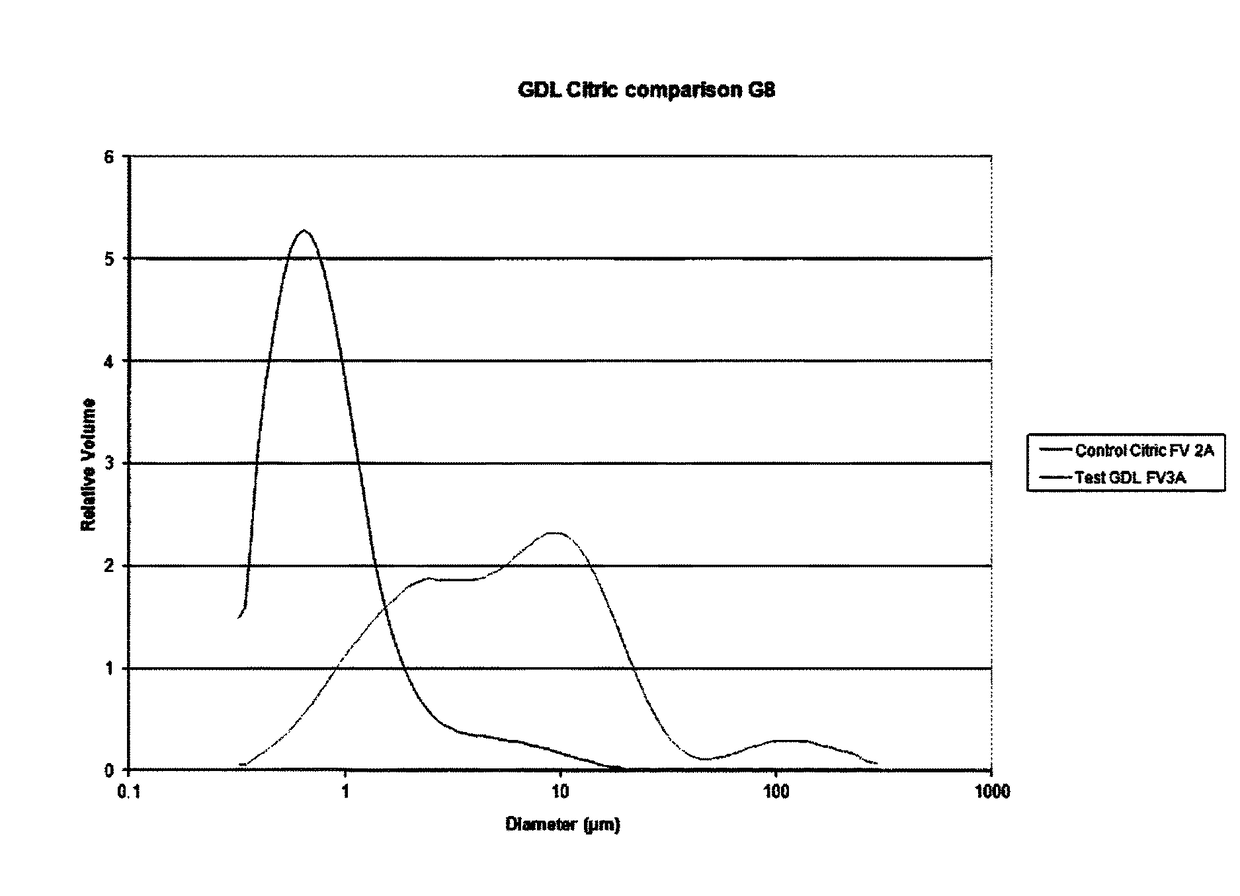
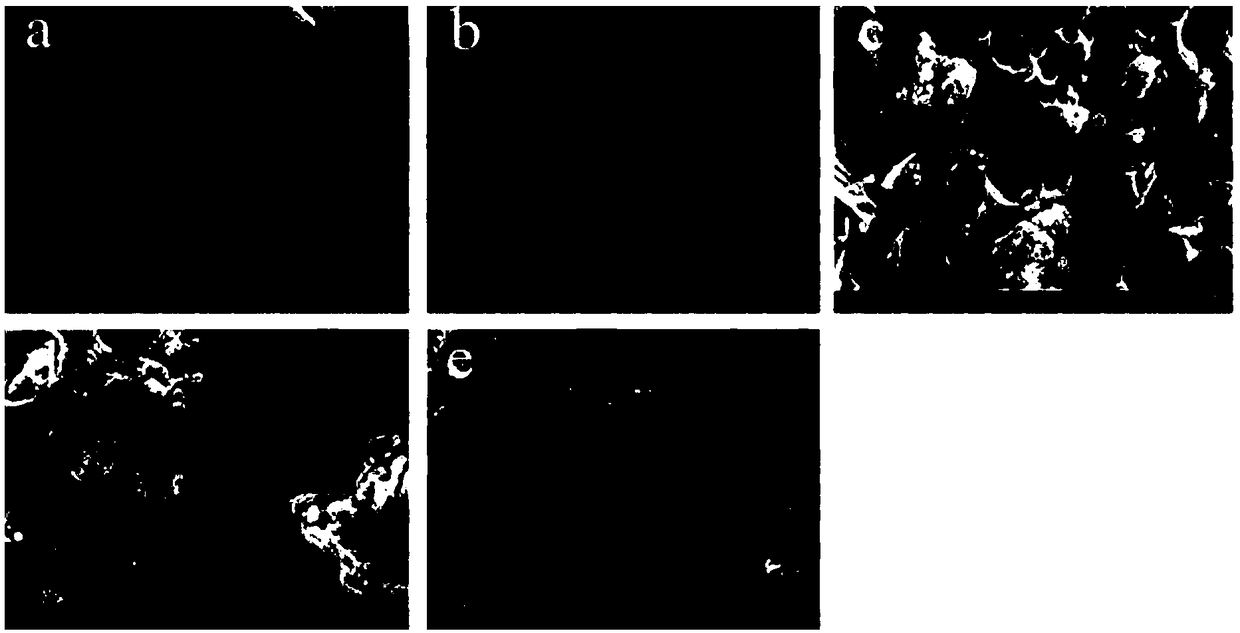
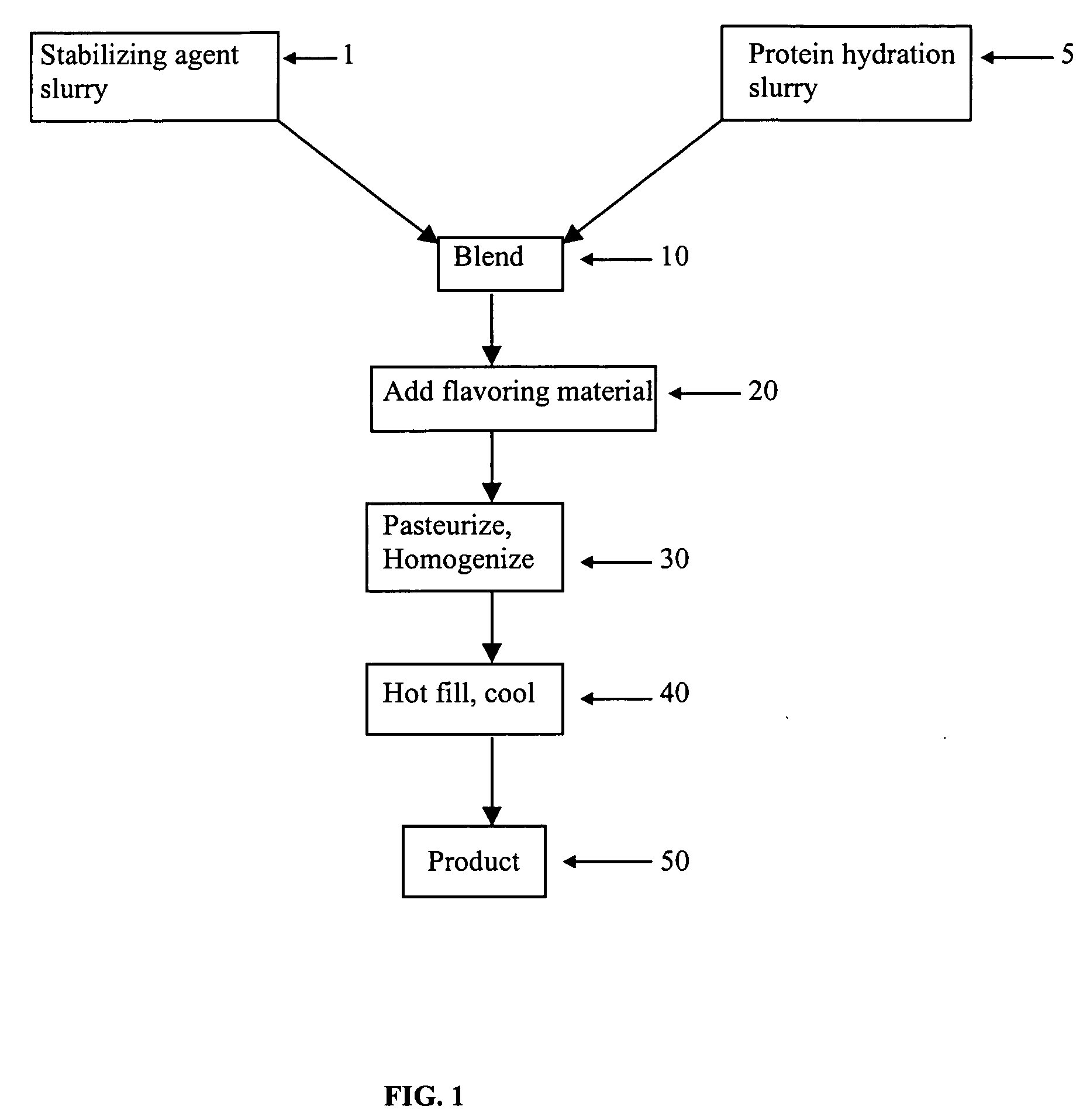
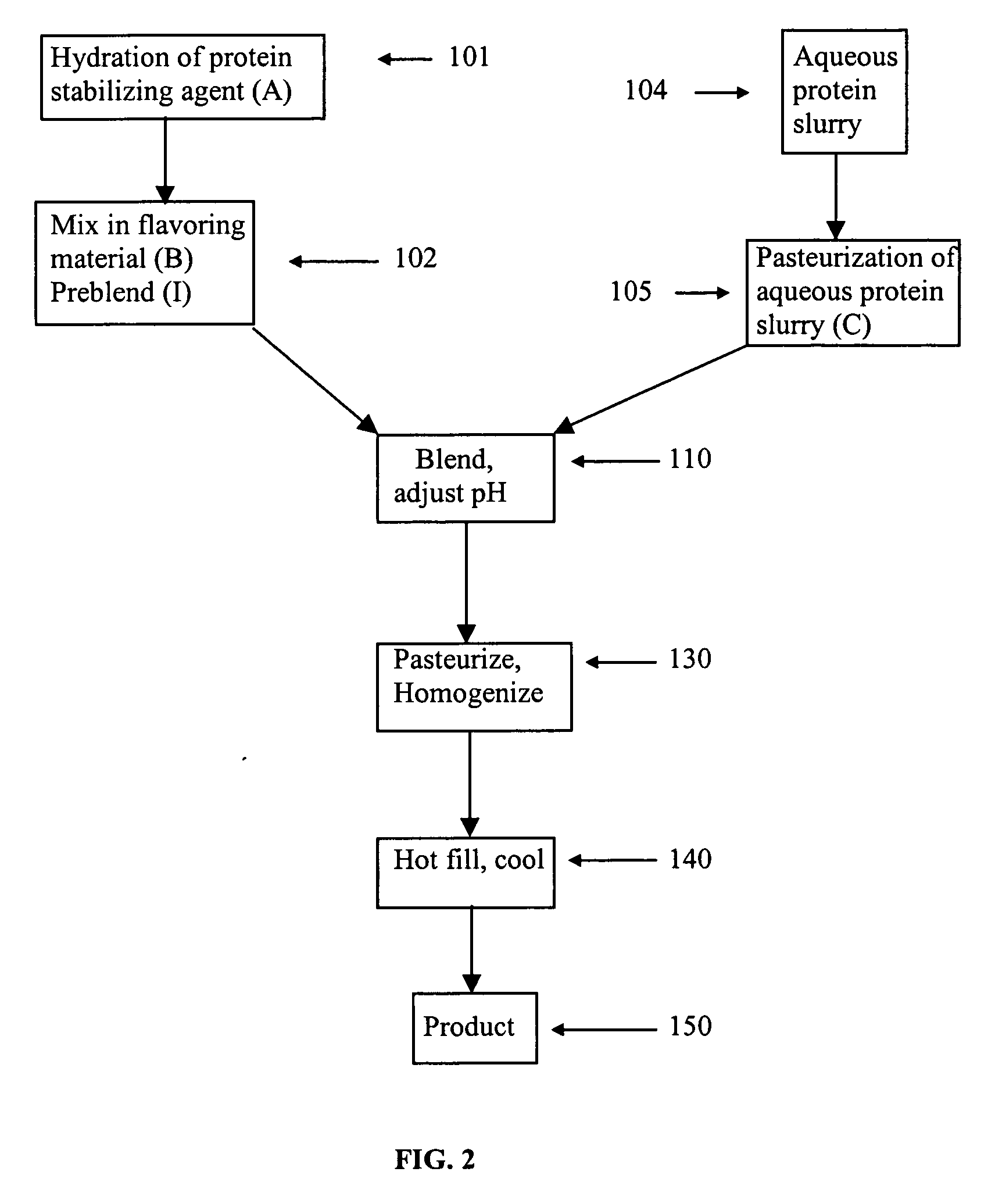
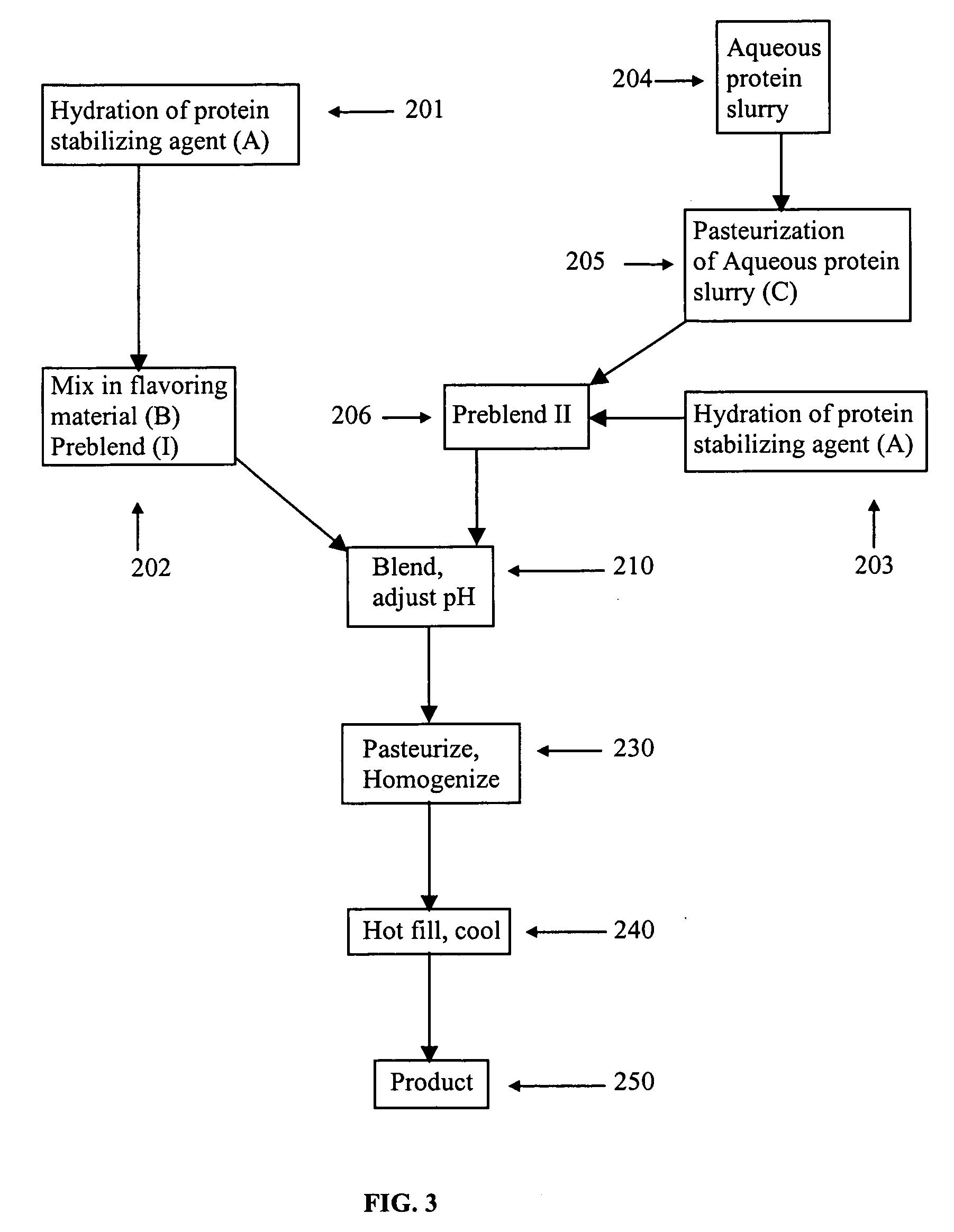
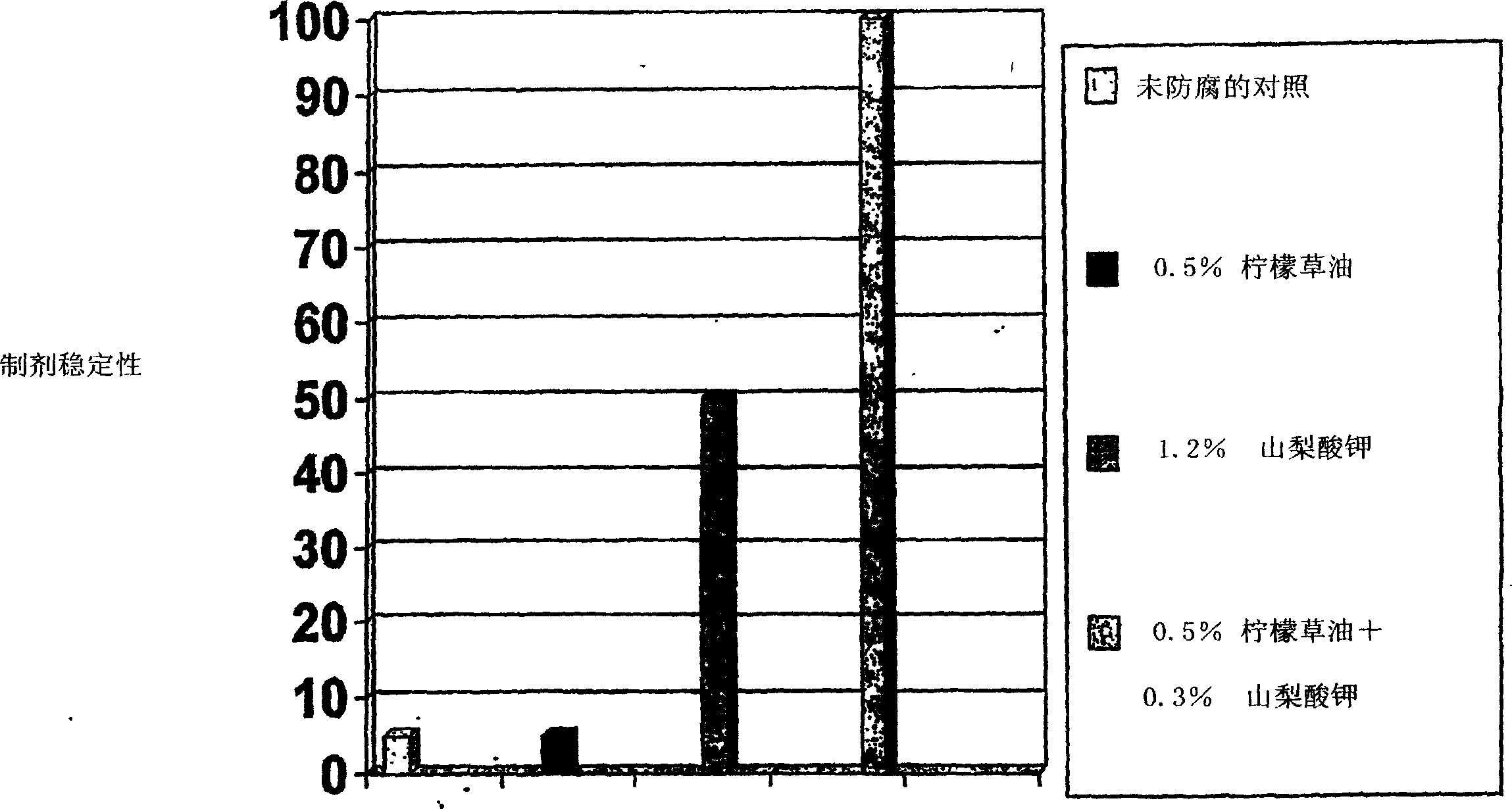
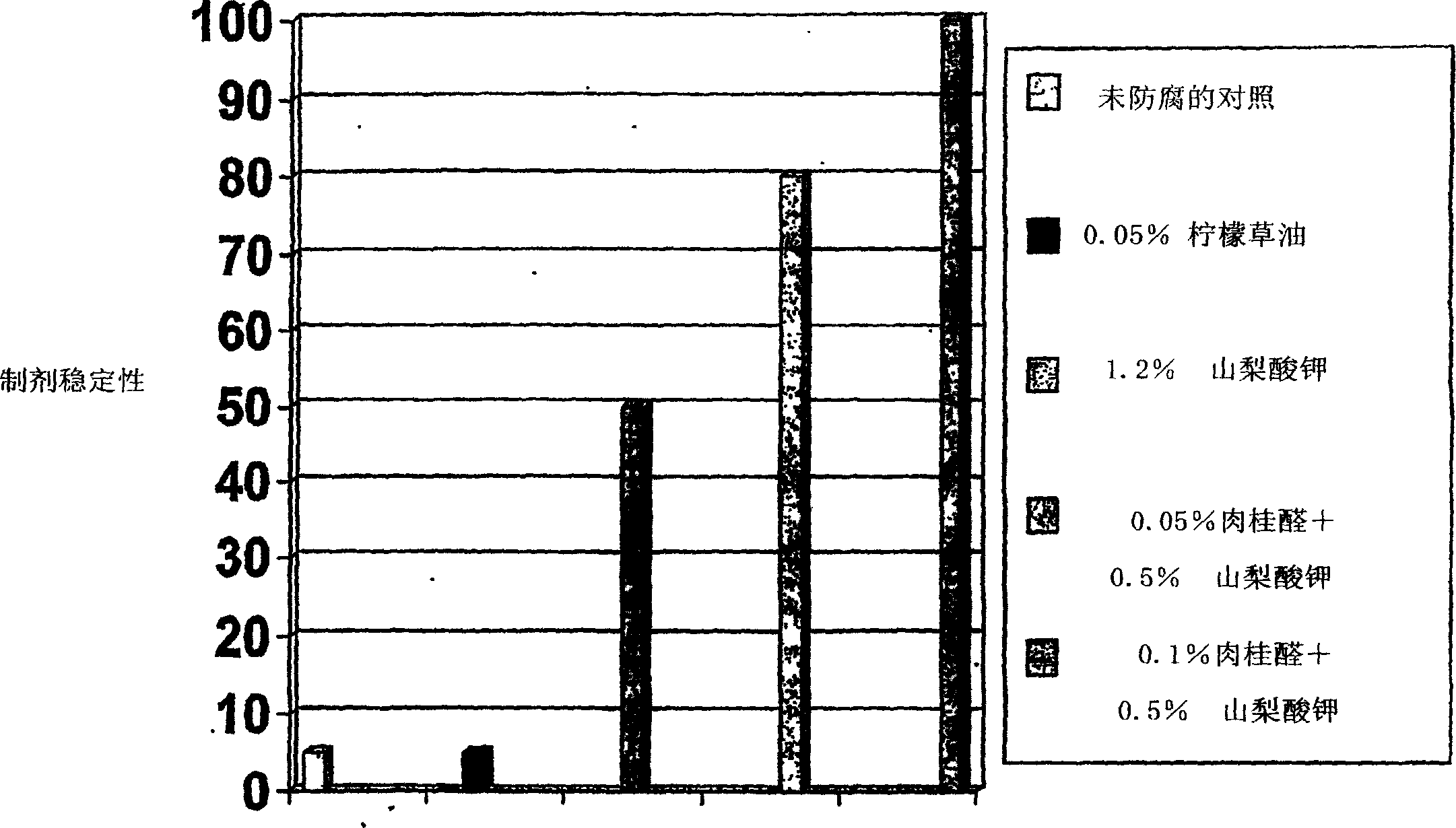
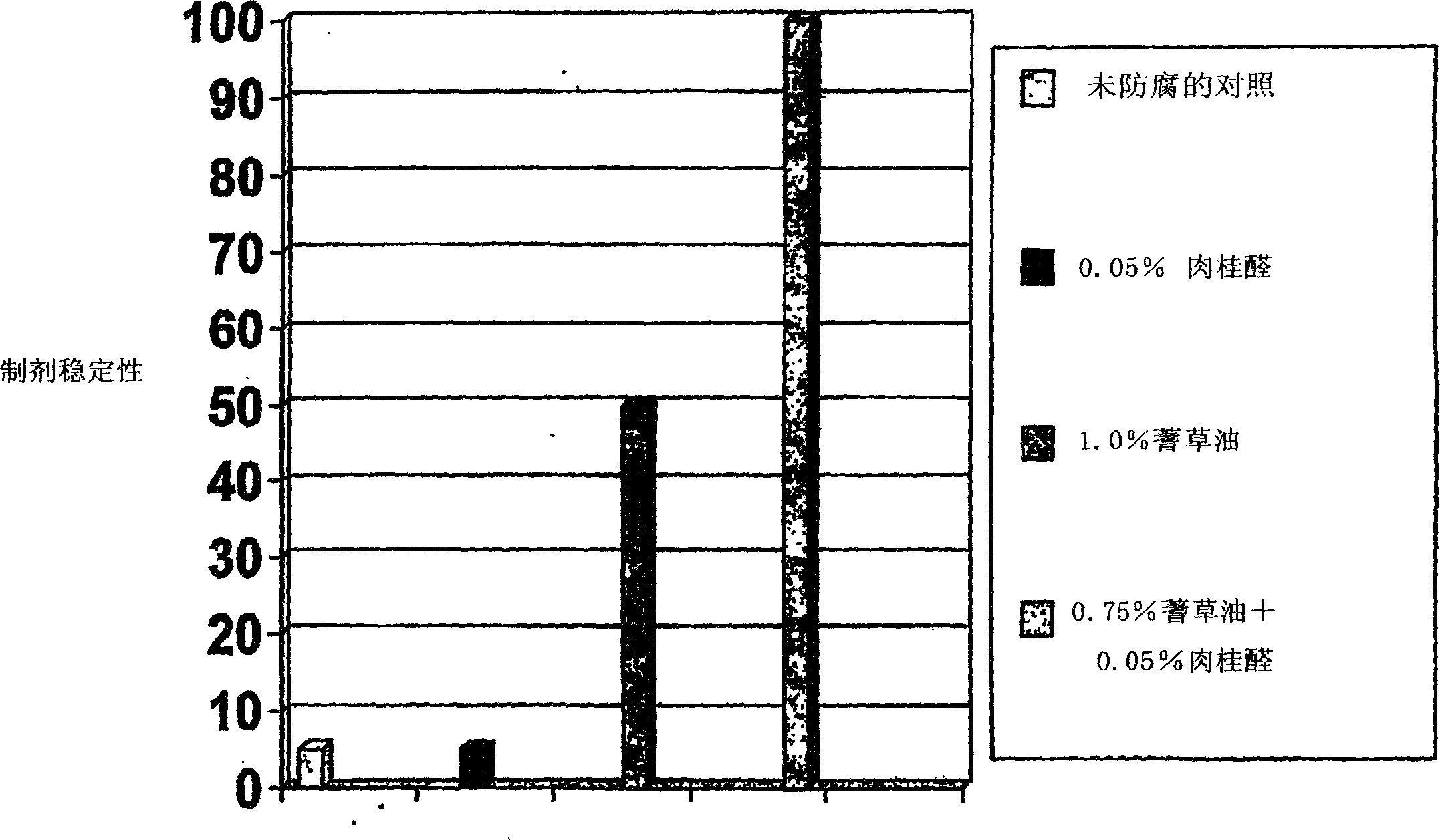
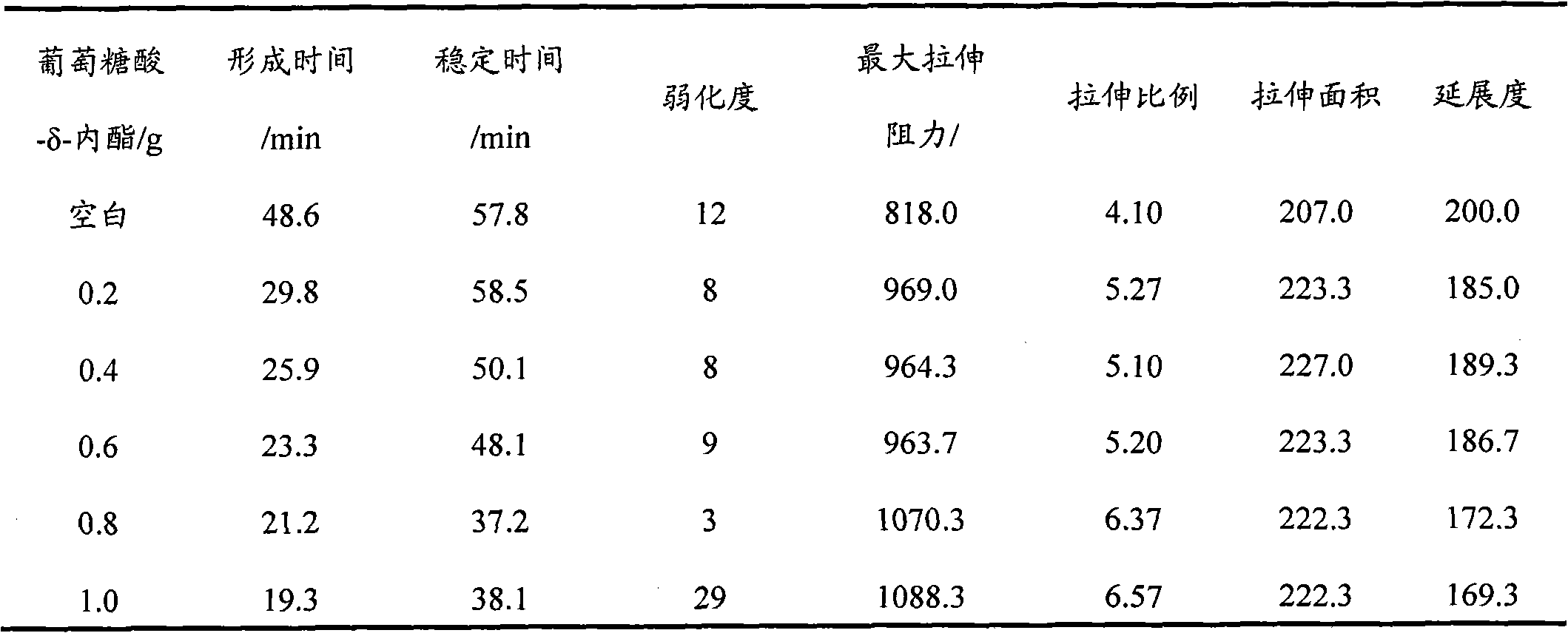
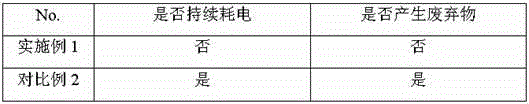
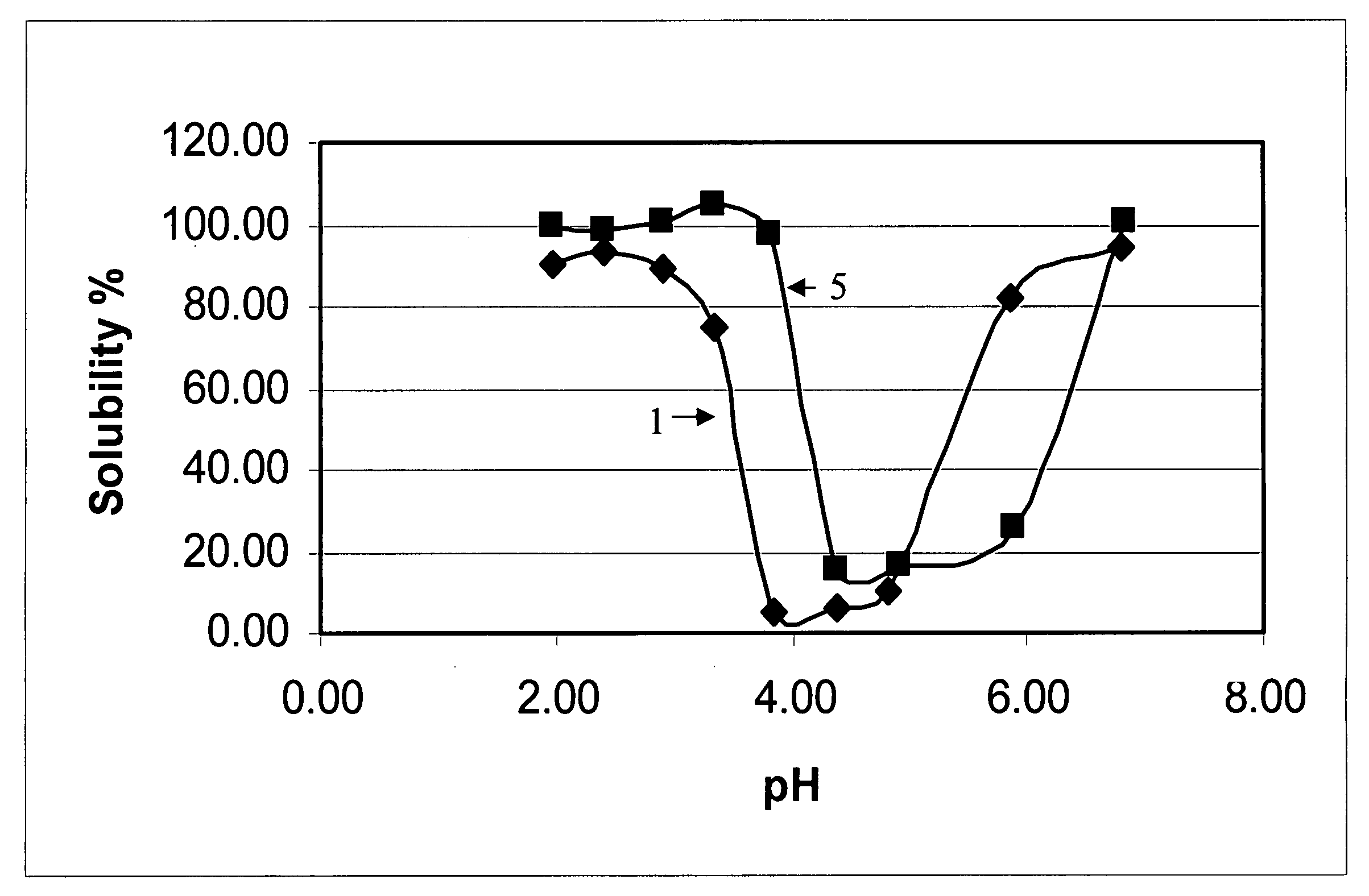
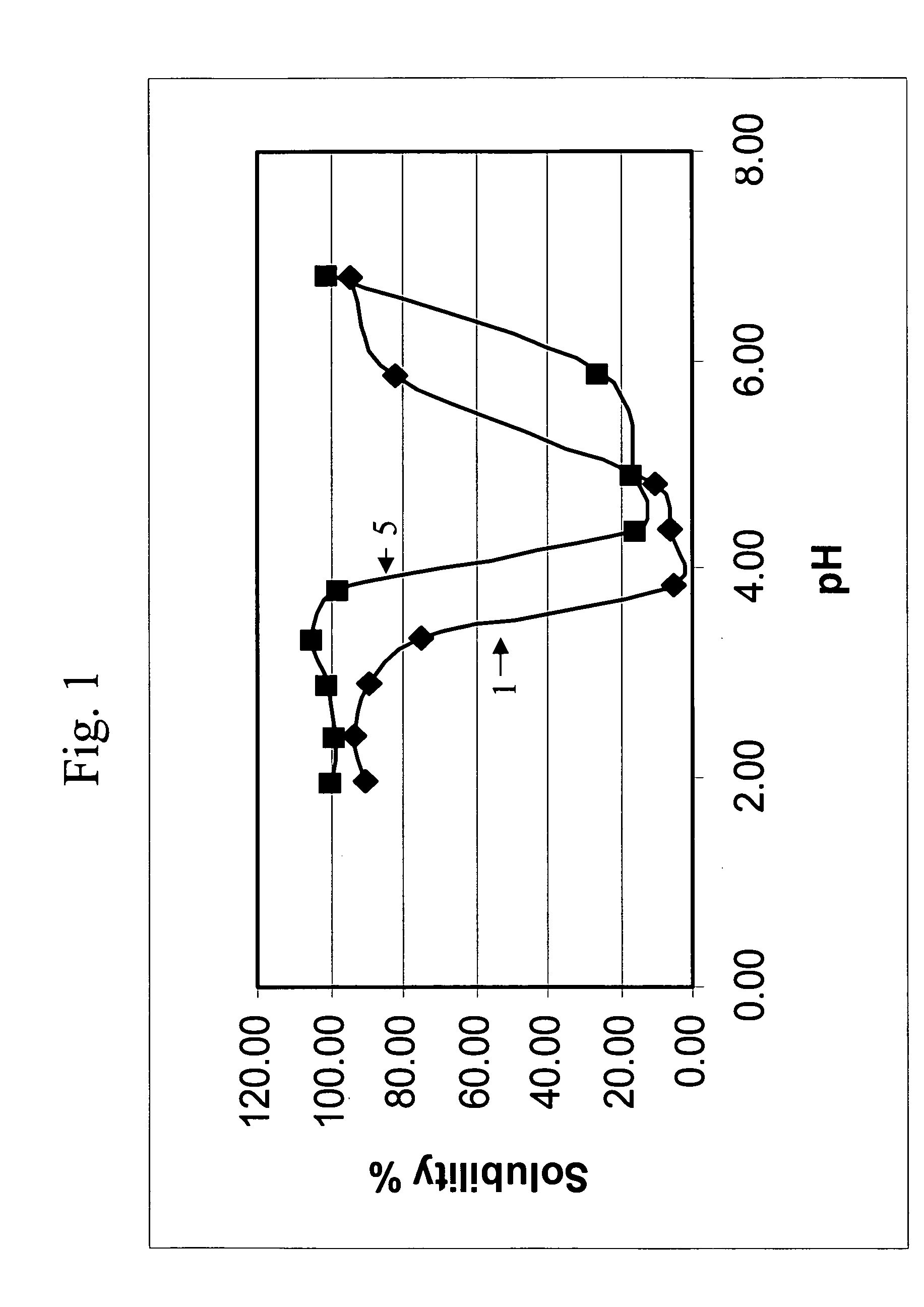
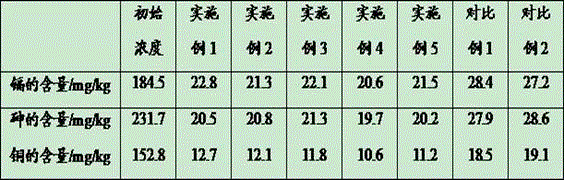
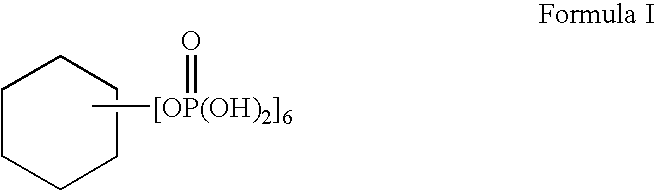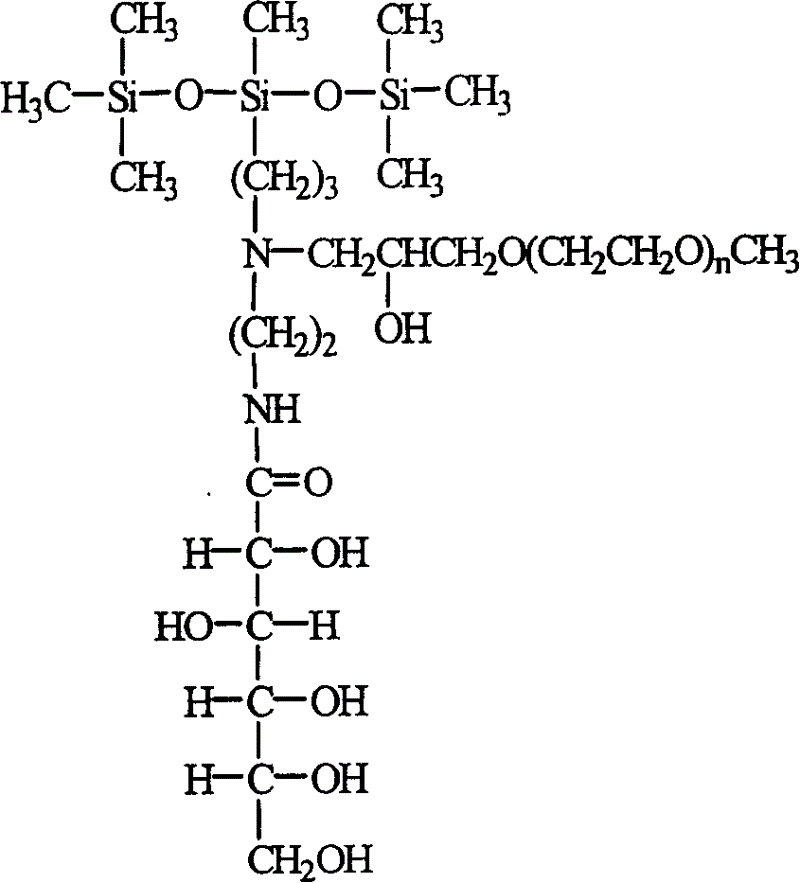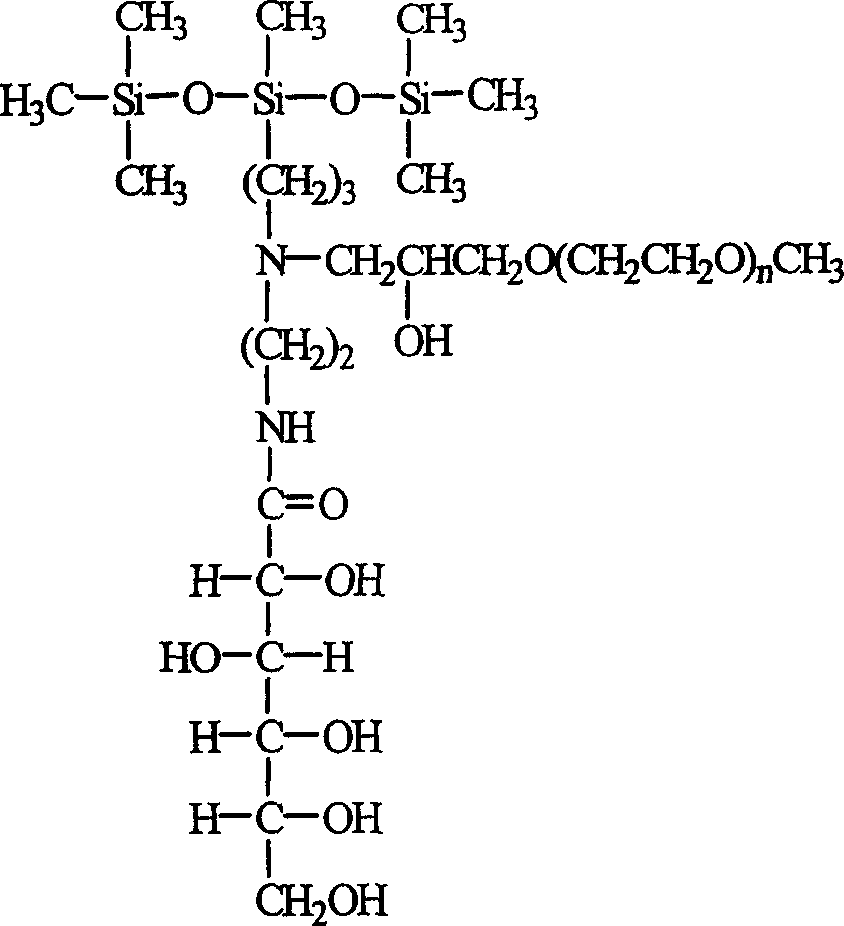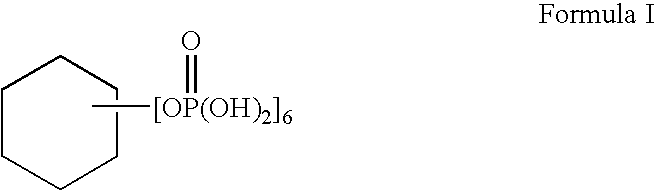Patents
Literature
254 results about "Delta-gluconolactone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
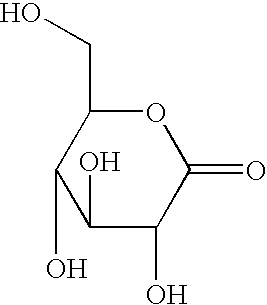
Glucono delta-lactone (GDL), also known as gluconolactone, is a food additive with the E number E575 used as a sequestrant, an acidifier, or a curing, pickling, or leavening agent. It is a lactone of D-gluconic acid.
Crayfish food as well as preparation method and production equipment thereof
InactiveCN103960697AGood health effectSilky meatWater/sewage treatmentOil/fat bakingVegetable oilAdditive ingredient
Crayfish food comprises ingredients in parts by weight as follows: 100 parts of crayfish, 50 parts of vegetable oil, 10.6-15.2 parts of spice, 0.3-0.5 parts of transglutaminase, 0.3-0.5 parts of nisin, 0.2-0.5 parts of konjac glucomannan, 0.2-0.4 parts of chitosan, 0.4-0.5 parts of lecithin and 0.08-0.16 parts of delta-gluconolactone. According to the crayfish food, crayfish balls are used for preparing instant food, crayfish shells are used for preparing chitosan, and raw materials are sufficiently utilized; transglutaminase in the raw materials prompts crosslinking of crayfish meat protein crosslinking amino acid, tenderness of a product is improved, natural food antiseptics such as nisin and the like meet requirements of people for food health, and at the same time, the guarantee period of the crayfish food is prolonged to 12 months; and defects that crayfish products which can be stored at the normal temperature are less, the guarantee period is short and the like are overcome, and the crayfish food has good market prospect.
