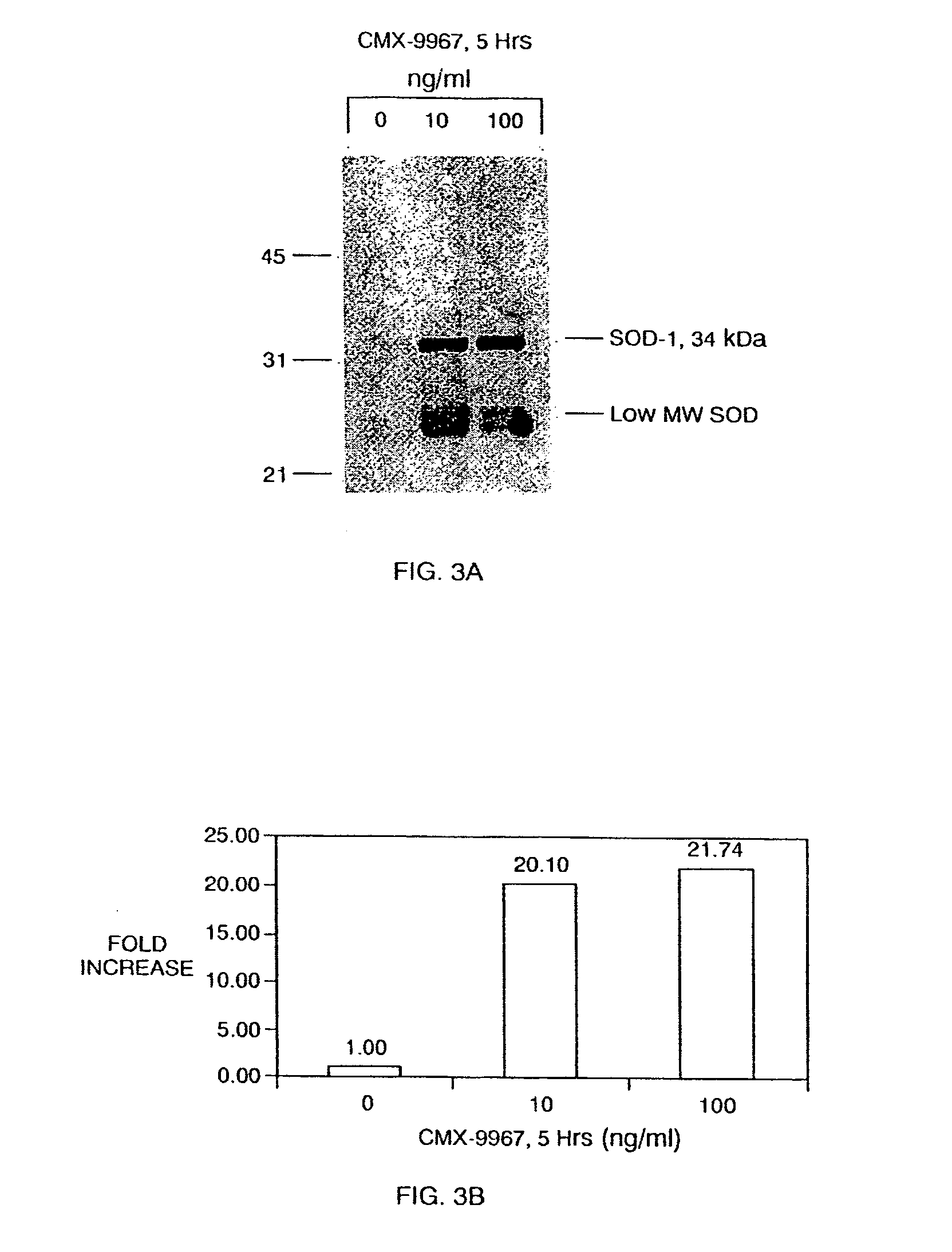
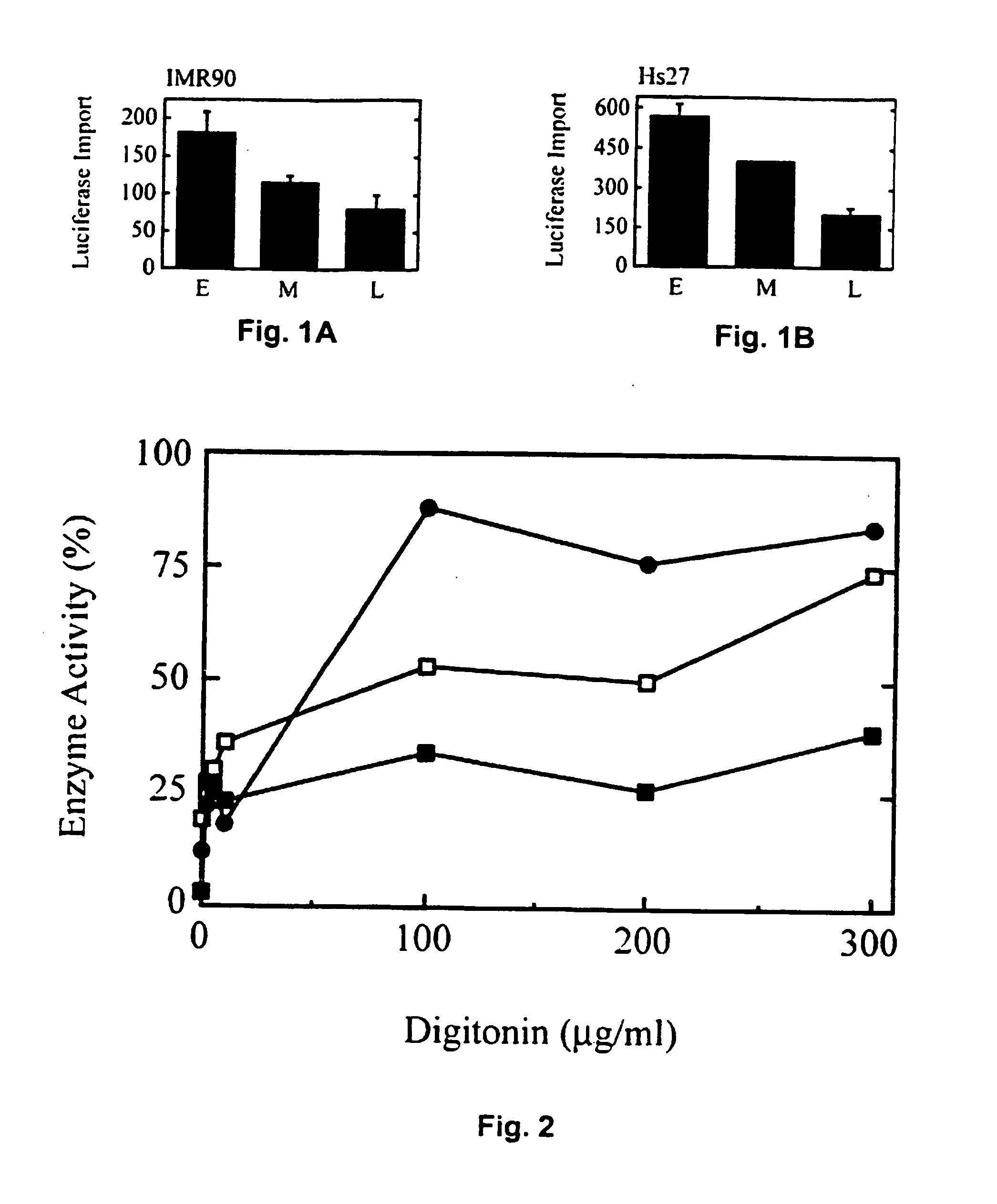
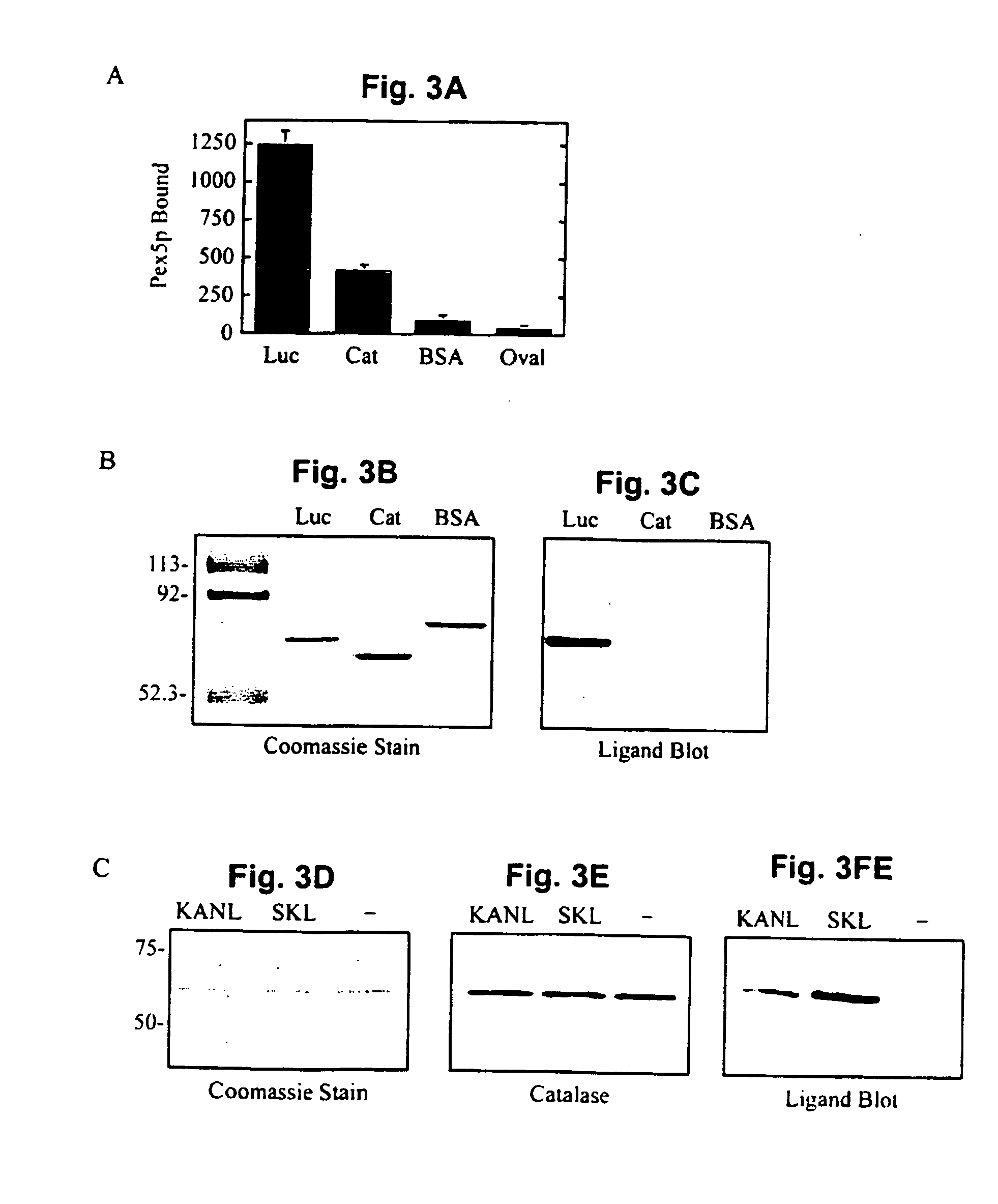
Patents
Literature
55 results about "Catalase T" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
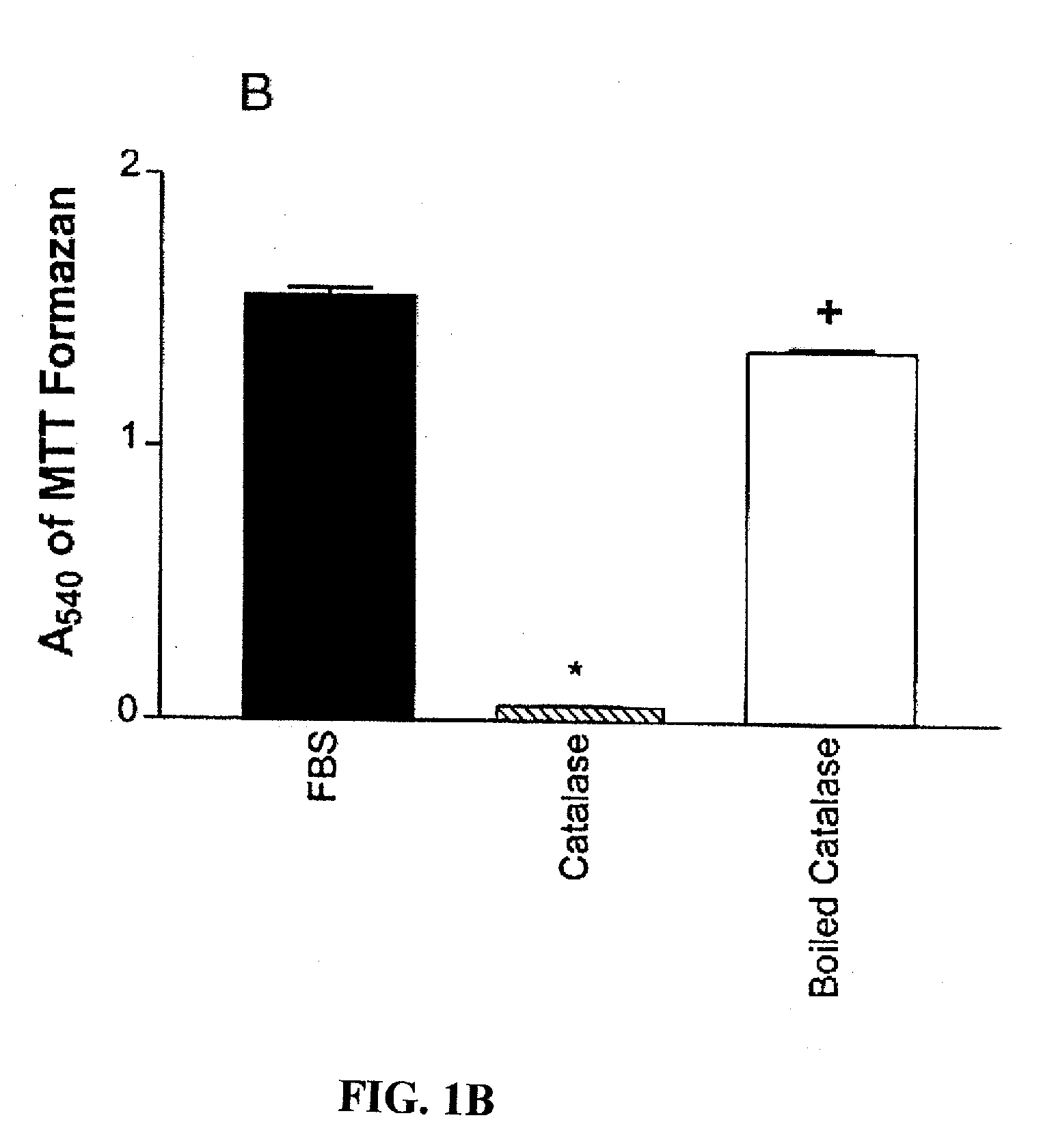
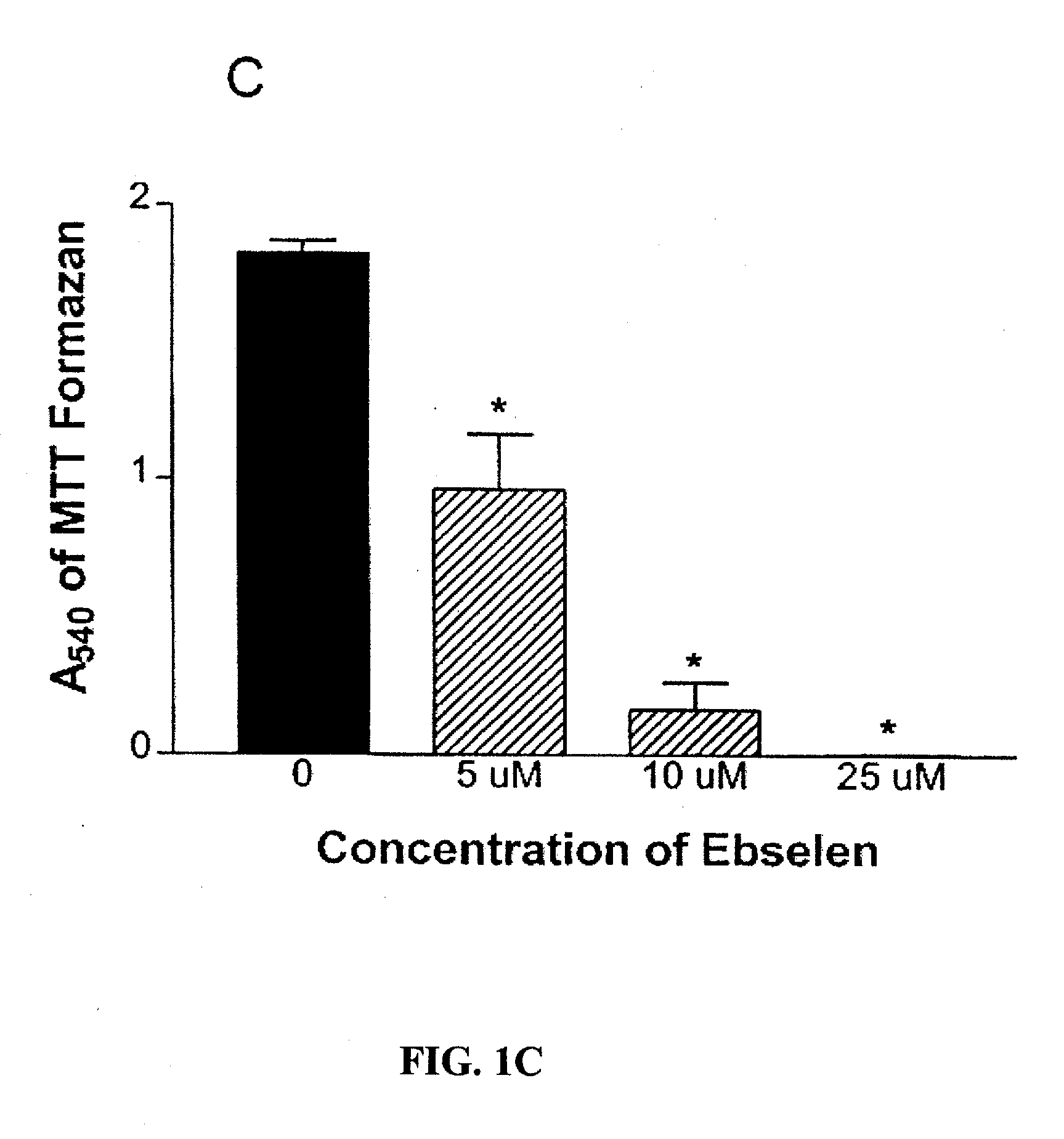
Catalase is a common enzyme found in nearly all living organisms exposed to oxygen (such as bacteria, plants, and animals). It catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. It is a very important enzyme in protecting the cell from oxidative damage by reactive oxygen species (ROS).
