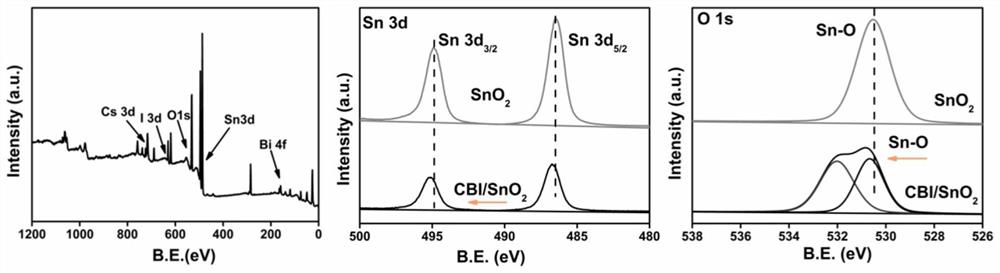
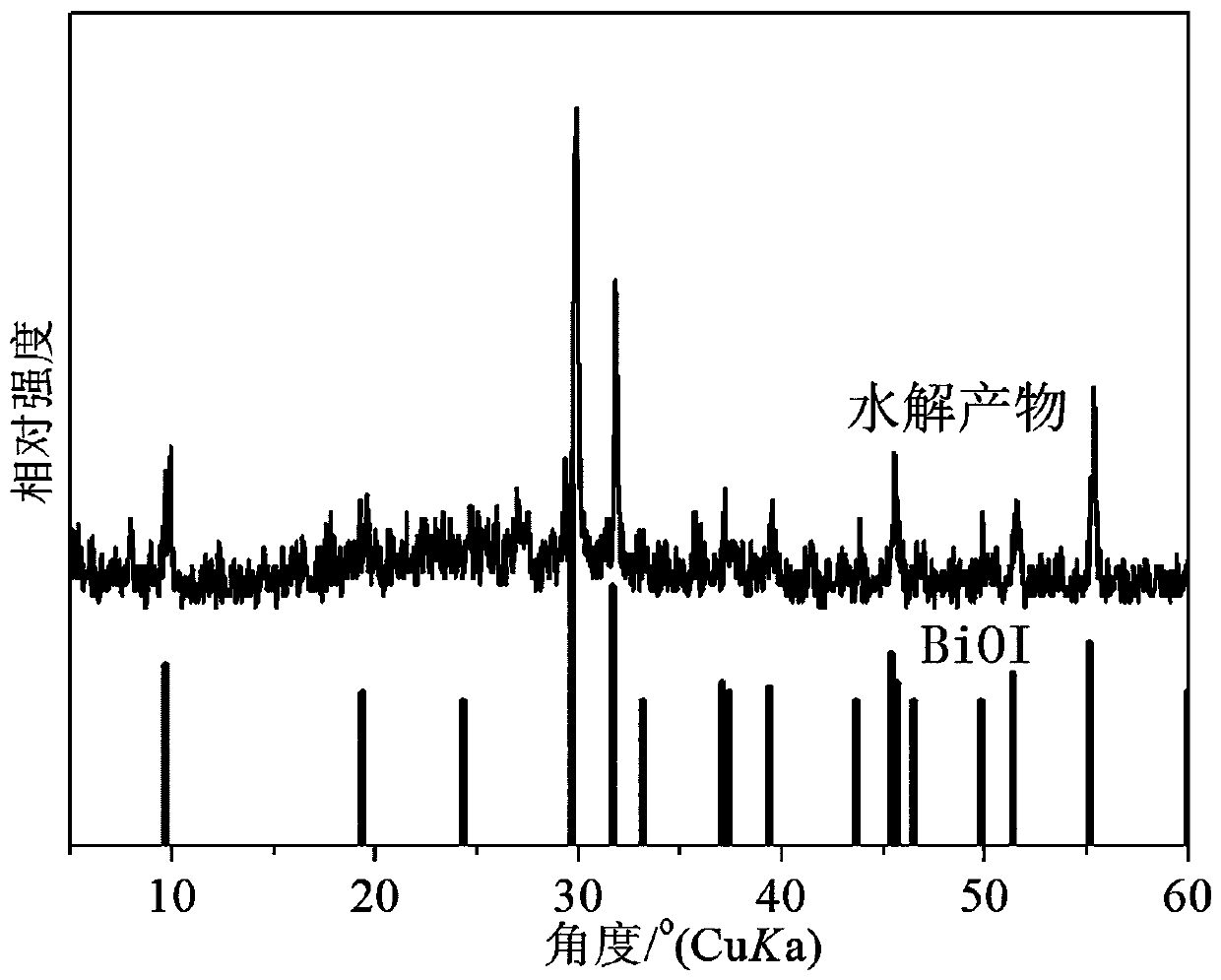
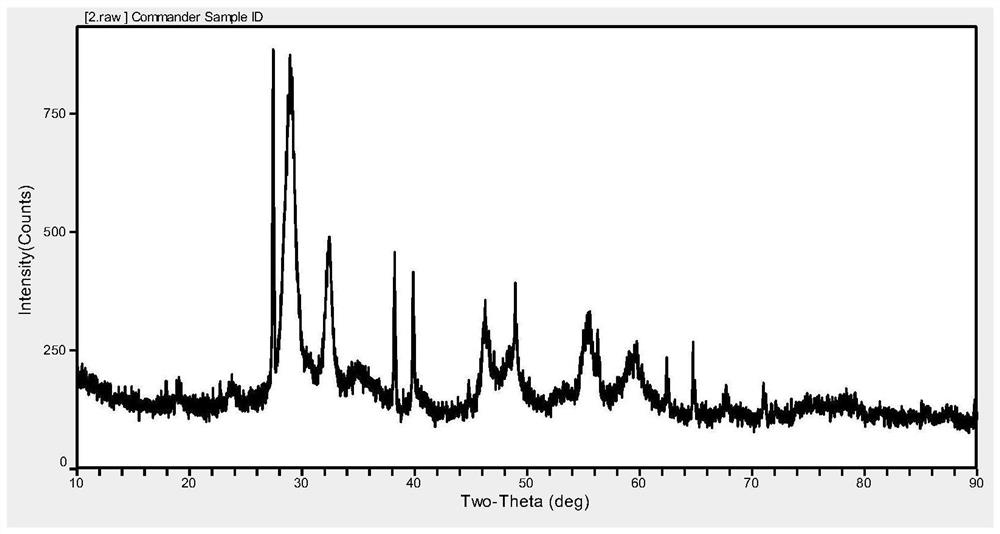
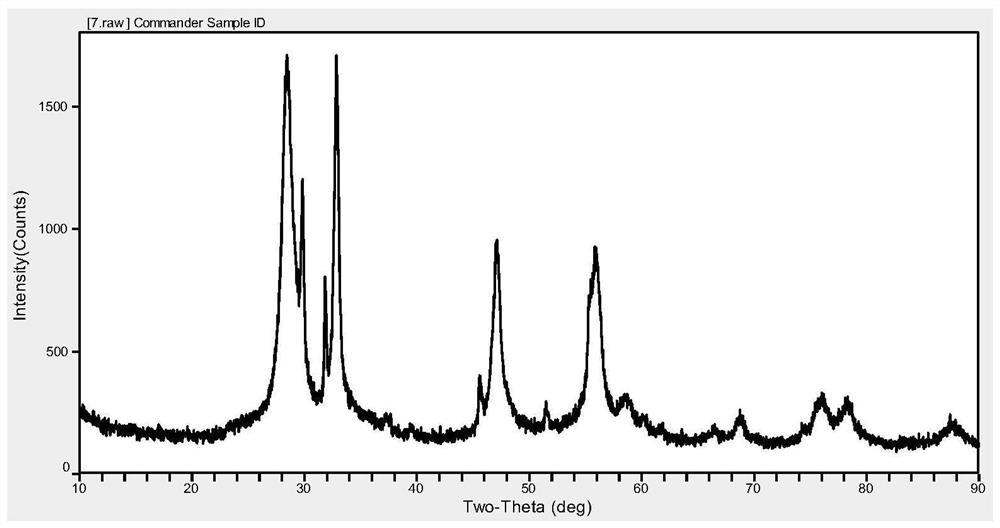
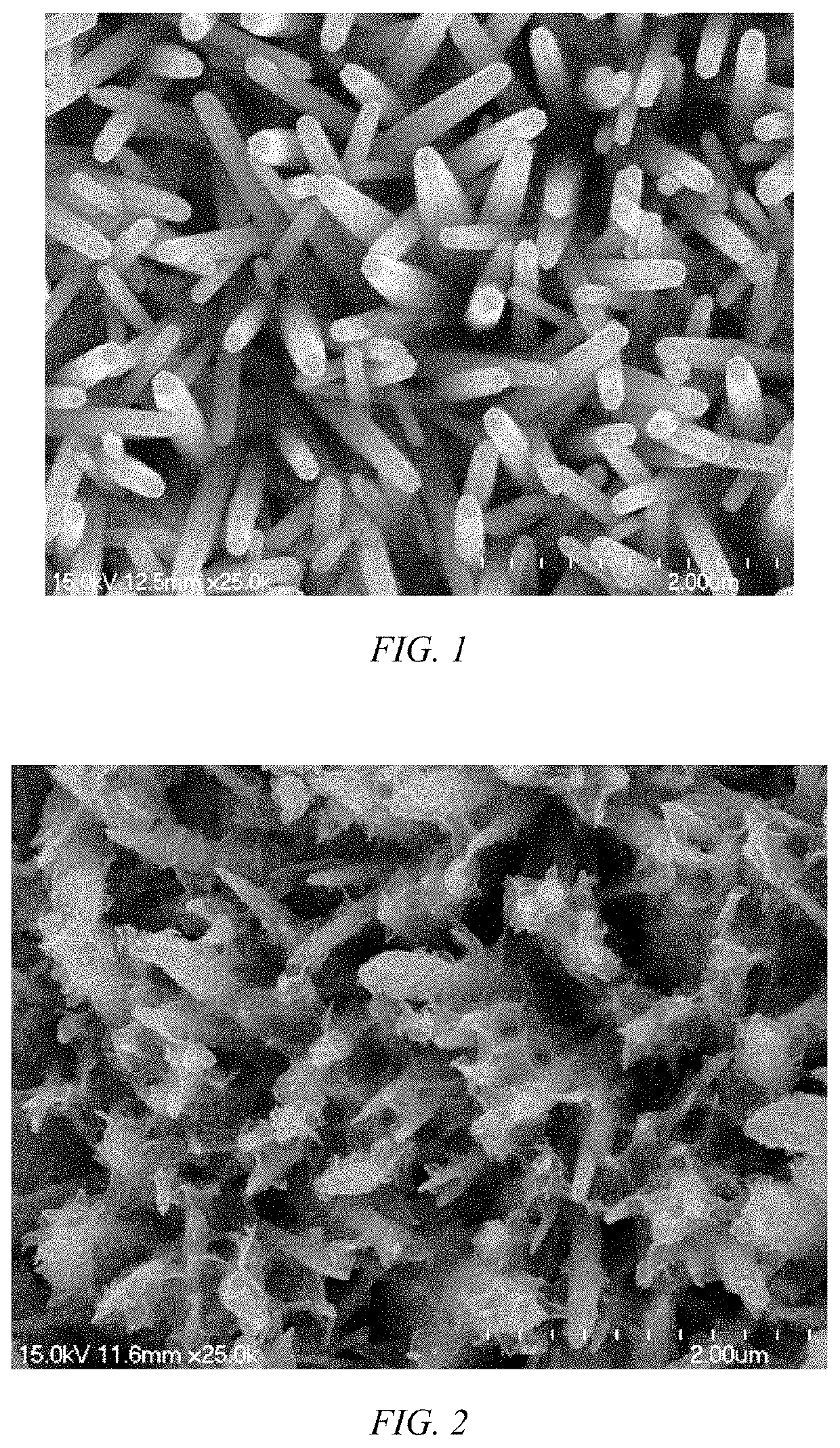
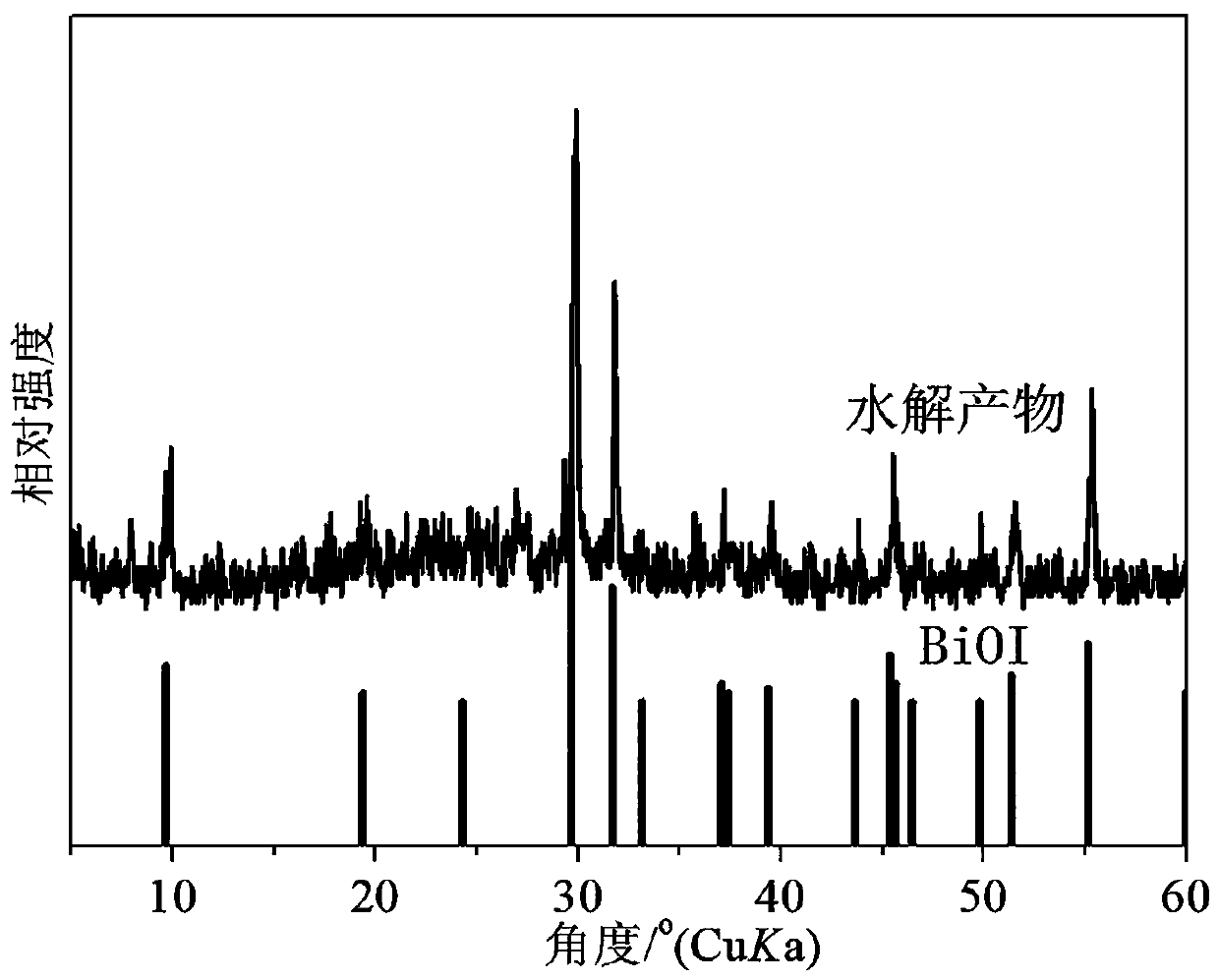
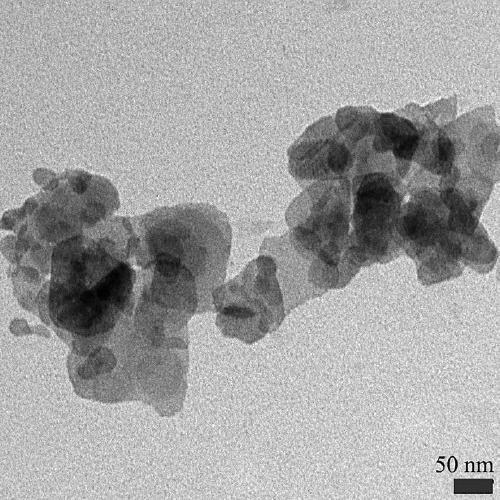
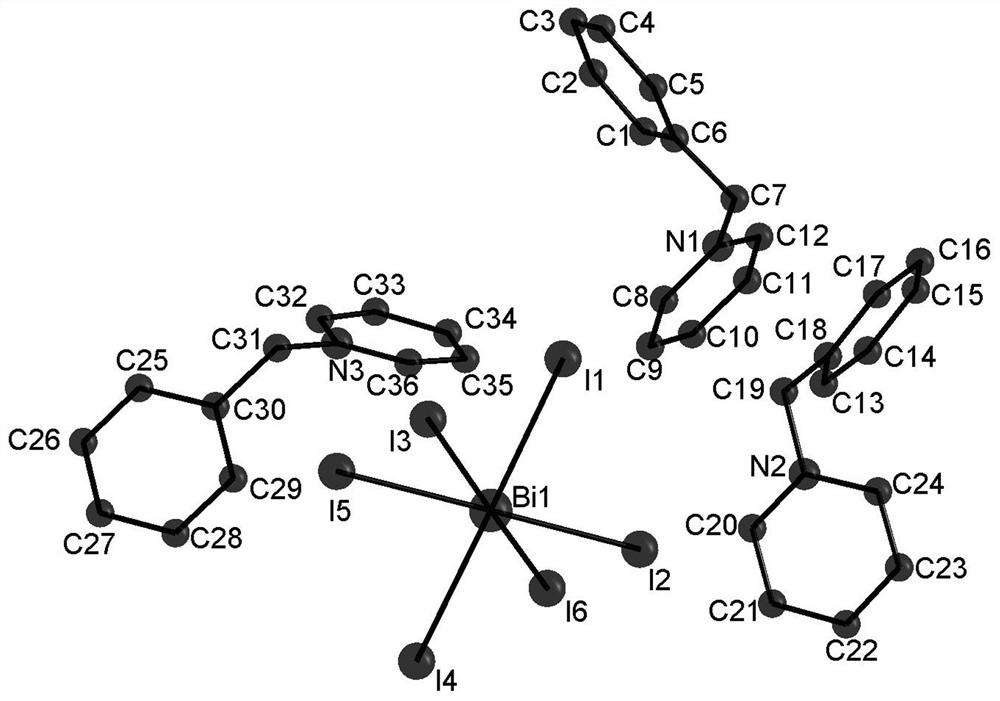
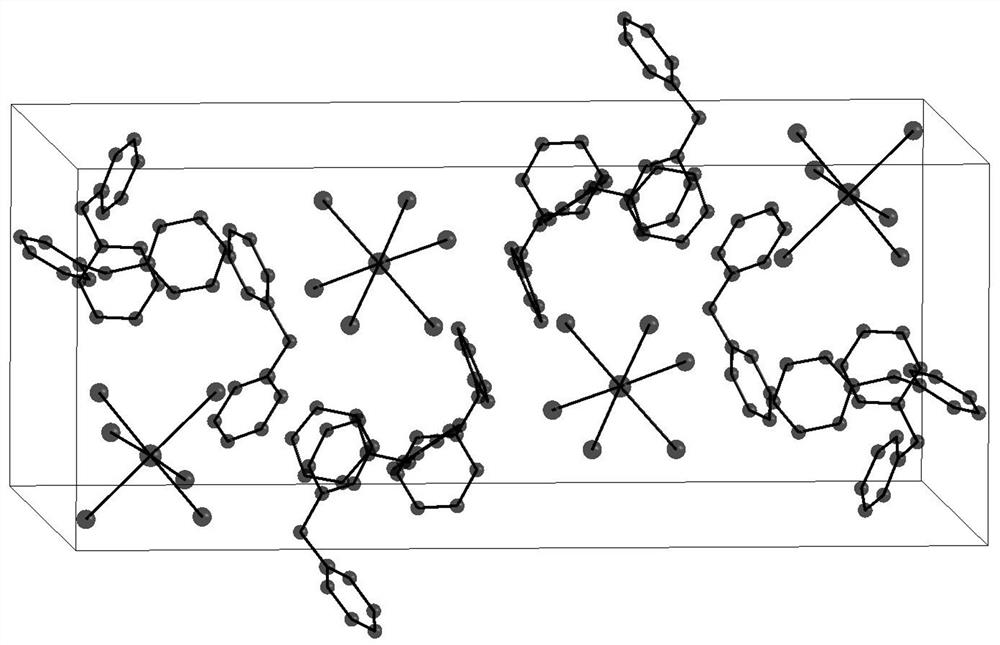
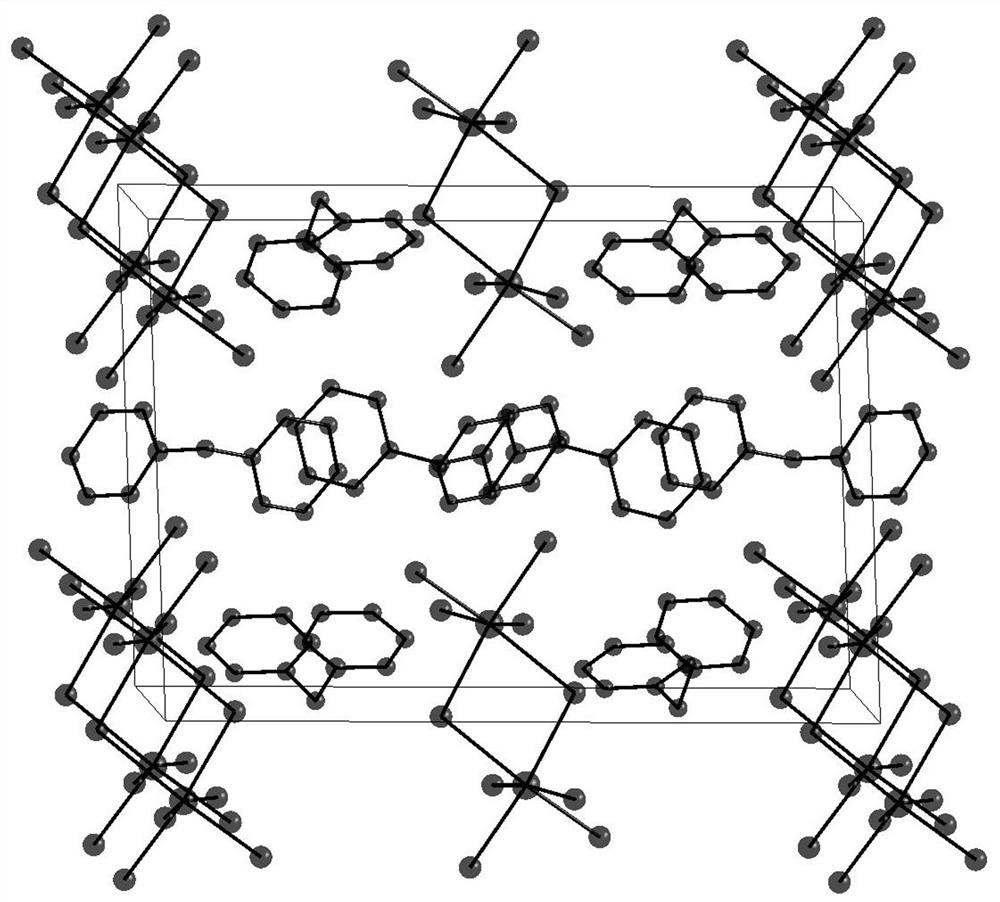
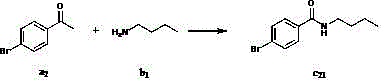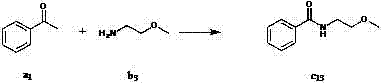Patents
Literature
64 results about "Bismuth iodide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
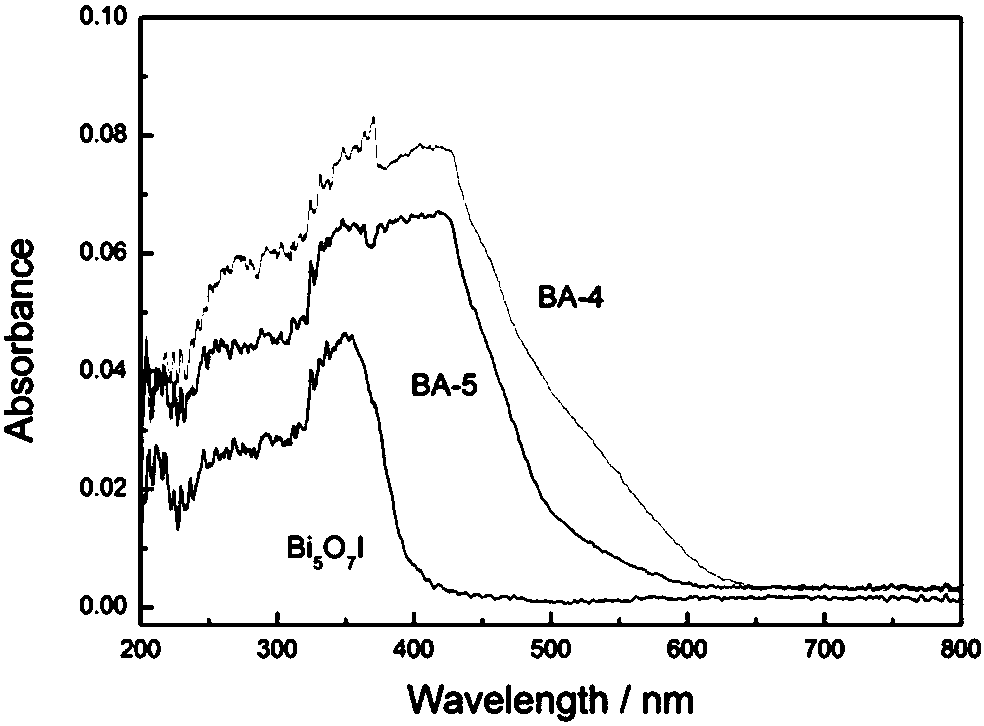
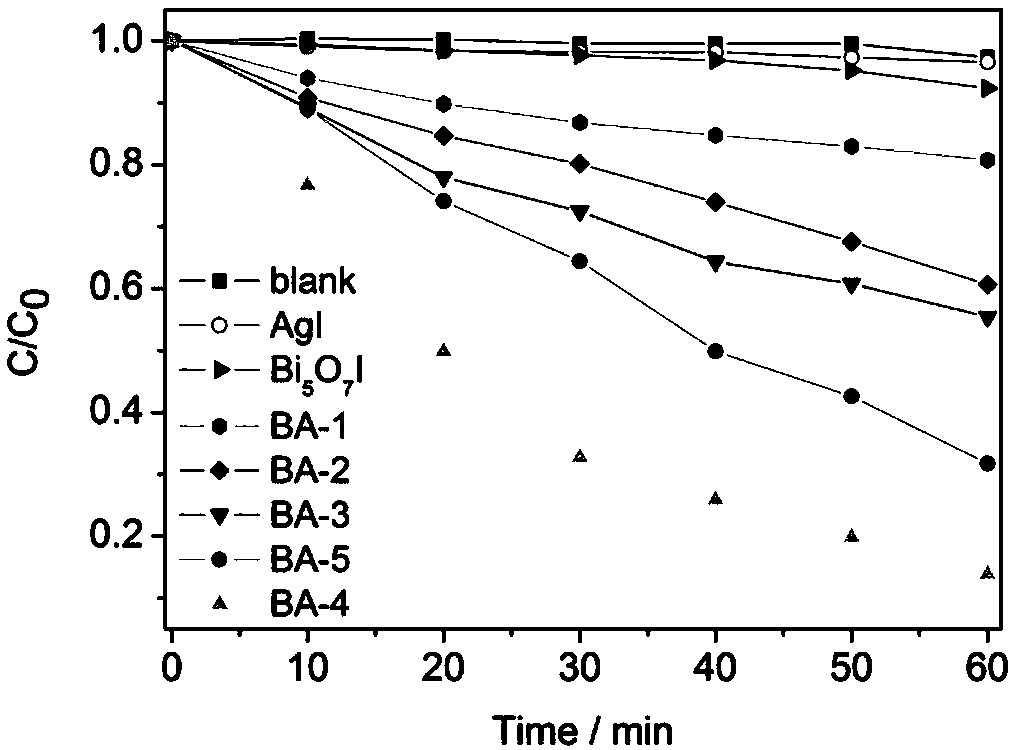
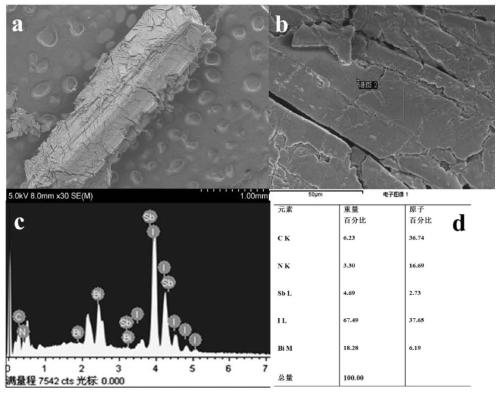
Bismuth(III) iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula BiI3. This gray-black solid is the product of the reaction of bismuth and iodine, which once was of interest in qualitative inorganic analysis.
Double-function negative electrode and applications of double-function negative electrode as all-vanadium flow battery negative electrode
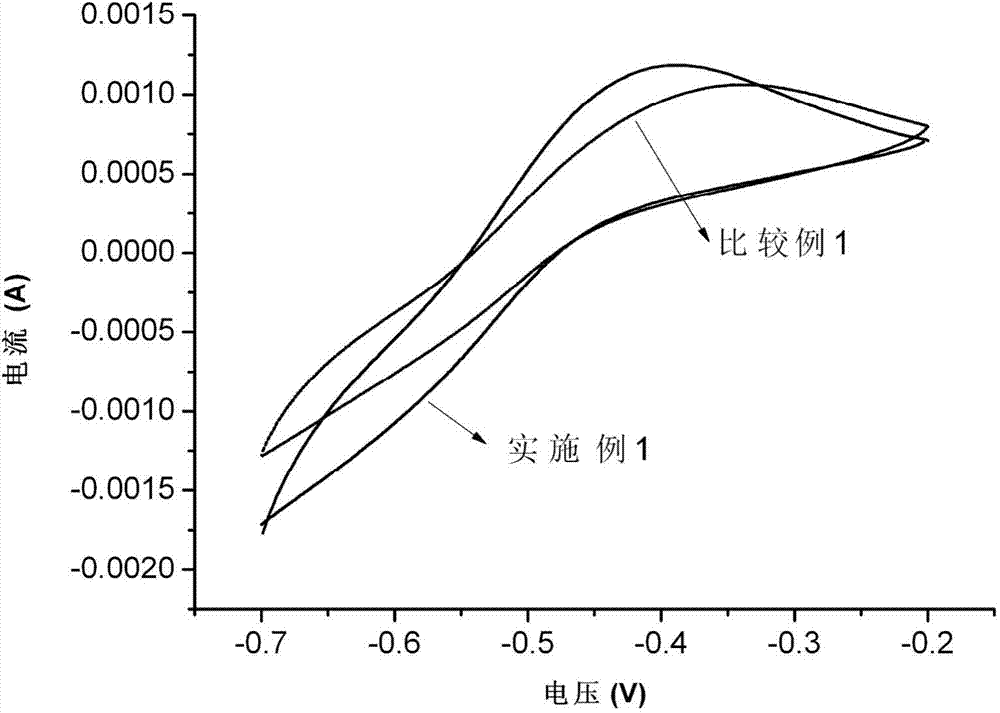
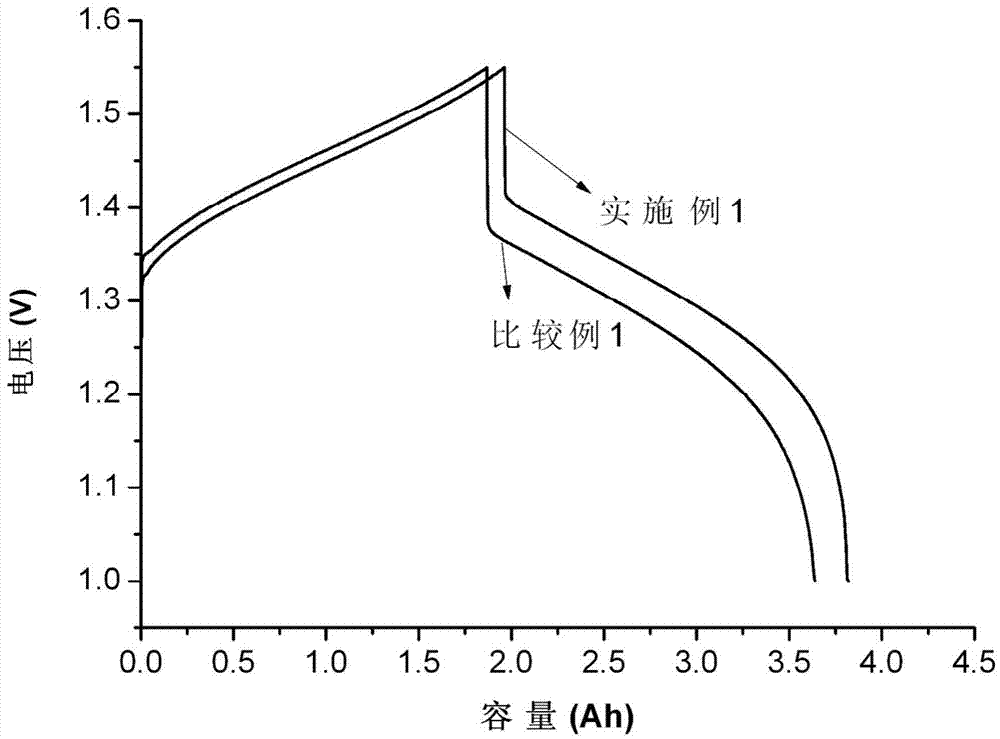
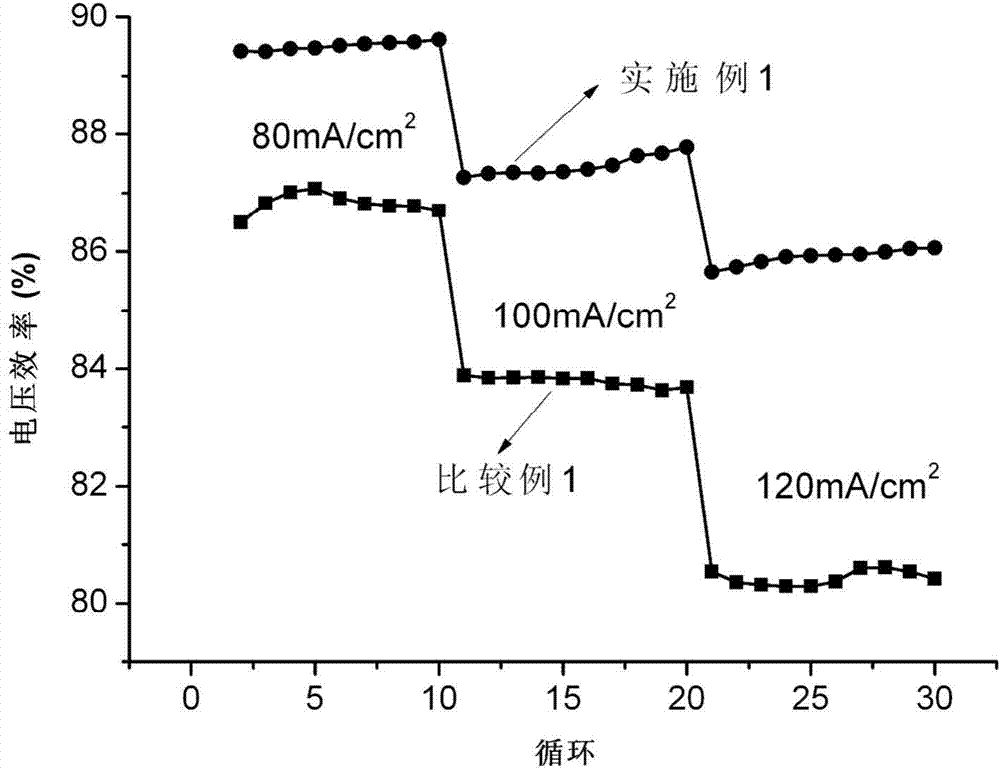
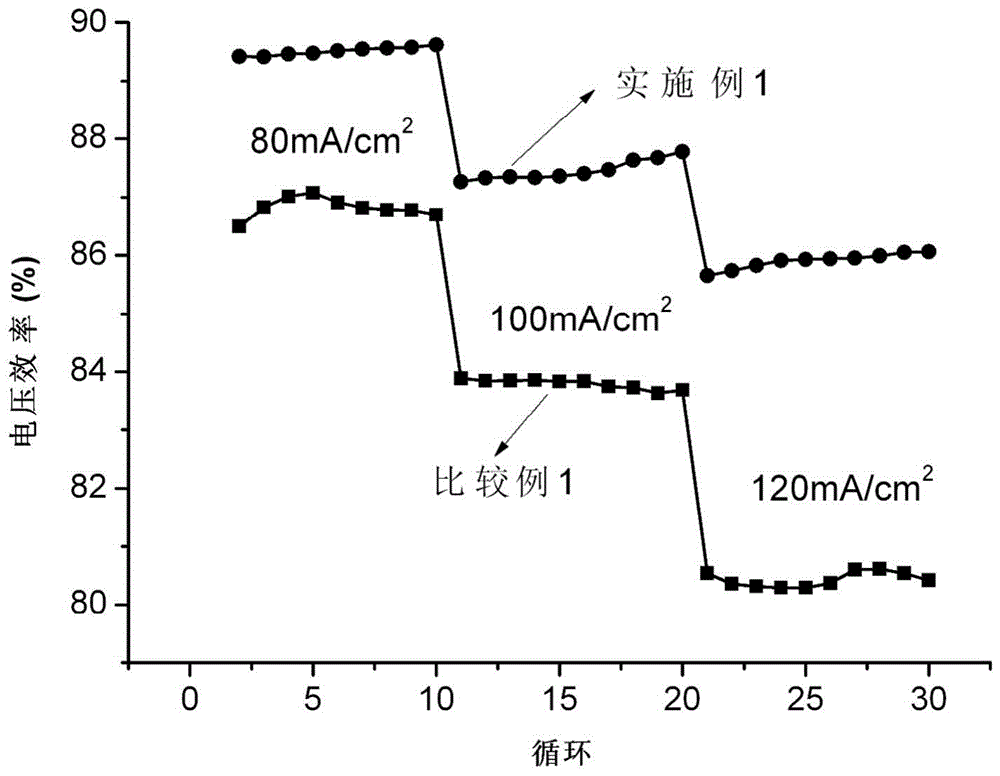
ActiveCN104518221AReduces electrochemical polarizationIncrease working current densityMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesFormateCharge transfer resistance
The invention relates to an all-vanadium flow battery double-function negative electrode, wherein a carbon material is adopted as a substrate, a Bi-containing electro-catalyst is modified on the surface of the substrate, the Bi-containing electro-catalyst is one or more than two selected from a Bi elementary substance, Bi2O3, a Bi halide and a Bi metal salt, the Bi halide is bismuth fluoride, bismuth trichloride, bismuth bromide, or bismuth iodide, and the Bi metal salt is bismuth sulfate, bismuth nitrate, bismuth phosphate, bismuth formate or bismuth acetate. According to the present invention, the electrode is suitable for the negative electrode of the all-vanadium flow battery, the electrocatalysis activity and the electrochemical reversibility of the electrode material on the V<2+> / V<3+> oxidation reduction reaction can be substantially improved, and the charge transfer resistance can be reduced; and the high hydrogen evolution overpotential is provided so as to inhibit the occurrence of the hydrogen evolution reaction and prolong the service life of the battery.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Wide band gap semiconductor composite detector plates for x-ray digital radiography
InactiveUS20050118527A1Direct signal conversionHigh sensitivitySolid-state devicesPhotomechanical apparatusParticulatesX-ray
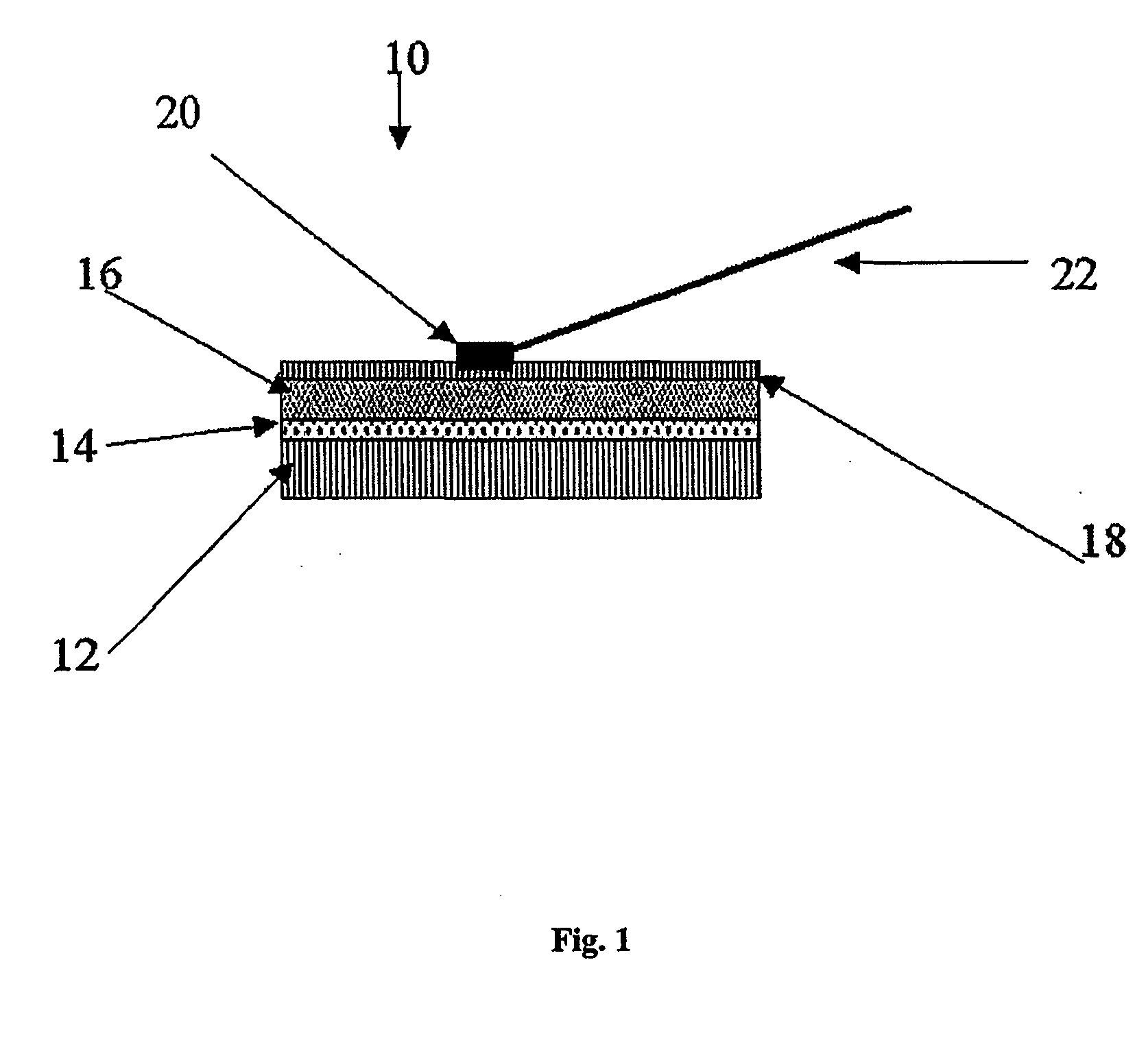
An imaging composition for radiation detection systems which includes an admixture of at least one non-heat treated, non-ground particulate semiconductor with a polymeric binder. The non-heat treated, non-ground particulate semiconductor is selected from mercuric iodide, lead iodide, bismuth iodide, thallium bromide and cadmium-zinc-telluride (CZT), and at least 90% of the semiconductor particulates have a grain size of less than 100 microns in their largest dimension. A radiation detector plate (10) for an imaging system includes a substrate (12) which serves as an electrode, at least one imaging composition layer (16) applied onto the substrate (12), and a second electrode (18) which is in electrical connection with the imaging composition (16) and connected (20, 22) to a high voltage bias.
Owner:REAL TIME RADIOGRAPHY
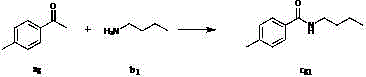
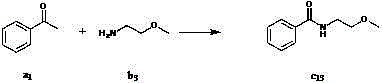
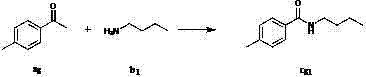
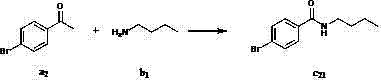
Method for preparing amide compound