Owner:顾炎林
Frozen confection product and a method of preparing such
ActiveUS9888706B2Improved textural and sensorial propertyGood creamy textureFrozen sweetsOther dairy technologyGlucono delta-lactoneDelta-gluconolactone
The present invention relates to a frozen confection product comprising glucono-delta-lactone. The present invention also relates to a method of producing a frozen confection product by adding glucono-delta-lactone to an ingredient mix and then homogenize, pasteurize, and freeze the mix. Preferably the method includes a post pasteurization acidification step. Preferably the method uses a standard freezing step followed by low temperature freezing.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Frozen confection product and a method of preparing such
ActiveUS20150245638A1Improved texturalImproved sensorial propertyFrozen sweetsOther dairy technologyGlucono delta-lactoneDelta-gluconolactone
The present invention relates to a frozen confection product comprising glucono-delta-lactone. The present invention also relates to a method of producing a frozen confection product by adding glucono-delta-lactone to an ingredient mix and then homogenize, pasteurize, and freeze the mix. Preferably the method includes a post pasteurization acidification step. Preferably the method uses a standard freezing step followed by low temperature freezing.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Non-fermentation type sour milk and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to non-fermentation type sour milk and a preparation method thereof. The non-fermentation type sour milk uses fresh cow milk as principal raw material. After being hydrolyzed by milk sugar, the