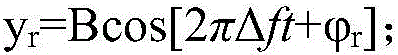Patents
Literature
211results about How to "Control consistency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Head for golf putter and golf putter
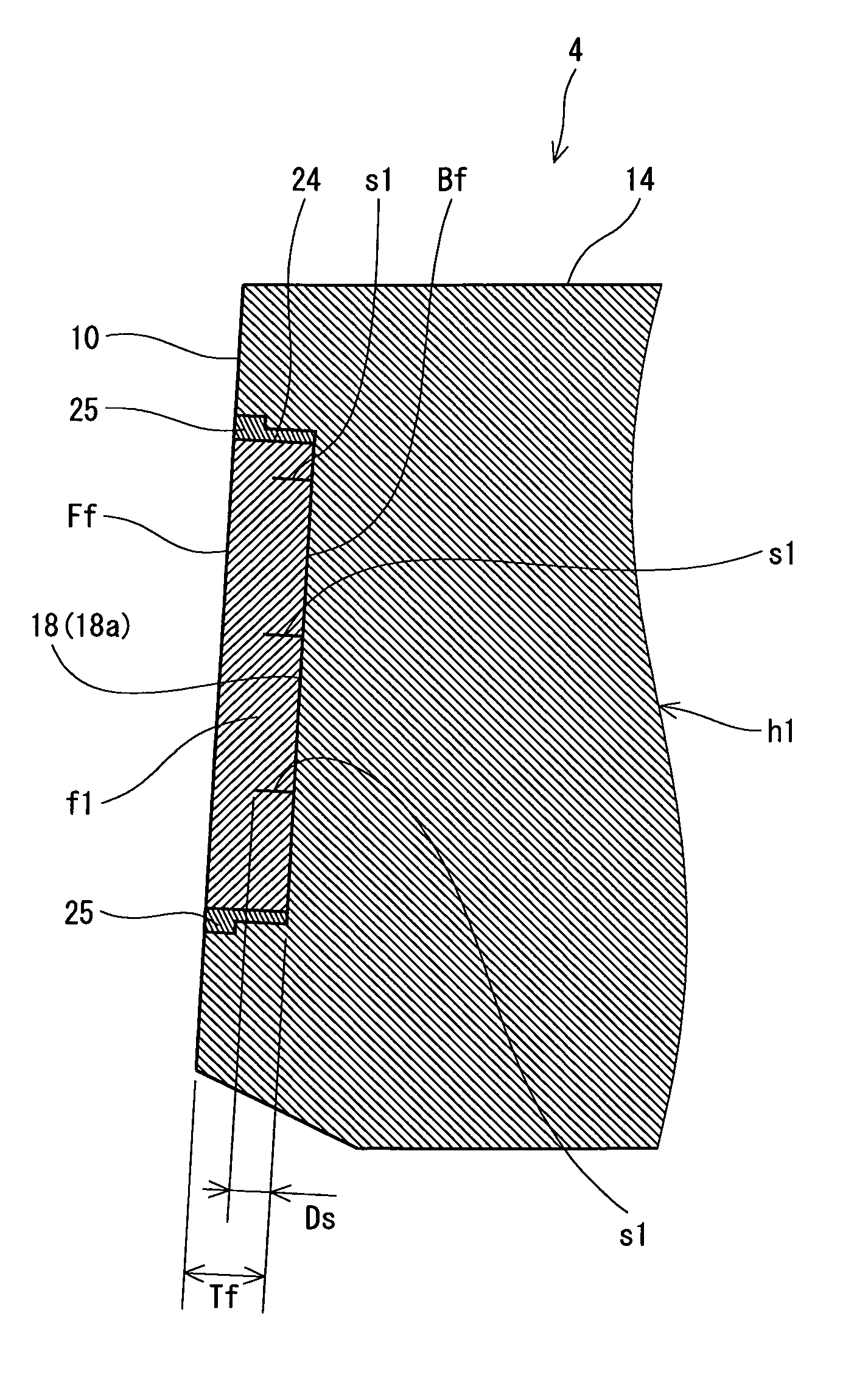
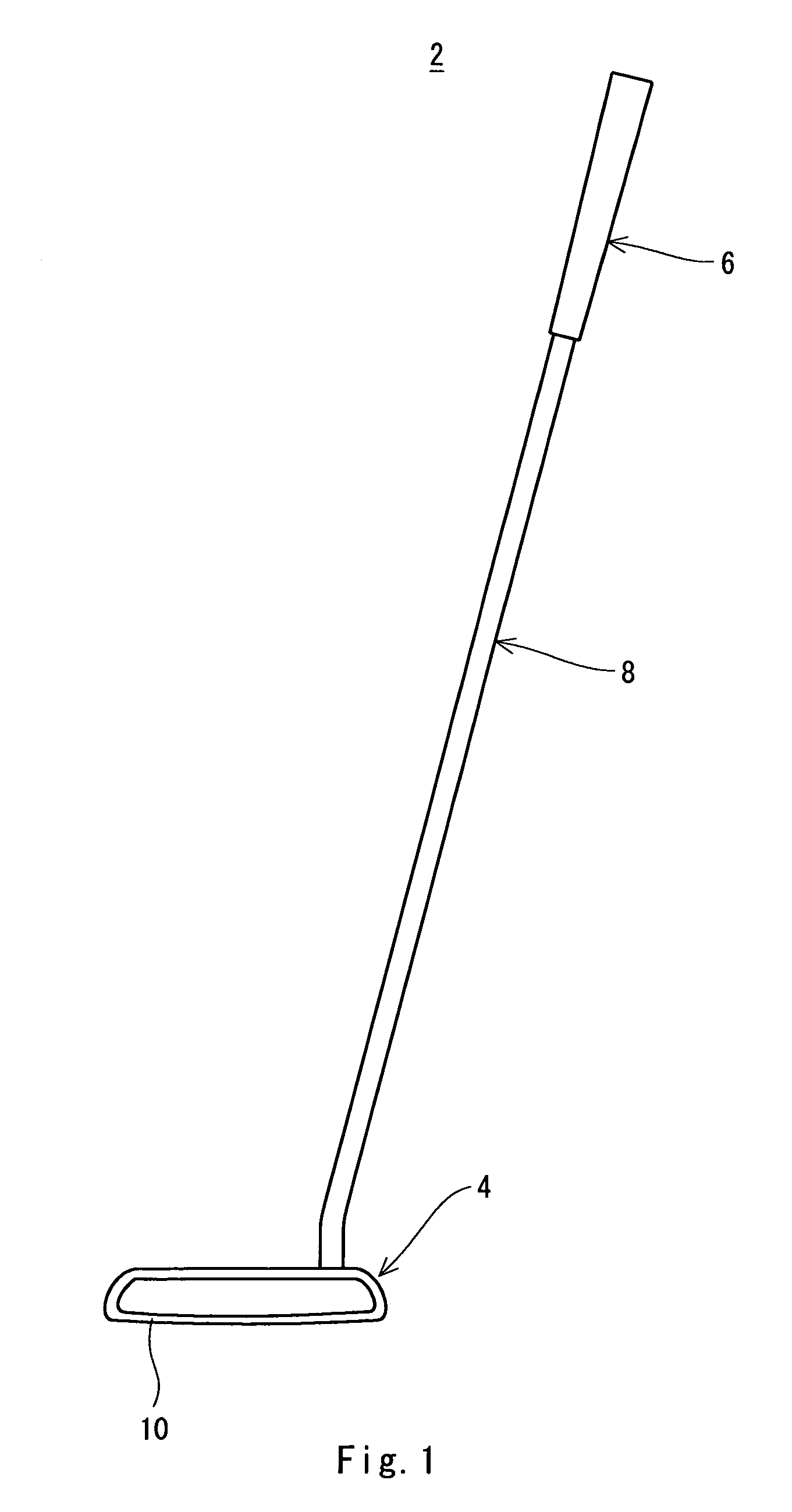
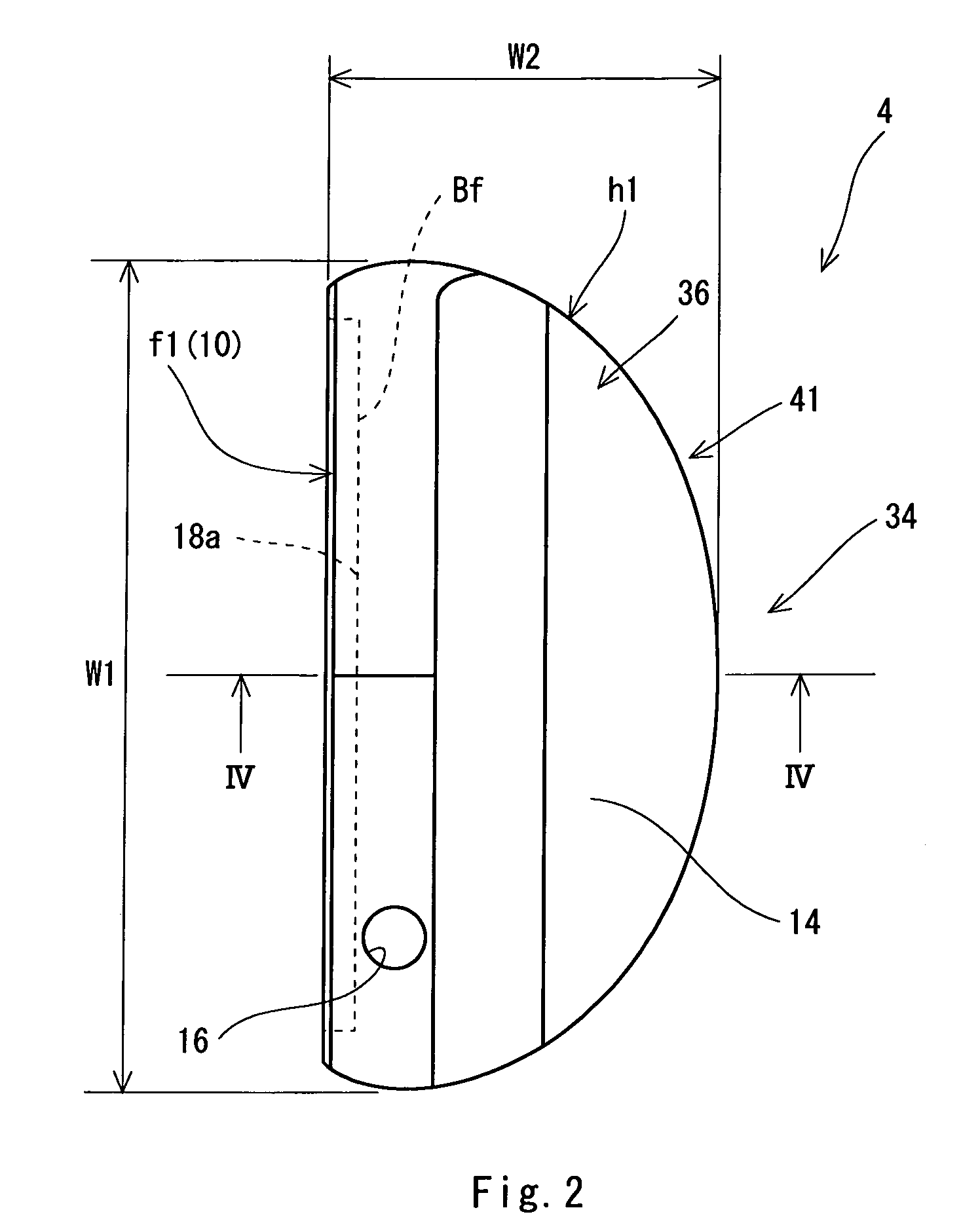
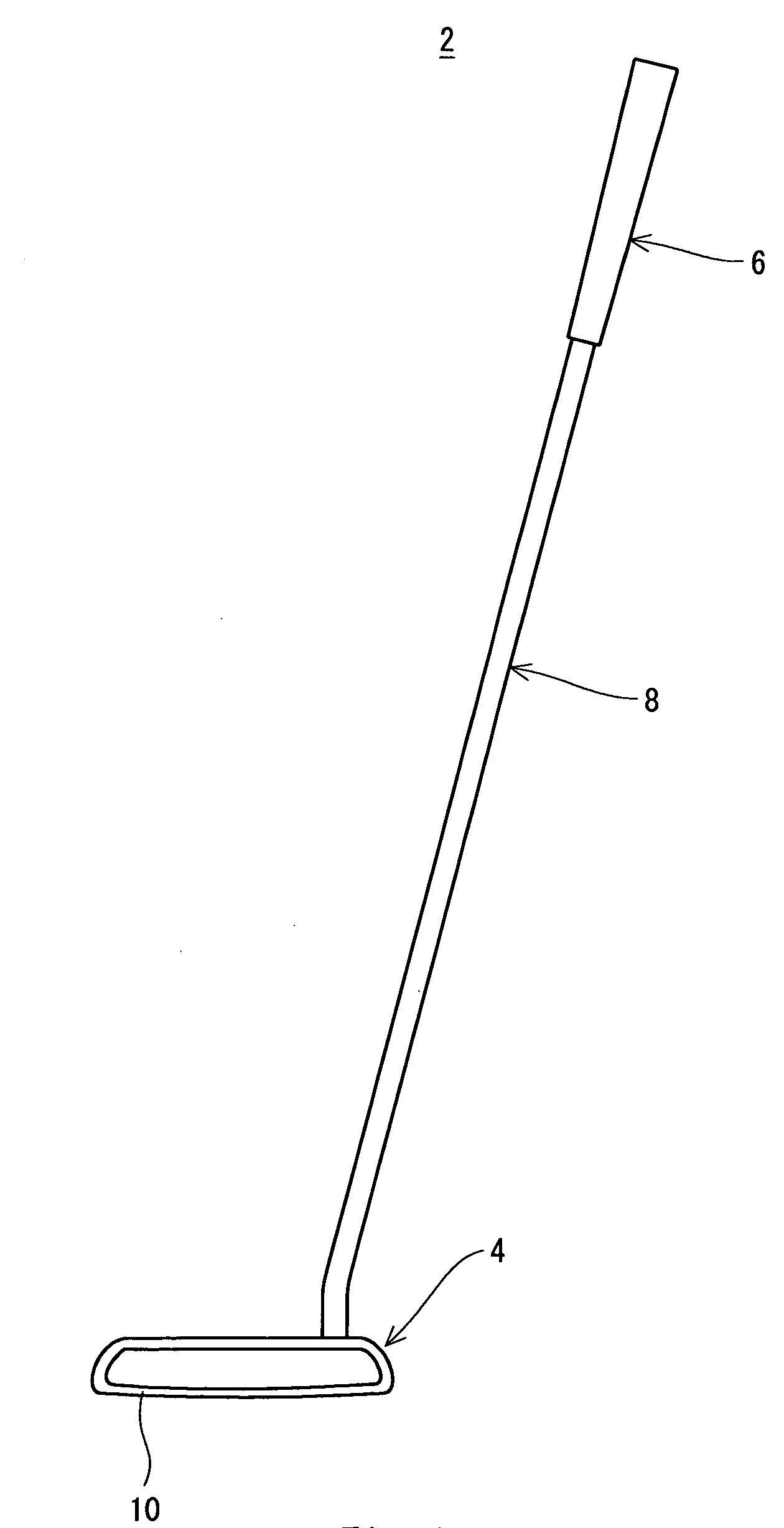
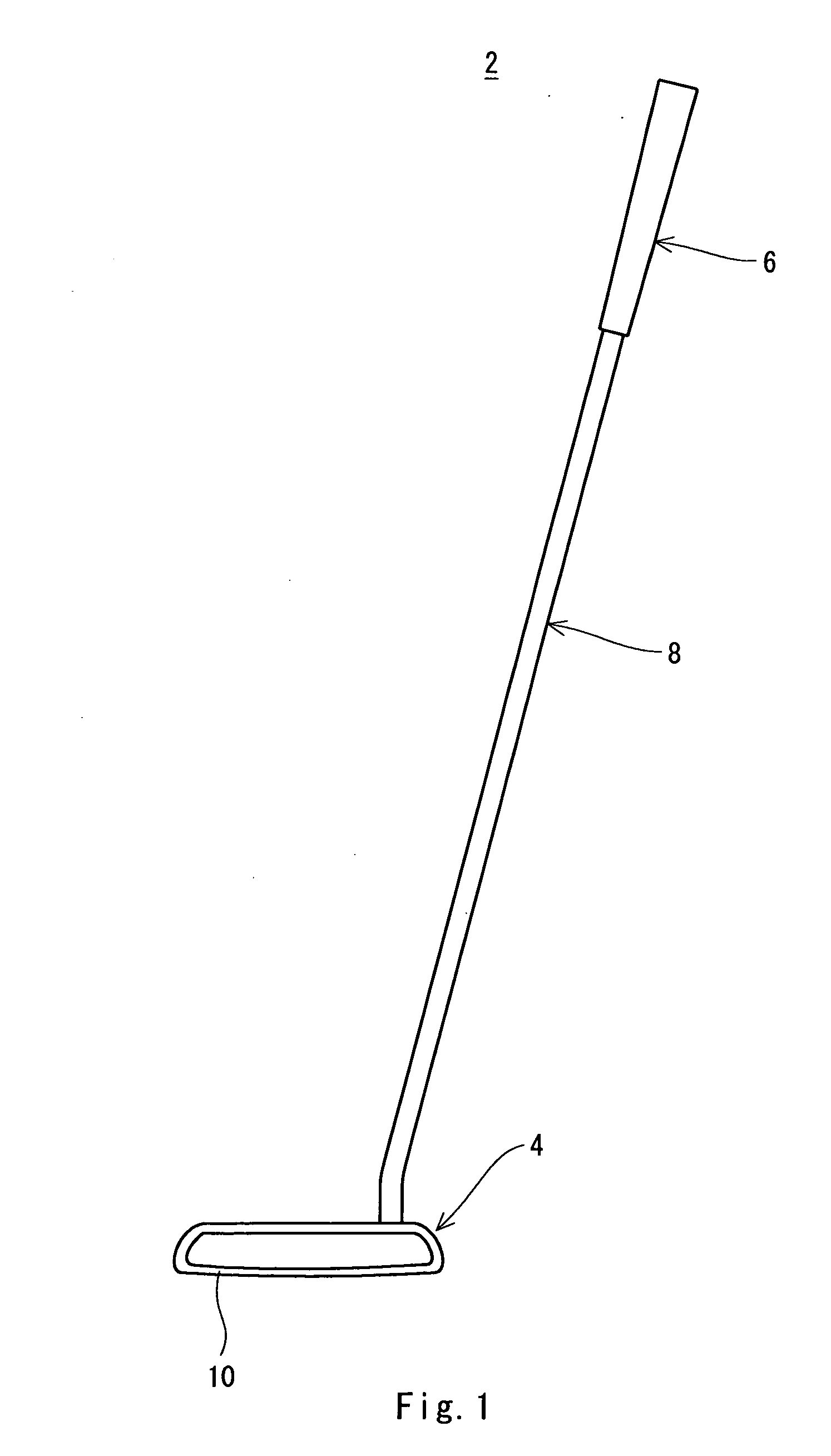
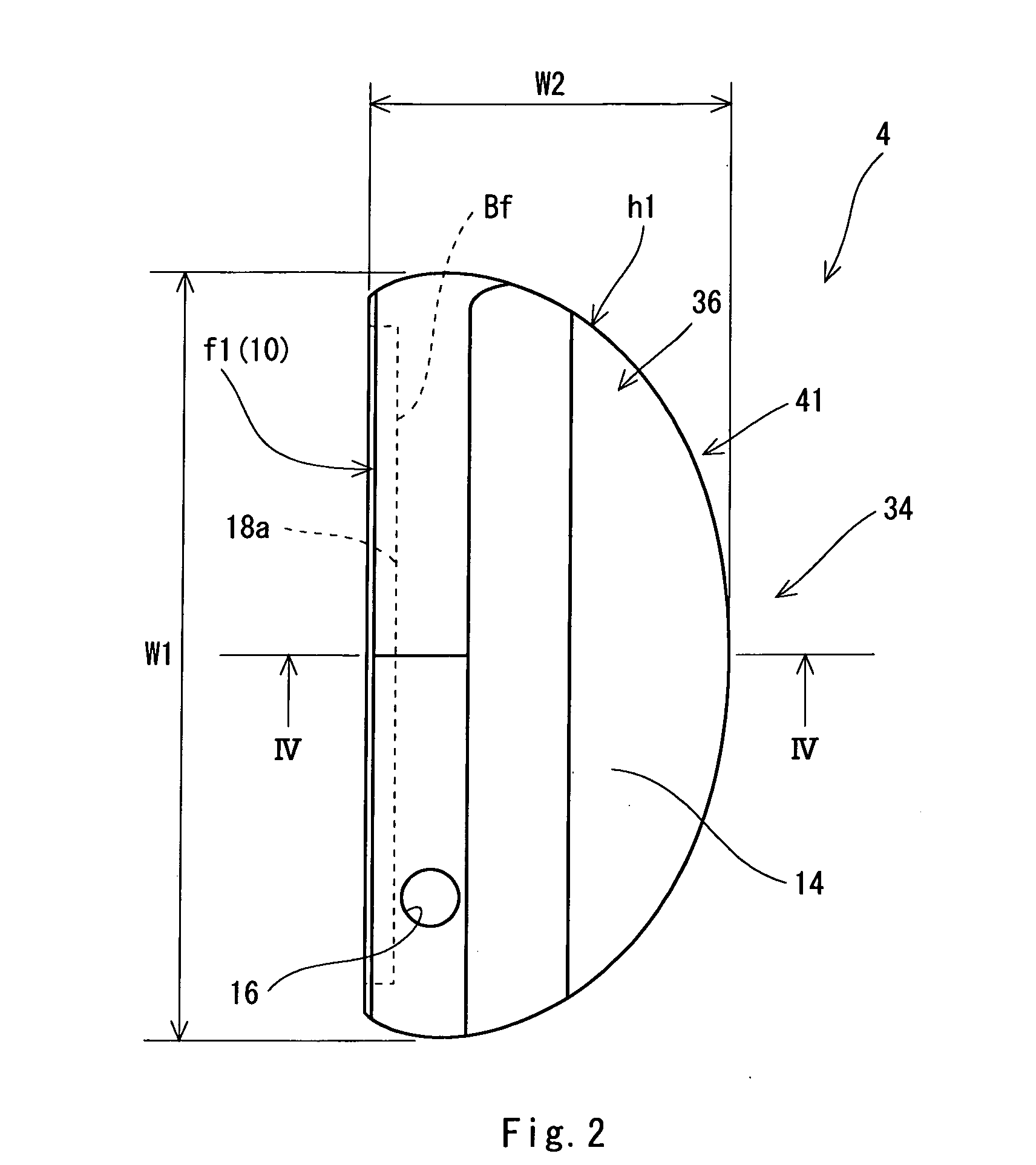
A golf putter (2) includes a head (4), a grip (6) and a shaft (8). The head (4) has a head body (h1) formed of a metal and a face member (f1) formed by an elastic material. A front surface (Ff) of the face member (f1) constitutes at least a part of a face surface (10). A siping (s1) is provided on a back surface (Bf) of the face member (f1). The siping (s1) is not provided on the front surface (Ff) of the face member (f1). It is preferable that the siping (s1) should be extended with bending. It is preferable that a ratio (Ds / Tf) of a depth (Ds) of the siping (s1) to a thickness (Tf) of the face member (f1) should be equal to or higher than 0.2 and should be equal to or lower than 0.8. It is preferable that a width (Ws) of the siping (s1) should be equal to or smaller than 1.0 mm.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Head for golf putter and golf putter
A golf putter (2) includes a head (4), a grip (6) and a shaft (8). The head (4) has a head body (h1) formed of a metal and a face member (f1) formed by an elastic material. A front surface (Ff) of the face member (f1) constitutes at least a part of a face surface (10). A siping (s1) is provided on a back surface (Bf) of the face member (f1). The siping (s1) is not provided on the front surface (Ff) of the face member (f1). It is preferable that the siping (s1) should be extended with bending. It is preferable that a ratio (Ds / Tf) of a depth (Ds) of the siping (s1) to a thickness (Tf) of the face member (f1) should be equal to or higher than 0.2 and should be equal to or lower than 0.8. It is preferable that a width (Ws) of the siping (s1) should be equal to or smaller than 1.0 mm.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
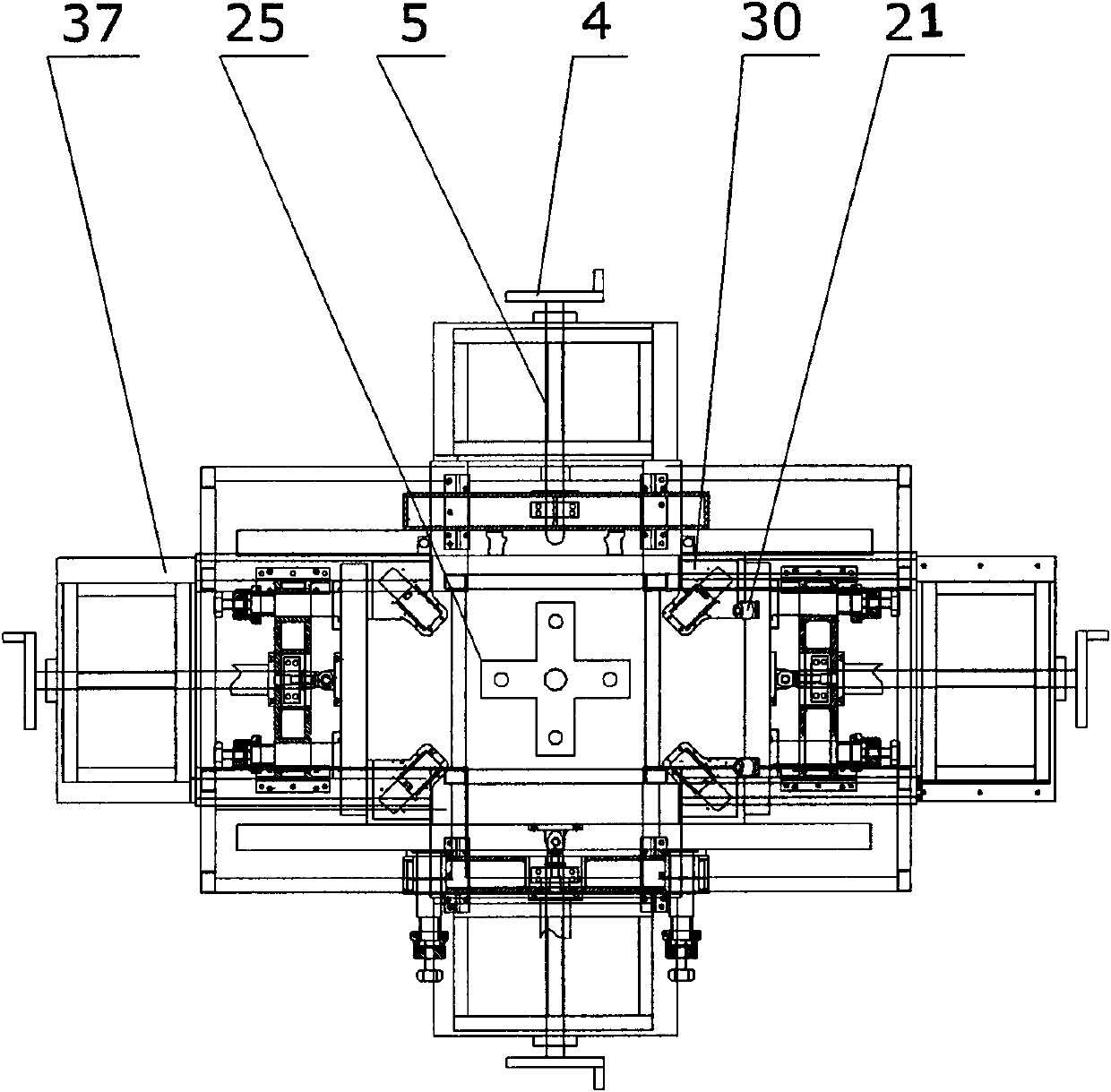
Solar cell assembly frame and angle assembling device and process thereof
InactiveCN102024868ARealize semi-automationNo need for manual handlingFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesDrive wheelEngineering
The invention discloses a solar cell assembly frame and angle assembling device and a process thereof, and relates to a solar cell assembly device. The invention provides the solar cell assembly frame and angle assembling device with good comprehensive use performance, scientific and reasonable structure, simple process and high automation degree. The device comprises a rack; the center of the rack is provided with a lifting mechanism; the sides of the lifting mechanism are provided with locking and adjusting mechanisms respectively, fixed on the rack and connected with movable supports; the movable supports are provided with frame assembling cross beams for connecting an upper guide plate and a lower guide plate respectively, the lower guide plate fixes an angle assembling bottom plate of an angle assembling cylinder and is connected with the frame assembling cross beam, and the angle assembling bottom plate fixed on the inner round angle of the rack is provided with an angle assembling mechanism; the upper guide plate of the frame assembling cross beam is provided with a transmission mechanism consisting of a motor, a telescopic pipe and a driving wheel set, and the two corresponding sides of the transmission mechanism are provided with positioning guardrails; and the transmission mechanism is connected with a frame closing mechanism.
Owner:YINGKOU JINCHEN MACHINERY
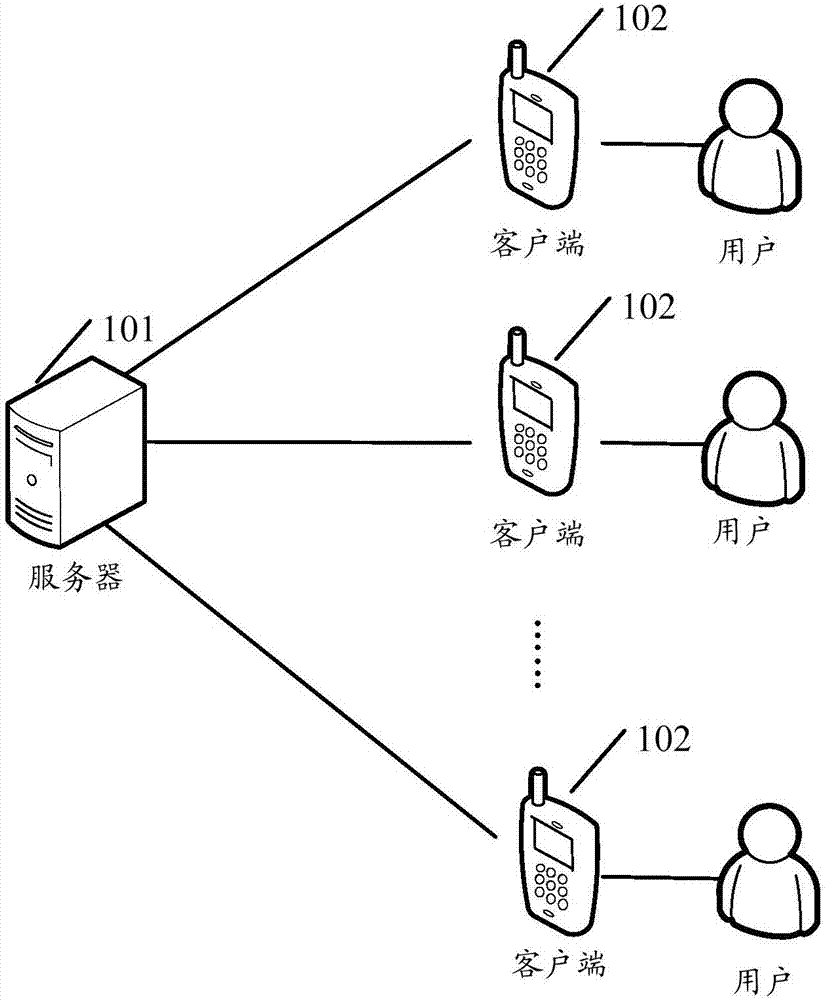
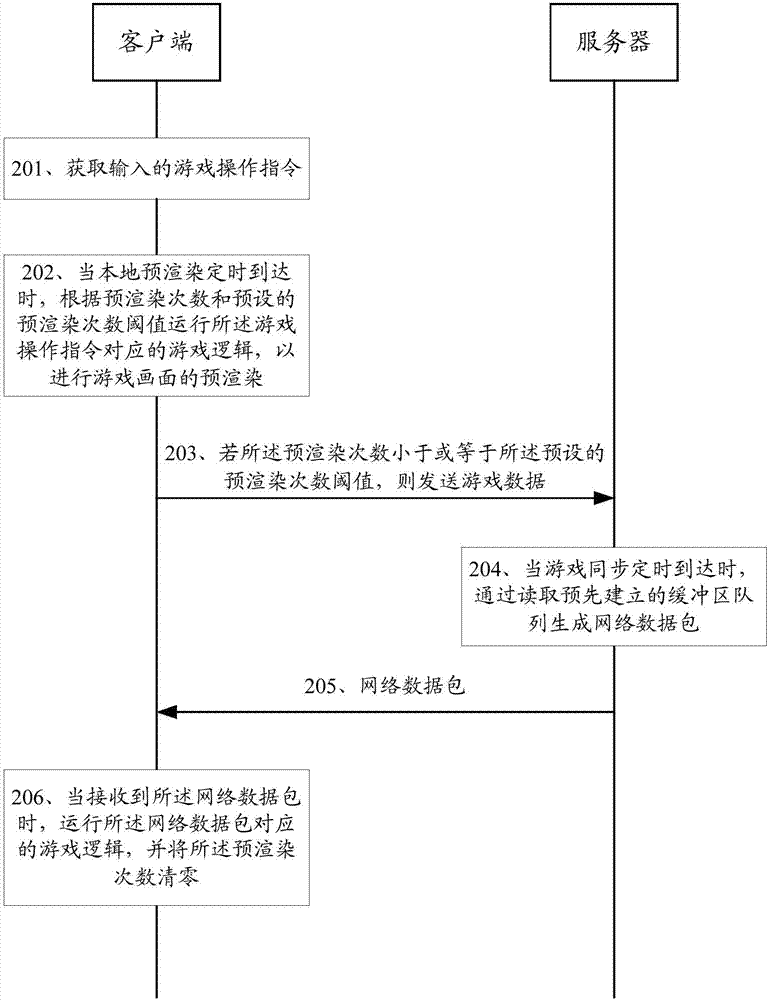
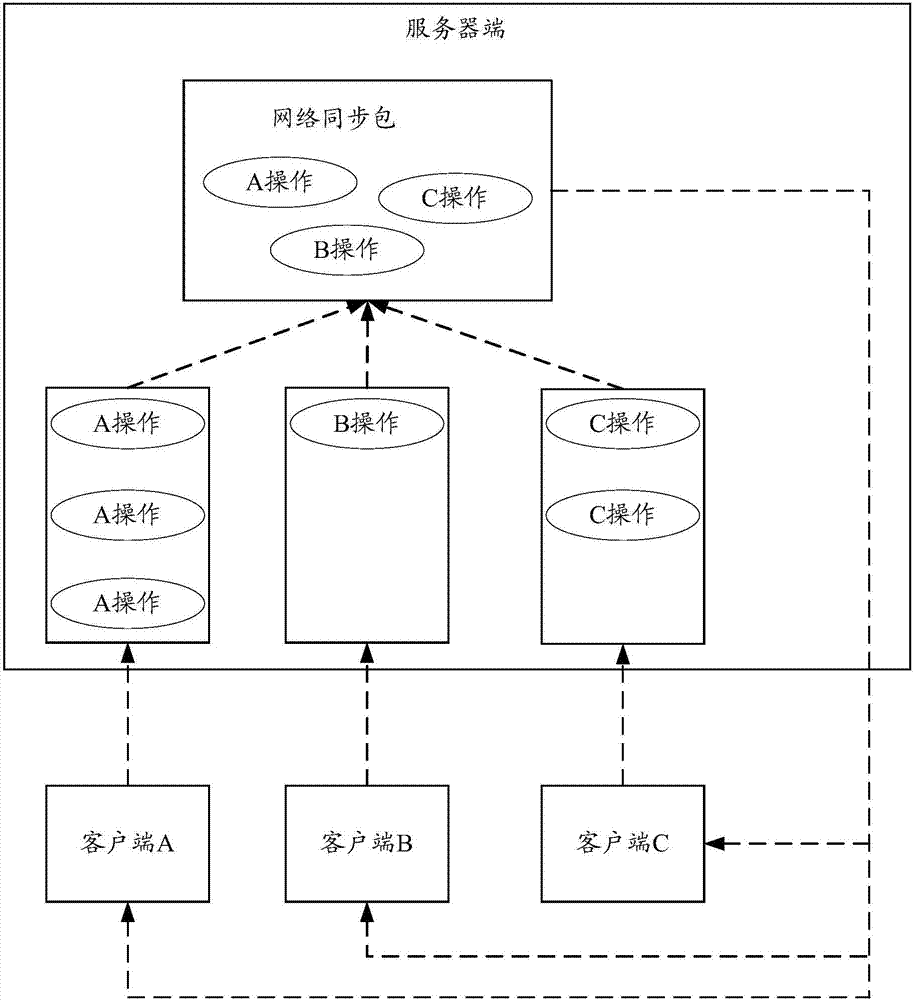
Game synchronization method, system and related device
ActiveCN107222510AControl fluencyControl consistencyVideo gamesTransmissionNetwork packetNetwork data
The embodiments of the invention provide a game synchronization method, a system and a related device. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an input game operation instruction; when the local pre-rendering time is up, running a game logic corresponding to the game operation instruction according to the number of pre-rendering times and a preset pre-rendering number-of-times threshold to pre-render game pictures; and when receiving a network data packet sent by a server, running a game logic corresponding to the network data packet to synchronize clients of which the game pictures are in the same game scene, and zeroing the number of pre-rendering times, wherein the network data packet includes game data sent by the clients. Through the embodiments of the invention, the smoothness and consistency of the game pictures can be controlled flexibly and efficiently, and the development cost of games can be reduced.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
