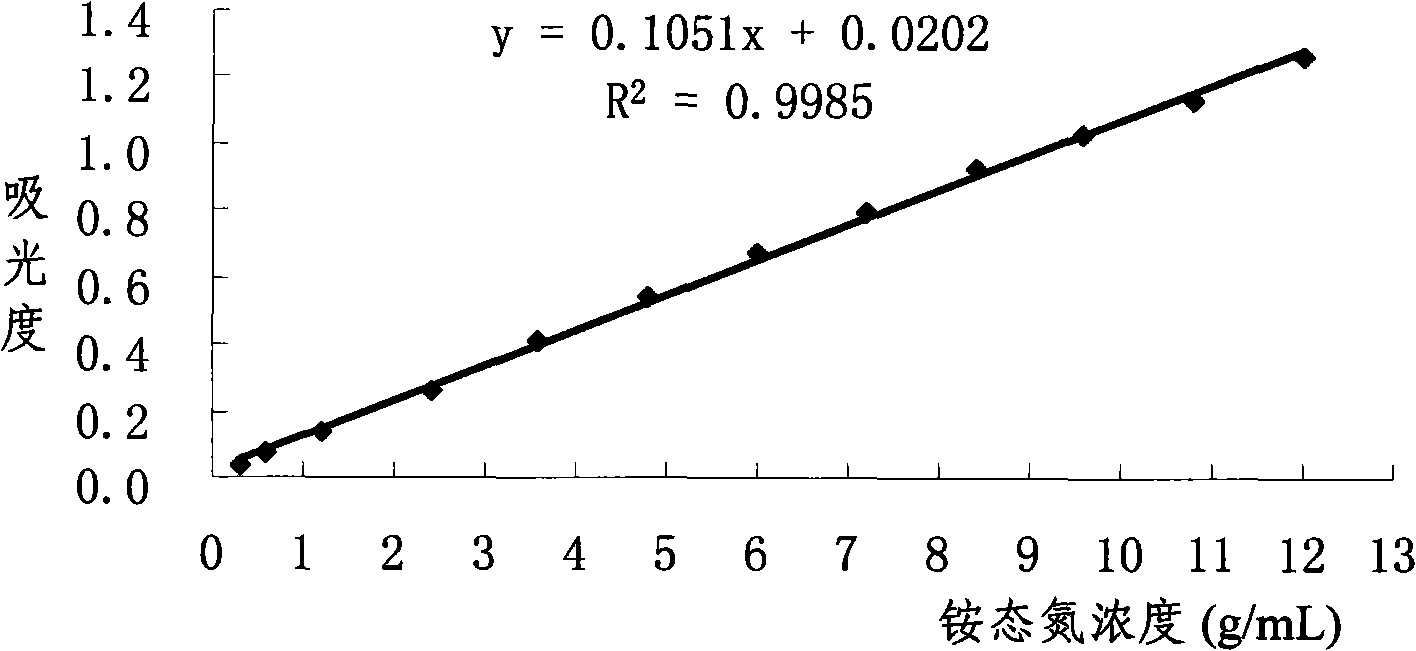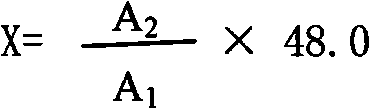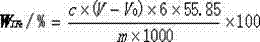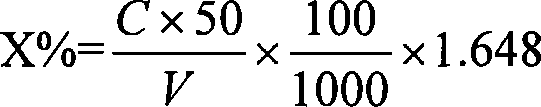Patents
Literature
95 results about "Mercury(II) chloride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mercury(II) chloride or mercuric chloride (historically "corrosive sublimate") is the chemical compound of mercury and chlorine with the formula HgCl₂. It is white crystalline solid and is a laboratory reagent and a molecular compound that is very toxic to humans. Once used as a treatment for syphilis, it is no longer used for medicinal purposes because of mercury toxicity and the availability of superior treatments.
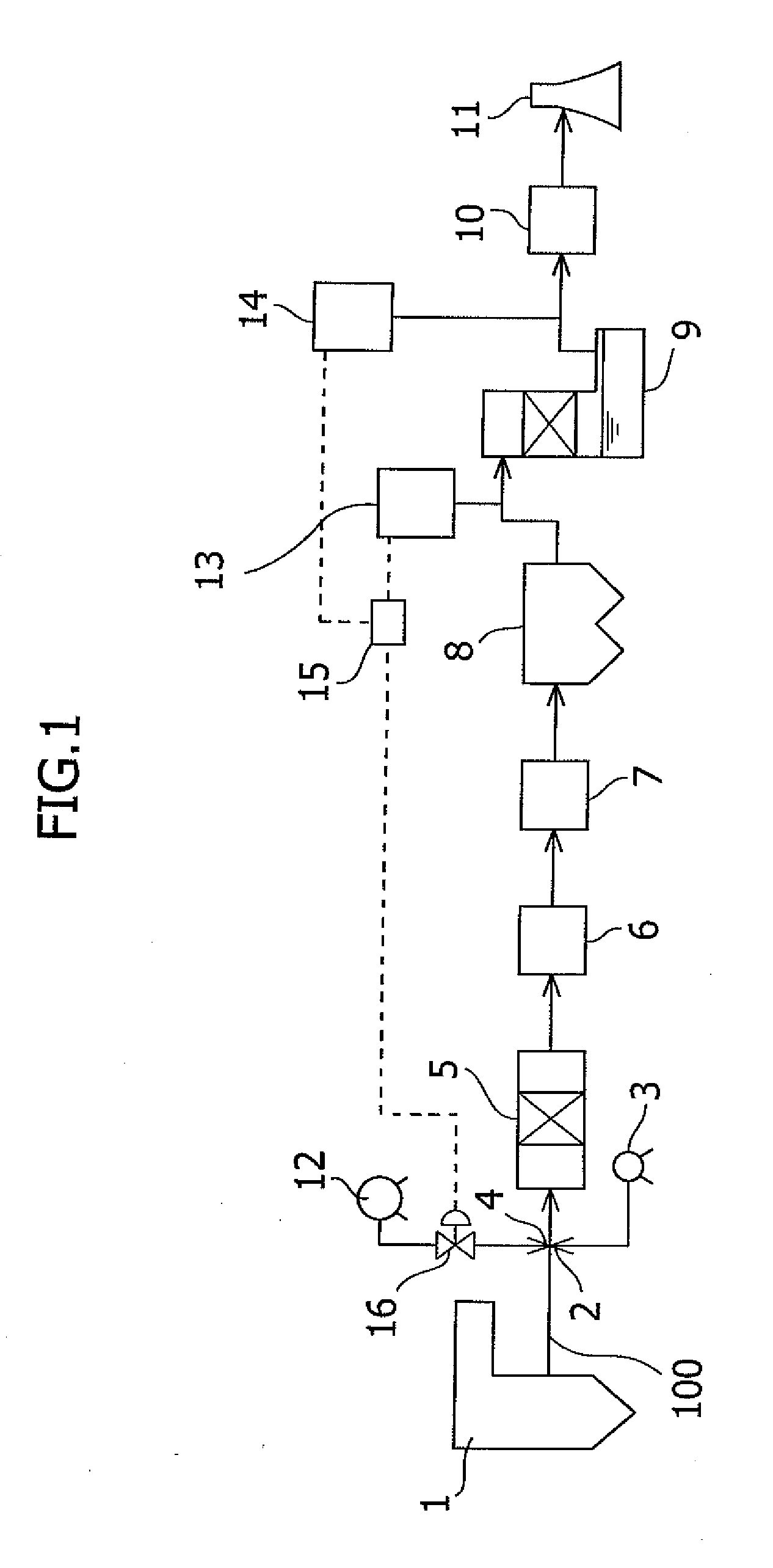
