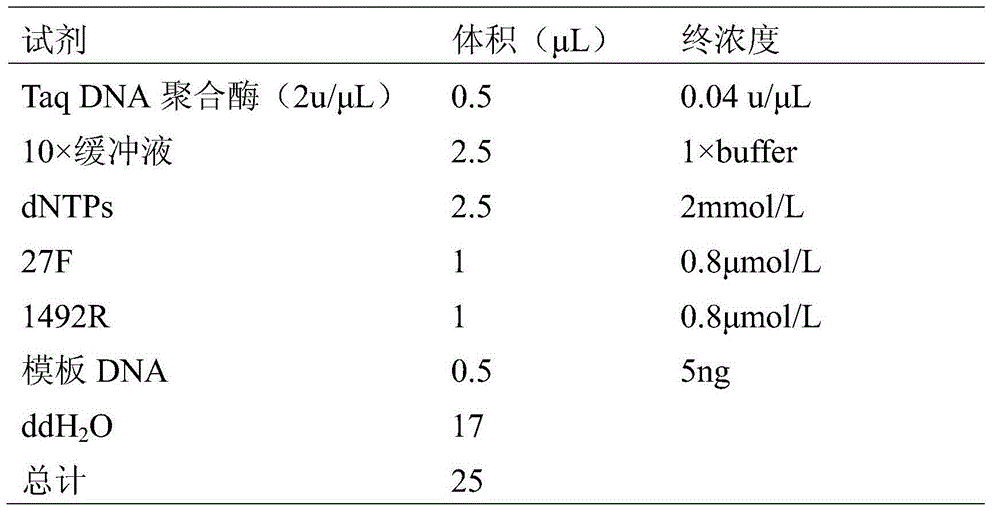
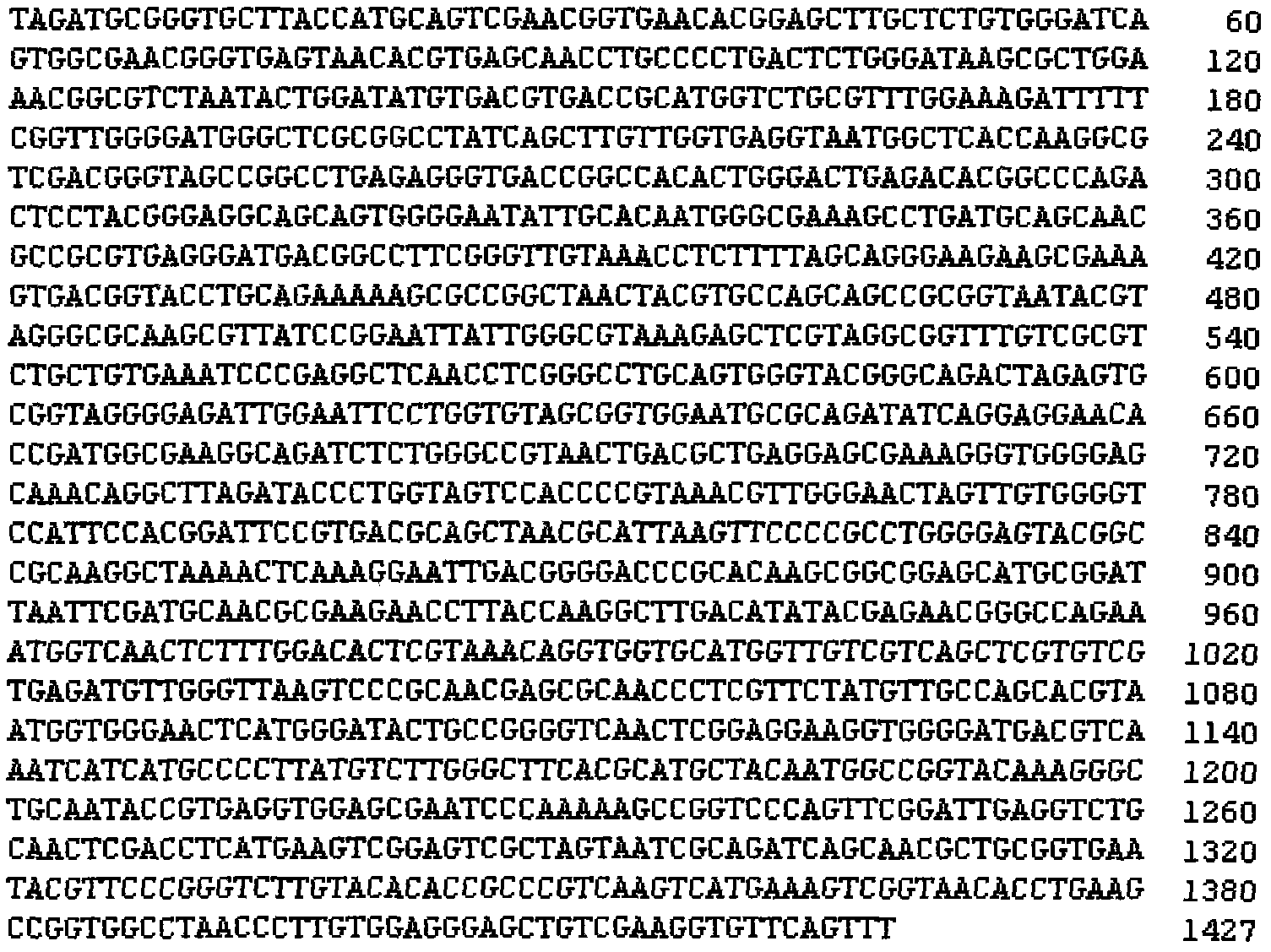Patents
Literature
64 results about "Microbacterium sp." patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Description and Significance. Microbacterium hatanonis is an aerobic, gram-positive, rod-shaped bacterium recently isolated in multiple brands of hairspray.[1] Originally thought to be a known Microbacterium species, 16S rRNA sequencing revealed that M. hatanonis is evolutionarily distinct from all formerly isolated organisms.
Fungicide for removing and/ or degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and application thereof
InactiveCN101851582AHigh removal rateBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationFungicidePolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
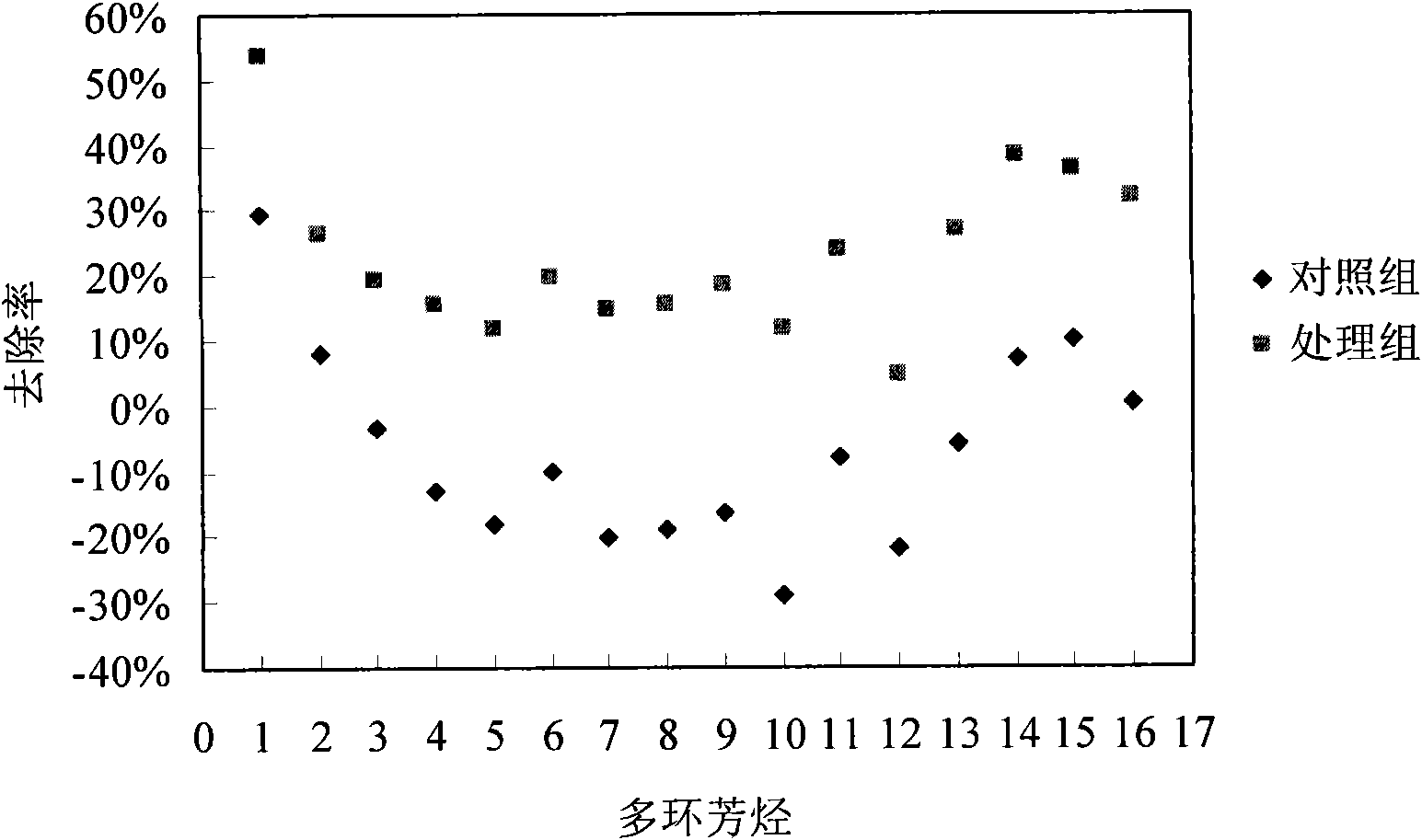
The invention discloses a fungicide for removing and / or degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and application thereof. The invention provides a fungicide of which the active ingredients are (Rhodococcus sp.) LU3 CGMCC No.3610, (Microbacterium sp.) LU1 CGMCC No.3581, (Ochrobacterium sp.) LU2CGMCC NO.3582 and (Bordetella sp.) LU4 CGMCC No.3611. The experiment of the invention shows: after four weeks, the strainaway rate of 16 types of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in soil added with the fungicide is averagely improved by 30% if being compared with that of soil which is not added with the fungicide, wherein the strainaway rate of six types of low-cyclic (two / three cyclic) polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon is averagely improved by 26%, and the stainaway rate of ten types of middle and high cyclic (more than four cycle) polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon is averagely improved by 32%.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Copper activation bacterium and method for plants renovation of soil pollution by heavy metal
InactiveCN101153273APromote activationImprove stress resistanceBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationGramSoil heavy metals
The invention relates to a copper activated bacterium and a method for strengthening the recovery to the heavy metal pollution in the vegetable soil, and belongs to the agricultural and environmental pollution treatment technical field. The JYC17 culture stain of heavy metal copper activated bacteria is the Microbacterium sp. The effective living microbial numbers of the liquid preparation are above a billion per millimeter, and the effective living microbial numbers of the solid preparation are 200 millions per gram. The using method is that: when the seeds of the plant are seminated in humid soil containing heavy metals, the bioremediation preparation of the JYC17 culture stain is inoculated, and 10 to 20mL of the bacteria liquid of 10<8> bacteria JYC17 / mLs is inoculated in each grams of soil once or in two times. The culture stain has good activation effect to the deposited copper in the solution and the activation rate up to above 73 percent. That the plant is implanted and the bioremediation preparation is inoculated in humid soil containing heavy metals promotes the absorption and the extraction of the plant to the heavy metal copper and improve the extraction and recovery efficiency.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Microbacterium and application thereof in degradation for organic pollutants
ActiveCN104745502ALow costNo secondary pollutionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesOxidative enzymeHydrolysis
The invention relates to a microbacterium and application thereof in degradation for organic pollutants, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The strain is obtained by separating and purifying from the sea mud of the South China Sea, is a variant of microbacterium, and named as Exiguobacterium profundum L20, and through authentication, the strain is a Gram-positive rod-shaped bacterium with a size of 1.1-1.2mum*1.4-3.2mum, which is peritrichous, sporeless, facultative anaerobic, positive with catalase, negative with oxidase, and is used for hydrolyzing gelatine, starch and the like, and the strain is collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Centre on March 20, 2014, with the collection number of CGMCC NO. 8944; through experimental verification, the strain has capacity of degrading bisphenol A, and a degradation rate of 90-100%, and can be applied to biodegradation for endocrine disruptor bisphenol A.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Microbacterium sp.T3 with tolerance on heavy metals and application thereof