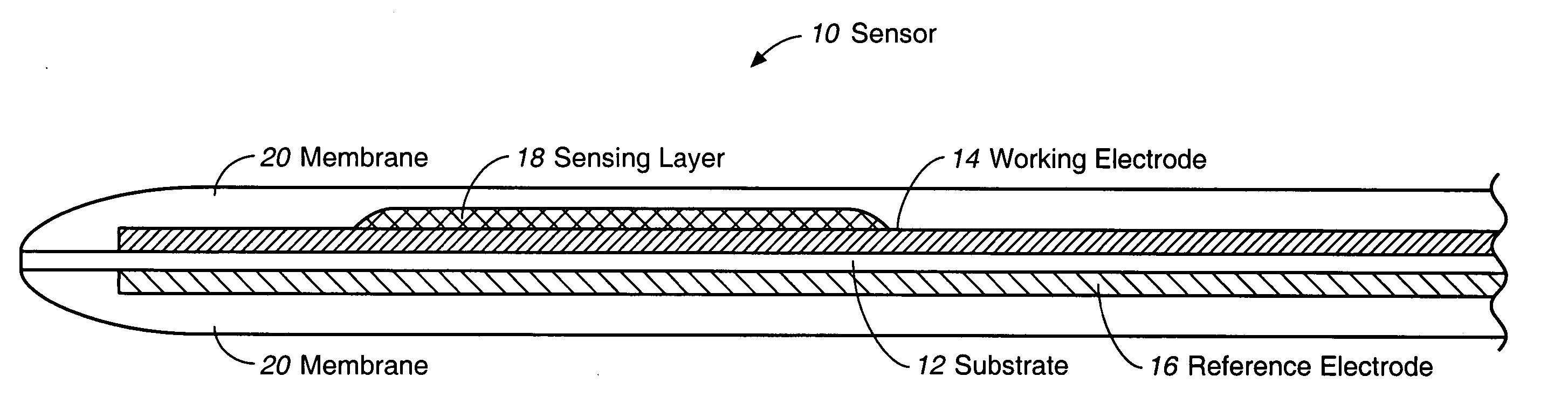
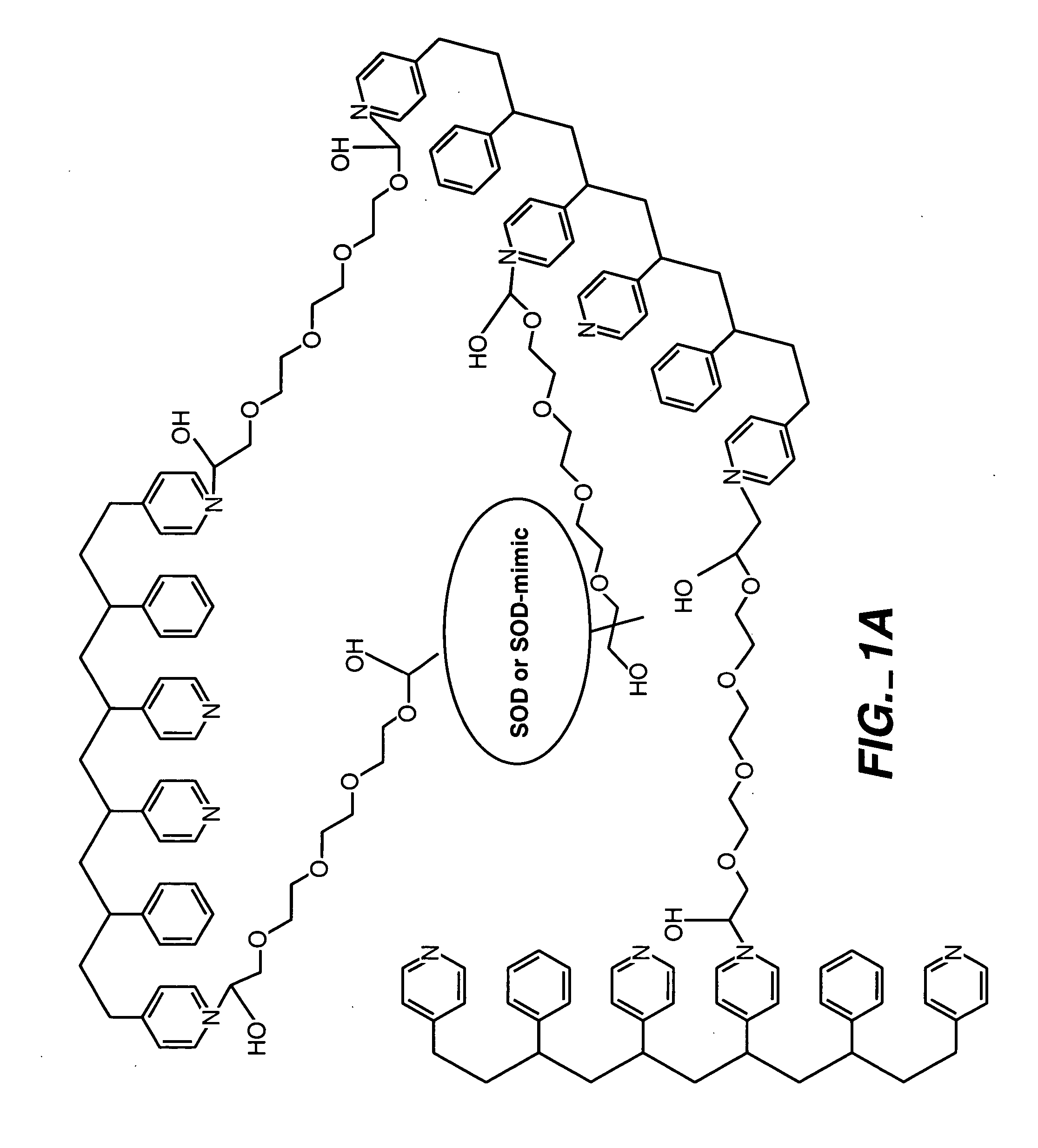
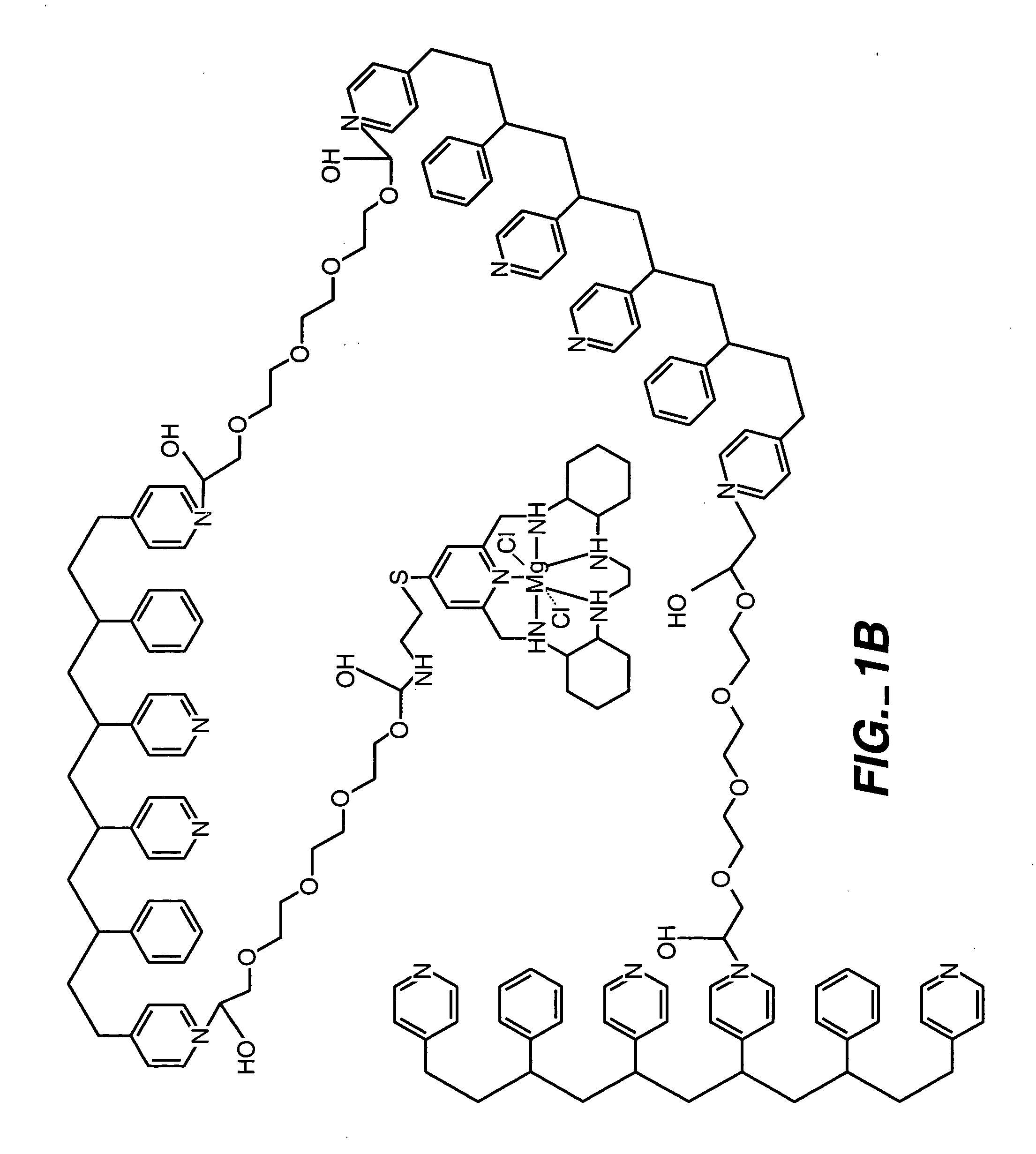
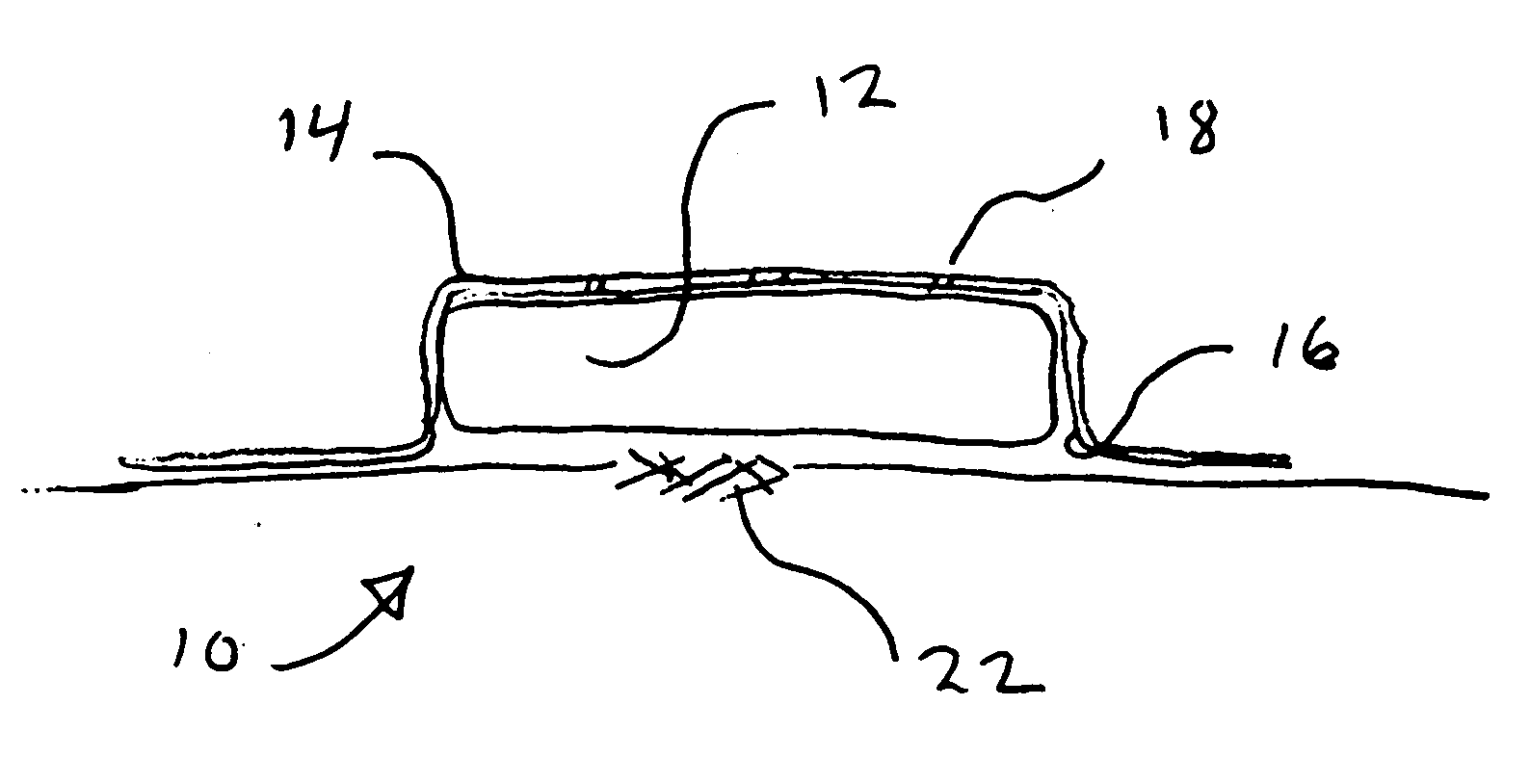
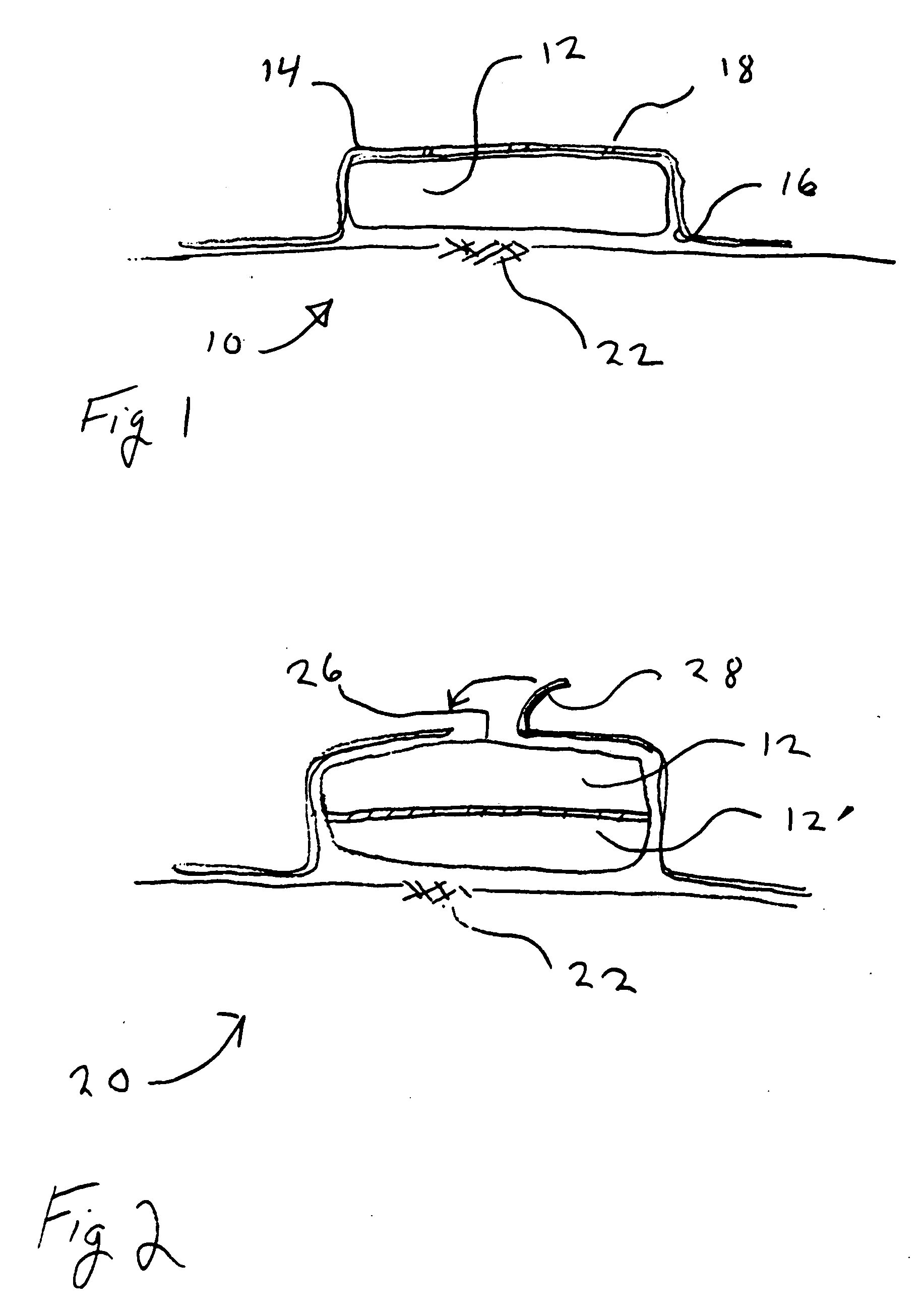
Membrane suitable for use in an analyte sensor, analyte sensor, and associated method
ActiveUS20050173245A1Facilitate linear responsivenessEasy CalibrationImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMetaboliteSuperoxide
A multifunctional membrane is provided. The multifunctional membrane is suitable for use in an analyte sensor. In a particular application, the multifunctional membrane may be used in connection with an amperometric biosensor, such as a transcutaneous amperometric biosensor. Some functions of the membrane are associated with properties of membrane itself, which is comprised of crosslinked polymers containing heterocyclic nitrogen groups. For example, the membrane, by virtue of its polymeric composition, may regulate the flux of an analyte to a sensor. Such regulation generally improves the kinetic performance of the sensor over a broad range of analyte concentration. Other functions of the membrane are associated with functional components, such as a superoxide-dismutating / catalase catalyst, either in the form of an enzyme or an enzyme mimic, that can be bound to the scaffold provided by the membrane. The effect of any such enzyme or enzyme mimic is to lower the concentration of a metabolite, such as superoxide and / or hydrogen peroxide, in the immediate vicinity of the sensing layer of the biosensor. Lowering the concentrations of such metabolites, which are generally deleterious to the function of the sensor, generally protects or enhances biosensor integrity and performance. The membrane is thus an important tool for use in connection with analyte sensors, amperometric sensors, biosensors, and particularly, transcutaneous biosensors. A membrane-covered sensor and a method for making same are also provided.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Disinfecting compositions and methods of making and using same
InactiveUS20050019421A1High kill rateUse of compositionBiocidePeroxide active ingredientsSolventBiology
The present invention provides a composition, comprising: greater than about 0.1% by weight hydrogen peroxide; an aromatic acid component; surfactant; optionally, a solvent; and a carrier. The composition of the invention is useful as a disinfecting composition for killing microorganisms such as bacterium (including Mycobacterium), spores and fungi. The composition provides a pathogenic bacteria kill rate of 99.9% in about 30 seconds when bacteria are exposed to the composition and is effective in providing a Mycobacterium kill of 106 with two minutes or less. Moreover, the compositions of the invention are generally more resistant to catalase deactivation than, for example, an aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide. The concentration of hydrogen peroxide within the composition may range from about 1% by weight to about 7% by weight and the concentration of aromatic acid component may range from about 0.1% by weight to about 5% by weight. The invention also provides a method for disinfection of a substrate utilizing the composition. The composition of the invention may be used in the foregoing method on a medical instrument, such as an endoscope or the like. Applying the compositions to a substrate may be accomplished in any of a variety of application methods such as by roll coating, dipping, spraying, or rotational tumbling. The composition may be applied to the substrate for a period of time ranging from about 30 seconds to about ten minutes. In this aspect, the invention can further comprise drying the substrate after removing the composition.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Oxygen releasing material
InactiveUS20060142684A1Promote wound healingSignificant propertyAbsorbent padsBandagesPolyvinyl alcoholOxygen
An oxygen releasing bandage or dressing is based on a stable complex between polyvinyl acetal and hydrogen peroxide. Medical grade polyvinyl acetal sponge is treated with hydrogen peroxide, thereby forming a complex between the acetal plastic and the hydrogen peroxide. The dressing material is then affixed to a wound preferably with an oxygen impermeable covering. Fluids from the wound are drawn into the sponge where catalase and other enzymes in the fluids breakdown the hydrogen peroxide to release oxygen. If treatment of relatively dry wounds is desired, catalyst solutions can be introduced into the bandage to stimulate production of oxygen. The bandages are stable for a prolonged period of time.
