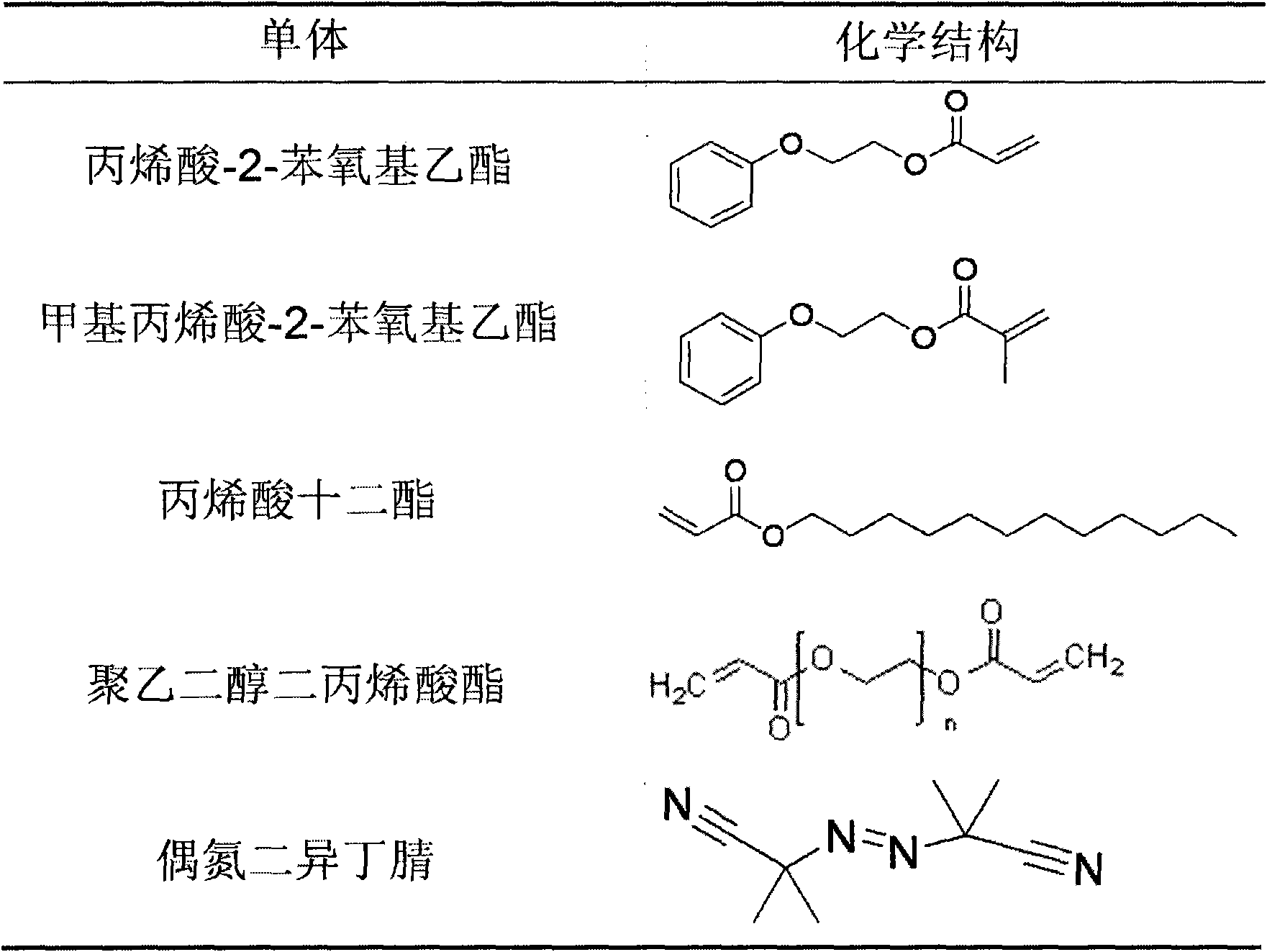
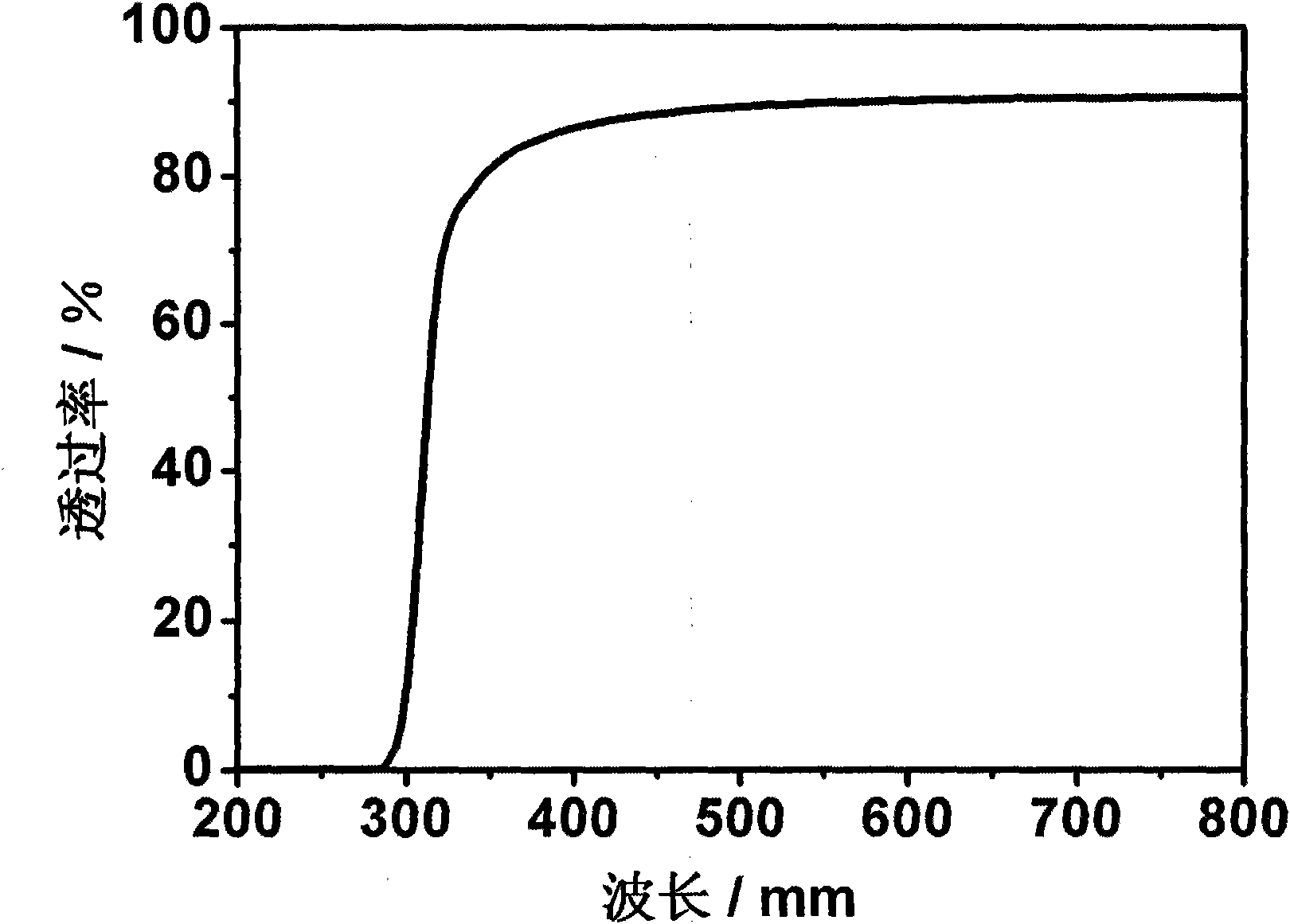
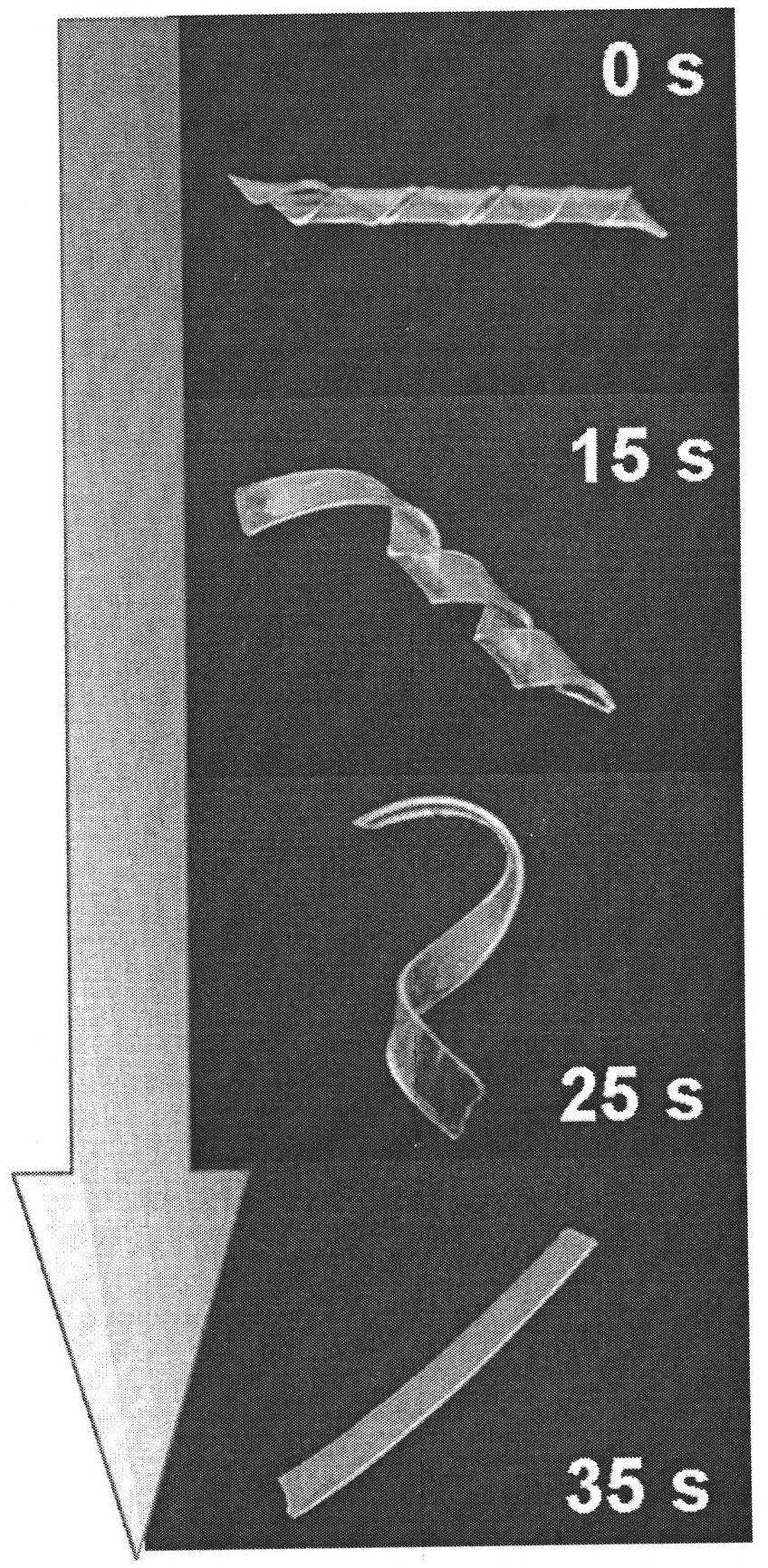
Patents
Literature
52 results about "Poly ethylene glycol diacrylate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
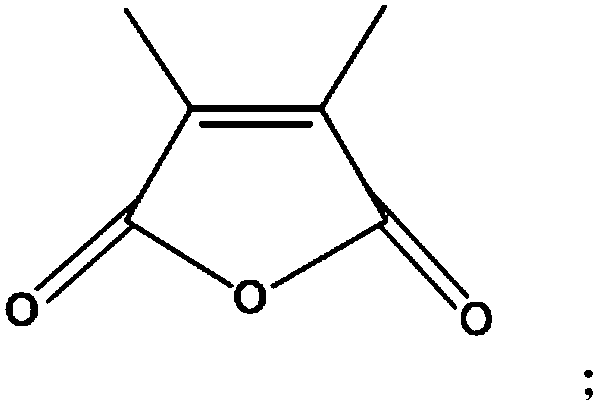
Ethylene glycol diacrylate (EGDA) is a crosslinking homobifunctional monomer. PEG-based cross-linked polymeric materials (hydrogels) are suitable carriers for drug delivery and various other biomedical applications. 1-3 Hoffman, A. S. Hydrogels for biomedical applications. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 64, 18–23 (2012).