ActiveCN102127516AHigh tolerance concentrationIncrease vitalityBacteriaWater contaminantsBacteriaHeavy metals
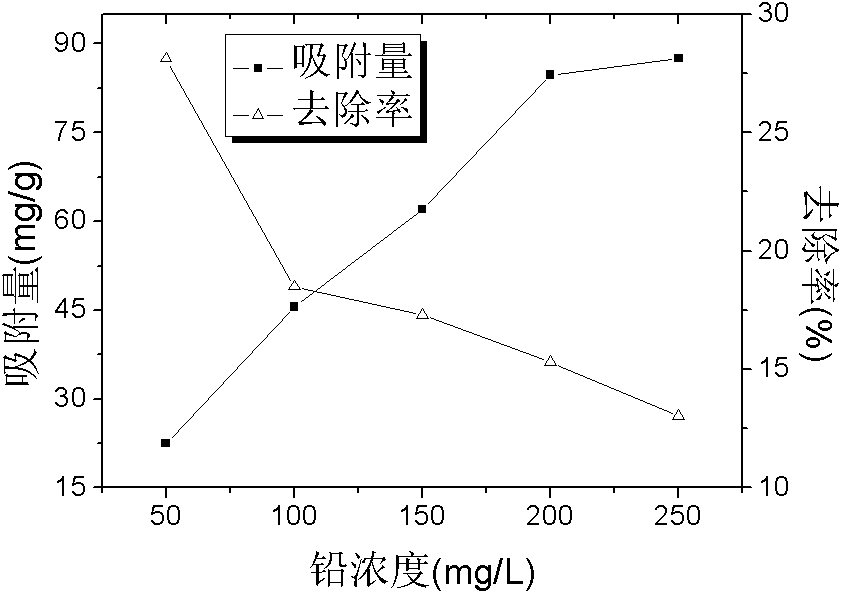
The invention discloses a Microbacterium sp.T3 with tolerance on heavy metals and application thereof. The Microbacterium sp.T3 is preserved with the number of CGMCCNo.4282. The bacterium can tolerate a plurality of heavy metals such as Pb<2+>, Cr<6+>, Mn<2+>, Zn<2+>, Cu<2+>, Ni<2+>, Cd<2+>, Co<2+>, Ag<+>, Hg<2+>, and the like, particularly has the tolerance concentration on the Pb<2+> and the Mn<2+> respectively reaching 2000mg / L and 1000mg / L. Strains are activated, cultured, collected, cleaned and dried to prepare an adsorbent in which heavy metals are removed. The maximum adsorption capacity on Pb<2+> as one of the heavy metals can reach 87.49mg / L.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Micro-ecological composite inoculant special for overcoming watermelon continuous cropping obstacle and application method
The invention belongs to the field of microbe fertilizers, and provides a micro-ecological composite inoculant special for overcoming watermelon continuous cropping obstacle and an application method so as to solve the problems that various method for overcoming watermelon continuous cropping obstacle possess responding defects. The inoculant is prepared by mixing bacillus laterosporus, bacillus amyloliquefaciens, bacillus circulans, propionibacterium shermanil, tree microbacterium sp., bacillus laevolacticus, trichoderma harzianum, trichoderma asperellum, trichoderma fasciculatum Bissett, paecilomyces lilacinus, streptomyces syringini, gordonia sp., tsukamurella sp. and conexibacter sp. according to a certain ratio. The composite inoculant guarantees watermelon quality safety and environment zero pollution, and helps to reduce peasant production cost, guarantee agricultural product quality safety and protect ecological environment. The composite inoculant effectively overcomes watermelon continuous cropping obstacle, and watermelon which is truly nuisance-free, pure in mouthfeel and high in sweetness is produced. The composite inoculant possesses significant meaning on watermelon production, watermelon peasant income increase, consumer health guarantee, environment pollution reduction and maintenance of agricultural sustainable development.
Owner:AGRI BIOTECH RES CENT OF SHANXI PROVINCE
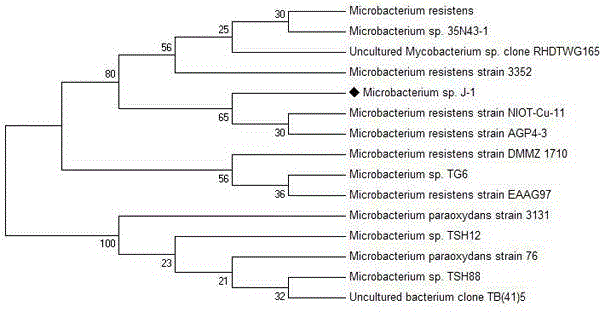
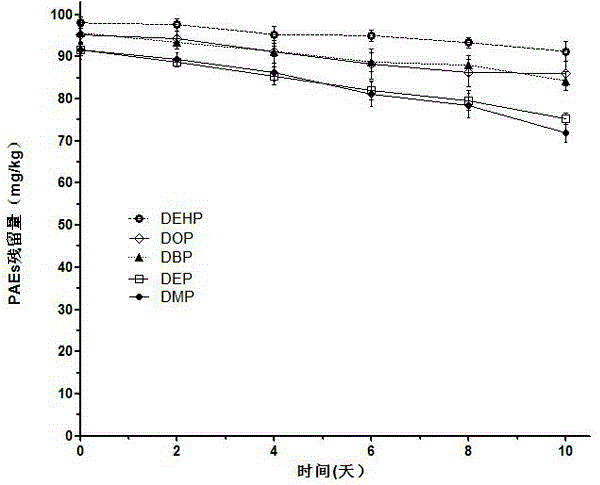
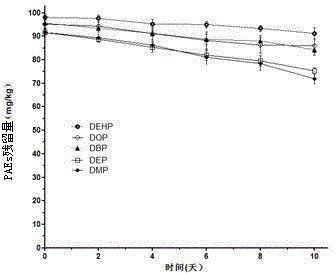
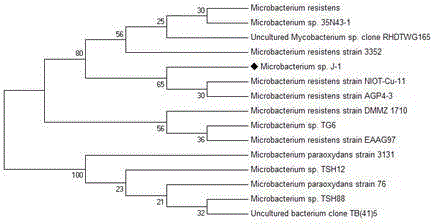
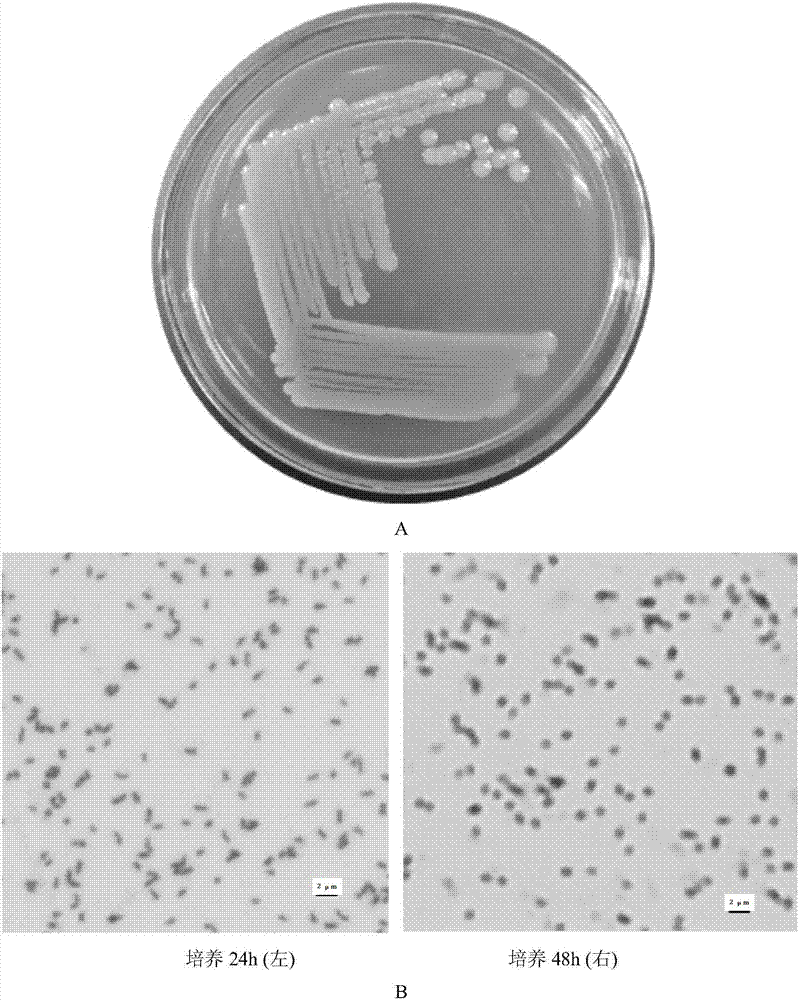
Microbacterium sp. J-1 used for degrading plurality of phthalic acid esters
ActiveCN104805033AEfficient degradation abilityWidely distributedBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationBacilliBacteroides species
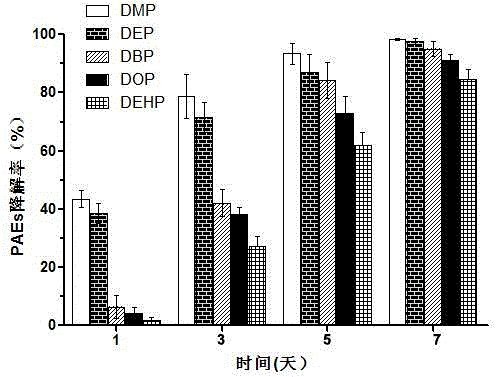
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental pollutant biological treatment, and specifically discloses microbacterium sp. J-1 used for degrading a plurality of phthalic acid esters (PAEs). The microbacterium sp. J-1 is preserved at China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on 22th, Jan., 2015, and preservation number is CCTCC No.M 2015055. The microbacterium sp. J-1 is capable of degrading a plurality of PAEs simultaneously; a problem that multi-effect bacteria in culture collection are insufficient is solved; the microbacterium sp. J-1 is widely distributed in the natural world; adaptability is high; and the invention also provides application research of the microbacterium sp. J-1 in polluted soil restoration, and technical support is provided for biological treatment of PAEs soil pollution.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
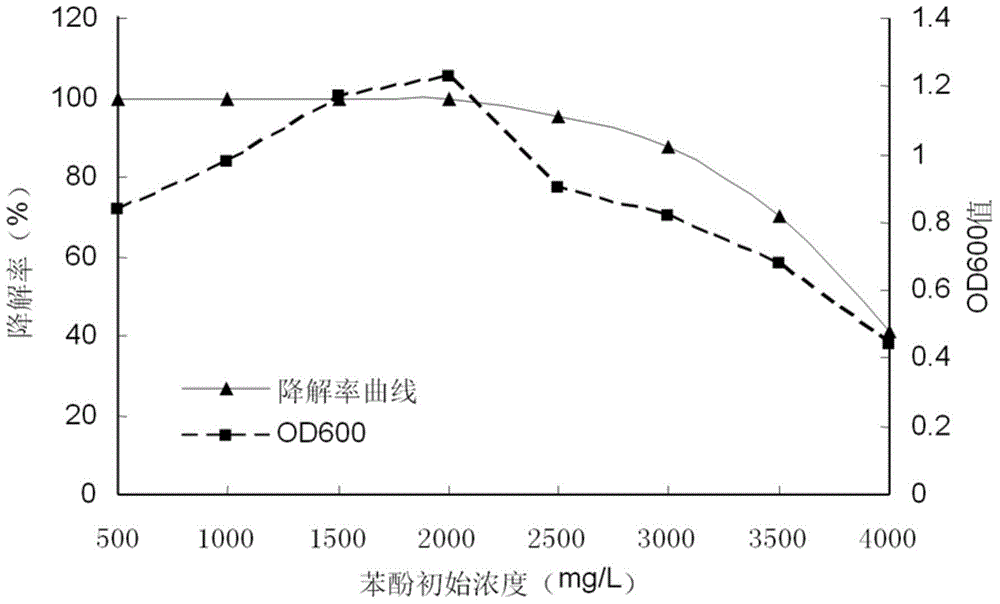
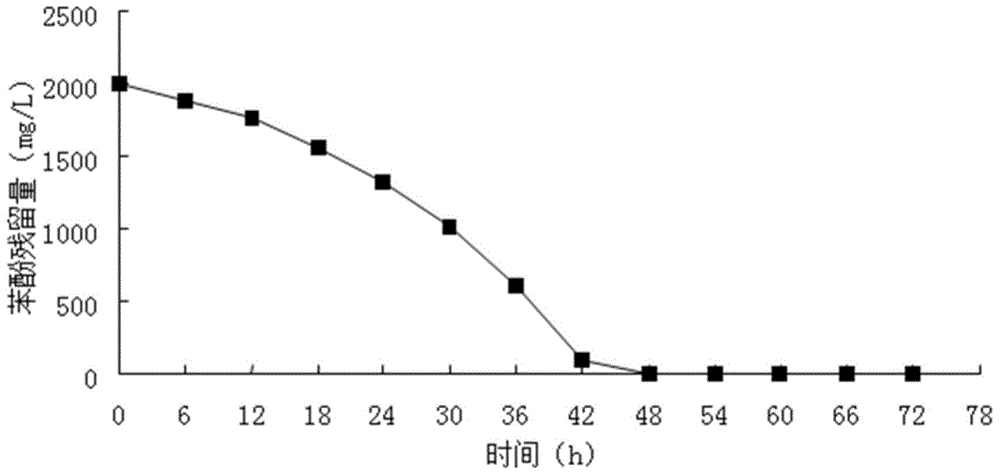
Microbacterium sp. strain and application thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of microbes, and concretely relates to a microbacterium sp. strain and a biological pure culture thereof, and application of the bacterial strain to degrade phenol. The microbacterium sp. strain is SY-PD-42, and has the preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2014101. The microbacterium sp. strain is capable of efficiently degrading phenols in wastewater, and also is capable of tolerating a phenol-containing solution with the phenol concentration up to 2500 mg / L.