cow milk is pasteurized and concentrated in vacuum to be 40 percent of the original volume. After the cow milk is cooled, probiotic powder is added. The invention has the core that transglutaminase is added at an optimal temperature; under the action of the transglutaminase, milk protein is connected together to form a protein network, thereby a uniform stable gelatin system is easily formed; delta-gluconolactone is then added, and the gelatin system and the delta-gluconolactone are heated at 35-40 DEG C in a water bath way for 2 to 3 hours so that the uniform, stable and exquisite non-fermentation type sour milk like a quark can be obtained. The invention has simple preparing process, no requirement for fermentation, and full utilization of resources. The non-fermentation type sour milk can be used as a base to develop various products, such as corn non-fermentation type sour milk for breakfast, jelly non-fermentation type sour milk, and the like, and can satisfy the requirements of consumers in nutrition, mouthfeel, texture, and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Phytase-treated acid stable soy protein products
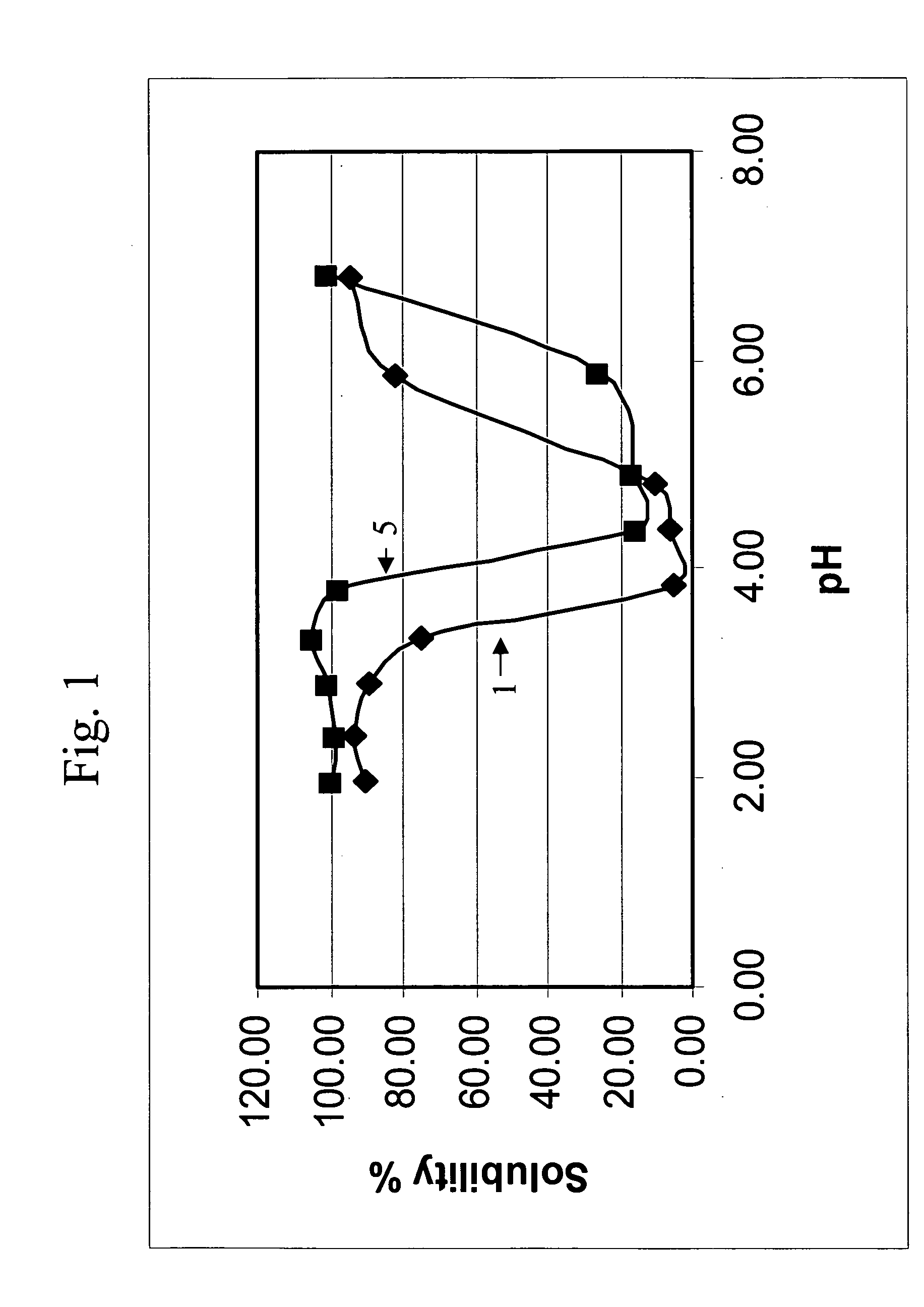
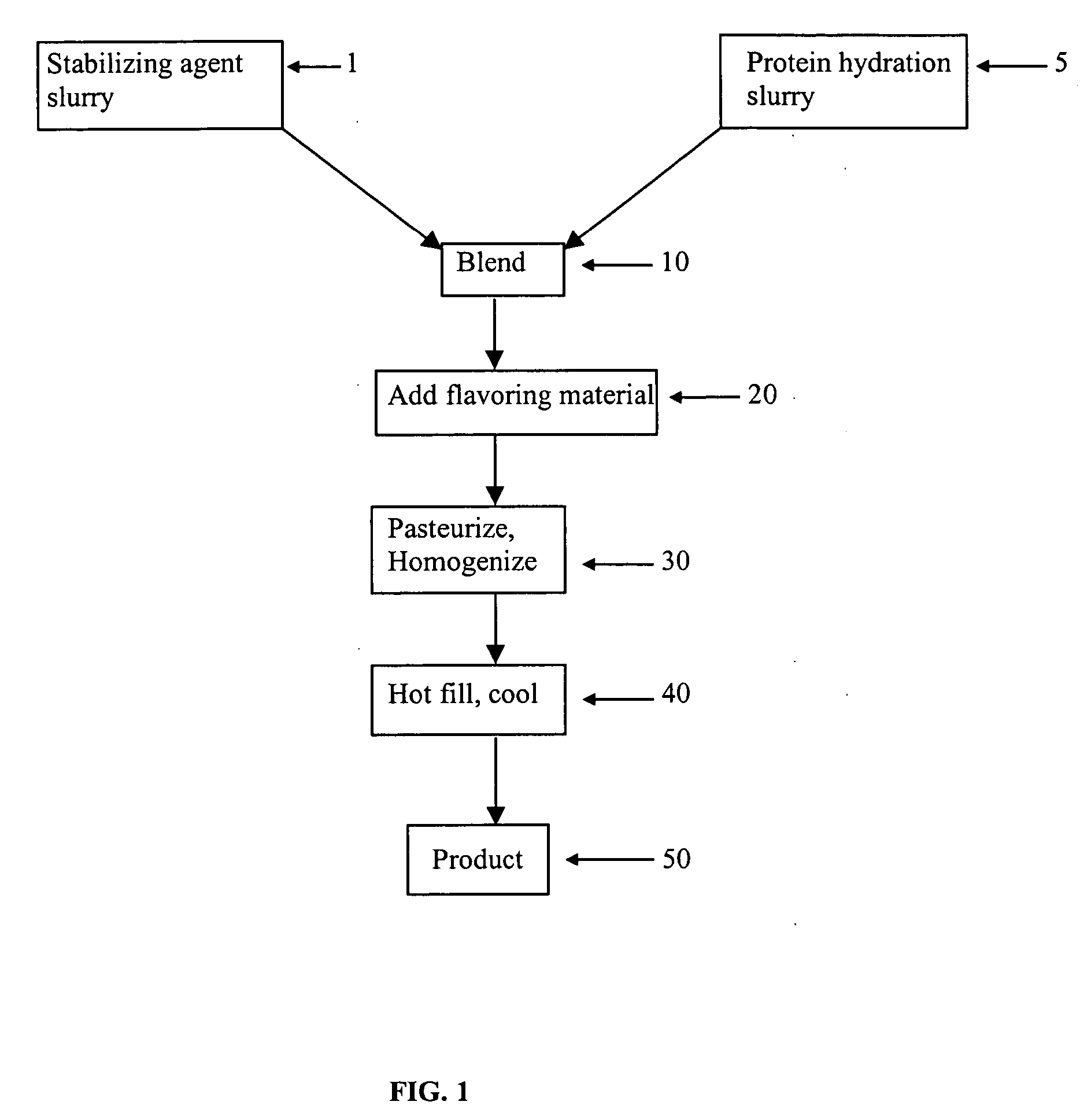
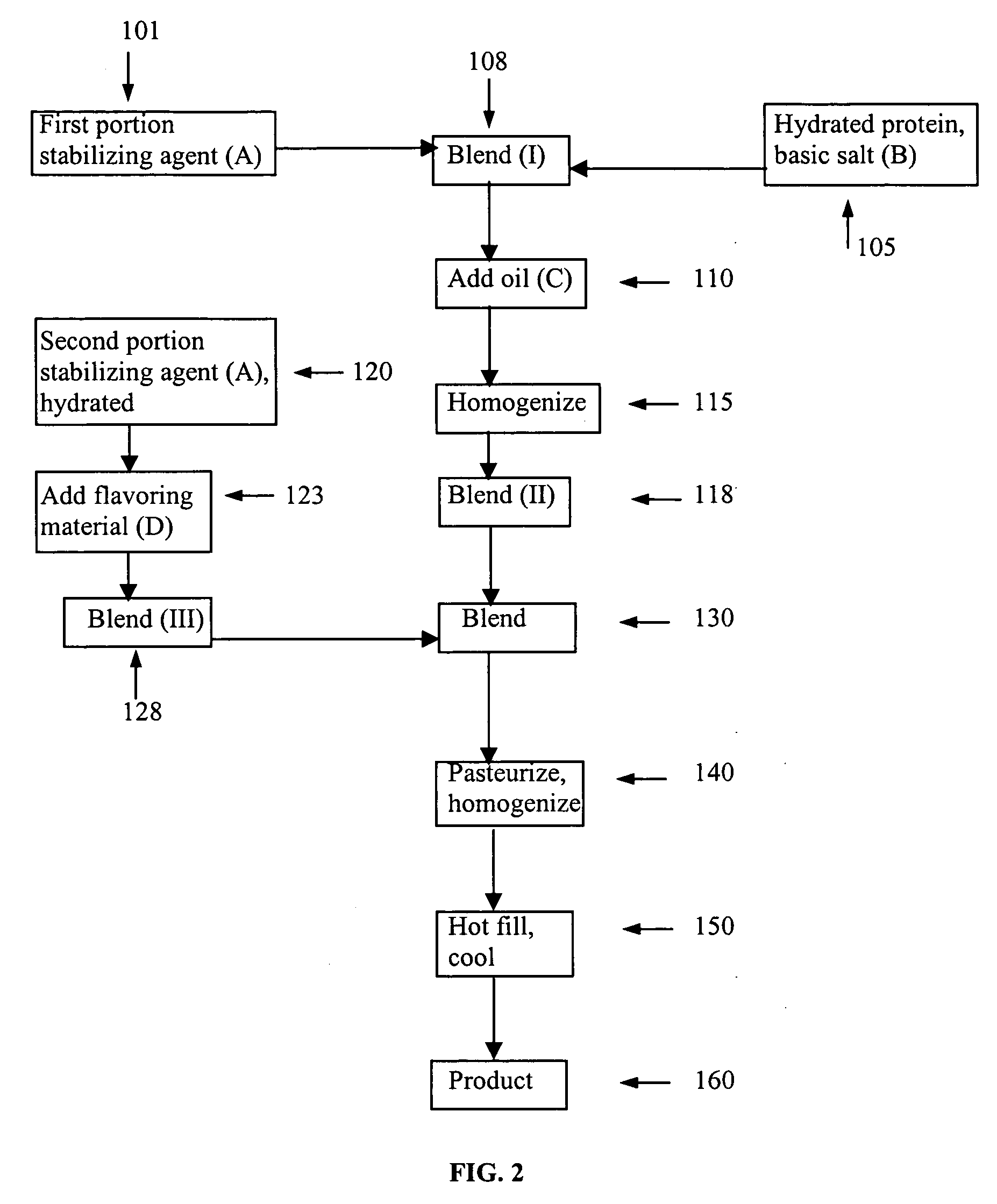
This invention is directed to an acidic beverage composition, comprising; (A) a hydrated protein material having a combination of an inositol-6-phosphate content, an inositol-5-phosphate content, an inositol-4-phosphate content and an inositol-3-phosphate content of less than 8.0 μmol / g, with (B) a hydrated protein stabilizing agent and (C) at least one acid comprising a fruit juice, a vegetable juice, citric acid, malic acid, tartaric acid, lactic acid, ascorbic acid, glucono delta lactone or phosphoric acid, wherein the acidic beverage composition has a pH of from 3.0 to 4.5.
Owner:SOLAE LLC
Acid beverage composition utilizing a protein and a vegetable oil and process for making same
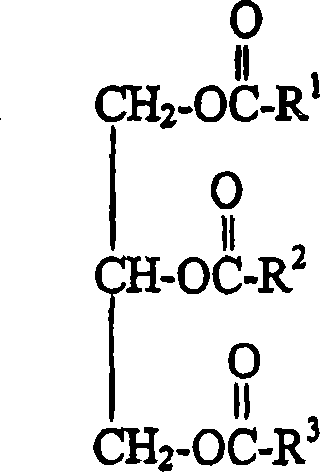