High strength injectable hydrogel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102718991AMacromolecular non-active ingredientsProsthesisBiocompatibility TestingPolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to a high strength injectable hydrogel and a preparation method thereof, and specifically relates to the hydrogel formed by using the double bond of polyethyleneglycol diacrylate (PEGDA) and the mercapto group of a sulfhydrylation natural polymer to undergo a Michael addition reaction and at the same time taking the nanoparticles of the triblock copolymer of polyethylene glycol and polycaprolactone (PEG-PCL-PEG) as a reinforcing agent. This kind of hydrogel has relatively high mechanical strength, is injectable hydrogel and degradable hydrogel with good biocompatibility, and has a high gelating speed. The hydrogel has the characteristics of cheap and easily available raw materials and simple preparation method, and therefore has a good application prospect in the biomedical field.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
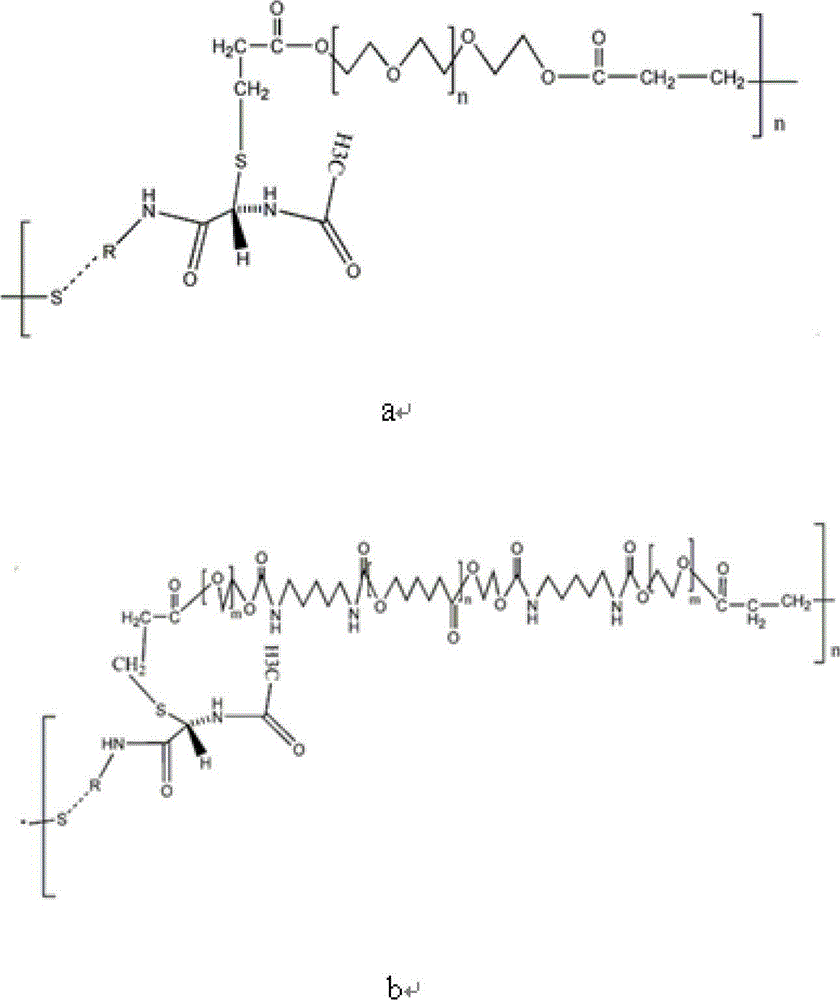
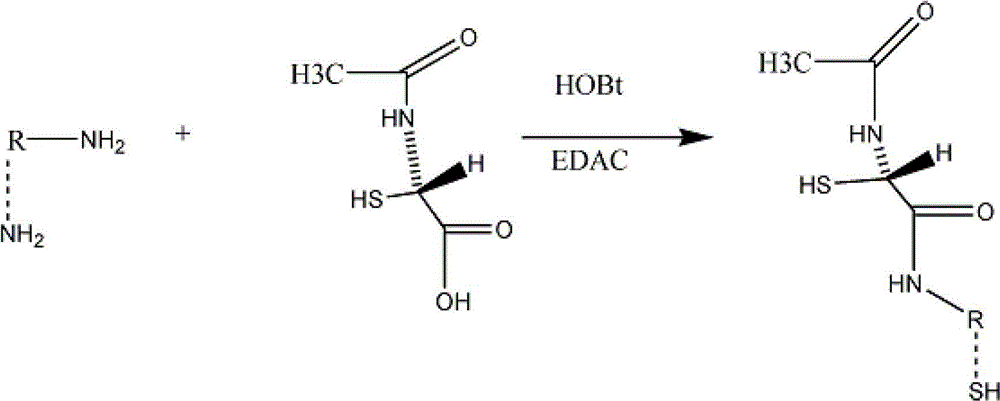
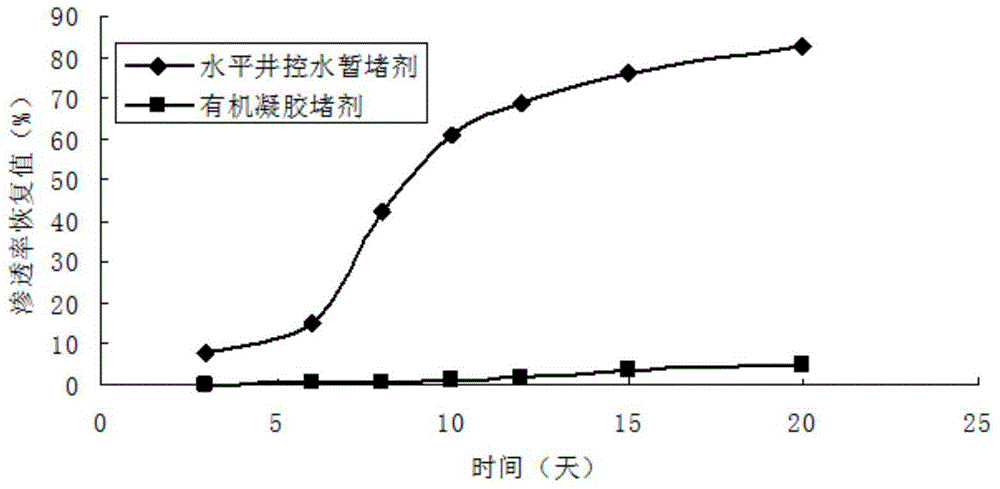
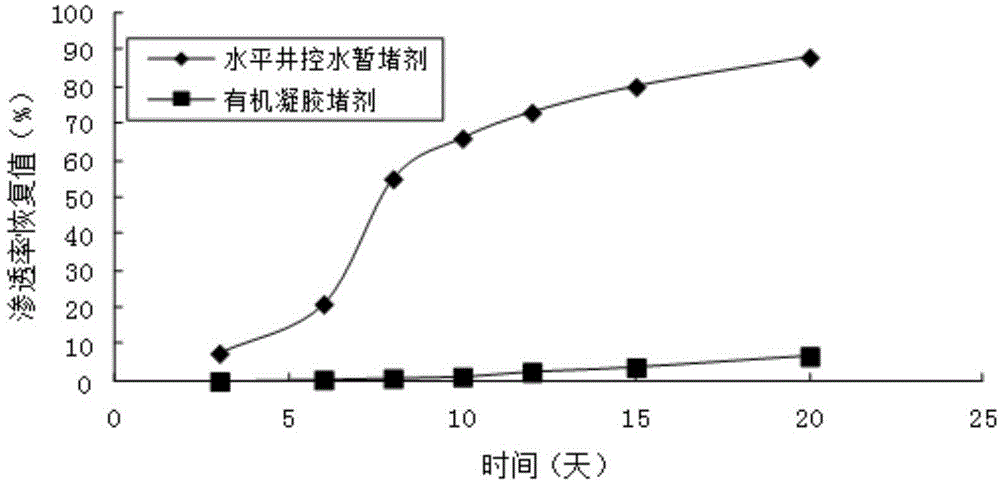
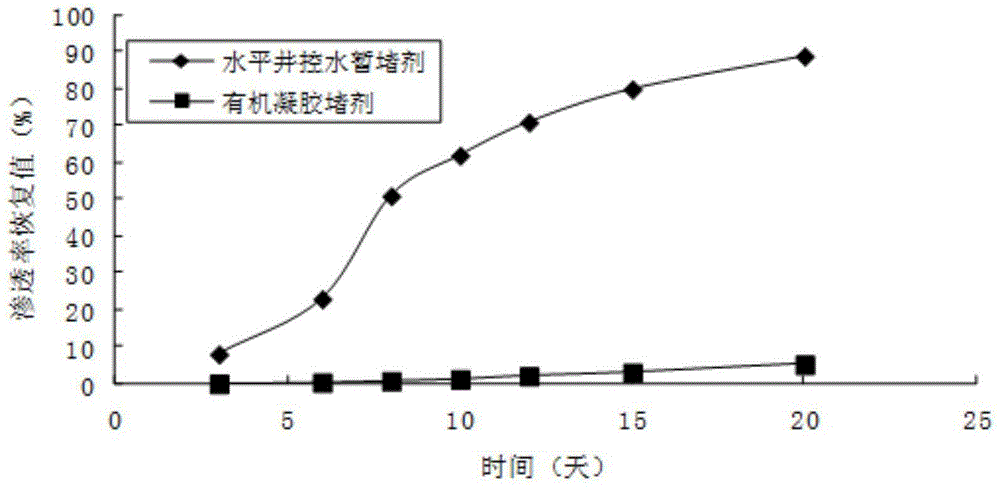
Temporary plugging agent for horizontal well water control, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104531115AReduce harmStrong blocking abilityDrilling compositionMass ratioMethylene bisacrylamide
The invention provides a temporary plugging agent for horizontal well water control, and a preparation method and application thereof. The temporary plugging agent for horizontal well water control comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 4-15 parts of acrylamide, 0.5-3 parts of polypropylene fiber, 1.5-4 parts of reinforcer, 0.5-1.0 part of composite crosslinking agent, 0.1-0.2 part of initiator and the balance of water, totaling 100 parts. The composite crosslinking agent is a mixture composed of polyethyleneglycol diacrylate and N,N-methylene-bis acrylamide in a mass ratio of 10:(1-4). The preparation method of the temporary plugging agent comprises the following steps: sequentially adding the acrylamide, polypropylene fiber, reinforcer and composite crosslinking agent into water, stirring uniformly, adding the initiator, and standing to react for 1-3 hours, thereby obtaining the temporary plugging agent. The invention also provides application of the temporary plugging agent in horizontal well water control. The temporary plugging agent provided by the invention has the characteristics of high gelling viscosity, controllable degradation time, thorough degradation and the like, can plug the high-permeability zone and implement adjustable degradation time, and can lower the damage to the reservoir.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
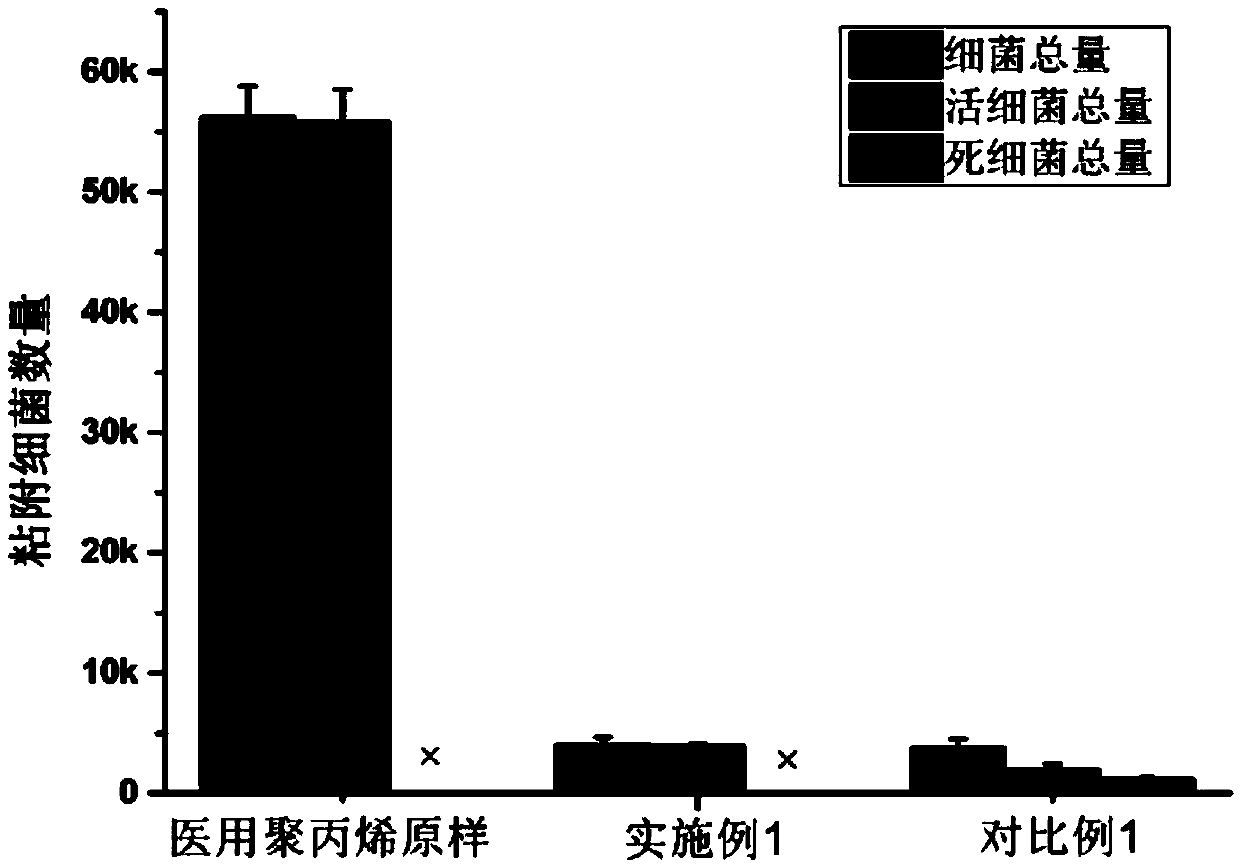
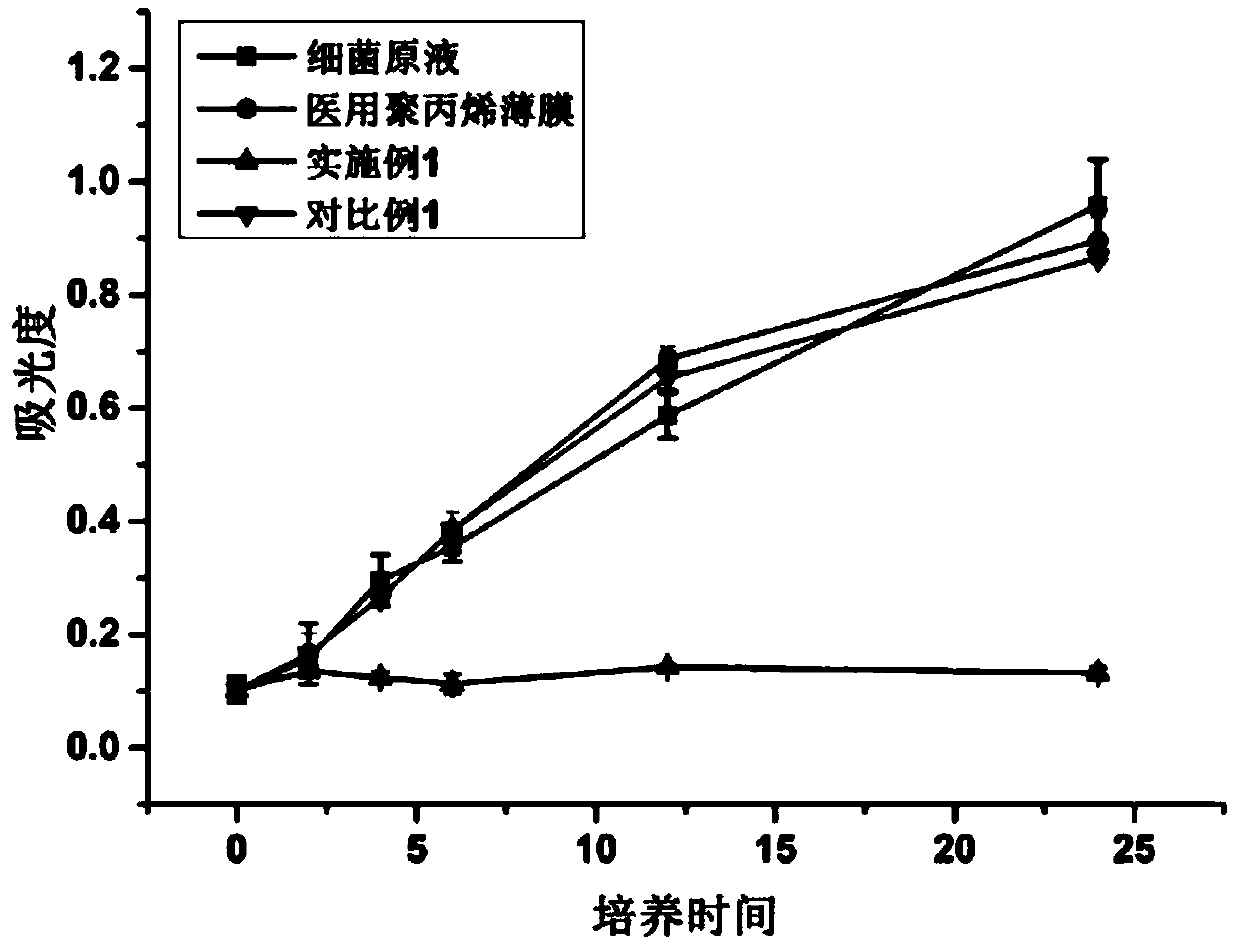
Anti-infection coating and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a preparation method of anti-infection coating. The preparation method comprises the following steps of (a) performing photoinitiator painting treatment on the surfaces of a medical macromolecule material to obtain a base material; (b) placing the base material obtained in the step (a) in a mixed solution comprising adhesion-resistant monomers, pH responsiveness polymerizingmonomers and polyethylene glycol diacrylate, and performing an ultraviolet cross-linking reaction to obtain a material having gel coating on the surface; and (c) performing antibiotic chemical loading on the material having gel coating on the surface obtained in the step (b) so as to obtain the anti-infection coating. According to the preparation method provided by the invention, a specific technology and a specific condition are adopted, and the anti-infection coating is obtained. The anti-infection coating has dual functions of resisting bacterium adhesion and controlling antibiotics to release for sterilization, so that bacterium adhesion can be effectively reduced, controllable release of antibiotics as required can be realized, and the problems that the bacterium-resistant effect ispoor in persistence caused by too fast antibiotic release and bacteria produce drug tolerance caused by random release of the antibiotics can be solved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Frame sealant composition, liquid crystal pollution prevention method, liquid crystal display panel and display device