Owner:中国中化股份有限公司 +1
Applications of Microbacterium sp. J-1 in degradation of plurality of phthalic acid esters
ActiveCN104805036AEfficient degradation abilityWidely distributedBacteriaWater contaminantsActivated sludgeSewage
The invention belongs to the technical field of environment pollutant biological treatment, and specifically discloses applications of Microbacterium sp. J-1 in degradation of a plurality of phthalic acid esters (PAEs). The bacterial strain is obtained by the inventors of the invention for the first time via separation from activated sludge of sewage treatment plants, and is capable of realizing high efficiency degradation on a plurality of PAEs in polluted environment, and especially on short chain PAEs, so that application prospect of the bacteria strain on remediation of soil polluted by the plurality of PAEs is promising.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
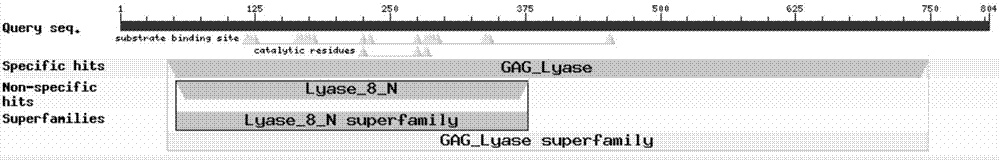
Microbacterium, broad spectrum glycosaminoglycan lyase expressed by microbacterium, and coding gene and applications of broad spectrum glycosaminoglycan lyase
ActiveCN106906161AEfficient preparationBroad substrate specificityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesChondroitin Sulfate C
The present invention relates to microbacterium, broad spectrum glycosaminoglycan lyase expressed by the microbacterium, and a coding gene and applications of the broad spectrum glycosaminoglycan lyase. According to the present invention, the Microbacterium sp. WS15 strain is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on December 05, 2016, and has the preservation number of CGMCC No.13421, wherein the address is Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 3# Court No.1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing; and the glycosaminoglycan lyase TT16 is firstly obtained from the genome of Microbacterium WS15, can degrade the hyaluronic acid with no sulfation modification, can further degrade chondroitin sulfate A (CS-A), chondroitin sulfate C (CS-C) and chondroitin sulfate E (CS-E) being subjected to different sulfation modifications, and is the broad spectrum glycosaminoglycan lyase.
Owner:济南唐泰生物科技有限公司
Method for producing liquid organic fertilizer by fermentation of poultry feathers with microbes
InactiveCN106116765ARich in nutrientsRich in amino acidsBio-organic fraction processingMagnesium fertilisersKeratinChemistry
The invention discloses a method for preparing liquid organic fertilizer with an efficient feather degrading bacterium stenotrophomonas maltophilia (Microbacterium sp. TSMC-99). The method is realized by a series of steps: pretreatment of raw materials, preparation of fermenting bacteria of organic fertilizer, optimization of fermenting conditions and production of liquid organic fertilizer. The method makes the most of the poultry feather protein source to produce the liquid organic fertilizer by fermentation, can relieve the insufficiency of organic fertilizer in China, and also can solve the environmental problem caused by a large backlog of feathers. The liquid organic fertilizer produced by microbial fermentative degradation of feather keratin contains rich amino acid and polypeptide and is efficient and environment-friendly green fertilizer; the method has the advantages of mild production conditions, environment friendliness, simple operation, easy popularization and low cost and makes waste profitable; and the technical indexes of the prepared liquid organic fertilizer conform to specifications in the industry standard 'NY525-2012 Organic Fertilizer' of the Department of Agriculture.
Owner:TAISHAN MEDICAL UNIV
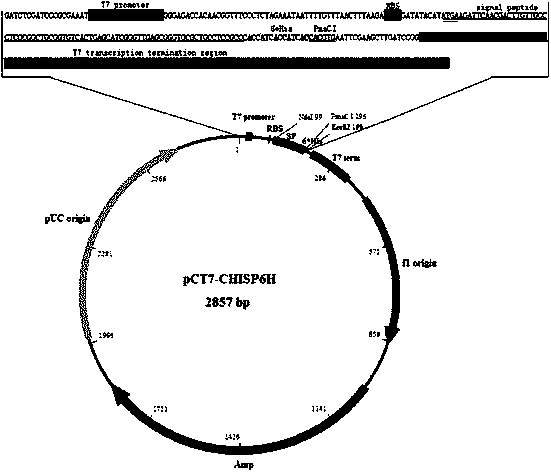
Vector for efficiently secreting and expressing heterogenous protein, and its application
InactiveCN104342445AImprove build efficiencyShorten the timeBacteria peptidesEnzymesSequence signalSolubility
