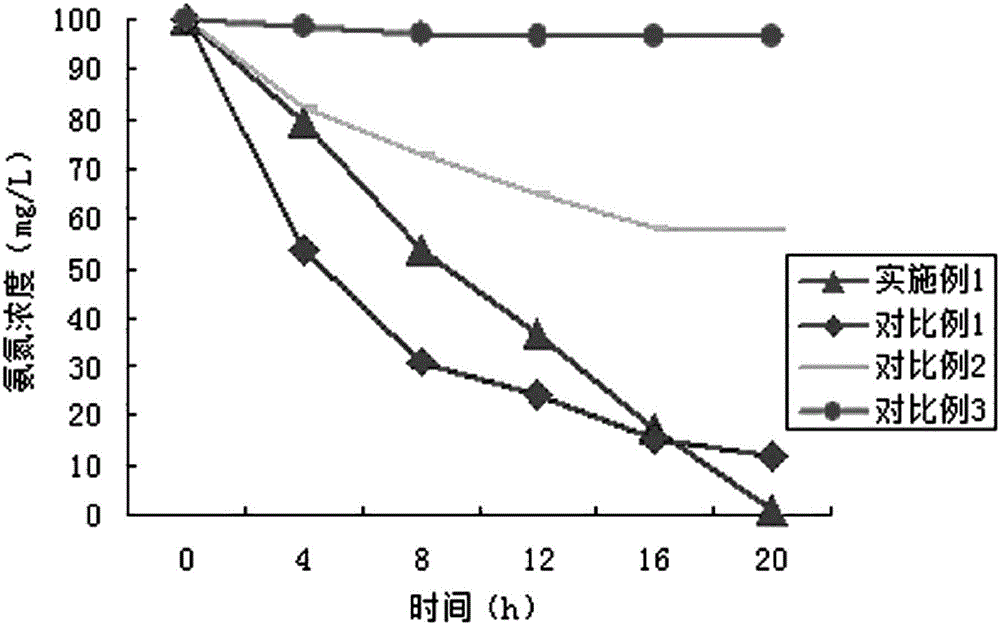
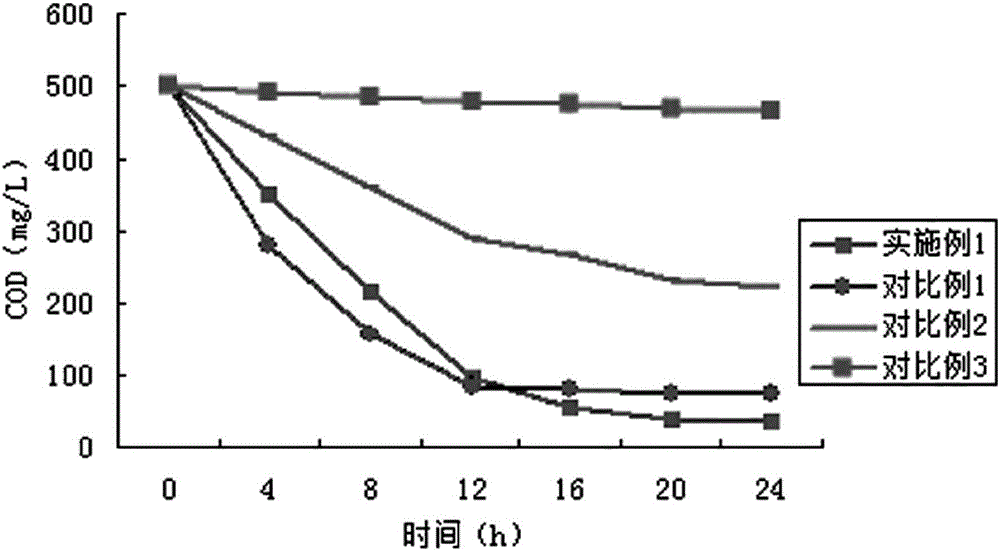
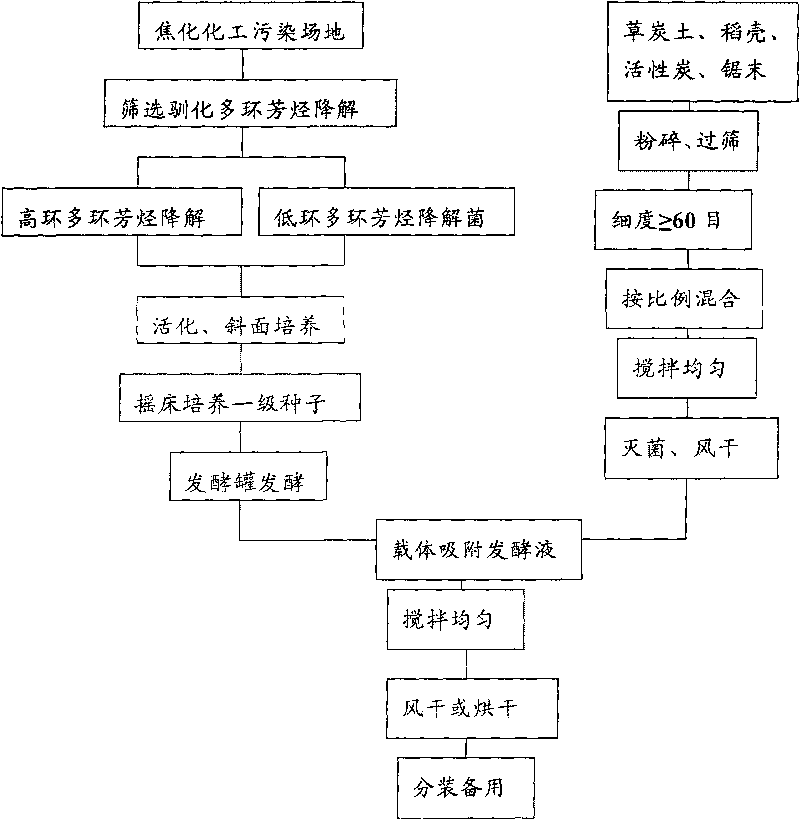
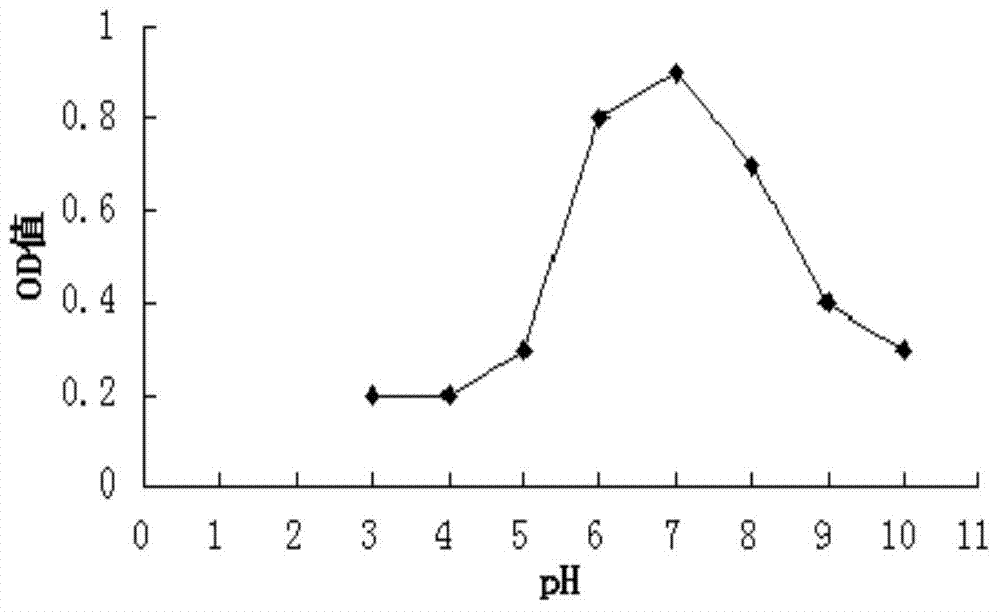
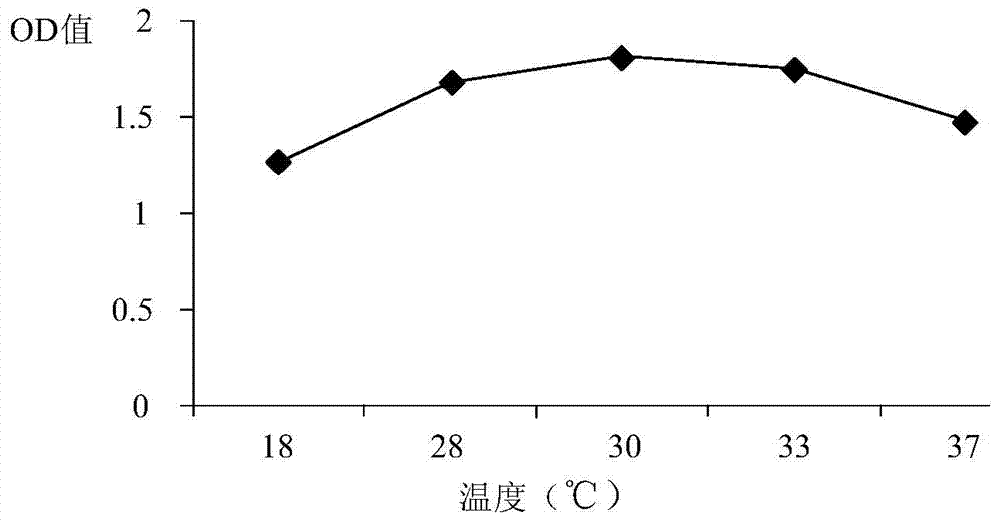
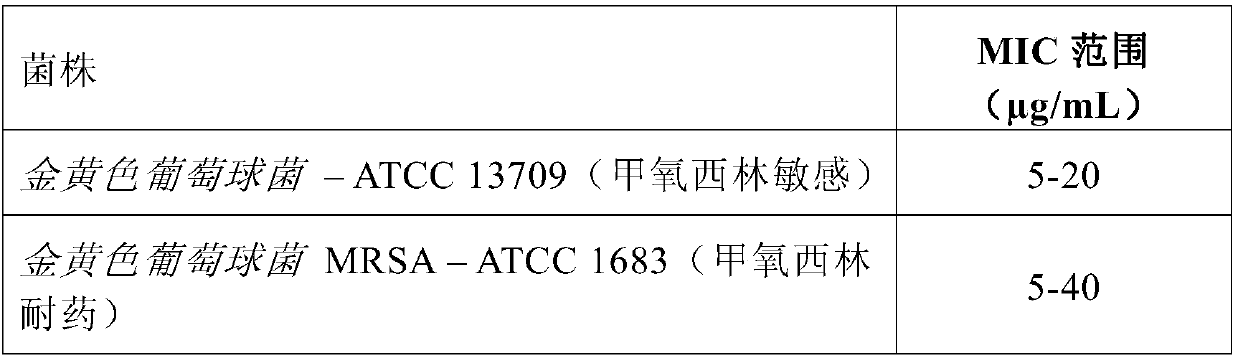
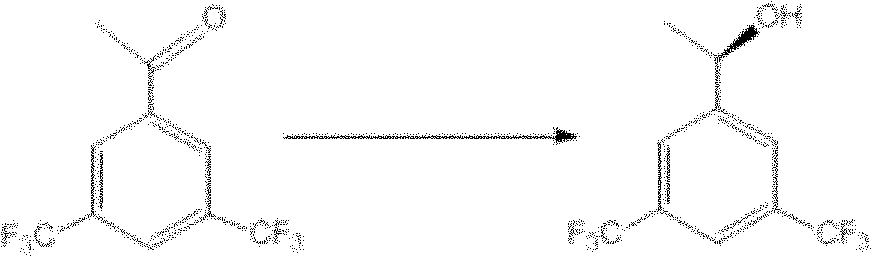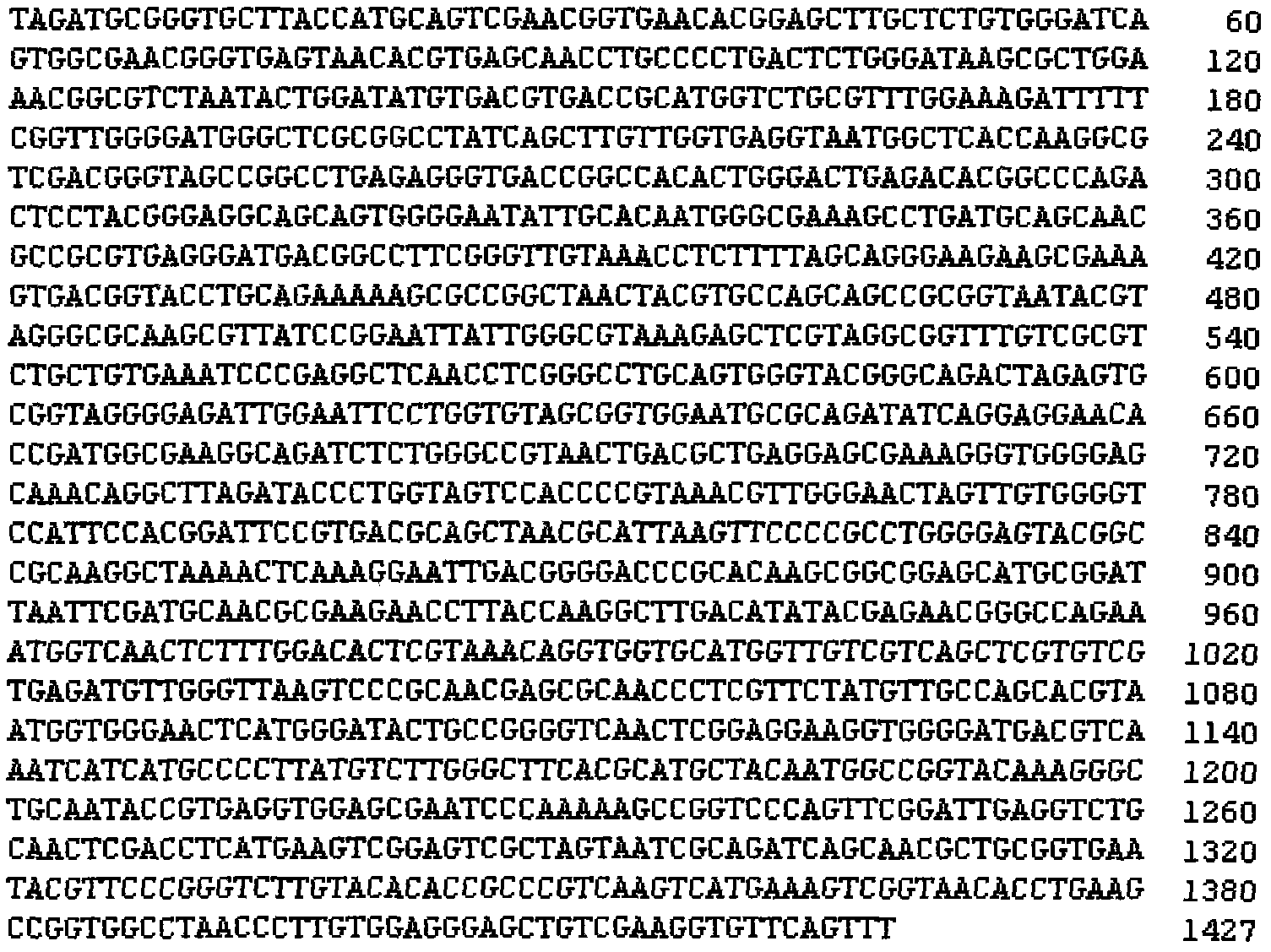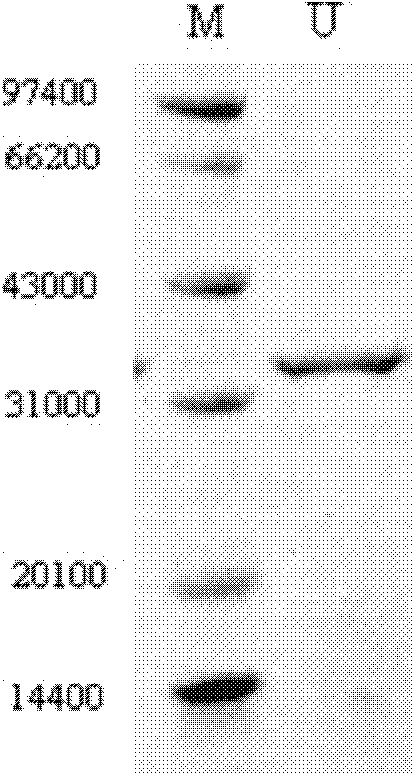Patents
Literature
69 results about "Microbacterium species" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
As of 2015, it contains 96 species: Microbacterium aerolatum. Microbacterium agarici. Microbacterium amylolyticum. Microbacterium aoyamense. Microbacterium aquimaris. Microbacterium arabinogalactanolyticum. Microbacterium arborescens.
