Patents
Literature
346results about How to "Improve sintered density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
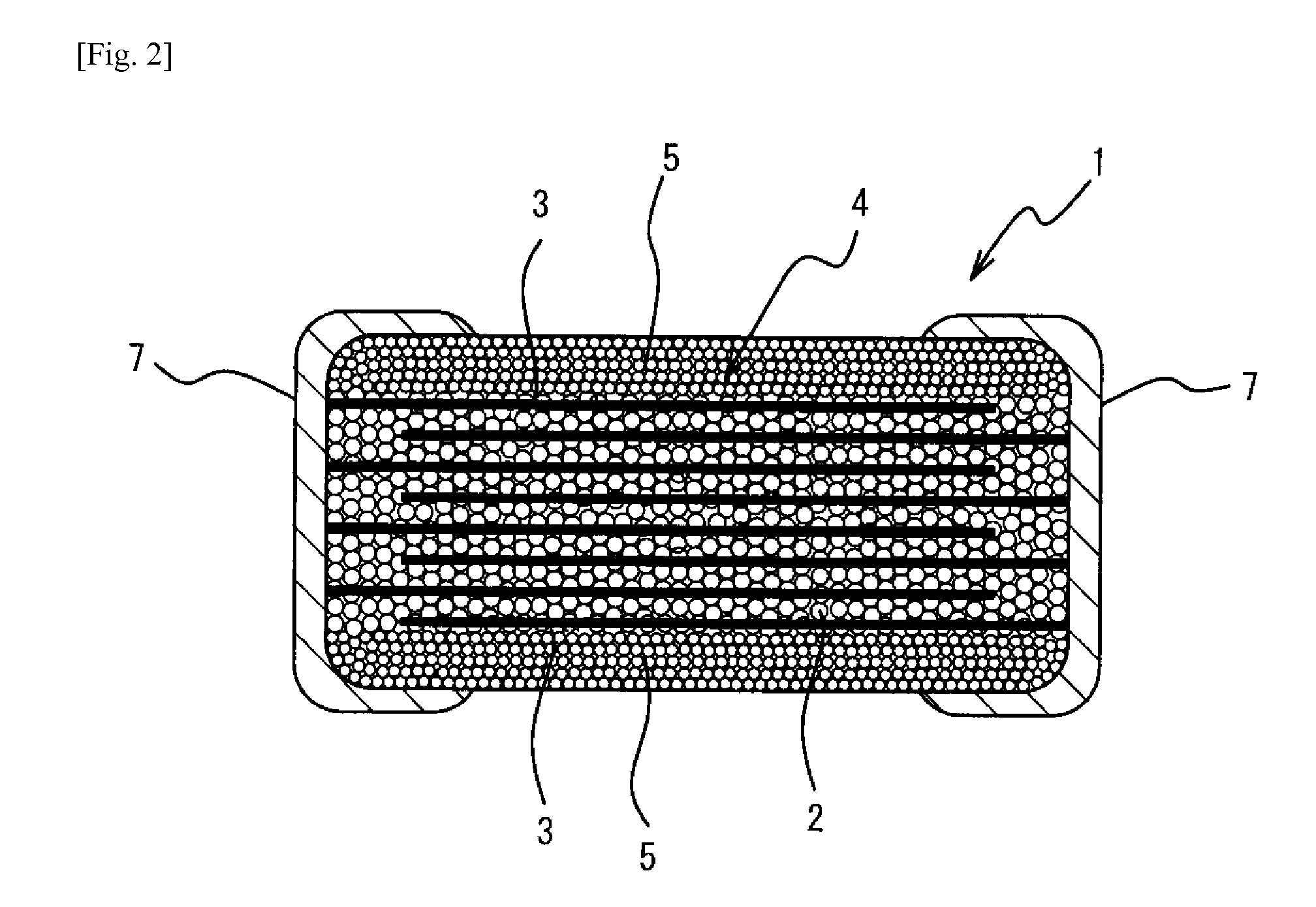
Laminated ceramic capacitor
ActiveUS20120262840A1Improved moisture resistancePrevent generation of crackFixed capacitor dielectricStacked capacitorsCrystalliteDielectric layer
The laminated ceramic capacitor has a laminate block made of alternately laminated ceramic dielectric layers and internal electrodes, a pair of cover layers, laminated on top and bottom of the laminate block, ceramic bodies formed on both side faces of the laminate block, and a pair of external electrodes that are electrically connected to the internal electrodes, wherein the average grain size of the ceramic dielectric grains constituting the ceramic body is smaller than the average grain size of the ceramic dielectric grains constituting the ceramic dielectric layer in the laminate block.
Owner:TAIYO YUDEN KK
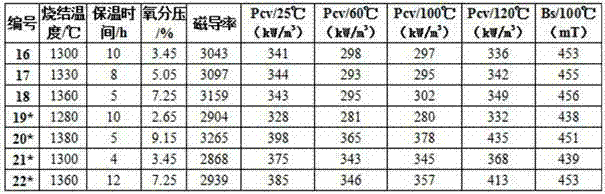
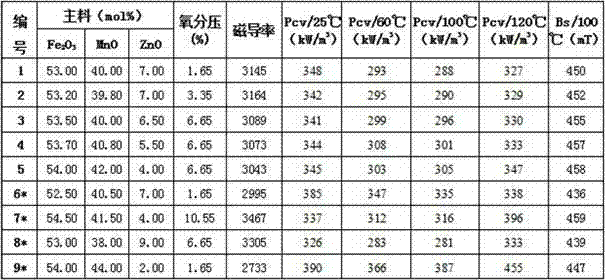
Ni-free MnZn ferrite magnetic core with double characteristics and manufacture method
ActiveCN103496963AOvercome the inability to take into account multiple featuresImprove performanceFerrite (magnet)Condensed matter physics
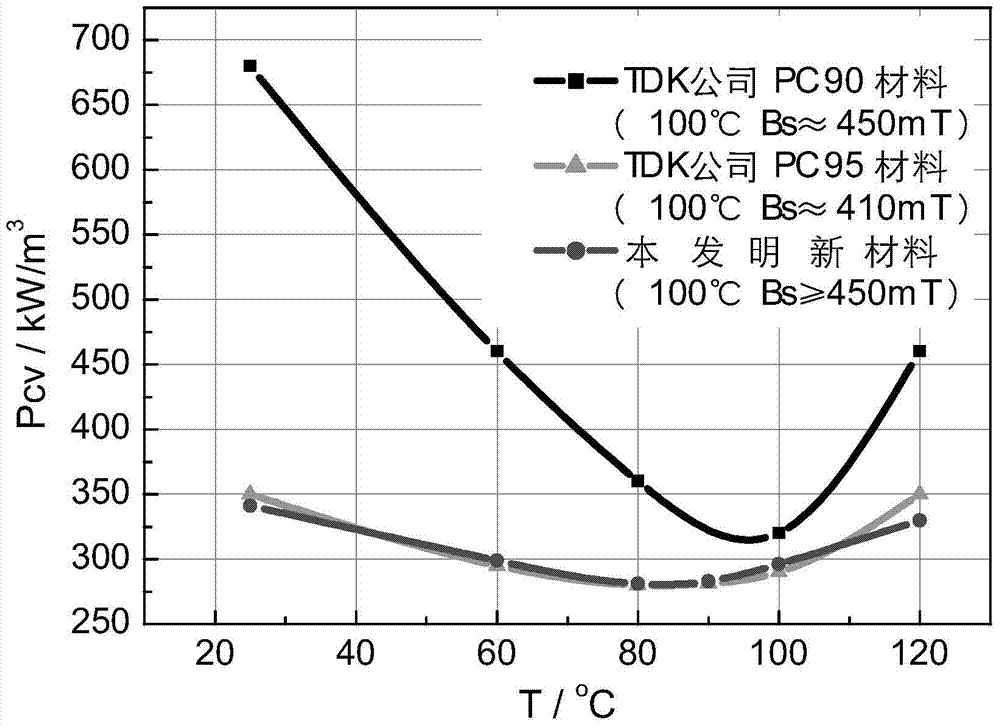
The invention provides a Ni-free MnZn ferrite magnetic core with double characteristics and a manufacture method thereof, wherein the double characteristics mean high temperature and high Bs, and wide temperature and low loss. The ferrite magnetic core comprises main components and auxiliary components. The main components comprise: 53 mol%-54 mol% of Fe2O3, 39 mol%-42 mol% of MnO and 4 mol%-7 mol% of ZnO; and the auxiliary components comprise: Co2O3 or CoO or Co3O4 as a first auxiliary component, SiO2 and CaCO3 as a second auxiliary, and a third auxiliary component which is one or more selected from MoO3, TiO2, SnO2, Nb2O5, V2O5, Sm2O3 and ZrO2. The provided MnZn ferrite magnetic core with double characteristics has unit volume loss Pcv (100kHz, 200mT) less than 350 kW / m<3> at the temperature of 25 DEG C to 120 DEG C, lowest loss of 300 kW / m<3> at the temperature of about 90 DEG C, and saturation magnetic flux density up to 450 mT at the temperature of 100 DEG C.