InactiveCN102746077AMild reaction conditionsMeet the requirementsOrganic compound preparationSulfonic acid esters preparationSodium iodidePotassium iodine
The invention discloses a method for preparing an amide compound, which comprises the steps of configuration of reaction system. Methyl ketone, amine, catalyst, an oxidizing agent and solvent are use, wherein the general formula of the methyl ketone is RCOCH3, and R is selected from one kind of C6-C14 aryl group, C2-C8 alkenyl group, and five-or six-membered heterocyclic group; the amine is primary amine; the catalyst is selected from one kind of potassium iodide, iodine, tetramethyl ammonium iodide, tetrabutyl ammonium iodide, tetrahexyl ammonium iodide, bismuth iodide, lithium iodide, phenyl trimethyl ammonium iodide, benzyl trimethyl ammonium iodide or sodium iodide; the oxidizing agent is tert-butyl hydroperoxide; the solvent is selected from one kind of water, dichloromethane, ethyl acetate, toluene, 1,2-dichloroethane, 1,1,1-trichloroethane, acetonitrile, and isopropanol. The methyl ketone, the catalyst and the amine are added into the reaction system under the temperature of 0 DEG C and stirred for 5 minutes, and then the oxidizing agent is added to react for 2-48 hours to obtain the amide compound. The method provided by the invention is green, moderate, high in selectivity and wide in application range.
Owner:云梦星联物流有限公司
Preparing method of methyl amino bismuth iodide photovoltaic film
The invention relates to a preparing method of methyl amino bismuth iodide photovoltaic film. The method includes: mixing methylamine and hydroiodic acid, allowing reaction at low temperature, performing evaporating and drying to obtain methylamine iodine powder, dissolving the methylamine iodine powder and bismuth iodide powder in dimethyl formamide or V-butyrolactone solution, performing heating and stirring to allow dissolution, subjecting a substrate to spin-coating, and performing heating and crystallizing at set temperature so as to obtain the methyl amino bismuth iodide film. The method has the advantages of simplicity in process, low cost, good environment friendliness, ease of large-scale production and the like. The methyl amino bismuth iodide prepared by the method has bandgaps in a visible light area, I-V curve testing of a solar cell device prepared shows that photoelectric conversion performance is good, and the method is applicable to the field of solar cell photovoltaics.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of silver iodide/platy bismuth-rich type bismuth iodide composite photocatalytic material
ActiveCN108187700AMild conditionsLess time and energy consumptionPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationHeterojunctionSilver iodide
The invention discloses a preparation method of a silver iodide / platy bismuth-rich type bismuth iodide composite photocatalytic material. The method includes the steps that firstly, Bi(NO3)3 5H2O andKI serve as raw materials, BiOI is prepared through a chemical precipitation method, BiOI powder is evenly dispersed in water, NaOH serves as a precipitation transforming agent, AgNO3 serves as a silver source, under a stirring condition, a sodium hydroxide solution and a silver nitrate agent are sequentially dropwise added into BiOI turbid liquid, and a AgI / Bi5O7I composite is generated through an in-situ deposition / precipitation transforming method. According to the AgI / Bi5O7I composite prepared through the method, AgI tightly binds to Bi5O7I, heterojunctions are formed, and excellent photocatalytic activity is generated under the synergistic effect of AgI and Bi5O7I. The preparation method is carried out at room temperature, has moderate conditions, and is short in reaction time, easy and convenient to operate and capable of being used for large-scale industrial production, and energy saving and environmental protection are achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Bismuth iodide two-dimensional material and preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN107093560ASynthetic heterostructureImprove performanceMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionTube furnace