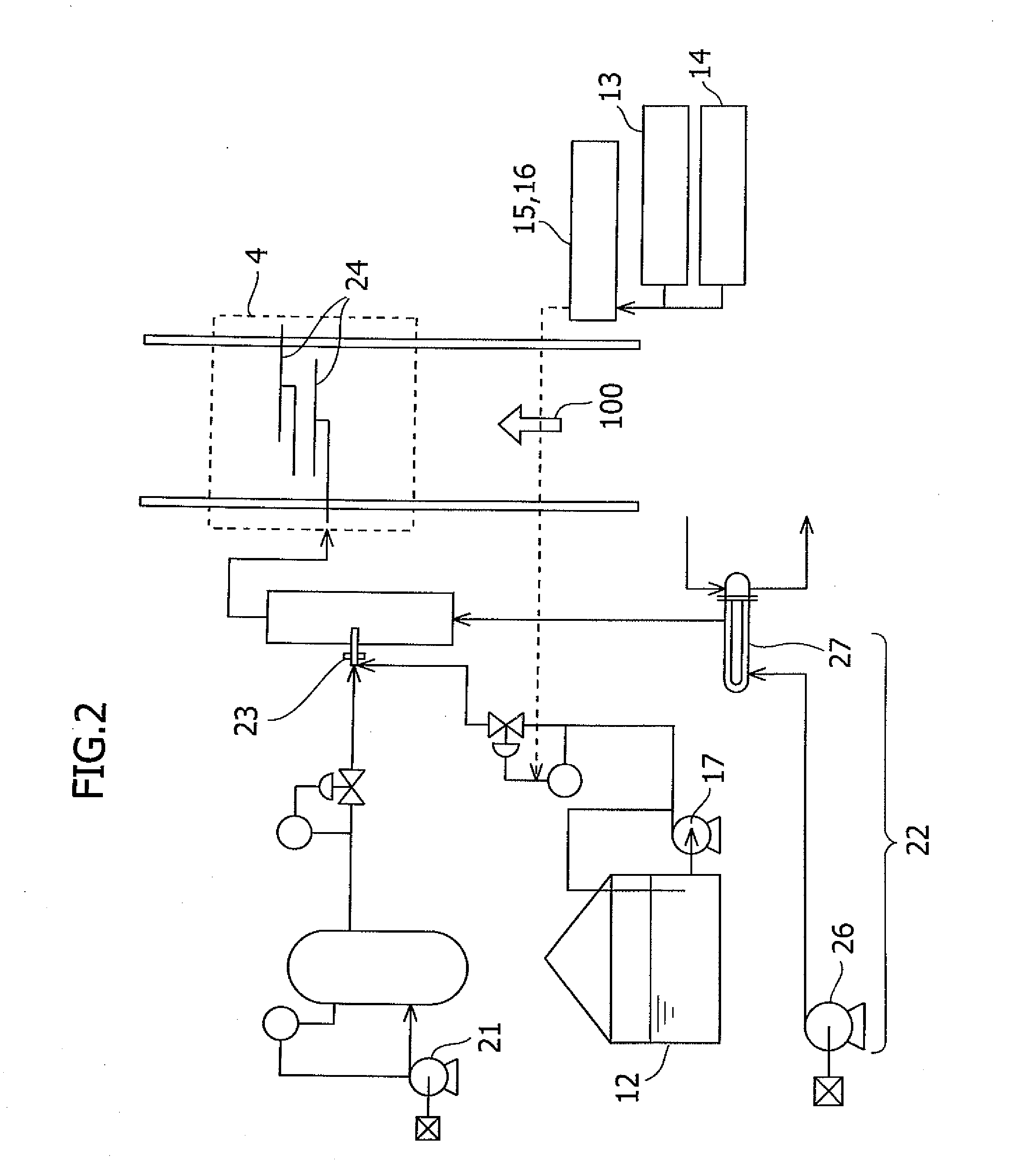
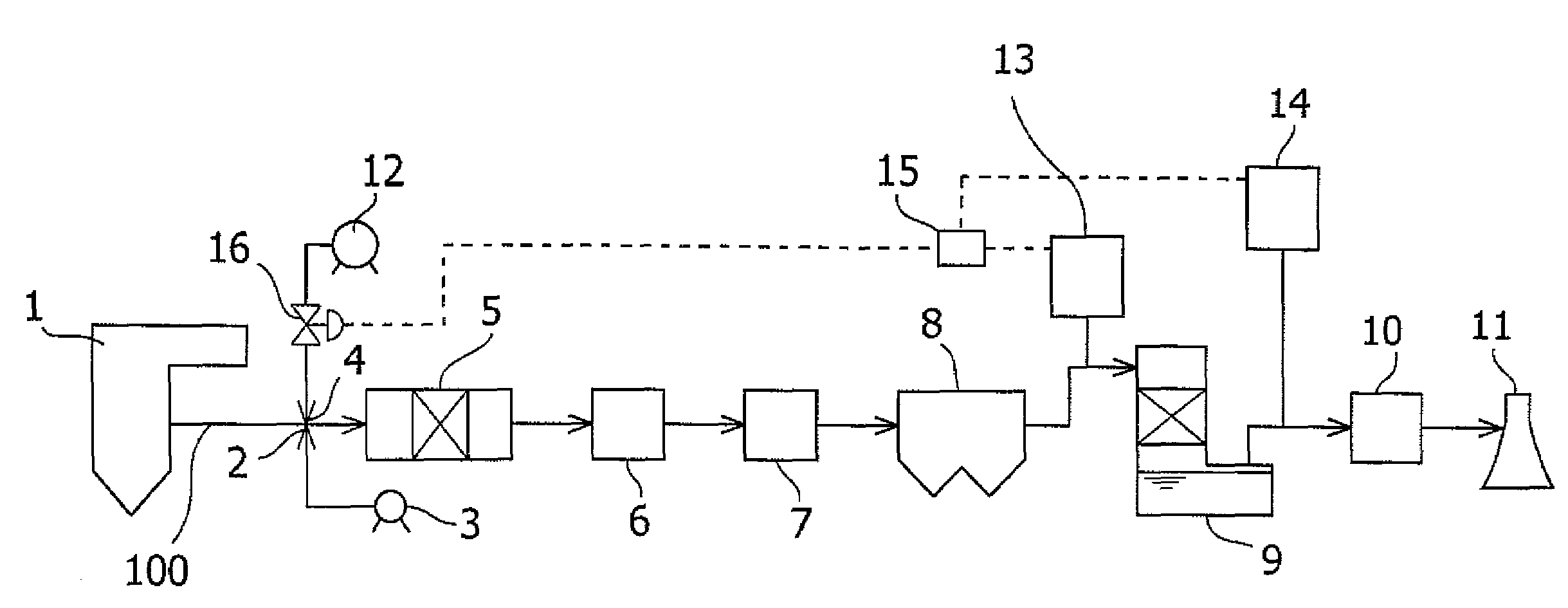
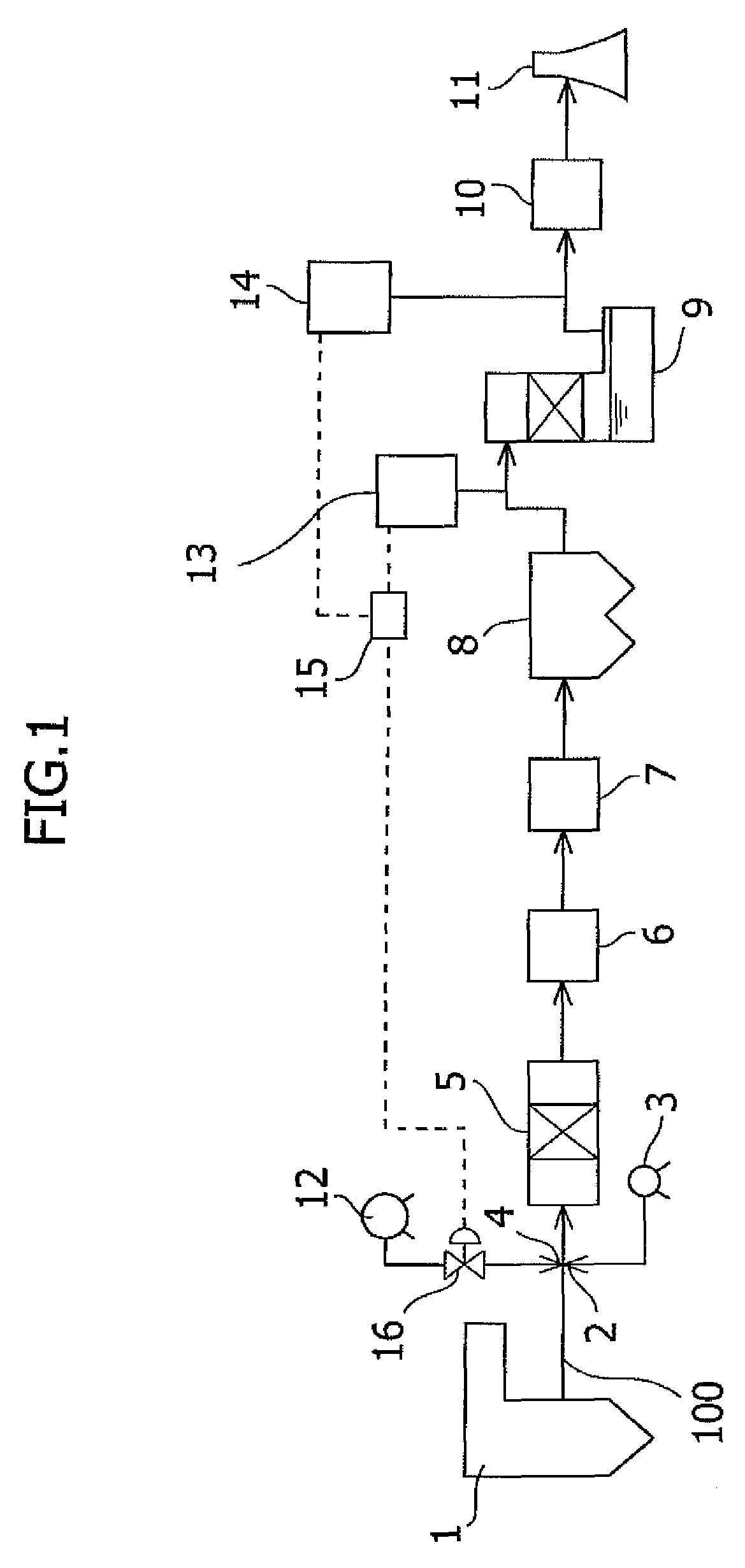
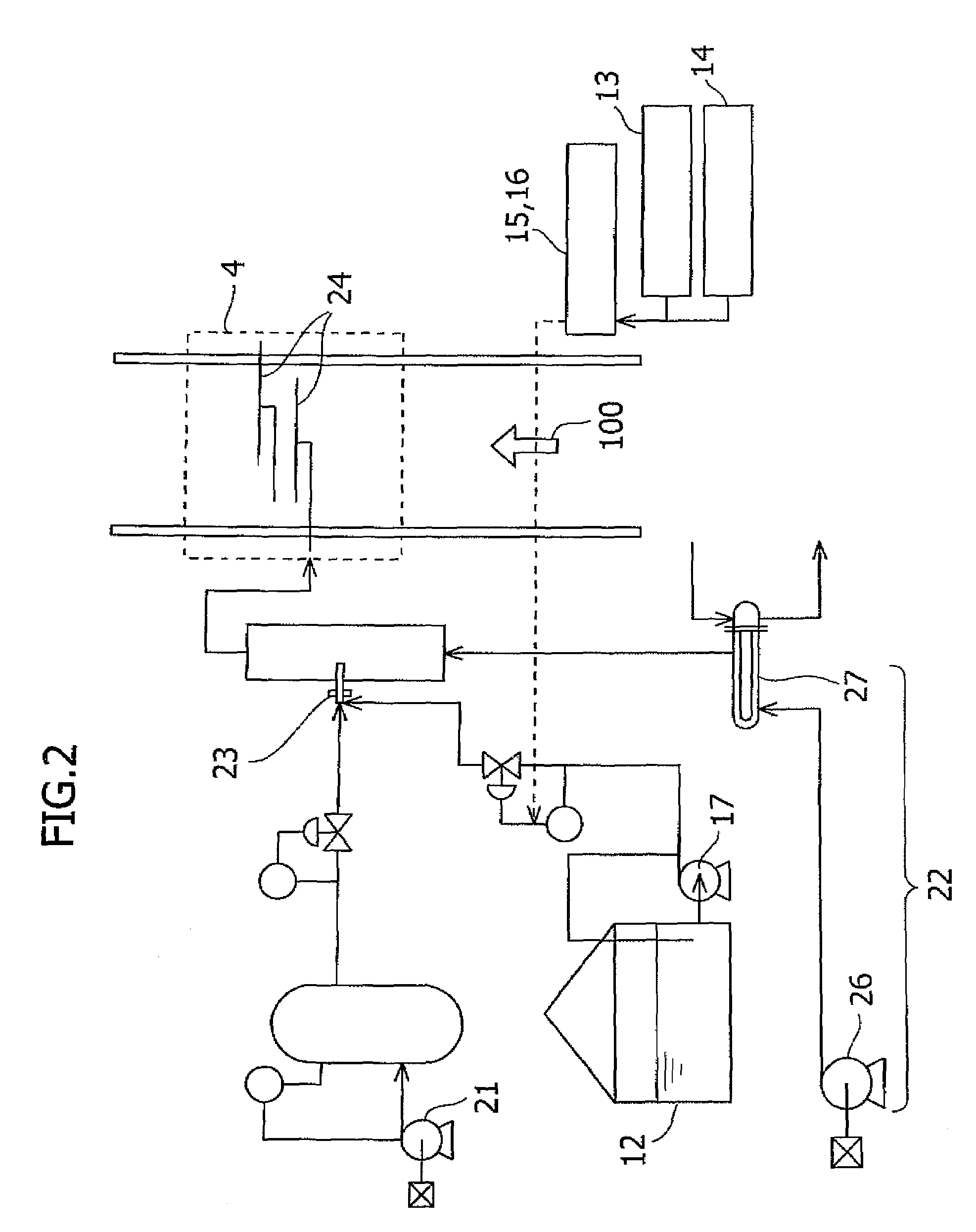
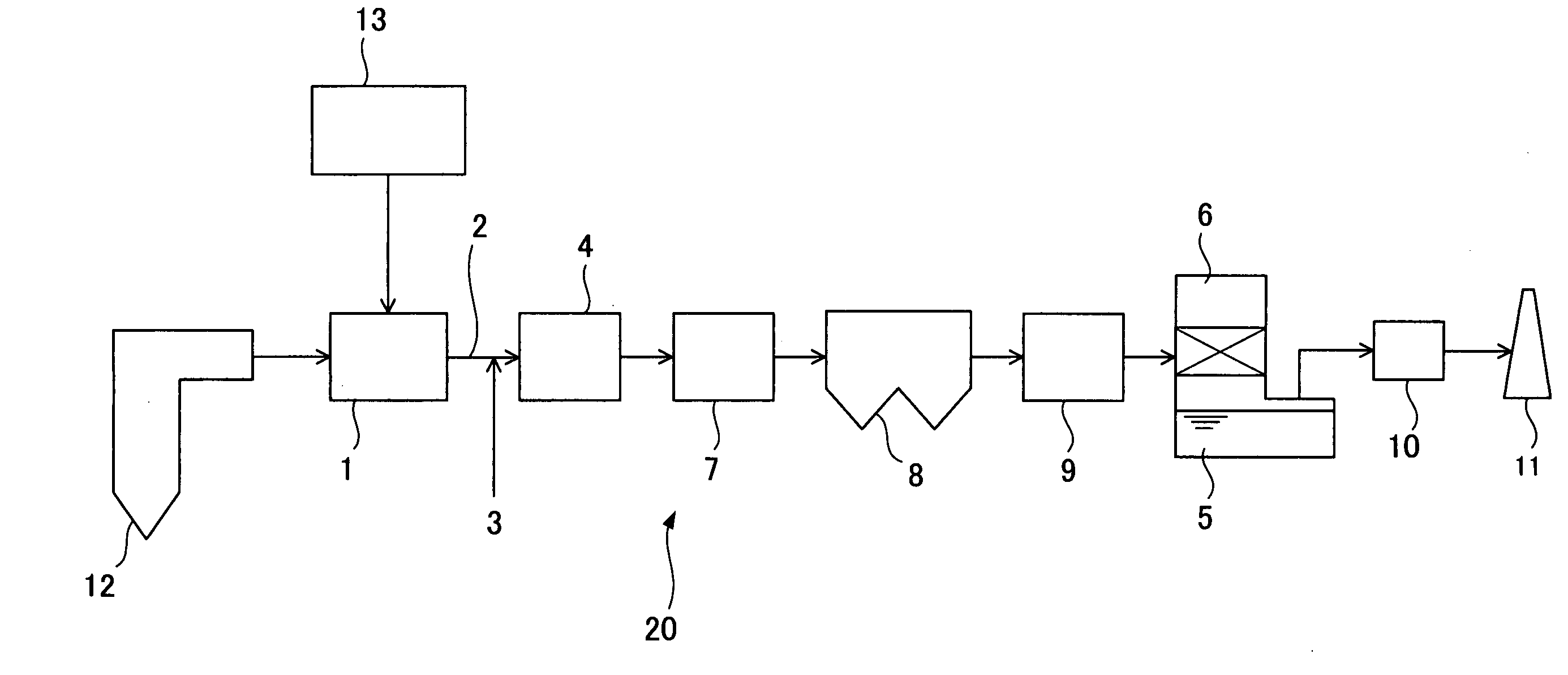
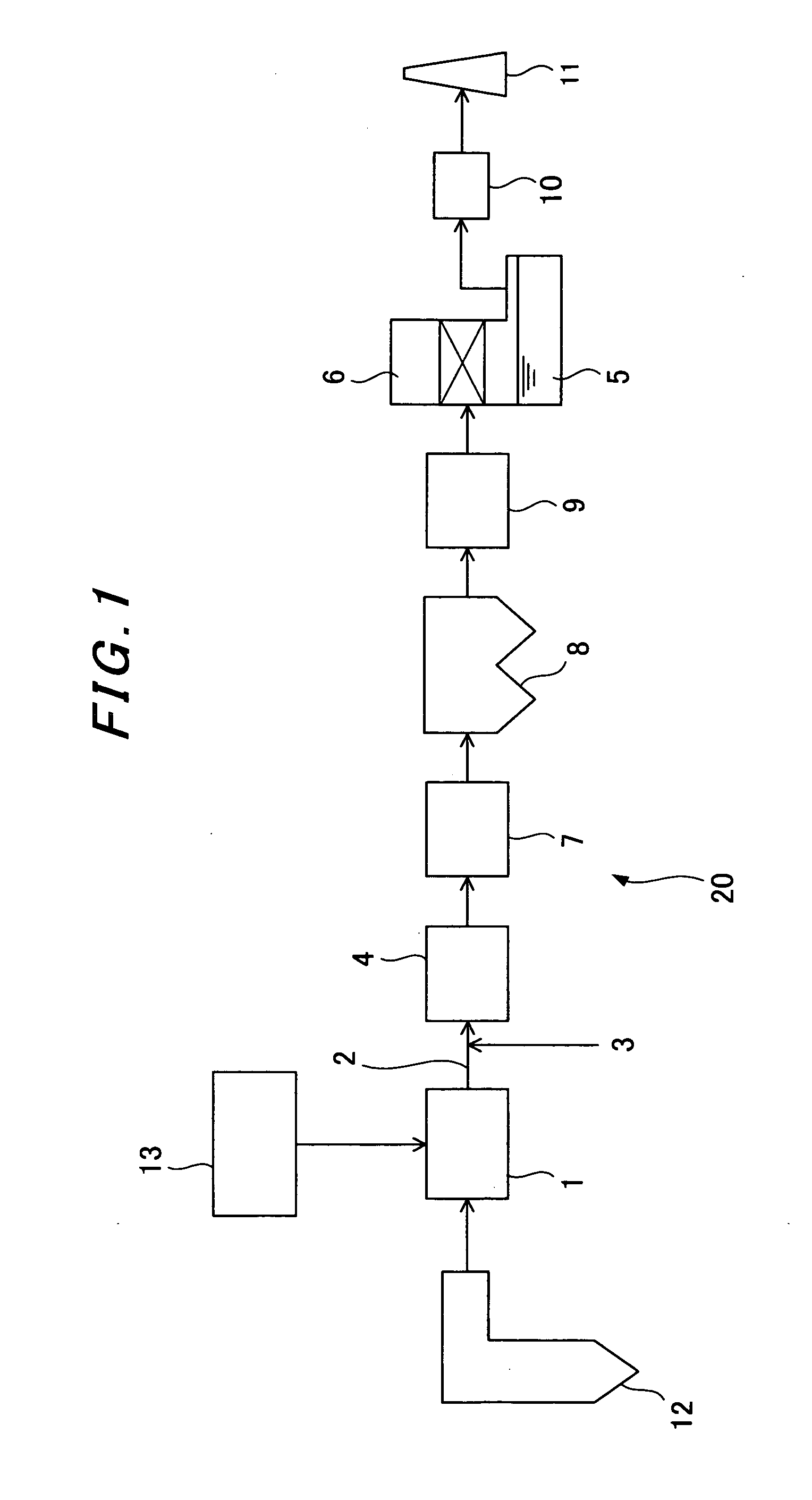
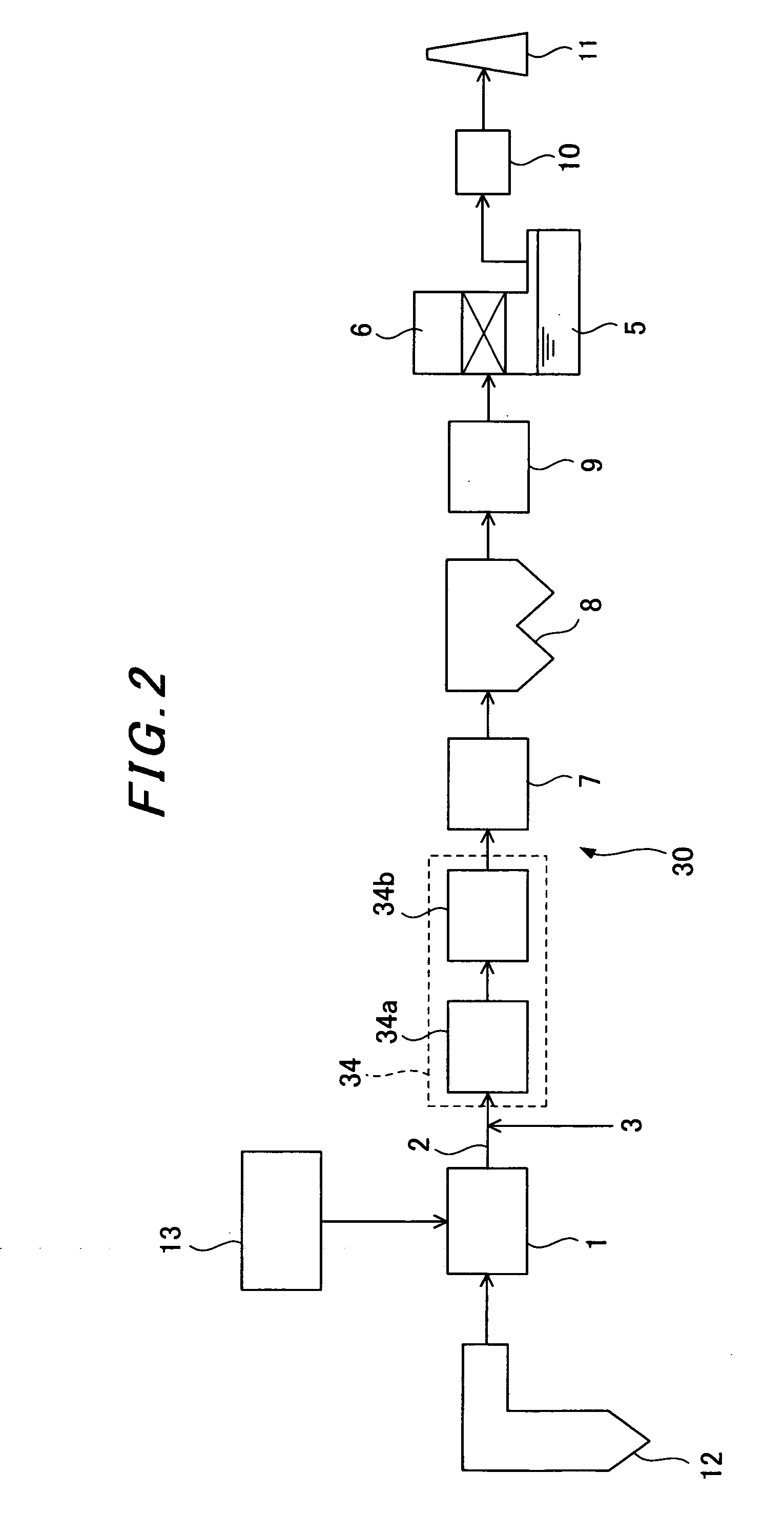
Sorbents for Removal of Mercury from Flue Gas
InactiveUS20070092418A1Enabling useLow costGas treatmentSolid waste managementParticulatesAlkaline earth metal
Metal sulfides having a micro-porous structure are disclosed for use as sorbents for removal of mercury from flue gas. Systems are disclosed for making and using micro-porous particulates at least partially composed of alkaline earth metal and transition metal sulfides as sorbents. Calcium sulfide micro-porous powders derived from the high temperature reduction of calcium sulfate and calcium sulfite are disclosed to be reactive substrates for a group of sorbents for adsorption of mercury from the myriad of coal combustion flue gases produced by the utilities industry, as well as from natural gas and gaseous and liquid hydrocarbons. Controlled addition of one or more of polyvalent metal ions, chloride ions, polysulfide ions, and sulfur to the micro-porous calcium sulfide substrate produces the sorbent. The sorbents are useful for cost-effectively adsorbing elemental mercury and oxidized mercury species such as mercuric chloride from flue gases, including those containing acid gases (e.g., SO.sub.2, NO and NO.sub.2, and HCI), over a wide range of temperatures.