InactiveCN102702987AReduce spreadImprove anchoring abilityOther chemical processesLayered productsDisplay deviceEngineering
The invention provides frame sealant composition, a liquid crystal display unit and a liquid crystal pollution prevention method using the frame sealant composition. The frame sealant composition comprises, by weight, 20-30 parts of ultraviolet double-bond polymeric monomer, 15-20 parts of thermally polymerized monomer, 5-20 parts of polymerizable oligomer, 0.1-5 parts of optical initiator, 10-20 parts of thermal curing agent and 0-20 parts of granulated additive. The polymerizable oligomer is polyethyleneglycol diacrylate or derivatives thereof. The polymerizable oligomer reacts with polymer of the ultraviolet double-bond polymeric monomer to generate network high polymer, and accordingly anchorage of the network high polymer on surrounding unreacted thermally polymerized monomers is enhanced effectively, and pollution of liquid crystal by the frame sealant is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING BOE OPTOELECTRONCIS TECH CO LTD
Pressure sensitive adhesive, preparation method thereof and protective films using same
ActiveCN101962525AImprove overlay performanceReduce polarityLiquid surface applicatorsFilm/foil adhesivesTectorial membraneAcrylic resin
Owner:KUNSHAN BYE MACROMOLECULE MATERIAL CO LTD
Nano gold doped integral material for enriching glycoprotein and applications thereof
ActiveCN103877949AImprove hydrophilicityReduce non-specific adsorptionOther chemical processesPeptide preparation methodsGlycidyl methacrylateGold particles
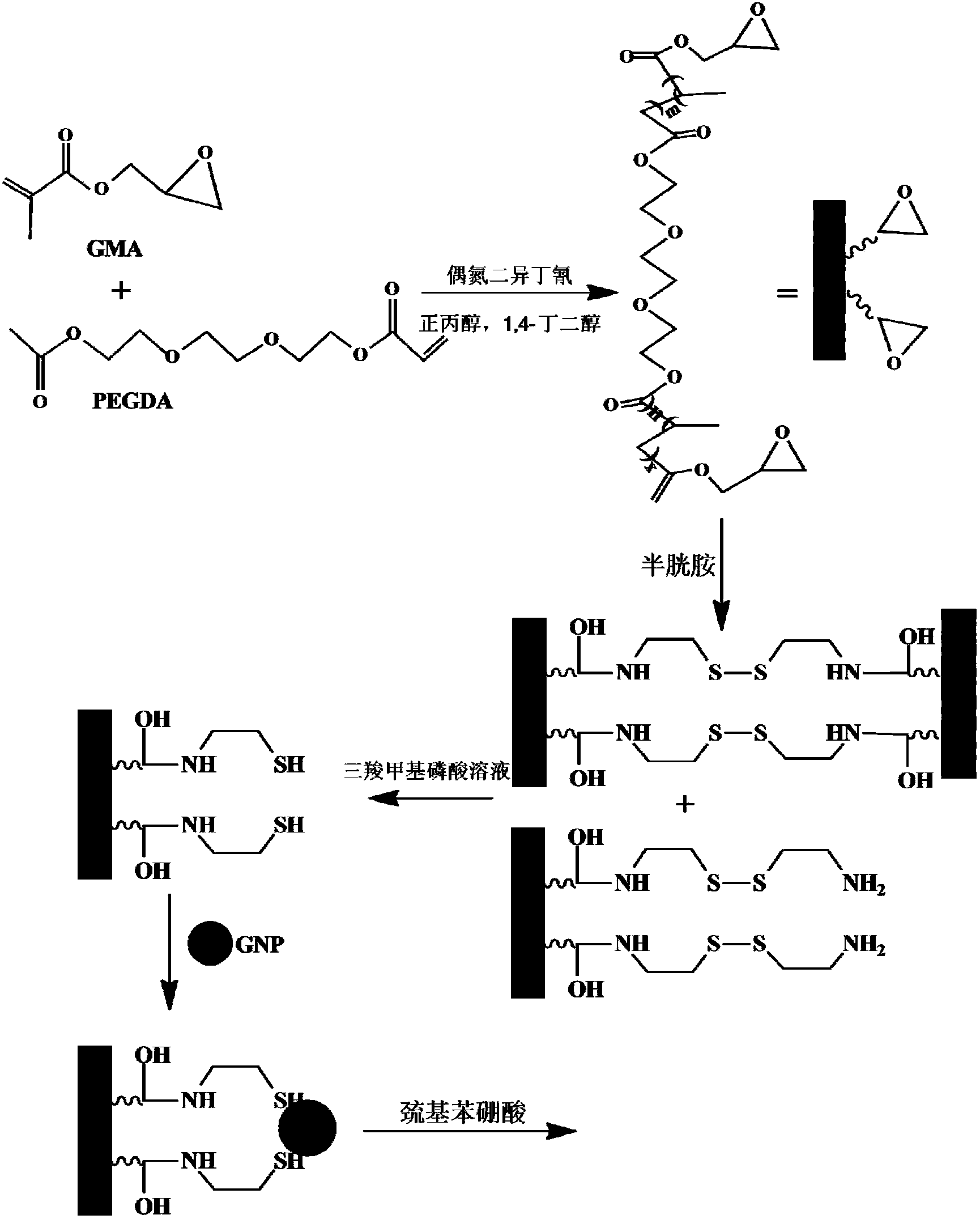
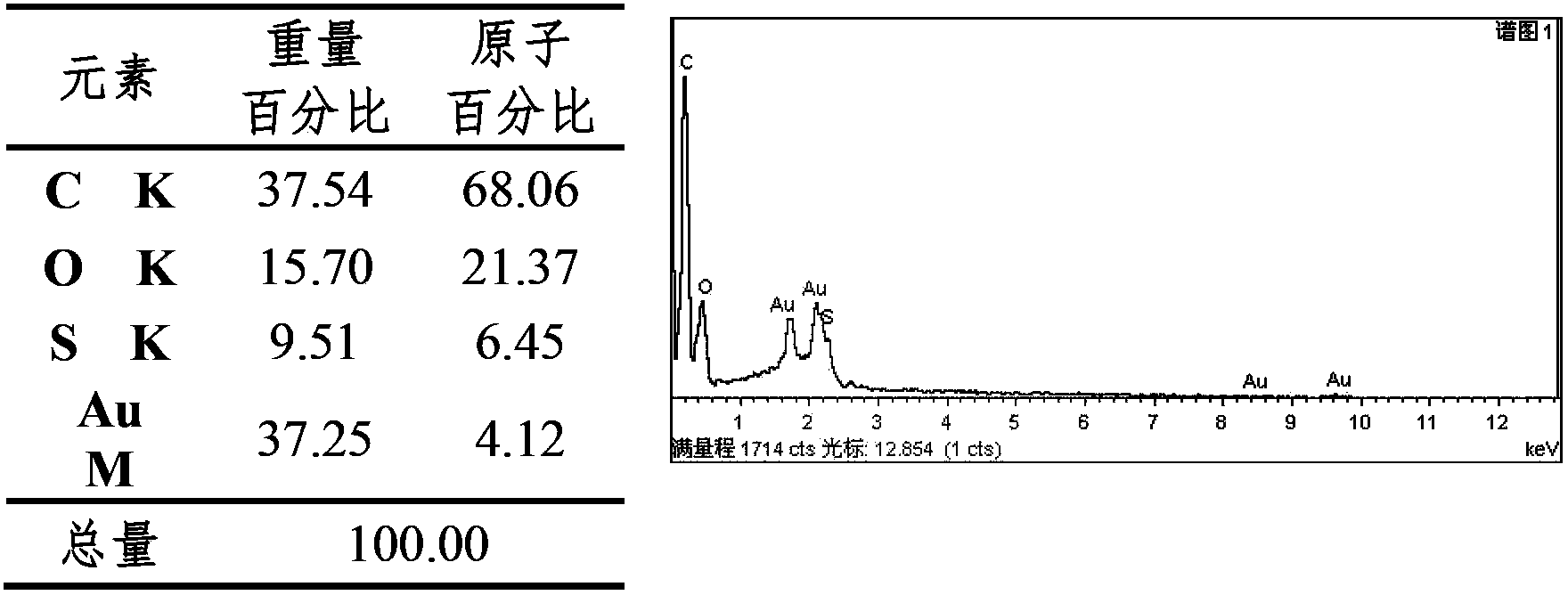
The invention relates to a preparation method of a nano gold doped integral material for enriching glycoprotein. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) and polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA) as the monomers to synthesize a hydrophilic polymer integral material substrate through an in-situ polymerization method; utilizing the epoxy groups in the substrate surface to enrich the substrate surface with mercapto groups through a chemical derivatization method, then modifying the substrate surface with nano gold particles; finally co-modifying 4-mercaptophenylboronic acid and mercaptoethylamine on the nano gold surfaces on the substrate, and enriching glycoprotein on the basis of phenylboronic acid affinity chromatography. The hydrophilicity of the monomer polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA) is utilized so as to reduce the non-specific adsorption of substrate on proteins, and thus the enrichment selectivity is improved. At the same time, the high specific surface area of nano particles is utilized at the same time, thus the enrichment capacity is increased, and finally the high-efficient and high-selective enrichment of glycoprotein is achieved.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing magnetic-induced discoloration polymeric fibers
The present invention relates to a method for preparing magnetic-induced discoloration polymeric fibers. The method comprises: adopting ferrocene, acetone, and hydrogen peroxide as starting raw materials; adopting a solvothermal method to prepare ferroferric oxide nanospheres; dispersing the ferroferric oxide nanospheres into an acetone solvent to obtain a dispersion liquid; uniformly mixing the dispersion liquid and polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA); evaporating the acetone solvent; adding an ultraviolet light initiator to obtain a polymer monomer emulsion (Fe3O4 / PEGDA); and placing polymer fibers in a magnetic field, and adopting an ultraviolet light polymerization method to polymerize the Fe3O4 / PEGDA on the surfaces of the polymer fibers to obtain the magnetic-induced discoloration polymeric fibers. The structural color fibers prepared by the method of the present invention have excellent optical properties, and can be used for preparation of magnetic field regulated photonic crystal fibers, photonic crystal sensors, and the like. The method of the present invention has characteristics of simple operation, good effect, and no requirement of chemical dyes, and provides important reference values for reduction of environmental pollution on dyeing and finishing industry.