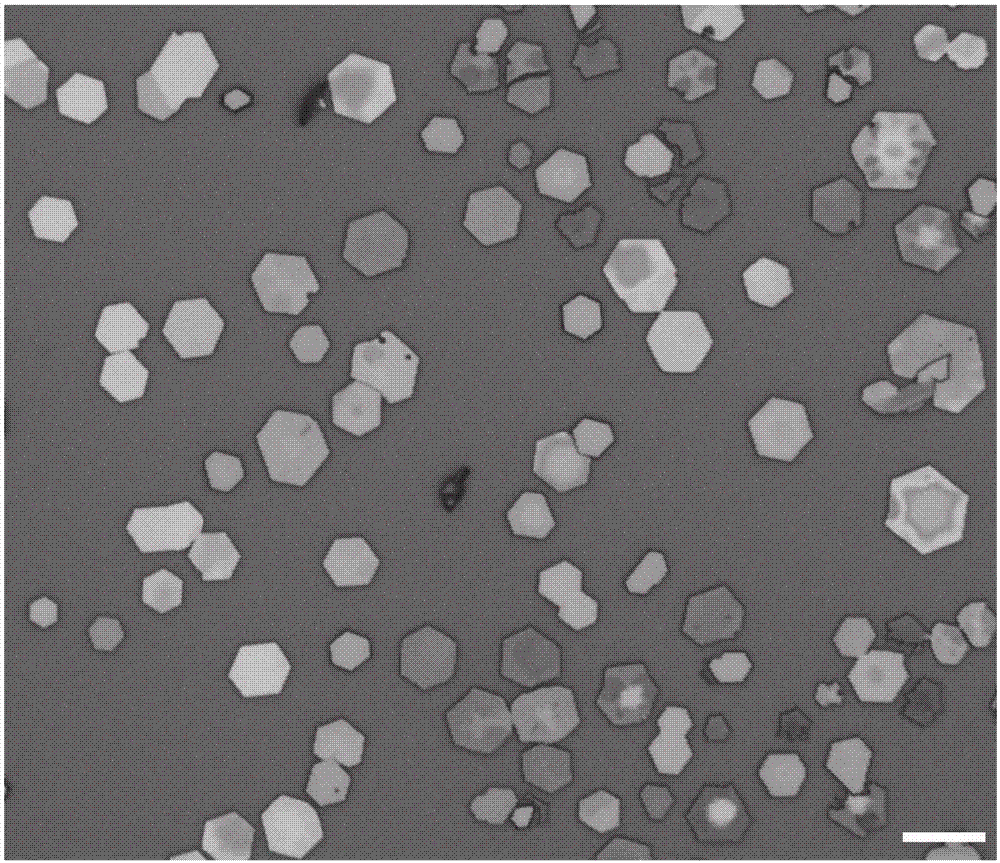
The invention relates to a preparation method of a bismuth iodide two-dimensional material and electrical and optoelectronic devices made of the material. A novel bismuth iodide nanosheet two-dimensional material is obtained through expansion. The preparation of a vertical heterojunction and electrical and optoelectronic devices offers new possibilities for the discovery of novel electrical and optoelectronic device equipment. The method comprises the following steps: placing a porcelain boat containing bismuth iodide powder in a constant temperature zone of a single-temperature-zone tubular furnace; setting the temperature of the constant temperature zone to 305-360 DEG C; taking empty Si / 300nmSiO2 and Si / 300nmSiO2 with WSe2 / WS2 nanosheets grown thereon as a growth substrate of the two-dimensional material, and placing the Si / 300nmSiO2 in a variable temperature zone or room temperature zone on the downstream of the furnace; setting the flow rate of carrier gas (argon) to 5-225sccm; and obtaining a bismuth iodide two-dimensional material through fast growth at constant temperature for 10-15min or by moving a silicon wafer through a magnet. The BiI3 two-dimensional material is prepared by depositing Cr (20nm) and Au (80nm) through electron beam lithography. The bismuth iodide nanosheet prepared using the method has a good hexagonal shape, has thickness of 10-120nm, is 3-10 microns in size, is monocrystal, and is of high quality. The hetero junction preparation method is simple and feasible.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
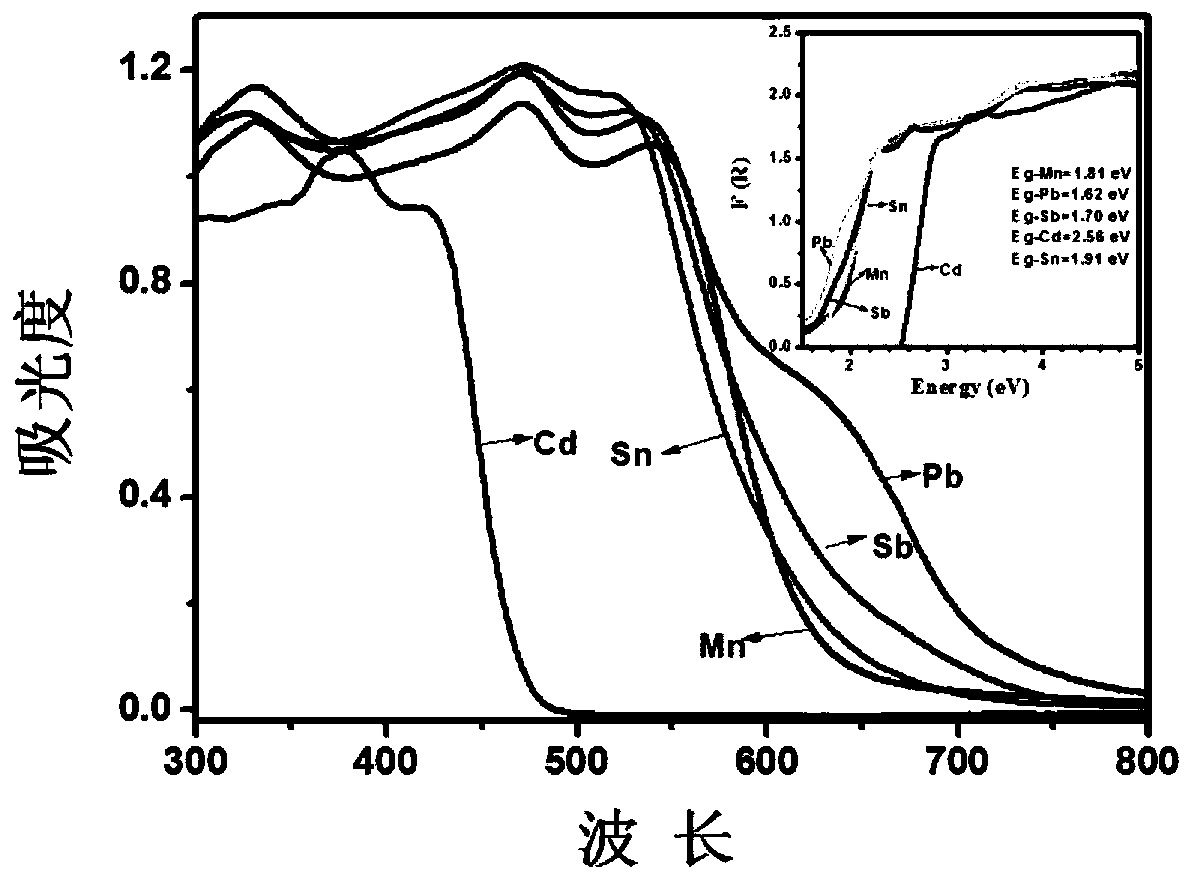
Lead-free all-inorganic perovskite cesium bismuth iodide thin film/n-type silicon heterojunction photodetector and preparation method thereof
PendingCN109256471AReduce manufacturing costImprove stabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention discloses a lead-free all-inorganic perovskite cesium bismuth iodide thin film / n-type silicon heterojunction photodetector and a preparation method thereof. The n-type silicon substrateis used as the base region of the photodetector, and the n-type silicon base electrode is disposed on the lower surface of the n-type silicon substrate; the upper surface of the n-type silicon substrate is covered with the insulating layer, and the insulating layer is covered with calcium Titanium ore CsBi3I10 film contact electrode, a perovskite CsBi3I10 film is deposited on the perovskite CsBi3I10 film contact electrode, and a part of the film forms an ohmic contact with the perovskite CsBi3I10 film contact electrode, and the remaining portion and the n-type silicon substrate surface are notcovered with the insulating layer to form a HeterojunctionThe photoelectric detector of the invention has the advantages of simple process, low cost, stable property, large current switching ratio and fast response speed.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Synthetic method of non-lead double perovskite nanocrystals
InactiveCN110003907ANo pollution in the processLow costNanoopticsLuminescent compositionsCesium iodideExciton