InactiveUS20050233051A1Color stableInhibit coloringMalt preparationFood preparationGlucono delta-lactoneVegetable oil
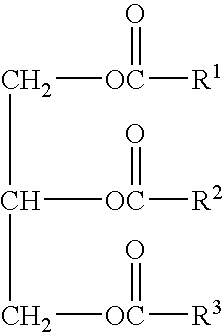
This invention is directed to an acid beverage composition, comprising; (A) a hydrated protein stabilizing agent; (B) a protein material; (C) a triglyceride comprising a vegetable oil triglyceride, a genetically modified vegetable oil triglyceride or a synthetic triglyceride oil of the formula wherein R1, R2 and R3 are aliphatic groups and contain from about 7 up to about 23 carbon atoms; and (D) a flavoring material comprising a fruit juice, a vegetable juice, glucono delta lactone, phosphoric acid or the sodium salts or acids of citric acid, malic acid, tartaric acid, lactic acid and ascorbic acid; wherein the acid beverage composition has a pH of from 3.0 to 4.5. Also disclosed is a process for preparing an acid beverage composition.
Owner:SOLAE LLC
Polyglycol modified trisilicate containing glucose amide group and preparation method
A polyethanediol modified trisiloxane containing glucosylamido used as the assistant of agricultural chemical to decrease the surface tension of water is prepared through catalytic reaction between hexamethyldisiloxane and aminosilane to obtain aminotrisiloxane, reacting on lactone gluconate in methanol to obtain trisiloxane containing glucosylamido, and modifying it by polyethanediol method glicideether.
Owner:CHINA RES INST OF DAILY CHEM IND
Method for separating cow milk beta-casein and whey protein at low temperature through microfiltration to simulate composition of human lactoprotein
ActiveCN106417888ARealize targeted regulationEfficient separationMilk preparationProtein composition from milkGlucono delta-lactoneAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to a method for separating cow milk beta-casein and whey protein at the low temperature through microfiltration to simulate composition of human lactoprotein. Skim milk, whole milk, dried skim milk, concentrated