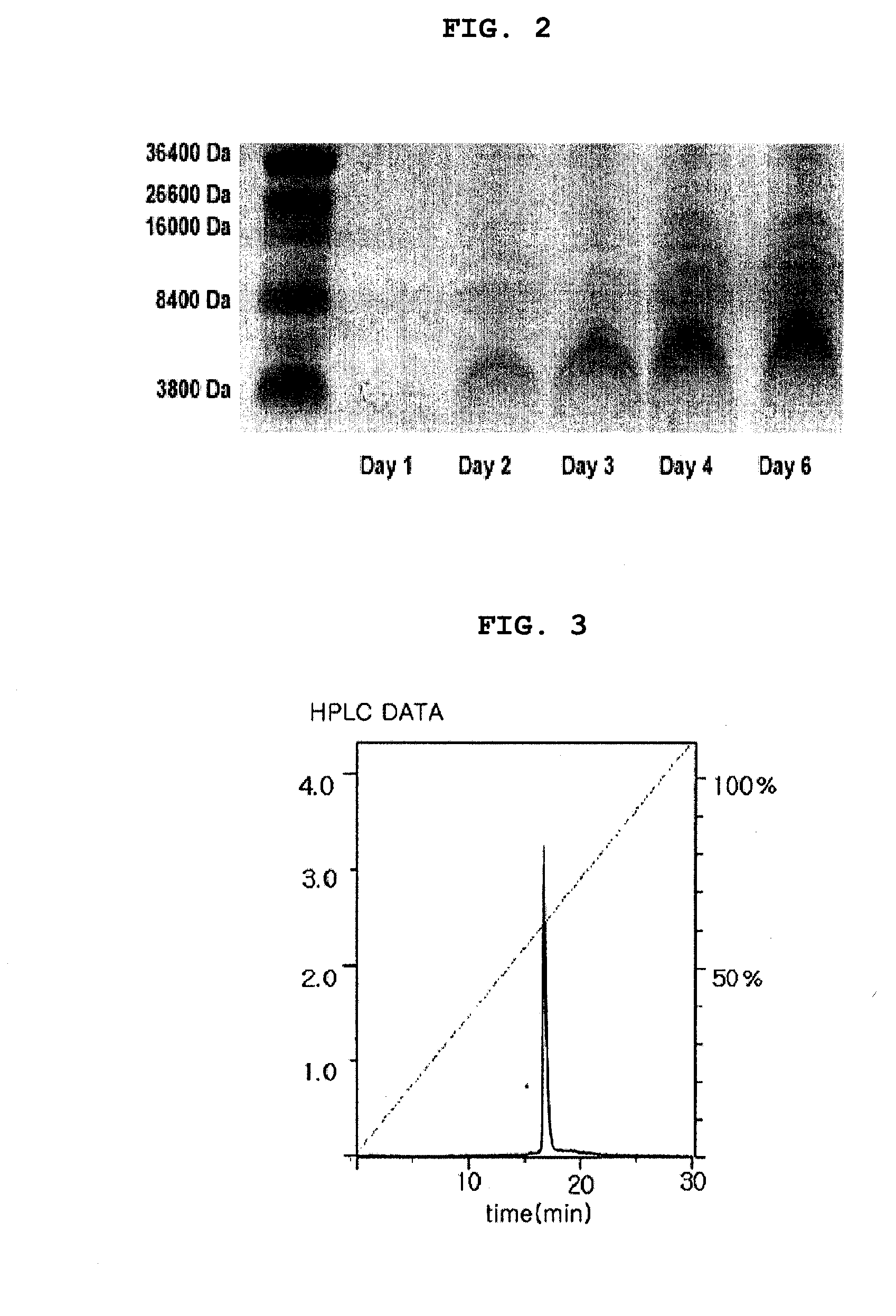
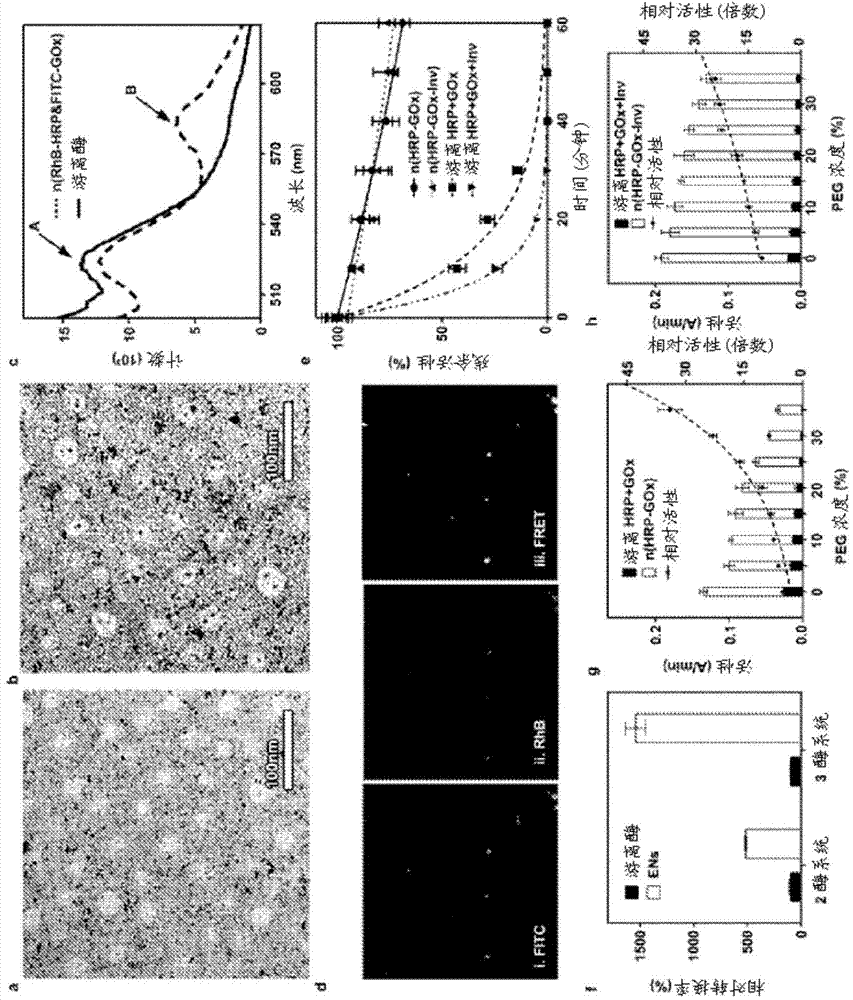
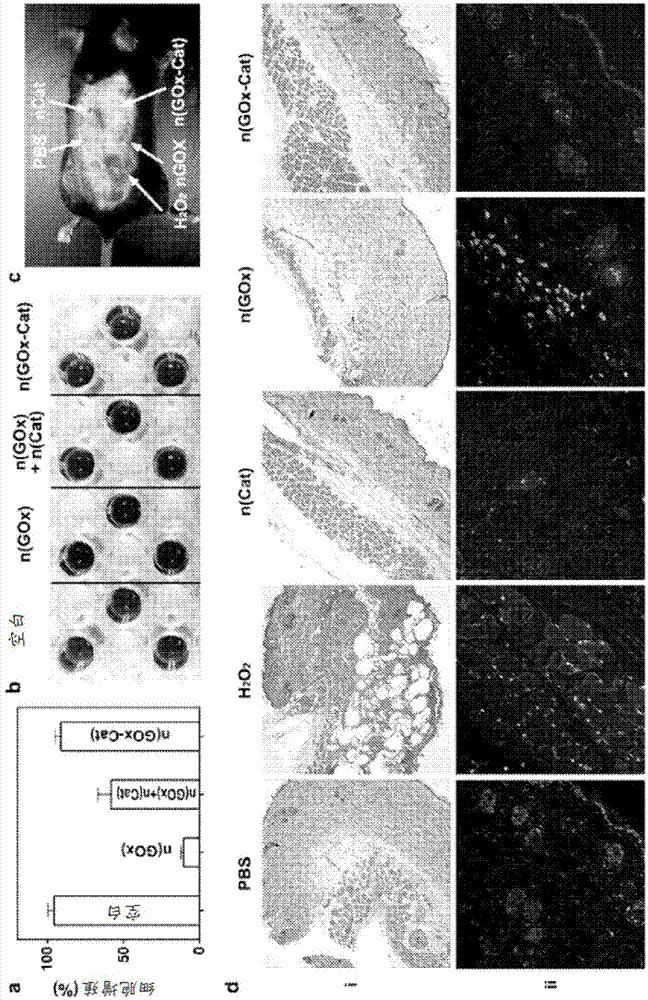
Patents
Literature
61 results about "Alcohol oxidase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
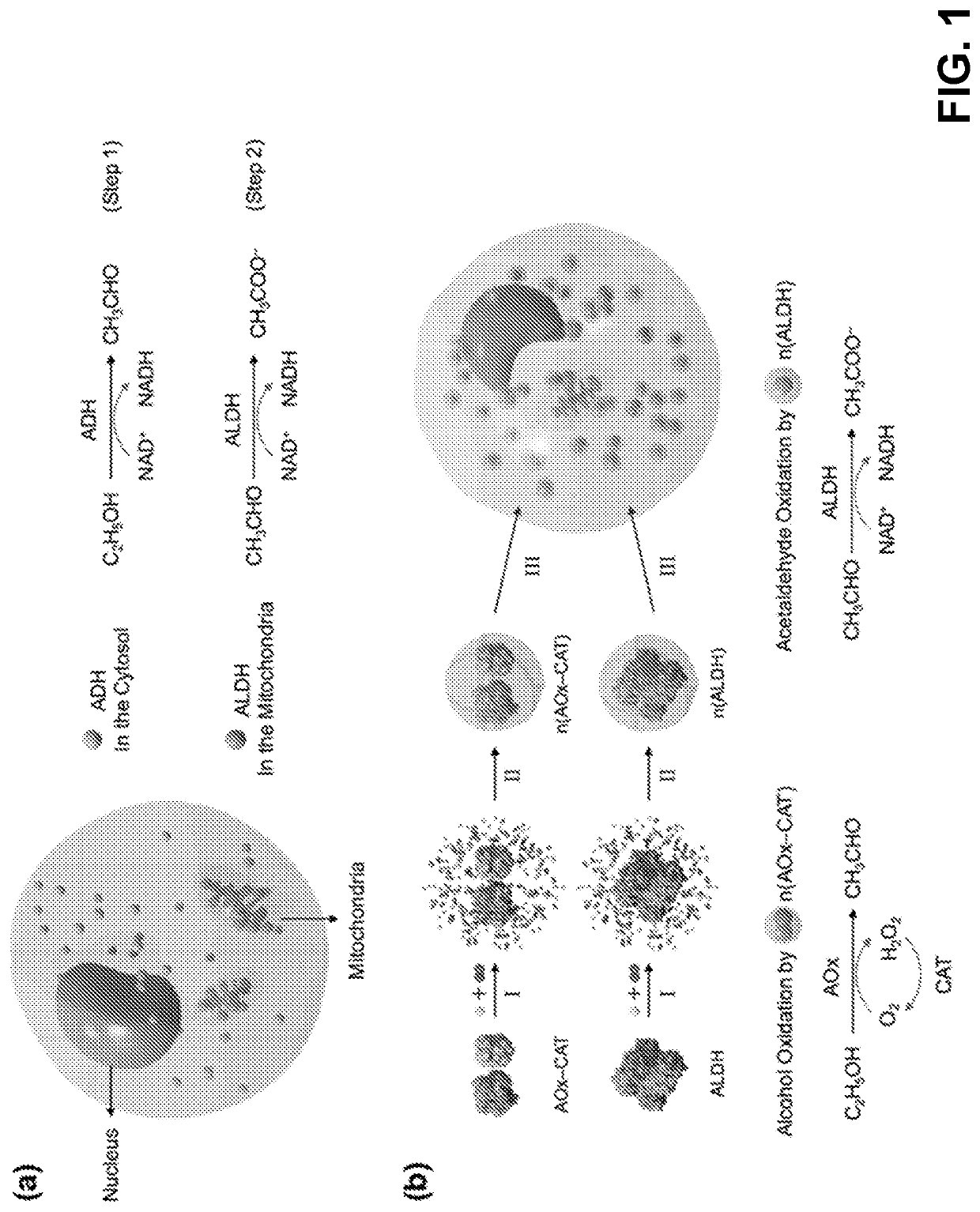
In enzymology, an alcohol oxidase (EC 1.1.3.13) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction a primary alcohol + O₂ ⇌ an aldehyde + H₂O₂ Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are primary alcohol and O₂, whereas its two products are aldehyde and H₂O₂. This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on the CH-OH group of the donor with oxygen as the acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is alcohol:oxygen oxidoreductase.