The invention relates to an expression vector in the gene engineering field, and concretely relates to a vector for efficiently secreting and expressing a heterologous protein, and its application. An encoding signal peptide for efficiently secreting and expressing the heterologous protein is represented by a base sequence in SEQID NO.1. The vector for efficiently secreting and expressing the heterologous protein contains a specific nucleotide sequence, the sequence is the nucleotide sequence of a promoter and the encoding signal peptide; structure diagrams comprise a promoter sequence, a nucleotide sequence encoding the signal peptide, a 6*His tag sequence and a PmaCI restriction enzyme site; and the promoter is a T7 promoter, and the encoding signal peptide is a chitosan enzyme signal peptide of microbacterium (Microbacterium sp.OU01). The vector can efficiently secreting and expressing exogenous gene and also can effectively improve the water solubility of expression products, and a recombinant protein with biological activity can be obtained by using affinity chromatography one-step purification.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
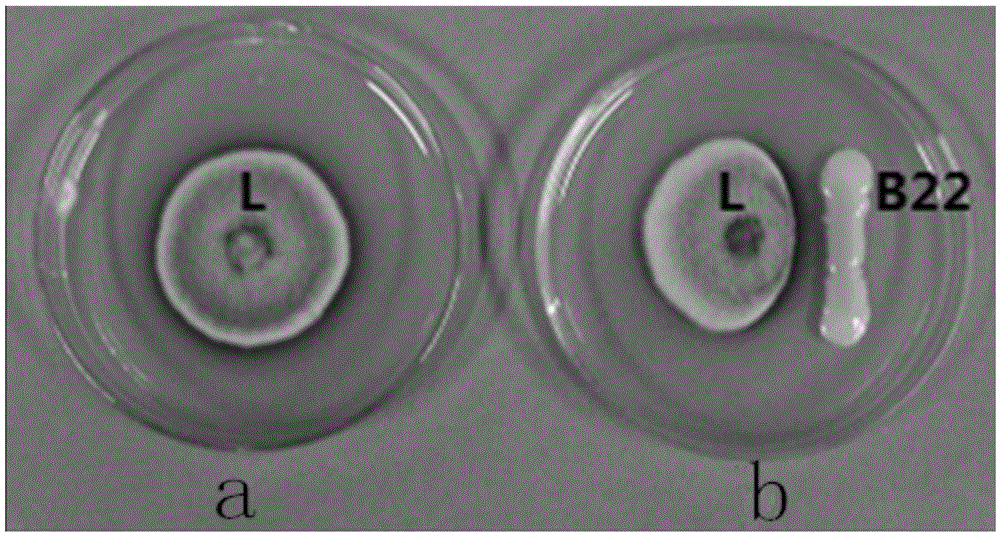
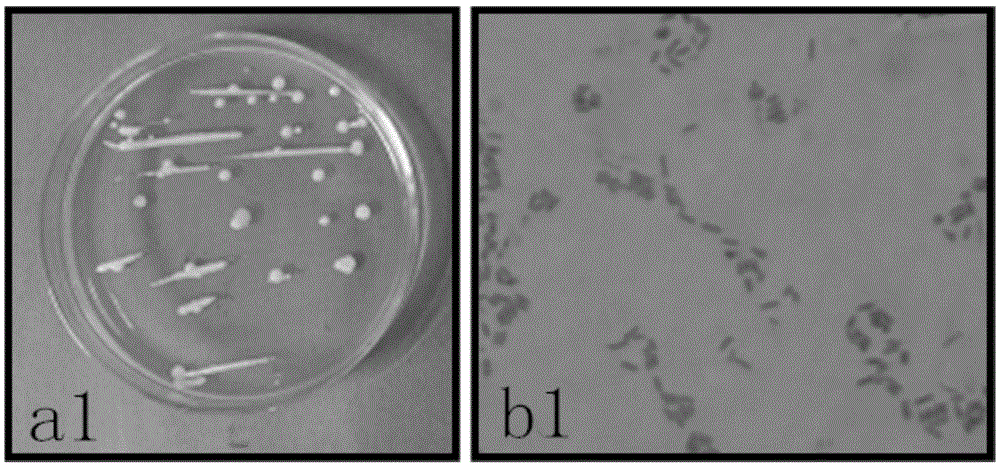
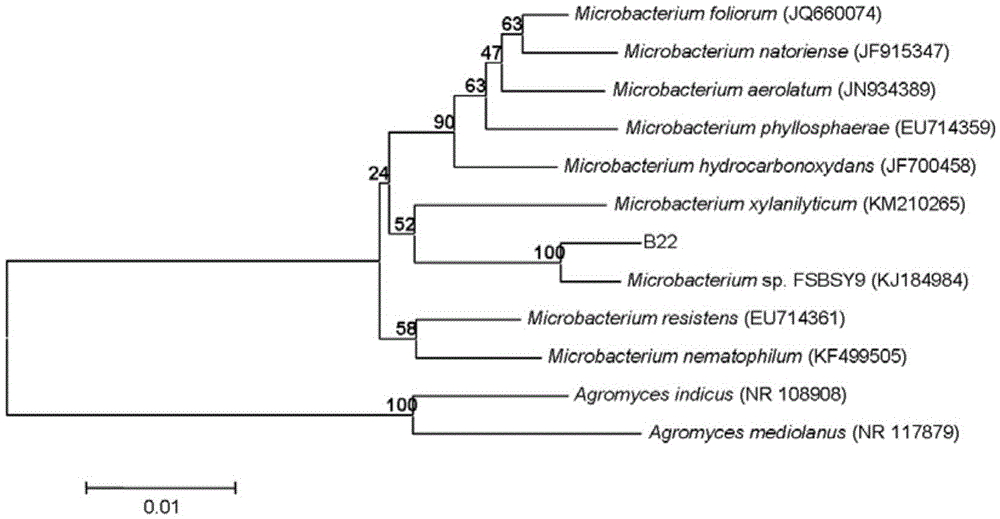
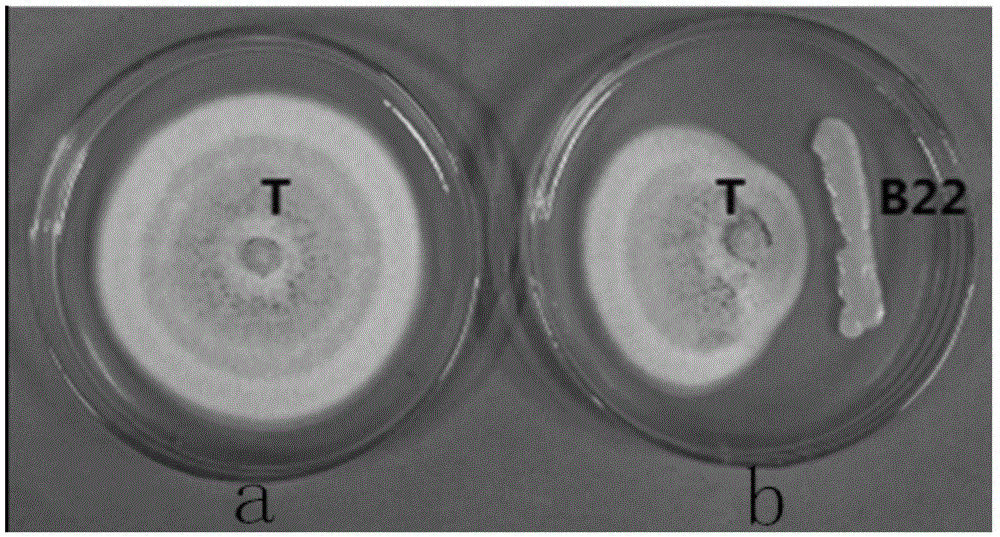
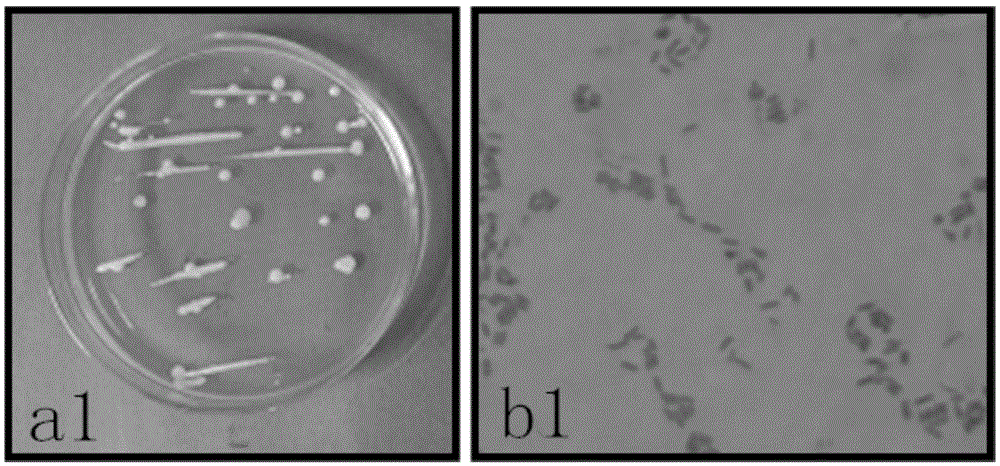
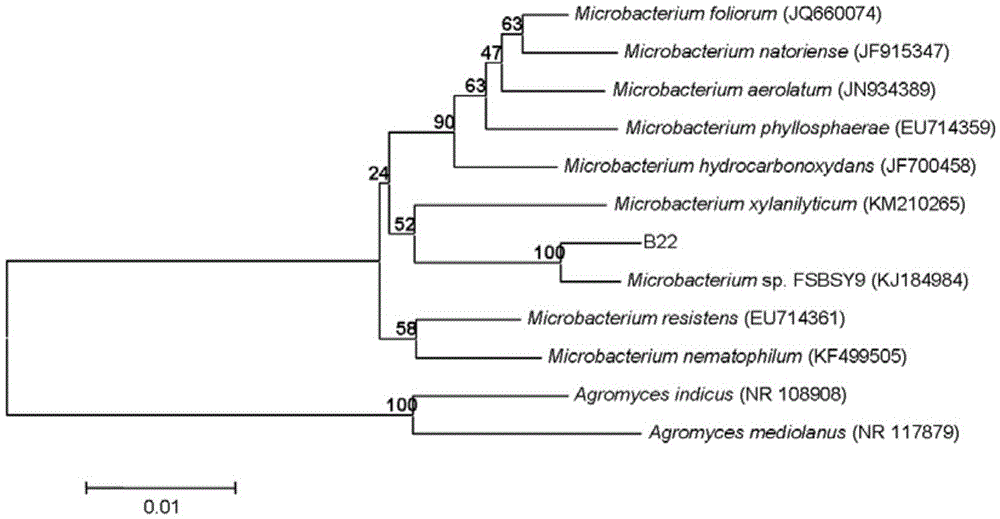
Application of sophora tonkinensis endogenetic bacterium B22 in prevention and treatment of panax notoginseng black spot
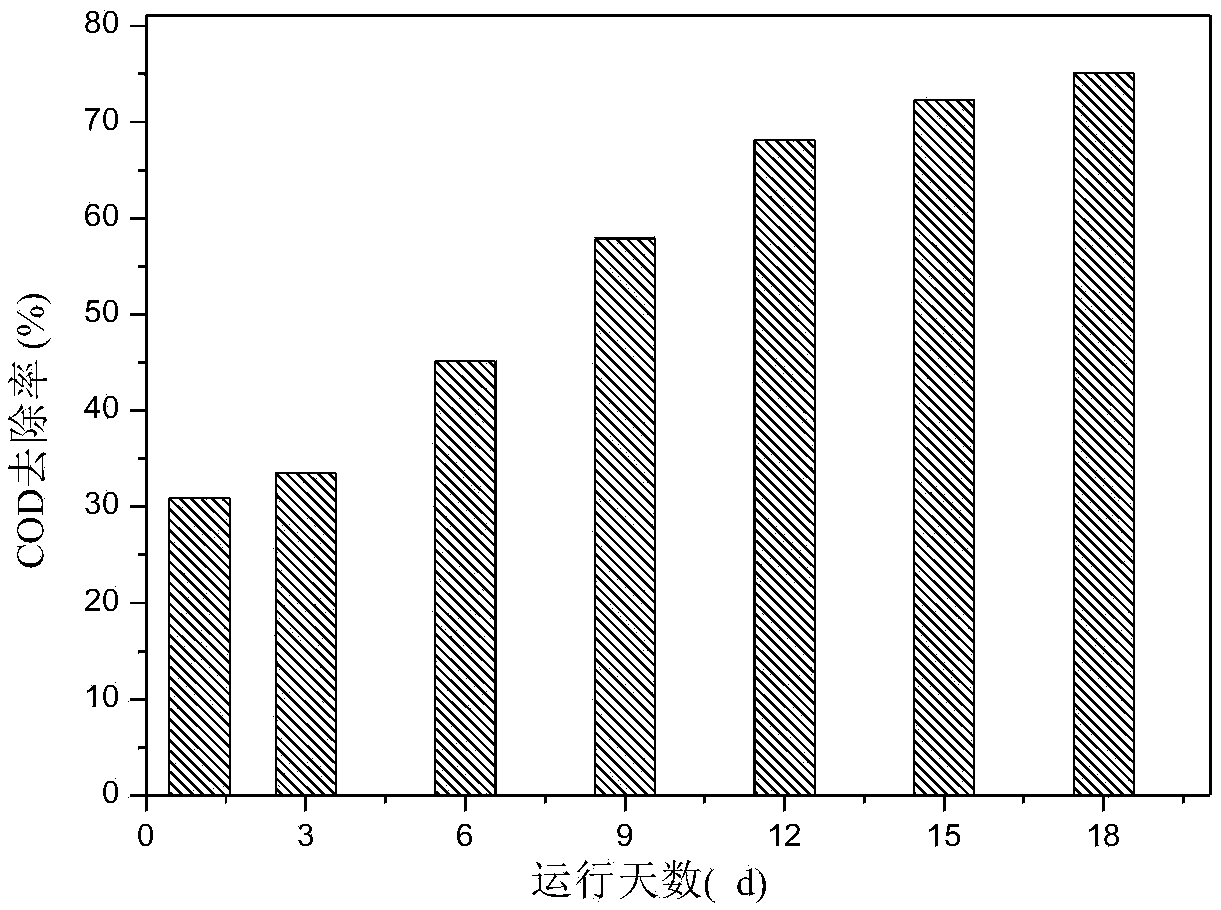
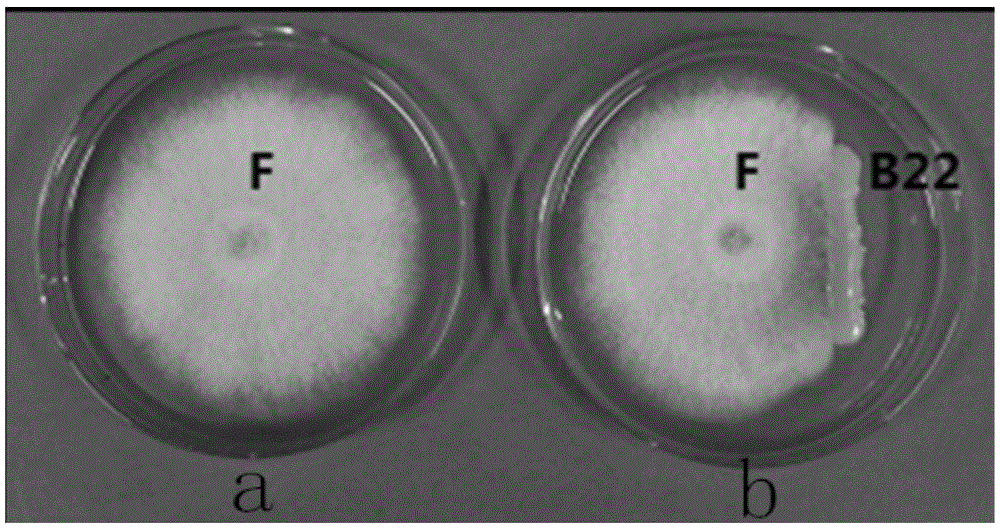
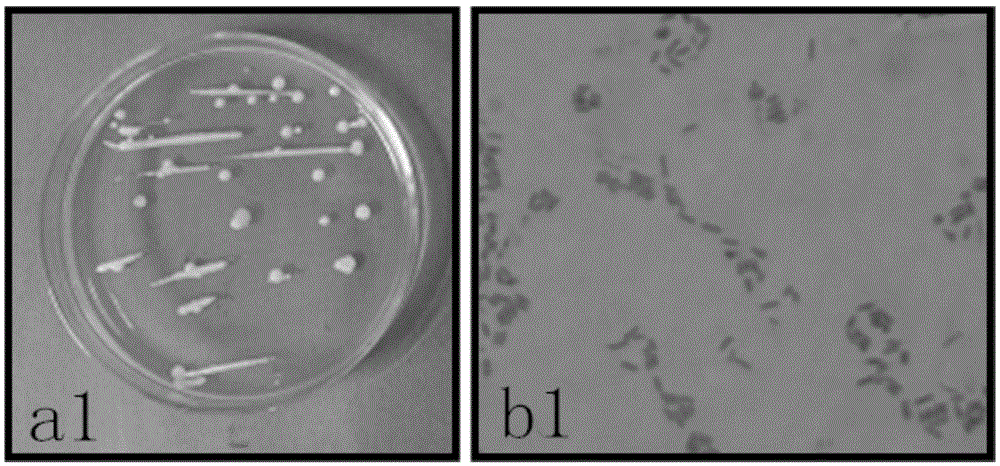
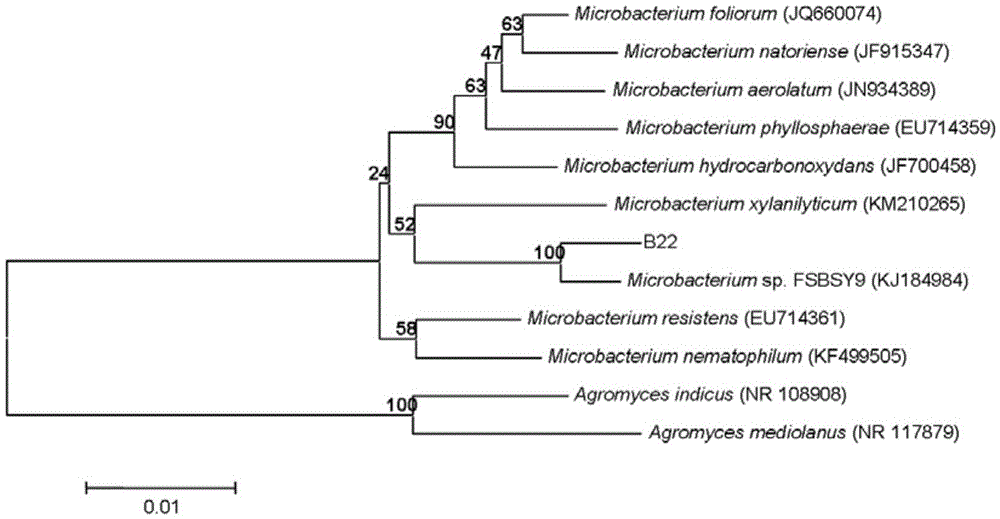
The invention discloses sophora tonkinensis endogenetic bacterium B22. The sophora tonkinensis endogenetic bacterium B22 has the type name of Microbacterium sp. B22, a 16S rDNA gene sequence table of the Microbacterium sp. B22 is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1, and the Microbacterium sp. B22 is collected by the General Microorganisms Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, which is located at Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 3#, 1# Courtyard, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, on September 29, 2015 and has the collection number of CGMCC No. 11463. According to the sophora tonkinensis endogenetic bacterium B22, the endogenetic bacterium Microbacterium sp. B22 is obtained through being separated from roots of a medicinal plant, i.e., Sophora tonkinensis and carrying out screening for the first time and has a powerful inhibiting action on Alternaria panax Whetzel, and thus a broad application prospect is brought to the field of biological control on panax notoginseng fungal diseases.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Microbial strain and application thereof
ActiveCN102719369AImprove qualityLower nicotine levelsTobacco treatmentBacteriaTobacco nicotineBiotechnology
The invention discloses a microbial strain and an application thereof, particularly relates to a tobacco nicotine degrading microbacterium GYC29 (Microbacterium sp.GYC29) with CCTCC of NO:M2010311 and an application of the microbacterium in tobacco. The strain disclosed herein can decompose and utilize nicotine in the growth process. According to the invention, by adding the ferment liquor of the strain or thallus with the additional amount of 1-5 % of the weight of the tobacco leaves in the tobacco with the water content of 10-50 % and fermenting for 6-72 h, the nicotine content of the tobacco leaves is reduced by 2-33%, the irritation of the tobacco leaves is obviously reduced, the miscellaneous gases are reduced, the smoke becomes pure and mild, and the sensory quality is obviously improved; the degradation of tobacco nicotine is realized by using microbes, the nicotine content of tobacco raw materials can be regulated properly, and the applicability of the tobacco leaves is raised.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO GUANGXI IND
