Patents
Literature
135 results about "Zymase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Zymase is an enzyme complex that catalyzes the fermentation of sugar into ethanol and carbon dioxide. It occurs naturally in yeasts. Zymase activity varies among yeast strains. Zymase is also the brand name of the drug pancrelipase.
Production method of biological polypeptide used for feed
ActiveCN102239960AIncrease the depth of fermentationIncrease the degree of hydrolysisAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsBiotechnologyImmunity
Owner:湖北邦之德牧业科技有限公司
Prepn and use of enzyme prepn for use in hemp degluing industrial process
InactiveCN1374398ANo pollution in the processImprove working conditionsBacteriaBacteriological rettingBreaking strengthMicroorganism
The present invention relates to the field of microbial engineering technology. The enzyme preparation is prepared through the process including slant culture and storing, shaking culture, seeding tank culture and fermenting tank production of high enzyme activity bacteria strain. Bacillus subtilis of No.13 strain and preservation number CCTCC No.M200038 is selected. The hemp degumming process includes the fermentation of enzyme liquid filtering residue, diluting bacteria liquid to 3-6 times, regulating the pH value of fermented enzyme liquid in degluing tank to 7.5-9.0, hemp material pre-treatment, degumming with degumming liquid for 2-10 hr. The process of the present invention has no environmental pollution, and can produce hemp top with length, fineness and breaking strength superior to those of chemical process.
Owner:山东省纤维检验局 +2
Mutant of glutamine transaminase expressed by active form
ActiveCN107574159AAchieve active expressionSimplify production stepsFungiTransferasesBacterial strainMutant
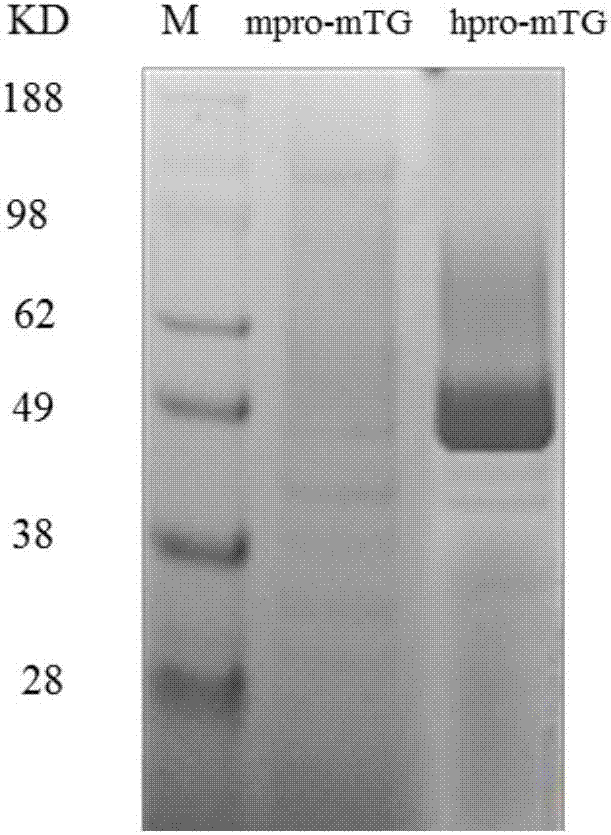
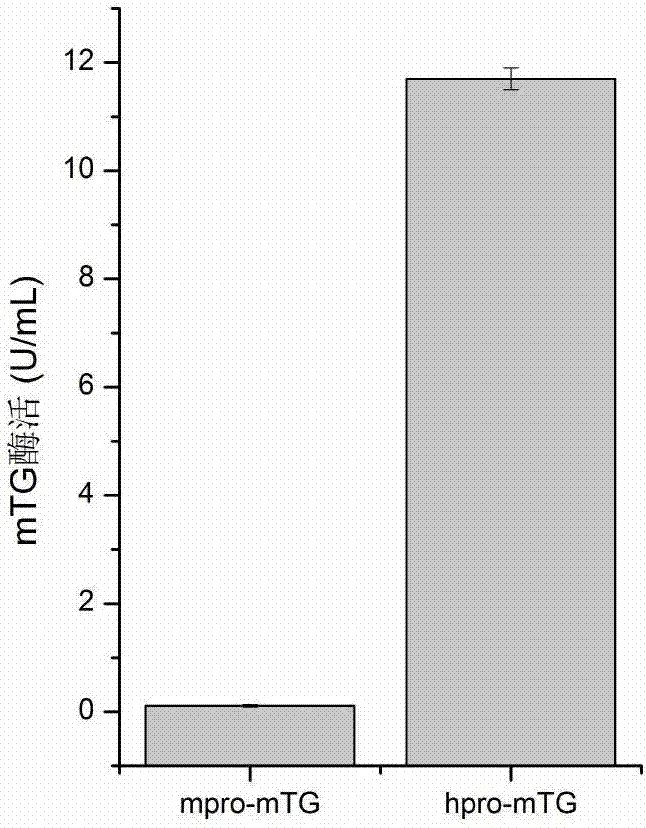
The invention discloses a mutant of glutamine transaminase expressed by an active form, and belongs to the field of gene engineering and fermentation engineering. A genetically engineered bacterium po1h / hpro-mTG of high-output glutamine transaminase is structured by using yarrowia lipolytica as a host. The bacterial strain is high in enzyme production level; the fermenting enzyme activity of a shake flask is up to 11.7 U / mL, and improved by 106 times in comparison to that before transformation; the fermenting enzyme activity of a fermenting tank is up to 43.7 U / mL. Through co-expressing proteases TAMEP and hpro-mTG, the activity expression of glutamine transaminase is realized; the fermenting enzyme activity of the shake flask can reach 6.7U / mL, and the fermenting enzyme activity of the fermenting tank can reach 21.4U / mL. The fermenting enzyme production level of the recombinant bacteria is high, the production cost of the glutamine transaminase is reduced; the mutant is good for the industrial production of the glutamine transaminase.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Lactose-free acidified milk and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a lactose-free acidified milk and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) uniformly mixing raw milk, a stabilizer, a sweetener and saccharomycete lactase at the temperature of 35-45 DEG C to obtain a mixed solution A, wherein the additive amount of saccharomycete lactase is larger than or equal to 0.03%; (2) homogenizing, sterilizing and cooling the mixed solution A to obtain a mixed solution B; (3) achieving synchronous enzymolysis and fermentation of the mixed solution B through a leavening agent and mold lactase at the temperature of 35-45 DEG C, wherein the additive amount of mold lactase is larger than or equal to 0.03%, and the total additive amount of the two enzymes is larger than or equal to 0.1%, and cooling the mixed solution B subjected to enzymolysis and fermentation to obtain the lactose-free acidified milk. According to the invention, the biological enzymolysis technology is adopted, and different lactases are added in different stages through the two-stage process, so that the content of lactose in the acidified milk is effectively reduced, and the internationally specified lactose-free standard is reached. The lactose-free acidified milk is good in texture properties, excellent in taste and flavor, rich in nutrition and easy to absorb.
Owner:BRIGHT DAIRY & FOOD
Bacillus coagulans L-H7 and application thereof
ActiveCN110724651AMeet basic fermentation requirementsLower pHBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyArginine
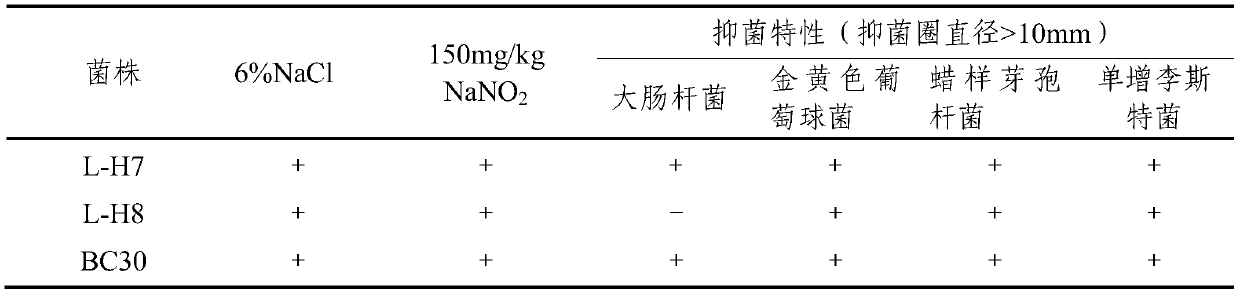
The invention provides bacillus coagulans L-H7 and an application thereof. The preservation number of the bacillus coagulans L-H7 is CGMCC No.18662. When glucose is fermented with a strain L-H7, acidis produced, but gas is not produced, viscosity is not produced, arginine does not produce ammonia, amino acid decarboxylase is feminine, H2S is not produced, protease and lipase are produced, high-concentration sodium chloride and high-concentration sodium nitrite can be borne, growth of food-borne pathogenic bacteria can be effectively restrained, besides, a fermentation enzyme system is rich, and activity of protease, esterase, glycosidase and the like is high. Compared with lactic acid bacteria trophosome, the bacillus coagulans L-H7 is higher in survival rate in digestion environment, andprobiotic effects can be effectively exerted. When the bacillus coagulans L-H7 instead of lactic acid bacteria is used for preparing low-salt fermented sausages, acid can be quickly produced, the bacillus coagulans L-H7 is dominant in fermentation, flavor defects of the low-salt fermented sausages can be effectively made up, and the quality of the fermented sausages can be improved.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Fermenting enzymolysis agent for soybean meal fermentation and application thereof
ActiveCN105614023AIncrease nutritionImprove digestion and absorption rateAnimal feeding stuffMycoproteinAdditive ingredient
The invention provides a fermenting enzymolysis agent for soybean meal fermentation and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of feed fermenting agents. The fermenting enzymolysis agent consists of microorganism strains, enzyme preparations, an accessory ingredient and a carrier. According to the fermenting enzymolysis agent, seven types of beneficial bacteria and three types of enzyme preparations are combined, 72-hour aerobiotic, microaerobic and anaerobic fermentation and enzymolysis are performed on crushed soybean meal and a small amount of corn flour, so that antinutritional factors in the soybean meal are eliminated, cell walls are broken, non-protein nitrogen is converted into mycoprotein, proteins are decomposed into polypeptide and small peptide, more Vitamin B is generated, the nutrition performance of the soybean meal is comprehensively improved, and thus the soybean meal becomes a feed protein source capable of partially replacing a feed protein source for import fish meal feed.
