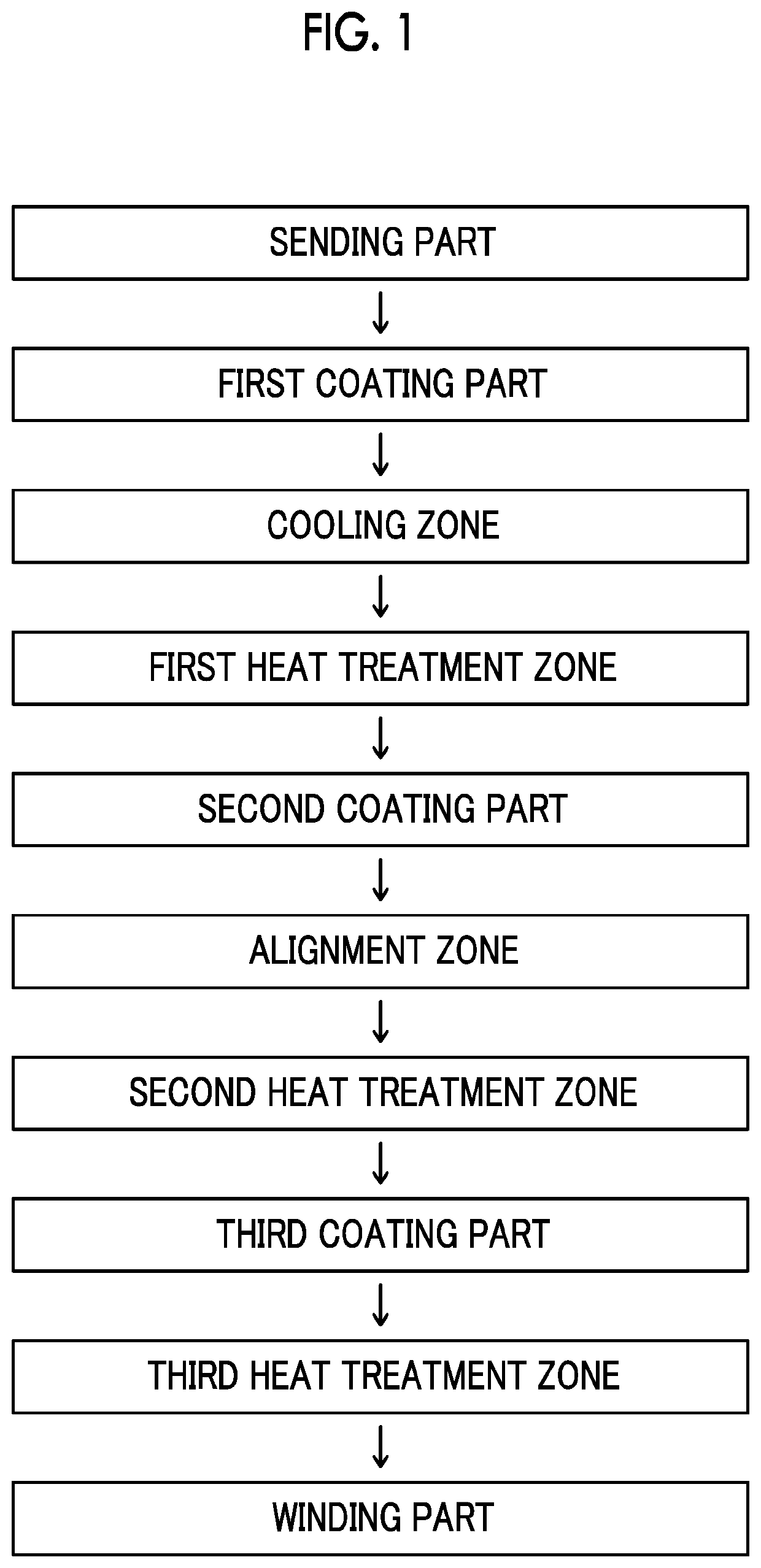
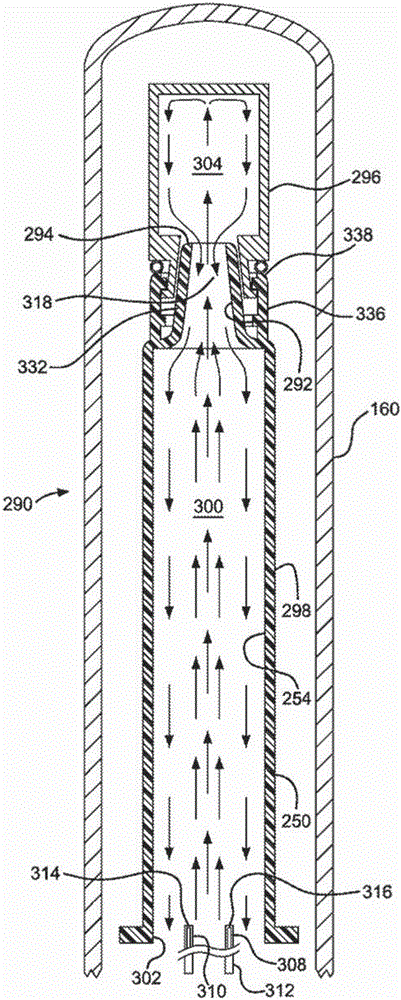
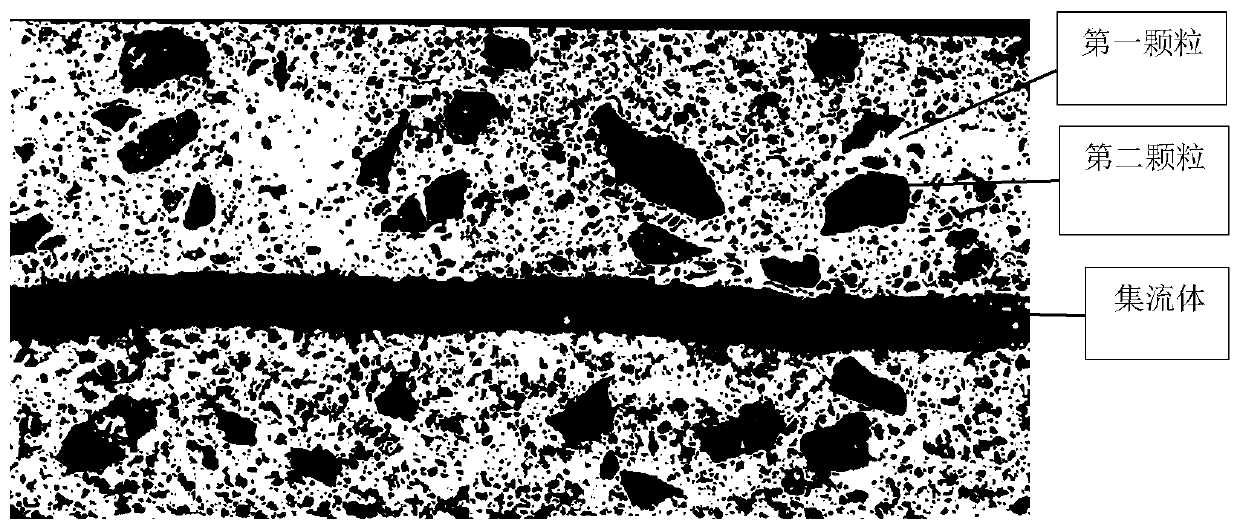
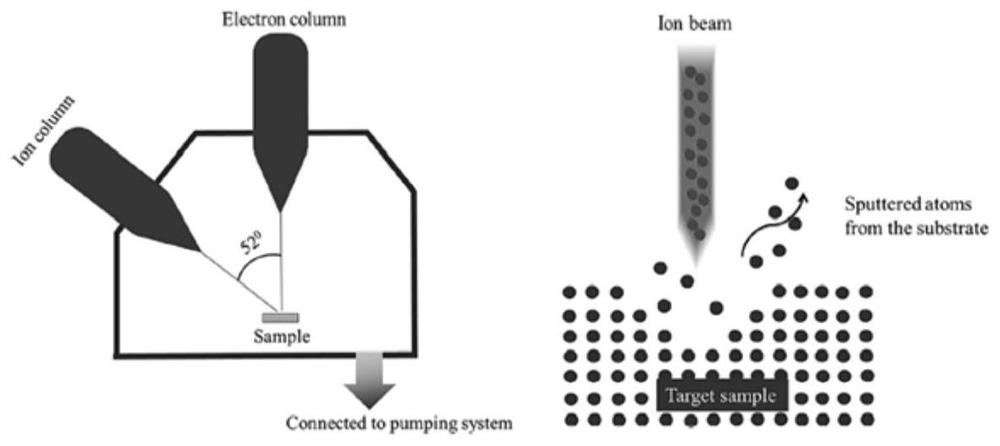
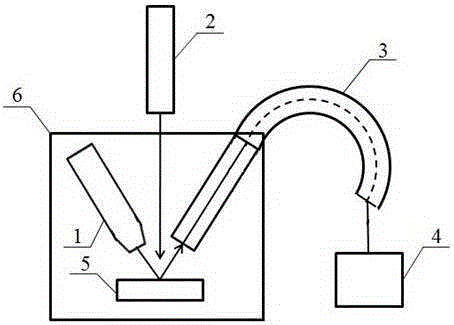
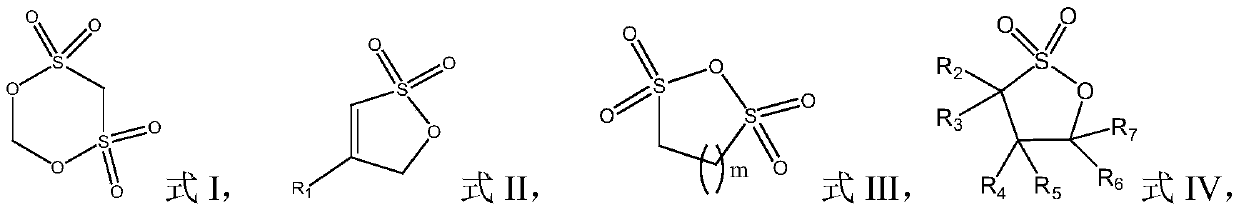Patents
Literature
157 results about "Electron energy spectrum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electrophotographic photosensitive member, process cartridge, and electrophotographic apparatus
ActiveUS9029054B2Long-term variationElectrographic process apparatusNitrogenElectron transporting layer
An electron transporting layer is a cured layer including carbon atoms, nitrogen atoms and oxygen atoms. When ratios of the number of carbon atoms, ratios of the number of nitrogen atoms, and ratios of the number of oxygen atoms are analyzed at 10 points by an X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (ESCA), the respective standard deviations, σ(C), σ(N) and σ(O), of the ratios of the number of carbon atoms, the ratios of the number of nitrogen atoms and the ratios of the number of oxygen atoms satisfy the following expressions (1) to (3):σ(C)≦1.5 (1),σ(N)≦1.5 (2),andσ(O)≦1.5 (3).
Owner:CANON KK
Magnetic tape having characterized magnetic layer
ActiveUS10839850B2Avoid it happening againImprove surface smoothnessMagnetic materials for record carriersTape carriersCoated surfaceMagnetic tape
Provided is a magnetic tape in which an Ra measured regarding a surface of a magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 1.8 nm, Int(110) / Int(114) of a hexagonal ferrite crystal structure obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical squareness ratio of the magnetic tape is 0.65 to 1.00, the back coating layer includes one or more kinds of component selected from the group consisting of fatty acid and fatty acid amide, and a C—H derived C concentration calculated from a C—H peak area ratio of C1s spectra obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis performed on the surface of the back coating layer at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees is equal to or greater than 35 atom %.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording and reproducing device
ActiveUS20210090599A1Improve running stabilityBase layers for recording layersRecord information storageNon magneticFerromagnetism
The magnetic recording medium includes a non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer including a ferromagnetic powder, in which one or more kinds of component selected from the group consisting of a fatty acid and a fatty acid amide are included in a portion of the magnetic layer side on the non-magnetic support, and a C—H derived C concentration calculated from a C—H peak surface area ratio in C1s spectra obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis performed on a surface of the magnetic layer at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees, after pressing the magnetic layer at a pressure of 70 atm is 45 atom % or more.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
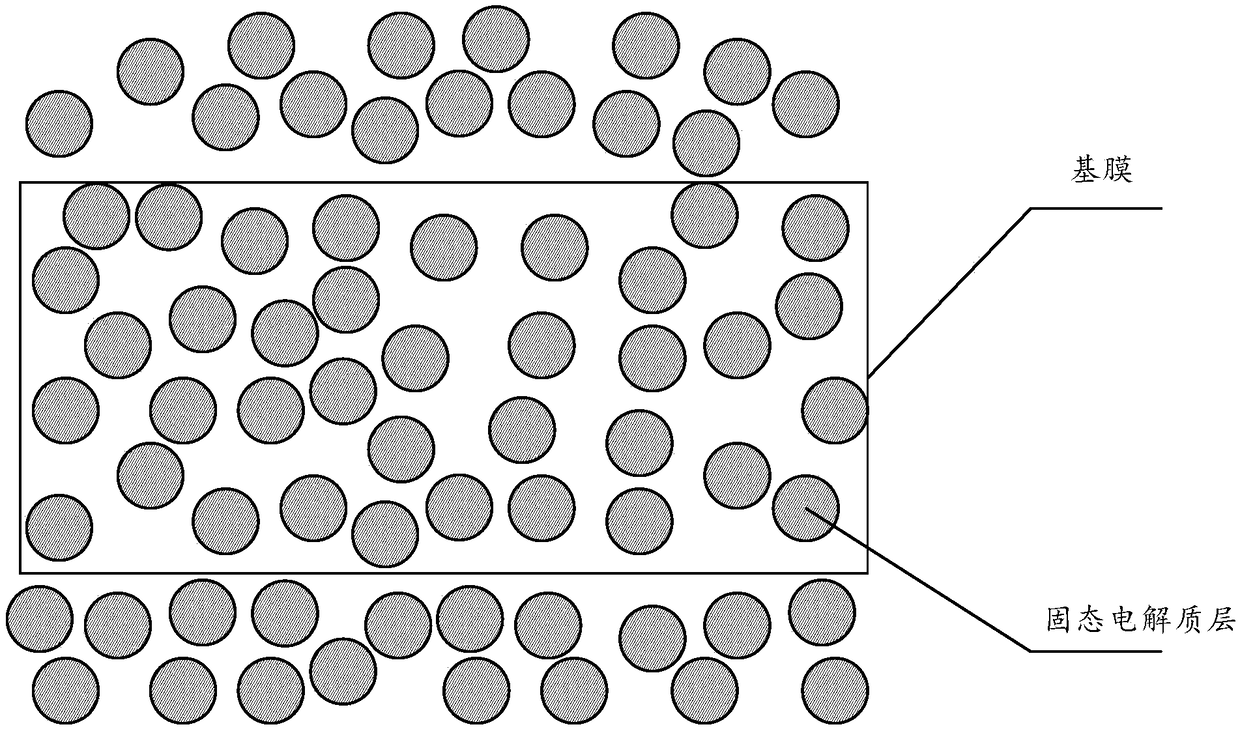
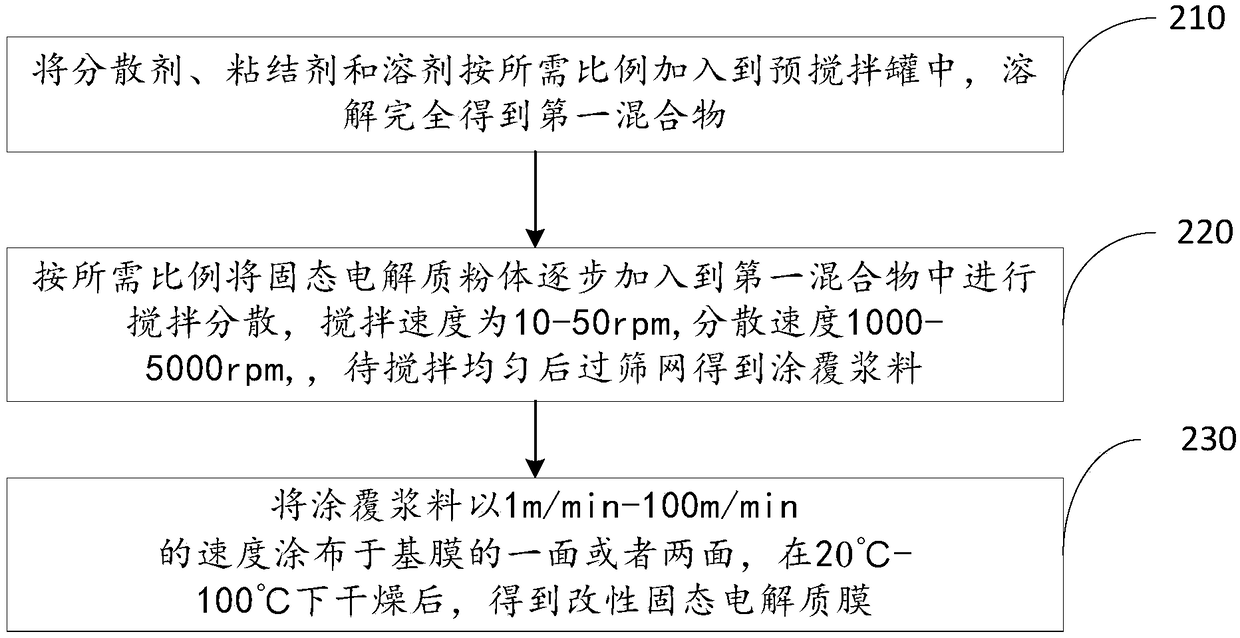
Modified solid electrolyte membrane, preparation method thereof and lithium battery
InactiveCN109494390AImprove liquid absorption performanceUniform thicknessSolid electrolytesLi-accumulatorsSolid state electrolyteChemical physics
The invention discloses a modified solid electrolyte membrane, a preparation method thereof and a lithium battery. The modified solid electrolyte membrane comprises a basic membrane and a solid electrolyte layer. The solid electrolyte layer is formed by a coating slurry which is coated on the basic membrane or is coated on the basic membrane and even permeate into the basic membrane, a thickness ratio of a coating layer on the basic membrane to the basic membrane is 10:1-1:10, the thickness of the coating layer is in a range of from 1 micrometer to 10 micrometers, and the density of the coating layer is in a range of from 50% to 100%. The solid electrolyte layer is formed by a NAS I CON type solid electrolyte material, have practical size smaller than 1 micrometer and is specifically represented as Li1+xAxB2-x(PO4)3, wherein x is in a range of from 0 to 0.6, A is one or more of Al, Y, Ga, Cr, In, Fe, Se or La, B is one or more of Ti, Ge, Ta, Zr, Sn, Fe, V or hafnium element Hf, and after the solid electrolyte membrane is circularly formed, a photoelectronic energy spectrum of an X-ray of the solid electrolyte membrane has a peak between 685eV to 690eV.