Bacterial strain for treating high concentrated organic wastewater, microorganism bacterium agent and application thereof
ActiveCN105368737AHigh organic loadStrong impact resistanceBacteriaBiological water/sewage treatmentMicroorganismTreatment field
The invention discloses a bacterial strain for treating high concentrated organic wastewater, a microorganism bacterium agent and application thereof. The bacterial strain specifically comprises Gordonia sp. Y-1 (the preservation registration number is CGMCC NO.10791) and Microbacterium sp. Y-3 (the preservation registration number is CGMCC NO.10792), and the Gordonia sp. Y-1 and the Microbacterium sp. Y-3 are mixed according to the proportion of 1:1-3 to perform magnifying fermentation so as to obtain the bacterium agent with the concentration of 1*109-1*1011 CFU / mL. The Y-1 and the Y-3 of the bacterial strain and the microorganism bacterium agent can maintain the better organic matter degradation capacity and can be used in the treatment field of pollutant reduction and degradation of high concentrated organic wastewater.
Owner:CNOOC TIANJIN CHEM RES & DESIGN INST +1
Application of sophora tonkinensis endophytic bacterium B22 in preventing and controlling panax notoginseng root rot
The invention discloses a sophora tonkinensis endophytic bacterium B22. The sophora tonkinensis endophytic bacterium B22 is classified and named as Microbacterium sp. B22, wherein the 16S rDNA gene sequence table of the strain is as described by SEQ ID NO.1, the depository authority is the General Microbiological Collection Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, the depository address is Institute of Microbiology, Building 3, No.1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, the depository date is 29 September 2015, and the depository number is CGMCC No.11463. According to the sophora tonkinensis endophytic bacterium B22 provided by the invention, a strain of sophora tonkinensis endophytic bacterium Microbacterium sp. B22 is separated and screened from the root of a medicinal plant sophora tonkinensis for the first time, the Microbacterium sp. B22 has strong inhibiting effect on panax notoginseng fusarium solani, and a wide application prospect is created for the biological prevention and control field of panax notoginseng fungal diseases.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
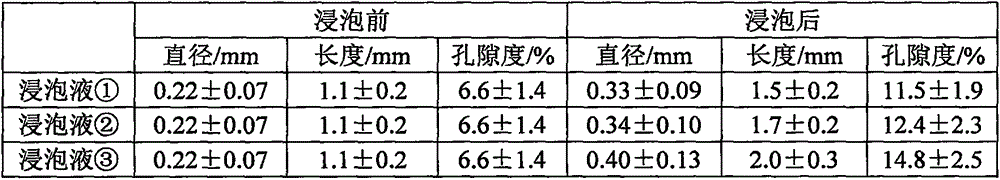
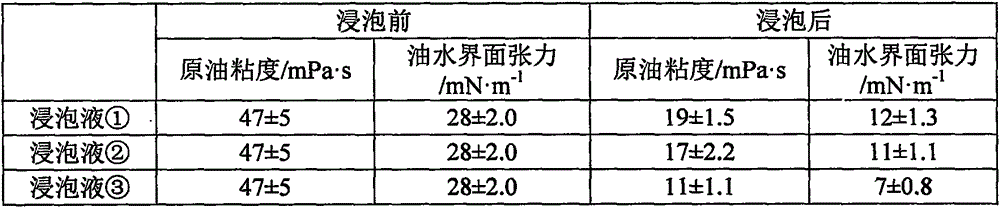
Method for improving crude oil recovery ratio in dolomite reservoir by using microbial flora
InactiveCN105567204AEnhanced Oil RecoveryIncreased pore diameterDrilling compositionEscherichia coliPseudomonas putida
The invention relates to a method for improving a crude oil recovery ratio in a dolomite reservoir by using microbial flora, wherein the microbial flora include pseudomonas aeruginosa, bacillus cereus, bacillus subtilis, microbacterium sp., escherichia coli, pseudomonas putida and bacillus licheniformis; the microbial flora are compounded according to the ratio, and through expansion culture and fermentation culture, a fermentation liquid of the microbial flora is prepared; the fermentation liquid is mixed with injected water, a nutrient solution is added into the mixed solution, the mixed solution is injected into a dolomite reservoir core, and after the injected microbial flora act on the dolomite reservoir core, crude oil recovery is performed. The microbial flora can increase the core pore diameter, length and porosity, and lowers the crude oil viscosity and oil-water interfacial tension, so as to improve the crude oil recovery ratio of the dolomite reservoir; moreover, the method has the advantages of simple fermentation process, low cost, simple operation, and high input / output ratio, is suitable for large-scale industrial production, and has good application prospects.