Owner:江门安磁电子有限公司
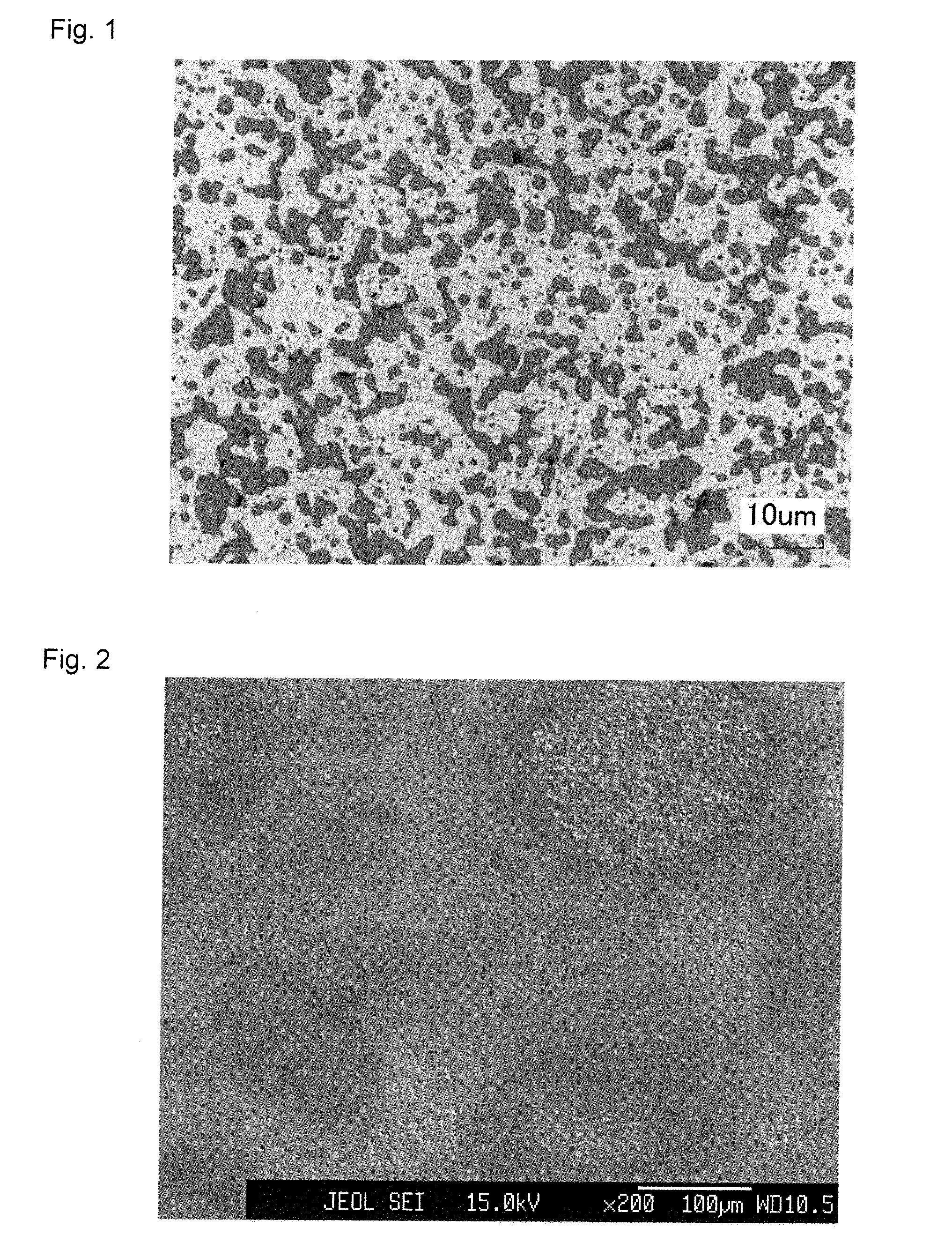
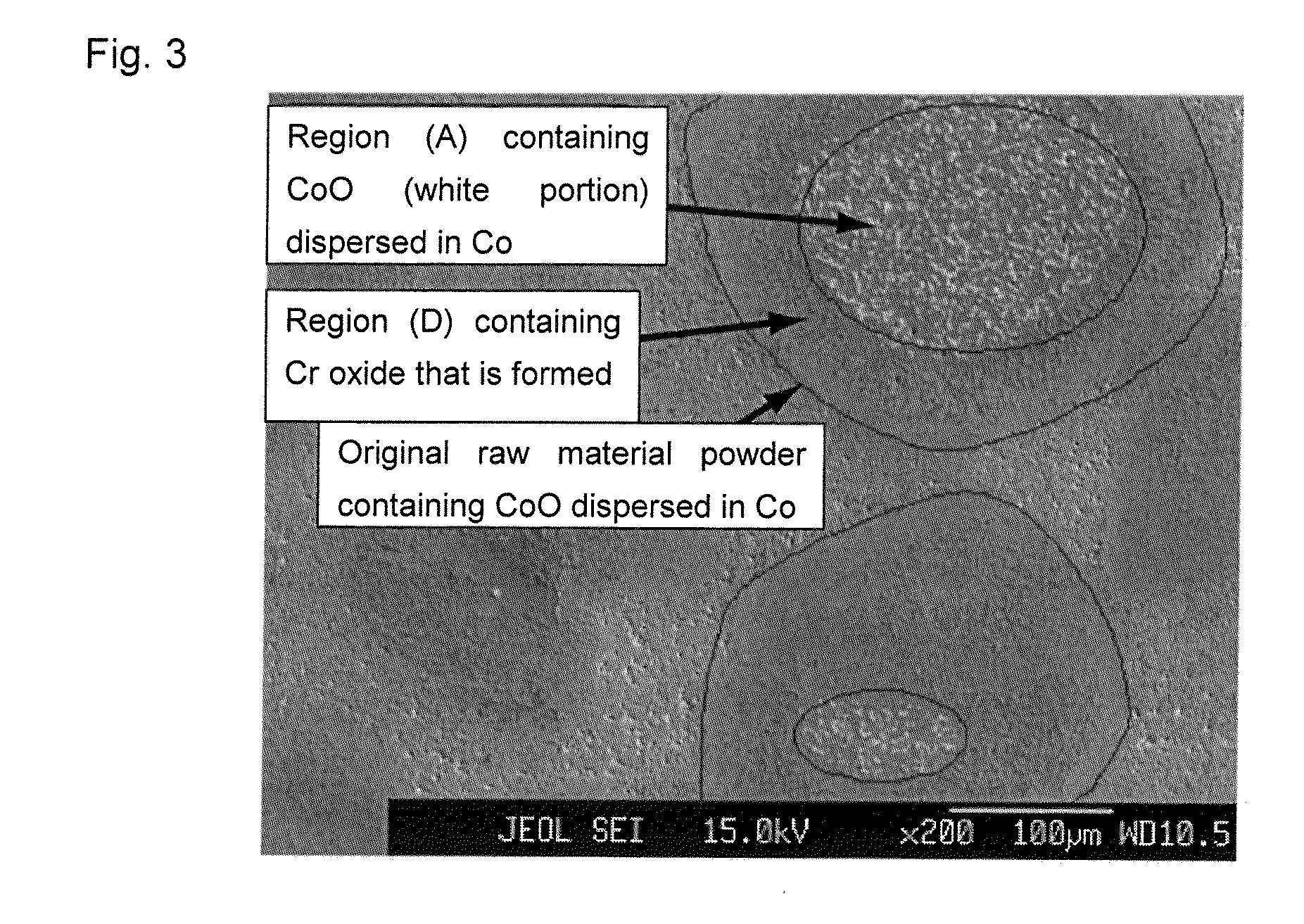
Sintered Compact Sputtering Target
InactiveUS20130213802A1Reduce generationSufficient sintered densityCellsVacuum evaporation coatingPowder mixtureMetal
A sintered compact sputtering target is provided and contains Co and Cr as metal components and includes oxides dispersed in the structure formed of the metal components. The structure of the sputtering target has a region (A) containing Co oxides dispersed in Co and a region (D) containing Cr oxides in a periphery of the region (A). In addition a method of producing the above referenced sintered compact sputtering target is provided and includes the steps of mixing a powder prepared by pulverizing a sintered compact containing Co oxide dispersed in Co, a Co powder, and a Cr power and pressure-sintering the resulting powder mixture to provide a sputtering target.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
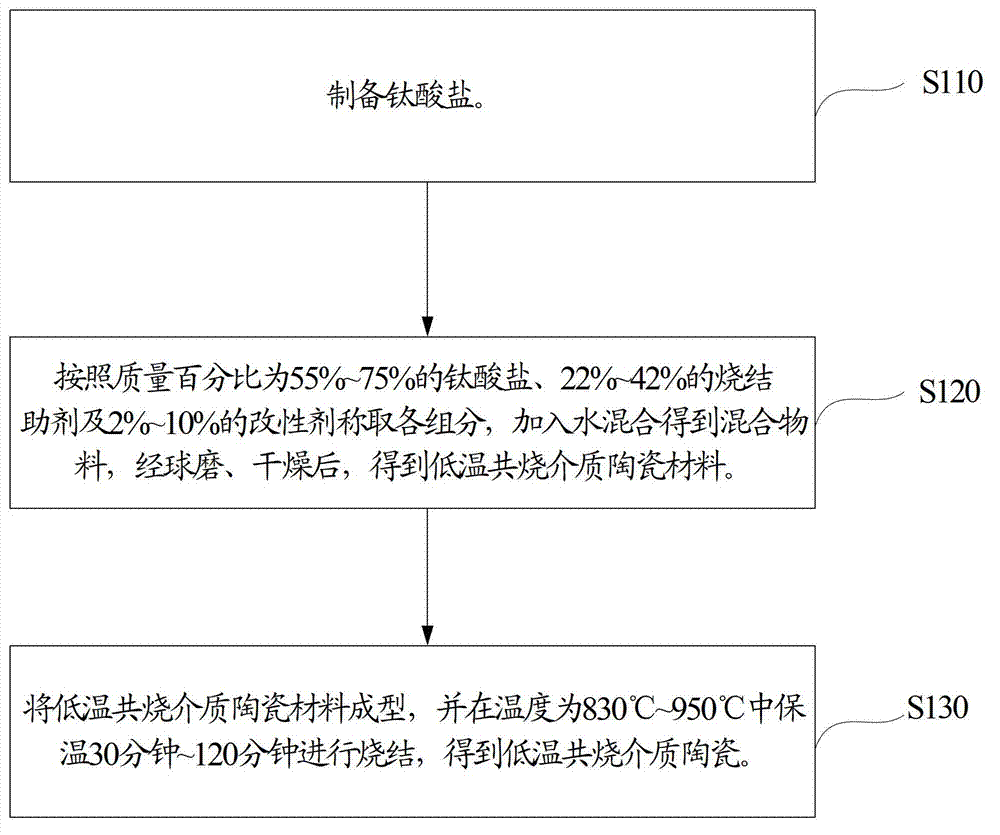
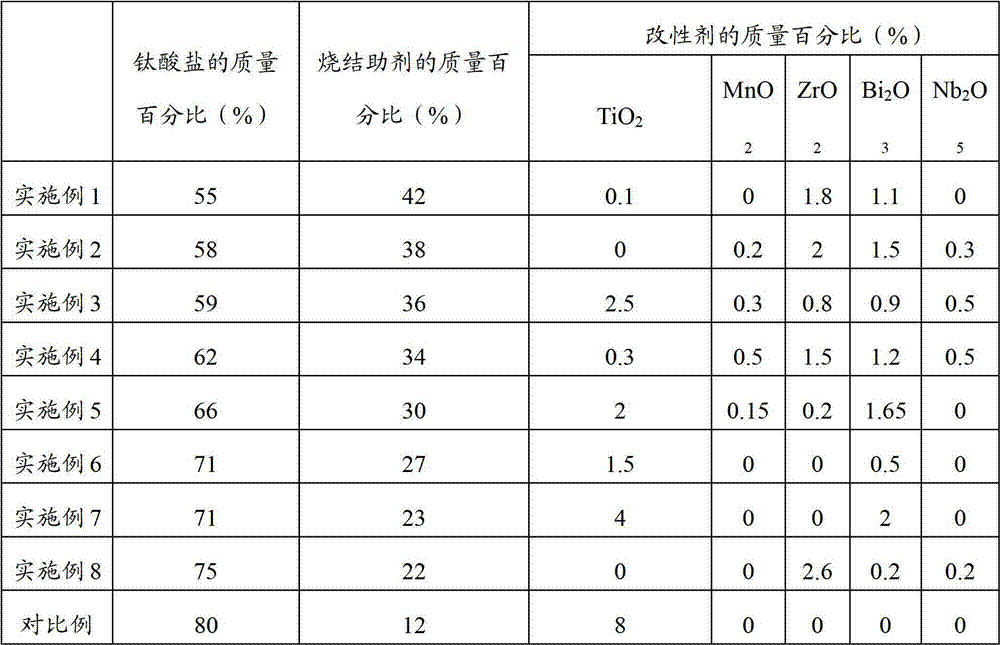
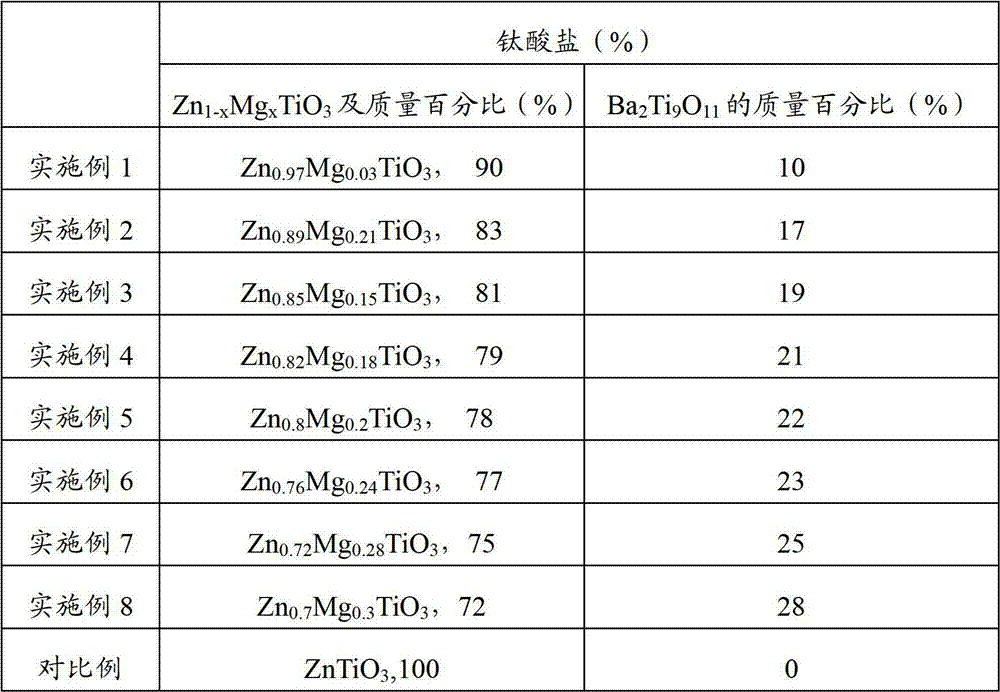
Method for preparing low-temperature cofired dielectric ceramic and material and sintering aid of low-temperature cofired dielectric ceramic
The invention relates to a sintering aid for a low-temperature cofired dielectric ceramic material. The sintering aid comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 40 to 55 percent of silicon dioxide, 5 to 16 percent of boron oxide, 12 to 17 percent of zinc oxide, 5 to 15 percent of aluminum oxide, 3 to 10 percent of lithium oxide, 0 to 5 percent of copper oxide, 0 to 5 percent of cobaltosic oxide and 3 to 8 percent of oxides of which the general formula is R2O3, wherein R may be at least one of lanthanum, neodymium, samarium and dysprosium. By the sintering aid for the low-temperature cofired dielectric ceramic material, the low-temperature cofired dielectric ceramic material can be sintered at temperature of between 830 and 950 DEG C, and the dielectric performance of the low-temperature cofired dielectric ceramic is improved effectively. In addition, the invention also provides the low-temperature cofired dielectric ceramic material and a method for preparing the low-temperature cofired dielectric ceramic.