Owner:LIYANG TIANMU PILOT BATTERY MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
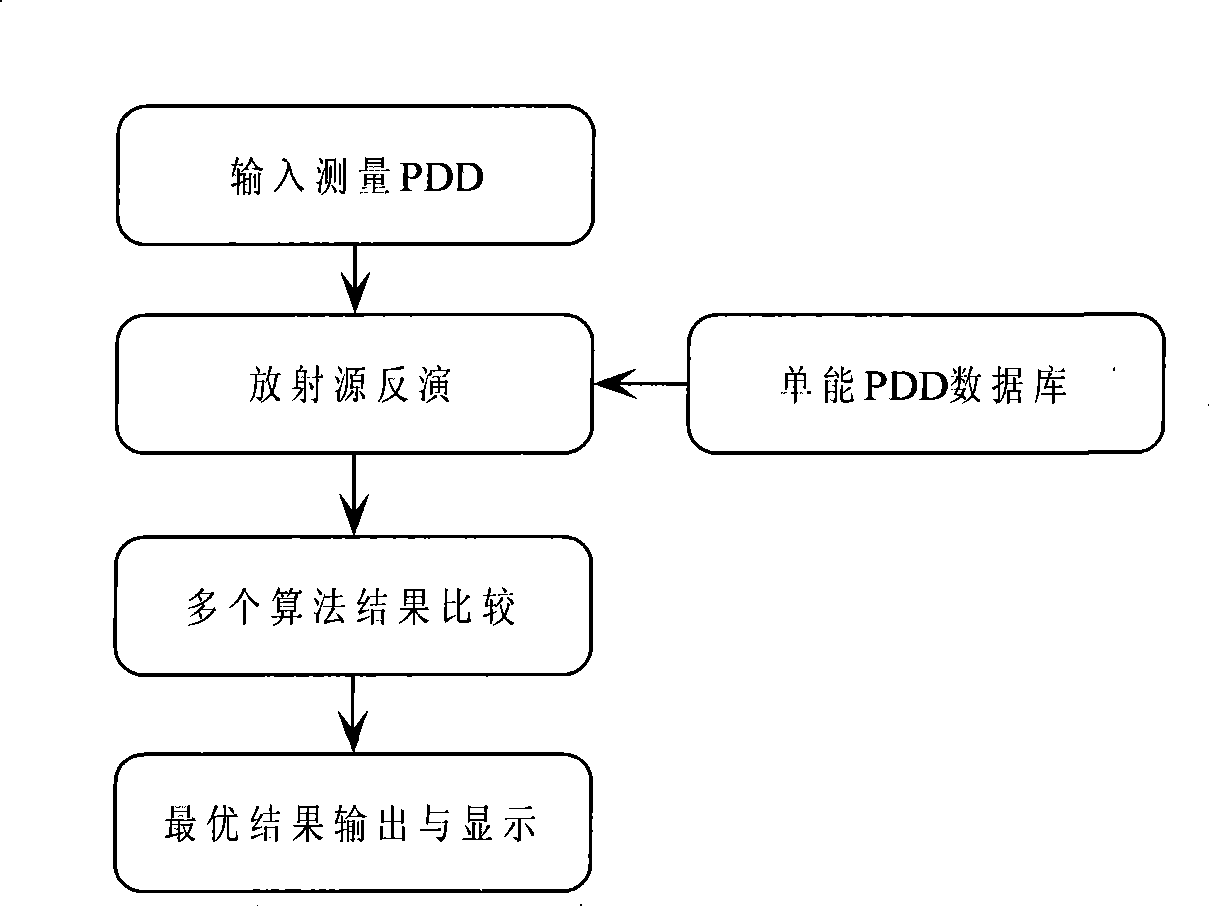
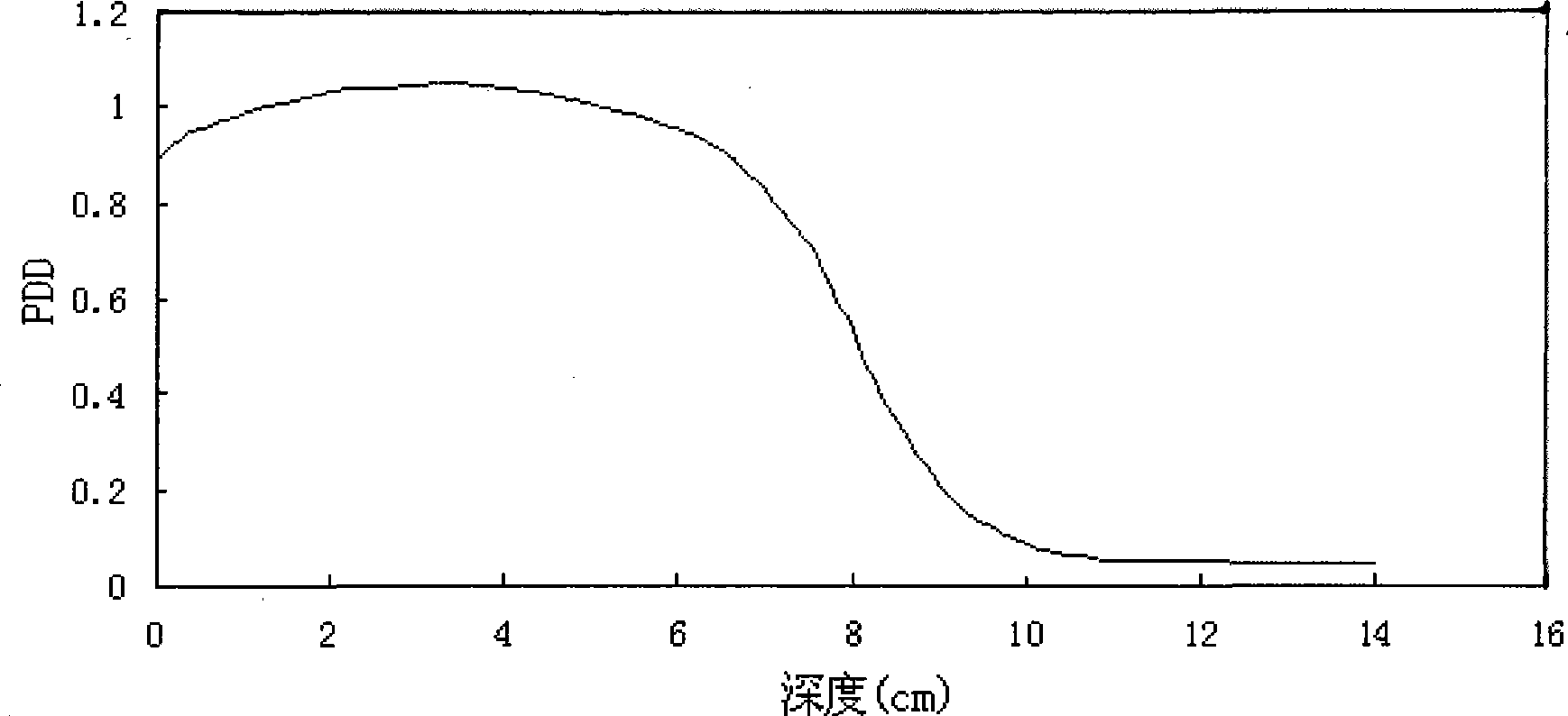
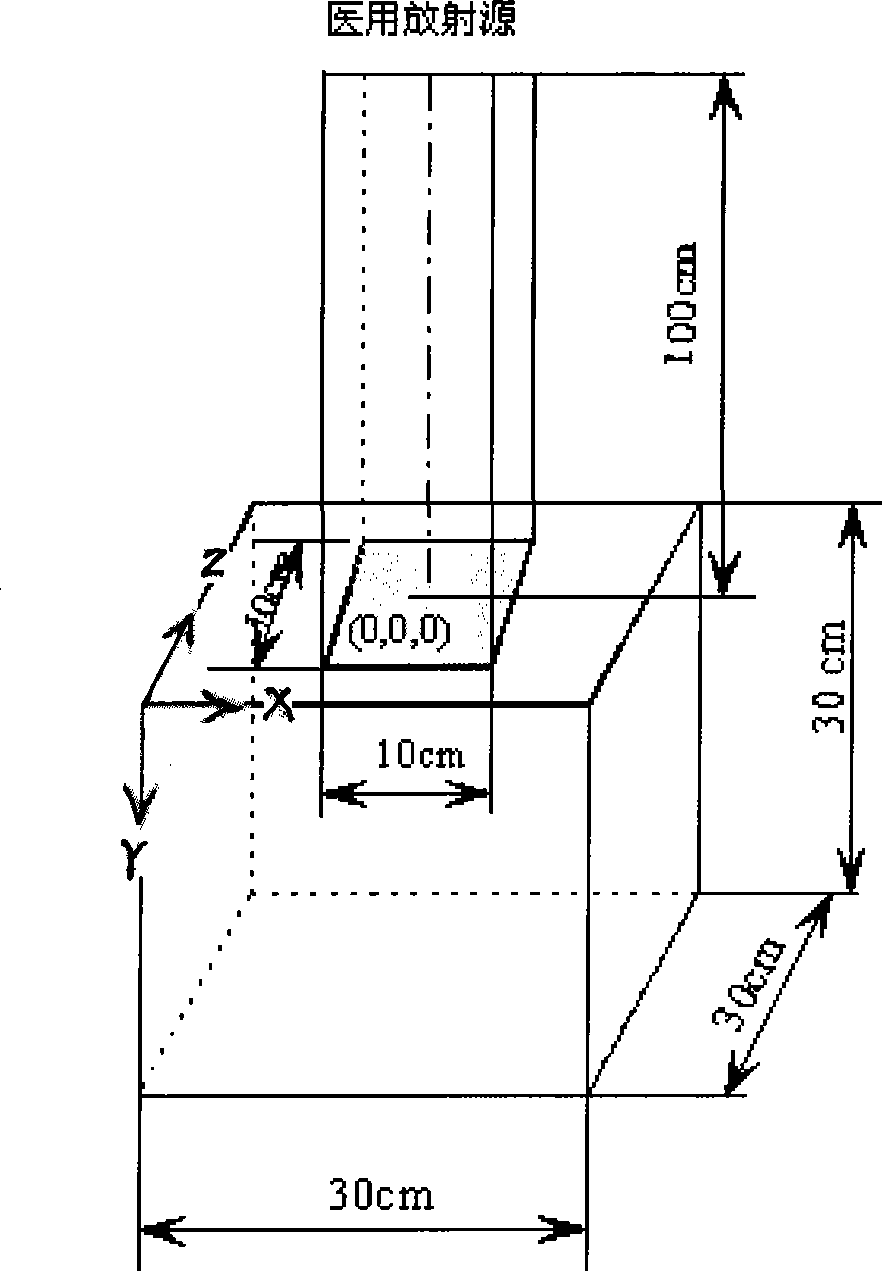
Radioactive source inversion method based on multi-algorithm
InactiveCN101477205ARebuild pollutionAccurate Radiation Source SpectroscopyX-ray spectral distribution measurementDosimetersPollutionDose calculation
The invention discloses a method for inversing a radiation source, which is to measure a PDD curve by a water tank or other radiation dosimetry measuring equipment. Information of the high accuracy radiation source can be acquired by the method, including photon energy spectrum, or proton energy spectrum, or electron energy spectrum and photon pollution and other radiation information. The method has the advantages that: the information of the photon energy spectrum, the electron energy spectrum, the proton energy spectrum, photon pollution and other radiation source information of the radiation source can be simultaneously reestablished; the defect that the prior energy spectrum calculation method can not accurately acquire multiple radiation source information can be overcome; while the accurate energy spectrum of the radiation source is accurately acquired, the information of the photon pollution and other information can be acquired; correct information of the radiation source can be provided for dose calculation; information of scattered or continuous energy spectrum and the photon pollution can be acquired; and the accurate radiation source can be realized by a plurality of algorithms so as to solve the problem that the prior single algorithm can not ensure that the inverse of the energy spectrum has a solution.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Magnetic tape having characterized magnetic layer and magnetic recording and reproducing device
ActiveUS20210358521A1High environmentIncrease temperatureMagnetic materials for record carriersTape carriersMagnetic tapeRefractive index
The magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic support, in which the magnetic layer includes one or more components selected from the group consisting of fatty acid and fatty acid amide, a C—H derived C concentration calculated from a C—H peak area ratio of C1s spectra obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis performed on a surface of the magnetic layer at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees is equal to or greater than 45 atom %, and an absolute value ΔN of a difference between a refractive index Nxy measured regarding an in-plane direction of the magnetic layer and a refractive index Nz measured regarding a thickness direction of the magnetic layer is 0.25 to 0.40.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Detection device of space electrons
ActiveCN102508281AReduce power consumptionHigh resolutionX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentSignal processing circuitsAnalog processing circuits
The invention discloses a detection device of space electrons, which belongs to the field of detection of space charged particles. Equipment used by the device comprises a detector and a signal processing circuit, wherein the detector comprises a probe, a heavy metal housing and a metal base; and the probe mainly comprises a light-blocking sheet, a detection unit D1, a detection unit D2, a scintillator framework, a photomultiplier tube and an analog processing circuit board. According to a method disclosed by the invention, a space 0.1-1MeV electron energy spectrum can be detected; and the detector designed by utilizing the method has the characteristics of miniaturization, low power consumption, high resolution and high efficiency, and is convenient to be carried on a spacecraft for detection.