milk protein powder and the like are taken as raw materials, decalcification pretreatment is performed with the adoption of citrate, glucono-delta-lactone and other chelating agents or an acidifier, microfiltration and filter wash are performed with the adoption of a ceramic membrane or a polyethersulfone membrane and the like under the low-temperature (0-15 DEG C) condition, beta-casein and whey protein are selectively enriched into a permeating liquid, the permeating liquid is subjected to spray drying and dewatering after lactose and mineral substances are removed through ultrafiltration and concentration, and high-protein powder containing rich beta-casein and whey protein is prepared. An adopted technical process has the characteristics of being environment-friendly, efficient, high in operability, good in safety and the like and is suitable for large-scale industrial production. The obtained compound protein powder can serve a novel functional lactoprotein ingredient to replace whey protein and is used for research and development of infant food such as formula milk powder and the like, so that the protein molecule composition of the compound protein powder is closer to that of human lactoprotein.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
High-efficiency broad-spectrum food composite preservative
The invention provides a high-efficiency broad-spectrum food composite preservative and aims to solve the technical problem that most of the food preservatives now used in food processing are potassium sorbate and sodium benzoate, cannot achieve ideal preservation effect when use alone due to certain limitation to antibacterial spectrum and suffers certain limitation on use. The key point of the preservative lies in that the preservative contains nisin, natamycin, potassium sorbate, sodium diacetate and sodium dehydroacetate or also one or all of d-sodium erythorbate and d-glucono-delta-lactone. The use of the preservative is to be added in various foods.