Owner:GUANGDONG FENGHUA ADVANCED TECH HLDG
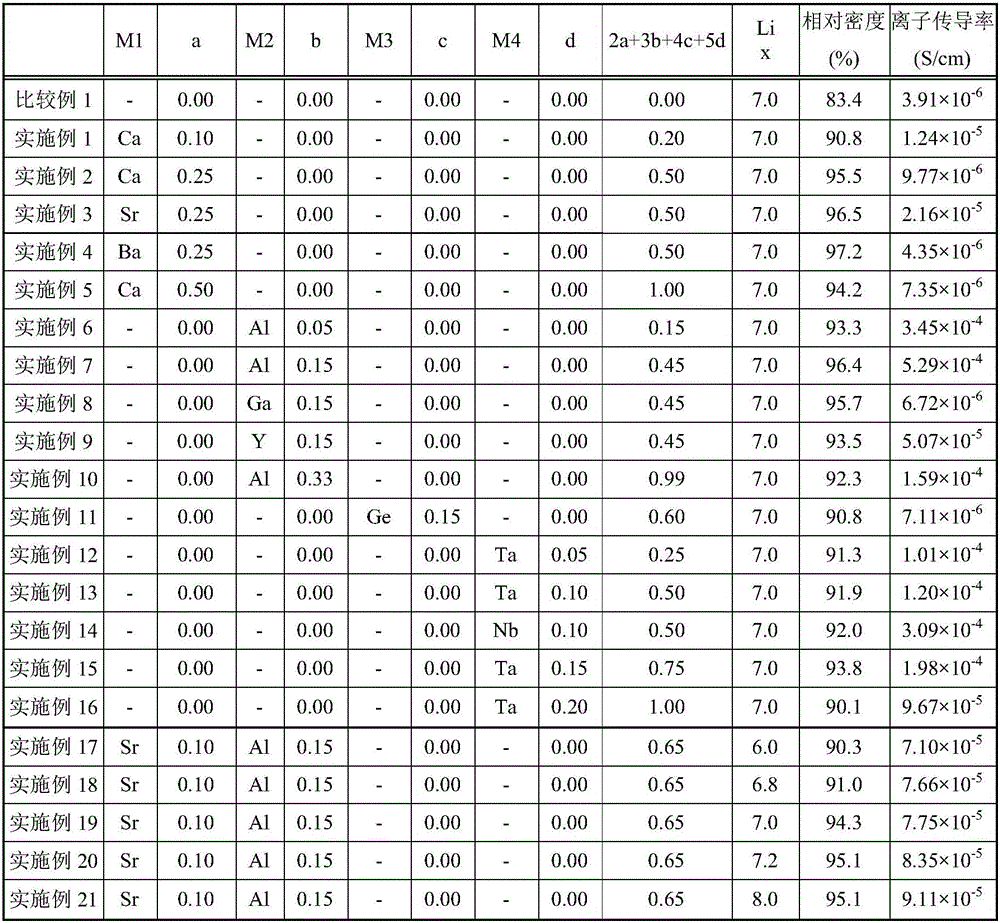
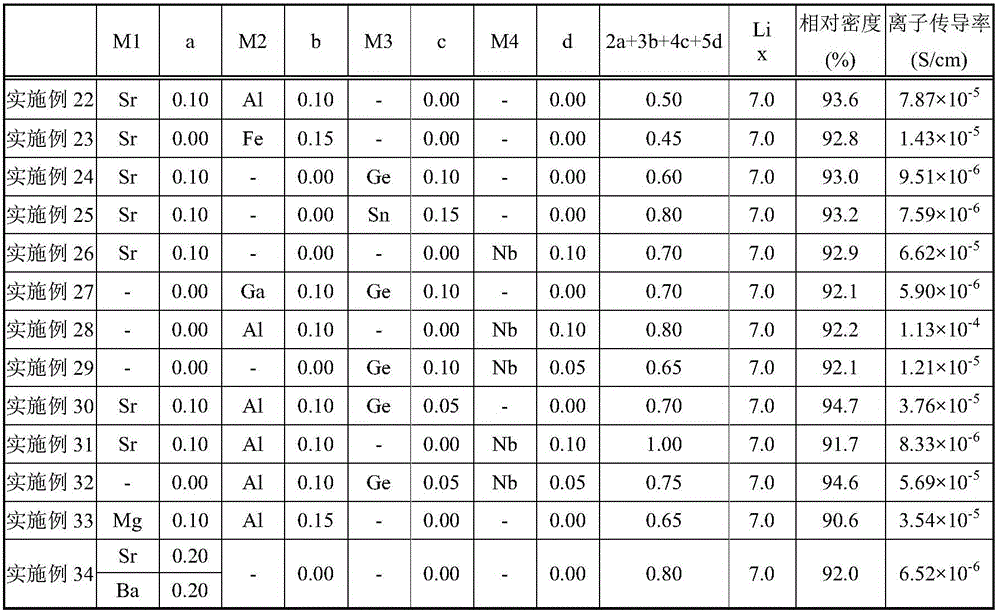
Garnet-type Li-ion conductive oxide
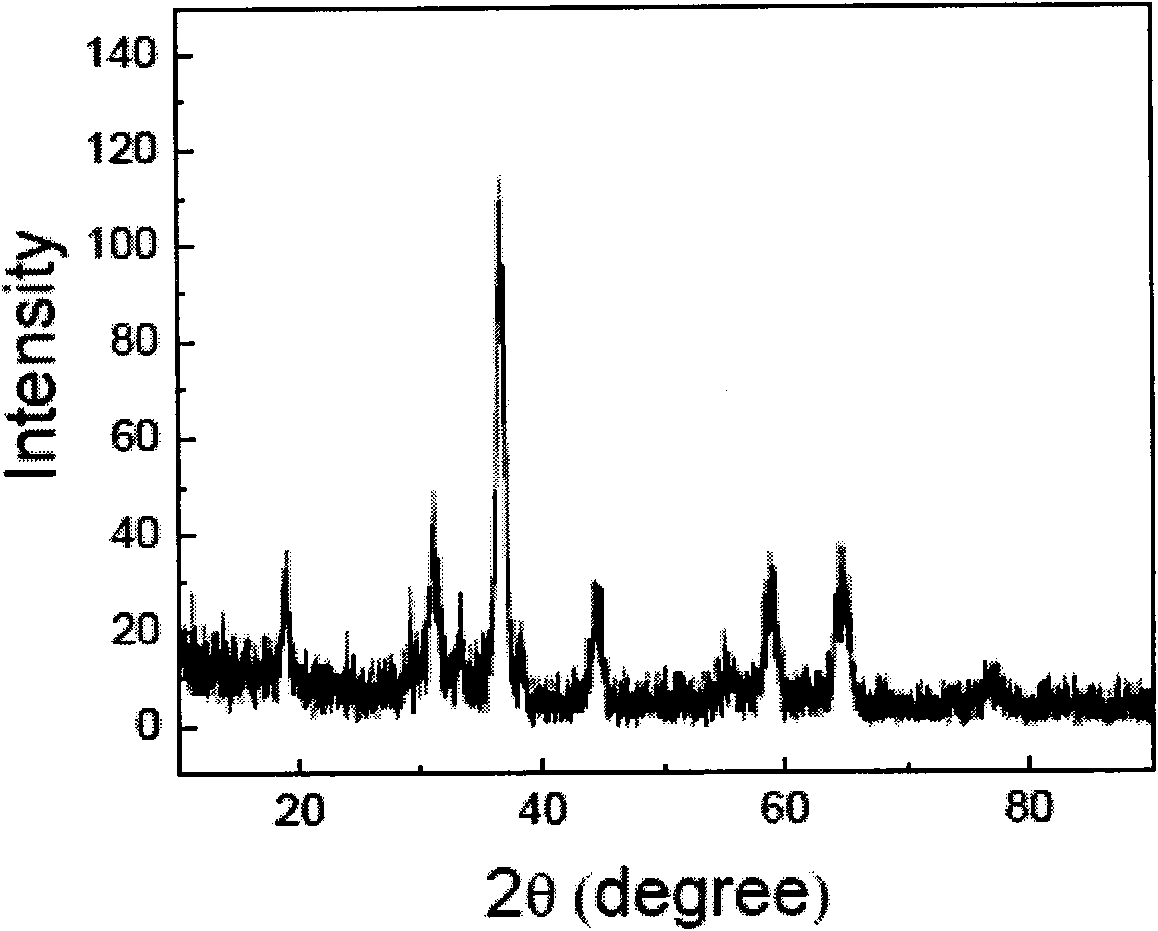
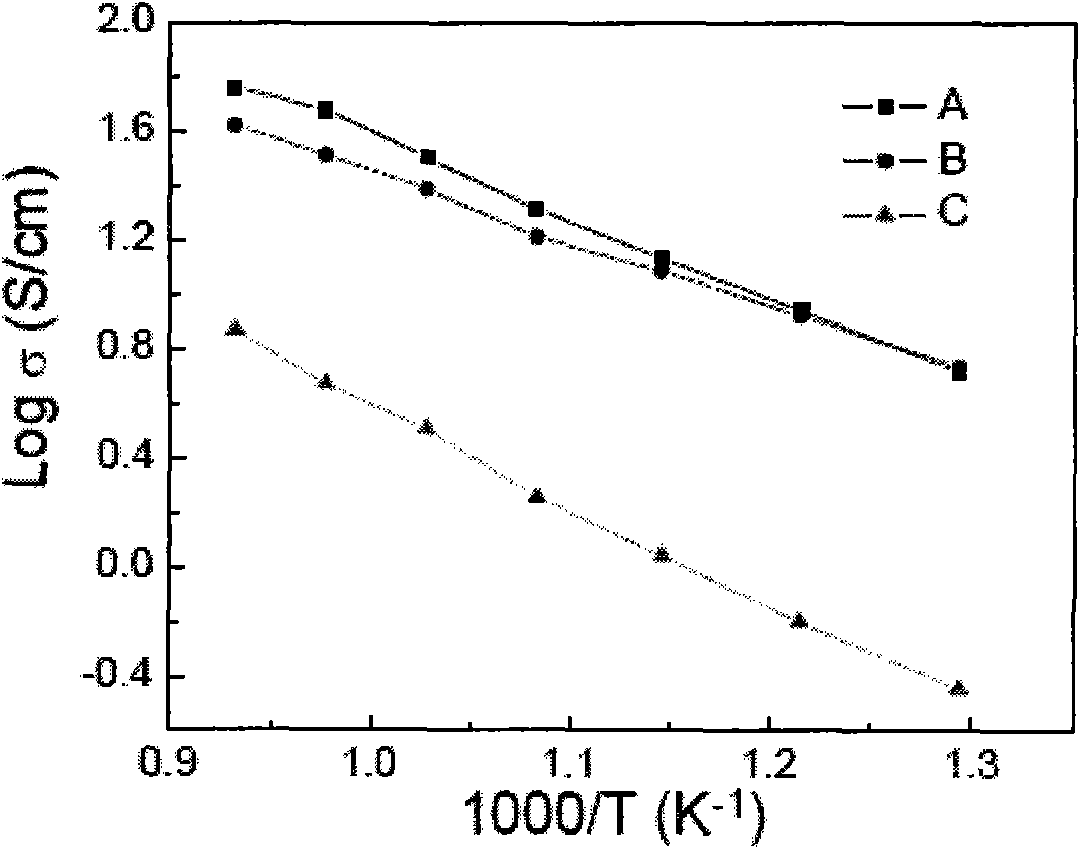
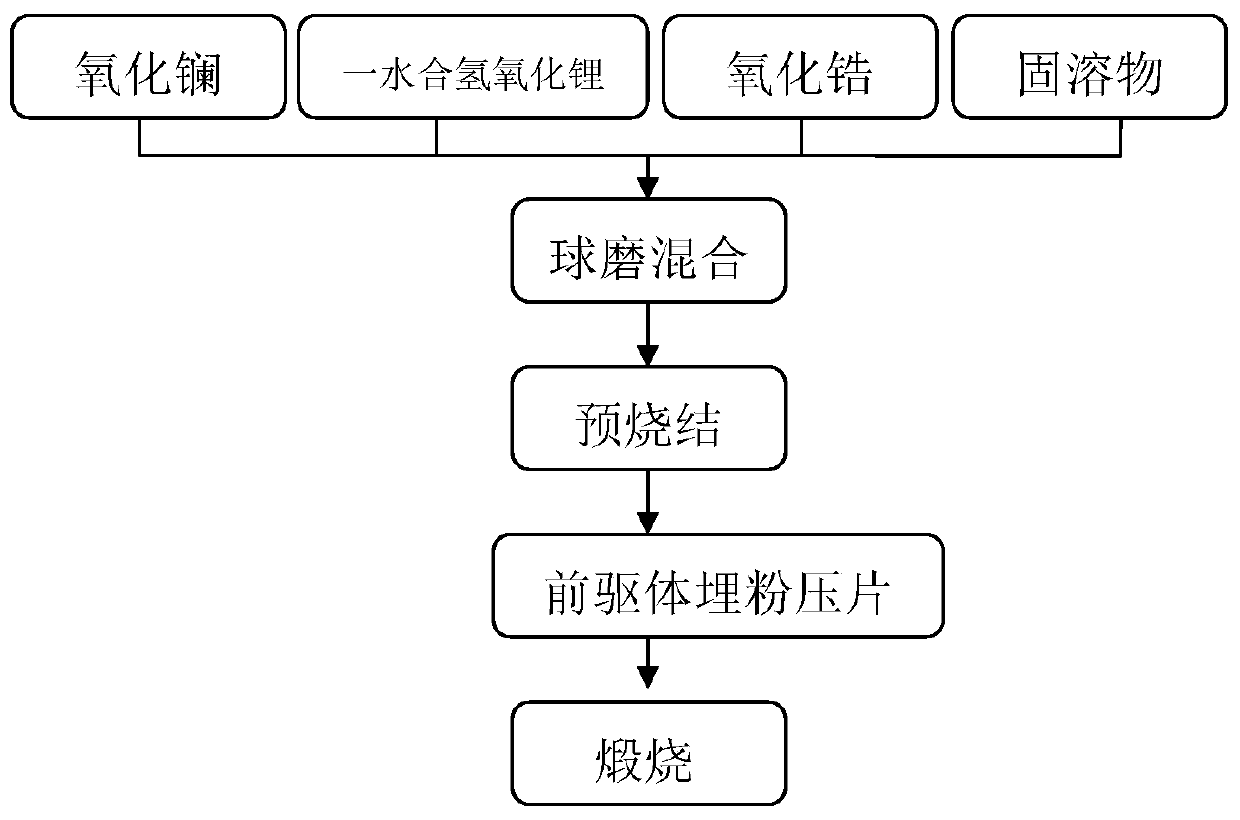
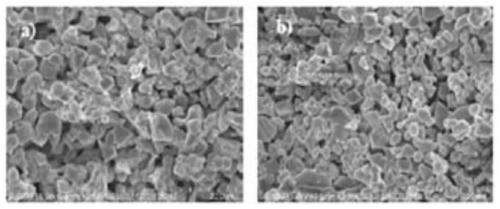
ActiveCN105977527AImprove sintered densityHigh ion conductivitySecondary cellsElectrolyte immobilisation/gelificationMaterials scienceIon
The invention provides a garnet-type Li-ion conductive oxide, that is, Li7La3Zr2O12, and the garnet-type Li-ion conductive oxide has relatively high sintered density and high ionic conductivity. The garnet-type Li-ion conductive oxide is formed by Li, La, Zr, and O. The garnet-type Li-ion conductive oxide is characterized by containing at least one element respresented by M1, M2, M3, and M4. The M1, M2, M3, and M4 represent the following elements. M 1 is more than one element selected from of Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, and Zn. M2 is more than one element selected from Al, Ga, Co, Fe, and Y. M3 is more than one element selected from Sn and Ge. M4 is more than one element selected from Ta and Nb.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
