Patents
Literature
40 results about "Gallium sulfide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gallium sulfide may refer to: Gallium sulfide, Ga₂S₃ Gallium sulfide, GaS
Device and method for emitting output light using group IIB element selenide-based and group IIA element gallium sulfide-based phosphor materials
InactiveUS20050156510A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesGallium sulfidePhosphor
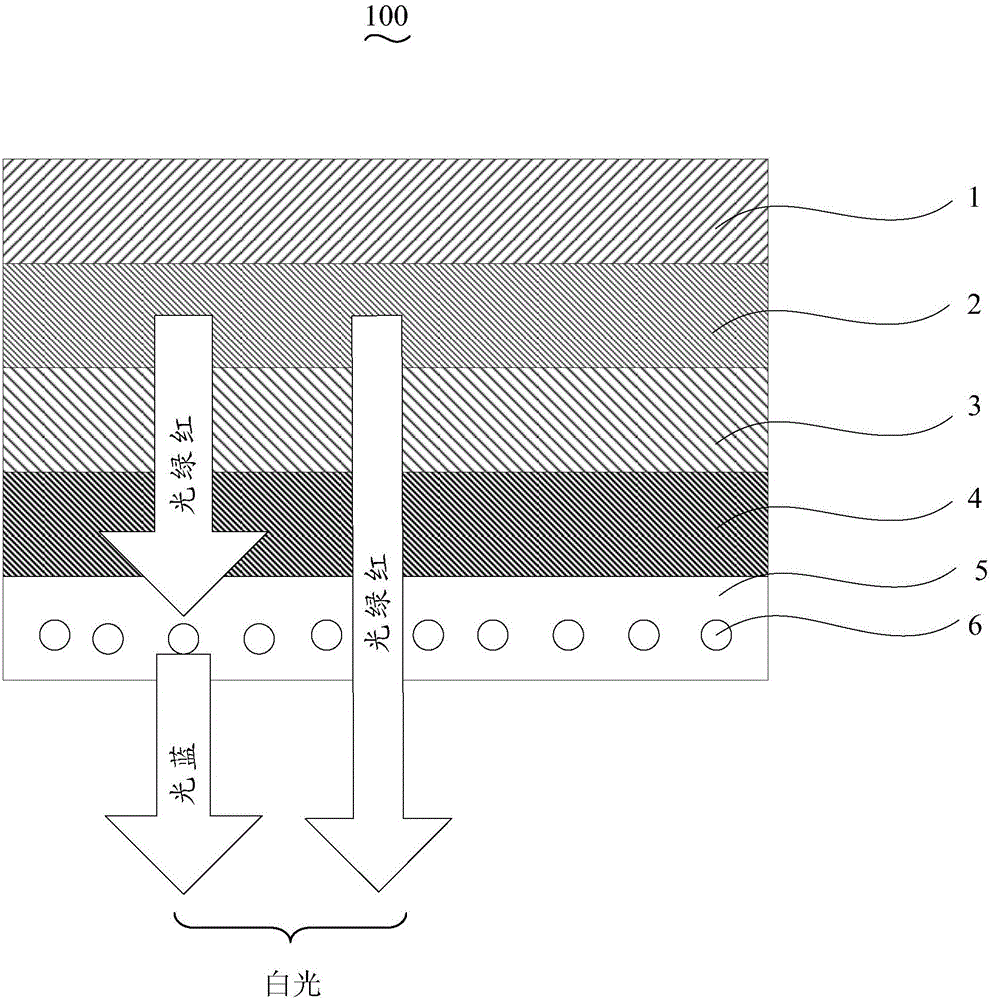
A device and method for emitting output light utilizes a mixture of Group IIB element Selenide-based phosphor material and Group IIA element Gallium Sulfide-based phosphor material in which the Group IIA element includes Calcium, Strontium and / or Barium to convert some of the original light emitted from a light source of the device to longer wavelength light to change the optical spectrum the output light. Thus, the device and method can be used to produce white color light. The mixture of Group IIB element Selenide-based and Group IIA element Gallium Sulfide-based phosphor materials is included in a wavelength-shifting region optically coupled to the light source, which may be a blue light emitting diode (LED) die.
Owner:AVAGO TECH ECBU IP (SINGAPORE) PTE LTD +1
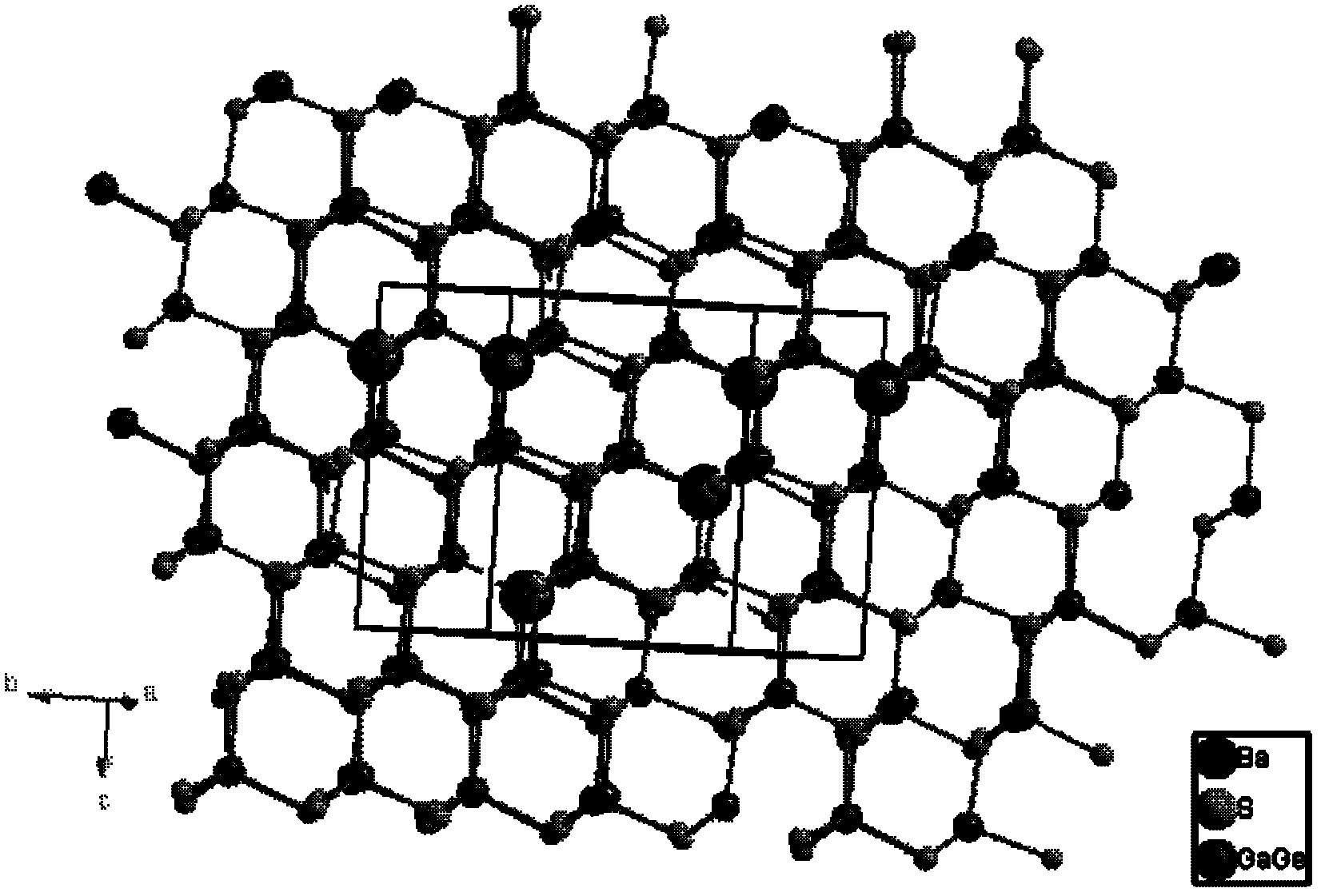
Novel non-linear optical crystal gallium germanium barium sulfide, and growing method and application thereof
ActiveCN102383196AHigh hardnessImprove mechanical propertiesPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsNonlinear optical crystalMiddle infrared
The invention provides novel non-linear optical crystal gallium germanium barium sulfide, and a growing method and application thereof. The chemical formula is BaGa2GeS6 (short for BGGS). The novel non-linear optical crystal gallium germanium barium sulfide has the chemical formula of BaGa2GeS6, has an asymmetrical center structure and belongs to a trigonal crystal system, wherein the space group is R3; and cell parameters are that: a=9.5967(5) Angstrom, b=9.5967(5) Angstrom, c=8.6712(7) Angstrom, alpha=90 degrees, beta=90 degrees, gamma=120 degrees, Z=1, and V=691.62 Angstrom3. The clock multiplier factor of the BaGa2GeS6 is 0.8 time that of AgGaS2. The BGGS compound is obtained by sintering at high temperature through a solid phase synthesis method. The BGGS monocrystal can grow successfully by a crucible descending method. The BaGa2GeS6 has a non-linear optical effect, is not dissolved in dilute acid, has high chemical stability, can be widely applied in various non-linear optical fields, and can develop non-linear optical application of a middle infrared band.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing flexible optical detector on basis of two-dimensional functional material