Owner:CHEM PROD CORP
Method for removing mercury in exhaust gas
InactiveUS7521032B2Amount of catalyst can be reducedIncreased durabilityCombination devicesGas treatmentDecompositionExhaust fumes
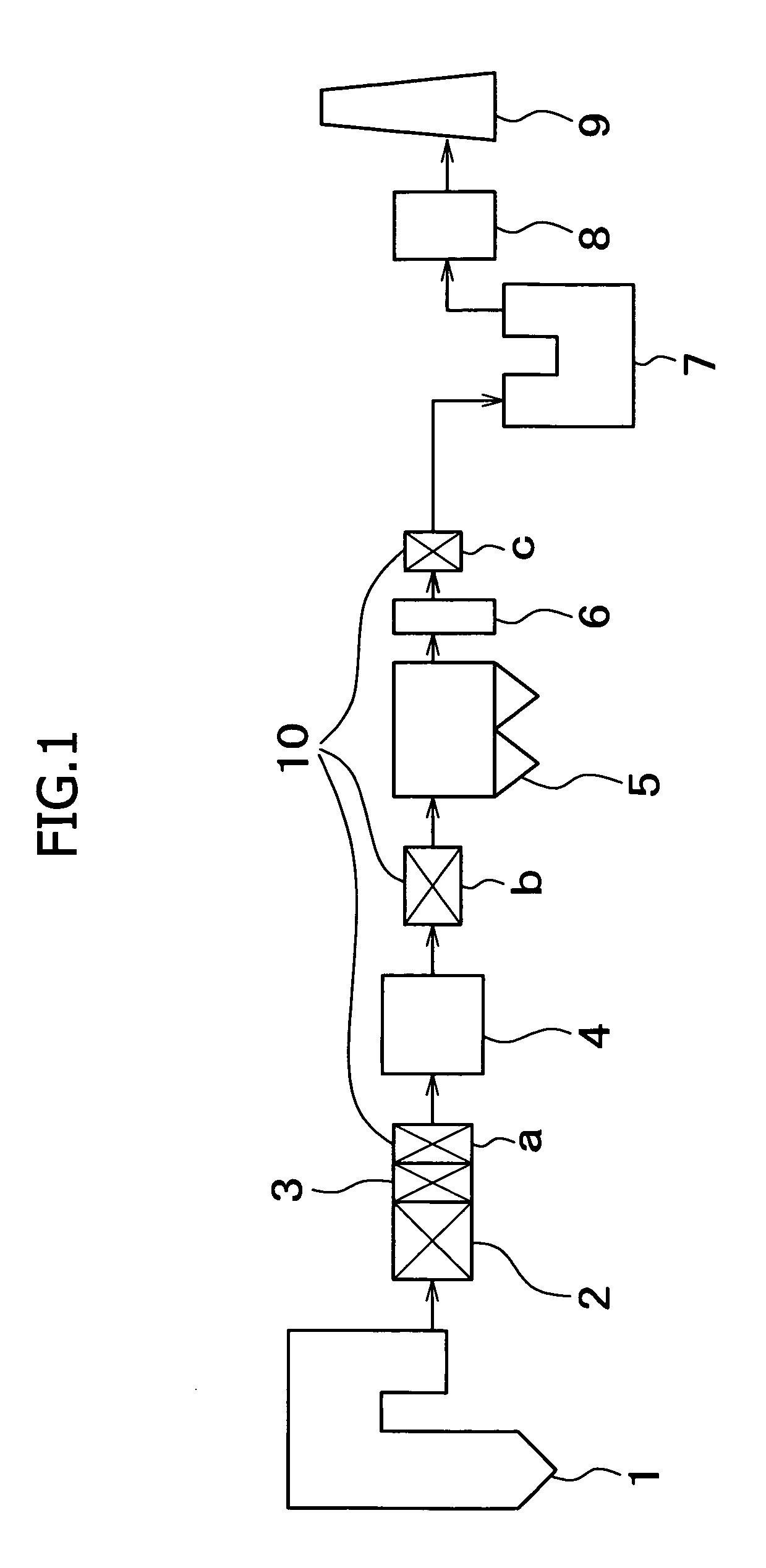
The present invention provides a system for removing mercury in exhaust gas, in which mercury is removed from exhaust gas of a boiler, characterized in that between a denitrification apparatus and a wet type desulfurization apparatus, an NH3 decomposition catalyst and a mercury oxidation catalyst are provided, and mercury having been oxidized into mercury chloride is removed by the wet type desulfurization apparatus. Also, it provides a method for removing mercury in exhaust gas, characterized in that the mercury removing method includes an NH3 decomposition process and a mercury oxidation process, which are provided between the denitrification process and a wet desulfurization process, and mercury having been oxidized into mercury chloride is removed in the wet desulfurization process.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HITACHIPOWER SYST LTD
Mercury removal system and mercury removal process
ActiveUS20070202020A1Improve reliabilityReduce operating costsCombination devicesNitrogen compoundsFlueSulfur oxide
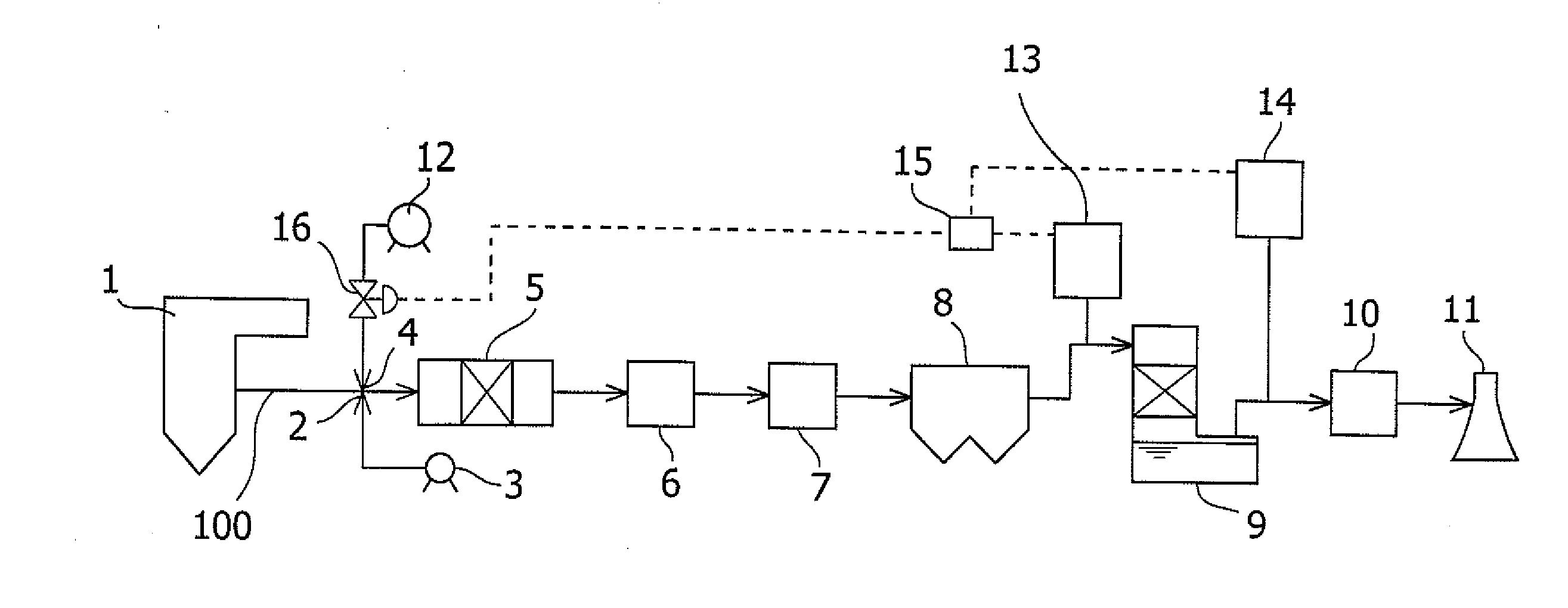
Provided is a system for removing mercury from a mercury-containing exhaust gas, which contains a mercury chlorinating agent feed unit for feeding a mercury chlorinating agent to an flue exhaust gas containing nitrogen oxide, sulfur oxide and mercury, a reductive denitration unit for reducing the nitrogen oxide, and a desulfurization unit for removing the sulfur oxide, characterized in that the mercury chlorinating agent feed unit further comprises a heating unit for heating a non-gaseous agent for mercury chlorination which is in the non-gaseous form under normal temperature and normal pressure or a gasifying unit for obtaining a gaseous agent for mercury chlorination from the non-gaseous agent for mercury chlorination. The present invention makes it possible to provide a mercury removal process and system which have high reliability and can be operated at a low cost.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
Mercury removal system and mercury removal process
ActiveUS7544338B2Improve reliabilityReduce operating costsCombination devicesNitrogen compoundsFlueSulfur oxide
Provided is a system for removing mercury from a mercury-containing exhaust gas, which contains a mercury chlorinating agent feed unit for feeding a mercury chlorinating agent to an flue exhaust gas containing nitrogen oxide, sulfur oxide and mercury, a reductive denitration unit for reducing the nitrogen oxide, and a desulfurization unit for removing the sulfur oxide, characterized in that the mercury chlorinating agent feed unit further comprises a heating unit for heating a non-gaseous agent for mercury chlorination which is in the non-gaseous form under normal temperature and normal pressure or a gasifying unit for obtaining a gaseous agent for mercury chlorination from the non-gaseous agent for mercury chlorination. The present invention makes it possible to provide a mercury removal process and system which have high reliability and can be operated at a low cost.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
Composite metal chloride catalyst and its production process
ActiveCN1814345AReduce dosageThe dosage can be greatly reduced when theCatalyst activation/preparationMetal chlorideActivated carbon
This invention is a complex metal chloride catalyst. Its carrier is active carbon with void ratio>=0.56cm3 / g, specific surface area>= 1000m2 / g, mechanical strength>=90%, and it is made by absorbing mercuric chloride and zinc chloride under condition of 92-96 degree centigrade. Computing as weight percentage, the mercuric chloride is 2-8%, zinc chloride 1-15%. Its advantage is that 1. Mercuric chloride content is low, but activity and stability is boosted 5-20% and 10-20% comparing to existing mercuric chloride catalyst. 2. Mercuric chloride using level can be reduced according to the boost of activity and stability and the catalyst activity is not reduced, and catalyst producing cost is reduced, mercury resource consumption is reduced. Otherwise, catalyst useful life can be prolonged, its dosage can be reduced, and catalyst replacing time is economized, so vinyl chloride producing cost is reduced. 3. Catalyst consumption is few, mercury drain is few. So the damage of drained mercury to environment and product is lightened.