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Injectable temperature-sensitive magnetic nano emulsive gel and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106729709AGood lookingUniform sizeDispersion deliveryEnergy modified materialsChemistryPoly ethylene glycol diacrylate
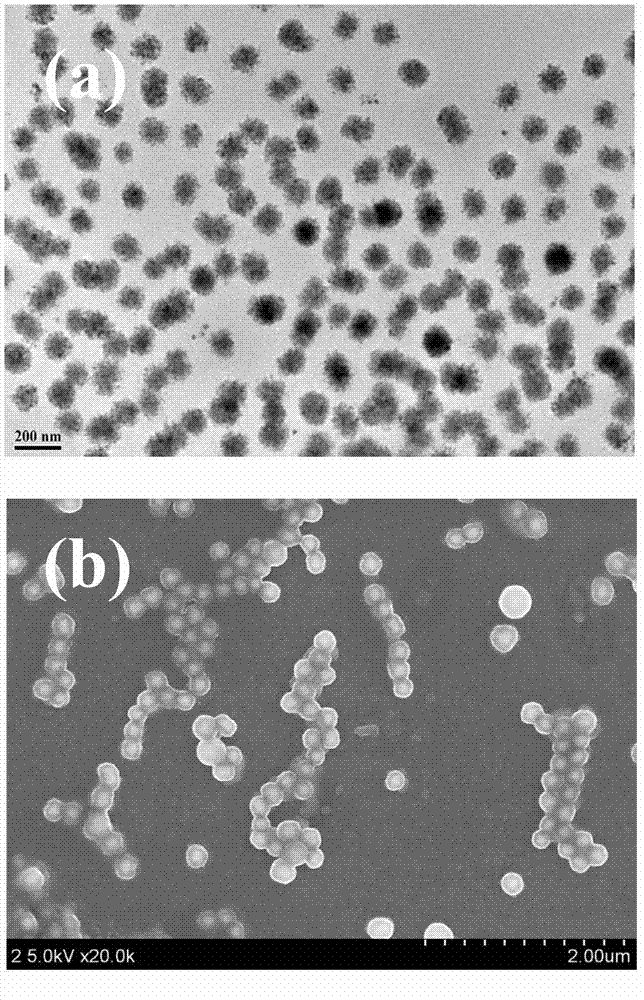
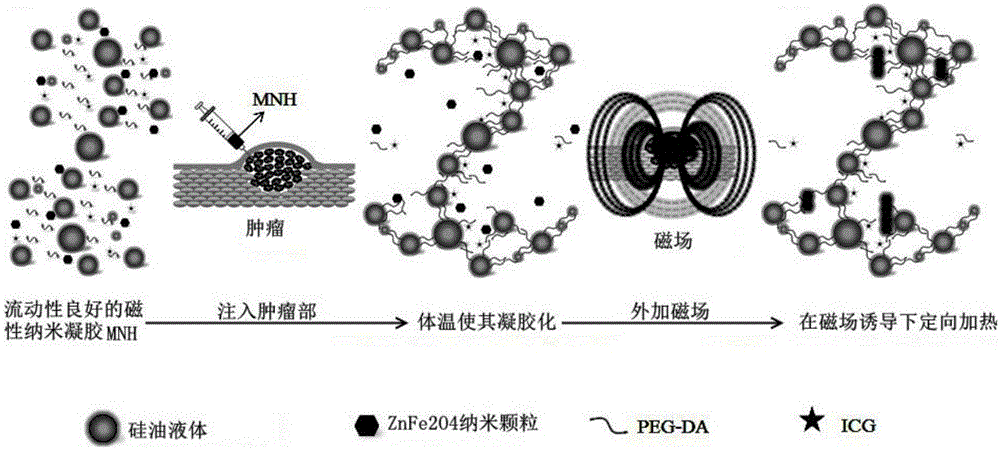
The invention discloses a preparation method of an injectable temperature-sensitive magnetic nano emulsive gel. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by taking a mixture of silicone oil and ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles as an oil phase and an aqueous solution where lauryl sodium sulfate is dissolved as an aqueous phase, dropwise adding the oil phase into the boiling aqueous phase while stirring to form an initial emulsion; performing uniform nanocrystallization on the initial emulsion by using an ultrasonic cell crusher to obtain a magnetic nanoemulsion; dropwise adding polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEG-DA) into the magnetic nanoemulsion under a low temperature condition, performing uniform ultrasonic dispersion, and fully cooling the mixture to obtain the magnetic nano emulsive gel which is good in flowability at normal temperature (less than 25 DEG C) and is gelatinized at body temperature (37 DEG C). The magnetic nano emulsive gel prepared by the invention can be injected in situ in a subcutaneous tumor of a mouse under guidance of an image and is gelatinized and fixed in the part of tumor, without leaking from an injection hole or diffusing to peripheral normal tissues and blood vessels; by applying an alternating magnetic field, the ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles generate heat to cause thermal ablation of tumor tissues for necrosis and exfoliation. The method has a wide application prospect in solid tumor interventional thermotherapy.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
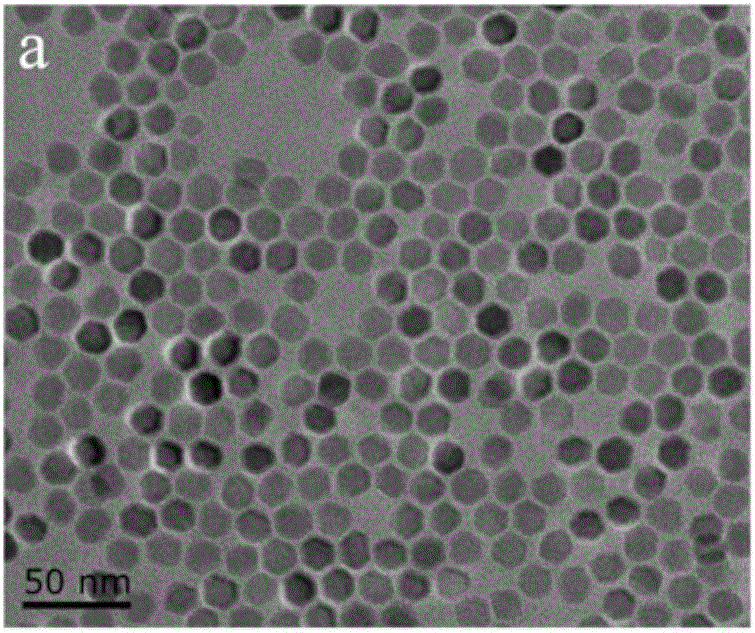
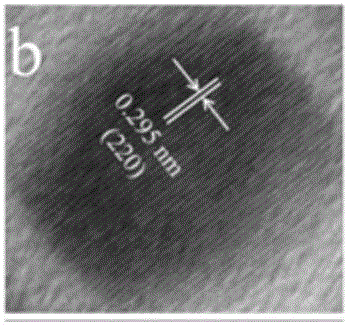
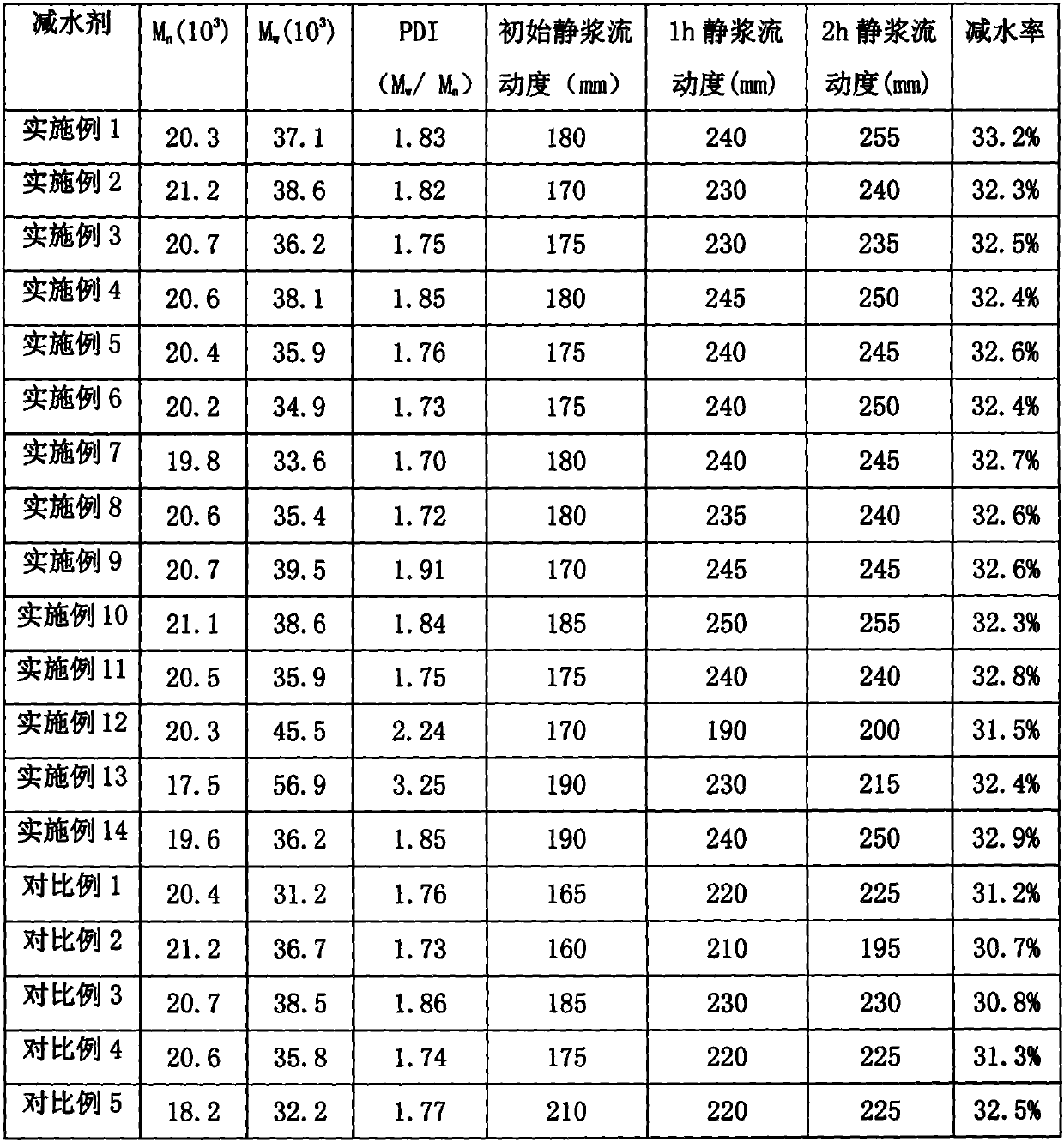
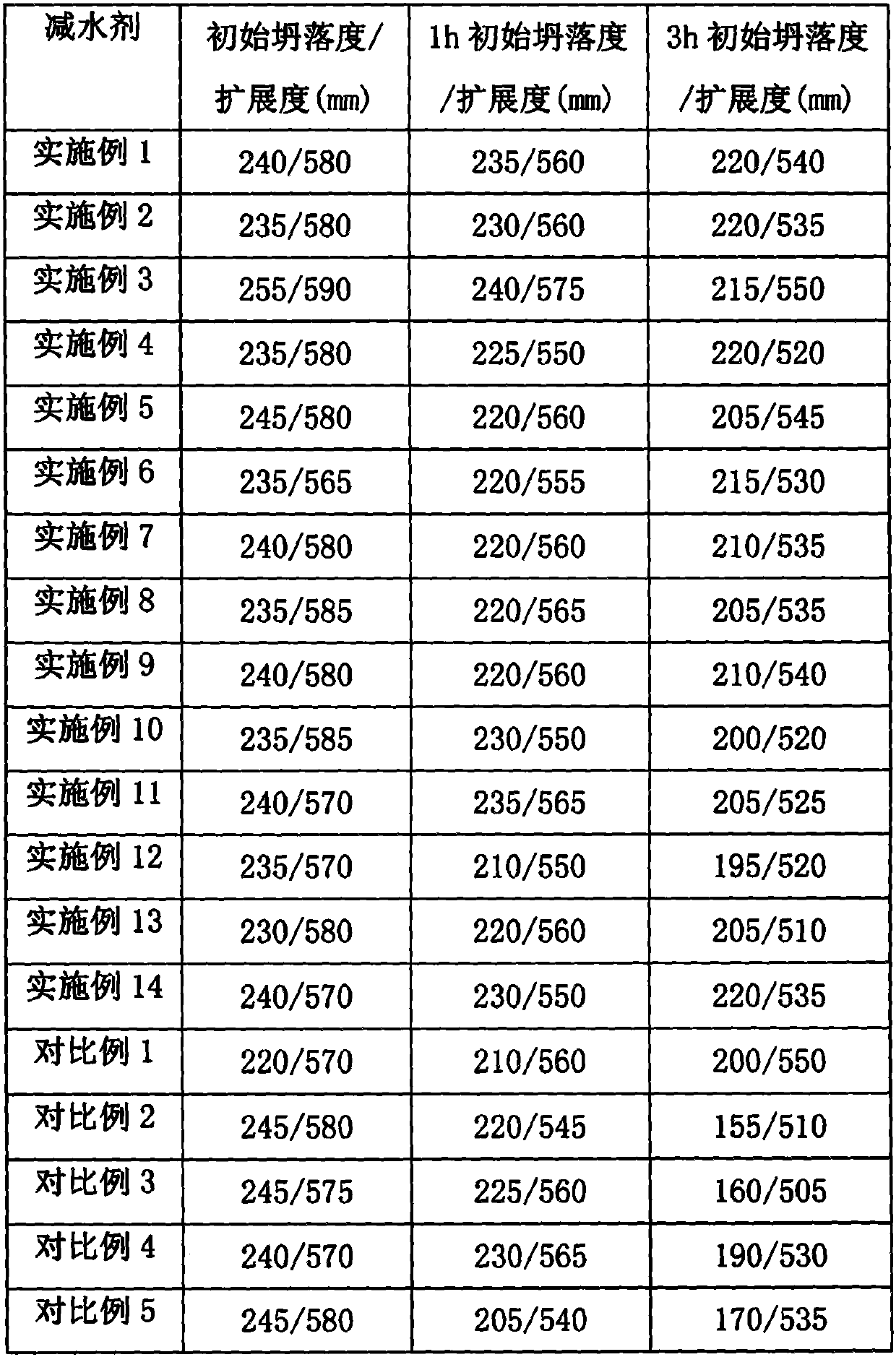
High-slump-retaining coagulation-retarding type polycarboxylate water reducing agent and preparation and application thereof
The invention discloses a high-slump-retaining coagulation-retarding type polycarboxylate water reducing agent and a preparation method and application thereof. The water reducing agent is prepared from, by molar part, 10-30 parts of small-molecule unsaturated carboxylic acid, 3-8 parts of ester of small-molecule unsaturated carboxylic acid, 1-5 parts of salt of small-molecule unsaturated carboxylic acid, 2-6 parts of polyethylene glycol diacrylate, 1-5 parts of an unsaturated polyether macromonomer, 8-20 parts of an acrylamide monomer, an initiator and a chain transferring agent, wherein theacrylamide monomer is a group consisting of three monomers including acrylamide (AM), 2-acrylamide-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid (AMPS) and 2-acryloylamino-2-phenylethanesulfonic acid (AMSS). The molecular structure of the water reducing agent is designed according to the construction demands for workability and slump retaining performance, and the high-slump-retaining coagulation-retarding type polycarboxylate water reducing agent with excellent comprehensive performance is finally obtained. During construction, a high water reducing rate can be achieved by applying a low dosage of the water reducing agent, the construction can be guaranteed, the slump retaining performance is excellent, the slump is basically not changed within 3 hours, and the water reducing agent has wide applicabilityin concrete construction.
