Patents
Literature
99 results about "Atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
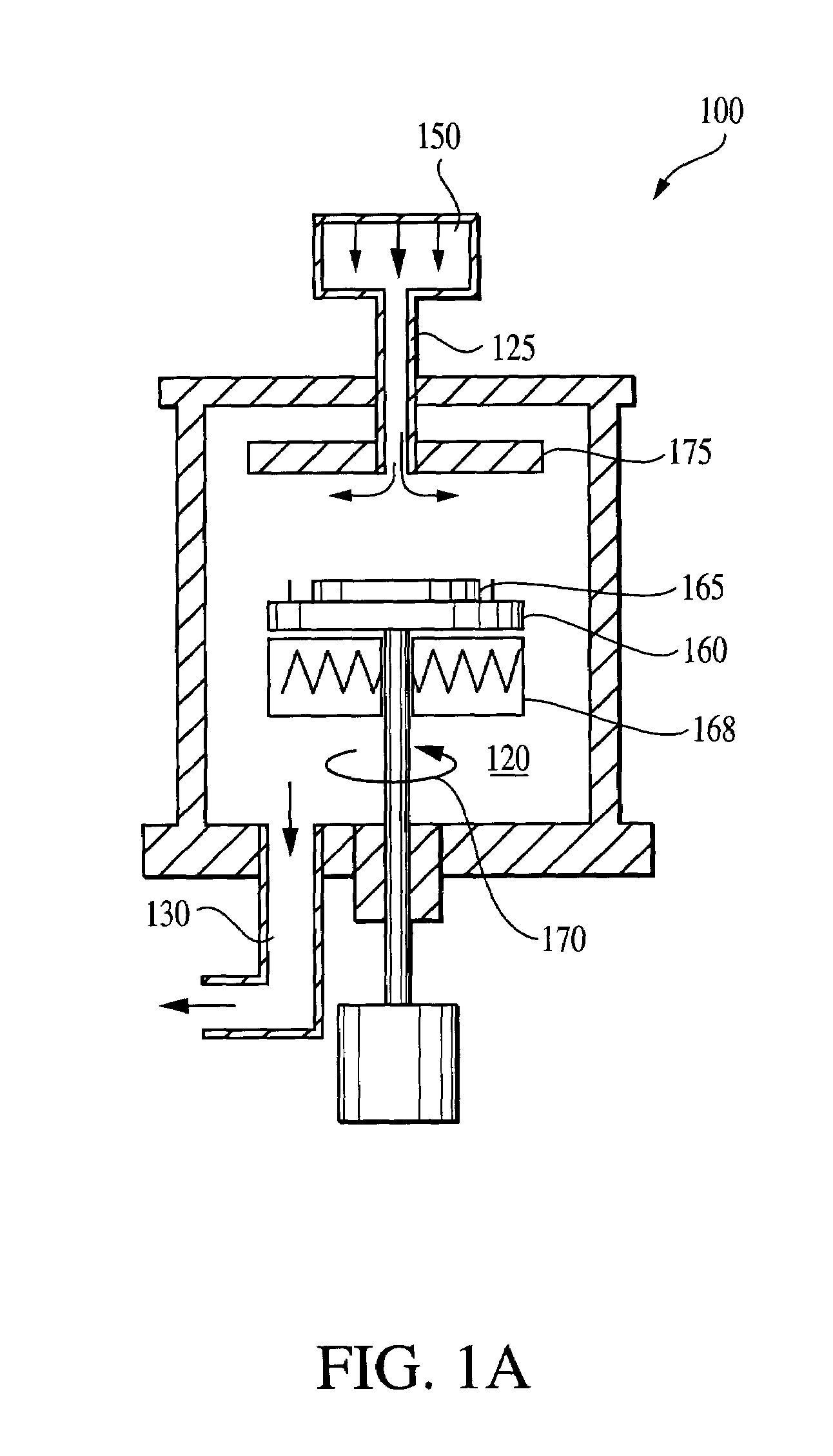
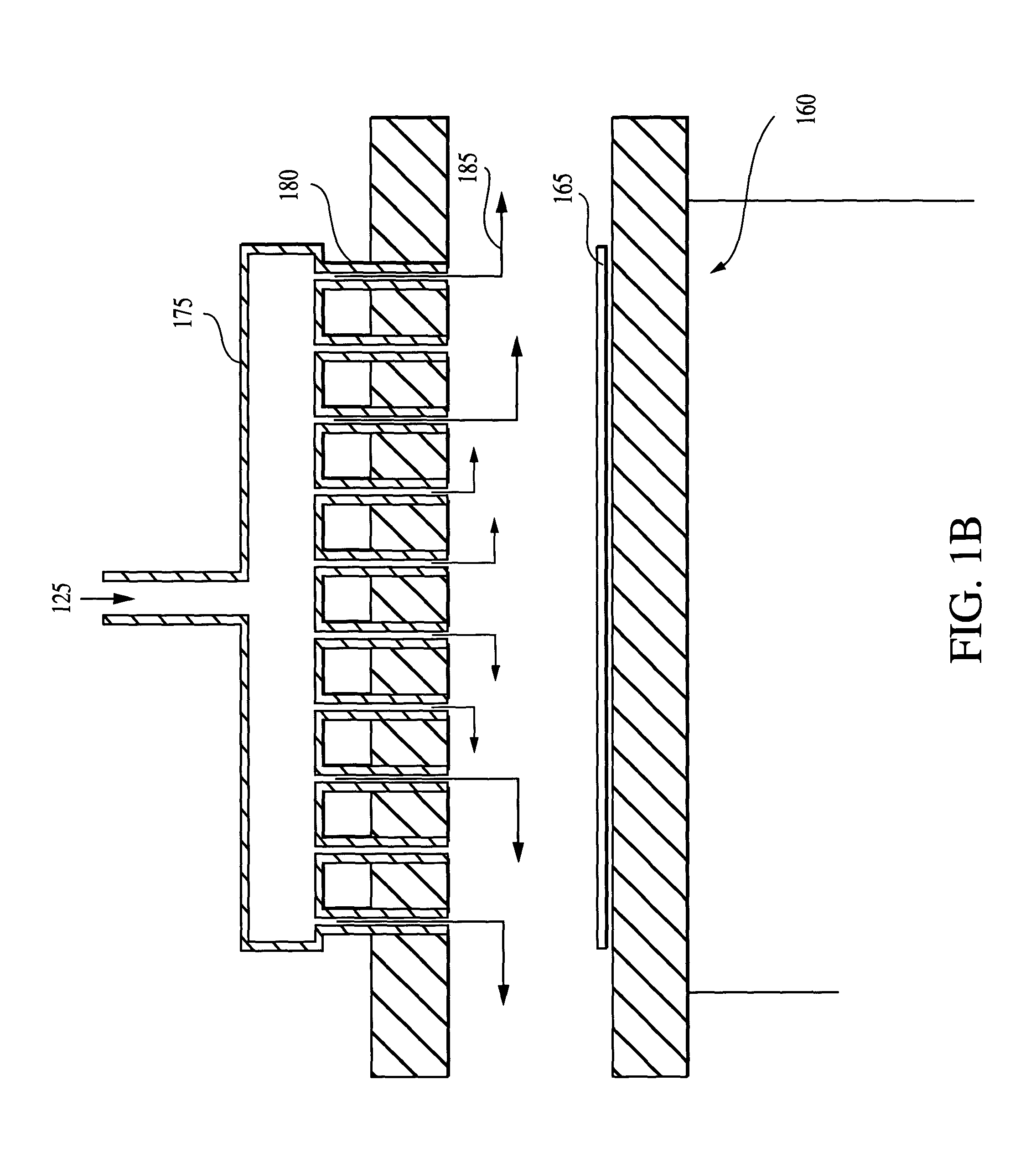
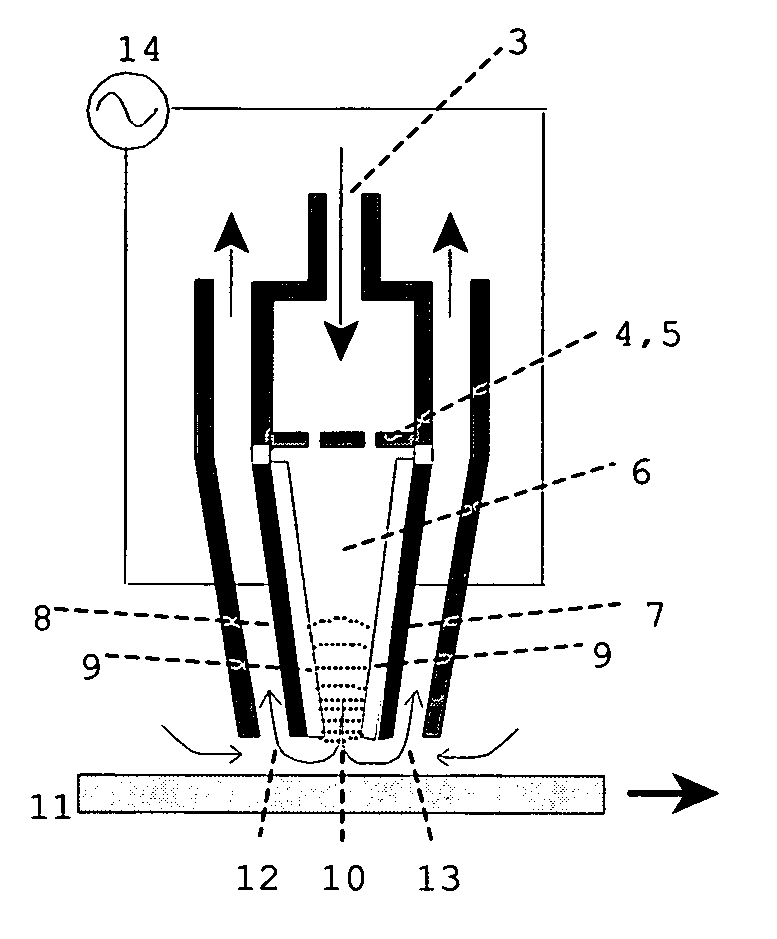
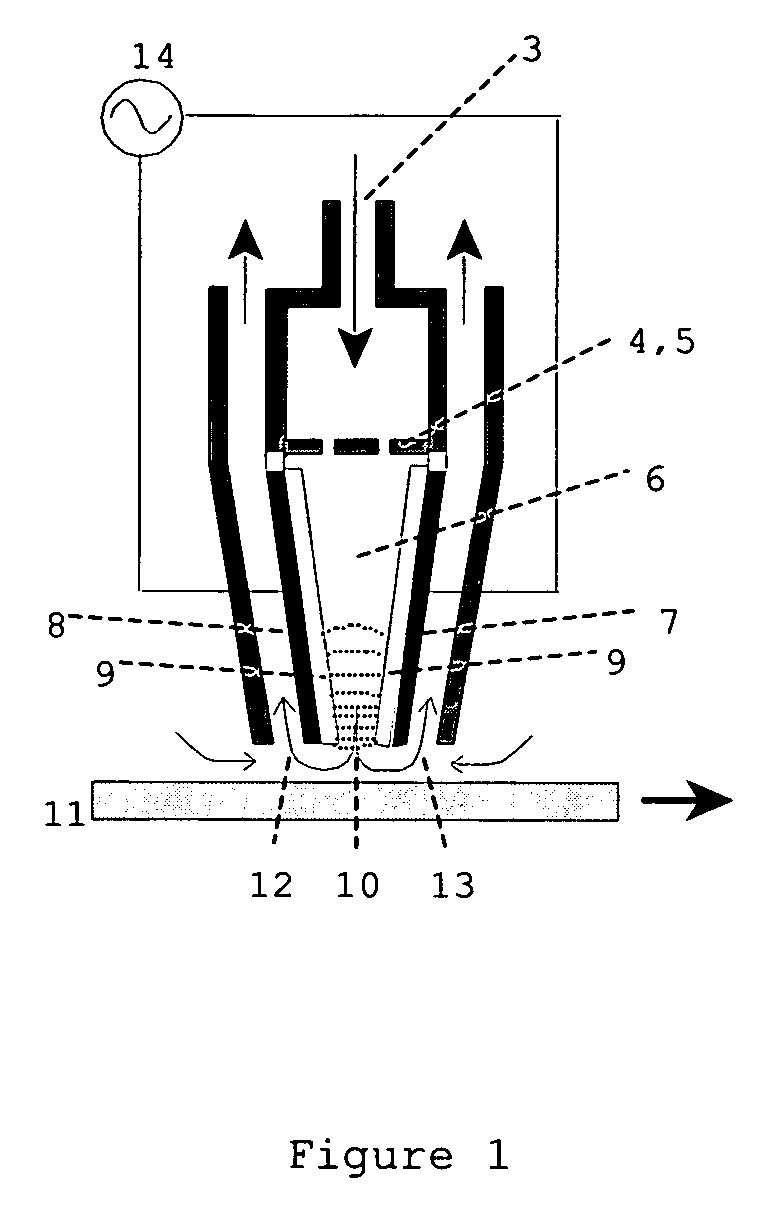
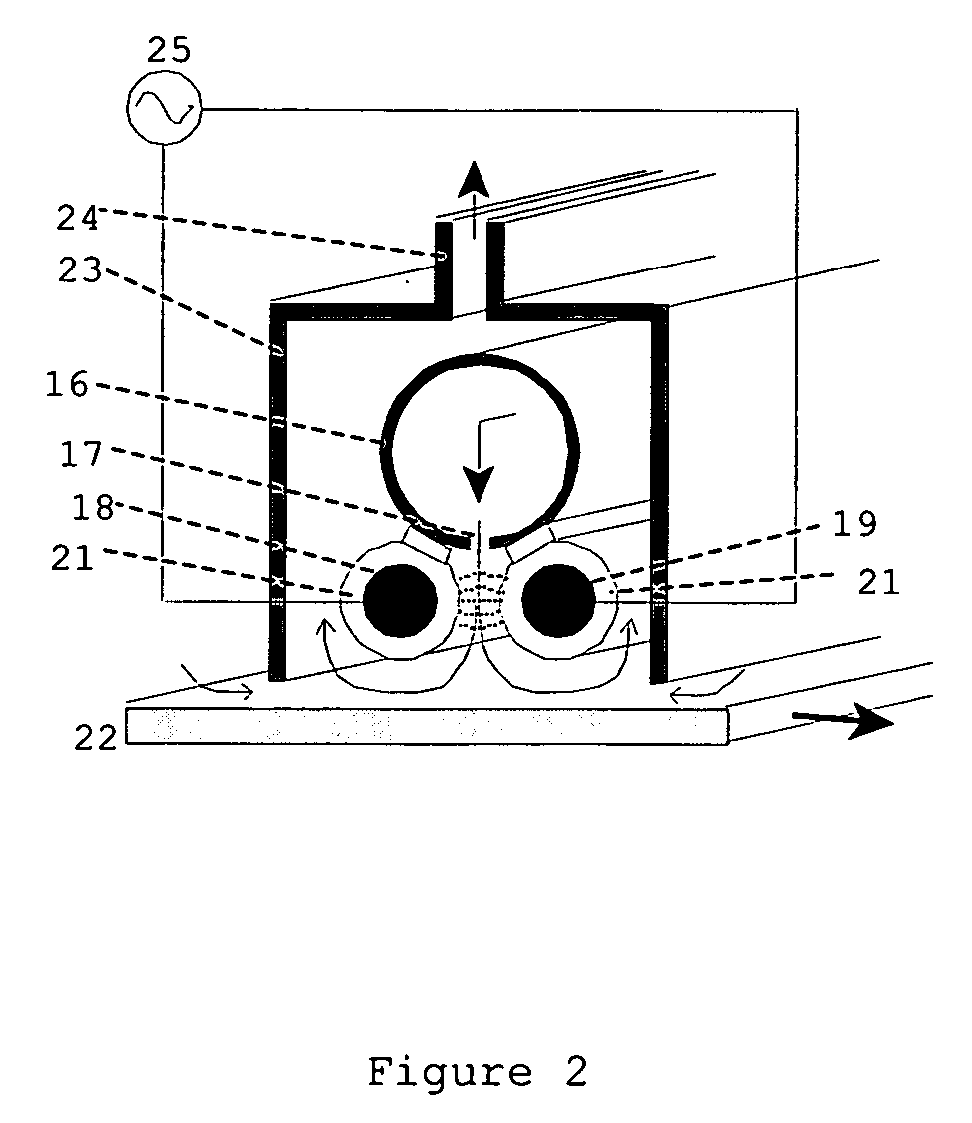
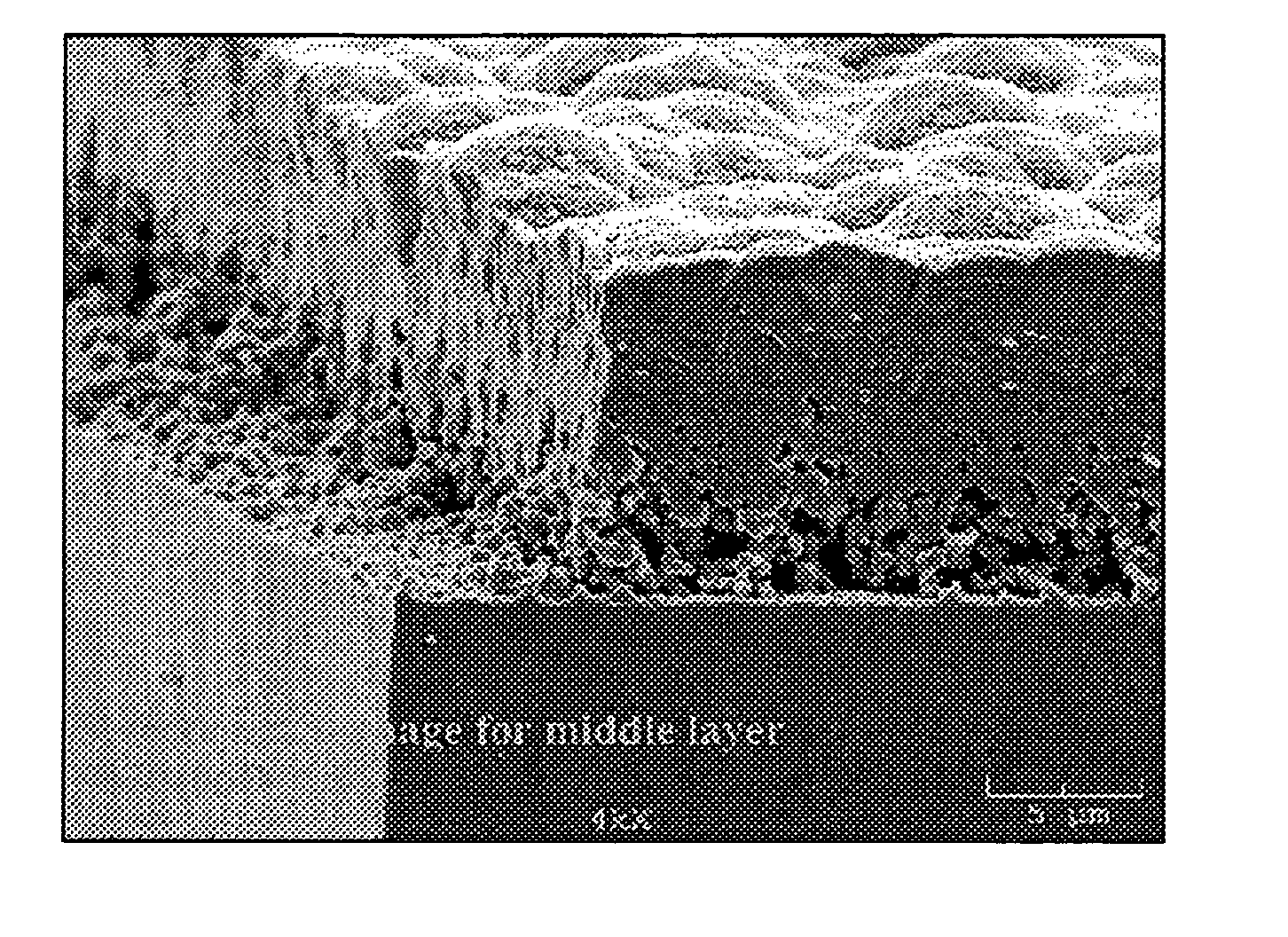
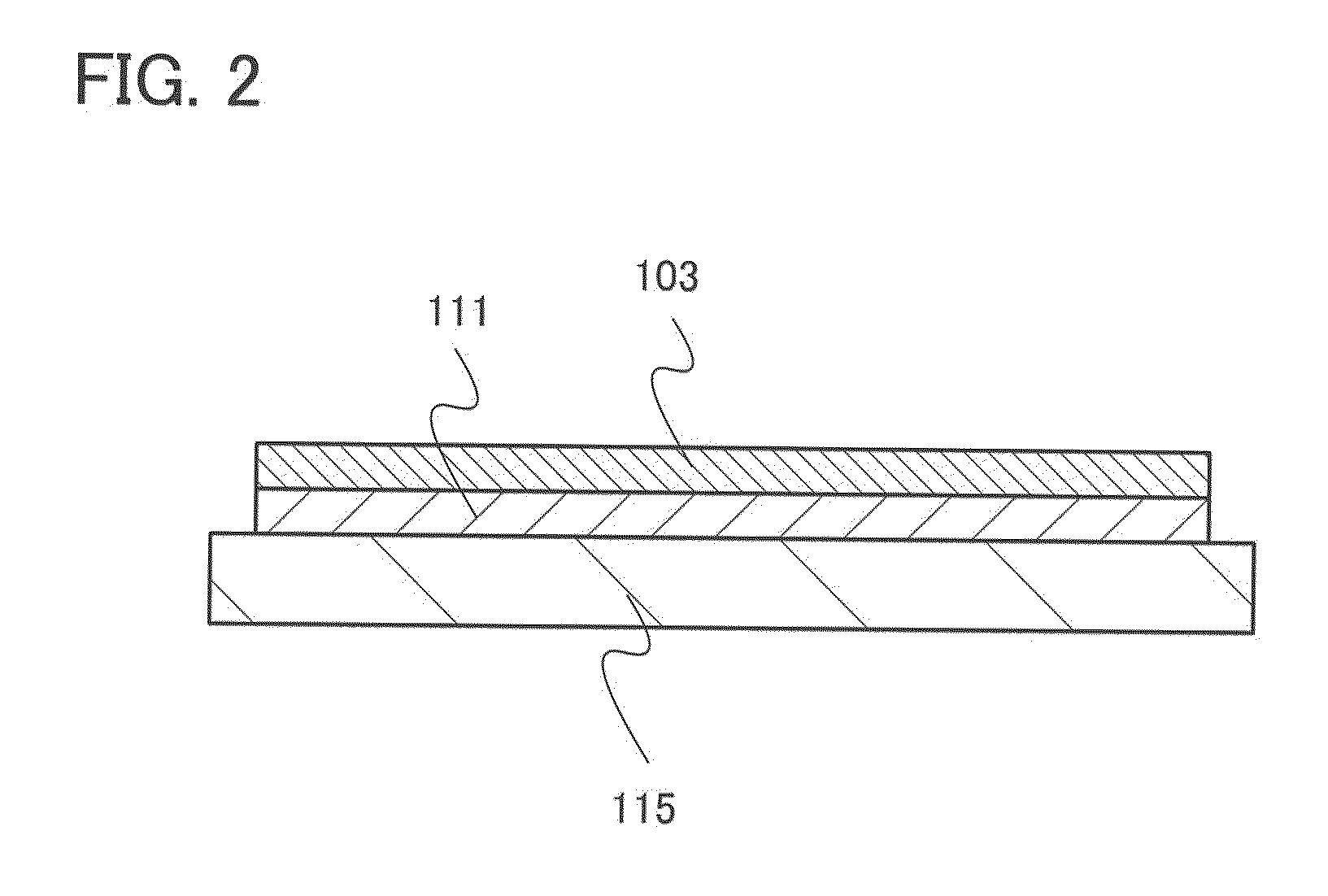
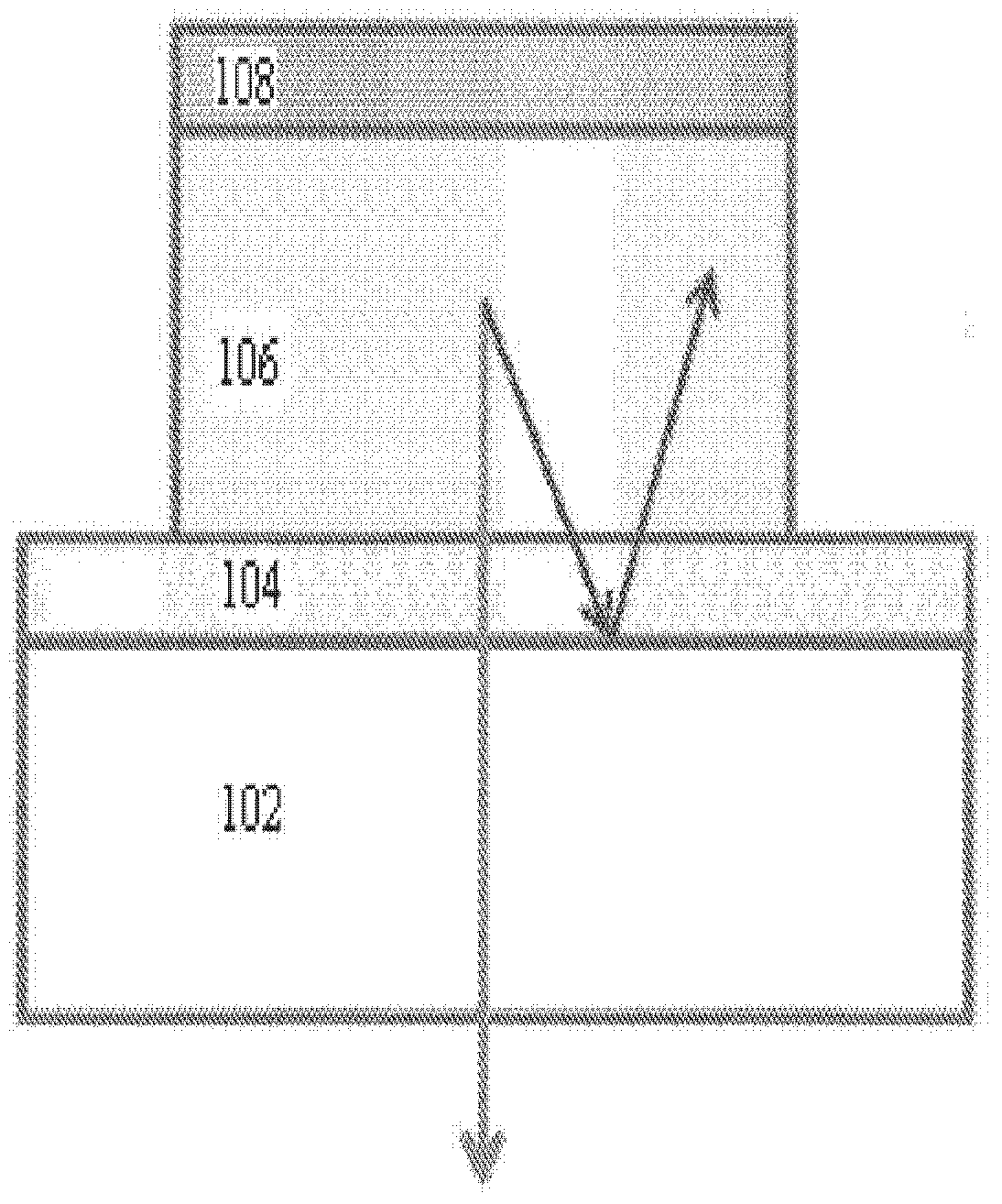
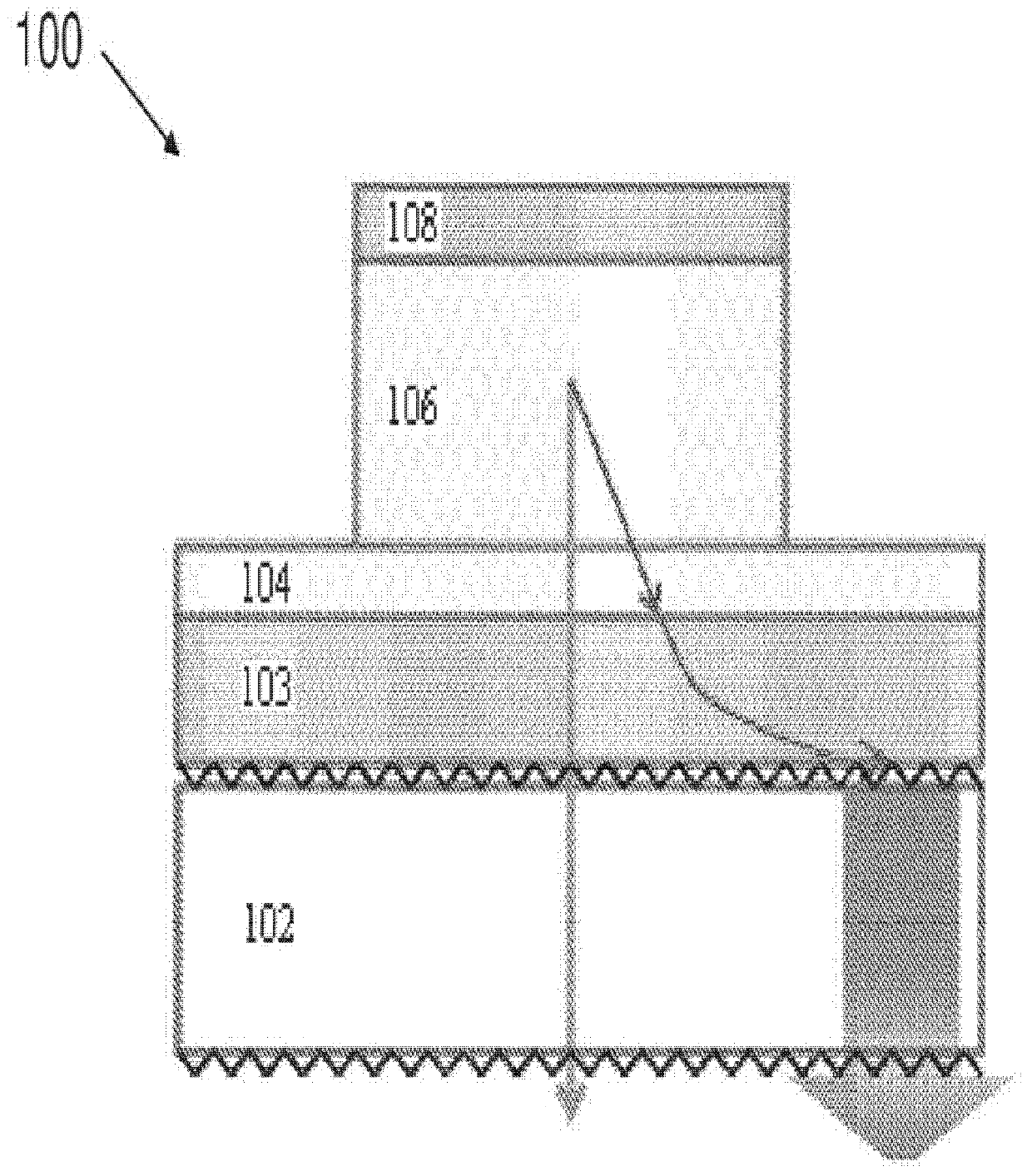
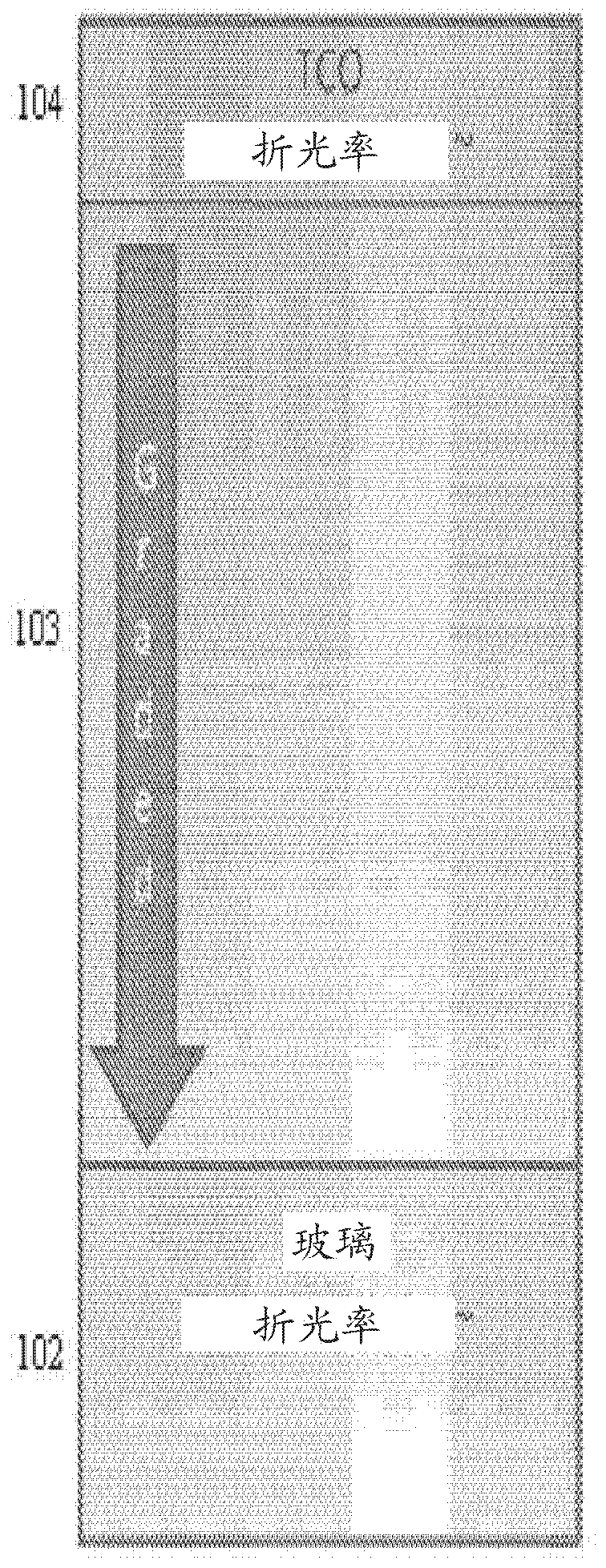
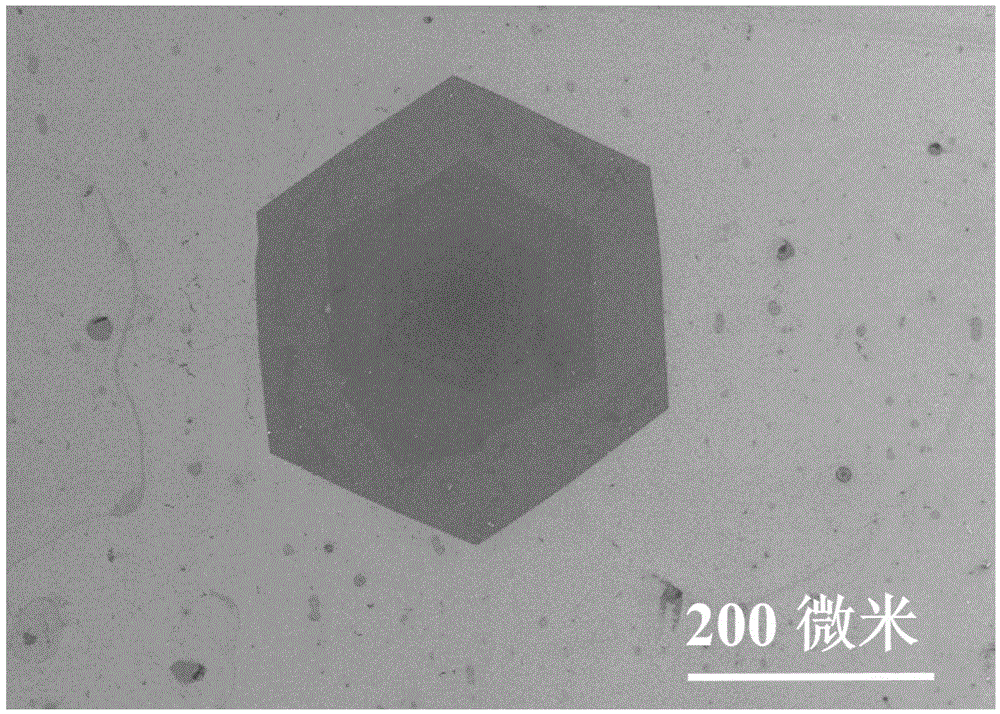
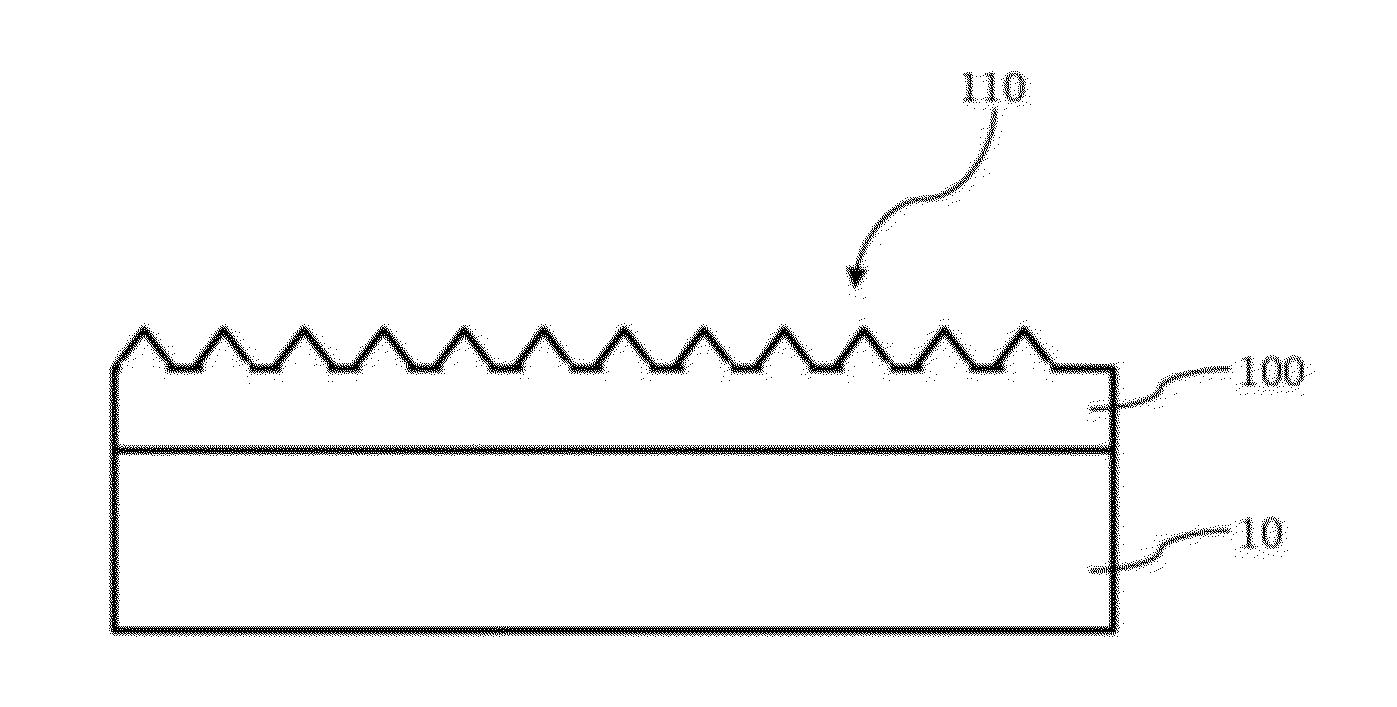
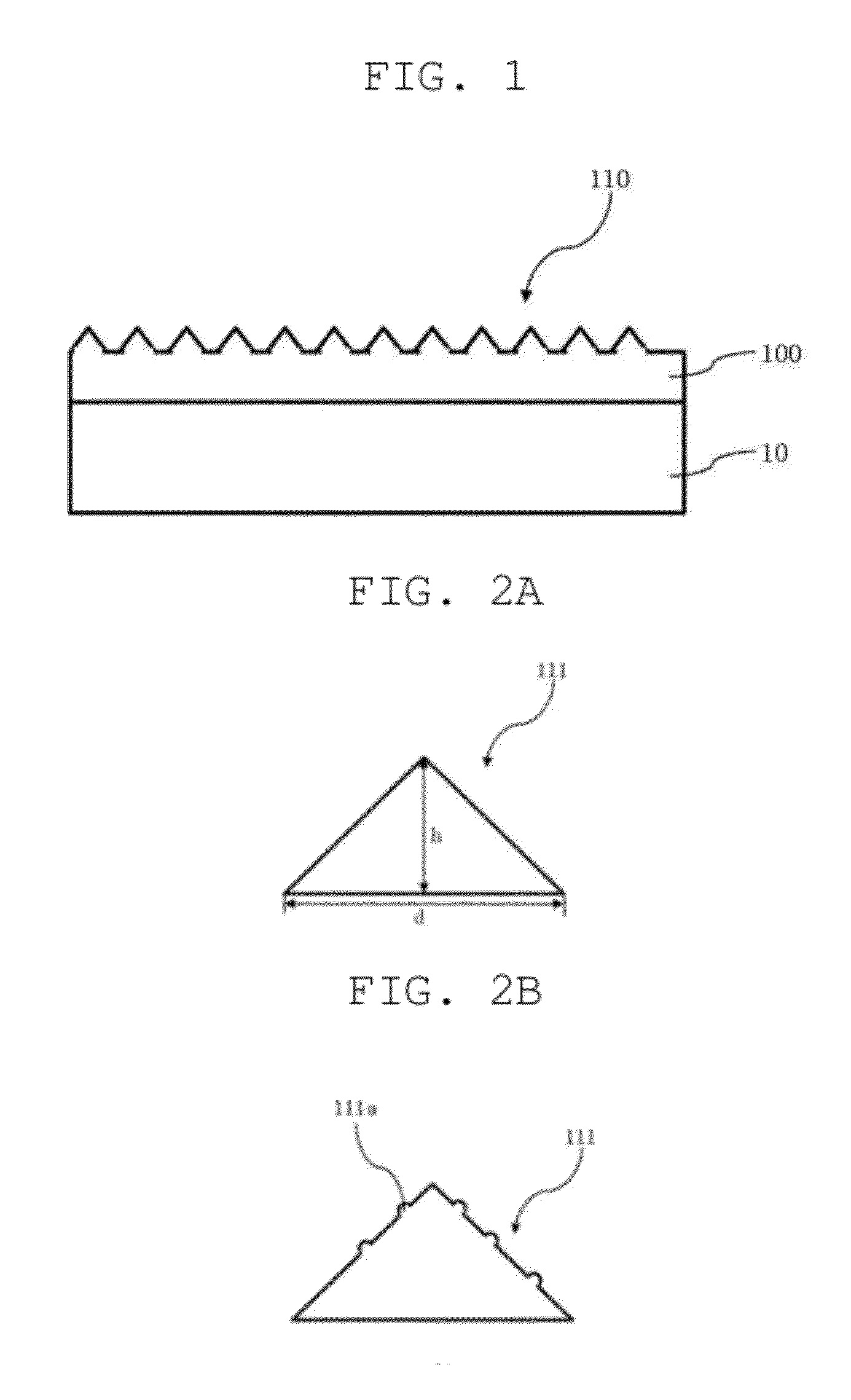
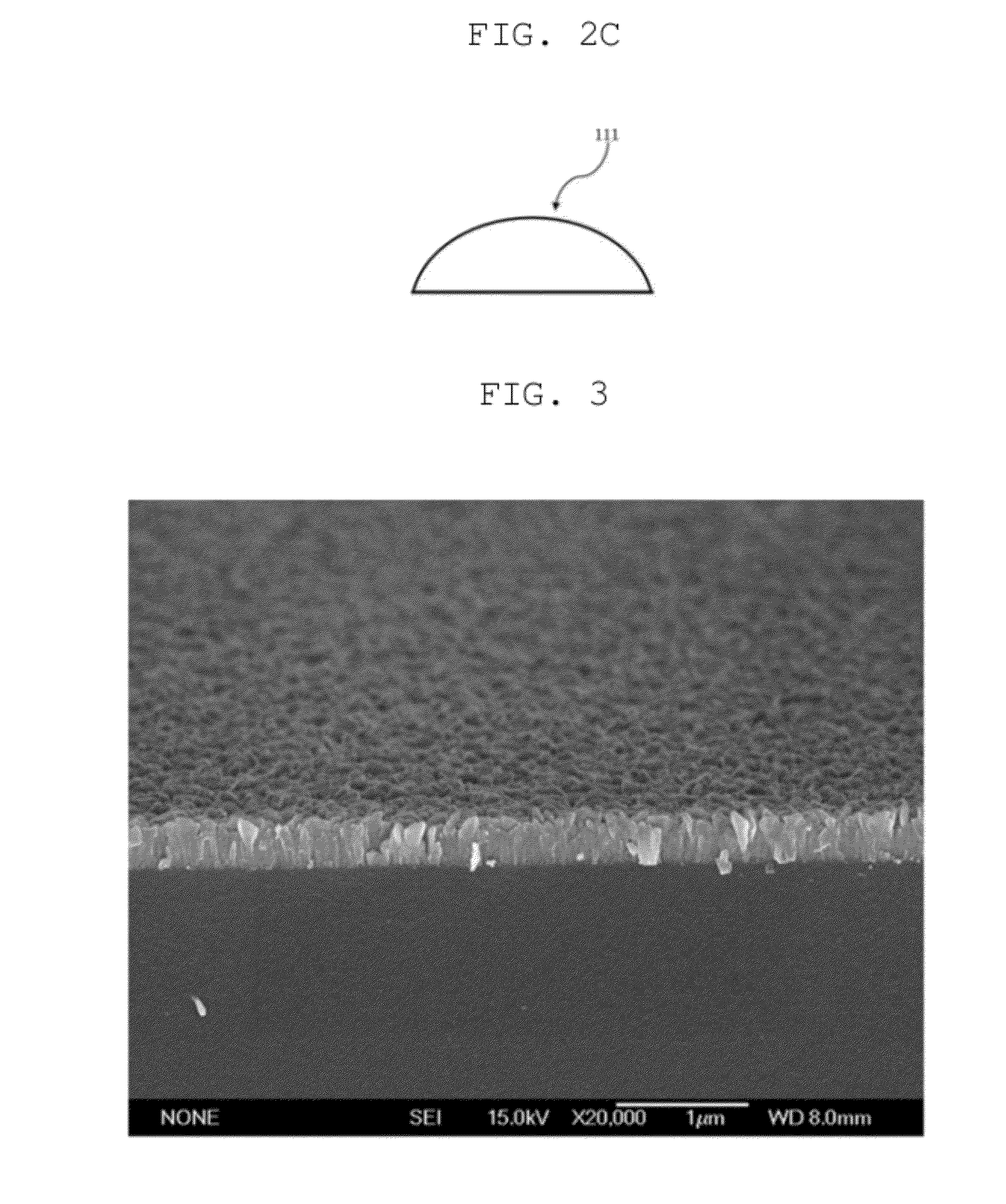
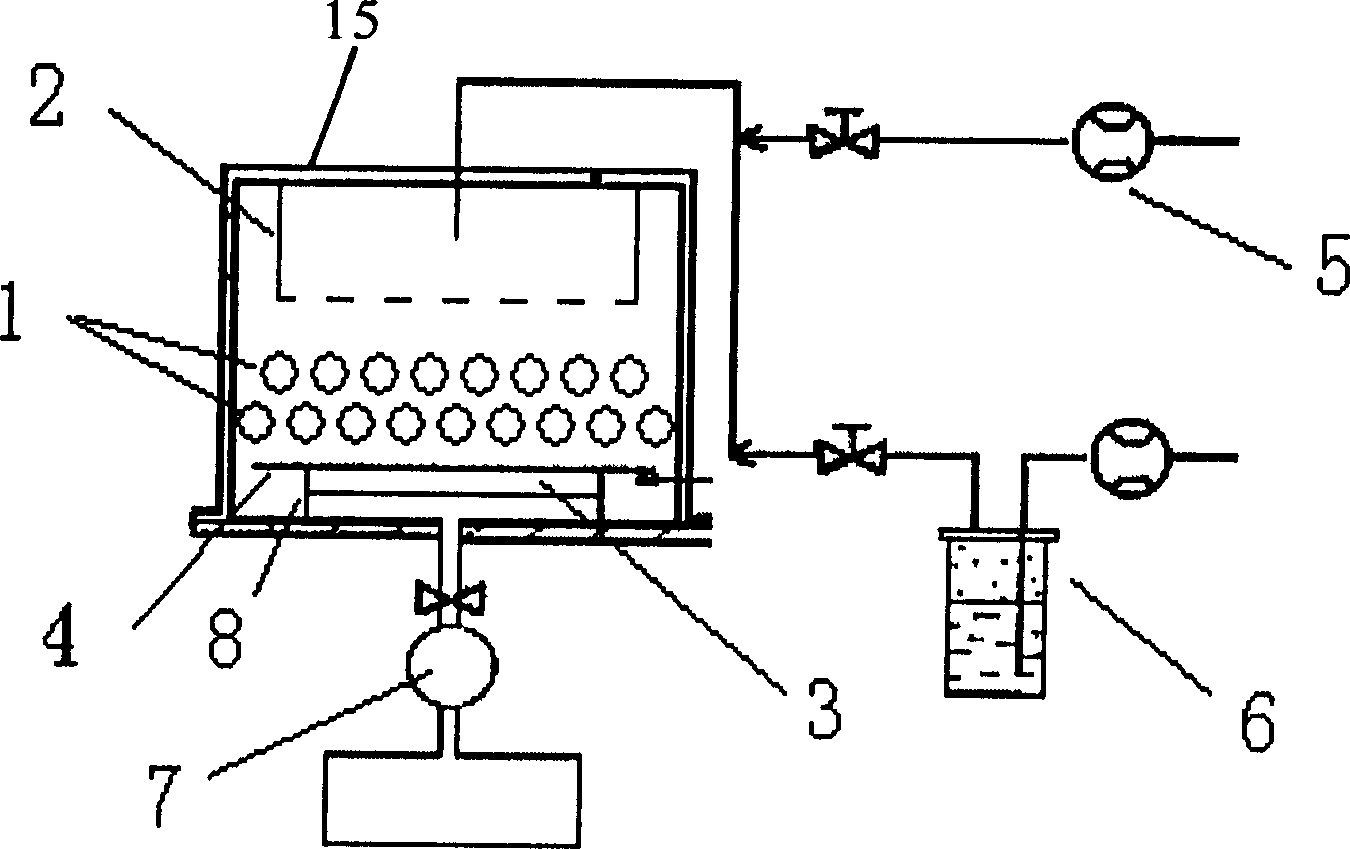
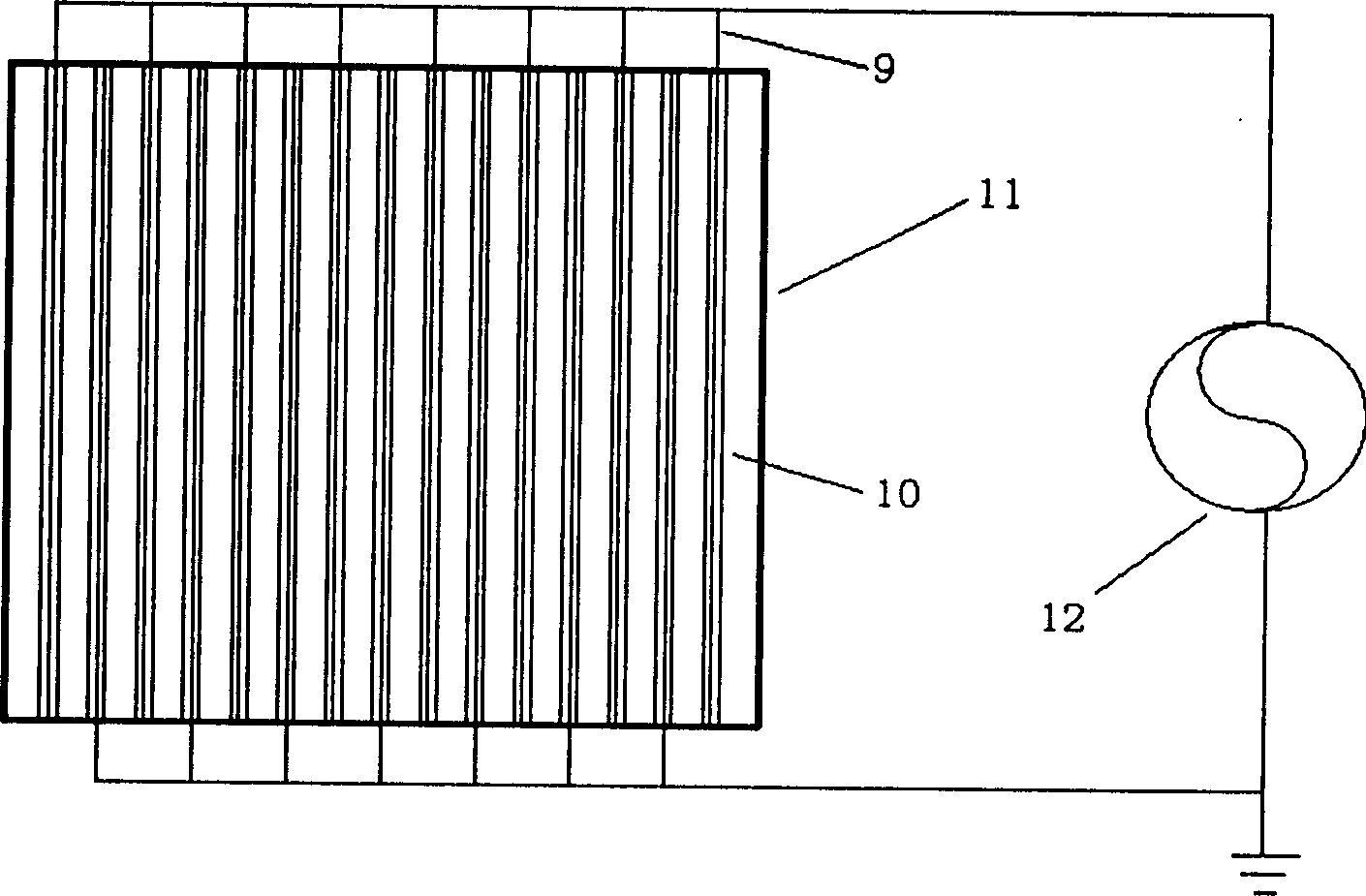
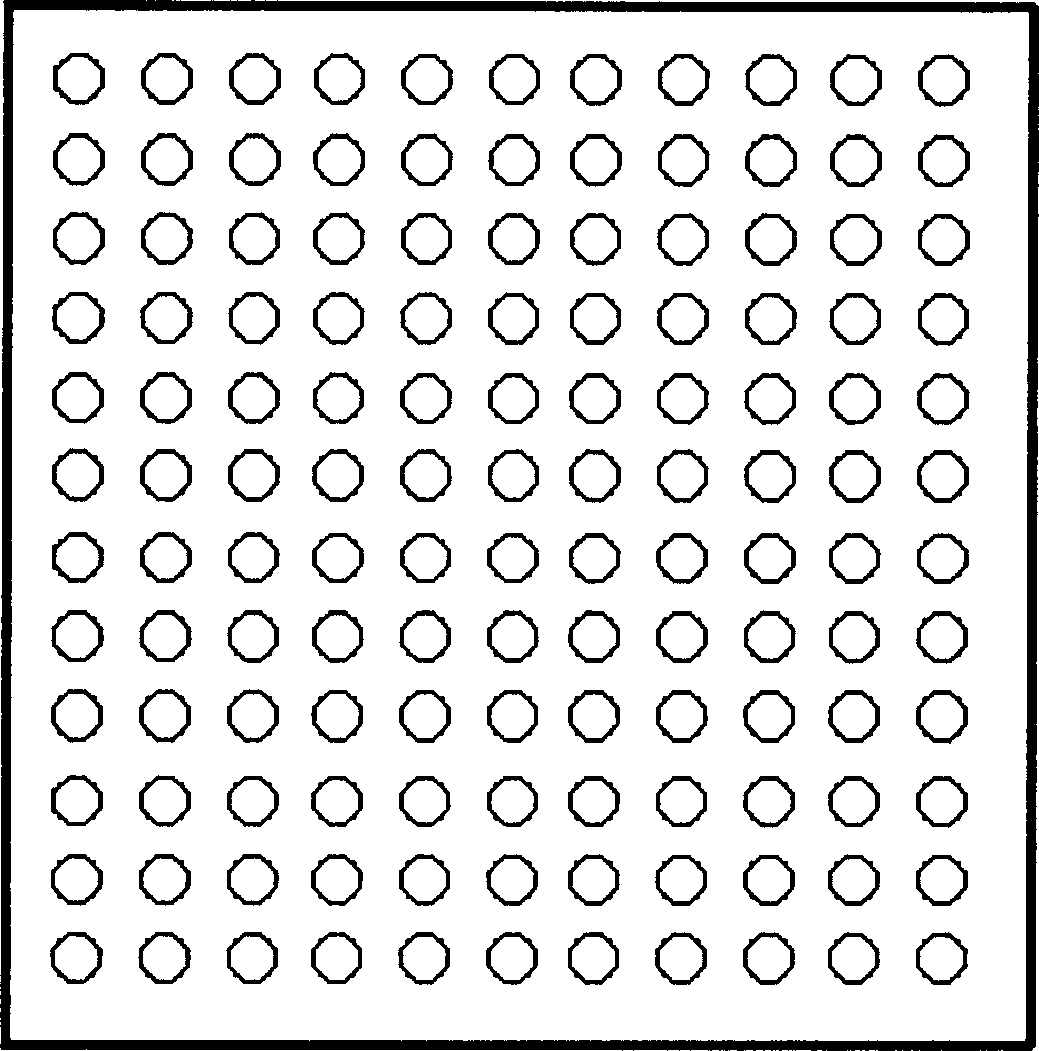
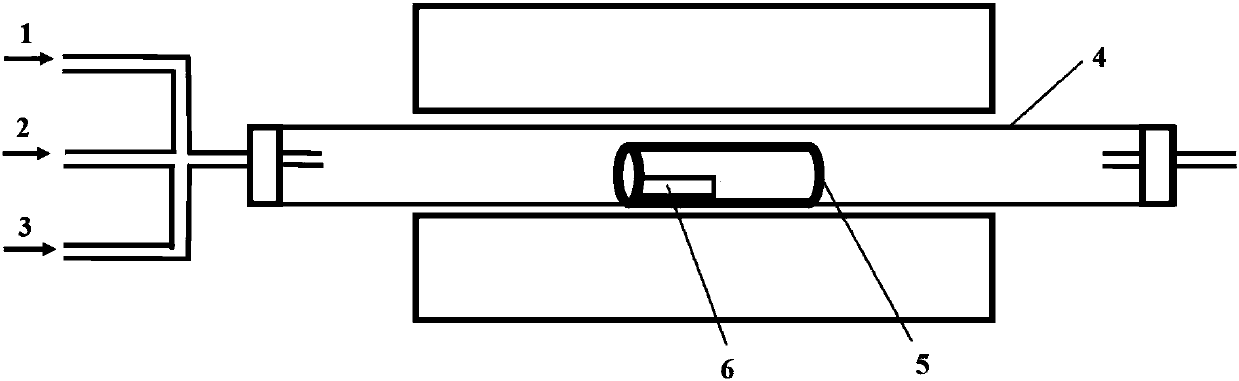
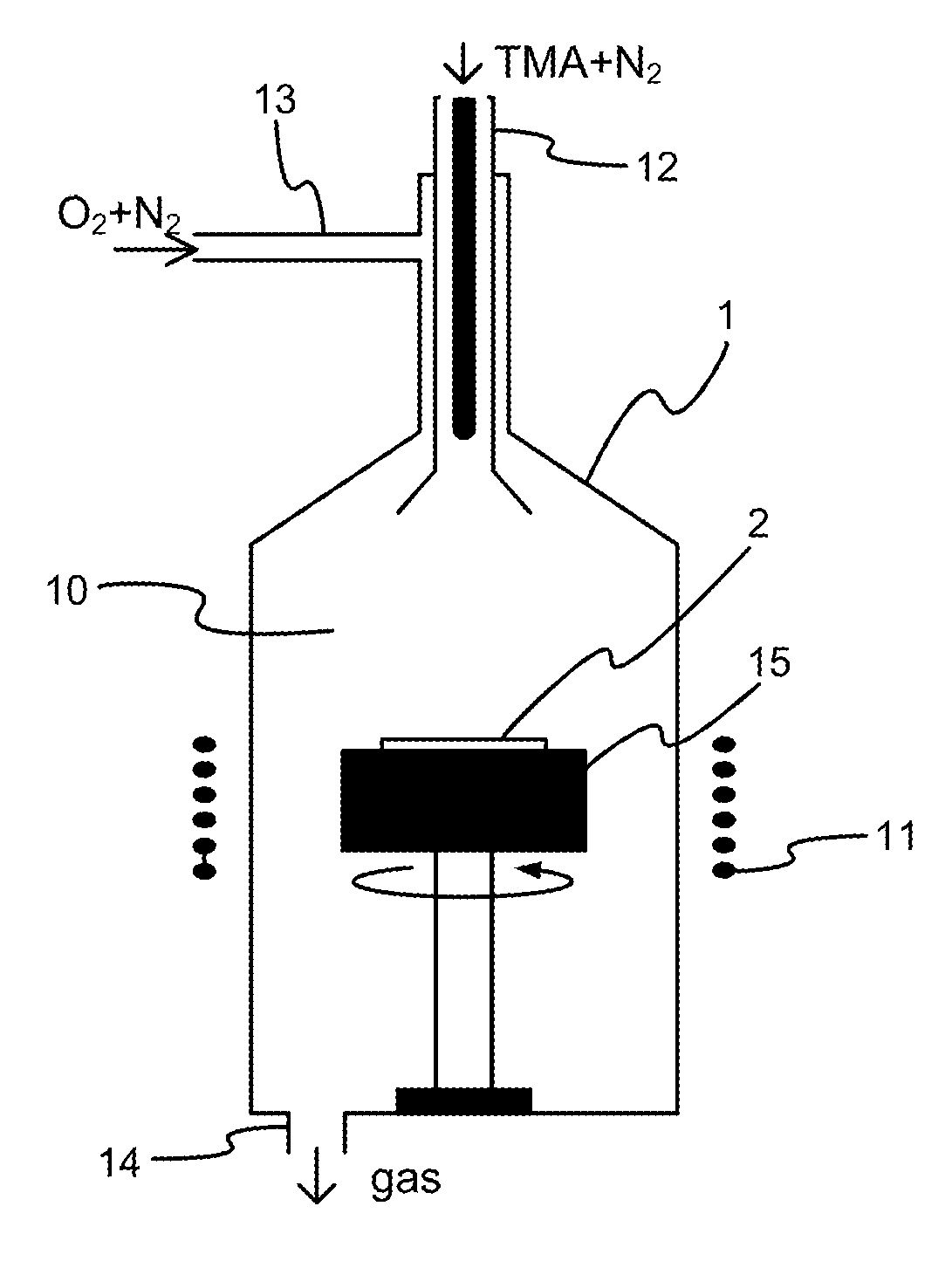
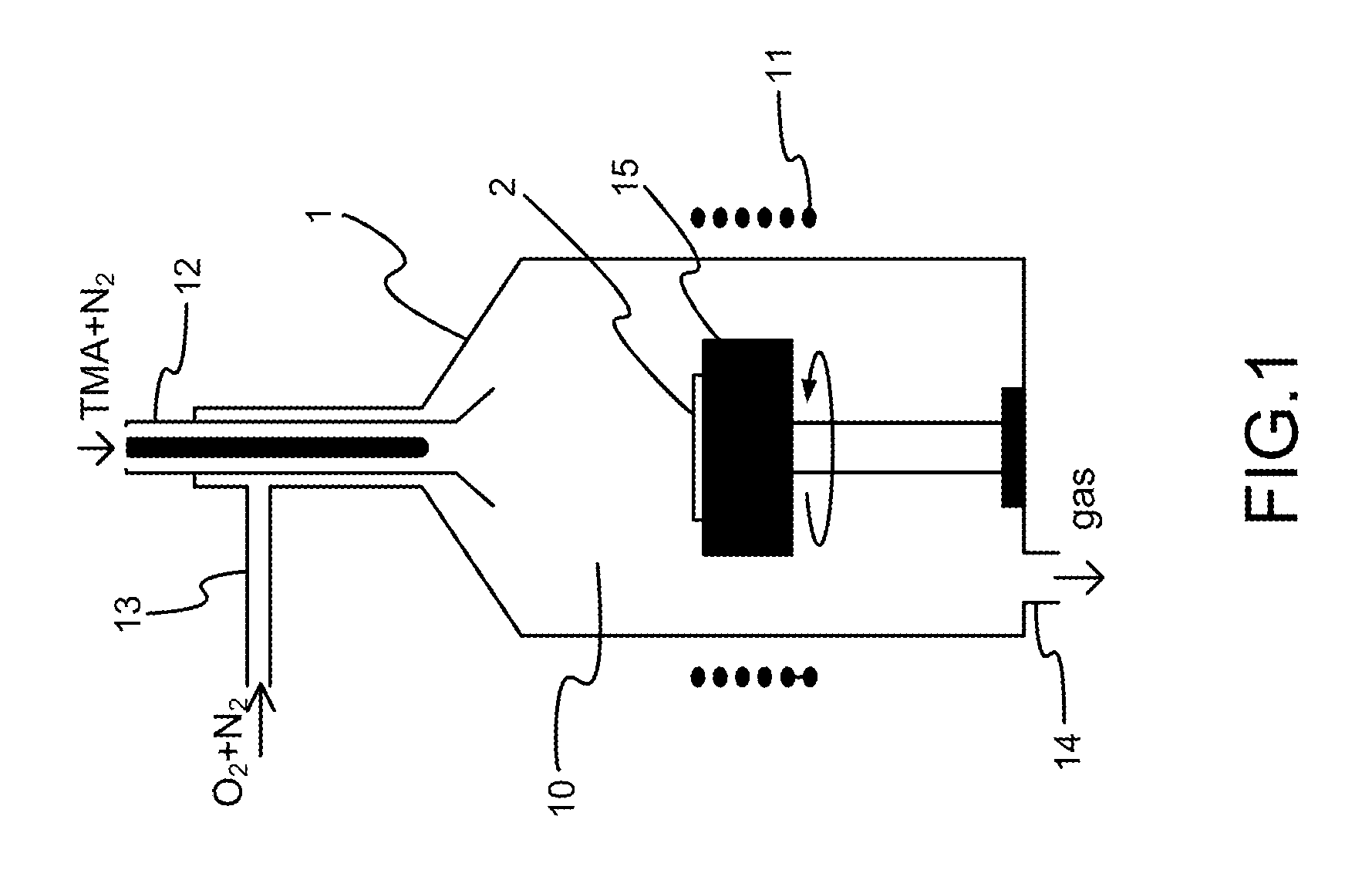
In atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition a layer of material several microns (10 -6 m) thick is deposited on a receiving surface. The picture below shows a reaction chamber during the reaction used in semiconductor wafer processing. The uniformity of the deposited layer is crucial to the performance of microelectronic devices.
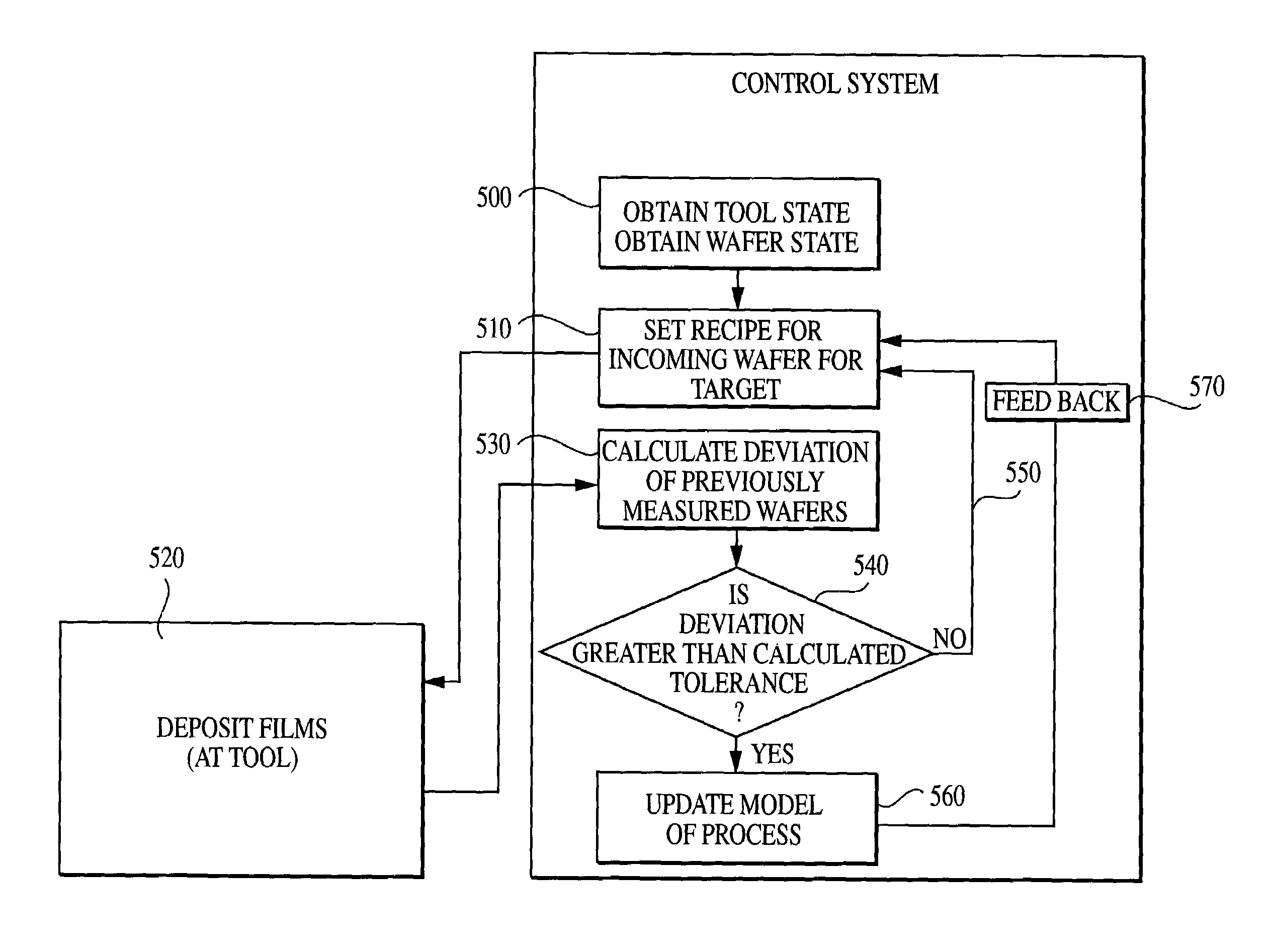
Method of feedback control of sub-atmospheric chemical vapor deposition processes