Owner:湖州环农微生物技术研究所 +1
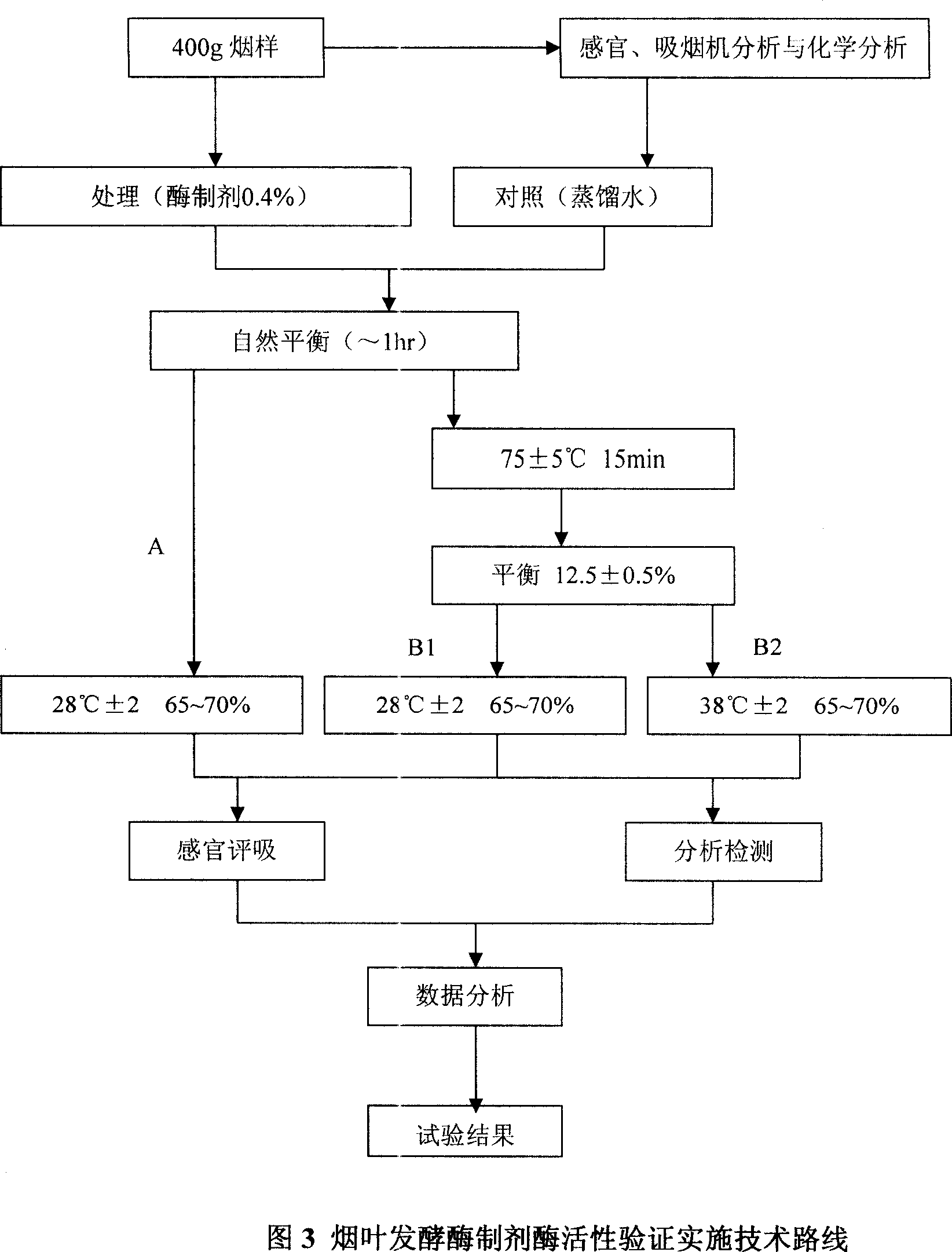
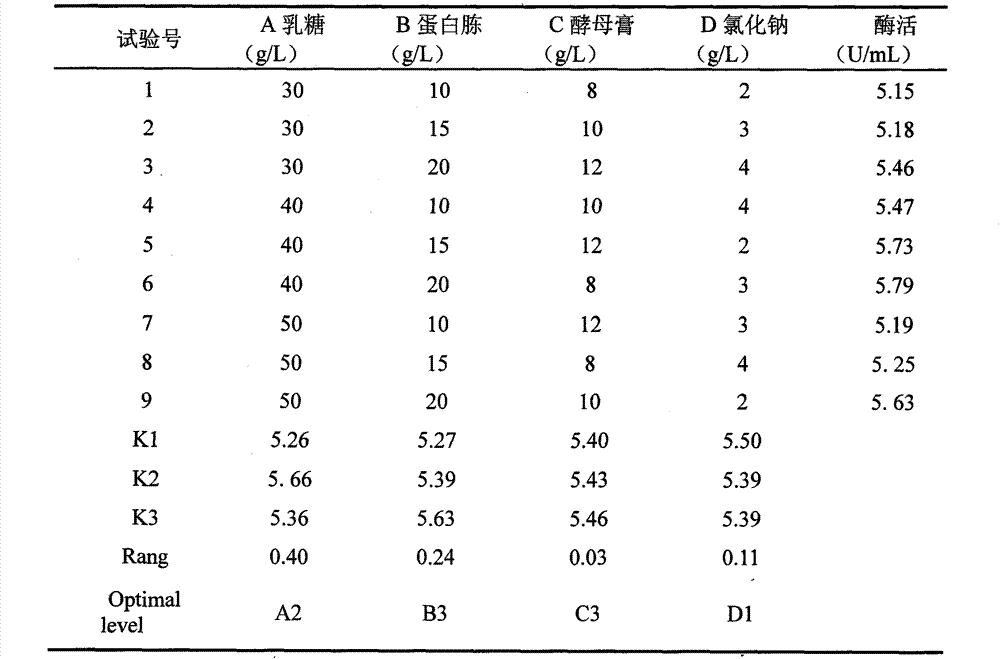
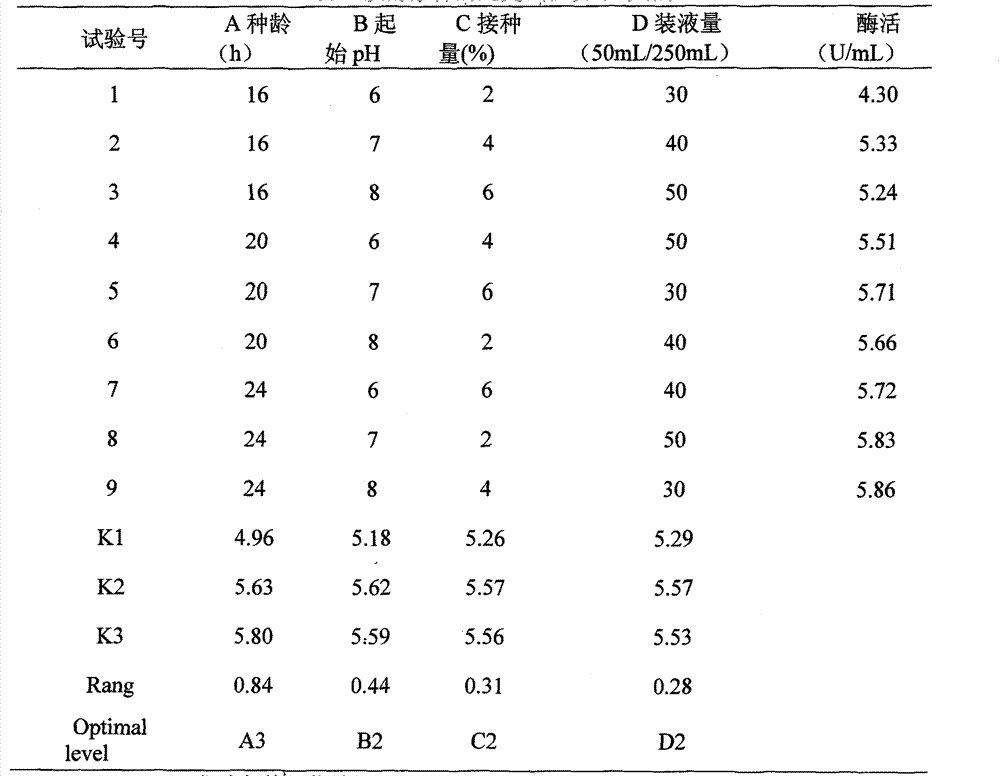
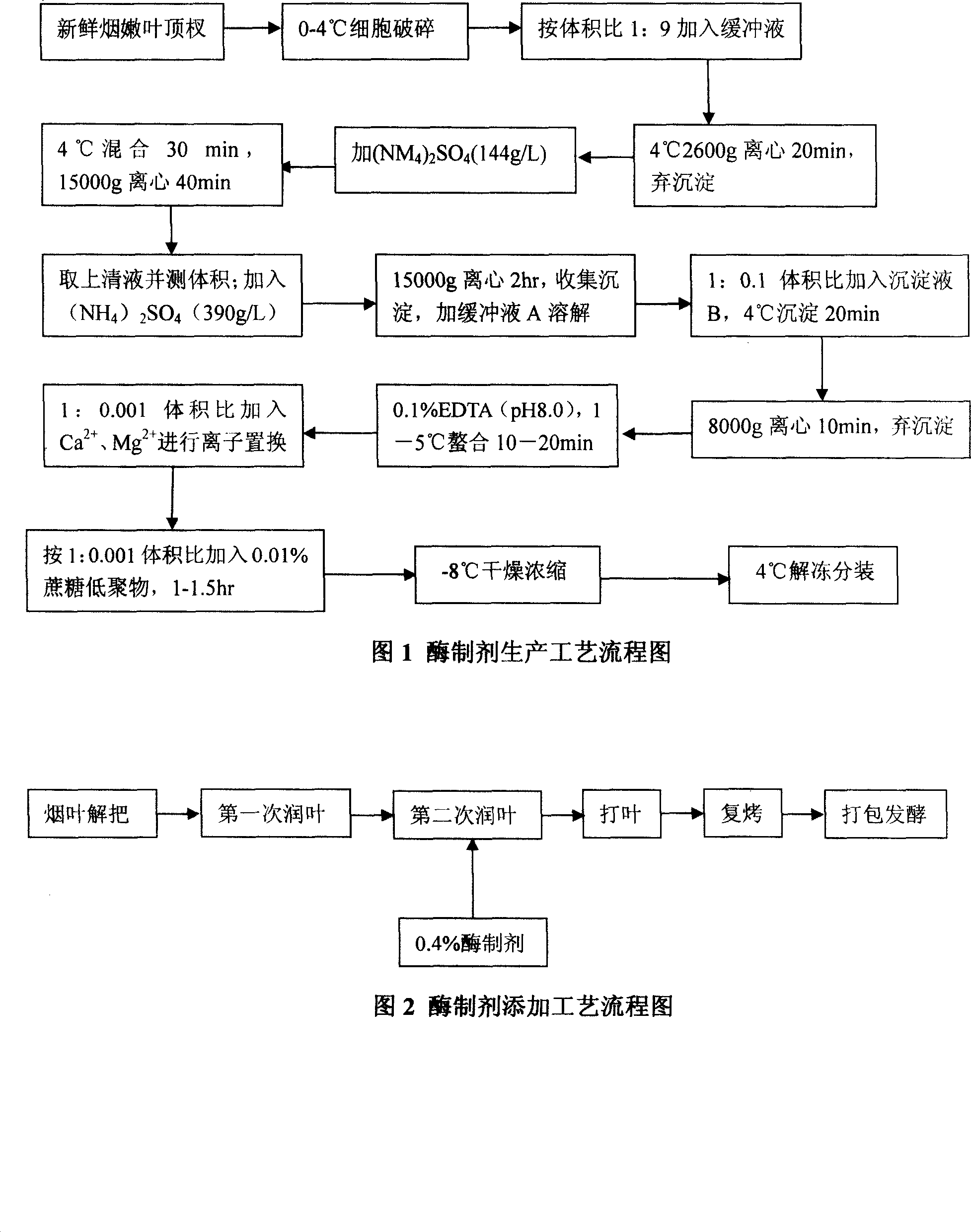
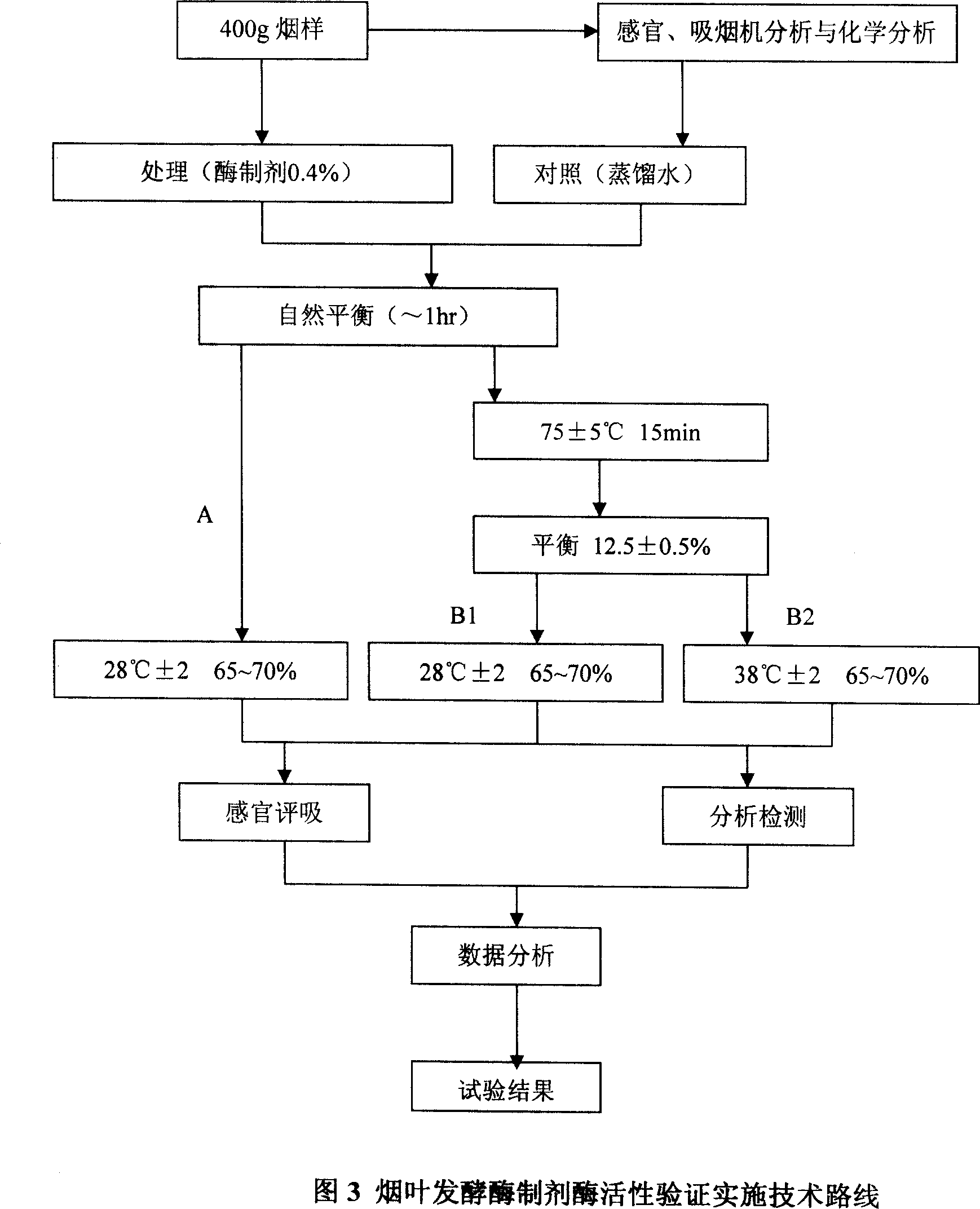
Method for producing tobacco leaf fermenting enzyme preparation
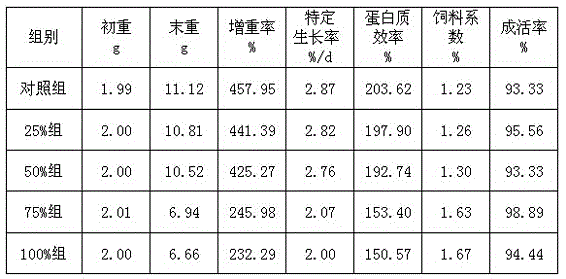
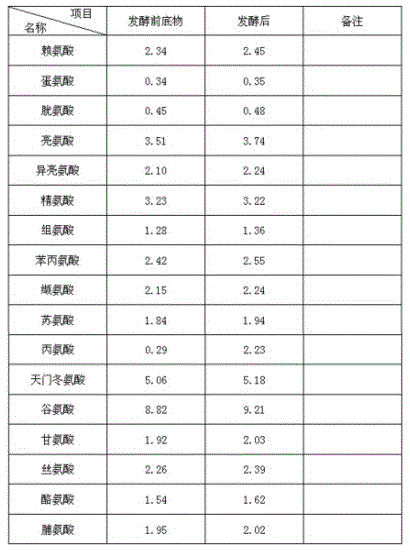
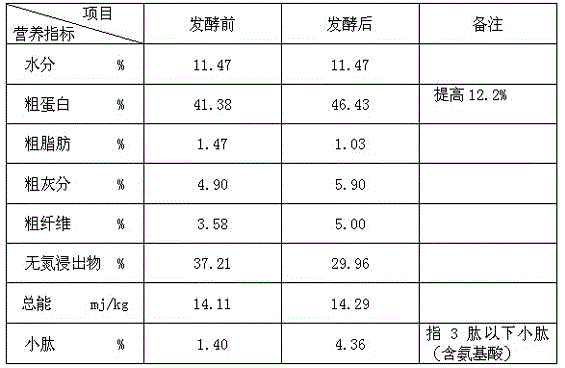
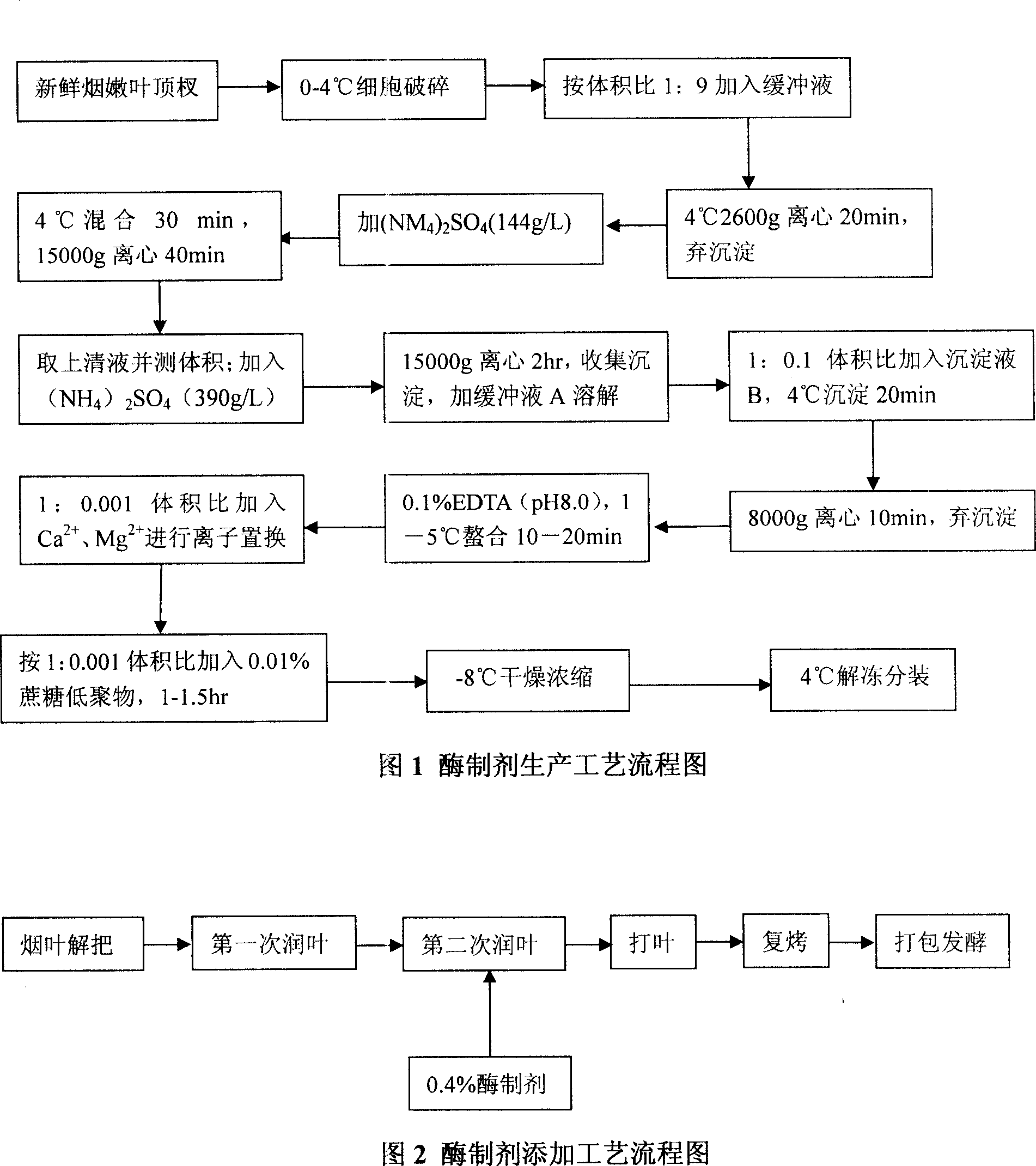
InactiveCN101144073AGood application effectIt has the characteristics of high temperature resistance of rebaking lineTobacco treatmentEnzymesBiotechnologySaccharum
The present invention relates to a novel tobacco leaf fermenting enzyme preparation production method which aims to solve the technical problems that how the quality of the tobacco leaf fermenting product is improved and how the reactivity protection of the tobacco leaf fermenting enzyme preparation is realized in the natural fermenting field of the tobacco leaf. The enzyme preparation consists of glucoseoxidase, chlorophyl oxidase, carotenoid oxidase, protease, and nicotine-degradation enzyme. Through the cell disruption of fresh leaves, (NH 4) 2 SO 4 is utilized to operate the second fractional precipitation to obtain crude enzyme fluid, an enzyme molecule adopts Ca 2 + and Mg 2 + to operate the metal ion exchange, to accomplish the molecule modification; a macro molecule combination modification is accomplished through adopting 0.01 percent of cane sugar low molecular polymer, thereby prolonging the half life period of an enzyme preparation, and obviously improving the high temperature resistant ability. The experimental result employed by the enzyme preparation indicates that the nicotine is decreased by 9.3 percent, the total nitrogen is decreased by 5.7 percent, the protein is decreased by 7.1 percent; cigarette smoke condensates are decreased by 8.4 percent, the tar content is decreased by 5.1 percent, cigarette smoke nicotine content is decreased by 28.0 percent, and the carbon is decreased monoxide by 1.6 percent. The enzyme preparation is employed when the tobacco is wet for the second time before defolat and redrying.
Owner:谢勇 +2
ª—- carrageenin catabolic enzymes , its preparing process and application
The invention is an enzyme, and its characteristic: it can degrade k-carrageenan to prepare oligo-carrageenan and degrade beta-1, 4-indican bond of k-carrageenan, therefore called k-carrageenan degrading enzyme, its molecular weight is 30,000Da. When preparing it, using 2216E culture medium to make shaking bottle culture on the sea Cytophaga sp at 28-35deg.C, then centrifugating the culture solution to obtain fermentation enzyme solution, ultrafiltering and concentrating the enzyme solution, then using 40-80% (NH4)2SO4 for salting-out and collecting protein deposit, and freeze-drying. It can effectively degrade k-carrageenan, be used to prepare oligo-carrageenan, and compared with chemical method, it has simple preparing coursee, high product yield, stable quality, and ensures the activity research and development of oligosaccharide, etc.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Prepn and use of enzyme prepn for use in hemp degluing industrial process
InactiveCN1188513CNo pollution in the processImprove working conditionsBacteriaBacteriological rettingMicroorganismPulp and paper industry
The present invention relates to the field of microbial engineering technology. The enzyme preparation is prepared through the process including slant culture and storing, shaking culture, seeding tank culture and fermenting tank production of high enzyme activity bacteria strain. Bacillus subtilis of No.13 strain and preservation number CCTCC No.M200038 is selected. The hemp degumming process includes the fermentation of enzyme liquid filtering residue, diluting bacteria liquid to 3-6 times, regulating the pH value of fermented enzyme liquid in degluing tank to 7.5-9.0, hemp material pre-treatment, degumming with degumming liquid for 2-10 hr. The process of the present invention has no environmental pollution, and can produce hemp top with length, fineness and breaking strength superior to those of chemical process.
Owner:山东省纤维检验局 +2
Method for producing forage plant protein by carrying out enzyme synergy fermentation and enzymolysis on plant protein
ActiveCN104068269APromote digestionThe process is simple and easy to controlFood processingAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologySmall peptide