InactiveCN102664218AEasy to separateEasy transferFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor materialsAdhesive
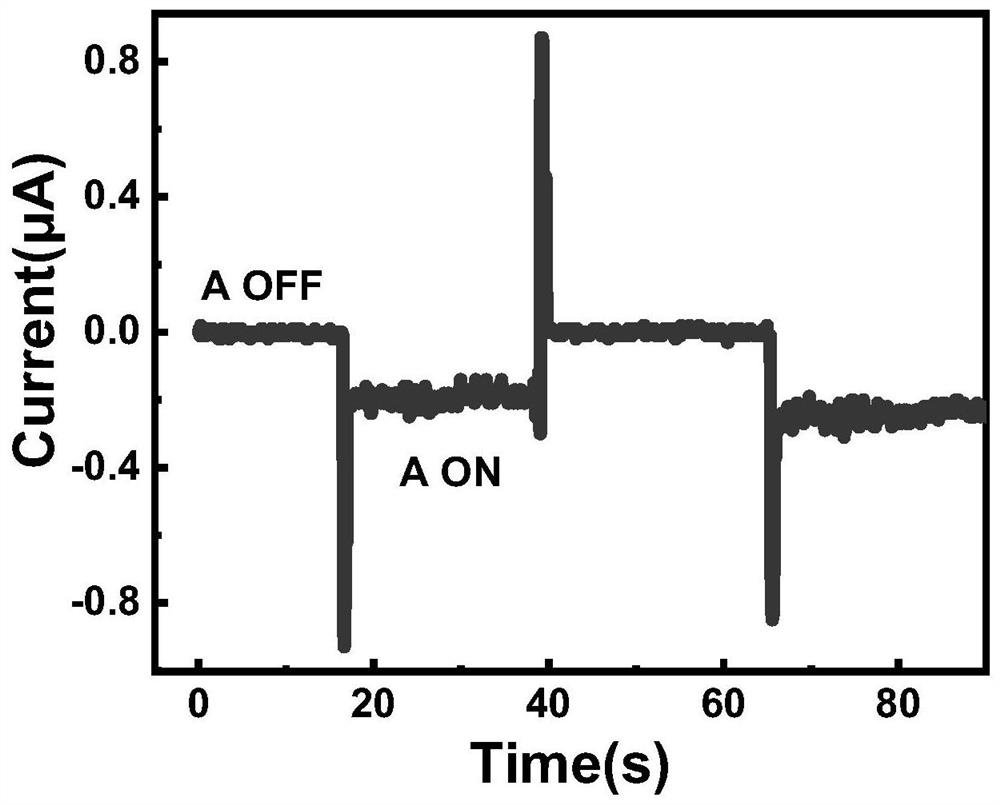
The invention discloses a method for preparing a flexible optical detector on the basis of the two-dimensional functional material, which relates to a preparation method for the optical detector. The method mainly aims to solve the technical problems that the conventional flexible optical detector has high photolithographic process technology cost and has difficulty in realizing mass production. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) preparing semiconductor materials, i.e. single crystal gallium selenide or single crystal gallium sulfide; 2) sticking and stripping on the surface of the semiconductor material by a scotch adhesive tape; 3) transferring the two-dimensional semiconductor material to a substrate; 4) covering a copper mask to the substrate processed in the step 3), depositing a gold metal layer and a chrome layer, removing the mask, and carrying out annealing processing; and 5) screening electrode couples with photoelectronic response to ultraviolet light in an optical detector semiconductor obtained in the step 4) to obtain the flexible optical detector prepared on the basis of the two-dimensional functional material. The ultraviolet light response degree of the optical detector is above 100AW<-1>. The flexible optical detector can be used as a microelectronic device and a photosensitive device to be used for the field of information transmission and storage.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
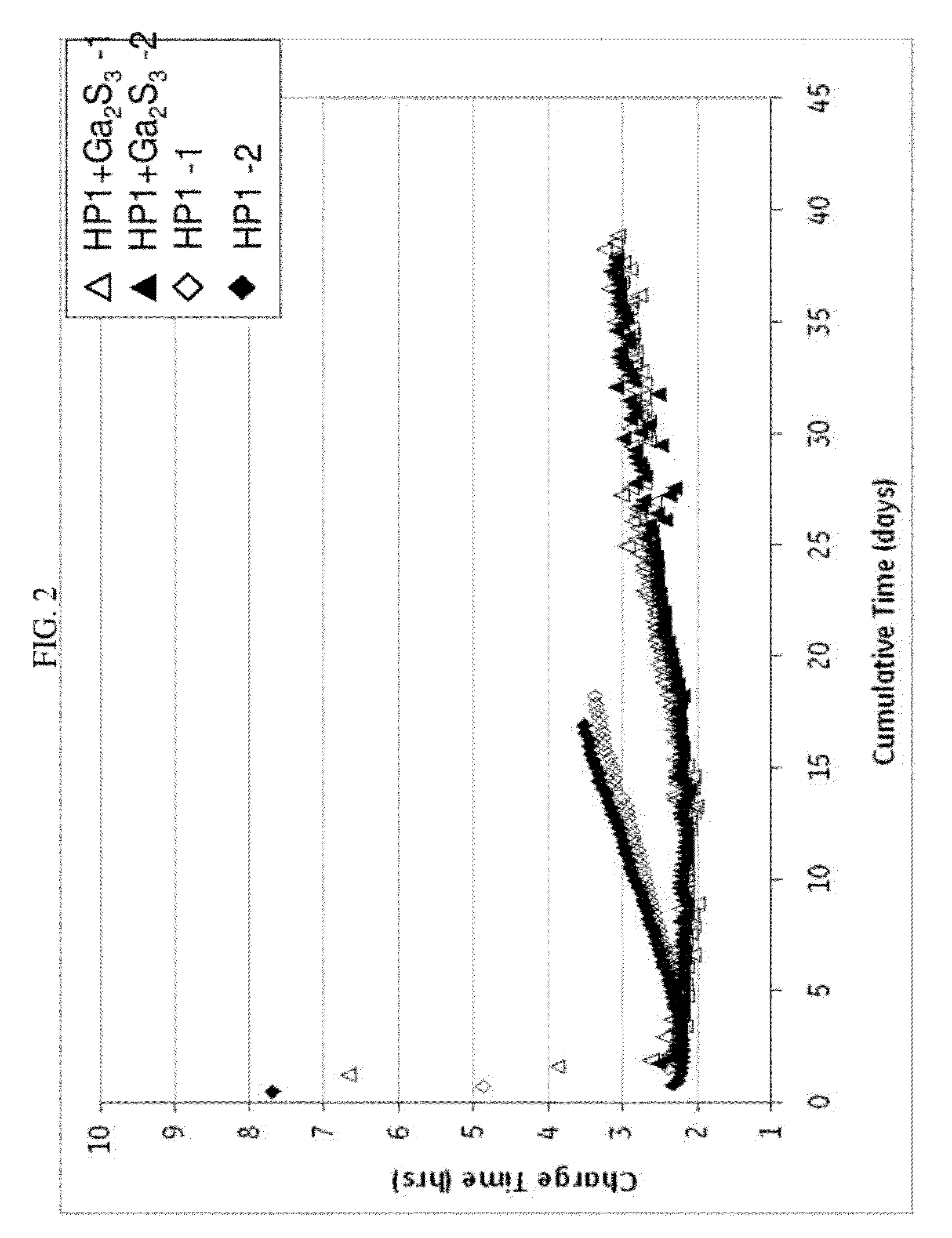
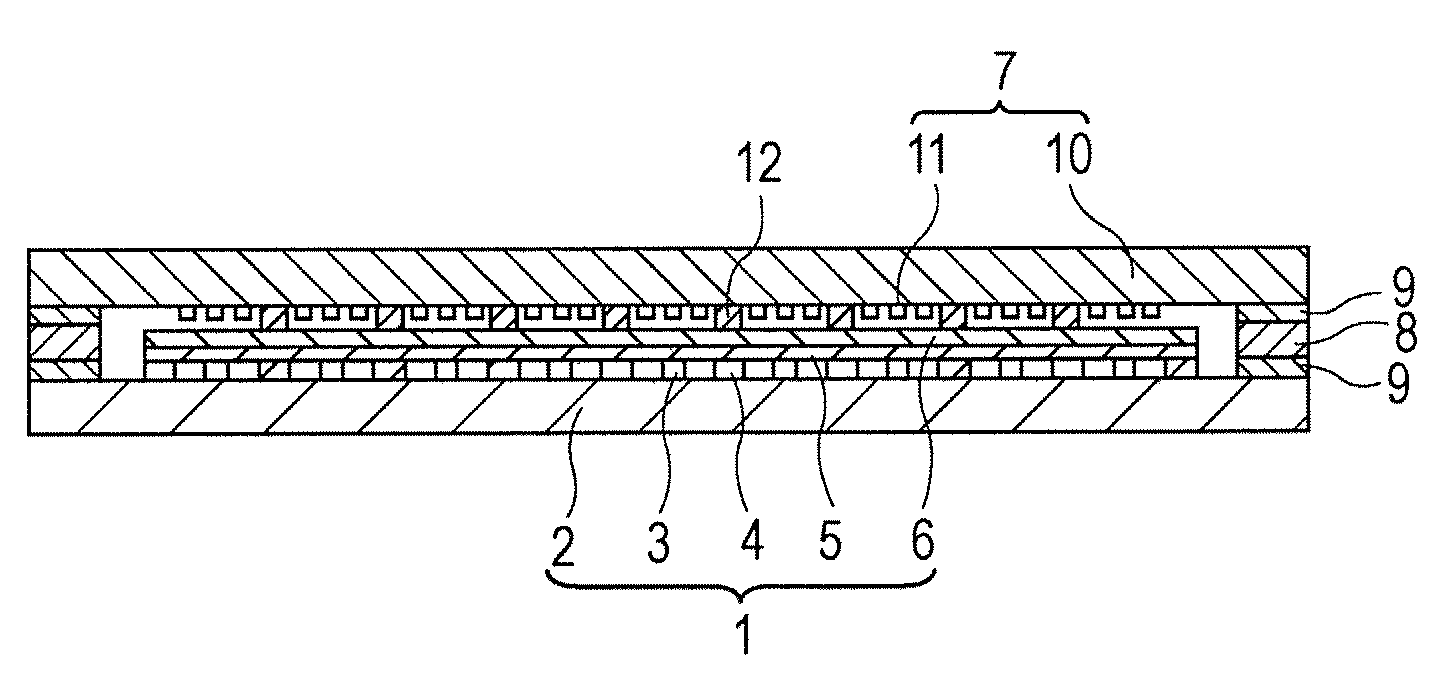
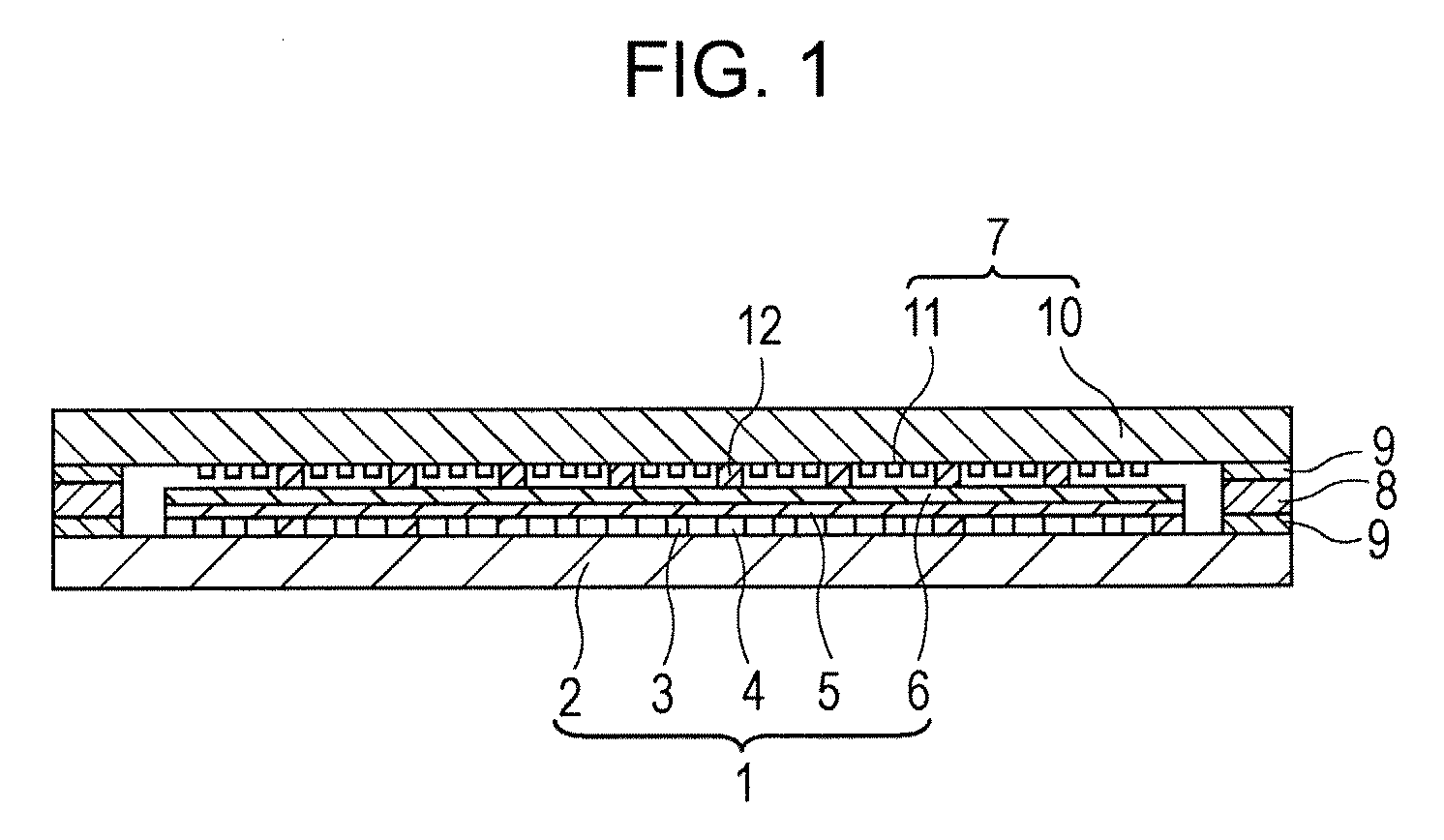
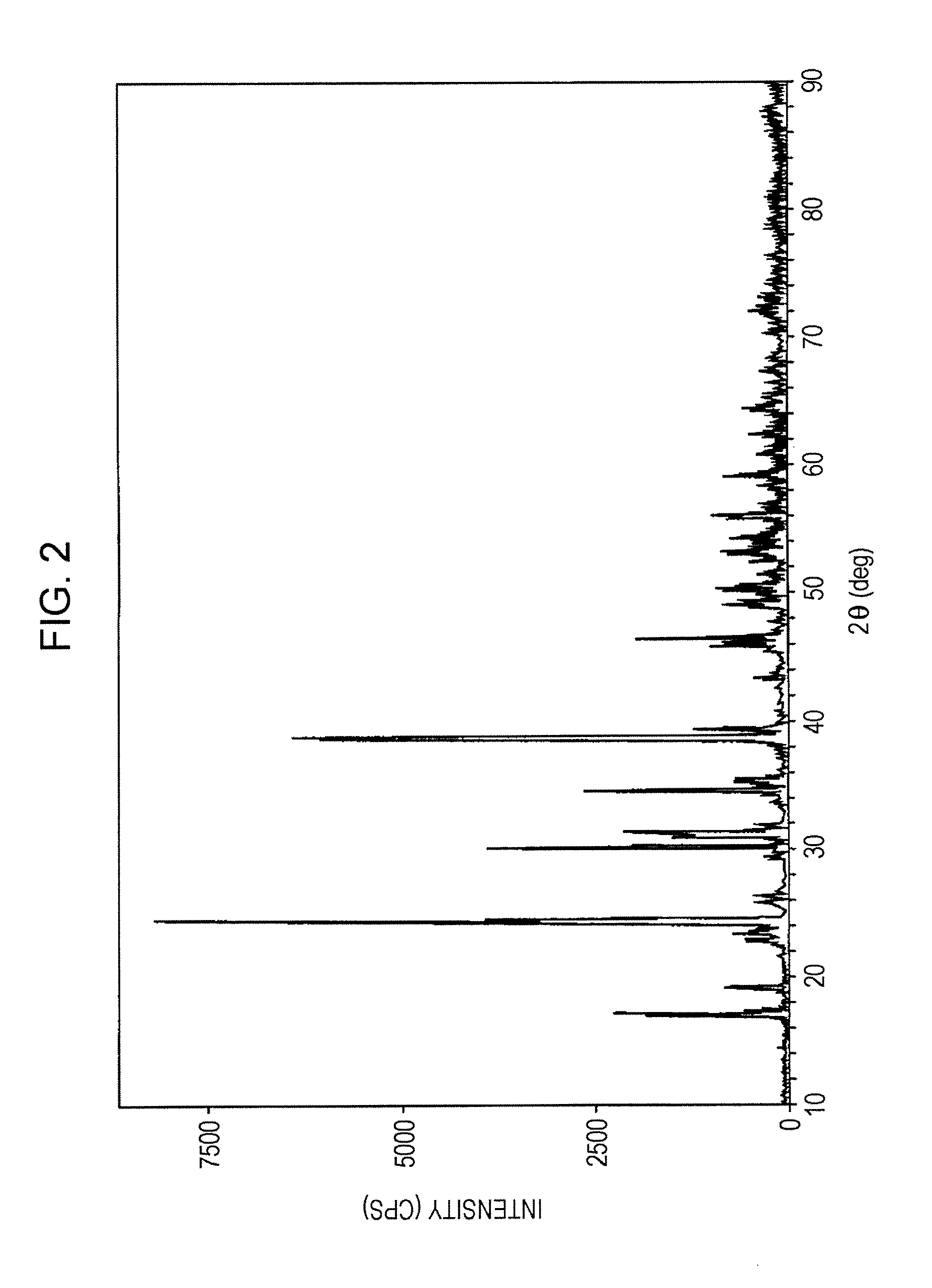
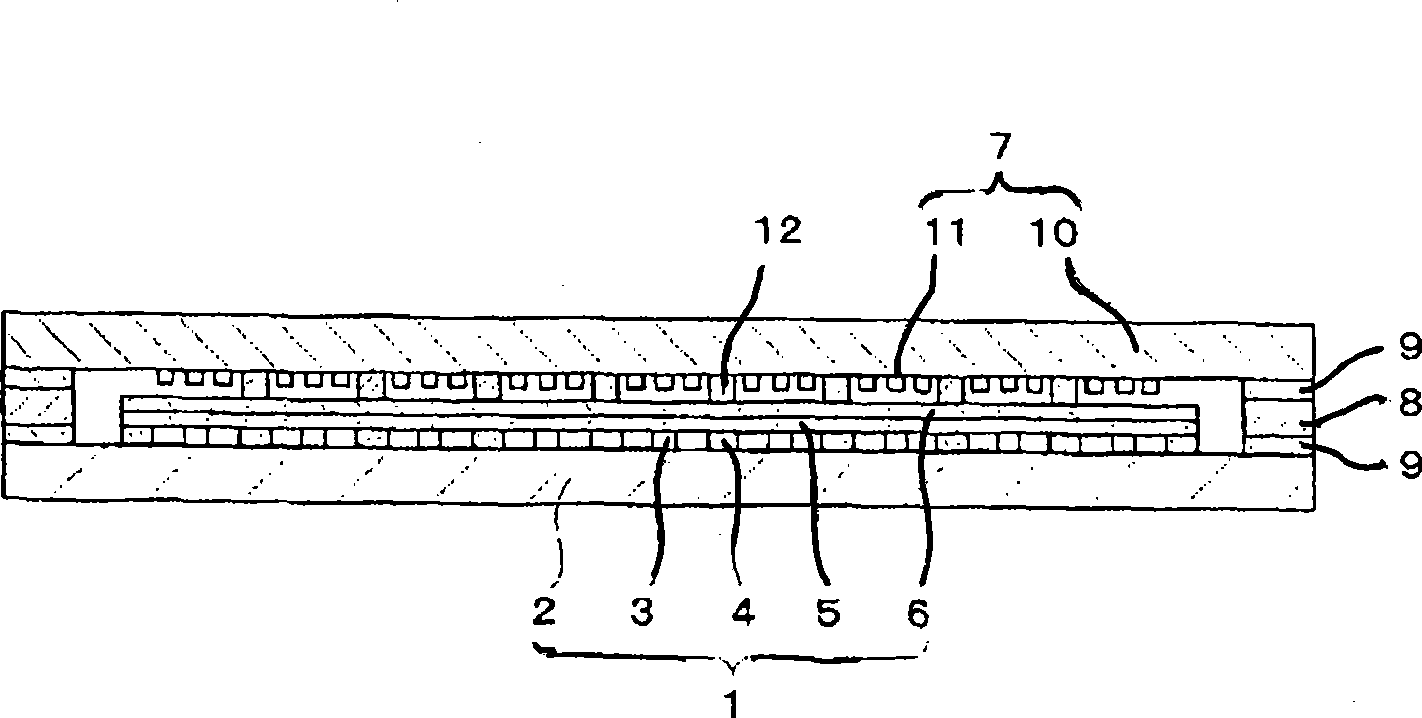
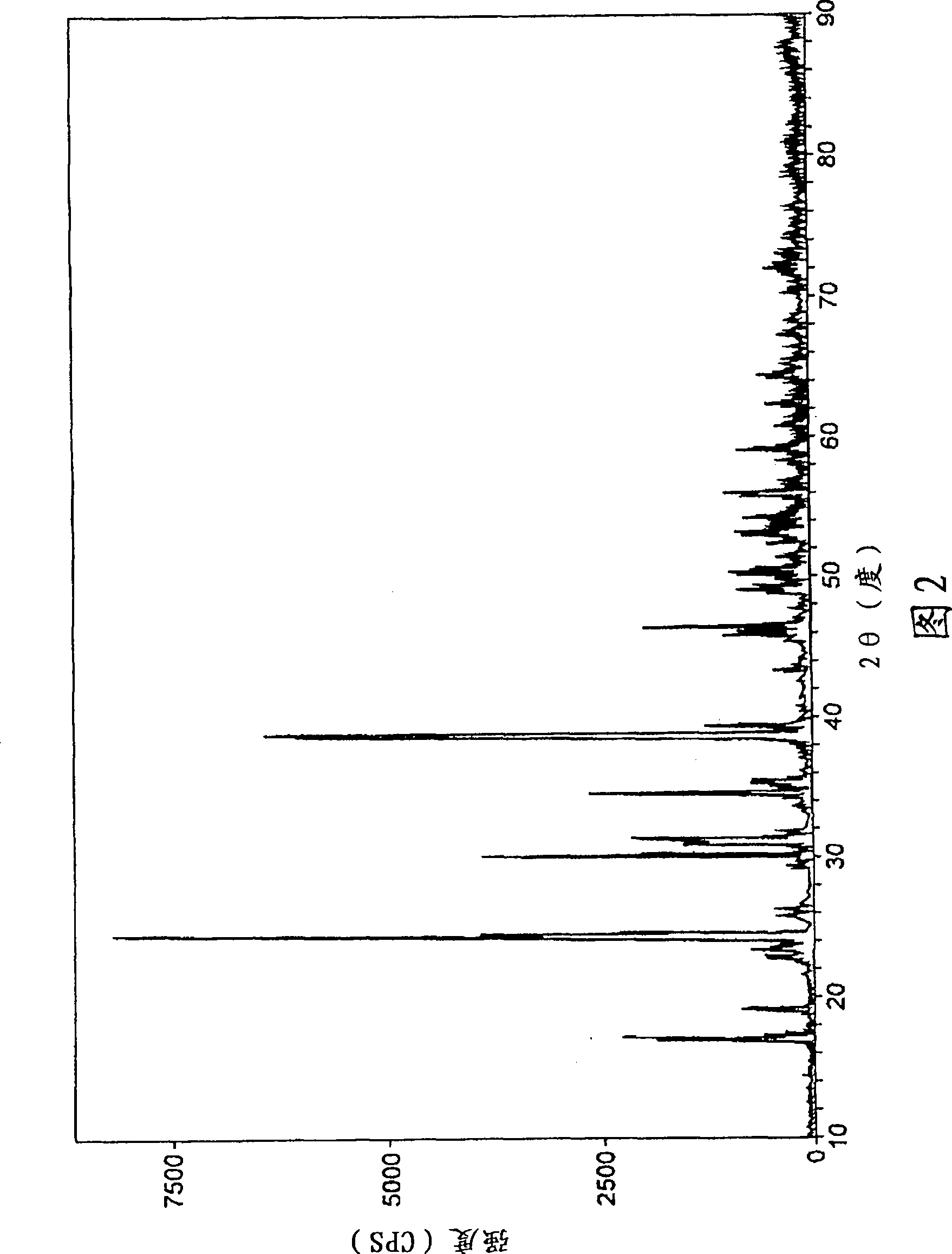
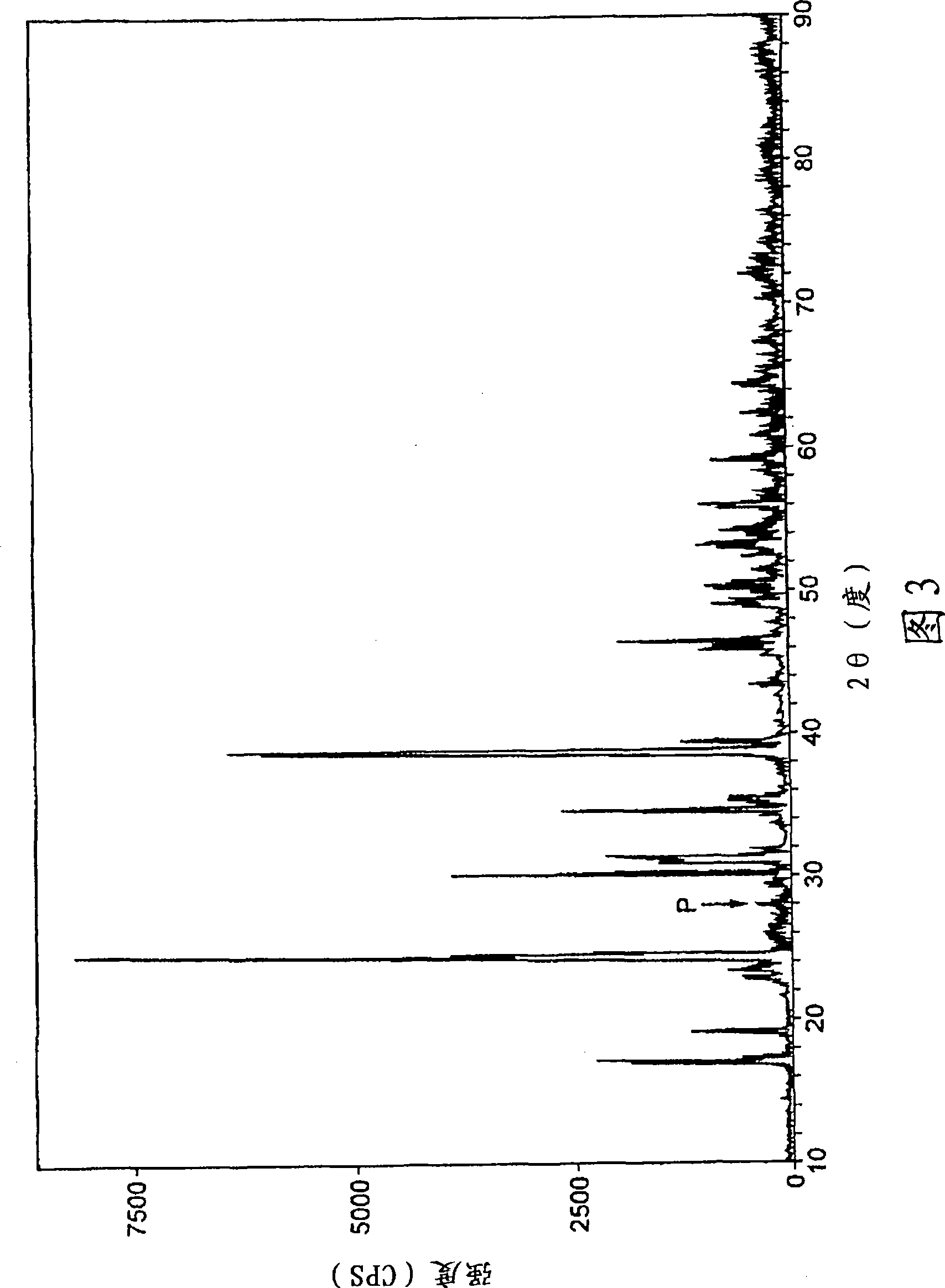
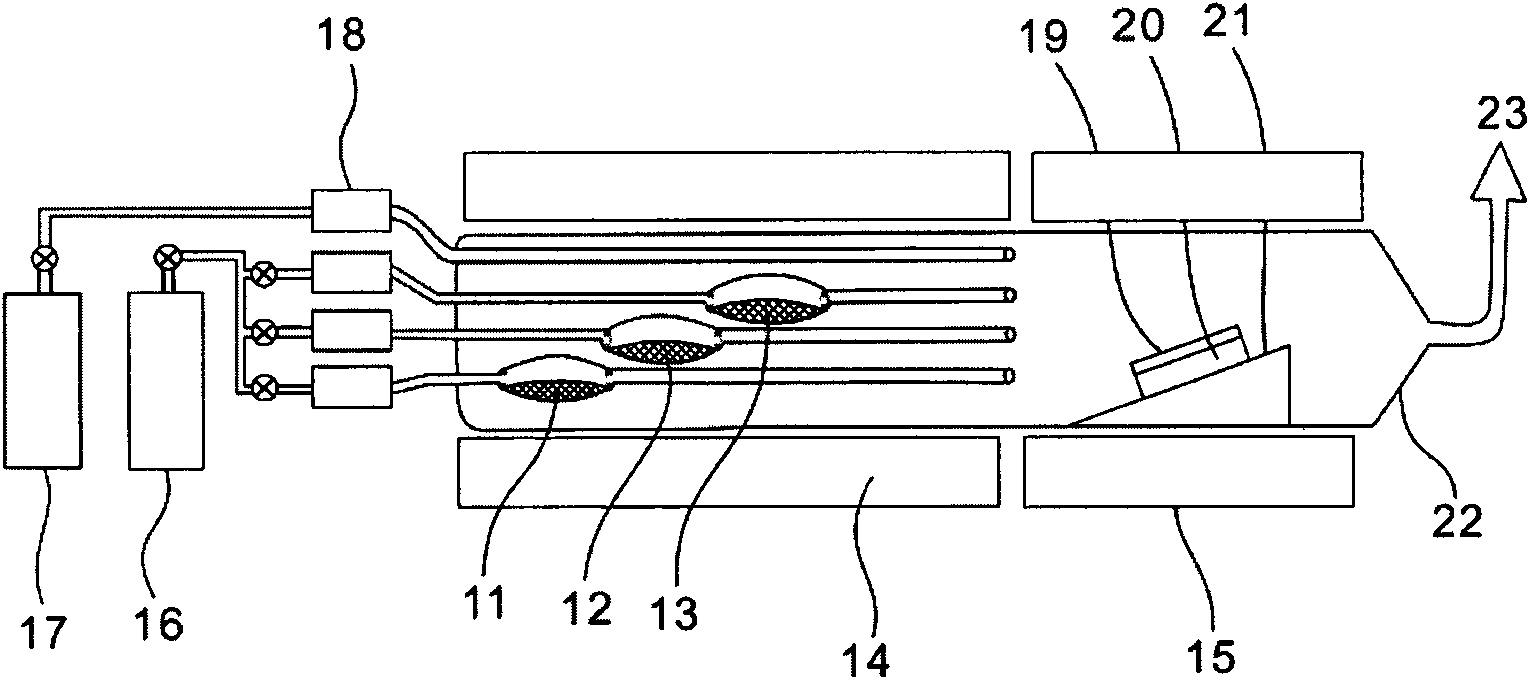
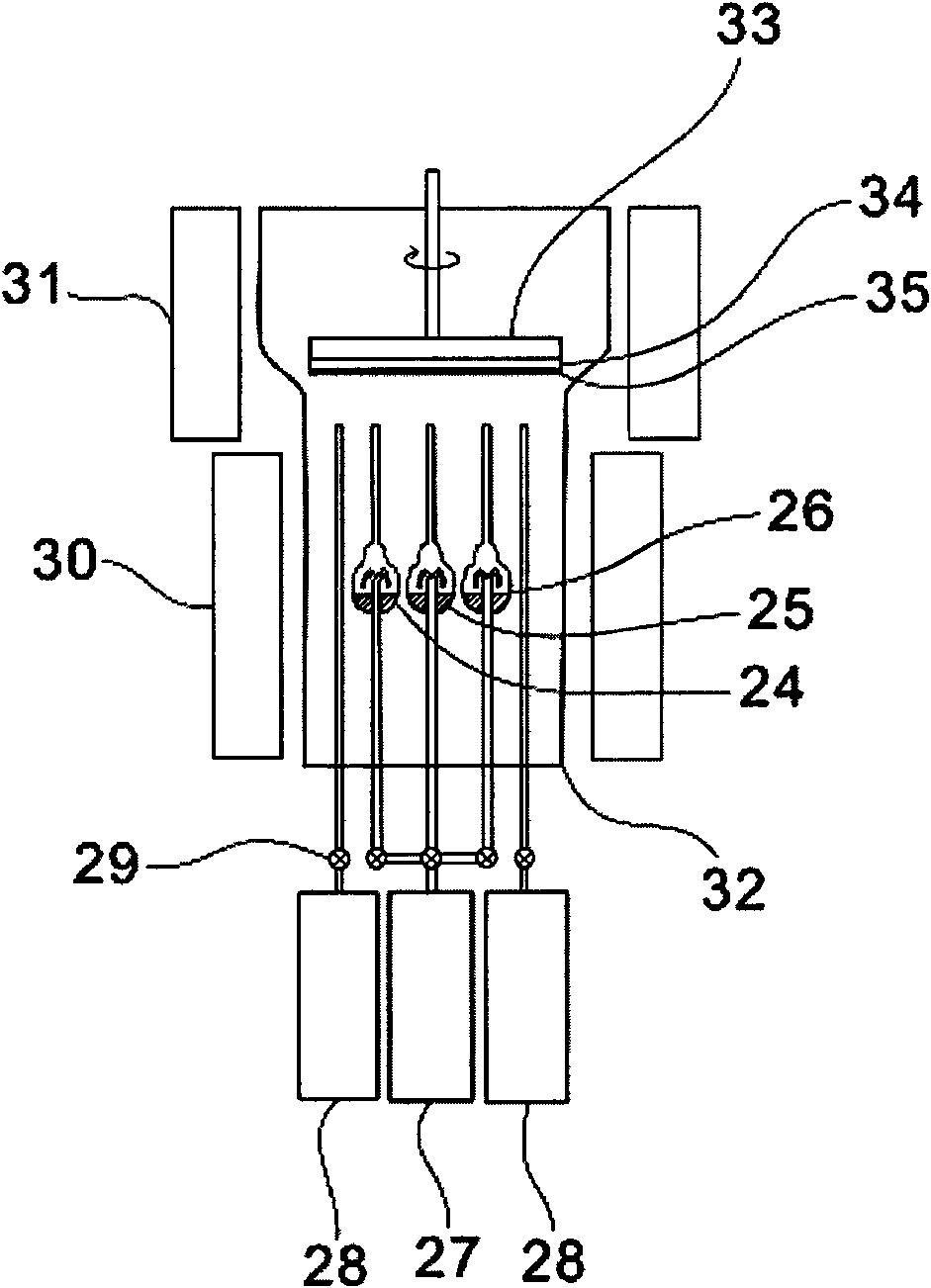
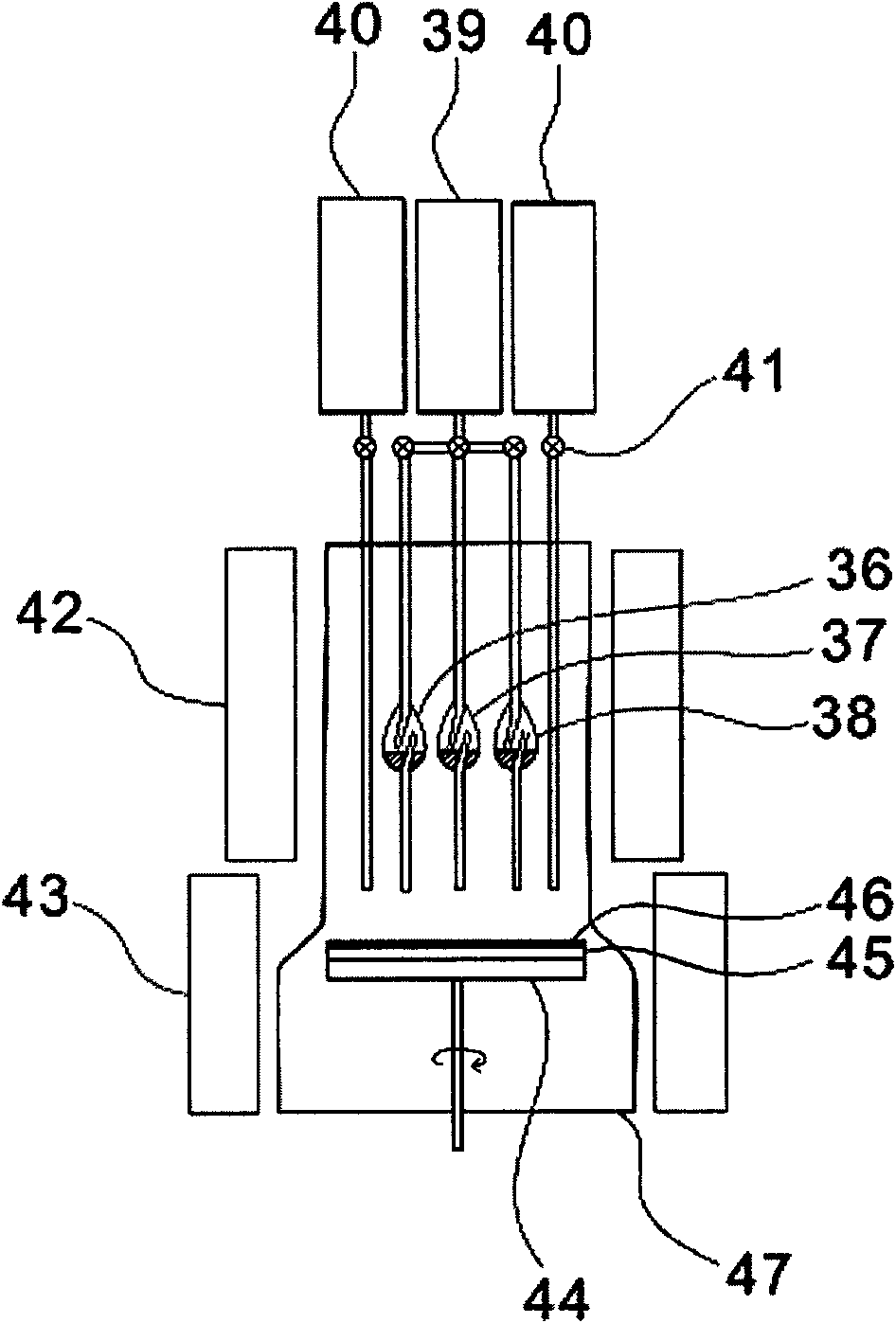
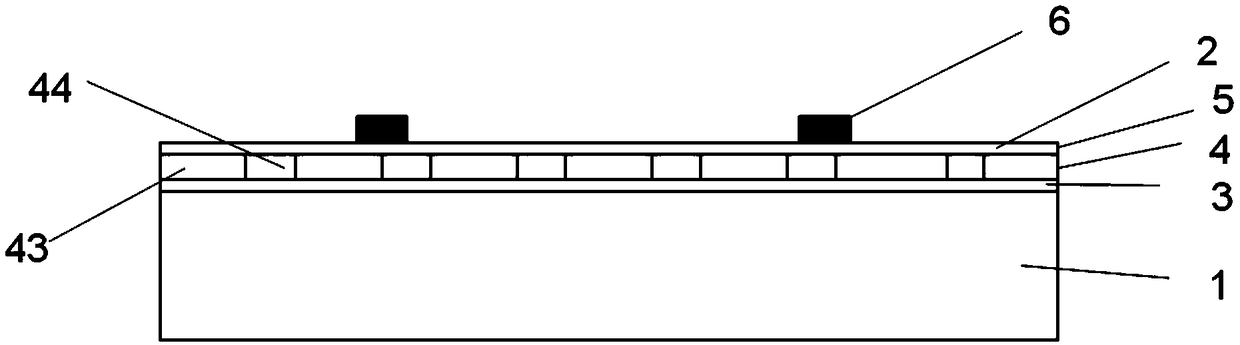
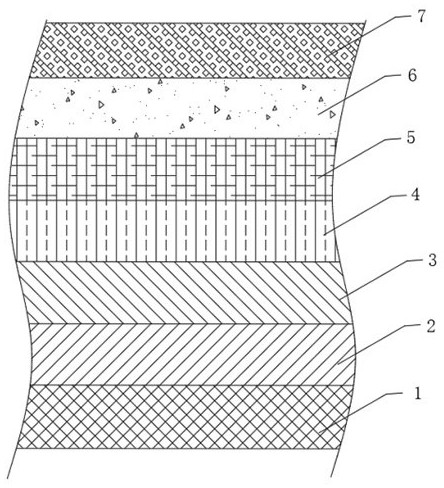
Optical waveguide[[s]] and optical fiber perform including gallium, lanthanum, sulfur, oxygen, and fluorine
InactiveUS7016593B2Improve thermal stabilityImprove propertiesGlass making apparatusCladded optical fibreGallium sulfideLanthanum fluoride