InactiveUS7201936B2Improve wafer-to-wafer uniformityImprove within-wafer uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementComputer controlGas phaseEngineering
A method of film deposition in a sub-atmospheric chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process includes (a) providing a model for sub-atmospheric CVD deposition of a film that identifies one or more film properties of the film and at least one deposition model variable that correlates with the one or more film properties; (b) depositing a film onto a wafer using a first deposition recipe comprising at least one deposition recipe parameter that corresponds to the at least one deposition variable; (c) measuring a film property of at least one of said one or more film properties for the deposited film of step (b); (d) calculating an updated deposition model based upon the measured film property of step (c) and the model of step (a); and (e) calculating an updated deposition recipe based upon the updated model of step (d) to maintain a target film property. The method can be used to provide feedback to a plurality of deposition chambers or to control a film property other than film thickness.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for growing graphene film by using low-temperature chemical vapor deposition
ActiveCN103184425AReduce roughnessReduce nucleation densityPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesGas phaseMaterials science
The invention relates to a method for preparing a graphene film in a low-temperature condition. The method at least comprises the following steps: (1), performing smooth treatment on a metal substrate; (2), performing doping of a chemical reagent on the surface of the metal substrate obtained in the step (1); (3), under a protective atmosphere, performing annealing treatment on the metal substrate obtained in the step (1); (4), contacting the metal substrate with a carbon source, and performing chemical vapor deposition in the low-temperature condition to obtain the graphene film; and optionally, after the step (4), performing step (5), stopping heating, cooling to the room temperature, and taking out the metal substrate with the graphene film thereon, wherein the chemical reagent is a precursor salt of metal. The method for growing the graphene film is low in growth temperature, low in cost, high in industrialized feasibility and wide in select range of the substrate, and can prepare the complete single-layer or multi-layer graphene film with high quality.
Owner:WUXI GRAPHENE FILM +1
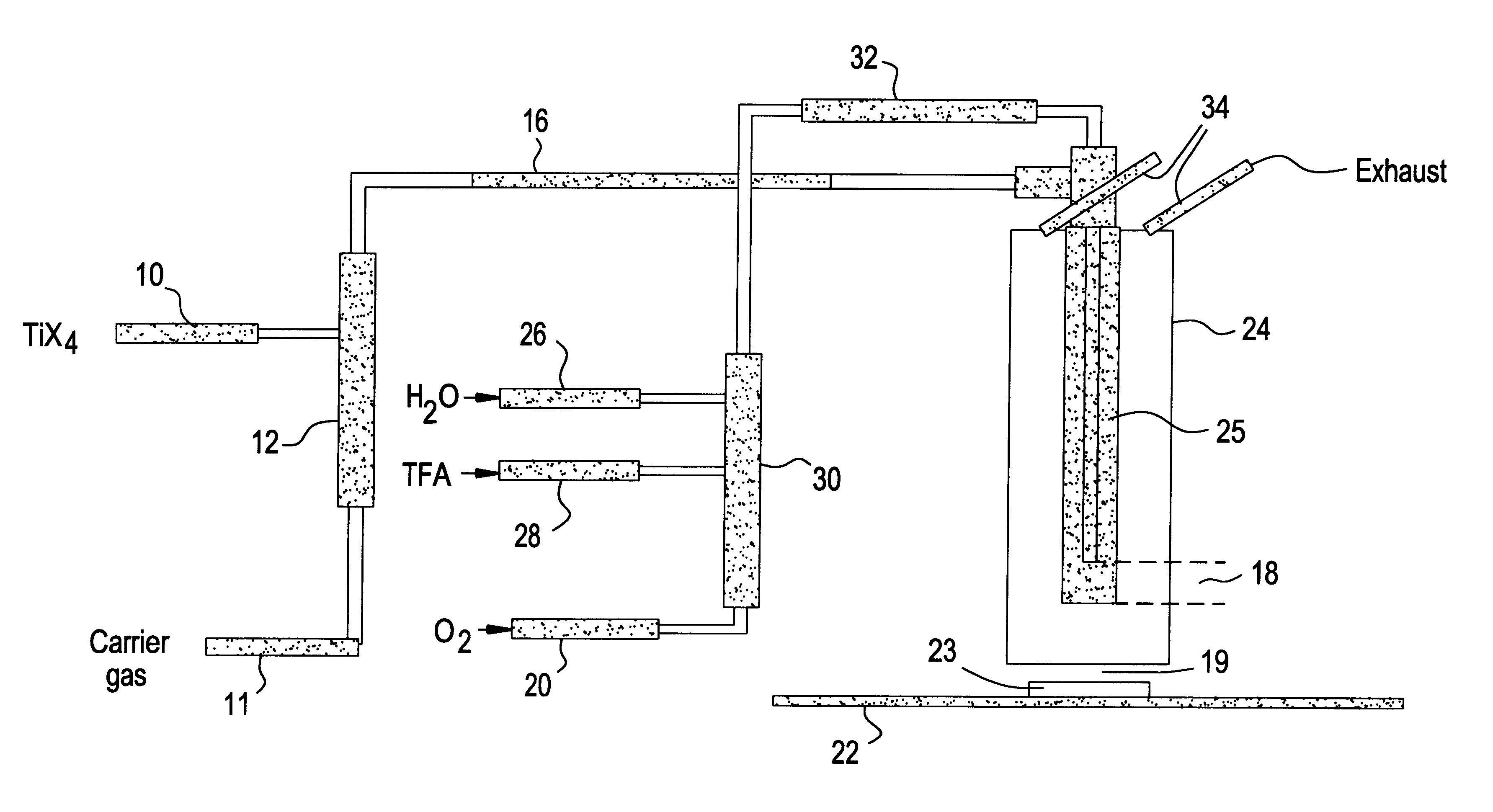
Preparation of fluorine modified, low haze, titanium dioxide films
InactiveUS6268019B1Improve propertiesDegradation of optical propertySpecial surfacesChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseRefractive index
