coal chemical industry enterprise is effectively increased.
Owner:陕西宏远流体控制设备有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com