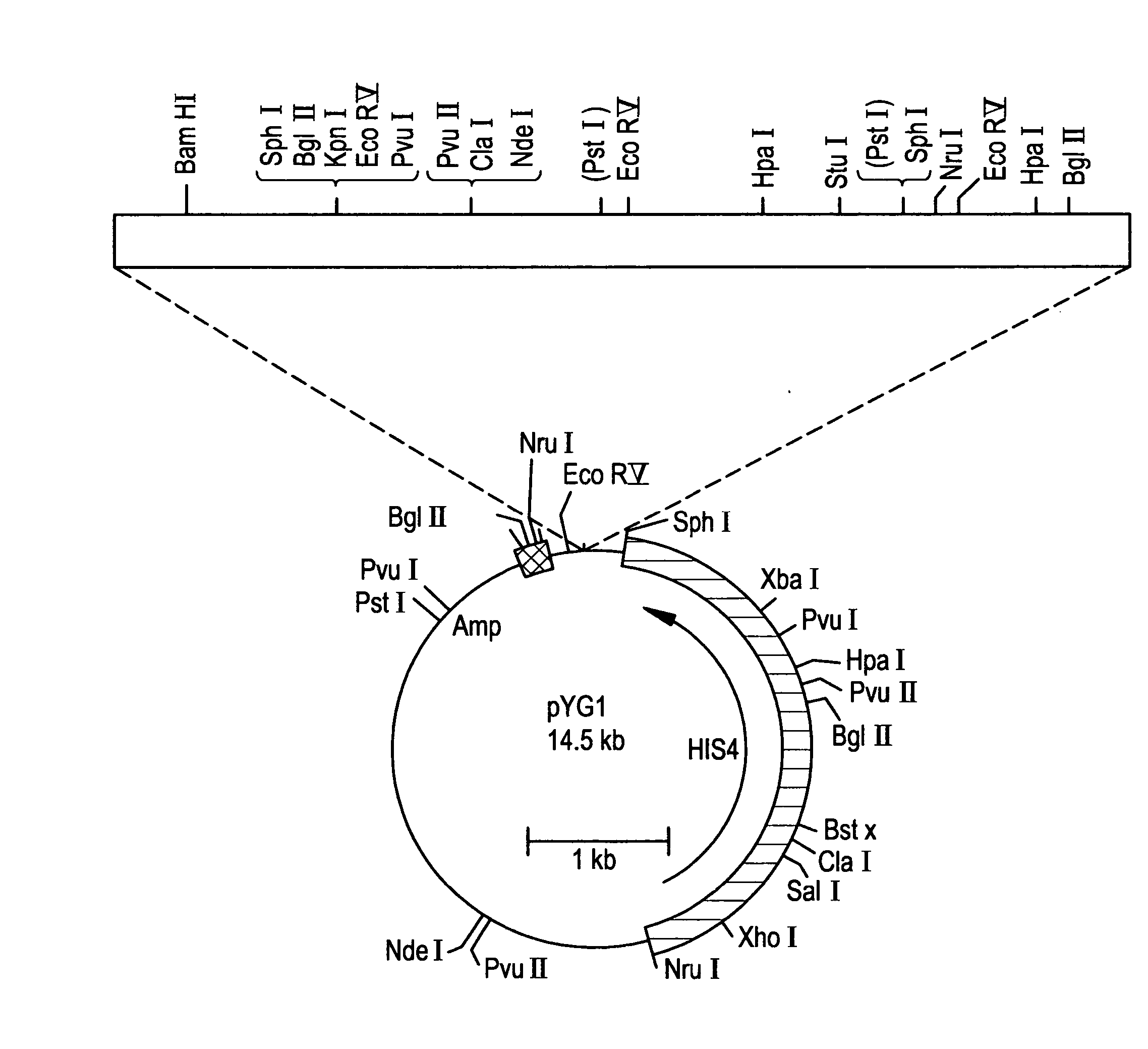
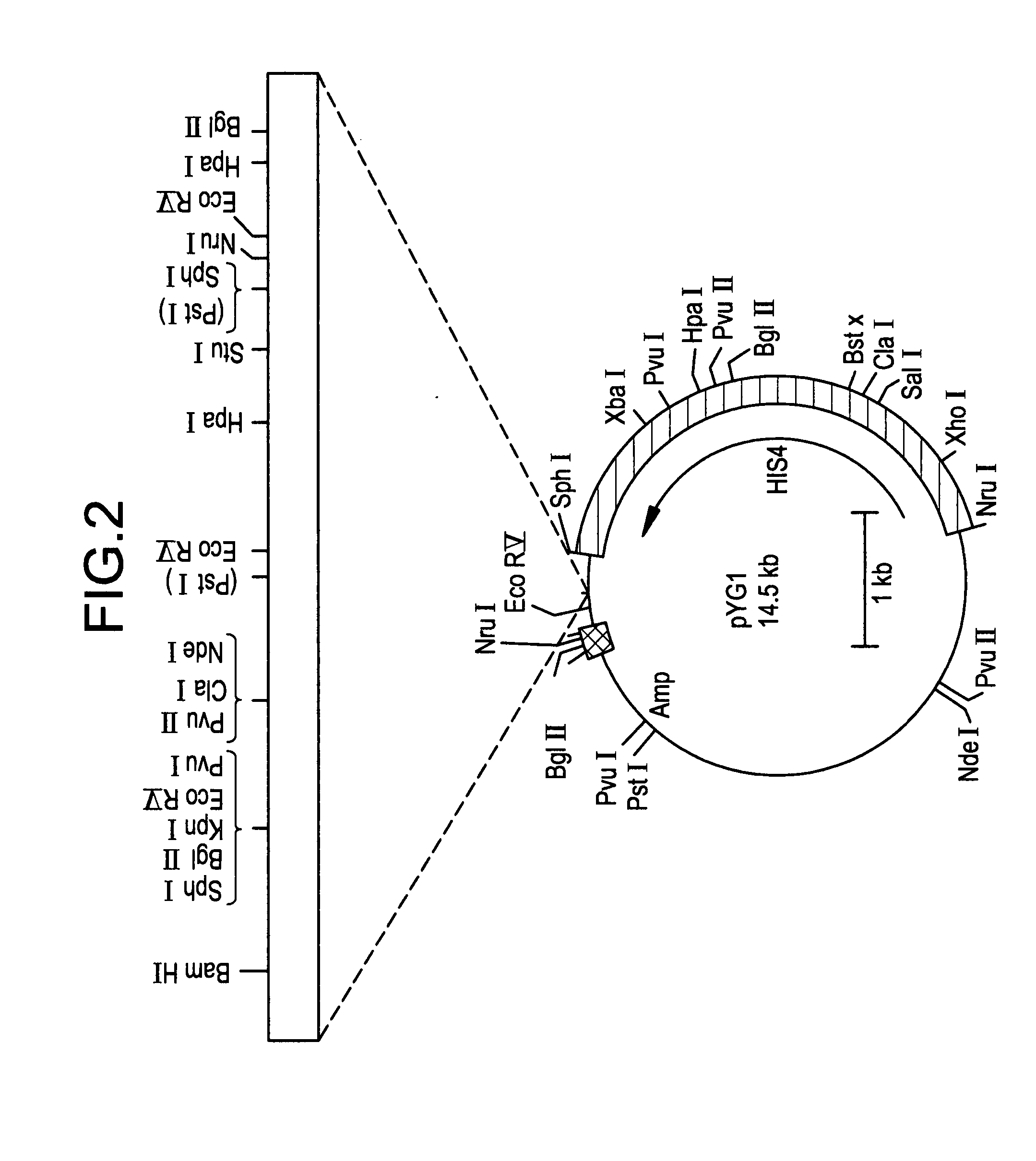
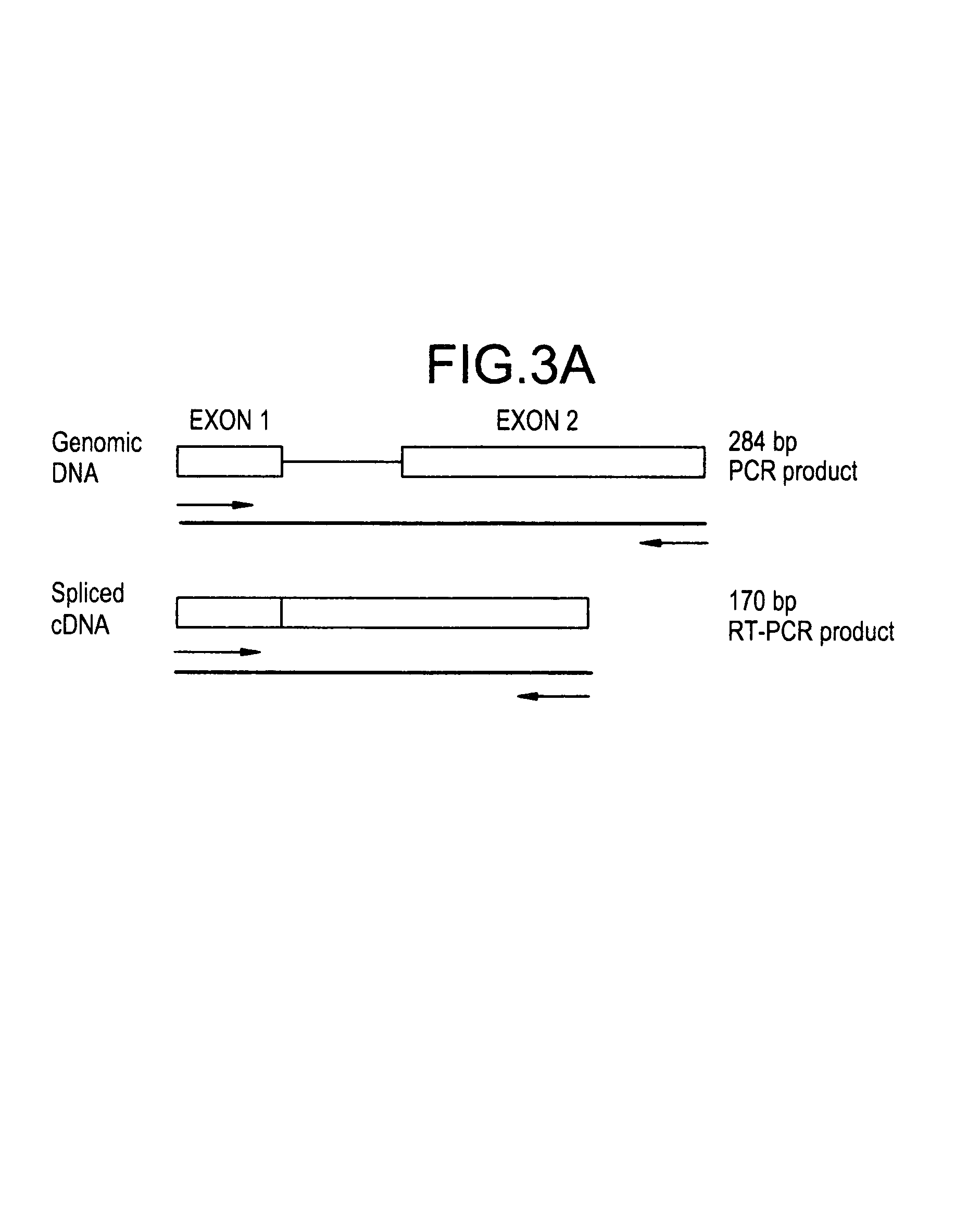
Formaldehyde dehydrogenase genes from methylotrophic yeasts
InactiveUS20070298500A1Microbiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesMethyl groupAmmonium sulfate
Owner:RES CORP TECH INC
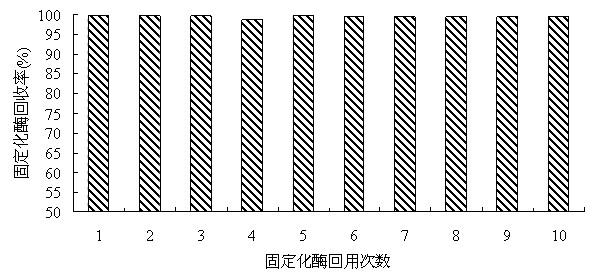
Method for producing L-2-aminobutyric acid by double immobilized multi-enzyme systems
InactiveCN102517351AImprove recycling ratesImprove regeneration efficiencyChemical industryFermentationEnzyme systemOxidative enzyme
The invention discloses a method for producing L-2-aminobutyric acid by double immobilized multi-enzyme systems. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps that 1, threonine dehydrogenase and leucine dehydrogenase are fixed on reversely-dissoluble pH-sensitive polymer carriers so that a co-immobilized multi-enzyme system is obtained; and 2, alcohol oxidase, formaldehyde dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenlyase are fixed on reversely-dissoluble pH-sensitive polymer carriers so that a co-immobilized coenzyme regeneration system is obtained. The method for producing L-2-aminobutyric acid by the double immobilized multi-enzyme systems utilizes dissolution reversibility of co-immobilized enzymes, realizes effective separation of the co-immobilized enzymes and products, improves accessibility between the co-immobilized enzymes and reactants, improves recovery and utilization rates of threonine dehydrogenase, leucine dehydrogenase, alcohol oxidase, formaldehyde dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenlyase, improves coenzyme regeneration efficiency, reduces follow-up separation purification processes, simplifies a process flow and reduces a production cost.
Owner:李鑫
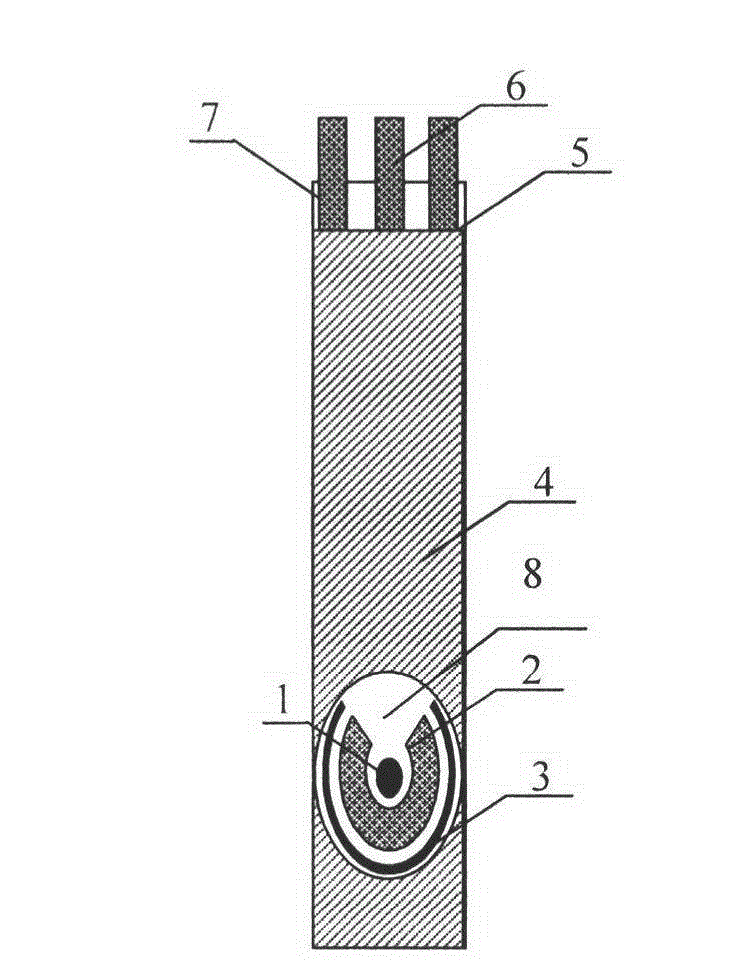
Spittle alcoholicity test strip and production method thereof
InactiveCN102384971AOutstanding FeaturesHighlight significant progressBiological testingAlcohol oxidaseAqueous alcohol
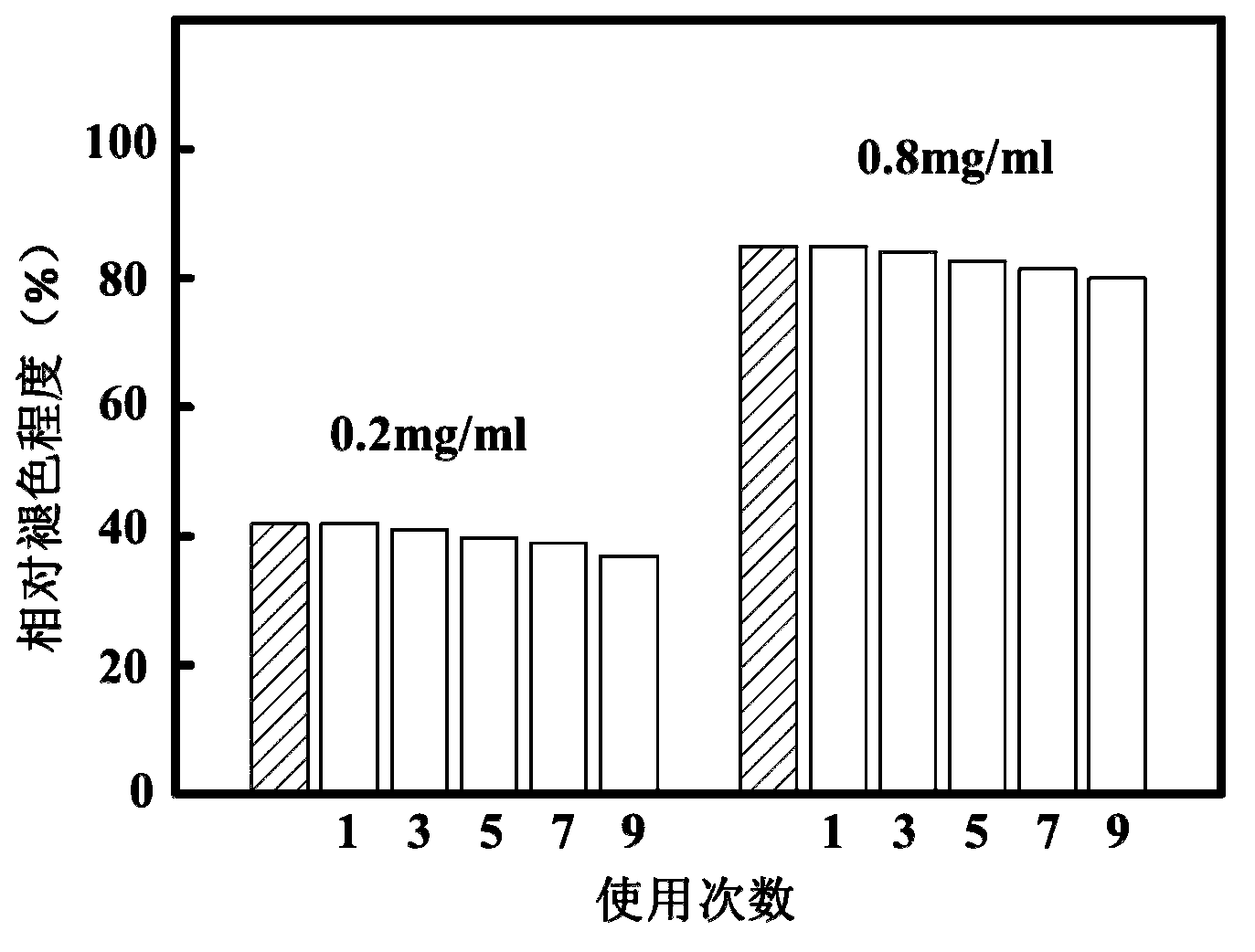
The invention provides a spittle alcoholicity test strip and a production method thereof. The test strip comprises a substrate and a reaction test strip which is adhered to the surface at one side surface of the substrate; and the reaction test strip is dry filter paper which is soaked in a color-developing agent solution and a bi-enzymatic reaction liquid in sequence. The production method comprises the following steps of: soaking the filter paper in the color-developing agent solution and then drying the filter paper by means of being protected from light at a room temperature to obtain developing filter paper; and soaking the developing filter paper into the bi-enzymatic reaction liquid and then drying the developing filter paper by means of being protected from the light at the room temperature to obtain the reaction filter paper. The bi-enzymatic reaction liquid contains alcohol oxidase with the activity unit of 80 U / ml, peroxidase with the activity unit of 80 U / ml, bovine serum albumin which accounts for 1.6% of the total weight of the bi-enzymatic reaction liquid, trehalose which accounts for 1.5% of the total weight of the bi-enzymatic reaction liquid, and the balance of 0.3 M phosphate buffer with the pH value of 7.5. The test strip has the advantages of fastness and accuracy in detection, high sensitivity and good stability. Furthermore, the production method is simple, practical and very reliable.