An optical waveguide includes a clad of clad glass and a core of core glass. The clad glass includes gallium, lanthanum, and sulfur. The clad glass may include gallium sulfide and lanthanum oxide. The clad glass may also include lanthanum fluoride. The core glass includes gallium, lanthanum, sulfur, oxygen, and fluorine. The core glass may include gallium sulfide, lanthanum oxide, and lanthanum fluoride. An optical fiber perform is also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
H-molybdenum trioxide/bis-metal sulfide composite material, preparation method and application
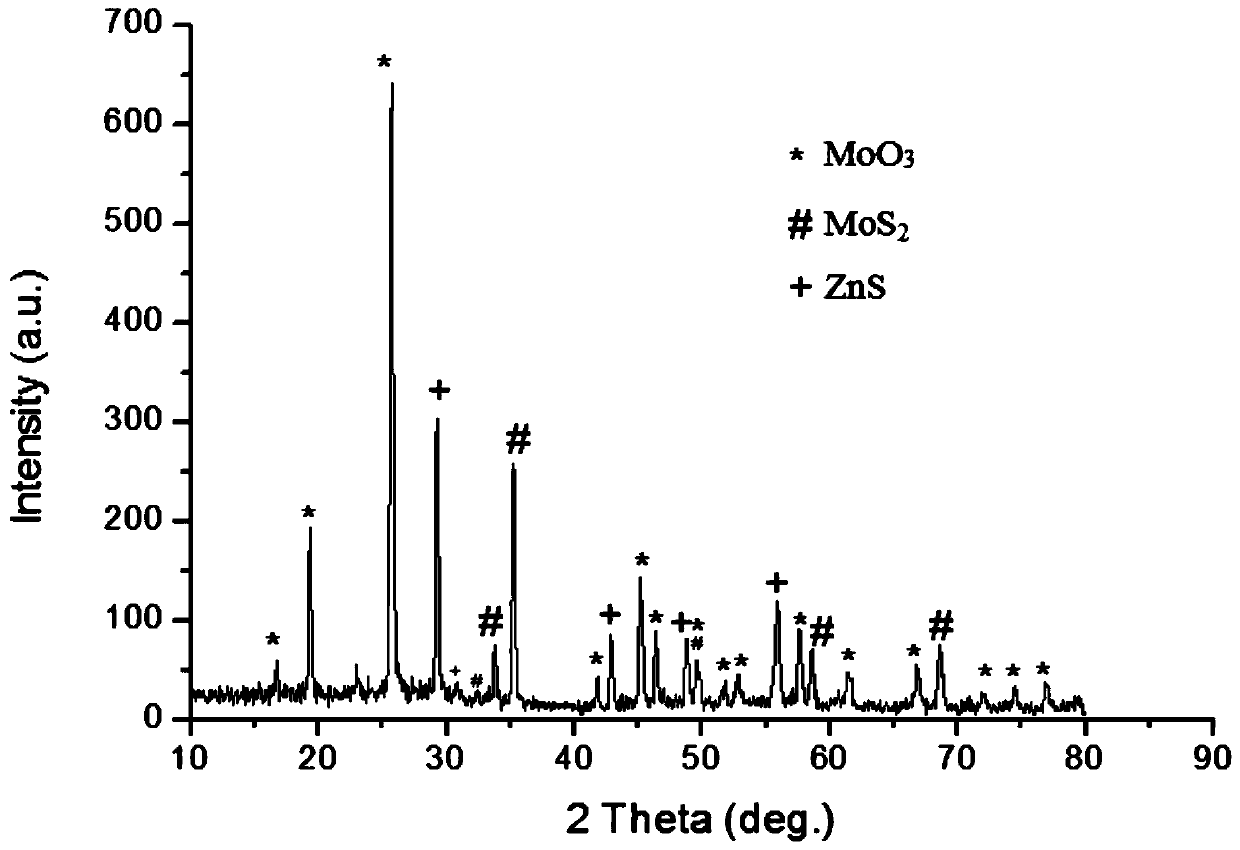
ActiveCN110681400ABroaden the response rangeImprove efficiencyPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationGallium sulfidePhoto catalytic
The invention discloses an h-molybdenum trioxide / bis-metal sulfide composite material, a preparation method and an application, and belongs to the technical field of photo-catalytic composite materials. The h-molybdenum trioxide / bis-metal sulfide composite material is composed of hexagonal prism-like molybdenum trioxide, namely h-MoO3, and two metal sulfides, wherein one metal sulfide is 2H-molybdenum disulfide, namely 2H-MoS2, and the other metal sulfide is zinc sulfide, nickel sulfide, gallium sulfide, or copper sulfide. The h-molybdenum trioxide / bis-metal sulfide composite material has readily available raw materials, low cost, and simple preparation process, and has great industrial application values as a photo-catalytic composite material in a wastewater treatment process.
Owner:NEIJIANG NORMAL UNIV
Composition and energy storage device
ActiveUS20120183829A1Cell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersCell electrodesCobaltAlkali metal halide
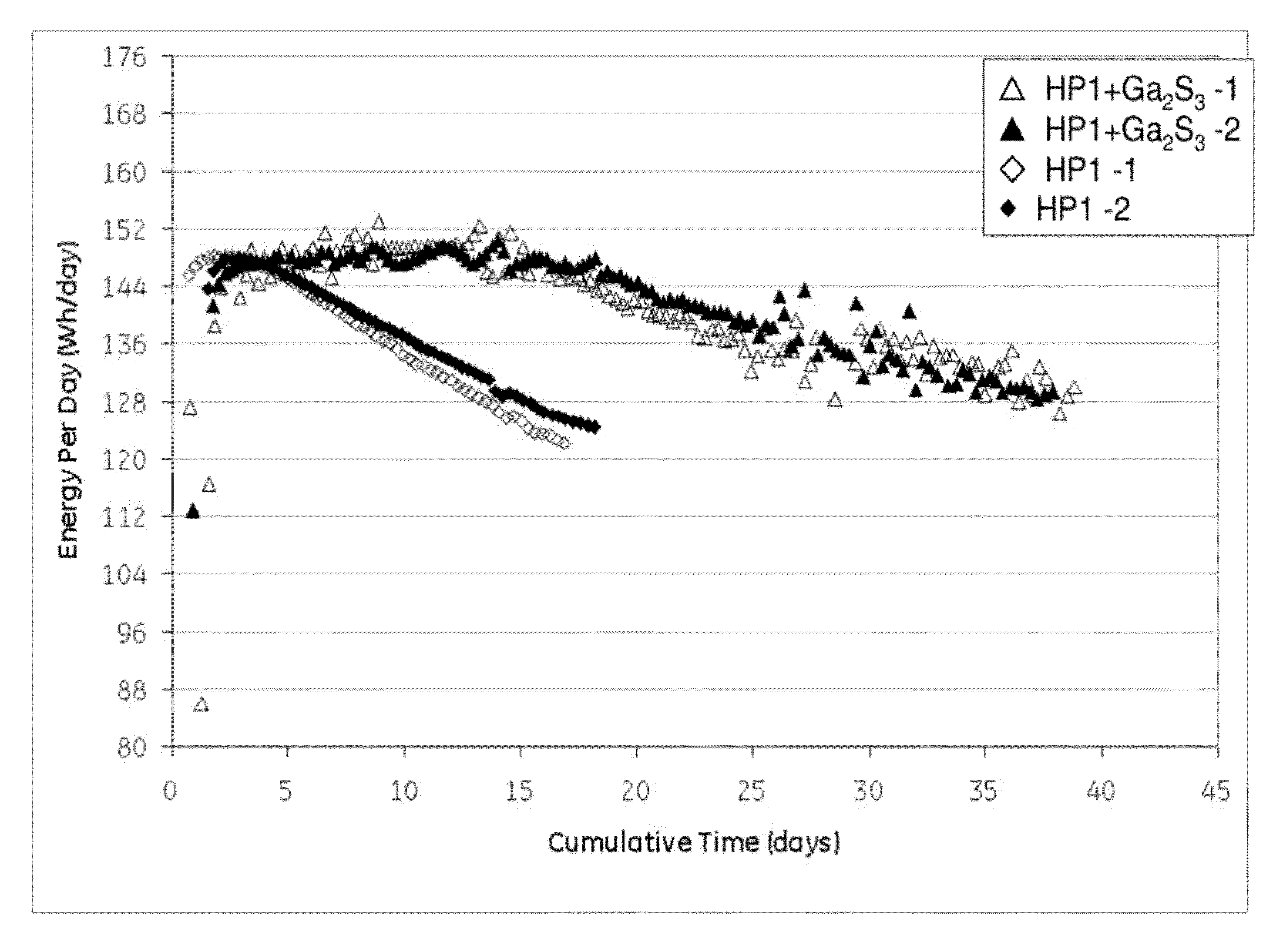
In one embodiment, a cathode composition comprises a transition metal and / or a transition metal salt, wherein the transition metal is selected from the group consisting of nickel, iron, cobalt, chromium, manganese, molybdenum, zinc, and antimony, and a combination comprising at least one of the foregoing; an alkali metal halide; an electrolyte salt comprising an alkali metal halide and a metal halide; and a sulfide compound selected from the group consisting of gallium sulfide, antimony sulfide, and a combination comprising at least one of the foregoing. An energy storage device comprising the electrode composition is also provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Phosphor for Display and Field Emission Display
InactiveUS20090039759A1Improve luminous efficiencyIncrease brightnessDischarge tube luminescnet screensCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesGallium sulfideDisplay device