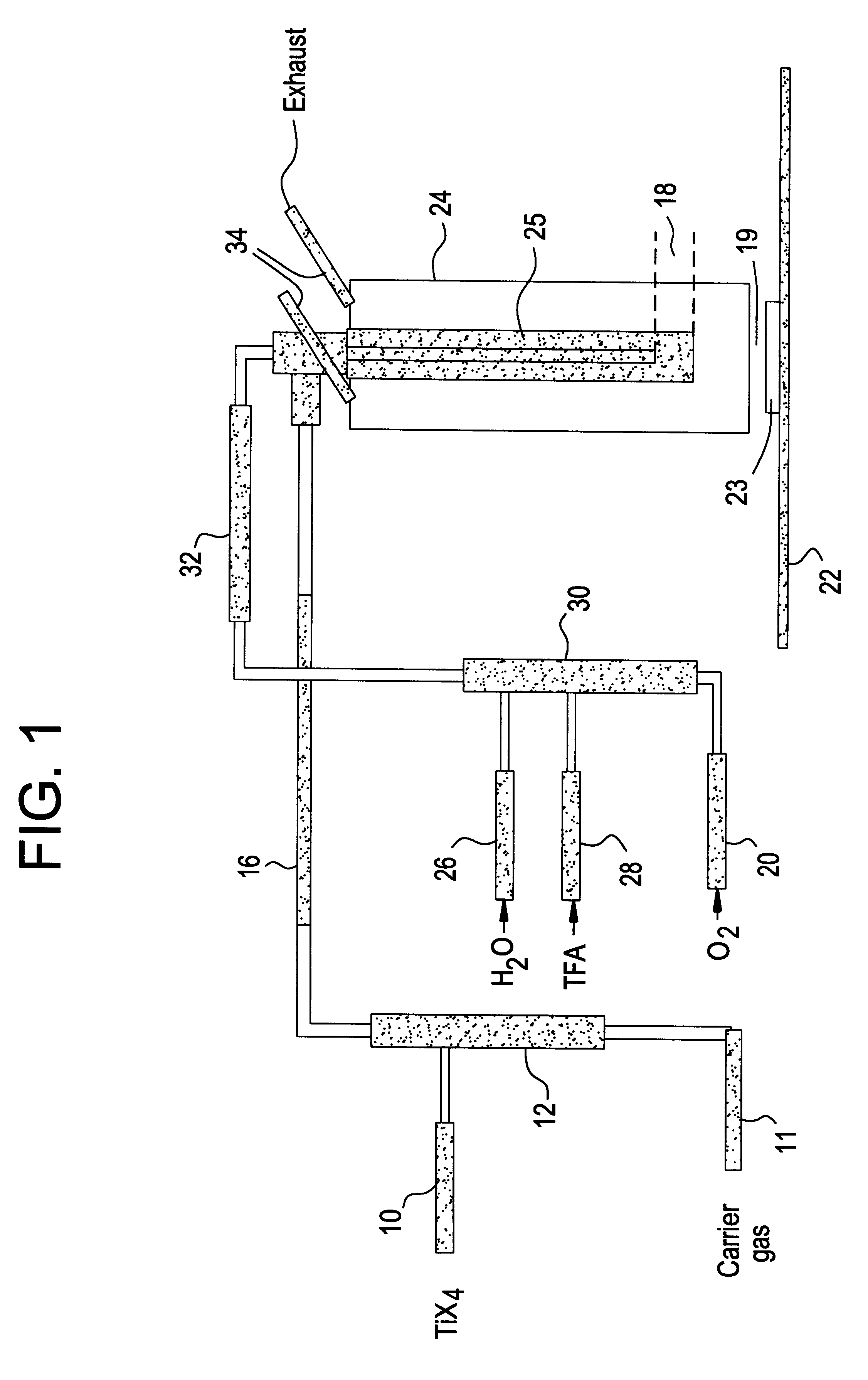
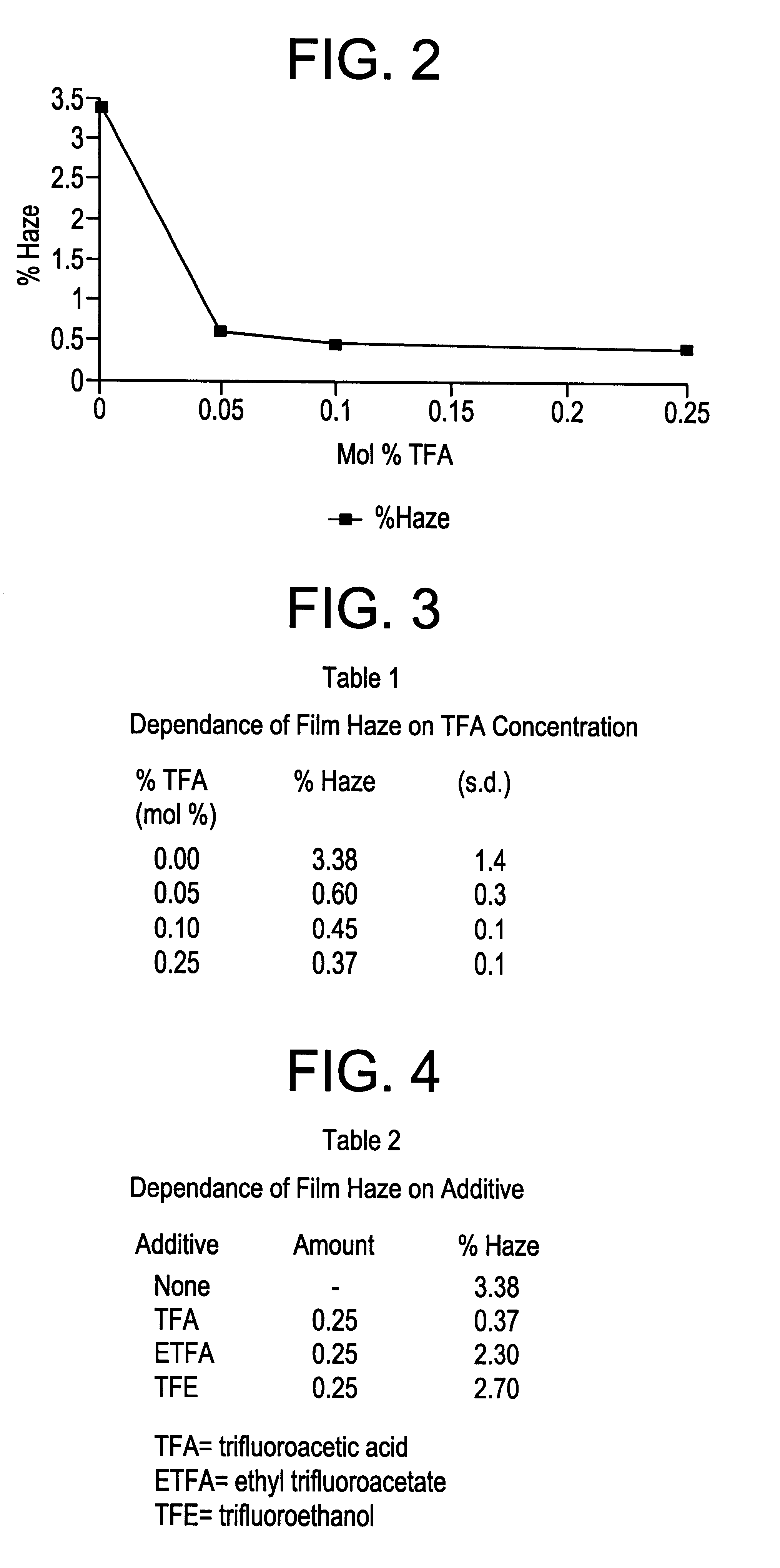
The present invention concerns the deposition of fluorine modified, titanium dioxide films (TiO2) onto hot glass by atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition (APCVD) using TiCl4 vapor. The invention is also suitable for depositing other metallic oxide films from their metallic halides such as SnCl4, GeCl4, and VCl4. The present invention provides a process that deposits a novel, fluorine modified, titanium dioxide film (TiO2) onto hot glass by atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition using TiCl4 vapor. The process uses injection of TiCl4 into a hot, nonoxygen containing carrier gas and blends the carrier gas and TiCl4 vapor with an oxygen containing gas stream containing a haze reducing quantity of a fluorine containing compound before contacting a surface of hot glass with the blended mixture. The process is capable of depositing a fluorine modified, TiO2 film at deposition rates exceeding 900 Å per second. The crystalline phase of the fluorine modified film is essentially anatase. The film has a haze of less then 1% and a refractive index of greater than or equal to about 2.48. Also provided is an apparatus for practicing the process and a novel coated glass.