Owner:那风换 +1
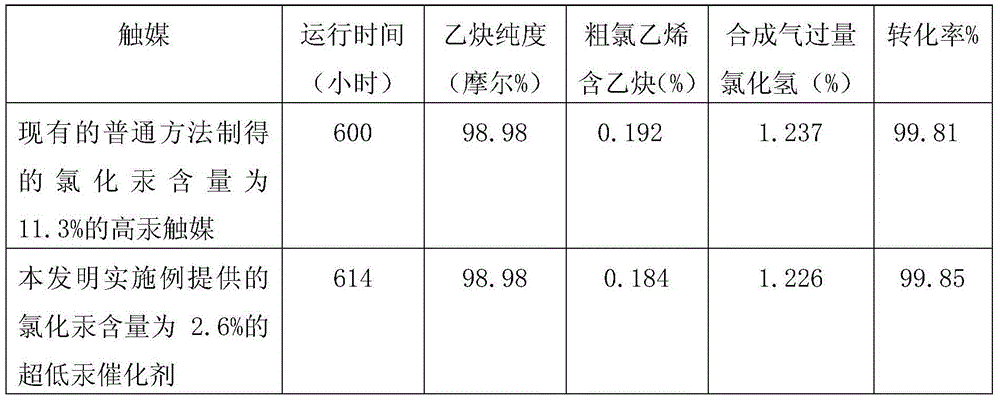
Ultralow-mercury catalyst and production process thereof
InactiveCN103551139AReduce manufacturing costLow in Mercury ChlorideCatalyst carriersPreparation by halogen halide additionVoid ratioPotassium
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG KECHUANG ADDITIVES CO LTD
Gold-containing catalyst for preparing vinyl chloride by using acetylene method as well as preparation method and application of catalyst
InactiveCN102327777ANo pollution in the processThere will be no deactivationMolecular sieve catalystsPreparation by halogen halide additionMicro structureEthyl Chloride
The invention discloses a gold-containing catalyst for preparing vinyl chloride by using an acetylene method as well as a preparation method and application of the catalyst. The catalyst contains a gold element, a lanthanum element, a cobalt element, a co-catalytic metal element and a carrier with a porous micro-structure. The gold accounts for 0.3%-2% by mass of the catalyst; the gold element in the catalyst comes from gold chlorides or gold nitrates; the cobalt element comes from chlorides of the cobalt or cobalt nitrates; and the lanthanum element comes from lanthanum chlorides or lanthanum nitrates. The catalyst disclosed by the invention in use is free from inactivation phenomenon caused by sublimation of industrial catalyst mercury chloride, has no pollution to the environment, overcomes defects of high toxicity and high pollution of the conventional industrial catalyst mercury chloride, has the characteristics of simple preparation method, high conversion rate of the acetylene and selectivity of the vinyl chloride, long service life up to 1000 hours or more, high temperature resistance, and high intensity and is renewable, and the conversion rate of the acetylene and selectivity of the vinyl chloride approximate to or exceed the technical indexes of the mercury chloride catalyst.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV +1
Preparation method of low-mercury catalyst for preparing vinyl chloride
ActiveCN102151573ALow costHigh activityPreparation by halogen halide additionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsEnvironmental resistanceEvaporation
The invention provides a novel preparation method of a low-mercury catalyst for preparing vinyl chloride from acetylene. In the method, treated coal carbon is taken as a carrier, the vacuum impregnation method is used for loading a small amount of mercury chloride and other auxiliaries on the carrier, and rotary evaporation and other drying ways are performed to obtain the novel catalyst. Compared with a high-mercury catalyst and a precious metal catalyst which is researched and developed currently, the carrier coal carbon, and the auxiliaries related to the catalyst disclosed by the invention are lower in cost, the catalyst is safer and more environment-friendly, the adopted process is simple, and the production period is short. In the application of preparing vinyl chloride by hydrochlorinate of acetylene, the low-mercury catalyst represents excellent activity and selectivity and can be regarded as an excellent substitute for the current mainstream high-mercury catalyst.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Kit and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104181155AHigh acceptanceNon-traumaticMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorCervical lesionMetabolite
The invention discloses a kit for detecting sulfydryl metabolite in urine prompting the cervical lesion and a preparation method thereof. The kit comprises a reference agent, a testing agent and a color developing agent, wherein the reference agent is a mercuric chloride solution or a mercury sulfate solution, and the color developing agent is a phosphotungstic acid reagent; the kit is prepared in a sterility packaging manner. The remarkable increment of sulfydryl metabolite in female urine is proved to prompt the cervical lesion. The kit can detect the content of the sulfydryl metabolite at a preclinical phase and a clinical phase, the positive rate and accuracy for detecting the cervical cancer are high, the missed diagnosis can be avoided, a subject is prevented from being wounded and crossly infected, and instruments and equipment are not needed; the detection process is simple, the acceptance of the subject is high, the manpower and material resource can be greatly saved, workload of the examination personnel can be remarkably alleviated, the bottleneck that the screening number cannot reach the standard can be effectively broken through, and the kit is particularly suitable for surveying the cervical cancer in a wide range.
Owner:CHENGDU XUHUA BIOLOGICAL TECH
Mercury chloride catalyst regenerated by oxychlorination method
InactiveCN101288850AEliminate poisonEliminate carbon depositsPhysical/chemical process catalystsCyclic processAdditional values
The invention discloses a chlorine-oxidation method for regenerating mercuric chloride catalyst, comprising the steps as follows: (1) screening; (2) activation reaction: 1000kg of screened waste mercuric chloride catalyst which complies with the requirement of particle size (the content of mercuric chloride is 3.0-4.5%) is taken as benchmark, arranged in an activator and prepared as dipping solution in a material distribution container I. The dipping solution is pumped into the activator, dipped and activated for 30 minutes under the conditions of the temperature of 15-40 DEG C and 0.1MPa of normal pressure, arranged in the material distribution container I, and pumped into the activator after 1-3kg of chlorine is pumped into the dipping solution, so as to complete a dipping and circulation process; the dipping and circulation process is repeated till that the colour of the dipping solution turns from green to pale brownish yellow; the dipping solution is then arranged in the material distribution container I and taken as circulation motor liquor used for the next material distribution; (3) dipping and adsorbing; (4) drying and cooling. The method of the invention has the advantages of short process flow, lower energy consumption, higher recovery and utilization additional value and utilization ratio of effective component, lower production cost and being more beneficial to environmental protection.