The invention discloses a synthetic method of non-lead double perovskite nanocrystals. The synthetic method comprises the following steps: taking DMF as a solvent for dissolving cesium iodide, sodiumiodide and bismuth iodide reactants to obtain a precursor solution; using isopropanol as an anti-solvent; and adding the precursor solution into the anti-solvent, and taking a supernate after centrifugalization to obtain a cubic type nanocrystal material, of which the chemical formula is Cs2NaBiI6 and the exciton peak is 509nm. The Cs2NaBiI6 perovskite nanocrystals are synthesized for the first time. The precursor solution is injected to the anti-solvent capable of being intersoluble by selecting elements which are relatively high in abundance and small in toxicity in earthcrust and adopting aprinciple of an LARP method which is relatively simple in process and relatively low in demand of experimental environment. The precursor substance separates out crystals. The materials used in synthesis are rich in resource and low in cost, and can be produced on a large scale. The prepared nanocrystal light-emitting material has a perovskite structure and an adjustable light-emitting range, sothat the nanocrystals become a low cost quantum dot light-emitting material with a development potential.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
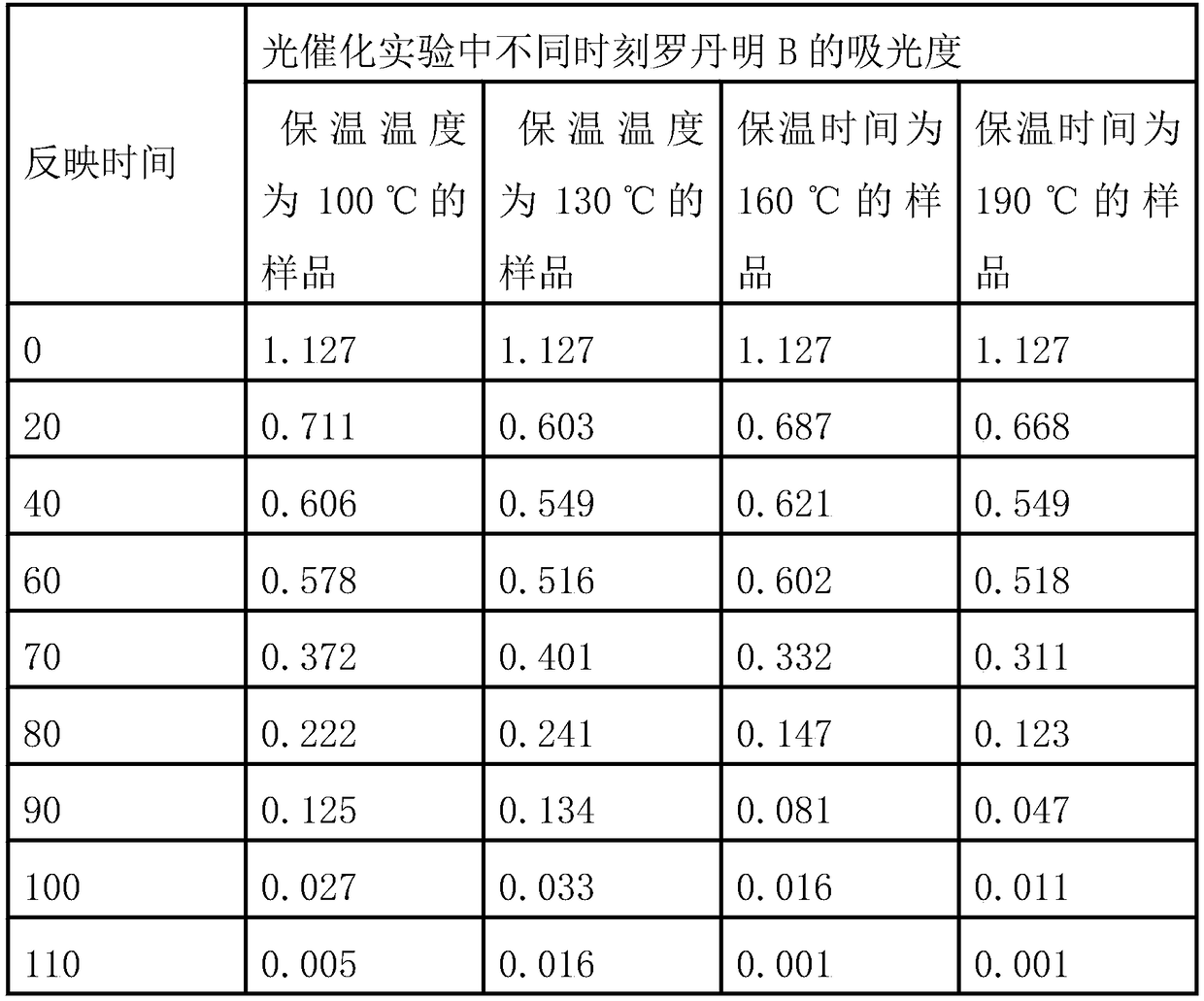
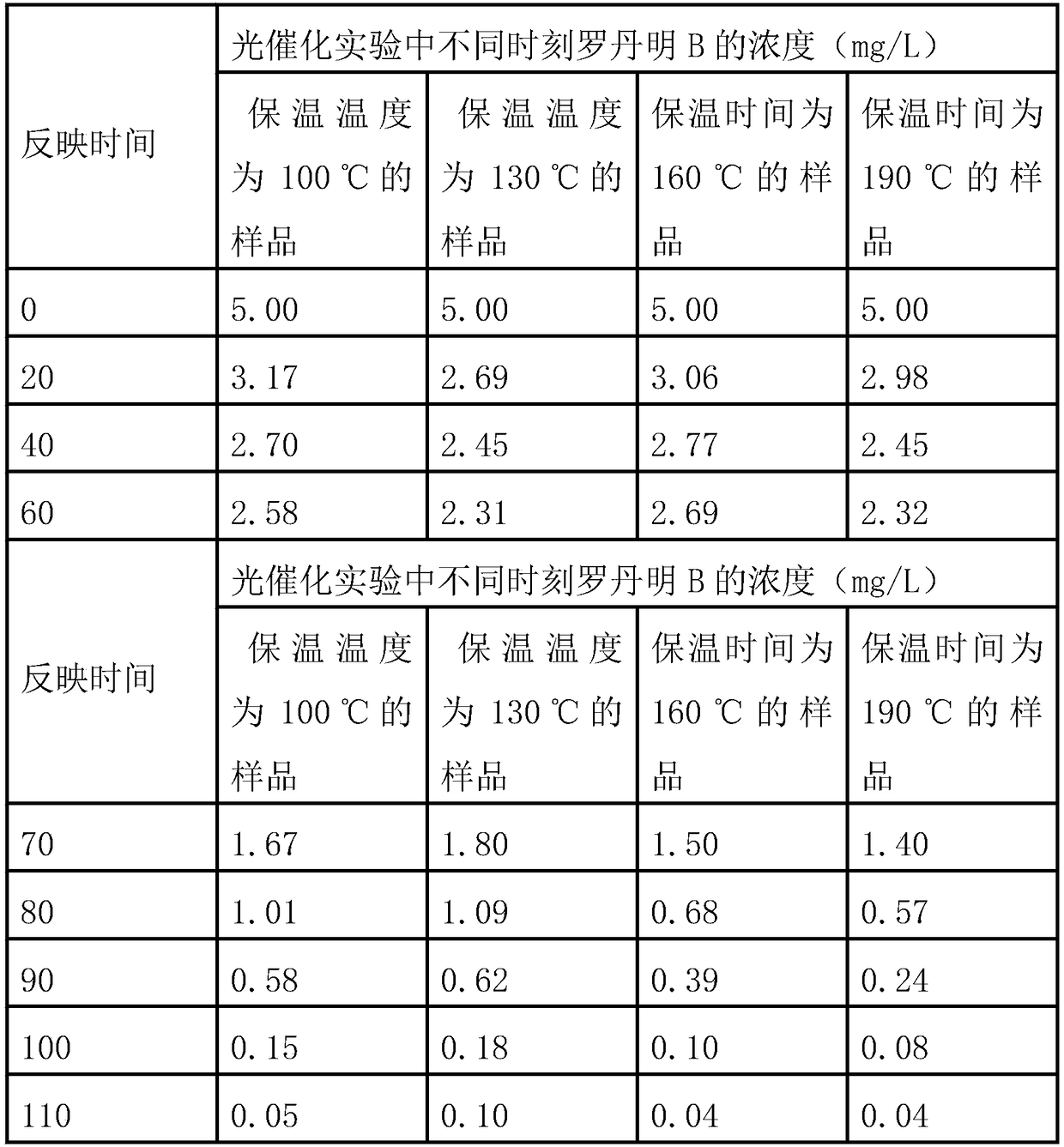
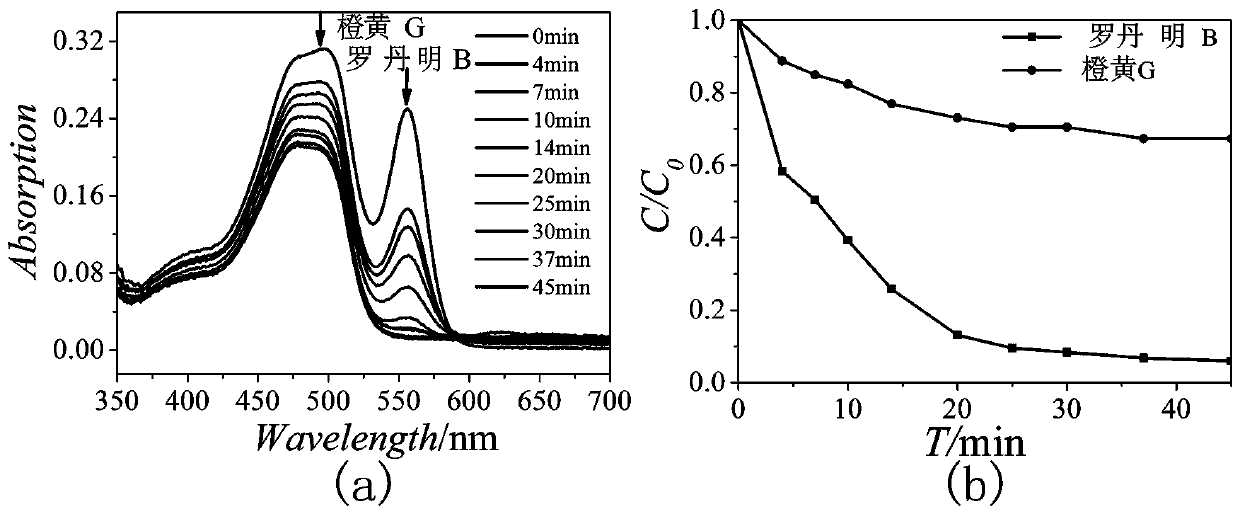
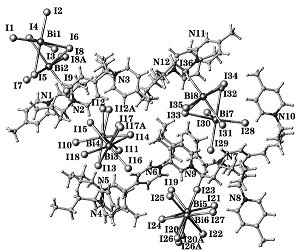
Preparation and application of bismuth iodine hybrid material for selective color fading of rhodamine B
InactiveCN108586538ASynthesis conditions are simpleNo pollution in the processOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsOrganic chemistry methodsIodineHybrid material
The invention discloses synthesis of a bismuth iodine based inorganic-organic hybrid material and an application of the hybrid material in selective color fading of rhodamine B. The purpose of the invention is to synthesize the inorganic-organic hybrid material (Habtz)BiI4 which can conveniently, quickly, efficiently and selectively fade color of the rhodamine B, wherein abtz represents 2-aminobenzothiazole. Bismuth iodide, 2-aminobenzothiazole, ethanol and hydroiodic acid can be selected as reaction raw materials, and a single crystal of the compound (Habtz)BiI4 is obtained under the solvothermal synthesis condition. The (Habtz)BiI4 disclosed by the invention has excellent properties, and can be used for chemical selective treatment of the rhodamine B in a dye waste liquid without any energy provided by the outside.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
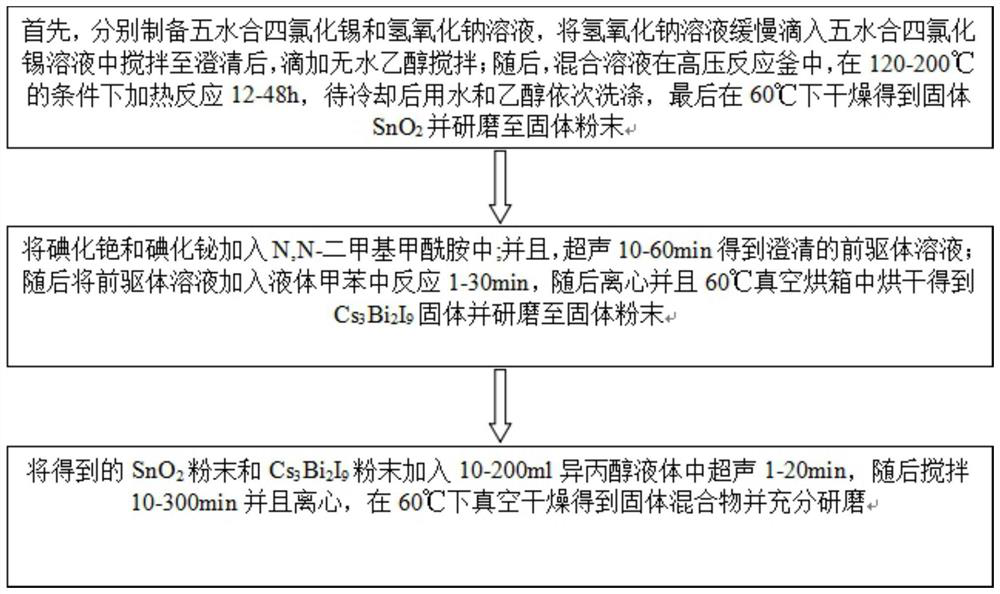
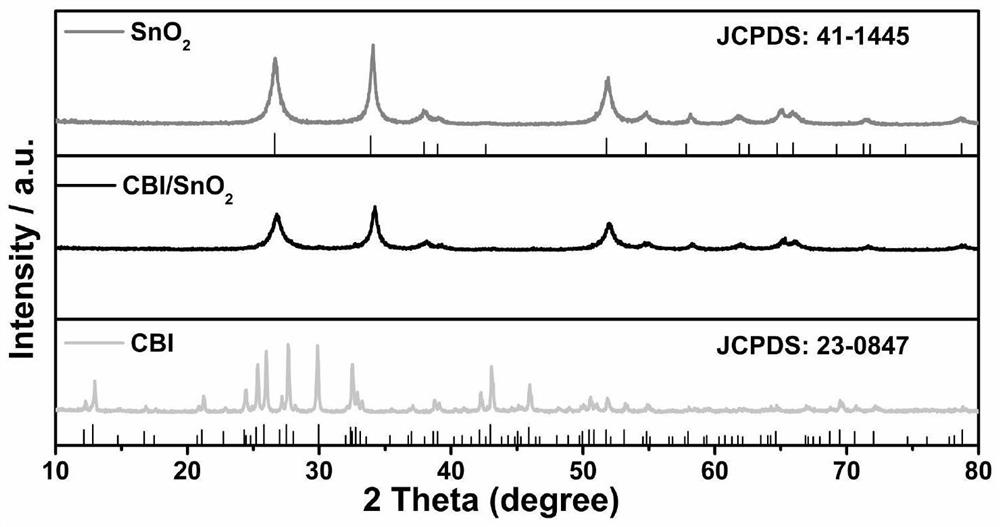
Metal oxide and halide perovskite quantum dot heterojunction visible-light-driven photocatalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113275026AEasy to operateMild reaction conditionsGas treatmentPhysical/chemical process catalystsHeterojunctionHydration reaction
The invention discloses a preparation method of a metal oxide SnO2 and halide perovskite quantum dot Cs3Bi2I9 heterojunction visible-light-driven photocatalyst, which comprises the following steps of (1) preparing a tin tetrachloride pentahydrate solution and a sodium hydroxide solution, dropwise adding the sodium hydroxide solution into the tin tetrachloride pentahydrate solution, stirring, dropwise adding absolute ethyl alcohol, stirring, heating, reacting, then washing, drying and grinding, (2) adding cesium iodide and bismuth iodide into N, N-dimethylformamide, and performing ultrasonic treatment to obtain a precursor solution, then adding the solution into toluene for reaction, and then centrifuging, drying and grinding, and (3) adding the two kinds of powder into isopropanol liquid for ultrasonic treatment, then stirring and centrifuging, drying and grinding to obtain the heterojunction visible-light-driven photocatalyst. The method for preparing the heterojunction photocatalyst is easy to operate, mild in reaction condition, low in equipment requirement and free of a complex synthesis device, and the catalyst is applied to nitrogen oxide degradation and can remarkably improve the nitrogen oxide removal efficiency.