Microbacterium oxydans for degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and application thereof
ActiveCN104342392ALow viscosityLow freezing pointBacteriaTransportation and packagingPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonMicrobial enhanced oil recovery
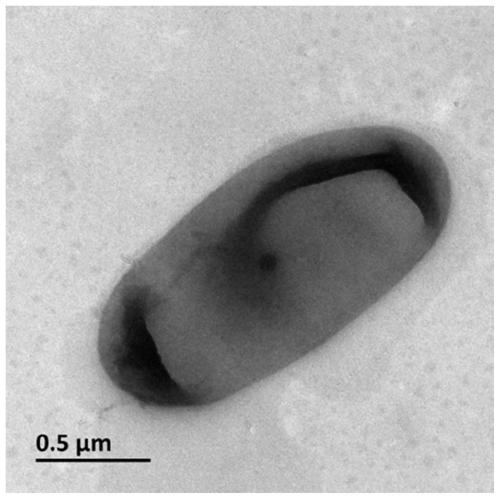
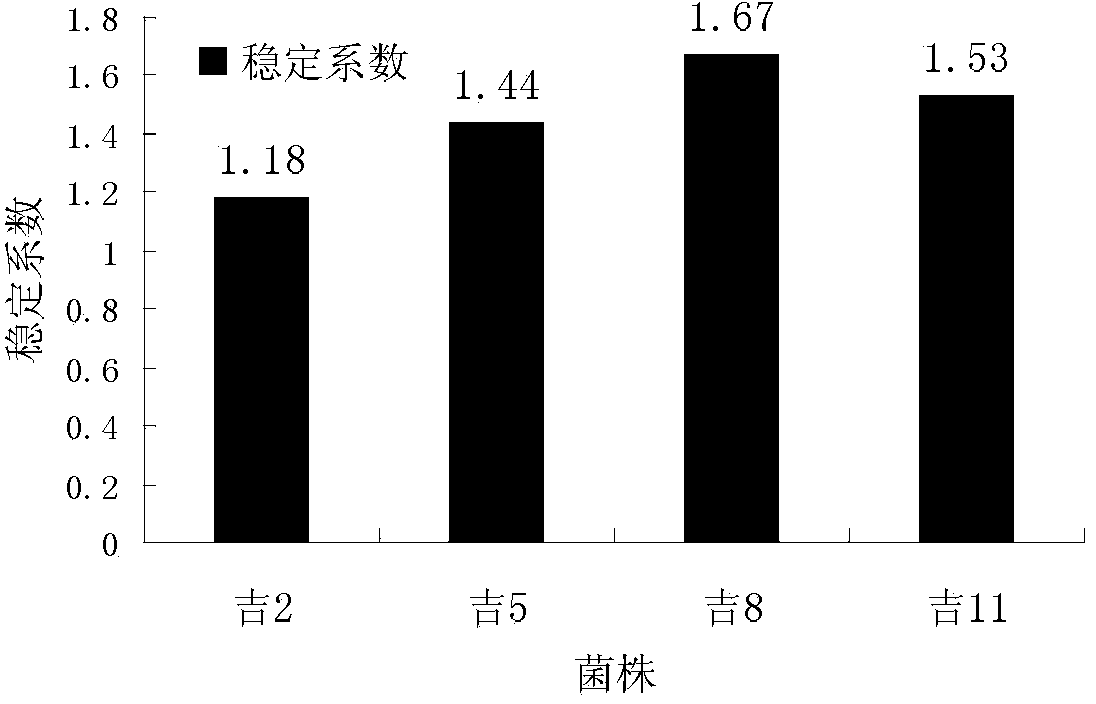
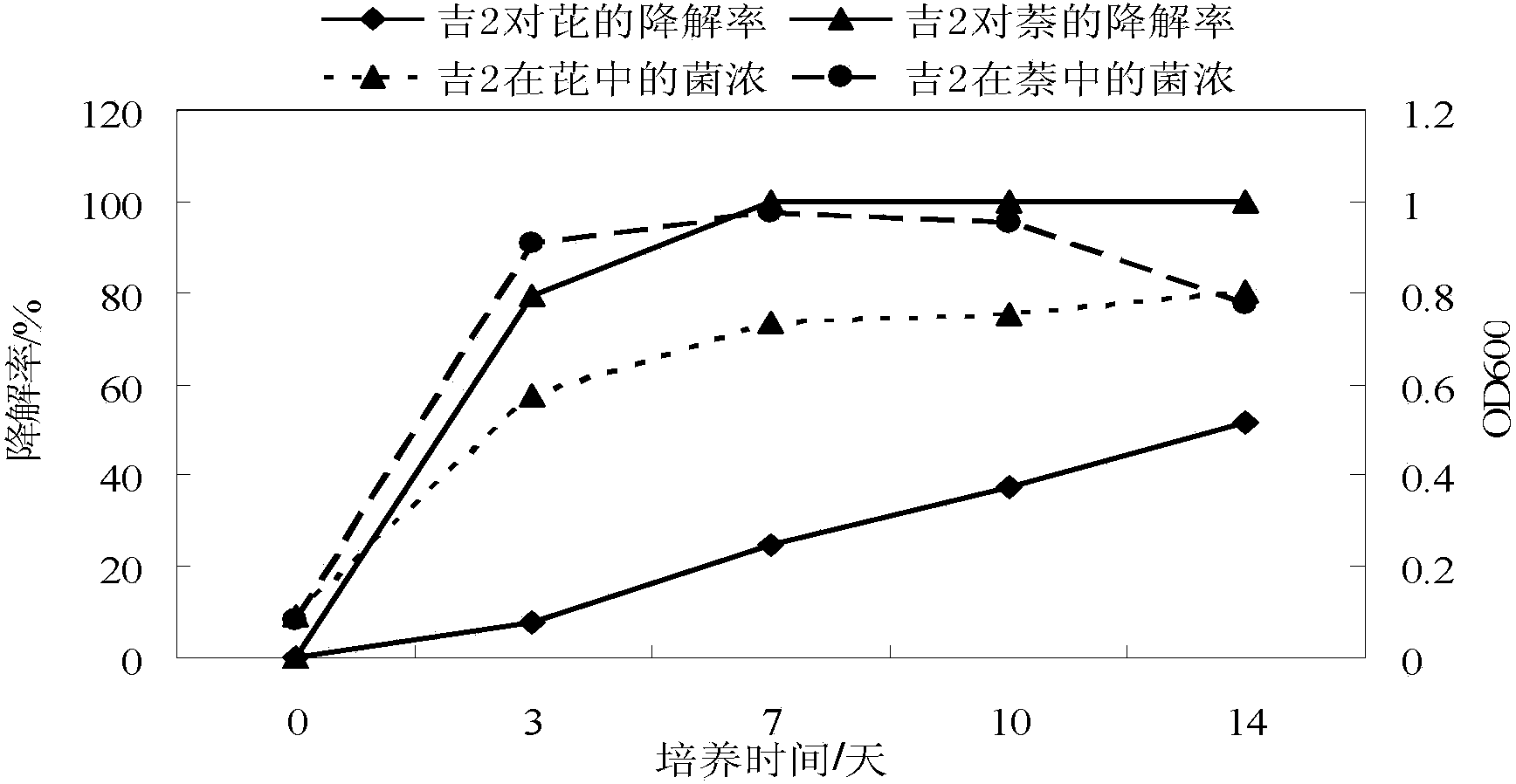
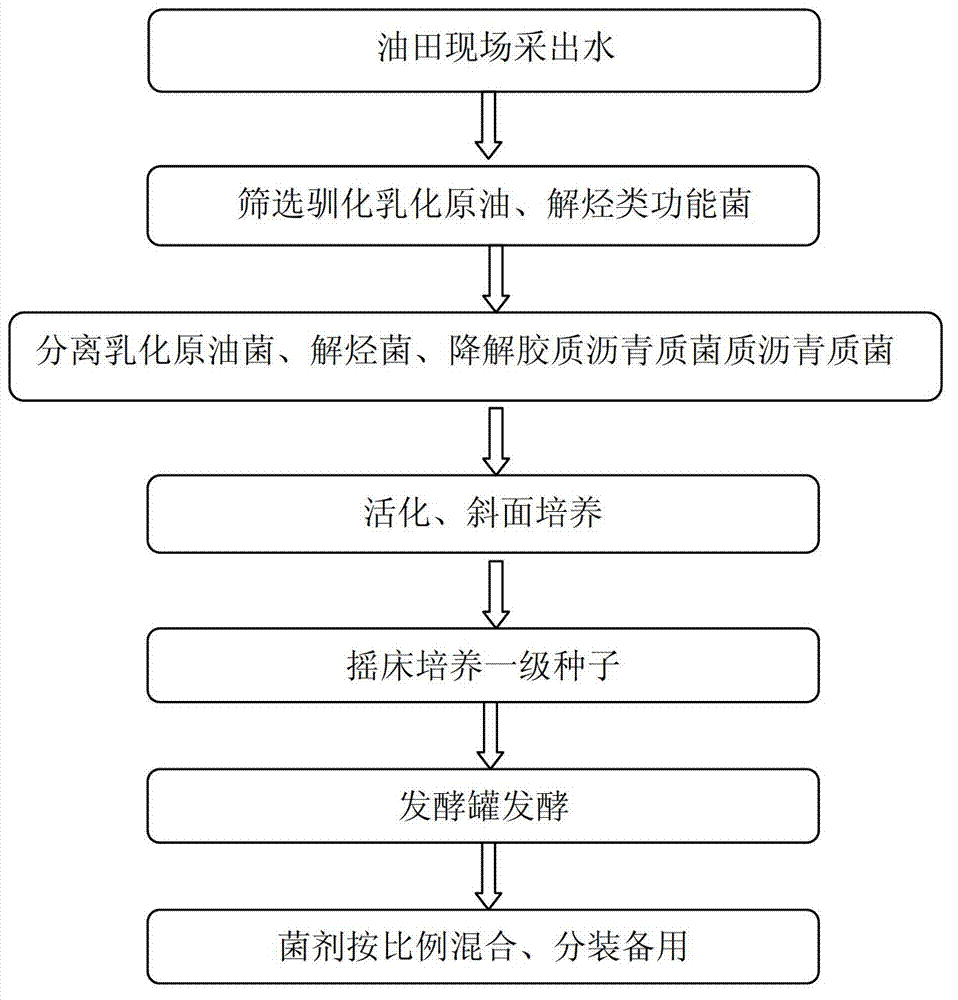
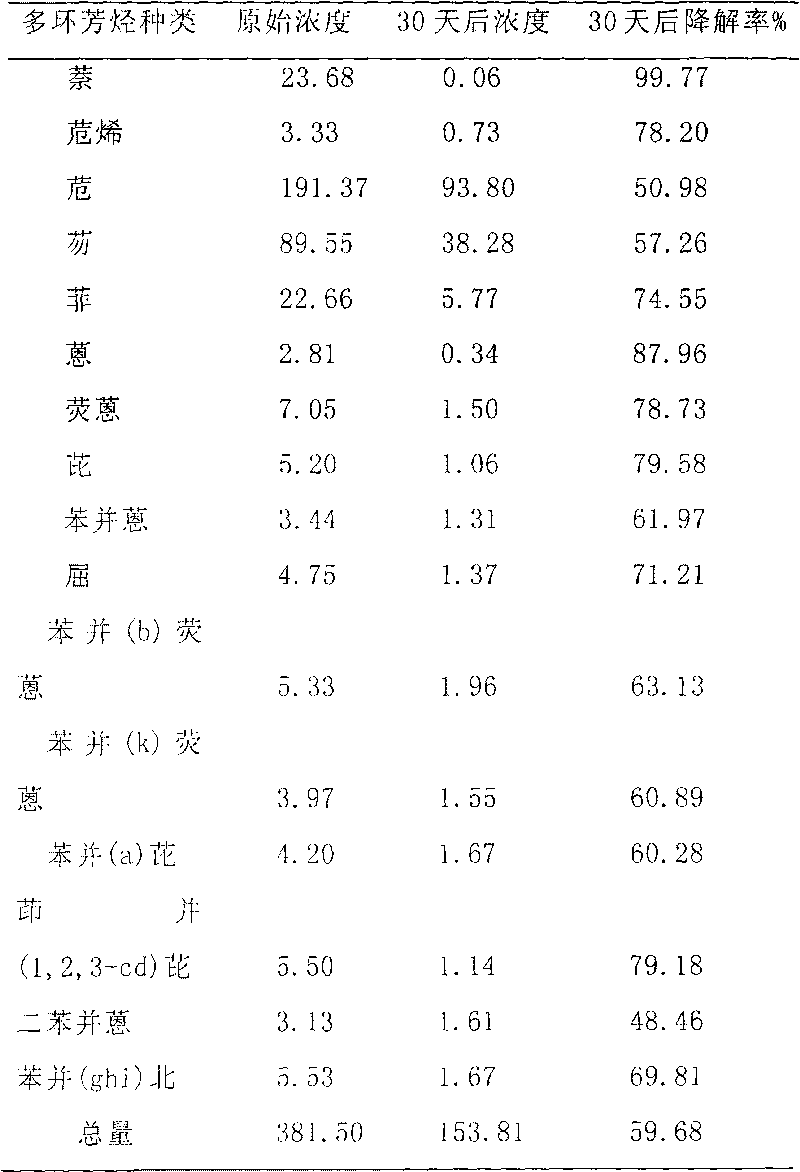
The invention provides a microbacterium oxydans for degrading a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and the application thereof. Particularly, the invention provides a microbacterium oxydans Ji2 strain with a preservation number of CGMCC No.9072 and the application effect of the microbacterium oxydans in emulsifying and degrading crude oil and the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and performing indoor physical simulation oil displacement. According to the microbacterium oxydans strain, the crude oil can be emulsified and degraded under aerobic and anaerobic conditions by taking the crude oil or the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon as the only carbon source and energy source, the degradation rate of the degraded polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, such as naphthalene is up to 100 percent, and analysis on the degraded crude oil shows that aromatic hydrocarbon and colloid, which are the components of the crude oil, are mainly degraded. The stain can be used for degrading the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in an environment by the performance of the stain, and can also be applied to microbial enhanced oil recovery, and the oil recovery is improved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Mixed bacterial agent for reducing viscosity of thick oil, as well as preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN102925397ARapid viscosity reductionHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPseudomonasBiological activation
The invention relates to a mixed bacterial agent for reducing viscosity of thick oil, as well as a preparation method and a use thereof, belonging to the technical field of crude oil recovery. The mixed bacterial agent for reducing the viscosity of the thick oil comprises xanthomonas, pseudomonas, microbacterium and bacillus, and the volume ratio of fermentation solutions of all bacterial genera is (20-100):(40-180):(30-100):(10-80). The preparation method comprises the following steps: respectively fermenting and mixing first-stage seed solutions of all bacteria: (1) getting strains from sources: extracting the strains out of water of Bohai sea gulf, and taking thick crude oil as a carbon source for acclimation and screening; (2) preparing the first-stage seed solutions: respectively activating on a peptone-yeast slant culture medium and transferring into a liquid peptone-yeast culture medium for shaking and activation; and (3) preparing a fermentation solution of mixed bacteria: respectively transferring the first-stage seed solutions of the strains into a fermentation culture medium for culture, wherein the living bacteria count in the mixed bacteria is 10<8>-10<10> bacteria / ml. The mixed bacterial agent for reducing the viscosity of the thick oil is used for reducing the viscosity of the crude oil. The mixed bacterial agent for reducing the viscosity of the thick oil, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages of high activity, rapid growth, no secondary pollution, good viscosity-reducing effect and the like.
Owner:E TECH ENERGY TECH DEV CORP
Ammonia nitrogen-removed compound microorganism microbial agent and application thereof
ActiveCN106676038APromote degradationImprove stabilityBacteriaWater contaminantsMicrobial agentOxygen
The invention discloses an ammonia nitrogen-removed compound microorganism microbial agent. The ammonia nitrogen-removed compound microorganism microbial agent is prepared from Providencia rettgeri, Microbacterium lactium, Lactobacillus delbrueckii and Rhodococcus coprophilus in a volume ratio of 5 to 2.5 to 1 to 5. The invention further discloses application of the compound microorganism microbial agent in ammonia nitrogen-containing wastewater treatment. The four bacteria are reasonably matched and are combined by virtue of an adsorption method and an embedding method to form immobilized cell particles, so that the ammonia-nitrogen degradation capacity and stability of the compound microorganism microbial agent are remarkably enhanced; a dominant bacterial community can be immediately formed after the compound microorganism microbial agent is applied to denitrification and treatment process of sewage, river way landscape water and the like, the treatment time is short, and ammonia and nitrogen indexes of the sewage are rapidly decreased; and meanwhile, the compound microorganism microbial agent has an aerobic denitrification function and further has relatively good effect of removing COD, and accumulation of nitrite and nitrate is avoided.
Owner:江苏绿境环保工程有限公司
Mixed bactericide for restoring places polluted by polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons, preparation method and application method
InactiveCN101735996AHigh activityLoose textureImmobilised enzymesWater contaminantsPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonHigh activity