Owner:WANSHAN HONGJING MERCURY
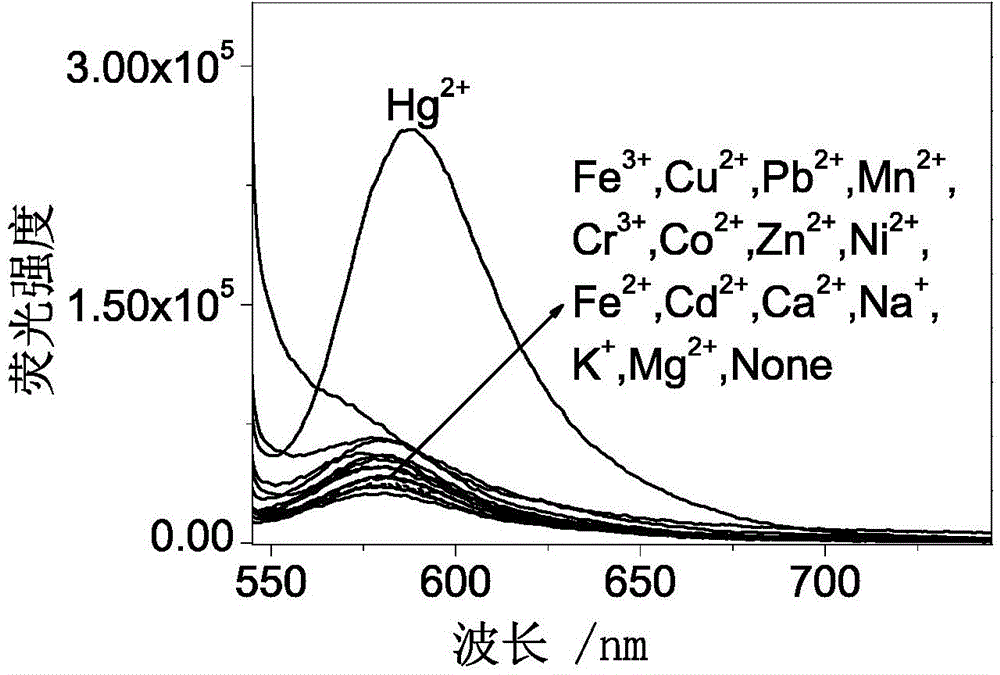
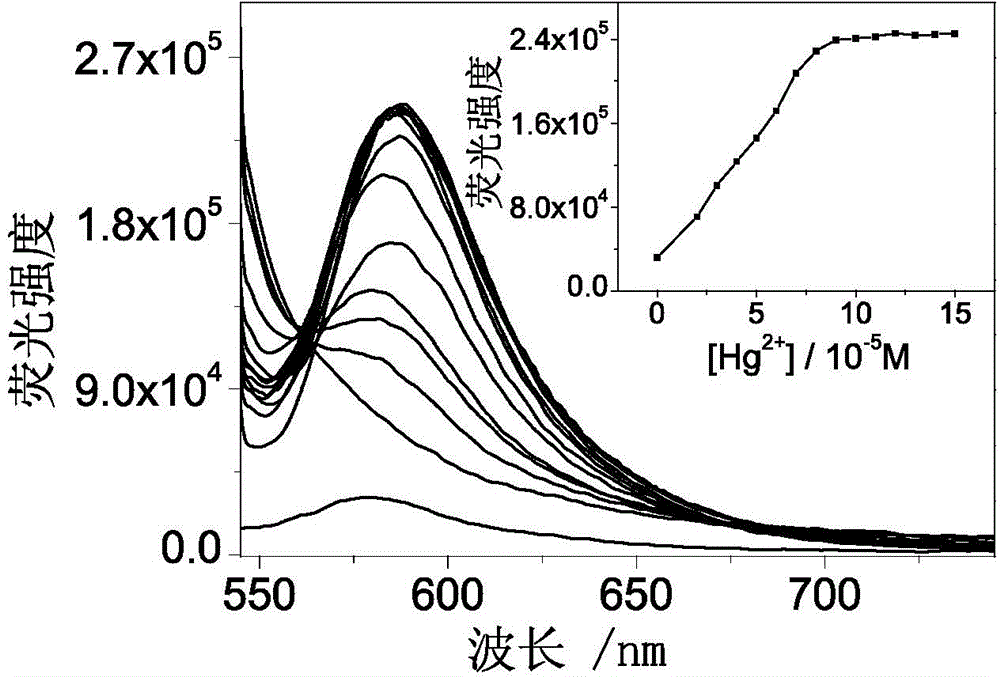
Fluorescent probe made of rhodamine B, diethylenetriamine and PITC (phenyl isothiocyanate) as well as preparation method and application thereof
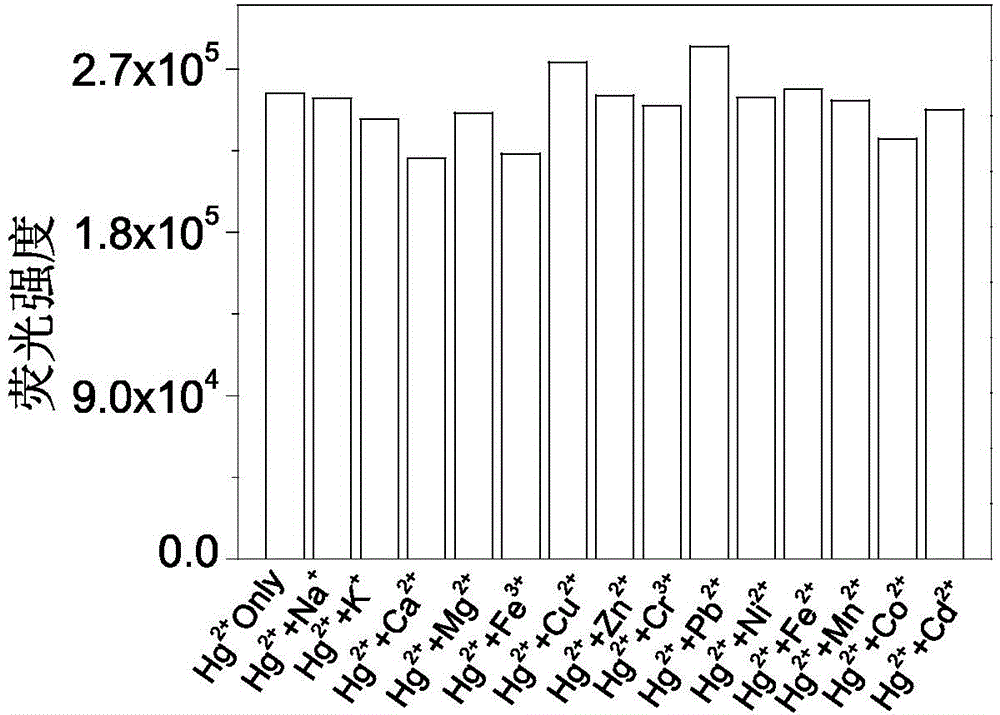
InactiveCN104098581AHigh selectivityHigh detection sensitivityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluoProbesMercuric ion
The invention discloses a fluorescent probe made of rhodamine B, diethylenetriamine and PITC (phenyl isothiocyanate) as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. Specifically, rhodamine B and diethylenetriamine react firstly to form a spiro amide structure with a stable property, a nitrogen bridging fragment is introduced, and the mixture then reacts with PITC so as to introduce a sulfur atom. By means of sulphophile affinity of mercury ions, each molecule of a novel rhodamine B-phenylthiourea derivative (namely, mercury ion fluorescent probe RDTU) obtained through the scheme can be combined with two mercury ions, so that the fluorescent probe has higher selectivity and detection sensitivity. The molecules of the fluorescent probe can perform detection in a neutral buffer solution especially in water phase. Additionally, the molecules of the fluorescent probe can detect the mercury ions from mercury chloride, and has better practicability.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Activating and recovering method of waste mercuric chloride catalyst
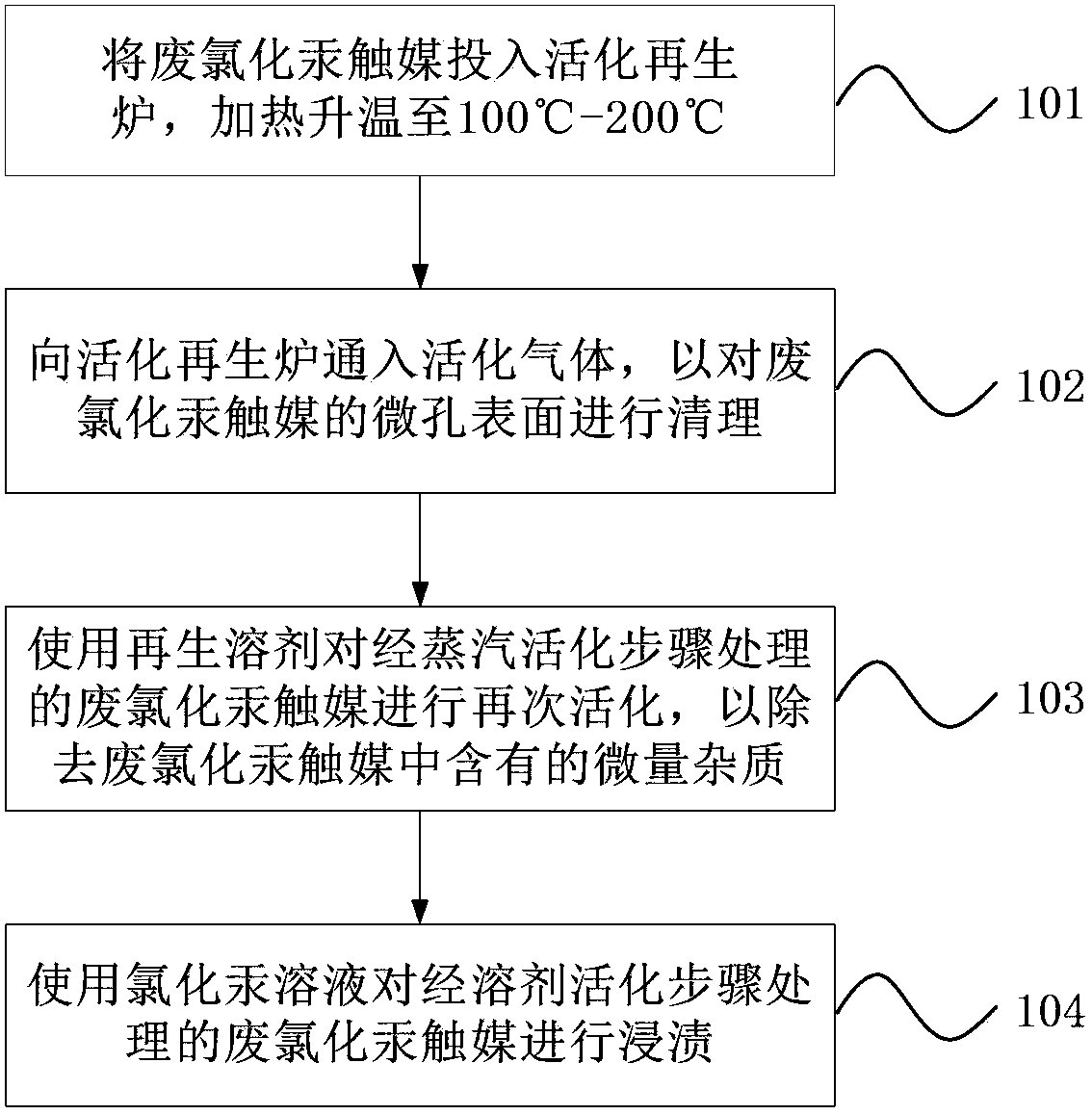
ActiveCN104138767AEfficient recyclingImprove protectionPhysical/chemical process catalystsSteam activationBiological activation
An activating and recovering method of a waste mercuric chloride catalyst is provided. The method includes: a low-temperature carbonization step, namely a step of adding the waste mercuric chloride catalyst into an activation regeneration furnace and heating to 100-200 DEG C; a step of steam activation, namely a step of feeding an activating gas into the activation regeneration furnace so as to clean micropore surfaces of the waste mercuric chloride catalyst; a step of solvent activation, namely a step of activating the waste mercuric chloride catalyst again by using a regenerating solvent so as to remove a trace amount of impurities in the waste mercuric chloride catalyst; and a step of regenerating the mercuric chloride catalyst, namely a step of dipping the waste mercuric chloride catalyst with a mercuric chloride solution. The method can effectively recover and reutilize the waste mercuric chloride catalyst. Compared with the prior art, the method is advantageous in that: on the one hand, the waste mercuric chloride catalyst is free of innocent treatment, and on the other hand, the waste mercuric chloride catalyst can be reutilized, thus effectively reducing the production cost, increasing the production efficiency and facilitating environment protection.
Owner:贵州省万山银河化工有限责任公司
Novel nessler's reagent and method for rapidly measuring soil ammonium nitrogen
InactiveCN101319999AControl pHSlow down chemical reactionsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPotassium hydroxideColor reaction
The invention discloses a novel Nyquist reagent and a method using the reagent for rapidly determining soil ammonium. The main improvement of the novel Nyquist reagent lies in that proper amount of solid potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide is directly added in solution after the complete reaction of potassium iodide and mercuric chloride during the preparation; the novel Nyquist reagent is used for determining the soil ammonium; tartaric acid potassium sodium alkaline solution is used as masking agent, the novel Nyquist reagent is added in Arabic gum medium solution for the color reaction with ammonium ions. Alkaline is added for adjusting the alkalinity of a color reaction system for the colorimetric determination after the color is stable. The Nyquist reagent has the advantages of wide linear range, long shelf life, color stability and easy preparation. The determination method of the invention has the advantages of easy operation, good reproducibility, small error and rapid test speed and is applied to bases and agricultural extension departments.
Owner:河南农大迅捷测试技术有限公司
Method for eliminating tissue culture seedling pollution
InactiveCN102726290AEliminate pollutionEasy to addPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsEconomic benefitsAntibiotic Y
The invention relates to a method for eliminating tissue culture seedling pollution, and the method is characterized by including the following steps of: (1) adding a sodium hypochlorite solution into a culture medium used for culturing tissue culture seedlings; (2) transferring a polluted tissue culture seedling to the sodium hypochlorite solution-containing culture medium; (3) repeating step (1) and (2), and conducting transfer several times so as to eliminate pollution; and (4) culturing the pollution eliminated tissue culture seedling. The method of the invention has the advantages that: compared with other antibiotics, the sodium hypochlorite solution adopted in the invention is convenient to add and can be subjected to autoclaving along with the culture medium; compared with mercuric chloride, the sodium hypochlorite solution has no secondary pollution, and tissue culture seedling pollution can be effectively eliminated; and the method can be used to save polluted tissue culture seedlings in tissue culture seedling species preservation and rapid propagation of seedlings for production, thus boasting substantial ecological and economic benefits.