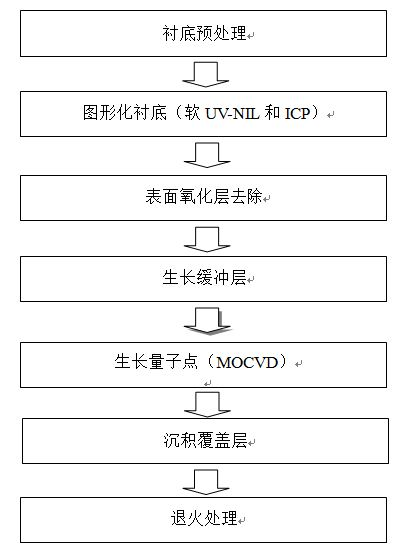
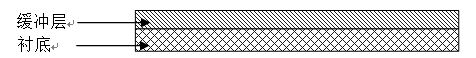
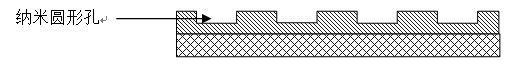
Manufacture method of large-area highly uniform sequential quantum dot array
InactiveCN101830430AReduce sizeSmall sizeNanostructure manufactureUltravioletInductively coupled plasma
The invention relates to a manufacture method of a large-area highly uniform sequential quantum dot array. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a nanopore graphic array on a substrate by adopting soft ultraviolet nano imprint lithography (UV-NIL) and an inductively coupled plasma (ICP) technology; and growing quantum dots in a self-organizing way by using a prepared graphical substrate as a template and using a metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) system. The invention realizes the low-cost, consistent and batched preparation of the large-area highly uniform sequential quantum dot array and can be applied to manufacture of devices such as quantum dot lasers, quantum dot memories, quantum dot solar batteries, quantum dot LEDs, single photon emitters, and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
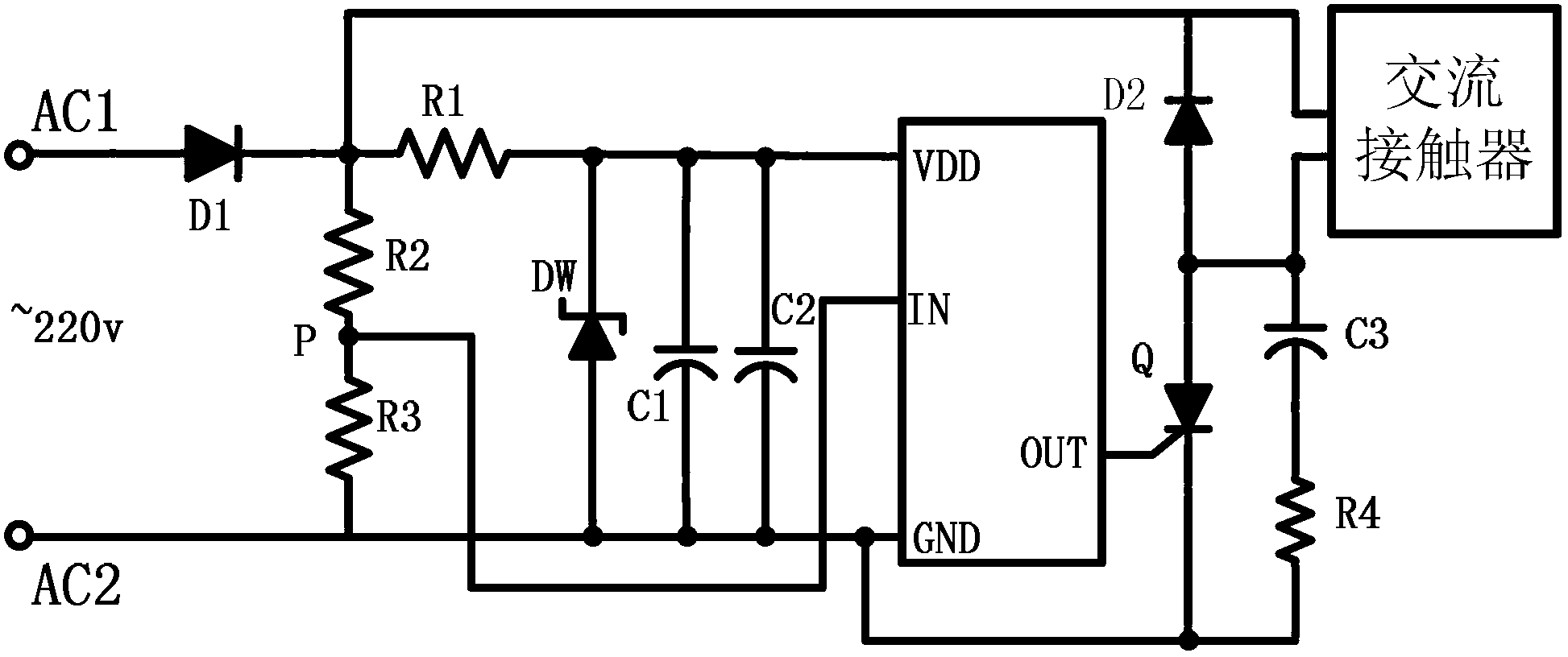
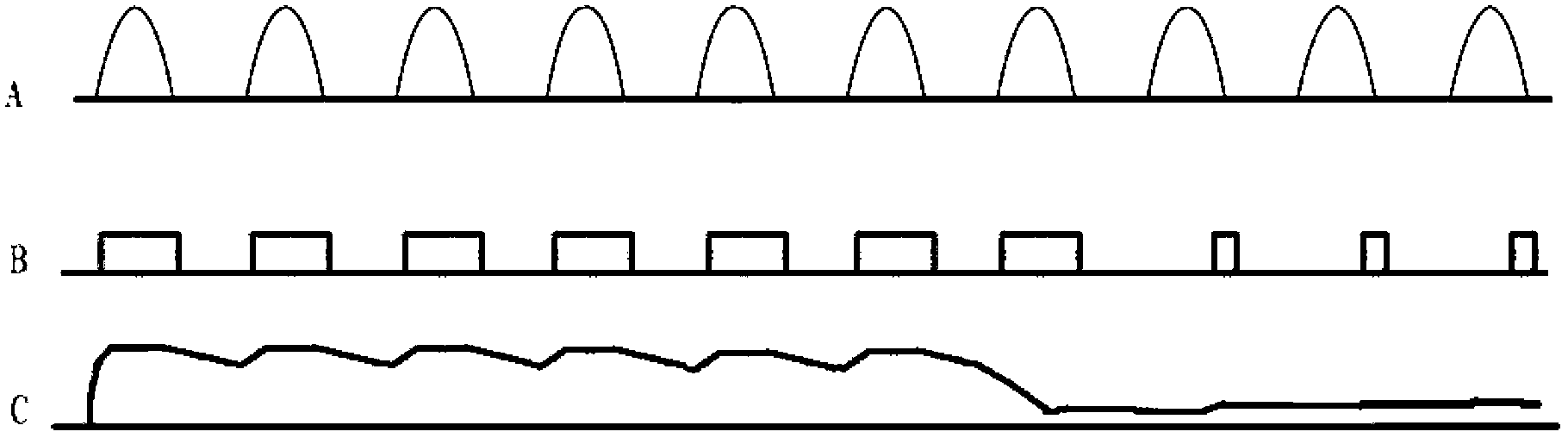
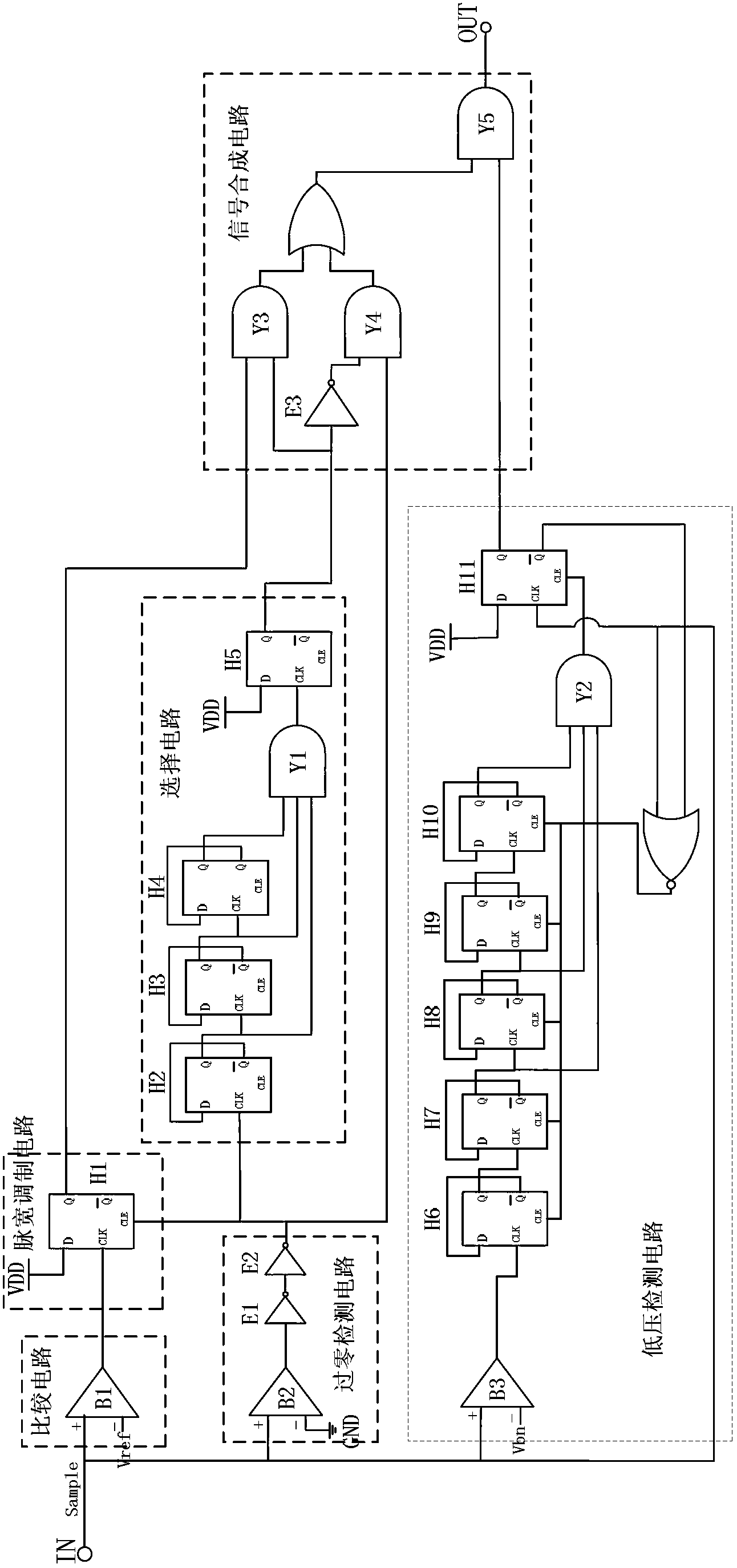
Economizer of alternative-current contactor
The invention discloses an economizer of an alternative-current contactor, and the economizer comprises a peripheral circuit which is connected with the alternative-current contactor and a signal processor which is connected with the peripheral circuit; the signal processor comprises a comparison circuit, a zero-crossing detection circuit, a pulse width modulation circuit, a selection circuit, a low-voltage detection circuit and a signal synthesis circuit. Due to the adoption of the economizer, narrow pulse of small current passing through the alternative-current contactor can be changed along with the variation of external voltage, the width of the narrow pulse is reduced while the external voltage is increased, the current passing by the economizer is reduced, and thus the burning of the coil caused by the overlarge current can be avoided. When the external voltage is dropped, the width of the narrow pulse outputted by the economizer is increased, the current passing by the alternative-current contactor is correspondently increased, and thus the disconnection of the alternative-current contactor because of reduced current can be prevented; and moreover, the power consumption of the alternative-current contactor can be further reduced, and the burning of a contactor coil because of over-current can be avoided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
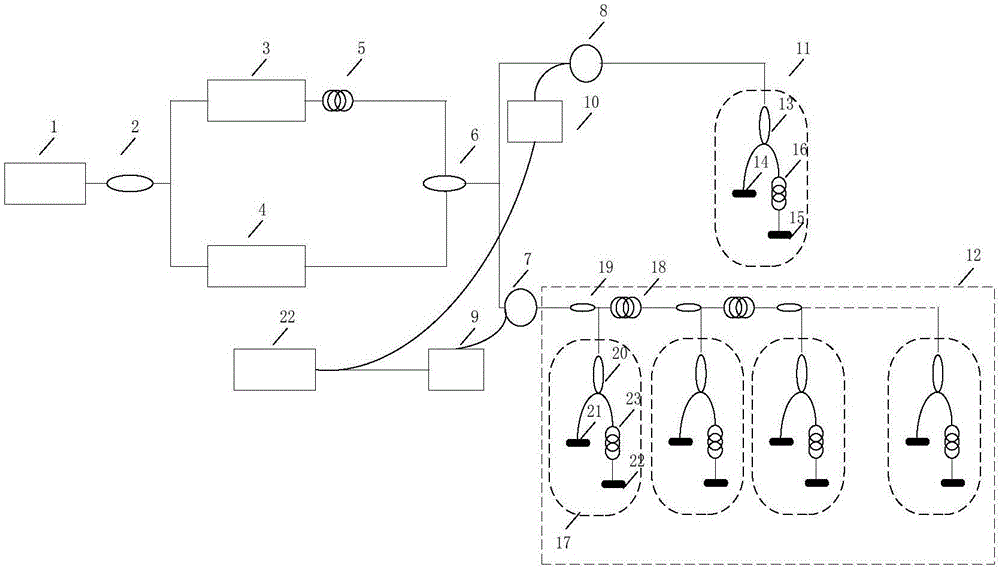
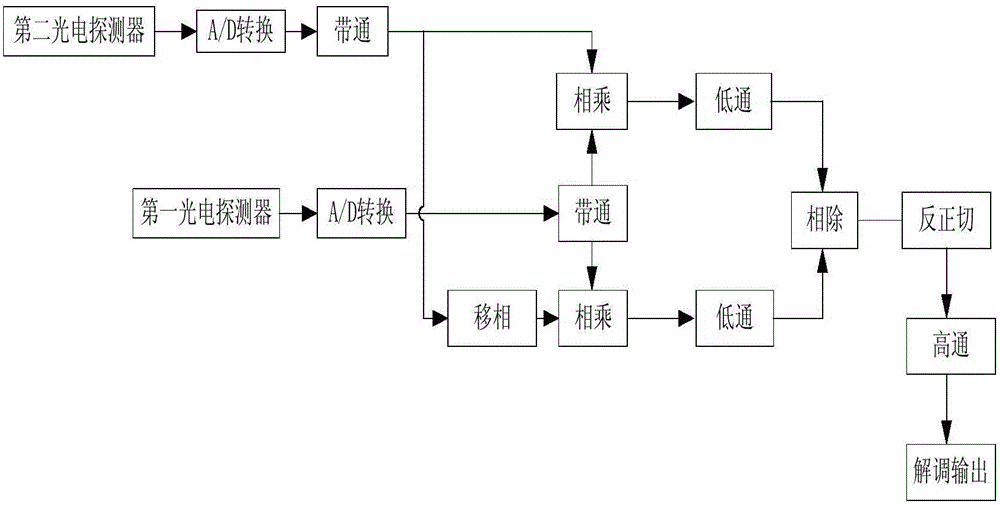
Heterodyne-interference-type optical fiber hydrophone time division multiplexing array and demodulation method
ActiveCN106052843AIncrease the carrier frequencyLarge dynamic rangeSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansHydrophonePhotovoltaic detectors
A heterodyne-interference-type optical fiber hydrophone time division multiplexing array and a demodulation method are disclosed. The optical fiber hydrophone time division multiplexing array comprises a narrow linewidth laser, a first coupler, a first acoustic-optical modulator, a second acoustic-optical modulator, a first optical fiber delay ring, a second coupler, a first circulator, a second circulator, a first photoelectric detector, a second photoelectric detector, a reference probe and a hydrophone sensing array. The sensing array adopts a parallel structure. Pulse light enters into each probe of the array through the delay ring in a time sharing mode so as to generate a sensing light signal. The reference probe is used for generating a reference light signal. The sensing light signal and the reference light signal are collected by the photoelectric detectors and then are converted into analog electronic signals. A signal demodulation module is used to carry out analog-to-digital conversion on the signals respectively. An arc tangent algorithm is used to resolve a submarine sound signal perceived by the sensing array.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
Three-dimensional semiconductor device and fabrication method thereof