The invention provides a mixed bactericide for restoring places polluted by polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons, a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of environment pollution restoration engineering. The strains used by the bactericide are Bordetella, Ochrobactrum, Rhodococcus, Achcromobacter, Herbaspirillum and Microbacterium which are mixed according to the ratio of 21-101:40-200:22-102:20-100:1:2 for fermentation to obtain a bacterial liquid, and the bacterial liquid is mixed with solid carriers according to the mass ratio of 0.5-1:1 to obtain a solid bactericide which has the effective living bacteria count of 108-1011 / g. The mixed bactericide in the invention can effectively remove polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons polluting soils and water, and has the advantages of high activity, rapid growth and propagation, strong adaptability, no generation of secondary pollution and the like.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
Immunomodulator, immunomodulator food
InactiveUS6506388B1Protection from damageLow viscosityOrganic active ingredientsBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteroidesDecomposition
An immunomodulator having suppressive activity on IgE antibody production is provided and contains bacterial cells, or their decomposition materials. It can be taken as a food. Bacterial cells such as Corynebacterium, Brevibacterium, Microbacterium, or bacterial cells of mutant strains of these bacteria, or decomposition products of these bacteria are used.
Owner:ASAMA CHEM +2
(+) gamma-lactamase with activity on splitting racemate gamma-lactam as well as coded gene and application thereof
InactiveCN101921742AWith absolute selectivityFungiBacteriaGamma-lactamaseMicrobacterium hydrocarbonoxydans
The invention discloses a (+) gamma-lactamase with activity on splitting racemate gamma-lactam as well as a coded gene and application thereof, wherein the (+) gamma-lactamase and the coded gene thereof derive from Microbacterium hydrocarbonoxydans, and the application refers to hydrolysis and splitting of the racemate gamma-lactam by the (+) gamma-lactamase. The (+) gamma-lactamase refers to a protein in (a) or (b) as follows: (a) a protein formed by the amino acid residue sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 in a sequence table; and (b) the protein which has activity on splitting racemate gamma-lactam and derives from the SEQ ID NO:1 by the steps of carrying out substitution and / or deletion and / or adding of one or more amino acid residue sequences on the amino acid residue sequences of the SEQ ID NO:1 in the sequence table. By utilizing the (+) gamma-lactamase to hydrolyze and split the racemate gamma-lactam, (-) gamma-lactam with the optical purity of 99.5 percent can be obtained with the yield larger than 39 percent.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
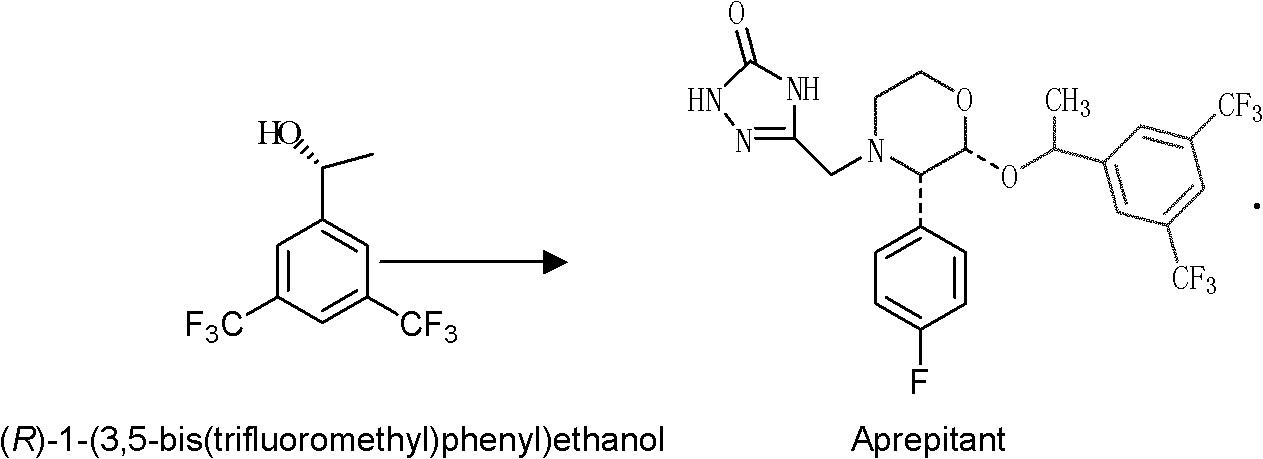
Microbacterium oxydans and method for preparing chiral bis(trifluoromethyl) phenyl ethanol by using same
ActiveCN102382780AEasy to manufactureMild reaction conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobacterium oxydansBuffer solution
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological catalysis, and relates to microbacterium oxydans and a method for preparing optically pure (R)-1-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl) phenyl] ethanol by using the microbacterium oxydans. The preservation number of the microbacterium oxydans C3 is CCTCC M2010179. The microbacterium oxydans is cultured at the temperature of 27-33 DEG C for 24-48 hours, and then substrate 3,5-bis-trifluoromethyl acetophenone is added to convert auxocyte; or the culture bacterium is collected and is resuspended in a buffer solution, and then the substrate is added to convert resting cells so as to generate a target product, namely the optically pure (R)-1-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl) phenyl] ethanol. The microbacterium oxydans has the advantages of easiness in industrialization, easiness in preparation of a catalyst thereof, mild reaction conditions and high conversion efficiency.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
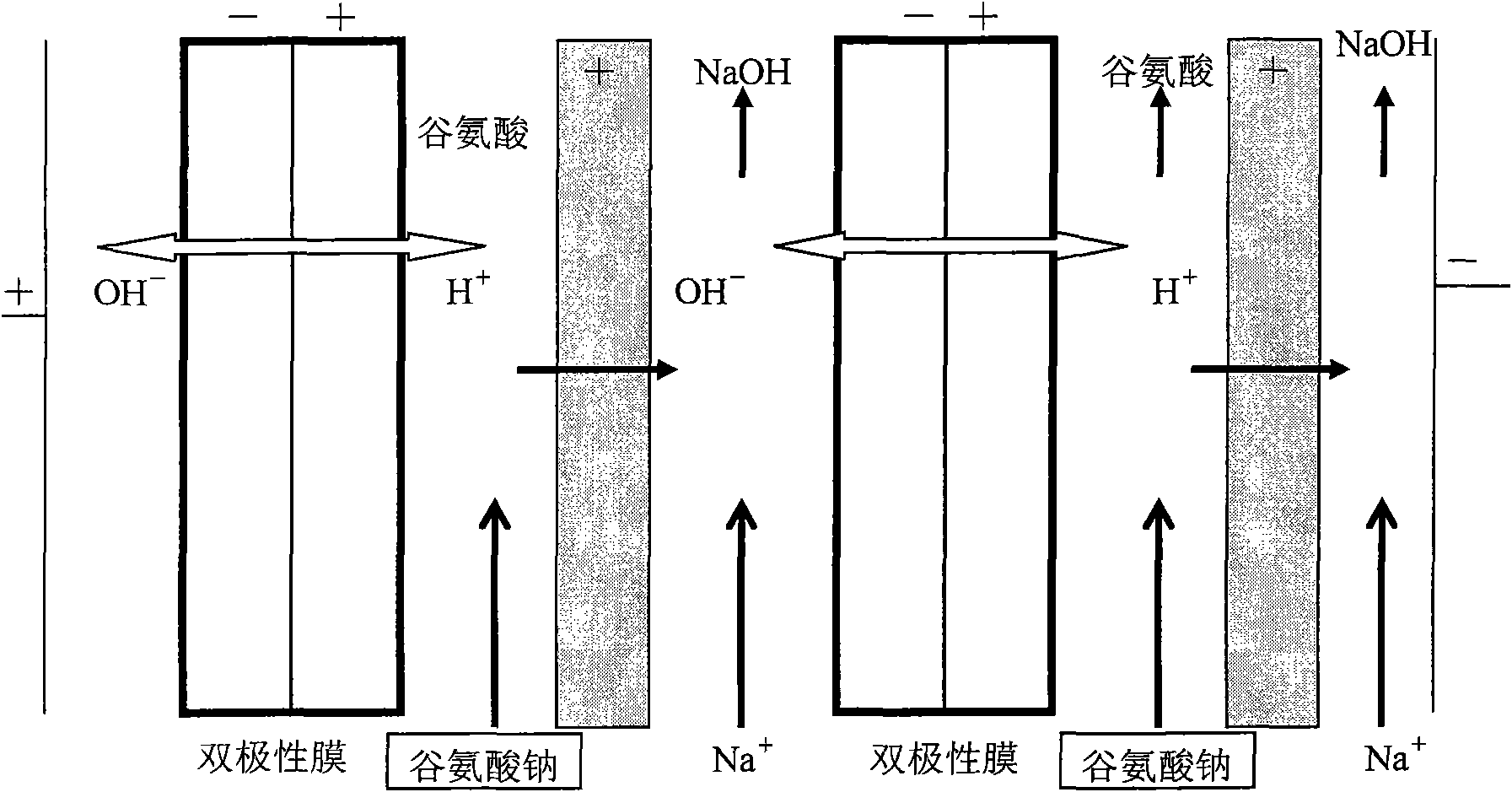
Method for extracting glutamic acid from glutamic acid fermentation liquor by bipolar membrane electroosmose process
InactiveCN101580859ANo pollution in the processEasy to operateOrganic compound preparationMicroorganism based processesHydrolysateUltrafiltration
The invention discloses a method for extracting glutamic acid from glutamic acid fermentation liquor by bipolar membrane electroosmose process. The method includes the following steps: a. microbacterium is used in a fermentation cylinder for the fermentation of proportioned raw materials of hydrolysate of the starch sugar, corn steep liquor, magnesium sulfate, disodium hydrogen phosphate, ureophil and potassium chloride, the steps of strain inoculation, water adding, air agitation fermentation and a certain temperature and pH value maintenance are carried out in a fermentation process, and glutamic acid fermentation liquor can be obtained after a certain period of fermentation; b. after being neutralized by sodium hydroxide, the glutamic acid fermentation liquor obtained in step a is processed by ultrafiltration to remove bacterial strain, protein and other impurities to obtain sodium glutamate liquor; and c. the glutamic acid obtained after the bipolar membrane electrodialysis separation of the sodium glutamate obtained in step b is processed by active carbon decolorization and concentrative crystallization to obtain the finished product. The method has the advantages of simple process, low energy consumption, small volume of equipment and easy operation, the rate of conversion can be as high as 99 percent, the byproduct-dilute sodium hydroxide solution can be circularly utilized, environmental pollution is not generated, and the energy consumption is lower.