Owner:NO 510 INST THE FIFTH RES INST OFCHINA AEROSPAE SCI & TECH
Low-temperature environmentally-friendly preparation method of nitrogen edge doped graphene
The invention relates to a low-temperature environmentally-friendly preparation method of nitrogen edge doped graphene, and belongs to the field of novel carbon nano-materials. The preparation method is characterized in that graphite powder and a nitrogen-containing polymer solid are mixed and subjected to continuous ball milling at a certain ball milling speed under the normal temperature and normal pressure so as to obtain a nitrogen edge doped graphene nanosheet, wherein no liquid agents are added during preparation. By analyzing through a scanning electron microscope and an atomic force microscope, the product is a lamellar structure which is uniform in dispersion and less than 1 nanometer in thickness. The analysis result of an X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy shows that the prepared product contains nitrogen, carbon, oxygen and other elements, and therefore, that the nitrogen edge doped graphene nanosheet is successfully prepared can be verified.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Surface-coated cermet cutting tool with hard coating layer having excellent chipping resistance
ActiveUS7273665B2Improve impact performanceImprove wear resistancePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesGas phaseChemical vapor deposition
There is provided a surface-coated cermet cutting tool with a hard-coating layer having excellent chipping resistance. The surface-coated cermet cutting tool is formed by coating, on a surface of a tool substrate made of WC-based cemented carbide or TiCN-based cermet, a hard-coating layer including the following upper and lower layers (a) and (b): (a) as the lower layer, a Ti compound layer having at least one or two of a TiC layer, a TiN layer, a TiCN layer, a TiCO layer and a TiCNO layer, all of which are deposited by chemical vapor deposition, the titanium compound layer having a total average thickness of 3 to 20 μm, and (b) as the upper layer, a heat-transformed α-type Al oxide layer formed by carrying out a heat-transforming treatment in a state that titanium oxide particulates satisfying the composition formula: TiOY, (where value Y is 1.2 to 1.9 in an atomic ratio to Ti when measured by Auger Electron Spectroscopy) and chemically deposited as a transformation starting material are dispersedly distributed on a surface of an Al oxide layer having a κ-type or θ-type crystal structure deposited by chemical vapor deposition and satisfying the composition formula: (Al1-XZrX)2O3 (where value X is 0.003 to 0.05 in an atomic ratio when measured by an electron probe micro-analyzer (EPMA)) to thereby transform the crystal structure of the Al oxide layer having the κ-type or θ-type crystal structure into an α-type crystal structure, the heat-transformed α-type Al oxide layer having an average thickness of 1 to 15 μm.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS CORP
Hard x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy arrangement and system
ActiveUS20200103358A1Effective protectionOptimizationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesSpectroscopyParticle physics
The present invention relates to a hard X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (HAXPES) system comprising an X-ray source providing a beam of photons which is directed through the system so as to excite electrons from an illuminated sample. An X-ray tube is connected to a monochromator vacuum chamber in which a crystal is configured to monochromatize and focus the beam onto an illuminated sample. A hemispherical electron energy analyser is mounted onto the analysis chamber. An air gap is provided between the X-ray tube and the monochromator chamber, which air gap is provided with a first radiation trap to shield the ambient air from the radiation when the air gap is illuminated with X-rays from the source.
Owner:SCIENTA OMICRON AB
Preparation and application of Nd<3-x>CoxNbO7-zincosilicate molecular sieve composite porous nanometer catalytic material
ActiveCN104646003AWater/sewage treatment by irradiationMolecular sieve catalystsElemental compositionX-ray
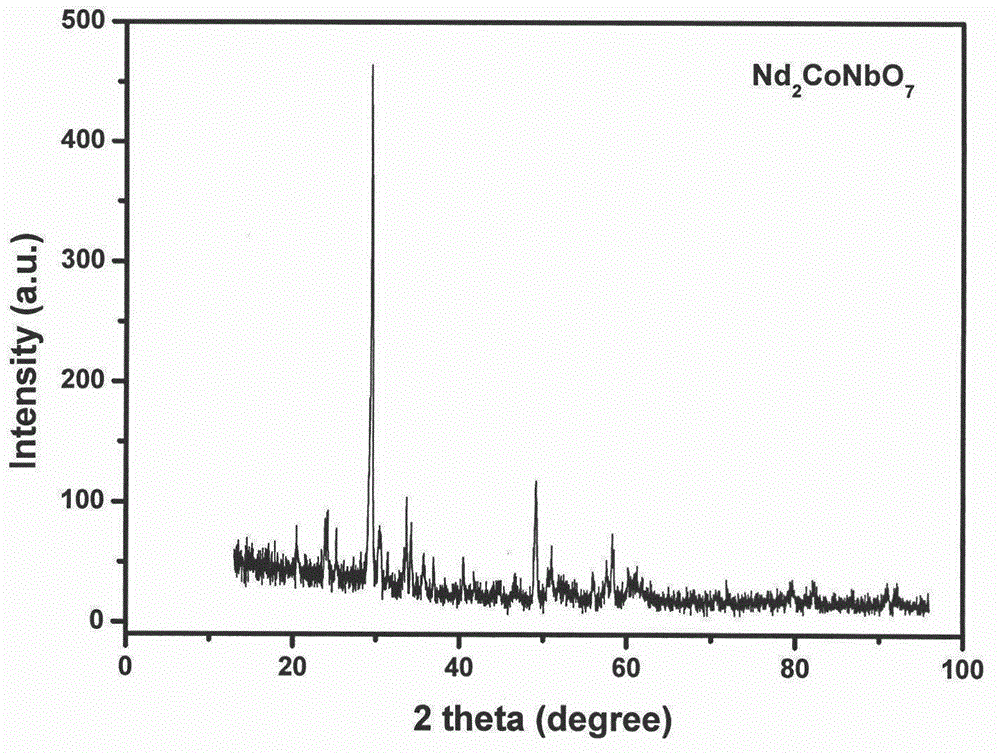
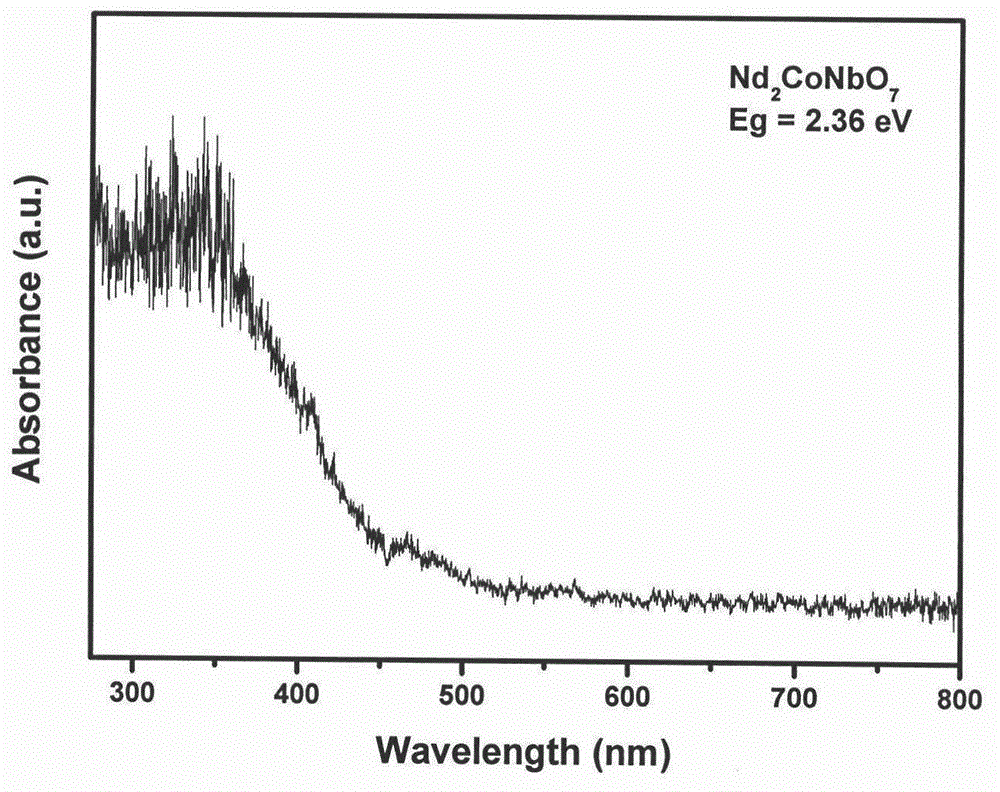
According to the invention, a powder catalytic material Nd<3-x>CoxNbO7 (x being greater than or equal to 0.5 and less than or equal to 1) is prepared by adopting a supercritical hydrosynthesis method and a chemical vapor condensation and deposition method; a composite porous nanometer catalytic material Nd<3-x>CoxNbO7 (x being greater than or equal to 0.5 and less than or equal to 1) -zincosilicate molecular sieve is prepared by adopting an impregnating and baking method; and a novel photoelectrode Nd<3-x>CoxNbO7 (x being greater than or equal to 0.5 and less than or equal to 1) is prepared. The three novel materials are represented: tissue morphology analysis is performed by a transmission electron microscopy, and results show that catalyst particles are irregular in shape, with the average particle size of 150 nm; phase analysis is performed by an X-ray diffractometer, and results show that Nd2CoNbO7 has a single phase, and relatively high crystallinity; the chemical speciation of the surface of the catalyst and the elementary composition of a microcell as well as the structural characteristics of an electronic shell are discussed by an X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; and a characteristic absorption edge of the Nd2CoNbO7 is determined by a UV-Vis diffuse reflection spectroscopy to obtain the band gap width of the Nd2CoNbO7 which is 2.412 eV. Finally, the catalyst is used for decomposing water to produce hydrogen, and carrying out catalytic degradation on organic pollutants such as microcystic toxins, methylene blue and sulfamethoxazole in a water body under visible light. Experimental results show that the catalyst prepared according to the invention is good in catalytic effect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for detecting lithium extraction of negative electrode of lithium ion battery
ActiveCN105203566AFix security issuesSimple methodMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionOrganic solventElectrical battery
The invention discloses a method for detecting lithium extraction of a negative electrode of a lithium ion battery. The method comprises the steps of 1, disassembling a to-be-detected lithium ion battery, taking out a negative electrode slice, and clearly cleaning the negative electrode slice by using an organic solvent; 2, soaking the negative electrode slice in an organic solution of metal salt Mn<+>, enabling Mn<+> and extracted lithium to be subjected to sufficient replacement reaction, taking out the negative electrode slice after the replacement reaction is completed, and then cleaning the negative electrode slice by using the organic solvent to obtain the clean negative electrode slice; 3, carrying out qualitative or quantitative analysis on a product M through an energy spectrum analyzer, X-ray diffraction, an X-ray fluorescence spectrum, or an X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, an atomic absorption spectrum or an inductive coupling high-frequency plasma by the negative electrode slice after the replacement reaction, and further determining whether the negative electrode is in the lithium extraction or not and the relative size of the lithium extraction amount. According to the method disclosed by the invention, whether the negative electrode of the lithium ion battery has the lithium extraction or not can be accurately detected, so that the situation that the safety of the lithium ion battery is affected due to the lithium extraction of the negative electrode can be avoided, the service life of the lithium ion battery is prolonged, the safety of the lithium ion battery is increased, the operation is simple and convenient, and the detection accuracy is higher.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for measuring attosecond X-ray pulses and application of method
The invention discloses a method for measuring attosecond X-ray pulses and application of the method. According to the method disclosed by the invention, each measured related phase of a photoelectron is determined by using a parameterized computing formula, and the shape of a pulse and a concrete time structure are rebuilt through one step by using an analytical photoelectron spectrum unscrambling technology; and the time domain characteristics of the attosecond X-ray pulses can be rebuilt from each measured photoelectron spectrum without a large amount of time resolution measurements of a photoelectron spectrum and without a redundant iterative computation and an experimental data fitting process. The time uncertainty of a pulse measurement result is computed from energy bandwidth values of the pulses by using the parameterized formula. Because a direct relation among attosecond pulse time characteristics, important laser parameters (such as peak strength, electric field envelope shape, phase, carrier-envelope phase and the like), atomic or molecular ionization power and the photoelectron spectrum is established by a transformation equation, the method can be used for computing unknown parameters from each known parameter value.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Reflective mask blank, reflective mask and method of manufacturing reflective mask
ActiveUS20130078554A1Highly precise transfer patternGood optical performanceOriginals for photomechanical treatmentBinding energySurface layer
The present invention is a reflective mask blank used to fabricate a reflective mask, which has a laminated structure of a multilayer reflective film, an absorber film and an etching mask film in this order on a substrate, wherein the etching mask film comprises a material containing chromium, the absorber film comprises a material containing tantalum, a highly oxidized layer is formed on the surface layer of the absorber film on the opposite side from the substrate, and a Ta 4f narrow spectrum of the highly oxidized layer when analyzed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy has a maximum peak at a binding energy of more than 23 eV.