Owner:ATOCHEM OF NORTH AMERICA INC
Discharge-enhanced atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition
InactiveUS20060040067A1Increase depositionNot easy to scaleChemical vapor deposition coatingPlasma techniqueElectricityNoble gas
A discharge-enhanced CVD apparatus and method utilizes a nozzle containing electrodes to generate a high voltage electrical discharge at or near atmospheric pressure in the absence of a stabilizing or arc-suppressing noble gas. Reactants are passed directly through or / and under the discharge before being directed to the surface of a substrate to be coated.
Owner:ARKEMA INC
Two-dimensional heterojunction solar cell and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN104218114ALow costImprove efficiencyFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationHeterojunctionNew energy
The invention belongs to the technical field of new energy and relates to a solar cell and a manufacturing method thereof, in particular to a two-dimensional heterojunction solar cell and a manufacturing method thereof. The manufacturing method includes manufacturing graphene and two-dimensional transition metal sulfide films by an atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition method; compositing the graphene and two-dimensional transition metal sulfide films, leading out to form a two-dimensional heterojunction solar cell by a metal electrode. The two-dimensional heterojunction solar cell has the advantages of simple structure, large area, low cost and high efficiency. The manufacturing method is simple and low in manufacturing cost and has potential application value in the technical field of new energy. Particularly, a flexible solar cell is obtained and has higher application value as compared with an existing silicon solar cell.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Reactive flow deposition and synthesis of inorganic foils
Sub-atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition is described with a directed reactant flow and a substrate that moves relative to the flow. Thus, using this CVD configuration a relatively high deposition rate can be achieved while obtaining desired levels of coating uniformity. Deposition approaches are described to place one or more inorganic layers onto a release layer, such as a porous, particulate release layer. In some embodiments, the release layer is formed from a dispersion of submicron particles that are coated onto a substrate. The processes described can be effective for the formation of silicon films that can be separated with the use of a release layer into a silicon foil. The silicon foils can be used for the formation of a range of semiconductor based devices, such as display circuits or solar cells.
Owner:NANOGRAM
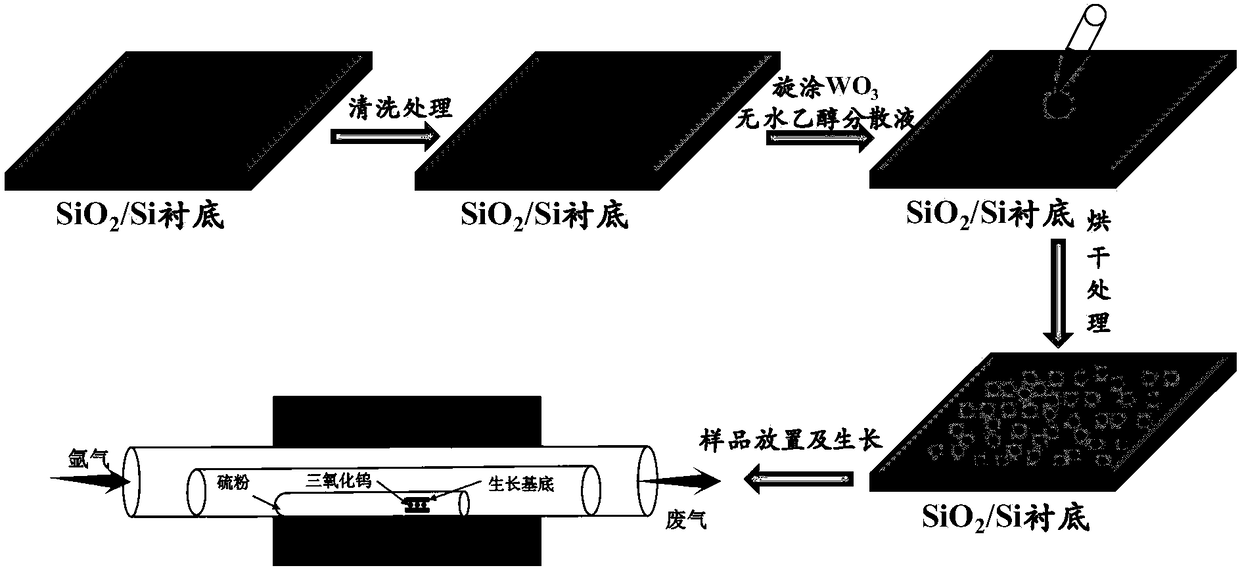
Preparation method for large-area single-layer tungsten disulfide film based on atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition and product
ActiveCN108559972AFast preparationPrepare to repeatChemical vapor deposition coatingFilm baseGas phase
The invention relates to a preparation method for a large-area single-layer tungsten disulfide film based on atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition and a product. The preparation process comprises SiO2 / Si substrate cleaning, spin coating of a WO3 anhydrous ethanol dispersion solution, substrate drying treatment, sample placement and tungsten disulfide film growth. By the adoption of the method, WO3 precursor is uniformly dispersed on a substrate by spin coating of the WO3 anhydrous ethanol dispersion solution, a single-ended-closed small-caliber quartz tube is placed in a quartz tube growth chamber, and the amount of S powder and WO3 precursor participating in a nucleation and film growth process is effectively controlled, so that the prepared tungsten disulfide film has the largearea, single layer and large size. The method has the beneficial effects of being quick and repeatable and is significant in preparation of the large-area single-layer tungsten disulfide film.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
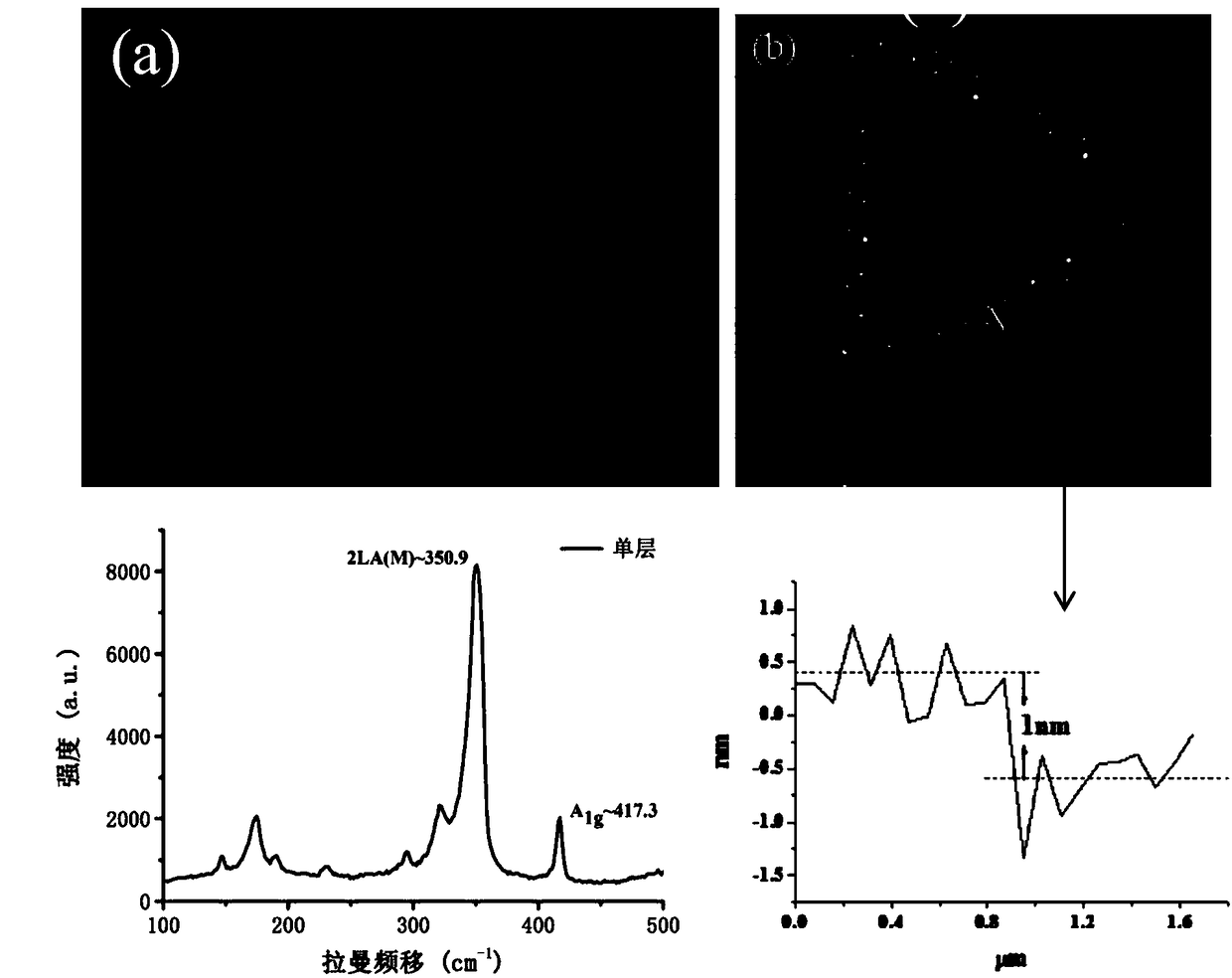
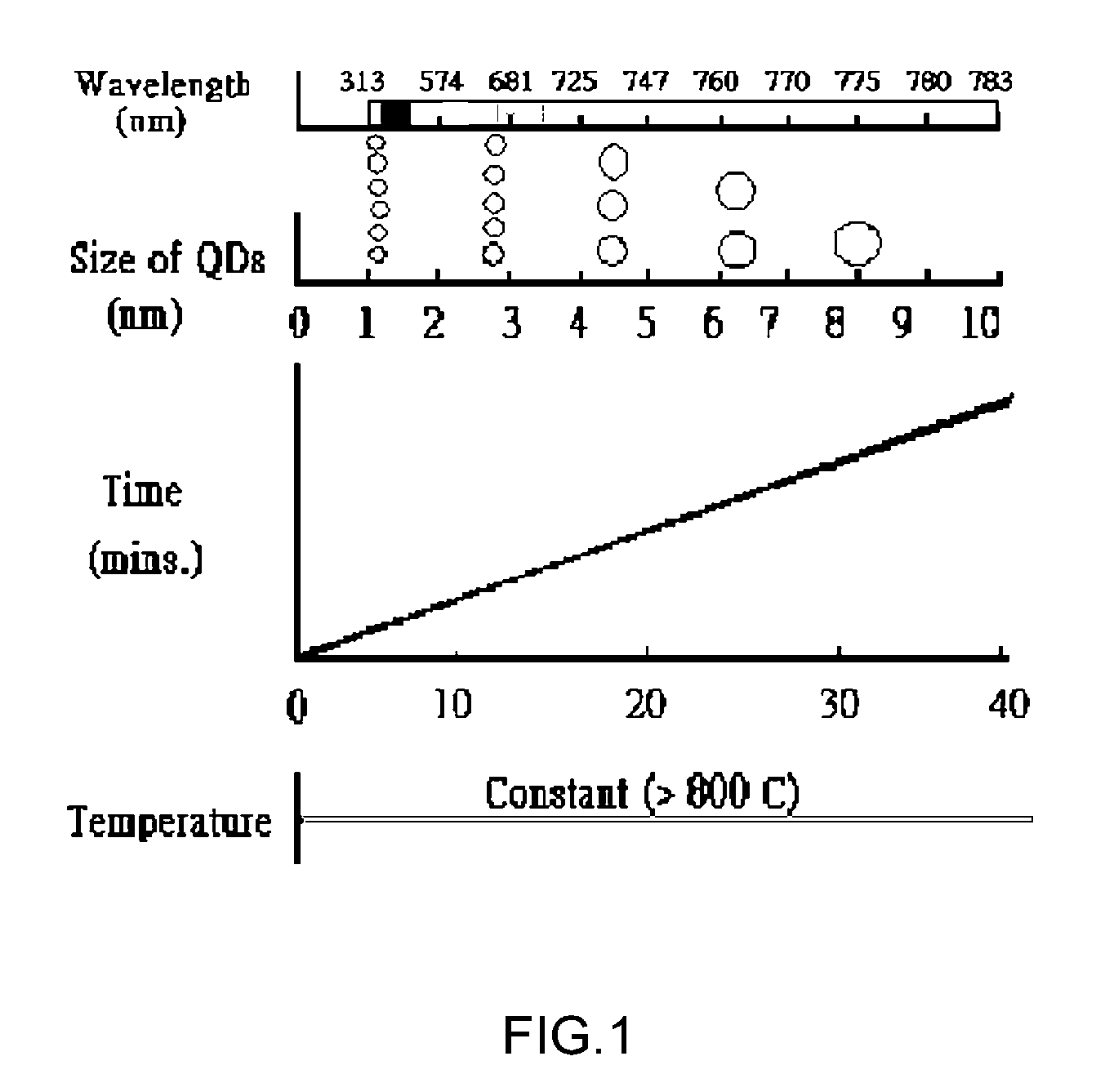
Method for preparing an optical active layer with 1~10 nm distributed silicon quantum dots
InactiveUS7358101B2NanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitritePhotoluminescence
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
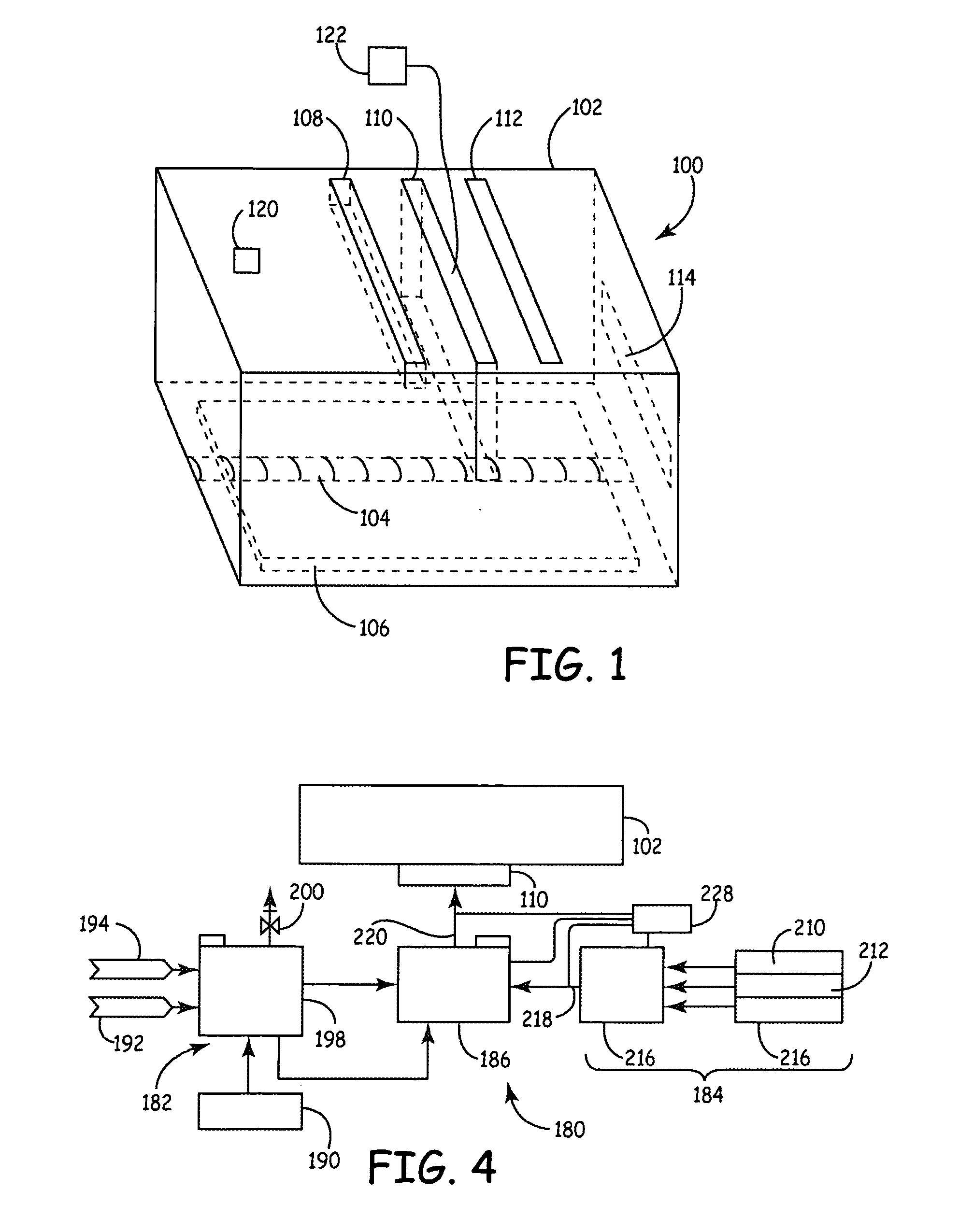
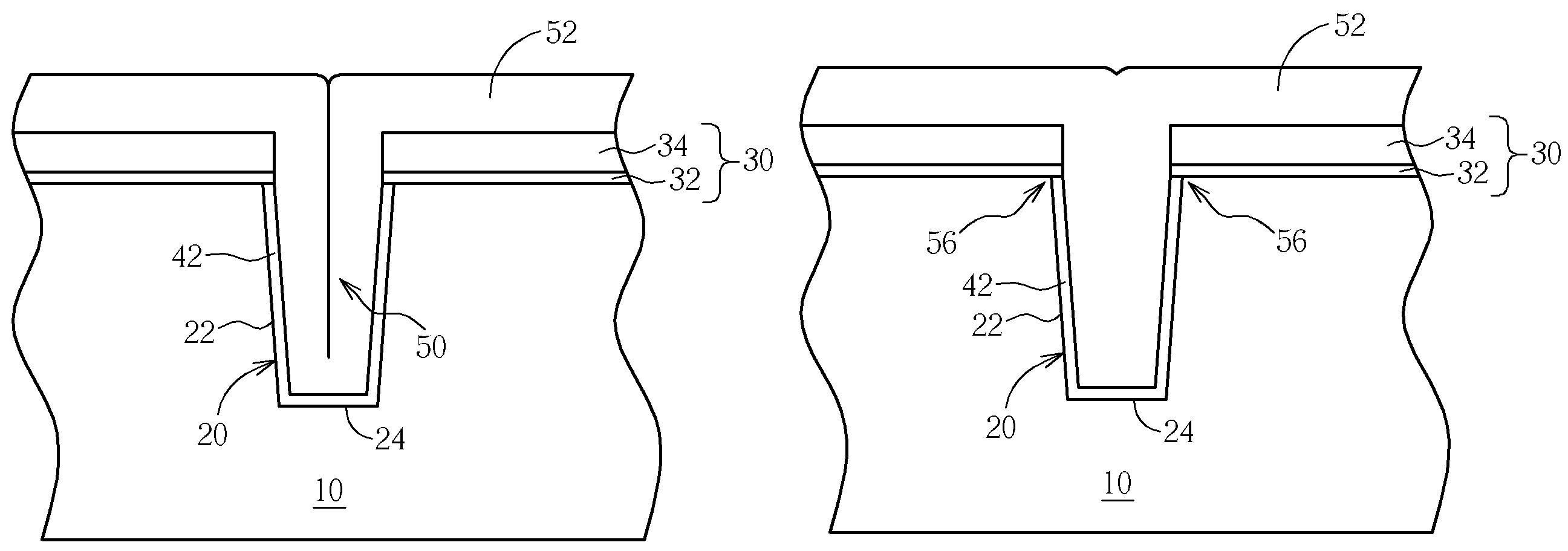
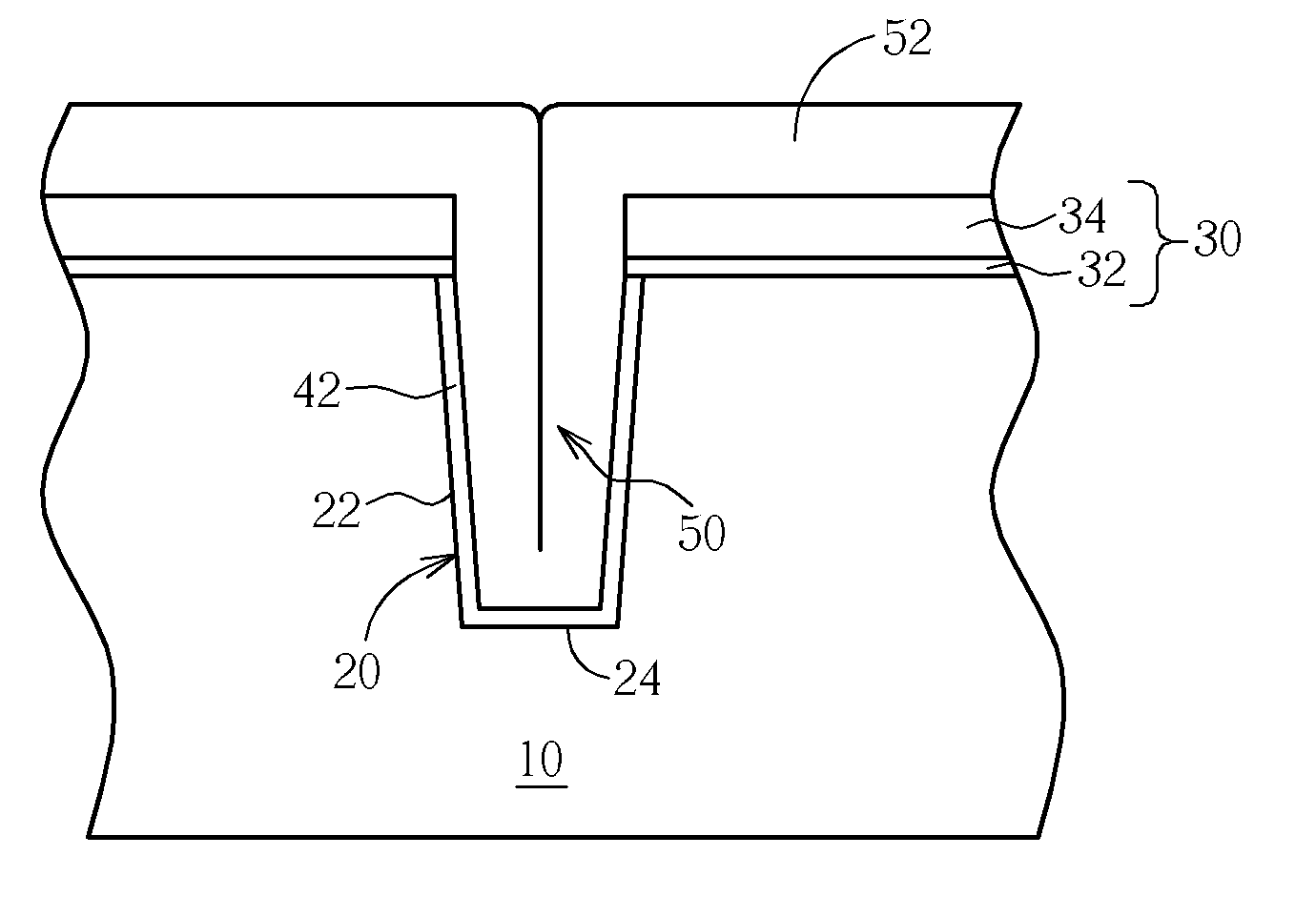
Seamless trench fill method utilizing sub-atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition technique
ActiveUS7238586B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon oxideAtmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition
A seamless trench fill method utilizing ozone-assisted sub-atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition (SACVD) technique is provided. After the deposition of a SACVD silicon oxide film, the substrate is subjected to a steam anneal that is performed under H2 / O2 environment at a relatively lower temperature ranging between 500° C. and 800° C. for a time period of no less than 30 minutes. The seam defect in the trench is effectively eliminated by this low-temperature steam anneal. To densify the SACVD silicon oxide film, a subsequent N2 anneal is carried out at a higher temperature, for example, 1050° C.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Seamless trench fill method utilizing sub-atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition technique
ActiveUS20070020875A1Eliminate seam defectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon oxideAtmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition
A seamless trench fill method utilizing ozone-assisted sub-atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition (SACVD) technique is provided. After the deposition of a SACVD silicon oxide film, the substrate is subjected to a steam anneal that is performed under H2O2 environment at a relatively lower temperature ranging between 500° C. and 800° C. for a time period of no less than 30 minutes. The seam defect in the trench is effectively eliminated by this low-temperature steam anneal. To densify the SACVD silicon oxide film, a subsequent N2 anneal is carried out at a higher temperature, for example, 1050° C.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Energy storage device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20110289767A1Improve discharge performanceHybrid capacitor electrodesFinal product manufactureWhiskersCrystalline silicon
An energy storage device whose discharge capacity can be improved and a method for manufacturing the energy storage device are provided. A method for manufacturing an energy storage device, in which a metal element is dispersed over a current collector, and a crystalline silicon layer including a whisker is formed as an active material layer over the surface of the current collector on which the metal element is dispersed by low pressure chemical vapor deposition (LPCVD) in which heating is performed using a deposition gas containing silicon. Having whiskers in the active material layer as described above, the surface area of the active material layer is increased; thus, the discharge capacity of the energy storage device can be increased.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Internal optical extraction layer for OLED devices