Owner:INST OF SUBTROPICAL AGRI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microbacterium, broad spectrum glycosaminoglycan lyase expressed by microbacterium, and coding gene and applications of broad spectrum glycosaminoglycan lyase
ActiveCN106906161AEfficient preparationBroad substrate specificityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesChondroitin Sulfate C
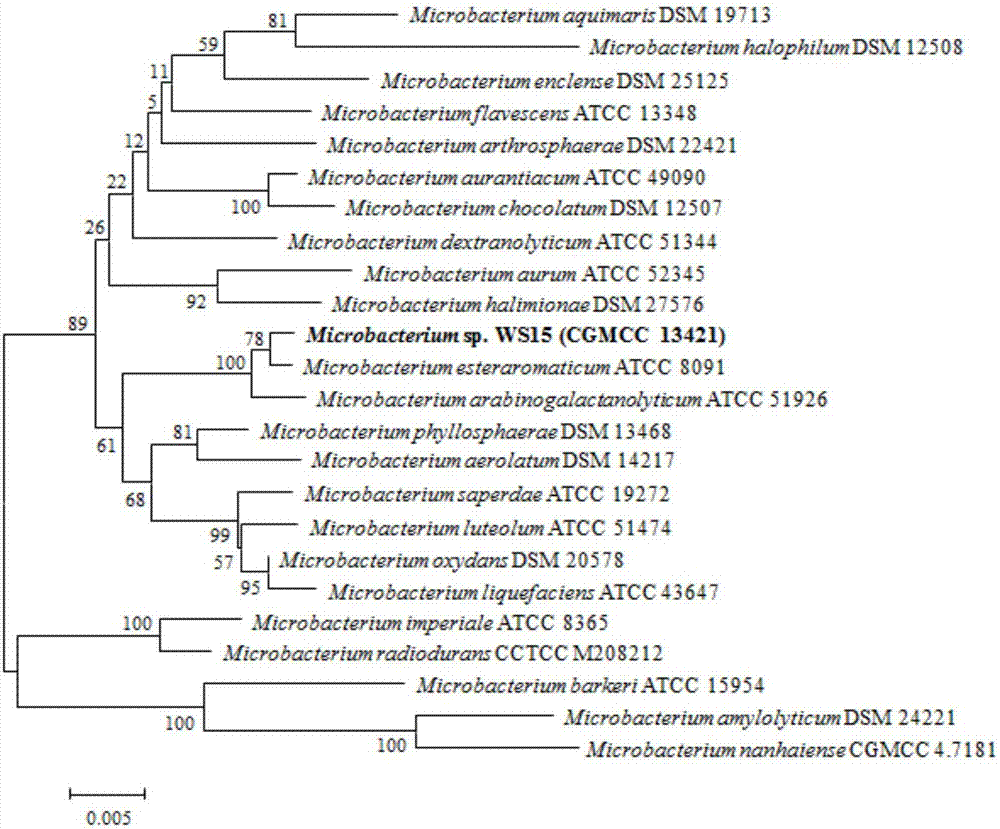
The present invention relates to microbacterium, broad spectrum glycosaminoglycan lyase expressed by the microbacterium, and a coding gene and applications of the broad spectrum glycosaminoglycan lyase. According to the present invention, the Microbacterium sp. WS15 strain is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on December 05, 2016, and has the preservation number of CGMCC No.13421, wherein the address is Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 3# Court No.1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing; and the glycosaminoglycan lyase TT16 is firstly obtained from the genome of Microbacterium WS15, can degrade the hyaluronic acid with no sulfation modification, can further degrade chondroitin sulfate A (CS-A), chondroitin sulfate C (CS-C) and chondroitin sulfate E (CS-E) being subjected to different sulfation modifications, and is the broad spectrum glycosaminoglycan lyase.
Owner:济南唐泰生物科技有限公司
Peach gum hydrolase producing strain and application in preparation of peach gum polysaccharide thereof
InactiveCN101701198ARich in economic valueShort hydrolysis cycleBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementHydrolysisHydrolase
The invention discloses a peach gum hydrolase producing strain and an application in preparation of peach gum polysaccharide thereof. The peach gum hydrolase producing strain belongs to microbacterium, is named microbacterium A5. The microbacterium was conserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on august 7, 2009 and the CCTCC NO is M209174. The strain of the invention can be used to effectively produce peach gum hydrolase used for degrading peach gum so as to obtain peach gum polysaccharide with large economic value. The strain of the invention can be utilized to produce peach gum through enzyme method, wherein the hydrolysis period is short, the relative molecular mass distribution of the product is narrow, no environmental pollution is caused, and the method is easy to control. The invention provides a new gum biotechnological process with more environmental friend and uniform product quality so as to facilitate the sustainable development of the society, promote the comprehensive utilization of wastes of Chinese agricultural culture and have wide market prospect.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
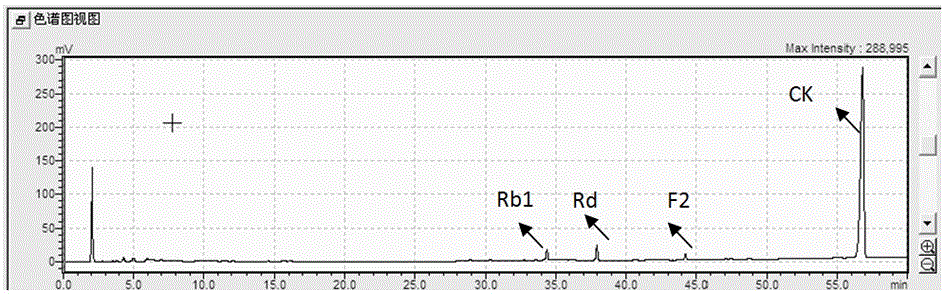
Method for preparing rare ginsenoside CK from protopanaxadiol ginsenoside through fermentation of microbacterium oxydans
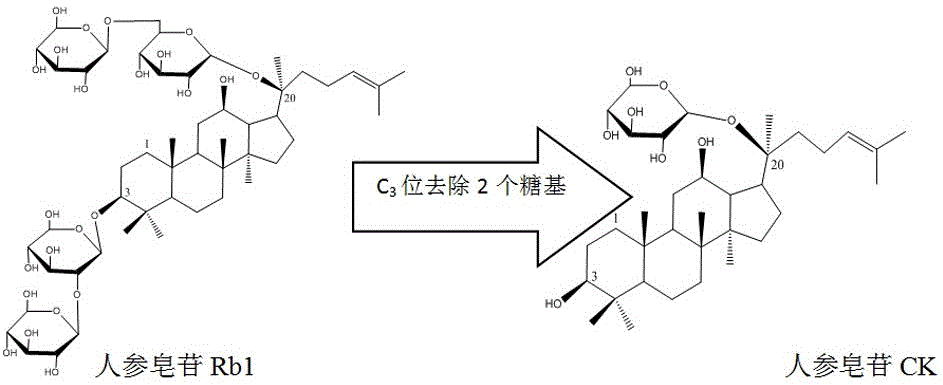
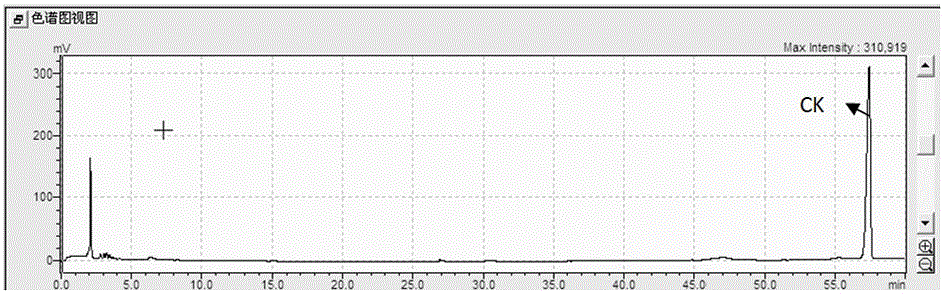
ActiveCN105838770AEasy to trainImprove catalytic performanceMicroorganism based processesFermentationChromatographic separationProtopanaxadiol
The invention relates to a method for preparing rare ginsenoside CK from protopanaxadiol ginsenoside through fermentation of microbacterium oxydans, in particular to a method for preparing 20-O-beta-D-glucopyranose-20-protopanaxadiol ginsenoside from protopanaxadiol ginsenoside Rb1, Rd and the like converted by utilizing fermentation of microbiological strains in a fully-automatic fermentation tank, belongs to the technical field of medicine, and comprises the steps: (1) fermentation cultivation of bacterial strains; conversion of raw materials Rb1, Rd and the like by utilizing fermented microorganisms and taking heteropolyacid HxYW12O40.nH2O with a Keggin structure as a catalyst, wherein Y is selected from P, Si, Fe or Zn, x is 3 or 4, and n is a positive integer ranging from 0 to 30; (3) preparative chromatographic separation and purification of conversion products, so as to finally obtain a compound with the chemical name being 20-O-beta-D-glucopyranose-20-protopanaxadiol ginsenoside.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Bacteria compsite inoculum used in lignin decomposition
The invention relates to a bacteria composite inoculum used in lignin decomposition. The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganism. With the inoculum, a current problem of a lack of lignin decomposition bacterial composite strain is solved. The composite inoculum comprises, by weight, 25-30 parts of pseudomonas ACCC11691 fermentation broth, 15-25 parts of pseudomonas stutzeri DSM6084 fermentation broth, 25-35 parts of microbacterium DSM20618 fermentation broth, and 20-25 parts of acinetobacter DSM9318 fermentation broth. Effective viable cell numbers in the four bacteria fermentation broths are all higher than 10<9> / mL. The composite inoculum provided by the invention provides a substantial decomposition effect upon lignin. The invention provides an application basis for papermaking pulping processes with cellulose as a main raw material, and provides a research basis for bacterial decomposition of lignin.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG BAYI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Microbial strain and application thereof
ActiveCN102719369AImprove qualityLower nicotine levelsTobacco treatmentBacteriaTobacco nicotineBiotechnology
The invention discloses a microbial strain and an application thereof, particularly relates to a tobacco nicotine degrading microbacterium GYC29 (Microbacterium sp.GYC29) with CCTCC of NO:M2010311 and an application of the microbacterium in tobacco. The strain disclosed herein can decompose and utilize nicotine in the growth process. According to the invention, by adding the ferment liquor of the strain or thallus with the additional amount of 1-5 % of the weight of the tobacco leaves in the tobacco with the water content of 10-50 % and fermenting for 6-72 h, the nicotine content of the tobacco leaves is reduced by 2-33%, the irritation of the tobacco leaves is obviously reduced, the miscellaneous gases are reduced, the smoke becomes pure and mild, and the sensory quality is obviously improved; the degradation of tobacco nicotine is realized by using microbes, the nicotine content of tobacco raw materials can be regulated properly, and the applicability of the tobacco leaves is raised.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO GUANGXI IND