Owner:SHANBROM TECH
Single amino acid based compounds for counteracting effects of reactive oxygen species and free radicals
InactiveUS20050130881A1Eliminate reduce prevent generationDetoxifying ROS and free radicalsAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCompound (substance)Antioxidative enzyme
Single amino acid compounds and methods for upregulating expression of a gene encoding an antioxidative enzyme, such as superoxide dismutase or catalase, to counteract harmful oxidative effects of reactive oxygen species and other free radicals are described. The single amino acid compounds may be used in compositions and methods to treat or prevent diseases and conditions characterized by undesirable elevation of reactive oxygen species and other free radicals.
Owner:ISCHEMIX
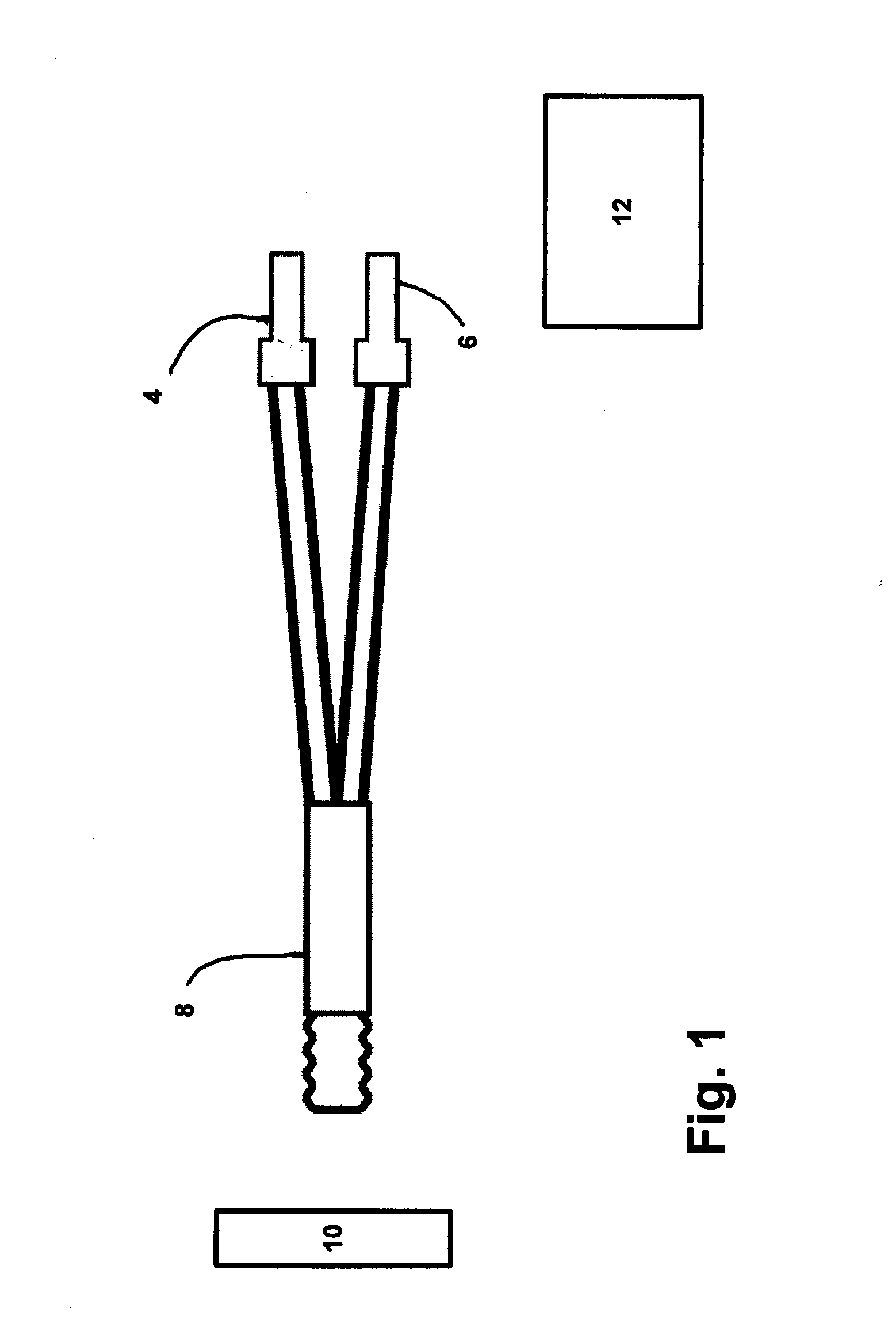
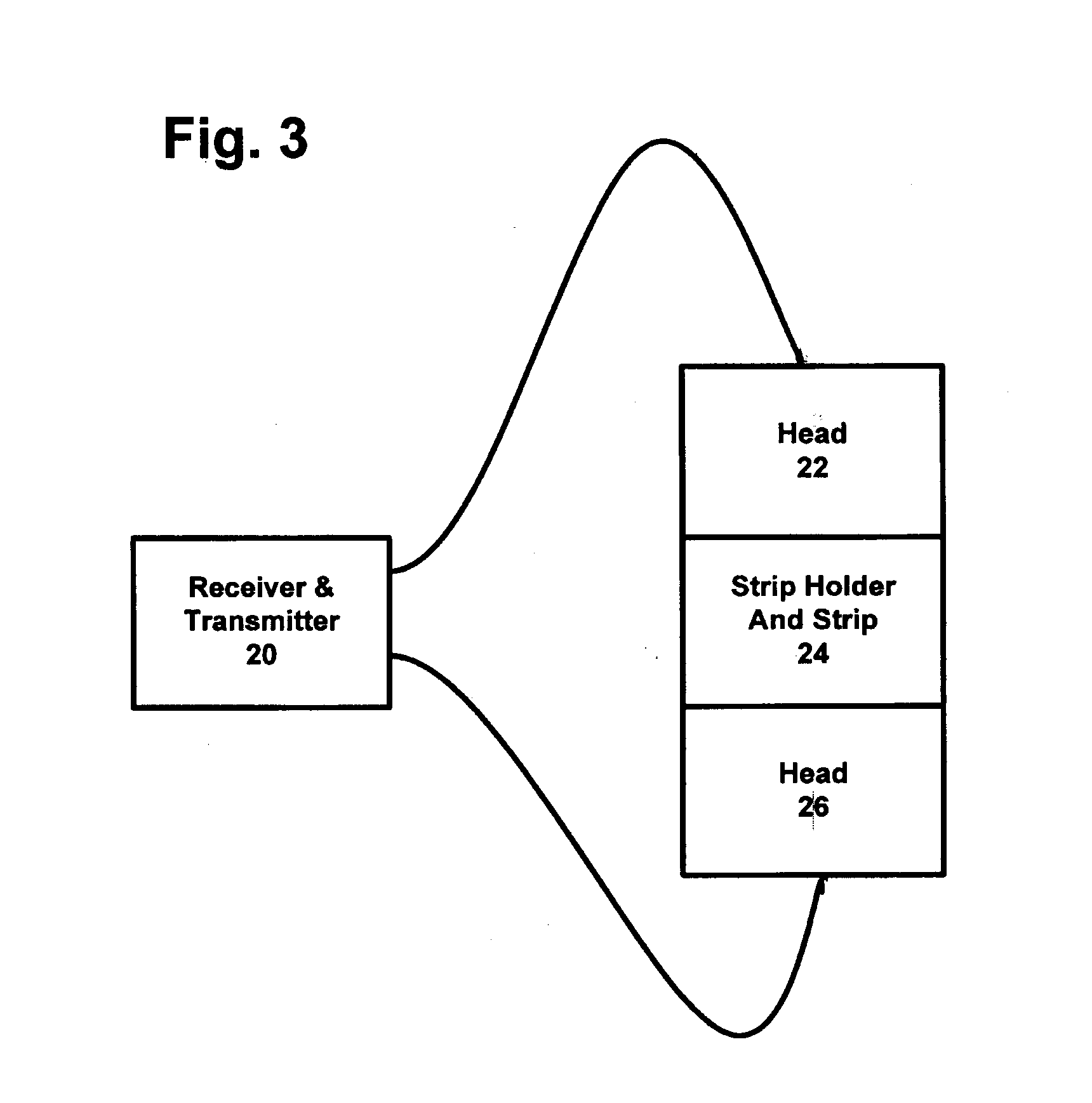
Method of measuring the concentration of hydrogen peroxide, peroxyacetic acid, chlorinated compounds and other aqueous oxidizer compounds
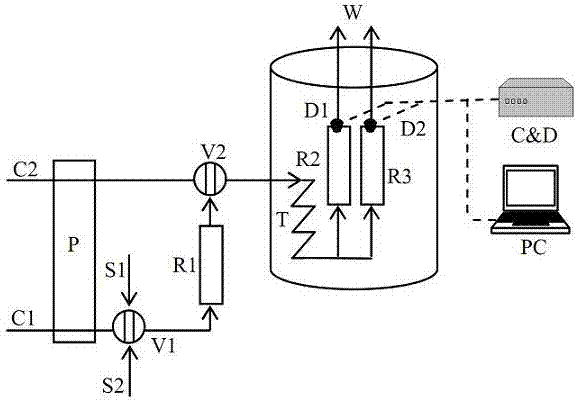
InactiveUS20060257964A1The process is simple and accurateEasy to storeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFiberLight-emitting diode
In some embodiments of the apparatus detects the concentration of a substance selected from the group consisting of hydrogen peroxide, peroxyacetic acid, chlorinated compounds and other aqueous oxidizer compounds. The light source may be a laser, or light emitting diode. The source may be part of a transmitter and the detector may be part all of a receiver. The apparatus may further include a data logger cooperating with the light detector. The enzyme coated strip may be a strip coated with catalase and the the strip may be an inert paper. In some cases the enzyme coated strip changes color as a function of the concentration of the substance. The apparatus may further including fiber-optic cable cooperating with said light detector to detect transmitted light from the enzyme coated strip and a fiber-optic cable and / or a fiber optic cable cooperating with said source to direct light on the enzyme coated strip. The invention also includes the method for measuring the concentration of a substance which includes providing an enzyme coated strip, projecting a light beam on the enzyme coated strip, and detecting light from the enzyme coated strip.