Owner:YANGTZE DELTA REGION INST OF UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINE HUZHOU +1
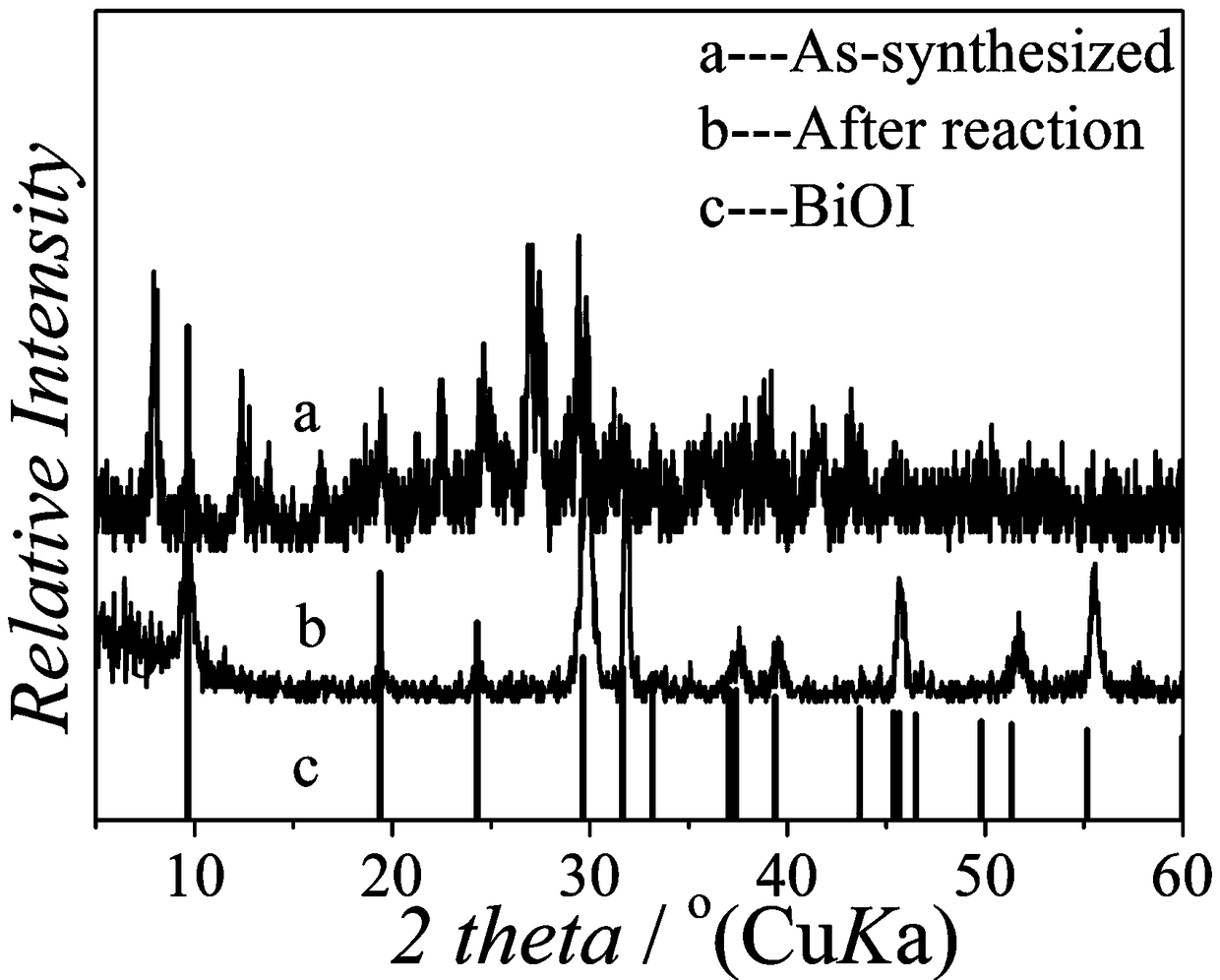
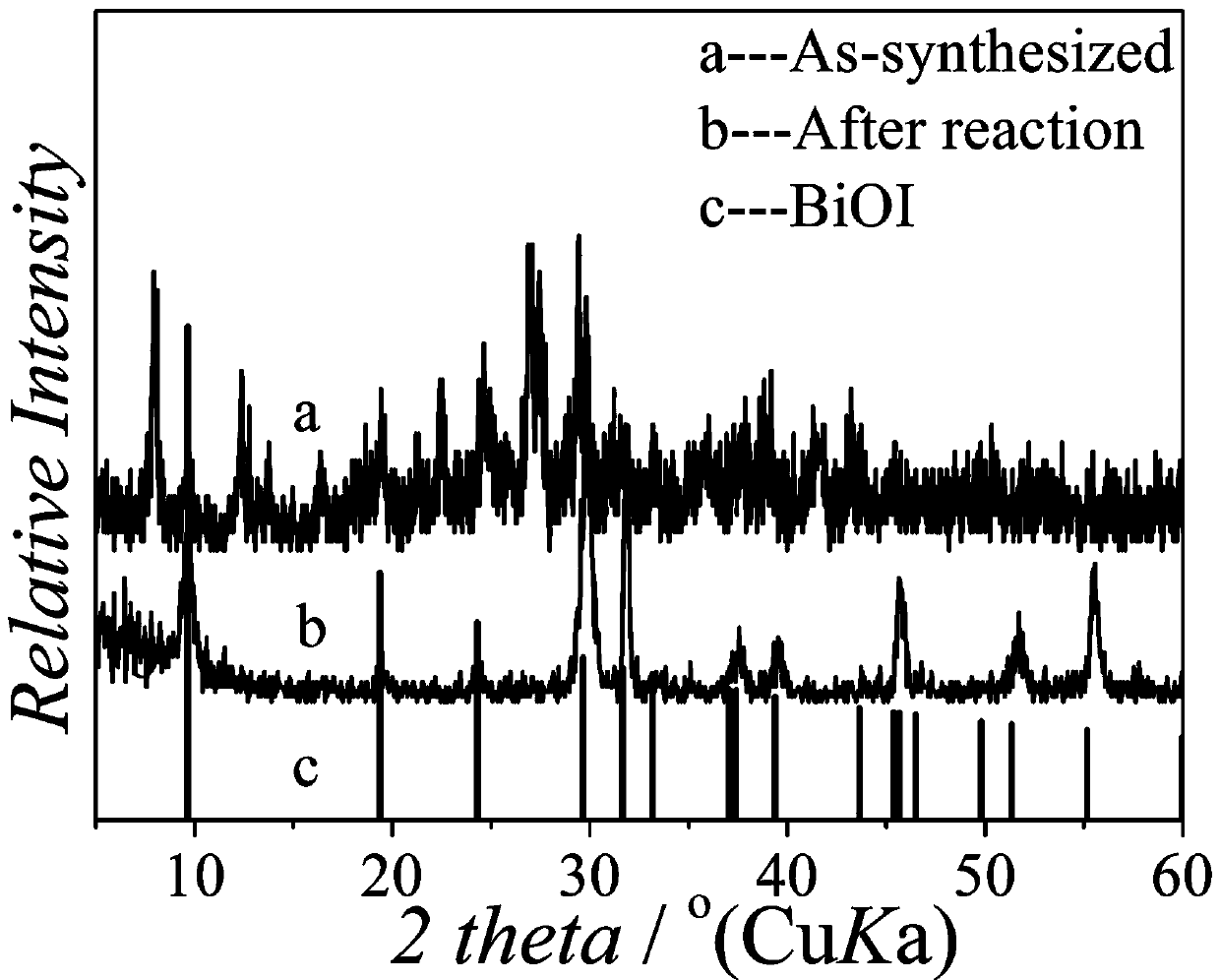
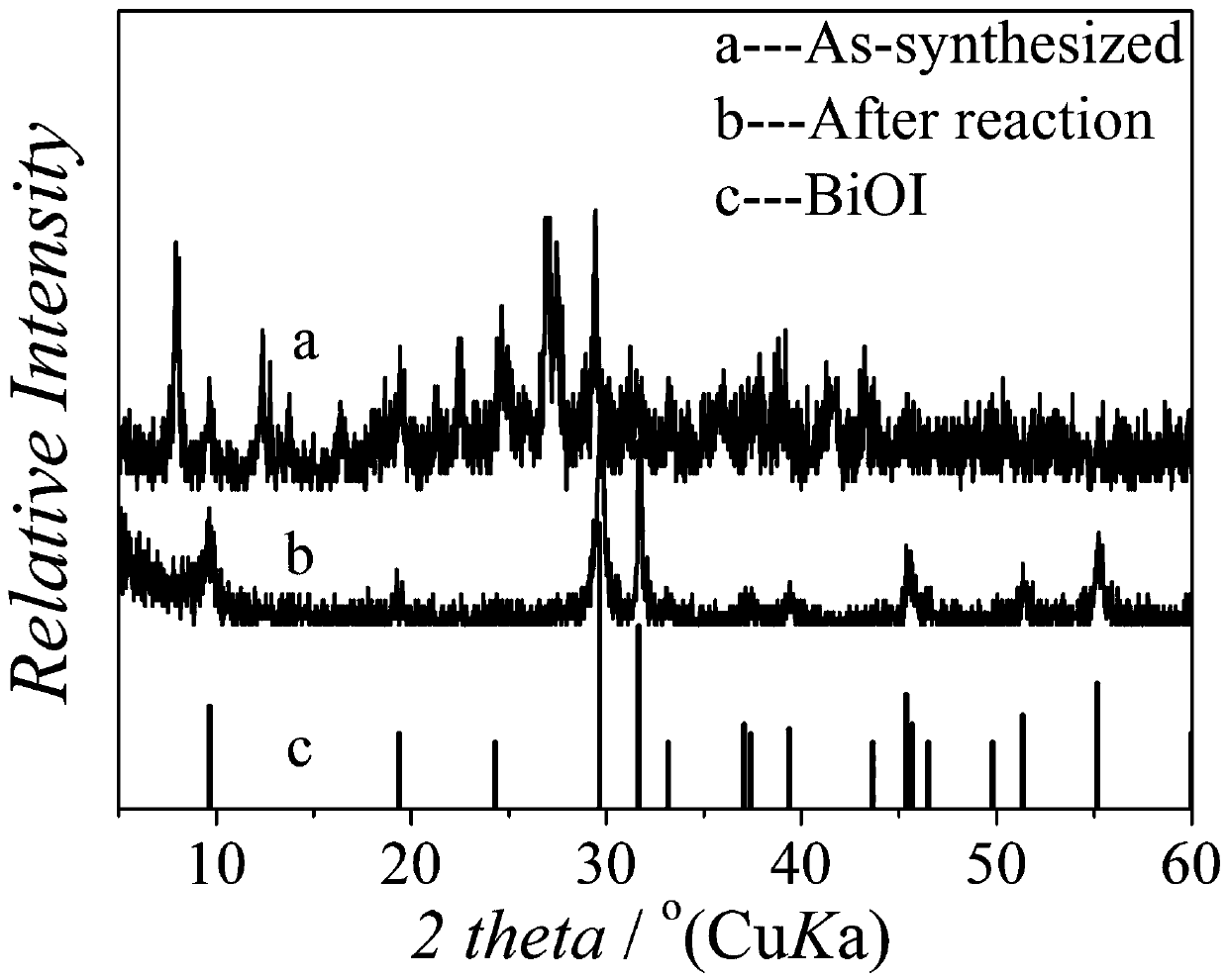
Synthesis of bismuth iodine hybrid material and application to preparation of BiOI nano-sheet
InactiveCN107686130AEasy to operateEasy to shapeIodide preparationBismuth compoundsHybrid materialIodine
The invention relates to synthesis of a bismuth iodine hybrid material and application to preparation of a BiOI nano-sheet, and aims to synthesize the bismuth iodine hybrid material, wherein the bismuth iodine hybrid material can be directly applied to hydrolysis to prepare the BiOI nano-sheet. A bismuth iodine based hybrid (Habtz)BiI4 is prepared by taking bismuth iodide and 2-aminobenzothiazoleas reaction raw materials and taking mixed liquid of ethanol and hydroiodic acid as a reactant and a solvent and under the solvothermal condition, wherein the abtz is 2-aminobenzothiazole. The bismuthiodine hybrid material is simple to prepare, the raw materials are low in price and the yield is high. The hybrid material serving as a precursor can be hydrolyzed rapidly without adding other reaction raw materials in distilled water and without adjusting the pH value of the reaction, so that simple and efficient preparation of the BiOI nano-sheet is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
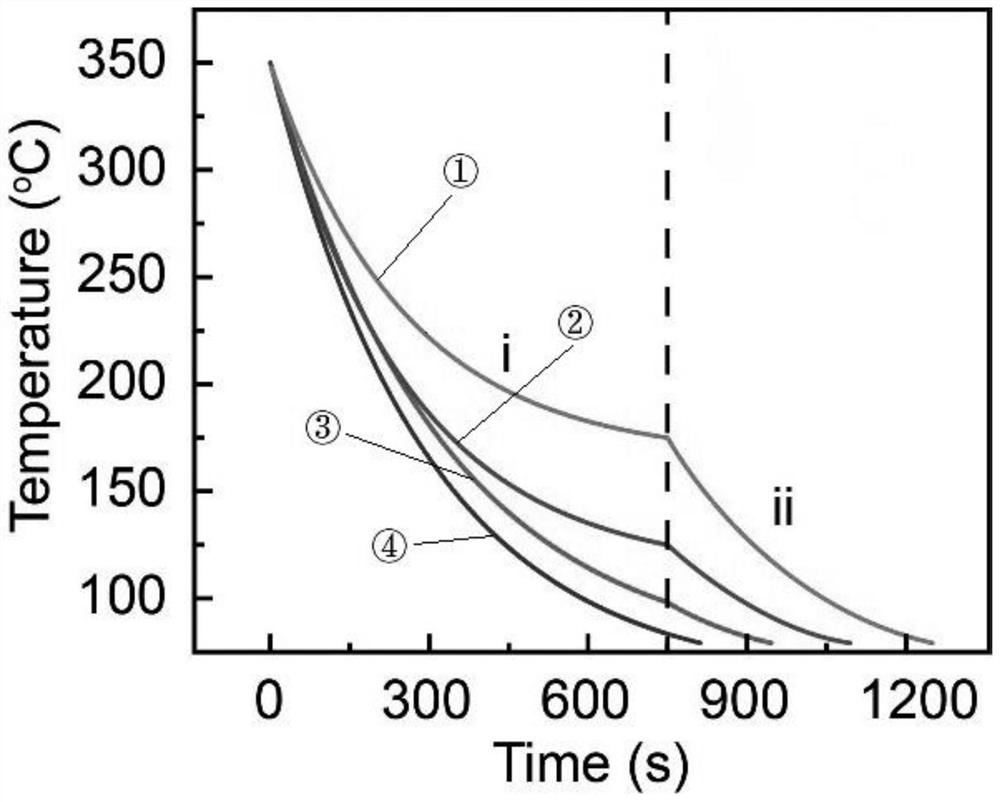
Metal layer molten pool heat transfer characteristic simulation material, preparation method and application
ActiveCN111430051ASimulation is accurateReliable simulationNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringPrandtl numberMolten salt
The invention discloses a metal layer molten pool heat transfer characteristic simulation material, and a preparation method and application thereof. The metal layer molten pool heat transfer characteristic simulation material comprises metal bismuth and bismuth iodide, and the Pr of the metal layer molten pool heat transfer characteristic simulation material under the condition of 500 DEG C is 0.08-0.12. The preparation process of the metal layer molten pool heat transfer characteristic simulation material comprises the following steps: preparing a bismuth iodide molten salt; heating the metal bismuth until the metal bismuth is completely molten, and continuously heating to a temperature T; slowly adding the prepared bismuth iodide molten salt into the molten metal bismuth for multiple times at the temperature T; and completely melting the bismuth iodide crystals on the surface layer of the metal bismuth to obtain the metal layer molten pool heat transfer characteristic simulation material. The Pr number of the metal layer molten pool heat transfer characteristic simulation material provided by the invention in a working state is 0.08-0.12, is closer to the Prandtl number of a real material; therefore, the real material of the metal layer can be simulated more accurately and reliably, the heat transfer characteristic of the metal layer of the metal layer molten pool in the reactor prototype lower end socket can be reflected more accurately, the uncertainty of the heat transfer relational expression obtained through experiments is effectively reduced, and data support is provided for formulation and implementation of a melt in-reactor retention strategy.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
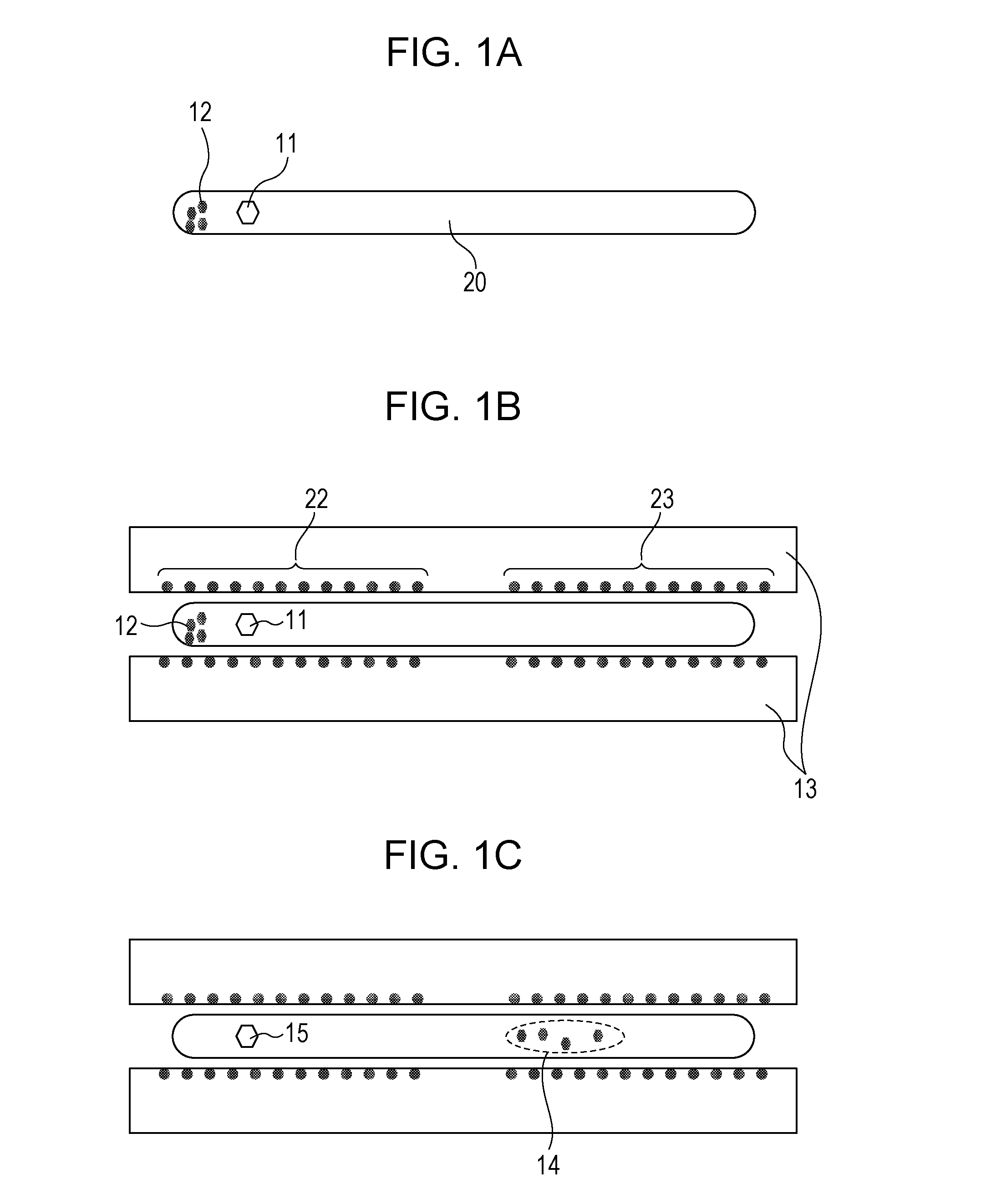
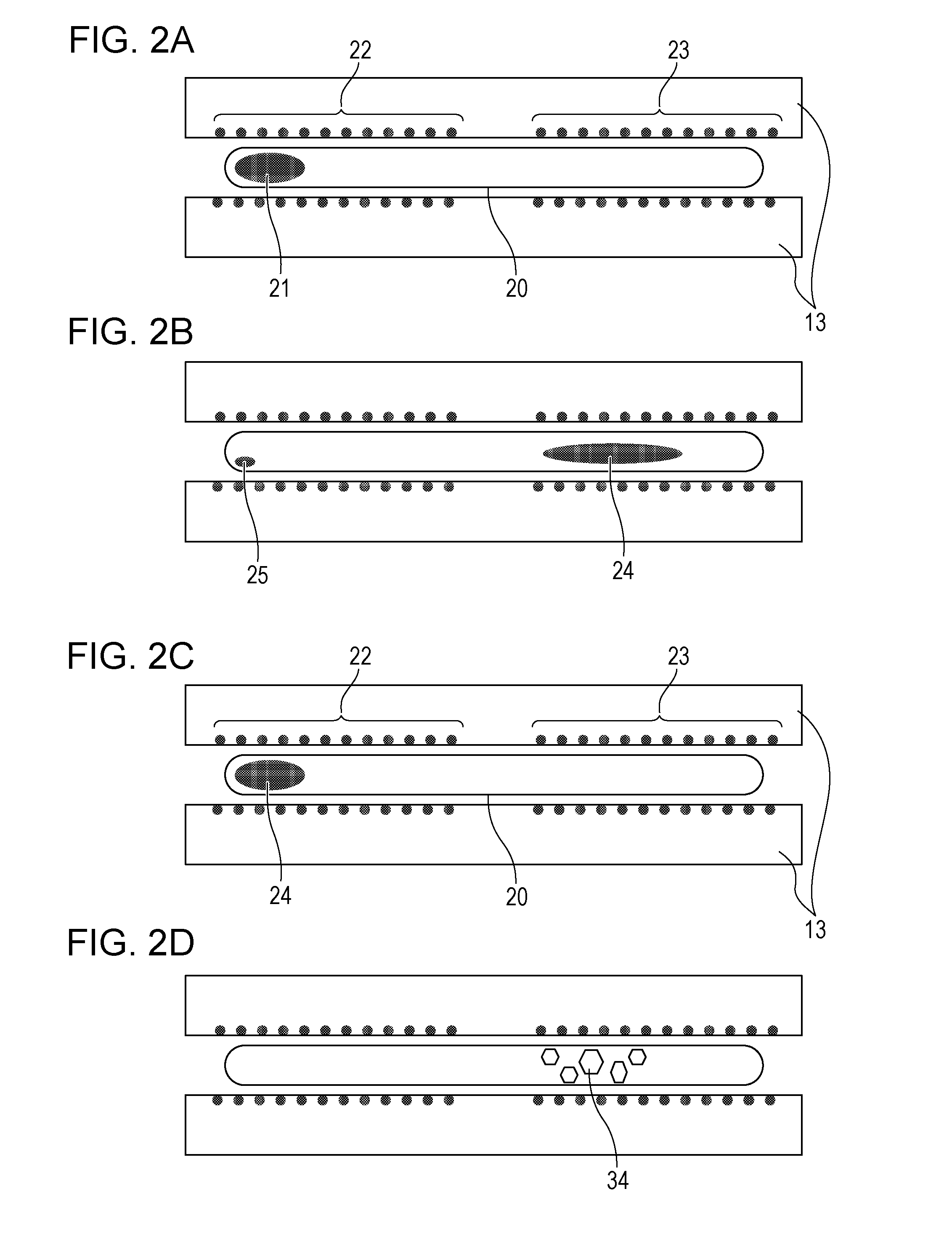
Method for preparing bismuth iodide article and method for manufacturing radiation detecting element
A method for preparing a bismuth iodide article includes heat-treating bismuth iodide at a temperature less than the melting point of bismuth iodide in an atmosphere containing iodine.