Disclosed is a phosphor for displays which is characterized by being composed of a europium-activated thiogallate phosphor represented by the following chemical formula: SrGa2S4:Eu. This phosphor is also characterized by containing no gallium sulfide (Ga2S3) and being a green phosphor which emits light when excited by an electron beam having an accelerating voltage of 5-15 kV. Consequently, this invention provides a phosphor for displays having high luminance, which emits light when excited by a pulse electron beam having an accelerating voltage of 5-15 kV.
Owner:CANON KK
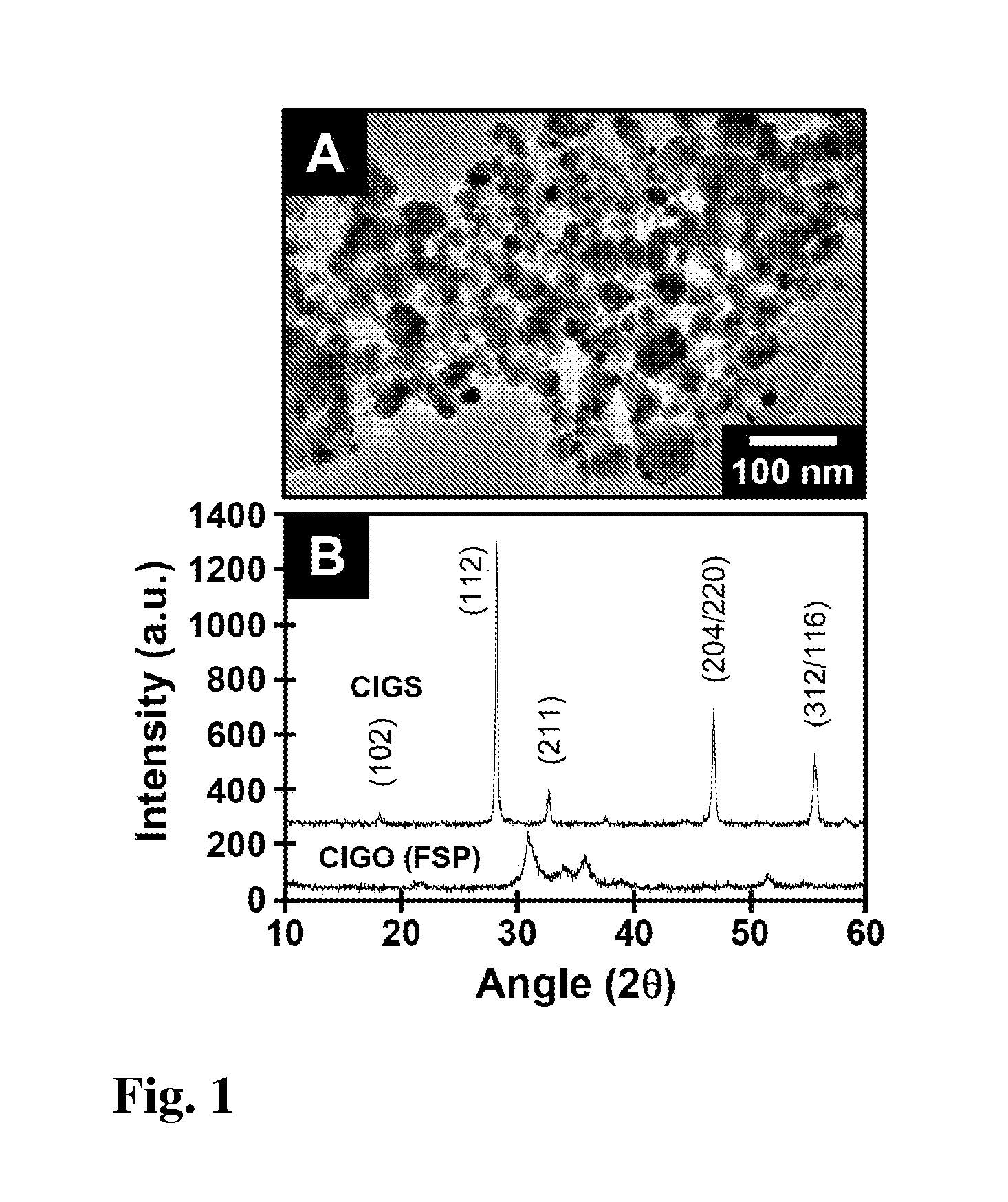
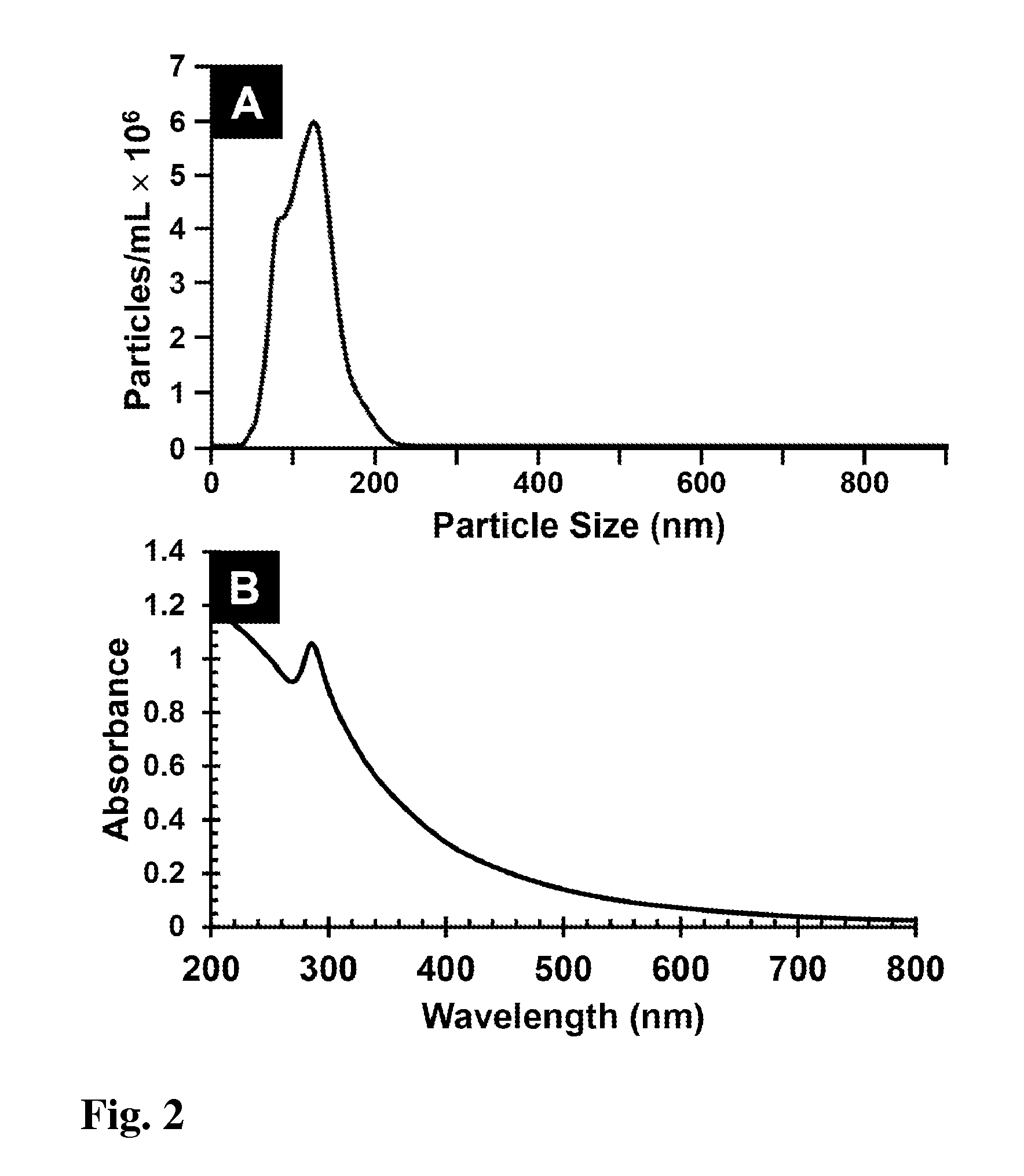
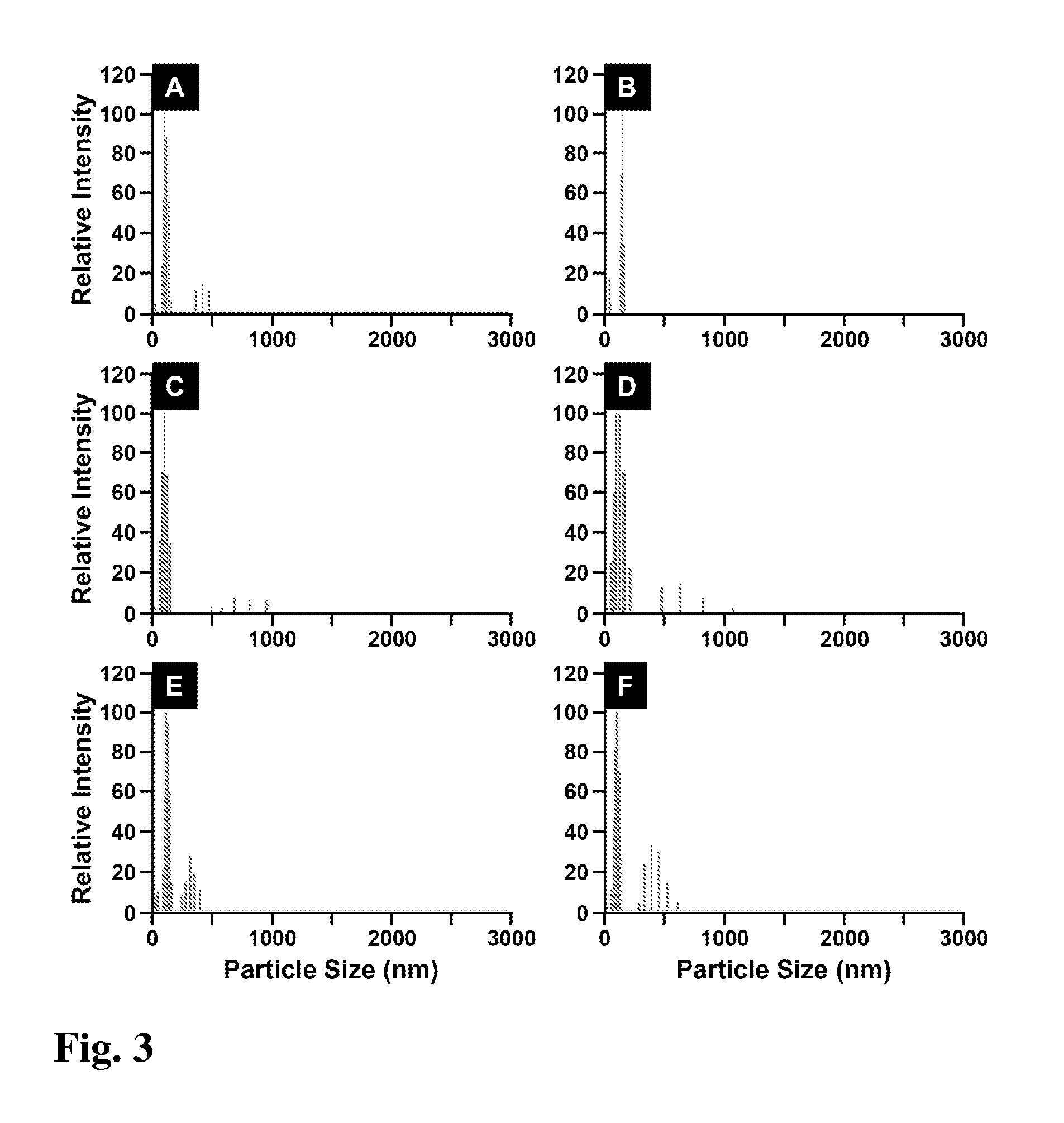
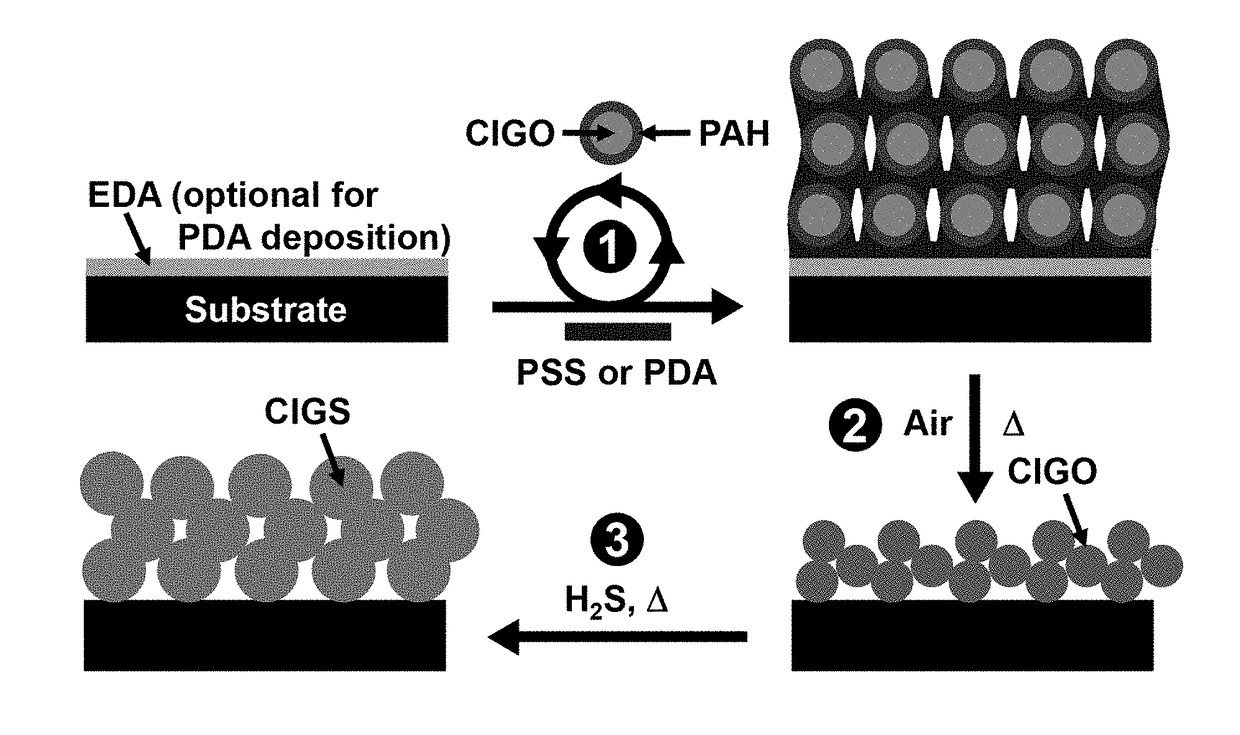
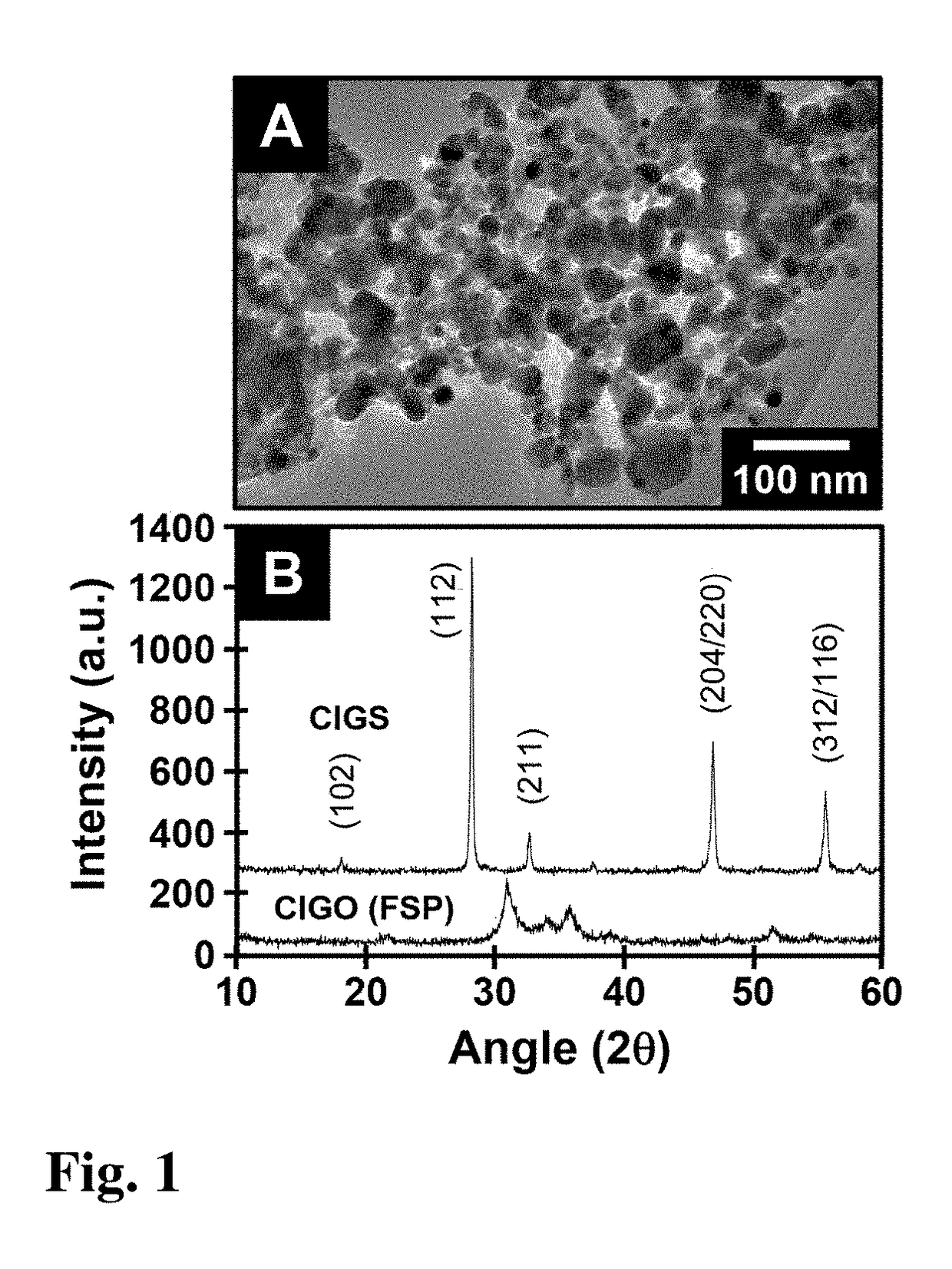
Method for fabrication of copper-indium gallium oxide and chalcogenide thin films
InactiveUS20150295106A1Simpler and cheapHigh capital expenseFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumMaterials science
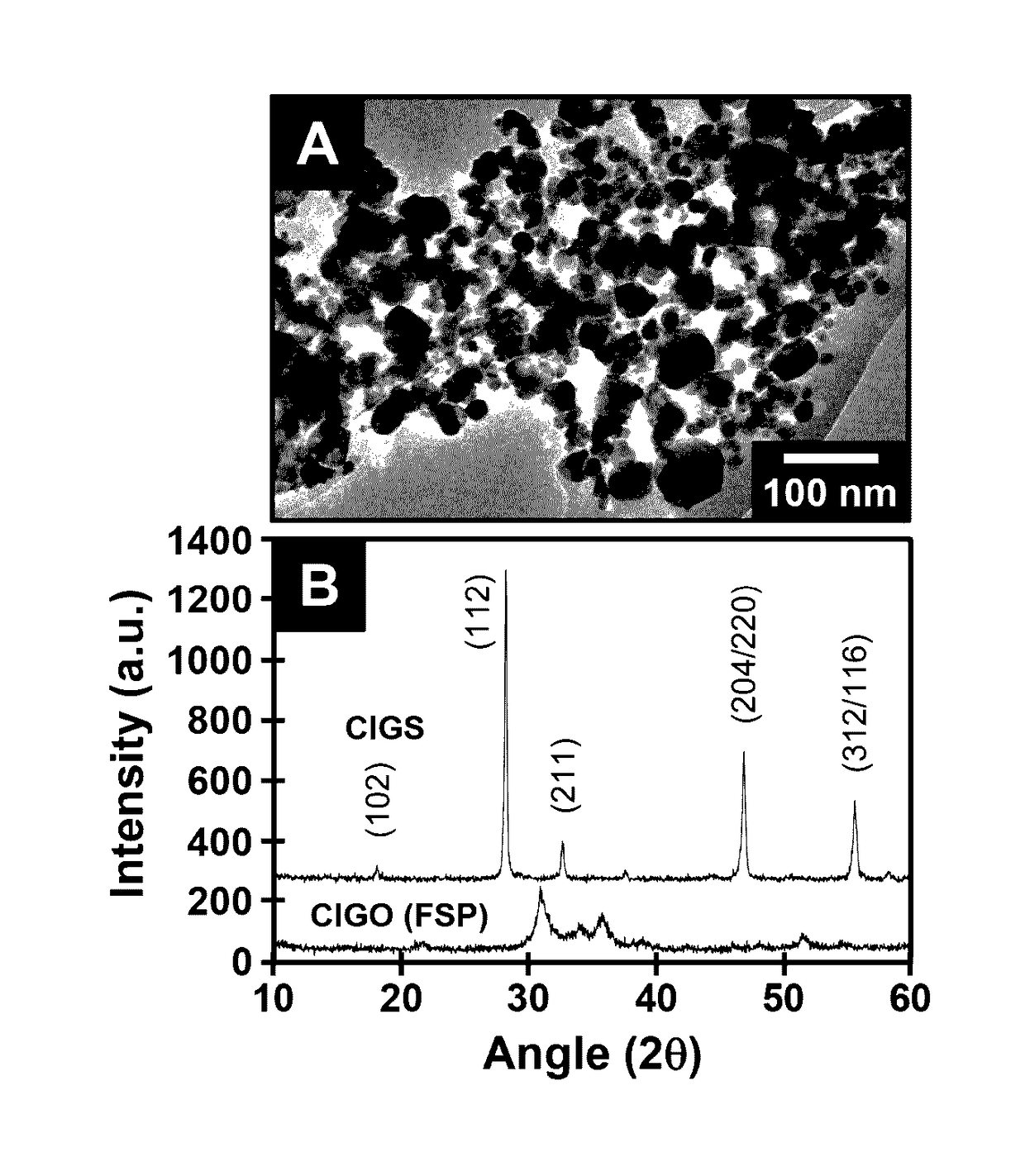
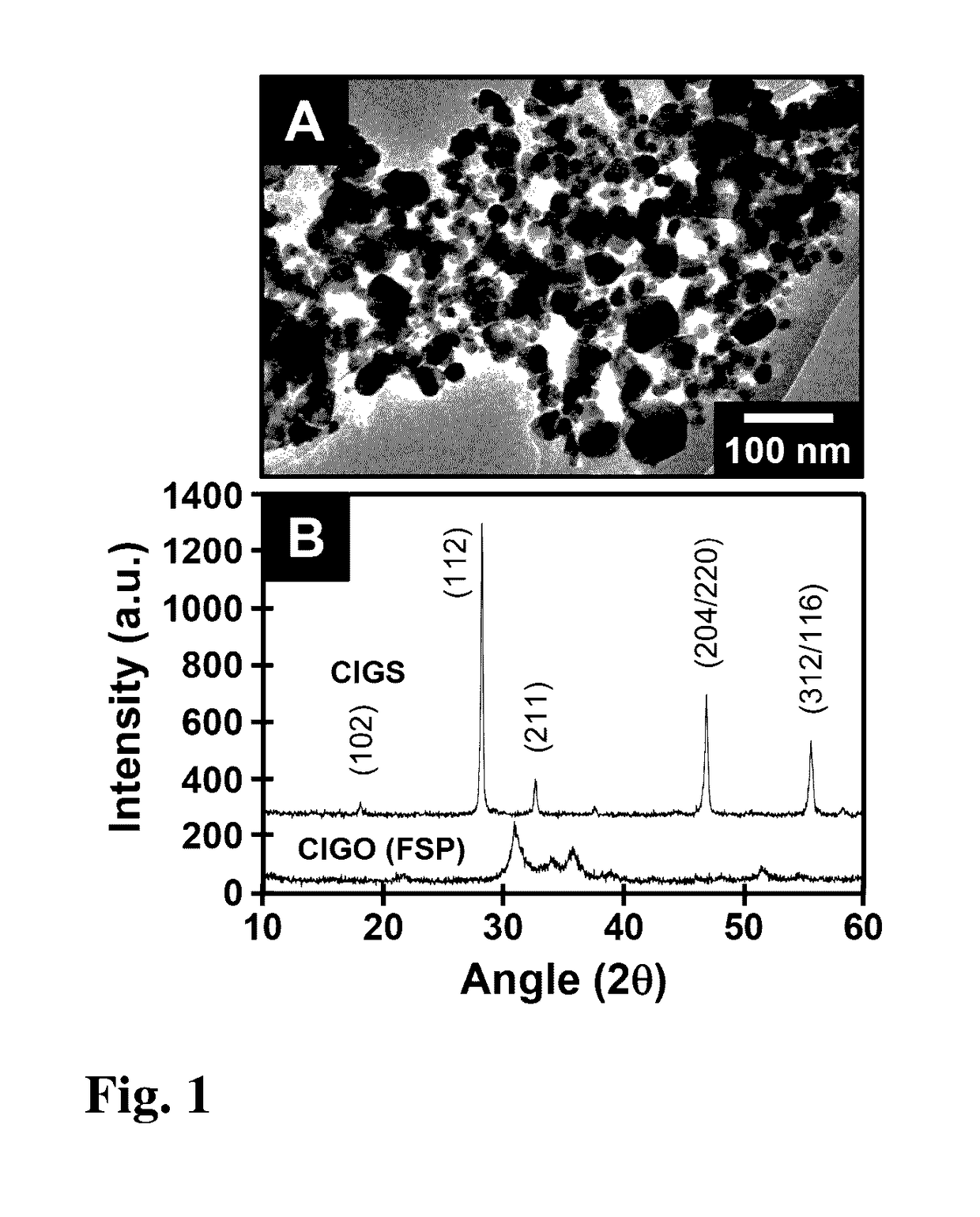
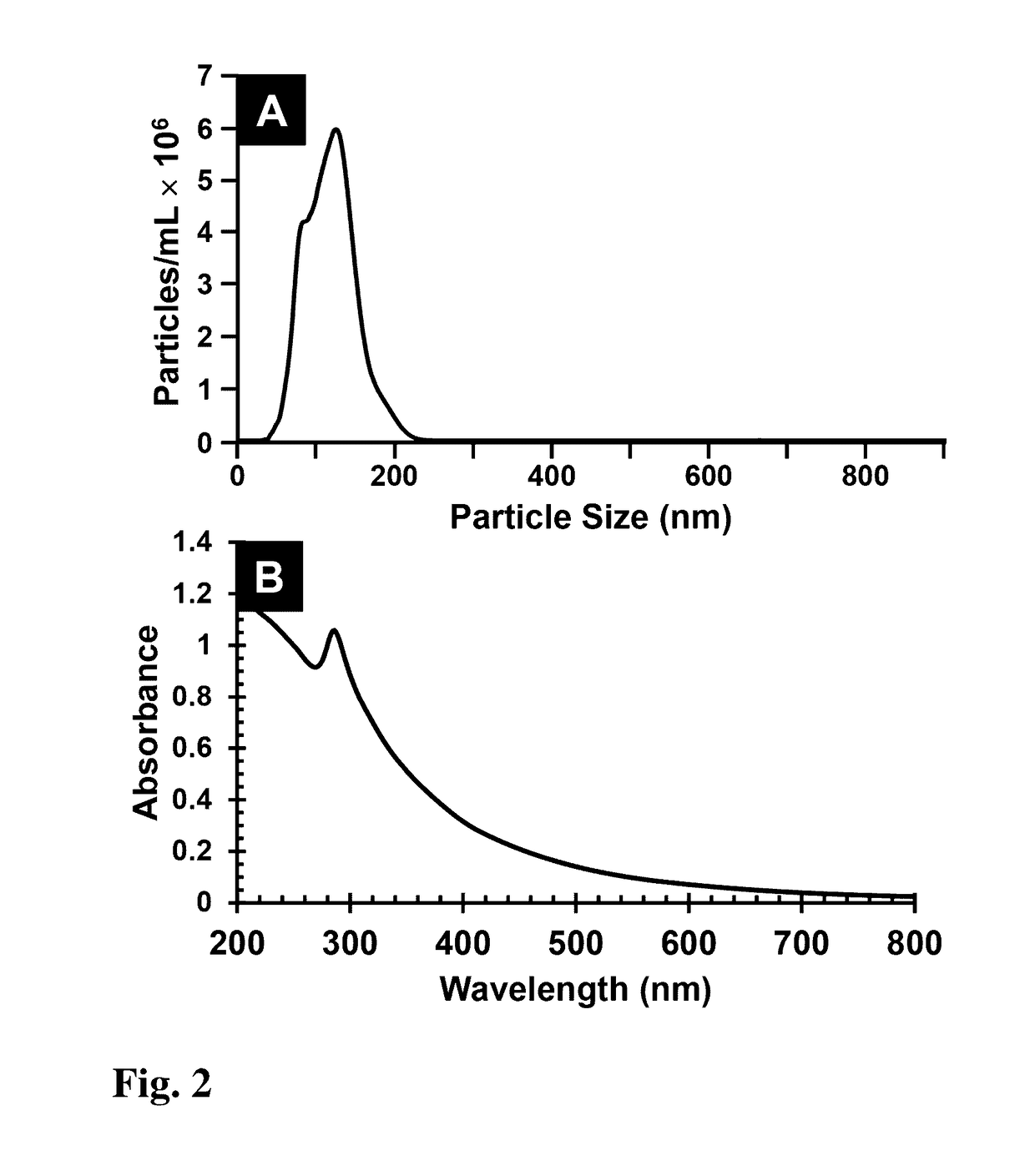
A composition of matter and method of forming copper indium gallium sulfide (CIGS), copper indium gallium selenide (CIGSe), or copper indium gallium telluride thin film via conversion of layer-by-layer (LbL) assembled Cu—In—Ga oxide (CIGO) nanoparticles and polyelectrolytes. CIGO nanoparticles are created via a flame-spray pyrolysis method using metal nitrate precursors, subsequently coated with polyallylamine (PAH), and dispersed in aqueous solution. Multilayer films are assembled by alternately dipping a substrate into a solution of either polydopamine (PDA) or polystyrenesulfonate (PSS) and then in the CIGO-PAH dispersion to fabricate films as thick as 1-2 microns. After LbL deposition, films are oxidized to remove polymer and sulfurized, selenized, or tellurinized to convert CIGO to CIGS, CIGSe, or copper indium gallium telluride.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Phosphor for display and field emission display
InactiveCN101389732AImprove luminous brightnessImprove luminous efficiencyImage/pattern display tubesLuminescent compositionsGallium sulfideField emission display
Disclosed is a phosphor for displays which is characterized by being composed of a europium-activated thiogallate phosphor represented by the following chemical formula: SrGa2S4:Eu. This phosphor is also characterized by containing no gallium sulfide (Ga2S3) and being a green phosphor which emits light when excited by an electron beam having an accelerating voltage of 5-15 kV. Consequently, this invention provides a phosphor for displays having high luminance, which emits light when excited by a pulse electron beam having an accelerating voltage of 5-15 kV.