Owner:郑州炜盛电子科技有限公司
Preparation method of test paper for detecting alcohol content in saliva and test paper prepared thereby
InactiveCN1837821ASignificant advantagesSignificant beneficial effectMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological testingSolid-state chemistryPhosphate
This invention relates to a preparation method of test paper for detecting alcohol content in saliva and test paper prepared thereby. Wherein, using pure cotton pulp filter paper as the bottom carrier of test paper; with solid chemistry technique, adding in turn the tetramethyl benzidine, phosphate buffer, HRP, alcohol oxidase and BSA on the paper, and multiple-step vacuum drying. This invention is safe and reliable for test, can read result directly with color-matching card, and has well repeatability for wide application.
Owner:丁国兴
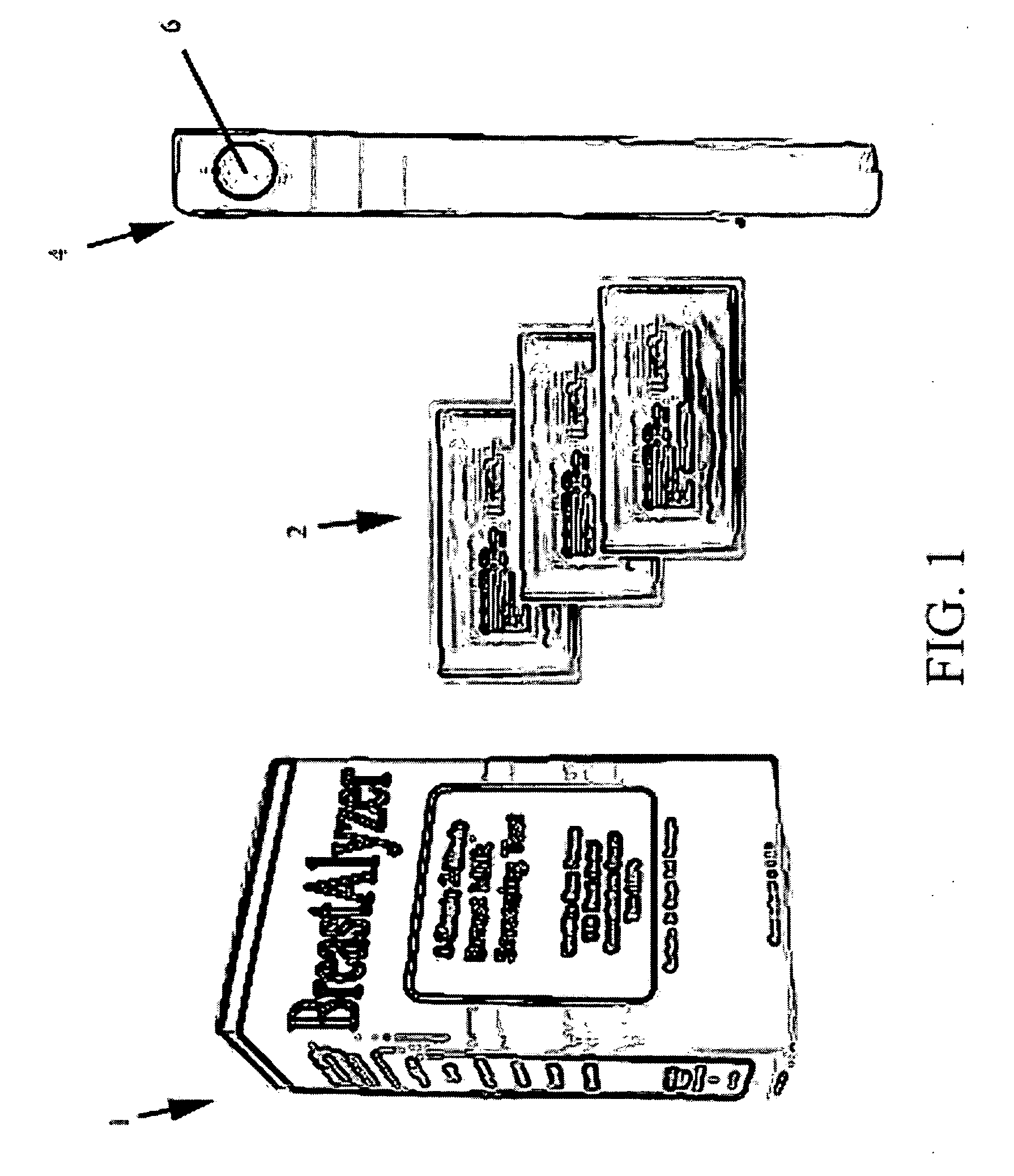
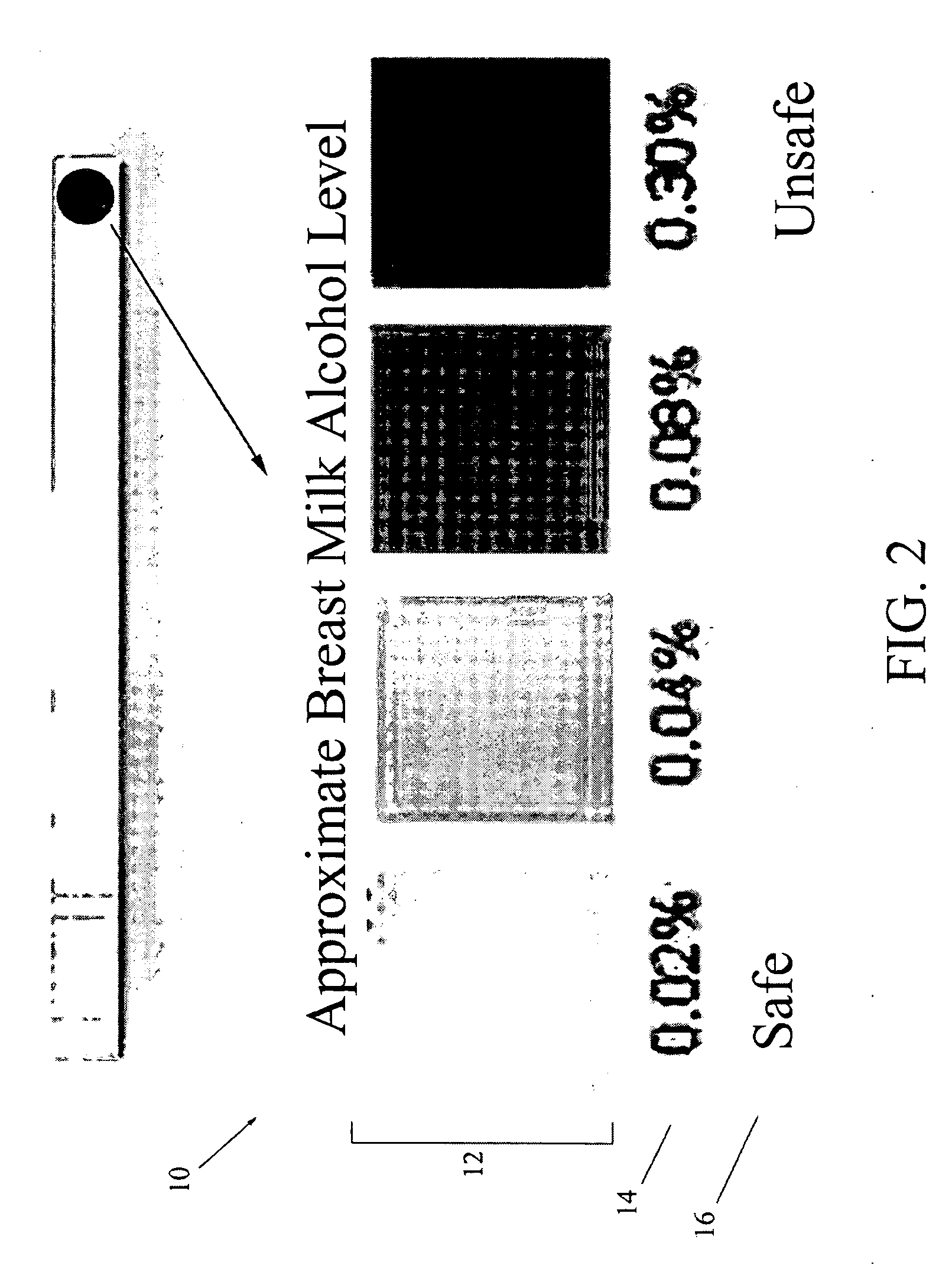
Alcohol-in-breast milk analysis test kit
InactiveUS20070077168A1Easy to useAnalysis using chemical indicatorsAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionBreastfeeding (mother)Color changes
The present invention is a test kit comprising a plurality of individually-sealed test strips, each for detecting the presence and intensity of alcohol in breast milk. Each test strip is formed from a porous (absorbent) carrier matrix, and a color-change reagent resident on the carrier matrix. The color-change reagent comprises an alcohol oxidase enzyme and a hydrogen donor indicator that changes color when oxidized. In addition, a comparative color chart is provided, including a plurality of color swatches, a numerical scale of blood alcohol concentration, and a quantitative safe / not safe warning. The reagent on the test strip indicates the presence of alcohol in breast milk. The test kit includes a number of test strips and a color chart to allow breast feeding mothers to ascertain the concentration of alcohol in their breast milk to ensure that breast milk fed to infants is free of alcohol.
Owner:SZALCZYK BRYARLY A
Engineering strain for biologically producing ferulic acid and establishing method of engineering strain
ActiveCN103820375AAvoid poisoningEffective implementation methodBacteriaFermentationEscherichia coliAlcohol oxidase
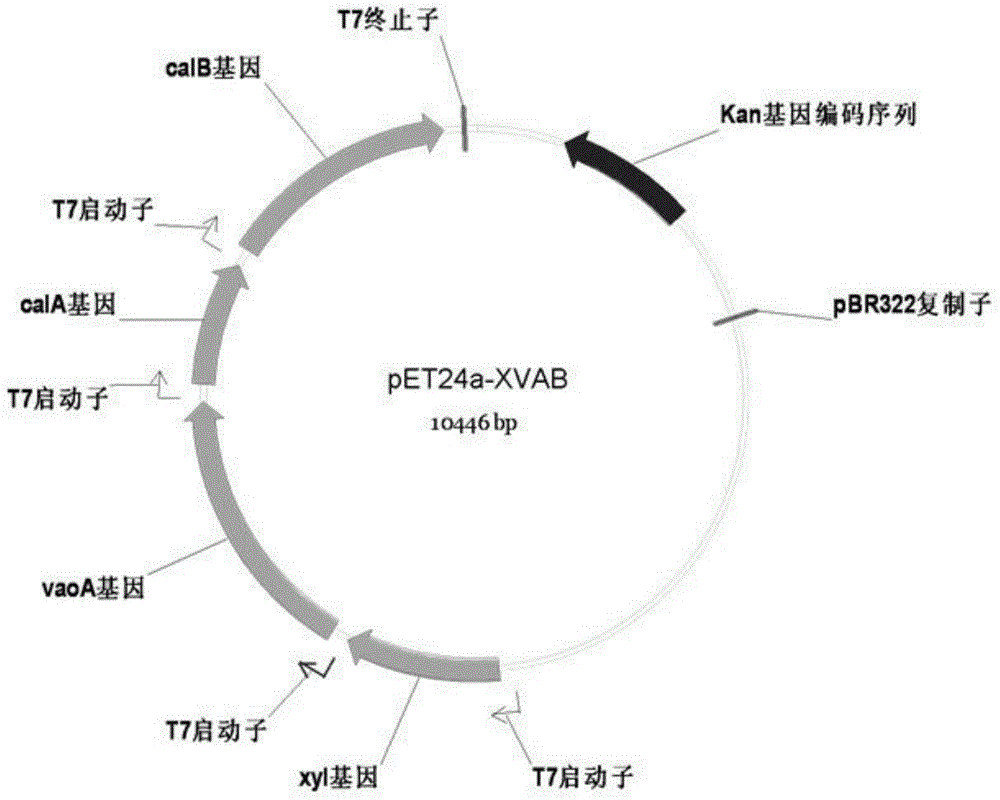
The invention discloses an establishing method of an engineering strain for biologically producing ferulic acid and application of the engineering strain in production of the ferulic acid. The engineering strain enables a vanillyl alcohol alcohol oxidase gene, a coniferyl alcohol dehydrogenase gene and a coniferyl aldehyde dehydrogenase gene to be connected in series and multiply strongly expressed in escherichia coli by using a T7 promoter, and then eugenol is catalyzed to generate the ferulic acid through enzymatic reaction. Through the bioconversion method of the ferulic acid, poisoning of substrate eugenol to a production strain is avoided; the characteristics of simple process and high conversion rate are achieved.