ActiveCN105355602AControl consistencyOvercome the current bottleneckSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerPower flow
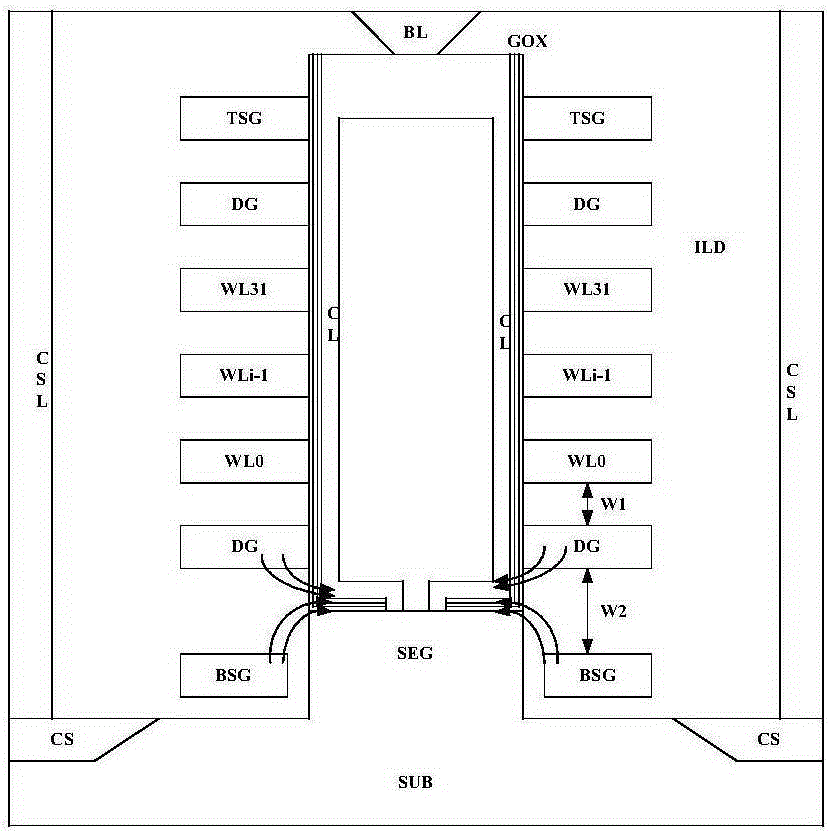
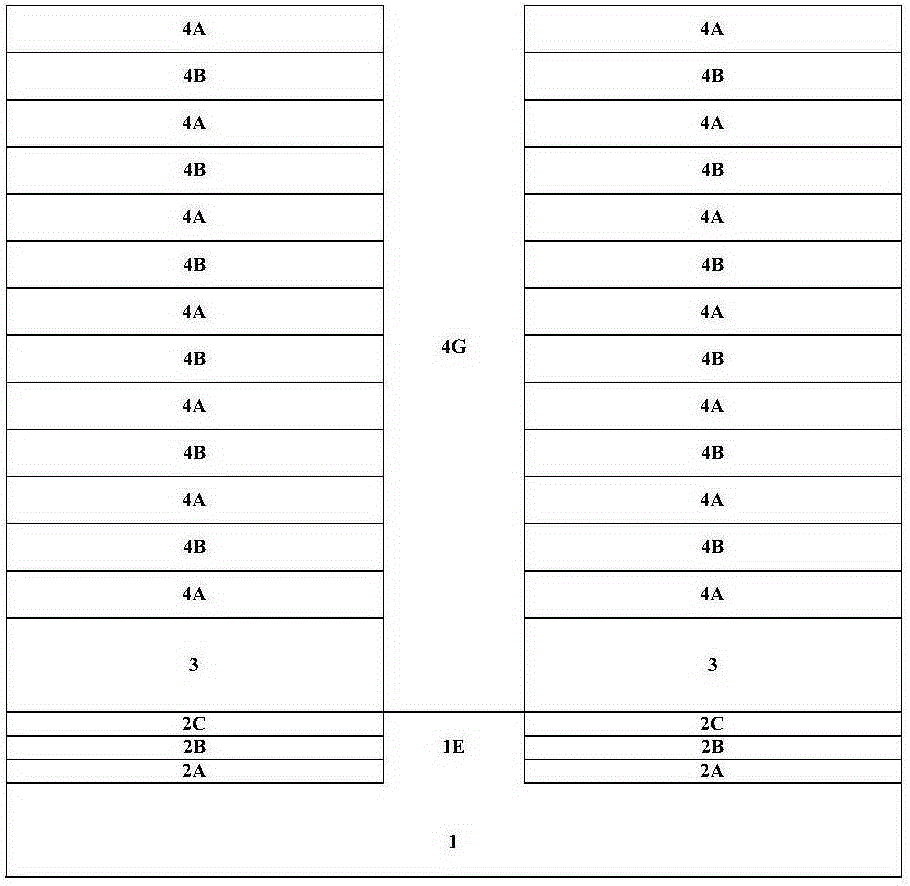
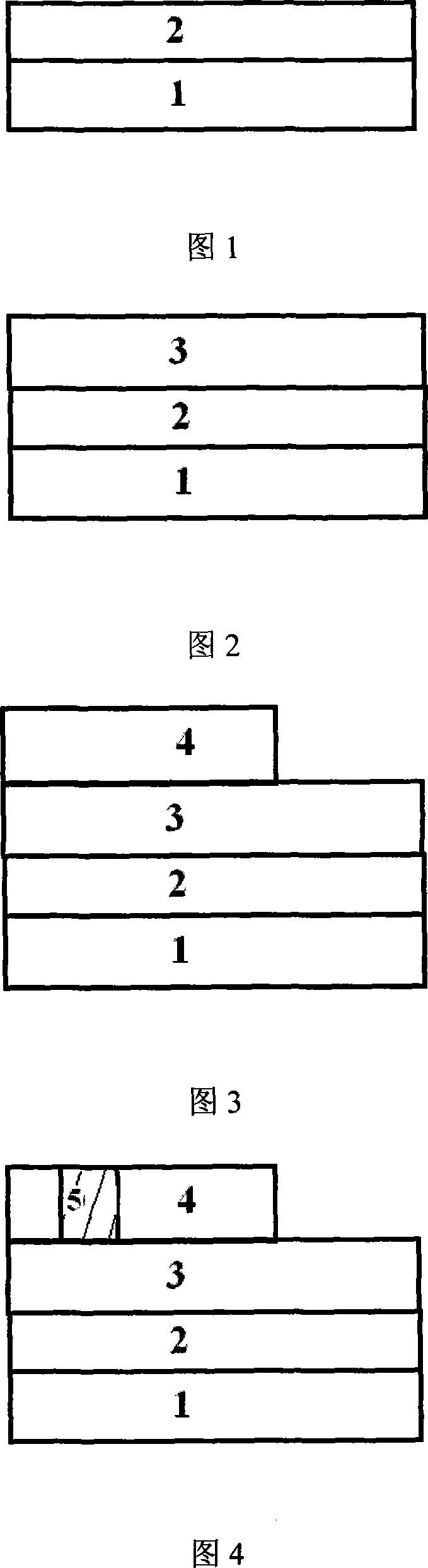
A three-dimensional semiconductor device comprises a plurality of storage units. Each storage unit comprises a channel layer, a bottom grid conductive layer, a floating gate layer, a plurality of second insulation layers, a plurality of grid conductive layers, a grid dielectric layer, a drain and a source, wherein the channel layer is arranged in a direction perpendicular to the surface of a substrate; the bottom grid conductive layer is arranged in a first insulation layer stack and arranged on a side wall of the channel layer; the floating gate layer is arranged on the first insulation layer stack and arranged on the side wall of the channel layer; the plurality of second insulation layer and the plurality of grid conductive layer are arranged on the floating grid layer and alternatively stacked along the side wall of the channel layer; the grid dielectric layer is arranged on the side wall of the channel layer; the drain is arranged at the top of the channel layer; and the source is arranged in the substrate between adjacent two storage units of the plurality of storage units. A floating gate which is not led out is embedded into the three-dimensional semiconductor device, a voltage is induced on the floating gate through voltage coupling on a near leading-out grid, thus, silicon epitaxial growth (SEG) and channel inversion of a poly-silicon contact region are assistantly completed, the current bottleneck of the region is overcome, the channel current is increased, and the consistency of threshold voltages of a field effect transistor (FET) near to the floating gate is effectively controlled.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Phase change memory unit with loop phase change material and its making method
ActiveCN101101961AEasy to operateReduce power consumptionElectrical apparatusDigital storagePhase-change memoryNanoscopic scale
The invention is concerned with the structure of the phase change memorizer device unit and its making method, with the cycle phase change material made of the heating electrode and the up electrode as the information saving carrier. The cycle phase change material is made of the proper film making technique and the nanometer processing, educed through the up and down electrode and integrated with the switch and the periphery circuit to prepare the nanometer scale phase change memorizer device unit. It is because of the thickness of the wall of the cycle phase change material is controllable within the nanometer scale range, the cross section area of the phase change material can be really small to improves the current density and the thermal efficiency of the phase change material available changing area that reduces the operating current of the phase change memorizer device unit and it's power consumption.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
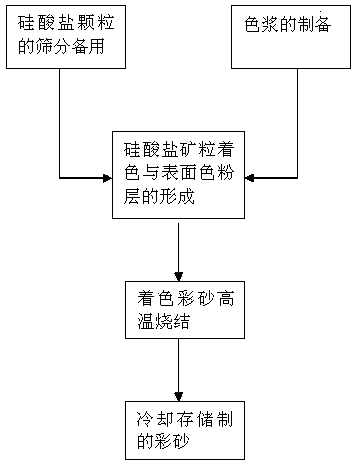
High-temperature sintered painted sand and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses high-temperature sintered painted sand and a preparation method thereof. The painted sand comprises silicate mineral particles and a surface toner layer, wherein the surface toner layer is formed by calcining color paste wrapping the surface of the silicate mineral particles at high temperature. The preparation method comprises the following steps: selecting and screening the silicate mineral particles; preparing the color paste, namely mixing water glass, kaolin, industrial borax and inorganic pigment with water according to the required color situation, and performing ball-milling; mixing the prepared color paste with the silicate mineral particles according to a weight ratio in a rotary drum furnace, and drying; after mixing and drying through the rotary drum furnace, calcining at high temperature, and after the calcining process is finished, feeding to the outlet of a calcining furnace; cooling and storing, namely cooling finally to prepare the high-temperature sintered painted sand. According to the preparation method, the operation is easy, the continuous production can be performed, the color adjustment of the painted sand is easy to control, the color consistency control of the painted sand can be ensured, the production is simple and quick, the cumbersome process in which frits need to be used is removed by optimization, the energy consumption is reduced, and the large-scale application is facilitated.