The invention relates to a method for producing a forage plant protein by carrying out enzyme synergy fermentation and enzymolysis on a plant protein. The method is characterized in that enzyme for the fermentation and the enzymolysis comprises a complex enzyme preparation and microbial strains; a plant protein raw material for the fermentation and the enzymolysis is extracted from residual processed meal or grains after two or more kinds of plant seeds are compressed or fermented. The method comprises the steps of preparing the materials, inoculating and mixing the materials, carrying out the fermentation, carrying out the enzymolysis, drying, cooling, crushing and carrying out product detection, so as to finally obtain a forage plant protein product, wherein the content of small peptide of the forage plant protein product is 10-40% of that of the proteins of the forage plant protein product. The method has the advantages that the key technical problems of high labor intensity, difficulty in control, instable quality, low production efficiency, high energy consumption and the like in the solid state fermentation process of the plant proteins can be solved, the industrialization of a fermented plant protein product can be effectively promoted, and the economic benefit can be increased.
Owner:湖北邦之德牧业科技有限公司
Chitosanase gene csnbaa, chitosanase and preparation method and application of chitosanase
PendingCN112430615ARich varietyRich sourcesFungiMicroorganism based processesNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
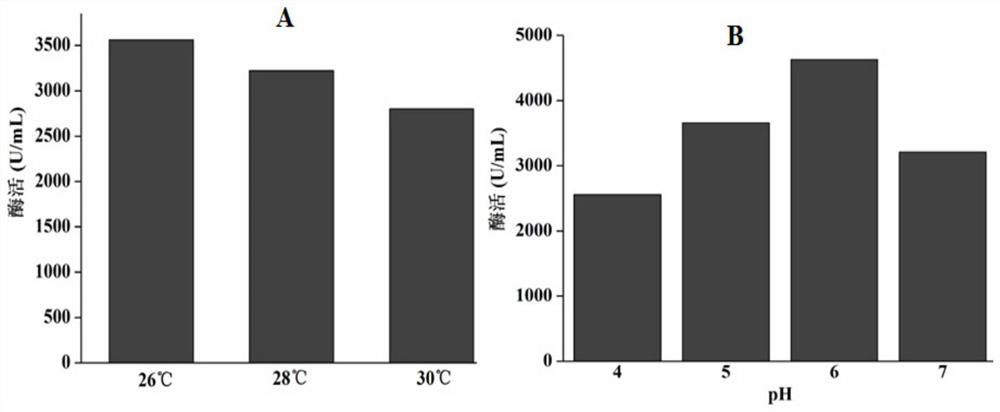
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and particularly relates to a chitosanase gene csnbaa, chitosanase and a preparation method and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the chitosanase gene csnbaa is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and the chitosanase gene csnbaa is obtained by comprehensively optimizing the sequence of chitosanase derived from Bacillus atrophaeus.The amino acid sequence of the chitosanase CsnBaa is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, so that not only are the types and source ways of chitosanase enriched, but also the fermentation enzyme activity can reach 4630 U / mL, and the chitosanase CsnBaa shows good stability in a relatively wide temperature range and a relatively wide pH range and has good application prospect and industrial value.
Owner:深圳润康生态环境股份有限公司 +2
Method for preparing hesperetin monoglucoside by fermentation, enzymolysis, extraction and coupling
ActiveCN102925364AImprove conversion rateReduce manufacturing costFungiMicroorganism based processesFusarium nivaleChemistry
The invention discloses a method for preparing hesperetin monoglucoside by fermentation, enzymolysis, extraction and coupling, belonging to the technical field of biochemical substances extraction. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a nutrient solution; preparing a strain seed solution; preparing fermentation liquor for producing the hesperetin monoglucoside; culturing the fermentation liquor for producing the hesperetin monoglucoside; carrying out resin adsorption, back flow, discharging and feeding on the fermentation liquor; and eluting and collecting resin. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the Fusarium nivale HESPER strain CGMCCNo.6238 is adopted as a culture, and the hesperetin monoglucoside is prepared by continuous culture fermentation, hesperidin enzymolysis, extraction and coupling, thus the hesperetin monoglucoside is effectively prevented from being degraded into hesperetin, the yield is enhanced, and the production cost is reduced. The method disclosed by the invention can be popularized and applied to related areas and enterprises.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Device for preparing fertilizer from kitchen garbage
InactiveCN111499424AGood for fallingSimple structureBio-organic fraction processingClimate change adaptationAgricultural engineeringBiology
The invention discloses a device for preparing a fertilizer from kitchen garbage. The device comprises a fermentation box; a crushing cavity is formed in the fermentation box, a solid-liquid separation cavity is formed in the lower side of the crushing cavity, a stirring cavity is formed in the lower side of the solid-liquid separation cavity, drying cavities are symmetrically formed in the left side and the right side of the stirring cavity, a fermentation cavity is formed in the lower side of the stirring cavity, an enzyme storage cavity is formed in the rear side of the fermentation cavity,and a granulation cavity is arranged on the left side of the fermentation cavity. Kitchen garbage is crushed through crushing rollers and oil stains are removed from the kitchen garbage; excessive water is discharged through solid-liquid separation, the separated kitchen garbage is dried, a fermentation enzyme can be quantitatively added during fermentation, then the kitchen garbage is fermentedinto a fertilizer, out-pushing, vibration and granulation of the fertilizer are controlled through a motor, and control is simpler and faster.