Owner:深圳市五山新材料股份有限公司
Injectable bone cement and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104645418AGood injectabilityImprove anti-collapse performanceProsthesisInjectable boneBiocompatibility Testing
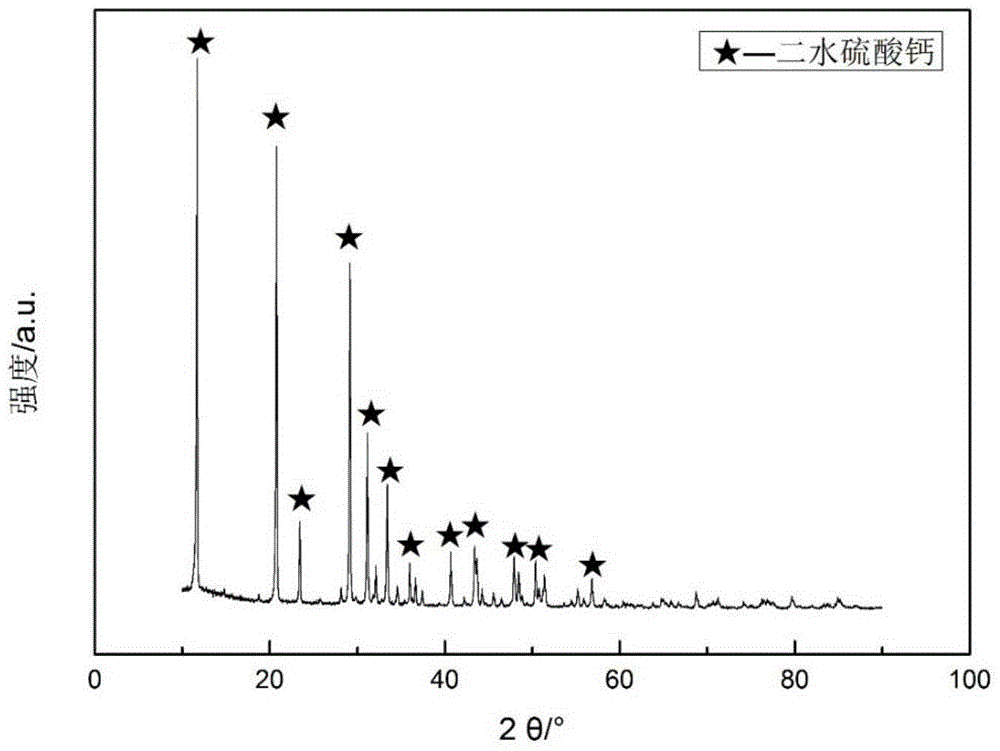
The invention relates to an injectable bone cement and preparation method thereof. The injectable bone cement comprises powder and curing liquid, wherein the powder is composited of calcium sulfate hemihydrate and polyethylene glycol diacrylate, and the curing liquid is sulfhydrylated hyaluronic acid aqueous solution or sulfhydrylated chitosan aqueous solution. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: preparing the powder of calcium sulfate hemihydrate and polyethylene glycol diacrylate inproportion; adding the curing liquid according to the liquid-to-solid ratio of 0.4-1.0mL / g, mixing and stirring evenly, and curing at room temperature to form the injectable bone cement. Sulfhydrylated hyaluronic acid and sulfhydrylated chitosan are liable to form intramolecular and intermolecular disulfide bonds under neutral condition and have higher degree of crosslinking and viscoelasticity; thus, injectable property, collapse resistance and mechanical property of the bone cement are improved. Meanwhile, the bone cement provided by the invention also has good biocompatibility and biodegradablity, and can be used for filling and repair for various bone defects. The injectable bone cement and the preparation method thereof are used in the field of tissue engineering and medicine.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Electrically responsive intelligent hydrogel, preparation method thereof, and manipulator type soft-bodied robot
ActiveCN110563971ARealize the clamping effectAchieve releaseProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsCross linked hydrogelsPoly ethylene glycol diacrylate
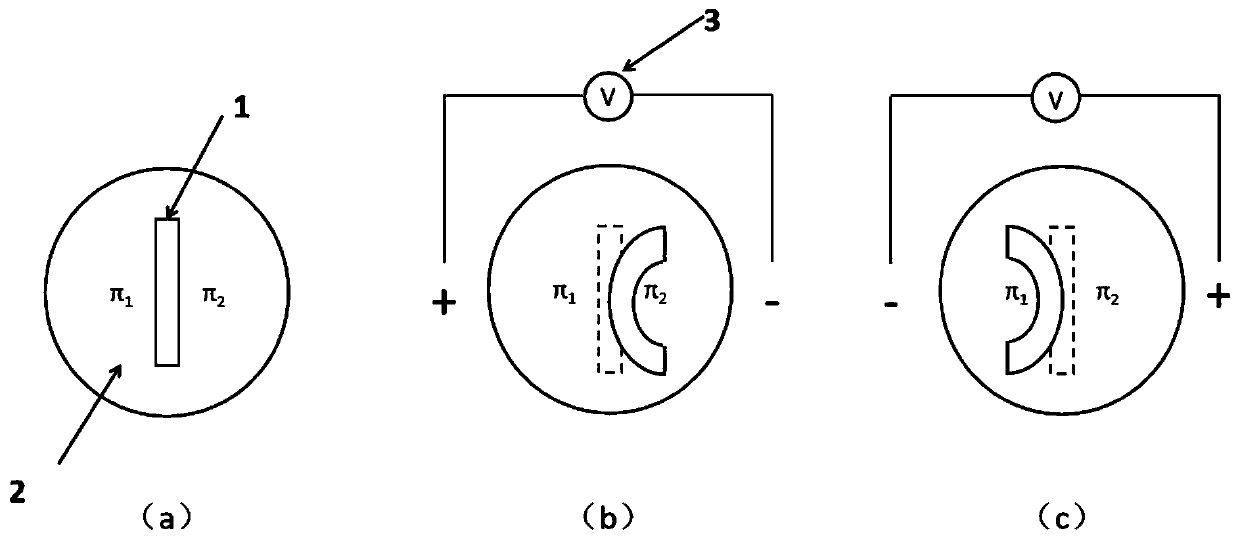
The invention belongs to the technical field of soft-bodied robots, and particularly relates to an electrically responsive intelligent hydrogel, a preparation method thereof, and a manipulator type soft-bodied robot. The electrically responsive intelligent hydrogel is a double-network cross-linked hydrogel formed by compounding polyethylene glycol diacrylate and acrylic acid; the hydrogel has theelectric response performance of bending towards an electric field cathode under the action of an electric field in an electrolyte solution; the hydrogel is applied in the manipulator type soft-bodiedrobot, and clamping and releasing of objects can be achieved through mutual cooperation and coordination of hydrogel fingers.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV +1
Ophthalmic implanted material with shape memory function and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101785874ARegulatory mechanicsTuning shape memory propertiesProsthesisPolyethylene glycolNitrogen gas
The invention relates to an ophthalmic implanted material with the shape memory function and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of biomedical materials. Thermally polymerizable acrylate monomers are used as the basic material, and the mol ratio thereof is 10.0-98.0%; polyethylene glycol diacrylates or polyethylene glycol dimethyl acrylates, which have different molecular weights, are used as the cross-linking agent, and the mol ratio thereof is 2.0-90.0%; and thermal initiator accounts for 0.2-1.0% of the total mass. The thermally polymerizable monomers, the thermal initiator and the cross-linking agent are uniformly mixed under the protection of nitrogen gas, then the mixture is injected into a mold to be subject to the thermal polymerization reaction at the temperature of 70-90 DEG C for 24-48 hours, and the Soxhlet extraction is adopted to remove the unreacted monomers and oligomers to obtain the ophthalmic implanted material with the shape memory function. The invention has the advantages that the prepared material has the shape memory property, the memory property transition temperature of the material can be adjusted to the body temperature, and the material has large deformation extent and higher light transmittance in visible light areas.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
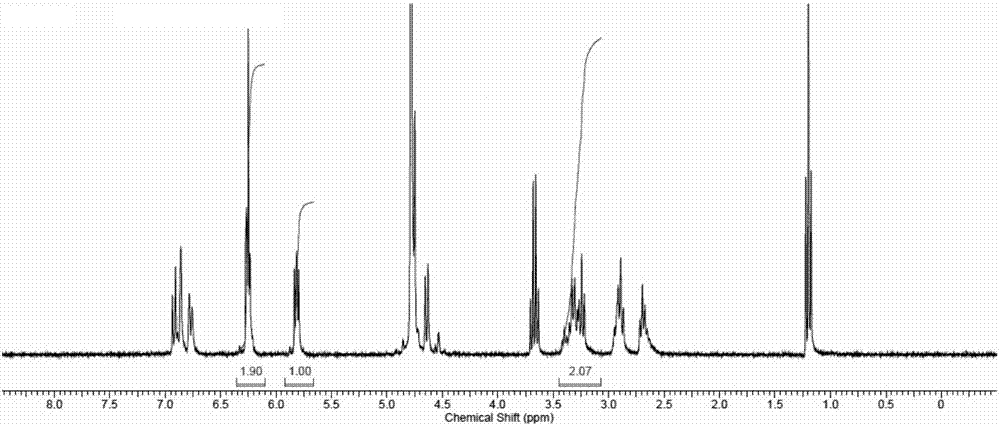
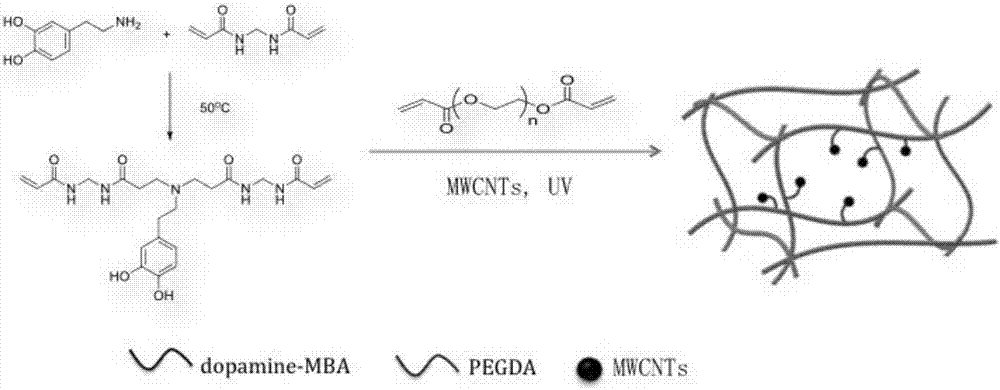
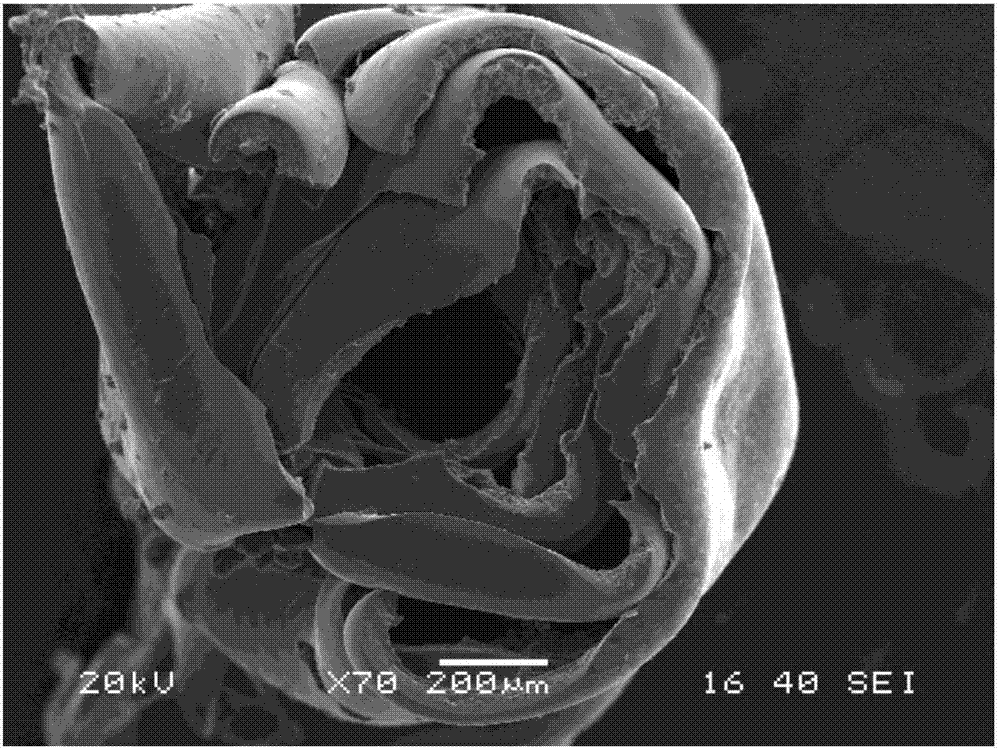
Production method and product of novel multiwalled carbon nanotube-dopamine-polyethyleneglycol diacrylate hydrogel film
The invention relates to a production method and a product of a novel multiwalled carbon nanotube-dopamine-polyethyleneglycol diacrylate hydrogel film. The method concretely comprises the following steps: 1, adding dopamine into a cross-linking agent solution under an anoxic condition, stirring the dopamine and the cross-linking agent solution at 45-55 DEG C in a shady place for 1-3 d, and freeze-drying the obtained solution to obtain a dopamine cross-linking agent; 2, adding a multiwalled carbon nanotube solution to the dopamine cross-linking agent, uniformly mixing the multiwalled carbon nanotube solution and the dopamine cross-linking agent, and adding polyethyleneglycol diacrylate and a photoinitiator to the obtained mixed solution to prepare a precursor solution; and 3, preparing the hydrogel from the precursor solution. The multiwalled carbon nanotube-dopamine-polyethyleneglycol diacrylate hydrogel film produced in the invention self-folds during transition from a dry environment to a water-containing environment, is independent from the concentration of the multiwalled carbon nanotube-dopamine, has the characteristics of self coiling, conductivity, cell adhesion ability and biocompatibility, affects cell differentiation, has a bone- and nerve tissue-like form after self-coiling, and has application potential in the biomedical science field.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