Owner:SHANDONG YANTAI AGRI SCHOOL
High-stability composite mercury catalyst for hydrochlorination of acetylene
InactiveCN102085485AHigh catalytic activityReduce dosagePhysical/chemical process catalystsPreparation by halogen halide additionManganeseGadolinium
The invention discloses a high-stability composite mercury catalyst for hydrochlorination of acetylene. The catalyst comprises the following components: 100 parts of active carbon serving as a carrier, 1-15 parts of mercuric chloride serving as a main catalytic component and 1-10 parts of auxiliary component, wherein the auxiliary component is one of chlorides of cobalt, manganese and gadolinium or a mixture of multiple of the chlorides, or one of chlorides of bismuth, cadmium and copper or a mixture of multiple of the chlorides. According to the invention, the problems of the current mercuric chloride catalyst that the mercury consumption during production is excessively large and the environmental pollution is serious are solved. The activity of the composite mercury catalyst disclosed by the invention is improved by 5-50% compared with that of the pure mercuric chloride catalyst, the utilization efficiency of the catalyst can be effectively improved, the production cost is lowered, and the mercury pollution is reduced.
Owner:XINJIANG CORPS MODERN GREEN CHLOR ALKALI CHEM ENG RES CENT LTD +1
Comprehensive processing method of vinyl chloride synthetic gas
ActiveCN102516022AHigh removal rateShort processChlorine/hydrogen-chloridePreparation by halogen halide additionHigh concentrationSyngas
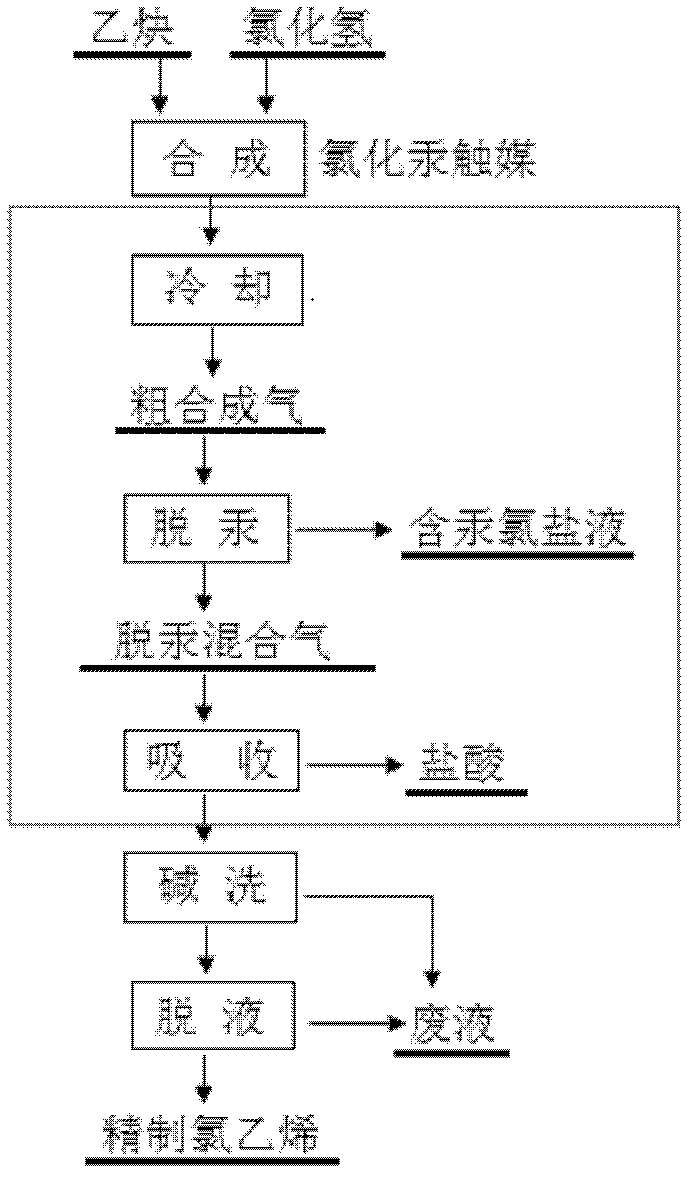
The invention discloses a comprehensive processing method of vinyl chloride synthetic gas. Under the effect of a mercuric chloride catalyst, acetylene gas and hydrogen chloride are subject to a reaction, such that crude vinyl chloride synthetic gas is produced; the crude vinyl chloride synthetic gas is subject to mercury removing by using a high-concentration chloride containing hydrochloric acid; hydrogen chloride is absorbed by using water; the crude vinyl chloride synthetic gas is then subject to steps such as alkali washing and dehydration, such that refined vinyl chloride is obtained, and requirements of mercury recovering, qualified industrial hydrochloric acid production and vinyl chloride refining are directly achieved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Composite metal chloride catalyst and production process thereof
InactiveCN103691460AReduce contentDo not reduce dosagePhysical/chemical process catalystsPreparation by halogen halide additionPorosityEthyl Chloride
The invention discloses a composite metal chloride catalyst. The catalyst is prepared by adopting active carbon with the porosity being more than or equal to 0.58cm<3> / g, the specific area being more than or equal to 1200m<2> / g and the mechanical strength being more than or equal to 95% as a carrier and absorbing mercury chloride, zinc chloride, calcium chloride and barium chloride under the condition with the temperature of 90-98 DEG C, wherein the content of the mercury chloride is 2.5-6.5% and the content of the zinc chloride is 1-15%. The catalyst disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the activity and the stability are respectively improved by 5-20% and 10-20% compared with the existing catalyst containing 10.5-12.5% of mercury chloride; under the condition without reducing the activity of the catalyst, the used amount of the mercury chloride can be greatly reduced, the production cost of the catalyst can be greatly reduced, the consumption of a mercury source can be greatly reduced, the service life of the catalyst also can be greatly prolonged, the used amount of the catalyst can be greatly reduced, the time for replacing the catalyst can be greatly saved, so that the production cost of vinyl chloride is greatly reduced; in production, the catalyst consumed is less and the lost mercury is less, the pollution of the lost mercury to the environment and the hazard caused by the mercury entering a product to the product can be obvious reduced.
Owner:李世禄
Method for rapidly determining content of total iron in nitrided ferrovanadium
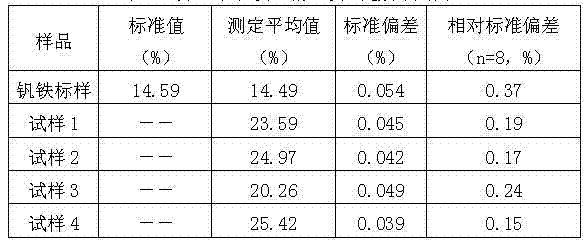
InactiveCN103091450AGuaranteed accuracyDetection speedChemical analysis using titrationPreparing sample for investigationFerric hydroxideBoiling point
The invention discloses a method for rapidly determining the content of total iron in nitrided ferrovanadium. The method comprises the steps of: 1, decomposing a nitrided ferrovanadium sample by an alkali fusion method to obtain an alkali fusion sample; 2, leaching the alkali fusion sample by hydrochloric acid, adding sodium hydroxide to a leaching solution for precipitation, and filtering and separating the solution to obtain a ferric hydroxide precipitate; 3, acidifying the ferric hydroxide participate by hydrochloric acid, heating the acidified precipitate to a boiling point, dropwise adding stannous chloride to the heated precipitate to reduce ferric iron into ferrous until the stannous chloride is excessive; and 4, oxidizing the excessive stannous chloride by mercuric chloride, titrating the oxidized stannous chloride by a potassium dichromate standard solution with sodium diphenylaminesulfonate being an indicator, thus calculating the content of the total iron of the nitrided ferrovanadium sample. The method is capable of separating vanadium and ferrum and eliminating interference of high vanadium to determination of the total iron, thereby ensuring the accuracy of a determination result. The method is used for directly determining the content of the total iron in the nitrided ferrovanadium, the detection time is shortened from original 10h to 1h, and the detection speed is greatly enhanced. The method has the characteristics of being direct, simple, convenient and feasible.
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
Apparatus and method for treating discharge gas
ActiveUS20070140939A1Increased cost of treatmentEfficient removal of mercuryCombination devicesGas treatmentTreatment costsOxide sulfur
The invention provides a discharge gas treatment apparatus and method which prevent increase in treatment cost and which attain efficient removal of mercury contained in a discharge gas. The discharge gas treatment apparatus, for treating a discharge gas containing nitrogen oxide, sulfur oxide, metallic mercury, and hydrogen chloride, includes a cooling apparatus for controlling the temperature of the discharge gas to a predetermined temperature in accordance with the hydrogen chloride concentration of the discharge gas; an NOx removal catalyst unit for reducing nitrogen oxide contained in the discharge gas for removal thereof and for causing reaction between mercury and hydrogen chloride contained in the discharge gas to thereby form mercury chloride, the discharge gas having been controlled to the predetermined temperature and having been introduced to the apparatus, with ammonia being added thereto; and a wet-format desulfurization apparatus, disposed on the downstream side with respect to the NOx removal catalyst unit, for removing sulfur oxide and mercury chloride contained in the discharge gas through dissolving sulfur oxide and mercury chloride in a liquid absorbent. The apparatus has a simple structure and prevents an increase in treatment cost.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Method for determining sodium chloride content in phosphate using spectrophotometry
ActiveCN101078681AReduce maintenance workloadSimple methodMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSpecial data processing applicationsIon contentSodium phosphates
The invention discloses a method of measuring sodium chloride content in phosphate by spectrophotometry, which solves the problem that chloride ion in phosphate added in utility boiler can not be controlled effectively so that steam and water quality is deteriorated. It is provided with convenient operation, easy operation and accurately measuring sodium chloride content in phosphate quickly so on. The method is that 0.2% of mixed solution of mercury thiocyanate and methyl alcohol is added in standard solution of chloride ion to generate mercuric chloride and release SCN-; then 0.15mol / L-2.5mol / L of mixed solution of mercury thiocyanate and perchloric acid is added to generate stable jacinth complex compound, of which absorbency A deducting blank absorbency A0, namely A-A0 and the chloride ion content has the smooth curve relation; on the curve linear relation chloride ion content is fetched in the range of 0-1000CI- mu g / L to build the equation of the absorbency (A-A0) and the chloride ion content C, namely (A-A0)=a+bC; after certain tri-sodium phosphate solution is fetched to measure absorbency blank absorbency is deducted; the standard curve is calculated or checked to obtain chloride ion content; then sodium chloride content in phosphate is obtained.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY +1
Method for extracting mercury from heavy-metal-related acid mud
ActiveCN106893865AEfficient separationAvoid pollutionProcess efficiency improvementSelenium/tellurium oxyacid saltsPotassium chlorateSediment
The invention particularly relates to a method for extracting mercury from heavy-metal-related acid mud, belonging to the technical field of resources and environment. The method comprises the following steps that step 1, the heavy-metal-related acid mud and hydrochloric acid are added into water and are heated; then potassium chlorate is added; reaction is performed at certain temperature to obtain a mixed liquid containing mercuric chloride; step 2, alkali is added in for neutralization to control pH, so that a mixed solution containing mercuric oxide sediment and Na2SeO3 is obtained; solid-liquid separation is performed, and a selenium-containing solution enters a selenium separation system for recycling selenium; step 3, the mercury oxide sediment obtained through separation in the step 2 is dried and is rectified by adopting a continuous vacuum rectification method; and generated mercury steam is condensed and recycled to obtained refined mercury. According to the method, a wet technique is adopted for processing, so that high-efficient separation of mercury and selenium is realized; then the high-purity mercury product is manufactured through continuous vacuum rectification; and smoke pollution caused by direct roasting of the acid mud is avoided.