Owner:临海永存智能技术有限公司
Trichoderma reesei bacterial strain for expressing saccharifying enzyme
ActiveCN103614303AHigh catalytic efficiencyReduce manufacturing costFungiMicroorganism based processesBacterial strainTrichoderma reesei
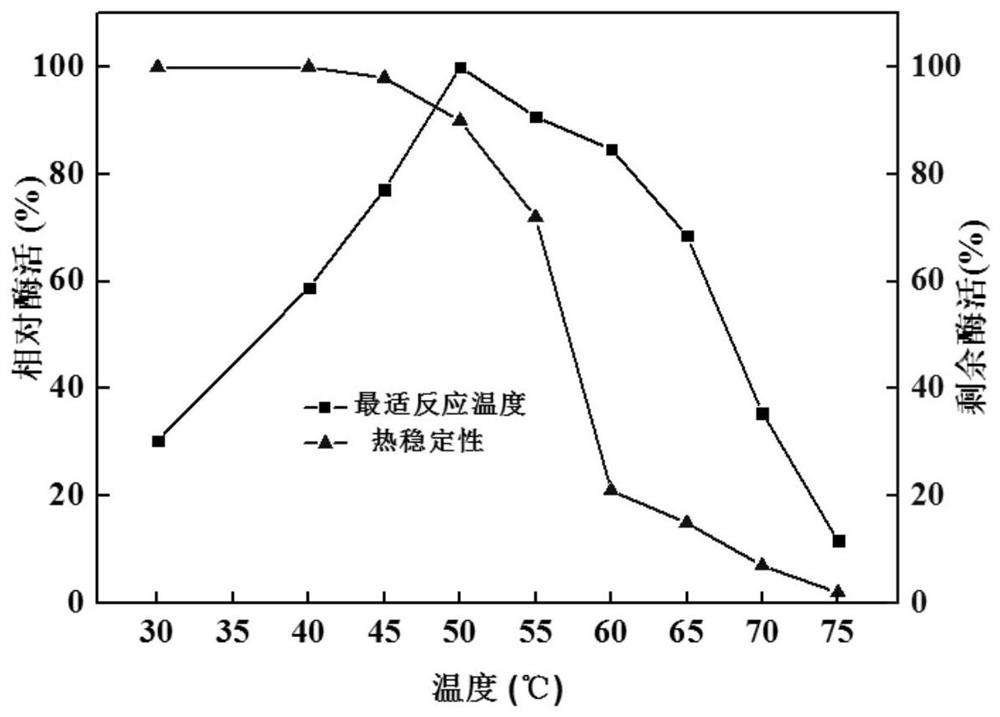
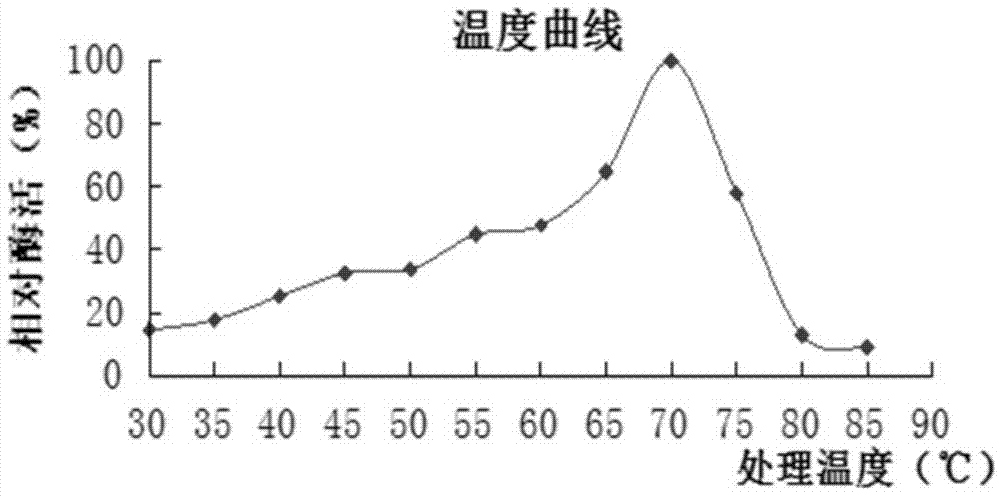
The invention aims at providing a trichoderma reesei bacterial strain for producing saccharifying enzyme. The trichoderma reesei bacterial strain is trichoderma reesei HDGAU-1 (Trichoderma reesei HDGAU-1) with a preservation number of CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) NO: M2013584. The trichoderma reesei bacterial strain disclosed by the invention can efficiently express the saccharifying enzyme, and fermentation enzyme activity is as high as 4000 U / ml which is improved by 54% in comparison with that before mutation, and protein amount exceeds 2.1 g / L which is improved by about 50% in comparison with that before mutation. According to the invention, production cost of the saccharifying enzyme can be greatly lowered by utilizing the trichoderma reesei bacterial strain to produce the saccharifying enzyme, and wide application of the saccharifying enzyme is facilitated. Moreover, the saccharifying enzyme recombinant and expressed by the trichoderma reesei bacterial strain disclosed by the invention has an optimum acting temperature of 70 DEG C and an optimum acting pH of 5.5, has catalytic efficiency higher than that of the common saccharifying enzyme from aspergillus niger at present, is more high temperature resistant, can effectively shorten saccharifying time and can lower production cost.
Owner:QINGDAO VLAND BIOTECH GRP
Aspergillus niger strain producing alpha-amylase, and its application
ActiveCN104004729AIncrease specific volumeImprove textureFungiMicroorganism based processesAspergillus clavatusAlpha-amylase
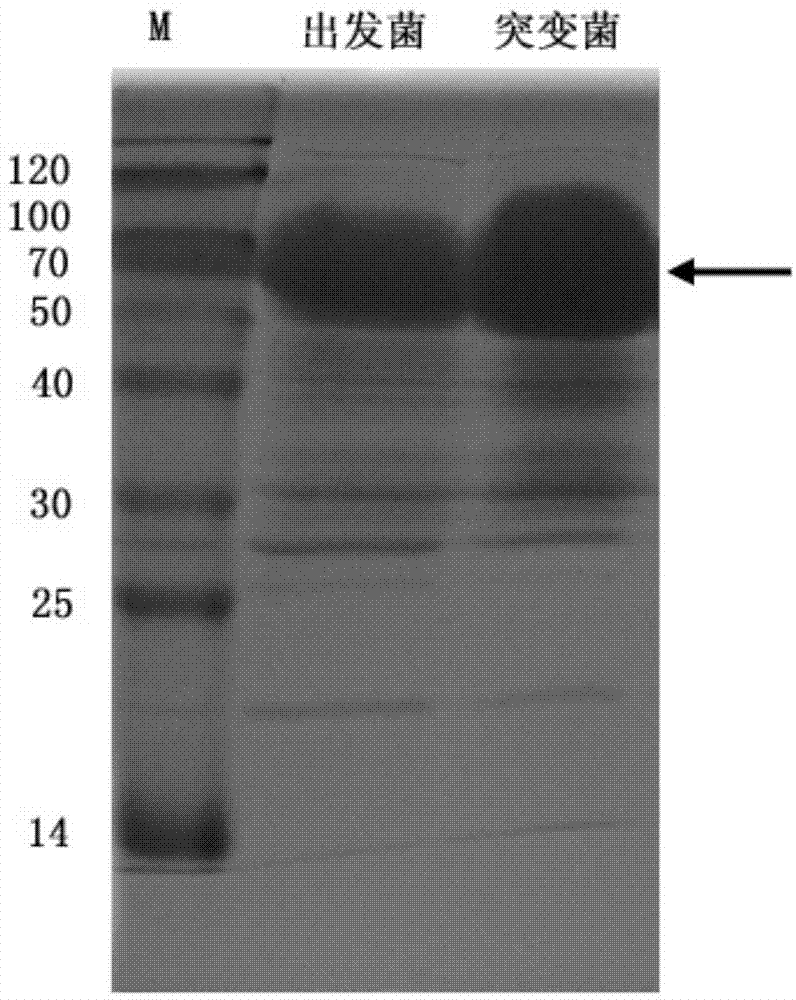
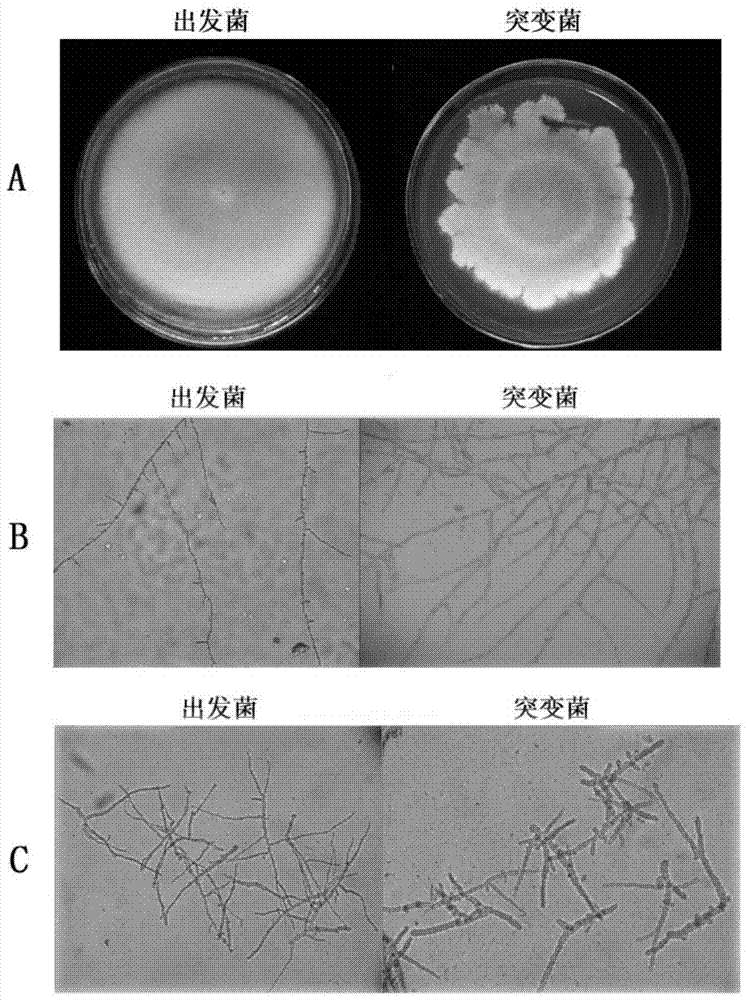
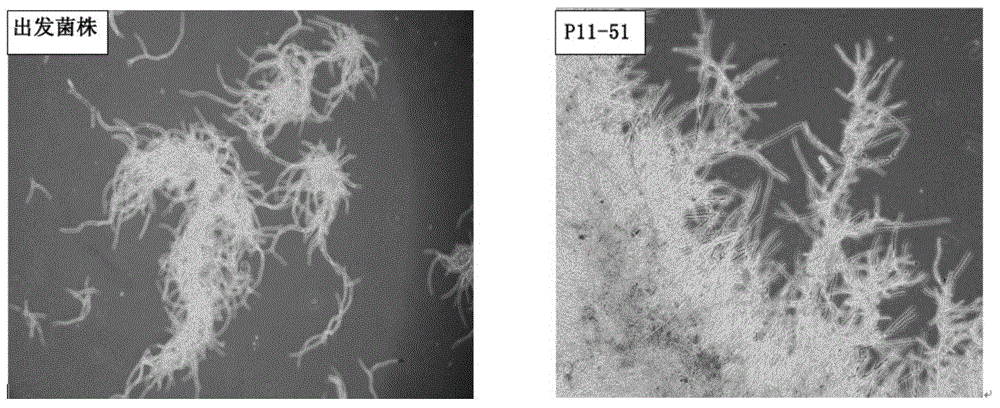
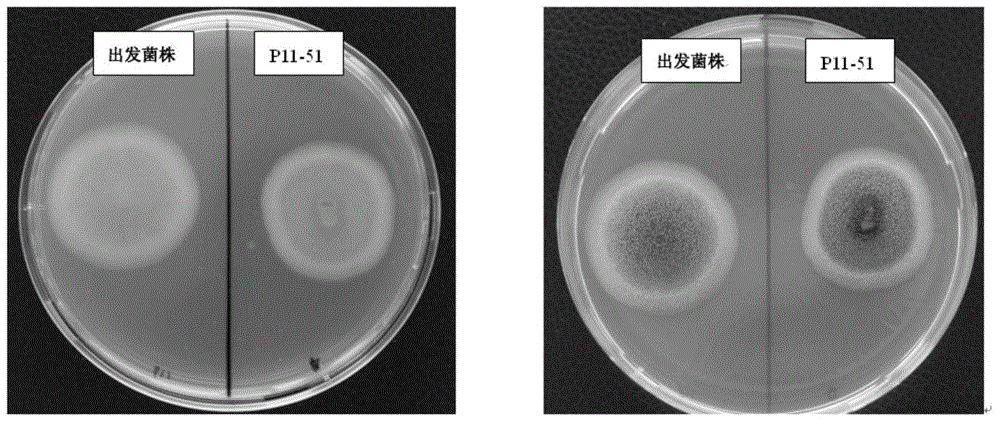
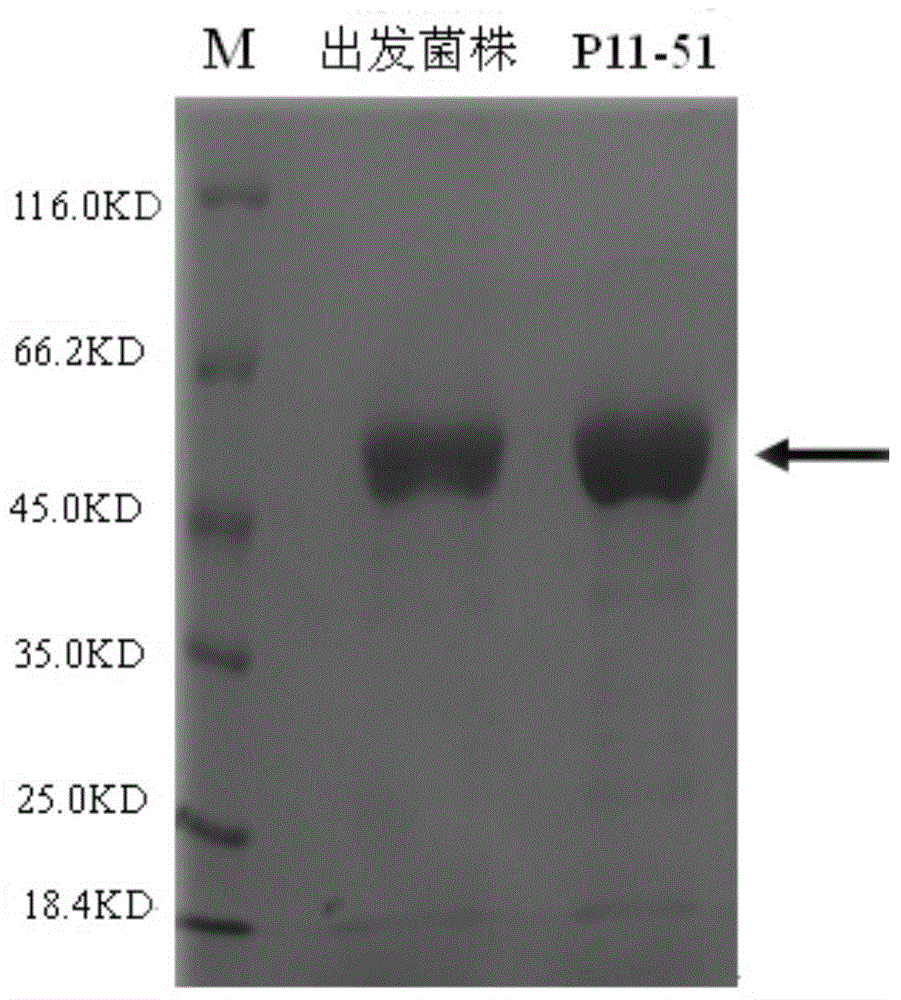
The invention provides an alpha-amylase. The amino acid sequence of the alpha-amylase is SEQ ID NO:1. The invention also provides Aspergillus niger P11-51 expressing the alpha-amylase. The strain number of the Aspergillus niger P11-51 is CCTCC NO:M2014017. The mutated strain Aspergillus niger P11-51 obtained through ultraviolet mutagenesis can efficiently express alpha-amylase from Aspergillus clavatus, and the fermenting enzyme activity of the Aspergillus niger P11-51 is 486.65CU / mL, and is 1.99 times that of an original strain. The Aspergillus niger P11-51 is a food safety bacterium (GRAS), and alpha-amylase produced by the Aspergillus niger P11-51 can be widely applied in the food processing field. The alpha-amylase can increase the specific volume of bread by 10-15%, reduces the hardness of bread crust and bread crumb, improves the quality of bread, improves the baking quality of the bread, improves the size of the volume, improves the mouthfeel of the bread, and makes particles soft.