Owner:SHENYANG HONGMEI BIOTECH
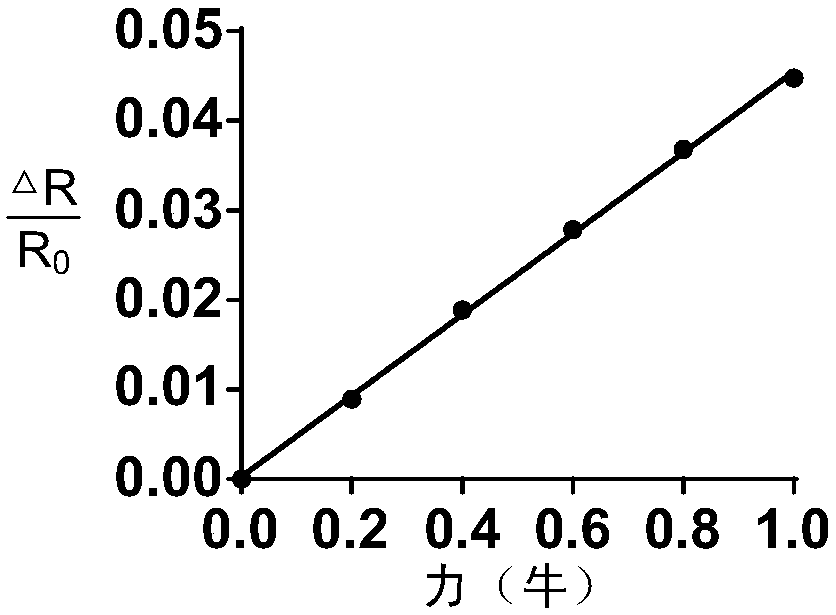
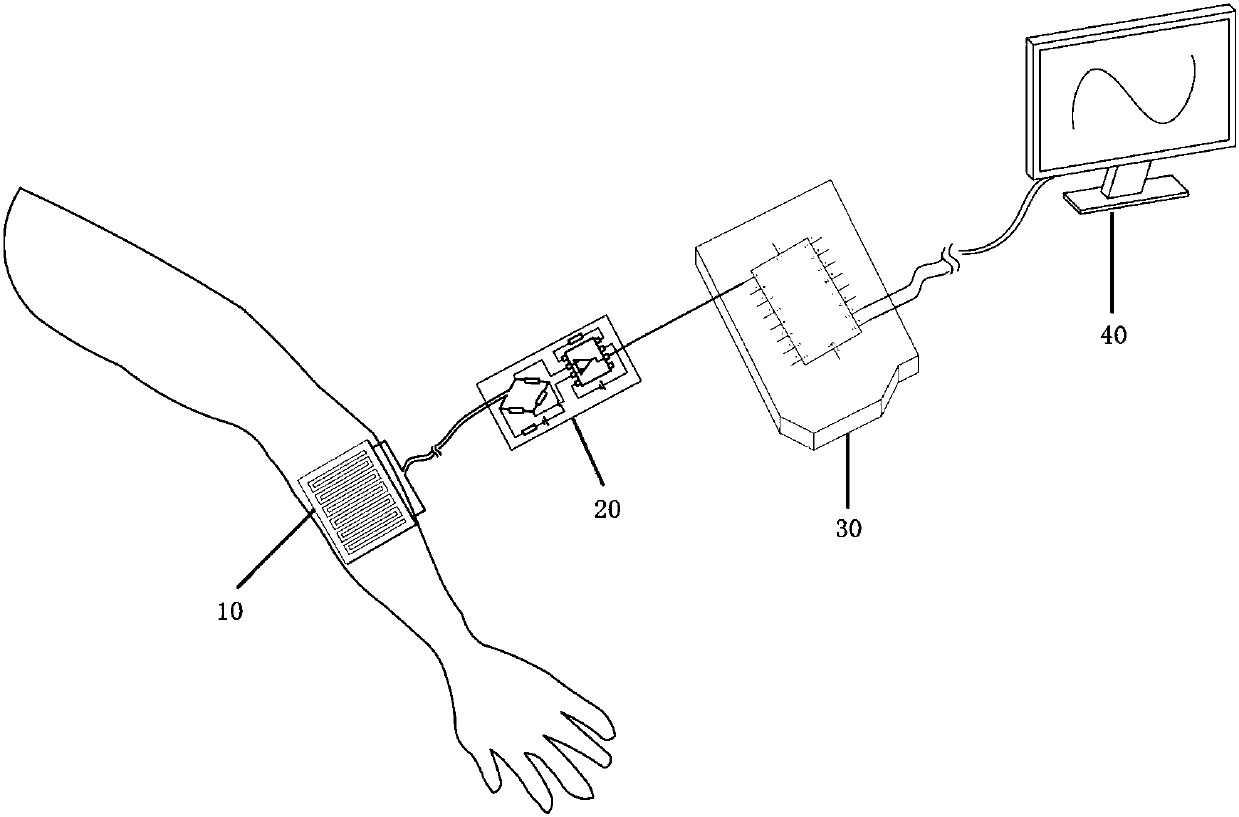
Flexible force tactile sensor based on transparent biomaterial, sensitive element and preparation methods of flexible force tactile sensor and sensitive element
ActiveCN107941386AGood for mechanical analysisGood biocompatibilityForce measurement using piezo-resistive materialsEthylenediamineGlucono delta-lactone
The invention belongs to the technical field of sensing, and in particular relates to a flexible force tactile sensor based on a transparent biomaterial, a sensitive element and preparation methods ofthe flexible force tactile sensor and the sensitive element. The sensitive element comprises a water-retaining layer substrate and hydrogel wrapped with the water-retaining layer substrate, wherein solute of the hydrogel is prepared from sodium alginate, ethylenediamine tetraacetate disodium calcium and glucono delta-lactone according to a mass ratio of 2 to (0.5-1.5) to (0.5-1.5), wherein the mass concentration of the sodium alginate is 2-6%. The sensor comprises the sensitive element, a measuring circuit, an analog-to-digital (AD) conversion circuit and a display device which are sequentially connected in a wired or wireless way. According to the preparation method, the ionic-crosslinked sustained release system hydrogel is used as a sensor main body, and calcium ions in ethylenediaminetetraacetate disodium calcium are slowly released by using the glucono delta-lactone, ionic crosslinking is formed by the calcium ions and a sodium alginate monomer, the water molecules are connectedinside a mesh structure, and then certain water conservation measures are utilized, so that the moisture emission is reduced, and the stability of the sensor is maintained.
Owner:ANHUI MEDICAL UNIV
Mini-salami sausage with tea fragrance and preserved fruit flavor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103340435AObvious sweetness of preserved fruitObvious tea aromaFood preparationGlucono delta-lactoneVitamin C
The invention discloses a mini-salami sausage with a tea fragrance and a preserved fruit flavor and a preparation method thereof. The mini-salami sausage is prepared by the following raw materials, in parts by weight: 50-60 of beef, 30-40 of pork lean, 15-25 of lardo, 2-3 of a stellaria yunnanensis powder, 2-3 of preserved cherries, 1-2 of kumquat cakes, 1-3 of a hawthorn seed powder, 3-5 of green tea wine, 2-3 of table salt, 1-2 of white sugar, 0.2-0.4 of an edible soy protein, 0.3-0.5 of glucose, 0.01-0.15 of sodium nitrite, 0.01-0.15 of vitamin C, 0.2-0.3 of carrageenan, 0.01-0.02 of glucono-delta-lactone, 0.02-0.03 of sodium tripolyphosphate, and 0.04-0.05 of a fermentation agent. The stellaria yunnanensis powder, the preserved cherries, the kumquat cakes, the hawthorn seed power and the green tea wine selected and used in the mini-salami sausage are rich in nutrition and significant in nourishing function, are added to the sausage, thereby adding unique flavors, having certain nutrition and health care effects, preventing certain diseases, and simultaneously increasing appetite.
Owner:于习和
Fast deep-fried dough stick leavening agent and method for fast making deep-fried dough sticks
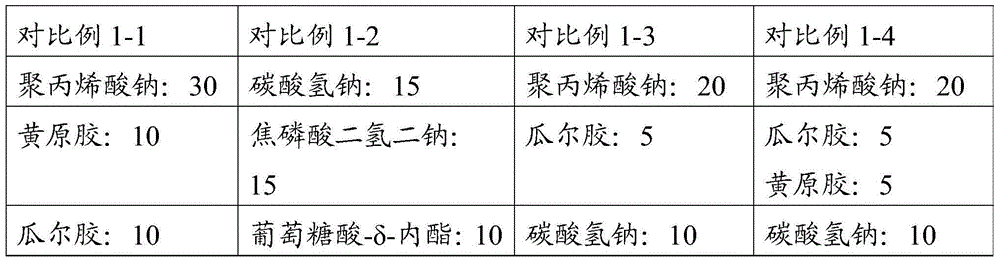
InactiveCN103828878AThere is no problem of excessive aluminumSolve the problem of excessive aluminum contentDough treatmentBakery productsSodium bicarbonateGlucono delta-lactone
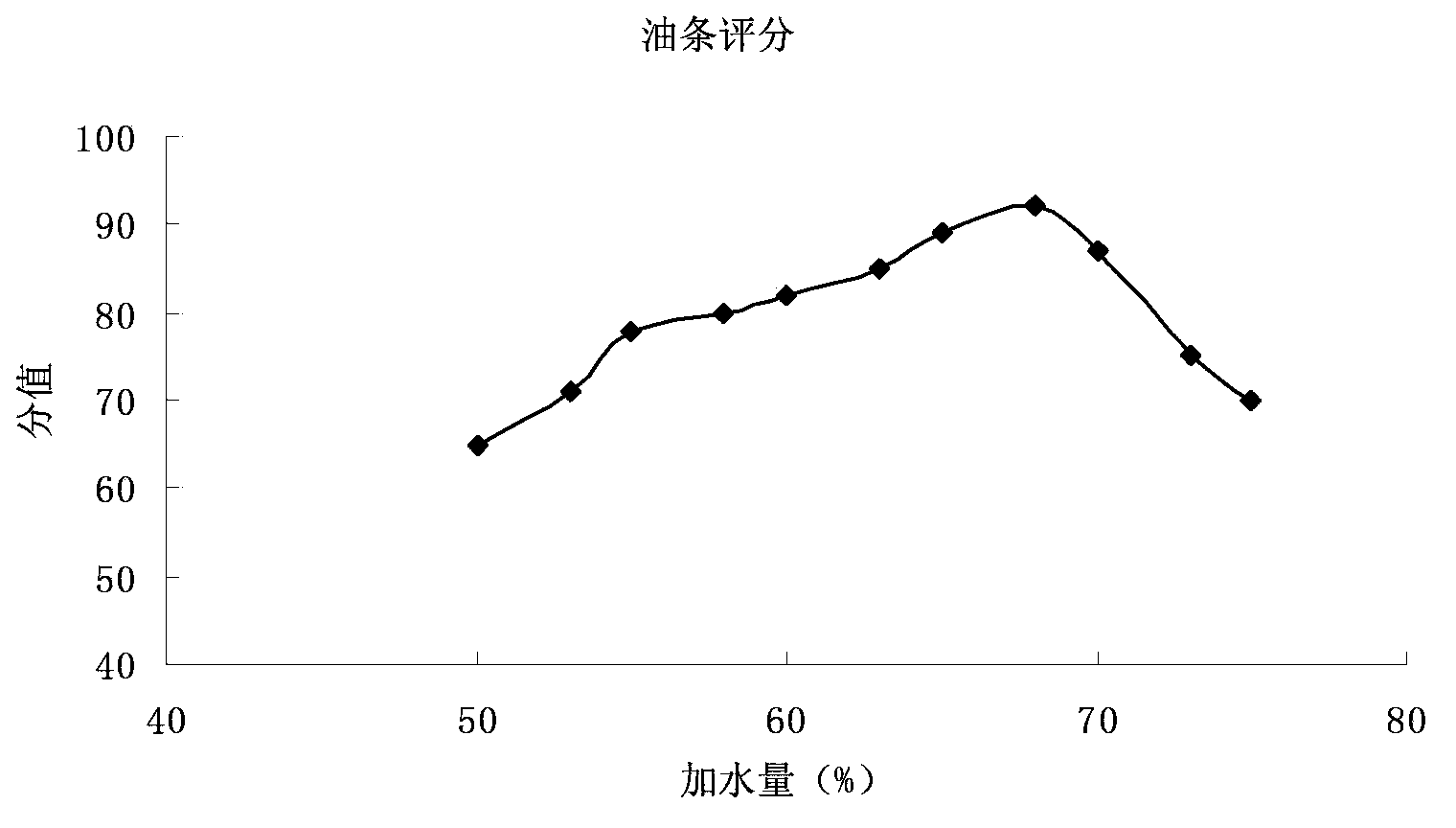
The invention relates to a fast deep-fried dough stick leavening agent and a method for fast making deep-fried dough sticks. The fast deep-fried dough stick leavening agent comprises, by weight, 20%-60% of sodium bicarbonate, 5%-15% of glucono-delta-lactone, 1%-20% of sodium dihydrogen phosphate, 1%-20% of malic acid and 1%-20% of citric acid, wherein the total of the weight percentages of all the constituents is 100% actually. The method includes the steps that 100 parts of flour, 2-3 parts of fast deep-fried dough stick leavening agents, water, table salt and sugar are prepared by weighing; paste is evenly stirred till slight gluten appears and is then cut into small dough pieces, the surfaces of the small dough pieces are brushed over with butter and covered with thin films, and the small dough pieces are subjected to standing for 15-33 min; the dough pieces having been being subjected to standing are taken out and stretched into long strips, the long strips are subjected to standing and are then cut into small segments, and every two small segments are pressed together; formed dough pieces are deep-fried till the surfaces of the dough pieces turn golden yellow. By means of the fast deep-fried dough stick leavening agent and the method for fast making the deep-fried dough sticks, the speed of making the deep-fried dough sticks is improved, the quality of the deep-fried dough sticks is improved, and adverse effects on the human body are reduced.