Owner:湖州百肽诺生物科技有限公司
Process for preparing phytase by efficiently fermenting recombinant pichiapastoris
InactiveCN101892206AEfficient fermentation productionImprove fermentation enzyme activityHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPhytase
The invention discloses a process for preparing phytase by efficiently fermenting recombinant pichiapastoris and a special batch fermentation culture medium thereof. The process comprises a thalli growth stage and an exogenous gene induction expression stage and relates to promoters such as an alcohol oxidase promoter, a methanol promoter and the like. The culture medium in a fed-batch fermentation stage adopts a low-salt formula which comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 3 to 6 percent of carbon source, 1.5 to 3 percent of nitrogen source, 0.8 to 1.0 percent of magnesium sulfate, 0.5 to 1.0 percent of potassium sulfate and 0.3 to 0.4 percent of monopotassium phosphate, wherein fermentation temperature is between 27 and 30 DEG C; and fermentation pH is between 4.5 and 5.5. Methanol induction in the exogenous gene induction expression stage is performed in five stages. The preparation process of the invention has the advantages of lower cost and higher phytase fermentation activity.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
Reagent strip for detecting alcohol content in saliva, preparation method of reagent strip and kit
ActiveCN107607730AImprove solubilityAvoid decompositionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological testingReagent stripSolubility
The invention belongs to the technical field of detection of alcohol in saliva and discloses a reagent strip for detecting the alcohol content in saliva, a preparation method of the reagent strip anda kit. The reagent strip contains bovine serum albumin and sodium alginate. The bovine serum albumin has good solubility, can be dissolved into a buffer solution at the normal temperature and can be uniformly mixed with alcohol oxidase and a horse radish peroxidase solution, so that the decomposition and nonspecific adsorption of enzyme are prevented; and sodium alginate has viscidity and can be tightly adsorbed to the surface of the bovine serum albumin after being mixed with the bovine serum albumin. The bovine serum albumin and sodium alginate are commonly used as an additive of alcohol oxidase and horse radish peroxidase, so that the oxygen and moisture in air are effectively isolated, the decomposition and nonspecific adsorption of enzyme are prevented, the false positive phenomenon generated in a detection process of a product is avoided, and the product has excellent stability.
Owner:NANTONG EGENS BIOTECH
Electrochemical ethyl alcohol sensor based on ethyl alcohol oxidase and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN105223253AHigh selectivityHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesLow activityAlcohol
The invention relates to an electrochemical ethyl alcohol sensor based on ethyl alcohol oxidase and a preparing method thereof. The sensor is provided with three electrodes, the working electrode is covered with an ethyl alcohol oxidase film, ethyl alcohol in sample gas is selectively oxidized into acetaldehyde by means of the ethyl alcohol oxidase, and current generated through oxidization of acetaldehyde on the working electrode has a linear relation with the concentration of ethyl alcohol. An enzyme catalyst layer of the ethyl alcohol oxidase film is not conductive and is an electrochemical inactive layer, and all reactions relevant to enzyme have no direct relation with the current of the working electrode of the electrochemical sensor. Catalytic reaction products of enzyme are diffused into the working electrode for further reaction, and then electrochemical current is generated and has a linear relation with the concentration of ethyl alcohol. The working electrode of the sensor is a low-activity material. The response time of the ethyl alcohol sensor is short, test results are accurate, the ethyl alcohol sensor makes no obvious response to other organic gas but has extremely high selectivity and sensitivity to ethyl alcohol, and the ethyl alcohol sensor can better meet the requirement for ethyl alcohol detection in complicated environments.
Owner:SHENZHEN METERAGE SCI & TECH DEV CO LTD
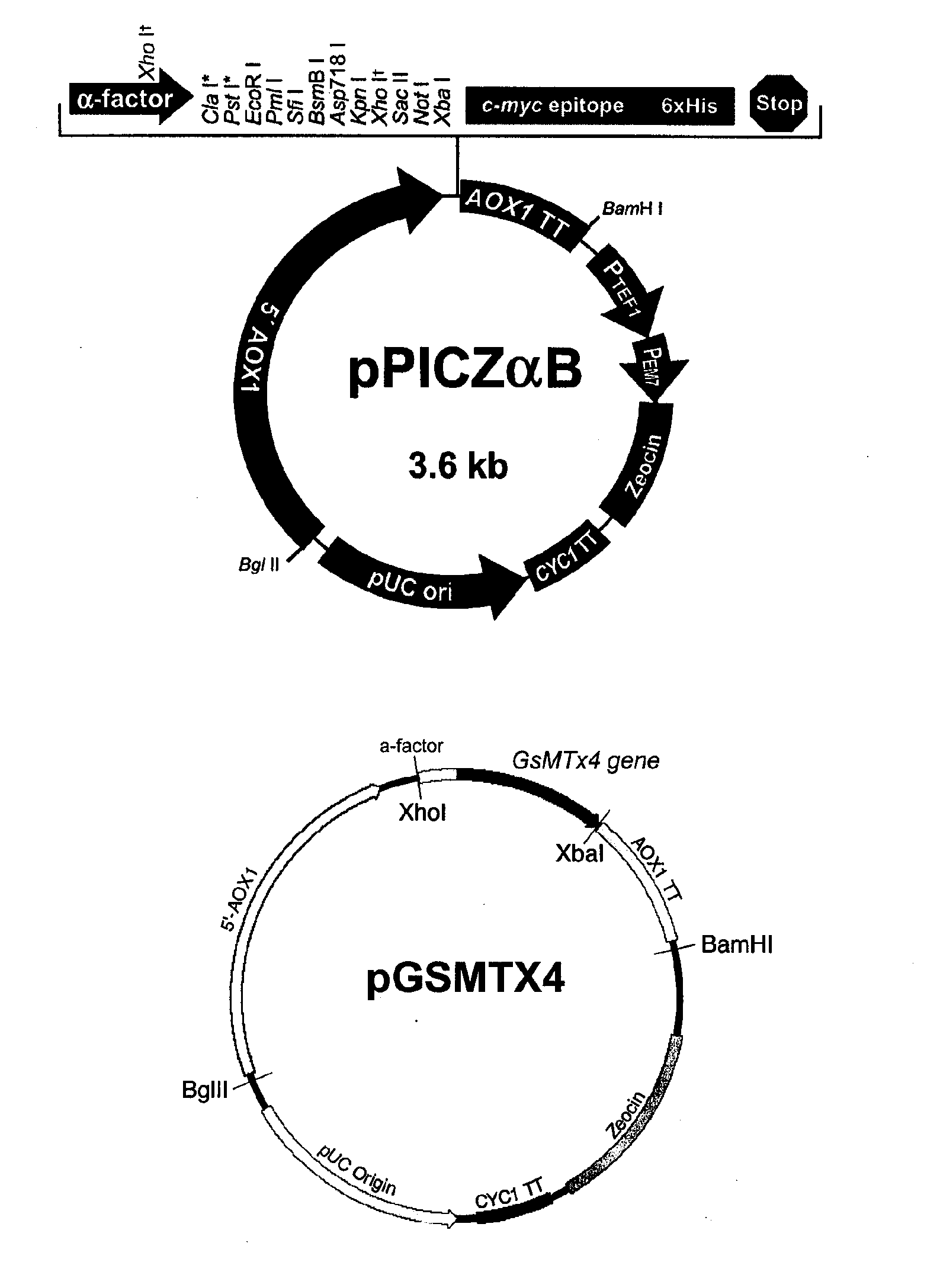
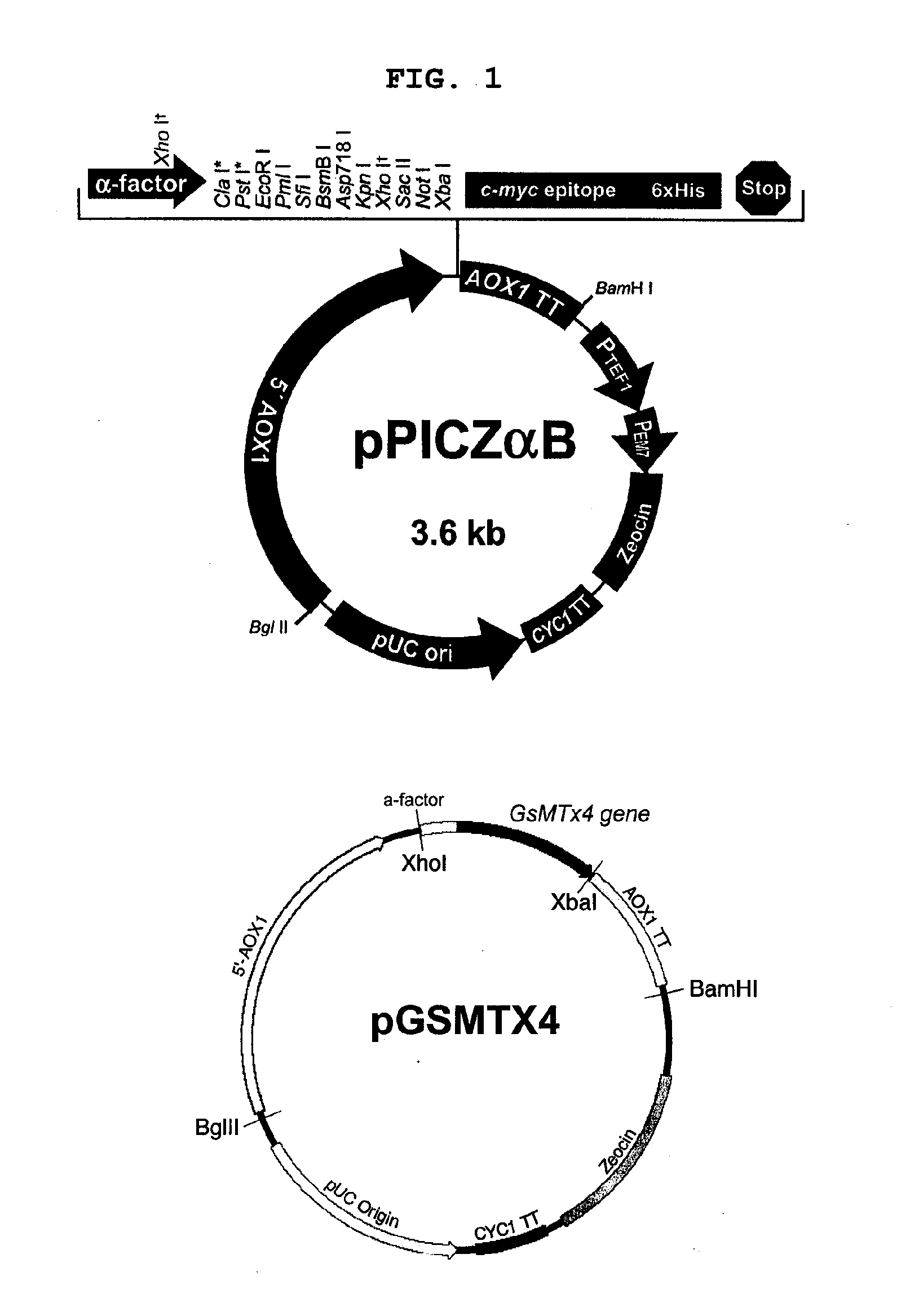
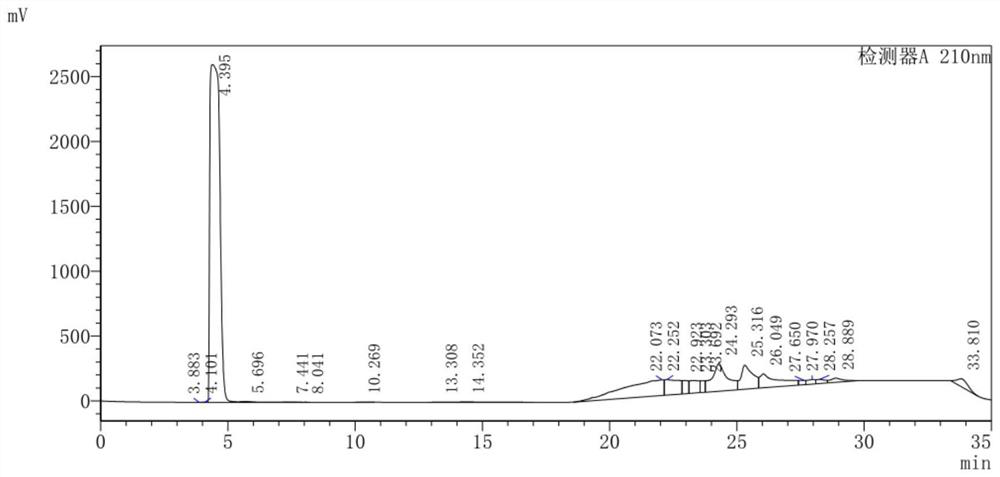
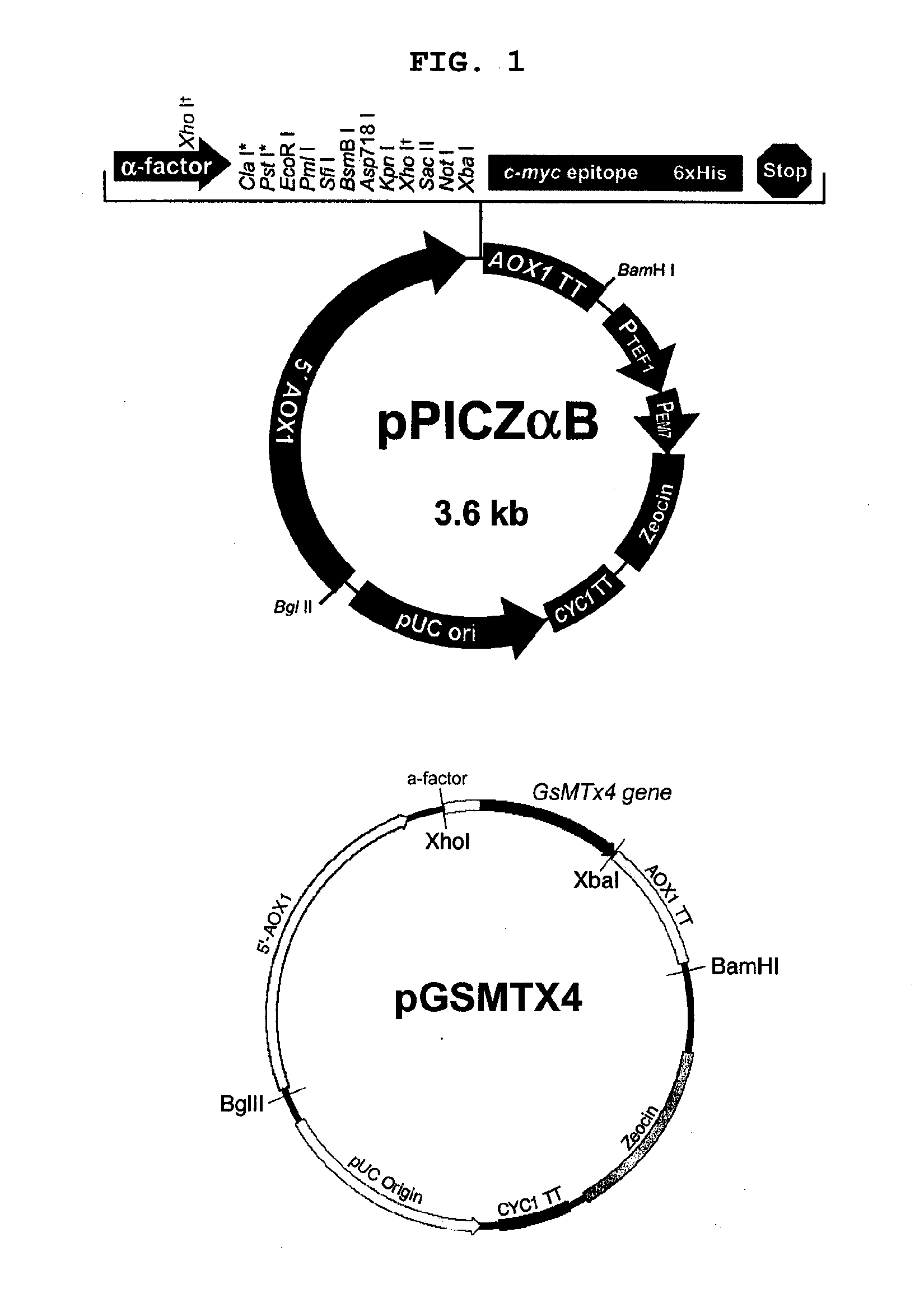
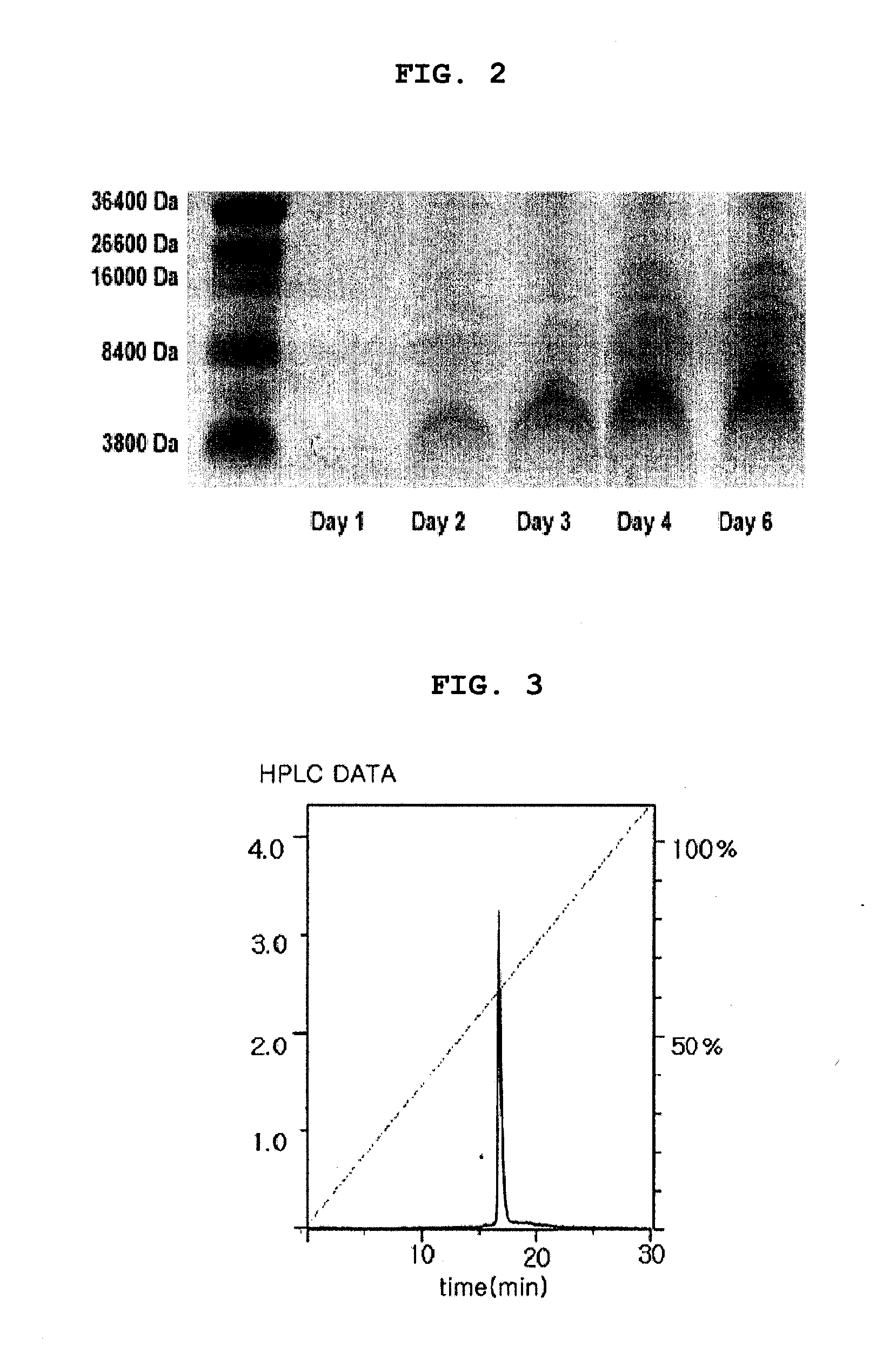
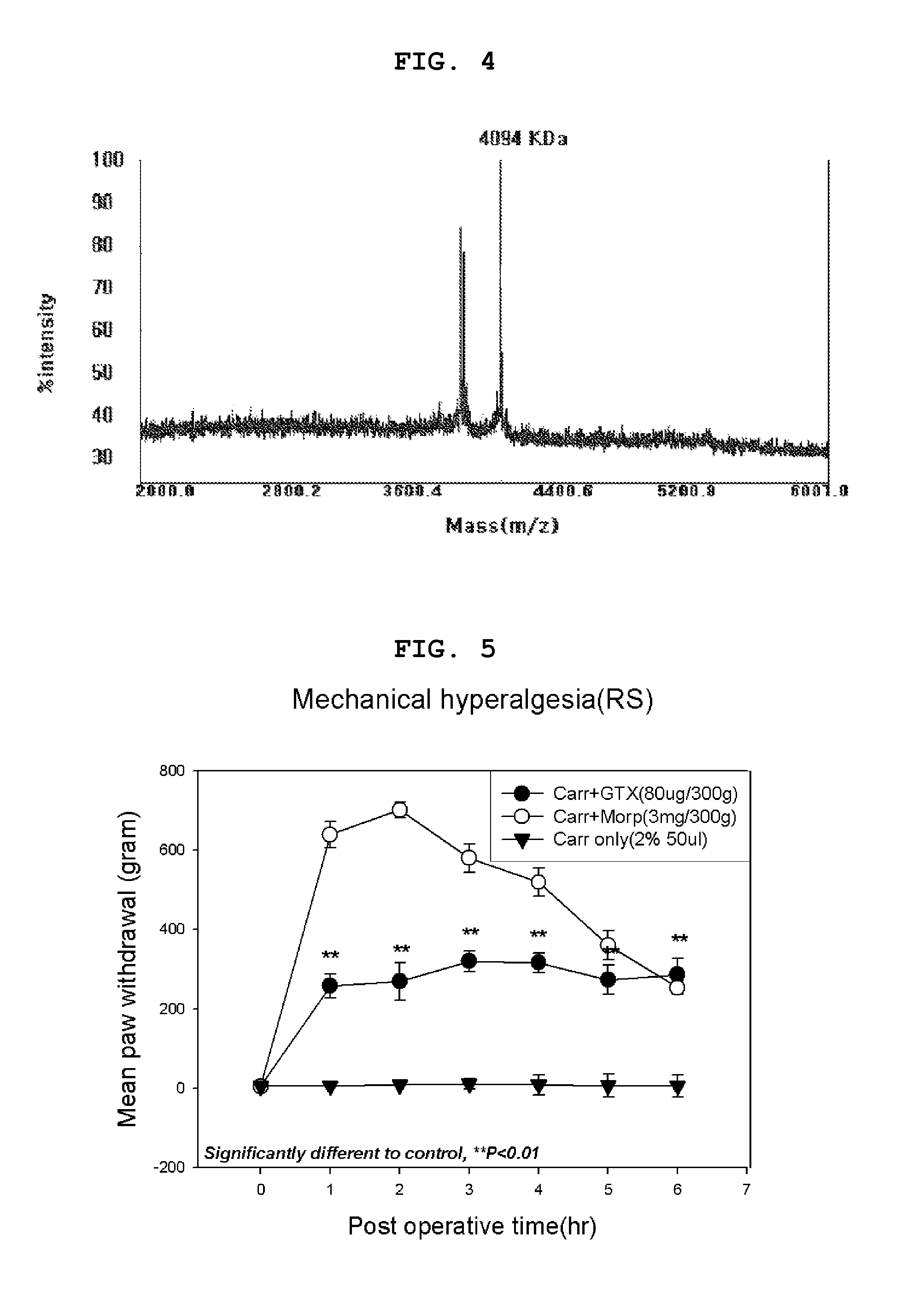
Method For Preparing Recombinant Peptide From Spider Venom and Analgesic Composition Containing The Peptide
InactiveUS20090023183A1Effective activityEffective functionSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseMechanosensitive ion channel
The present invention relates to a method for producing a recombinant, spider toxin peptide and analgesic compositions containing said peptide. More specifically, the present invention relates to a method in which the gene for GsMTx4 is subcloned into a vector, so that it is linked to a secretion signal sequence of the alpha factor and under the control of methanol-inducible alcohol oxidase (AOX) promoter to construct a recombinant yeast expression plasmid. Yeast cells are transformed with this plasmid to produce the GsMTx4 peptide and analgesic compositions containing said peptide. The recombinant yeast expression system of the present invention affords a more stable method for producing GsMTx4 than its natural route. Thus the GsMTx4 peptide and its derivatives produced by the method of this invention can be used in the cure of related diseases such as heart failure as the peptide specifically inhibits mechanosensitive ion channels.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Oral delivery of enzymes by nanocapsules for targeted metabolism of alcohol or toxic metabolites