Owner:HOYA CORP
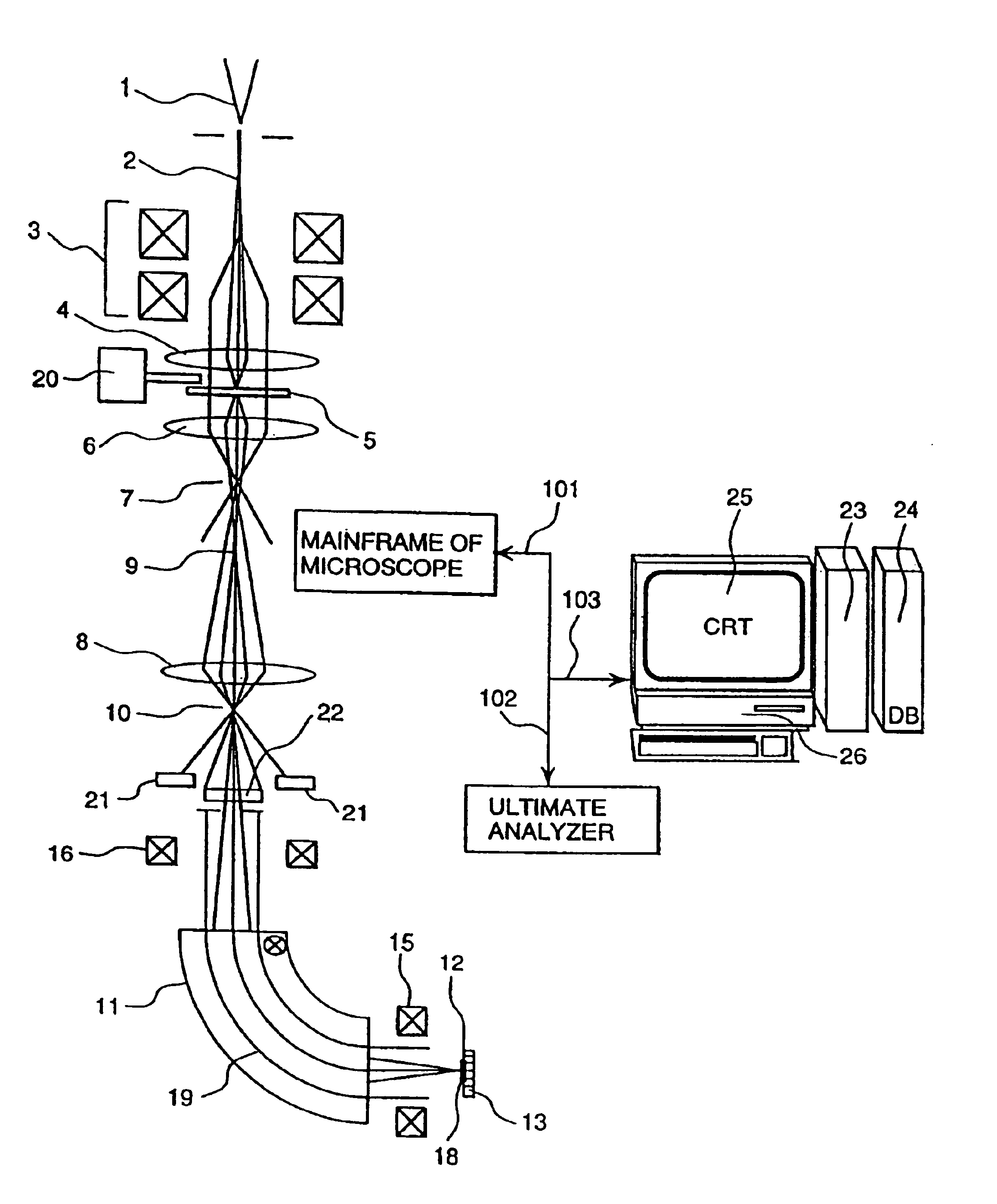
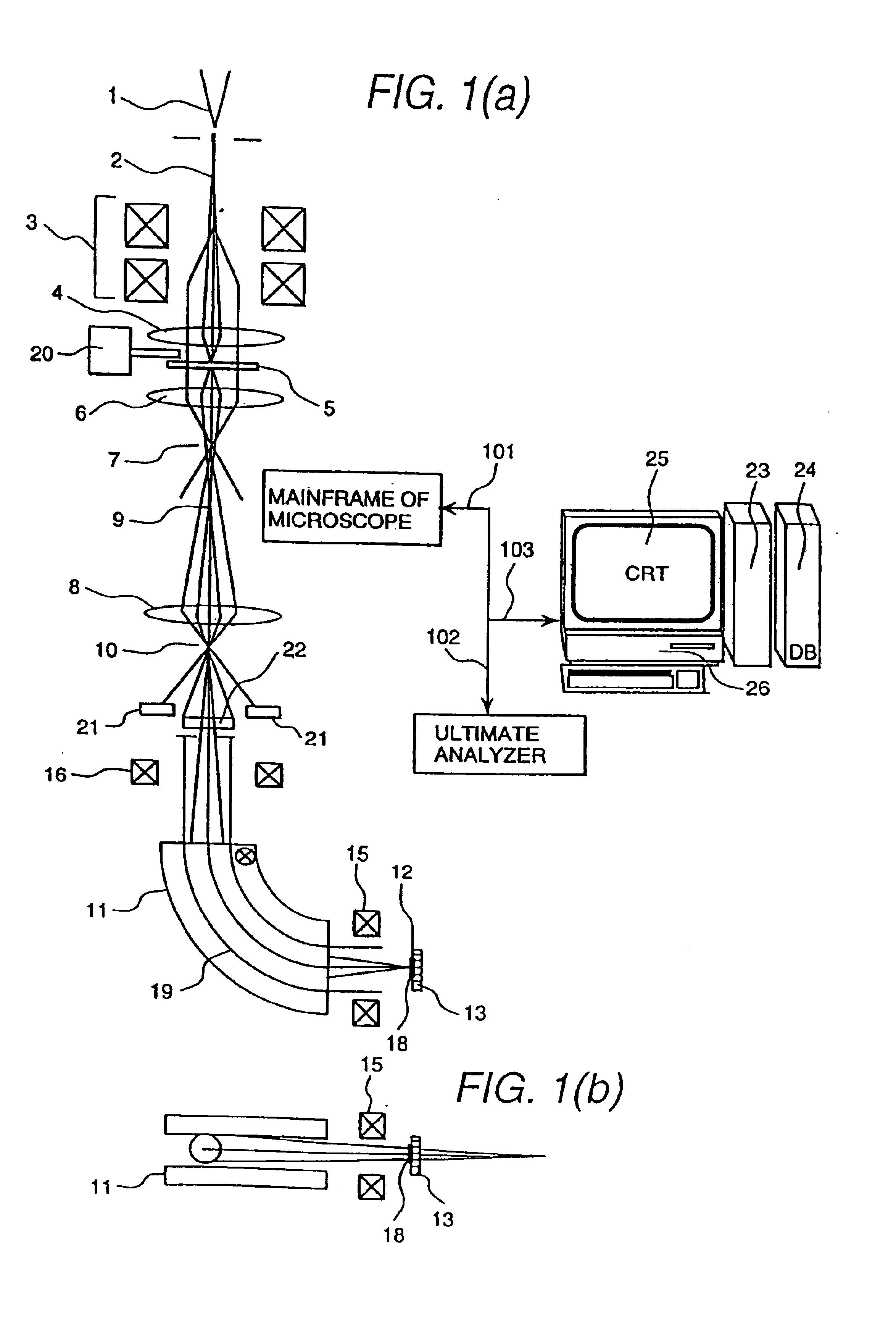
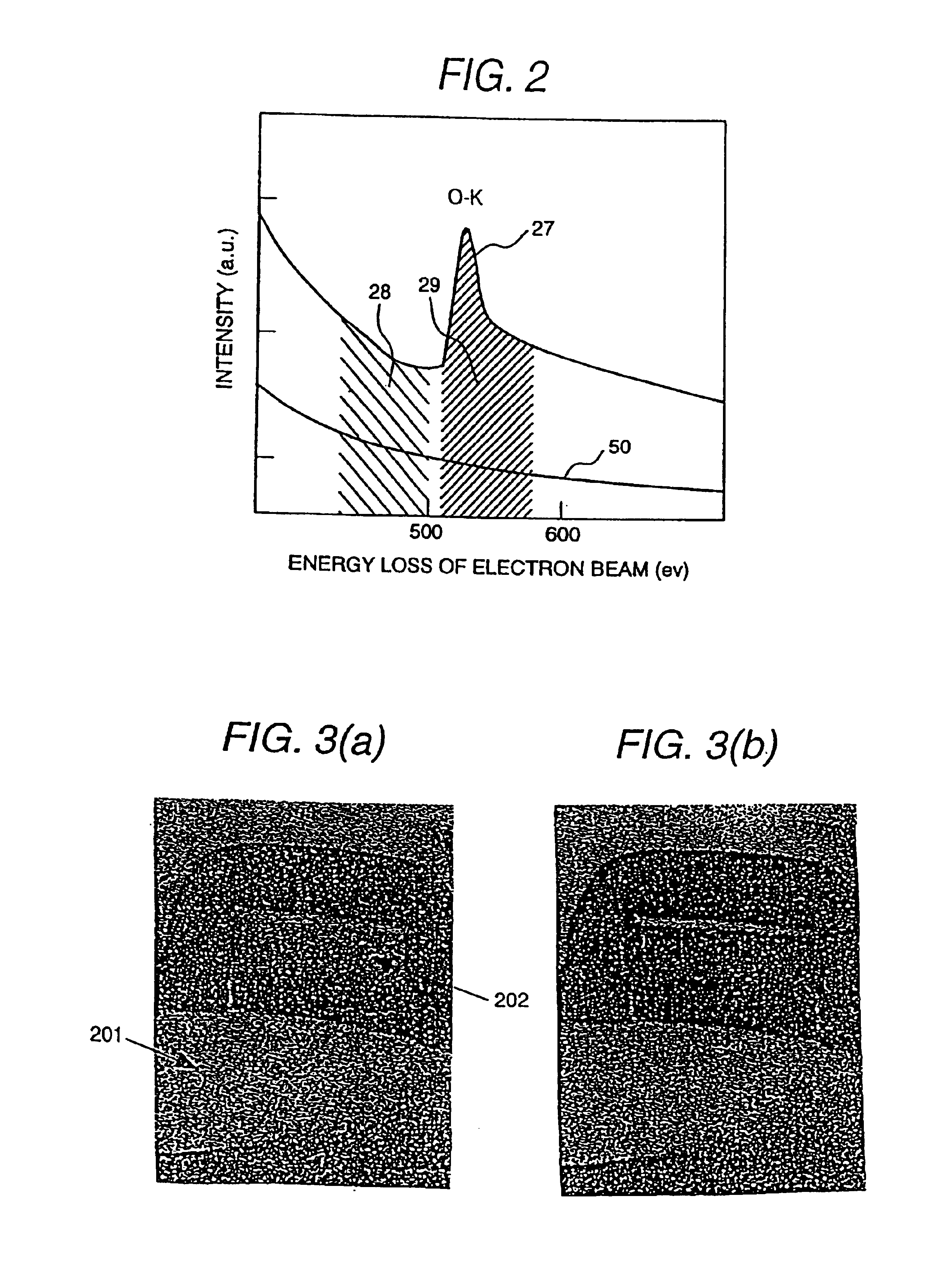
Ultimate analyzer, scanning transmission electron microscope and ultimate analysis method
InactiveUS6933501B2Increase contrastImprove accuracyPhotoelectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationConventional transmission electron microscopeEnergy dispersion
The present invention provides an ultimate analyzer which displays an element distribution image of an object with high contrast and high accuracy. A scanning transmission electron microscope and a method of analyzing elements using the ultimate analyzer is also provided. The ultimate analyzer comprises a scattered electron beam detector for detecting an electron beam scattered by an object; an electron spectrometer for energy dispersing an electron beam transmitted through the object; an electron beam detector for detecting said dispersed electron beam; and a control unit for analyzing elements based on an output signal of the electron beam detected by the electron beam detector and an output signal of the electron beam detected by the scattered electron beam detector.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
SiOx BARRIER FOR PHARMACEUTICAL PACKAGE AND COATING PROCESS
Disclosed is a container comprising a thermoplastic wall defining an inner cavity. The wall supports a SiOx composite barrier coating or layer arranged between the wall and the inner cavity, wherein x is 1.8-2.4. High-resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) shows that one interface exists between the composite barrier coating or layer and the wall or a substrate. In one aspect, the interface has O3-Si-C covalent bonds accounting for at least 1 mol% of the proportion of O3-Si-C covalent bonds and SiO4 bonds. In another respect, the interface has chemical shift of Si 2p with the bond energy (eV) lower than the bond energy of SiO4 bonds. The result is a closely attached composite barrier coating or layer having high degree of adhesion with the substrate. The invention also provides a method of applying the composite barrier coating or layer.
Owner:SI02 MEDICAL PRODS
Electrolyte and electrochemical device
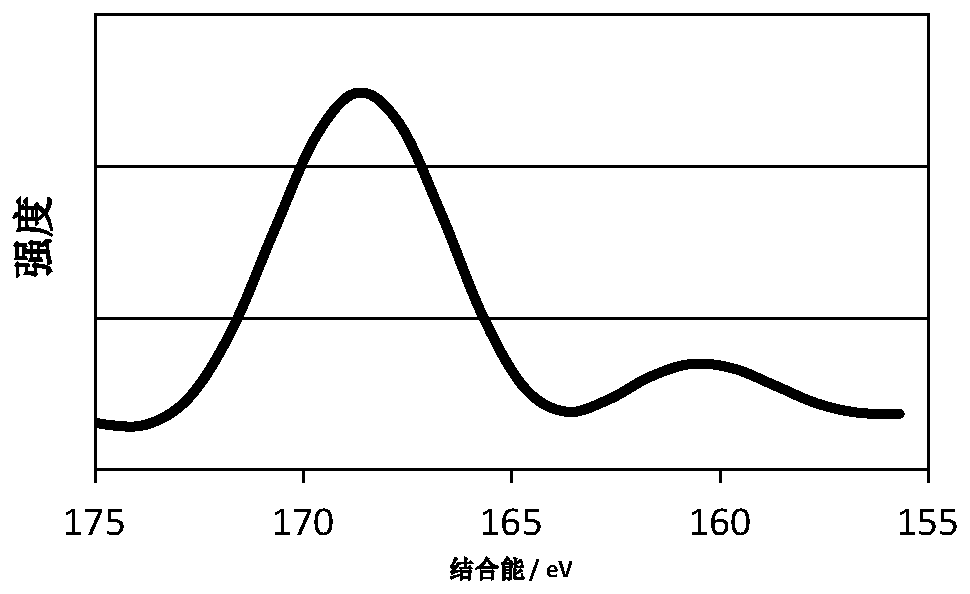
The invention provides an electrolyte and an electrochemical device. The electrochemical device comprises a positive electrode, a negative electrode, an electrolyte and an isolating membrane, whereinthe positive electrode comprises a positive electrode current collector and a positive electrode active material layer arranged on the positive electrode current collector, the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of the positive electrode active material layer has a peak in a range of 164 eV to 175 eV, and the electrolyte retention amount of the electrochemical device is 1.0 g / Ah to 4.0 g / Ah. According to the electrochemical device and the electrolyte, the cycle performance, the over-discharge storage performance and the safety performance of the electrochemical device can be improved.