Owner:QINGDAO VLAND BIOTECH GRP
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens for high production of neutral protease
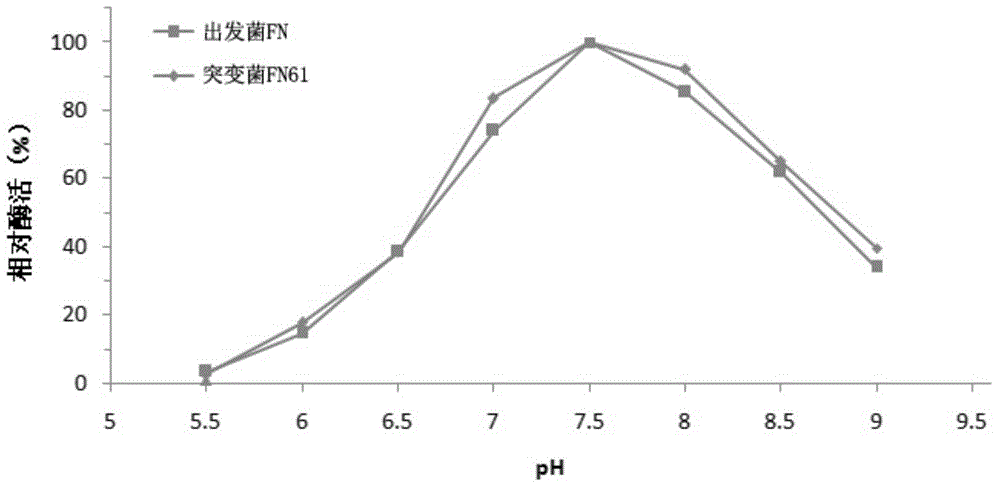
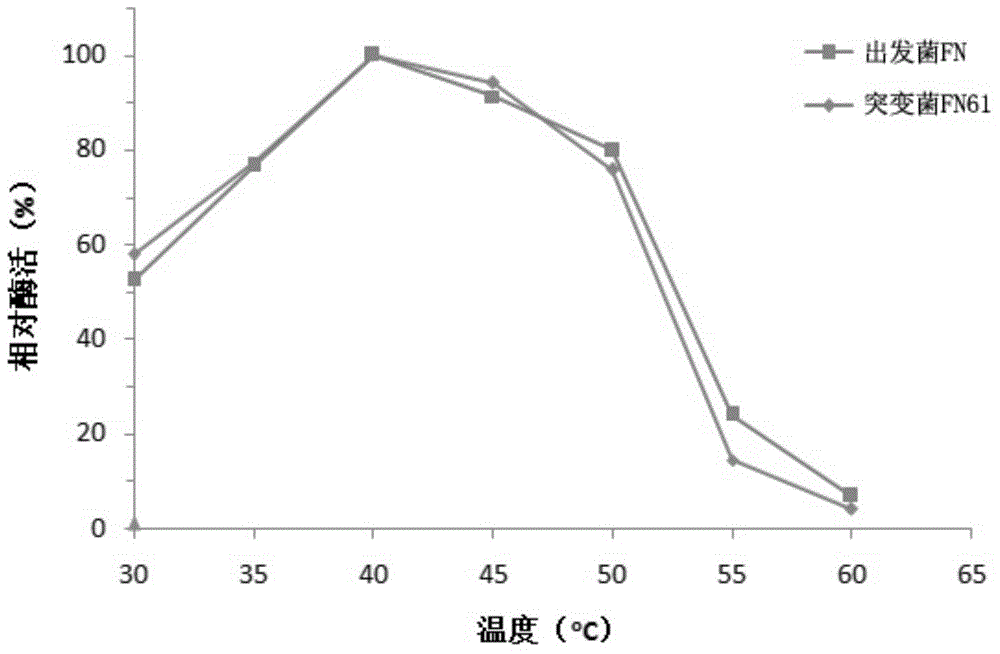
The invention relates to the technical field of functional microorganism screening, and in particular relates to a mutant strain, namely bacillus amyloliquefaciens FN61, which is obtained through ultraviolet mutagenesis, wherein the preservation number of the mutant strain is CCTCC NO: M2015527. The mutant strain can be used for significantly improving the yield of neutral protease, and fermenting enzyme activity in a 20L tank can reach up to14135U / ml, which is 42% higher than that of an initial strain. The optimum action pH of the neutral protease produced by the mutant strain is 7.5, which is consistent with the initial strain, but relative enzyme activity of the protease produced by the mutant strain is generally higher than that of the initial strain with a pH range of 6.5-8.5, showing that the protease produced by the mutant strain more sui table than the initial strain to play a role in a neutral condition; and the optimum action temperature of the protease produced by the mutant strain is at 40 DEG C, which is equal to that of the initial strain, so that an unexpected technical effect is achieved. The neutral protease produced by the mutant strain FN61 disclosed by the invention can be widely applied to the fields of feed and food processing; and the neutral protease is broad in prospect.
Owner:WEIFANG KANGDIEN BIOTECH +1
Wet state yeast culture movable fermentation method with distillers grains as raw materials
InactiveCN104982648ANo pollution in the processImprove processing stabilityAnimal feeding stuffFiberCrude fibre
A wet state yeast culture movable fermentation method with distillers grains as raw materials comprises the following steps of batching, activation of culture, inoculation mixing, temperature-controlled fermentation, enzymolysis wall breaking and product postprocessing. The product postprocessing comprises inspection, packaging and finished products. The method adopts the bacterium and enzyme synergetic fermentation and enzymolysis technology with microzyme, protease and cellulose combined, the technology is good in stability and free of mold pollution, and products are safe. A two-step method temperature control technology is adopted, the number of microzyme is large after cultivating, enzymolysis is thorough, yeast wall breaking is sufficient, and the nutritive value is higher. The content of coarse fibers is more than 30% lower than conventional distillers grains and like products, the current situation that the conventional distillers grain products is only suitable for cud chewers is avoided, the using aspects of products are broadened, and market expansion is facilitated.