Owner:CANON KK
Method for adjusting morphology, band gap and stability of bismuth iodide-ethylene diamine hybrid material through doping projects
InactiveCN109824519AThe synthesis process is simpleMild reaction conditionsPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsSemiconductor materialsEngineering
The invention discloses a method for adjusting morphology, band gap and stability of a bismuth iodide-ethylene diamine hybrid material through doping projects. The method aims at research on methods for performing metal element doping on the hybrid material (NH3CH2CH2NH3)Bi2I10 to adjust morphology, optical band gap and stability of the hybrid material to finally obtain hybrid materials with different band gaps, which can be further applied to the fields of organic-inorganic hybrid perovskite solar batteries and semiconductor materials. The method comprises performing adjustment within a certain range on the band gap of an originally prepared narrow-band-gap organic-inorganic low-dimension hybrid material (NH3CH2CH2NH3)Bi2I10. The method for adjusting morphology, band gap and stability ofthe bismuth iodide-ethylene diamine hybrid material through the doping projects has the advantages of being simple in synthesis, mild in reaction conditions, low in cost, good in repeatability, continuously adjustable in optical band gap within a relatively wide range, high in stability and the like, thereby having a good industrialization prospect.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Asymmetric bismuth catalysis system, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109590024AAchieve activationTo achieve the purpose of activationOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsOxonium ionPhosphoric acid
The invention provides an asymmetric bismuth catalysis system, a preparation method and an application thereof, relates to the technical field of asymmetric catalysis and provides an asymmetric bismuth catalysis system. By adoption of the asymmetric bismuth catalysis system, the problem of high Substrate specificity of the bismuth catalysis system is solved. The asymmetric bismuth catalysis systemcomprises a metal activity center and a chiral ligand, wherein the metal activity center is selected from one or more of bismuth acetate, bismuth hydroxide, bismuth bromide or bismuth iodide; the chiral ligand is selected from chiral phosphoric acid. The asymmetric bismuth catalysis system is used for catalyzing multiple types of asymmetric transformations such as asymmetric allylation of ketoneand imine, asymmetric allylation of oxonium ions and asymmetric reaction of imine and phenolic substrates and the like.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
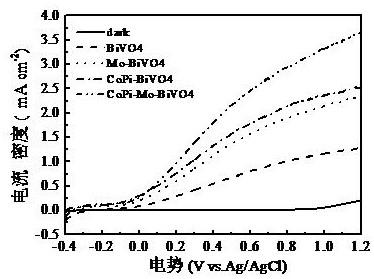
A kind of preparation method of cobalt phosphide modified molybdenum doped bismuth vanadate photoelectrode
ActiveCN109402656BDelayed self-recombinationHigh densityEnergy inputCoatingsBismuth vanadateCatalytic decomposition
The invention discloses a method for preparing a molybdenum-doped bismuth vanadate photoelectrode modified by cobalt phosphide. First, a bismuth iodide oxide photoelectrode is prepared on the surface of a conductive glass by a deposition method, and a vanadium source and molybdenum are added dropwise on the bismuth iodide oxide photoelectrode. source solution, after annealing and cleaning, the molybdenum-doped bismuth vanadate photoelectrode was obtained, and then in the three-electrode system, cobalt phosphide was deposited on the surface of the molybdenum-doped bismuth vanadate photoelectrode through photo-assisted electrodeposition, and the new bismuth vanadate photoelectrode was obtained. The invention also discloses the application of the composite bismuth molybdovanadate photoelectrode in photoelectric catalytic water decomposition. The photoelectrode prepared by the present invention is used for photoelectrocatalytic water splitting to produce hydrogen. Doping molybdenum can effectively increase the concentration of carriers and increase the photocurrent, while electrodeposition of cobalt and phosphorus can effectively delay the recombination loss in the photoelectrode and increase the The lifetime of the photogenerated carriers can promote the oxygen evolution reaction on the surface of the photoelectrode, thereby improving the solar-to-hydrogen conversion efficiency of the semiconductor photoelectrode.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
A dual-functional negative electrode and its application as negative electrode for all-vanadium redox flow battery
ActiveCN104518221BReduces electrochemical polarizationIncrease working current densityMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesFormateCharge transfer resistance
A dual-functional negative electrode for an all-vanadium redox flow battery, the dual-functional negative electrode is based on a carbon material, and its surface is modified with a Bi-containing electrocatalyst, and the Bi-containing electrocatalyst is Bi simple substance, Bi2O3, Bi halide or Bi One or more than two kinds of metal salts; Bi halides are bismuth fluoride, bismuth chloride, bismuth bromide or bismuth iodide; Bi metal salts are bismuth sulfate, bismuth nitrate, bismuth phosphate, bismuth formate or bismuth acetate . This electrode is suitable for the negative electrode of the all-vanadium redox flow battery, which can greatly improve the electrocatalytic activity and electrochemical reversibility of the electrode material for the V2+ / V3+ redox reaction, reduce the charge transfer resistance; it also has a high hydrogen evolution overpotential, It can inhibit the occurrence of hydrogen evolution reaction and prolong the working life of the battery.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
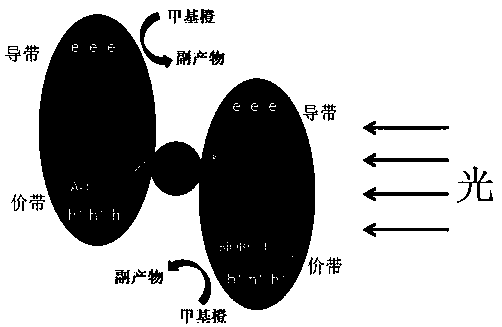
Z-type photocatalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109046396AImprove catalytic effect is weakImprove efficiencyPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationSilver iodideHalogen
The invention discloses a Z-type photocatalyst as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The Z-type photocatalyst is shown as BiOYnI1-n / Ag / AgI-x, wherein Y is halogen; x is the molar ratio of silver to iodine, and the value of x ranges from 0 to 1; n is 0 to 1; n is not equal to 1. The Z-type photocatalyst is prepared by doping silver and silver iodide into bismuth iodide, thereby improving the defects of weaker catalytic action and lower catalytic efficiency caused by higher conduction band energy level of the bismuth iodide, and remarkably improving the catalytic activity andcatalytic efficiency of the Z-type photocatalyst. Moreover, the preparation method of the Z-type photocatalyst is simple, and the photocatalytic performance of the photocatalyst can be adjusted by controlling the using amount of soluble silver salt and illumination conditions and controlling the content of silver and silver iodide.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for measuring bismuth content in colloidal bismuth pectin or colloidal bismuth pectin-contained preparation
InactiveUS20180017497A1Strong specificityGood repeatabilityAntibacterial agentsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBismuth / pectinPotassium
Provided is a method for measuring the bismuth content in a colloidal bismuth pectin or a colloidal bismuth pectin-contained preparation. A protonic acid is used to dissociate bismuth from a colloidal bismuth pectin, the principle of the characteristic reaction between bismuth and potassium iodide to produce yellow potassium bismuth iodide is used; ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry is for measurement; an external standard method is for calculation. The method has strong specificity, a good linear relationship, high accuracy, good repeatability and high sensitivity. The method is able to act as a quality control method for bismuth in a colloidal bismuth pectin or a colloidal bismuth pectin-contained preparation to effectively control the product quality.
Owner:SHANXI ZHENDONG ANTE BIOPHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Method for preparing amide compound
InactiveCN102746077BMild reaction conditionsHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationSulfonic acid esters preparationSodium iodidePotassium iodine
The invention discloses a method for preparing an amide compound, which comprises the steps of configuration of reaction system. Methyl ketone, amine, catalyst, an oxidizing agent and solvent are use, wherein the general formula of the methyl ketone is RCOCH3, and R is selected from one kind of C6-C14 aryl group, C2-C8 alkenyl group, and five-or six-membered heterocyclic group; the amine is primary amine; the catalyst is selected from one kind of potassium iodide, iodine, tetramethyl ammonium iodide, tetrabutyl ammonium iodide, tetrahexyl ammonium iodide, bismuth iodide, lithium iodide, phenyl trimethyl ammonium iodide, benzyl trimethyl ammonium iodide or sodium iodide; the oxidizing agent is tert-butyl hydroperoxide; the solvent is selected from one kind of water, dichloromethane, ethyl acetate, toluene, 1,2-dichloroethane, 1,1,1-trichloroethane, acetonitrile, and isopropanol. The methyl ketone, the catalyst and the amine are added into the reaction system under the temperature of 0 DEG C and stirred for 5 minutes, and then the oxidizing agent is added to react for 2-48 hours to obtain the amide compound. The method provided by the invention is green, moderate, high in selectivity and wide in application range.
Owner:云梦星联物流有限公司
Preparation method of floating bead loaded bismuth oxyiodide catalyst
InactiveCN108906087AHigh catalytic efficiencyImprove performanceCatalyst carriersPotassium iodineCoal
The invention provides a preparation method of a floating bead loaded bismuth oxyiodide photocatalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: pouring coal ash into a beaker containing water, after stirring, standing and separating out floating bead particles floating on the water surface; and soaking the separated floating bead particles in dilute nitric acid; after 10-14 hours, filtering and drying to obtain floating beads; mixing bismuth nitrate pentahydrate, potassium iodide and polyvinylpyrrolidone into a reaction container containing ethylene glycol to obtain a substrate liquid, and stirring the base liquid; under the condition of continuous stirring, adding the floating beads and a pH adjusting liquid into the soluble substrate liquid to obtain an adherence liquid; andfiltering the adherence liquid to obtain the adhered floating beads; drying the adhered floating beads and carrying out heat preservation to obtain the concentrated floating beads; rinsing and filtering the concentrated floating beads, and drying to obtain a finished product. The preparation method of the floating bead loaded bismuth oxyiodide photocatalyst solves the problem that in the prior art, bismuth iodide particles are fine, and the separation process is relatively complicated.