Owner:NINGDE AMPEREX TECH
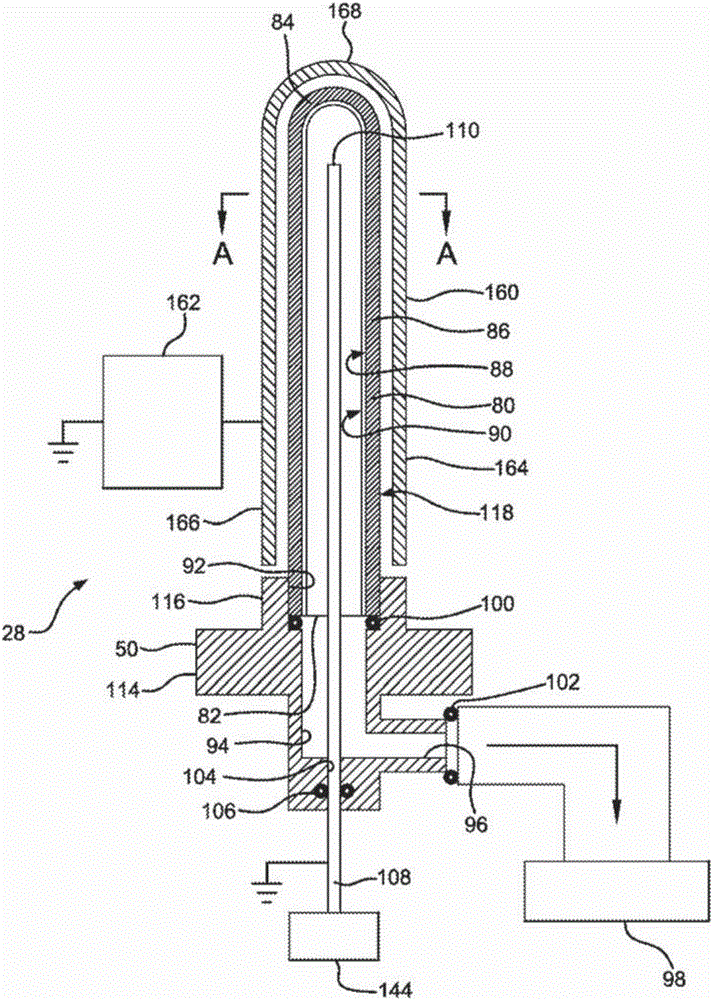
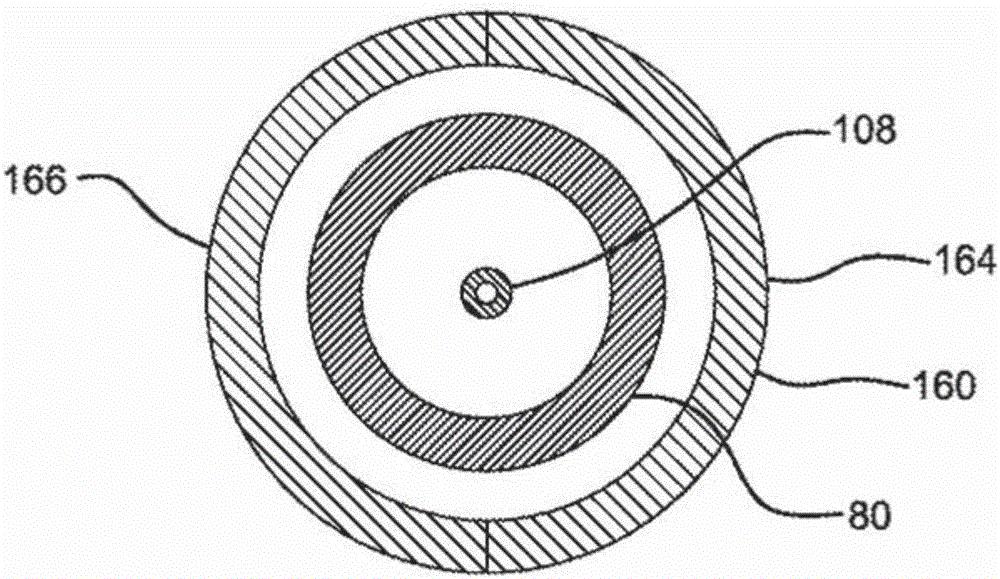
Hard X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Apparatus
InactiveUS20160327499A1Increase productionIncrease photoelectron collection efficiencyMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionHard X-raysFocal position
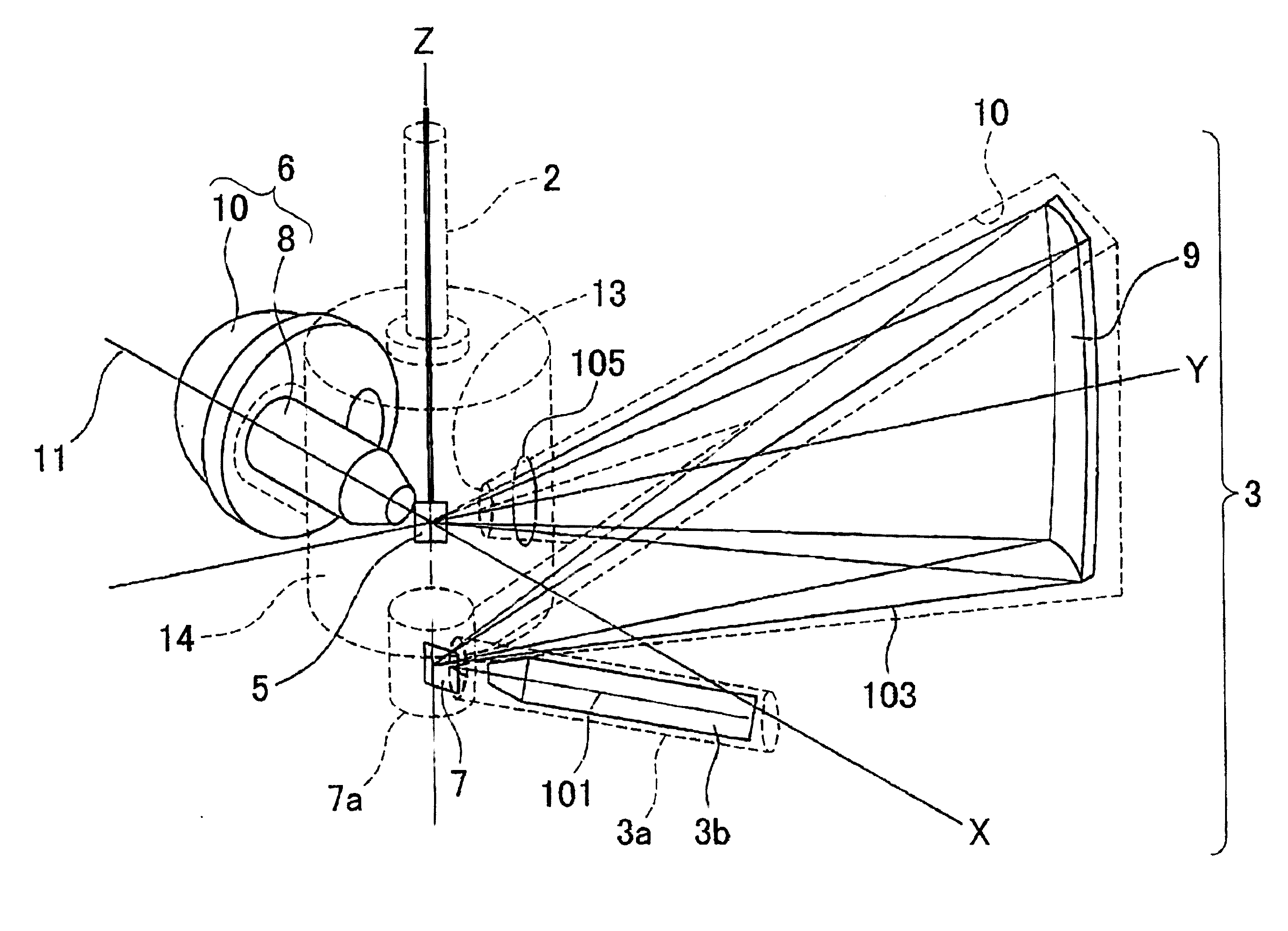
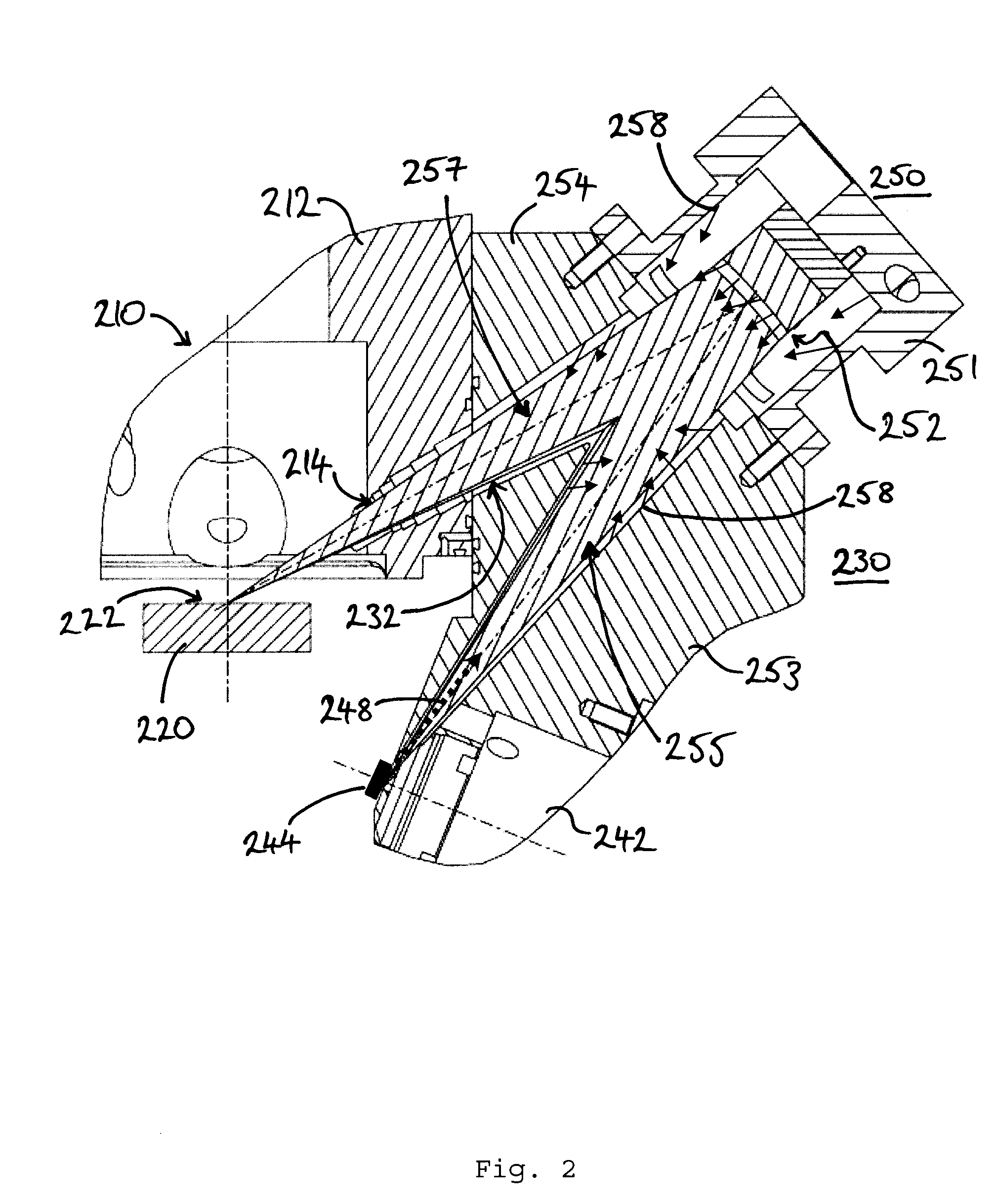
[Problem]The present invention aims to solve the problems that size of X-ray monochromater crystal assembly is restricted and the vacuum of the X-ray source and the vacuum of the analysis chamber cannot be separated.[Solution]A hard X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy apparatus comprises an X-ray source, an analyzer, a sample manipulator, an analysis chamber, and vacuum evacuation systems, wherein, in a three-dimensional space defined by a XYZ rectangular coordinate axis system, a plate-like sample is arranged to be rotatable around the Z-axis by said sample manipulator (2), wherein said X-ray source comprises an electron gun (3b) which accelerates and focuses electrons, a target which is irradiated with the electrons accelerated and focused by the electron gun to generate an X-ray, monochromater crystal assembly, wherein the monochromater crystal assembly meets the Bragg condition of X-ray diffraction in X-Y plane to diffract / reflect and monochromatize the X-ray generated in said target and extract characteristic X-rays only, and on the other hand, the electron-beam-irradiation position on the target-center of the monochromater crystal assembly-center of the sample is arranged on the Rowland circle to minimize focusing aberration to the sample, the monochromater crystal assembly is located on a circle having a radius twice as large as that of the Rowland circle in a X-Y plane, preferably electron-beam-irradiation position on said target and the center of the sample are located on each of two focuses of an ellipse coming in contact with said Rowland circle in the center of the monochromater crystal assembly, said monochromater crystal assembly has a toroidal surface in Z axial direction acquired by rotating said ellipse coming in contact with said Rowland circle around a straight line connecting the electron-beam-irradiation position on said target and the center of the sample, and, a vacuum vessel for installing these components, wherein the monochromater crystal assembly used for monochromatization with diffraction and reflection of said X-ray source is located on the Rowland circle together with said target and said sample to meet the condition that the dispersed X-ray beam concentrates on the surface of the sample with the minimum aberration, wherein said Rowland circle is located to be orthogonal to the surface of the sample, wherein an optical axis of said analyzer is placed to be perpendicular (in X axial direction) to the incident direction (in Y axial direction) of the X-ray or within a range of ±36 degree angle in a X-Y plane and within a range of ±49 degree angle in a X-Z plane, wherein the sample is such that said X-ray diffracted and reflected by a reflection surface is located on focus positions on the surface of said sample and is obliquely incident on the surface of said sample, so that the spot of said X-ray elongatedly extends along a line in substantially parallel to Y axis (substantially perpendicular to X axis), and wherein an aperture of a slit provided at the entrance of said analyzer is arranged in parallel to a direction where said X-ray spot on the sample surface elongatedly extends.