Owner:河北地质大学
Complex microbial inoculant for degradation of chlorohydrocarbon and application thereof
InactiveCN104830726AEfficient degradationImprove toleranceBacteriaWater contaminantsMicroorganismMicrobial inoculant
The present invention relates to a complex microbial inoculant for degradation of chlorohydrocarbon and application thereof. The complex microbial inoculant includes 10-30% of methylocystis sp.JTA, 20-40% of methylobacterium sp.R1, 10-30% of microbacterium sp.DH and 5-20% of cupriavidus sp.SWA1. The invention employs co-metabolism and direct oxidation of a variety of microorganisms to achieve efficient degradation on the chlorohydrocarbon hard to degrade, effectively solves the problems of incomplete degradation or higher toxicity of product after dechlorination in the anaerobic degradation of chlorohydrocarbon, and is expected to achieve new breakthroughs in engineering application of chlorohydrocarbon biodegradation.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
2,4-dinitrotoluene sulfonate efficient degradation strain Microbacterium sp.X3 and application thereof
ActiveCN108277175AOvercome defectsOvercome deficienciesBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationNitro compoundMicroorganism
The invention discloses a 2,4-dinitrotoluene sulfonate efficient degradation strain Microbacterium sp.X3 and application of the 2,4-dinitrotoluene sulfonate efficient degradation strain Microbacteriumsp.X3. The strain is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on September 15, 2017, and the preservation number is CGMCC NO.14586. The invention further discloses a method for screening the 2,4-dinitrotoluene sulfonate efficient degradation strain and a use method applying the strain to degrading the TNT red water and soil polluted by the red water. The strain iscultured to the logarithmic phase and is then inoculated to the polluted soil, the concentrations of 2,4-DNT-3-SA and 2,4-DNT-5-SA in the polluted soil are respectively 500 mg / Kg, and the removal rateof two 2,4-dinitrotoluene sulfonates both reach 100% after the treatment for 4-6 days. The strain has excellent application in the remediation of the organic polluted soil polluted by nitrocompounds.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF COLLABORATIVE INNOVATION
Application of sophora tonkinensis endophytic bacterium B22 in preventing and controlling panax notoginseng anthracnose
The invention discloses a sophora tonkinensis endophytic bacterium B22. The sophora tonkinensis endophytic bacterium B22 is classified and named as Microbacterium sp. B22, wherein the 16S rDNA gene sequence table of the strain is as described by SEQ ID NO.1, the depository authority is the General Microbiological Collection Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, the depository address is Institute of Microbiology, Building 3, No.1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, the depository date is 29 September 2015, and the depository number is CGMCC No.11463. According to the sophora tonkinensis endophytic bacterium B22 provided by the invention, a strain of sophora tonkinensis endophytic bacterium Microbacterium sp. B22 is separated and screened from the root of a medicinal plant sophora tonkinensis for the first time, the Microbacterium sp. B22 has a strong inhibiting effect on panax notoginseng colletotrichum gloeosporioides, and a wide application prospect is created for the biological prevention and control field of panax notoginseng fungal diseases.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Complex microbial agent capable of efficiently degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and application of complex microbial agent
ActiveCN109370931APromote degradationShort fermentation timeBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationAcenaphthyleneMicrobial agent
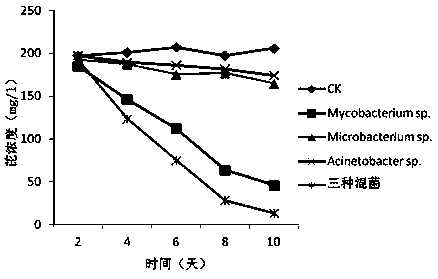
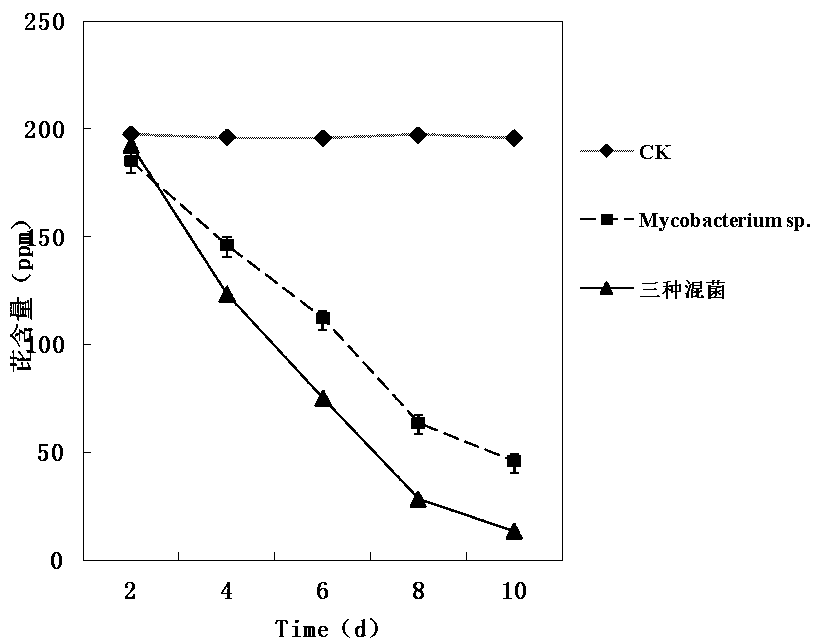
The invention provides a complex microbial agent capable of efficiently degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. The active ingredients include Mycobacterium sp. having a collection number of CGMCCNo. 6531, Acinetobacter sp. having a collection number of CGMCC No. 6532, and Microbacterium sp. having a collection number of CGMCC No. 6530. The complex microbial agent can take the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, such as fluorine, naphthalene, anthracene, acenaphthene, acenaphthylene, dibenzothiophen, carbazole, chrysene, phenanthrene, pyrene, fluoranthene, benzofluoranthrene, benzanthraceneor benzopyrene as the unique carbon source. The complex microbial agent disclosed by the invention is capable of obviously improving the degradation effect of single colony on organic contaminated soil, the fermentation time of three strains is short, the effect is obvious, and the cost is low. Therefore, the complex microbial agent has strong application prospects and popularization value on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon heavy contaminated soil and water.
Owner:北京市科学技术研究院资源环境研究所
Mixed bacteria for promoting acacia nodulation and nitrogen fixation and application thereof
ActiveCN110527653APromote photosynthesisSynergistic stacking effectBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMicroorganismNodulations
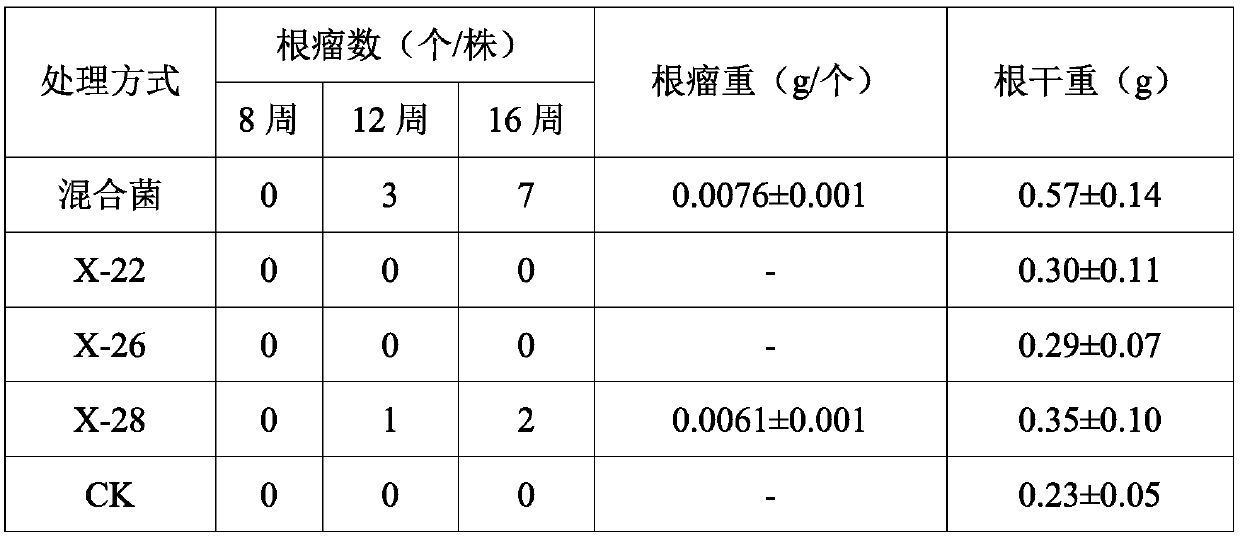
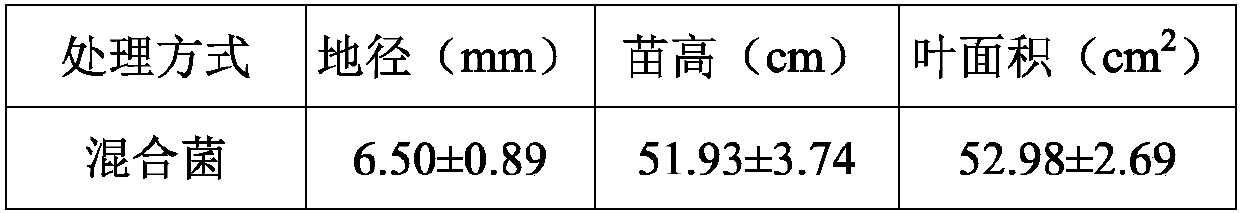
The invention discloses mixed bacteria for promoting acacia nodulation and nitrogen fixation and an application thereof, which belong to the technical field of microorganisms. The mixed bacteria can be prepared from Kocuria sp. X-22, Microbacterium sp. X-26 and Bacillus sp. X-28, all the bacteria are preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), the preservation numbers are CCTCC No: M 2019237, CCTCC No: M 2019238, and CCTCC No: M 2019239 respectively. The mixed bacteria are added to the periphery of the acacia seedlings, and compared with a single-bacteria treatment groupand a sterile treatment group, the synergistic superposition effect can be achieved, the nodulation rate and symbiotic nitrogen fixation level of acacia are obviously increased, and photosynthesis ofacacia is promoted.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Microorganisms for assimilating oils or fats, etc. and methods for treating waste liquids and deodorizing by using the same
The microorganisms for assimilating oils, fats or an organic waste material, etc. according to the present invention can efficiently decompose waste oils, fats or organic waste materials, etc. contained in a waste liquid and reduce concentrations of such waste oils, fats or organic waste materials, etc. to a level lower than a given standard level. The microorganisms for assimilating waste oils, fats or organic waste materials, etc. to be used for the present invention include strains belonging to genus Sphingomonas, genus Nocardia, genus Microbacterium or genus Bacillus or a mixture of the strains belonging to genera Sphingomonas, Nocardia, Microbacterium and / or Bacillus. The present invention is further directed to a method for treating waste liquids containing waste oils, fats or organic waste materials, etc. by using the microorganisms for assimilating oils, fats or organic waste materials, etc. or to a method for deodorizing offensive odors resulting from such waste liquids.