Owner:江苏益元泰生物技术有限公司
Alpha-AmyL (Amylase) mutant with increased activity and coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN106754826AReduce the cost of fermentation productionGreat application potentialFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAlpha-amylase
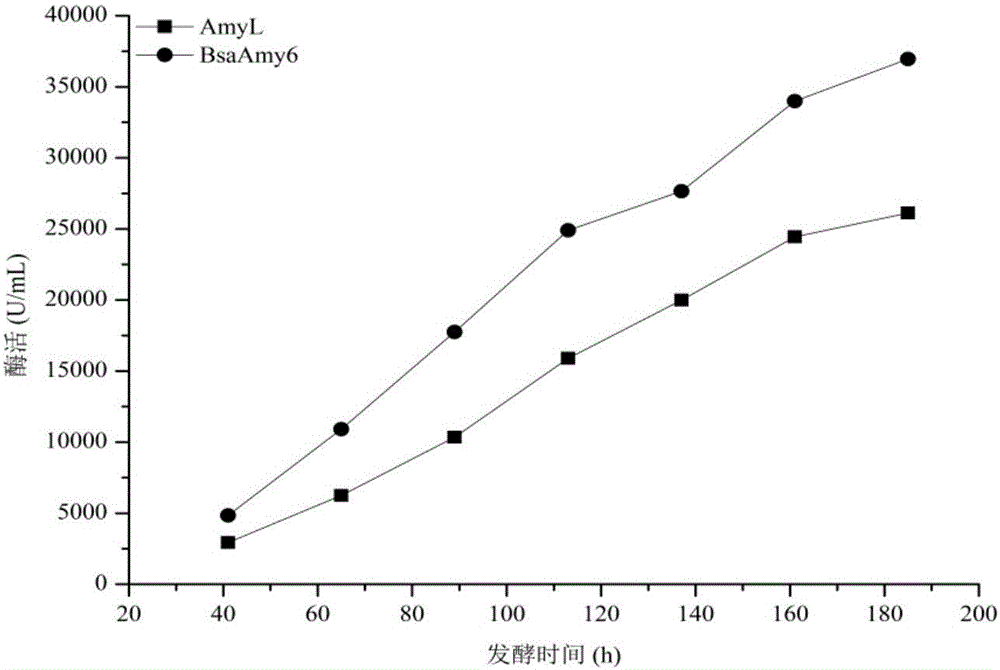
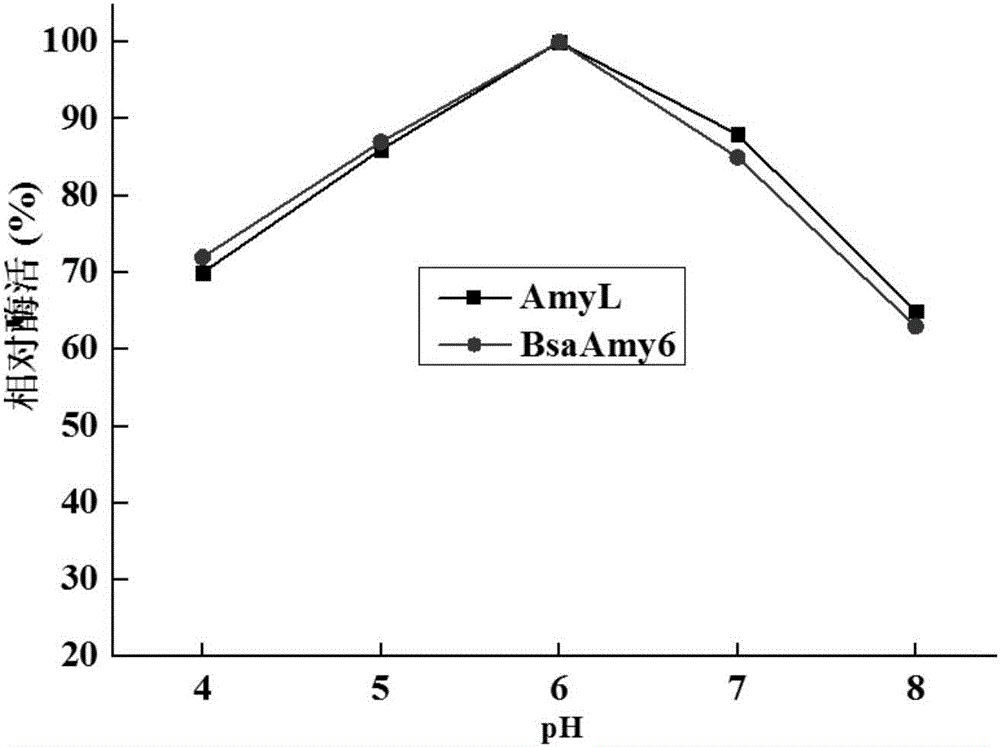
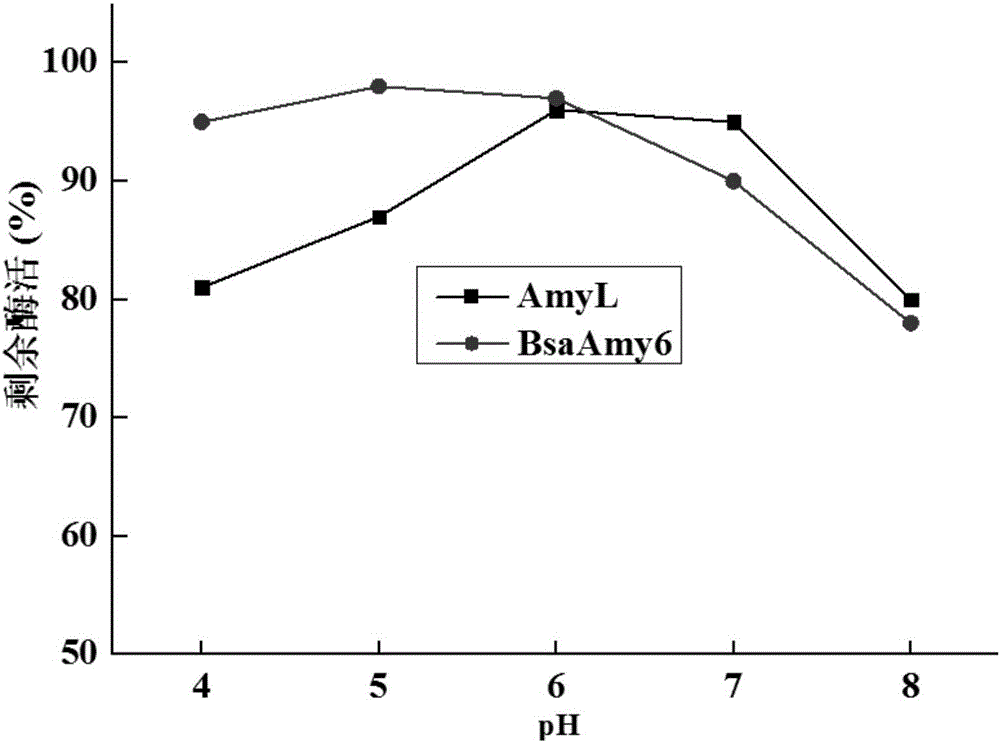
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, and in particular to an alpha-AmyL (Amylase) mutant with increased activity and a coding gene and application thereof. An amino acid sequence of the mutant is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. The fermentation enzyme activity of an improved alpha-AmyL strain is up to 36900 U / mL, and compared with an alpha-AmyL producing strain before improvement, the fermentation enzyme activity is increased by 41.5 percent. According to mutant BsaAmy6 (Bacillus Salsus Alpha-Amylase 6) and recombinant engineering bacterium, the fermentation production cost is greatly reduced, and a foundation is laid for further industrial application.
Owner:内蒙古溢多利生物科技有限公司
Method for preparing chitosan through composite fermentation and enzymatic hydrolysis
The invention discloses a method for preparing chitosan through composite fermentation and enzymatic hydrolysis. The method comprises the following steps: drying crab shell or shrimp shell, and crushing; fermenting; carrying out enzymatic hydrolysis calcium removal and protein removal; and carrying out enzymatic hydrolysis for acetyl removal, washing with water, drying, and crushing. Compared with the prior art, the above enzymatic hydrolysis method has the advantages of realization of calcium removal and protein removal in a same step, substantial improvement of the production efficiency, no use of a strong aid, low energy consumption, no pollution and environmental protection. A free calcium solution obtained after the enzymatic hydrolysis can be recovered to prepare an organic calcium preparation, so all products can be reasonably used to generate substantial economic values.
Owner:TIANJIN TIANSHI BIOLOGICAL DEV
Method for screening and culturing Rahnella sp.R3 producing low-temperature lactase
The invention relates to a screening and culturing method of Rahnella sp.R3. The method adopts a bacterial enrichment medium (1 / 4TSB) and lactose as substrates, takes X-Gal as a color developing agent, and performs agar identification plate primary screening and fermentation enzymatic activity determination secondary screening to obtain the high-yield low-temperature lactase strain Rahnella sp.R3. Single factor experiment and orthogonal experiment analysis is conducted to obtain the optimal fermentation enzyme production formula and fermentation condition, and finally the flask-shaking fermentation level can reach 5.92U / mL.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Digestive pig feed
InactiveCN107960548APromote decompositionImprove digestibilityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffFiberAnimal science
The invention discloses digestive pig feed which comprises, by weight, 100-200 parts of bean pulp, 30-50 parts of bone meal, 150-200 parts of wheat meal, 30-50 parts of maize meal, 50-100 parts of pine tree leaves, 30-40 parts of salt, 2-3 parts of probiotics, 30-50 parts of pulverized lime, 5-10 parts of fruit and vegetable enzyme powder, 30-50 parts of traditional Chinese medicine residues and 10-25 parts of fermentation enzyme. The raw materials are fermented twice to obtain the digestive pig feed. By the aid of biphasic effects of enzyme and the traditional Chinese medicine residues, the digestibility of the digestive pig feed is improved, the physique of pigs is enhanced, pork quality is improved, the feed is fermented twice by the aid of the enzyme and other functional enzyme, and the content of crude fibers in the feed is decreased, so that the pigs more easily absorb the pig feed.
Owner:LANGFANG RUIKANG FEED CO LTD
Method for producing tobacco leaf fermenting enzyme preparation
InactiveCN101144074AIt has the characteristics of high temperature resistance of rebaking lineHas high temperature propertiesTobacco treatmentEnzymesBiotechnologySaccharum
The present invention relates to a novel tobacco fermenting enzyme preparation production method. The purpose is to solve the technical problems that how improve the quality of the tobacco fermenting product is improved and how the reactivity protection of the tobacco fermenting enzyme preparation is realized in the natural fermenting field of tobacco. The enzyme preparation consists of a glucoseoxidase, a chlorophyl oxidase, a carotenoid oxidase, a protease, and a nicotine-degradation enzyme. Through the cell disruption of fresh leaves, (NH 4) 2 SO 4 is utilized to operate the second fractional precipitation to obtain crude enzyme fluid, an enzyme molecule adopts Ca 2 + and Mg 2 + to operate the metal ion exchange, to accomplish the molecule modification; a macro molecule combination modification is accomplished through adopting 0.01 percent of cane sugar low molecular polymer, thereby prolonging the half life period of theenzyme preparation and obviously improving the high temperature resistant ability. The experimental result employed by the enzyme preparation indicates that the nicotine is decreased by 9.3 percent, the total nitrogen is decreased by 5.7 percent, the protein is decreased by 7.1 percent; cigarette smoke condensates are decreased by 8.4 percent, the tar content is decreased by 5.1 percent, the cigarette smoke nicotine content is decreased by 28.0 percent, and the carbon monoxide is decreased by 1.6 percent. The enzyme preparation is employed when the tobacco leaf is wet for the second time before defolat and redrying.
Owner:云南万芳生物技术有限公司 +2
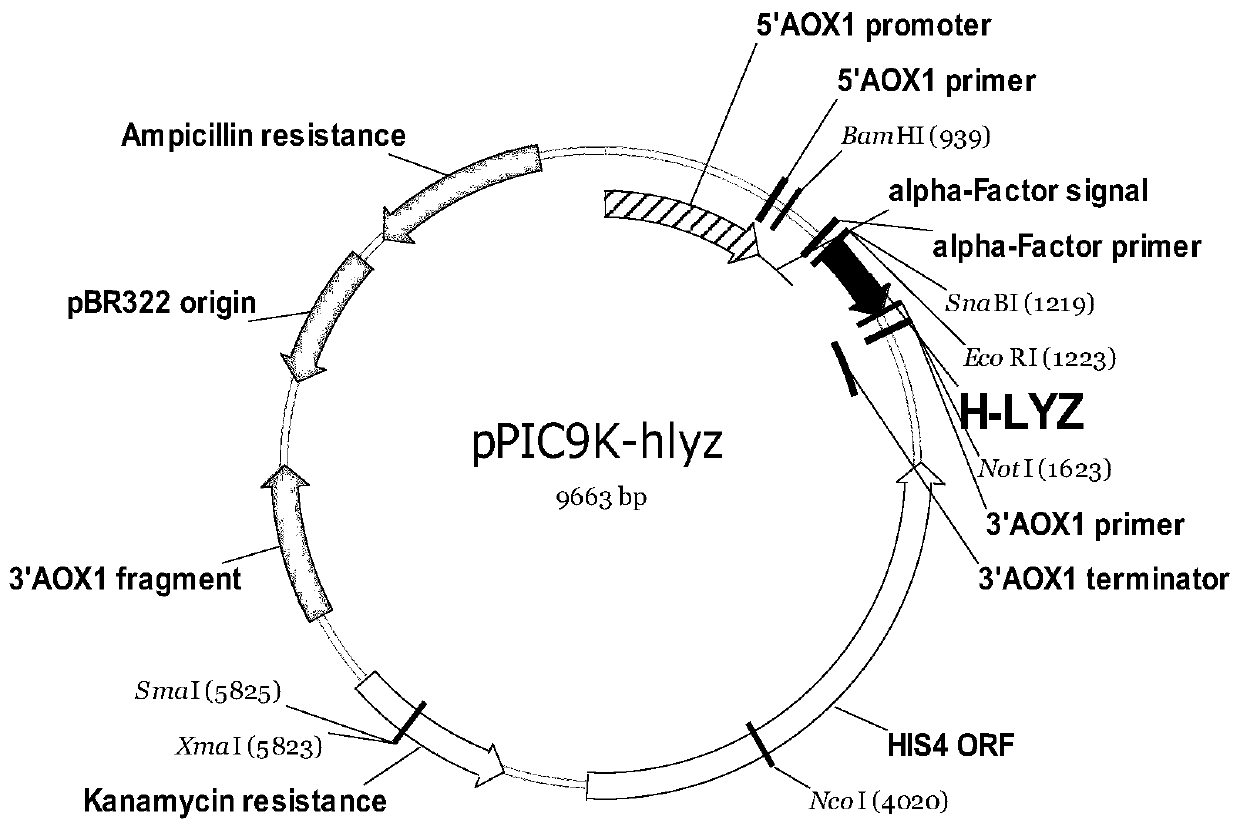
Recombinant pichia pastoris engineering bacterium containing high-copy-number humanized lysozyme gene and application thereof
InactiveCN110903991AIncrease enzyme activityFood safetyFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisMicrobiology
The invention discloses a recombinant pichia pastoris engineering bacterium containing a high-copy-number humanized lysozyme gene and application thereof. The recombinant pichia pastoris engineering bacterium is obtained by integrating a lysozyme gene shown in SEQ ID NO.1 with a pichia pastoris genome with a high copy number. According to the invention, a two-plasmid-mediated recombinant bacteriumconstruction method is adopted to obtain a recombinant bacterium with a copy number of 15; and the lysozyme produced by the recombinant bacterium has high enzyme activity, and the fermentation enzymeactivity is 180-220 KU / mL within 120-140h.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SILVER ELEPHANT BIO ENG +1
High expression lipase gene and secretory expression vector and application thereof
The invention discloses a high expression lipase gene and a secretory expression vector thereof, belonging to the genetic engineering field. The DNA sequence of the lipase gene is SEQIDNO.1; or under strict condition, lipase gene DNA is a DNA molecule which hybridizes with DNA sequences limited by the SEQIDNO.1 and codes protein possessing lipase activity. The invention also discloses a method for producing lipase utilizing the lipase gene; constructed engineering bacteria overcome long term defects of low expression level and enzyme activity of the lipase. Enzyme activity can be as high as 123.4 U / mL in shaking flask fermentation, increasing about 11 times compared with that of initial recombinant strains; enzyme activity in 7 L pot fermentation methanol induction for 84h is about 7062.5 U / mL, increasing about 56.2 times compared with that of the shaking flask fermentation. The invention has a wide application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI CUTSEQ BIOMEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Technology for preparing functional xylo-oligosaccharide by comprehensively utilizing wheat straw
InactiveCN104928331AHigh yieldHigh puritySugar derivativesMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPhytase
The invention discloses a method for extracting xylo-oligosaccharide from wheat straw. The wheat straw, an agricultural and sideline product, is used as a raw material, and a microbial fermentation technology and a biological enzyme technology are utilized for preparing xylo-oligosaccharide which has the functions of promoting bifidobacterium to proliferate, preventing constipation, lowering the content of cholesterol, protecting the liver and the like. The quality of the obtained xylo-oligosaccharide product meets the xylo-oligosaccharide industrial standard request, efficient utilization of the straw is achieved, the utilization value of the straw is increased, and a good popularization prospect is achieved. The method for extracting the xylo-oligosaccharide from the wheat straw has the advantages that the preparation technology combining compound microorganism solid fermentation and ultrasonic-assisted enzymolysis is adopted, so that the yield of the xylo-oligosaccharide is increased; ultrasonic-assisted enzymolysis is adopted for removal of proteins and starch and enzymolysis of phytase and mannose, and therefore the purity of the xylo-oligosaccharide product is remarkably improved; multi-bacteria mixed fermentation is adopted, so that the capacity of fermentation and enzymolysis of xylan is improved; the production technology is simple, energy consumption is low, environmental pollution is avoided, the investment is small, and mass production is easy to conduct.