Owner:CHANGZHOU HONGCHENG SAND
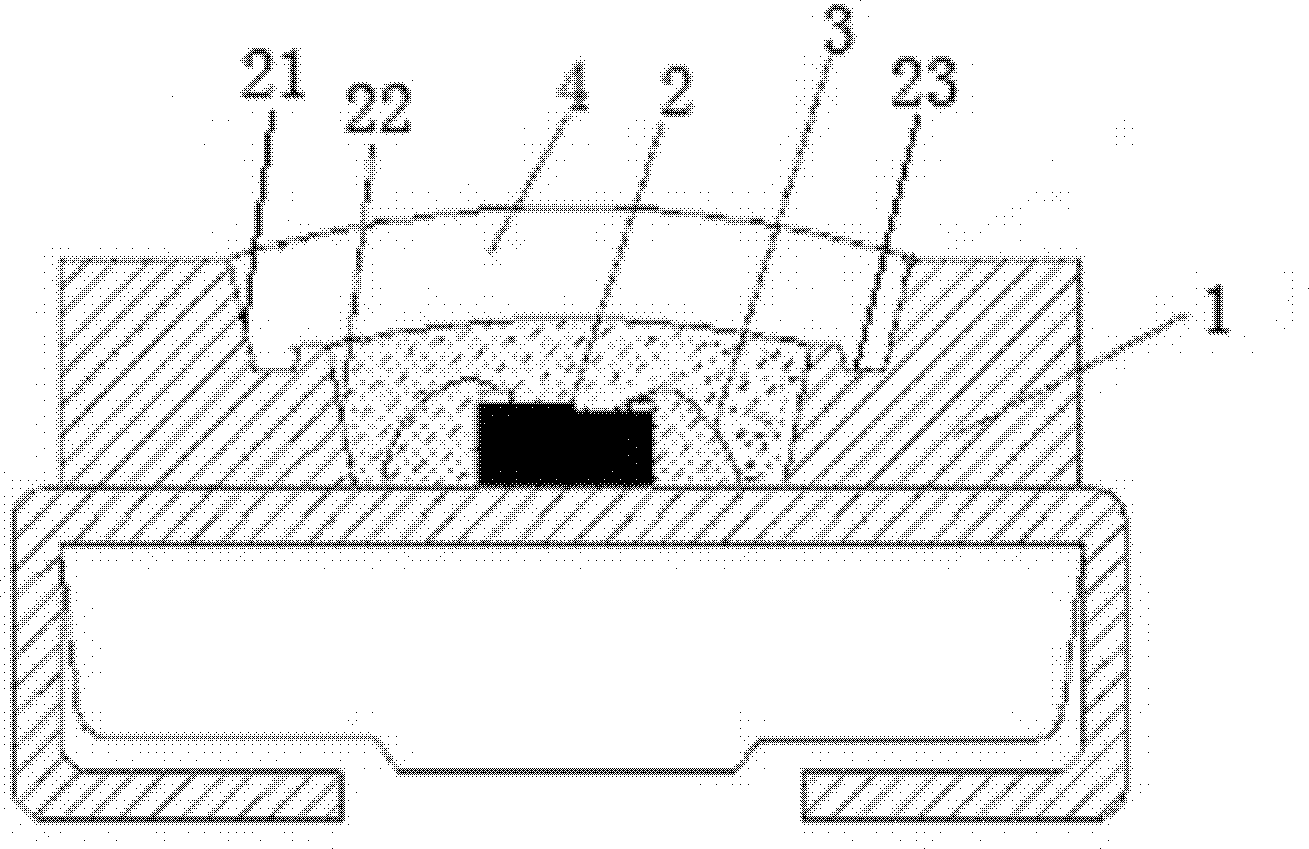
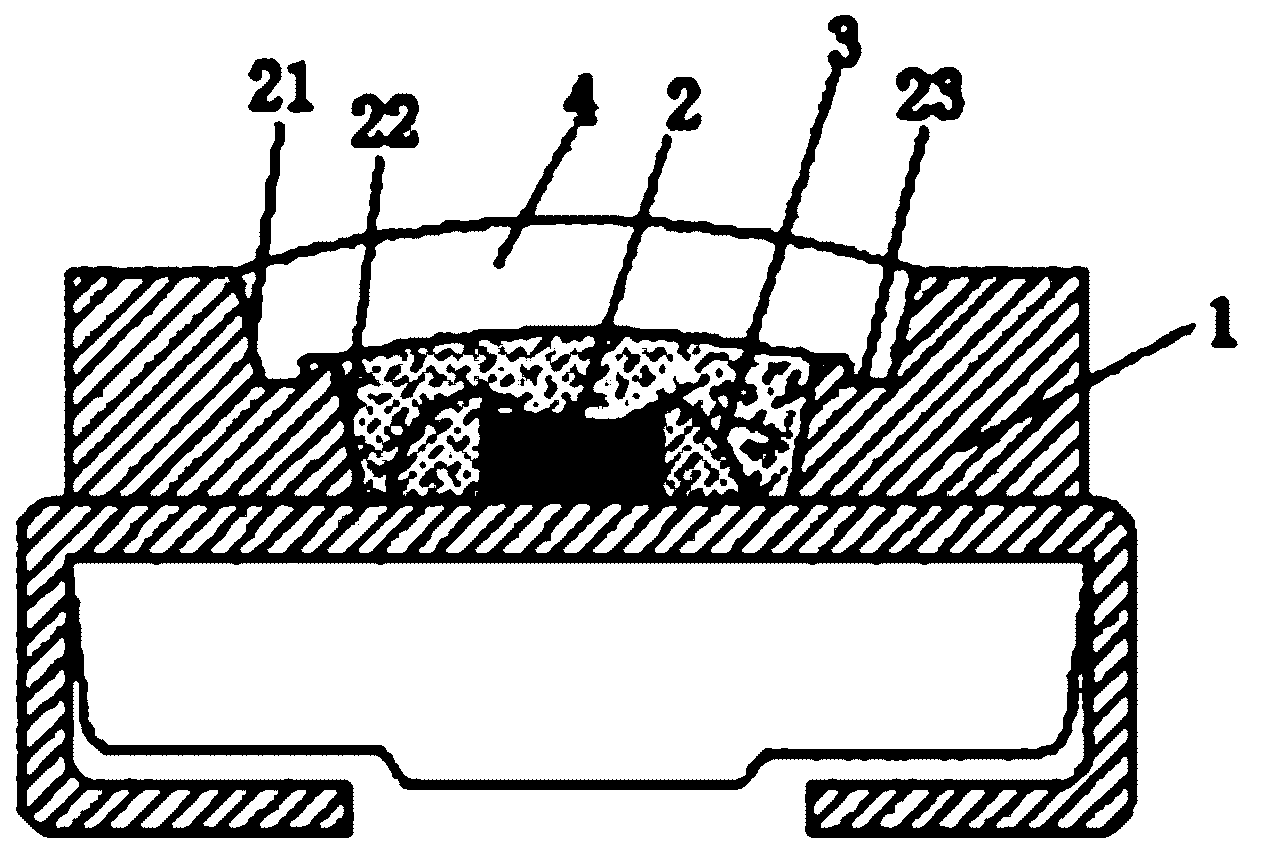
Manufacturing method and special die for one-step-formed multi-curved-face integral bullet-proof plates
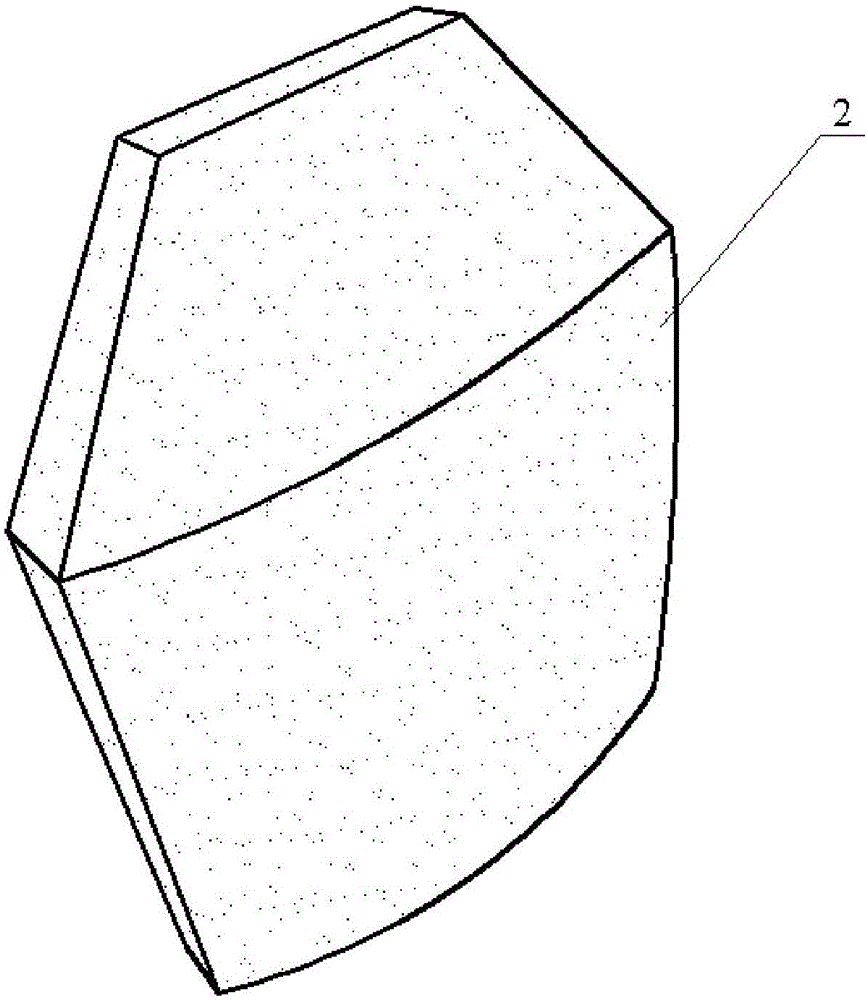
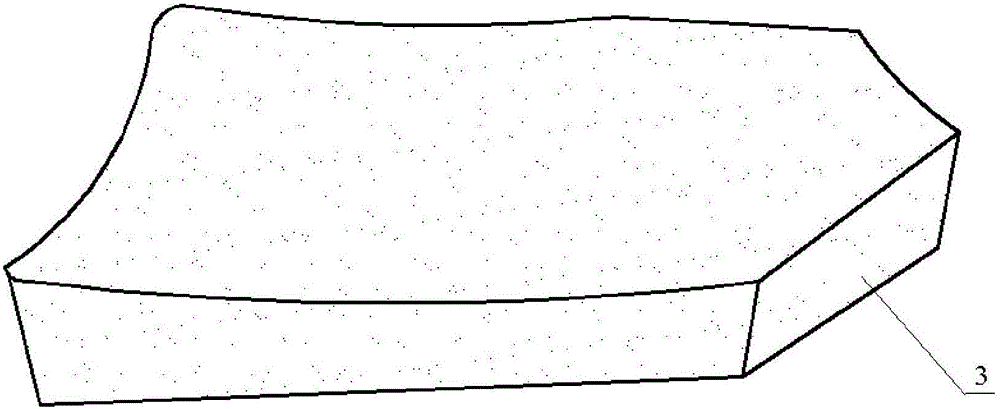
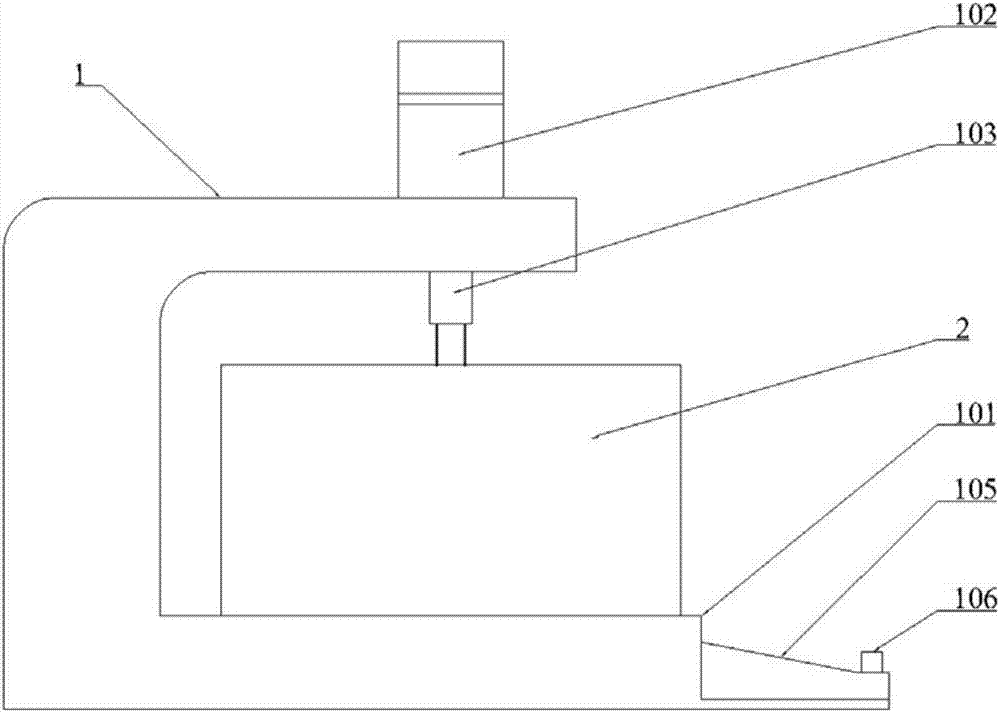
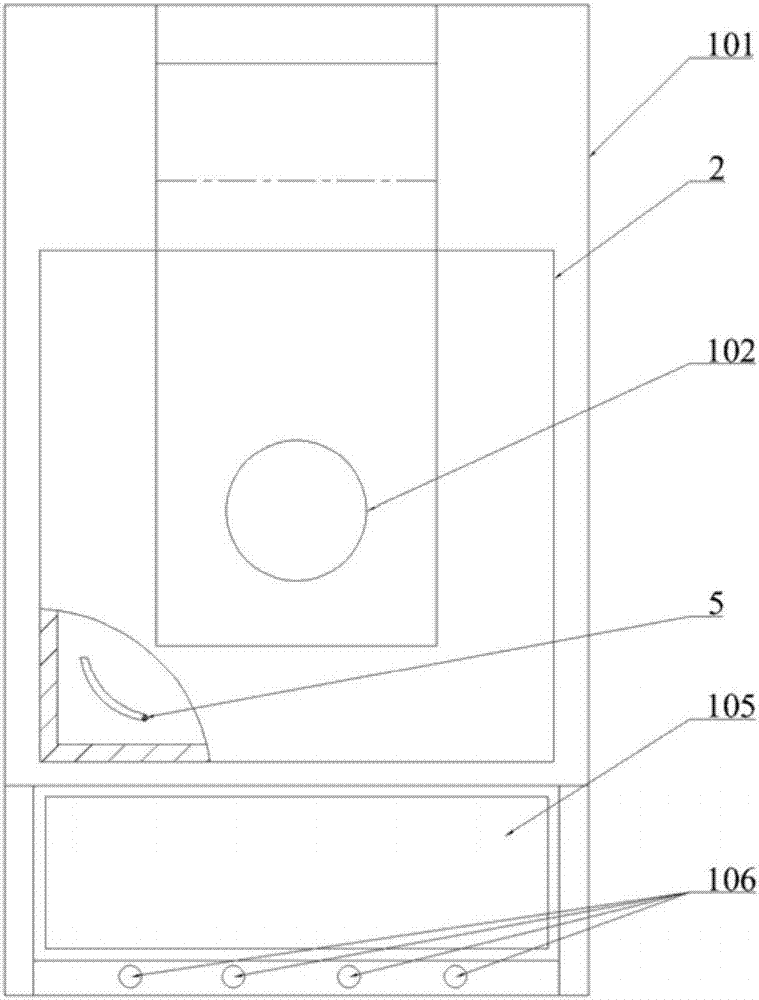
ActiveCN105777133AControl consistencyGood sintered densityMouldsMould auxillary partsComing outSemi automatic
The invention discloses a special die for one-step-formed multi-curved-face integral bullet-proof plates. The special die comprises an upper punch (2), a lower punch (3), an outer die (4) and a plug block (5). A die cavity (41) is formed in the outer die (4) and is communicated with two ends of the outer die (4). An opening (42) used for charging is formed in the top of the outer die (4) and is matched with the plug block (5) in shape. The die cavity (41) is communicated with the opening (42). The upper punch (2) is connected with an upper die plate of a semi-automatic horizontal press machine, and the lower punch (3) is connected with a lower die plate of the semi-automatic horizontal press machine. The upper punch (2) and the lower punch (3) can get into or come out of the die cavity (41) under the drive of the upper die plate and the lower die plate. The invention further provides a manufacturing method for the one-step-formed multi-curved-face integral bullet-proof plates by the special die.