Owner:KANBIKEN
Root nodule growth-promoting microbacterium X-18 and application thereof
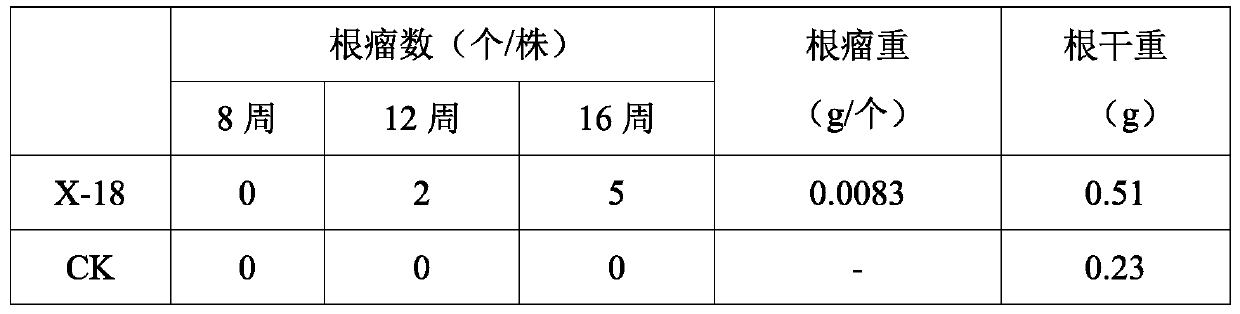
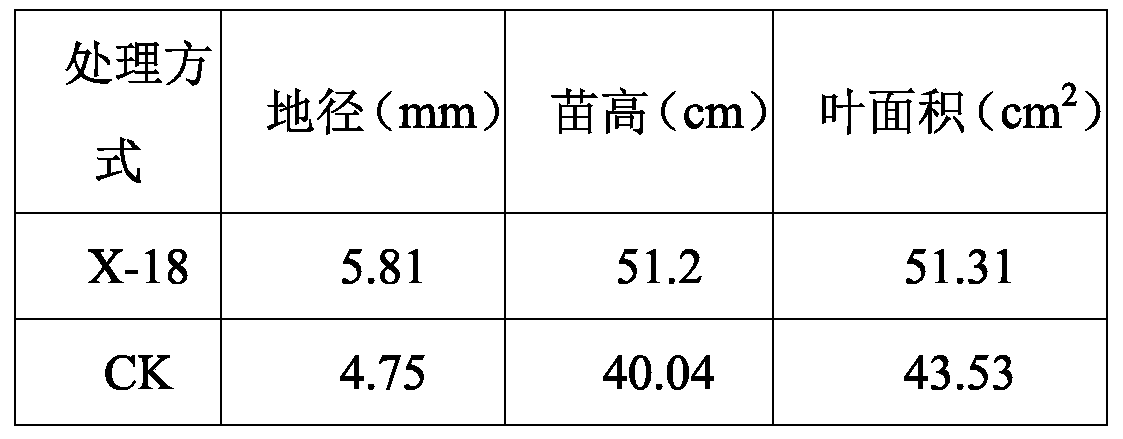
ActiveCN110551664APromotes effective nitrogen fixationThe ability of symbiotic nitrogen fixation is obviously exertedBiocidePlant growth regulatorsNitraria billardiereiMicroorganism
The invention discloses a root nodule growth-promoting microbacterium X-18 and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. A root nodule growth-promoting bacterium is classified and named as microbacterium sp. X-18, is deposited in The preservation date is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection with a preservation date being April 8th, 2019, a preservation number being CCTCC NO: M2019236 and a preservation address being Wuhan University in China. The microbacterium X-18 disclosed by the invention is applied to black locust as leguminous plants, canpromote effective nitrogen fixation of the black locust and provides nitrogen required by growth of he black locust to enable the symbiotic fixation ability of the root nodule growth-promoting bacteria with the plants to be obviously exerted, so that growth and development of black locust plants are promoted, and a development prospect is good.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria having effect of promoting growth of plants and isolated culture and application of hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria
InactiveCN110229762APromote growthImprove stress resistancePlant growth regulatorsBiocideBacteroidesBiotechnology
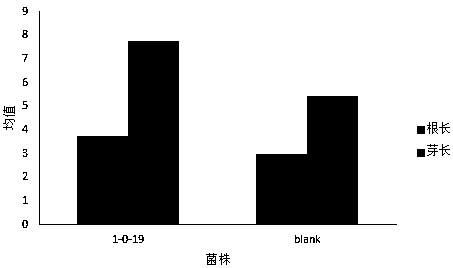
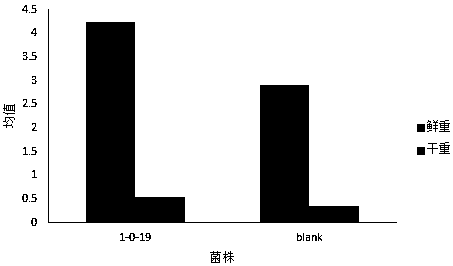
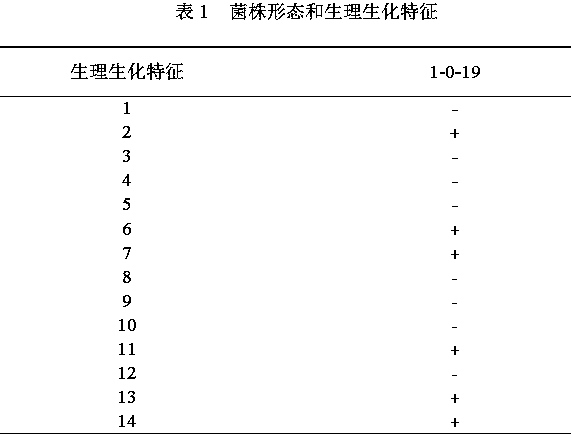
The invention discloses microbacterium Microbacterium1-0-19. The strain is isolated from a place nearby Tongchuan overpass, Yaozhou district, Tongchuan city, Shanxi province, and is classified into microbacterium bacteria based on physiological and biochemical characteristics and 16SrDNA analysis. Medicago sativa rhizosphere soil is used as a research object, and hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria are isolated through a continuous hydrogen inflating device; and through shape observation, physiological and biochemical identification and 16SrDNA identification of the hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria, the classification status of the hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria is determined. The optimal strain is fermented in a laboratory, and a hydrogen bacterium preparation is prepared. The biological preparation canbe used for agricultural production to promote growth of plants, increase yield, increase fertilizer effects and increase the stress tolerance capacity of the plants.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Microbacterium for cassava nitrogen fixation and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105907670APromote accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNitrogen accumulationFermentation
The invention discloses microbacterium for cassava nitrogen fixation and a preparation method and application thereof. The microbacterium belongs to Microbacterium sp. and is preserved in CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) on March 7, 2016, and a preservation serial number is CGMCC NO.12182. A biological agent with the microbacterium as an active component is prepared by tube culture and liquid fermentation culture. By application of the microbacterium and the biological agent thereof, nitrogen contents of roots, stems and leaves of cassava seedlings can be remarkably increased, nitrogen accumulation in an early growth stage of cassava is benefited, and high application value in cassava production is achieved.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Microbacterium capable of degrading decabromodiphenyl ether as well as domestication method and application thereof
ActiveCN110511881APromote degradationImprove environmental adaptabilityBacteriaWater contaminantsMicroorganismDecabromobiphenyl ether