Owner:BIOSAFE SYST
Method for the preparation of L-amino acids from D-amino acids
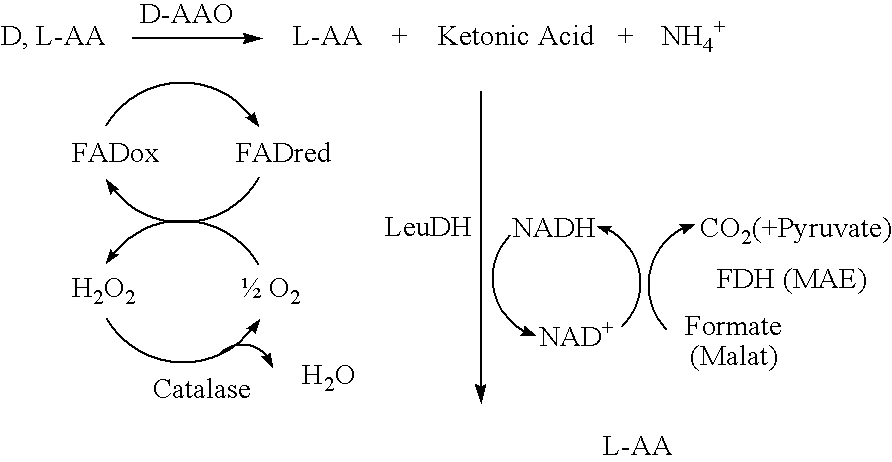
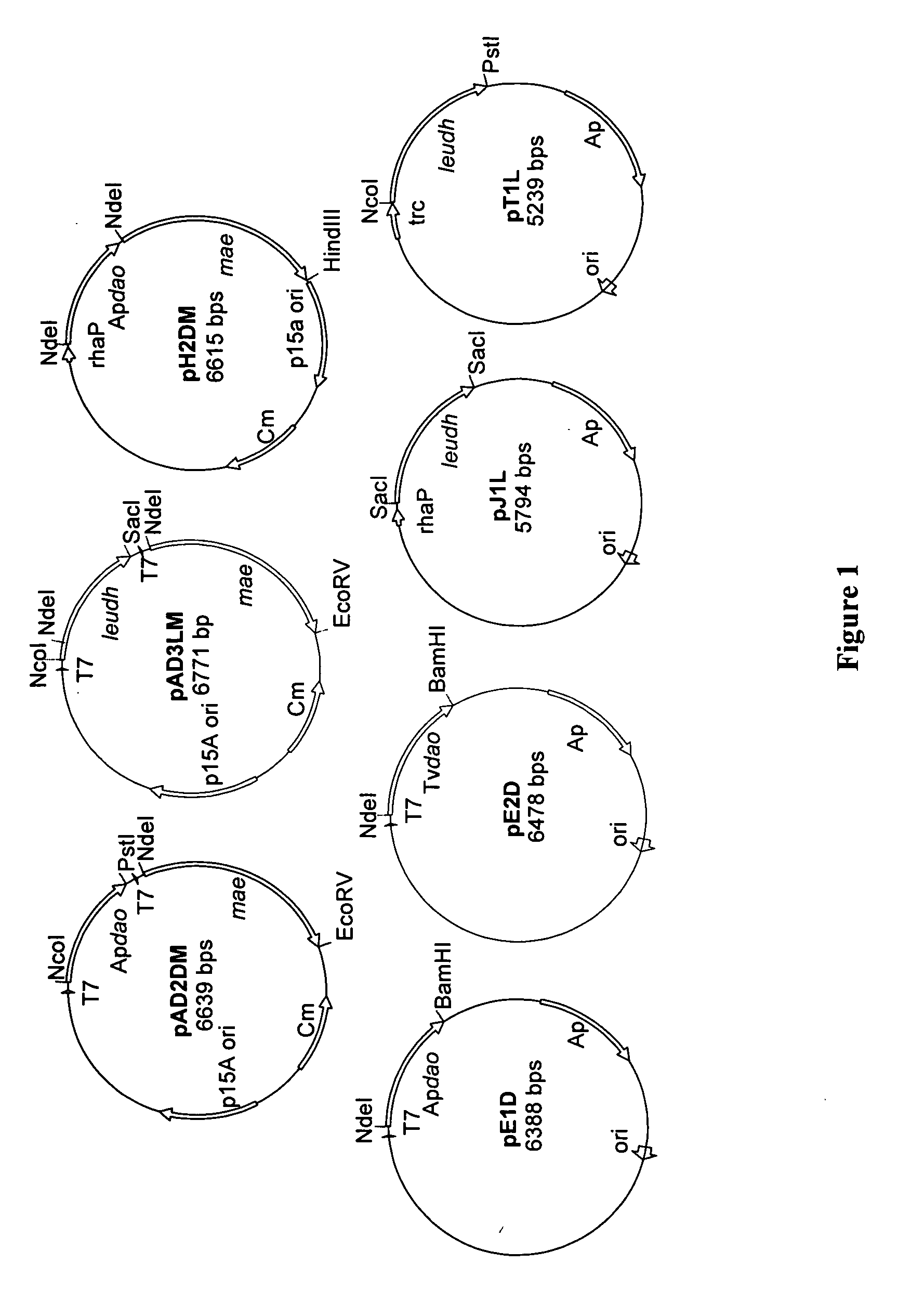
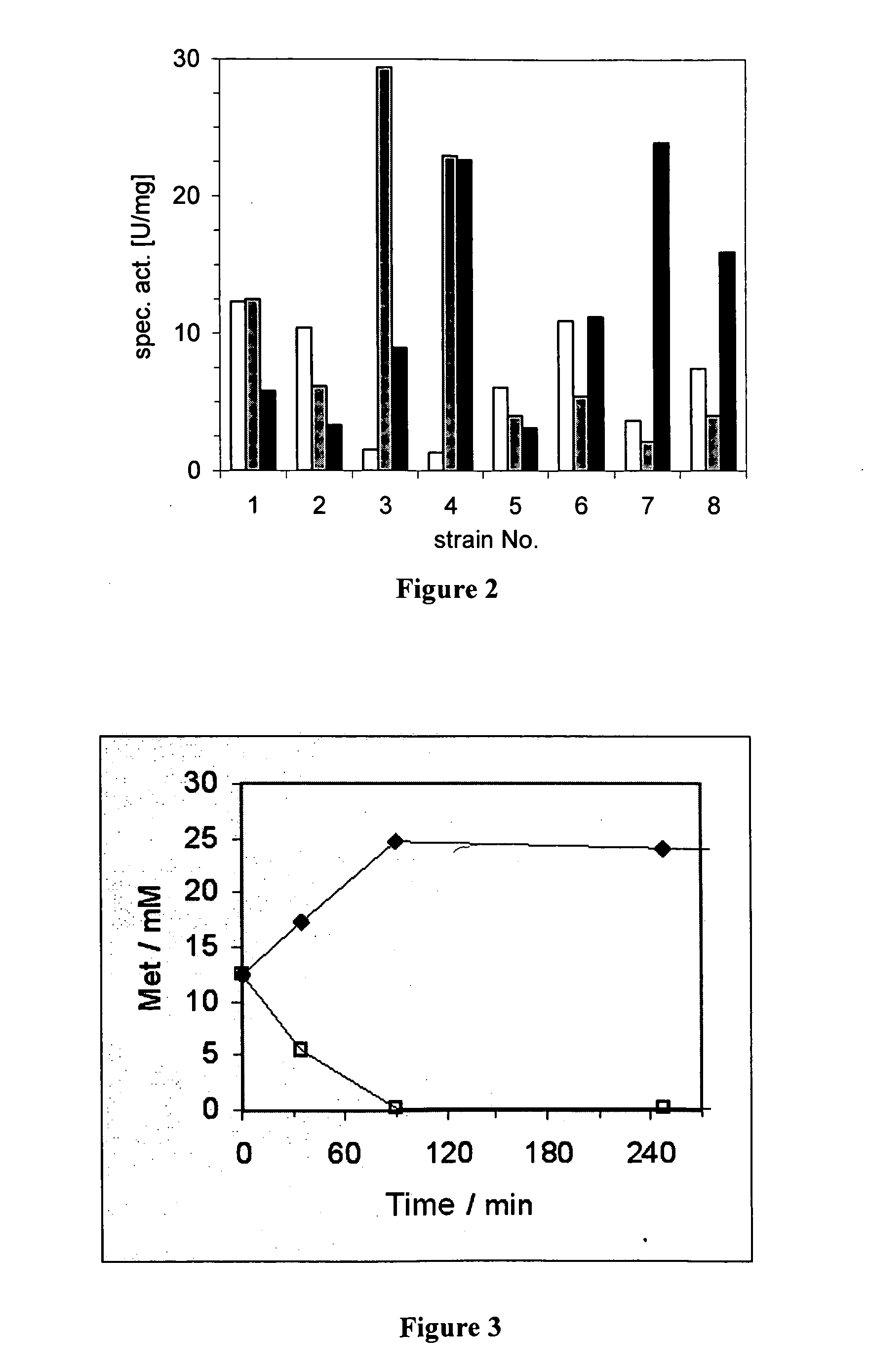
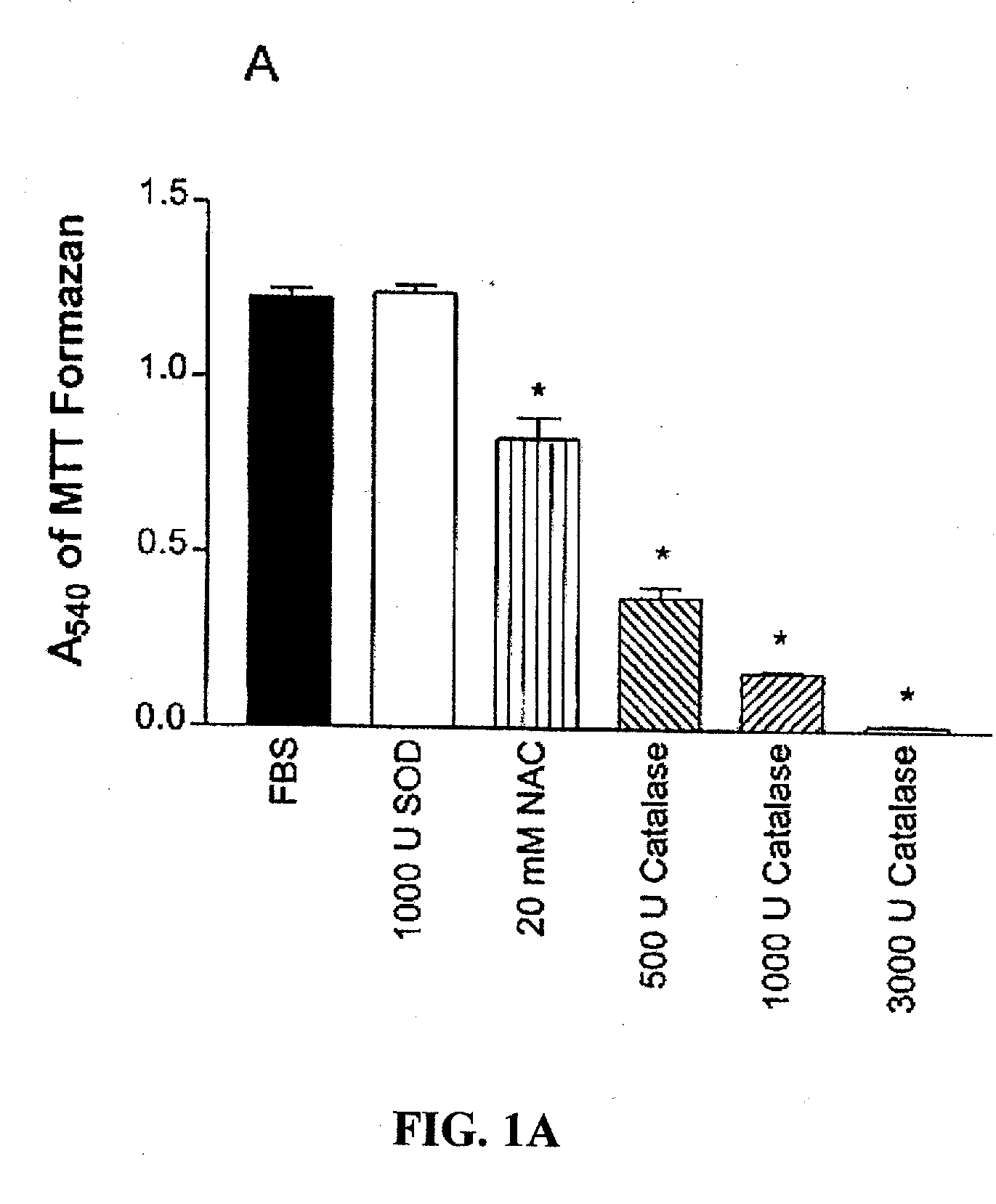
The invention relates to recombinant microorganisms which, in comparison to the starting organism, have a higher concentration or activity of a D-amino acid oxidase, of an L-amino acid dehydrogenase, of an NADH cosubstrate regenerating enzyme and, if necessary, of a catalase. The invention also includes methods for preparing L-amino acids from D-amino acids using of these microorganisms.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Enzymatic reactions in the presence of keto acids
Owner:ENTERIS BIOPHARMA
Method of Treating Cancer
InactiveUS20070142462A1Lower Level RequirementsInhibition of activationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPatient needOncology
Methods for treating cancer are provided including administering a patient needing treatment a therapeutically effective amount of one or more antioxidants selected from the group of catalase, N-acetylcysteine, glutathione peroxidase, salen-transition metal complexes, dicumarol, and derivatives thereof.
Owner:THE UNIV OF UTAH
Degradation bacteria for carbendazim pesticide residue and bacterial agent produced thereby
InactiveCN1827764AEasy to useReduce production and use costsBacteriaPesticide residueBacterial strain
The invention provides a carbendazim pesticide residue degrading bacteria and a prodegradant, which belongs to biological high-tech domain. The used bacterial strain DJL-6 is judged as Rhodococcus sp. The main biological feature is: G+, the thallus is of ball rod and atrichosis; the reaction between catalase and V-P is positive; the oxidase reaction is negative; the barley sugar, carubinose, citrate, acetamide and agedoite can be used as unique carbon source or nitrogen source to carry out its growth, but the lactin and bitter almond acid can not be used as unique carbon source to carry out its growth; and the bacterial colony is orange when cultivated on LB culture medium. The pesticide residual quantity of the crop can be reduced by more than 95 % by directly applying the degrading bacteria product, which solves the overproof pesticide residue problem, and can produce non-toxic and nuisanceless environmental farm product.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Oxygen scavenging system
InactiveUS20050221029A1Extended shelf lifeLower Level RequirementsEnvelopes/bags making machineryOther chemical processesSodium bicarbonateGram
The oxygen scavenging system of the subject invention contemplates a composition, system and appurtenant methodology for substantially eliminating elemental oxygen from packaged oxygen sensitive products. The composition or scavenging agent includes an oxidoreductase enzyme, a suitable energy source or substrate for the enzyme, and a buffer. The composition binds oxygen when exposed to moisture, thereby reducing the level of oxygen in a closed (e.g., sealed) space such as a food package or the like. More particularly and preferably, the composition includes glucose oxidase in an amount of between 1 and 100 activity units (U) per gram, catalase in an amount of between 1 and 300 activity units (U) per gram, dextrose in an amount of between about 20 and 99 percent by weight, and sodium bicarbonate in an amount of between about 1 and 80 percent by weight.
Owner:NUTRICEPTS
Method for treating ship ballast water
InactiveUS20060289364A1Easy dischargeWater treatment compoundsNature of treatment waterBiological bodyIodine
Owner:KATAYAMA CHEM WORKS CO LTD
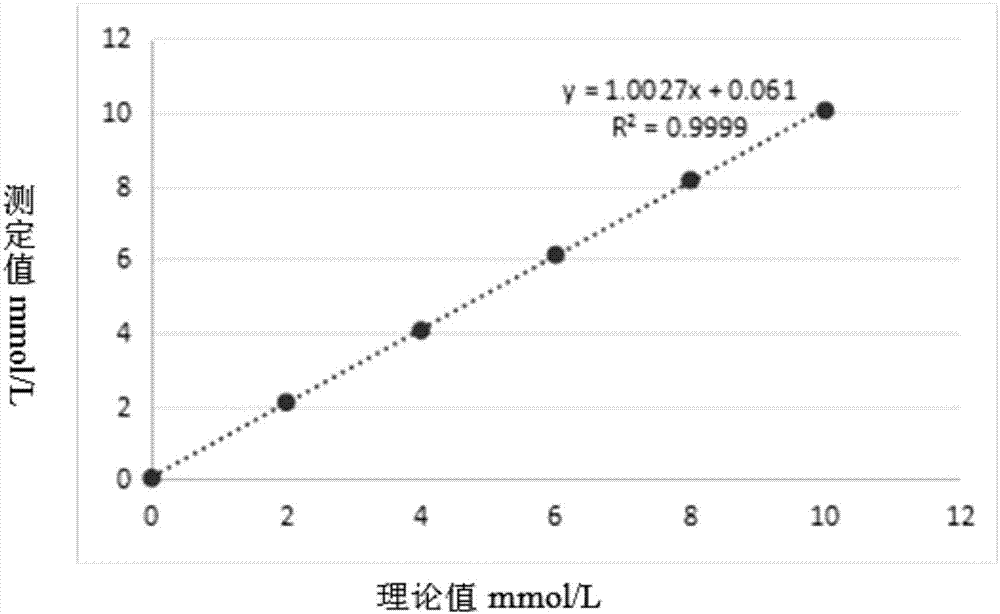
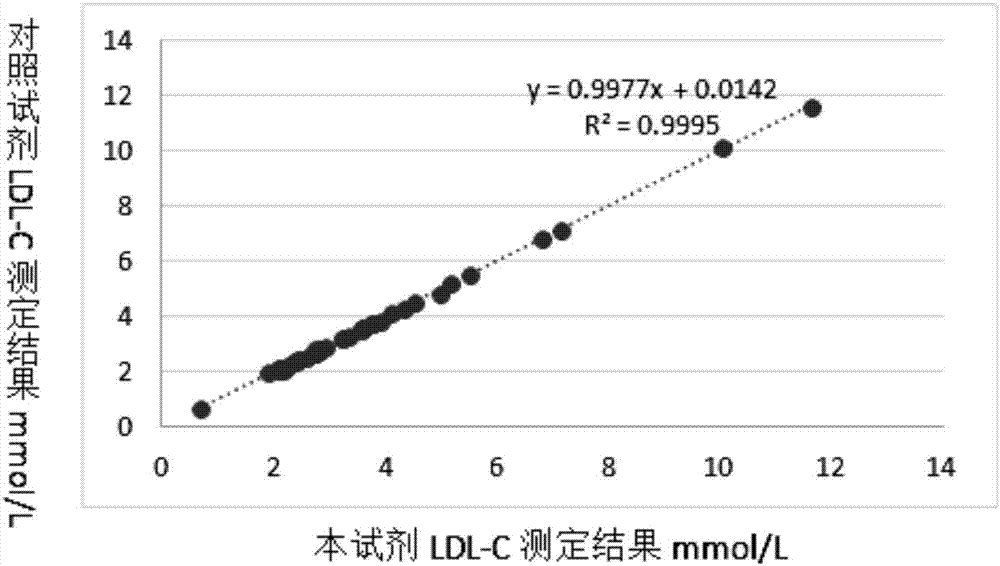
Detection kit for LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol and use method of detection kit
ActiveCN107505272AImprove accuracyNo precipitationColor/spectral properties measurementsPeroxidasePolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a detection kit for LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol and a use method of the detection kit, relates to the field of biochemical detection and aims to provide a detection kit, having high stability, accuracy and precision as well as low toxicity, for LDL cholesterol and a use method of the detection kit. The kit comprises a reagent 1 and a reagent 2, wherein the reagent 1 is prepared from a surfactant, polyethylene glycol, SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate), Emulgen A9 series, CHOD (cholesterol oxidase), CHER (cholesterol esterase), ascorbic acid oxidase, CAT (catalase), 4-AAP (4-aminoantipyrine) and the like; the reagent 2 is prepared from octylphenyl polyethylene glycol, cholate, a compound stabilizer, bovine serum albumin, POD (peroxidase), TOPS (sodium 3-(N-ethyl-3-methylanilino)propanesulfonate) and the like. The proclin series added to the kit is a novel biological preservative, has good compatibility with various enzymes, better stability and low toxicity, and the stability of the reagents is maintained.