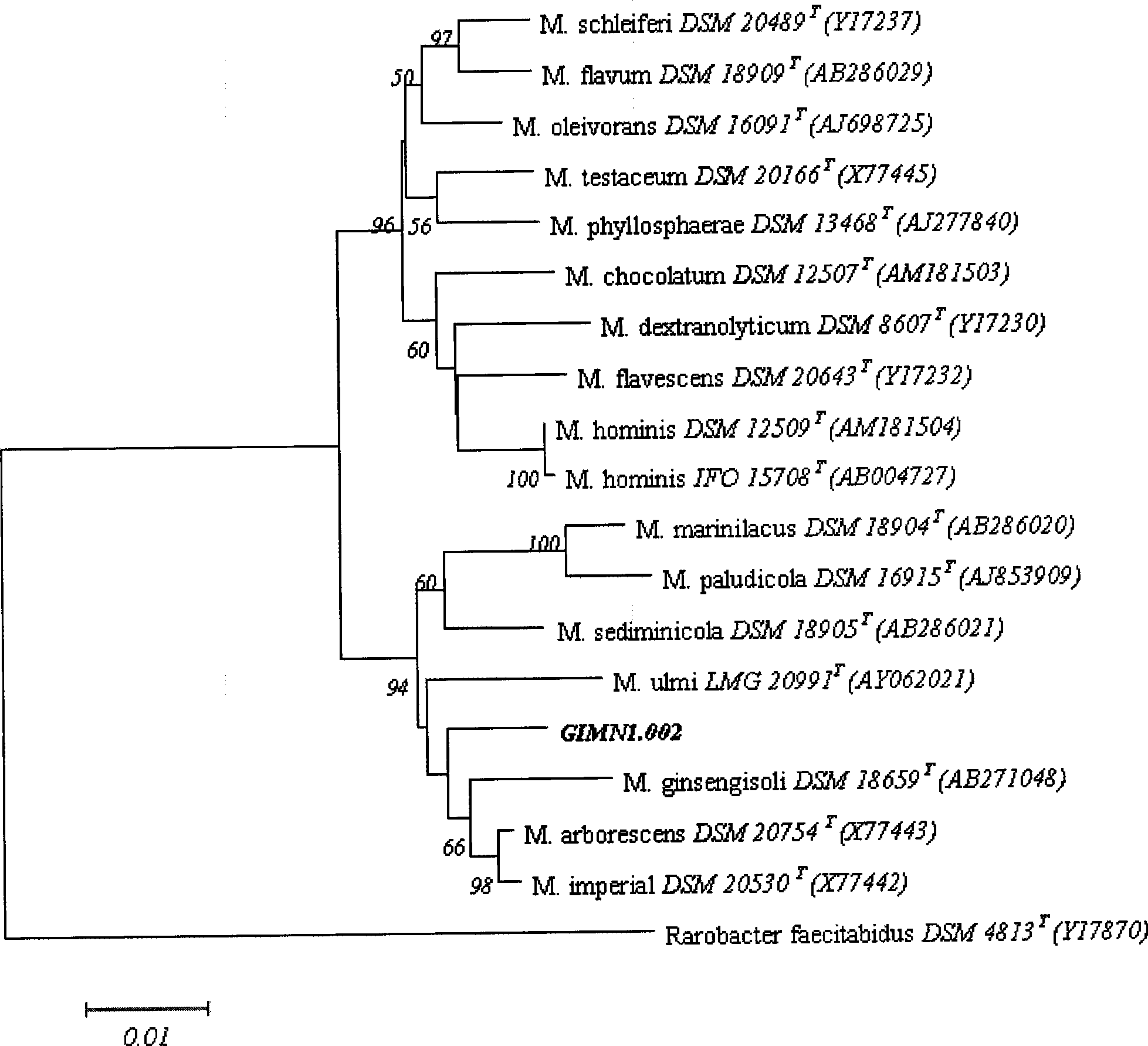
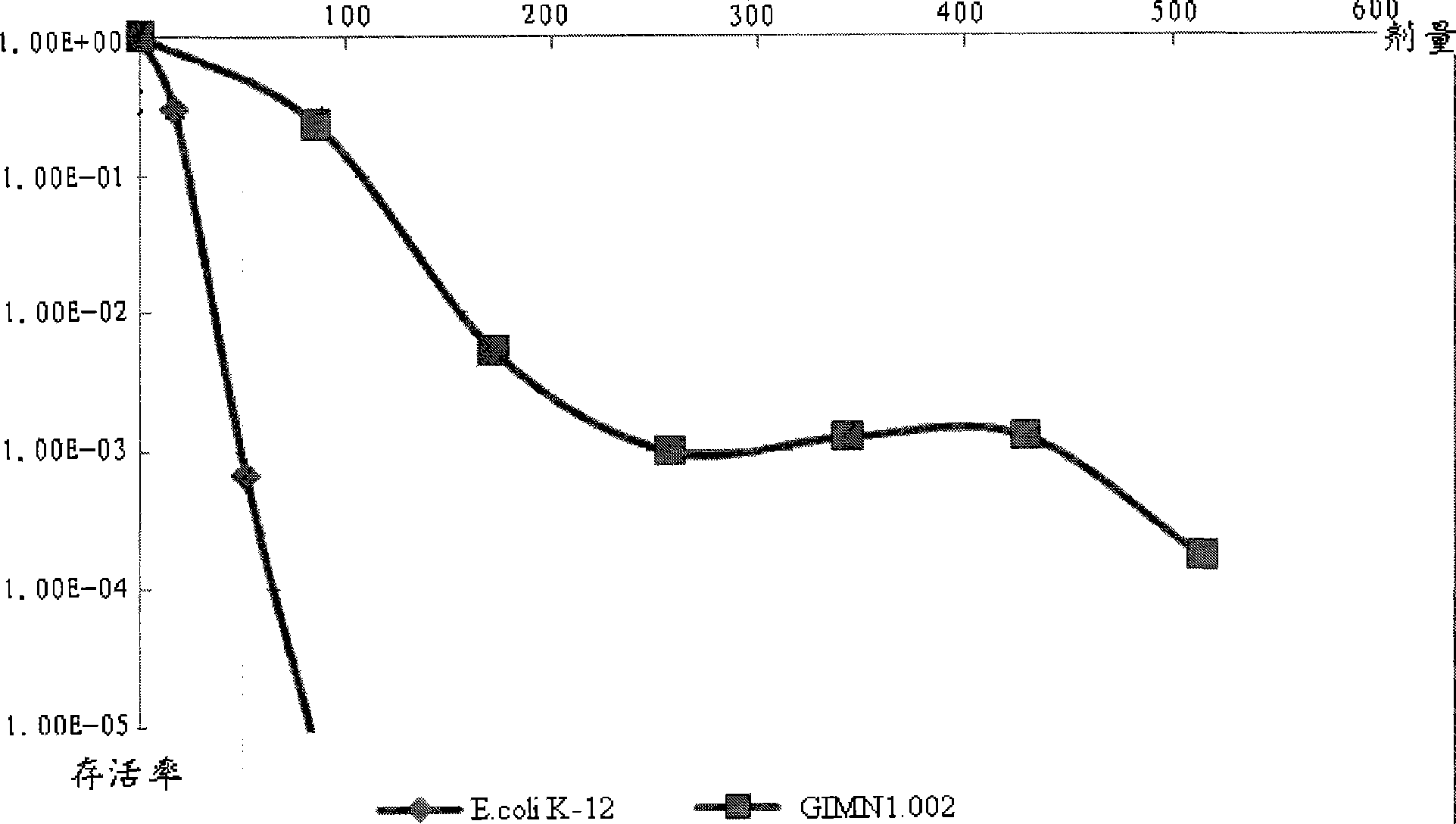
Radiation resistant microbacterium and use thereof
ActiveCN101481672AStrong resistance to UV radiationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRadiation resistantMicrobiology
The invention discloses a radioresistant Microbacterium radiodurans GIMN1.002 and uses thereof, the bacterium has been collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection, the collection date is 11.10.2008 and the collection number is CCTCC No.M208212. The ability of the inventive radioresistant Microbacterium radiodurans to resist the ultraviolet radiation is significant for researching on repair molecular mechanism of DNA damage thereof and for promoting the development of new DNA technologies in environmental protection, biomediation, human health, etc.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
(+)-gamma-lactamase from microbacterium as well as coding gene and application of (+)-gamma-lactamase
The invention discloses (+)-gamma-lactamase from microbacterium as well as a coding gene and an application of the (+)-gamma-lactamase, and belongs to the field of enzyme engineering. The (+)-gamma-lactamase is the following protein (a) or (b): (a): a protein containing an amino acid residue sequence as shown in SEQ ID:1; (b) a protein which has racemate gamma-lactamase splitting activity, contains the amino acid residue sequence as shown in SEQ ID:1 and is obtained through substituting and / or deleting and / or adding at least one or more amino acid residues. The (+)-gamma-lactamase further comprises a coding gene of the (+)-gamma-lactamase. The invention provides (+)-gamma-lactamase with activity of efficiently splitting racemate gamma-lactamase and a coding gene of the (+)-gamma-lactamase, which are expected to be applied to the industry. The enzyme has low requirements on temperature, can reach maximal activity at 20-30 DEG C, is very good in stability tolerance, and low in energy consumption when applied to the industry. The method for splitting racemate gamma-lactamase by utilizing the (+)-gamma-lactamase is simple and convenient, good in operability and small in pollution.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Compositions for improving the flavor of alcoholic beverage made from grape
It is intended to provide novel compositions usable in improving the flavor of an alcoholic beverage made from grapes typified by wine. Namely, a composition usable in improving the flavor of an alcoholic beverage made from grapes which contains the culture of a strain belonging to a genus Aspergillus, Penicillium, Rhizopus, Rhizomucor, Talaromyces, Mortierella, Cryptococcus, Microbacterium, Corynebacterium or Actinoplanes and being capable of producing diglycosidase.
Owner:AMANO ENZYME INC +1
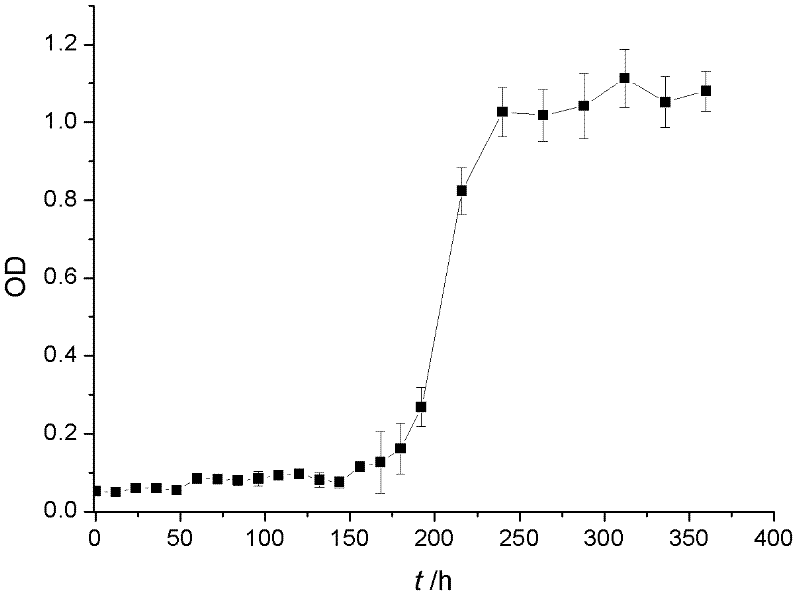
Space microbacterium oxydans LCT-H6
The invention relates to space microbacterium oxydans LCT-H6, in particular to a space microorganism which is obtained through separation of condensed water in a 'Shenzhou 9' spacecraft return capsule with a space technology. The space microbacterium oxydans LCT-H6 is characterized in that microbacterium oxydans LCT-H6 is an aerobic gram-positive bacterium, has the closest genetic relationship with microbacterium maritypicum, and the space microbacterium oxydans LCT-H6 has corrosion capability for four polymer materials including epoxy resin, ester type polyurethane, ether type polyurethane and vulcanized natural rubber. The space microbacterium oxydans LCT-H6 is clarified on the level of genomics, the total length of a whole genome sequence of LCT-H6 proves to be 4.11 Mbp, the content of GC is 67.65%, protein of the space microbacterium oxydans LCT-H6 is classified and noted as the class-22 COG family, and COG containing a largest amount of protein has functions on 'energy generation and conversion', 'amino acid transportation and metabolism', 'sugar transportation and metabolism', 'inorganic salt ion transportation and metabolism' as well as 'translation, ribosome structure and forming'.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
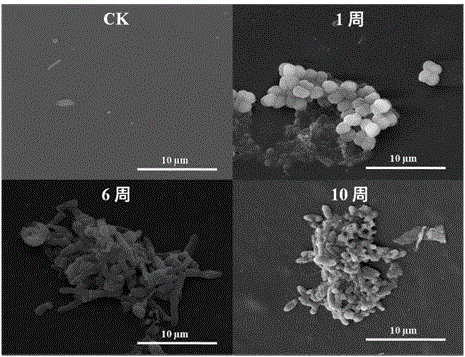
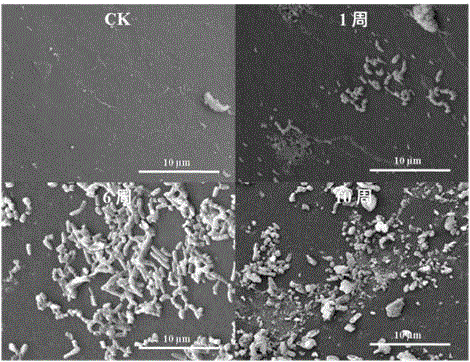
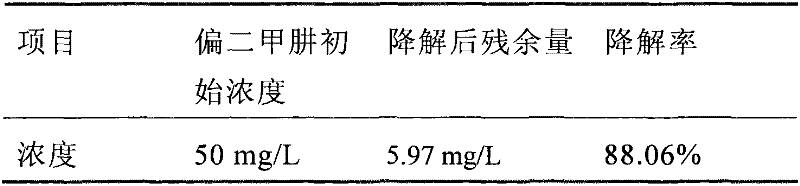
Microbacterium 18 for degrading unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine and unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine method therewith
InactiveCN102367426AImprove degradation rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesUnsymmetrical dimethylhydrazineSugar
The invention discloses a microbacterium 18 for degrading unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine, and provides a method for degrading unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine with the microbacterium 18. The method comprises the steps of: inoculating a microbacterium 18 strain in a slant culture medium composed of tryptone, malt extract, bacto peptone and agar for culturing so as to obtain a slant culture; inoculating the slant culture in a container loaded with a seed culture medium composed of tryptone, malt extract, and bacto peptone for culturing so as to obtain a seed solution; inoculating the seed solution in a container loaded with a substrate solution composed of cane sugar, NaCl, K2HPO4, KH2PO4, MgSO4, CaCl2, FeSO4, H3BO3, ZnSO4 and unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine for culturing, and conducting degradation at a temperature of 28-37DEG C for 72h. With the microbacterium 18 and the method that are provided in the invention, the degradation rate of unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine can reach 88.06%.