Owner:KOBAYASHI KEISUKE +1
Electron spectroscopy system
ActiveUS20190096627A1Maintain throughputHigh momentum and energy resolutionStatic energy spectrometersElectron spectroscopyRadio frequency
An electron spectroscopy system and method are disclosed. In another aspect, an ultrabright and ultrafast angle-resolved electron spectroscopy system is provided. A further aspect of the present system employs an electron gun, a radio frequency cavity and multiple spectrometers. Yet another aspect uses spectrometers in an aligned manner to deflect and focus electrons emitted by the electron gun. Moreover, an ultrafast laser is coupled to an electron spectroscopy system. A bunch of monochromatic electrons have their energy compressed and reoriented in an additional aspect of the present system. A further aspect of the present electron spectroscopy system employs adaptive and / or adjustable optics to optimize both time and energy compression. Another aspect provides at least two RF lenses or cavities, one before a specimen and one after the specimen.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
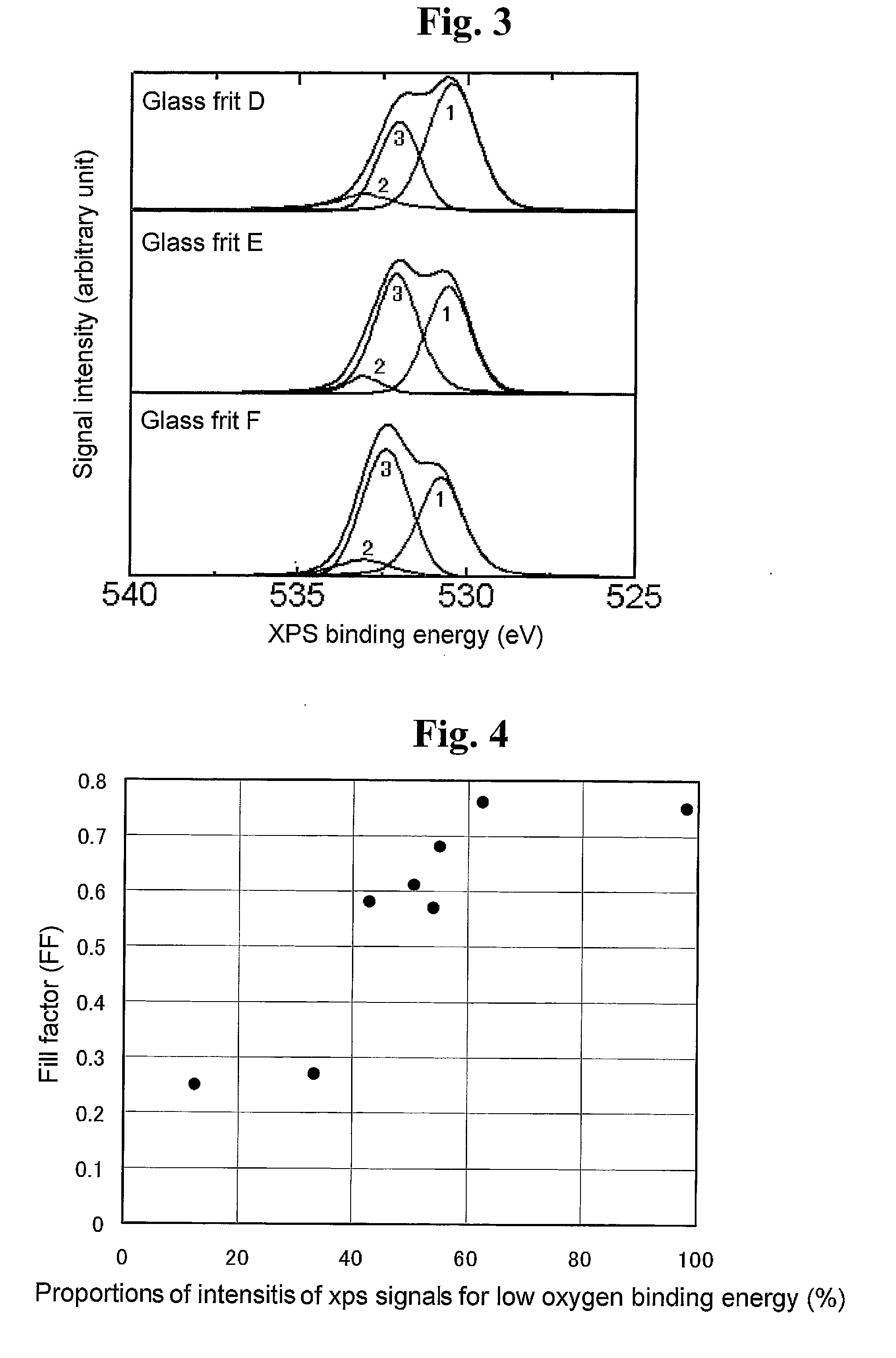
Conductive pastes for forming solar cell electrodes
InactiveUS20130312825A1Good solar cell characteristicFinal product manufactureConductive materialX-rayOxygen
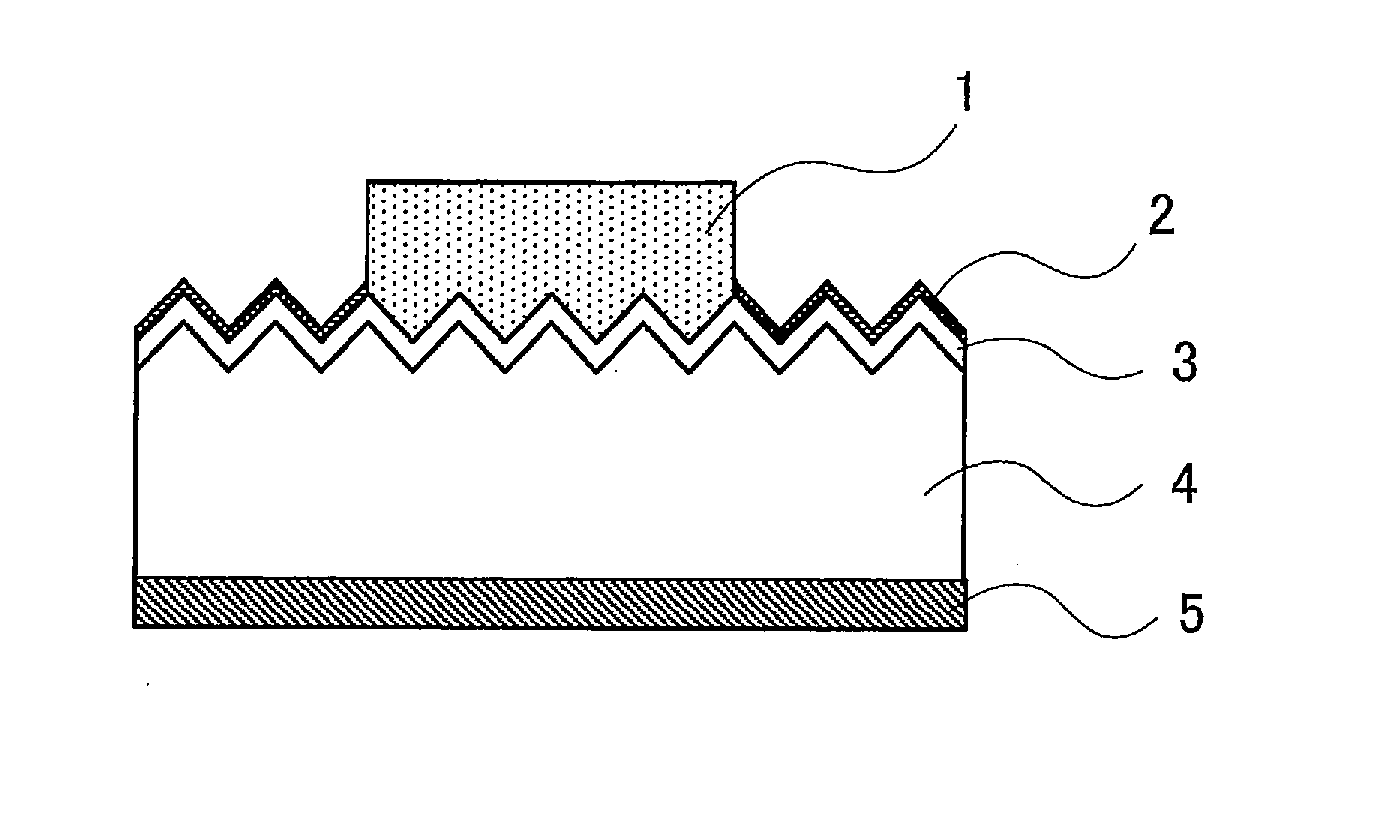
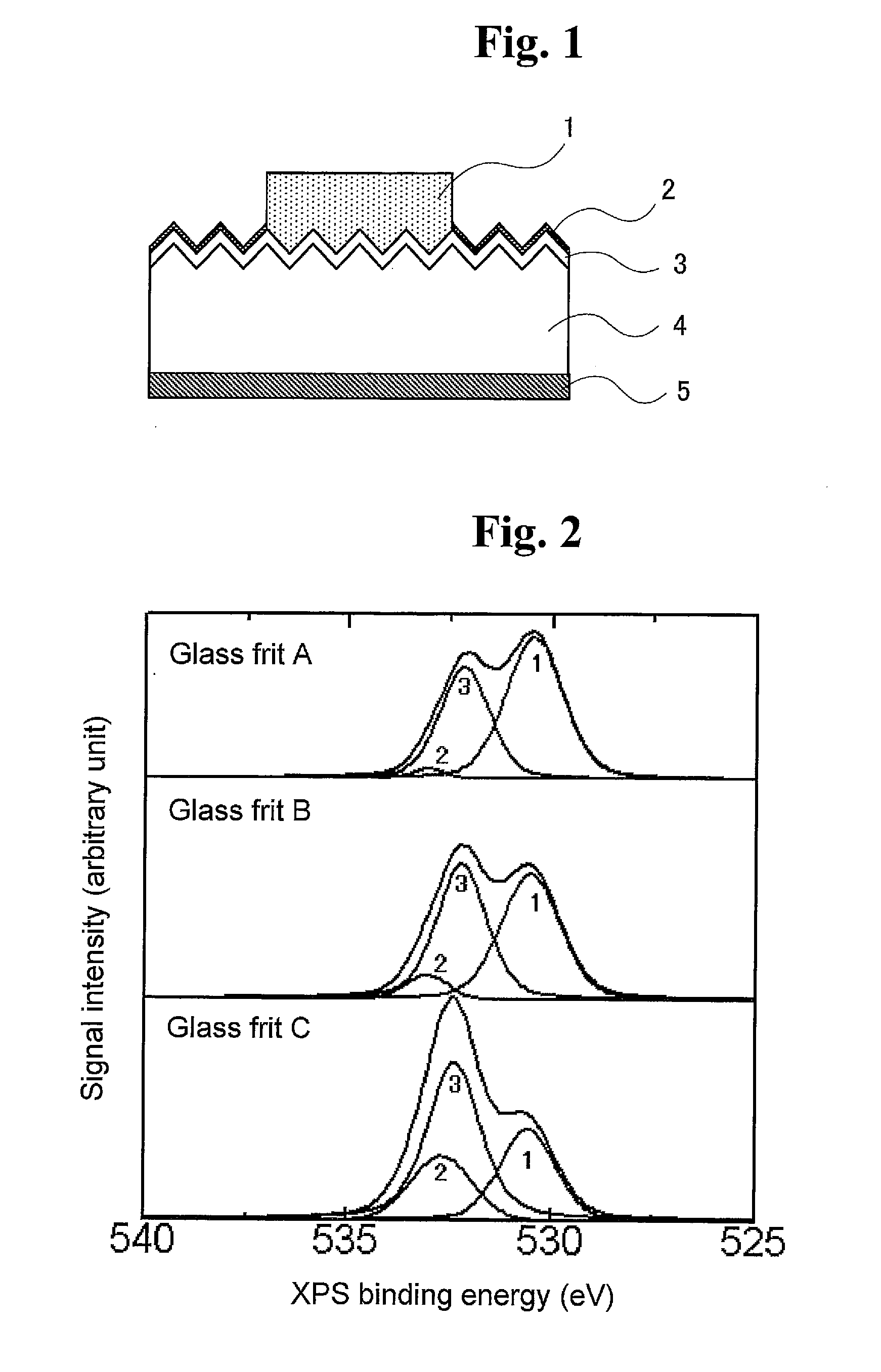
The invention relates to a process for manufacturing solar cells. The manufacturing process of the invention comprises the steps of printing a conductive paste onto an n-type silicon layer of a crystalline silicon substrate or onto an antireflection film on the n-type silicon layer, and drying and firing the conductive paste to form an electrode. The conductive paste comprises a conductive powder, a glass frit and an organic vehicle. The glass frit comprises at least one oxide. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of the glass fit gives a spectrum representing binding energies of oxygen in which the signal intensity of a peak with a peak top at a range from 529 eV to less than 531 eV has a proportion of 40% or more relative to the total of signal intensities from 526 eV to 536 eV.
Owner:NAMICS CORPORATION
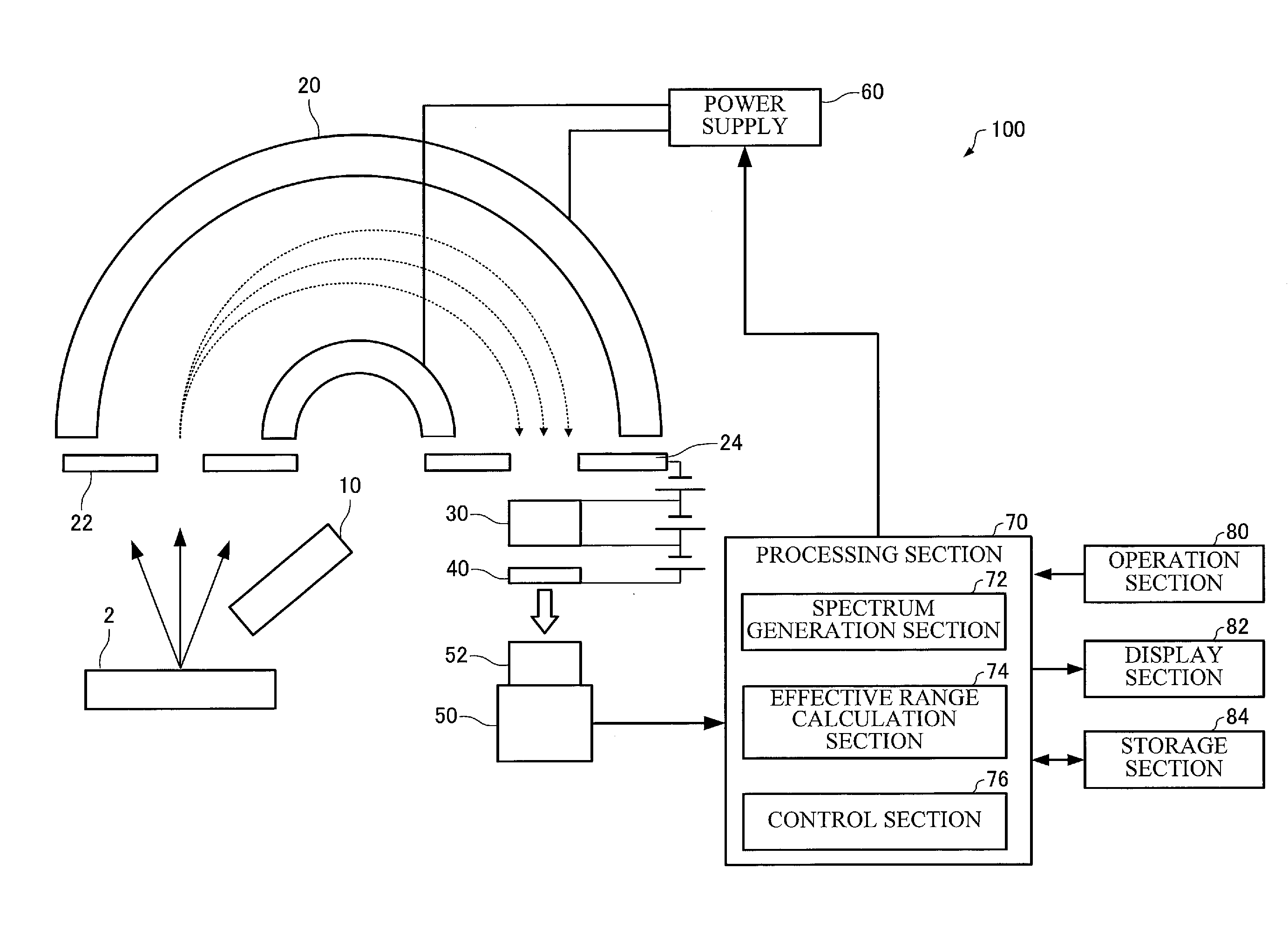
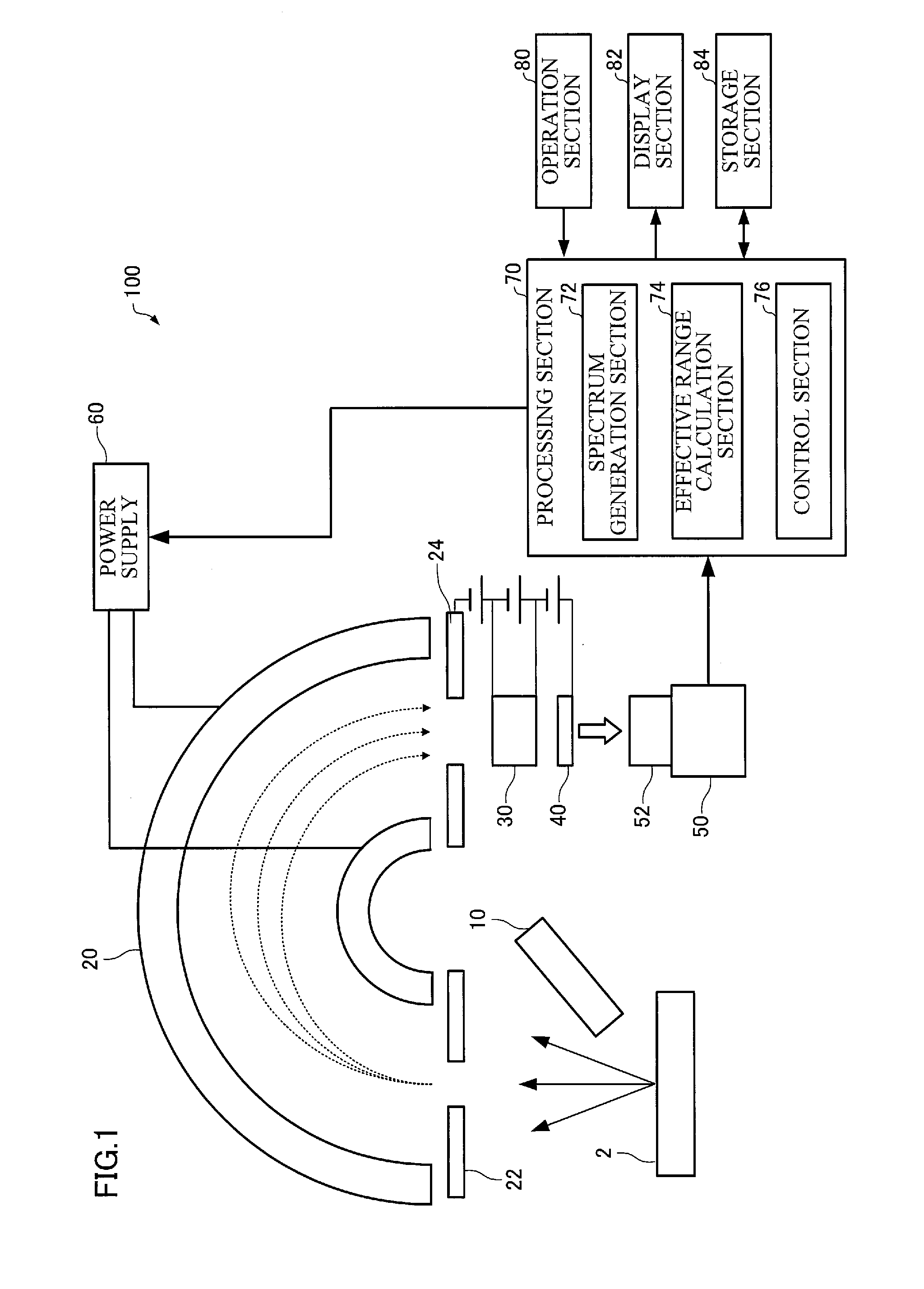
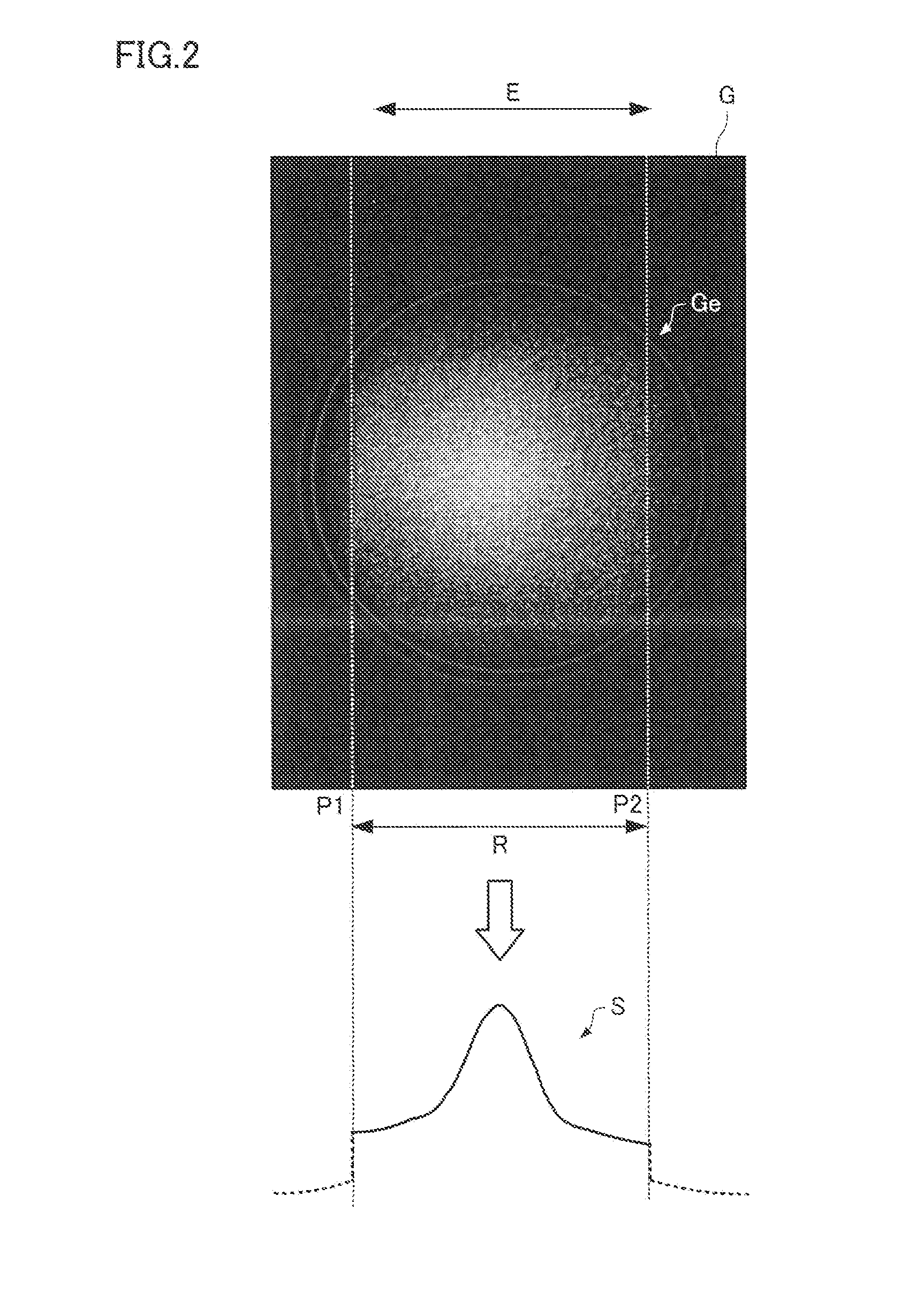
Electron Spectrometer and Measurement Method
ActiveUS20160268119A1Accurately effective rangeAccurate calculationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationImaging particle spectrometryCamera imageFluorescence
An electron spectrometer includes: an energy analyzer section that energy-analyzes electrons emitted from a specimen; a micro-channel plate that amplifies the electrons analyzed by the energy analyzer section; a fluorescent screen that converts the electrons amplified by the micro-channel plate into light; a camera that photographs the fluorescent screen; and an effective range calculation section that calculates an effective range of the fluorescent screen within a camera image photographed by the camera, the effective range calculation section performing a process that acquires a plurality of the camera images photographed while causing the energy analyzer section to analyze the electrons with a different center energy, a process that converts the plurality of camera images respectively into a plurality of spectra, and a process that calculates the effective range of the fluorescent screen within the camera image based on the plurality of spectra.