Owner:CANON KK
Method for fabrication of copper-indium gallium oxide and chalcogenide thin films
InactiveUS20170200840A1Simpler and cheapHigh capital expenseFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumMaterials science
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Composition and energy storage device
ActiveUS8697279B2Cell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersSolid electrolyte cellsCobaltAlkali metal halide
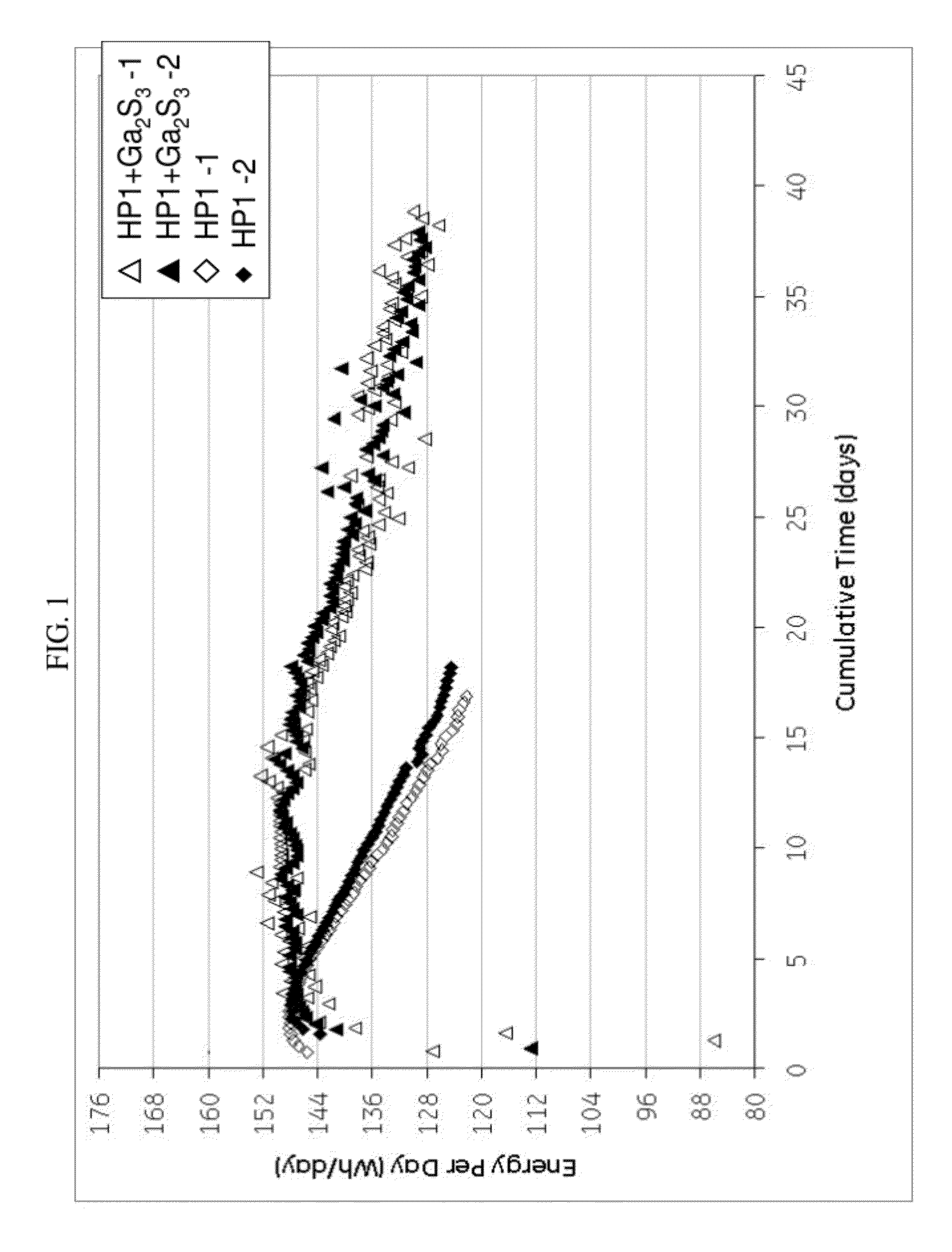
In one embodiment, a cathode composition comprises a transition metal and / or a transition metal salt, wherein the transition metal is selected from the group consisting of nickel, iron, cobalt, chromium, manganese, molybdenum, zinc, and antimony, and a combination comprising at least one of the foregoing; an alkali metal halide; an electrolyte salt comprising an alkali metal halide and a metal halide; and a sulfide compound selected from the group consisting of gallium sulfide, antimony sulfide, and a combination comprising at least one of the foregoing. An energy storage device comprising the electrode composition is also provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
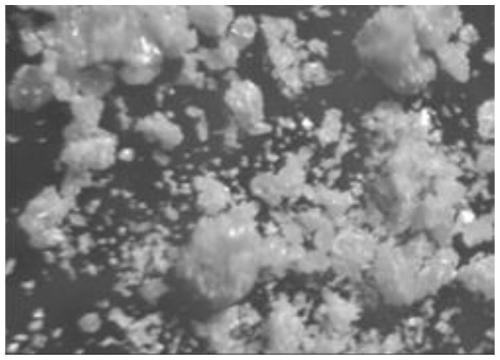
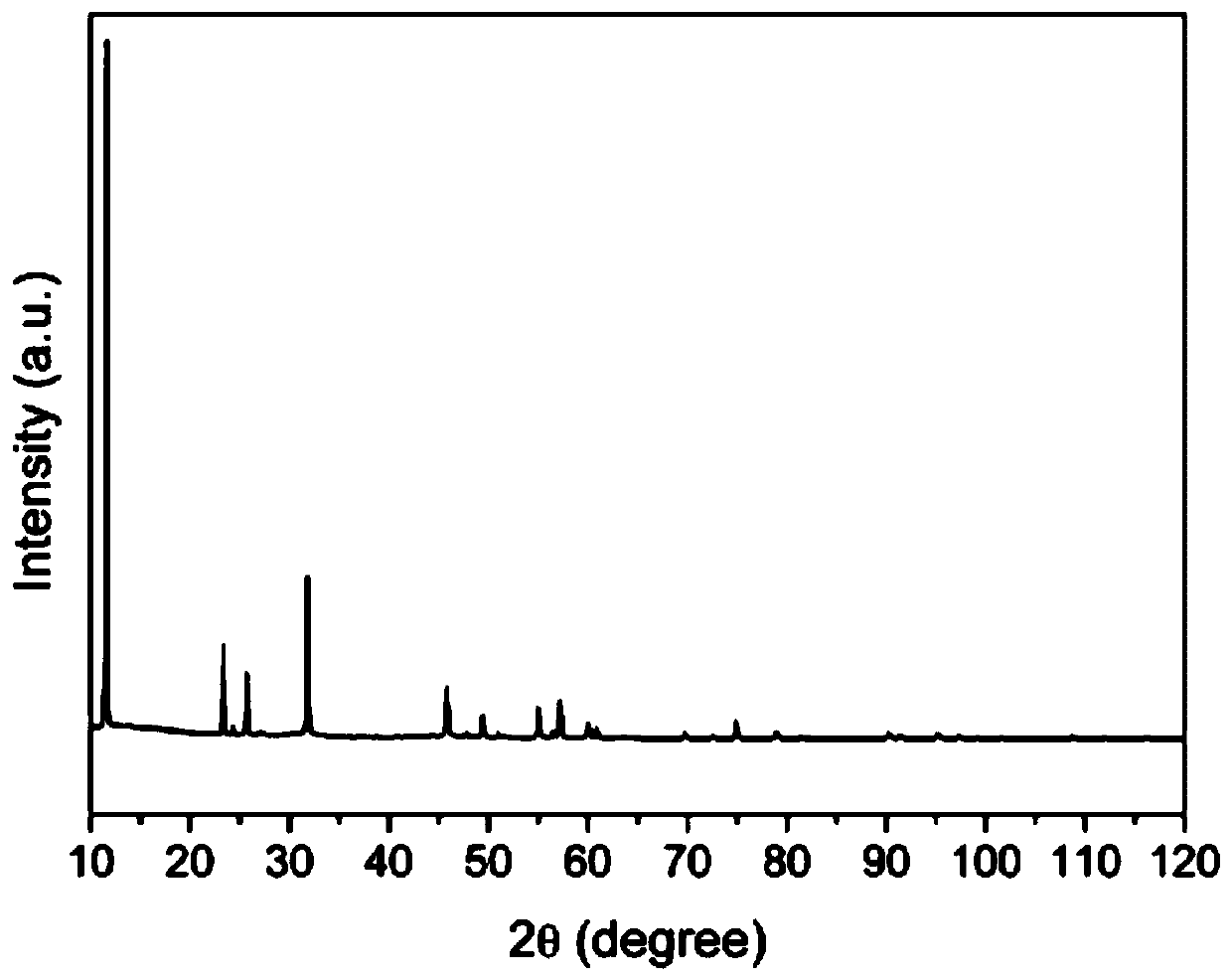
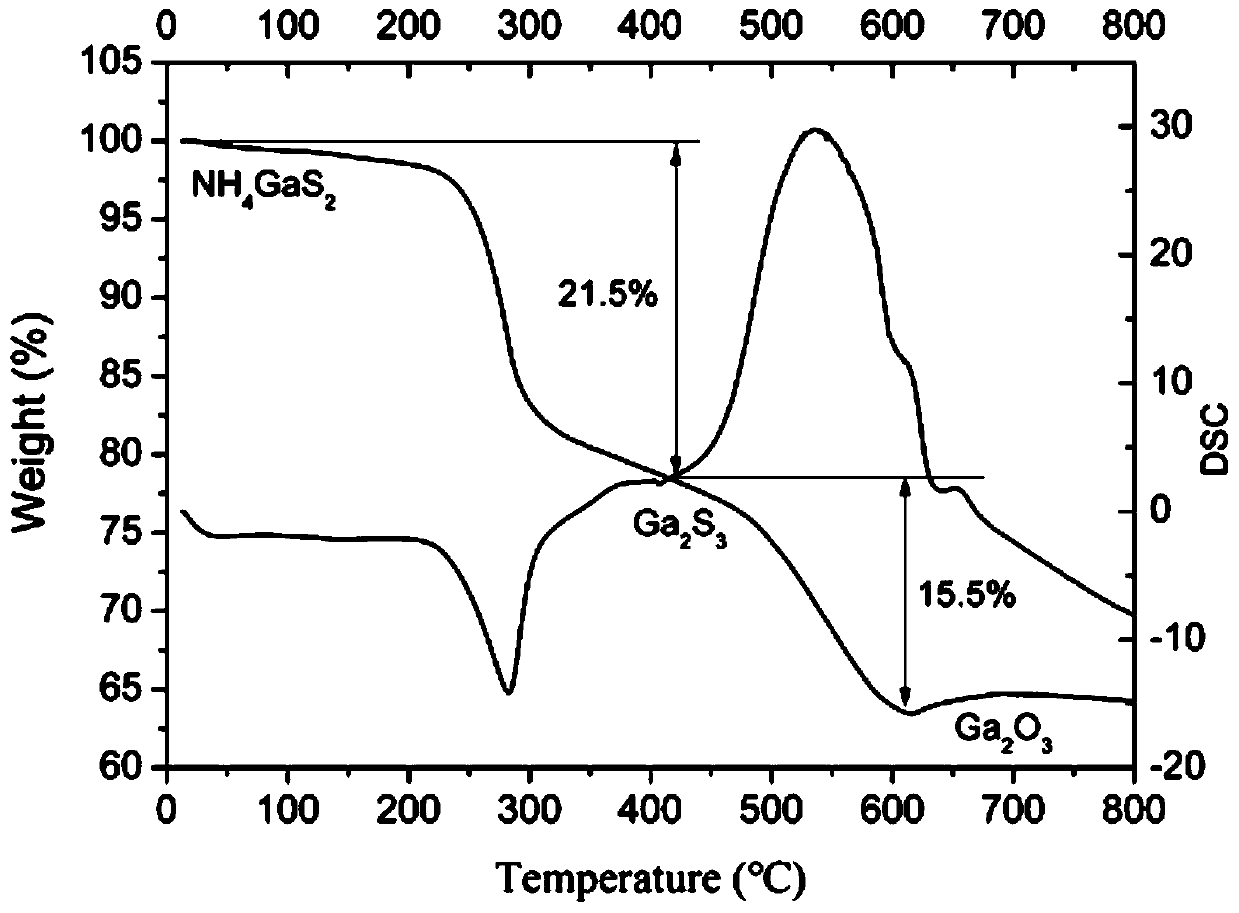
Compound NH4GaS2 and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110054212ASimple methodLow costPhysical/chemical process catalystsGallium/indium/thallium compoundsThioureaOxalic acid
The invention provides a compound NH4GaS2 and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method includes: mixing gallium oxide and thiourea evenly and adding the gallium oxide and thiourea to a reactor; adding oxalic acid and sealing the reactor; heating the reactor for reaction to obtain white granular crystal, namely the compound NH4GaS2, after reaction. The compound NH4GaS2 is synthesized by adopting the simple thiourea oxalate method which is simple and easy to implement, the method does not need to be carried out under harsh vacuum reaction conditions, raw materials arecheap and easy to obtain, and low cost, low energy consumption and easy industrial production are achieved; the compound has good photocatalytic activity for hydrogen production under simulated sunlight and can be used as raw material for the synthesis of other gallium sulfides, and good application prospect is achieved.
Owner:YANGTZE NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Photoelectric detector based on copper indium gallium
ActiveCN107731943AFulfil requirementsHigh sensitivityPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesPhotovoltaic detectorsGallium sulfide
The present invention provides a novel photoelectric detector based on copper indium gallium selenium and copper indium gallium sulfide. According to the composite functional layer, a contact part ofthe copper indium gallium selenium and the copper indium gallium sulfide is changed into copper indium gallium selenium sulfide, a composition is gradually changed in a transverse direction, the functional layer is modified, the electrical performance is adjusted to meet requirements of the photoelectric detector, the sensitivity of the detector is further improved, and the stability of the sensoris greatly improved.
Owner:宝应电工厂
Method for preparing chalcopyrite thin-film solar cells
InactiveCN102610689AHigh purityReduce manufacturing costFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesIndiumOxygen
The invention discloses a method for preparing chalcopyrite thin-film solar cells. The method comprises the following steps of: (a) by using a non-vacuum manufacture procedure, carrying out in-situ reaction on metals such as copper, indium, gallium and the like and hydrogen chloride or chlorine so as to form reaction precursors, and then reacting the reaction precursors with hydrogen selenide or hydrogen sulfide; (b) preparing light absorption layers of selenium / copper-indium-gallium sulfide and selenium / copper-zinc-tin sulfide thin-film solar cells in cooperation with a vapor-phase epitaxial growth technique; and (c) preparing buffer layers and transparent conductive layers of the thin-film solar cells in cooperation with oxygen. By using the method disclosed by the invention, high-purity chalcopyrite thin-film solar cells can be prepared, and the production cost is greatly saved.
Owner:黄崇哲
Light sensitive energy-saving street lamp
ActiveCN104515102ALow costGood weather resistanceMechanical apparatusElectric circuit arrangementsIridiumHafnium
The invention discloses a light sensitive energy-saving street lamp. A sensor is arranged at the top of the street lamp and can control on and off the street lamp according to the intensity of visible light, a light sensitive resistor is arranged in the sensor and comprises an upper electrode layer, a lower electrode layer and a middle light sensitive material layer, and the light sensitive material layer comprises gallium sulfide, cadmium sulfide, zinc sulfide, copper sulfide, beryllium sulfide, strontium sulfide, germanium oxide, niobium oxide, hafnium, iridium and Y4-x-yLuxFeyO6. A light sensitive material is low in manufacturing cost, resistant to ageing, wide in application field and beneficial to large-scale popularization and application, has excellent weather resistance and corrosion resistance and has strong compatibility with the sensor, the light sensitive energy-saving street lamp can automatically sense the visible light, can be automatically turned on and turned off according to the intensity of the visible light and conforms to the advocated trend of energy conservation and environmental protection, and resources are reasonably distributed and used.
Owner:JIANGSU TIWIN OPTO ELECTRONICS TECH
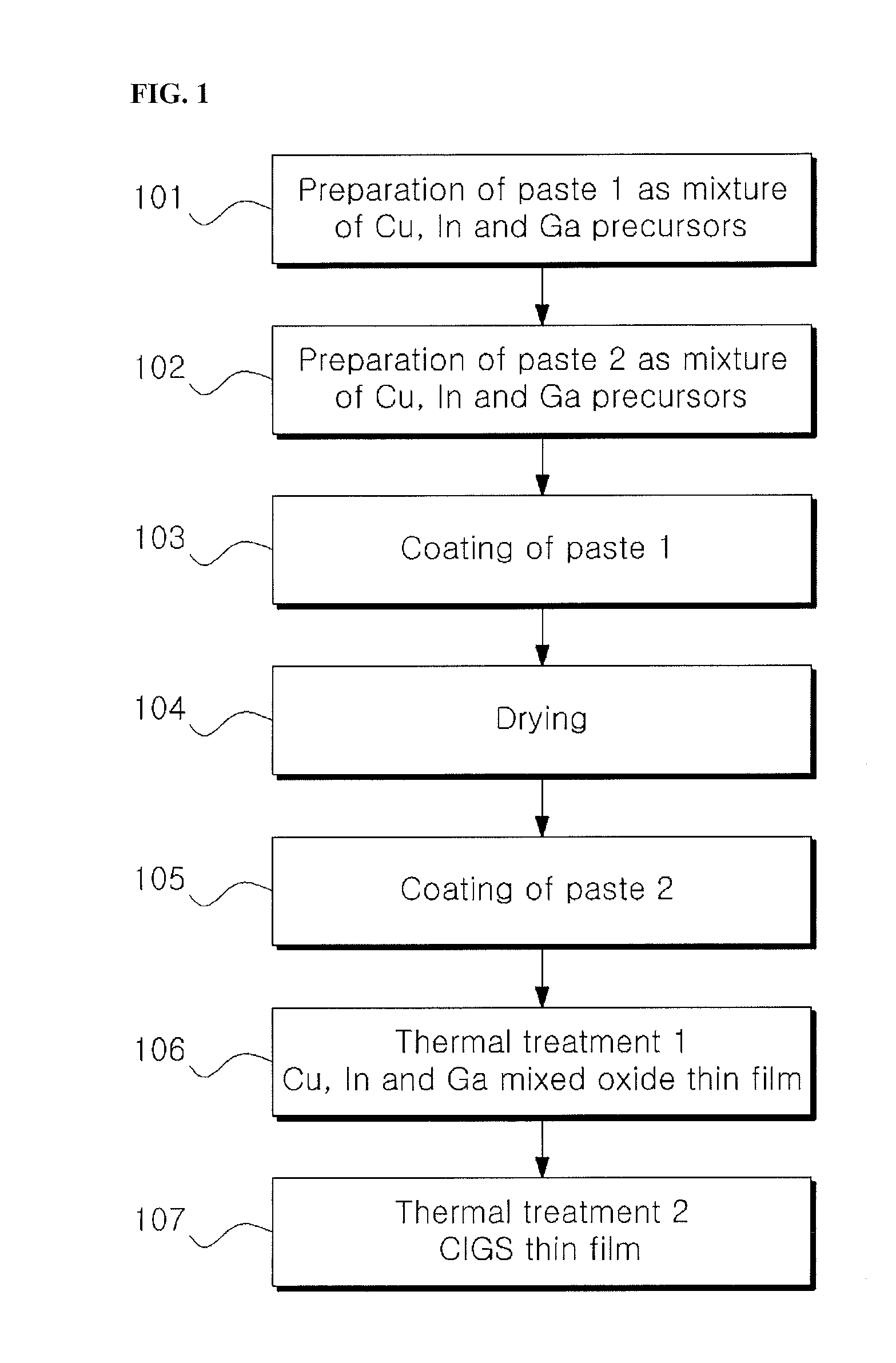
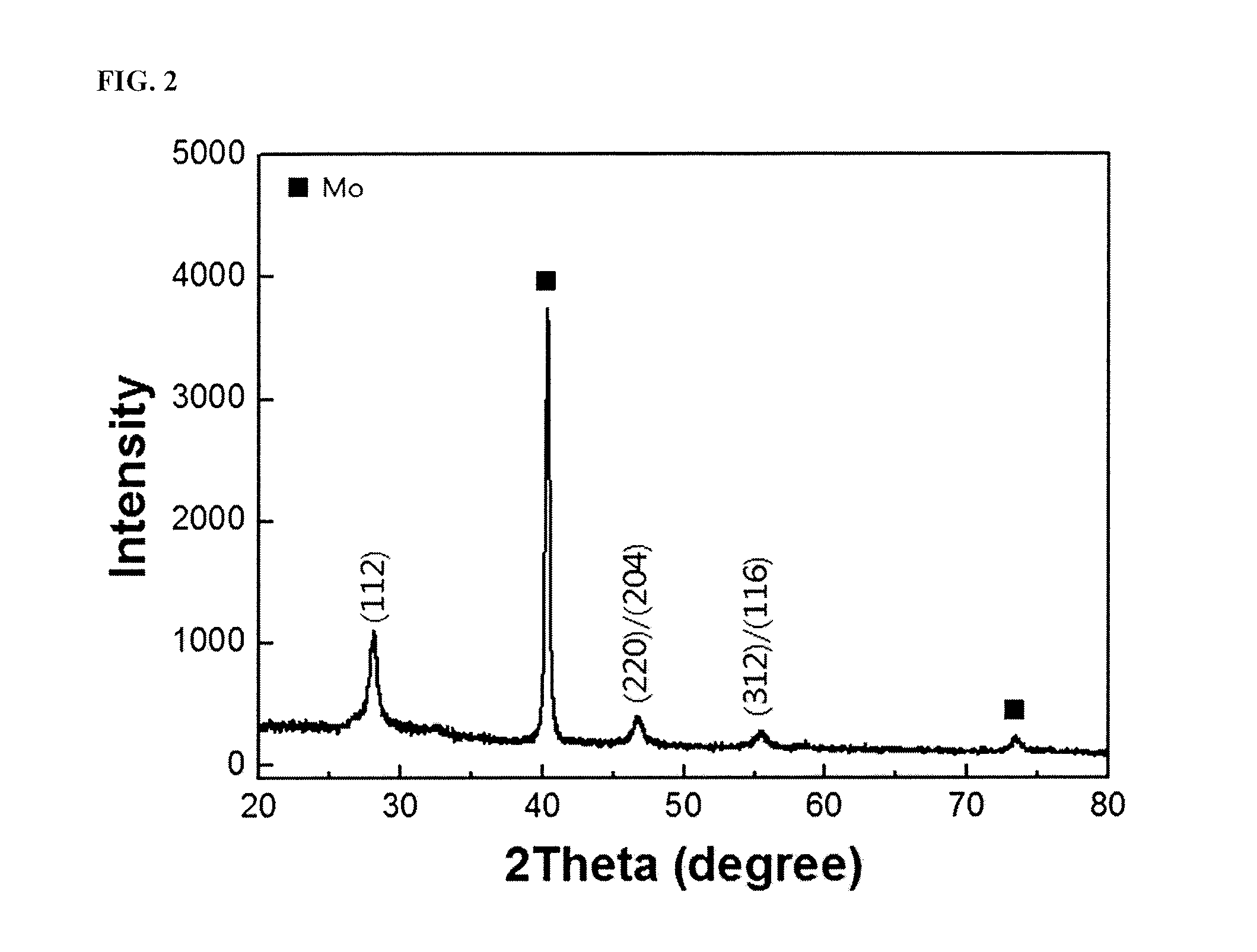
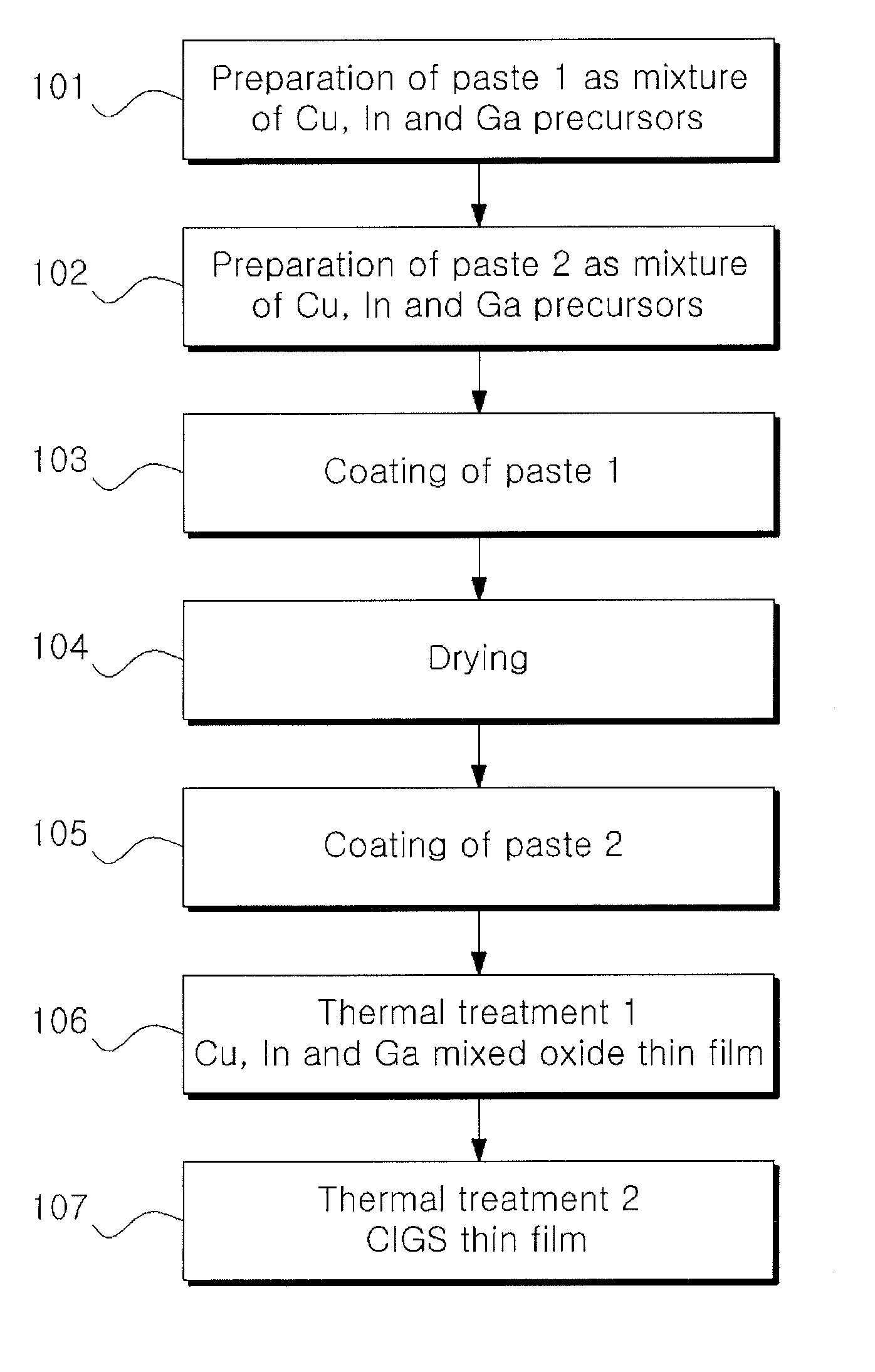
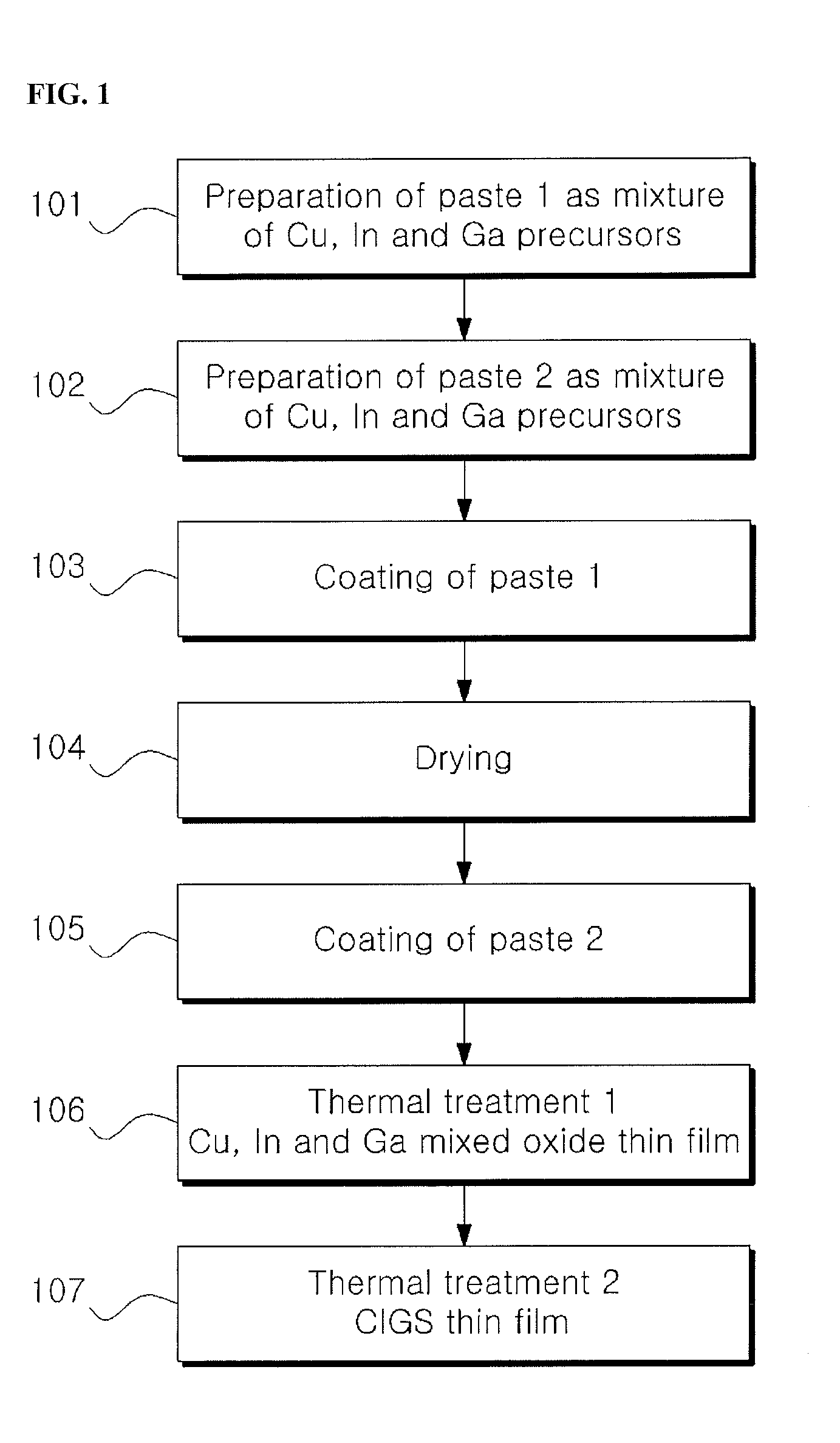
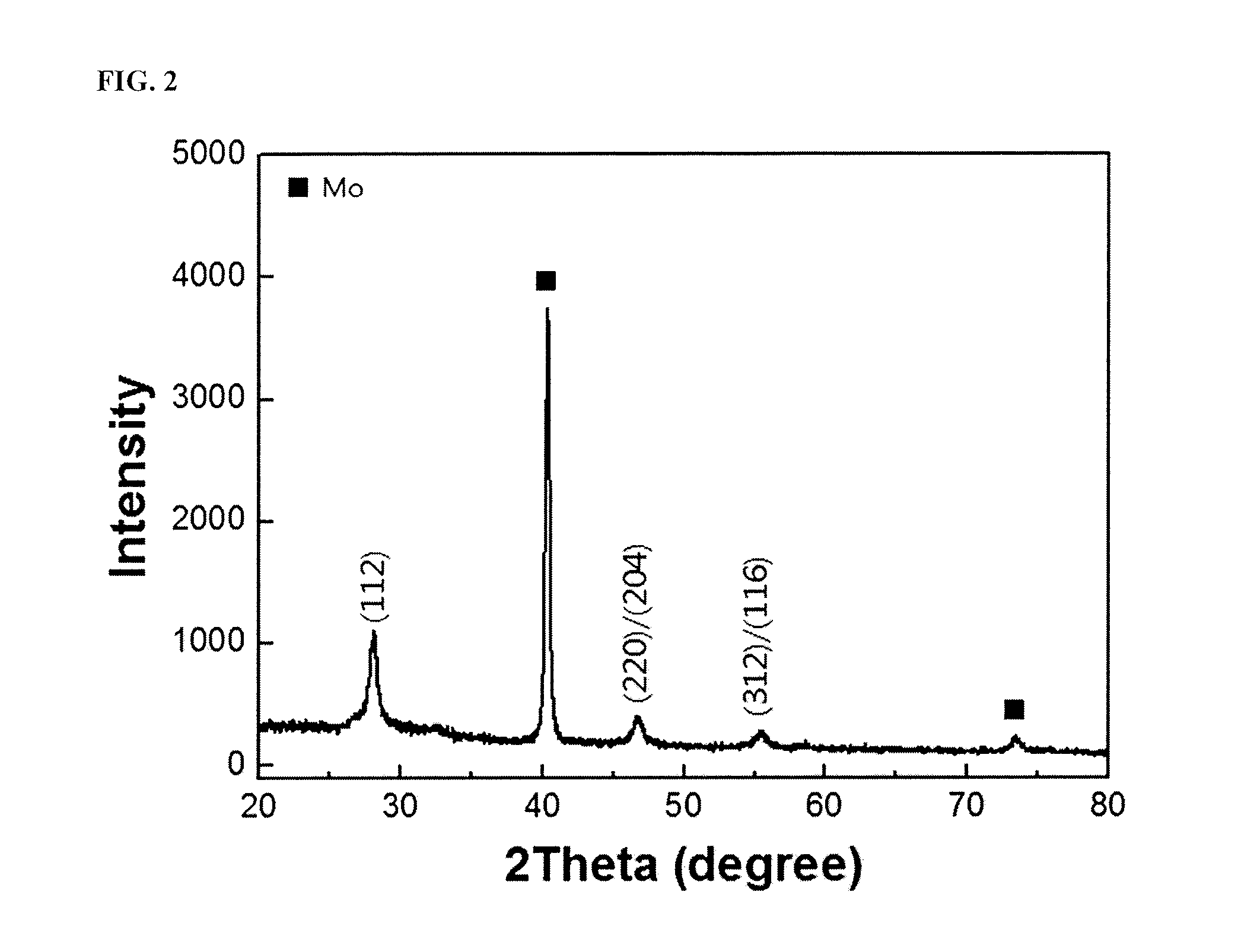
Methods for producing chalcopyrite compound thin films for solar cells using multi-stage paste coating
ActiveUS20140070347A1Low costHigh spreading rateSulfur compoundsSolid-state devicesIndiumGallium sulfide