Owner:LOGISTICS DEPT ANTIEPIDEMIC ARMY OF THE GENERAL ARMAMENT DEPT PLA
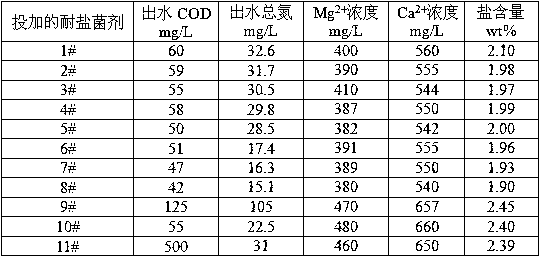
Microbial agent with high salt resistance, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108118008AEfficient removalImprove removal rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh resistanceStaphylococcus cohnii
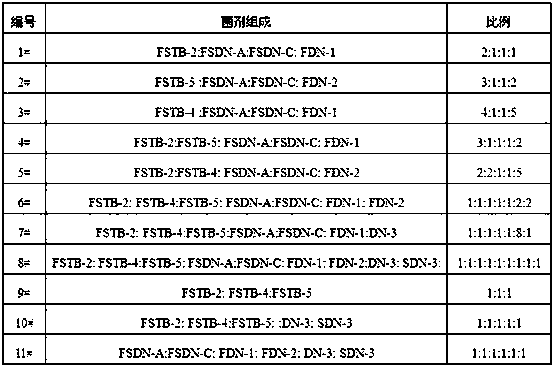
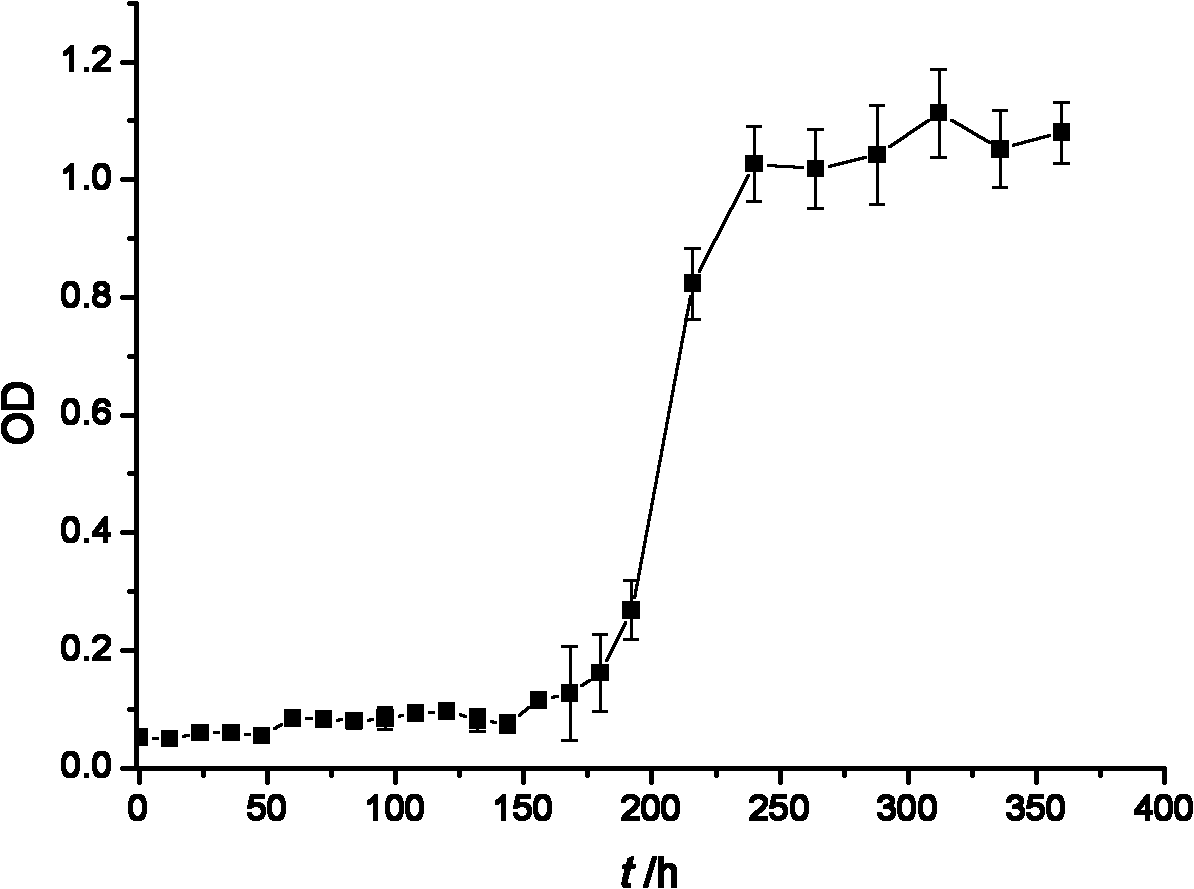
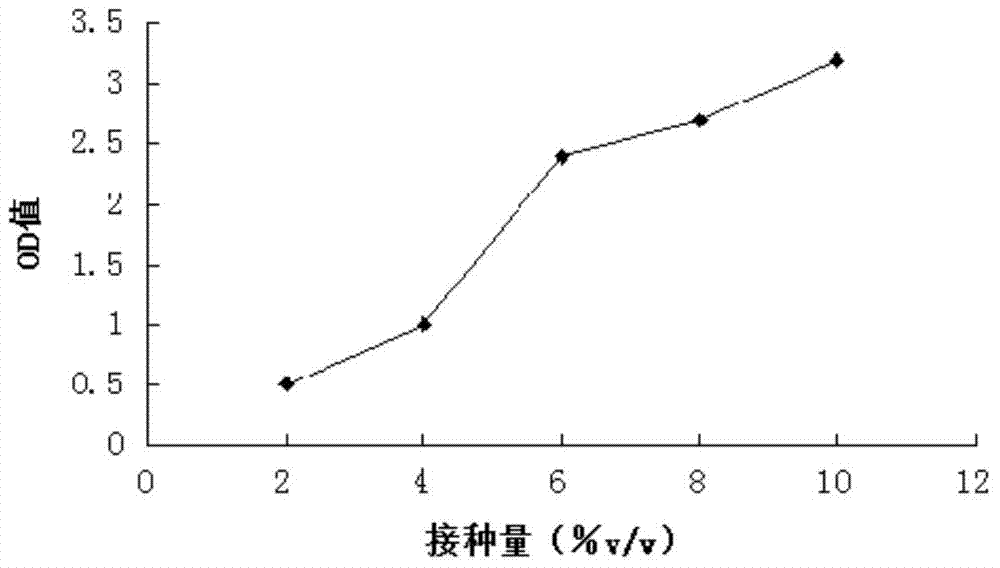
The invention relates to a microbial agent with high salt resistance. The microbial agent comprises at least one of selected from a group consisting of Paracoccus sp. FSTB-2, Microbacterium kitamienseFSTB-4 and Pseudomonas stutzeri FSTB-5, also comprises Kocuria palustris FSDN-A and Staphylococcus cohnii FSDN-C, and further comprises at least one of selected from a group consisting of Arthrobacter creatinolyticus FDN-1 and Flavobacterium mizutaii FDN-2. The invention also discloses a preparation method and application of the above microbial agent. The microbial agent can be directly used fortreating total nitrogen and COD in high-salt wastewater, and can also be added to various biochemical reaction structures to improve microbial composition, optimize the salt tolerance of a microbial system in wastewater treatment and enhance the capability of the system in removing total nitrogen and COD.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Microbacterium and application of microbacterium in conversion of reed straw hydrolysate to prepare microbial flocculant
ActiveCN110205268AIncrease productionReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationHydrolysate
The invention discloses a microbacterium and an application of microbacterium in conversion of a reed straw hydrolysate to prepare a microbial flocculant. The microbacterium is classified as Microbacterium trichothecenolyticum BWL1091, and a preservation number is CGMCC No. 14436. A method of preparing the microbial flocculant comprises the following steps: inoculating the strain in a seed liquidmedium, and preparing the seed liquid by shaking table culture at 37 DEG C; transferring the seed liquid to a ratio of 1% to a fermentation medium taking the 650 mL / L reed straw hydrolysate as a solecarbon source, and performing shaking table culture at a constant temperature of 30 DEG C; centrifuging a fermentation broth, and collecting a supernatant for use as a liquid microbial flocculant; adding 2-time volumes of pre-cooled anhydrous ethanol to the liquid microbial flocculant, and collecting the precipitate by centrifugation, and performing freeze drying to obtain the solid microbial flocculant. The microbacterium of the invention can tolerate a high concentration of reed straw hydrolysate, and can utilize the rich reducing sugar in the reed straw hydrolysate as the sole carbon sourceto ferment and produce the microbial flocculant, the output can reach up to 7.53g / L, the production process is simple, and the cost is low.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Microbacterium capable of utilizing methane and applications thereof
InactiveCN102071160AImprove oxidation activityHigh affinityBacteriaDispersed particle separationMicrobiologyMicrobacterium species
The invention relates to a microbacterium capable of utilizing methane and the applications thereof. The CCTCC NO of the microbacterium is M2010099. The microbacterium can be used to prepare the methanogen absorbent, the garbage treatment agent and the biocatalyst. The microbacterium overcomes the application problems that the methane oxidizing bacteria have low microbial density, the cultivation of the bacteria is difficult to enlarged, etc; and the microbacterium has higher affinity to methane. The microbacterium is especially suitable for man-made methane sources such as domestic garbage landfills and rice fields and can be widely popularized.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Azo dye orange II degrading bacterium and inocula produced from same
ActiveCN104195066AResidue reductionReduce manufacturing costBacteriaWater contaminantsMicroorganismMicrobacterium oxydans
The invention discloses an azo dye orange II degrading bacterium and an inocula produced from the same. The bacterial strain is bacterial strain L-11 of microbacterium oxydans, is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center since 8th, May, 2014, the preservation address is No. 3, No. 1 yard, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing City, and the preservation number is CGMCC NO.9130. The main biological characteristics comprise that the bacterium colony is circle and is not transparent, the bacterium colony is white after being cultured for 1-3 days and is yellow after being continuously cultured, the liquid culture color is yellow, the optimum culture temperature is 28-30 DEG C, and the optimum pH is 7.2. The bacterium belongs to actinomyces. The degrading bacterium L-11 is capable of enabling the azo dye orange II residual quantity to be reduced by 80% or more. The azo dye orange II degrading bacterium inocula has the advantages of low production cost, usage convenience and good removing effect, and is applicable to pollution treatment of water and soil.