Owner:WHITMAN BIOTECH NANJING
Preparation method of highly sensitive photoelectrochemical sensor for detecting microRNA
ActiveCN110412097AIncrease surface areaEnhance photoelectric signalMaterial electrochemical variablesBismuth sulfideBismuth vanadate
The invention discloses a highly sensitive paper-based photoelectrochemical sensor for detecting microRNA. A paper chip is prepared by means of a wax printing technology, gold nano-particles are grownin situ in a hydrophilic working area to achieve functionalization of the paper chip, a cuprous oxide / bismuth sulfide / bismuth vanadate tertiary sensitizer is modified subsequently, and microRNA is captured through a fixed hairpin DNA chain; by means of identification of specificity and digestion effect of duplex-specific nuclease, signal amplification on microRNA is achieved, and then by means ofa multibranched hybrid chain, platinum nanoparticles are embedded into a main part of the chain, branch parts form a chlorhematin / G-tetrad structure, and a DNA concatemer with catalase bological characteristics is formed; signal amplification is further achieved, thus preparation of the photoelectrochemical sensor is completed, and highly sensitive and accurate detection on microRNA is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Atmosphere heavy metal pollution prewarning method using muskeg catalase as marking article
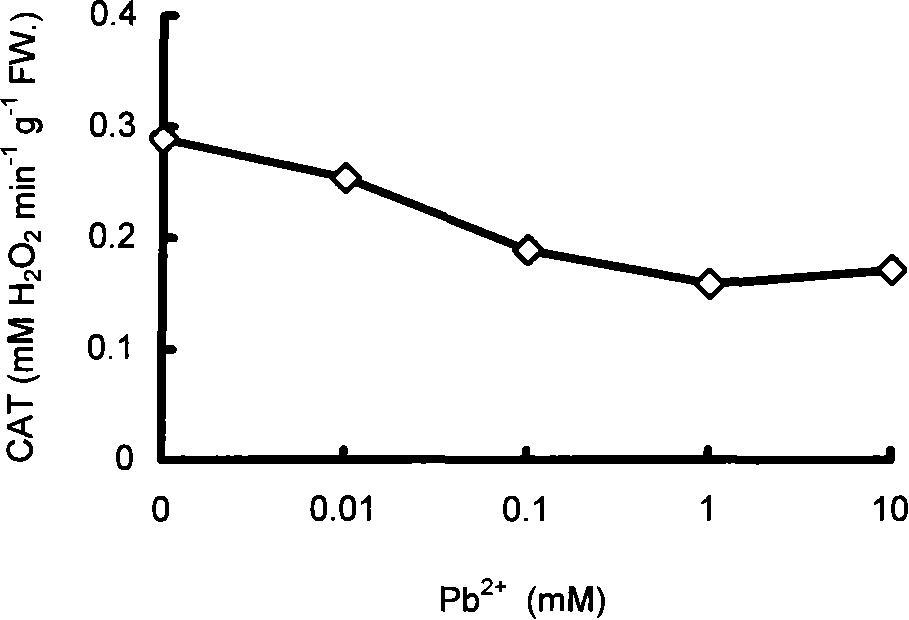
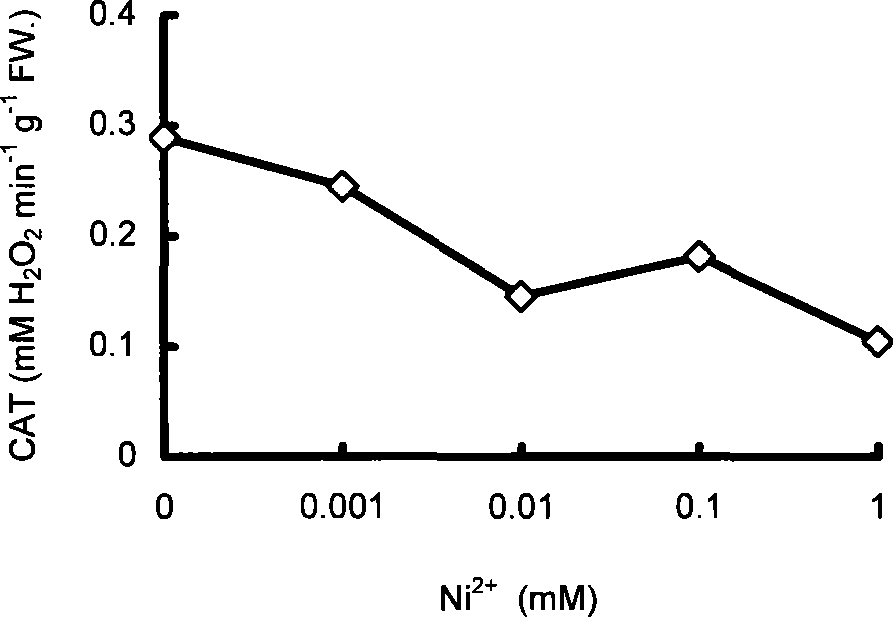
InactiveCN101251531AThe method is sensitive and efficientSimple and fast operationColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingMossMetal contamination
The invention relates to an environmental protection technical field, in particular to a method for the early detection of the heavy metal pollution in air by taking the moss catalase as a marking object; the steps of the method are as follows: firstly mosses are collected, and the catalase is extracted from the mosses, finally the catalase is analyzed and the extent of the heavy metal pollution in air is judged according to the activity of the catalase. Because the activity of the catalase of the mosses is analyzed and the extent of the heavy metal pollution in air is judged according to the activity of the catalase, the invention has the advantages of flexibility, high efficiency, easy operation and low cost; the method has good early warning effect for the heavy metal pollution in the air, and is particularly applied to conditions in which pollutants are too low to cause morphological changes of plants.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
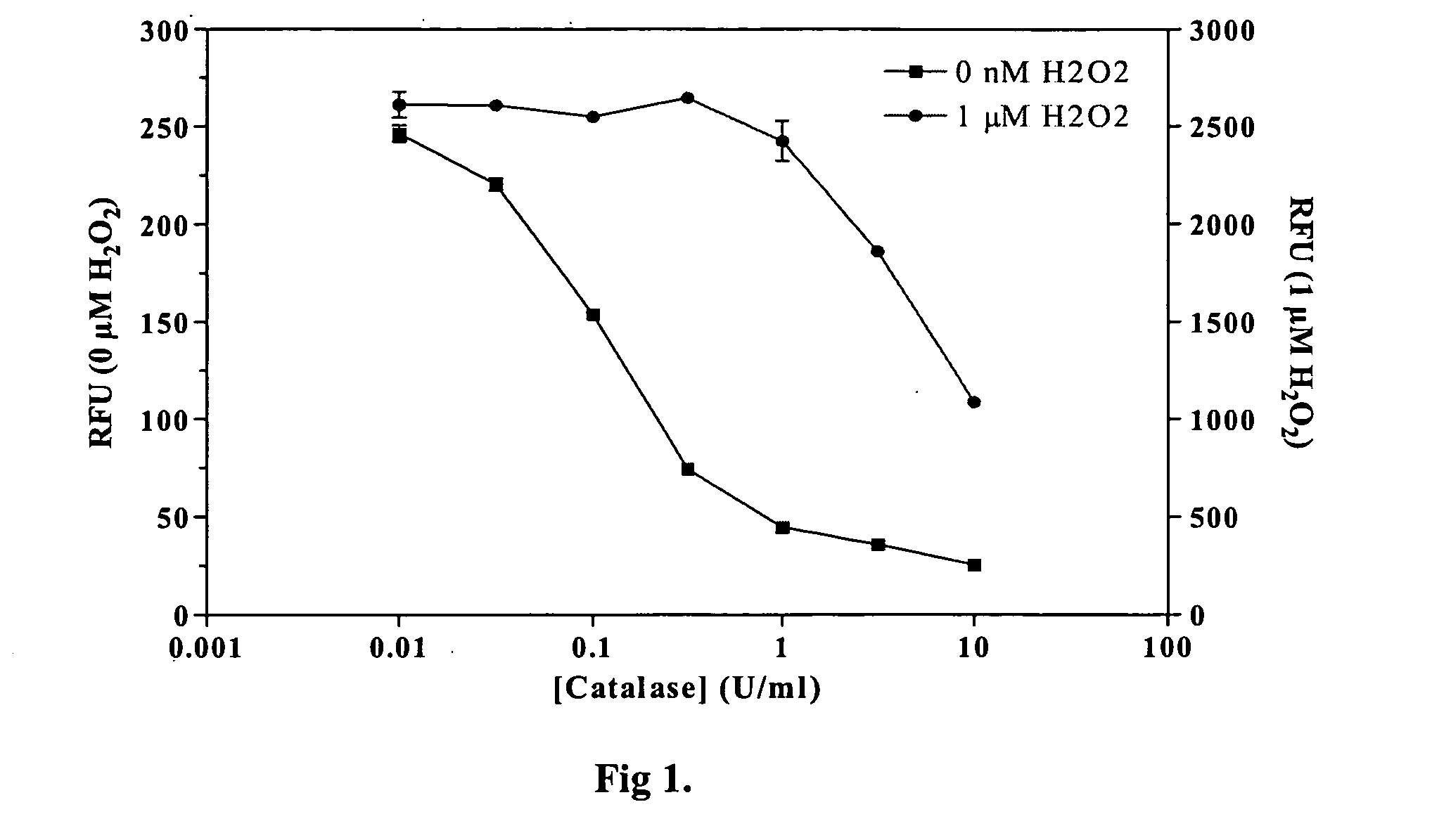
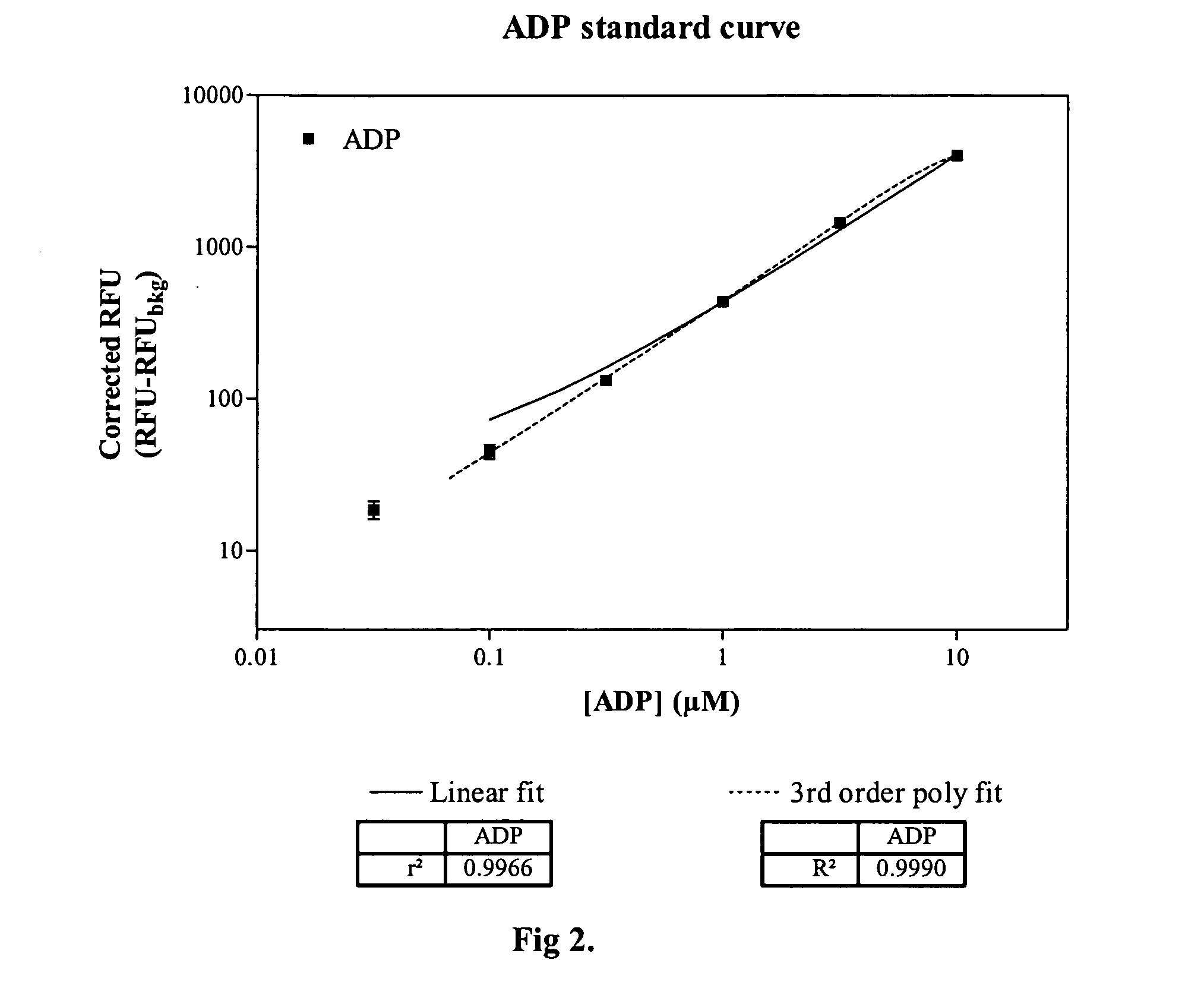
ADP detection using an enzyme-coupled reaction
ActiveUS20060199238A1Minimize contaminationMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulinsFluorescencePeroxidase
Methods and compositions are provided for determining ADP in the presence of ATP. These comprise including among the assay reagents at least one of the correcting components creatine phosphokinase and phosphocreatine, pyruvate kinase and phosphoenolpyruvate, peroxidase and a non-interfering peroxidase substrate, and catalase. One aspect of the method employs formation of hydrogen peroxide from the ADP by pyruvate kinase, phosphoenolpyruvate and pyruvate oxidase. The hydrogen peroxide is then determined. A combined reagent having all of the reagents may optionally include a peroxidase when the hydrogen peroxide is to be enzymatically determined. A peroxidase substrate is added to the sample in conjunction with the peroxidase substrate reagent, the mixture incubated and depending on whether the peroxidase substrate is a fluorescer or chemiluminescer, the mixture may be illuminated with excitation light and the emitted light determined as a measure of the ADP in the sample.
Owner:DISCOVERYX CORP
Method for improving activity of reactive oxygen species scavenging enzymes
InactiveUS20100037353A1Increase volumeIncrease enzyme activityBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsBiological bodyRos scavenging
A highly safe, inexpensive and widely utilizable method, which has a mechanism backed by scientific grounds, for improving an activity of ROS (reactive oxygen species)-scavenging enzyme group; An increase in the amount of an enzyme or promotion of an enzyme activity of the ROS scavenging enzyme group such as superoxide dismutase, catalase or peroxidase is caused in an organism having the ROS-scavenging enzyme with one or two or more kinds of substances selected from the group consisting of erythritol, mannitol, sorbitol and xylitol in 0.01-10% administration concentration.
Owner:B FOOD SCI
Calorimetric method for detecting pesticides by using acetylcholin esterase
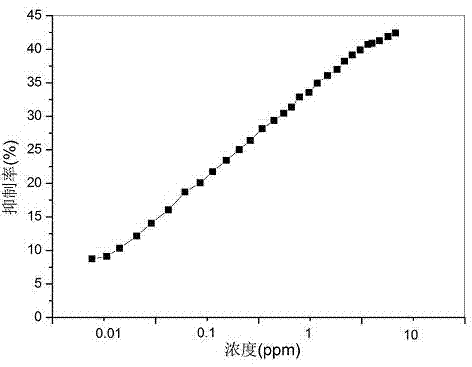
InactiveCN103196952AHigh strengthHigh sensitivityMaterial heat developmentPesticide residueReaction rate
The invention relates to a calorimetric method for detecting pesticides by using acetylcholin esterase. According to the technical scheme, an enzymatic inhibition method and cascade reaction are adopted; the acetylcholin esterase is suppressed by pesticides, so that the enzymatic reaction rate is reduced; the quantity of choline products is reduced and is in direct proportion to the suppression degree; and furthermore, the amount of the choline can be obtained by cascade reaction heat of choline oxidase and catalase. By using the cascade reaction, the intensity of an original thermal signal as well as the detection sensitivity and the detection resolution are greatly improved, the detection limit is reduced, and the detection accuracy is effectively improved; a pesticide detection calorimetric method based on the acetylcholin esterase is realized; the advantages of high sensitivity of the acetylcholin esterase to organophosphorus and carbamic acid ester type pesticides and no interference caused by electrochemical active substances or colors and turbidity of the sample on the calorimetric method are integrated; the in-site quick pesticide residue detection is facilitated; and the large-scale application is facilitated.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
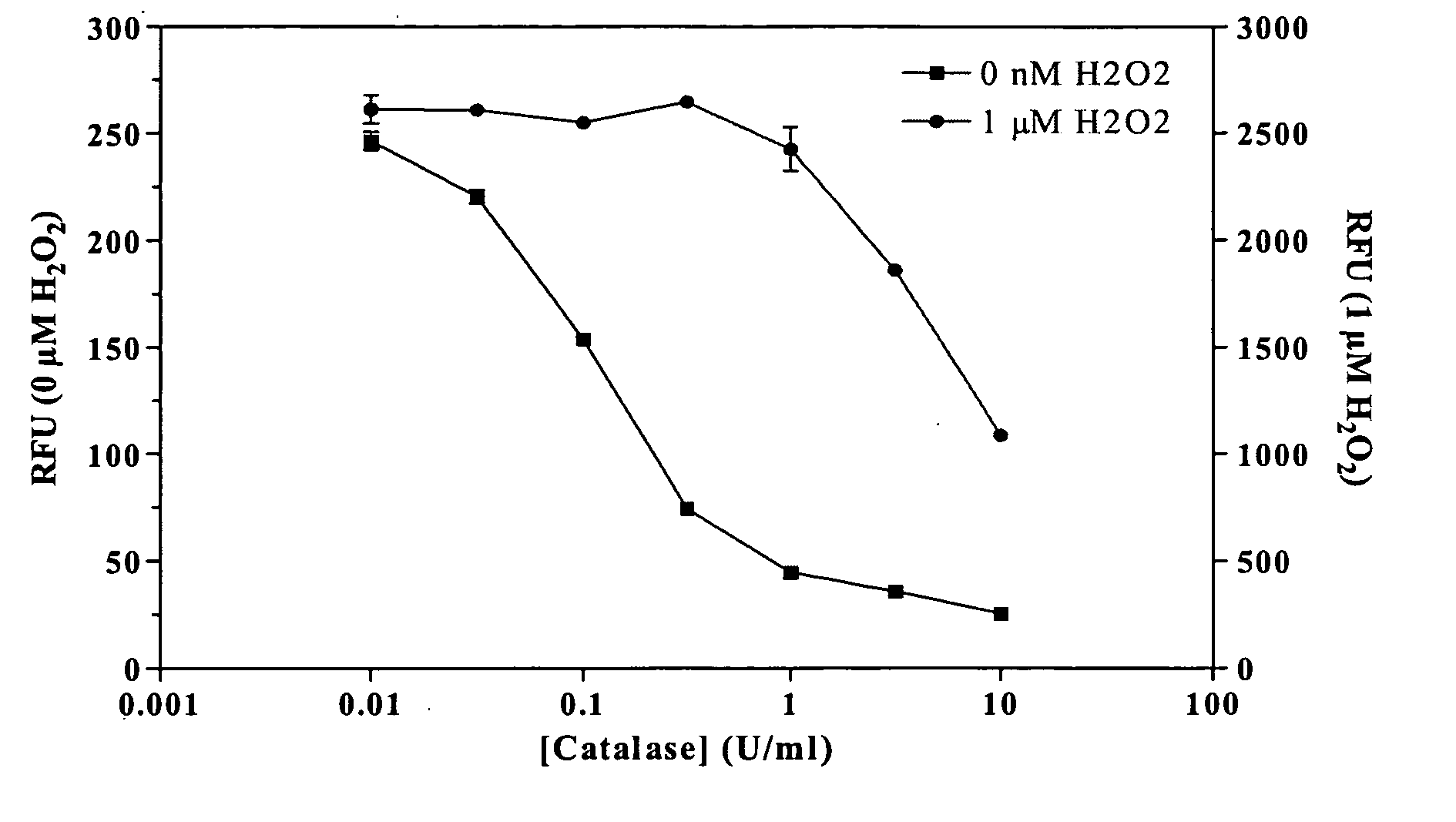
Method for detecting activity of catalase
InactiveCN104297185AThe detection method is accuratePracticalColor/spectral properties measurementsWater bathsPhosphate
The invention relates to a method for detecting activity of catalase, belonging to the field of enzymatic activity detection methods. The method for detecting activity of catalase comprises the following steps: diluting a catalase standard substance into a standard solution with a series of catalase activity concentrations, adding 10mL of chlorine peroxide phosphate buffer solution in a 100mL iodine measuring flask, putting the iodine measuring flask in water bath at 25 DEG C and carrying out heat preservation, then adding 2mL of a standard enzyme solution, accurately carrying out heat preservation for 3 minutes, instantly adding 2mL of 0.5mol / L sulfuric acid to end reaction, adding 2mL of 0.5mol / L sulfuric acid into a contrast tube of a contrast reaction solution to end reaction, and then adding the enzyme solution; then extracting 0.1mL of the reaction solution, adding 2.9mL of a peroxidase-dianisidine solution in a test tube and shaking to be uniform, firstly carrying out zero adjustment by a blank test tube in 436microns by virtue of a spectrophotometer at 25 DEG C, then detecting absorbancy of each reaction solution test tube to obtain a curve about the relation between the standard enzymatic activity and the absorbancy. The test enzyme is processed by the same method, so that the enzymatic activity of the test enzyme can be obtained according to the absorbancy and the standard curve. The detection method has the characteristics of being accurate, high in practicability, simple in instrument requirement and suitable for operation in the conventional condition; the detection method belongs to one reliable method of color rendering methods for detecting the activity of the catalase.