Owner:QINGDAO JIARUI BIOLOGICAL TECH
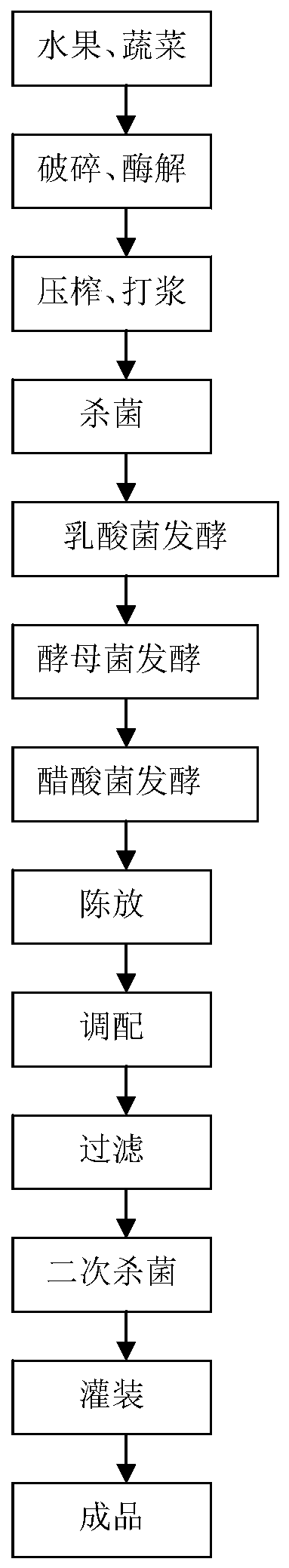
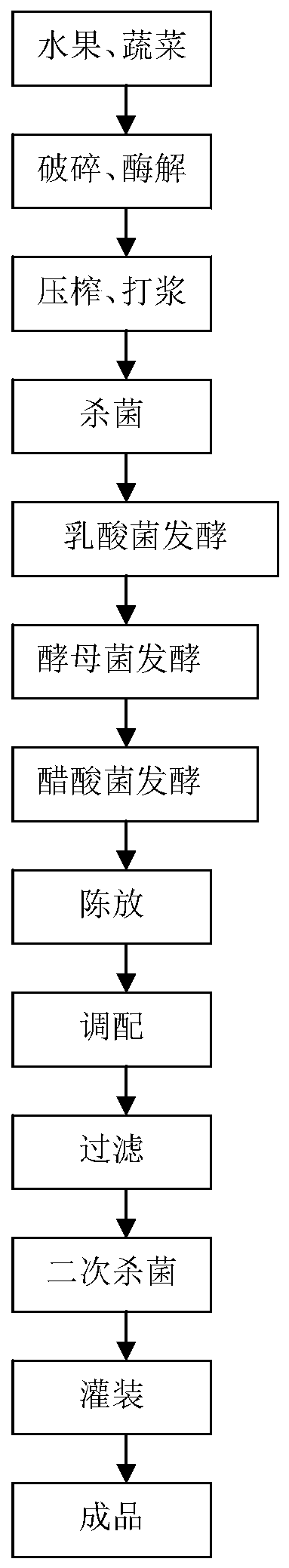
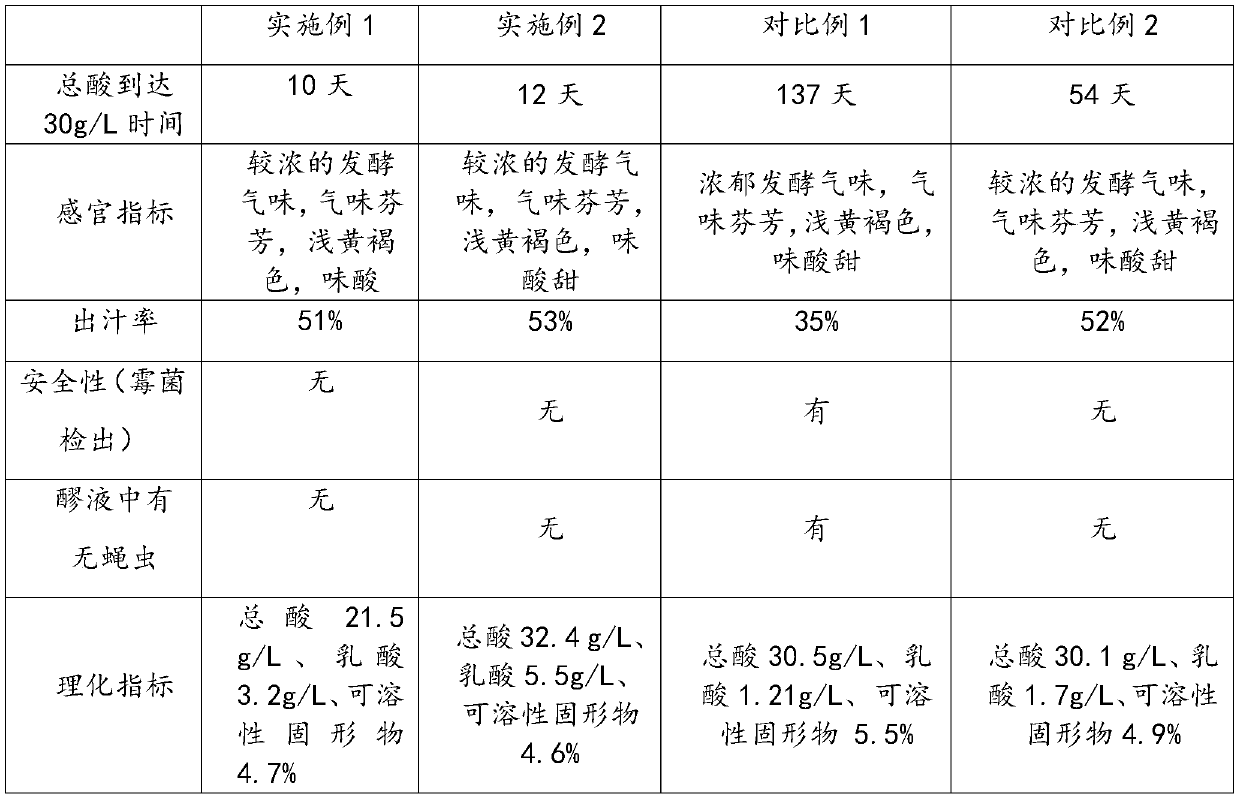
Preparation method of composite fruit and vegetable enzyme and composite fruit and vegetable enzyme
PendingCN111165798AIncrease the juice yieldImprove securityFood ingredient as antioxidantBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The invention relates to the field of drink foods and in particular relates to a preparation method of a composite fruit and vegetable enzyme and the composite fruit and vegetable enzyme. The preparation method comprises the following steps: crushing a fruit and vegetable raw material, and performing enzymolysis so as to obtain a fermentation stock solution; adjusting the total sugar of the fermentation stock solution to 40-60g / L, performing sterilization, cooling the fermentation stock solution to 37-39 DEG C, and performing lactobacillus fermentation, yeast fermentation and acetic acid bacterium fermentation in sequence; and filtering supernate obtained after fermentation is completed, and performing secondary sterilization, so as to obtain the composite fruit and vegetable enzyme. According to the method, the fruit and vegetable raw material is subjected to crushing, enzymolysis and sterilization, lactic acid bacteria, yeast and acetic acid bacteria are sequentially inoculated to implement stage fermentation, and a certain number of solids in the fruit and vegetable raw material can be decomposed and converted through enzymolysis, so that the juice yield can be increased; and bydefining fermentation sequences and fermentation conditions of lactobacillus fermentation, yeast fermentation and acetic acid bacterium fermentation, different bacteria can be dominant bacteria at different stages of fermentation, fermentation can be benefited, and the fermentation time can be greatly shortened.
Owner:江西仁仁健康产业有限公司
Strain for producing D-psicose 3-epimerase and application thereof
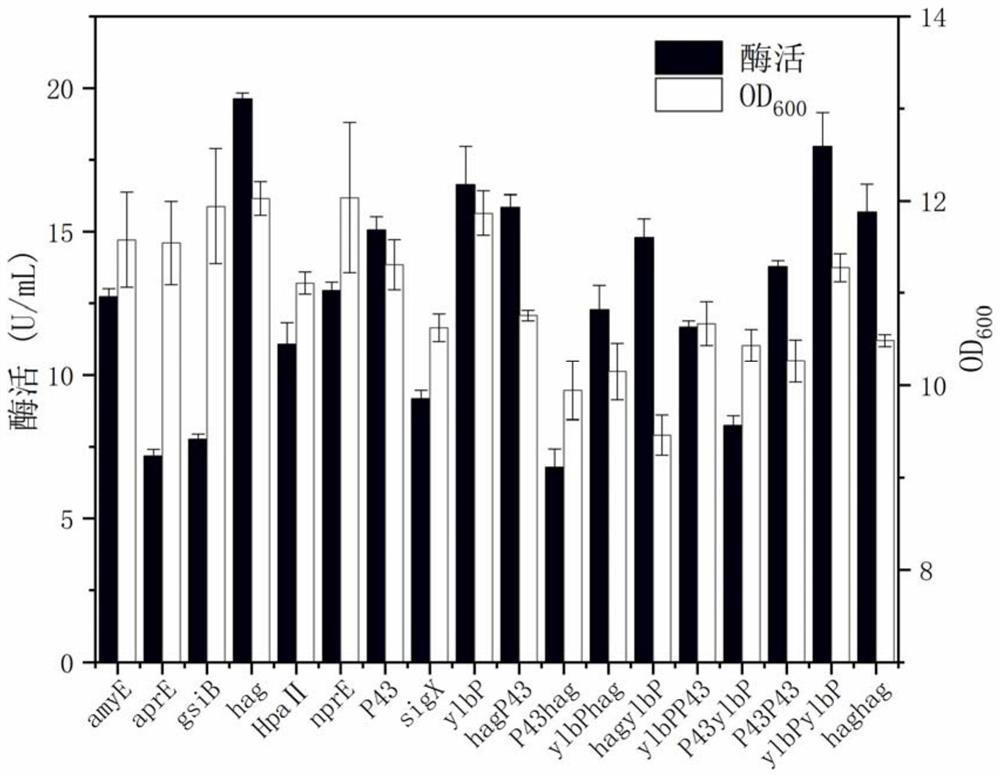
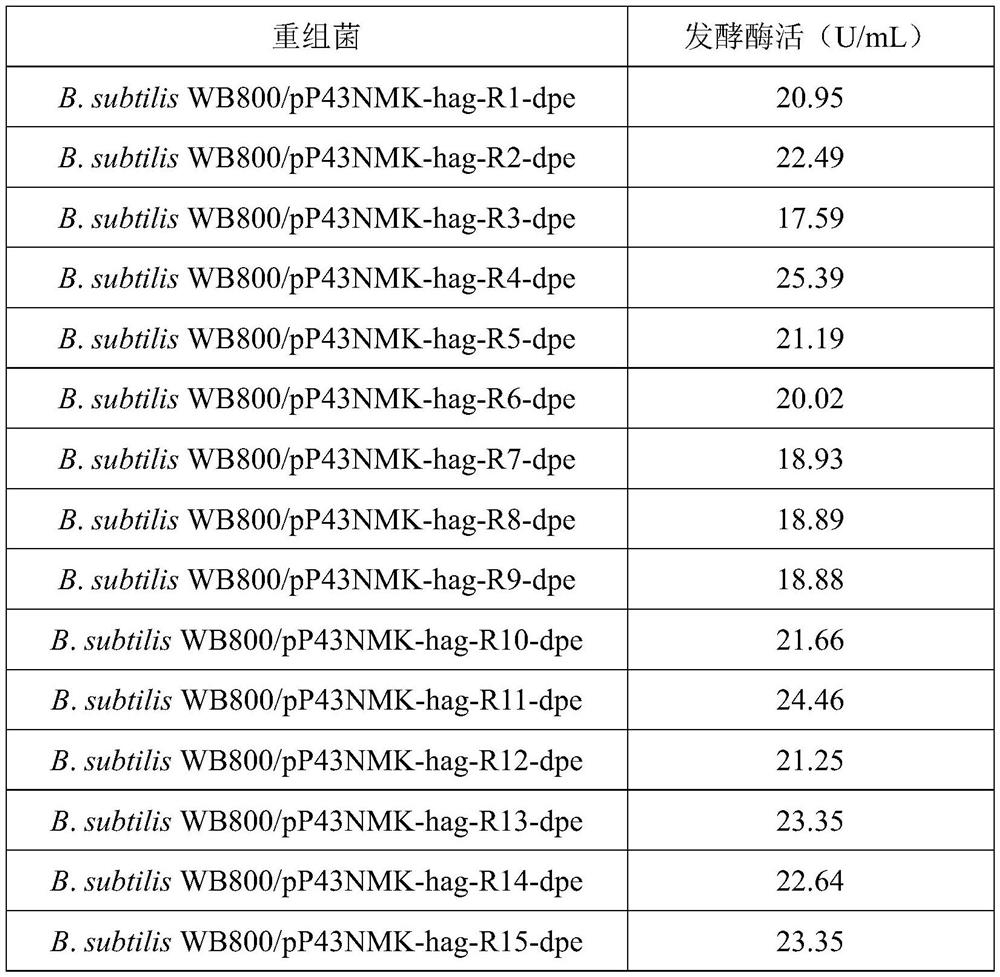
The invention discloses a strain for producing D-psicose 3-epimerase and application of the strain, and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The invention provides a method for screening a promoter and improving the expression quantity of D-psicose 3-epimerase through RBS optimization of the promoter. According to the recombinant bacillus subtilis constructed by using the vectors pP43NMK-hag and pP43NMK-hag-RBS4 provided by the invention, the enzyme activity of the target gene D-psicose 3-epimerase is improved, and the enzyme activity after modification is respectively 1.30 times and 1.69 times of the enzyme activity of the original vector. The invention also provides an antibiotic-free vector and an antibiotic-free recombinant bacillus subtilis strain, and the highest fermentation enzyme activity of a shake flask is 24.72 U / mL by adopting the antibiotic-free strain B.subtilis 1A751-dal- / pP43NMK-hag-RBS4-dpe-dal provided by the invention.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Microbial fermentation method for preparing lysozyme from hermetia illucens larvae and application
PendingCN111990529AShorten the breeding cycleImprove survival rateFood processingClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyLiver atrophy
The invention discloses a microbial fermentation method for preparing insect soluble pulp from hermetia illucens larvae. The method comprises the following steps: beating hermetia illucens old maturelarvae into fresh insect pulp; adding 0.5% of high-activity compound bacteria into the fresh insect pulp; and carrying out fermentation and enzymolysis composite reaction at 30-35 DEG C to prepare fluid insect soluble pulp. The method has the advantages that: scientific matching is achieved, the insect soluble pulp is close to natural bait, a foundation is laid for providing a healthy body for aquatic products in the whole process, the survival rate is increased, and the bait falling coefficient is low; high-quality amino acid is rapidly supplemented and absorbed and is a substitute raw material for crude protein coating, digestive enzyme conversion is not needed, the liver load is reduced, and the liver atrophy phenomenon is eliminated; and the water quality is stabilized, the water quality is not polluted, algae pouring is not easy, the heavy water color does not need to be worried too much, and zymophyte organic acid has a certain detoxification effect on algae, nitrite, hydrogen sulfide, chloride ions and the like.