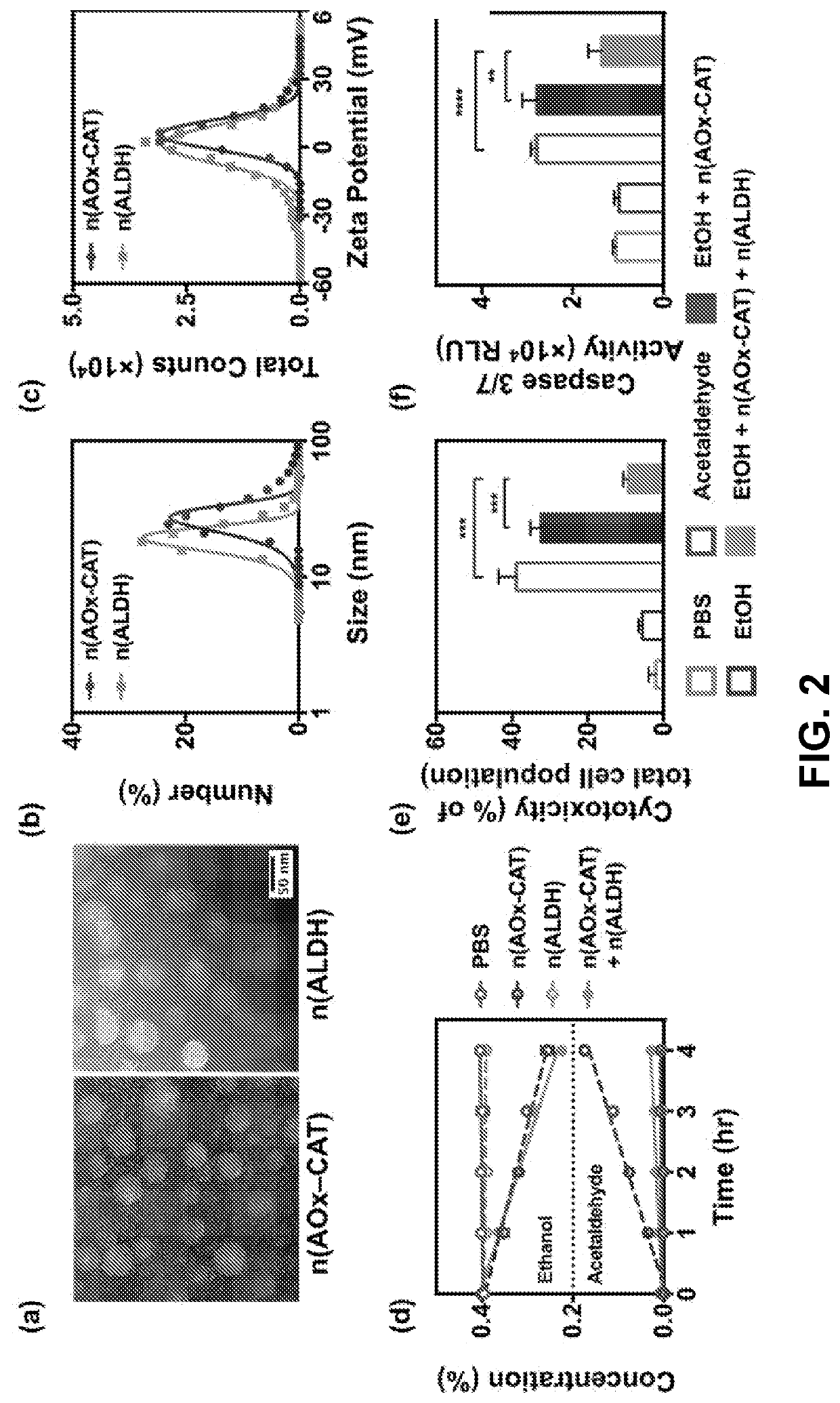
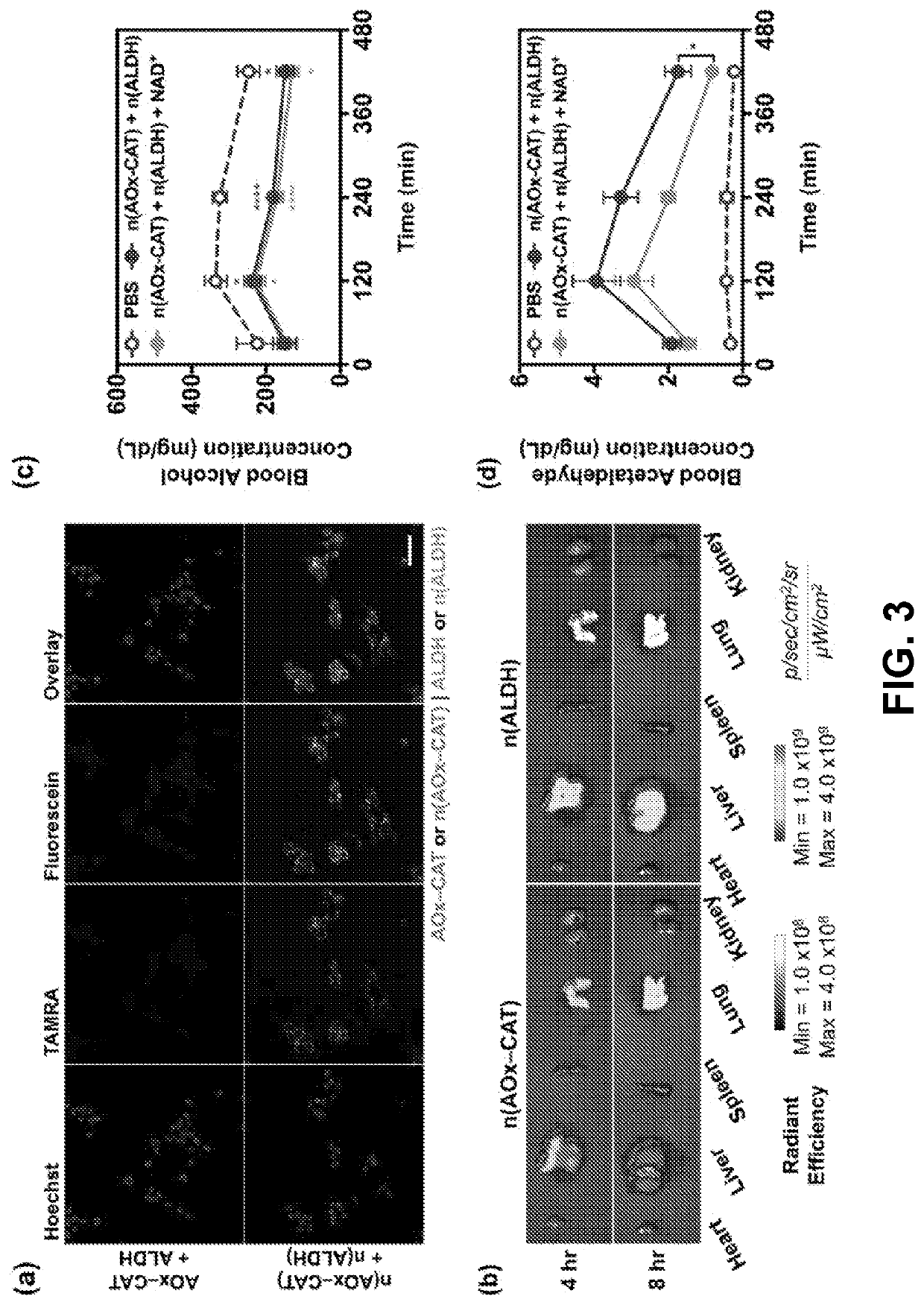
InactiveCN103781475APeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsMetaboliteAlcohol oxidase
The invention disclosed herein includes nanocomplexes that are designed include enzymes that have complementary functional attributes and methods for using these nanocomplexes. Illustrative examples include nanocomplexes that comprise both an alcohol oxidase enzyme as well as a catalase enzyme. These nanocomplexes can be used in methods designed to lower blood alcohol levels in vivo, and / or to break down the toxic byproducts of alcohol metabolism. Consequently these nanocomplexes can be used to treat a variety of conditions resulting from the consumption of alcohol, including for example, acute alcohol intoxication.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Preparation method of immobilized enzyme nanofiber membrane for detecting alcohol content in spit
InactiveCN103232987AEffectively fixedFixed a lotImmobilised enzymesMicrobiological testing/measurementMulti sitePolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a preparation method of an immobilized enzyme nanofiber membrane for detecting the alcohol content in spit. The preparation method comprises the steps of: covalently binding alcohol oxidase through a polymer such as polyethylene glycol or polyethyleneimine as an arm molecular multi-site; further fixing a plurality of subunits of the alcohol oxidase by the polyethyleneimine, polylysine, poly-histidine or chitosan and the like through physical action among charges; then absorbing indigo blue as a chromogenic substrate; generating hydrogen peroxide after ethanol in a sample is oxidized by the alcohol oxidase in detection; leading the indigo blue to fade by the hydrogen peroxide, and conveniently calculating the ethanol concentration in the sample by comparing the fading degree of the indigo blue with a standard color atla. The preparation method is high in sensitivity, simple and convenient to operate, and low in price, can be repeatedly used for a plurality of times, and can be conveniently used for investigating and treating drunk driving by a law-enforcing department; and the reliable evidence is provided for the law enforcement process.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Deliquescent-polyelectrolyte-based full-solid-state ethanol gas sensor enzyme electrode and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102944597AMiniaturizationImprove intelligenceMaterial electrochemical variablesReaction layerPolycarbonate
The invention relates to a deliquescent-polyelectrolyte-based full-solid-state ethanol gas sensor enzyme electrode and a manufacturing method thereof. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: on a matrix made of an insulating material, preparing a printed electrode composed of a working electrode, a reference electrode and a counter electrode by screen printing technology; coating a polycarbonate insulator on the surfaces in the middle; coating a reaction layer composed of graphene, deliquescent polyelectrolyte and alcohol oxidase on the working electrode; and coating a deliquescent solid polymer film among the working electrode, counter electrode and reference electrode to obtain the biological enzyme electrode. The invention provides an enzyme electrode for gas-state ethanol detection; and the enzyme electrode can implement high-selectivity detection of ethanol gas without using any liquid electrolyte in the use process, thereby integrally enhancing the properties and practicality of the ethanol gas biosensor.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Ferulic acid producing engineering strain, construction method and biotransformation method
ActiveCN104928224AEffective implementation methodThe implementation method is simpleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEugenol
The invention discloses a ferulic acid producing engineering strain, a construction method and a biotransformation method. The provided engineering strain integrates a novel enzyme coupling system, a strong promoter is used to co-express a pandan alcohol oxidase gene, a coniferyl alcohol dehydrogenase gene and a coniferyl aldehyde dehydrogenase gene in escherichia coli, and eugenol is catalyzed through enzymatic reaction to generate ferulic acid. In the system, a xylose reductase is simultaneously coupled, xylose is reduced in a production process, meanwhile, oxidation type coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate are regenerated, and coenzyme balance of a ferulic acid biotransformation system is kept, so that the transformation rate and the yield of the product, i.e. the ferulic acid are improved. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that an effective and simple implementation method for safe biotransformation of a medical intermediate product, i.e. the ferulic acid is provided, the transformation rate is up to over 95 percent, the concentration of the ferulic acid (end-product) is 11g / L, and the method has a relatively high industrialization value.
Owner:湖州百肽诺生物科技有限公司
Alcohol quantitative analysis method based on double-enzyme-inorganic nanoflower composite material
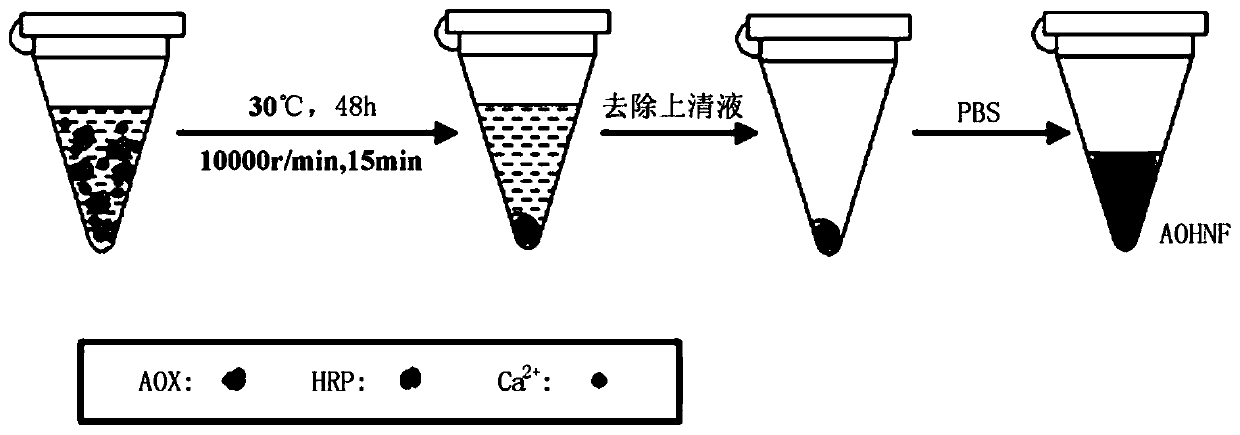
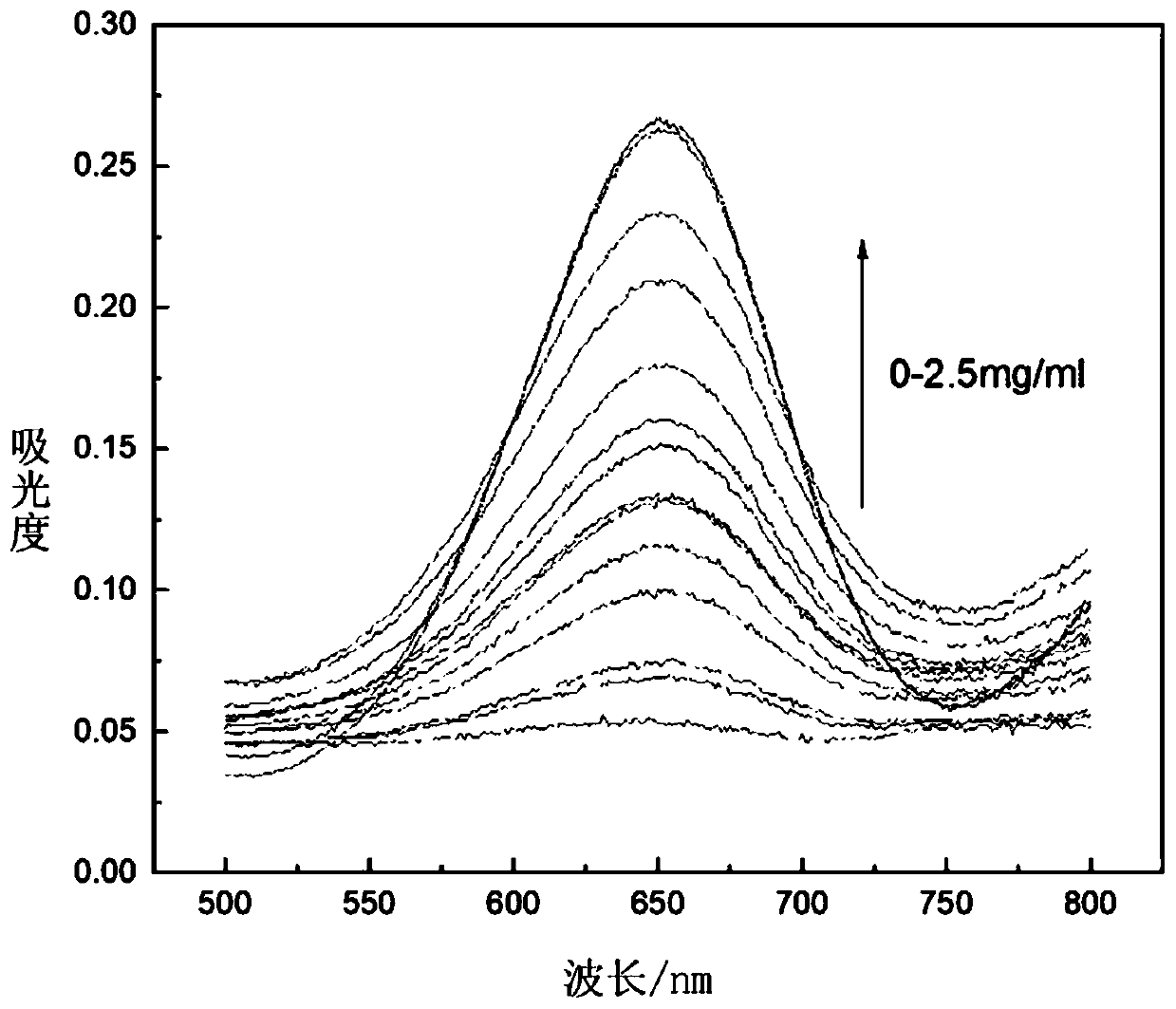
ActiveCN110006885AHigh activityImprove stabilityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsAlcoholPhosphate
The invention discloses an alcohol quantitative analysis method based on a double-enzyme-inorganic nanoflower composite material. The method comprises the following steps: adding alcohol oxidase (AOX), horse radish peroxidase (HRP) and CaCl2 solution into a phosphate buffer solution, standing and reacting at room temperature to obtain the double-enzyme-inorganic nanoflower composite material (AOHNF). The reaction conditions are simple, and the enzyme activity and stability of the obtained material are remarkably enhanced. Alcohol in the solution is catalyzed and oxidized by using AOX to generate H2O2, TMB is catalyzed by using HRP to react with H2O2 to enable the solution to be blue, and the absorbance of the absorption wavelength at 650 nm is measured, so that the alcohol concentration inthe solution is obtained. The analysis method is simple to operate and high in detection result sensitivity. Double enzyme-based method disclosed by the invention The alcohol quantitative analysis method based on the double-enzyme-inorganic nanoflower composite material has the characteristics of simplicity in operation, high sensitivity, good stability and the like, and has a good development prospect.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Diesel oil improver component containing biological enzyme and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103421552AImprove catalytic performanceHigh-speed catalytic performanceLiquid carbonaceous fuelsFuel additivesAldehyde oxidasePeroxidase
The invention provides a diesel oil improver component containing biological enzyme, which comprises cetane number improver and biological enzyme, wherein the weight part ratio of the cetane number improver to the biological enzyme is 1:(0.01-1); the biological enzyme is the mixture of sulpho enzyme, alcohol oxidase, aldehyde oxidase, amine oxidase, sulfhydryl oxidase, methyl mercaptan oxidase, methyl naphthoquinone oxidase, peroxidase, ferrochelatase, decarboxylase, aldolase, oxyacid lyase, demethylase, alcohol dehydratase, acid dehydratase, esters dehydratase, desulfhydrase, desulfurization methyl enzyme, cobalt chelating enzyme and magnesium chelating enzyme. According to the diesel oil improver component containing the biological enzyme, provided by the invention, the high speed catalytic performance can be realized under the temperate environment through utilizing properties of the biological enzyme, and the component is combined with the conventional cetane number improver for use, the catalytic combustion efficiency of the cetane number improver in diesel oil is greatly improved, and the combustion performance of the diesel oil is further improved.
Owner:英杰惠能(北京)能源新技术有限公司
Breast milk ethanol screening system and method
A test kit detects presence of ethanol alcohol in human breast milk. The test kit includes an alcohol oxidase reactive in the presence of ethanol alcohol in breast milk and oxygen, an indicator having a visible color when not subjected to oxidizing agent, in sufficient amount for visible observance, and a peroxidase reactive in the presence of acetaldehyde and peroxide, to yield oxidizing agent, in sufficient amount to induce change to the visible color of the hydrogen donor indicator. The test kit is a sealed pack containing a test strip. The test strip is for one-time use, and disposable after testing. The test strip is handled by a tester, typically a breast-feeding mother. The mother contacts her breast milk lactate with testing portion of the test strip. The testing portion selectively reacts to alcohol, and not other components of breast milk. A reactive agent of the testing portion of the test strip changes color in the presence of alcohol. The mother observes the result to determine if there is presence of alcohol in the breast milk.
Owner:UPSPRING
Method for synthesizing fludarabine phosphate through biological catalysis
PendingCN113584104AImprove conversion rateHigh yieldTransferasesOxidoreductasesReaction temperaturePhosphoric acid
The invention relates to a method for preparing fludarabine phosphate by an enzyme method. Fludarabine phosphate is prepared by taking fludarabine as a raw material through an enzyme catalytic reaction in the presence of inorganic salt and coenzyme; an enzyme used in the enzyme catalysis reaction is selected from at least one of phosphotransferase, aldoketoreductase, alcohol oxidase or alcohol dehydrogenase; the pH value of the enzyme catalytic reaction is 7.3-7.6, the reaction temperature is 37 DEG C, and the reaction time is 1-4 hours; the coenzyme is ATP. According to the invention, fludarabine phosphate is prepared by adopting a novel enzymatic process, so that the technical problems existing in some existing chemical processes are solved, and the process is improved compared with the existing enzymatic preparation process; the production cost is reduced; the process is environment-friendly and reaction conditions are mild.
Owner:JIANGSU OCEAN UNIV +1
Ethanol concentration detection kit by using circulatory enzyme method and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102901727AQuick responseHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorReagent stripEthanol dehydrogenase
The invention provides an ethanol concentration detection kit by using a circulatory enzyme method and a preparation method thereof. The kit comprises a reagent strip and a standard comparison card, wherein the reagent strip is of a filter paper strip with the width of 0.5-1cm, the filter paper strip contains immobilized alcohol oxidase, alcohol dehydrogenase, reduction type coenzyme I, horseradish peroxidase, 4-acetoxyazetidinone, an aniline analog and a coloring stabilizer, and the standard comparison card comprises coloring comparison area with different ethanol concentrations. When the kit is used for detecting the ethanol concentration, the operation is simple and sanitary, the speed is fast, the sensitivity is high and the stability is high; and the kit is easy to carry and particularly suitable for field detection.