Disclosed are methods for producing chalcopyrite compound (e.g., copper indium selenide (CIS), copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS), copper indium sulfide (CIS) or copper indium gallium sulfide (CIGS)) thin films. The methods are based on solution processes, such as printing, particularly, multi-stage coating of pastes or inks of precursors having different physical properties. Chalcopyrite compound thin films produced by the methods can be used as light-absorbing layers for thin-film solar cells. The use of the chalcopyrite compound thin films enables the fabrication of thin-film solar cells with improved efficiency at low costs.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing copper gallium sulfide photoelectric thin film from copper chloride
InactiveCN106024976ALower requirementImprove continuityFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationGallium sulfideCopper chloride
The invention provides a method for preparing a copper gallium sulfide photoelectric thin film from copper chloride, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of photoelectric thin films for solar cells. The copper gallium sulfide photoelectric thin film is obtained through the following steps of: firstly, cleaning a glass substrate and then putting CuCl2.2H2O, Ga(NO3)3.xH2O and CH3CSNH2 into a solvent for mixing evenly; obtaining a precursor thin film on a glass sheet through a spin-coating method, drying the precursor thin film and putting the precursor thin film into a closed container with hydrazine hydrate; preventing a precursor thin film sample from being in contact with the hydrazine hydrate and arranging the closed container with the sample into an oven for heating and heat preservation treatment; and finally taking out the sample to soak for 24 hours and then drying the sample to obtain the copper gallium sulfide photoelectric thin film. A high-temperature and high-vacuum condition is not needed; the method is low in demands on instruments and equipment, low in production cost, high in production efficiency and easy to operate; the obtained copper gallium sulfide photoelectric thin film has relatively good continuity and uniformity; the main phase is a CuGaS2 phase; by the novel technology, the component and the structure of a target product are easy to control; and a low-cost production method capable of achieving industrialization is provided for preparation of the high-performance copper gallium sulfide photoelectric thin film.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
Method for preparing copper gallium sulfide photoelectric thin film from copper sulfate
InactiveCN106024977ALower requirementImprove continuityFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationGallium sulfideHydrazine compound
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
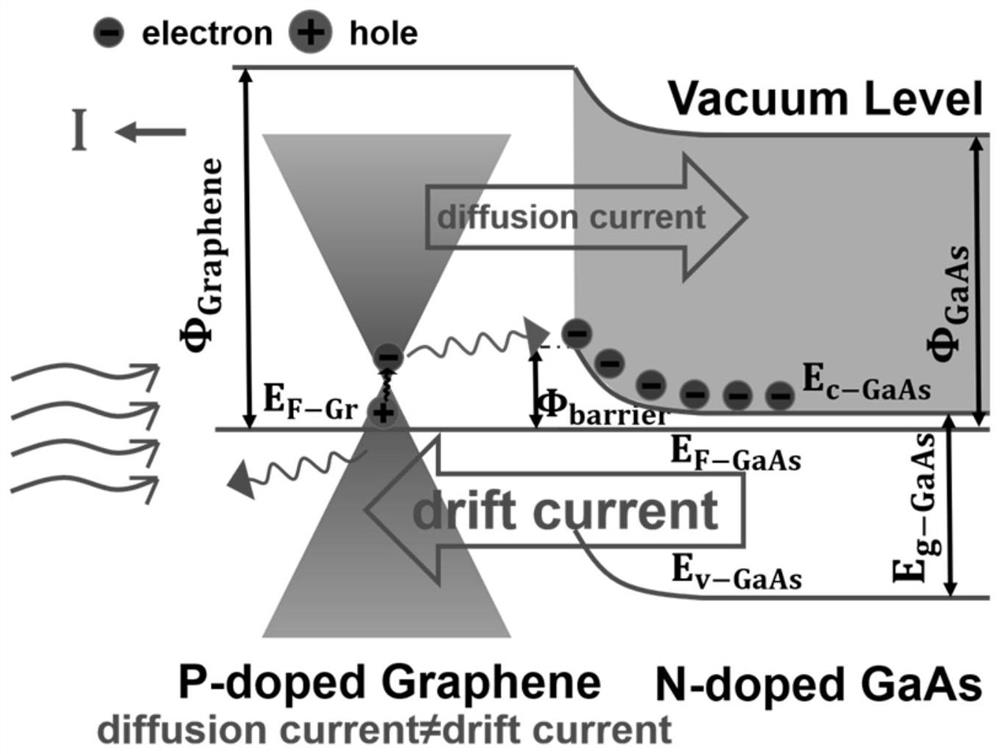
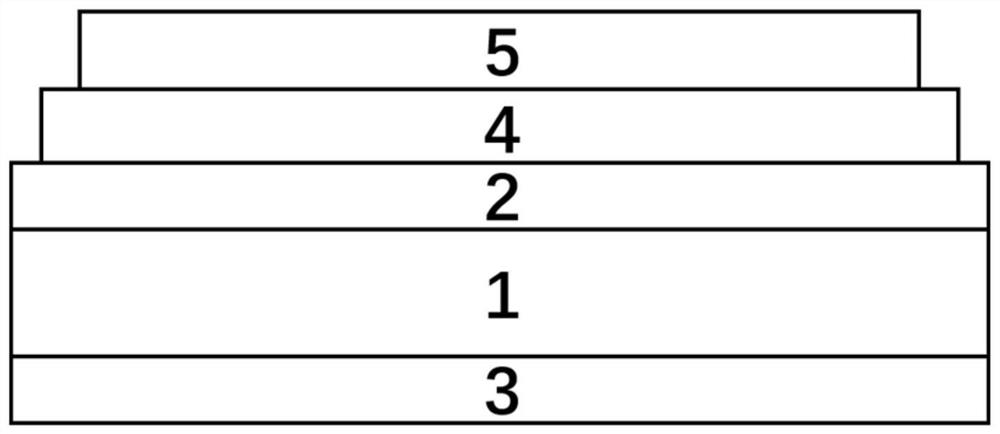
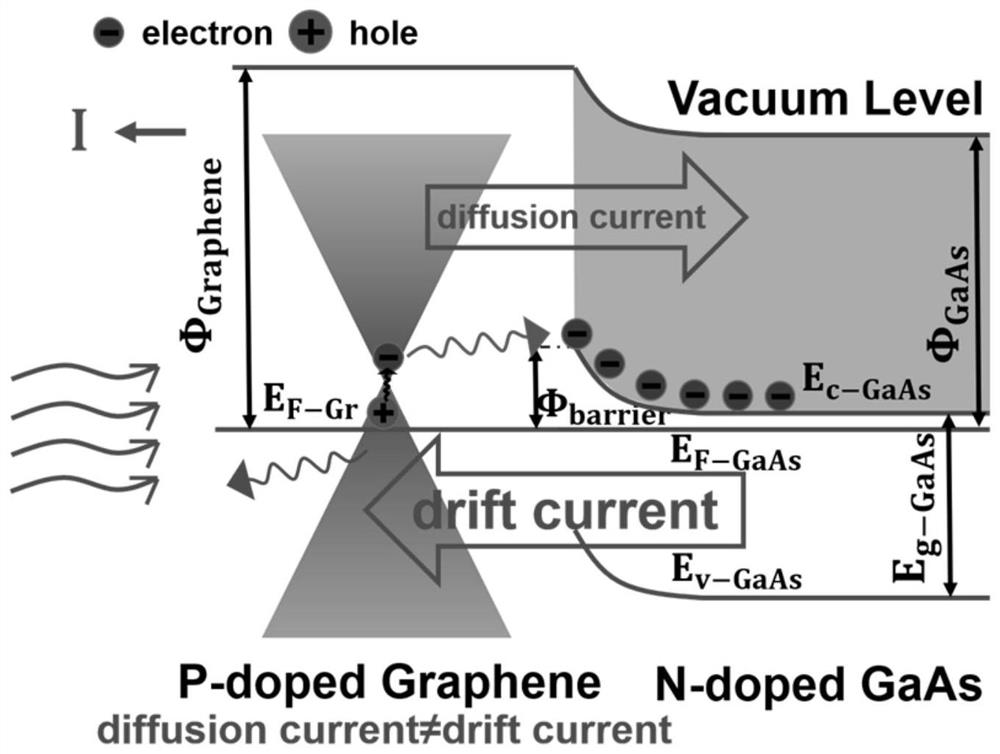
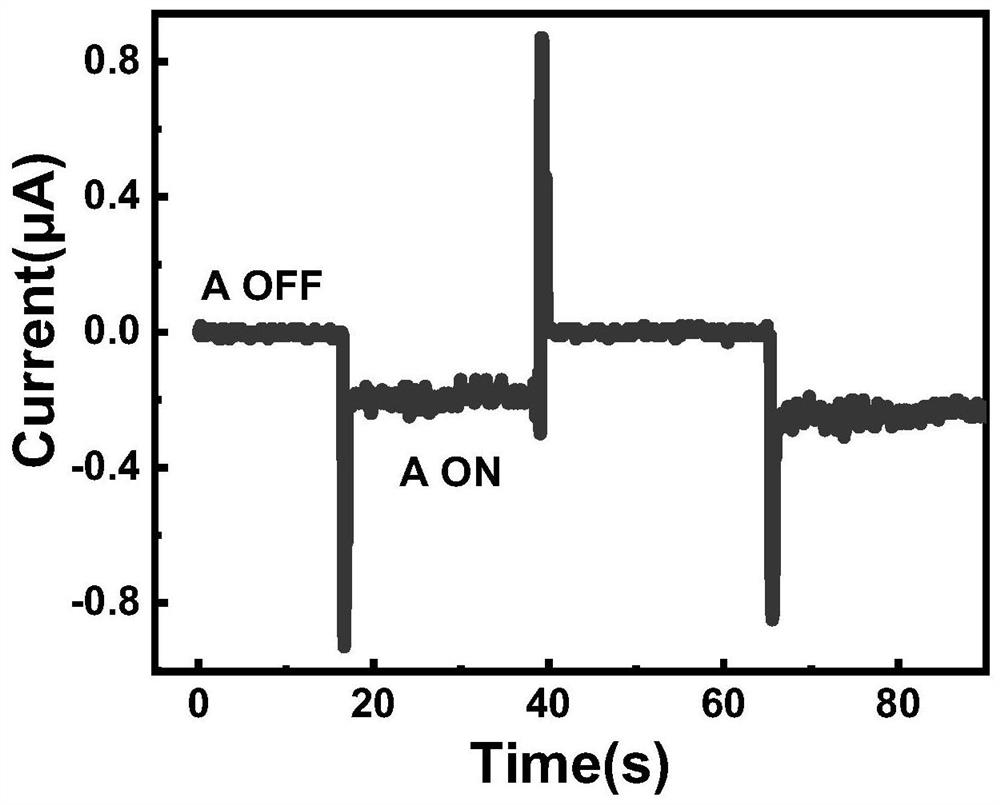
Graphene/monatomic layer GaS/GaAs radio generator and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN111641275AGood for long runWork lessCircuit arrangementsSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionSchottky barrier
The invention relates to a radio power generation device and discloses a graphene / monatomic layer GaS / gallium arsenide radio generator. A layer of monatomic layer GaS is formed on a gallium arsenide substrate passivated by ammonium sulfide, a layer of graphene is attached to the layer of monatomic layer GaS, a first electrode and a side electrode are arranged, and the graphene is in direct contactwith a monatomic layer gallium sulfide surface of gallium arsenide to form a heterojunction. The key point of the generator lies in that graphene contacts gallium arsenide passivated by ammonium sulfide to form a Schottky junction and a Schottky barrier, t radio frequency waves (sub-6G) emitted by an emission source can be collected, the quantum property of the radio frequency waves stimulates hot electrons in the graphene, and a tunneling process occurs to form a current. External radio frequency waves are directly converted into direct-current electric energy, and electric energy can be provided for electronic equipment such as wearable equipment and sensors anytime and anywhere. Compared with traditional wireless charging equipment, the generator is more flexible, higher in efficiencyand simple in device structure.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Methods for producing chalcopyrite compound thin films for solar cells using multi-stage paste coating
ActiveUS8841160B2Low costDense surfaceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumCopper selenide
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Graphene/single atomic layer gas/gaas radio generator and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN111641275BGood for long runWork lessCircuit arrangementsSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionSchottky barrier
The invention relates to a radio power generation device, and discloses a graphene / single atomic layer GaS / gallium arsenide wireless generator. A layer of single atomic layer GaS is formed on a gallium arsenide substrate passivated by ammonium sulfide, and then attached A layer of graphene, with a first electrode and a side electrode, direct contact between the graphene and the single atomic layer gallium sulfide surface of gallium arsenide to form a heterojunction; Gallium contacts form a Schottky junction and create a Schottky barrier that collects radio frequency waves (sub-6G) emitted by the source. The quantum nature of the radio frequency waves excites hot electrons in the graphene and tunnels them The process forms an electric current. The invention directly converts external radio frequency waves into DC power, and can provide power to electronic devices such as wearable devices and sensors anytime and anywhere. Compared with traditional wireless charging equipment, the generator is more flexible, has higher efficiency, and has a simpler device structure.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