Owner:嘉兴华吉环保科技有限公司
Use of microbacterium strains for the production of antibacterial agents
InactiveCN108026546AHas antibacterial activityEfficient and effective productionBiocideBacteriaBacteroidesAntibacterial activity
Owner:DEINOBIOTICS
Microbacterium capable of utilizing methane and applications thereof
InactiveCN102071160BImprove oxidation activityHigh affinityBacteriaDispersed particle separationChemistryMicrobacterium species
The invention relates to a microbacterium capable of utilizing methane and the applications thereof. The CCTCC NO of the microbacterium is M2010099. The microbacterium can be used to prepare the methanogen absorbent, the garbage treatment agent and the biocatalyst. The microbacterium overcomes the application problems that the methane oxidizing bacteria have low microbial density, the cultivationof the bacteria is difficult to enlarged, etc; and the microbacterium has higher affinity to methane. The microbacterium is especially suitable for man-made methane sources such as domestic garbage landfills and rice fields and can be widely popularized.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
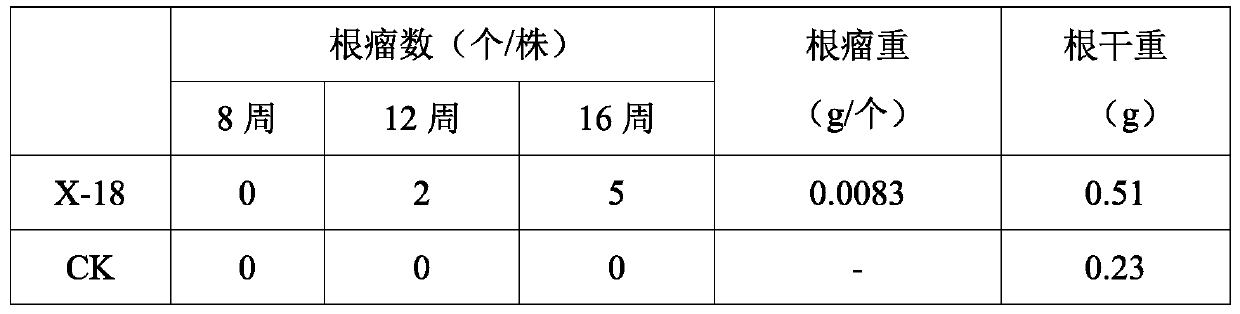
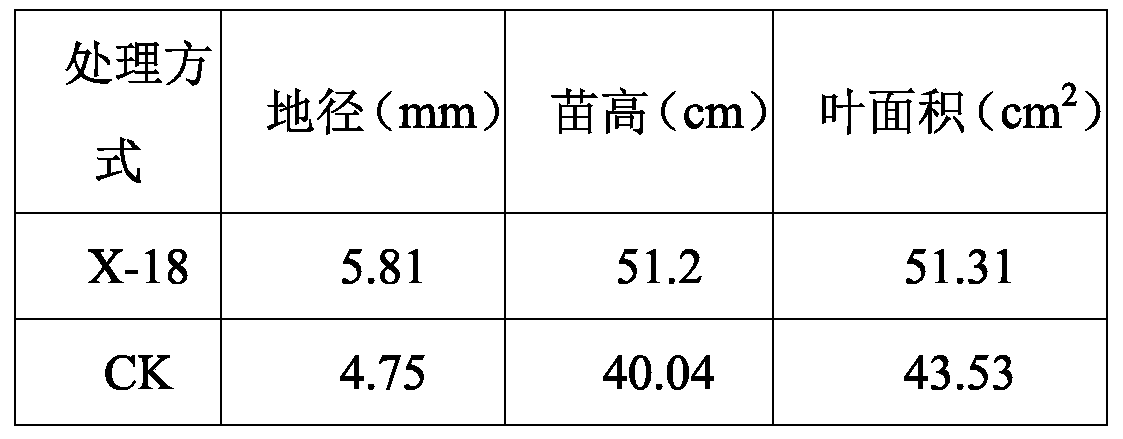
Root nodule growth-promoting microbacterium X-18 and application thereof
ActiveCN110551664APromotes effective nitrogen fixationThe ability of symbiotic nitrogen fixation is obviously exertedBiocidePlant growth regulatorsNitraria billardiereiMicroorganism
The invention discloses a root nodule growth-promoting microbacterium X-18 and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. A root nodule growth-promoting bacterium is classified and named as microbacterium sp. X-18, is deposited in The preservation date is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection with a preservation date being April 8th, 2019, a preservation number being CCTCC NO: M2019236 and a preservation address being Wuhan University in China. The microbacterium X-18 disclosed by the invention is applied to black locust as leguminous plants, canpromote effective nitrogen fixation of the black locust and provides nitrogen required by growth of he black locust to enable the symbiotic fixation ability of the root nodule growth-promoting bacteria with the plants to be obviously exerted, so that growth and development of black locust plants are promoted, and a development prospect is good.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
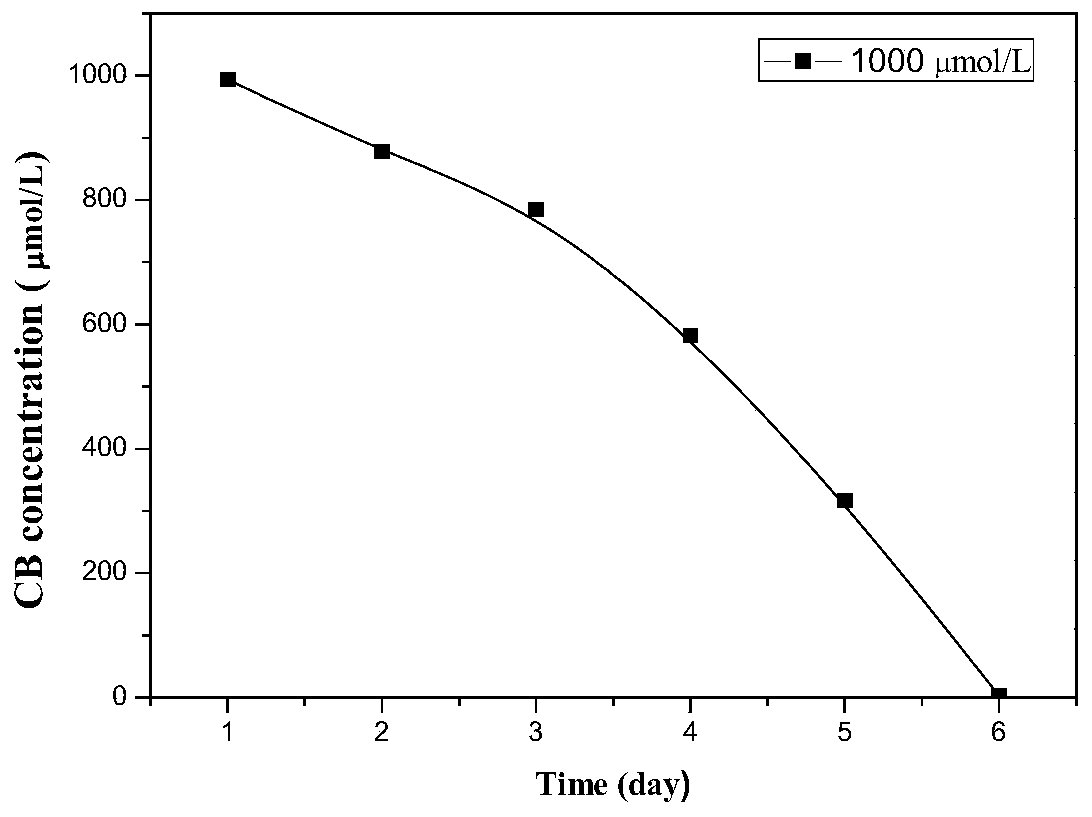
Microbacterium oxydans and application thereof in degrading organic pollutants
ActiveCN110229766AEfficient purificationPollution efficientGas treatmentBacteriaInorganic saltsChlorobenzene
The invention discloses microbacterium oxydans and application thereof in degrading organic pollutants. The application method comprises the following steps: inoculating an inorganic salt culture solution with microbacterium oxydans, adding organic pollutants, and carrying out degradation reaction under the conditions of 25-35 DEG C, 160 rpm and pH value of 6-8 to realize the degradation of organic matters. The microbacterium oxydans of the invention can degrade chlorobenzene. Under aerobic condition, the microbacterium oxydans can degrade chlorobenzene with an initial concentration of 500-2000 [mu]mol / L, wherein the removal rate is 100%, and the average degradation rate is as high as 334.16549 [mu]mol / (L x h). Under anaerobic condition, the microbacterium oxydans can degrade chlorobenzenewith an initial concentration of 500-1500 [mu]mol / L, wherein the removal rate is 100% too. The microbacterium oxydans can realize high-efficiency purification of chlorobenzene in industrial wastewater and waste gas, and has the advantages of low pollution, easy popularization and low purification cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Microbe bacteria agent for treatment of refinery waste water, its preparation method and application