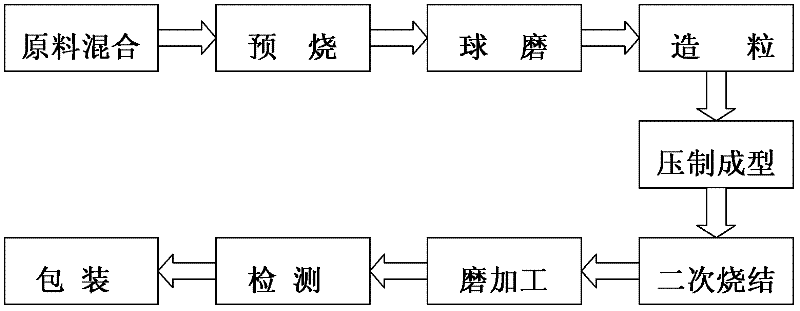
Method for producing soft magnetic ferrite core
InactiveCN102643083AImprove permeabilityLow dissipation factorEdge grinding machinesPolishing machinesInitial permeabilitySoft magnet
The invention discloses a method for producing a soft magnetic ferrite core. The method comprises the following steps of: mixing of raw materials, pre-sintering, ball milling, compression moulding, secondary sintering, grinding and detection, wherein an integral magnetic-attraction double-sided grinding machine is adopted in the grinding process. The magnetic core produced by the method has high magnetic conductivity and low loss factor, and energy sources can be saved; the magnetic core has uniform color, flat end surface and bright and clean surface; the ball milling as well as the uniformity and sphericity of the mixed material are improved; a low-temperature sintering technology is adopted, the heating rate and cooling rate of each stage are adjusted, the ferrite transformation of the material is promoted, and the grain size can be effectively controlled; and the initial permeability and temperature characteristic are improved.