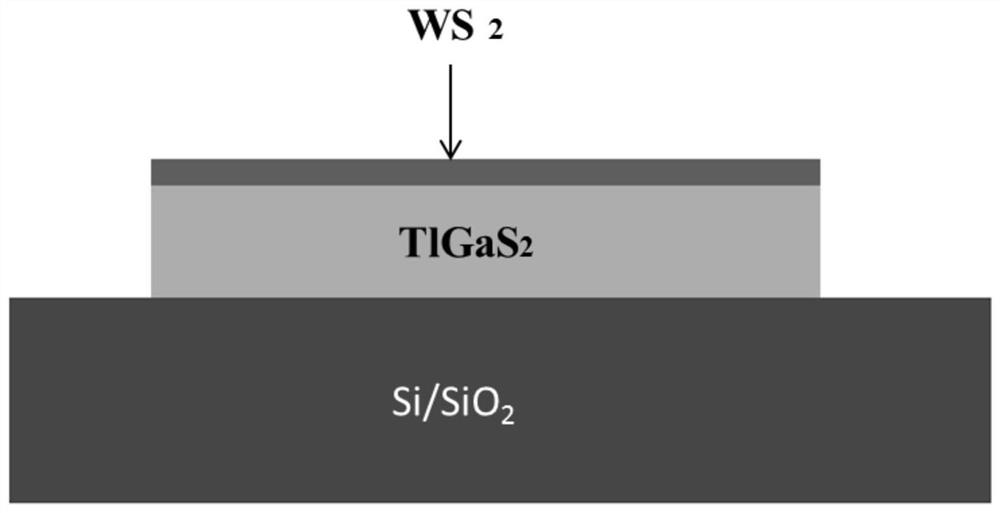
Composite material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN114335212AImprove carrier lifetimeSimple processFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionGallium sulfide
The invention provides a composite material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The composite material comprises: a substrate; the gallium thallium sulfide layer is arranged on the substrate; the single-layer tungsten disulfide layer is arranged on the gallium thallium sulfide layer and at least partially covers the gallium thallium sulfide layer, and the single-layer tungsten disulfide layer and the gallium thallium sulfide layer form a heterojunction. According to the invention, gallium thallium sulfide and single-layer tungsten disulfide are combined to form a heterojunction for regulating and controlling the service life of the carrier of the single-layer tungsten disulfide for the first time, and the composite material provided by the invention can obviously prolong the service life of the carrier of the single-layer tungsten disulfide.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF RADIO METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT
A near-infrared sulfide long-lasting luminescent material and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN110028958BAfterglow implementationSimple preparation processIn-vivo testing preparationsLuminescent compositionsGallium sulfideSulfidation
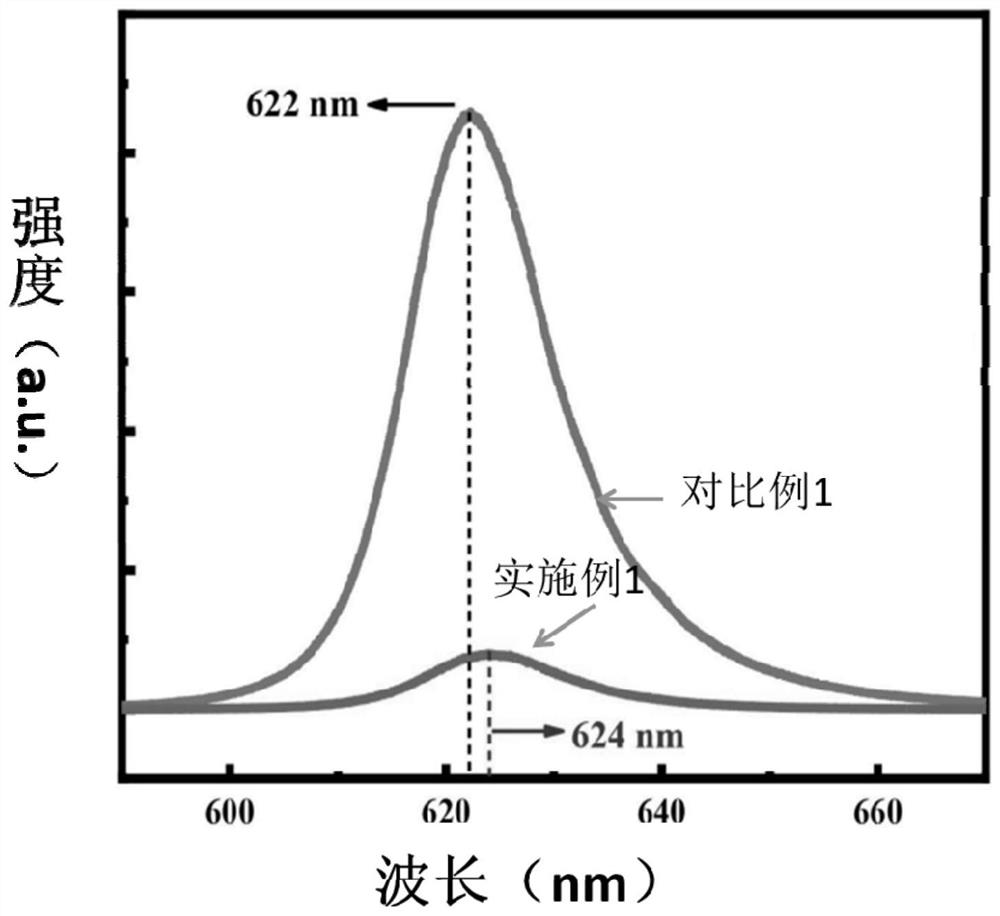
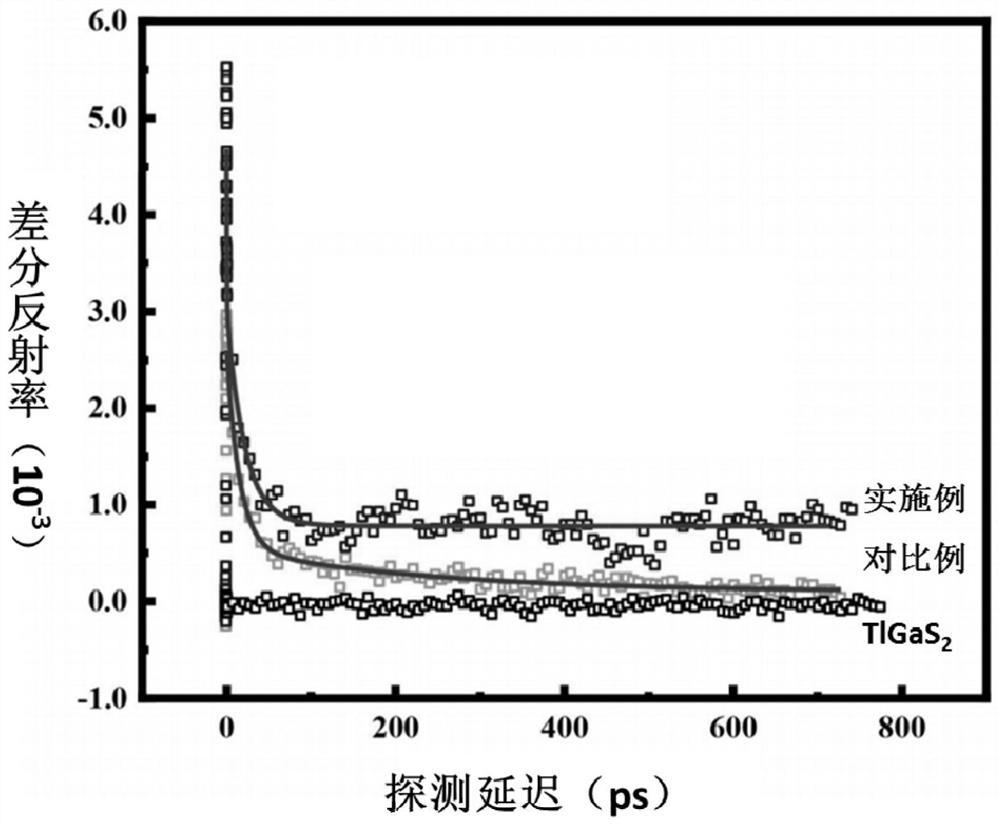
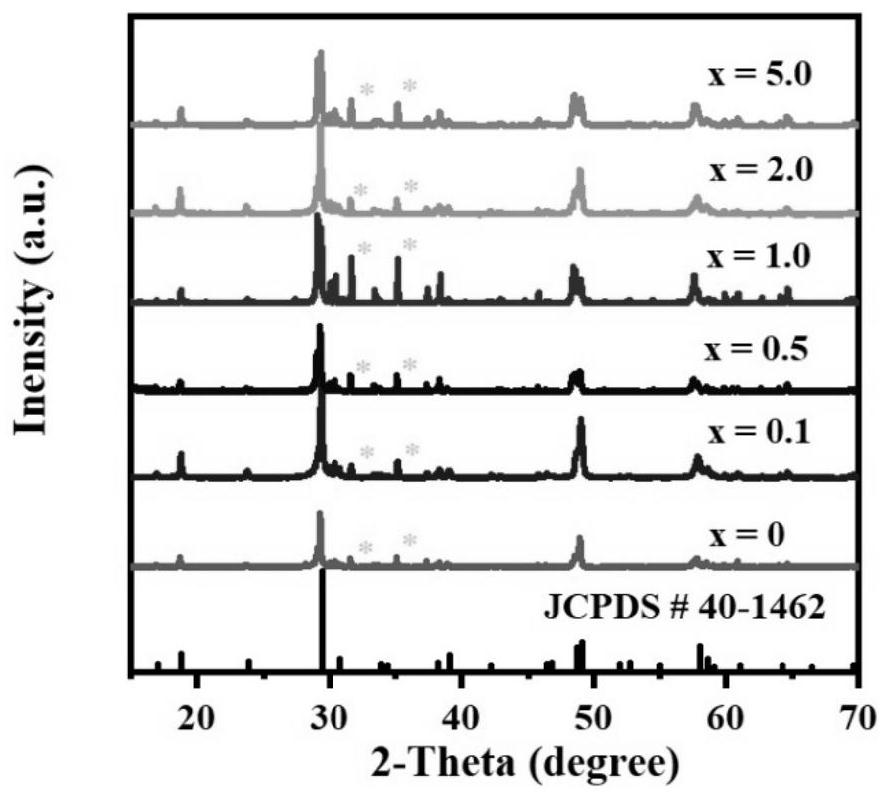
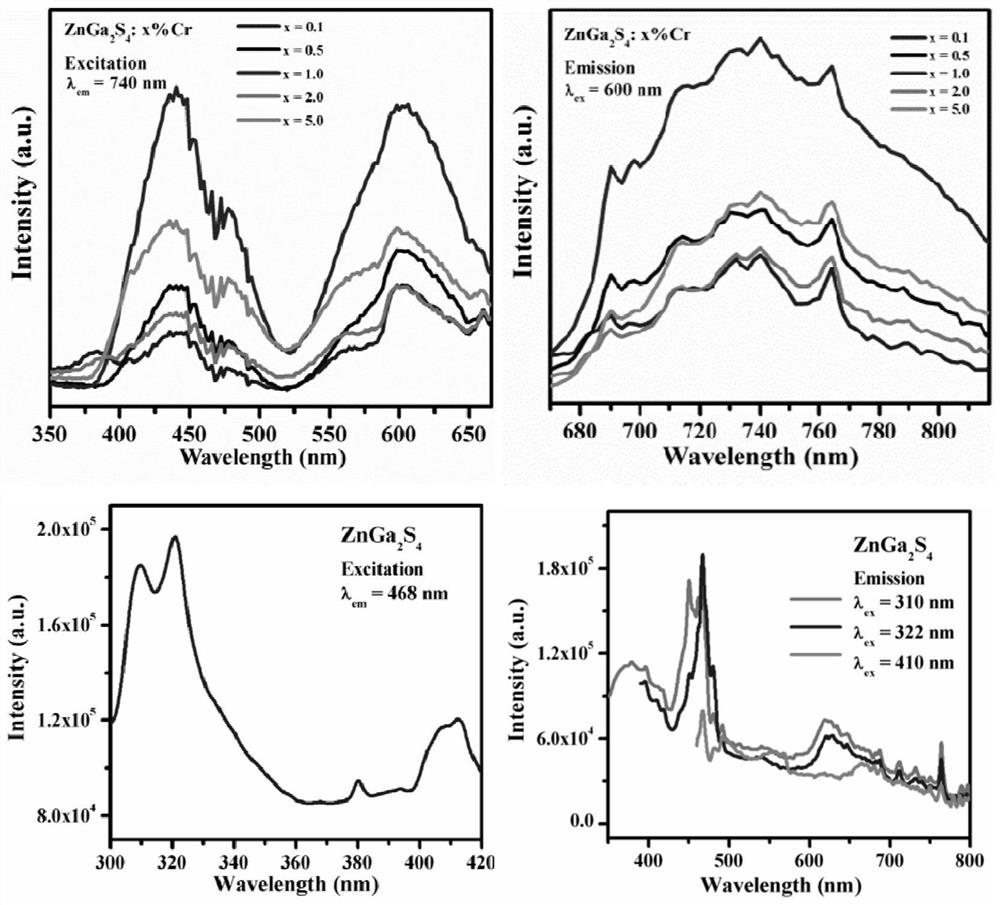
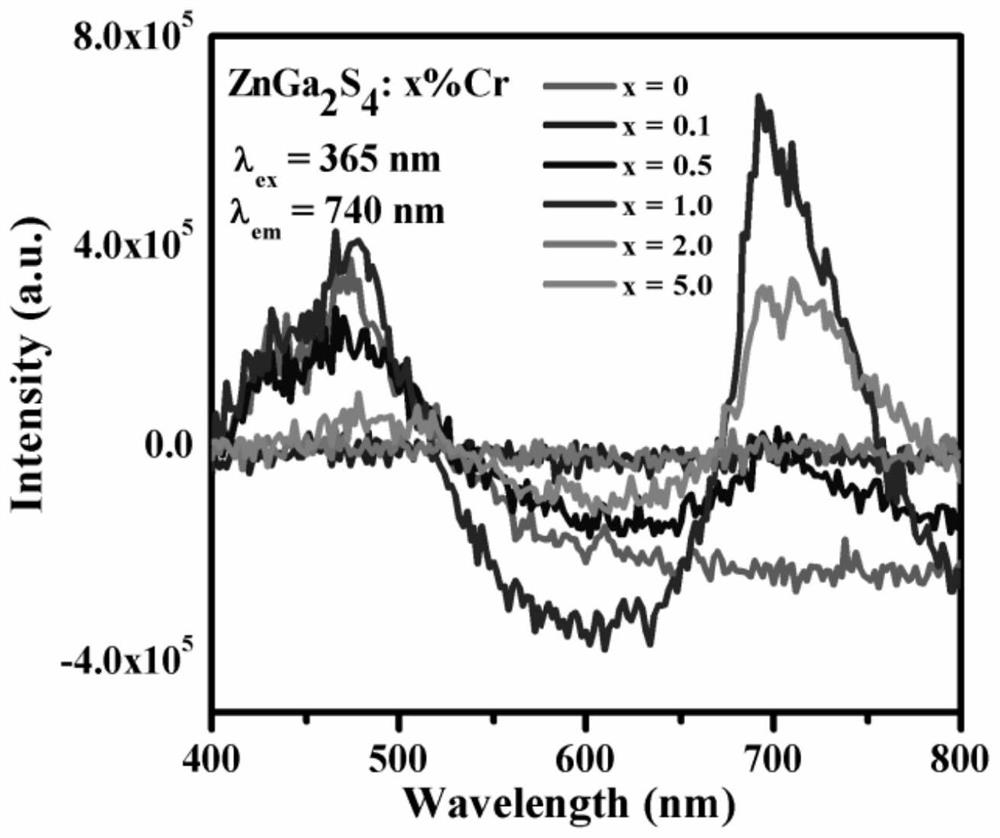
The invention discloses a near-infrared sulfide long afterglow luminescent material, which uses ZnGa 2 S 4 As the substrate, the substrate is doped with 0.1-5.0mol% Cr 2 o 3 , whose structural formula is =ZnGa 2 S 4 :xCr 3+ , x=0.1~5.0mol%. Grinding and mixing gallium sulfide, zinc sulfide and chromium oxide in a molar ratio of 1:1:0.0004-0.025 and putting them into a reaction vessel, calcining at 1100-1200°C for 2-4 hours in a sulfur atmosphere, cooling down , that is. The present invention achieves near-infrared long afterglow luminescence by doping trivalent chromium ions. The afterglow luminescence peak is located at the 740nm luminescence peak, and the afterglow decay time is as long as 600s. Application prospects.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Praseodymium-ytterbium co-doped zirconium gallium sulfide glass up-conversion luminescent material as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106118648ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRubidiumPhotoluminescence
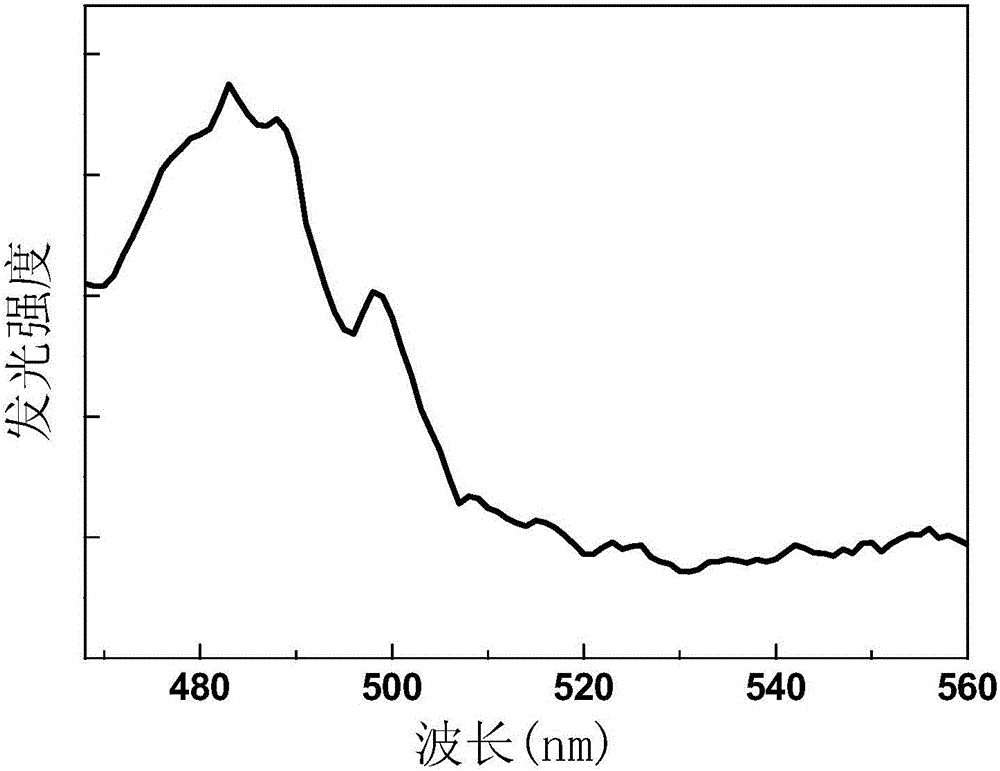
The invention discloses a praseodymium-ytterbium co-doped zirconium gallium sulfide glass up-conversion luminescent material of which the chemical formula is ZrS-Ga2S3-R2S: xPr<3+>, yYb<3+>, in the formula, R is at least one of a lithium element, a sodium element, a potassium element, a rubidium element and a caesium element; x is 0.01-0.06; and y is 0.01-0.04. In the photoluminescence spectra of the praseodymium-ytterbium co-doped zirconium gallium sulfide glass up-conversion luminescent material, the excitation wavelength of the praseodymium-ytterbium co-doped zirconium gallium sulfide glass up-conversion luminescent material is 578nm, a luminescent peak is formed by transition radiation of Pr<3+> ions from <3>P<0> to <3>H<4> in a wavelength zone of 483nm, and thus the material can be used as a blue luminescent material. The invention further provides a preparation method of the praseodymium-ytterbium co-doped zirconium gallium sulfide glass up-conversion luminescent material and an organic light-emitting diode using the praseodymium-ytterbium co-doped zirconium gallium sulfide glass up-conversion luminescent material.
Owner:郑甘裕
A copper indium gallium based photodetector
ActiveCN107731943BFulfil requirementsHigh sensitivityPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesIndiumPhotovoltaic detectors
The present invention provides a novel photoelectric detector based on copper indium gallium selenium and copper indium gallium sulfide. According to the composite functional layer, a contact part ofthe copper indium gallium selenium and the copper indium gallium sulfide is changed into copper indium gallium selenium sulfide, a composition is gradually changed in a transverse direction, the functional layer is modified, the electrical performance is adjusted to meet requirements of the photoelectric detector, the sensitivity of the detector is further improved, and the stability of the sensoris greatly improved.
Owner:宝应电工厂
A light-emitting diode epitaxial structure based on aluminum gallium nitride material and its manufacturing method
ActiveCN114497307BImprove output performanceImprove quantum efficiencySemiconductor devicesGallium sulfideUltraviolet lights
The invention relates to an epitaxial structure of a light emitting diode based on aluminum gallium nitride material and a manufacturing method thereof. The invention optimizes the light extraction structure for an ultraviolet light emitting diode based on tunneling effect. The UV light emitting diode using the n-p-n-type tunneling structure can effectively avoid the absorption of UV light by the traditional p-type gallium nitride in the pn structure of the UV diode, that is, the use of n-type aluminum gallium nitride (its aluminum Composition high enough that its band bandwidth is substantially transparent to UV light from the active layer) and a very thin layer of n-type or undoped gallium nitride (5 nm and below), and a layer of p-type nitrogen A carrier injection structure based on the tunneling effect of aluminum gallium sulfide (the aluminum composition of which is high enough that its energy band bandwidth is substantially transparent to ultraviolet light from the active layer). The ultraviolet light emitting diode with this structure needs to be combined with a new light extraction structure and technology to effectively extract the ultraviolet light absorbed in the traditional ultraviolet light emitting diode from the p surface.