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria having effect of promoting growth of plants and isolated culture and application of hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria
InactiveCN110229762APromote growthImprove stress resistancePlant growth regulatorsBiocideBacteroidesBiotechnology
The invention discloses microbacterium Microbacterium1-0-19. The strain is isolated from a place nearby Tongchuan overpass, Yaozhou district, Tongchuan city, Shanxi province, and is classified into microbacterium bacteria based on physiological and biochemical characteristics and 16SrDNA analysis. Medicago sativa rhizosphere soil is used as a research object, and hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria are isolated through a continuous hydrogen inflating device; and through shape observation, physiological and biochemical identification and 16SrDNA identification of the hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria, the classification status of the hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria is determined. The optimal strain is fermented in a laboratory, and a hydrogen bacterium preparation is prepared. The biological preparation canbe used for agricultural production to promote growth of plants, increase yield, increase fertilizer effects and increase the stress tolerance capacity of the plants.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
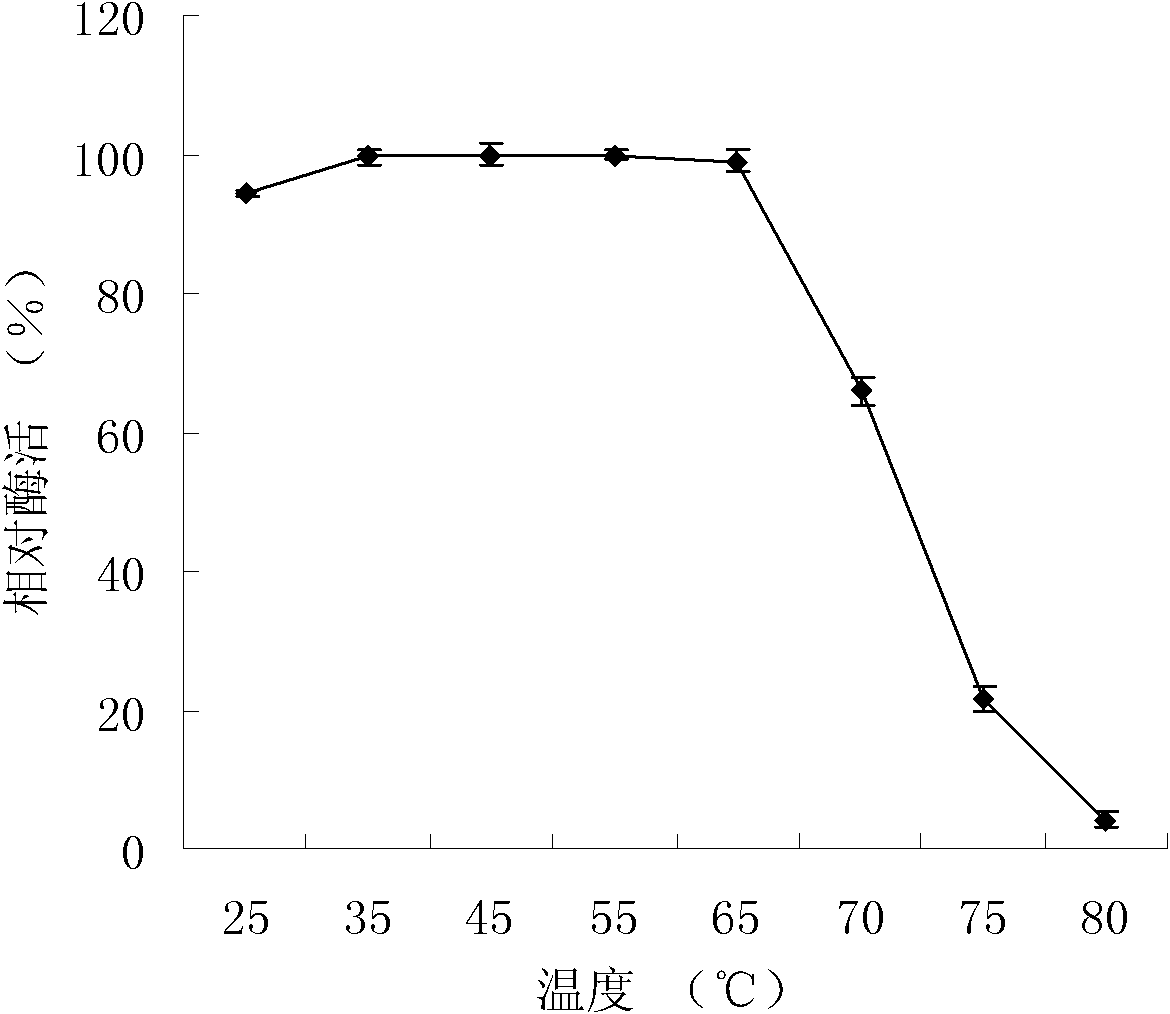
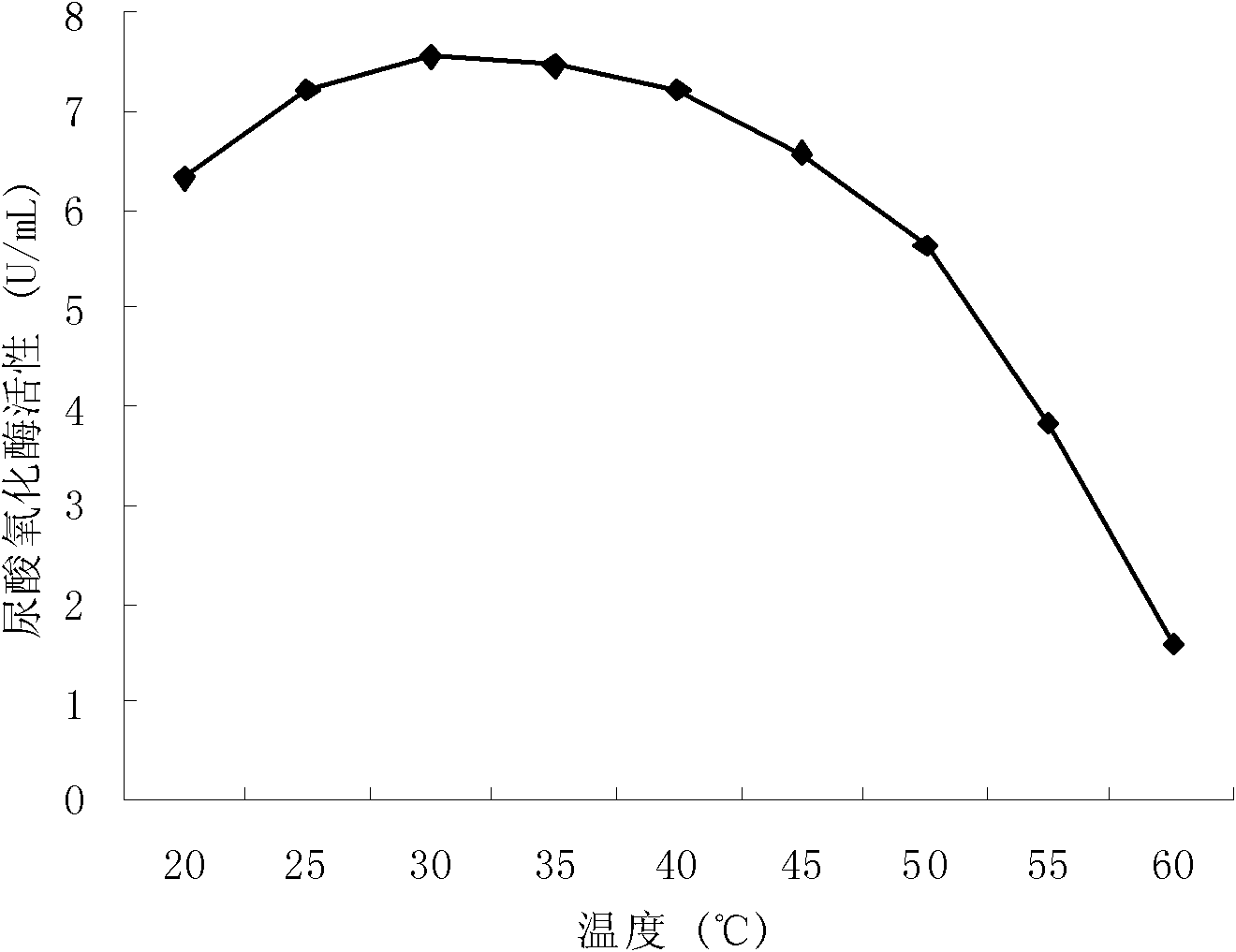
Heat-resisting urate oxidase gene of microbacterium category bacteria and application of same
InactiveCN102220354AImprove thermal stabilityImprove thermal characteristicsEnzymesFermentationBacteroidesNucleotide
The invention discloses the heat-resisting urate oxidase gene of microbacterium bacteria, comprising the nucleotide sequence presented in SEQ ID No.1. The invention also discloses a protein encoded by the gene, comprising the amino acid sequence presented in SEQ ID No.2. The invention also discloses the application of the heat-resisting urate oxidase gene of the microbacterium category bacteria: the gene is cloned in a vector so as to carry out induction expression, thus obtaining the heat-resisting urate oxidase with high activity.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
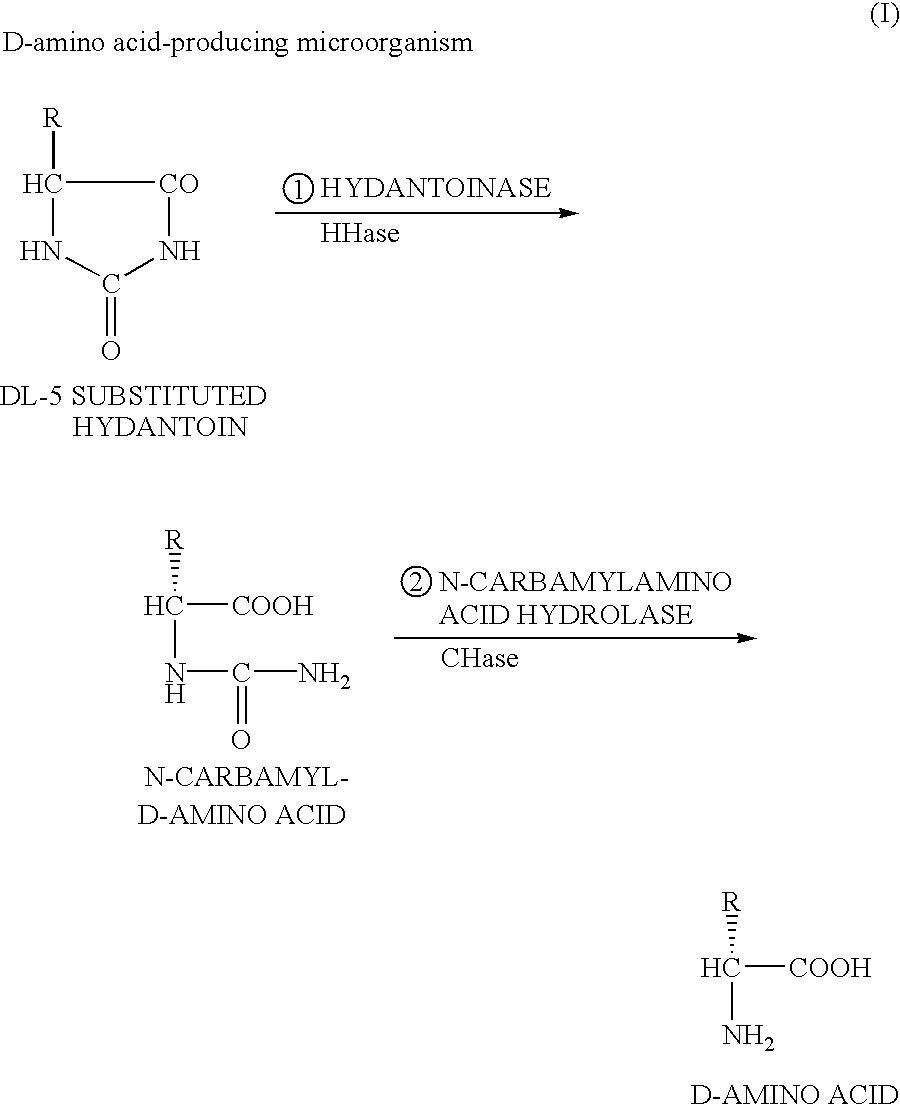
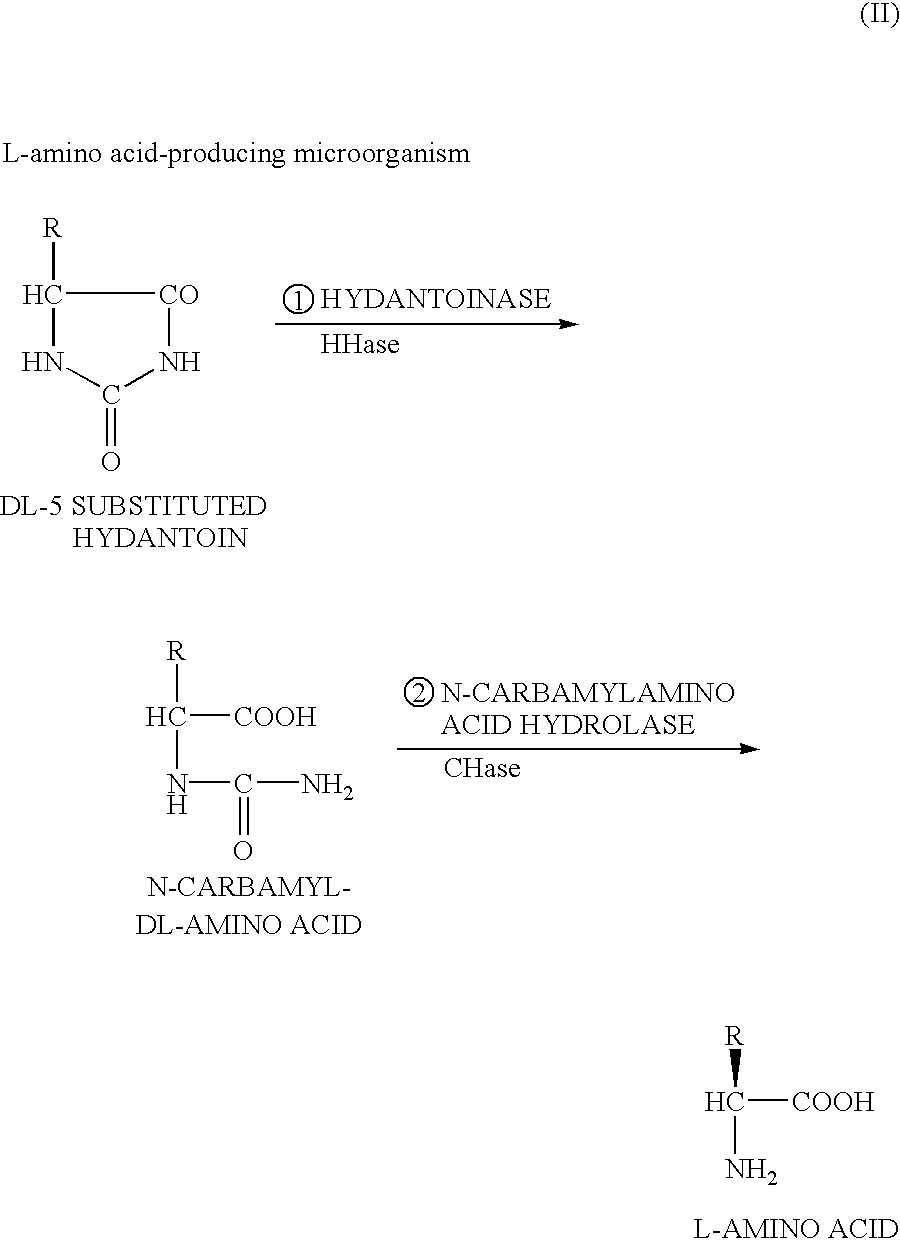
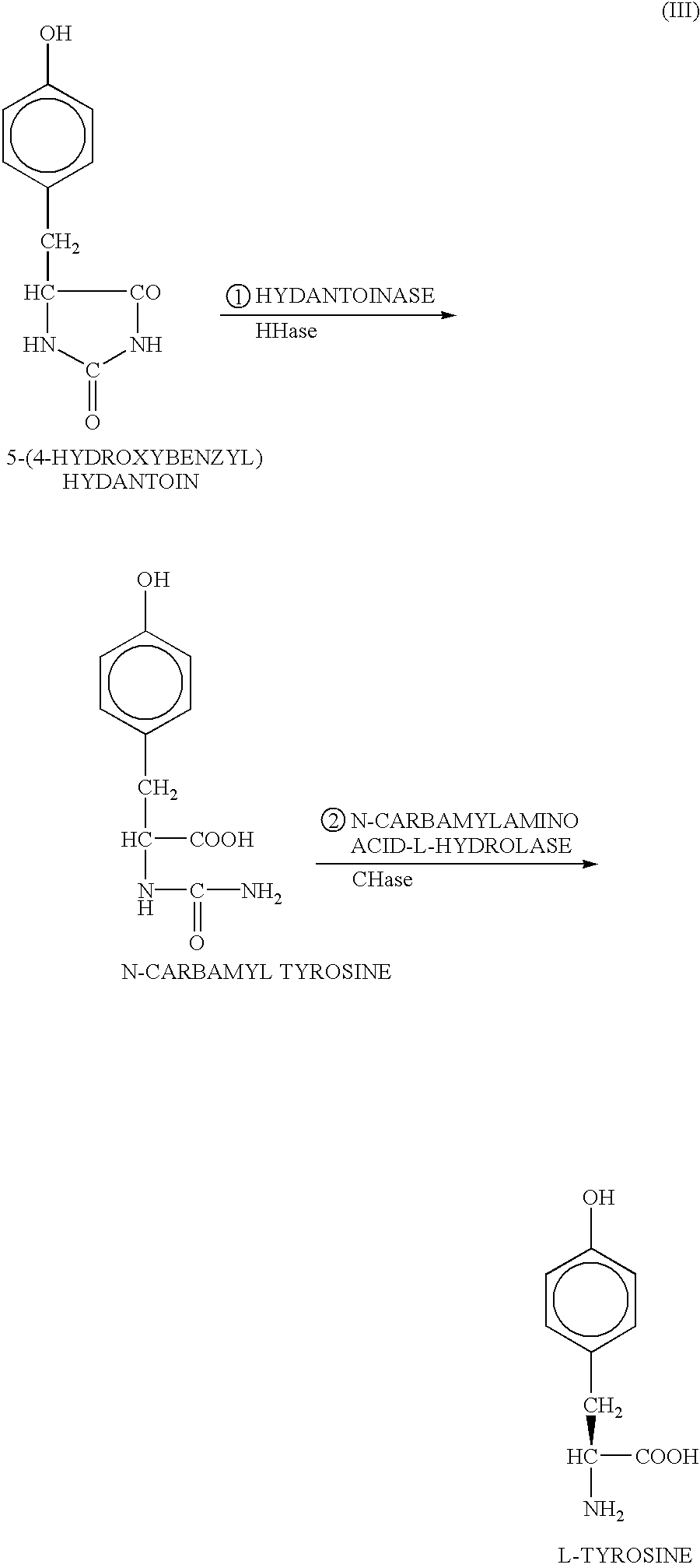
DNA encoding hydantoinase, DNA encoding N-carbamyl-L-amino acid hydrolase, recombinant DNA, transformed cell, method of producing protein, and method of producing optically active amino acid
The present invention provides a method of producing optically active amino acids from 5-substituted hydantoin by isolating a hydantoinase gene and an N-carbamyl-L-amino acid hydrolase gene involved in an ability to convert 5-substituted hydantoin or N-carbamylamino acid into optically active amino acids from a microorganism of the genus Microbacterium having the above ability and by improving gene amplification and transcriptional and translational activities thereby preparing a recombinant wherein the amount of the desired enzymes produced is increased. The hydantoinase gene is, for example, a DNA encoding for a protein having a hydantoinase activity, which has the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1 in the Sequence. The N-carbamyl-L-amino acid hydrolase gene is, for example, a DNA encoding for a protein having an N-carbamyl-L-amino acid hydrolase activity, which has the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:3 in the Sequence.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com