Owner:深圳市华世纪联合企业管理有限公司
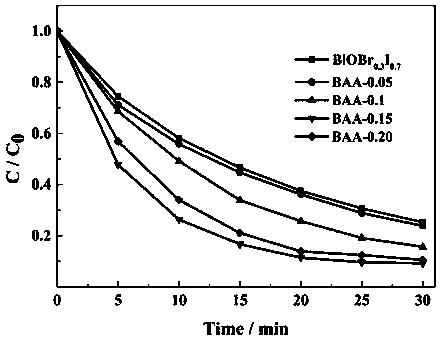
A kind of bismuth oxide/defective bismuth iodide composite material, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113042072BEasy to separateImprove photocatalytic performanceWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsGlycol synthesisComposite material
The invention provides a bismuth oxide / deficient iodine oxybismuth composite material, a preparation method and application thereof, the preparation method is firstly preparing Bi 2 o 3 , then Bi(NO 3 ) 3 ·5H 2 O and Bi 2 o 3 Dissolve in water and ethylene glycol, add water-soluble iodine salt and stir, then transfer to a hydrothermal reactor for reaction, cool to room temperature, wash, dry, grind and sieve, and finally calcined to obtain bismuth oxide / defective bismuth iodine oxybismuth composite material. The bismuth oxide / deficient iodine oxybismuth composite material of the invention is used for degrading propranolol in water. The preparation method of the present invention is simple, the conditions are mild, and the price is low, and the prepared Bi 2 o 3 / BiO 1.4 I 0.3 The composite material has a wide range of light absorption, which significantly improves the separation of photogenerated carriers, greatly improves the photocatalytic performance, and can realize the rapid and effective degradation of propranolol in water, the degradation rate and maximum adsorption of propranolol The amount is much higher than that of bismuth oxide and bismuth oxyiodide.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
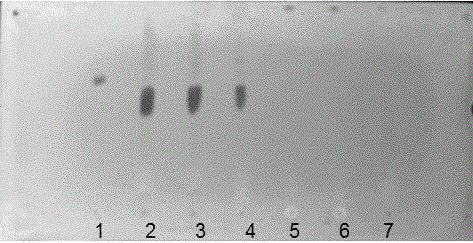
TLC method for identification of Eucommia ulmoides and preparations containing eucommia and application of potassium bismuth iodide solution
ActiveCN104807947BGood reproducibilityStrong specificityComponent separationBiotechnologyMedicinal herbs
Owner:HUNAN HANSEN PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
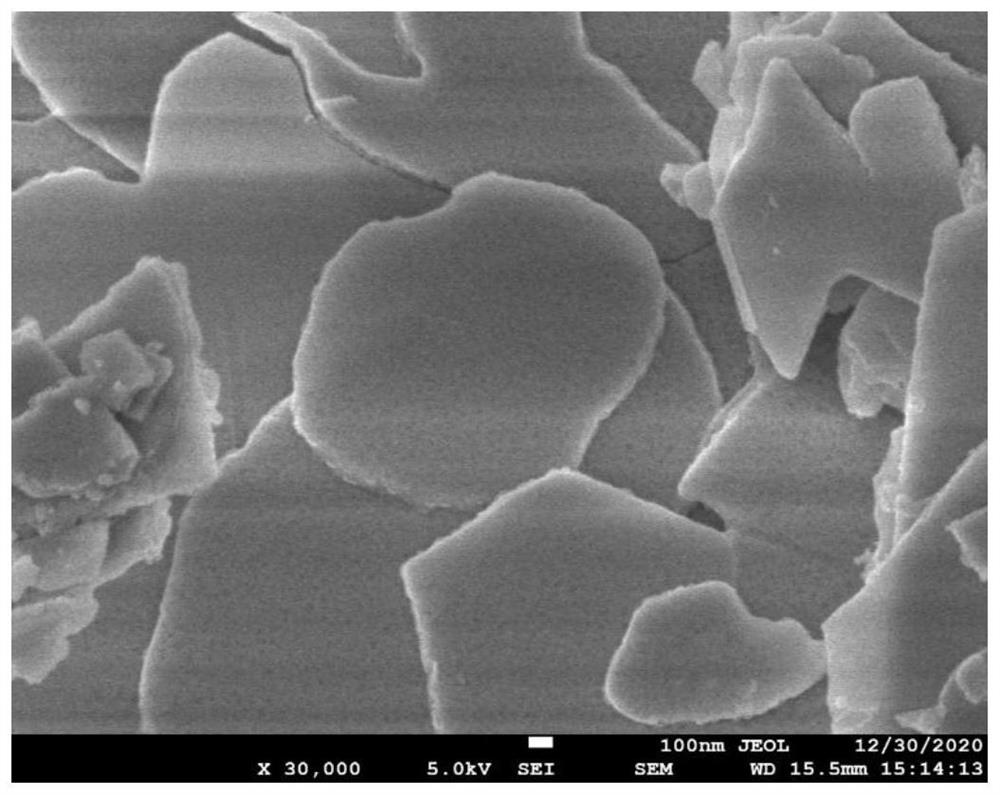
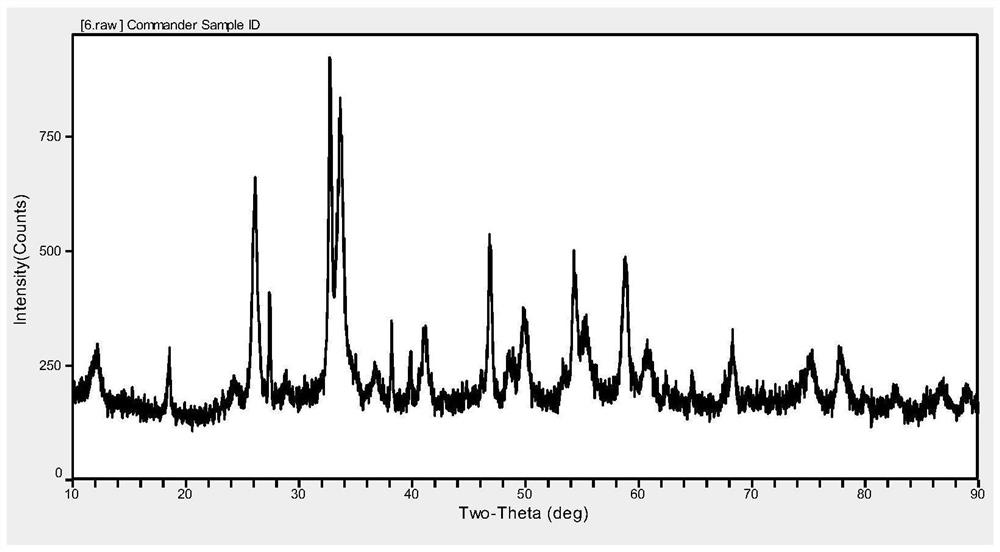
Preparation method of large-size two-dimensional bismuth iodide single crystal
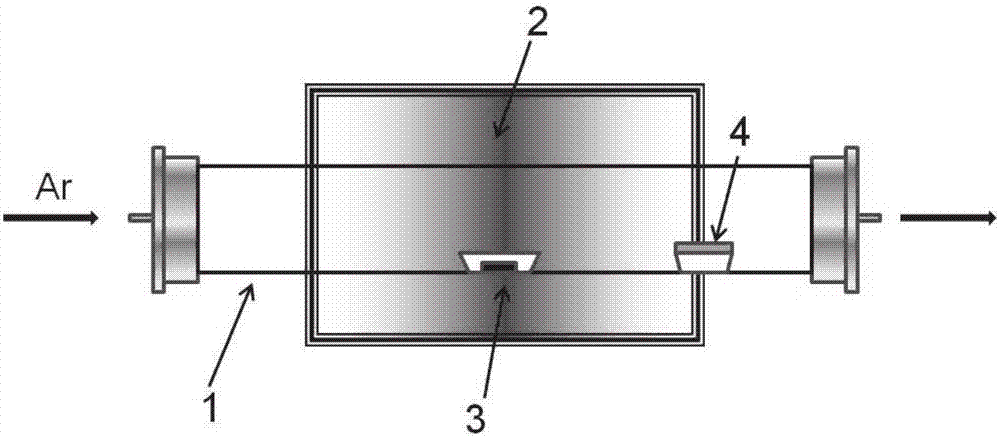
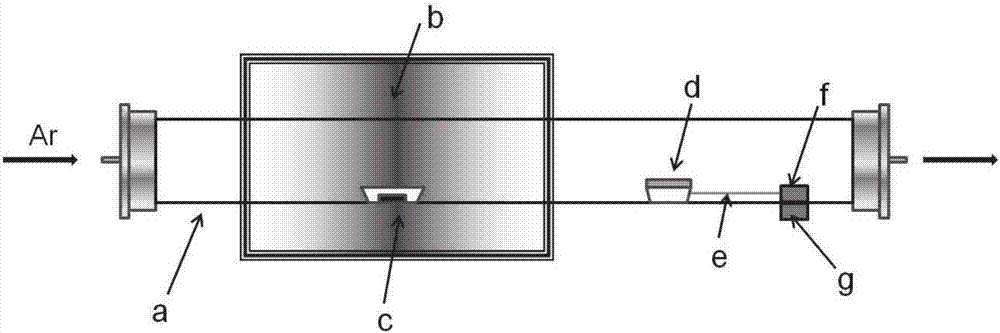
ActiveCN113652739ASolve sizeAddress controllabilityPolycrystalline material growthFrom condensed vaporsTube furnacePhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method of a large-size two-dimensional bismuth iodide single crystal. The method comprises the following steps: S1, putting bismuth iodide powder into a corundum boat with an opening at one end, and then inversely buckling a fluorophlogopite substrate on the corundum boat; s3, introducing argon and hydrogen into the tubular furnace, and making the gasified bismuth iodide diluted and subjected to a reduction reaction; s4, after the reaction is finished, making the gas phase trap moved to a heating belt at the tail end of the tube furnace for cooling, and in the cooling process, making gas in the corundum boat deposited on the fluorophlogopite substrate to form attachment; and S5, after the gas phase trap is completely cooled, obtaining the two-dimensional bismuth iodide single crystal. The preparation method of the large-size two-dimensional bismuth iodide single crystal solves the problems that the bismuth iodide single crystal prepared by the existing method is small in size and uncontrollable in thickness, the whole preparation process is simple, the operation is convenient, and the repeatability is good; and two-dimensional single crystal bismuth iodide with different thicknesses and sizes can be obtained by controlling the cooling rate.
Owner:化学与精细化工广东省实验室潮州分中心
A kind of preparation method of z-form bismuth-based photocatalyst
ActiveCN112973741BEfficient separationHigh redox potentialMaterial nanotechnologyWater/sewage treatment by irradiationSimple Organic CompoundsPtru catalyst
The invention relates to a preparation method of a Z-form bismuth-based photocatalyst, and belongs to the technical field of nanomaterials. By adding the bismuth salt and the iodine source into the solvent to dissolve completely or to disperse uniformly, a reaction solution containing the precursor of bismuth iodide is obtained after sufficient reaction; the composite phase substance and the reducing agent are added to the reaction solution prepared in step (1) to react , obtain a reaction solution with a reducing chemical atmosphere, containing bismuth iodide-composite phase precursor; heat the reaction solution obtained in step (2) with a solvent, and separate and dry the reaction solution after the solvent heat treatment to obtain the catalyst. . The catalyst can retain a high redox potential on the basis of effectively separating electron-hole pairs; compared with the heterojunction structure obtained without adding a reducing agent, it has the ability to complete the photocatalytic degradation of organic compounds such as rhodamine B faster. Effect.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
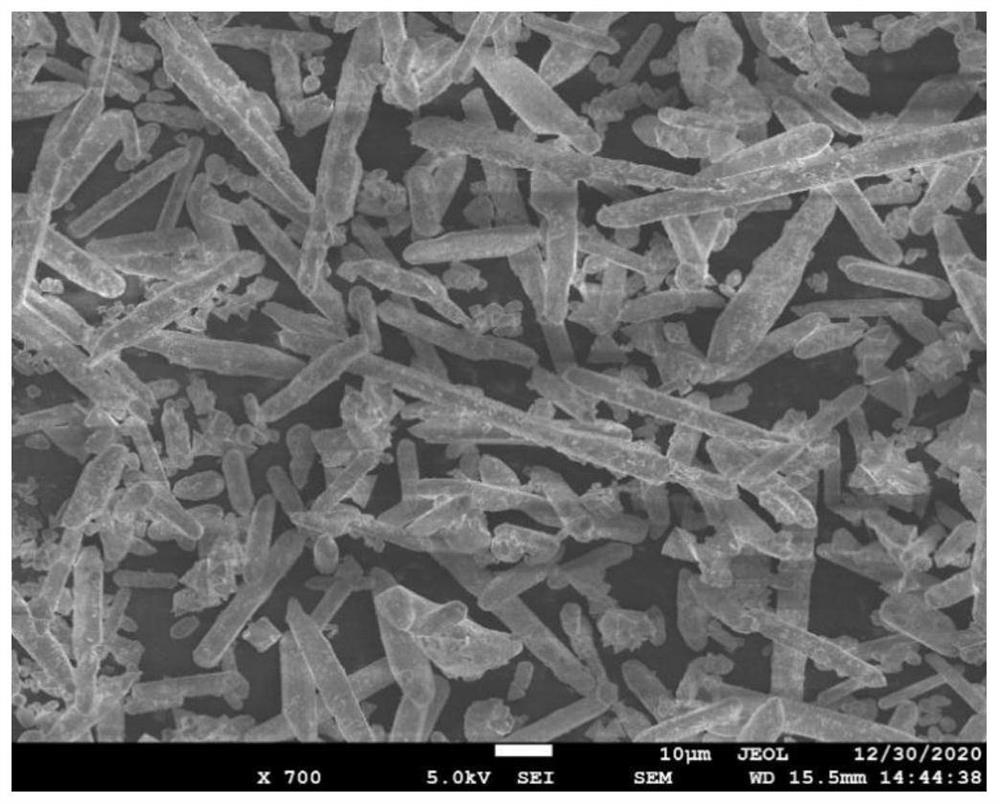
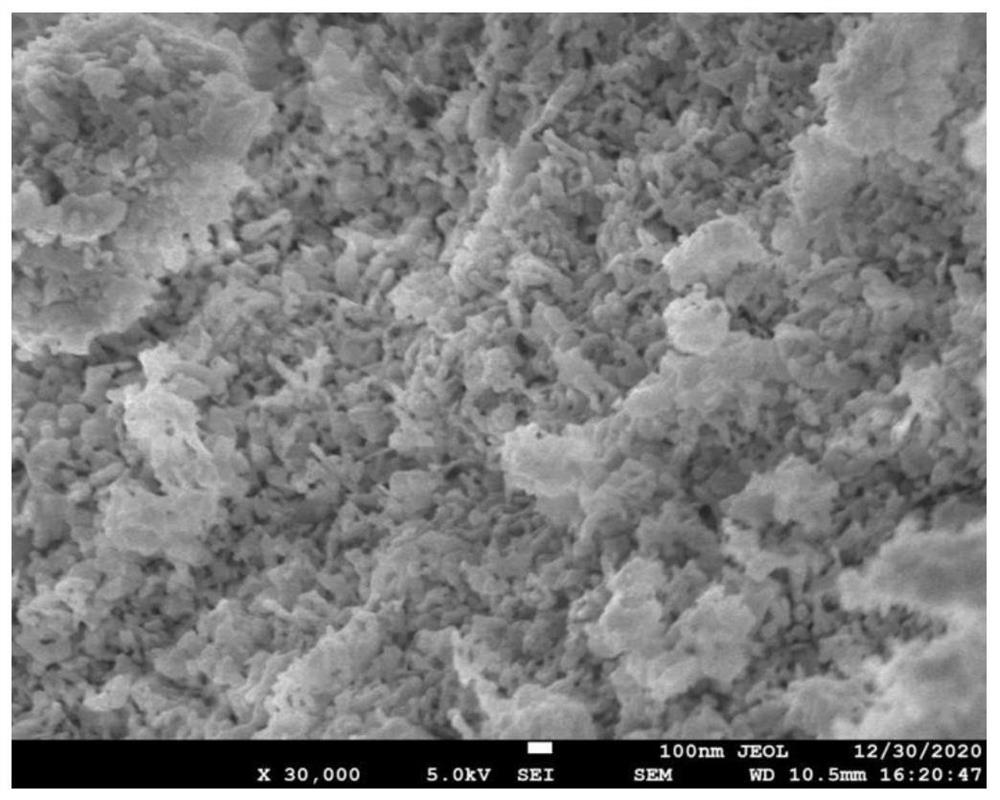
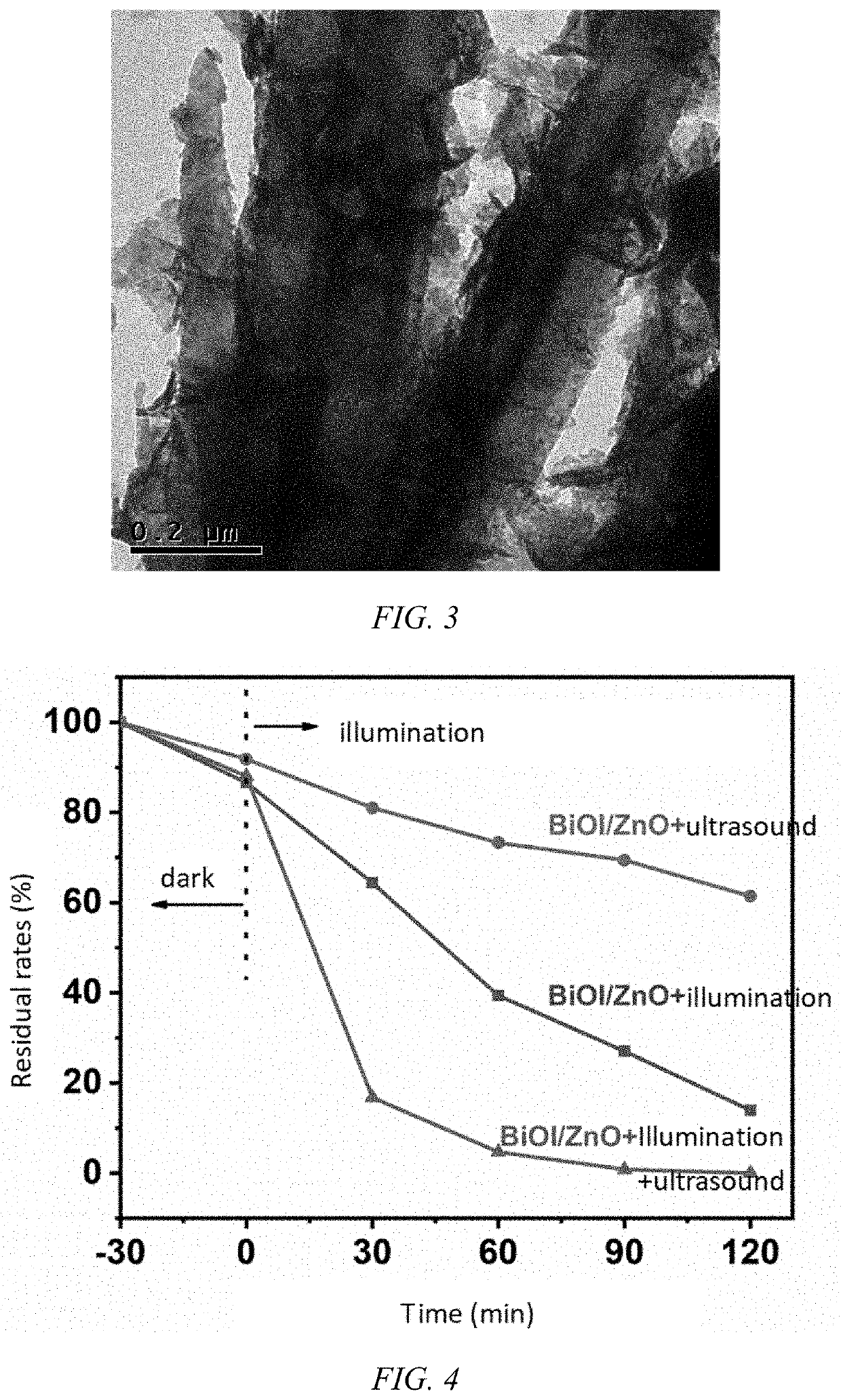
Bismuth iodide oxide / zinc oxide composite and preparation method therefor and application thereof in piezoelectric photocatalytic removal of organic pollutants
PendingUS20220347660A1The synthesis method is simpleMorphological rulesWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsOxide compositeZinc oxide nanorod