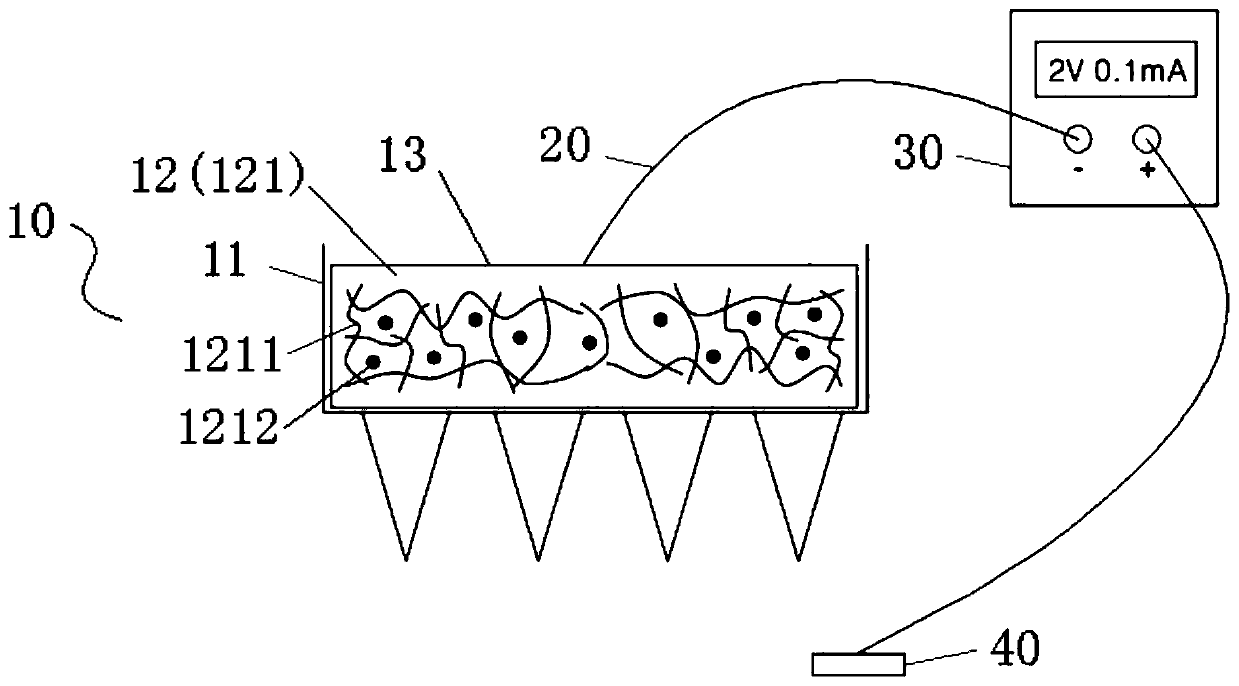
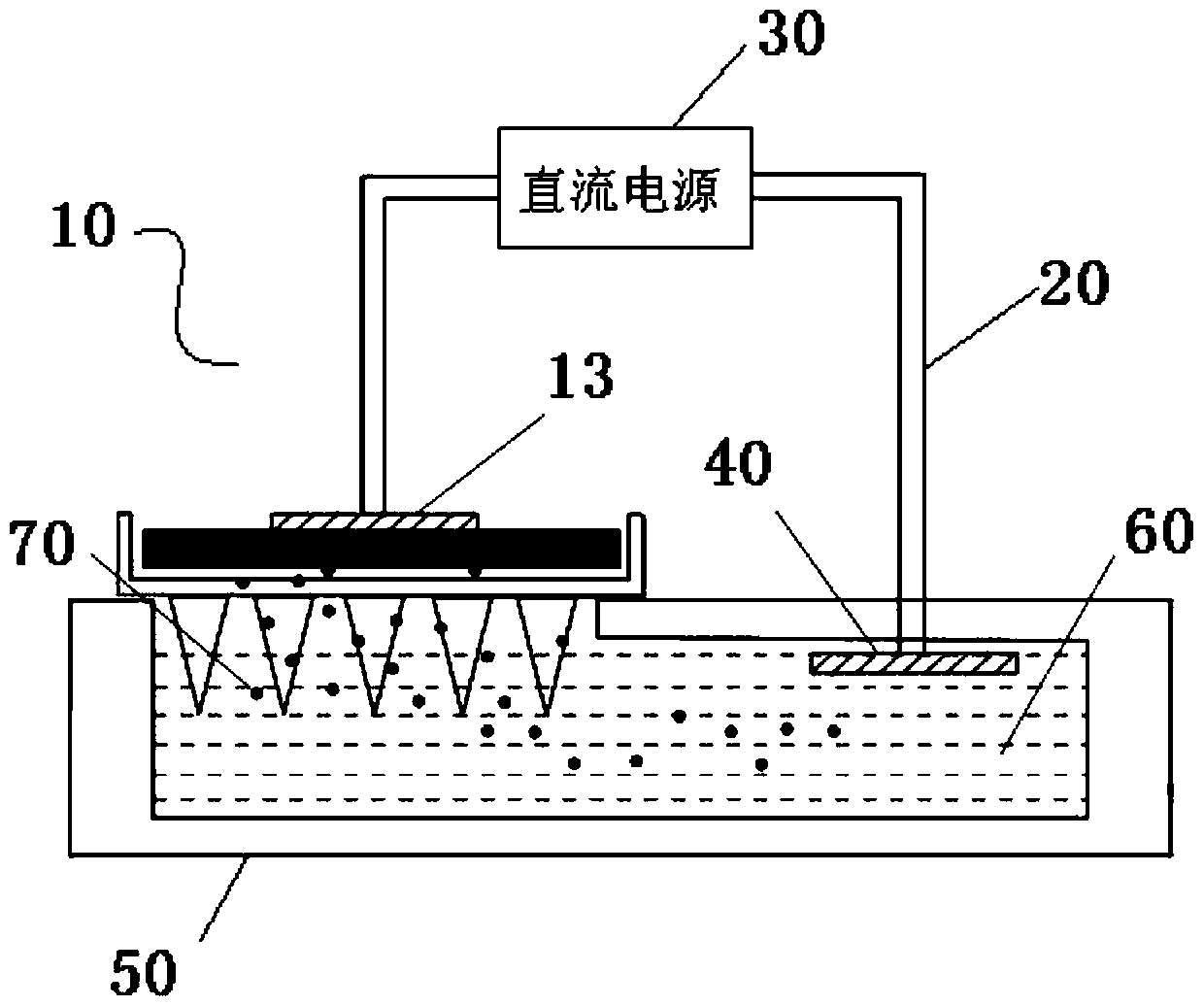
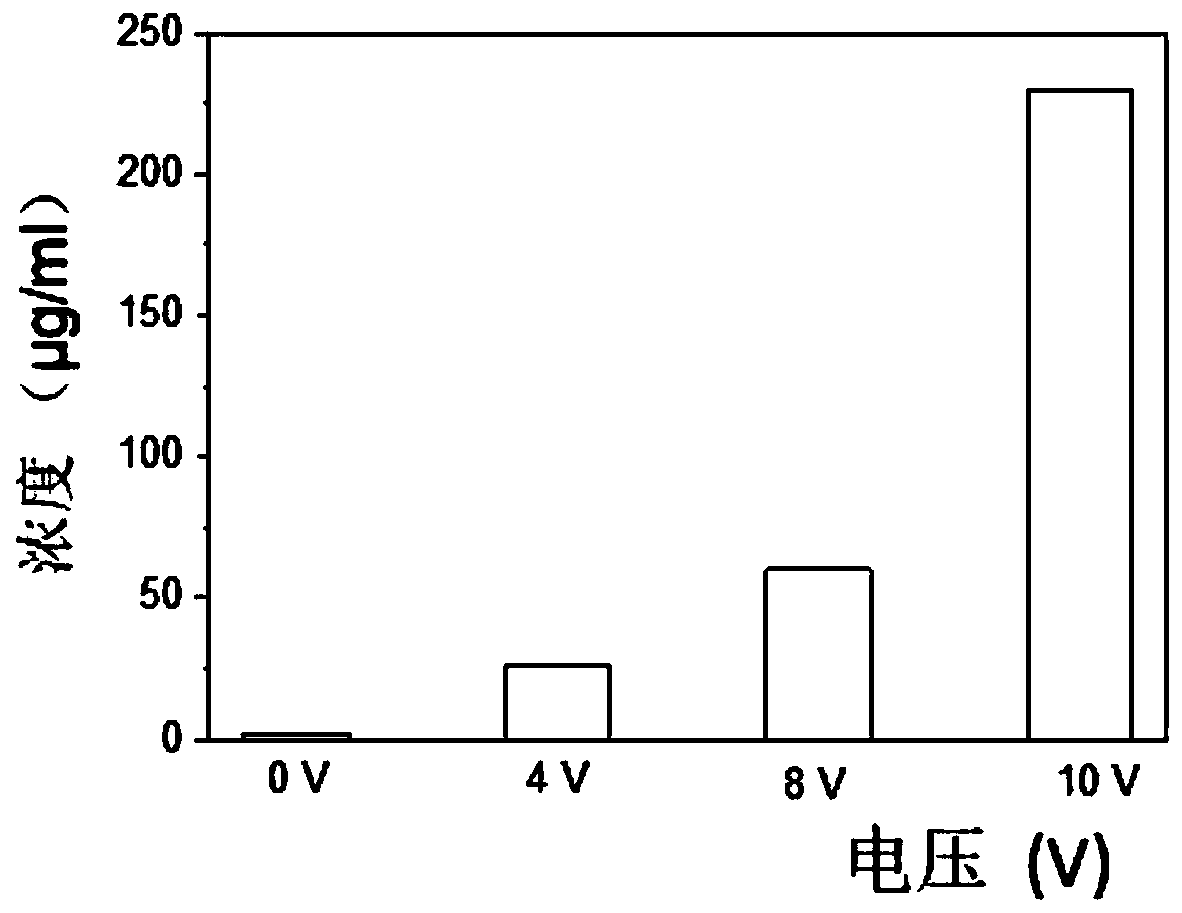
Transdermal precision drug-delivery device based on microneedle-type ionophoresis device and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110404161AIncreased percutaneous diffusion rateEasy to adjustElectrotherapyPeptide/protein ingredientsPolyethylene glycolBlood sugar
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical drug delivery devices, and specifically discloses a transdermal precision drug-delivery device based on a microneedle-type ionophoresis device.The transdermal precision drug-delivery device comprises a composite microneedle, a DC power source and a skin electrode sheet which are sequentially connected by wires, and the composite microneedlecomprises a microneedle patch and a controllableg drug-loading substrate. The microneedle patch is a hydrogel microneedle with a grid gap formed by crosslinking polyethylene glycol-crosslinked polyvinyl methyl ether-maleic acid. The drug-loading substrate comprises a photo-cured polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA) and a composite hydrogel coated with insulin, and a back surface of the compositehydrogel is provided with a microneedle electrode sheet. The drug delivery device efficiently realizes macro-molecule transdermal administration such as insulin, and greatly improves the transdermaldiffusion rate of insulin by ion electrophoresis. The device can achieve more precise and controllable administration by changing the voltage, current and time of ion electrophoresis, realizes intelligent release and termination of insulin, and more accurately regulate blood sugar.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
High-strength hydrogel with hydrogen bond strengthened ion driven shape memory, as well as preparation method and application of hydrogel
The invention discloses high-strength hydrogel with hydrogen bond strengthened ion driven shape memory, as well as a preparation method and an application of the hydrogel. According to the hydrogel, 2-vinyl-4,6-diamino-1,3,5-triazine and acrylic acid are used as monomers, polyethylene glycol diacrylate is used as a cross-linking agent, under the effect of an initiating agent, copolymerization is performed so that the hydrogel is prepared, wherein the mass ratio of the 2-vinyl-4,6-diamino-1,3,5-triazine to the acrylic acid is (1-10) to 1, the mass ratio of the monomers to the cross-linking agent is 2 to 1, and the solid content of gel is 15wt%. The hydrogel disclosed by the invention has very high tensile strength and high compression resistance, and has shape memory under the stimulus of ions and the function of without damaging removed cells. The preparation method is simple, and products are easy to store for a long term storage and transport for a long distance.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for preparing temperature-sensitive crosslinked fiber through low-temperature photopolymerization
InactiveCN104894673AHigh degree of fiber formationMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentFiberSmart hydrogels
The invention provides a method for preparing temperature-sensitive crosslinked fiber through low-temperature photopolymerization. The temperature-sensitive crosslinked fiber provided by the invention is obtained by carrying out low-temperature photopolymerization reaction on a temperature-sensitive photopolymerization monomer and poly(ethylene oxide) diacrylate under the initiation of a free radical photoinitiator, and can be used as a temperature-sensitive tissue engineering scaffold, intelligent hydrogel and a drug controlled release carrier. The method comprises the steps of dissolving the temperature-sensitive photopolymerization monomer, poly(ethylene oxide) diacrylate and the photoinitiator into water; carrying out low-temperature freezing to freeze water to form a crystal; and then, carrying out low-temperature illuminating and crosslinking as well as freeze drying to remove water to obtain the temperature-sensitive crosslinked fiber. The method has the characteristics of simple preparation process, high speed and capability of finishing material crosslinking and fiber forming processes through one-step reaction.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Thixotropic photocured hydrogel, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109851727AFast light curingHigh transparencyAdditive manufacturing apparatusHydrogenUltraviolet lights
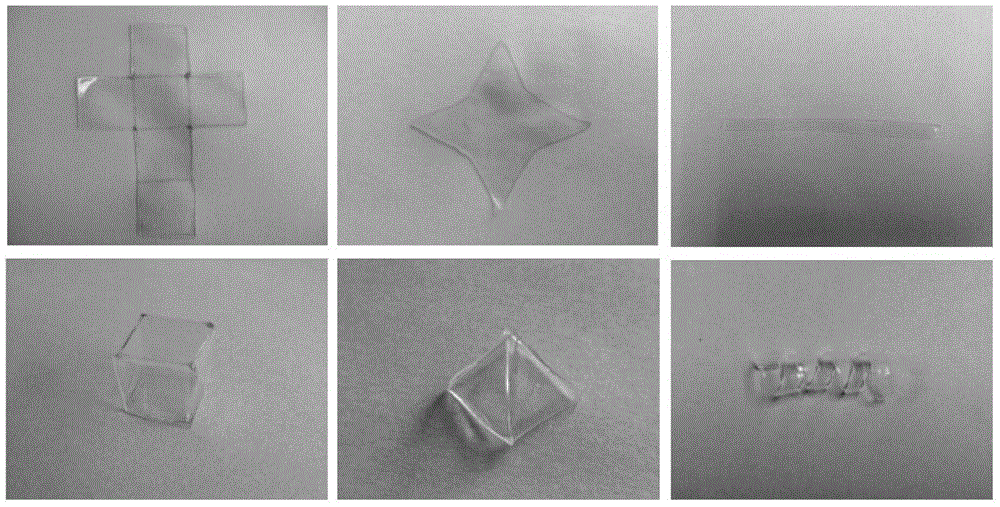