Owner:ANHUI TAIDE ELECTRONICS TECH
Method for preparing iron-based superconductor
InactiveCN101814344ASignificant magnetic anisotropyFirmly connectedSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesSolventCrystallite
The invention relates to a method for preparing an iron-based superconductor. The method comprises the following steps: correspondingly processing iron-based superconductor precursor powder to obtain a lumpish or strip sample; putting the lumpish or strip sample into an Ar atmosphere protected or vacuum intense magnetic field heat treatment furnace; preserving the heat under a magnetic field intensity of between 0.1 and 30 Tesla and at the temperature of between 500 and 1,500 DEG C for 0.1 to 100 hours; and cooling the sample to room temperature together with the heat treatment furnace to obtain an iron-based superconductor sample; or the method comprises the following steps: dispersing sintered iron-based superconductor powder in a solvent; ultrasonically mixing the powder and the solvent; keeping the mixture in a magnetic field with a magnetic field intensity of between 0.1 and 30 Tesla for 0.1 to 2 hours; evaporating the solvent; putting the iron-based superconductor powder which is treated in the magnetic field into an Ar atmosphere or vacuum heat treatment furnace; and preserving the heat at the temperature of between 500 and 1,500 DEG C for 0.1 to 100 hours to obtain the iron-based superconductor sample. The method can effectively improve the connectivity of crystalline grains, greatly enhances the critical current density, upper critical field and irreversible field of the iron-based superconductor and makes the practicability of the iron-based superconductor become possible.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Novel synergistic process and recipe for fabrication of a high integrity membrane electrode assembly of solid oxide fuel cell
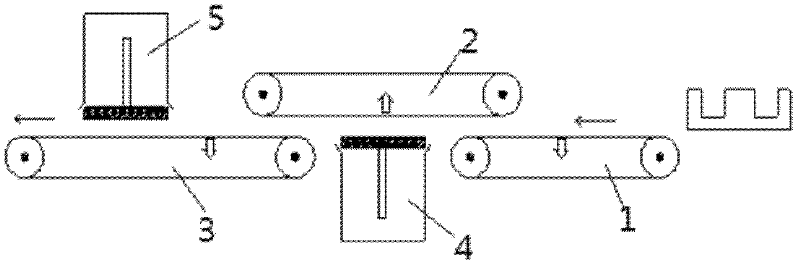
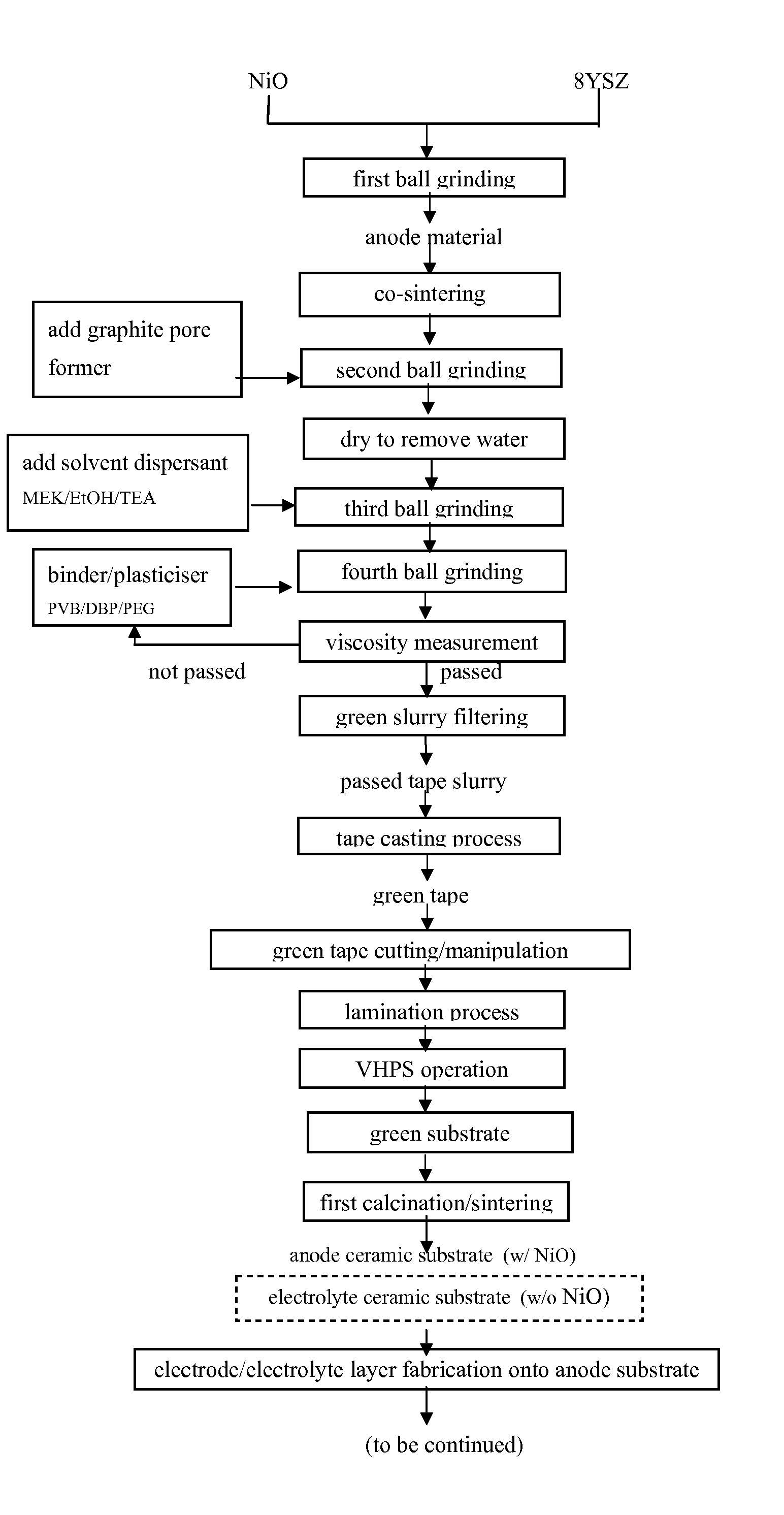
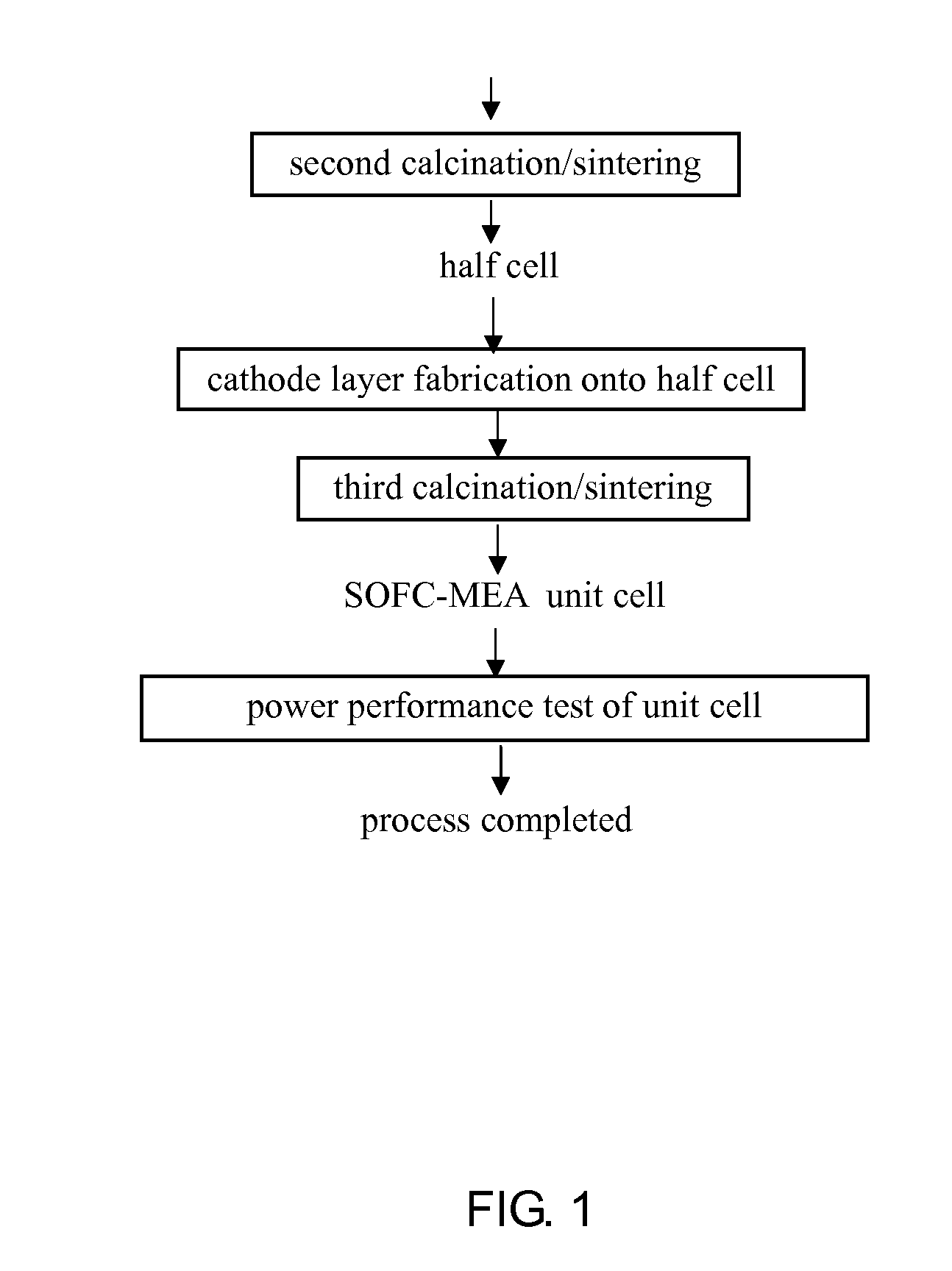
ActiveUS20090068373A1Improve integrityIncrease ratingsMolten spray coatingCell electrodesGreen tapeFuel cells
A recipe and two sequential processes for fabrication of electrode substrates of solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) are described in this invention. The typical recipe consists of 50˜86 wt % electrolyte (8YSZ) or 50˜80 wt % anode electrode (NiO / 8YSZ), 12˜22 wt % MEK (solvent 1), 5˜9 wt % EtOH (solvent 2), 1˜2 wt % TEA (dispersant), 0.5˜2 wt % DBP (plasticizer 1), 0.5˜2 wt % PEG (plasticizer 2), 3˜6 wt % PVB (binder), and 0.1˜10 wt % graphite (pore former). Two sequential processes include: 1. The process for preparation of the green tape slurry from materials of the recipe, 2. The synergistic process for fabrication of a high integrity membrane electrode assembly (MEA) of SOFC from the prepared electrode substrates.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
NiMnZn based ferrite
InactiveUS8282853B2Reduce the magnetic loss (core loss)High magnetic flux densityInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureManganese oxideIron oxide
A novel NiMnZn-based ferrite which can reduce magnetic loss (core loss) at a high frequency of about 2 MHz or higher and achieve higher saturated magnetic flux density while forming high sintered density is provided. The NiMnZn-based ferrite contains a main component comprising 54.0 to 57.5 mol % of iron oxide in terms of Fe2O3, 2.0 to 7.0 mol % of zinc oxide in terms of ZnO, 0.5 to 4.7 mol % of nickel oxide in terms of NiO, and a remainder of manganese oxide (in terms of MnO); and an accessory component comprising 100 to 1000 ppm by weight of Si in terms of SiO2, 800 to 3000 ppm by weight of Ca in terms of CaCO3, and 520 to 1000 ppm by weight of Nb in terms of Nb2O5 with respect to the main component; while having an average ferrite crystal particle size of 2.1 to 8.5 μm.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Pressureless sintering preparation method for boron carbide ceramic
The invention relates to a pressureless sintering preparation method for boron carbide ceramic, and coarse particle powder with the particle size larger than 2 micrometers is taken as raw materials. The method comprises the following steps that 70-80 wt % of boron carbide powder (D50>=2 micrometers), 4-8 wt% of carbon powder and 0.7-2 wt% of yttrium oxide powder are put into a ball mill mixing container, ball mill slurrying is performed after binding agents, dispersing agents and deionized water are added, and the solid phase content of obtained slurry is 25-45 wt%; the obtained slurry is prepared into granulating powder with a spray drying granulating machine; the granulating powder is pressed into green bodies by adopting a dry-pressing molding technology or isostatic cool pressing molding technology at 100-200 MPa; the green bodies are placed in a vacuum furnace, a vacuum or normal pressure sintering mode is adopted, heat preservation is performed for 0.5-5 h at the temperature of 2000 DEG C-2300 DEG C, sintering is completed, and then the boron carbide ceramic is obtained. According to the pressureless sintering preparation method for the boron carbide ceramic, due to the fact that the coarse particle boron carbide powder which is low in cost is adopted as the raw materials and the pressureless sintering technology capable of achieving scale production is adopted, the preparation cost of the boron carbide ceramic can be greatly lowered, and therefore the method is suitable for the fields of nuclear power, semiconductor equipment, armor protection and the like.