The invention discloses a microbacterium capable of degrading decabromodiphenyl ether as well as a domestication method and an application thereof. The microbacterium sp capable of degrading decabromodiphenyl ether is preserved in the Guangdong Province Microbial Culture Collection Center on April 19th, 2019, and a number of the microbacterium sp is GDMCC No: 60634. The domestication method is a method for increasing pollutants in a gradient mode, decabromodiphenyl ether is added into a culture medium, the concentration gradient of the decabromodiphenyl ether ranges from 10 mg / L to 100 mg / L, and domestication is conducted through the domestication method for increasing the concentration of the pollutants in the gradient mode. The microbacterium provided by the invention is high in environmental adaptability and relatively good in decabromodiphenyl ether degradation effect; and the cost of degrading pollutants by using the microbacterium is relatively low. The degradation rate of the microbacterium provided by the invention on decabromodiphenyl ether can reach 57.6% at most, the practical application value is high, and a reference can be provided for solving the problem of decabromodiphenyl ether pollution treatment.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
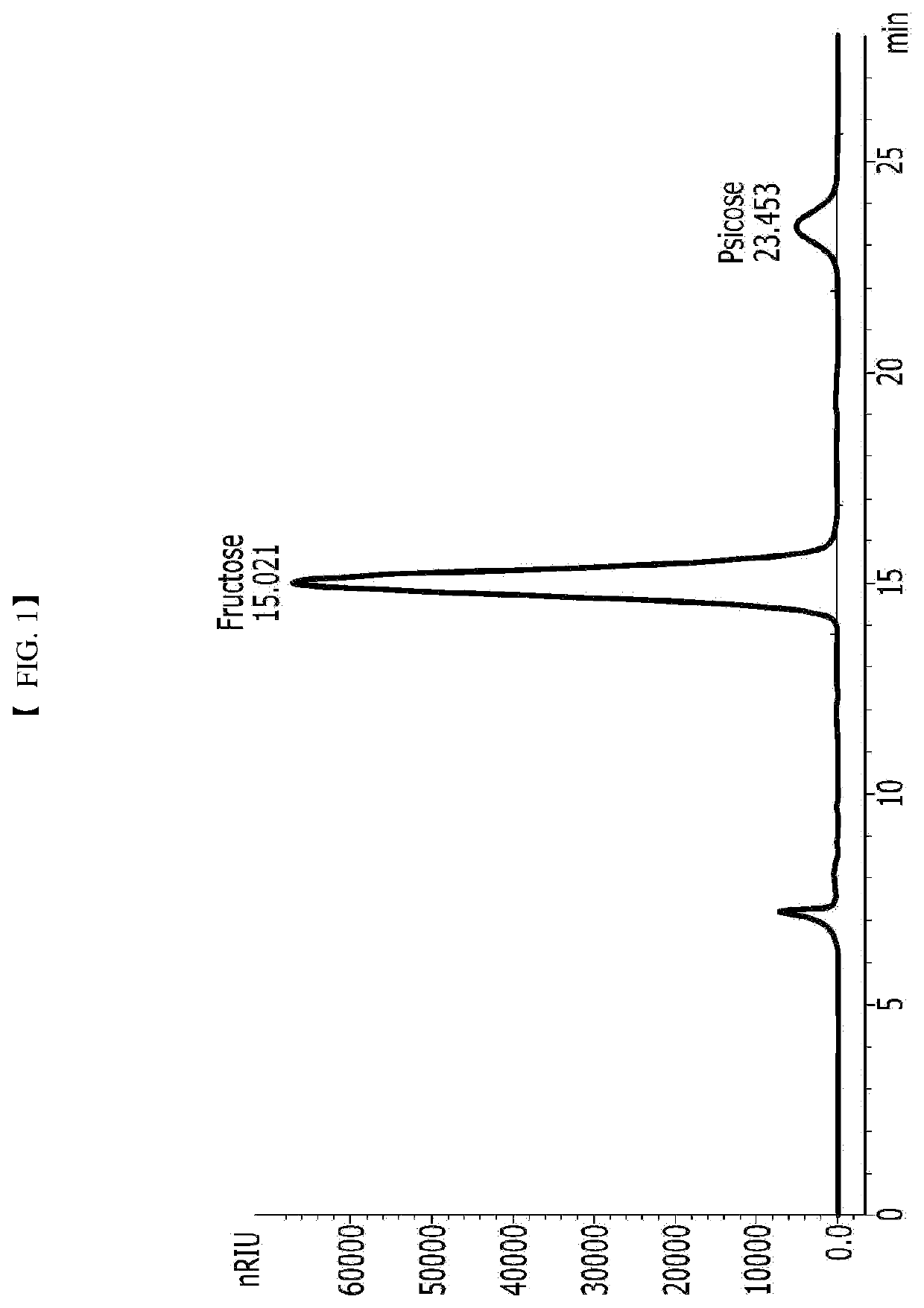
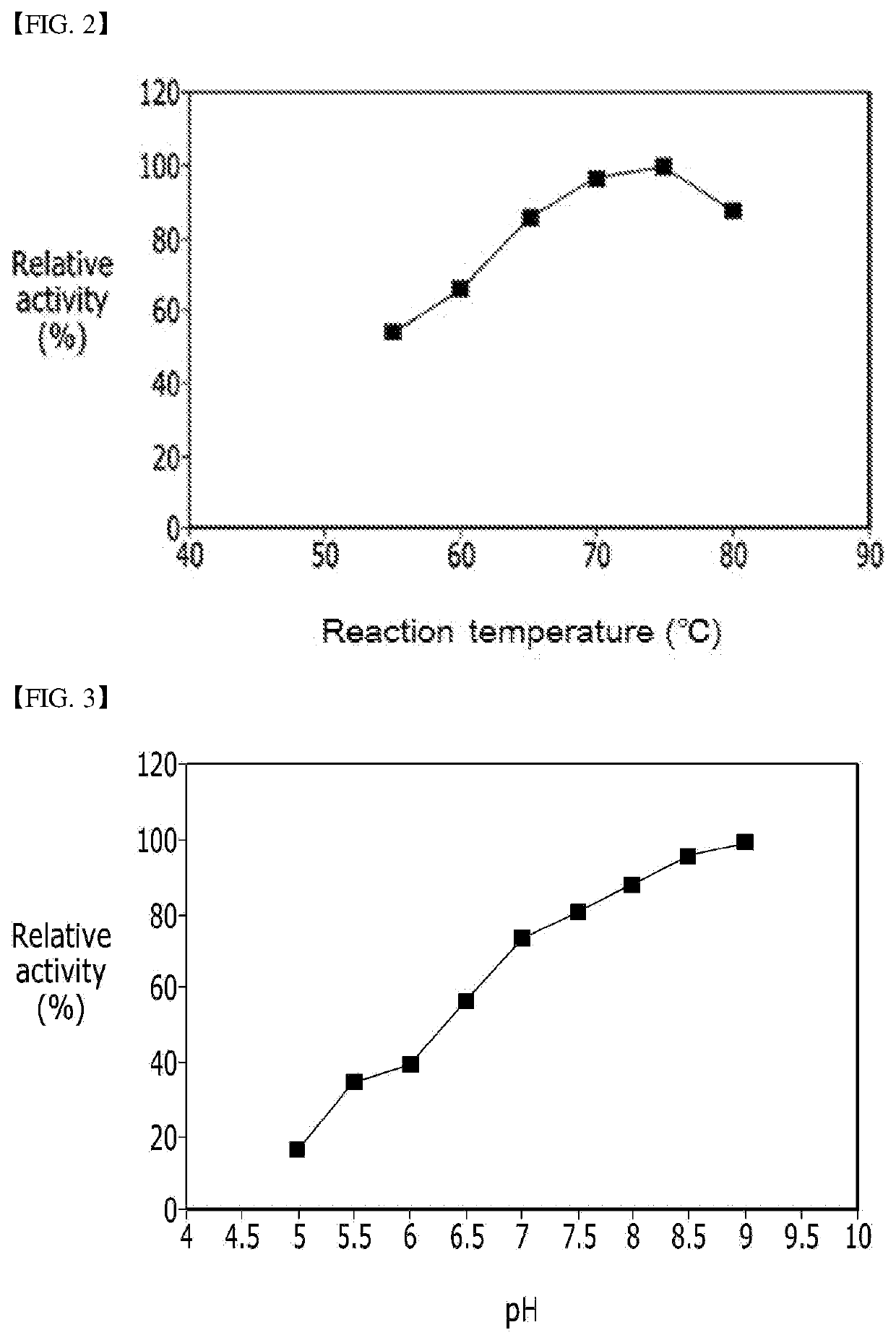
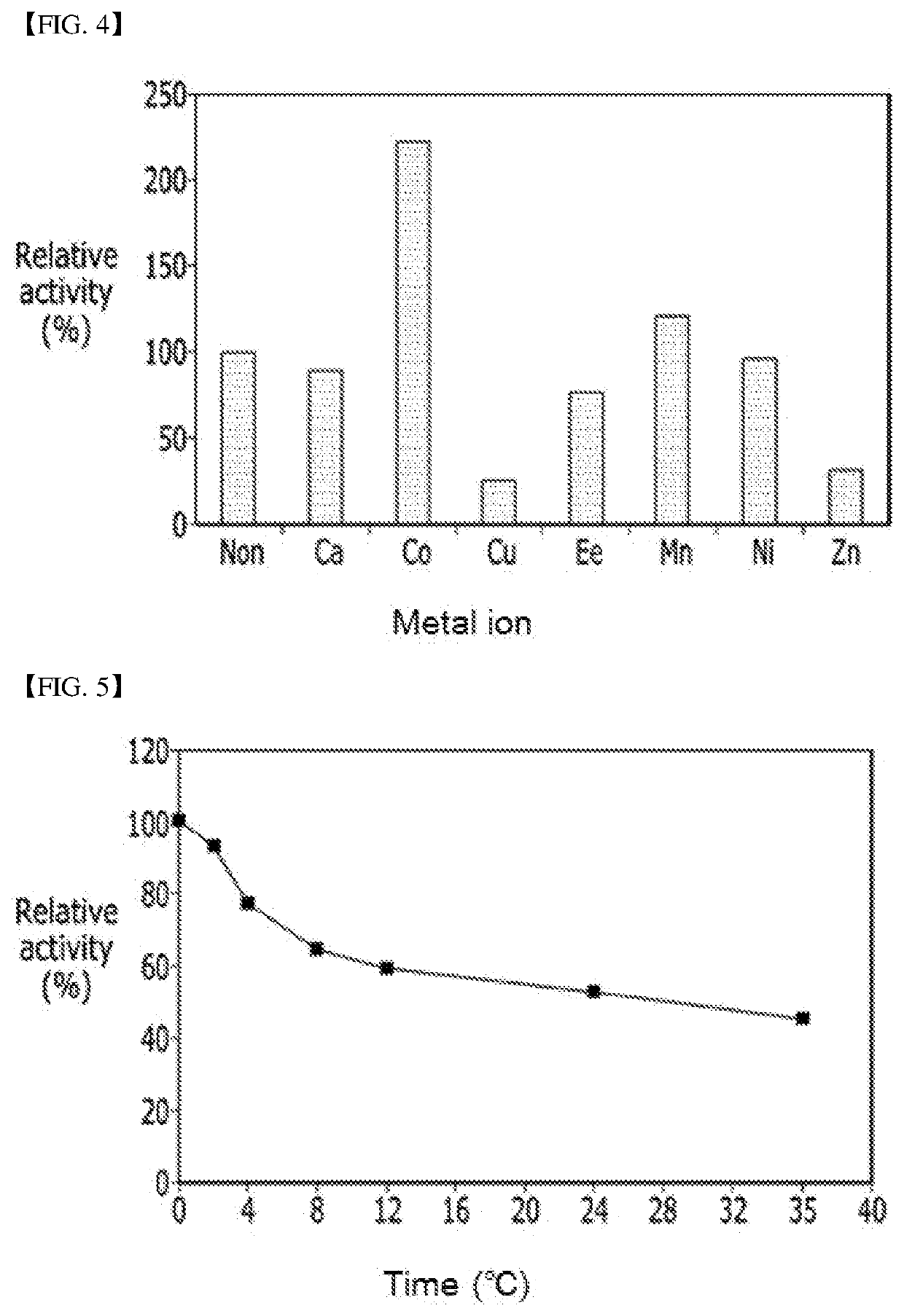
Microbacterium sp. strain and method for producing psicose by using same
The present invention relates to a newly isolated bacterium belonging to the genus Microbacterium, a composition for producing psicose comprising the strain, and a method for producing psicose using the same.
Owner:SAMSANG CORP
Preparation method of microbacterium for cassava nitrogen fixation
InactiveCN108587977APromote accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismNitrogen accumulation
The invention discloses a preparation method of microbacterium for cassava nitrogen fixation. The microbacterium belongs to Microbacterium sp.. The microbacterium is collected at the CGMCC on March 07th, 2016 under the number of CGMCC No.12182. A biological agent taking the microbacterium as an active substance is prepared through tube seed culture and liquid fermentation culture. By applying thestrain and the biological agent thereof in the seedling period of cassava growth, nitrogen content of cassava roots, stems and leaves can be increased remarkably, nitrogen accumulation at the early stage of cassava growth is facilitated, and the preparation method has great application value in cassava production.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Microbacterium capable of completely degrading zearalenone and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms and particularly relates to a microbacterium capable of completely degrading zearalenone and application thereof. The microbacterium capable of completely degrading zearalenone, discovered by the invention is named Microbacterium sp. FY1538. The Microbacterium sp. FY1538 belongs to Microbacterium sp. and is separated from turf on the bank of the Qinghai Lake of the Qinghai-Tibet plateau. Microbacterium sp. FY1538 is cultured in an LB culture medium with a pH value of 7.4 at a culture temperature of 30 DEG C for 48h in a shaking way by virtue of a shake flask at a rotating speed of 220rpm in the presence of methyl alcohol with a final concentration of 10 mu l / ml; the fermentation supernate has the capability of completely degrading zearalenone. The microbacterium provided by the invention can be applied to detoxification for mouldy crops such as mouldy corn.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Microbacterium and microbial reduction method thereof for repairing chromium-polluted soil
PendingCN114657090AReduce pollutionPromote sustainable developmentBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismChromium contamination
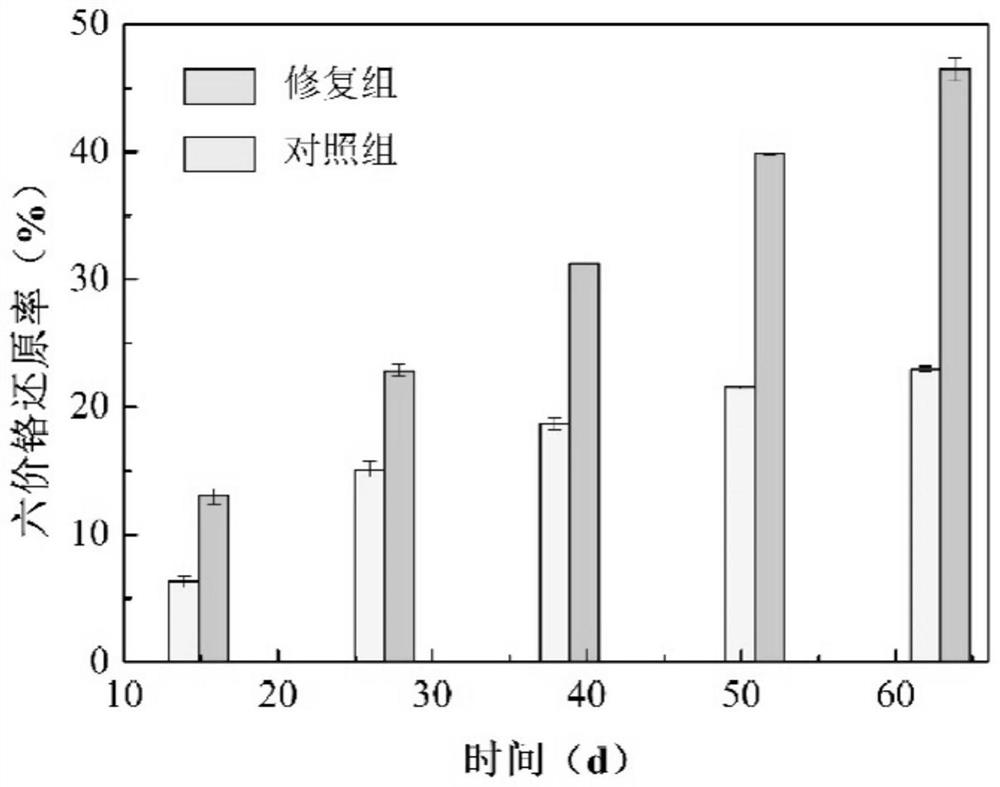
The invention provides a strain of microbacterium, the classification name of the microbacterium is Microbacterium sp.GRINML SWG1, the preservation unit is China Center for Type Culture Collection, the address is Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, the preservation date is August 6, 2021, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M2021992. The microbacterium provided by the invention can efficiently reduce soluble hexavalent chromium with different concentrations, and provides an experimental technology and a theoretical basis for applying a microbial reduction technology to chromium-contaminated soil remediation.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com