InactiveCN103518269ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRefractive indexLight emitting device
A light-emitting device, which improves the light output of an organic light emitting diode (OLED), includes at least one porous metal or metalloid oxide light extraction layer positioned between the substrate and the transparent conducting material layer in the OLED. The index of refraction of the light extraction layer and the light scattering may be tuned by changing the pore size, pore density, doping the metal oxide, adding an insulating, conducting or semiconducting component, or filling the pores, for example. A method for forming the light-emitting device includes forming at least one light extraction layer comprising a porous metal or metalloid oxide on a substrate, for example, using atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition (APCVD), and subsequently, forming a transparent conducting material on the light extraction layer.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA +1
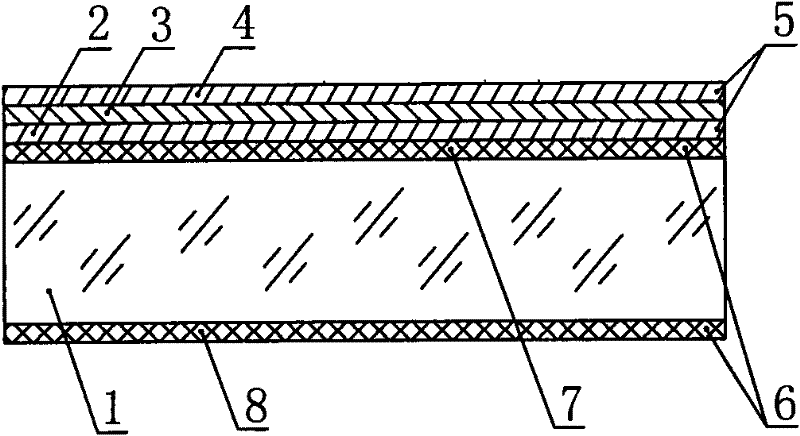
Conductive glass with double anti-reflective film surfaces for thin film solar battery and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102683433AImprove stabilityUniform and dense structureSemiconductor devicesGas phaseEvaporation
The invention relates to conductive glass with double anti-reflective film surfaces for a thin film solar battery and a preparation method of the conductive glass. According to the conductive glass, a metal layer (3) is clamped between a metallic oxide conductive layer (2) and a second metallic oxide conductive layer (4); a first anti-reflective film (7), the metallic oxide conductive layer (2), the metal layer (3) and the second metallic oxide conductive layer (4) are sequentially arranged on the surface at one side surface of a glass base material (1); and a second anti-reflective film (8) is arranged on the surface at the other side surface of the glass base material (1). The metallic oxide conductive layer is prepared on the glass base material through methods such as LPCVD (low pressure chemical vapor deposition) or PECVD (plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition) and the like; the metal layer is prepared by a magnetron sputtering or thermal evaporation method; the second metallic oxide conductive layer is prepared by a chemical vapor deposition method; and the anti-reflective films are prepared by a sol-gel method. The conductive glass provided by the invention has the advantages of good light transmission, strong conduction, high scattering degree, good film layer structure stability, high cost performance and low preparation cost.
Owner:CHANGZHOU ALMADEN
Method for preparing monocrystal double-layer graphene
InactiveCN105483824ASmall sizeEasy to operatePolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesSingle crystalNon oxidative
The invention discloses a method for preparing monocrystal double-layer graphene. The method comprises the following steps that 1, a copper catalyst is put into a reactor, non-oxidative gas is introduced into the reactor to enable the reactor to be full of the non-oxidative gas, and monocrystal copper or polycrystalline copper or a copper film is adopted as the copper catalyst; 2, the copper catalyst is heated to the target temperature, and then the temperature is kept constant for 30-120 minutes, wherein the target temperature ranges from 1000 DEG C to 1070 DEG C; 3, the copper catalyst is cooled to enable the temperature to reach 900 DEG C-500 DEG C or be kept constant, in the cooling or constant temperature process, the non-oxidative gas carrying a carbon source is introduced into the reactor, and then the monocrystal double-layer graphene can be obtained on the surface of the copper catalyst. Accordingly, the large-size monocrystal double-layer graphene is prepared on the copper catalyst through an isothermal or non-isothermal atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition method, and the method is convenient to operate, simple and practicable and can be applied to high-grade electronic devices and integrated circuits.
Owner:XINYANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Float online production method for low radiation film glass
The invention relates to a float online method for producing low-radiation film glass. The method comprises that: on a float glass production line, molten glass liquid floats in a tin groove and moves and is gradually cooled to form a glass strip; the glass strip leaves the tin groove and enters an atmosphere control chamber; in the atmosphere control chamber, a proplastid gas mixture consisting of silane, an oxygenous source and ethene uses inert gas as a carrier and is deposited on the surface of the float glass strip to form a shielding layer at speed of more than 300 / s by an atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition method; the glass deposited with the shielding layer is transported to an annealing furnace; the atomized proplastid gas mixture containing a tin source, a stibium source, a fluorine source, a phosphorus source, a catalyst and a stabilizing agent is introduced to the surface of the float glass strip deposited with the shielding layer in a region with a temperature of between 540 and 610 DEG C of the annealing furnace; and taking nitrogen gas as a carrier, a film layer with low radiation performance is formed on the glass strip plated with the shielding layer through pyrolysis reaction at speed of more than 300 / s.
Owner:CSG HOLDING
ZnO-BASED TRANSPARENT CONDUCTIVE THIN FILM FOR PHOTOVOLTAIC CELL AND MANUFACTURING METHOD THEREOF
InactiveUS20120270013A1Excellent textured surfaceFine surfaceRecord information storageOxide conductorsDopantTransparent conducting film
A zinc oxide (ZnO)-based transparent conductive thin film for a photovoltaic cell and a manufacturing method thereof, in which the transparent conductive thin film has an excellent textured surface and can be mass-produced. The ZnO-based transparent conductive film is formed on a substrate, is doped with a dopant, and has a textured surface. The textured surface has a plurality of protrusions. The manufacturing method forms the zinc oxide-based transparent conductive film on a substrate by atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition (APCVD) involving organic precursor gas and oxidizer gas.
Owner:SAMSUNG CORNING PRECISION MATERIALS CO LTD
Near infrared reflecting coatings on glass
Multi-layer solar control films composed of metal oxide, oxynitride, carbide, and / or oxycarbide layers are deposited on a substrate by atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition (APCVD). The film layers have alternating high / low refractive index. The coated substrate reflects near infrared (NIR) radiation, while transmitting a high level of visible radiation.