Owner:CHINA WEAPON SCI ACADEMY NINGBO BRANCH
Sodium-potassium niobate series substituted by bismuth-base calcium-titanium ore and preparing method
InactiveCN101024574AImprove performanceLead-free system with good performance has good environmental compatibilityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesElectricityManufacturing technology
The invention relates to a potassium niobate natrium series leadless piezoelectric ceramics and the manufacturing method. It is expressed by the general equation: (1-u)[(1-n)(LitNa1-w-t1Kw-t2)(Nb1-g-fTagSbf)O3+nBiMeO3]+uM. The invention has stable manufacturing technology and has great usefulness.
Owner:SENBA SENSING TECH CO LTD
Tungsten carbide material with Ni3Al as cementing phase and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101323925AReduce material costsLow priceIncreasing energy efficiencyCobaltConstant current
The invention relates to a plastic forming technique and a powder metallurgy technique and provides a tungsten carbide material which adopts Ni3Al as binder phase and a preparation method thereof. The tungsten carbide material adopts toughening intermetallic compound Ni3Al to substitute cobalt with traditional binder phase and contains the following components according to mass percentage: 86 to 95 percent of WC, 5 to 14 percent of toughening Ni3Al. The preparation method comprises the steps: ball grinding is carried out to the raw materials according to the percentages until the size of WC powder crystal grain is thinned to be less than 100nm; current rapid sintering method is adopted to form solidified ball grinding powder, and the conditions of current rapid sintering process are as follows: types of sintering current: square wave pulsed current or constant current; sintering pressure: 10MPa to 50MPa; sintering time: 2 to 8 minutes. The plastic forming technique, the powder metallurgy technique and the tungsten carbide material of the invention can not only save strategic material cobalt, reduce material cost, but also effectively improve the performance of high temperature resistant and corrosion resistant performance of the material and have good promotion and application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing high-density iron-base powder metallurgy parts
The invention provides a method for preparing high-density iron-base powder metallurgy parts, and belongs to the technical field of powder metallurgy molding. The compaction density of iron-base powder can be increased by utilizing the special stratified structure, the low friction factor and the good lubricating property of MoS2 (molybdenum disulfide). The method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing the iron powder with MoS2 powder, carrying out annealing treatment, and causing MoS2 to be uniformly distributed on the surface of the iron powder; and uniformly mixing annealed mixed powder with a certain amount of metal powder, graphite powder and the like, and pressing and sintering to obtain the high-density iron-base parts. In the pressing process, the friction force among powder particles is reduced and the friction state among the powder particles is improved through the MoS2, the pressing performance is increased, and the iron-base powder metallurgy parts with the density of 7.2g / cm3-7.5g / cm3 can be obtained. The method has the advantages that the pressing performance of the iron-base powder is improved; the high-density iron-base powder metallurgy parts is obtained on the premise of cost reducing; the friction factor is reduced, the loss of abrasive tools is decreased, and meanwhile, the adverse influence of sulphur on the iron-base parts does not exist; and the process is simple and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Powder Metallurgy Methods And Compositions
ActiveUS20090162236A1Faster rateImprove sintered densityTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusMetal powderPowder metallurgy
The present invention provides metal powder compositions for pressed powder metallurgy and methods of forming metal parts using the metal powder compositions. In each embodiment of the invention, the outer surface of primary metal particles in the metal powder composition is chemically cleaned to remove oxides in situ, which provides ideal conditions for achieving near full density metal parts when the metal powder compositions are sintered.
Owner:JOHNSON ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA
Multi-element sodium-potassium niobate series lead-free piezoelectric ceramic and preparing method
InactiveCN101024573AImprove performanceLead-free system with good performance has good environmental compatibilityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesManufacturing technologyGeneral equation
The invention relates to a multielement potassium niobate natrium series leadless piezoelectric ceramics and the manufacturing method. It is expressed by the general equation: (1-u)[(1-z-n)(LitNa1-w-t1Kw-t2)(Nb1-g-fTagSbf)O3+ z(Bi0.5Na0.5xK0.5 (1-x))TiO3+nBaTiO3]+uM. The invention has stable manufacturing technology and has great usefulness.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Mn-Co-doped spinel composite nanometer material and low-temperature sintering method thereof
ActiveCN101670999AHigh sintering activityImprove sintered densityCell electrodesIndividual molecule manipulationRare earthAlloy
The invention provides an Mn-Co-doped spinel composite nanometer material and a low-temperature sintering method thereof. The spinel material has the following chemical composition: Mn<1-m>(R)m<1+x>Co<2-x>O4 or Mn<1+x>Co<1-n>(R)n<2-x>O4, wherein x is less than or equal to 1 and more than or equal to 0, m is more than 0 and less than or equal to 0.2, n is more than 0 and less than or equal to 0.2,and R is one or a plurality of rare earth metal elements. The material can serve as high temperature oxidation resisting conductive coating material of a solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) alloy connectingboard or serve as high temperature oxidation resisting conductive coating material under other similar environments. Meanwhile, the invention initiates a low-temperature sintering method of spinel material, the spinel powder material which can be reduced is firstly reduced, tabletted and sintered, sintered blocks show higher sintering activity and obviously high conductivity at lower temperature,and the outstanding characteristic can be used for preparing high-density non-noble metal high temperature oxidation resisting conductive elements.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Coarse-grained powder based pressureless sintering boron carbide ceramic preparation method
The invention relates to a pressureless sintering boron carbide ceramic preparation method of using more than 2 microns of coarse-grained powder as a raw material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: putting 70-80 wt% of boron carbide (D50 is greater than or equal to 2 microns), 4-8 wt% of powdered carbon, 0.7-2 wt% of yttrium oxide powder and the balance a binder and a dispersant into a mixing container of a ball mill, adding deionized water and ball-milling for pulping so as to obtain slurry with solid content being 25-45 wt%; preparing granulation powder from the slurry by using a spray drying granulating machine; pressing the granulation powder at 100-200 MPa by a dry pressing or isostatic cool pressing process to generate a green body; and putting the green body into a vacuum furnace, and carrying out thermal insulation at 200-2300 DEG C for 0.5-5h to finish sintering by a vacuum or pressureless sintering mode so as to obtain boron carbide ceramic. As the low-cost coarse-grained boron carbide powder is used as the raw material, manufacturing cost of the boron carbide ceramic can be reduced greatly by the pressureless sintering process for large-scale production. The boron carbide ceramic is suitable for fields of nuclear power, semiconductor equipment, armor protection and the like.
Owner:YANTAI BRANCH NO 52 INST OF CHINA NORTH IND GRP
Conductive paste composition, preparation of electrode using same and solar cell comprising same
InactiveCN101728438ALower impedanceReduce contact resistanceFinal product manufactureActive material electrodesConductive pasteContact impedance
The invention relates to a conductive paste composition, preparation of electrode using the same and solar cell comprising the same. The conductive paste composition comprises a mixing powder comprising a micro conductive metal powder with average grain size of below 0.5Mum and a conductive metal powder with average grain size of between 0.5 to 10Mum, an inorganic viscosity resin and an organic medium. The conductive paste composition can have high sintered density during preparing the electrode material and less sintering shrinkage, thereby providing lower electrode line impedance and contact impedance and increased efficiency of the solar cell.