Owner:JEOL LTD
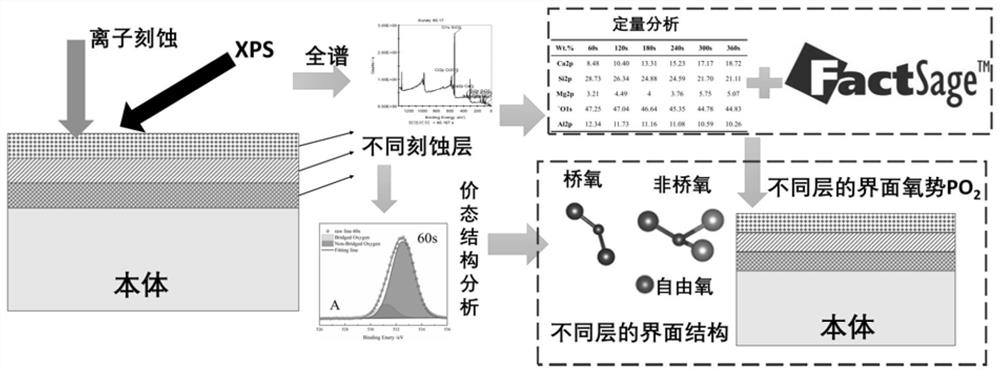
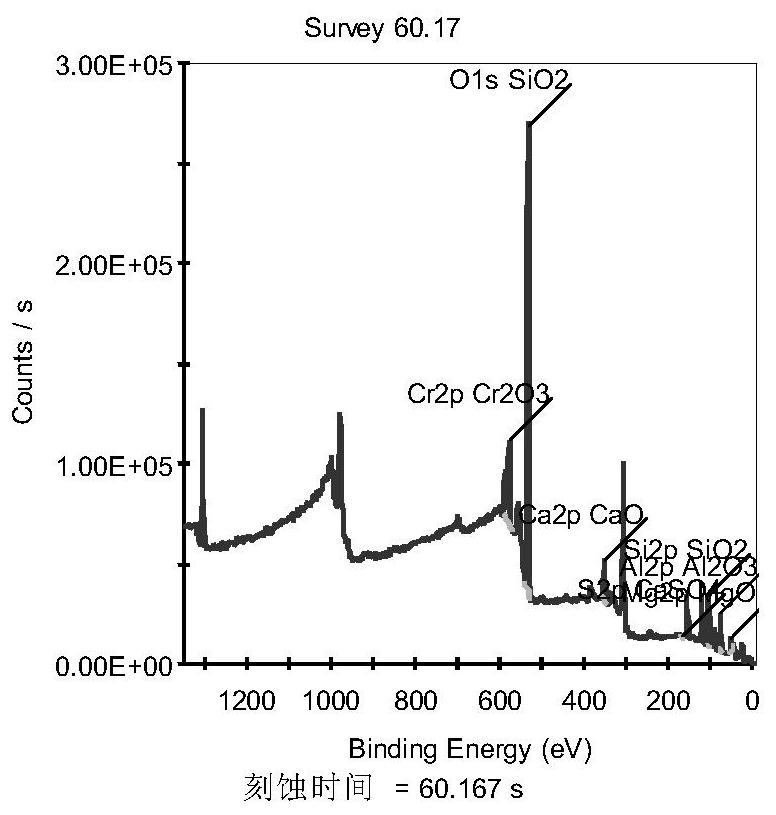
Method for directly obtaining oxygen potential and structure of material interface
ActiveCN112763527AEasy to implementImprove portabilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationComputational materials scienceChemical physicsOxygen potential
The invention discloses a method for directly obtaining oxygen potential and structure of a material interface, and belongs to the technical field of material interface research. The method comprises the following steps of: etching the surface of a fresh solid sample to form a to-be-detected sample interface; carrying out XPS detection on the to-be-detected sample interface by using an Al K alpha or Mg K alpha X-ray to obtain an X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy full spectrum and a target element high-resolution spectrum; according to full-spectrum quantification and high-resolution spectrogram fitting processing, obtaining element quantitative information and valence state distribution information of the to-be-detected sample interface; performing multivariate thermodynamic calculation according to the element quantitative information of the interface to obtain the interface oxygen potential of the to-be-detected sample interface; obtaining the structure information of the to-be-detected sample interface according to the valence state distribution information; and according to the etching information, obtaining structure changes of different depths. The method solves the problem that the interface oxygen potential and the interface structure are difficult to directly obtain.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Light and X-ray photoelectron energy spectroscopy synchronous analyzing and testing device
InactiveCN105259197ARealize physical property analysisAccurate study of physical propertiesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhoto irradiationParticle physics
The invention discloses a light and X-ray photoelectron energy spectroscopy synchronous analyzing and testing device. The device comprises an X-ray source arranged in a vacuum chamber, an electron transmission lens, an electron-energy analyzer and a detector, and the device further comprises an externally applied light source which comprises a light source probe, a light source generator and a light source controller; the light source generator is arranged outside the vacuum chamber and connected with the light source probe and the light source controller, light sent by the light source probe irradiates the surface of a sample, and the light source controller is arranged outside the vacuum chamber. According to the light and X-ray photoelectron energy spectroscopy synchronous analyzing and testing device, the externally applied light source is additionally arranged on the basis of an existing X-ray photoelectron energy spectroscopy technology, the situation that the externally applied light source and X-rays synchronously irradiate the surface of a material for physical property analysis is achieved, the application range of the X-ray photoelectron energy spectroscopy characterization analysis technology is extended, and therefore the physical property of the interior of the material can be accurately researched.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optoacoustic and surface photoroltaic dectecting method by surface electron-phonon interaction
InactiveCN1588001AAnalysis by material excitationColor/spectral properties measurementsElectrical conductorSemiconductor materials
The invention uses energy complementary relation of surface acoustooptic effect of conductor and semiconductor material and surface photovoltaic effect, combines results of optical acoustic spectrum and surface photovoltage spectrum, supplies a optical acoustic and photovoltaic detecting method of surface electron-phonon of conductor and semiconductor material. Using measuring method, can directly discuss; interaction of electron-phonon on surface and interface of conductor and semiconductor, and effective effective channel of radiationless de excitation course happened on surface and interface. The invention has properties of noncontiguous, nonpreprocessing, quick testing and high sensitivity, whose sensitivity can reach photovoltage spectrum multiply to the power. Atoms / cu cm which is usually higher than some standard energy spectrum or spectrum such as multiply PS or Auger electron energy spectrum several order of magnitude. The apparatus is simple and convenient, whose operation can be under room temperature and acoustooptic signal created by exciton in radiationless de excitation course can be observed, mostly important, it can supply information of electron-phonon on material surface and interface.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis system for surface analysis and method therefor
ActiveUS20080142707A1Prevent surfaceThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersX-rayIrradiation
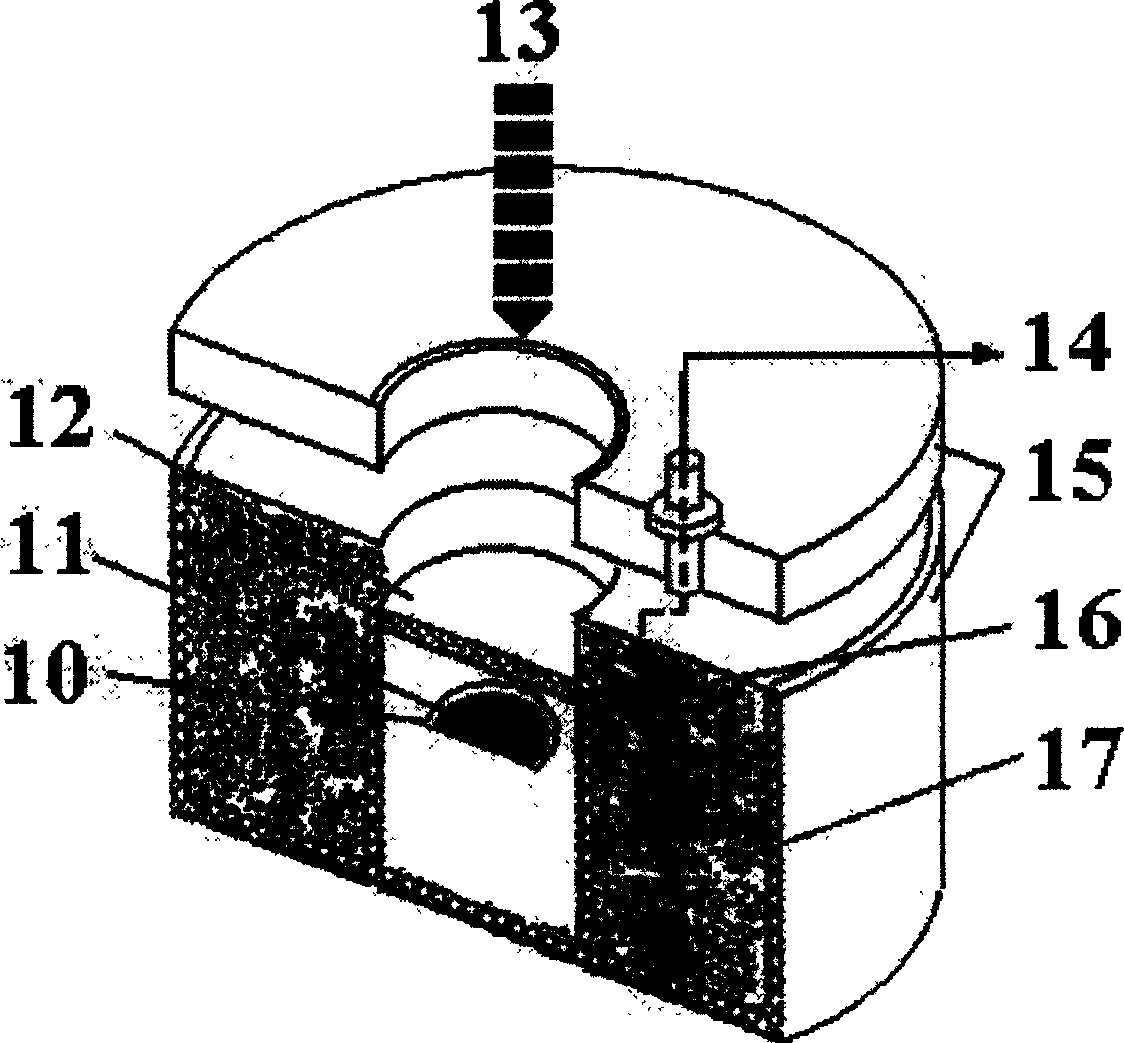
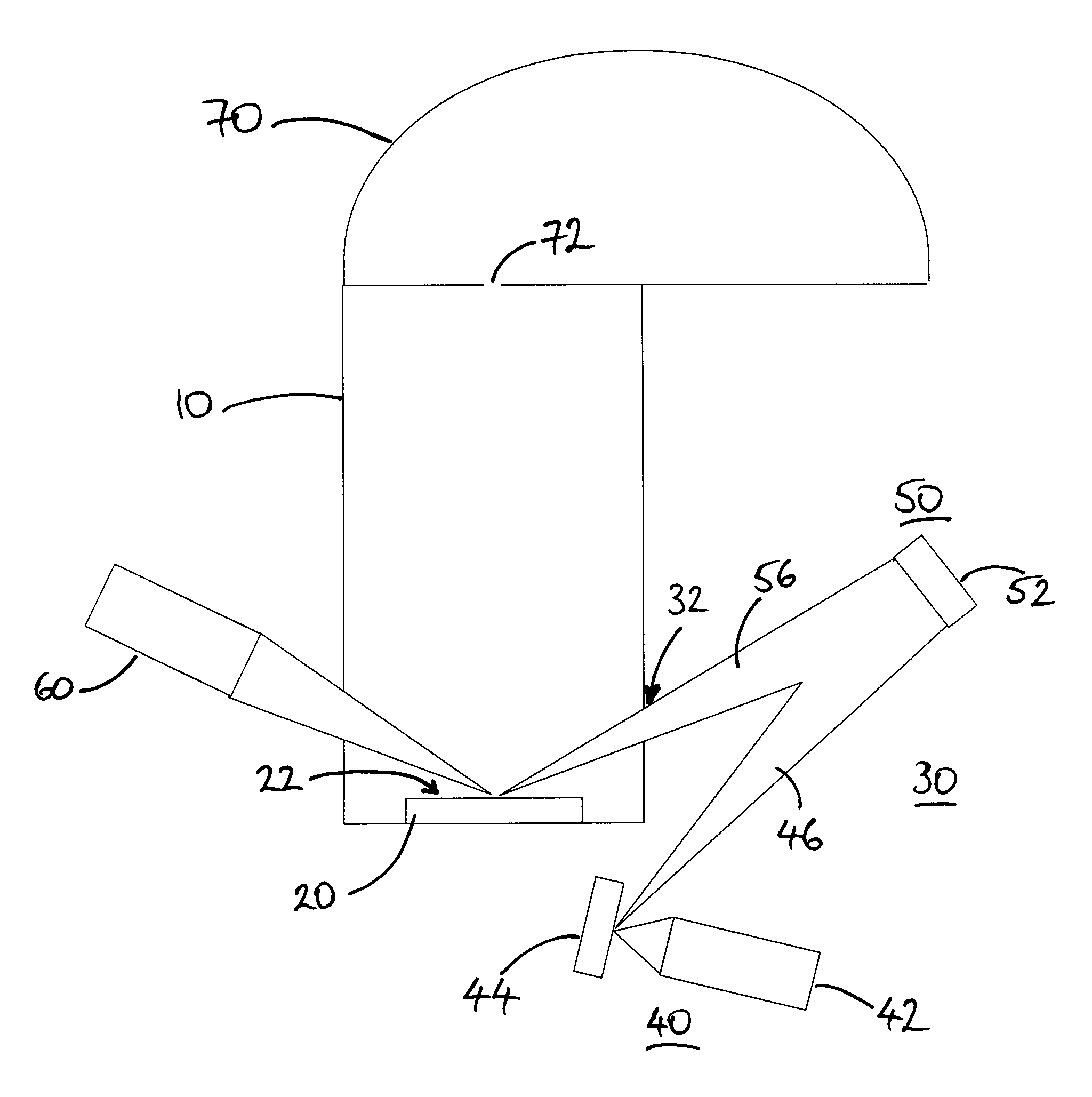
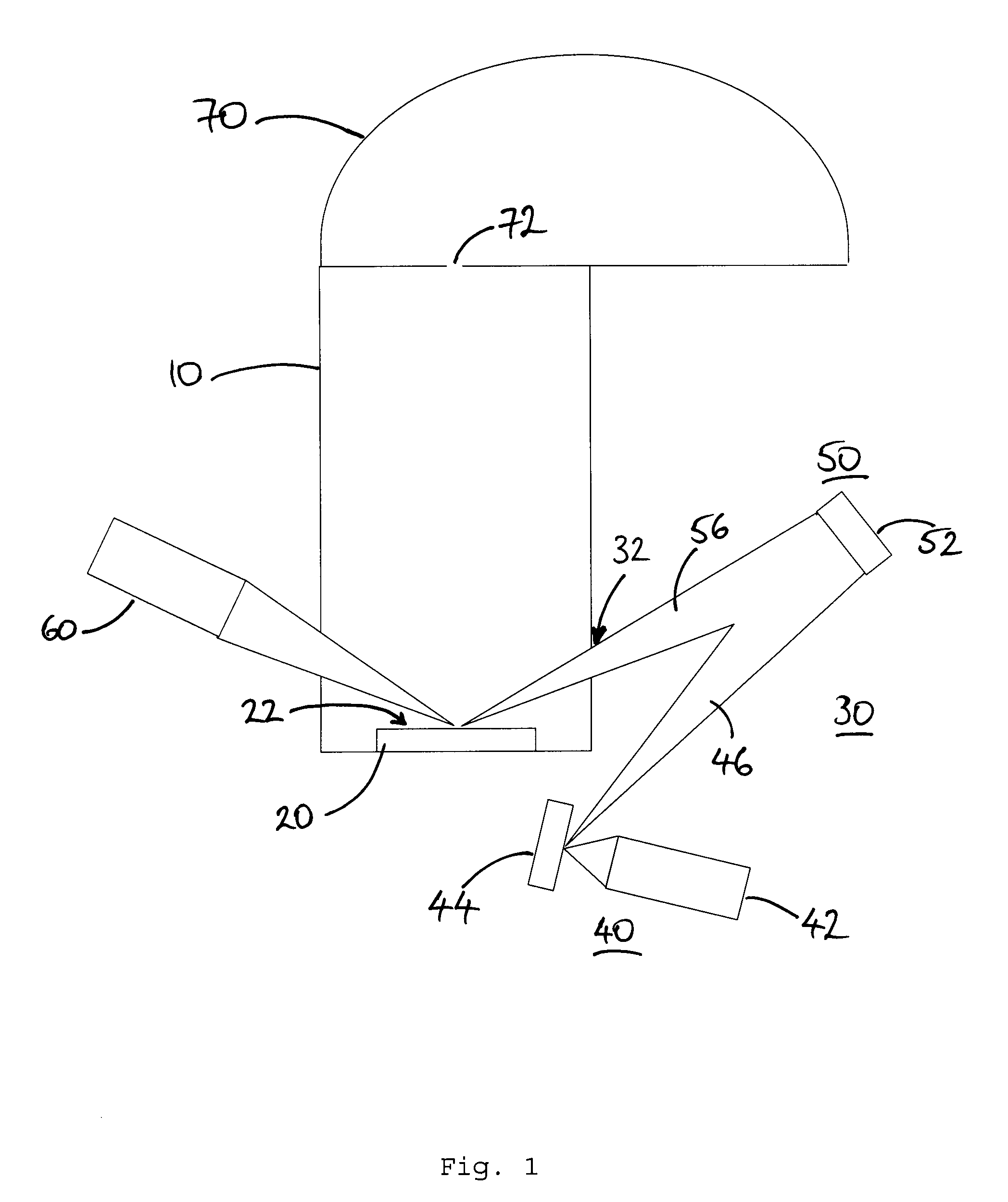