Owner:ANGELYEAST CO LTD
Preparation method for magnetic carbon aerogel
InactiveCN104998613AIdiosyncratic reactivityLow priceCatalyst carriersOther chemical processesGlucono delta-lactoneFreeze-drying
The invention relates to a preparation method for an aerogel, especially to a preparation method for a carbon aerogel. The invention aims to overcome the technical problems of high cost for raw materials and great toxicity in preparation in conventional preparation methods for the carbon aerogel. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding carboxymethylcellulose sodium and glucono delta-lactone into water and carrying out stirring until carboxymethylcellulose sodium and glucono delta-lactone are dissolved so as to obtain a colloidal liquid; adding a neutral ferric trichloride solution into the colloidal liquid, carrying out uniform mixing under stirring and then carrying out standing at room temperature so as to obtain gel; freezing the gel and then carrying out freeze drying so as to obtain a carboxymethylcellulose sodium aerogel; and carbonizing the carboxymethylcellulose sodium aerogel under the protection of N2 so as to obtain the magnetic carbon aerogel. The preparation method has the advantages of simple steps and no toxicity; and the prepared magnetic carbon aerogel has magnetism and a large specific surface area, can be repeatedly recycled, has active bright blue dye adsorption capacity of 59.98 mg / g and removal rate of as high as 42.38%, and is applicable to treatment of dye waste water.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Composite ecological coagulant and its preparation method and application in producing fruit and vegetable color bean curd
InactiveCN101283744ADeliciousGreat tasteCheese manufactureFood preparationGlucono delta-lactoneThreonine
The invention discloses an ecological compound coagulant, its production method and the use in producing colorful vegetable / fruit bean curd. The ecological compound coagulant contains the flowing components in weight parts: 20-30 weight parts of CaSO4, 0.8-1.5 weight parts of glucono-delta-lactone, 0.1-0.2 weight parts of calcium hydrogen phosphate, 0.05-0.1 weight parts of potassium tartrate, 0.3-0.4 weight parts of sodium hydrogen phosphate, 0.8-0.9 weight parts of fumaric acid, 0.15-0.25 weight parts of corn starch and 0.8-0.9 weight parts of surfactant. The surfactant is selected from lysine, methionine, tryptophan, phenylalanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, threonine, and a combination thereof. The coagulant ensures elasticity, chewiness and smooth mouthfeel of bean curd, and prevents the bean curd to be broken and cracked during the slicing or shredding process.
Owner:刘子余
Plastic gel material for preventing spontaneous combustion of coal
InactiveCN109364418AImprove water retentionImprove toughnessDust removalFire preventionSodium BentoniteGlucono delta-lactone
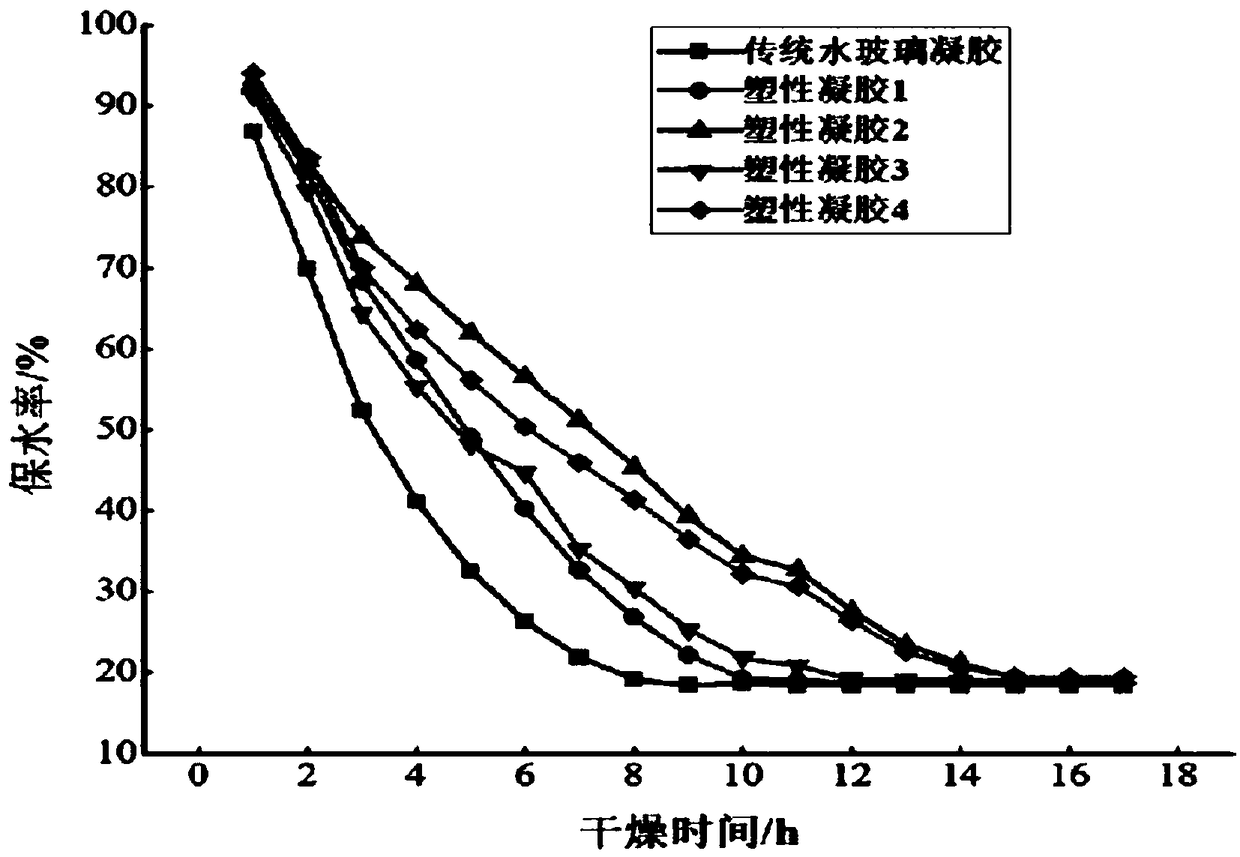
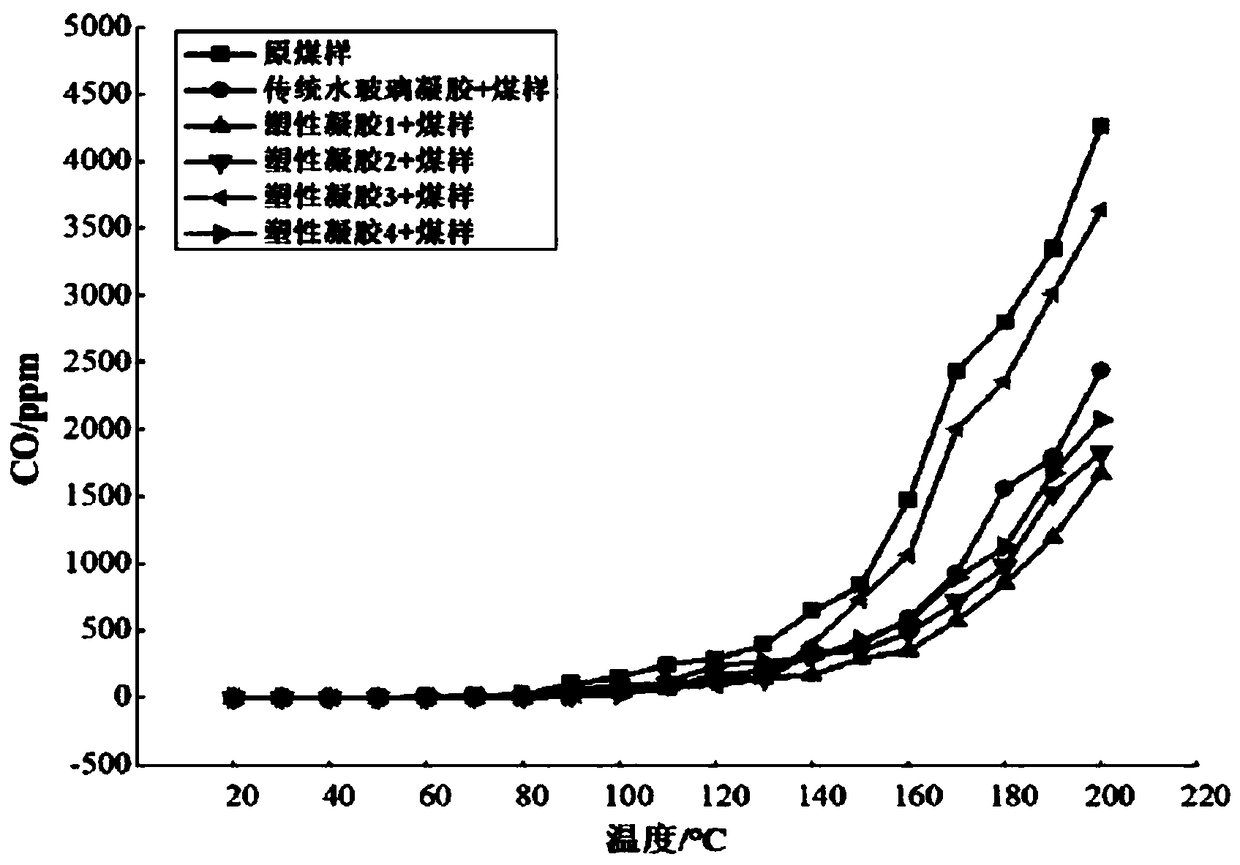
The invention provides a plastic gel material for preventing spontaneous combustion of coal. The plastic gel material for preventing spontaneous combustion of coal comprises water, a cross-linking agent, a toughening agent, a coagulant, an aggregate and a water glass, wherein the cross-linking agent (AlCit) is obtained by mixing a polymeric aluminium chloride solution and a citric acid solution ina certain ratio and then neutralizing the sodium hydroxide solution; the coagulant is potassium bicarbonate, sodium hydrogen carbonate, ammonium hydrogen carbonate, and one or more of sodium carbonate and glucono-delta-lactone (GDL); the toughening agent is one or more of pregelatinized starch, sodium alginate, carboxymethyl cellulose, and polyacrylamide; aggregate is fly ash or bentonite. The plastic gel material has better water retention, toughness and resistance properties, so that the problems of easy cracking and pulverization of the traditional inorganic silicon gel solid body after water loss is effectively solved, and the material cost is effectively reduced compared with the traditional gel. The plastic gel material can cover the surface of the burning coal body, significantly reducing the temperature of the fire source, the heat radiation and the amount of CO generated, and the fire extinguishing is stable, the re-ignition phenomenon does not occur. In addition, the plasticgel can adhere to the coal body cracks, achieving a good air leakage effect.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Acid beverage composition and process for making same utilizing an aqueous protein component
InactiveUS20050233052A1Reduce solubilityHigh protein concentrationVegetable proteins working-upFood preparationO-Phosphoric AcidGlucono delta-lactone
This invention is directed to an acid beverage composition, comprising; (A) a hydrated protein stabilizing agent; (B) at least one flavoring material comprising a fruit juice, a vegetable juice, citric acid, malic acid, tartaric acid, lactic acid, ascorbic acid, glucono delta lactone or phosphoric acid; and (C) a slurry of an aqueous protein material wherein the slurry of the aqueous protein material is prepared by a process, comprising; (1) preparing an aqueous extract from a protein containing material, (2) adjusting the pH of the aqueous extract to a value of from about 4 to about 5 to precipitate the protein material, (3) separating the precipitated protein material and forming a suspension of the precipitated protein material in water, (4) adjusting the pH of the suspension to a value of from about 4.0 to about 6.0 to form a slurry of an aqueous protein material, and optionally (5) pasteurizing the slurry of the aqueous protein material; wherein the acid beverage composition has a pH of from 3.0 to 4.5. Also disclosed are several processes for preparing an acid beverage composition.
Owner:SOLAE LLC
Antimicrobial compositions
InactiveCN1688329ACosmetic preparationsOrganic detergent compounding agentsBenzoic acidGlucono delta-lactone
The present invention provides an antimicrobial composition comprising an antimicrobial effective amount (such as a preservative, bactericidal, and / or fungicidal effective amount) of a mixture comprising at least two of: (a) lemon grass oil; (b) cinnamaldehyde, cinnamon oil, cinnamomum cassia, cinnamon extract, cassia leaf oil, 3,4-dihydroxycinnamic acid or salt thereof, or a mixture thereof; (c) sorbic acid, or a salt thereof; (d) erythorbic acid, or a salt thereof; (e) benzoic acid, or a salt thereof; (f) arabinogalactan, galactoarabinan, or a mixture thereof; (g) a hexahydro-iso-alpha-acid, tetrahydro-iso-alpha-acid, or a mixture thereof; (h) Achillea fragrantissima oils, Santolina fragrantissima oils, Forssk oils, Lavender cotton oils; and (i) Glucono Delta Lactone. The present invention also provides a product (preferably a product other than a foodstuff, pharmaceutical, or cosmetic) comprising a preservative effective amount of cinnamaldehyde or a mixture of cinnamaldehyde and one or more alkanol-dialkyl hydantoins.