Owner:浙江东新新材料科技有限公司
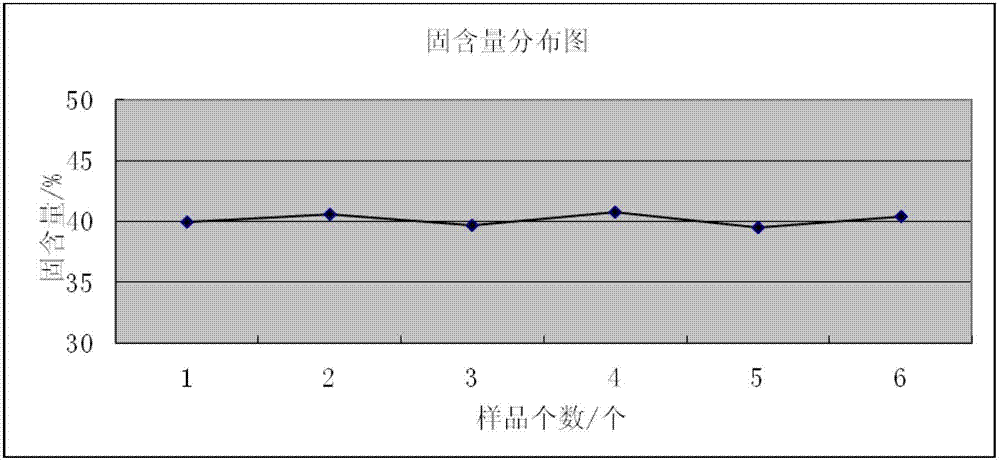
Method for assessing settleability and uniformity of lithium ion battery cathode slurry
ActiveCN102854083ASimple methodEasy to operateWeighing by removing componentCentrifugationRelative standard deviation
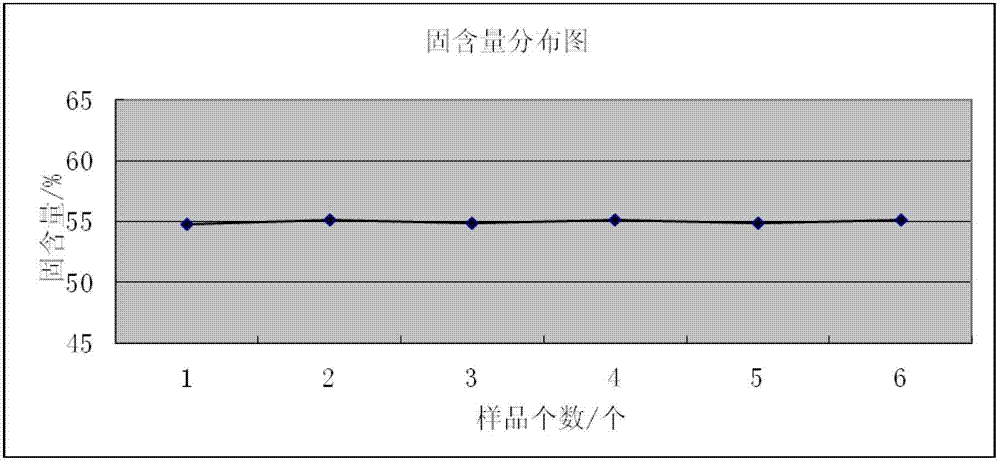
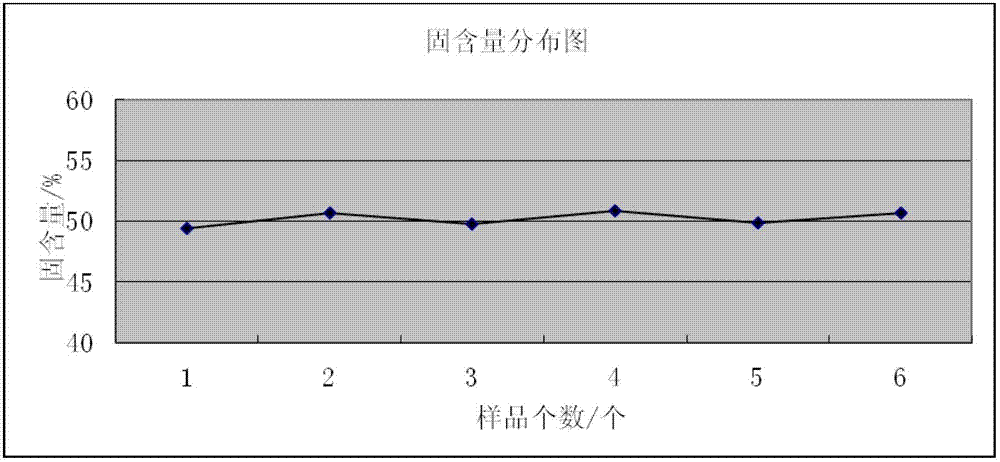
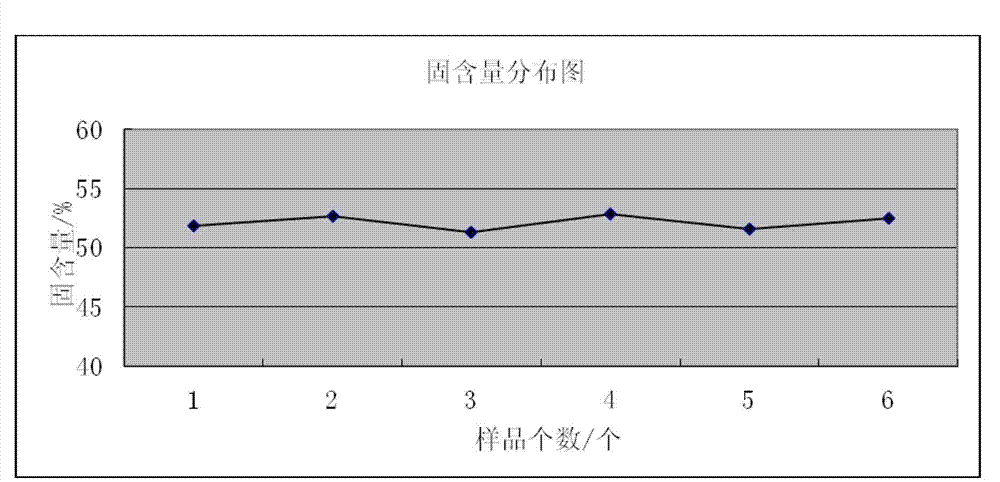
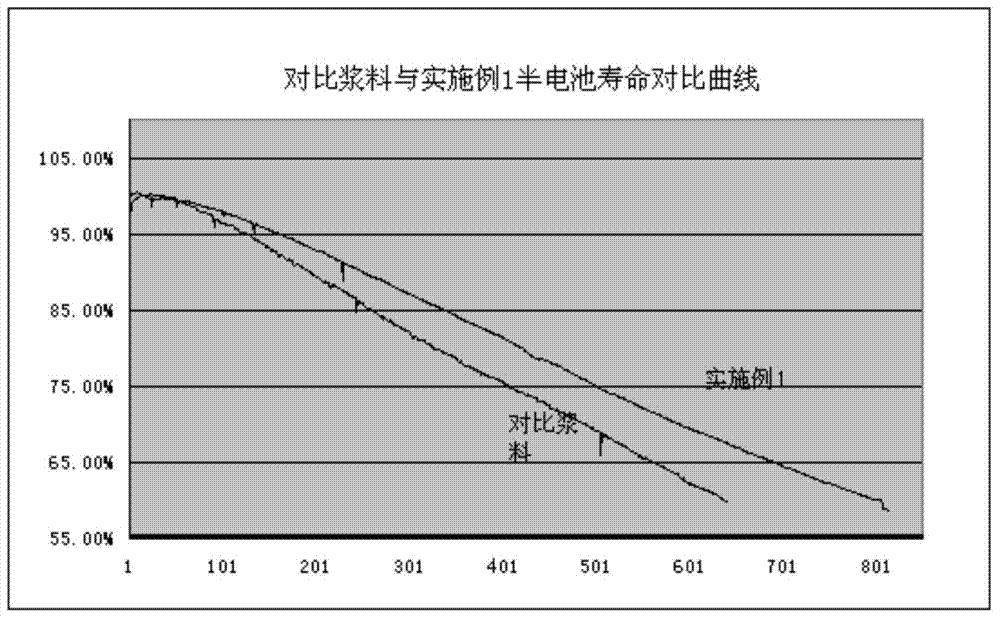
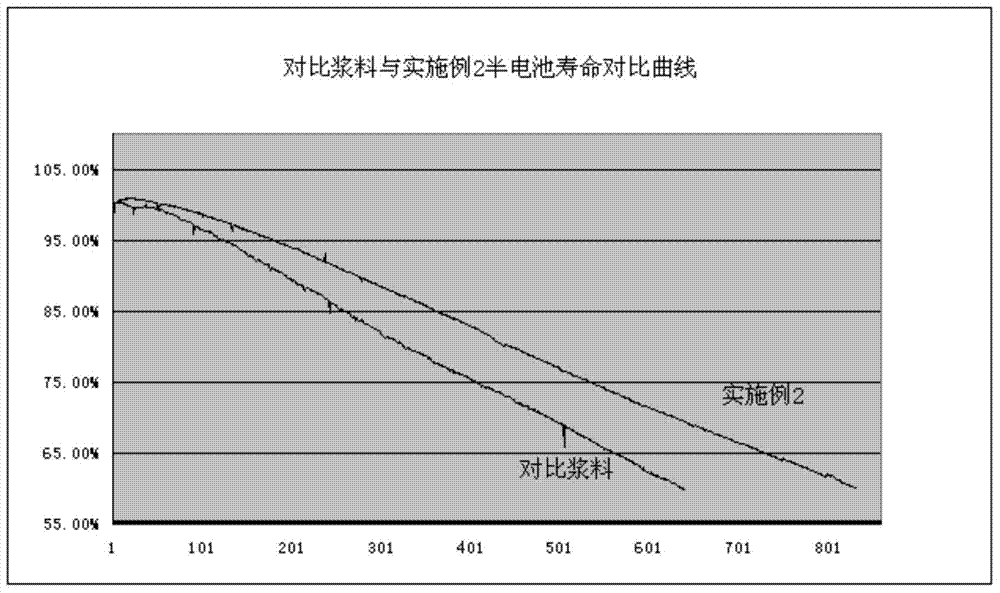
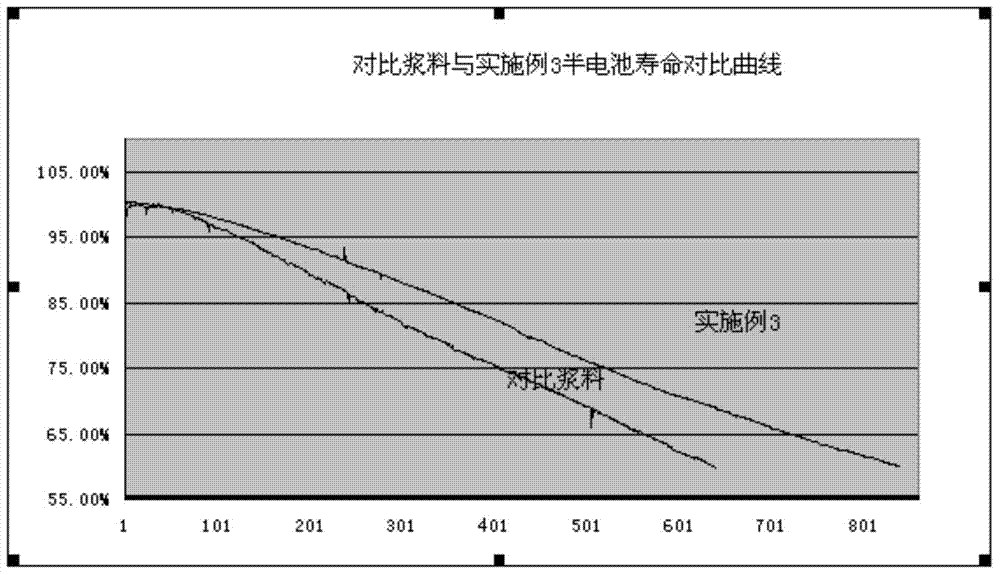
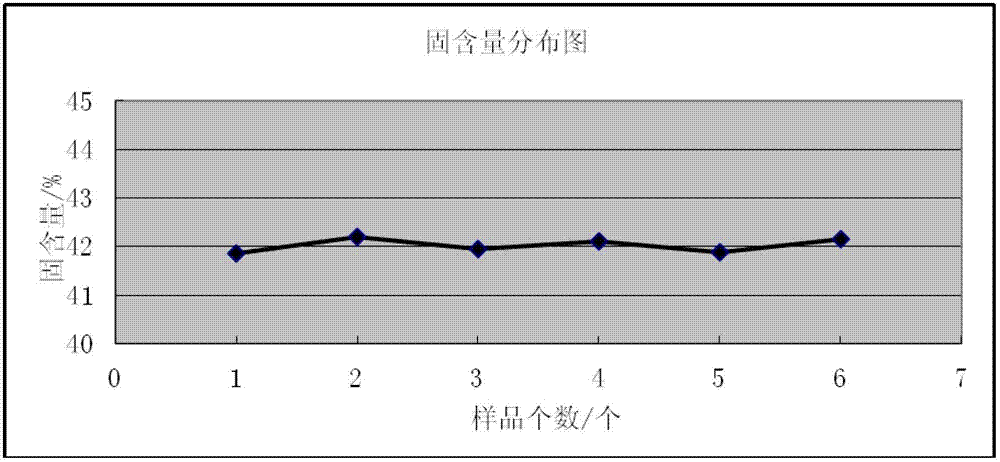
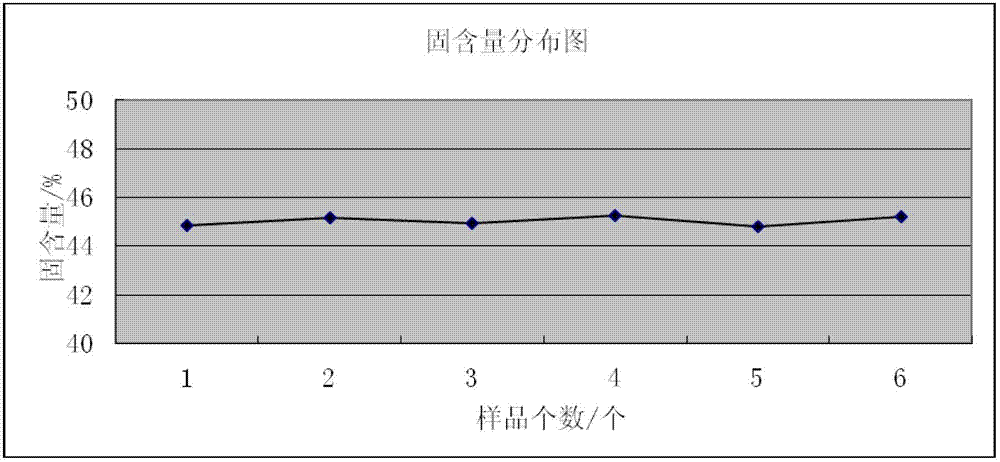
The invention discloses a method for assessing settleability and uniformity of lithium ion battery cathode slurry. The method comprises the following steps of taking samples from different positions of lithium ion battery cathode slurry, detecting solid contents of upper and lower layers in a centrifuge tube by a centrifugation method and assessing settleability and uniformity of the lithium ion battery cathode slurry according to relative standard deviation of the solid contents. The method has the advantages of simple processes, convenient operation, good reappearance, accurate data and high analysis efficiency and can be widely used in industries.
Owner:SHENZHEN DYNANONIC
Battery cathode slurry and preparation method of battery cathode slurry
InactiveCN103794798AImprove liquidityReduced charge and discharge performanceCell electrodesAntioxidantSlurry
The invention relates to battery cathode slurry and a preparation method of the battery cathode slurry. The battery cathode slurry comprises cathode active material, a conductive agent, a bonding agent, an antioxidant and a solvent, wherein the ratio of parts by weight among the cathode active material, the conductive agent, the bonding agent and the antioxidant is 100:(3.2-10):(0.8-2.4):(0.1-1); the conductive agent, namely, carbon black comprises graphene-doped superconductive carbon black and nickel powder. The slurry preparation process comprises the following two steps in the slurry preparation process: firstly preparing auxiliary liquid, standing until the bubbles of the auxiliary liquid are removed as much as possible, and then highly mixing the auxiliary liquid with alloyed powder to produce the battery with excellent performances.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
LTCC low temperature co-fired ceramic flat surface transformer
InactiveCN101789311AIncreasing the thicknessMiniaturizationTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsTransformers/inductances magnetic coresCapacitanceCoupling
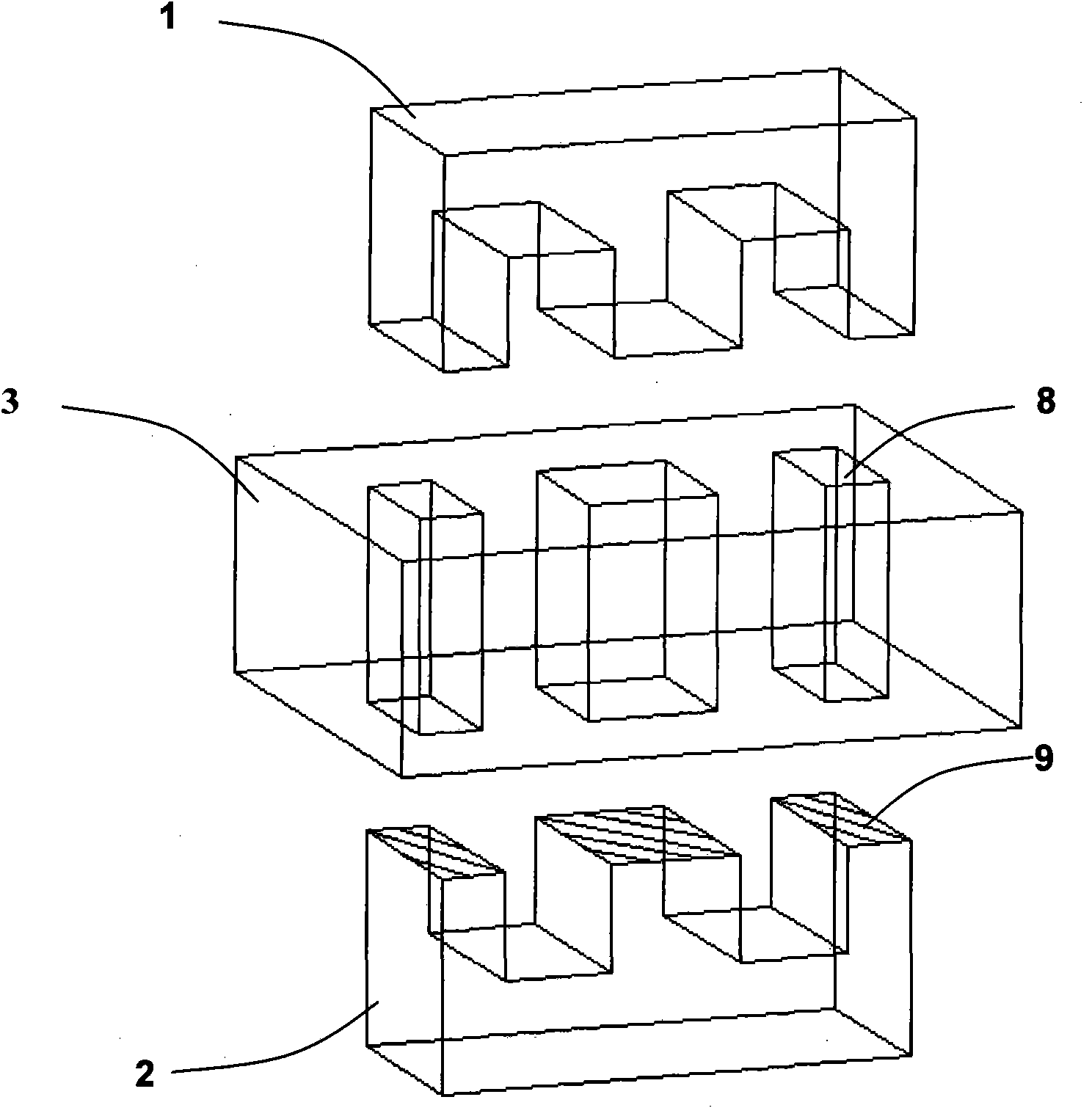
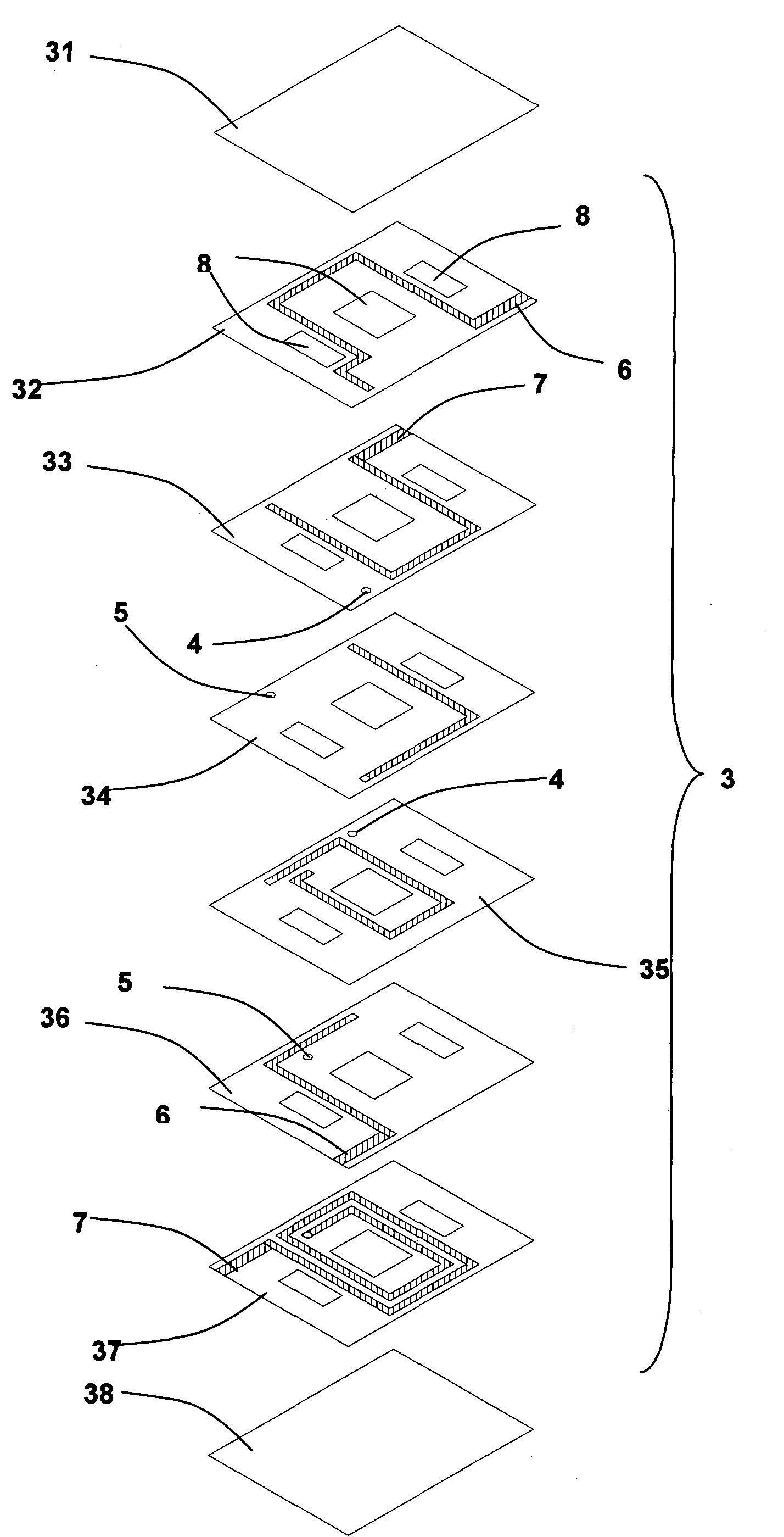
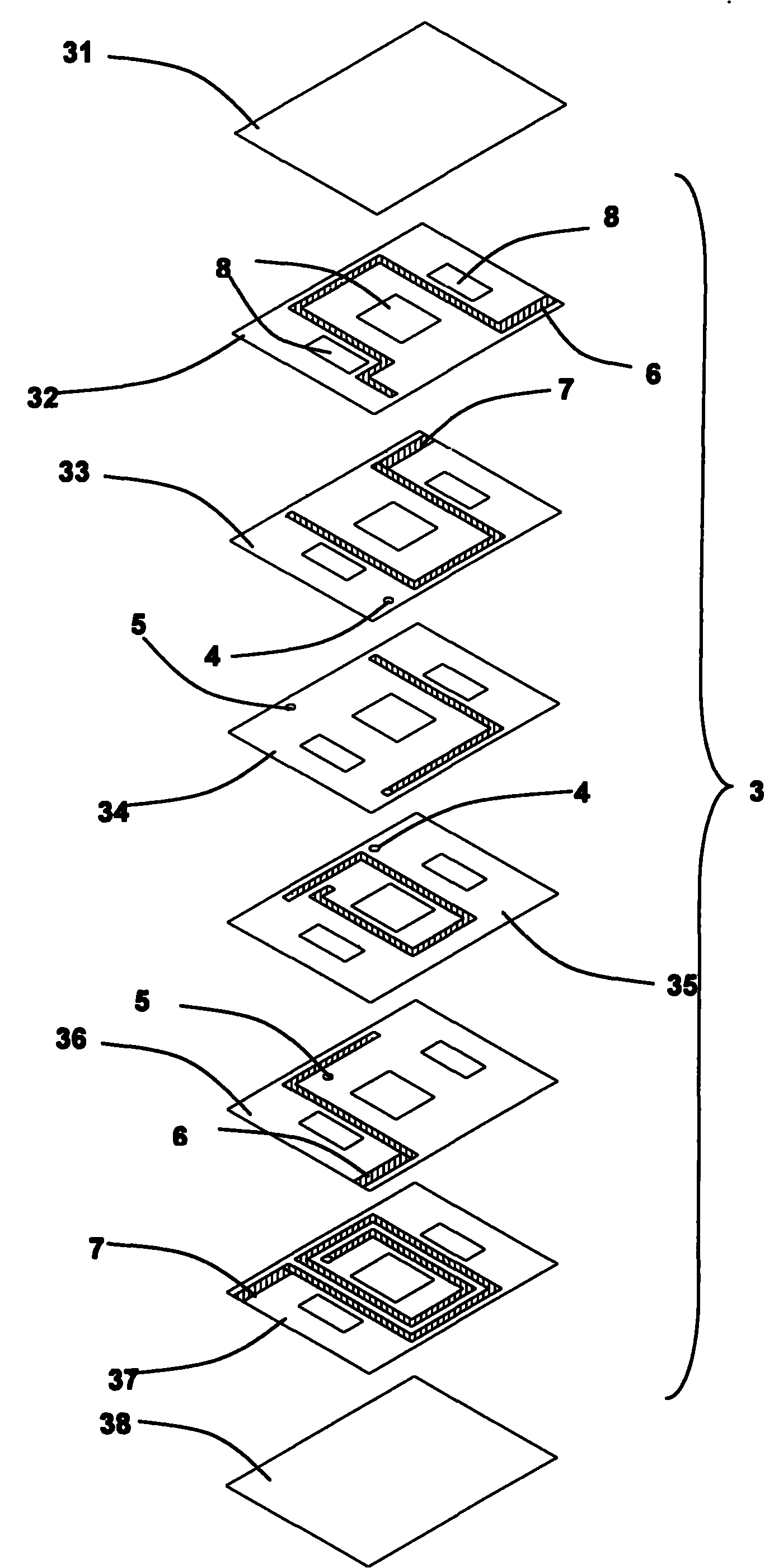
The invention relates to an LTCC low temperature co-fired ceramic planar transformer. The transformer comprises a ferrite magnetic core composed of an upper magnetic core and a lower magnetic core. The transformer is characterized in that the transformer also comprises an LTCC planar transformer base plate provided with at least one group of planar coil component, each planar coil component comprises a primary coil with high coupling coefficient and a secondary coil; the LTCC planar transformer base plate is provided with one or three penetrating holes used for assembling the ferrite magnetic core; and the upper and lower magnetic cores separately penetrate the penetrating holes from the upper and lower sides of the LTCC planar transformer base plate and are butted and adhered together to form the ferrite magnetic core. Compared with the traditional planar transformer, the LTCC low temperature co-fired ceramic planar transformer of the invention has the following beneficial effects: the transformer of the invention has low direct current impedance, leakage inductance and distributed capacitance and can satisfy the design requirement of the resonance circuit; and as the magnetic core has good magnetic shielding, the transformer can inhibit the radio frequency interference.