The invention discloses a thixotropic photocured hydrogel, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: fully mixing a rheological modifier with deionized water to obtain a mixture A; adding an acrylamide monomer and polyethyleneglycol diacrylate to the mixture A, and performing full stirring to obtain a mixture B; adding a free radicalphotoinitiator to the mixture B, performing full mixing, and carrying out vacuum defoaming to obtain a defoamed gel; and irradiating the defoamed gel with ultraviolet light or near ultraviolet lightto obtain the cured hydrogel. The thixotropic photocured hydrogel is a photocurable, thixotropic, transparent and soft novel printing medium, and can be printed to form a transparent, soft and photocured complex model; the hydrogen is endowed with the photocuring and thixotropic property, so the complex entity obtained after embedded 3D printing can be preserved; and the transparent and soft properties make the complex entity have great potential in medical surgery prediction.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
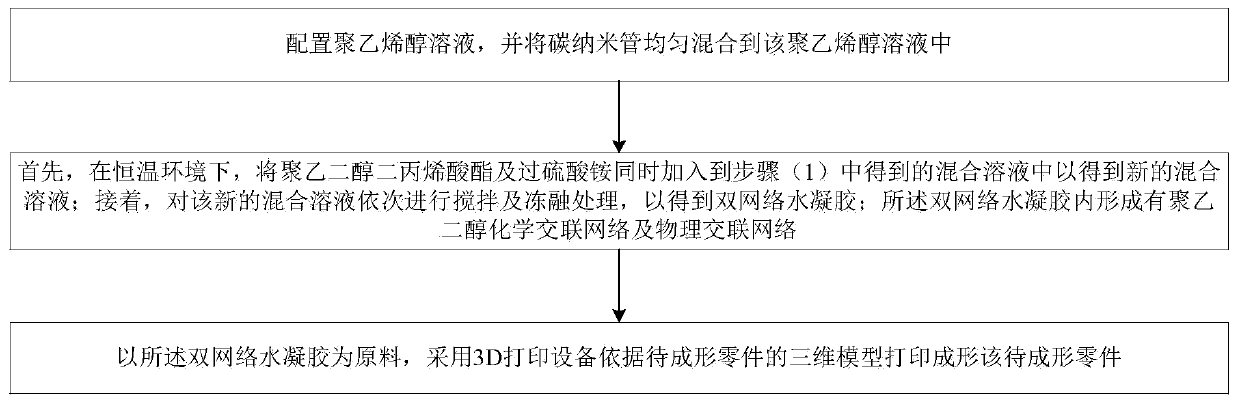
Performance regulation and forming method applicable to double-network intelligent hydrogel and product thereof
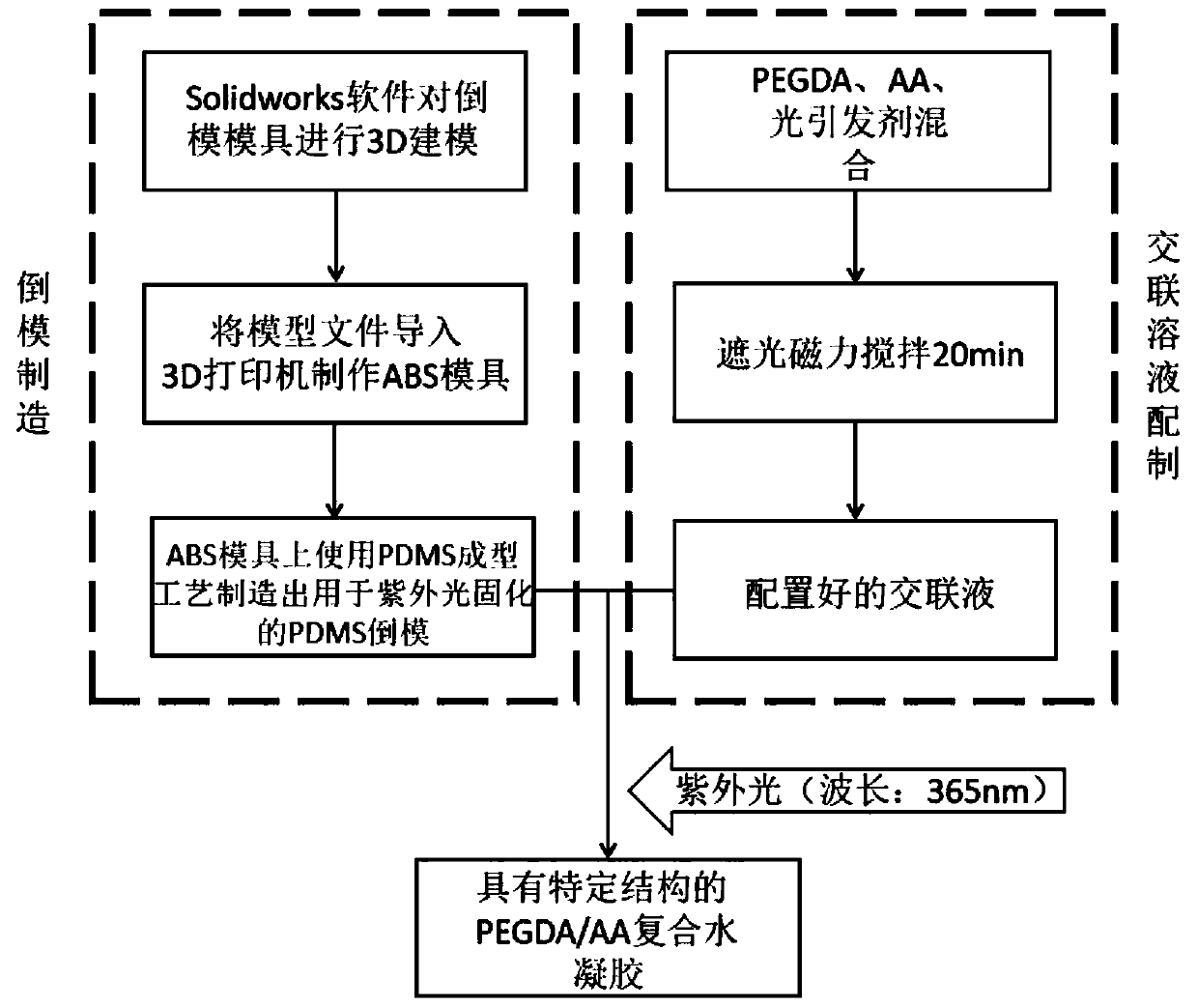
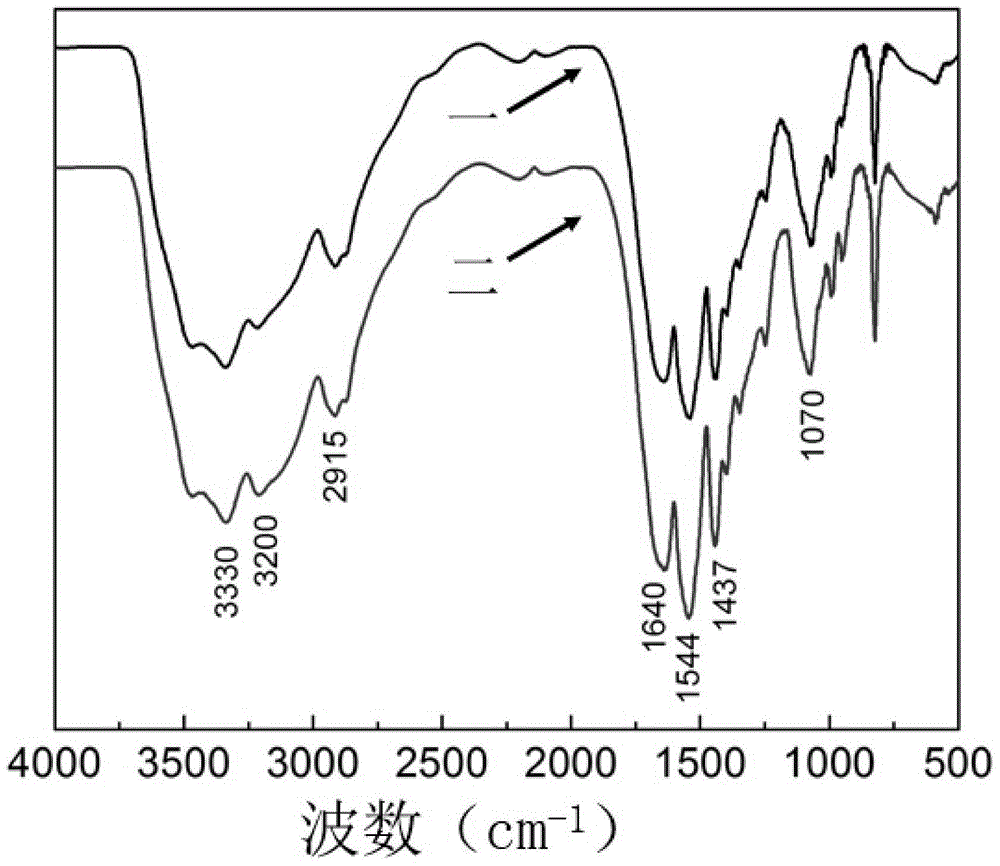
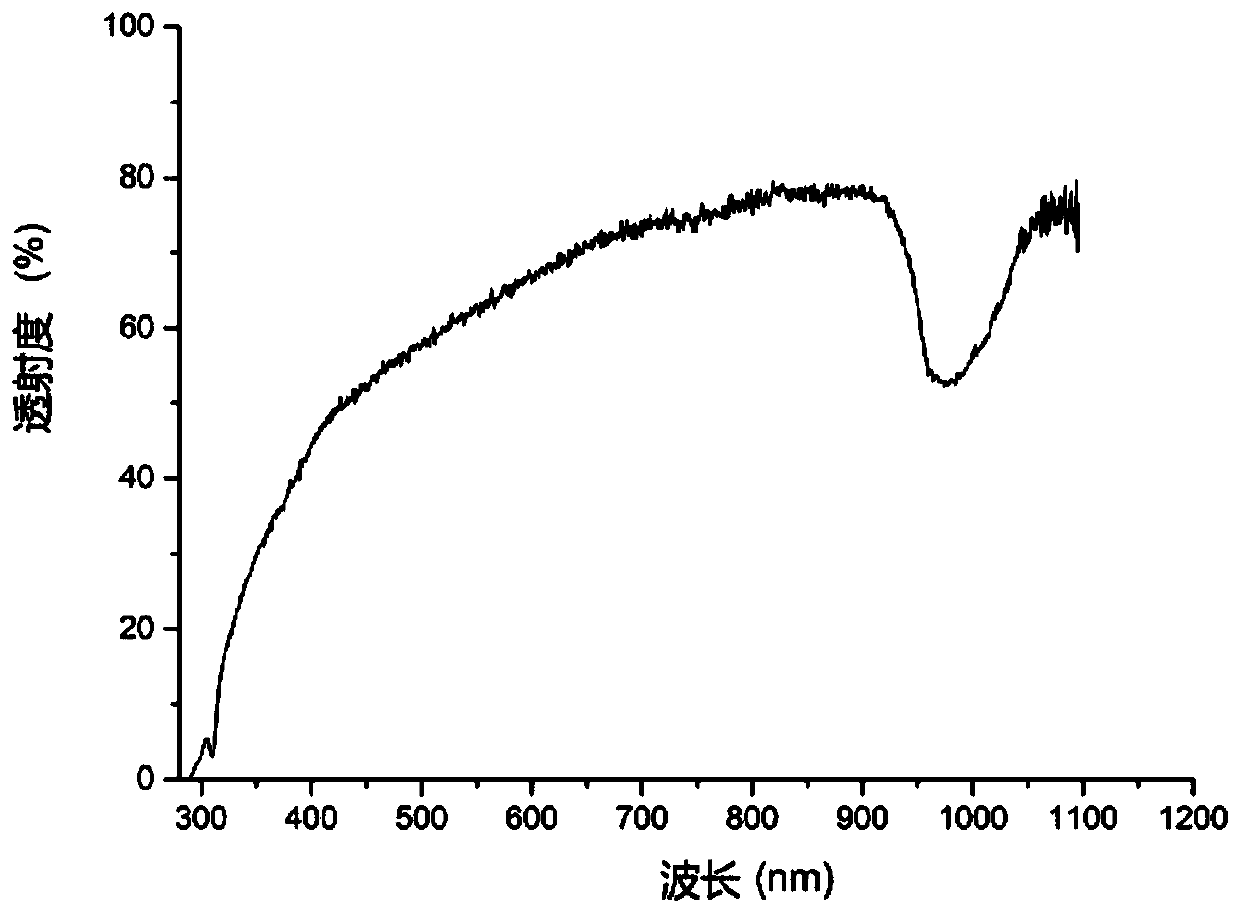
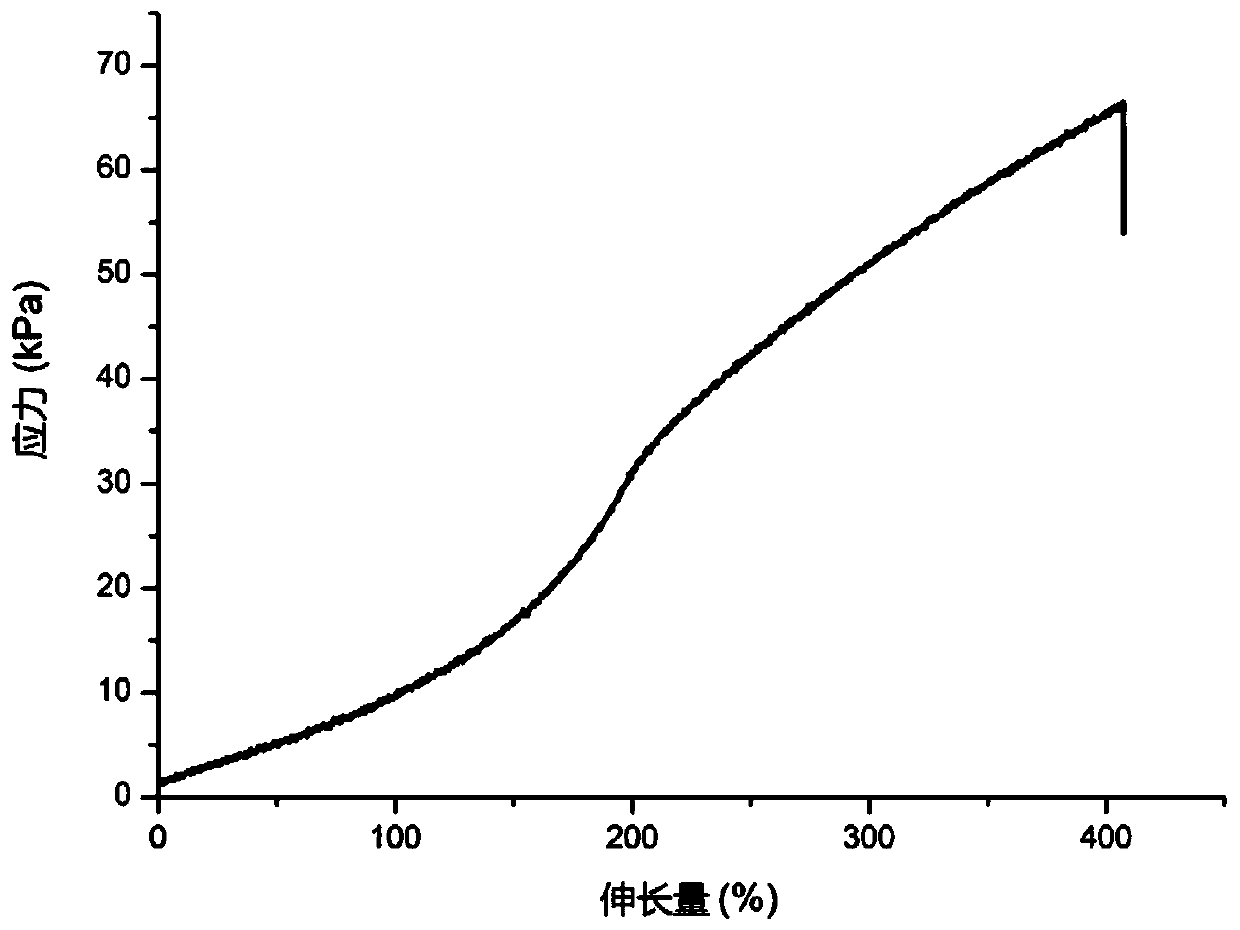
The invention belongs to the technical field of intelligent manufacturing, and discloses a performance regulation and forming method suitable for double-network intelligent hydrogel and a product thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a polyvinyl alcohol solution, and uniformly mixing carbon nanotubes into the polyvinyl alcohol solution; (2) first, simultaneously adding,in a constant temperature environment, polyethylene glycol diacrylate and ammonium persulfate into the mixed solution obtained in the step (1) to obtain a new mixed solution, and then, sequentially performing stirring and freeze thawing on the new mixed solution to obtain a double-network hydrogel, wherein a polyethylene glycol chemical crosslinking network and a physical crosslinking network areformed in the double-network hydrogel; and (3) taking the double-network hydrogel as a raw material, printing and forming a to-be-formed part according to a three-dimensional model of the to-be-formedpart by adopting a 3D printing device. The hydrogel provided by the invention not only has a controllable shape and good surface quality, but also has a good response degree, as well as good mechanical properties and electrical conductivity.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
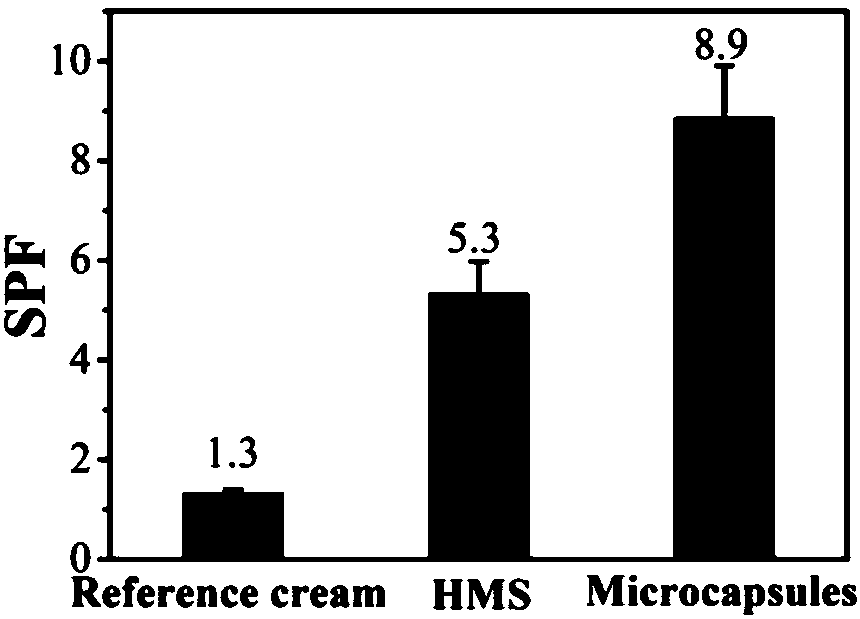
Sun protection microcapsule taking poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate as wall material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108066163ASimple methodFast wayCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsUltravioletWhite powder
The invention relates to a sun protection microcapsule taking poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate as a wall material and a preparation method thereof. The sun protection microcapsule comprises an oil phase and an aqueous phase, wherein the oil phase comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 5.0-30.0% of a core material and 0.01-0.4% of an initiator; the aqueous phase comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 0.5-3.5% of an emulsifier, 2.0-4.0% of poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate and 30.8-75.8% of deionized water. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing the oil phase, preparing the aqueous phase, and preparing the sun protection microcapsule. The method disclosed by the invention is simple, rapid and capable of preparing uniform microcapsules with different particle sizes; the prepared sun protection microcapsule adopts a white powder in a dry state, can be uniformly dispersed in products, has a wide application range, can be coated with multiple ultraviolet protecting agents and is prevented from being influenced by external environmental factors. The ultraviolet resistance of the ultraviolet protecting agents can be obviously improved.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Shape memory anti-tear hydrogel with carbon dioxide responsibility, as well as preparation method and application of shape memory anti-tear hydrogel
The invention discloses a shape memory anti-tear hydrogel with carbon dioxide responsibility and a preparation method. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking 2-vinyl-4,6-diamino-1,3,5-triazine and N,N-dimethyl acrylamide as monomers, taking polyethylene glycol acrylate as a cross-linking agent, and preparing the shape memory anti-tear hydrogel through copolymerization under an initiator, wherein the mass ratio of 2-vinyl-4,6-diamino-1,3,5-triazine to N,N-dimethyl acrylamide is (3:2)to(3:1). The hydrogel has strong stretch resistance, compression resistance, tearing resistance and notching resistance, meanwhile, the hydrogel has stimulative-responsibility on CO2, and has a shape memory function under the stimulation of CO2. The preparation method is simple, and the shape memory anti-tear hydrogel is easy to store for a long time and transport for a long distance.