Owner:LONZA LTD
Magnetic high-strength high-toughness hydrogel for membrane pollution washing and application method thereof
Magnetic high-strength high-toughness hydrogel for membrane pollution washing and an application method thereof are provided; sodium alginate is used as a framework; acrylamide and its derivatives areused as polymeric monomers; sodium silicate, the polymeric monomers and the sodium alginate are dissolved together in water; acrylamide polymerization is initiated by ultraviolet; calcium silicate nanoparticles are generated in situ in hydrogel by calcium ion crosslinking; calcium silicate having surface mesoporous silica gel is generated by soaking via glucono delta-lactone solution; the strength and stability of the hydrogel are improved accordingly. Nano calcium silicate evenly dispersed is generated by in-situ mineralization such that strength of the hydrogel is enhanced. Micro-nano magnetic particles are used as an enhancer to prepare microspheres via an injector; since the density of the micro-nano magnetic particles are very close to water in density and have high strength, high toughness and good stability, the hydrogel gains improved washing effect in jet or low washing process; the composite hydrogel with the silicate has significantly improved stability in water and has a good application prospect in the field of membrane pollution washing.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Frozen dough, manufacturing method and application thereof
ActiveCN101810204AReduce usageImprove securityDough treatmentPre-baking dough treatmentSodium bicarbonateCalcium biphosphate
The invention relates to dough for frozen pre-fried food and a preparation method thereof. The dough is prepared from compound leavening agent accessories such as gluconic acid-delta-lactone, calcium biphosphate, sodium bicarbonate, glycerol monolaurate and the like and flour. By means of analysis on the properties of the dough through flour stretching and rheological research, the dough of the invention is similar to the dough of the traditional alum formula on flour stretching property and rheological property; and the effects of single ingredients on the properties of the dough are mutually complementary and cooperative through single ingredient analysis so that the property of the dough of the invention is similar to that of the dough of the traditional alum formula. Moreover, compared with the deep-fried dough sticks of the traditional formula, the deep-fried dough sticks made of the dough of the invention have the advantage that various physicochemical indexes and sensory evaluation results are improved. Therefore, the dough enables the deep-fried dough sticks to be processed simply and conveniently, is favorable for developing markets, and produces good economic benefit.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +2
Bupropion hydrochloride solid dosage forms
InactiveUS20060020040A1BiocideOrganic active ingredientsGlucono delta-lactoneBupropion hydrochloride
The present invention relates to solid dosage forms that contain bupropion hydrochloride and glucono delta lactone or its corresponding open chain hydroxy acid derivative. The bupropion hydrochloride retains at least 80% of the bupropion hydrochloride potency after storage for three months at 40° C. and 75% relative humidity. The solid dosage form may be in the form of a tablet, a capsule, or a granulate with or without an immediate release profile, a modified release profile, or an extended release profile.
Owner:RANBAXY LAB LTD
Method and composition for gel mixture
InactiveUS20050118320A1Rate of gelling is determinedQuickly the pH of the product is loweredFood preparationGlucono delta-lactonePowder mixture
A quick-gel mixture is prepared from a liquid mixture and a powder blend. The liquid mixture is an alginate blended with sugar and solubilized in water and, optionally, ethyl alcohol. The powder blend is a mix of sugar, calcium, acids, and sodium citrate, which acts as a sequestering agent to control the release of calcium. The acids used are a combination of adipic and glucono delta lactone. The acids being used are slow-release-type acids and control the rate of gelling. The source of calcium is calcium glycerophosphate, which is readily soluble in the liquid phase and reacts with the alginate to form the gel. Granular sugar is used as a carrier and to solubilize the powder blend mix. To prepare the final product, the liquid mixture and the powder blend are combined and shaken for about 15 seconds. The gel sets in approximately 15 to 30 minutes.
Owner:J MANHEIMER
Production method of low-temperature sterilized surimi products capable of being storage at room temperature
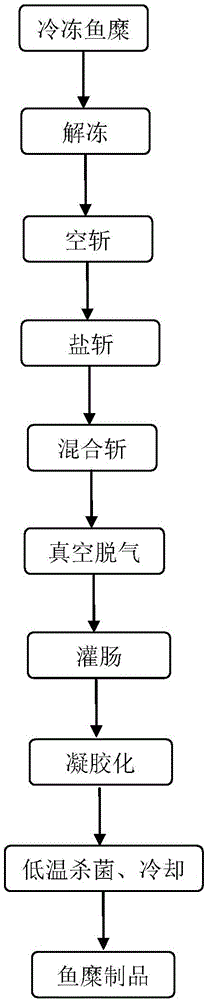
ActiveCN106509690APromote circulationLower pHMeat/fish preservation by freezing/coolingNutritive valuesMicroorganism
The invention provides a production method of low-temperature sterilized surimi products capable of being storage at room temperature. The production method of the low-temperature sterilized surimi products capable of being storage at room temperature comprises the following steps: carrying out thawing, carrying out air cut, carrying salt cut, carrying out mixed cut, carrying out vacuum degassing, carrying out filling so as to prepare sausages, carrying out gelatinizing, and carrying out low-temperature sterilizing. Glucono delta-lactone, as well as crushed ice, soy protein isolate, starch, locust bean gum, scallion and ginger juice, cooking wine, white pepper powder and edible salt, is added into the surimi products prepared by utilizing the production method so as to reduce the pH of the surimi gel and enhancing the bacteriostatic capacity of the surimi gel; thus, growth of most microorganisms can be inhibited. Moreover, a vacuum packing way is combined, and the sterilizing method is designed and optimized so as to achieve the purpose of normal-temperature storage; thus, the damages caused by high-temperature sterilizing on the qualities of the surimi are greatly reduced so as to improve the nutritive values and the edible values of the surimi products. Circulation of the surimi products and edible convenience of the consumers are thereby facilitated.
Owner:江苏里物食品科技有限公司
Candied cherry tomatoes and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses candied cherry tomatoes and a preparation method thereof. Cherry tomatoes, soybean oligosaccharides, xylo-oligosaccharide, white granulated sugar, glucono-delta-lactone, carboxymethyl cellulose sodium, citric acid, and potassium sorbate are used as the raw materials and subjected to the steps including: selecting of raw materials, cleaning, micro-wave water-removing, perforating, hardening, first solar energy-heat pump combined drying, micro-wave sugar permeability, secondary solar energy-heat pump combined drying, micro-wave sterilizing and vacuum packaging, and finally the candied cherry tomatoes which are round in shape, red and bright in color and fresh and sweet in taste are produced. The nutrients of the prepared candied cherry tomatoes are well maintained, and the candied cherry tomatoes have health-care efficacies of regulating the intestinal flora, promoting the growth of bifidobacterium, regulating immunity and preventing decayed tooth. Moreover, the preparation process is simple, and high in operability, and the solar energy-heat pump combined drying technology is adopted, so as to greatly shorten the production time and provide an energy-saving and environmental-protection path for deep processing of cherry tomatoes.
Owner:福建龙岩晋龙食品有限公司
Acid beverage composition utilizing a protein and a vegetable oil and process for making same
This invention is directed to an acid beverage composition, comprising; (A) a hydrated protein stabilizing agent; (B) a protein material; (C) a triglyceride comprising a vegetable oil triglyceride, a genetically modified vegetable oil triglyceride or a synthetic triglyceride oil of the formula (I) wherein R<1>, R<2> and R<3> are aliphatic groups and contain from about 7 up to about 23 carbon atoms; and (D) a flavoring material comprising a fruit juice, a vegetable juice, glucono-delta-lactone, phosphoric acid or the sodium salts or acids of citric acid, malic acid, tartaric acid, lactic acid and ascorbic acid; wherein the acid beverage composition has a pH of from 3.0 to 4.5. Also disclosed is a process for preparing an acid beverage composition.
Owner:SOLAE LLC
Self-rising flour
The invention relates to self-raising flour which comprises the raw materials of 98-99% of flour and 1-2% of compound raising agent. The raising agent is prepared by mixing and combining various raw materials according to a certain proportion, which ensures that actions of all components can suit well with each other. The raising agent plays a fermentation role by being added to the flour which subsequently acts and generates gas when water is added. Dry yeast which is rich in protein, enzyme and vitamin B complex such as nicotinic acid, folic acid, vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin B6, vitamin B12, and the like, is mainly used for properly prolong fermentation time. Sodium bicarbonate, delta-gluconolactone and primary calcium creasote are used for generating gas by interacting with each other, thus the flour can be fermented by being added with water. The flour has high eating quality, convenient use, simple operation, long quality guarantee period and wide application range.
Owner:郑州天地人面粉实业有限公司
Phytase-treated acid stable soy protein products
This invention is directed to an acidic beverage composition, comprising;(A) a hydrated protein material having a combination of an inositol-6-phosphate content, an inositol-5-phosphate content, an inositol-4-phosphate content and an inositol-3-phosphate content of less than 8.0 μmol / g, with(B) a hydrated protein stabilizing agent and(C) at least one acid comprising a fruit juice, a vegetable juice, citric acid, malic acid, tartaric acid, lactic acid, ascorbic acid, glucono delta lactone or phosphoric acid,wherein the acidic beverage composition has a pH of from 3.0 to 4.5.
Owner:SOLAE LLC
Method for preparing high-purity calcium gluconate from oyster shell
InactiveCN101434532AGuaranteed white colorMeet the requirements of high-purity calcium supplement productsCarboxylic acid salt preparationWater bathsOyster shells
The invention discloses a method for preparing calcium gluconate with high purity by utilization of oyster shells, which adopts a technical method that the oyster shells are cleaned, dried and comminuted to a grain size of 80 meshes to 120 meshes; under the conditions of constantly stirring and heating in water bath of 50 DEG C to 70 DEG C, the oyster shell powders are slowly added into a gluconic acid delta lactone solution and react for 2 hours to 5 hours, then a filtrate is subjected to vacuum concentration to a paste; and then edible alcohol is used for washing, crystal and recrystal are purified and finally the obtained crystal is dried to obtain white calcium gluconate with purity of more than 99 percent. The method has the advantages that the oyster shell powders do not need calcination and can be directly used for preparing the calcium gluconate which is the product with largest consumption for enriching the calcium in the human body; the adoption of the method of alcohol washing, crystallization and recrystallization not only can ensure that the calcium gluconate is white in color, but also can remove impurities. The purity of the product can achieve more than 99 percent so as to meet the requirements of calcium enriching products with high purity. The method is simple and practical, and has energy conservation and significant economic benefit.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Method for remedying Cd-As-Cu heavy metal polluted soil
The invention provides a method for remedying Cd-As-Cu heavy metal polluted soil. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, uniformly mixing hydrogen peroxide, oxysophocarpine, phosphoric acid, citric acid, palmitic acid, Tween 80 and deionized water to obtain a solution M, uniformly mixing bismuth phosphate, sodium sulfite, ferrous oxide, hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose and deionized water to obtain a solution N, and uniformly mixing bromelain, amylase, glucono-delta-lactone and deionized water to obtain a solution K; step 2, pulverizing the polluted soil, and performing cyclic leaching on the pulverized polluted soil by adopting the solution M; step 3, adding the solution N into the leached soil for uniform mixing; step 4, adding the solution K for uniform mixing and step 5, adding calcium molybdate, calcium oxalate, silkworm shell powder, chicken manure and fly ash for uniform mixing, and performing conservation. According to the method provided by the invention, the remedying effect on the Cd-As-Cu heavy metal polluted soil and the market prospect are good.
Owner:湖南科臣环境科技有限公司 +1
Seasoned tofu and method of producing the same
InactiveUS20090136634A1Great tasteMilk preparationAlcoholic beverage preparationGlucono delta-lactonePotassium ions
It is intended to provide seasoned tofu which has a favorable mouthfeel in “hardness” and “brittleness” and has been evenly seasoned throughout, and a method of producing the same. Seasoned tofu is produced by heating and coagulating seasoned soymilk containing soybean milk, a seasoning providing sodium ion and / or potassium ion and glucono delta-lactone as a coagulant wherein the concentration of soybean protein is 5.5% by mass or more and 8.5% by mass or less, the total concentration of the sodium ion and / or potassium ion is 0.05 mol / L or more and 0.154 mol / L or less and the concentration of the glucono delta-lactone is 0.4% by mass or more and 0.9% by mass or less.
Owner:MORINAGA MILK IND CO LTD
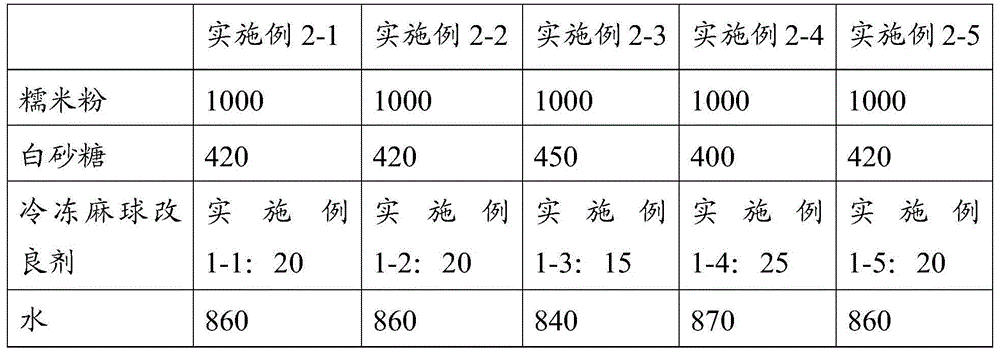
Frozen glutinous rice ball modifying agent, frozen glutinous rice ball raw bases, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106259595AGreat tasteIncrease breathabilityDough extruding machinesDough processingSodium bicarbonateGlucono delta-lactone
The present invention relates to the field of food and particularly discloses a frozen glutinous rice ball modifying agent, frozen glutinous rice ball raw bases, a preparation method and an application thereof. The modifying agent consists of the following components: (1) a compound thickener comprises sodium polyacrylate and other thickening agents, and the other thickening agents are selected from one or more than two of xanthan gum, guar gum and sodium carboxymethylcellulose; and (2) a compound swelling agent comprises sodium bicarbonate, disodium dihydrogen pyrophosphate and glucono-delta-lactone. The recipe of the frozen glutinous rice ball raw bases comprises the following raw materials: 1,000 parts by weight of glutinous rice flour, 400-450 parts of white granulated sugar, 15-25 parts by weight of the frozen glutinous rice ball modifying agent and 800-900 parts of water. The frozen glutinous rice ball modifying agent is used to prepare the frozen glutinous rice ball raw bases and the frozen glutinous rice balls. In the recipe, a combination of the compound thickening agent and the compound swelling agent is used, which improves the air holding capacity and freezing stability of the glutinous rice ball raw bases, so that the glutinous rice balls are better in mouthfeel and have broad application prospects.
Owner:ANGELYEAST CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com