Owner:SHENZHEN SUNLORD ELECTRONICS
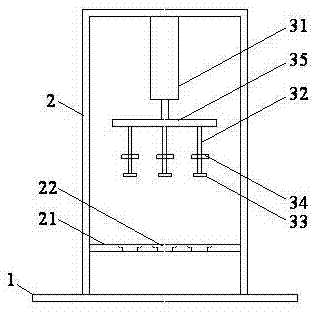
Parallel hydraulic type triaxial sample preparation device and sampling method thereof
ActiveCN102928267AImprove efficiencyEasy to unloadPreparing sample for investigationHollow cylinderEngineering
The invention discloses a parallel hydraulic type triaxial sample preparation device and a sampling method thereof, belonging to the technical field of soil mass mechanics performance testing. The parallel hydraulic type triaxial sample preparation device comprises a base, a door-shaped bracket, a hydraulic system, a sampling cylinder and a counter-force pad, wherein the door-shaped bracket is installed on the base; the hydraulic system is installed on the door-shaped bracket; a horizontal counter-force cross beam is installed at the lower part of the door-shaped bracket; a sample unloading round hole is formed in the counter-force cross beam; the hydraulic system comprises a hydraulic implementer, a pressure transmission rod, a push head, a stopper and a horizontal beam; the sampling cylinder is a cylindrical hollow cylinder body; and the counter-force pad comprises a counter-force cross plate, an upper side bulge and a lower side bulge. With the adoption of the parallel hydraulic type triaxial sample preparation device, the defect that a traditional sample preparation device cannot sufficiently compress the soil mass with uniform density is overcome; not only are the overall density of a sample and the consistency of the samples precisely controlled, but also 1-3 samples can be prepared once with high efficiency; and the samples can be unloaded conveniently.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
Hollow blade as well as manufacturing method and application thereof
InactiveCN108223019AQuality assuranceGuaranteed reliabilityBlade accessoriesMachines/enginesEngineeringMachining
The invention discloses a hollow blade as well as a manufacturing method and application thereof. The hollow blade comprises a cooling structure, an inner cavity and a transition structure, wherein the transition structure is located at the junction of the cooling structure and the wall surface of the inner cavity. Compared with the prior art, the blade avoids a sharp structure of the air film cooling structure of the inner cavity, the machining method can guarantee shape precision and consistency of the blade and the air film cooling structure, and occurrence of the back damage problems is thoroughly avoided from a process route layer, so that the quality and reliability of the blade are guaranteed.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Preparation method of anode active material
The invention provides a preparation method of an anode active material, which comprises the steps of: a, adding a titanium source and an organic carbon source in an organic solution with the pH value of 0-6 to prepare a mixture solution; b, adding an oxidizing agent in the mixture solution, reacting for 1-24h at a temperature of 20-80 DEG C, then separating and settling, washing with water, drying to obtain a titanium-containing precursor; and c, carrying out mixing and ball-milling on the titanium-containing precursor obtained in the step b and a lithium source, and then roasting in an inert gas. A lithium titanate composite material prepared by adopting the method disclosed by the invention has less impurity phases; the prepared nanometer lithium titanate particles are attractive in appearance; and the preparation method has the advantages of short time, low energy consumption, low cost, high yield, uniform particles of the prepared material, stable performance of the prepared material, simple and controllable process, and capability of realizing massive industrialized clean production.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Non-autoclaved lightweight thermal insulation particle aerated concrete block and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a non-autoclaved lightweight thermal insulation particle aerated concrete block and a preparation method thereof. The aerated concrete block comprises the following components:50 to 100 parts of cement, 0 to 37.5 parts of fly ash, 0 to 12.5 parts of superfine slag powder, 0 to 50 parts of light particles, 2 to 8 parts of a foaming agent, 0 to 5 parts of a coagulation accelerator, 0.025 to 0.175 part of a foam stabilizer, 0.2 to 1.4 parts of a water reducing agent, 0.1 to 0.7 part of a water repellent, 0 to 0.6 part of fibers and 30 to 60 parts of water. The aerated concrete block has the advantages of light weight, heat preservation and insulation, energy conservation, high strength, simple maintenance process and low cost, and solves the problems of non-ideal heatpreservation and insulation performance and complex maintenance process of the existing aerated concrete block.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +3
Sunscreen composition and a process for preparing it
InactiveUS7056496B2Control consistencyControlling sensationCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsSilicone ElastomersSun Protection Factors
The present invention includes a process of preparing an advanced cosmetic product by combining a high internal phase ratio (HIPR) emollient-in-water emulsion with a partial cosmetic formulation that typically contains water, a coloring agent, a fragrance, a rheology modifier, or a pH adjuster, or a combination thereof. The present invention also includes compositions directed to two particular subclasses of HIPR emollient-in-water emulsions, namely an HIPR silicone elastomer-in-water emulsion and an HIPR sunscreen-in-water emulsion and water-diluted dispersions thereof. The use of an HIPR emulsion of a cosmetic emollient provides a simple and flexible method of formulating the cosmetic product, due in part to the long shelf-stability of the HIPR emulsion (greater than 1 year), and the low quantity of water in the emulsion (typically less than 20% by volume based on the volume of emollient and water). The HIPR sunscreen-in-water emulsion can be formulated into an advanced cosmetic product with an improved sun protection factor (SPF) and critical wavelength.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Flowing water salt corrosion test device and test method of asphalt mixture
InactiveCN106959253AControl consistencyImprove reliabilityWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesTest chamberEngineering
The invention discloses a flowing water salt corrosion test device and test method of an asphalt mixture. The test device comprises a circular pressurization mechanism, a test chamber, a test bottle, a test piece fixing disc and a test piece fixing mould, wherein the test chamber is arranged on the circular pressurization mechanism; the test bottle is arranged in the test chamber; the test piece fixing disc is arranged in the test bottle; the test piece fixing mould is placed in the test piece fixing disc. The test method comprises the following steps: sample preparation, sample loading, testing, data analyzing, result assessment and the like. The test device and the test method have the beneficial effects that (1) a flowing water salt corrosion test is performed on a plurality of asphalt mixture Marshal test pieces simultaneously, so that the reliability of test data can be remarkably improved, and the test progress is greatly accelerated; (2) the high temperature stability, the low temperature anti-cracking ability, the water stability and the like of the asphalt mixture under a flowing water salt corrosion condition can be studied; (3) according to the test method, the influences of different salt corrosion conditions and vehicle load effects on the pavement performance of the asphalt mixture can be simulated more truly.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Method for assessing settleability and uniformity of lithium ion battery anode slurry
ActiveCN102854084ASimple methodEasy to operateWeighing by removing componentCentrifugationRelative standard deviation
The invention discloses a method for assessing settleability and uniformity of lithium ion battery anode slurry. The method comprises the following steps of taking samples from different positions of lithium ion battery anode slurry, detecting solid contents of upper and lower layers in a centrifuge tube by a centrifugation method and assessing settleability and uniformity of the lithium ion battery anode slurry according to relative standard deviation of the solid contents. The method has the advantages of simple processes, convenient operation, good reappearance, accurate data and high analysis efficiency and can be widely used in industries.
Owner:SHENZHEN DYNANONIC
Sintered NdFeB magnet having high integral magnetic performance and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108320902AImprove adhesionImprove liquiditySolid state diffusion coatingInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureAdhesion forceRare-earth element
The invention relates to a preparation method of a sintered NdFeB magnet having high integral magnetic performance. The preparation method comprises the following steps of (1) pre-processing a surfaceof the magnet; (2) uniformly spraying a layer of homogeneous paste containing a heavy rare-earth element, an adhesion force improvement agent and a plasticizer onto the surface of the magnet; and (3)performing drying, wherein a flexible coating layer with high adhesion force is formed on the surface of the sintered NdFeB magnet, and high-temperature permeation diffusion thermal processing and low-temperature tempering are performed on the magnet uniformly coated with the flexible coating layer. By forming the flexible coating layer on the surface of the sintered NdFeB magnet, the problem ofplating layer falling caused by turnover spraying of the magnet during mass production process is solved, and industrial preparation of the sintered NdFeB magnet having high integral magnetic performance can be achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHEENSEN MAGNETICS TECH CO LTD
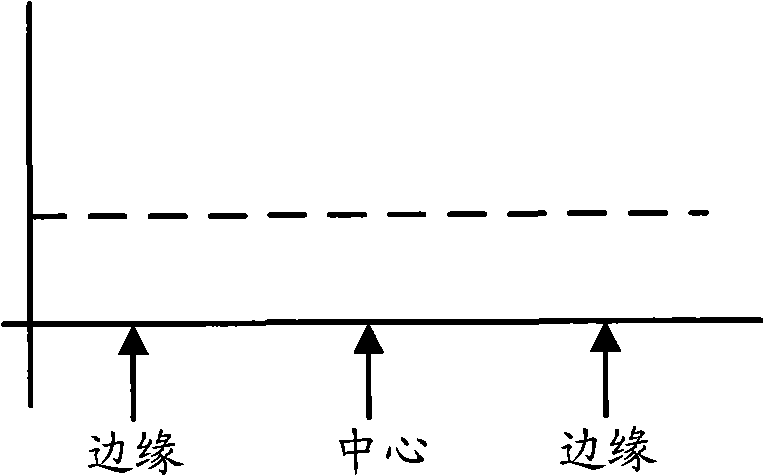
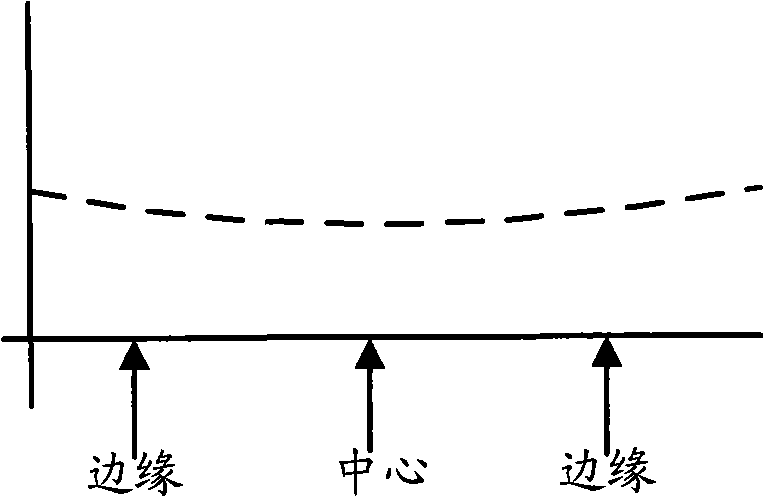
Photo-etching method
InactiveCN101344721AImprove uniformityControl consistencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical coating apparatusEngineeringPhotoresist
The invention discloses a lithography method, relating to the semiconductor manufacturing field and aiming at overcoming the defect of the traditional lithography method that the evenness of etched patterns is poor. The lithography method of the invention includes the following steps: a wafer to be processed is provided; photoresist is plated on the surface of an etched layer of the wafer and the thickness of the photoresist at the center of the wafer is different from that of the peripheral parts of the wafer; an exposure step is carried out; a development step is carried out; an etching step is carried out; and the remaining photoresist is removed. Compared with the prior art, the method can obtain a circuit pattern with better evenness and the unification for the etched patterns can be further controlled for the distortion states of position patterns on the wafer are identical and then the traditional methods such as the correction methods of optical approaching correction and exposure machine approaching correction, etc., can be conveniently adopted.