A bismuth iodide oxide / zinc oxide composite material, a preparation method therefor and an application thereof in piezoelectric photocatalytic removal of organic pollutants. The conductive substrate spin-coated with a zinc oxide seed solution is annealed and added to the precursor solution for reaction to obtain a zinc oxide nanorod array (ZnO NRs); the zinc oxide nanorod array is added into a bismuth iodide precursor solution for reaction to obtain the bismuth iodide oxide / zinc oxide composite material (BiOI / ZnO NAs). The composite material is put into an aqueous solution containing bisphenol A, adsorption is performed in the dark for half an hour, and then ultrasound and visible light are used together to remove organic pollutants in the water. After piezoelectric photocatalytic degradation of 90 minutes, bisphenol A in the aqueous solution is almost completely degraded.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
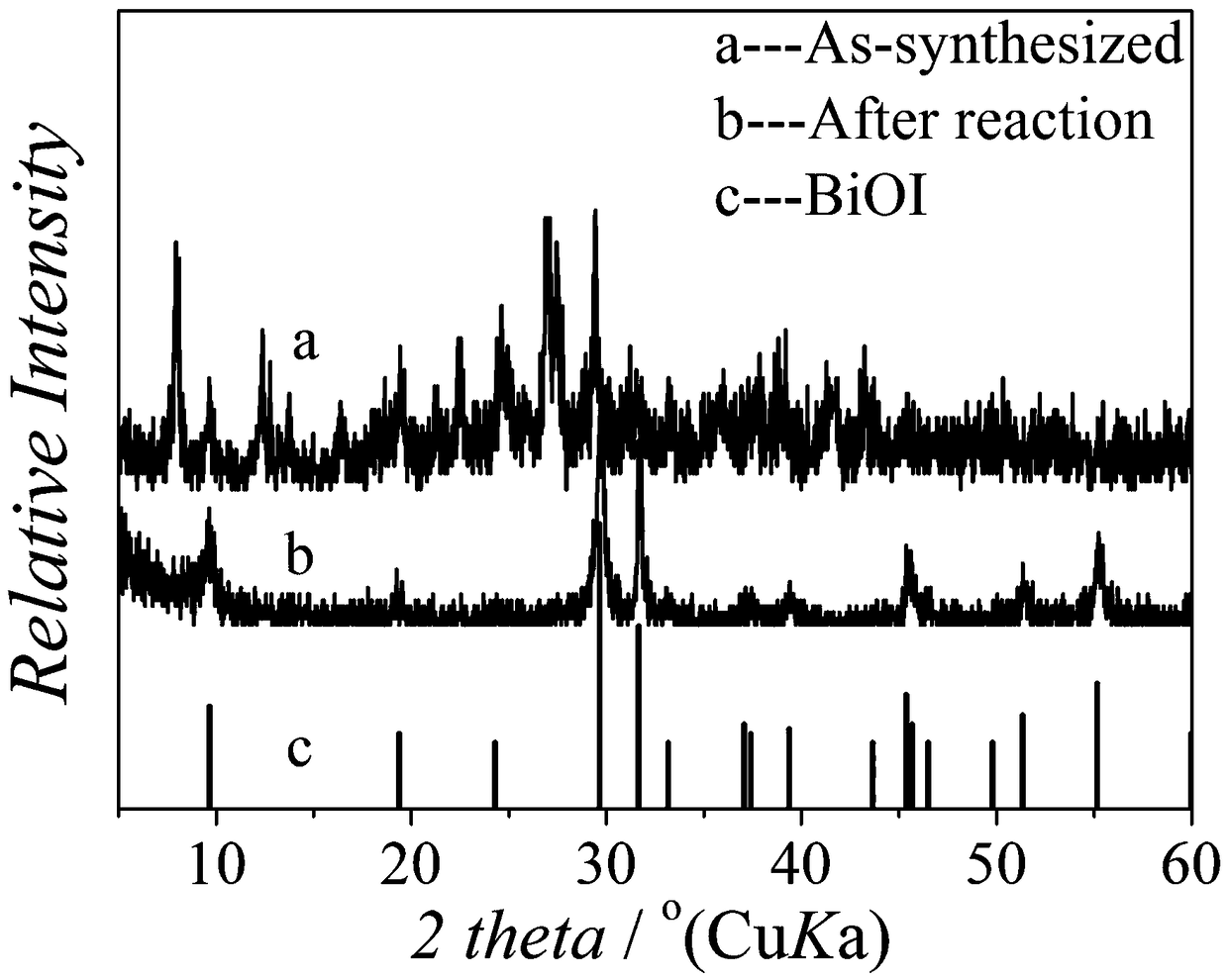
Synthesis of a bismuth-iodine hybrid material and its use in the preparation of bioi nanosheets
The invention relates to synthesis of a bismuth iodine hybrid material and application to preparation of a BiOI nano-sheet, and aims to synthesize the bismuth iodine hybrid material, wherein the bismuth iodine hybrid material can be directly applied to hydrolysis to prepare the BiOI nano-sheet. A bismuth iodine based hybrid (Habtz)BiI4 is prepared by taking bismuth iodide and 2-aminobenzothiazoleas reaction raw materials and taking mixed liquid of ethanol and hydroiodic acid as a reactant and a solvent and under the solvothermal condition, wherein the abtz is 2-aminobenzothiazole. The bismuthiodine hybrid material is simple to prepare, the raw materials are low in price and the yield is high. The hybrid material serving as a precursor can be hydrolyzed rapidly without adding other reaction raw materials in distilled water and without adjusting the pH value of the reaction, so that simple and efficient preparation of the BiOI nano-sheet is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
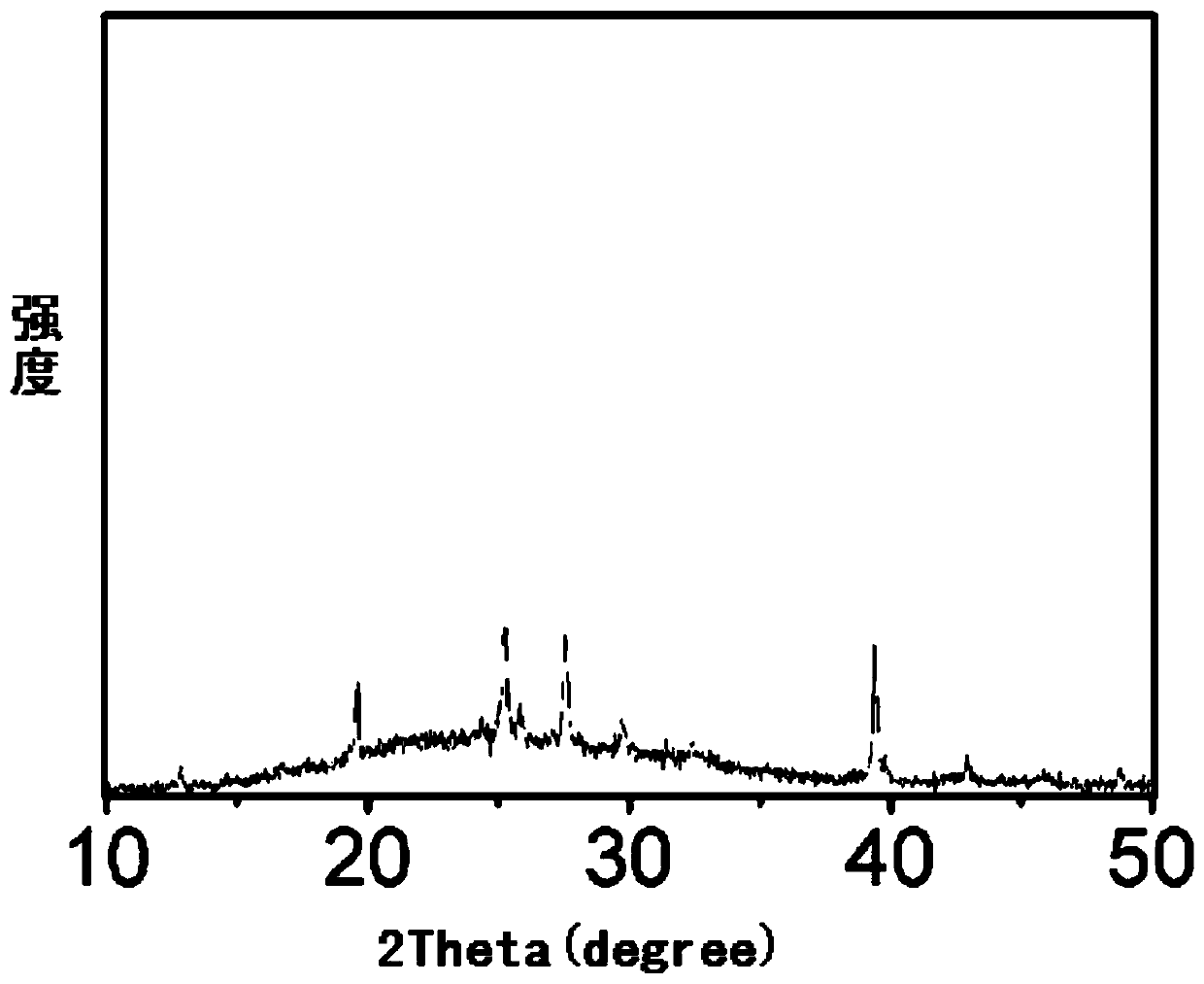
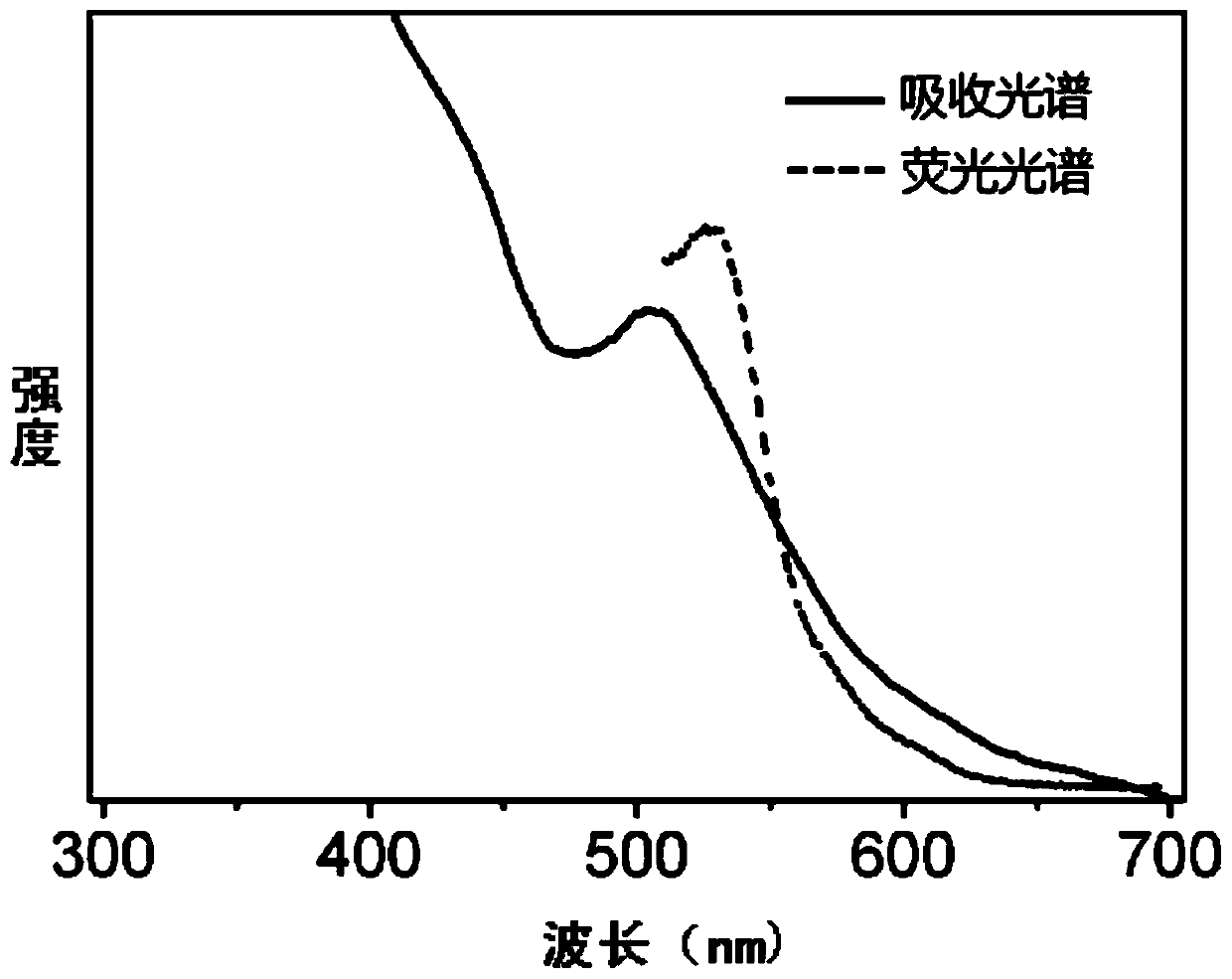
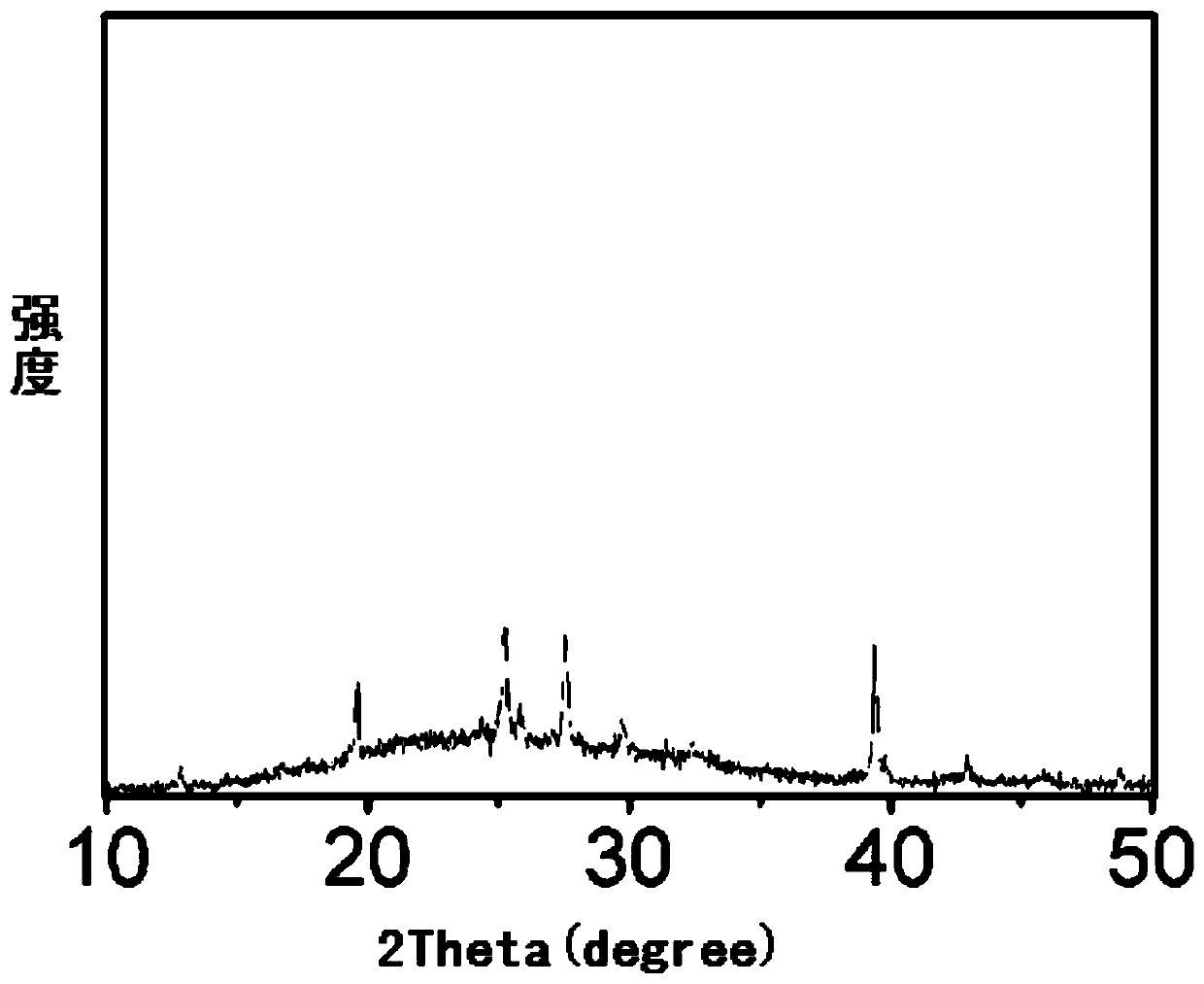
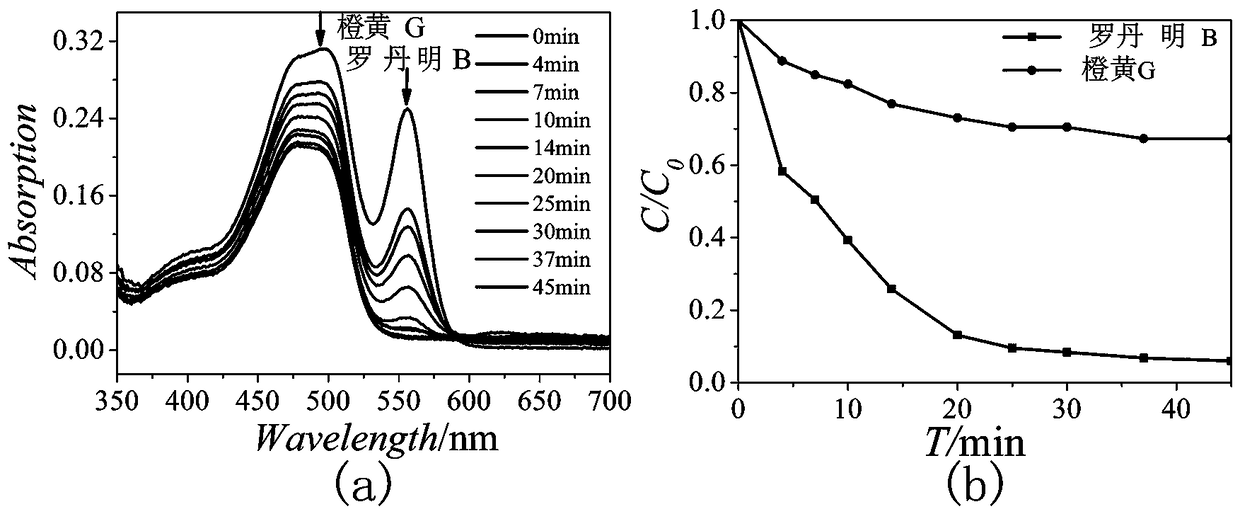
A bismuth iodide salt and its preparation method and application in fluorescence and photodegradation
ActiveCN112142650BEfficient use ofGood photodegradation effectWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsBenzoyl bromideIodide
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental protection functional materials, and specifically relates to a novel bismuth halide salt, which is a compound composed of hexaiodobismuth anion and benzylpyridinium cation. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking a certain amount of benzyl bromide and pyridine, Add an appropriate amount of solvent to mix and dissolve, stir and reflux, then evaporate and concentrate, and then wash with ether to obtain benzylpyridinium bromide; take BiI 3 Dissolve in an appropriate amount of concentrated iodic acid, take a certain amount of benzylpyridinium bromide salt and dissolve it in an appropriate amount of solvent, mix and stir the two solutions to reflux to obtain a clear filtrate, and freeze and crystallize to obtain a new type of bismuth iodide salt. The novel bismuth halide of the invention emits strong orange-red light under the irradiation of 365nm ultraviolet light, rapidly degrades rhodamine B and methyl orange under visible light, and has good cycle degradation efficiency. The invention also provides a preparation method of the novel bismuth iodide salt, the method has high yield, saves cost, is easy to operate, and is beneficial to industrialized production.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Preparation and application of a bismuth-iodine hybrid material capable of selectively decolorizing rhodamine b
InactiveCN108586538BSynthesis conditions are simpleNo pollution in the processOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsOrganic chemistry methodsThiazoleHybrid material
The invention discloses synthesis of a bismuth iodine based inorganic-organic hybrid material and an application of the hybrid material in selective color fading of rhodamine B. The purpose of the invention is to synthesize the inorganic-organic hybrid material (Habtz)BiI4 which can conveniently, quickly, efficiently and selectively fade color of the rhodamine B, wherein abtz represents 2-aminobenzothiazole. Bismuth iodide, 2-aminobenzothiazole, ethanol and hydroiodic acid can be selected as reaction raw materials, and a single crystal of the compound (Habtz)BiI4 is obtained under the solvothermal synthesis condition. The (Habtz)BiI4 disclosed by the invention has excellent properties, and can be used for chemical selective treatment of the rhodamine B in a dye waste liquid without any energy provided by the outside.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Bismuth iodine cluster hybrid semiconductor perovskite material based on 1-butyl-4-methylpyridinium cation
PendingCN114369058AEnhanced light absorptionModerate band gapOrganic chemistry methodsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsMethylpyridinium
The invention discloses a bismuth iodine cluster hybrid perovskite-like material based on a 1-butyl-4-methylpyridinium cation and a preparation method of the bismuth iodine cluster hybrid perovskite-like material. The perovskite-like compound hybrid material is synthesized from 1-butyl-4-methyl pyridine chloride, bismuth iodide and potassium iodide, the molecular structure of the perovskite-like compound hybrid material is (BMPY) 3 (Bi2I9), and in the formula, BMPY is a 1-butyl-4-methylpyridinium cation. The hybrid semiconductor material is a perovskite-like semiconductor material with moderate forbidden band width and good photoelectric response effect, and DFT calculation shows that the hybrid semiconductor material is a charge transfer salt. The material has the advantages of being cheap, completely free of lead and easy to purify, and has good solubility and stability. The material can be used as a semiconductor material in a halide-based perovskite photoelectric device.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com