An X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis system for analysing an insulating sample 20, and a method of XPS analysis. The system comprises an X-ray generating means 30 having an exit opening 32 and being arranged to generate primary X-rays 46,56 which pass out of the exit opening in a sample direction towards a sample surface 22 for irradiation thereof. It has been found that the X-ray generating means in use additionally generates unwanted electrons 258 which may pass out of the exit opening substantially in the sample direction and cause undesirable sample charging effects. The system further comprises an electron deflection field generating means 380,480,580 arranged to generate a deflection field upstream of the sample surface. The deflection field is configured to deflect the unwanted electrons away from the sample direction, such that the unwanted electrons are prevented from reaching the sample surface.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC INC
Metal-plated stainless steel material, and production method for metal-plated stainless steel material
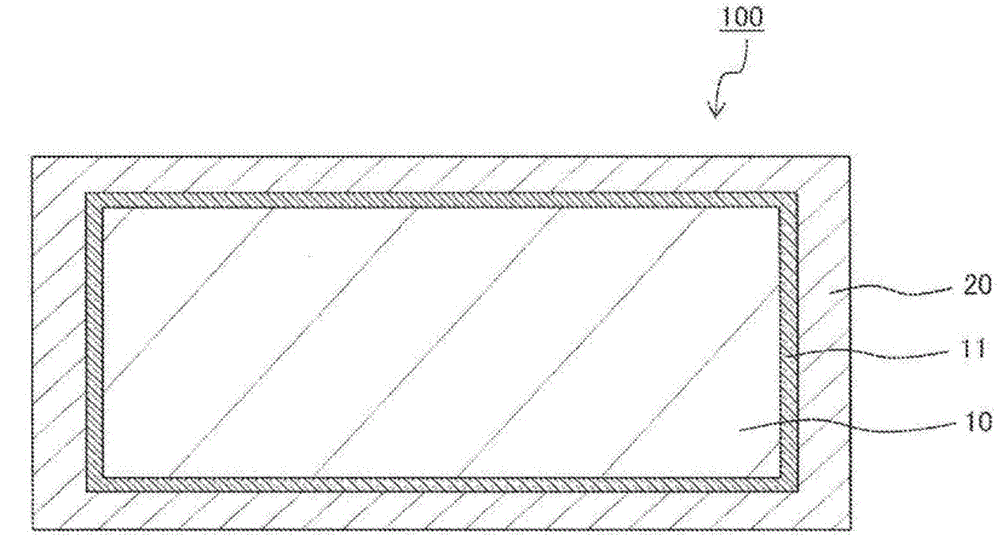
ActiveCN105556002AImprove corrosion resistanceImprove conductivityLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingSuperimposed coating processSS - Stainless steelAlloy
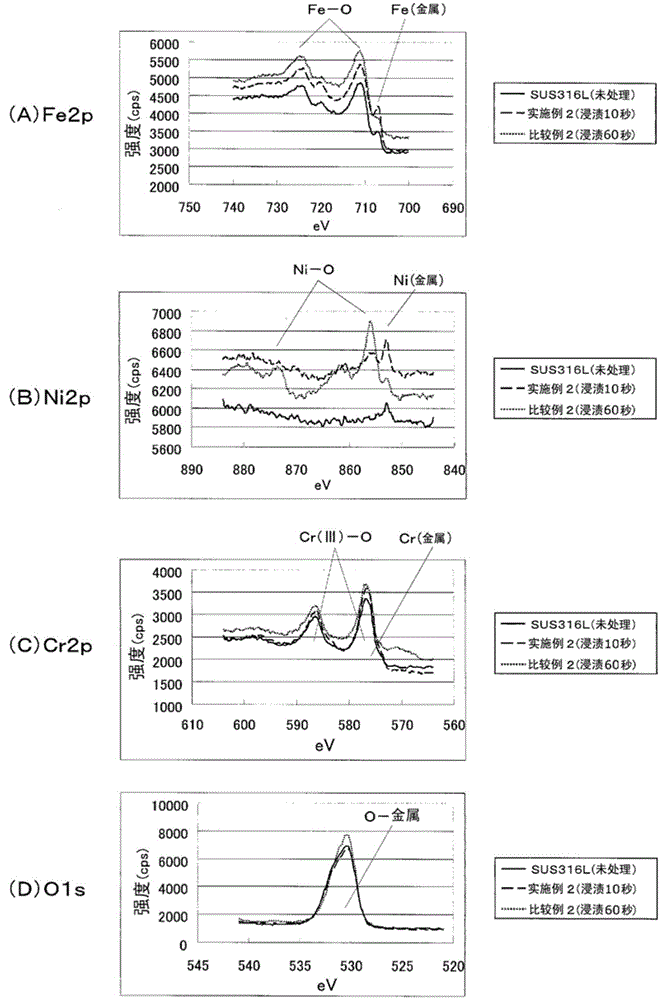
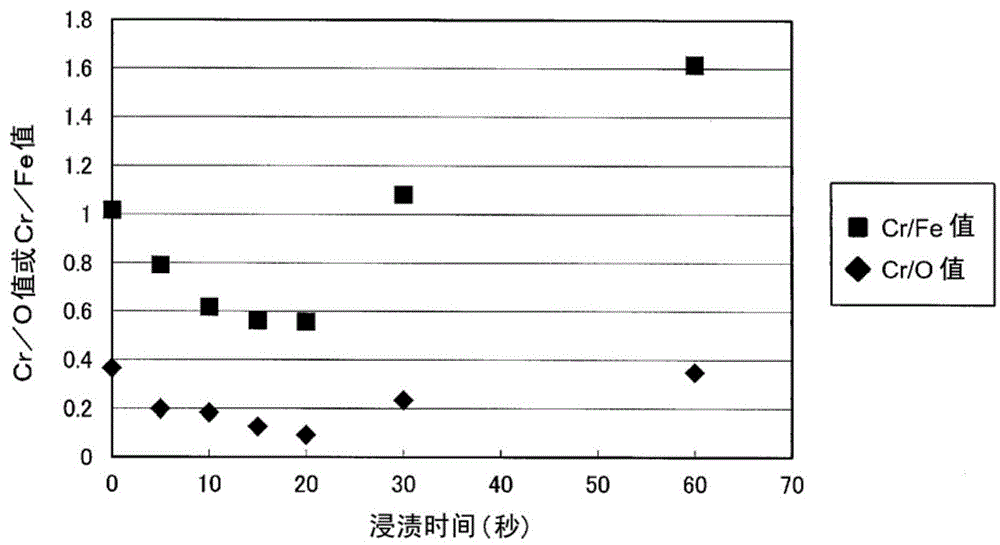
The invention provides a metal-plated stainless steel material and a production method for the metal-plated stainless steel material. The a metal-plated stainless steel material (100) is characterized by being provided with: a stainless steel plate (10) having, formed thereon, a passivation film (11) which has a Cr / O value in the range of 0.05-0.2, and a Cr / Fe value in the range of 0.5-0.8, said values being obtained by subjecting a surface of the passivation film (11) to Auger electron spectroscopy; and a metal-plating layer (20) formed upon the passivation film (11) on the stainless steel plate (10). The metal-plated stainless steel material (100) is further characterized in that the metal-plating layer (20) is configured from any one metal from among Ag, Pd, Pt, Rh, Ru, Cu, Sn, and Cr, or an alloy of these metals.
Owner:TOYO KOHAN CO LTD
Three-channel runaway electron energy spectrum measuring device under nanosecond pulse discharge
ActiveCN106597520AGood for studying uniformityRestricted areaX-ray spectral distribution measurementTime domainCoaxial cable
The invention relates to a three-channel runaway electron energy spectrum measuring device under nanosecond pulse discharge, comprising: a nanosecond pulse power supply, a discharge chamber, a runaway electron beam collector and an oscilloscope which are successively connected, wherein the runaway electron beam collector comprises three or more same coaxial collectors each having a signal output end and each being connected to the oscilloscope via a coaxial cable, the output end of the nanosecond pulse power supply is connected to the oscilloscope via a voltage divider. The three-channel runaway electron energy spectrum measuring device can measure the runaway electrons generated by discharging in different regions so as to analyze the time-domain distribution and the energy spectrum distribution of the runaway electrons in space, and can be widely applied to the theoretical analysis and application research of nanosecond pulse discharge.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Metal oxide thin film, method of producing same, and coating solution for forming metal oxide thin film used in said method
ActiveUS20160118253A1Increase the amount addedLow production costTransistorConductive materialBinding energyNitrogen
A metal oxide thin film according to the present invention has a peak which is attributed to 1s electrons of nitrogen in a binding energy range of 402 eV to 405 eV in an XPS spectrum obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, in which peak areas, which are obtained by separation of peaks having a peak energy of a metal-oxygen bond attributed to 1s electrons of oxygen, satisfy the following expression.0.9<D / E (1)(D represents a peak area of a component having a peak position in a binding energy range of 529 eV or higher and lower than 531 eV, and E represents a peak area of a component having a peak position in a binding energy range of 531 eV to 532 eV)
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Preparation method of Pd-PdH0. 706-PdO-NiOxHy/C core-shell electrocatalyst
InactiveCN111430732ASimple preparation processImprove production efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method of a Pd-PdH0. 706-PdO-NiOxHy / C core-shell electrocatalyst. The preparation method is a solvothermal method, and comprises the following steps of under an alkaline condition, taking tert-butyl alcohol as a solvent, heating by using a drying oven at 180 DEG C to prepare the Pd-PdH0. 706-coated PdO-NiOxHy / C core-shell composite catalyst; representing the morphology, structure, chemical state and composition of the catalyst by a transmission electron microscope, the X-ray diffraction, the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and the inductively coupled plasma emission spectroscopy; at 25 DEG C, and testing the electrocatalytic activity of the electrocatalyst on the methanol and ethanol under the alkaline condition. Results show that the activity of theobtained catalyst is the highest when the dosage of the 1M KOH solution is 10ml, and the peak current densities of the catalyst for catalyzing the electrochemical oxidation of methanol and ethanol respectively reach 592.1 mA mg <-1> Pd and 1504.0 mA mg <-1> Pd.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com