Owner:GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Interface, method and communication system for implementing interface data consistency
ActiveCN101119408AControl consistencyResolve gradingSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsTransmissionCommunications systemComputer module
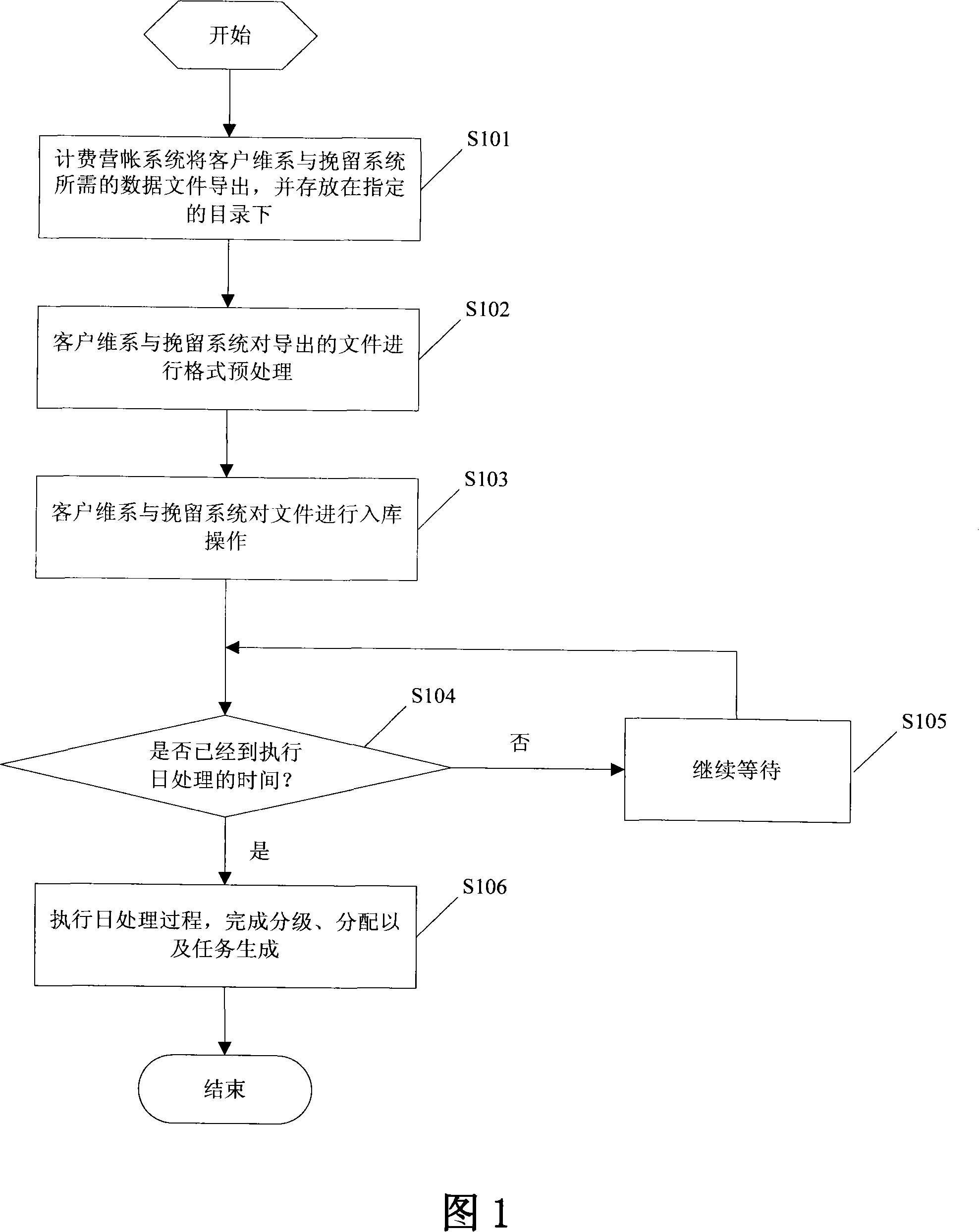
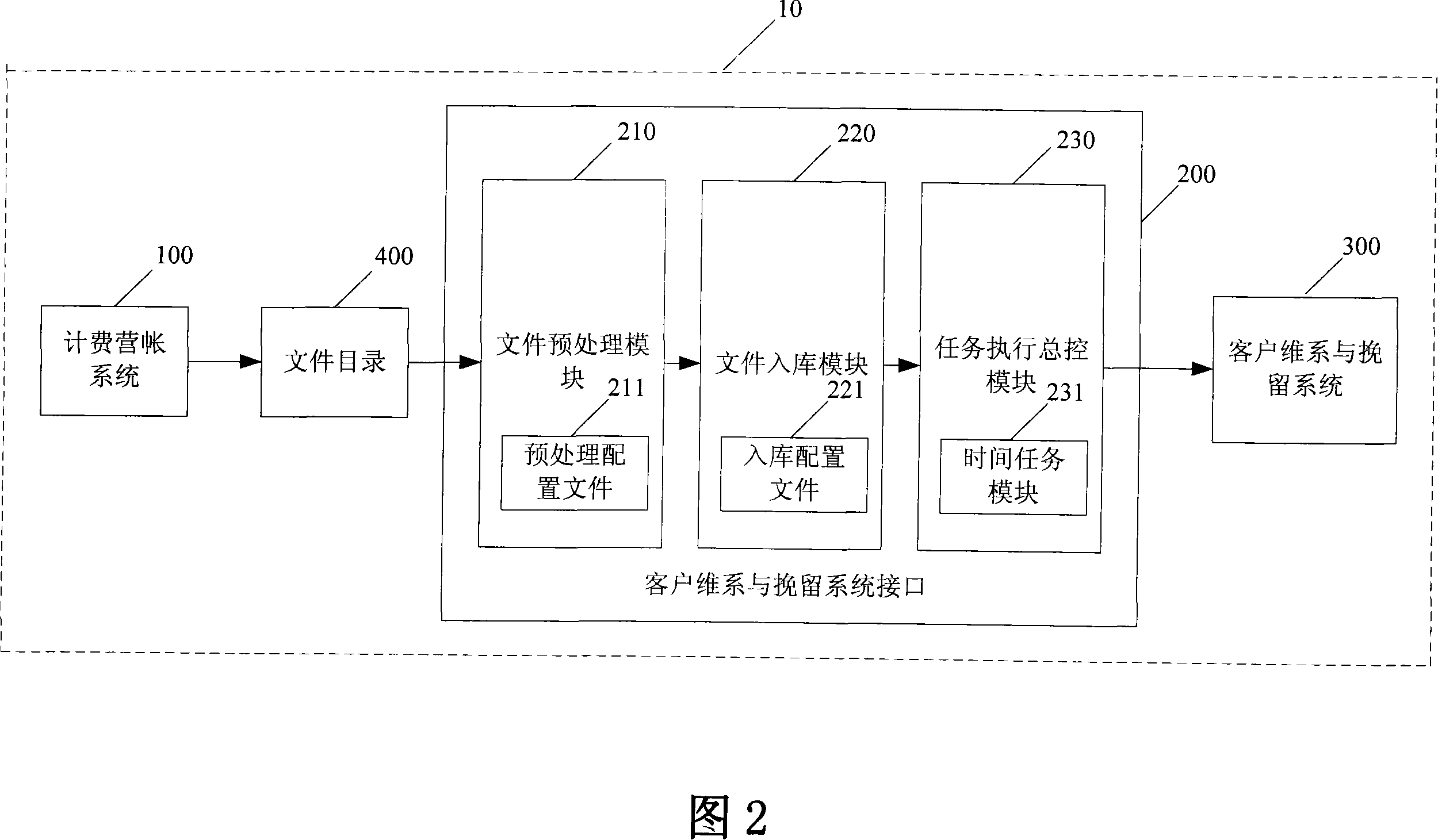
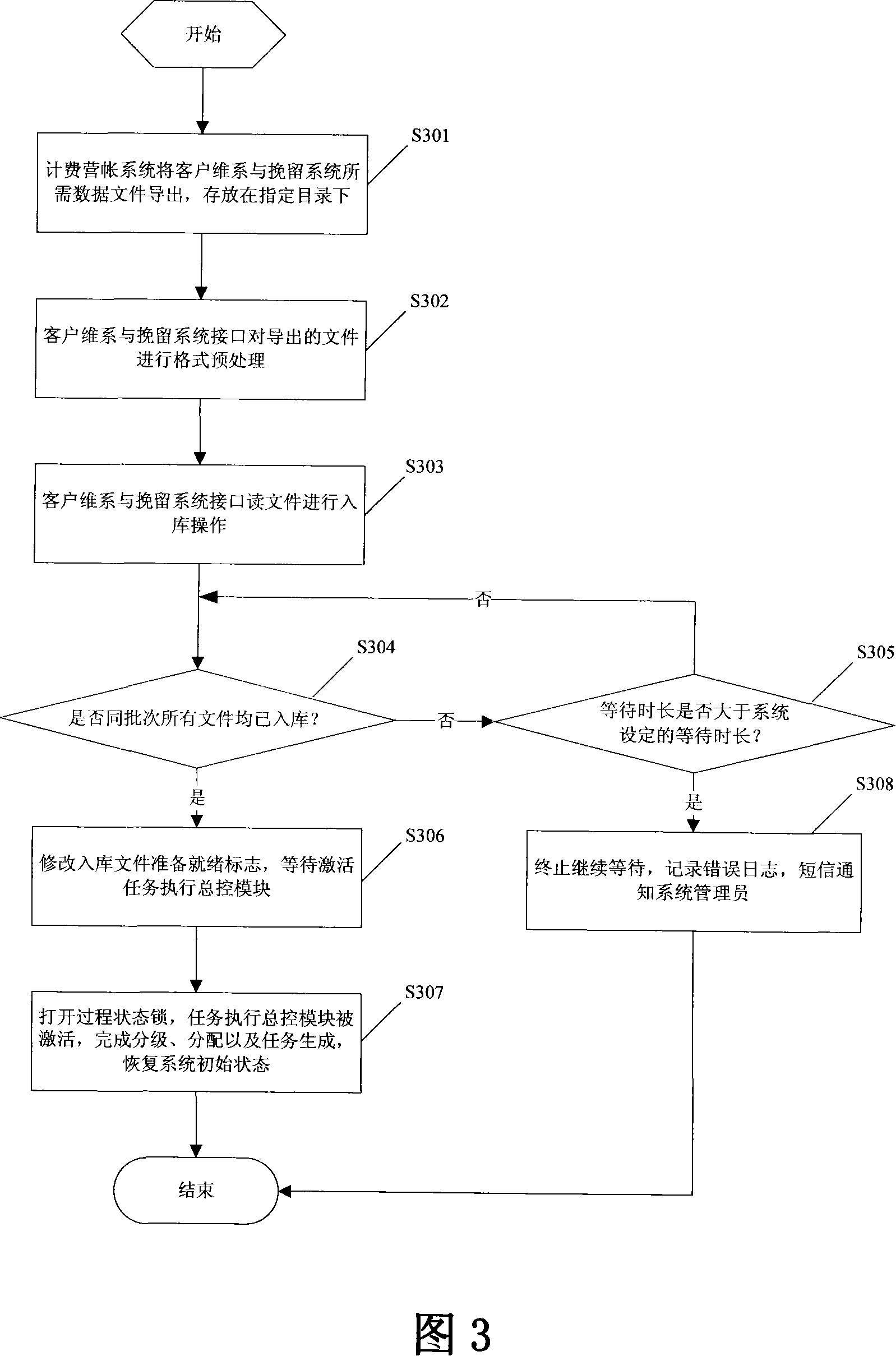
The present invention provides an interface, method and communication system which can realize the consistency of the interface data. The interface and accounting system is connected with the client retention and detention system. Wherein, the invention comprises a file pretreatment module for performing the format pretreatment to the information files which is outputted from the accounting system and required by the client retention and detention system and transforming the file format into the distinguishable format of the file entering module; a file entering module which imports the file after format pretreatment into a temporary interface table, after the file entering is finished, the file entering module modifies the ready sign of the file in the database to the finished state; a task execution central control module which timely reads the ready signs of the files in the database, once the ready sign becomes the finished state, the task execution central control module activates the subsequent task processing of the files and coordinates the execution of the subsequent task, after the task is finished successfully, the task execution central control module recovers the ready signs of the files.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF STATE GRID QINGHAI ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY
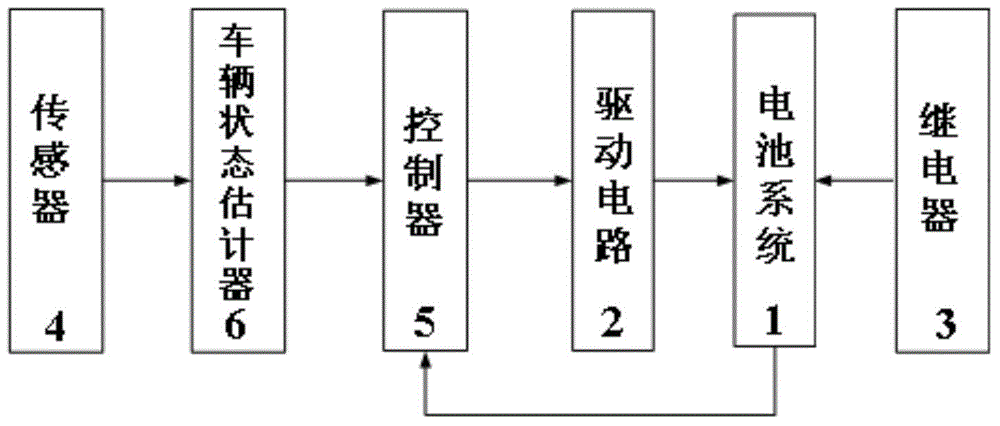
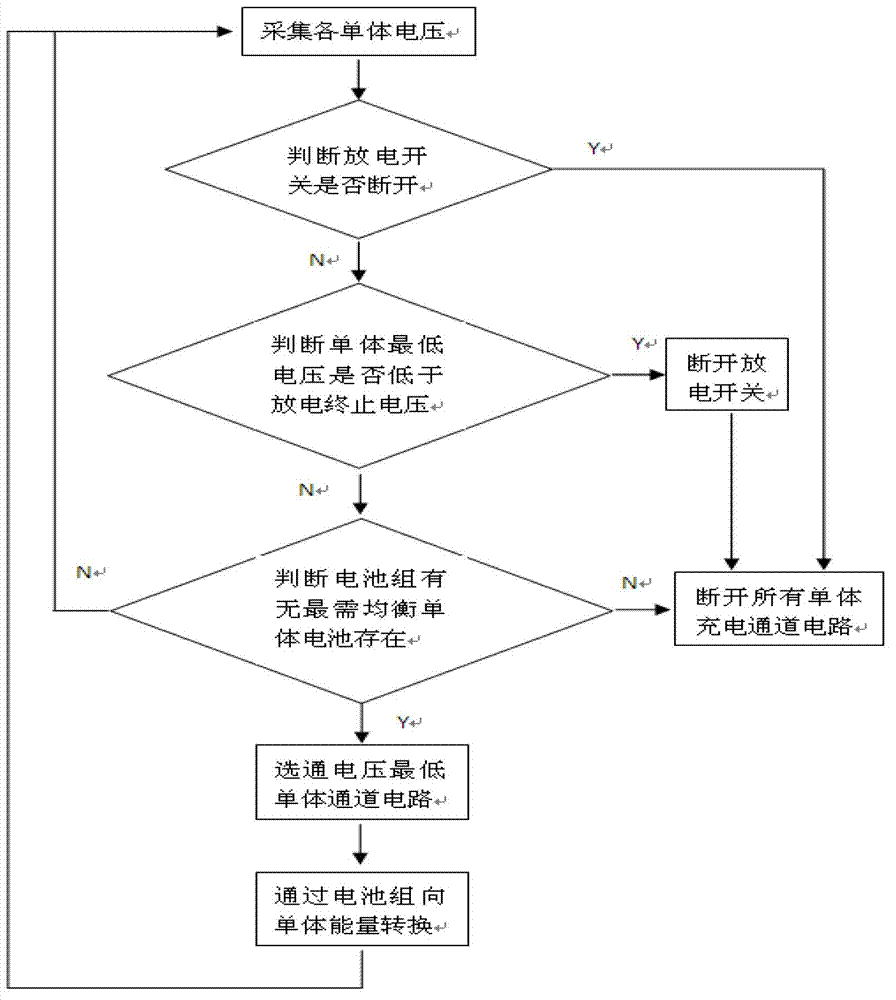
Safety system of electric car battery unit structure, and control method thereof
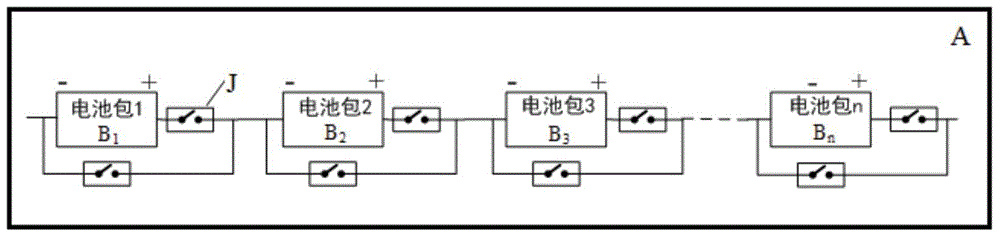
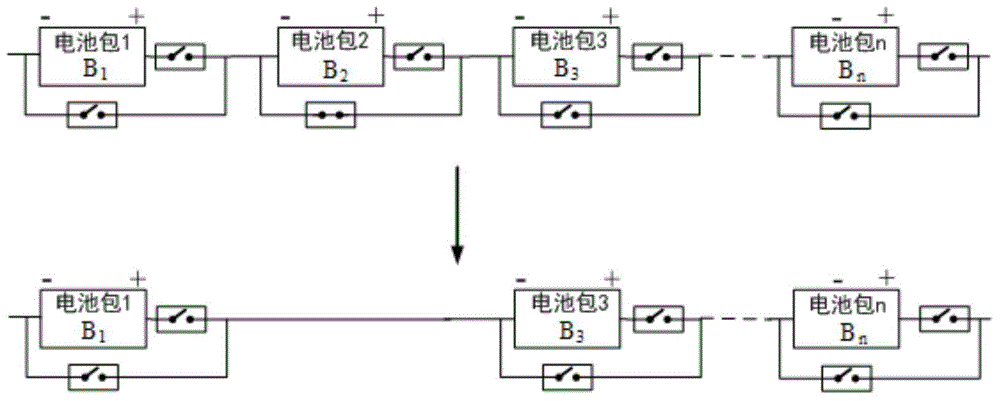
PendingCN106711519AControl consistencyReduce the voltage levelSecondary cells charging/dischargingCell component detailsUnit structureSafe system
The invention provides a safety system of an electric car battery unit structure, and a control method thereof. The safety system comprises a battery system, a driving circuit, a relay, a sensor, a controller and a car state estimator. The battery system comprises a battery box layer, a battery bag layer and a battery module layer. Turn-on or cut-off of battery units in the charge / discharge process guarantees the consistence of the battery units; transformation of the connecting mode of the battery system in the parking process reduces the voltage of the battery system and prevents latent high voltage dangers; and connection of battery cells is broken when battery liquid leakage, insulation damage or local short circuit appears in the running process in order to prevent the high voltage dangers, and some battery units are selectively cut off in the bumping process according to the bumping degree in order to prevent the high voltage dangers.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Surface mounting light-emitting diode (LED) with high sealing property and production method thereof
InactiveCN102194983AIncrease brightnessIncrease lumen valueSemiconductor devicesSurface mountingEffect light
The invention is suitable for the technical field of a light-emitting diode (LED) and discloses a surface mounting LED with a high sealing property and a production method thereof. The surface mounting LED with the high sealing property comprises a bracket and a chip arranged on the bracket, wherein the bracket is provided with a big bowl part and a small bowl part which are up-and-down stacked and communicated; the big bowl part is located above the small bowl part; the chip is attached in the small bowl part; the small bowl part is also internally provided with packaging colloid covering on the chip; and the big bowl part is internally provided with a seal colloid covering on the packaging colloid. The production method of the surface mounting LED with the high sealing property comprises the following steps: arranging the bracket which comprises the big bowl part and the small bowl part which are up-and-down stacked and communicated, and mounting the chip inside the small bowl part; then injecting packaging colloid to the inside of the small bowl part, and then injecting seal colloid to the inside of the big bowl part. According to the surface mounting LED with the high sealing property and the production method thereof, the lighting effect of the product is excellent, and the reliability of the product is good.
Owner:SHENZHEN REFOND OPTOELECTRONICS
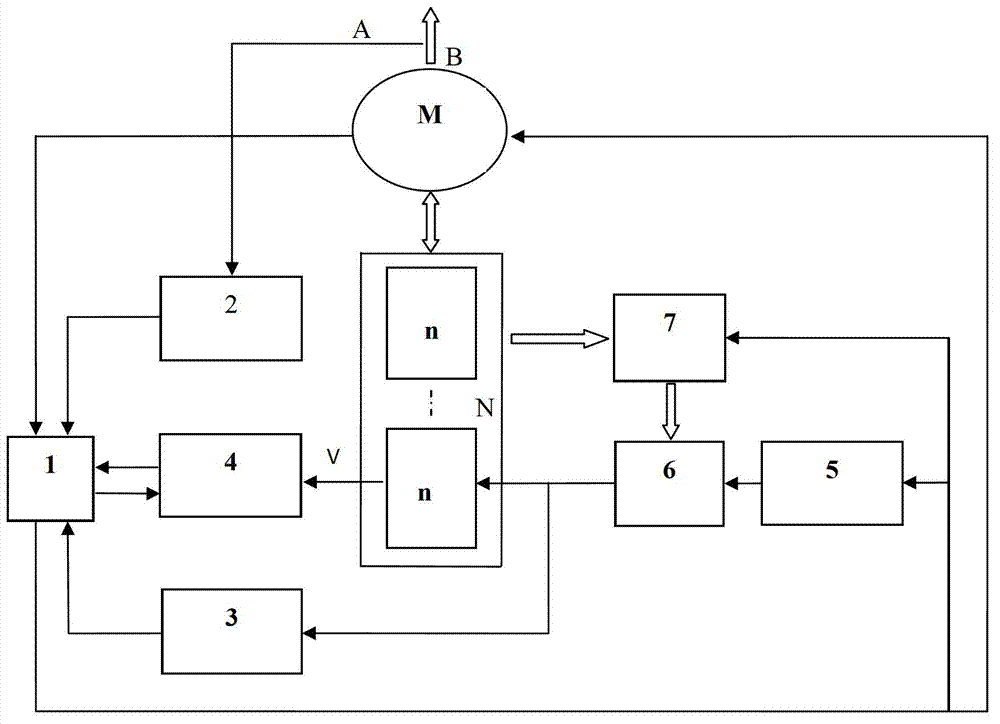
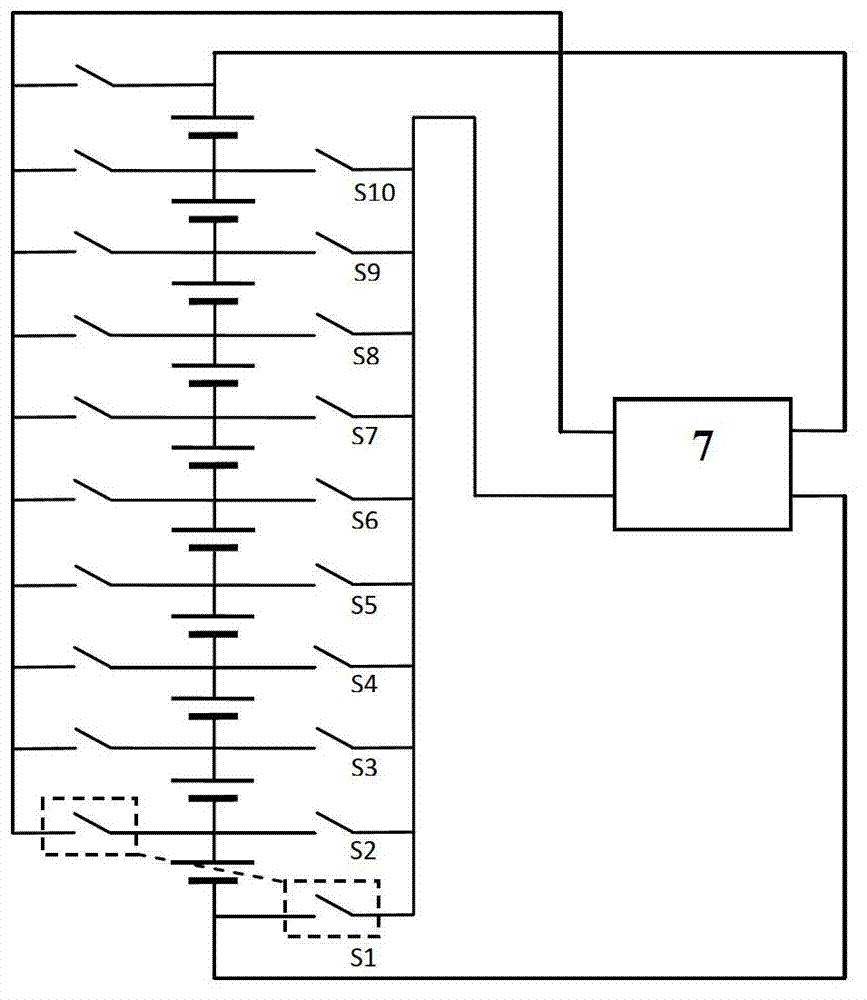
Voltage dynamic balance management system of power lithium battery pack
InactiveCN102761165APrevent overchargingPrevent overcurrentBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerElectrical batteryMicroprocessor
The invention provides a voltage dynamic balance management system of a power lithium battery pack, which relates to a charging and discharging balancing circuit of a series power battery pack. The voltage dynamic balance management system comprises a microprocessor, Hall sensor modules, channel selecting modules, a switch driving circuit module and a DC / DC (Direct Current / Direct Current) transformer, wherein the microprocessor is used for gating a single battery in the battery pack by a first channel selecting module; an input end of the DC / DC transformer is connected with two ends of the battery pack; an output end of the DC / DC transformer is connected with two ends of the single battery by the switch driving circuit module and the switch driving circuit module; an input end of a first Hall sensor module is connected with a charging current input end and a discharging current output end of a charging and discharging switch; an output end of the first Hall sensor module is connected with the microprocessor; an input end of a second Hall sensor module is connected with a balancing charging current output end of the switch driving circuit module; an output end of the second Hall sensor module is connected with an input port of the microprocessor; an input end of the switch driving circuit module is connected with an output end of a second channel selecting module; and an output end of the circuit driving circuit module is connected with two ends of the single battery of the battery pack.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Thermal cover plate used in nucleic acid amplification detector
ActiveCN103725602AAccurate compensationControl consistencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringNucleic acid
The invention relates to a thermal cover plate used in a nucleic acid amplification detector. The thermal cover plate comprises an upper cover plate and a lower press plate which are horizontally and oppositely arranged, wherein the upper cover plate and the lower press plate are fixedly connected through at least two springs; at least two probes are fixedly mounted on the lower press plate; displacement sensors capable of quantitatively measuring the displacement of the probes relative to the upper cover plate are fixedly mounted on the upper cover plate; the number of the displacement sensors is equal to that of the probes and the mounting positions of the displacement sensors correspond to those of the probes; at least one heating component and at least one temperature sensor which is capable of detecting the temperature of the lower press plate are fixedly mounted on the lower press plate. The problem that the nucleic acid reaction can be failed as the pressure cannot be controlled due to the fact that the conventional nucleic acid amplification detector is lack of a device which can accurately control the pressure is solved, and the pressure and the temperature can be accurately controlled.