Owner:湖南省环境保护科学研究院 +1
High-dispersity low-solid-mercury catalyst for hydrochlorination of acetylene and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107442175AGood dispersionImprove effective utilizationPreparation by halogen halide additionOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsDispersityCerium(IV) oxide
The invention discloses a high-dispersity low-solid-mercury catalyst for hydrochlorination of acetylene and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a nitrogen doped carrier with large specific surface area by taking coconut shells, melamine and pyrrole formaldehyde as raw materials, and preparing the catalyst in a substep ultrasonic impregnation-infrared drying way under vacuum condition by taking mercury chloride as a main catalytic active component, indium chloride as a synergistic catalytic promoter, potassium chloride as a mercury-fixing agent and nano cerium dioxide as a carbon-deposition-resistant agent. The catalyst disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of large specific surface area, high dispersity of active components, high utilization rate of mercury chloride, high catalysis conversion rate, good carbon-deposition-resistant effect and long service life.
Owner:贵州重力科技环保股份有限公司
Composite low-mercury complex catalyst used in vinyl chloride synthesis, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104338561AReduced sublimation lossHigh reactivityPreparation by halogen halide additionOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsActivated carbonPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a composite low-mercury complex catalyst used in vinyl chloride synthesis, and a preparation method thereof. According to the catalyst, active carbon is adopted as a carrier. An active component is a complex formed by an organic ligand and mercury chloride. A co-catalyst is one or more selected from potassium chloride, iron chloride, zinc chloride and copper chloride. According to the catalyst, polyethylene glycol or a crown ether compound is adopted as the ligand, and is subjected to a coordination reaction with mercury ions, such that a stable ring complex is formed, and mercury ions are anchored in active carbon pores. Therefore, mercury element sublimation loss is reduced. According to the invention, a step-by-step impregnation method is adopted. The preparation method is simple; catalyst activity is high; and catalyst stability is high.
Ultralow-mercury catalyst used for acetylene hydrochlorination
ActiveCN105032455AHigh activityImprove stabilityMolecular sieve catalystsPreparation by halogen halide additionZinc bromideCupric bromide
The invention discloses an ultralow-mercury catalyst, and particularly relates to a catalyst with the ultralow content of mercuric chloride and suitable for acetylene hydrochlorination to synthesize chloroethylene. The catalyst comprises a main activity component, auxiliary component A metal bromide, auxiliary component B metal bromide and carriers, wherein the main activity component is mercuric chloride, and the content of the mercuric chloride accounts for 0.5-4% of the total mass of the catalyst carriers; the auxiliary component A metal bromide includes one or more of cupric bromide, cobaltous bromide, manganous bromide, nickel bromide and zinc bromide, and the metal element content of the auxiliary component A metal bromide accounts for 0.1-15% of the total mass of the catalyst carriers; the auxiliary component B metal bromide includes one or more of potassium bromide, barium bromide, sodium bromide and lithium bromide, and the metal element content of the auxiliary component B metal bromide accounts for 0.01-10% of the total mass of the catalyst carriers; the carriers include activated carbon with the specific surface area of 300-2500 m<2> / g and molecular sieve, or silica gel, or zeolite or kieselguhr. While activity and stability of the ultralow-mercury catalyst are ensured, the mercury resource in the catalyst is brought into full play to reach the maximum use efficiency, and the novel ultralow-mercury catalyst is environmentally friendly.
Owner:XINJIANG CORPS MODERN GREEN CHLOR ALKALI CHEM ENG RES CENT LTD
Acetylene-hydrochlorinated novel low-solid mercury catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105032453ALarge specific surface areaImprove thermal stabilityPhysical/chemical process catalystsActivated carbonPotassium
The invention discloses an acetylene-hydrochlorinated novel low-solid mercury catalyst, and meanwhile, the invention also provides a preparation method for the acetylene-hydrochlorinated novel low-solid mercury catalyst. According to the preparation method, the novel low-solid mercury catalyst is obtained by taking coal-based activated carbon as a carrier, taking mercuric chloride as a main catalytic composition, taking zinc chloride and potassium chloride as auxiliary catalytic compositions and stabilizers, performing spraying and dipping, and drying in a gradient heating mode; the low-solid mercury catalyst disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high catalytic activity, high heat stability, short induction period, and good catalytic conversion effect.
Owner:贵州重力科技环保股份有限公司 +1
Rapid neuron staining method based on Golgi silver staining method
InactiveCN103471898AEffective detection meansOvercoming long-term operationsPreparing sample for investigationNervous systemMicroscopic observation
The invention discloses a rapid neuron staining method based on a Golgi silver staining method. The rapid neuron staining method based on the Golgi silver staining method is characterized in that according to mass volume ratio concentration, the aqueous solution with 5 % of potassium dichromate, the aqueous solution with 5 % of mercuric chloride and the aqueous solution with 5 % of potassium chromate are prepared into a Golgi silver staining solution in the volume ratio of 1:1:1, a brain tissue is soaked in the silver staining solution at 37 DEGCfor 36-48 hours, the soaked brain tissue is sliced on a vibrating slicer, tissue sections are arranged on a glass slide coated with gelatin, the tissue sections stay overnight, then conventional ammonia developing is conducted, gradient alcohol dehydration is conducted, the transparency process is conducted by xylene, finally, the tissue sections are sealed by netrual gum, and the tissue sections are observed through a microscope. According to the rapid neuron staining method based on the Golgi silver staining method, staining can be conducted on each encephalic region of the brain, the staining result is clear, details are obvious, and research staff can observe the neuron structure of the brain tissues conveniently, the convenient and fast means is provided for case analysis of nervous system lesions, and the rapid neuron staining method based on the Golgi silver staining method has significant meanings for the field of foundational research of neurology.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Hg-Ni catalyst used in synthesis of chloroethylene by using hydrochlorination of acetylene and preparation method for Hg-Ni catalyst
InactiveCN102872887ASimple processEasy to operatePhysical/chemical process catalystsPreparation by halogen halide additionBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTActive ingredient
The invention relates to a low-mercury catalyst used in preparation of chloroethylene by hydrochlorination reaction of acetylene. The low-mercury catalyst is prepared from mercuric chloride serving as an active ingredient and the other metal element, namely nickel chloride, wherein metal salts of the active ingredient can be nitrate, acetate, chloride and the like; the active ingredient is loaded by a porous carrier, and an asphaltic base, a coal base or husk active carbon serves as the porous carrier; and the active ingredient is loaded by an impregnation method.
Owner:代斌
Method for preparing zinc chloride and elementary mercury by using mercury-containing waste catalyst
The invention discloses a method for preparing zinc chloride and elementary mercury by using a mercury-containing waste catalyst and relates to the technical field of waste gas, waste water and industrial residue treatment and utilization of an organic industrial waste mercury catalyst. The zinc chloride and elementary mercury are prepared from waste mercury catalyst by the following three steps: firstly, filling the waste mercury catalyst into a sealed distiller for distillation to allow mercury to sublime into gas directly, and cooling to obtain liquid mercury chloride; reacting the obtained solution of mercury chloride with zinc particles to obtain mixed solution of zinc chloride and elementary mercury; secondly, performing suction-filtration on the mixed solution in a sealed manner to obtain an elementary mercury filter cake, and washing, dewatering and packaging to obtain an elementary mercury product; and finally, filling the obtained solution of zinc chloride into a normal pressure distiller for distillation, discharging saturated solution of zinc chloride, cooling, crystallizing, crushing and packing to obtain a zinc chloride crystal product. When the method is used, the pollution of waste mercury catalyst to the environment is prevented effectively, and high economic benefit is created at the same time.
Owner:何侠
Preparation method of low-mercury catalyst
ActiveCN106179428AImprove stabilityImprove efficiencyCatalyst activation/preparationActivated carbonPhysical chemistry
The invention provides a preparation method of a low-mercury catalyst. According to the preparation method of the low-mercury catalyst, the adsorption rate of activated carbon for chlorides such as mercuric chloride is increased under the condition of negative pressure, mercuric chloride is enabled to penetrate into the inner layer of the activated carbon more deeply, the stability and the use efficiency of the low-mercury catalyst are improved, and the service life of the low-mercury catalyst is prolonged; meanwhile, a chloride solution is uniformly mixed by the aid of the form of bubbles, the mixing effect is moderate, the good mixing effect is realized while crushing of the activated carbon is avoided, the original condition of inconsistent up-and-down concentrations of the chlorides and the solution is eliminated, the chlorides on the surface of the activated carbon are pushed inwards while the bubbles act on the activated carbon at the moment, so that the mercuric chloride further penetrates into the inner layer of the activated carbon, and the low-mercury catalyst with high quality and long service life is obtained.
Owner:NINGXIA JINHAI CHUANGKE CHEM TECH
Method using microwave heating to treat mercury-containing acid sludge
PendingCN109136566AEfficient recyclingOvercome efficiencyProcess efficiency improvementMercury halidesActivated sludgeMicrowave
The invention discloses a method using microwave heating to treat mercury-containing acid sludge and belongs to the technical field of solid waste treatment and recycling. The method includes: sequentially subjecting the mercury-containing acid sludge to drying and microwave heating under inert gas protection to obtain HgS-containing acid sludge and HgCl2 steam; subjecting the HgCl2 steam to condensation and dissolving with water to obtain a mercuric chloride solution for a mercury waste medium; subjecting the HgS-containing acid sludge to microwave calcining in oxygen atmosphere to obtain elemental mercury steam, and subjecting the obtained Hg steam to condensation to obtain pure elemental mercury. The method has the advantages by subjecting the mercury-containing acid sludge to microwaveheating, mercuric chloride and the elemental mercury can be efficiently recycled, and the method is simple in process flow, clean and environmentally friendly, cheap in raw materials and huge in environmental benefits and economic benefits.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com