Owner:ARKEMA INC
Graphene synthesis by suppressing evaporative substrate loss during low pressure chemical vapor deposition
InactiveUS20150050482A1Suppress evaporative lossMinimize evaporative lossPolycrystalline material growthSingle layer grapheneSimple Organic CompoundsThermal chemical vapor deposition
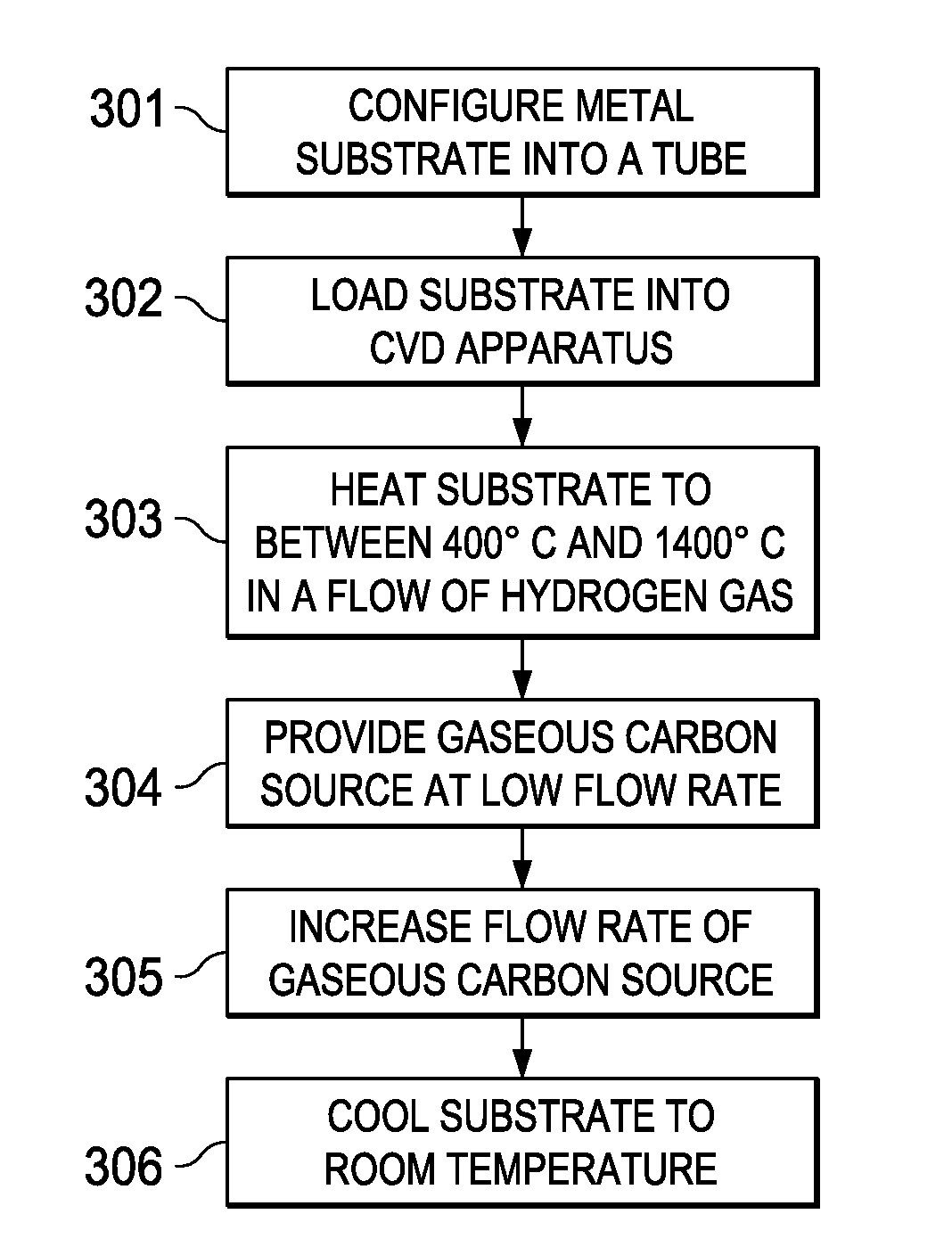
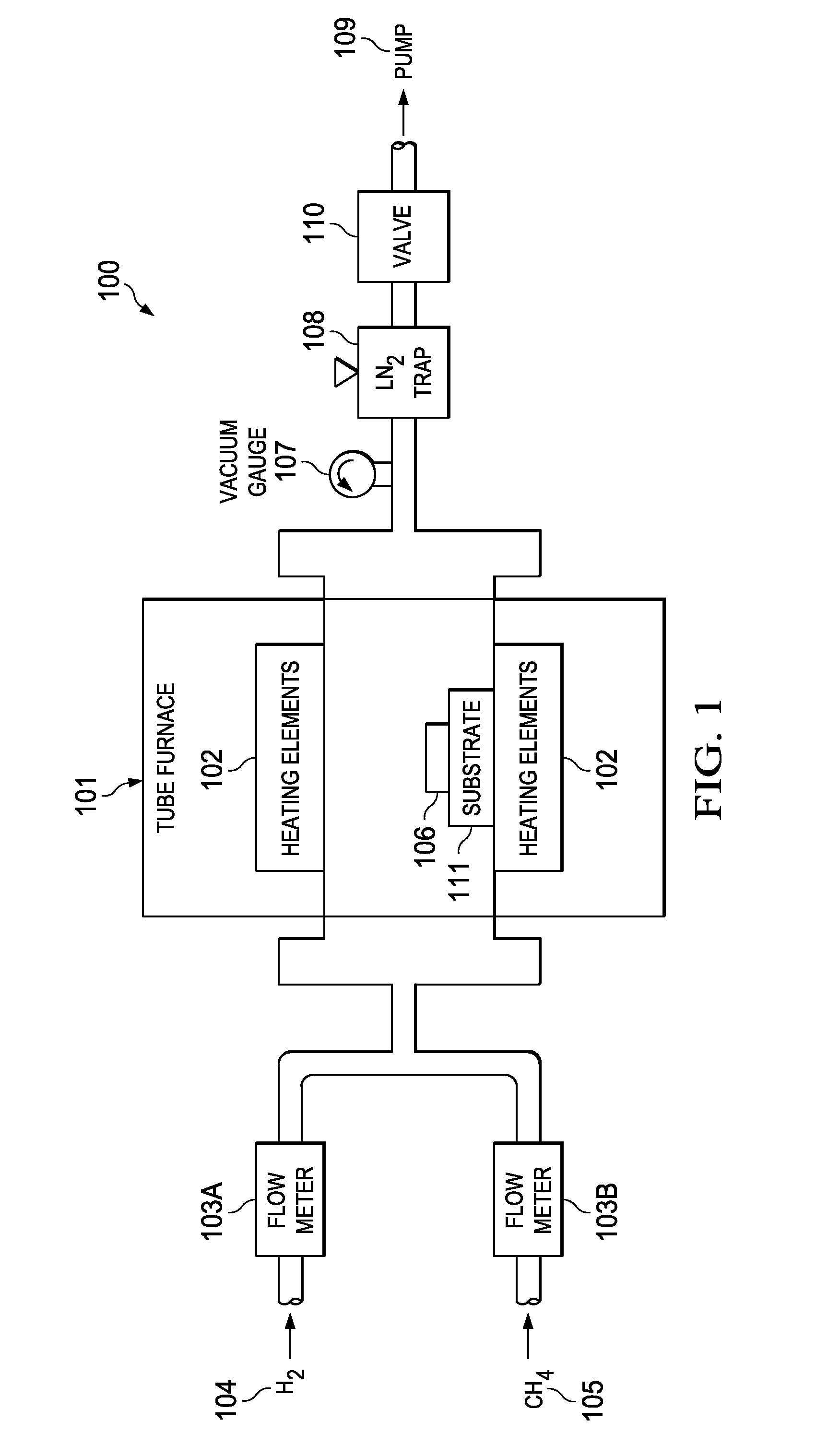
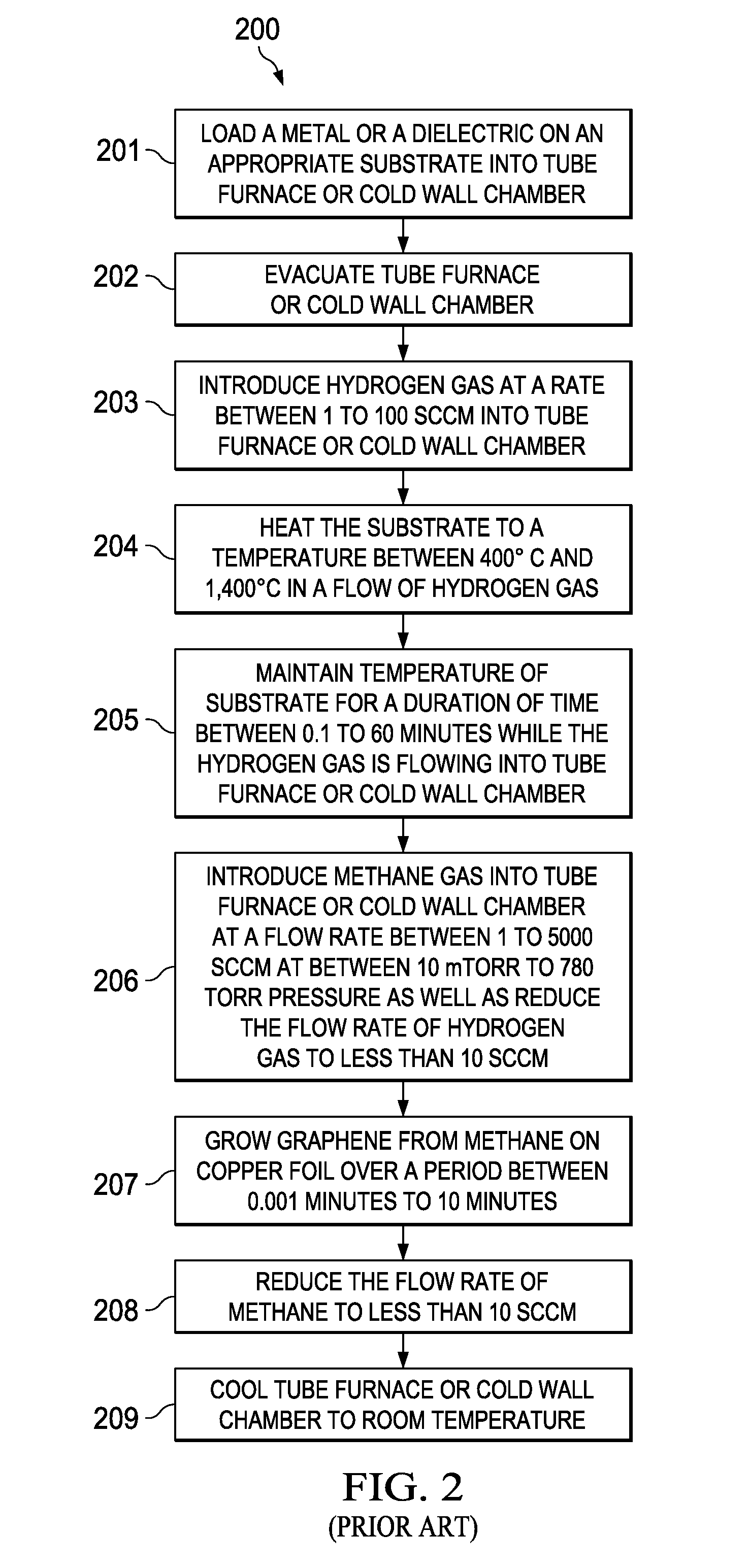
Method for synthesizing large single-crystal graphene films by suppressing evaporative substrate loss in chemical vapor deposition, and graphene films synthesized thereby. The substrate may be configured as a tube prior to exposure to an organic compound at high temperature. Low flow rate of the gaseous carbon source may be employed, and this flow rate may be increased after an initial nucleation period.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
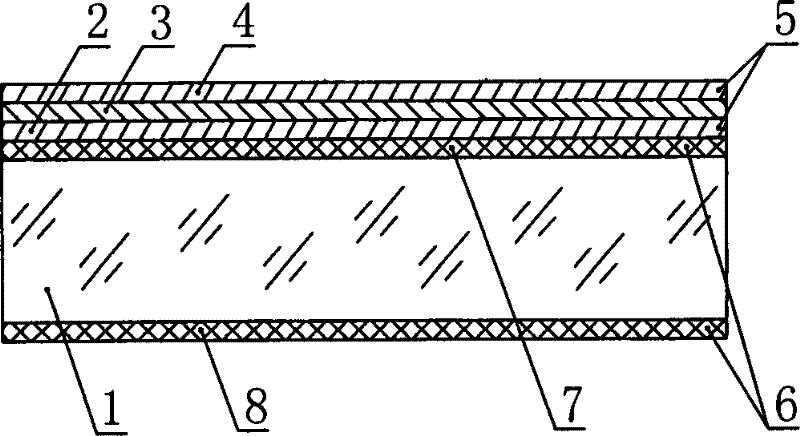
Composite passivated reflection reducing membrane for crystalline silicon solar cell and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101383382ASimple manufacturing processEfficient passivationFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationThermal sprayingGas phase
The invention relates to a composite passivation antireflective film used for a crystal silicon solar cell. The invention is characterized in that the composite passivation antireflective film is composed of a layer of amorphous silicon layer (2) and a layer of titanium dioxide layer (3), wherein the amorphous silicon layer (2) is directly deposited on the irradiation surface of a solar cell (1) and plays the role of surface passivation, and the titanium dioxide layer (3) is deposited on the amorphous silicon layer (2) and plays the role of reducing the reflection of light of the battery. The invention also relates to a method for preparing the passivation antireflective film, and the method comprises the following steps: firstly, the amorphous silicon layer (2) is deposited and prepared on the solar cell (1) by adopting a PECVD (plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition) process, and then the titanium dioxide layer is deposited on the amorphous silicon layer (2) by adopting an APCVD (atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition) process, or the titanium dioxide layer (3) is deposited on the amorphous silicon layer (2) by adopting a thermal spraying process.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
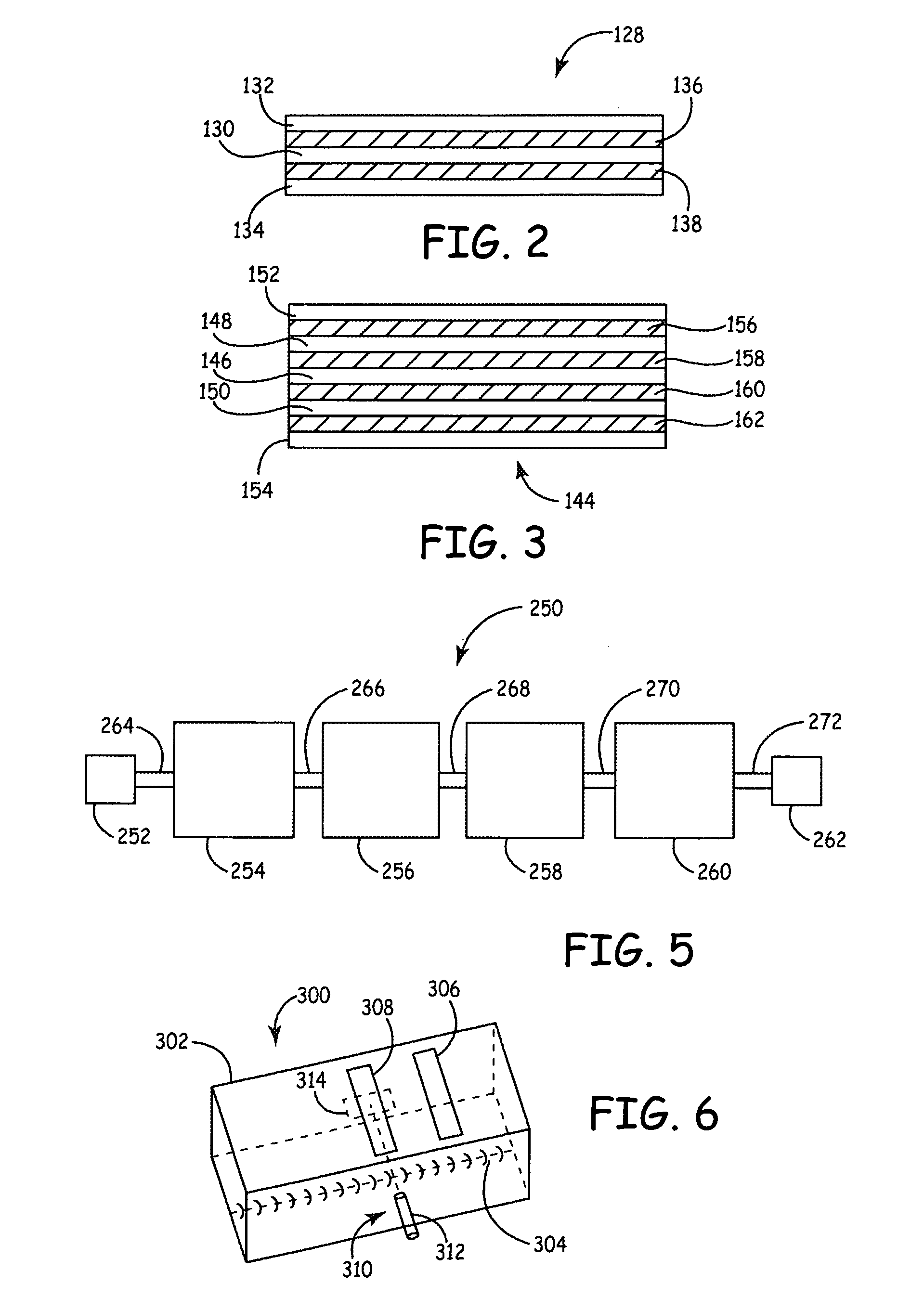
Deposition of silicon oxide by atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition
ActiveCN103958731AGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsChemical vapor deposition coatingSilicon oxideAtmospheric pressure
The invention provides methods for forming silicon oxide-containing layer(s) on a substrate, such as glass, by heating a substrate, vaporizing at least one precursor comprising a monoalkylsilane having an alkyl group with greater than two carbon atoms to form a vaporized precursor stream, and contacting a surface of the heated substrate with the vaporized precursor stream at about atmospheric pressure to deposit one or more layers comprising silicon oxide onto the surface of the substrate. The method is particularly useful for applying an anti-iridescent coating to glass in an online float glass process.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
Method of atmospheric pressure plane discharge chemical gaseous phase depositing nano-particular film and its device
InactiveCN1786262ARealize the structureDeposition stabilityChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseEngineering
The invention relates to an atmosphere pressure plane discharging chemical vapor deposition nanometer membrane granulose method and equipment. Its features are setting airflow divider in the reactor to make airflow uniformly flow through the discharging area and form film; setting different plane discharging unit in the reactor, increasing and reducing the cross distance to adjust deposited film component, and form crystalline state film; applying static high-voltage field to adjust forming predecessor and spatial configuration to adjust and control the film growth appearance.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Method for preparing large-area double-layer graphene film on insulated liner
ActiveCN107604338AReduce defectsImprove mobilityChemical vapor deposition coatingHydrogenComposite substrate
The invention discloses a method for preparing a large-area double-layer graphene film on an insulated liner. The method comprises the following steps: a composite liner is manufactured; the compositeliner comprises a copper pipe on an outer part and an insulated liner arrange in the copper pipe; the insulated liner is located in the range of the copper pipe; the copper pipe is made by curling acopper foil into a pipe shape; the composite liner is placed in a reactor, and mixed gas of argon and hydrogen is introduced into the reactor; the composite liner is heated, so that the copper pipe and the insulated liner in the composite liner both reach target temperature; then temperature is maintained constant for 30-120 min; temperature is continuously maintained constant, a gas carbon sourceis introduced into the reactor; and then the large-area double-layer graphene film can be obtained on the insulated liner under effect of a copper catalyst. According to the method, preparation of the large-area double-layer graphene film on the insulated liner is realized by utilizing a normal-pressure chemical vapor deposition method under catalysis effect of the copper foil; and the method isconvenient in operation and simple and feasible.
Owner:XINYANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Undoped oxide liner/BPSG for improved data retention
ActiveUS20050006693A1Improve data retentionImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesSilicon oxideEngineering
Semiconductor devices with improved data retention are formed by depositing an undoped oxide liner on spaced apart transistors followed by in situ deposition of a BPSG layer. Embodiments include depositing an undoped silicon oxide liner derived from TEOS, as at a thickness of 400 Å to 600 Å, on transistors of a non-volatile semiconductor device, as by sub-atmospheric chemical vapor deposition, followed by depositing the BPSG layer in the same deposition chamber.
Owner:INFINEON TECH LLC
Method of reducing metal impurities of upgraded metallurgical grade silicon wafer by using epitaxial silicon film
InactiveUS7972942B1Reduce impurity concentrationLow costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon chipAtmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition
Metal impurities of an upgraded metallurgical grade (UMG) silicon (Si) wafer are reduced. The UMG Si wafer having a 5N (99.999%) purity is chosen to grow a high-quality epitaxial Si thin film through atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition (APCVD). Through heat treating diffusion, the epitaxial Si film is used to form sink positions for the metal impurities in the UMG Si wafer. By using concentration gradient, temperature gradient and interface defect, individual and comprehensive effects are built for enhancing purity of the UMG Si wafer from 5N to 6N. Thus, a low-cost Si wafer can be fabricated for Si-based solar cell through a simple, fast and effective method.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
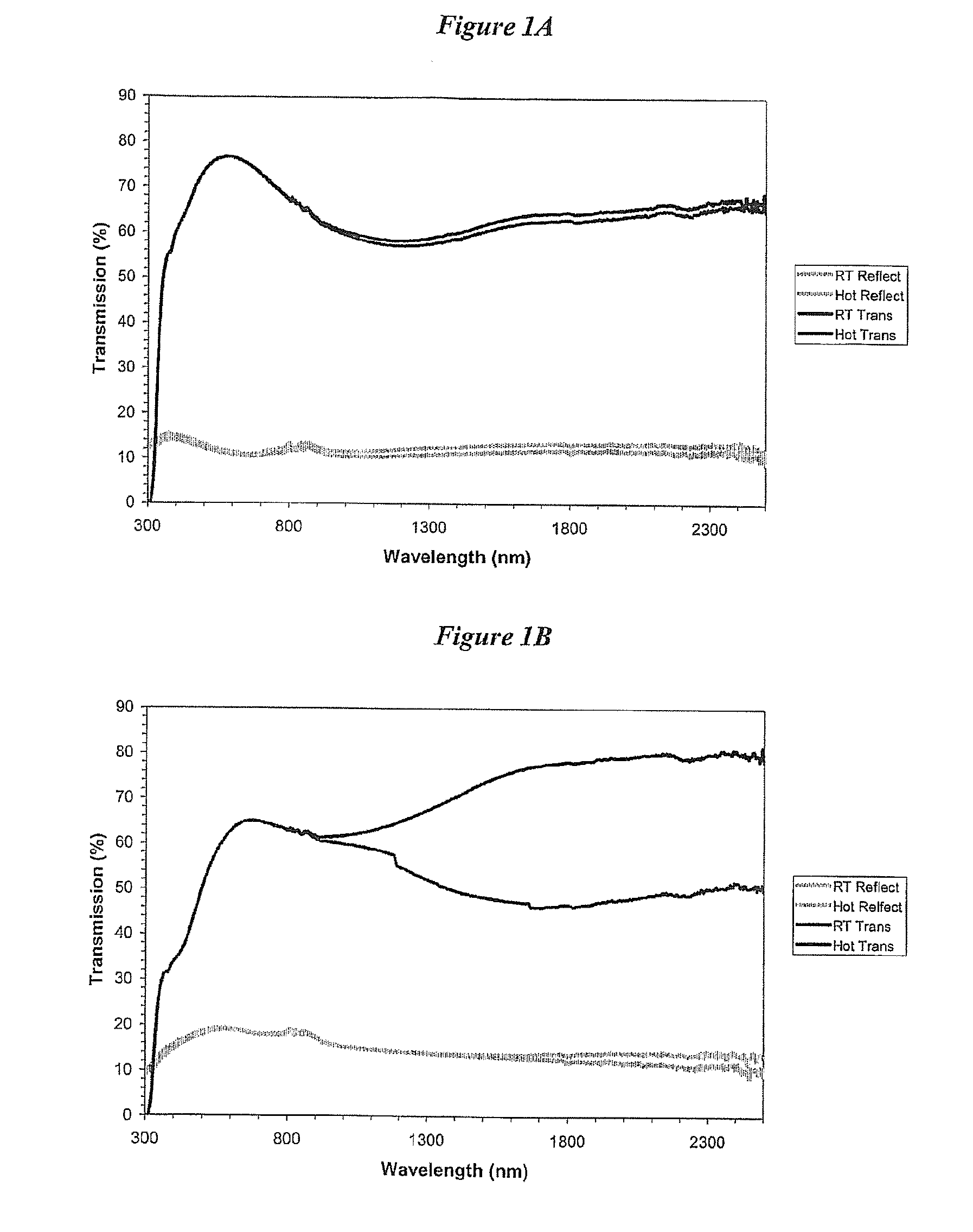
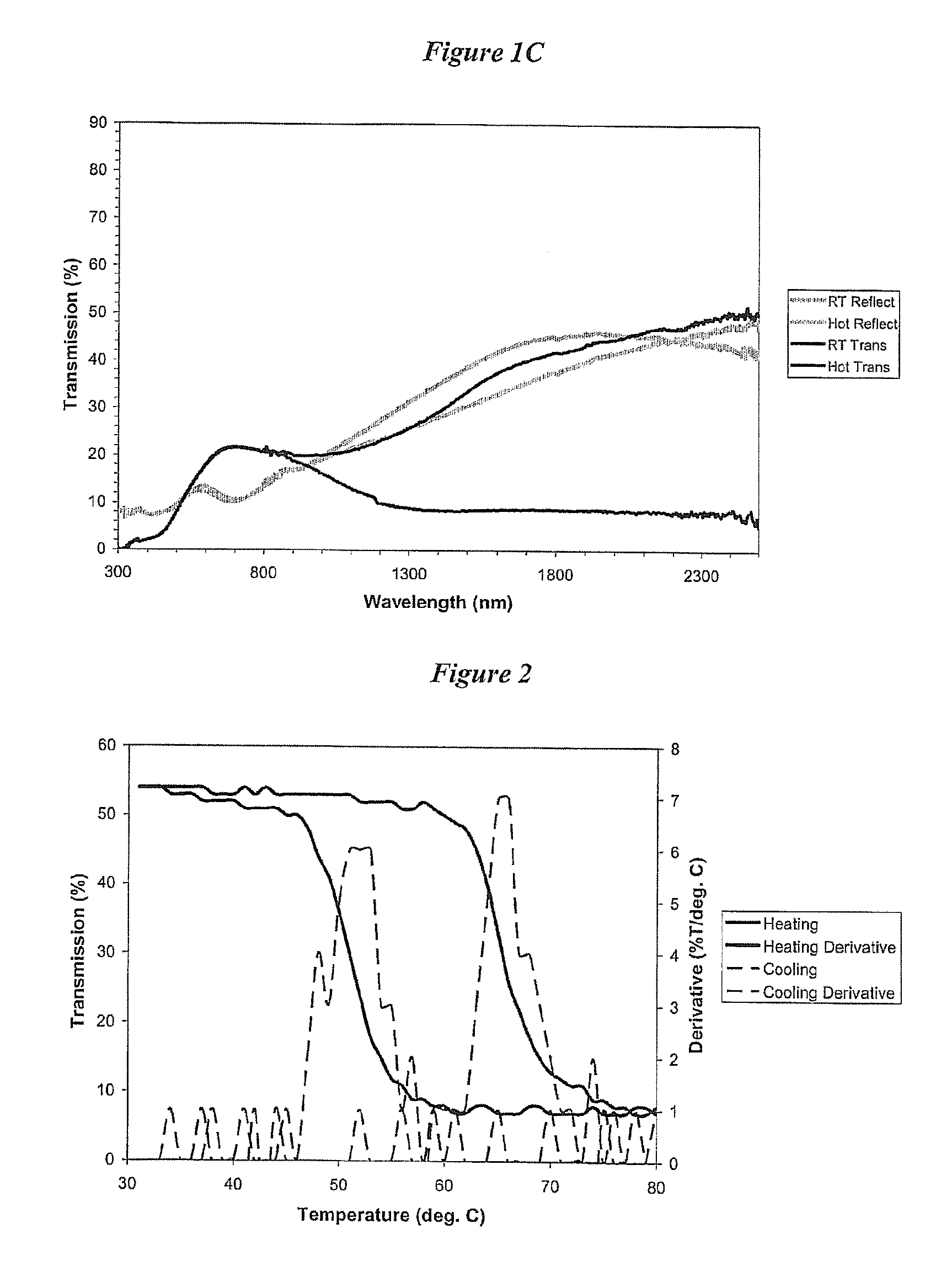
Thermochromic coatings ii
InactiveUS20100270519A1Quality improvementGood reproducibilityConductive materialMetal/alloy conductorsPhysical chemistryThin membrane
The invention provides improved conditions for atmospheric pressure chemical vapour deposition (APCVD) of vanadium (IV) oxide. Specifically, higher quality vanadium oxide (particularly in the form of films) can be obtained by employing concentrations of precursors in the APCVD reaction which are substantially less than those used previously. These conditions improve the reproducibility of the films obtained by APCVD and also prevent particulate formation in the manufacturing apparatus, which in previous work had caused blockages. The films obtained have improved visual appearance, especially colour, and / or have improved adhesion to a substrate. The obtained films also show a greater difference in transmission above and below the switching temperature than previous films. The invention also provides doped vanadium oxide, particularly with tungsten. Substrates (e.g. glass substrates) coated with a film of vanadium oxide are also provided. The vanadium oxide of the invention is useful for intelligent window systems, infrared modulators and data storage devices.