Owner:XIAN MIYI BIOTECH
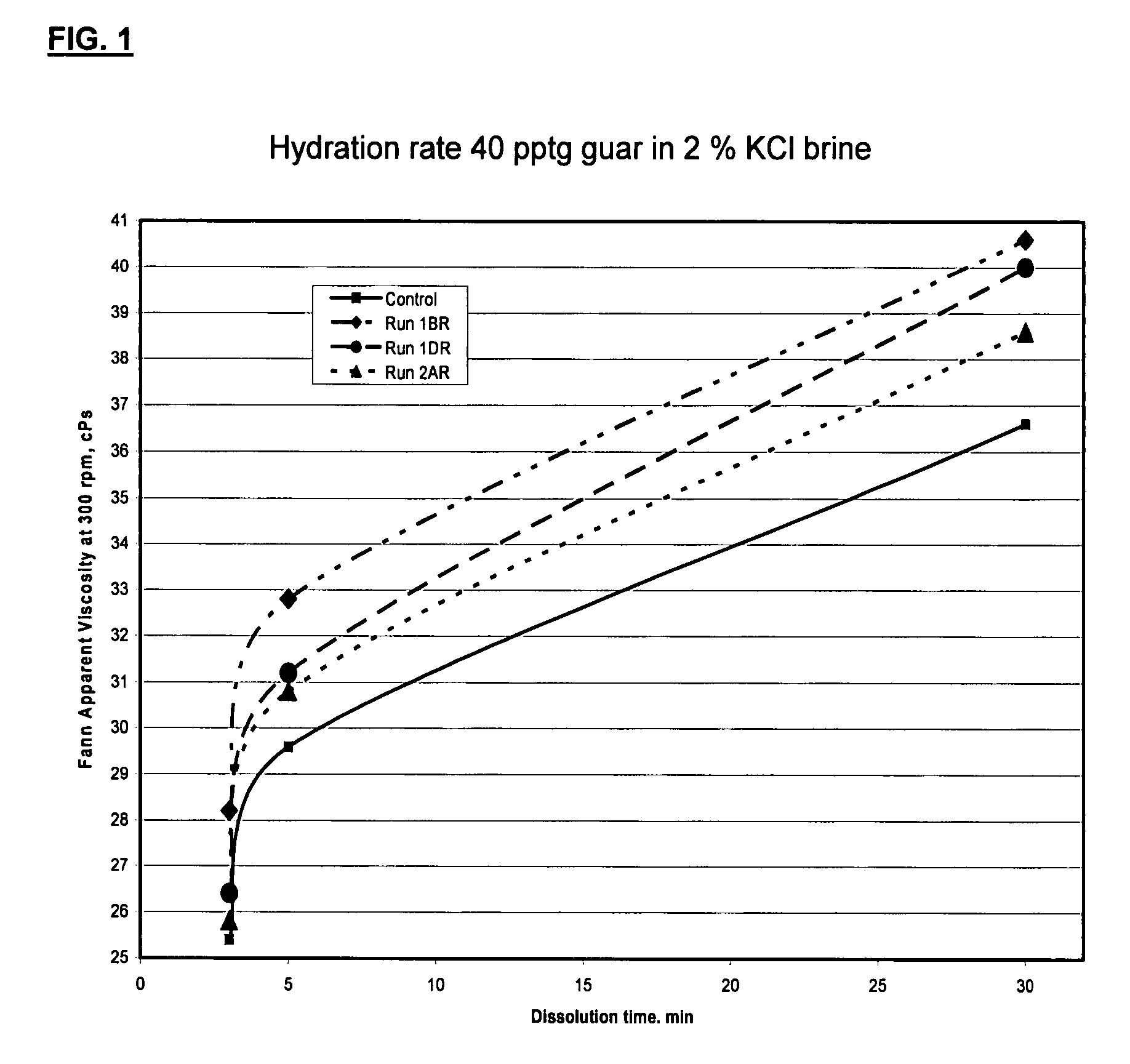
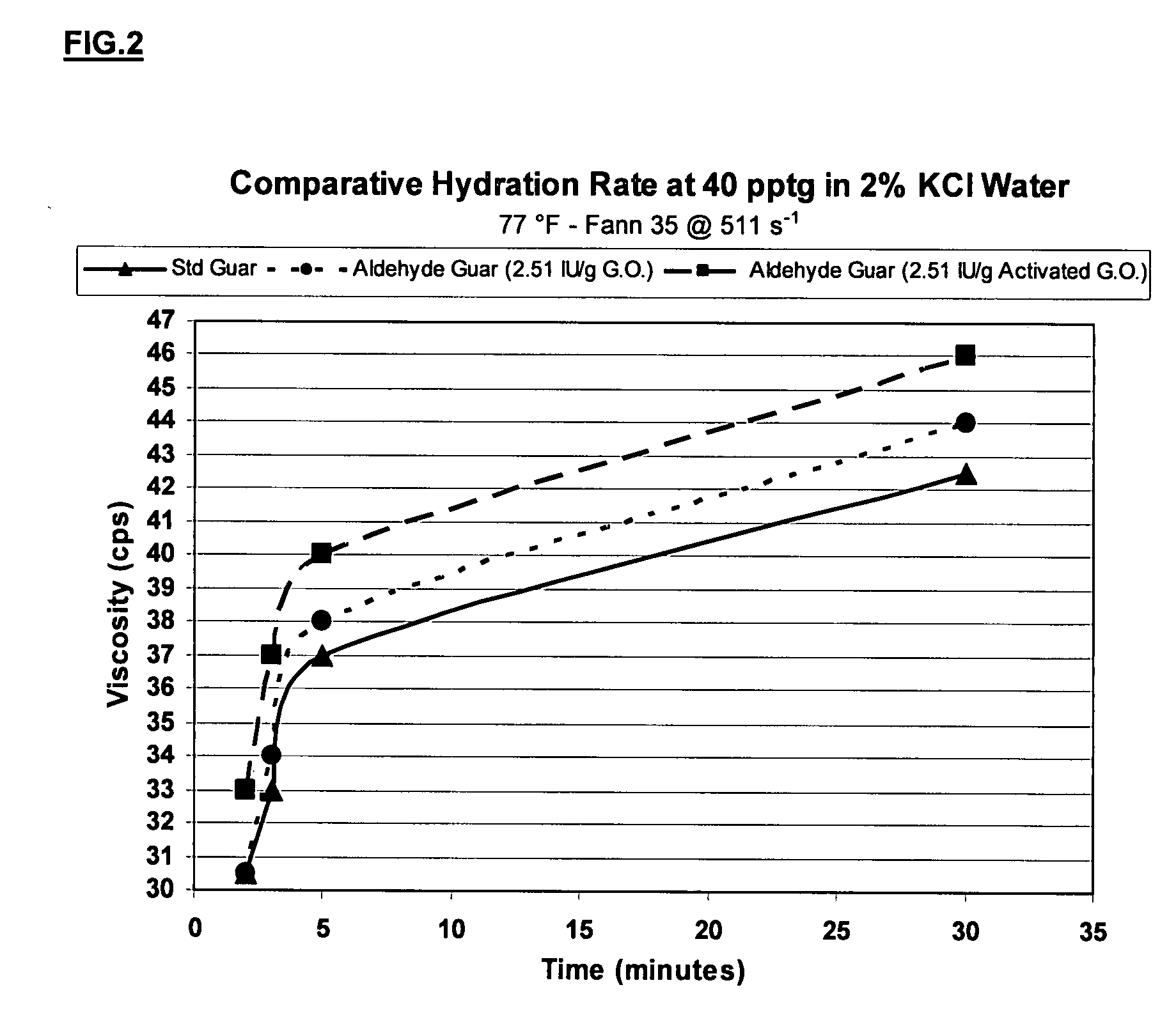
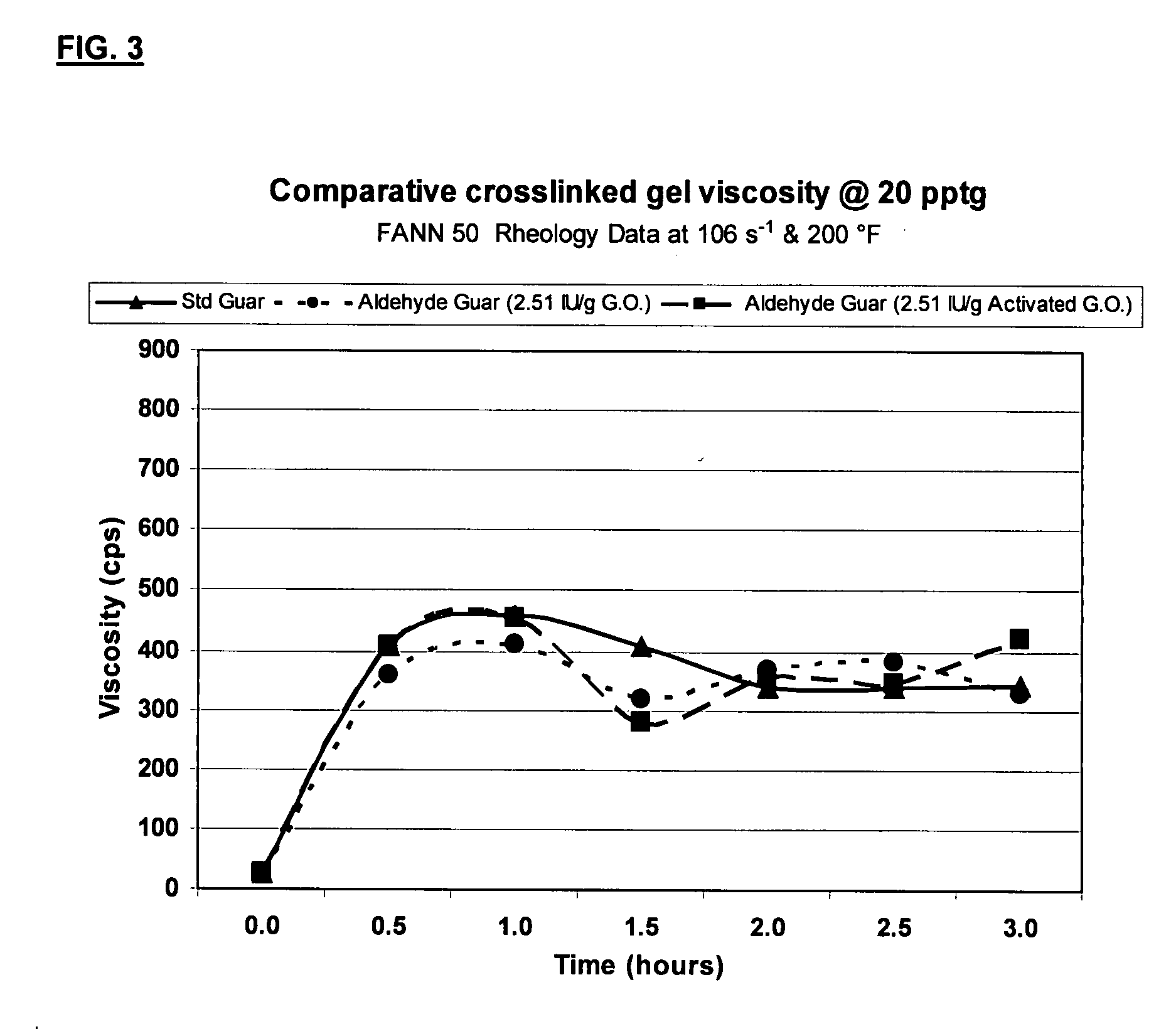
Oxidized guar for oilfield servicing fluids
ActiveUS20070275862A1High viscositySolve insufficient capacityFluid removalFlushingPeroxidaseHydraulic fracturing
An oilfield servicing fluid composition containing an aldehyde guar produced by enzymatic oxidation of a non-derivatized, straight guar or of a guar derivative. The enzyme used to oxidize the guar to the aldehyde guar is galactose oxidase, which may be combined with catalase or catalase and peroxidase. The aldehyde guar is useful as an effective gelling agent for oilfield servicing fluids such as hydraulic fracturing fluids and stimulation fluids.
Owner:HERCULES LLC
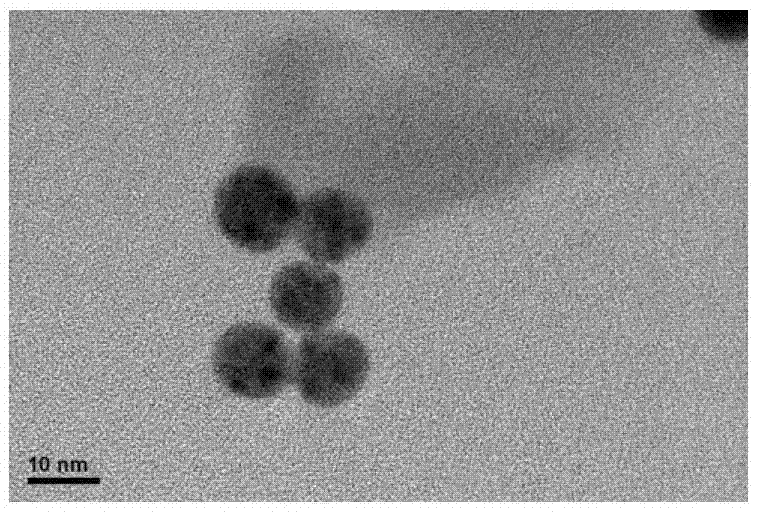
Process for preparing gold nano particles through reduction of chloroauric acid by catalase
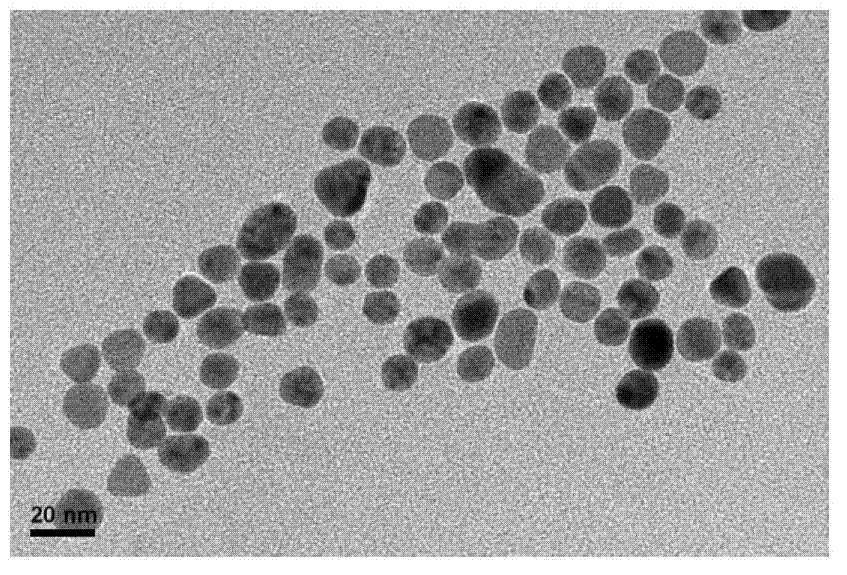
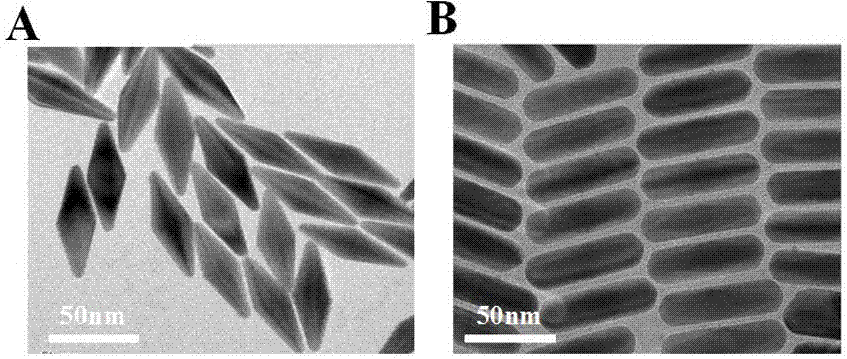
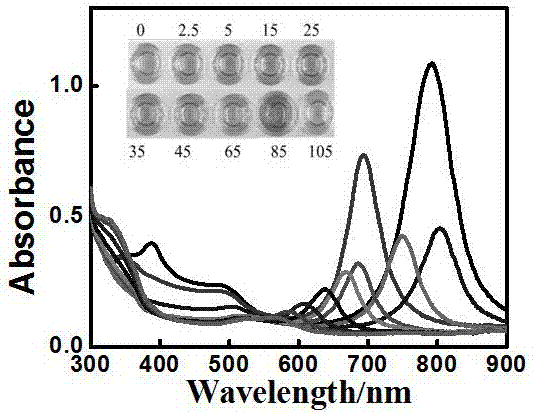
The invention discloses a process for preparing gold nano particles through reduction of chloroauric acid by catalase. The process comprises the steps of dropping a catalase solution into a chloroauric acid solution, and mixing uniformly; and adjusting the pH value of a mixed solution to be alkaline, reacting on the water bath condition of 20-37 DEG C, and obtaining gold nano particles through separation after the reaction is completed. According to the process, the catalase is introduced to serve as a reducing agent and a protective agent, reducing functional groups on the catalase are high in reducibility on the alkaline condition, the synthesis of gold nano particles is facilitated, and the produced gold nano particles are free from agglomeration on the high salinity condition (0.5MNaCl).