Owner:深圳市百科俊实业股份有限公司
Trichoderma harzianum strain from Tibet for producing cellulase and application of trichoderma harzianum strain
PendingCN110527634APromote degradationFast inductionFungiMicroorganism based processesResource developmentCellulose degradation
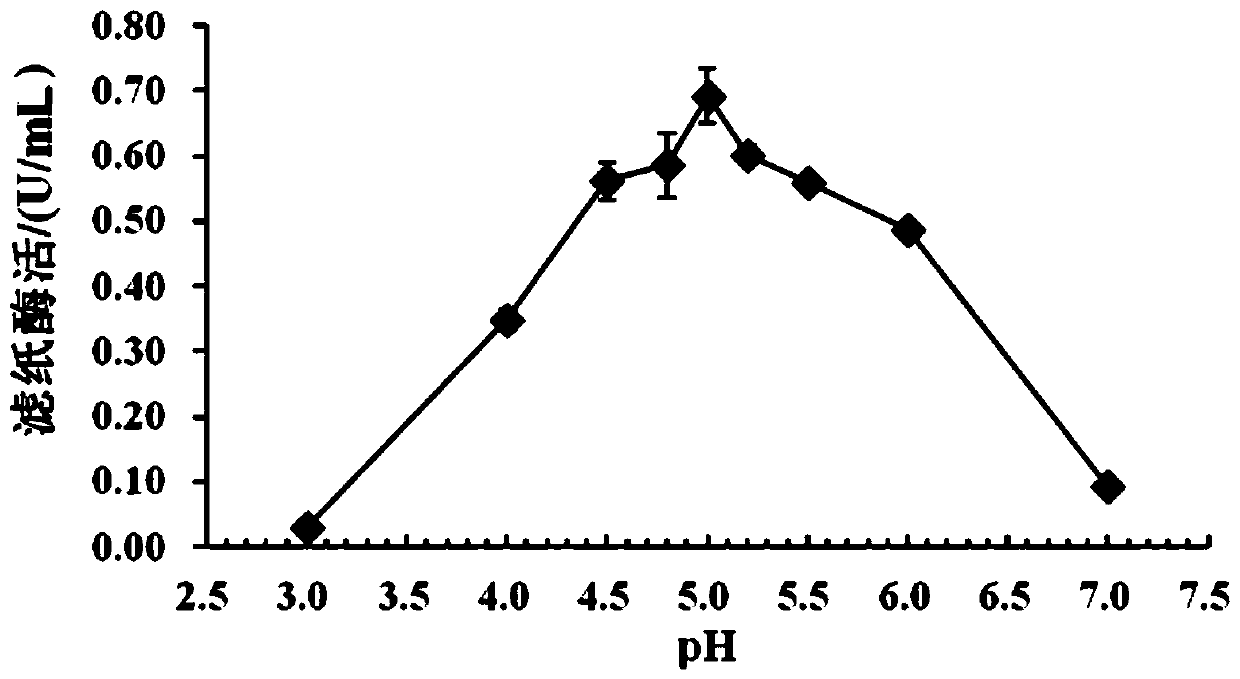
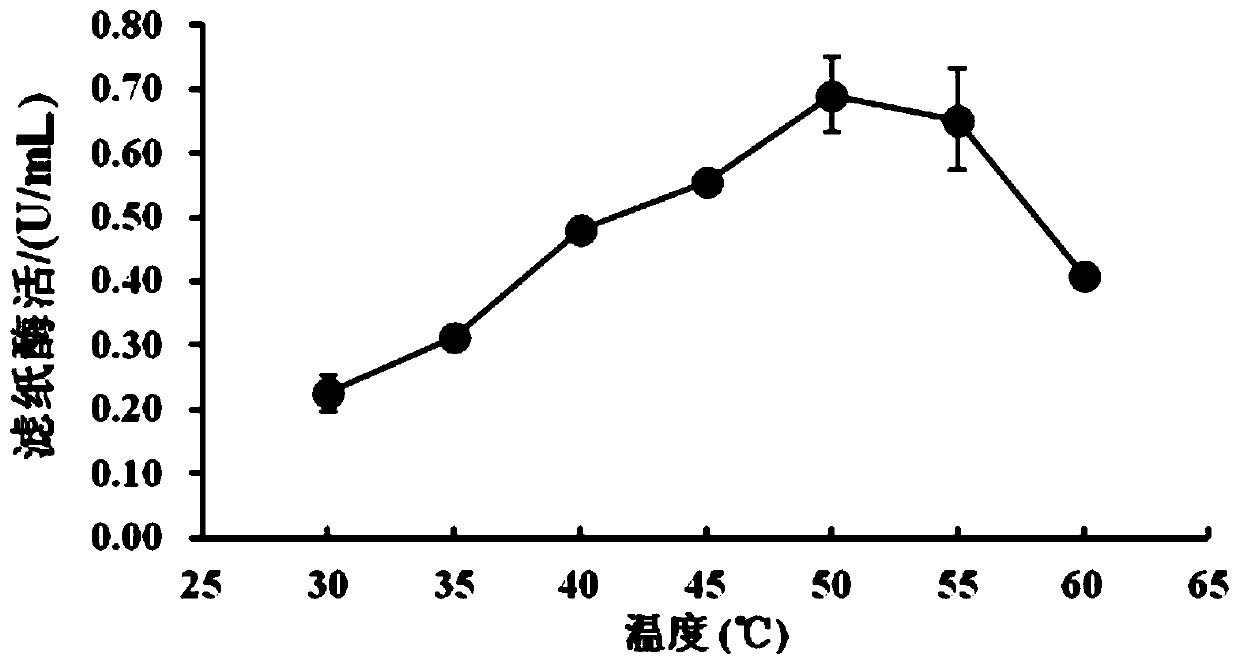
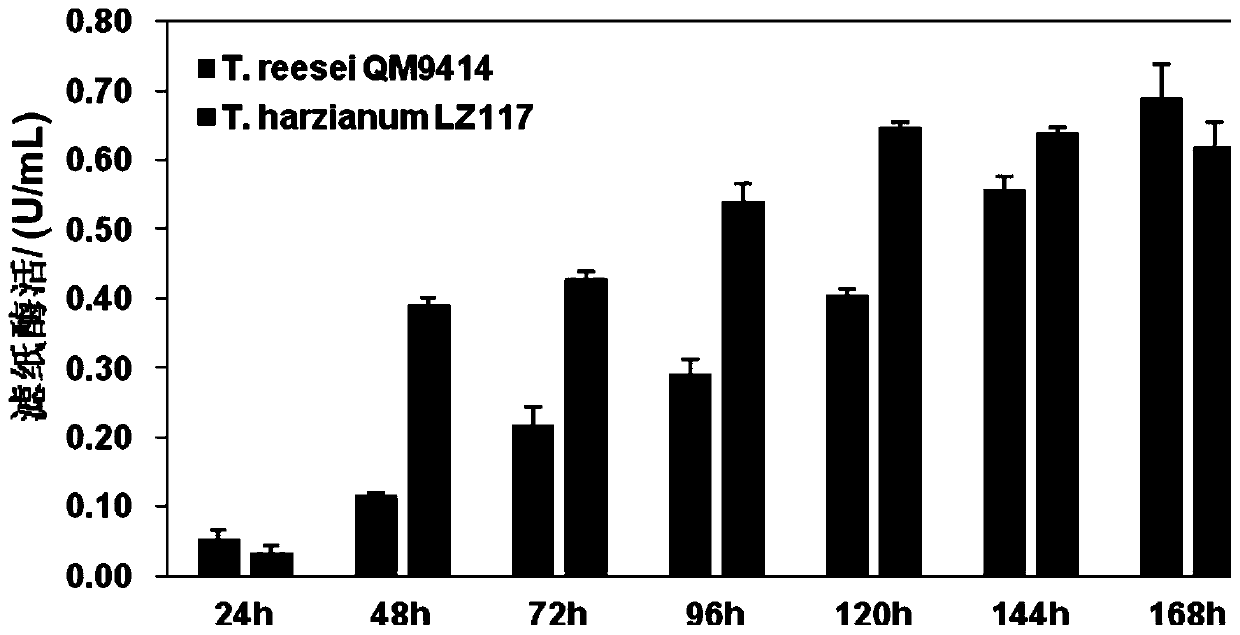
The invention discloses a trichoderma harzianum strain LZ117 from Tibet for producing cellulase. The preservation number of the trichoderma harzianum strain LZ117 is CGMCC No.17184, and the trichoderma harzianum strain LZ117 and a fermentation liquor thereof can be used for degrading lignocellulose biomass. A preparation method of the cellulase-containing fermentation liquor produced by the trichoderma harzianum strain LZ117 is also disclosed. According to the trichoderma harzianum strain LZ117 from Tibet for producing the cellulase, a new microbial resource is provided for degradation of thelignocellulose biomass; after the trichoderma harzianum strain LZ117 is cultured for 48 hours in a Mandels plate which adopts cellulose as a sole carbon source, obvious degradation transparent circlescan be shown; after culture is conducted in a 250 mL shake flask for about 120 hours, the fermentation enzyme liquor can achieve maximum filter paper activity, and high-activity cellulose degrading capability of the fermentation enzyme liquor is reflected; and the trichoderma harzianum strain LZ117 has high capability of degrading filter paper, preprocessed corn straw and preprocessed jerusalem artichoke straw, and accordingly has great application potentiality in the aspects of lignocellulose biomass resource development and utilization.
Owner:JALA GROUP CORPORATION +1
Novel phospholipase D and method for preparing functional phospholipids by using same
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering of enzymes, and specifically relates to a novel phospholipase D. The novel phospholipase D with improved specific enzyme activity isprepared through following steps: a phospholipase D mutant is obtained through error-prone PCR technology and overlapping PCR technology directed evolution in vitro; then expression of high-activityphospholipase D gene in a bacillus subtilis expression system, a bacillus amyloliquefaciens expression system and a bacillus licheniformis expression system is carried out respectively; and after expression, the specific enzyme activity of the high-activity phospholipase D is detected to be improved by 500% at most compared with that of wild phospholipase D. The highest fermentation enzyme activity values of the high-activity phospholipase D in the bacillus subtilis expression system, the bacillus licheniformis expression system and the bacillus amyloliquefaciens expression system are 319.1 U / mL, 952.2 U / mL and 1304.5 U / mL respectively; and phosphatidic acid, phosphatidylserine, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylglycerol and phosphatidylinositol can be effectively prepared by using thehigh-activity phospholipase D.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com