Owner:CHANGZHOU FUSHENG BIOTECH
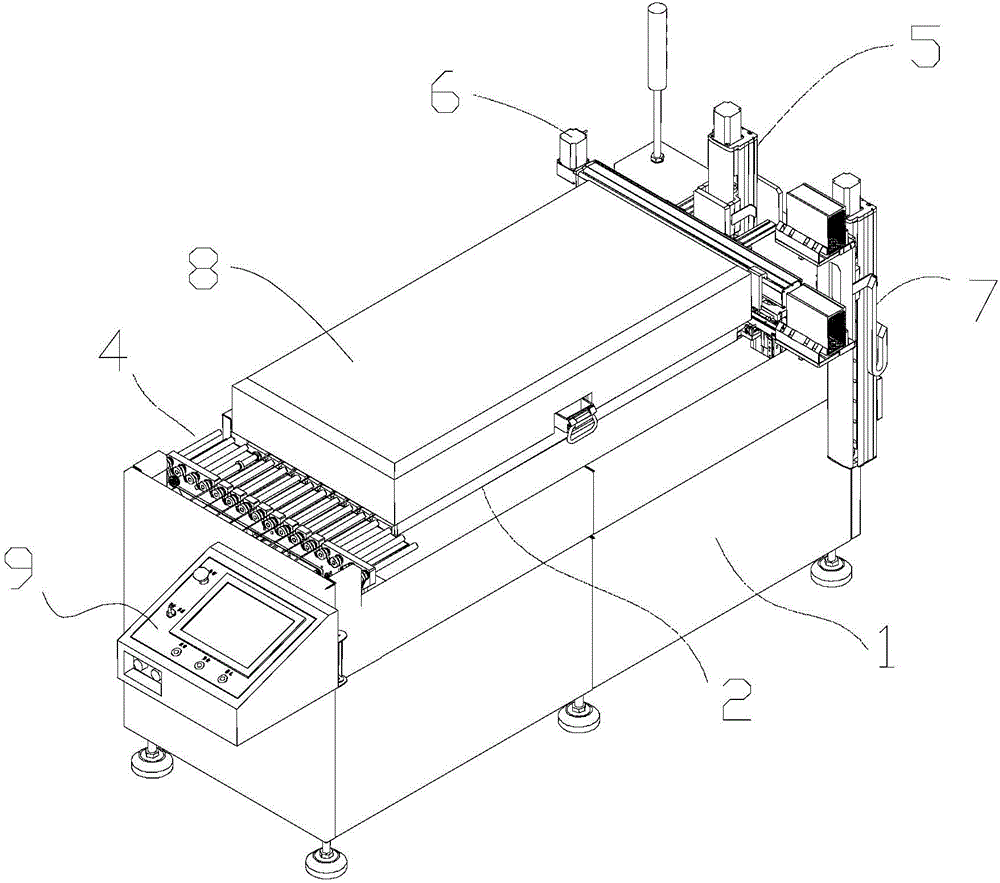
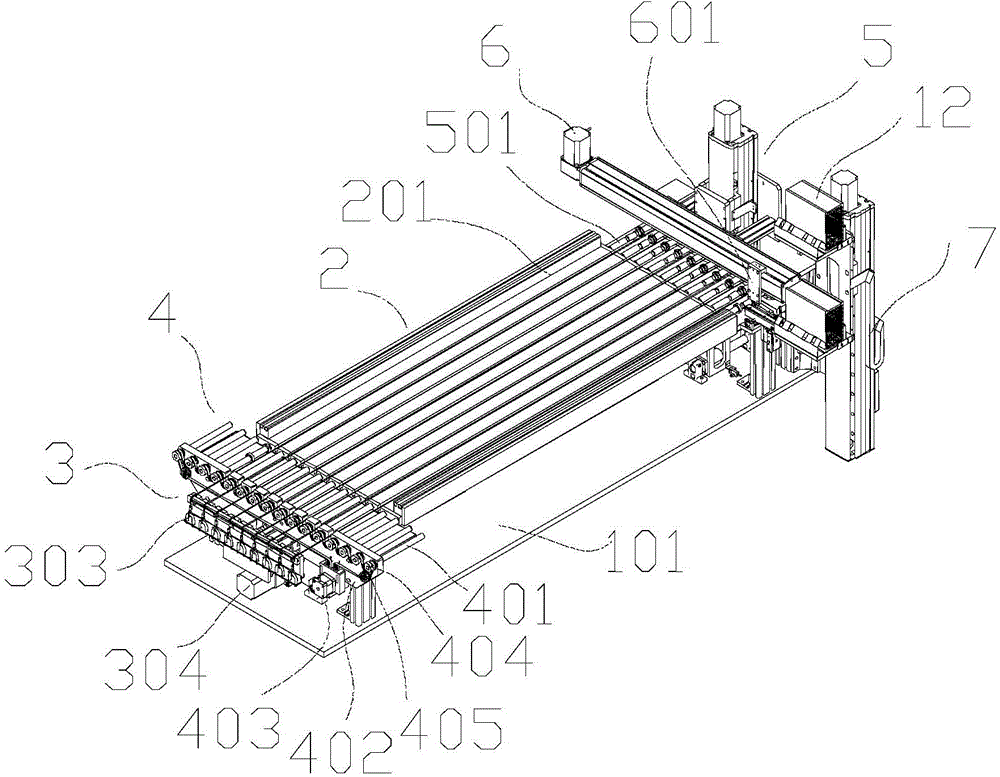
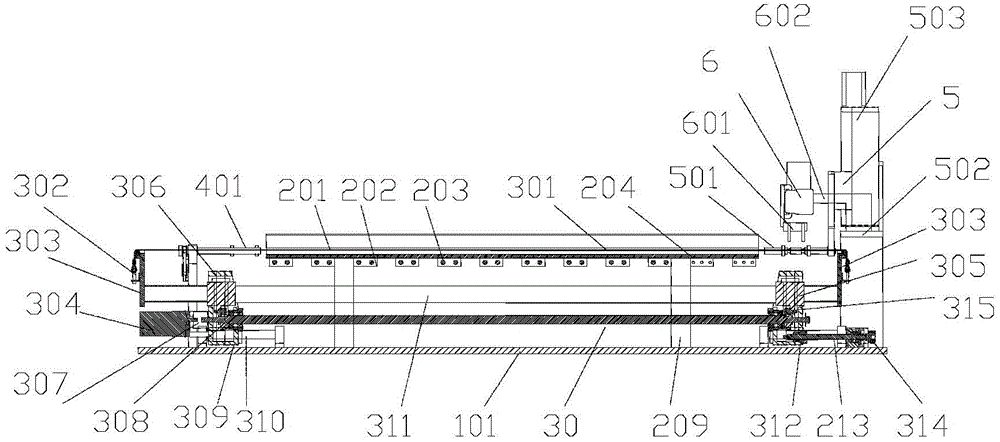
Tunnel-type hardening furnace for semiconductor device
ActiveCN104576454ATemperature controlControl consistencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectricityPower semiconductor device
The invention discloses a tunnel-type hardening furnace for a semiconductor device. The tunnel-type hardening furnace for the semiconductor device is characterized by comprising a hardening surface base platform, a heating platform, a conveying mechanism, a furnace cover and an electric control platform, wherein the heating platform is arranged on the hardening surface base platform and is used for heating the semiconductor device; the conveying mechanism spans over two ends of the heating platform and conveys the semiconductor device to the heating platform by using a steel wire as a conveying tool; the furnace cover is arranged on the heating platform and is used for forming a tunnel-type heating chamber in the hardening surface base platform; the electric control platform is electrically connected with the heating platform and the conveying mechanism and is used for controlling heating and automatic conveying of the hardening furnace. According to the tunnel-type hardening furnace for the semiconductor device, manpower can be saved, the production efficiency can be improved, and meanwhile, the consistency of product quality is controlled.
Owner:广东歌得智能装备有限公司
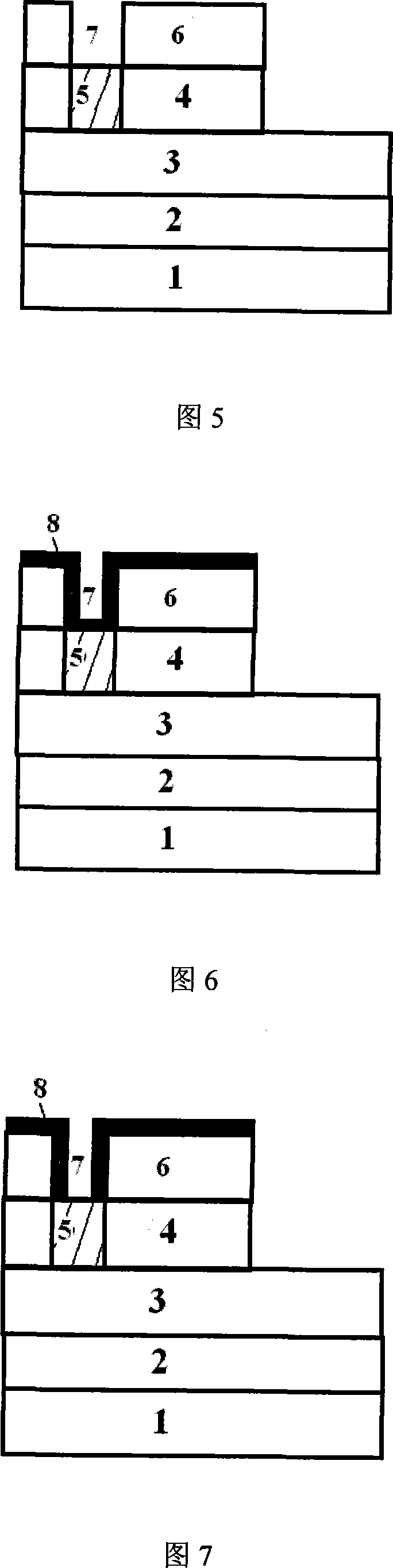
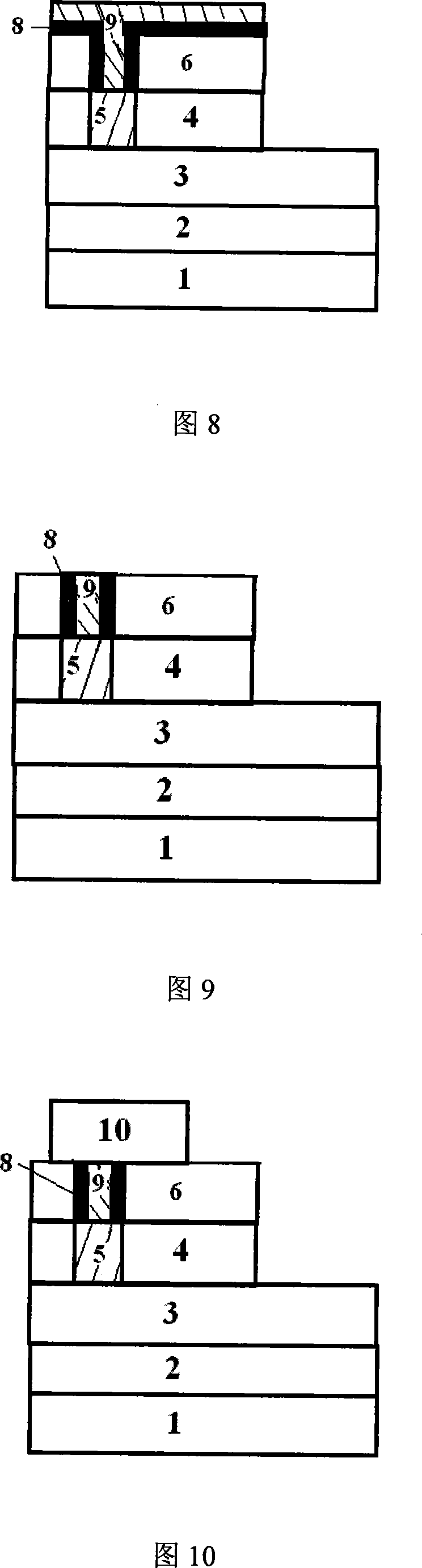
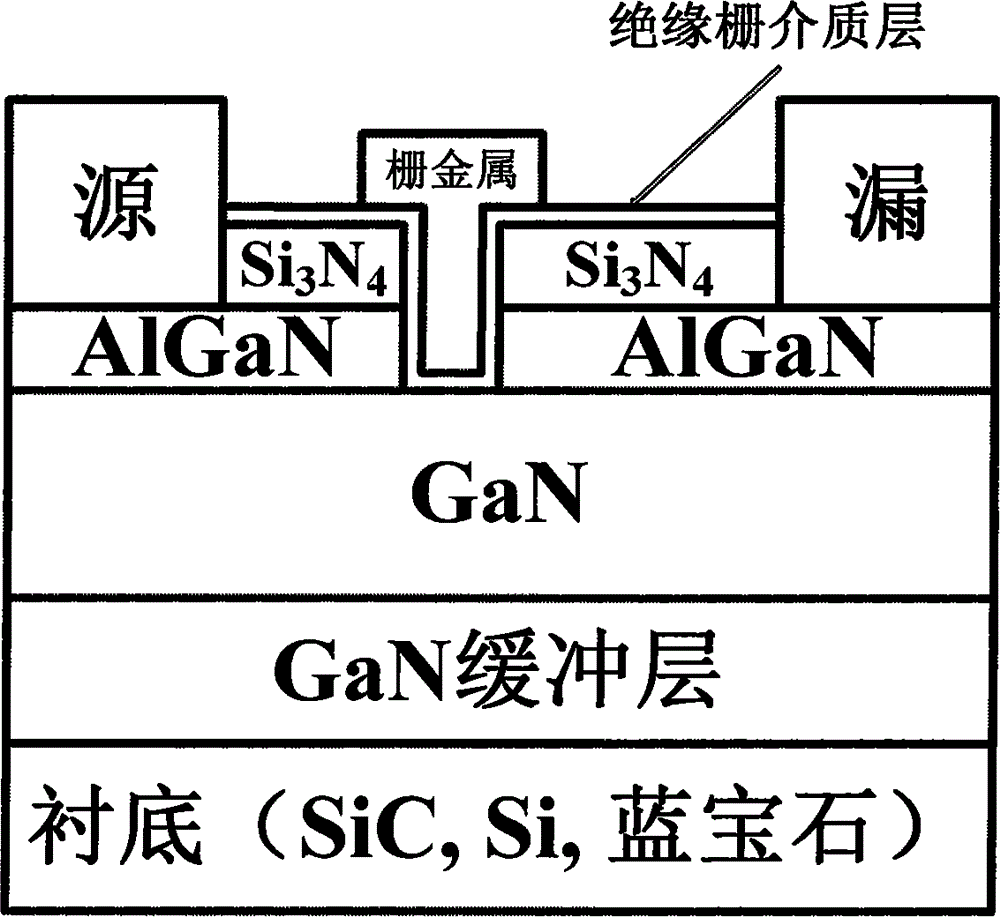
GaN-enhanced MOSFET formed based on digital wet grating etching technology and preparation method
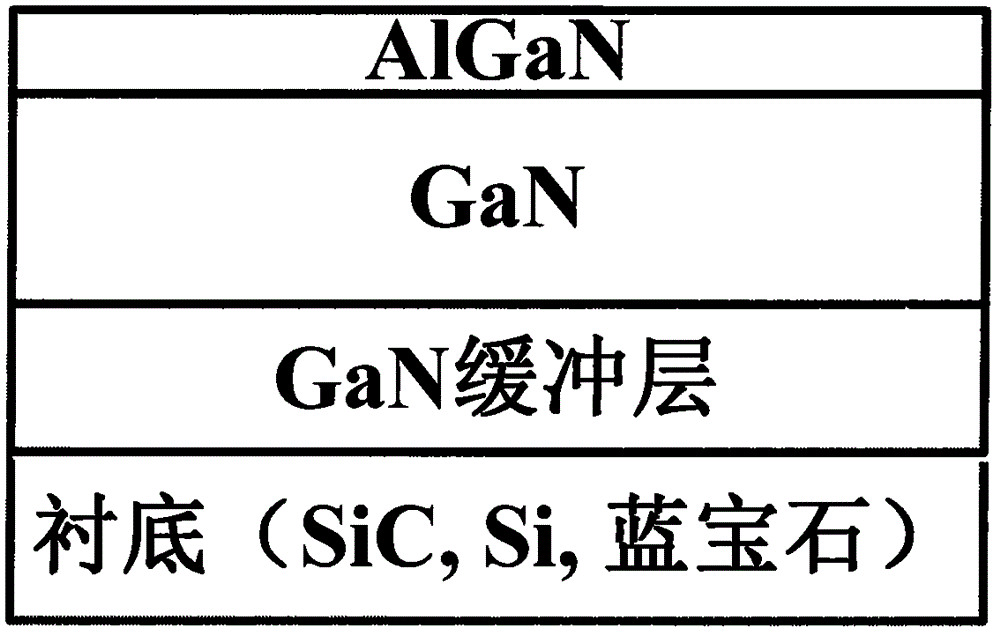
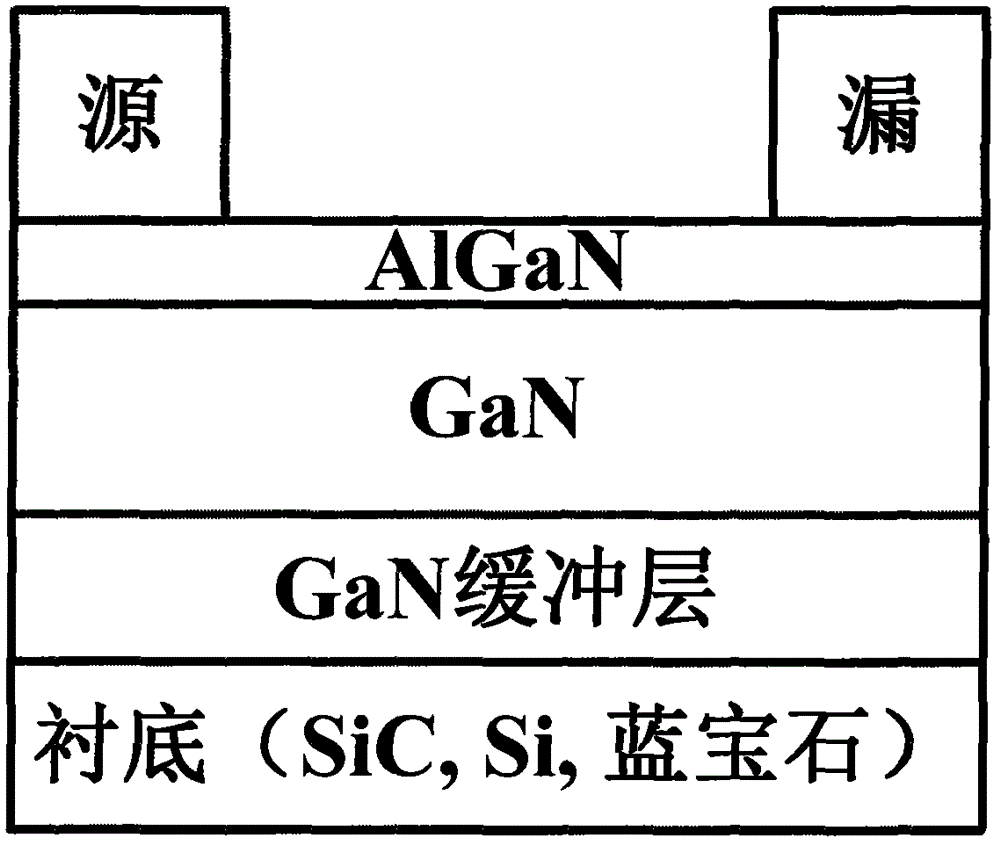
InactiveCN106158960AAvoid damageImprove surface topographySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETEtching
The invention provides a GaN-enhanced MOSFET formed based on a digital wet grating etching technology and a preparation method, and relates to the field of power electronic devices and high-efficiency power switches of wide-band-gap compound semiconductor materials. The GaN-enhanced MOSFET comprises a substrate, a GaN buffer layer, GaN, AlGaN, an etching mask dielectric layer and an insulated gate dielectric layer from bottom to top; a gate area is defined on the surface of a wafer; the etching mask dielectric layer below the gate area is etched away and the AlGaN layer is etched away by a wet process; and a source region and a drain region are arranged on the surface of the AlGaN to form a source and a drain respectively. The GaN-enhanced MOSFET has the beneficial effects that a gate trench area is etched by the wet process, so that the plasma damage is avoided, the surface shape and form of a gate trench are relatively good, the maximum leakage current density is improved, and the consistency of the grating etching depth and the threshold voltage can be controlled. The developed high-performance wet etching-based GaN-enhanced device can be used for the high-efficiency power switch and an RF power device.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com