Owner:XUZHOU LIYU ADVANCED TECH CO LTD
Method for fabrication of copper-indium gallium oxide and chalcogenide thin films
InactiveUS9608146B2Simpler and cheapHigh capital expenseSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationIndiumMaterials science
A composition of matter and method of forming copper indium gallium sulfide (CIGS), copper indium gallium selenide (CIGSe), or copper indium gallium telluride thin film via conversion of layer-by-layer (LbL) assembled Cu—In—Ga oxide (CIGO) nanoparticles and polyelectrolytes. CIGO nanoparticles are created via a flame-spray pyrolysis method using metal nitrate precursors, subsequently coated with polyallylamine (PAH), and dispersed in aqueous solution. Multilayer films are assembled by alternately dipping a substrate into a solution of either polydopamine (PDA) or polystyrenesulfonate (PSS) and then in the CIGO-PAH dispersion to fabricate films as thick as 1-2 microns. After LbL deposition, films are oxidized to remove polymer and sulfurized, selenized, or tellurinized to convert CIGO to CIGS, CIGSe, or copper indium gallium telluride.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
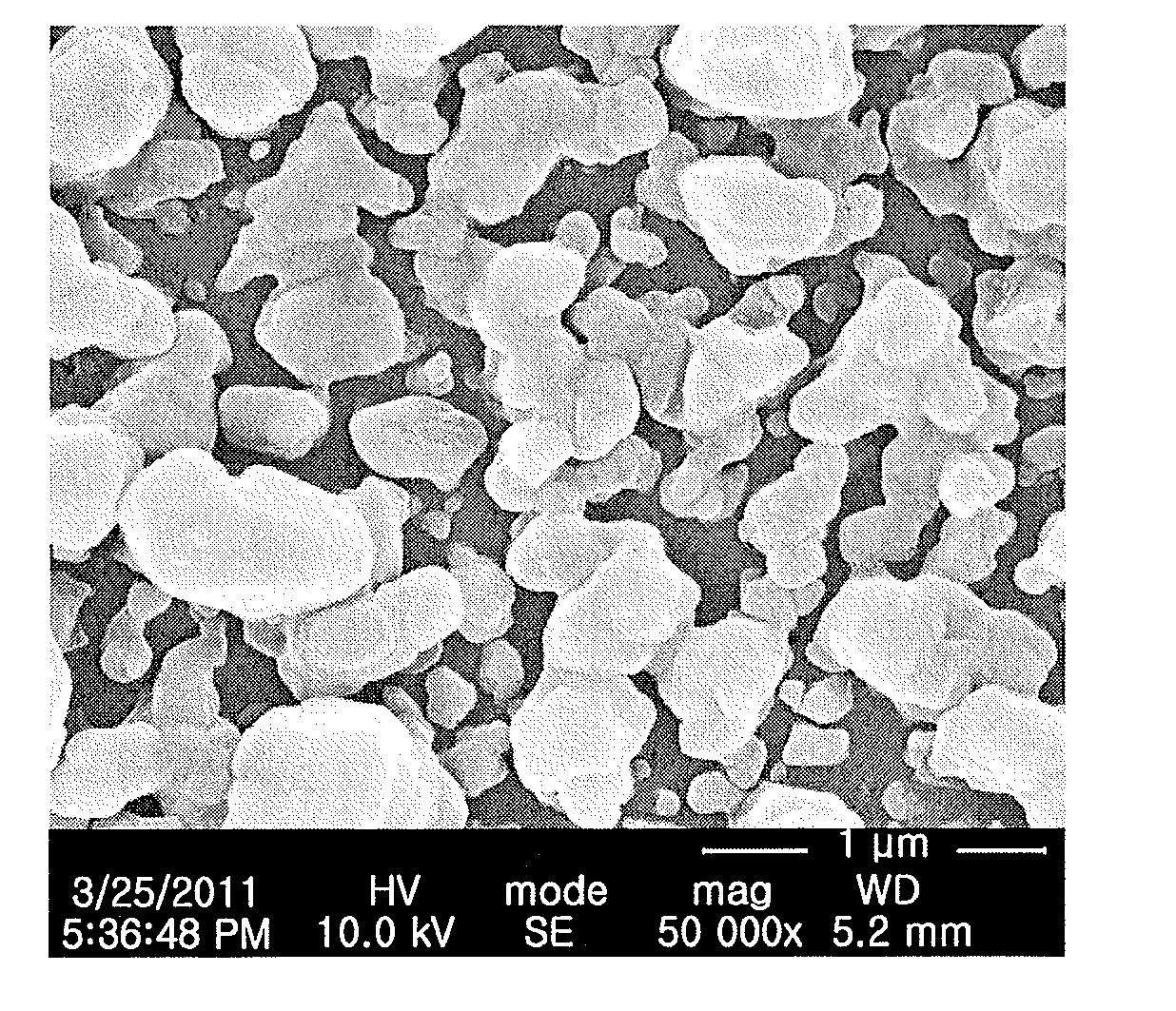
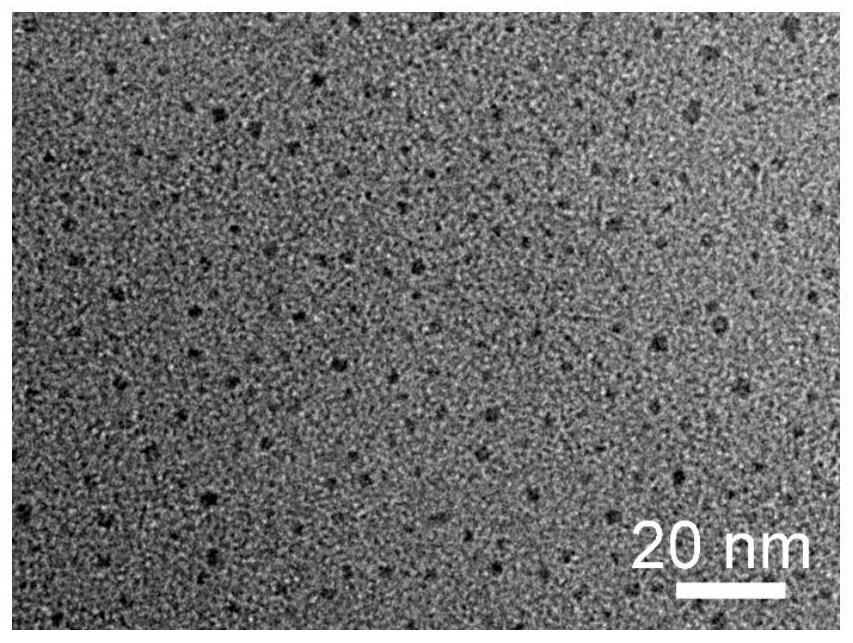
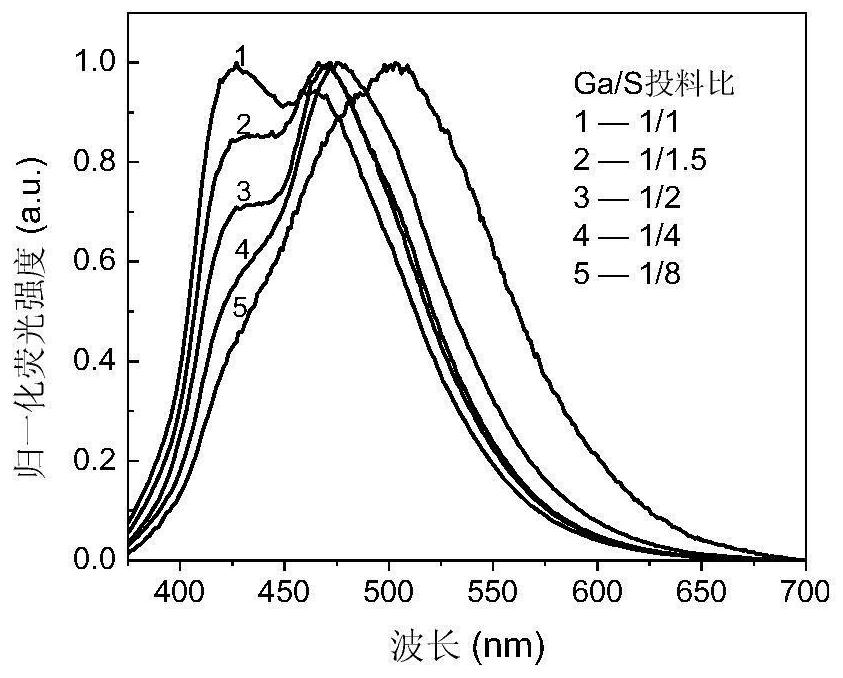
Gallium sulfide quantum dot material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109385272BEase of widespread commercial applicationSimple processLuminescent compositionsGallium sulfideUltraviolet lights
The invention discloses a gallium sulfide quantum dot material and a preparation method thereof. The material is gallium sulfide quantum dots, the chemical formula is Ga x S 3 , where 1≤x≤5, the chemical formula is Ga x S 3 The gallium sulfide quantum dots have a diameter of 1-8nm; the method is to mix four or mixed to obtain a mixed solution, and then the mixed solution is placed in an inert atmosphere and reacted at 220-300°C for 2-20min to obtain a reaction solution. After that, the molar ratio of the gallium source, solvent and precipitant in the reaction solution The ratio is 1:50-300:100-1400, adding solvent and precipitant successively to the reaction liquid cooled under an inert atmosphere to obtain a suspension, and then performing solid-liquid separation on the suspension to obtain a gallium sulfide quantum dot material . Its luminescence peak under the excitation of ultraviolet light is adjustable in the range of 420-505nm, and it is very easy to be widely commercialized and applied in the fields of light-emitting devices and ion detection.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
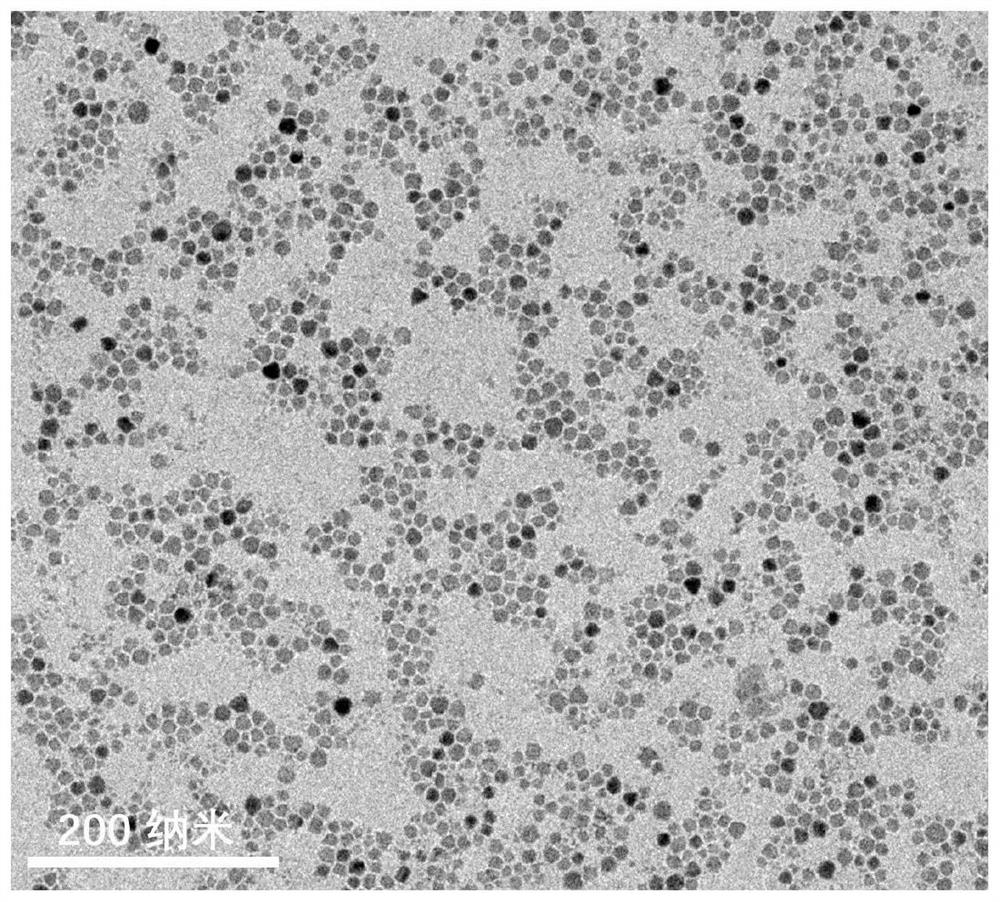
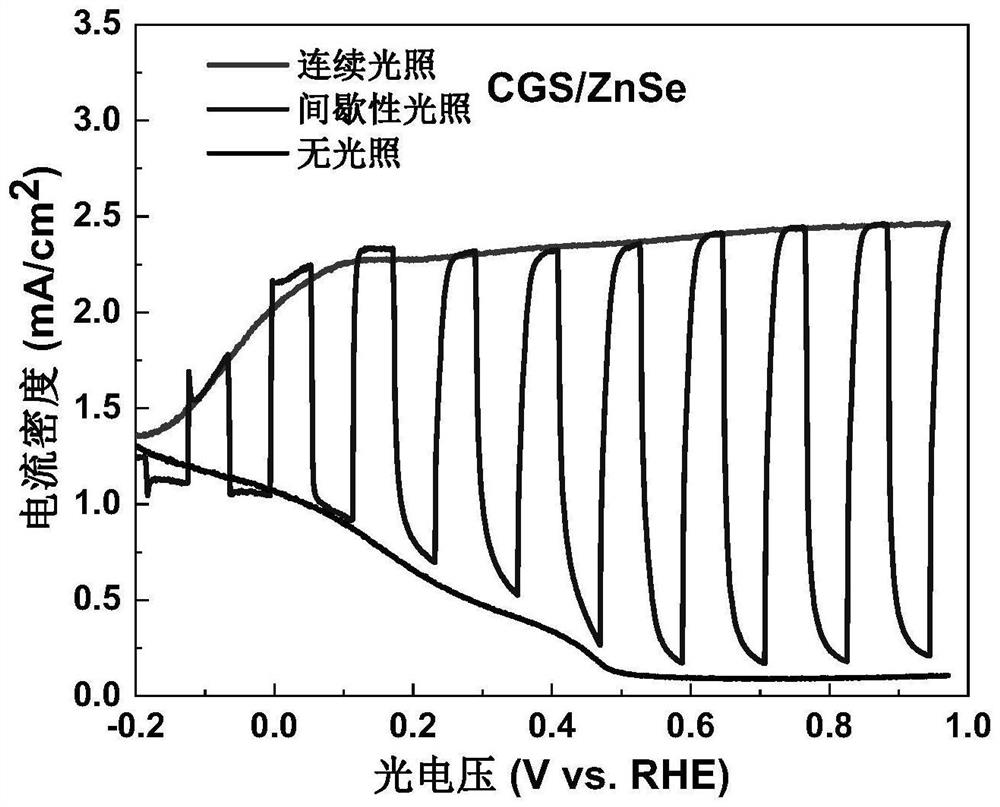
Copper gallium sulfide/zinc selenide core-shell structure quantum dot and preparation method and application thereof
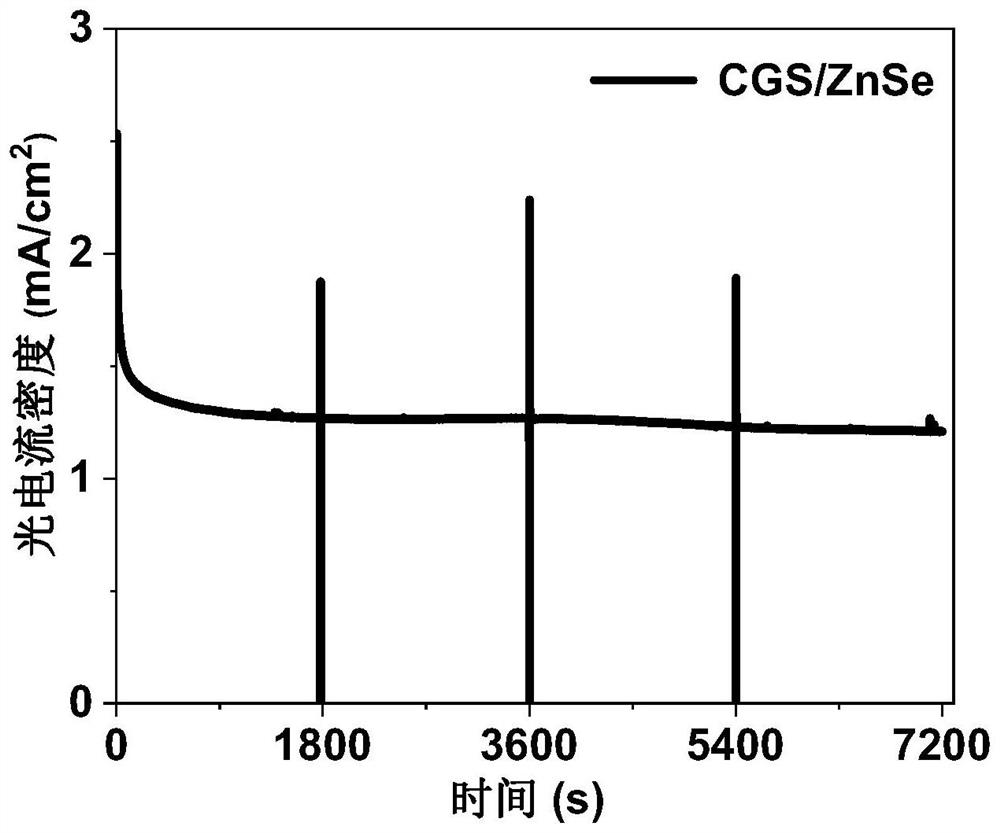
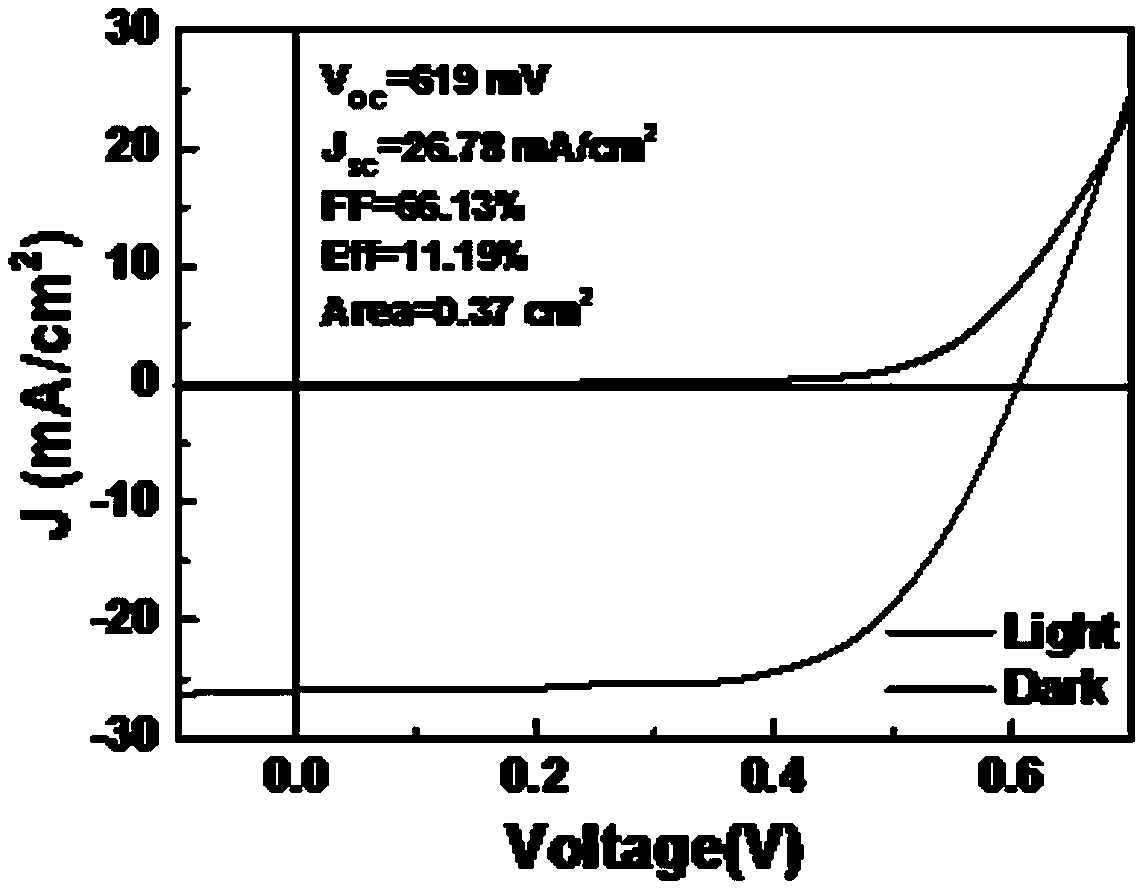
PendingCN114561215AIncrease the saturation photocurrentReduce surface defectsLight-sensitive devicesEnergy inputZinc selenideElectron injection
The invention discloses a copper gallium sulfur / zinc selenide core-shell structure quantum dot and a preparation method and application thereof, and the preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly synthesizing a CuGaS2 core quantum dot, and then synthesizing a ZnSe shell layer on the surface of the CuGaS2 core quantum dot. The ZnSe shell layer in the core-shell structure quantum dot effectively passivates a large number of surface defects of a CuGaS2 core, improves the stability and effectively inhibits non-radiative recombination, and compared with pure copper-gallium-sulfur quantum dots, the zinc selenide shell layer coating effectively improves the saturation photocurrent of a quantum dot photoelectrochemical cell. The core-shell structure quantum dot can be applied to hydrogen production of a photoelectrochemical cell, and more electrons can be injected into a photoanode, so that the photocurrent density is improved.
Owner:YANGTZE DELTA REGION INST OF UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINE HUZHOU
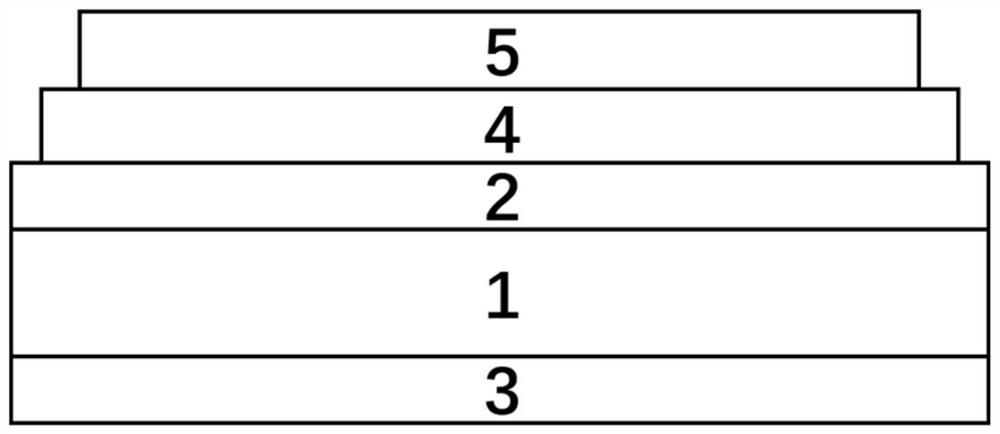
Method for improving efficiency of flexible copper indium gallium sulfide selenide thin film solar cell
ActiveCN110752272AReduce manufacturing costReduce the temperatureFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingTin thin filmsGrain boundary
The present invention belongs to the field of solar cell preparation, in particular to a method for improving efficiency of a flexible copper indium gallium sulfide selenide thin film solar cell. Thespecific steps are as follows: firstly, a molybdenum electrode is sputtered on a substrate; a CIGSSe precursor solution is prepared; the precursor solution is spin-coated on the substrate to prepare aCIGSSe prefabricated film, which is heated, selenized and annealed to obtain a CIGSSe film; then a cadmium sulfide film is prepared on the CIGSSe film; zinc oxide and indium doped tin oxide thin films are sputtered on the cadmium sulfide film in turn; finally silver electrode evaporation is carried out, then the flexible CIGSSe thin film solar cell is obtained. By introducing bismuth and potassium compounds into the CIGSSe precursor solution, the growth of CIGSSe crystals is promoted; grain boundary defects are passivated; and then the performance of the CIGSSe solar cell is improved. The invention is environmental, safe and low-cost, and the efficiency of the CIGSSe thin film solar cell is effectively improved.
Owner:XINYANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

![Optical waveguide[[s]] and optical fiber perform including gallium, lanthanum, sulfur, oxygen, and fluorine Optical waveguide[[s]] and optical fiber perform including gallium, lanthanum, sulfur, oxygen, and fluorine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/86095b83-535f-4d0f-8ec9-91d36fd5bd79/US07016593-20060321-D00000.png)
![Optical waveguide[[s]] and optical fiber perform including gallium, lanthanum, sulfur, oxygen, and fluorine Optical waveguide[[s]] and optical fiber perform including gallium, lanthanum, sulfur, oxygen, and fluorine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/86095b83-535f-4d0f-8ec9-91d36fd5bd79/US07016593-20060321-D00001.png)
![Optical waveguide[[s]] and optical fiber perform including gallium, lanthanum, sulfur, oxygen, and fluorine Optical waveguide[[s]] and optical fiber perform including gallium, lanthanum, sulfur, oxygen, and fluorine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/86095b83-535f-4d0f-8ec9-91d36fd5bd79/US07016593-20060321-D00002.png)