Owner:苏州奕方华知识产权运营有限公司
Method for raising disease resistance of paddy rice to rice blast by utilization of alginooligosaccharide
InactiveCN108812671AIncrease defense enzyme activityPromote growthPlant growth regulatorsBiocideDiseaseAgricultural science
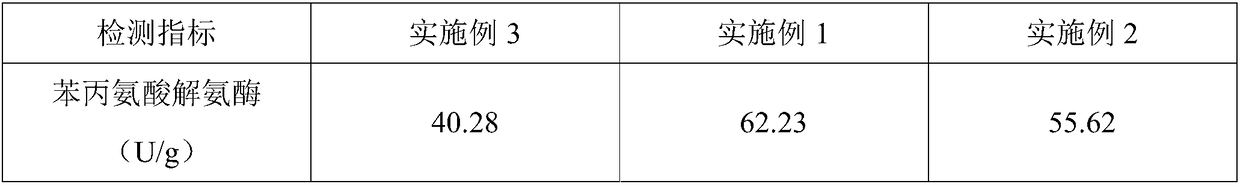
The invention provides a method for raising disease resistance of paddy rice to rice blast by the utilization of alginooligosaccharide. By spraying alginooligosaccharide during the rice seedling stage, activity of defensive enzymes--phenylalnine ammonialyase, catalase and peroxidase in the rice leaves is raised, and furthermore disease resistance of paddy rice to rice blast is enhanced. By the method, disease resistance of paddy rice is enhanced, and growth of paddy rice is promoted. Meanwhile, the method is simple and feasible and is beneficial to agricultural promotion and application.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Systems and Methods for Enzymatic Oxygen Removal
ActiveUS20120211372A1Microbiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow measurementElectrochemical responseOxidative enzyme
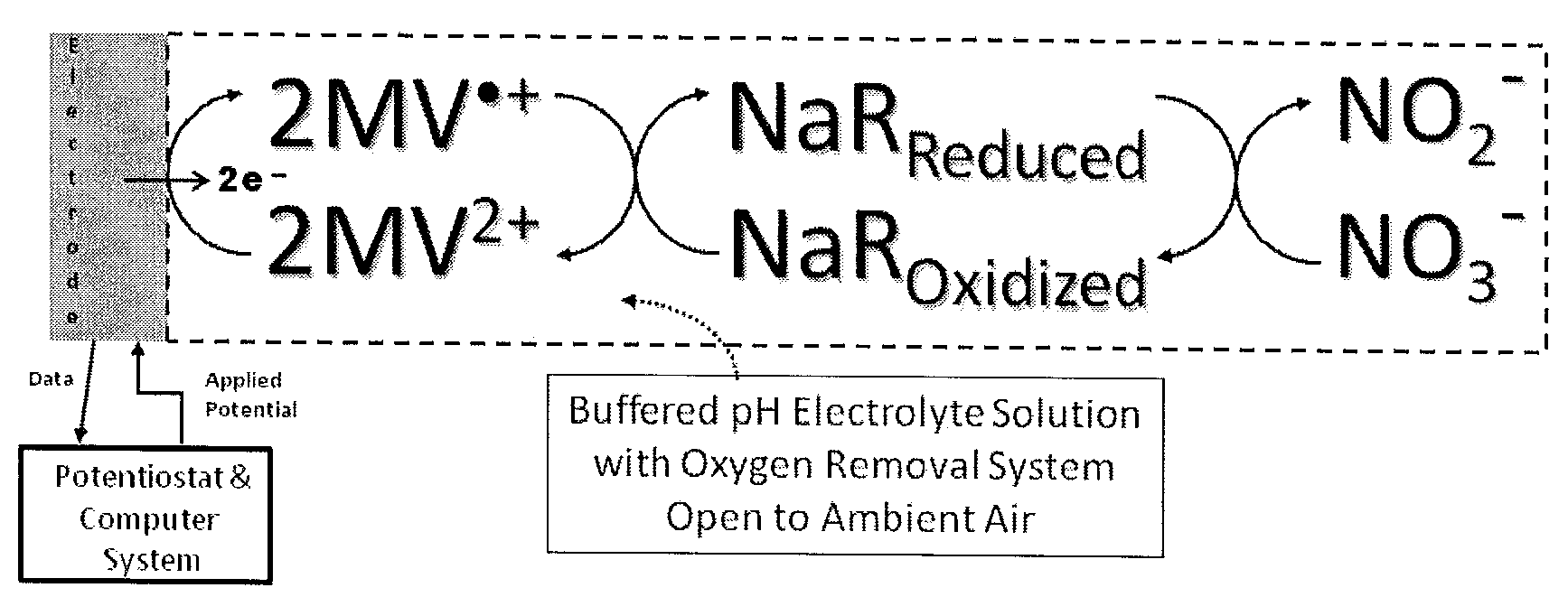
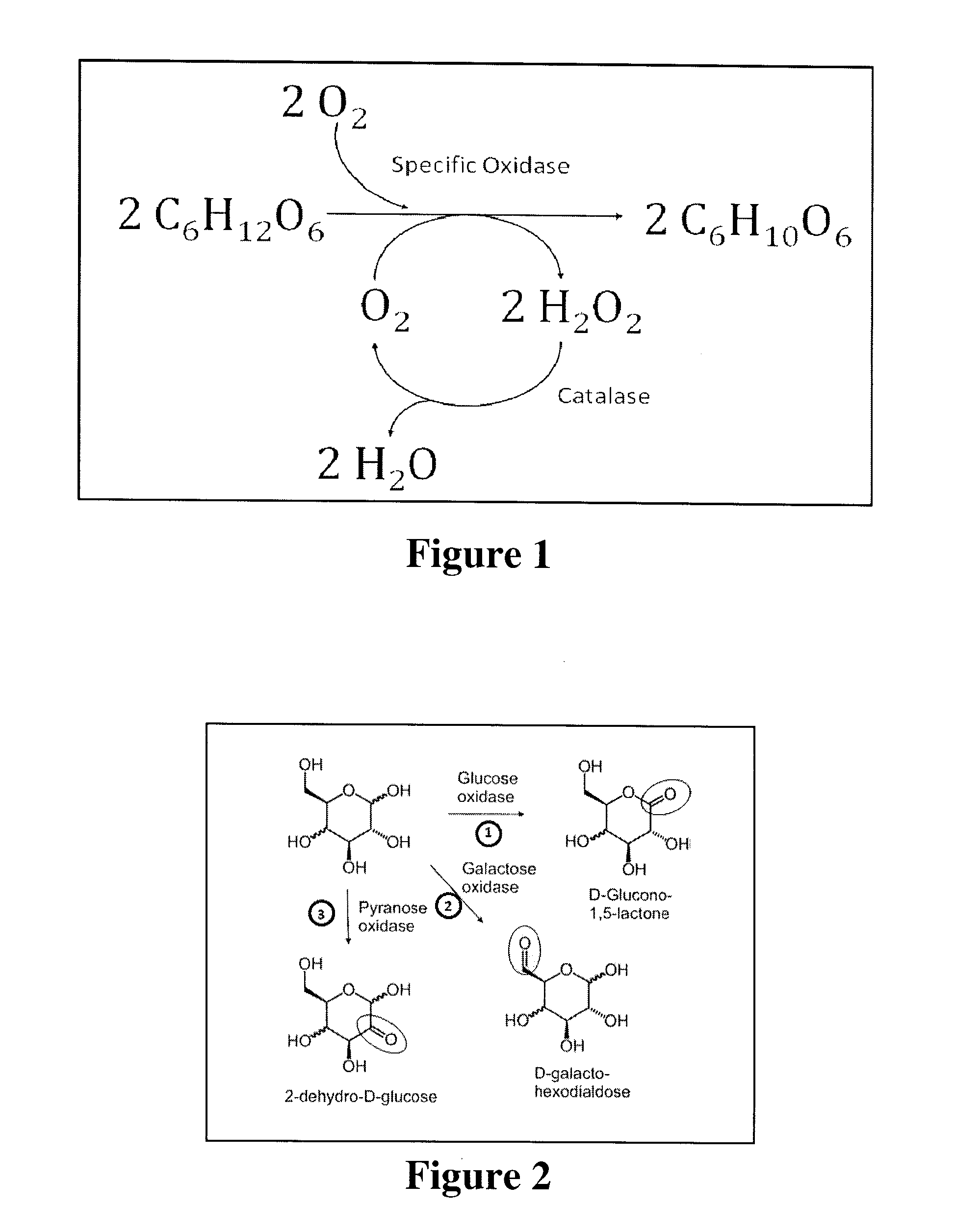
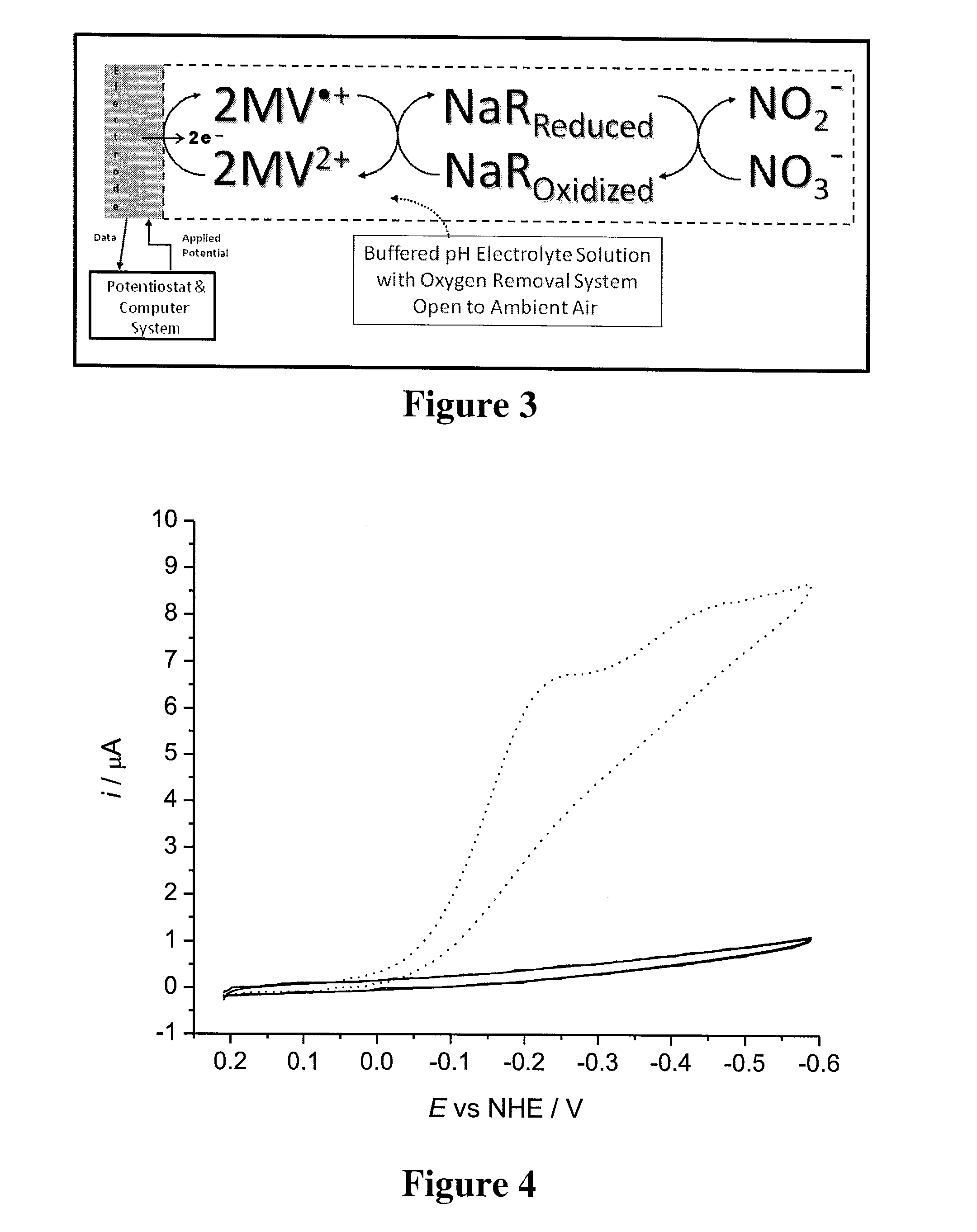
Systems and methods for oxygen removal from aqueous solutions are presented in which a bi-enzymatic reaction sequence recycles and depletes oxygen to extinction, preferably using an oxidase and a catalase as biocatalysts and a carbohydrate as co-substrate. Contemplated systems and methods are particularly advantageous in conjunction with electrochemical reaction systems in which oxygen would adversely interfere with the reaction system.
Owner:SILVER BEAR INC
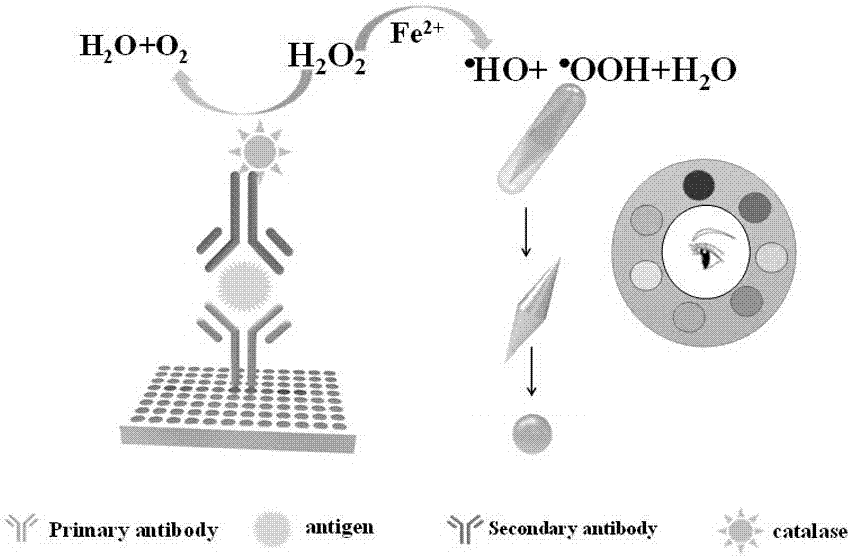
Visualized enzyme linked immunoassay method
InactiveCN107490682ARealize quantitative detectionSolve the shortcoming of single color changeMaterial analysisSilver plateColor changes
The invention discloses a visualized enzyme linked immunoassay method which comprises the following steps: (1) Au NBP@Ag nanorod preparation; (2) enzyme-linked immunoassay. According to the visualized enzyme linked immunoassay method, a primary antibody has been laid on a plate, antigen is added, then catalase modified secondary antibody compound is added, and then Fe2<+> and hydrochloric acid are added after the equivalent of hydrogen peroxide is added; then a silver plated gold cone nanorod is added to react, a series of fresh colors are observed in an etching process, and a target antigen is analyzed visually and semi quantitatively. The visualized enzyme linked immunoassay method disclosed by the invention can generate varieties of color change, solves the defect that color change in a traditional colorimetric method is single, achieves quantitative detection on a target object and further has quick reaction time and a good effect; thus, accuracy of the method for naked eye detection is greatly improved, and a detection limit is lower.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method for stabilizing percarboxylic acids in dispersions containing surfactants
InactiveUS20060178284A1Efficiently impededReduce decompositionInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsCosmetic preparationsSolubilityCarboxylic acid
A method for stabilizing particulate peroxycarboxylic acids, in particular imidoperoxycarboxylic acids, (such as, e.g., PAP), which are solid at an ambient temperature in a preferably aqueous dispersion containing surfactants. The dispersion is established in such a way that in the dispersed state a degradation of the peroxycarboxylic acids in the dispersion is prevented or at least reduced or retarded, or that the solubility of the peroxycarboxylic acids in the dispersion is diminished, in particular by minimizing the halide ion content, reducing the pH value to pH values ≦7, minimizing the content of free or active surfactants, minimizing the content of non-ionic surfactants, adding complexers, adding catalases or adding a solvent with a low solubility capability for peroxycarboxylic acids etc.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Compositions and methods for counteracting effects of reactive oxygen species and free radicals
InactiveUS20050090446A1Restore age-related reductionAntioxidative activityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntinoxious agentsDietary supplementAntioxidative enzyme
Peptide compounds and methods for upregulating expression of a gene encoding an antioxidative enzyme, such as superoxide dismutase or catalase, to counteract harmful oxidative effects of reactive oxygen species and other free radicals are described. The peptide compounds may be used to treat or prevent diseases and conditions characterized by undesirable elevation of reactive oxygen species and other free radicals, to upregulate AP-1 gene expression, and to treat pain. The peptide compounds may be used as components of pharmaceuticals and dietary supplements.