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
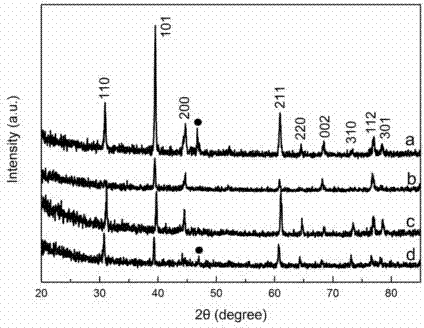
Preparation method of stannic oxide micro-nano materials based on APCVD (atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition) method
InactiveCN102951677ANo post-processing requiredAchieving controllable synthesisMaterial nanotechnologyTin oxidesPotassium borohydridePtru catalyst
The invention provideds a controllable preparation method of stannic oxide micro-nano materials of different shapes based on an APCVD (atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition) method. The controllable preparation method comprises the following steps of mixing a carbonaceous material and a solvent, grinding the mixture to be pasty, uniformly coating the pasty mixture on a resistance ring, and calcining the resistance ring with the pasty mixture to be served as a substrate of a deposition material; putting the resistance ring in a reaction chamber, firstly filling protective gas, secondly mixing a stannous chloride solution and a potassium borohydride solution to generate hydrogen stannide, charging carrier gas in the reaction chamber with the hydrogen stannide, heating the reaction chamber to a preset temperature and depositing for a while to stop the reaction; and continuously filling the protective gas till the resistance ring is cooled down, putting the cold resistance ring in a muffle furnace to calcine to obtain white stannic oxide materials on the substrate. According to the controllable preparation method of stannic oxide micro-nano materials of different shapes based on the APCVD method, disclosed by the invention, the controllable synthesis of the stannic oxide material is realized by changing the temperature, the time and the substrate of deposition; the utilized instruments are simple, the deposition is carried out under normal pressure so that the cost is low, and no catalyst is added so that the operation is easy; and therefore, the controllable preparation method hopefully becomes a common method for preparing multifunctional materials with high degree of crystallinity and special shapes.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
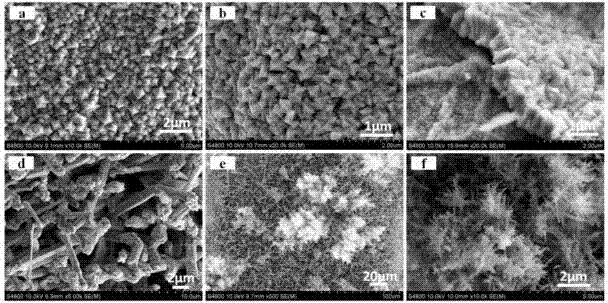
Petal-shaped molybdenum disulfide two-dimensional crystal material as well as preparation method and application thereof
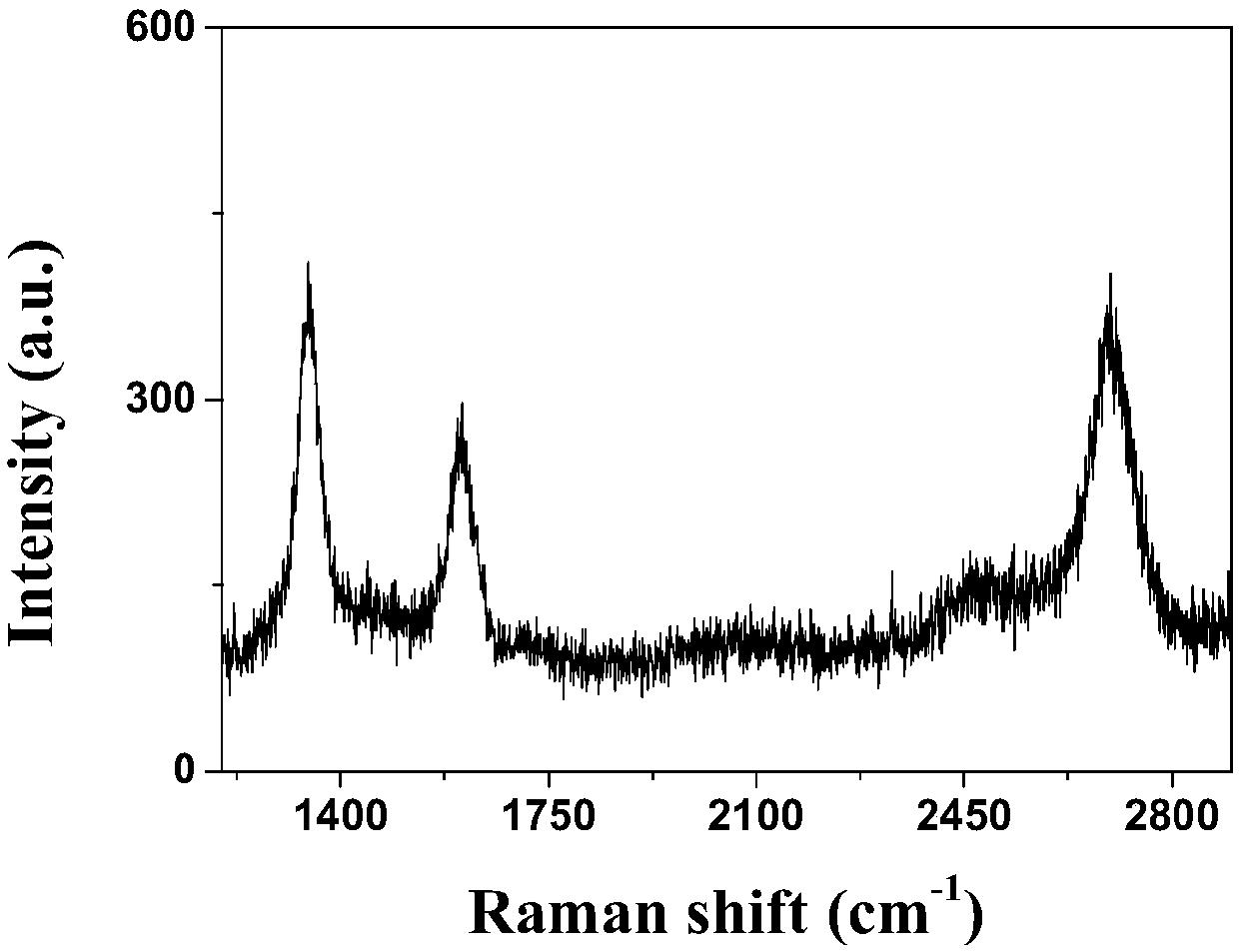
ActiveCN109881176AOptimal control methodEasy to increase or decrease the amountPolycrystalline material growthRaman scatteringChemical reactionTwo dimensional crystal
The invention discloses a petal-shaped molybdenum disulfide two-dimensional crystal material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. According to the method, an atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition method is adopted, and the petal-shaped molybdenum disulfide two-dimensional crystal material is grown on a substrate by heating a reactant for chemical reaction under an inert gas environment. The method has the advantages of simplicity and feasibility and operation convenience. The amount of the reactant is conveniently controlled in the experimental procedures, and uniform supply of a reactant molybdenum source is realized in a large-area range. The prepared product is controllable in morphology characteristic, stable in performance and good in crystallinity, and can be further used for preparing an SERS sensor with high sensitivity and good repeatability, and rapid trace detection on organic molecules is realized.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method of Fabricating Al2O3 Thin Film Layer
InactiveUS20130084715A1Simple and fast procedureReduce leakageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingPhotoelectric conversionSolar cell
An Al2O3 thin film layer is fabricated. Atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition (APCVD) is processed in a normal atmospheric pressure and a low temperature. On a surface of a p-type or n-type silicon crystal wafer having a purity between 5N (99.999%) and 9N (99.9999999%), the Al2O3 thin film layer is deposited and fabricated. The deposition and fabrication are done to obtain chemical passivation and field effect passivation. In this way, the present invention can be applied in solar cells and other photoelectric devices with reduced leakage of surface currents and improved photoelectric conversion.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
Preparation method for reinforced copper-based composite wire
ActiveCN111349905ASolve Component Quality Control IssuesSolve difficult-to-wet problemsTransportation and packagingApparatus for heat treatmentWire rodCopper-wiring
The invention relates to a preparation method for a reinforced copper-based composite wire. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: growing graphene on copper or copper alloy powder by adopting an atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition method; compacting the copper or copper alloy powder into an extrusion blank at a room temperature; carrying out hot extrusion to the extrusion blank to form an extrusion rod blank; drawing the extrusion rod blank at the room temperature to obtain a drawing wire; growing the graphene on the surface of the drawing wire by using the atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition method; cutting and bundling the drawing wire with the graphene growing on the surface, and repeating the hot extrusion process to the drawing wire and a roomtemperature drawing step for zero to many times; rapidly recrystallizing and continuously annealing to the bundling wire after repeated treatment, and then preparing the reinforced copper-base composite wire. The reinforced copper-based composite wire prepared by the invention has a low defect rate, and can form a graphene reinforced and micro-nano copper wire interpenetrating structure with goodinterface bonding to achieve the high strength and high conductivity target of graphene-copper composite material.
Owner:北京碳垣新材料科技有限公司
Atmospheric-pressure chemical vapor deposition coating reactor
ActiveCN104451601AInnovative design ideasEasy maintenanceChemical vapor deposition coatingLaboratory deviceMembrane reactor
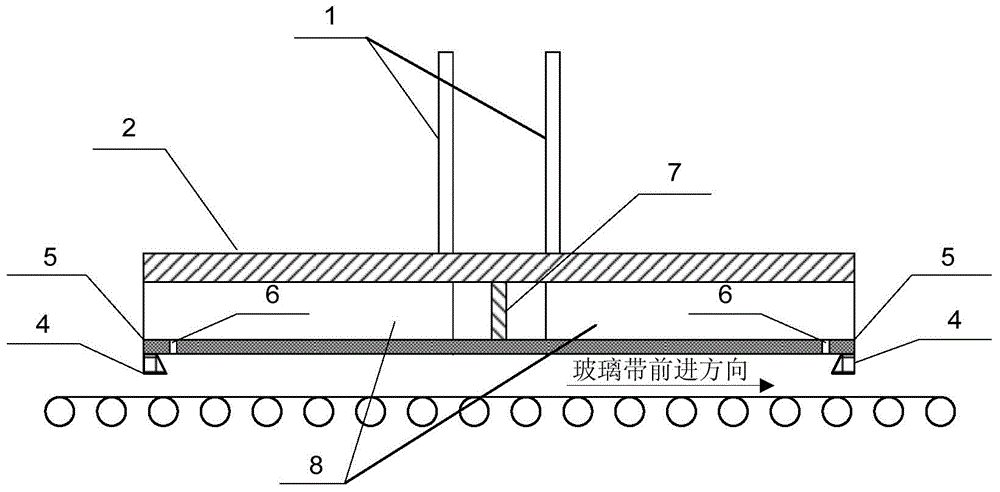
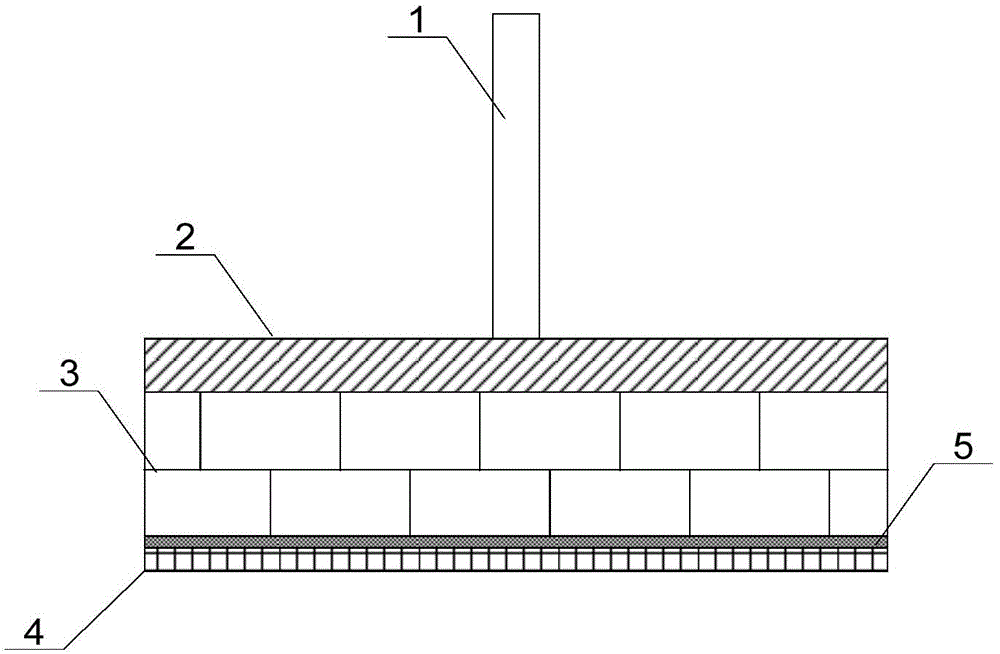
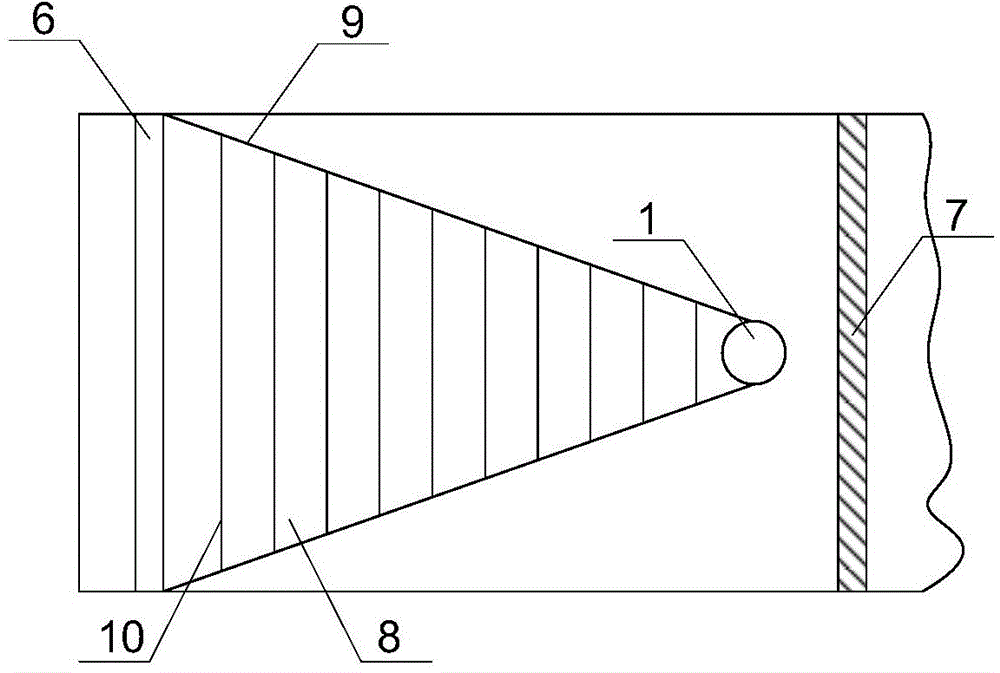
The invention discloses an atmospheric-pressure chemical vapor deposition coating reactor. The coating reactor is characterized in that a gas-mixing chamber having enhanced convection and a beam structure is designed inside the reactor; the bottom of the reactor structurally adopts high-temperature-resistant steel plates having good heat conductivity; the outlet of the gas-mixing chamber adopts a slit structure as a nozzle for coating gas in the reactor; a graphite stopper having a chamfer structure is mounted at the nozzle of the reactor; the gas inlet cavity and an exhaust cavity of the reactor adopt fully symmetrical structures; and the coating gas inlet and coating exhaust directions of the reactor can be interchanged. According to the atmospheric-pressure chemical vapor deposition coating reactor, by enhancing the convective heat transfer of the precursor gas, the thermal efficiency of the reaction is increased, the coating deposition reaction can be performed at a relatively low temperature, the energy consumption of the coating is reduced and the coating temperature window is widen. The coating reactor has the advantages of novel design idea, simple maintenance of the device, small investment and low cost and is suitable for application in industrial or laboratory devices.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com