Owner:鑫通家空间(天津)科技有限公司
Method for preparing pH-value-sensitive crosslinked fiber through low-temperature photopolymerization
InactiveCN104894672AHigh degree of fiber formationEasy to prepareMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentFiberSmart hydrogels
The invention provides a method for preparing pH-value-sensitive crosslinked fiber through low-temperature photopolymerization. The pH-value-sensitive crosslinked fiber provided by the invention is obtained by carrying out low-temperature photopolymerization reaction on a pH-value-sensitive photopolymerization monomer and poly(ethylene oxide) diacrylate under the initiation of a free radical photoinitiator, and can be used as a pH-value-sensitive tissue engineering scaffold, intelligent hydrogel and a drug controlled release carrier. The method comprises the steps of dissolving the pH-value-sensitive photopolymerization monomer, poly(ethylene oxide) diacrylate and the photoinitiator into water; carrying out low-temperature freezing to freeze water to form a crystal; and then, carrying out low-temperature illuminating and crosslinking as well as freeze drying to remove water to obtain the pH-value-sensitive crosslinked fiber. The method has the characteristics of simple preparation process, high speed and capability of finishing material crosslinking and fiber forming processes through one-step reaction.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Sunscreen microcapsule taking polyethylene glycol diacrylate and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108420739AGood biocompatibilityLittle side effectsCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBiocompatibility TestingUltraviolet
The invention discloses a sunscreen microcapsule taking polyethylene glycol diacrylate as a wall material and a preparation method of the sunscreen microcapsule. The microcapsule comprises the raw materials of a core material, an initiator, an emulsifying agent, polyethylene glycol diacrylate, and deionized water. The preparation method is as follows: using the emulsifying agent and part of deionized water to prepare an emulsifying agent aqueous solution, mixing the emulsifying agent aqueous solution, polyethylene glycol diacrylate and the rest of the deionized water to obtain an aqueous phase; mixing the core material and the initiator, evenly mixing under the heating condition to obtain an oil phase; adding the aqueous phase into the oil phase, shearing, forming an emulsion; introducingnitrogen into the emulsion, mechanically stirring, reacting to obtain the microcapsule. The polyethylene glycol diacrylate macromolecule is taken as a monomer, the monomer is non-toxic, is excellent in biocompatibility, contains two double bonds, and is crosslinked under the action of the initiator to form a three-dimensional network high polymer, so that the core material is wrapped to form the sunscreen microcapsule, and the side effect caused by the direct contact between the skin and a chemical ultraviolet protecting agent is reduced.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
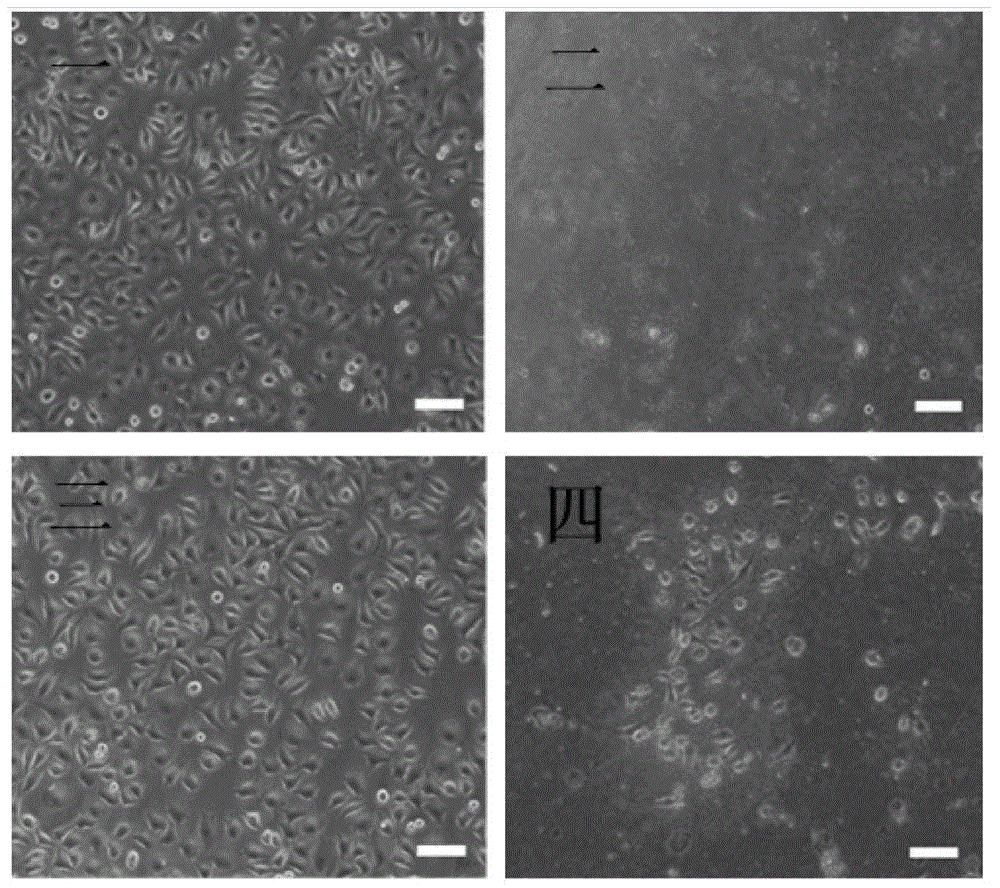
QK-polypeptide-encapsulating polylactide copolymer electrospinning fibrous membrane and preparing method
InactiveCN105107017AAchieve perfect coverageHigh activityPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsFiberN dimethylformamide
The invention relates to a QK-polypeptide-encapsulating polylactide copolymer electrospinning fibrous membrane and a preparing method. The preparing method of the polylactide copolymer electrospinning fibrous membrane includes the steps that a fibrous membrane body with the thickness of 50 micrometers to 200 micrometers is formed by polyethylene glycol-b-poly(lactide-co-epsilon-caprolactone) fibers with the diameter of 100 nm to 900 nm or poly(glycolide-co-epsilon-lactide) fibers with the diameter of 100 nm to 900 nm and chitosan gel particles encapsulated in the fibers, wherein the diameter of the chitosan gel particles is smaller than 100 nm; QK polypeptide, sulfhydrylation chitosan and polyethylene glycol 200 diacrylate are dissolved into a phosphate buffer solution to serve as a water phase (W); polylactide copolymers are dissolved into mixed solvents of chloroform and N,N-dimethylformamide to serve as an oil phase (O); the water phase is added into the oil phase, and stirring is carried out to form W / O dispersion liquid under the effect of emulsifying agents; electrospinning is carried out on the dispersing liquid to obtain the fibrous membrane. According to the QK-polypeptide-encapsulating polylactide copolymer electrospinning fibrous membrane and the preparing method, the preparing process is simple, the good biocompatibility and the good degradability are achieved, and the fibrous membrane and the preparing method can be used for the tissue engineering field and the in-situ drug sustained release field.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Polylactide electrospinning composite film for in-situ gel encapsulating and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102505350AEasy to makeGood biocompatibilityNon-woven fabricsSpinning solutions preparationFiberComposite film
The invention discloses a polylactide electrospinning composite film for in-situ gel encapsulating and a preparation method of the polylactide electrospinning composite film. The electrospinning composite film consists of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) or polyethylene glycol-b-poly(lactide-co-caprolactone) fibers and chitosan or gelatin gel particles in the fibers. The preparation method comprises the steps that: sulfydryl chitosan or sulfydryl gelatin and polyethyleneglycol diacrylate are dissolved in phosphate buffer liquid to be used as water phases; the poly(lactide-co-glycolide) or the polyethylene glycol-b-poly(lactide-co-caprolactone) is dissolved in mixed organic solvents to be used as oil phases; and the water phases are added to the oil phases, water / oil (W / O) dispersing liquid is formed through adding emulsifying agents under the stirring condition, and the electrospinning composite film is obtained through the electrospinning of the dispersing liquid. The polylactide electrospinning composite film and the preparation method have the advantages that the preparation process is simple, the prepared composite film has good biocompatibility, degradability, hydrophily and mechanical property, the medicine dumping is reduced, and the medicine release speed is adjustable and controllable. The polylactide electrospinning composite film and the preparation method are used for the tissue engineering and medicine release fields.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Synthesis method of hollow mesoporous silicon dioxide nano-drug capsule
InactiveCN106619570AAvoid leakage lossIncrease densityHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsDrug capsuleSynthesis methods
The invention belongs to the field of nano-drugs, and particularly relates to a synthesis method of a hollow mesoporous silicon dioxide nano-drug capsule. The synthesis method comprises the following steps: modifying hollow mesoporous silicon dioxide through an acrylic acid propyl ester group, dispersing the hollow mesoporous silicon dioxide into a drug-containing buffer solution, then adding polyethylene glycol diacrylate and ammonium persulfate serving as an initiator, and dripping N,N,N',N'-tetramethylethylenediamine serving as an accelerator to enable the polyethylene glycol diacrylate and the acrylic acid propyl ester group to generate polymerization reaction on the surface of the hollow mesoporous silicon dioxide to form a polymer coated layer. Loading of a drug and encapsulation of a nano capsule are completed in the drug-containing buffer solution, so that leakage of the drug in an encapsulation process can be avoided; the synthesis process is simple, and the coating thickness and the compactness can be adjusted.
Owner:XINYANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Alkyl acrylate-aromatic vinyl compound-vinyl cyanide compound copolymer with improved low-temperature impact strength and polycarbonate composition comprising the same
ActiveUS20160304651A1High impact strengthLow-temperature impact strengthCyanide compoundCompound (substance)
Disclosed are an alkyl acrylate-aromatic vinyl compound-vinyl cyanide compound copolymer which is prepared using a polyalkylene cross-linking agent such as polyethylene glycol diacrylate or polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate for a core of the alkyl acrylate-aromatic vinyl compound-vinyl cyanide compound copolymer and thus advantageously improves low-temperature impact strength of resins when the copolymer is applied to a polycarbonate resin composition, and the polycarbonate resin composition comprising the copolymer.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
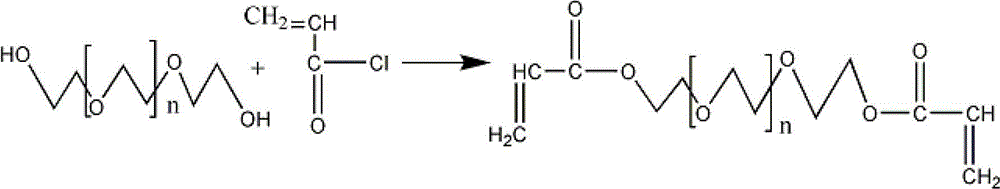
Preparation method and application of high-molecular weight polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA)
The invention provides a preparation method of high-molecular weight (greater than 3,000 Dalton) polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA), which comprises the following steps: fetching high-molecular weight polyethylene glycol (PEG) to react with an organic solvent and an elementary-substance metal; and adding a polymerization inhibitor, and purifying to obtain PEGDA of different yields. According to the method provided by the invention, the high-molecular weight PEG is adopted as a raw material, the use of the reagent with relatively high volatility and toxicity is avoided, the molecular elasticity is improved while the energy consumption is reduced, and the synthesis yield is improved.
Owner:广州市一杰医药科技有限公司
Method for rapidly preparing high-quality acrylamide gel film
The invention provides a method for rapidly preparing a high-quality acrylamide gel film. The method comprises the following steps: (a) a piece of glassware and two pieces of float glass are pretreated; (b) poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate is added to the glassware, then N-isopropylacrylamide and N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide are added and dissolved, an initiator and a catalyst are added, and the substances are ultrasonically mixed in an ice bath; (c) one piece of float glass is soaked in the initiator, the other piece of float glass is soaked in the catalyst, and the initiator and the catalystare uniformly dispersed on the surfaces of the corresponding float glass by ultrasonic waves; (d) one piece of float glass is placed on a water plane, an acrylamide prepolymer solution is added dropwise, then the other piece of float glass is pressed on the acrylamide prepolymer solution, and gelation is performed for 2-4 h. The film forming time of acrylamide gel is shortened effectively, the film forming quality is improved, and the defect that harsh film forming conditions and equipment are required by the conventional method is overcome.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
Preparation method for high-strength high-toughness micro polylactic acid product
The invention relates to the technical field of high polymer materials, in particular to a preparation method for a high-strength high-toughness micro polylactic acid product. The preparation method for the high-strength high-toughness micro polylactic acid product comprises the steps that polylactic acid, dicumyl peroxide and polyethylene glycol diacrylate are subjected to melt blending for 1-6 minutes at the temperature of 170-190 DEG C, and the micro polylactic acid product is prepared by using a micro injection molding method, wherein the weight part ratio of the polylactic acid to the dicumyl peroxide to the polyethylene glycol diacrylate is 100:0.3:(0.1-0.5); according to the micro injection molding process, the injection speed is 200-500 mm / s, the injection temperature is 170-190 DEG C, the injection pressure is 500-1200 bar, and the mold temperature is 50-100 DEG C. The polylactic acid product prepared by using the method is high in strength and toughness.
Owner:SHAANXI SCI TECH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com