Owner:ISCHEMIX
Method for chlorite removal
InactiveUS20070080116A1Reaction is slowSolve reductionSpecific water treatment objectivesWater contaminantsCHLORITE IONCompound (substance)
The invention is directed to a process for removing chlorite ion from a body of water containing unacceptably high levels of chlorite comprising adding to said body of water a chlorite removal chemical selected from the group comprising sodium dichloroisocyanurate dihydrate, sodium dichloroisocyanurate, trichloroisocyanurate, polyaluminum chloride, sodium permanganate, potassium permanganate, and catalase enzyme.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Method for detecting a plurality of catalase positive microorganisms
InactiveUS7674602B2Material analysis using acoustic emission techniquesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismHydrogen peroxide
This invention is directed to a method and kit for detecting microorganisms on a surface. The invention involves contacting a household surface with a cleaning composition comprising hydrogen peroxide and then placing an acoustic device in close proximity to the household surface to determine if the microorganisms are still present.
Owner:THE CLOROX CO
Promotion of peroxisomal catalase function in cells
InactiveUS20060141598A1Reduce accumulationExtend your lifePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifNervous disorderMetabolitePeroxisomal biogenesis
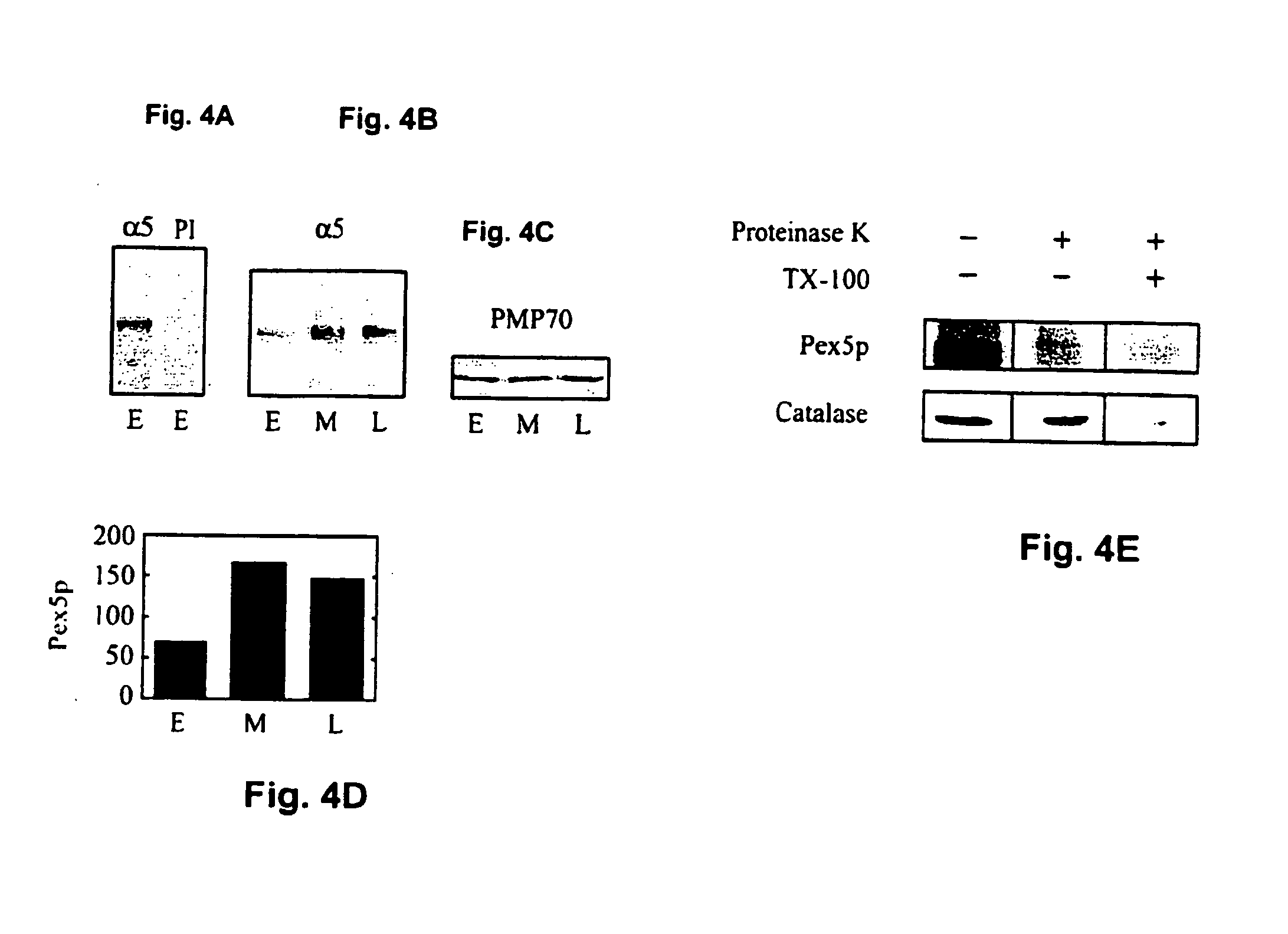
The molecular mechanisms of peroxisome biogenesis have begun to emerge: in contrast, relatively little is known about how the organelle functions as cells age. The present inventors characterized age-related changes in peroxisomes of human cells and showed that aging compromises peroxisomal targeting signal 1 (PTS1) protein import, with the critical antioxidant enzyme, catalase, especially affected. The number and appearance of peroxisomes are altered in these cells, and the organelles accumulate the PTS1-import receptor. Pex5p, on their membranes. Concomitantly, cells produce increasing amounts of the toxic metabolite, H2O2, and this increased load of reactive oxygen species (ROS) may further reduce peroxisomal protein import and exacerbate the effects of aging. Disclosed are novel compositions and methods for restoring catalase in peroxisomes by use of targeted catalase modified at its C-terminus and / or N-terminus, optionally in combination with polypeptides which promote cellular uptake of proteins, to prevent or overcome the changes that follows aging or that are associated with a number of diseases or disorders.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
Analytical method of ecological effect influence of domestic-garbage-leachate-contaminated soil
InactiveCN102590478AAvoid complex ingredientsOvercome limitationsEarth material testingEcological indicatorMoisture capacity
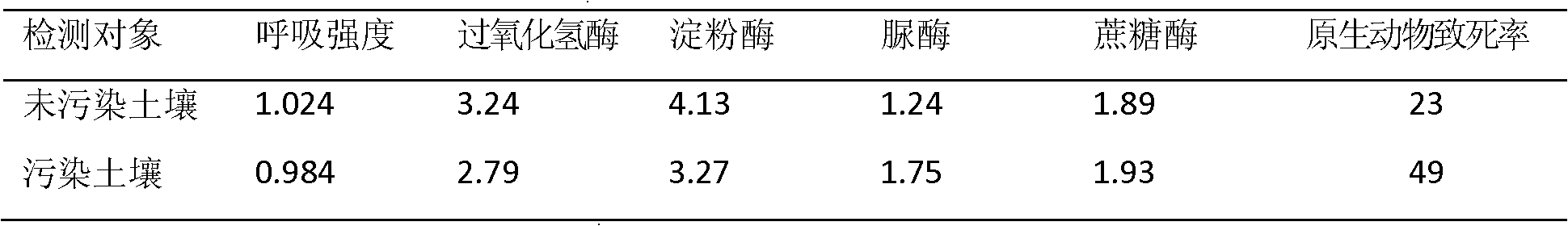
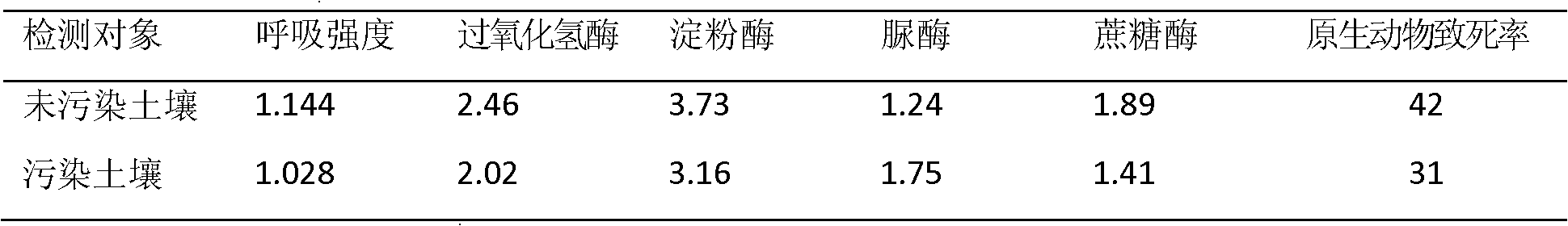
The invention relates to an analytical method of ecological effect influence of domestic-garbage-leachate-contaminated soil, comprising the following steps: 1. adjusting moisture contents of a contaminated soil sample and an uncontaminated soil sample to be 60% of field moisture capacity and culturing at the temperature of 20-30 DEG C; 2. selecting microbial activity indexes (respiratory intensity and soil enzymatic activity(catalase, amylase, urease and invertase)) and biotoxicity indexes (protozoon fatality rate) as ecological effect indexes of a soil sample; 3. comparing according to the difference of ecological indicators of the contaminated soil sample and the uncontaminated soil sample and analyzing the contaminated degree of the soil by the domestic garbage leachate. Indexes monitoring referred in the analytical method disclosed by the invention is convenient to operate and is easy to carry out, and can be a supplement for chemical index monitoring.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
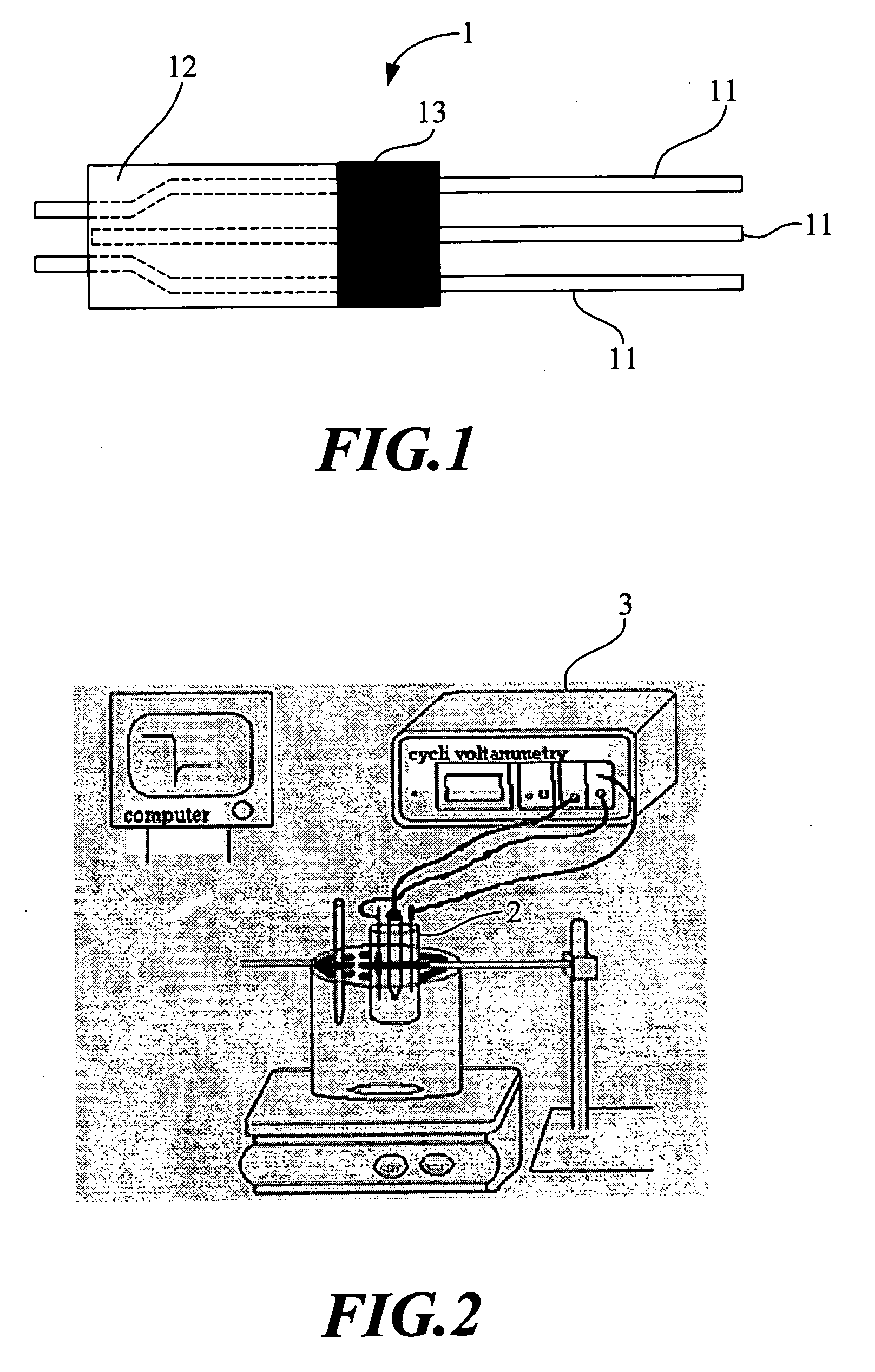
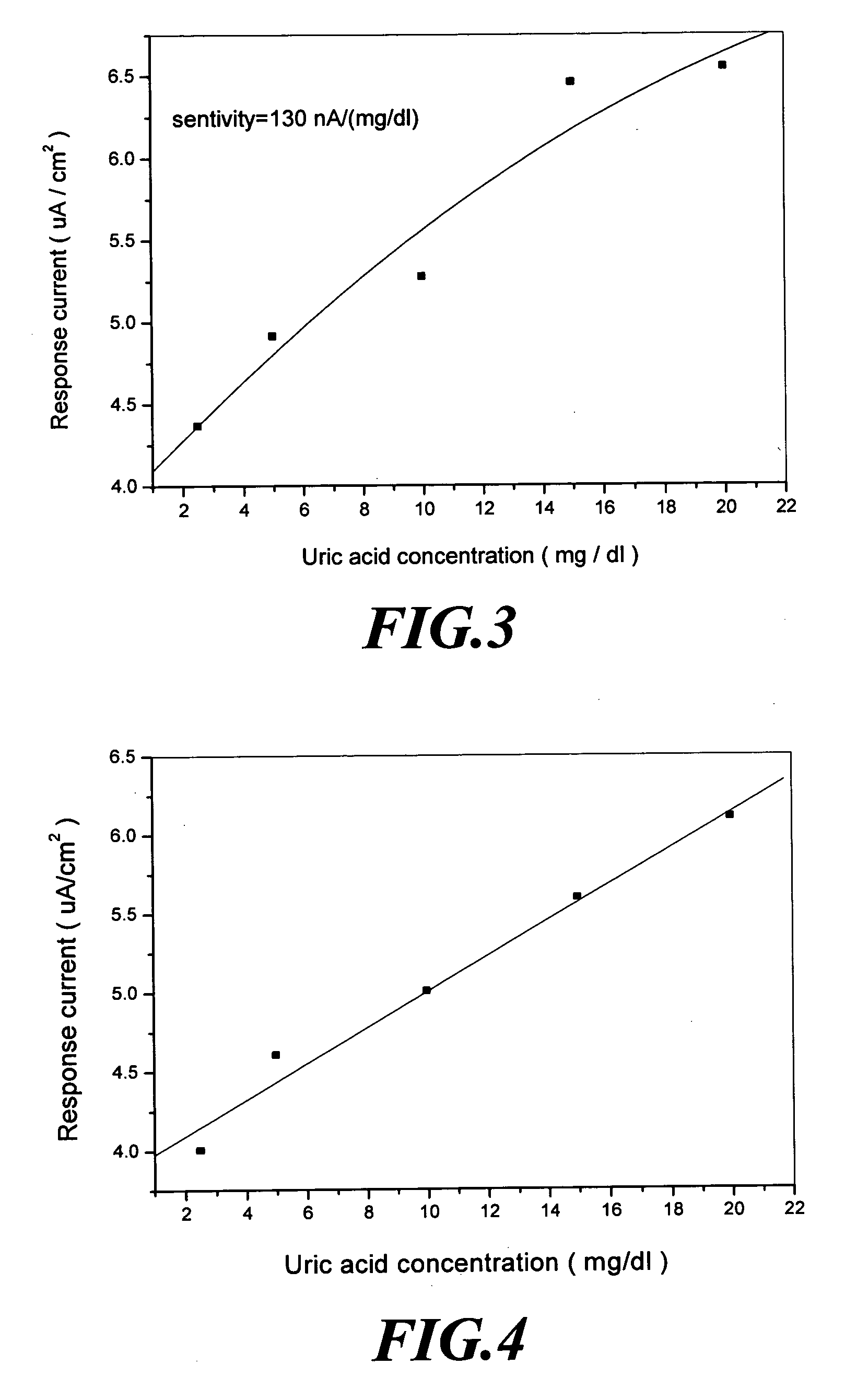
Amperometric sensor for uric acid and method for the same
InactiveUS20070240983A1Low costEasy to packImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFerrocenecarboxylic acidPolyacrylamide
An amperometric sensor for uric acid and a manufacturing method thereof are disclosed, in which polyacrylamide is used to fix catalase, uricase and ferrocenecarboxylic acid on a working electrode. In determining concentration of uric acid, hydrogen peroxide is produced when enzyme and uric acid react with each other and then a reduction current generated from enzyme on the electrode with an external voltage 200 mV applied is detected. In determining concentration of uric acid, a concentration range of 2.5-20 mg / dl is achieved and sensibility of the sensor in a linear portion is 5.17 uAcm−2(mg / dl)−1. In addition, reaction time required for the reaction between enzyme and uric acid is 5.17 uAcm−2(mg / dl)−1.
Owner:CHUNG YUAN CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com