Owner:CHINA MARITIME POLICE ACADEMY
Method for preparing recombinant peptide from spider venom and method for relieving pain
InactiveUS20120015886A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticMechanosensitive ion channelRecombinant peptide
The present invention relates to a method for producing a recombinant, spider toxin peptide and analgesic compositions containing said peptide. More specifically, the present invention relates to a method in which the gene for GsMTx4 is subcloned into a vector, so that it is linked to a secretion signal sequence of the alpha factor and under the control of methanol-inducible alcohol oxidase (AOX) promoter to construct a recombinant yeast expression plasmid. Yeast cells are transformed with this plasmid to produce the GsMTx4 peptide and analgesic compositions containing said peptide. The recombinant yeast expression system of the present invention affords a more stable method for producing GsMTx4 than its natural route. Thus the GsMTx4 peptide and its derivatives produced by the method of this invention can be used in the cure of related diseases such as heart failure as the peptide specifically inhibits mechanosensitive ion channels.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Inositol oxidase mutant, as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN108018265AHigh catalytic activityIncrease productionFungiBacteriaHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsWild type
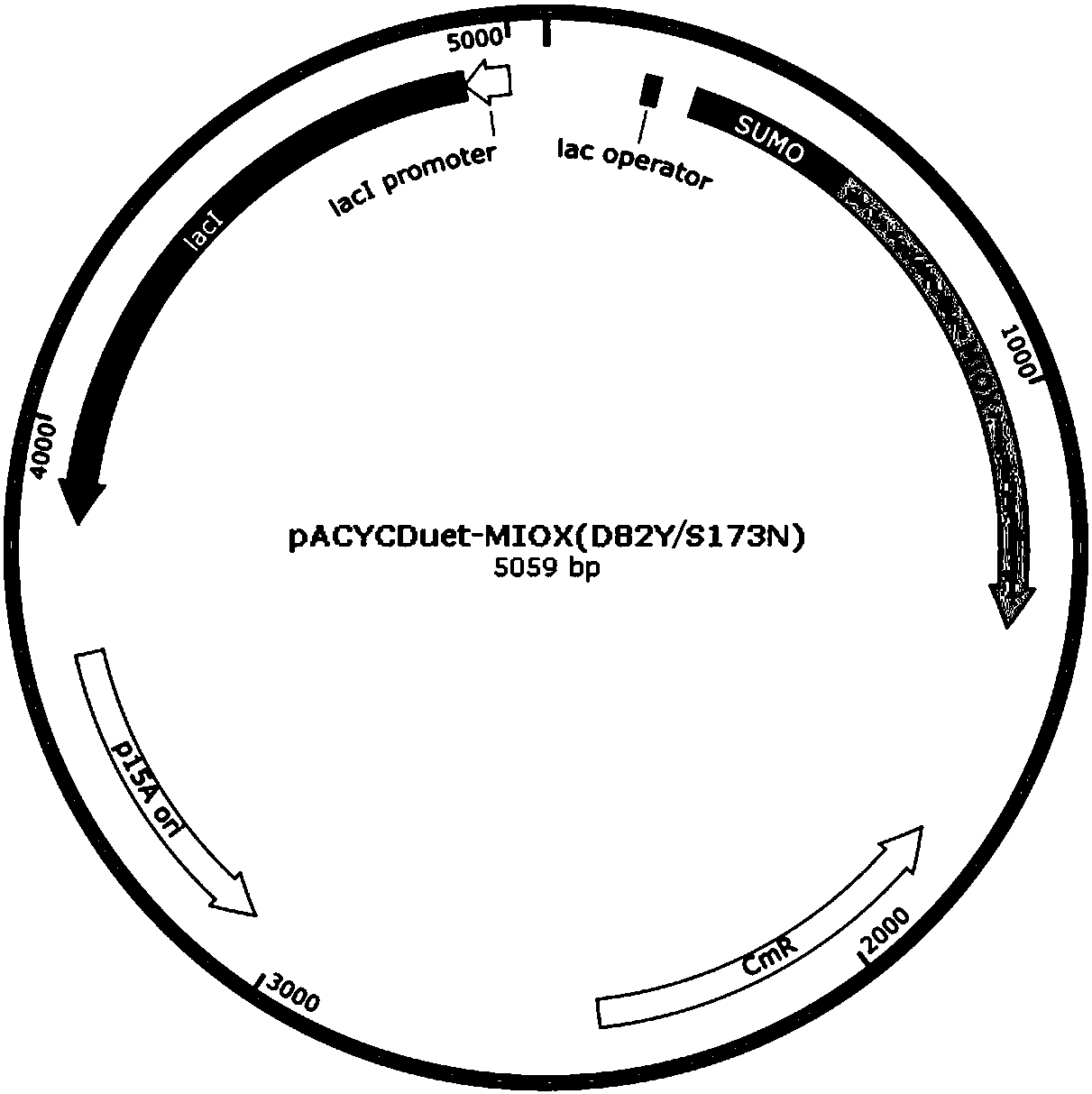
The invention relates to an inositol oxidase mutant, as well as a coding gene and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of gene engineering. According to the inositol oxidase mutant, plasmids pACYCDuet-MIOX-Udh containing wild inositol oxidase coding genes are adopted as a template, an error PCR technology is used to obtain an inositol oxidase MIOX random mutation library; a high GA yield inositol oxidase mutant can be obtained by high throughput screening of biosensor, and the inositol oxidase mutant has relatively high catalytic activity and can be applied to the fields of enzyme engineering, gene engineering, metabolic engineering and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
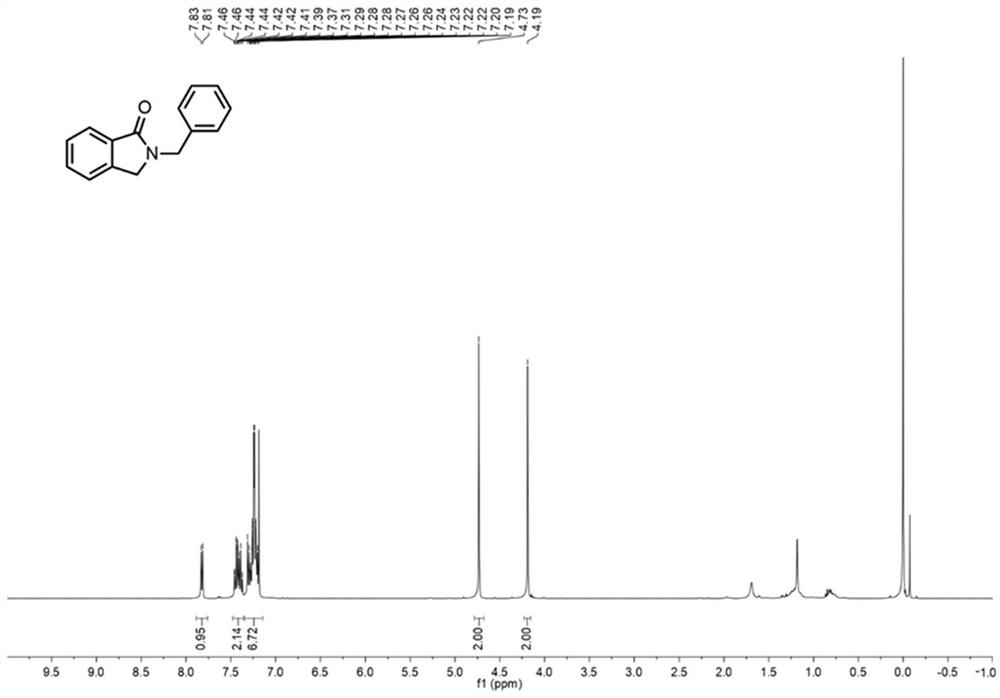
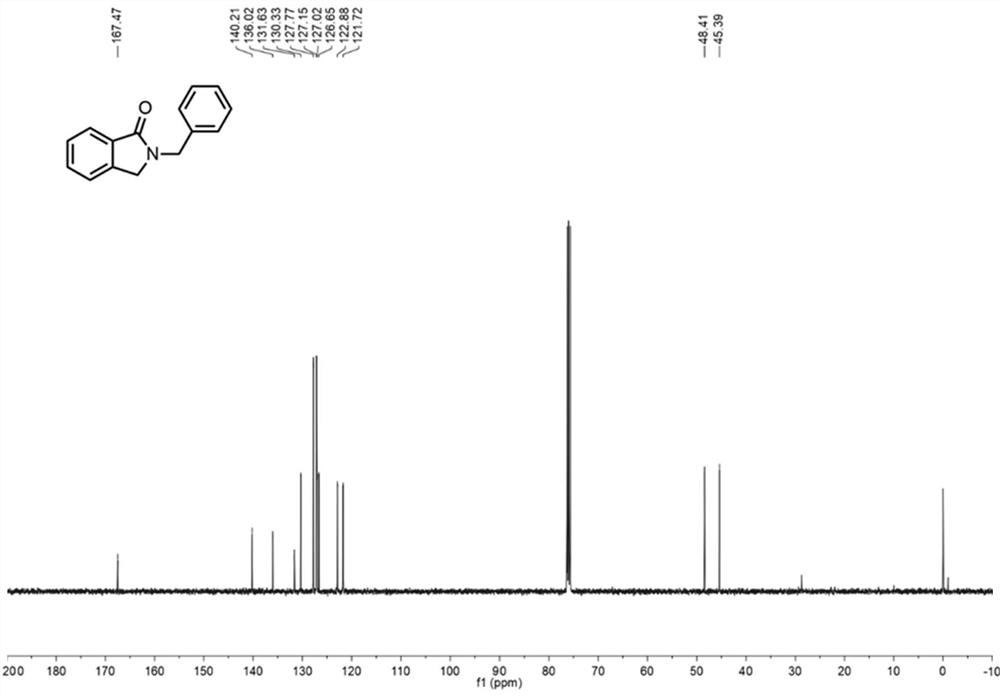
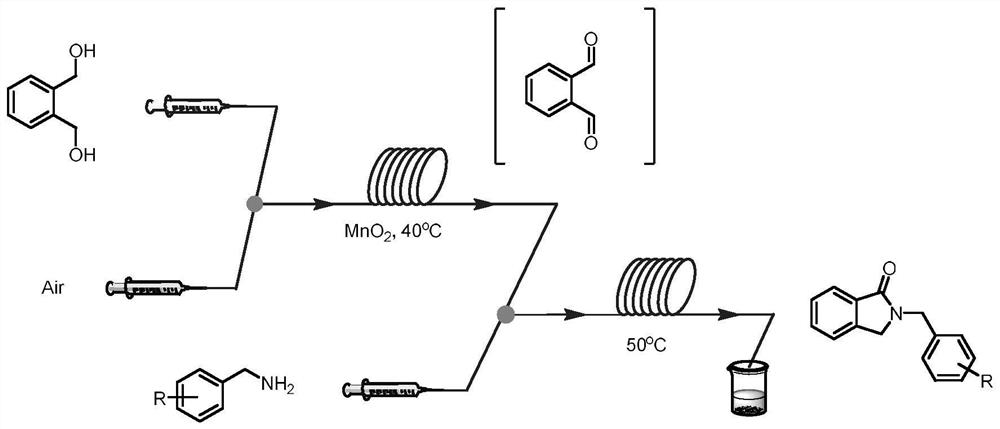
Method for continuously preparing 2-benzyl isoindolinone compound by adopting microchannel reactor
PendingCN113444752AShort reaction timeHigh reaction conversion rateOrganic chemistryFermentationFlavin adenine dinucleotidePtru catalyst
The invention discloses a method for continuously preparing a 2-benzyl isoindolinone compound by adopting a microchannel reactor, which comprises the following steps: (1) respectively and simultaneously pumping a mixed solution containing 1,2-Benzenedimethanol, alcohol oxidase, flavin adenine dinucleotide and hydrogen peroxide reductase and air into a microchannel reaction device; carrying out a first reaction in a first microreactor containing nano MnO2; and (2) respectively and simultaneously pumping the first reaction effluent and a benzylamine compound solution into a second microreactor, and carrying out a second reaction to obtain the 2-benzyl isoindolinone compound as shown in a formula IV. The method has the advantages of short reaction time, high reaction conversion rate, few side reactions, small toxicity and pollution, low production cost, good product quality and the like, does not use noble metal catalysis in the reaction process, is green, environment-friendly, energy-saving and efficient, is suitable for popularization and application, and solves the problems of long reaction time, harsh reaction conditions and need of noble metal catalytic catalyst in the prior art.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Formaldehyde dehydrogenase genes from methylotrophic yeasts
The present invention provides formaldehyde dehydrogenase genes (FLD) from methylotrophic yeasts. The FLD structural genes confer resistance to formaldehyde and are therefore useful as a selectable marker in methylotrophic yeasts. The FLD promoter sequences are strongly and independently induced by either methanol as sole carbon source (with ammonium sulfate as nitrogen source) or methylamine as sole nitrogen source (with glucose as carbon source). Induction under either methanol, methylamine or both provides levels of heterologous gene expression comparable to those obtained with the commonly used alcohol oxidase I gene promoter (PAOX1). The FLD promoter of Pichia pastoris (PFLD1) is an attractive alternative to PAOX1 for expression of foreign genes in P. pastoris, allowing regulation by carbon (methanol) or nitrogen (methylamine) source within the same expression strain. Yeast strains, expression cassettes, expression vectors, and host cells comprising an FLD gene promoter and 3′ termination sequence are also provided.
Owner:RES CORP TECH INC
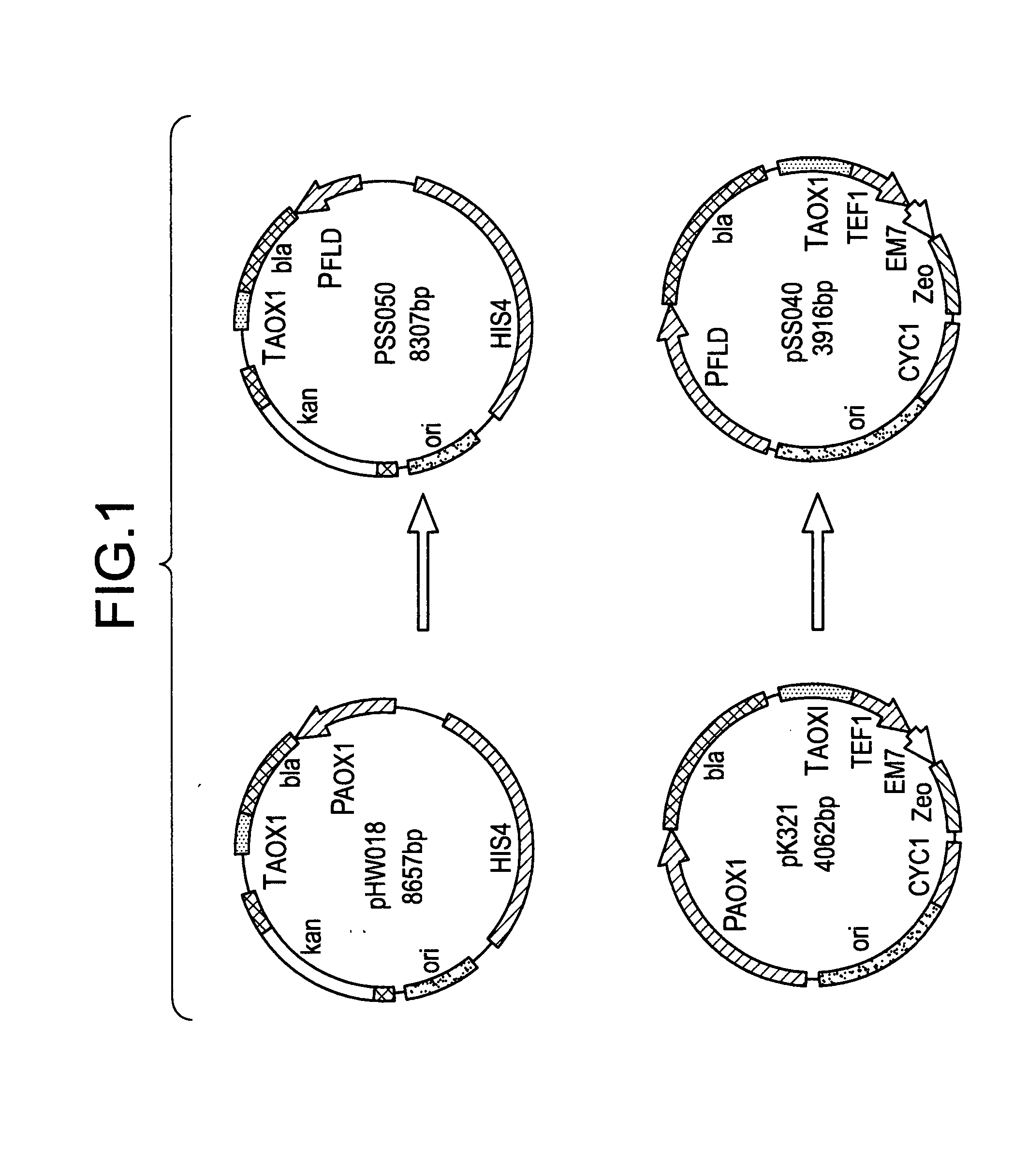
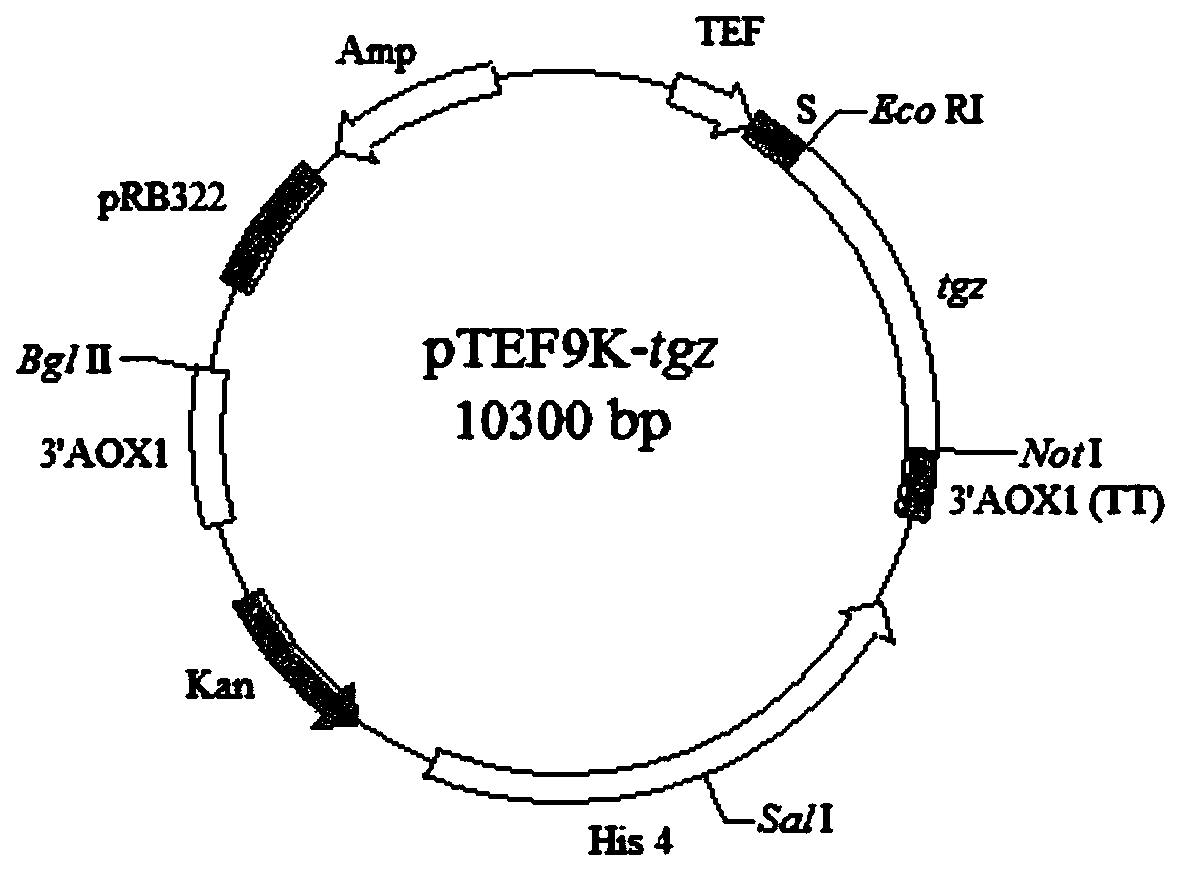
Recombinant pichia pastoris strain for regulating and controlling transglutaminase expression of zea mays through TEF1 promoter and construction method
InactiveCN109749948AEasy to trainStrong secretory abilityFungiTransferasesPichia pastorisBiotechnology
The invention relates to a recombinant pichia pastoris strain for regulating and controlling transglutaminase expression of zea mays through a TEF1 promoter. The recombinant pichia pastoris strain isa genetically engineered strain obtained in the mode that transglutaminase from the zea mays is transferred to pichia pastoris. According to the recombinant pichia pastoris strain, an alcohol oxidasepromoter PAOX1 in a pPIC9K plasmid is replaced by a promoter PTEF1 of a translation extension factor 1-alpha, the promoter PTEF1 is connected with a transglutaminase gene to form a loop, and a recombinant expression vector is constructed. The recombinant strain is easy to culture, high in secretion capacity and beneficial for mass transglutaminase expression, the enzyme activity can reach 479 mU / mL, and the recombinant pichia pastoris strain has the advantages of being safe and reliable and has important application prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) diagnosis/determination kit and method for determining inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) concentration
InactiveCN101620138AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsPhosphateEnzymatic Colorimetry
The invention relates to an inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) diagnosis / determination kit using the technology of an enzyme colorimetric method and an ELISA method, a method for determining inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) concentration and composition and components of a reagent, and belongs to the technical field of test and determination of medical science, food, and environment. The kit comprises the following main components: buffer solution, coenzyme, pyruvic acid, acetaldehyde, pyruvate oxidase, alcohol oxidase, alcohol dehydrogenase and a stabilizer. The method comprises the following steps: mixing a sample and the reagent according to a certain volume ratio to perform a series of enzymic reaction, and then placing reactants under a UV / visible light analyzer to test the ascending speed of absorbance at the position where the dominant wave length is 340nm to determine the inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) concentration.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
A hepatocyte-mimicking antidote for alcohol intoxication
InactiveUS20200405823A1Fast shippingHighly retained activityPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseAntidote
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for carrying out reductive amination reaction by adopting microchannel reaction device
ActiveCN113801025AShort reaction timeHigh reaction conversion rateAmino preparation from aminesOrganic compound preparationFlavin adenine dinucleotideNucleotide
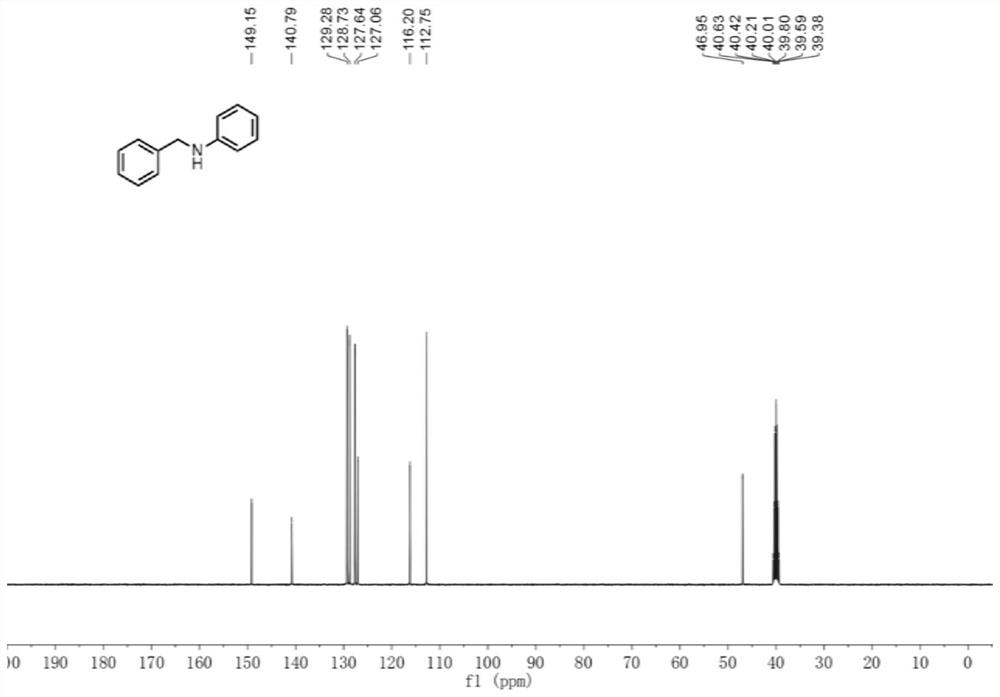
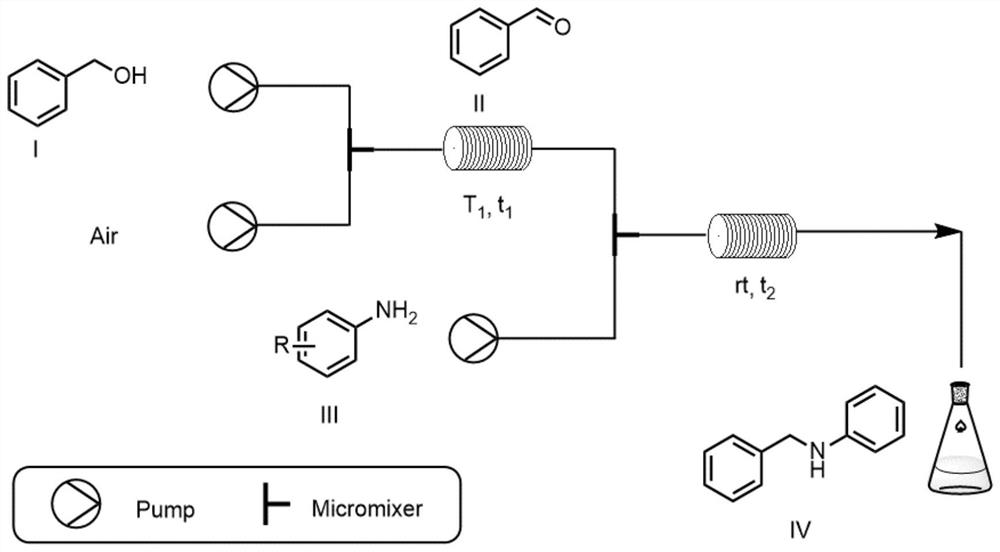
The invention discloses a method for carrying out reductive amination reaction by adopting a microchannel reaction device. The microchannel reaction device comprises a microreactor 1 and a microreactor 2 which are connected in series, and the method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a solution containing benzyl alcohol, alcohol oxidase, flavin adenine dinucleotide and hydrogen peroxide reductase as a first homogeneous solution, and preparing a solution of an aniline compound III as a second homogeneous solution; (2) mixing the first homogeneous solution with air, and simultaneously pumping a formed mixture into a microreactor 1 for reaction; and (3) mixing the reaction solution obtained in the step (2) with the second homogeneous solution, and simultaneously pumping a formed mixture into a microreactor 2 for reaction to obtain the N-benzylaniline compound as shown in a formula IV. The microreactor disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of high reaction safety, convenience in cleaning, easiness in amplification and the like. Meanwhile, compared with the prior art, the synthesis method has the advantages of simple, cheap and easily available initial materials, simple operation and high reaction efficiency, and is expected to be applied to industrial production.
Owner:NANJING ADVANCED BIOLOGICAL MATERIALS & PROCESS EQUIP INST CO LTD
Diesel oil improver component containing biological enzyme and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103421552BImprove catalytic performanceHigh-speed catalytic performanceLiquid carbonaceous fuelsFuel additivesPeroxidaseLyase
The invention provides a bioenzyme-containing diesel oil booster composition, comprising a cetane number improver and a bioenzyme at a weight ratio of 1:0.01-1; the bioenzyme is sulfonase, alcohol oxidase, aldehyde Oxidase, amine oxidase, sulfhydryl oxidase, methylmercaptan oxidase, menaquinone oxidase, peroxidase, ferrochelatase, decarboxylase, aldolase, oxoacid lyase, demethylation Mixture of enzymes, alcohol, acid, ester dehydratase, desulfhydrylase, desulfomethylase, cobalt chelatase, magnesium chelatase. A bio-enzyme-containing diesel oil booster composition of the present invention can realize high-speed catalytic performance in a mild environment by utilizing the characteristics of a bio-enzyme, and is used in combination with the existing cetane number improver, The catalytic combustion efficiency of the cetane number improver in diesel is significantly improved, and the combustion performance of diesel is further improved.
Owner:英杰惠能(北京)能源新技术有限公司
Recombinant pichia pastoris strain regulating expression of glutamine transaminase in Zea mays by using FLD1 promoter and construction method thereof
InactiveCN109929769AEasy to trainStrong secretory abilityFungiTransferasesBiotechnologyAlcohol oxidase
The invention relates to a recombinant pichia pastoris strain regulating expression of glutamine transaminase in Zea mays by using a FLD1 promoter and a construction method thereof. The recombinant pichia pastoris strain is a genetically engineered strain obtained by transferring a transglutaminase gene derived from Zea mays into pichia pastoris, the recombinant pichia pastoris strain is obtainedby replacing an alcohol oxidase promoter PAOX1 in the pPIC9K plasmids to a formaldehyde dehydrogenase promoter PFLD1, and connecting with the glutamine transaminase gene into a loop to form a recombinant expression vector. The recombinant strain is easy to culture has strong secreting capability, is beneficial to the large expression of glutamine transaminase, has the characteristics of safety andreliability, and has important application prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
A method for producing l-2-aminobutyric acid by a double-immobilized multi-enzyme system
InactiveCN102517351BImprove recycling ratesImprove regeneration efficiencyChemical industryFermentationL-2-Aminobutyric AcidAlcohol oxidase
The invention discloses a method for producing L-2-aminobutyric acid by double immobilized multi-enzyme systems. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps that 1, threonine dehydrogenase and leucine dehydrogenase are fixed on reversely-dissoluble pH-sensitive polymer carriers so that a co-immobilized multi-enzyme system is obtained; and 2, alcohol oxidase, formaldehyde dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenlyase are fixed on reversely-dissoluble pH-sensitive polymer carriers so that a co-immobilized coenzyme regeneration system is obtained. The method for producing L-2-aminobutyric acid by the double immobilized multi-enzyme systems utilizes dissolution reversibility of co-immobilized enzymes, realizes effective separation of the co-immobilized enzymes and products, improves accessibility between the co-immobilized enzymes and reactants, improves recovery and utilization rates of threonine dehydrogenase, leucine dehydrogenase, alcohol oxidase, formaldehyde dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenlyase, improves coenzyme regeneration efficiency, reduces follow-up separation purification processes, simplifies a process flow and reduces a production cost.
Owner:李鑫
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com