Owner:DAEJOO ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CO LTD +1
Solid-solution-doped LLZO inorganic oxide solid electrolyte and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111116198AImprove compactnessHigh ion conductivitySecondary cellsElectrolytesLithium oxideElectrical battery
A solid-solution-doped LLZO inorganic oxide solid electrolyte is prepared from the following preparation raw materials in percentage by mass: 49 to 54% of lanthanum trioxide (La2O3), 29 to 33% of lithium hydroxide (LiOH), 12 to 14% of zirconium dioxide (ZrO2) and 2 to 4% of tetraethoxysilane, and can further comprise one or more of 0%-8% of aluminum oxide (Al2O3), 0%-8% of niobium oxide (Nb2O5) and 0%-8% of tantalum oxide (Ta2O5). The inorganic oxide solid electrolyte has the advantages of high compactness and high ionic conductivity. The organic oxide solid electrolyte prepared by the methodcan be used for preparing an all-solid-state power ion battery with high discharge capacity, and the obtained all-solid-state battery has excellent performance, high power density, high energy densityand good safety. The obtained all-solid-state battery can replace a traditional lithium ion battery, is particularly suitable for electric transport vehicles, electric power storage and the like, andhas a good application prospect.
Owner:GUANG DONG DONGBOND TECH CO LTD
High-stability garnet microwave ferrite magnetic sheet and preparation method thereof
PendingCN111187064AHigh dielectric constantReduce the anisotropy coefficient KInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufacturePorosityMicrowave
The invention belongs to the technical field of magnetic materials, and discloses a high-stability garnet microwave ferrite magnetic sheet and a preparation method thereof. The material composition ofthe high-stability garnet microwave ferrite magnetic sheet is Y<3-f-2d-a>Gd<f>Ca<2d+a>Bi<e>Fe<5-a-b-c-d-sigma>SnInMn<c>V<d>O<12>, wherein a is more than 0 and no more than 0.7; b is more than 0and no more than 0.7; c is more than 0 and no more than 0.6; d is more than 0 and no more than 1.5; e is more than 0 and no more than 0.6; f is more than 0 and no more than 0.8; and sigma is more than 0 and no more than 0.4. According to the high-stability garnet microwave ferrite magnetic sheet, Bi<3+> ions are added into the material, so the dielectric constant of the material is improved, anda Curie temperature is increased; and in addition, SnO<2>, In<2>O<3>, SnO<2> and In<2>O<3> are added into the material, so the anisotropy coefficient K of the material can be reduced, and the ferromagnetic resonance linewidth Delta(H) of the material is reduced. In terms of the process, high-pressure sintering is adopted to replace normal-pressure sintering, so sintering density is improved, the porosity of the material is reduced, and the ferromagnetic resonance linewidth Delta(H) of the material is reduced. Thus, the problem that the temperature coefficient of the material is poor is solved,and the material is guaranteed to have low ferromagnetic resonance linewidth Delta(H), high dielectric constant and high Curie temperature.
Owner:HENGDIAN GRP DMEGC MAGNETICS CO LTD
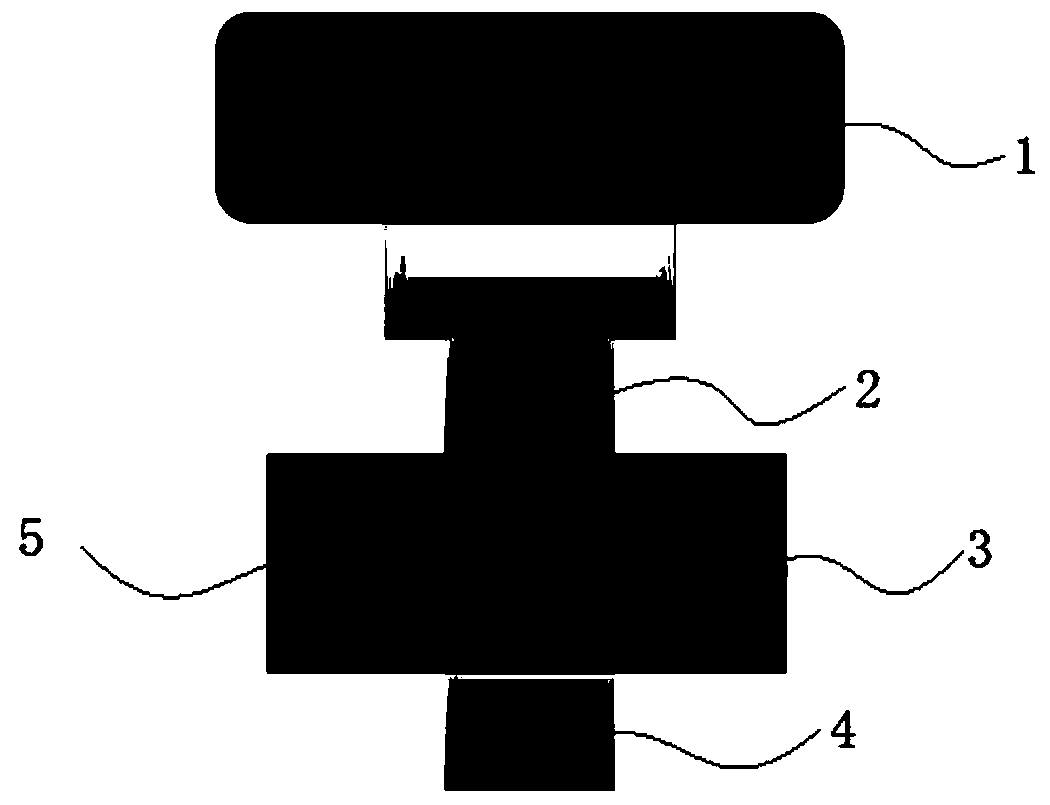
Dynamic pressure electric pulse double-field control sintering furnace and sintering method
ActiveCN105135873ALower sintering temperatureShorten the sintering timeMuffle furnacesMaintainance of heating chambersElectrical impulseDynamic pressure
The invention relates to a dynamic pressure electric pulse double-field control sintering furnace and a sintering method. The sintering furnace comprises a furnace body, a dynamic pressure system, a pulse current generator and a sintering controller. The furnace body is connected with the dynamic pressure system and the pulse current generator. The dynamic pressure system and the pulse current generator are both connected to the sintering controller. A die is arranged in the furnace body. The dynamic pressure system comprises an upper press head electrode, a lower press head electrode, an upper press head, a lower press head, a constant pressure control module, a dynamic pressure control module and a pressure master control module. The dynamic pressure system is connected with the sintering controller. The pulse current generator is connected with the upper press head electrode and the lower press head electrode and connected with the sintering controller as well. The sintering controller controls the dynamic pressure system and the pulse current generator to generate the adjustable dynamic pressure for a material to be sintered and conduct plasma pulse current sintering on the material to be sintered. The dynamic pressure electric pulse double-field control sintering furnace and the sintering method can be widely applied to sintering of the high-performance material.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Silicon carbide ceramic paste for photocuring and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110451985AImprove curing depthReduce clumpingAdditive manufacturing apparatusCeramic sinteringDispersity
The invention discloses silicon carbide ceramic paste for photocuring and a preparation method thereof. The paste is prepared by mixing SiC mixed powder, a dispersing agent, a monomer, a compatilizerand a photoinitiator, wherein the surface of the SiC mixed powder is coated with a SiO2 layer, so that the refractive index difference between the final paste and light-cured resin is reduced, and then printing efficiency is further improved. SiO2 can improve the solid phase content of the whole slurry, so that the sintering density of sintered ceramic and the mechanical property of finally formedceramic can be improved during subsequent ceramic sintering. Through addition of the dispersing agent into the slurry, the agglomeration phenomenon of the slurry can be reduced, the dispersity is improved, and the solid phase content of the whole slurry can be increased. Verification finds that the solid phase content in the paste can finally reach 40%-60%.
Owner:NAT INST CORP OF ADDITIVE MFG XIAN
Preparation method of high-density garnet type inorganic solid electrolyte material
InactiveCN108899581AImprove sintered densityEasy to operateFinal product manufactureElectrolytesMuffle furnaceLanthanum
The invention relates to a preparation method of a high-density garnet type inorganic solid electrolyte material. The preparation method of the high-density garnet type inorganic solid electrolyte material comprises the following steps: (1) weighing a lithium source, a lanthanum source, a zirconium source and a tantalum source, adding ethanol, and carrying out ball-milling to obtain a powder mixedraw material; (2) calcining the powder mixed raw material in a high-temperature muffle furnace, and grinding and sieving after calcining to obtain uniformly granular precursor powder; (3) carrying out tabletting forming on the precursor powder to obtain precursor tablets, covering the precursor tablets with the precursor powder and sintering in the high-temperature muffle furnace, and cooling toa room temperature in the furnace to obtain inorganic solid garnet type electrolyte plates; (4) carrying out dipping treatment on the inorganic solid garnet type electrolyte plates by using dipping fluid, wherein the dipping fluid is a deionized aqueous solution of a mixture of the lithium source, the lanthanum source, the zirconium source and the tantalum source; and (5) drying a sample subjectedto dipping treatment, and calcining the sample in the high-temperature muffle furnace to obtain the high-density garnet type inorganic solid electrolyte material.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Special molybdenum powder used for automatic forming and preparation method thereof
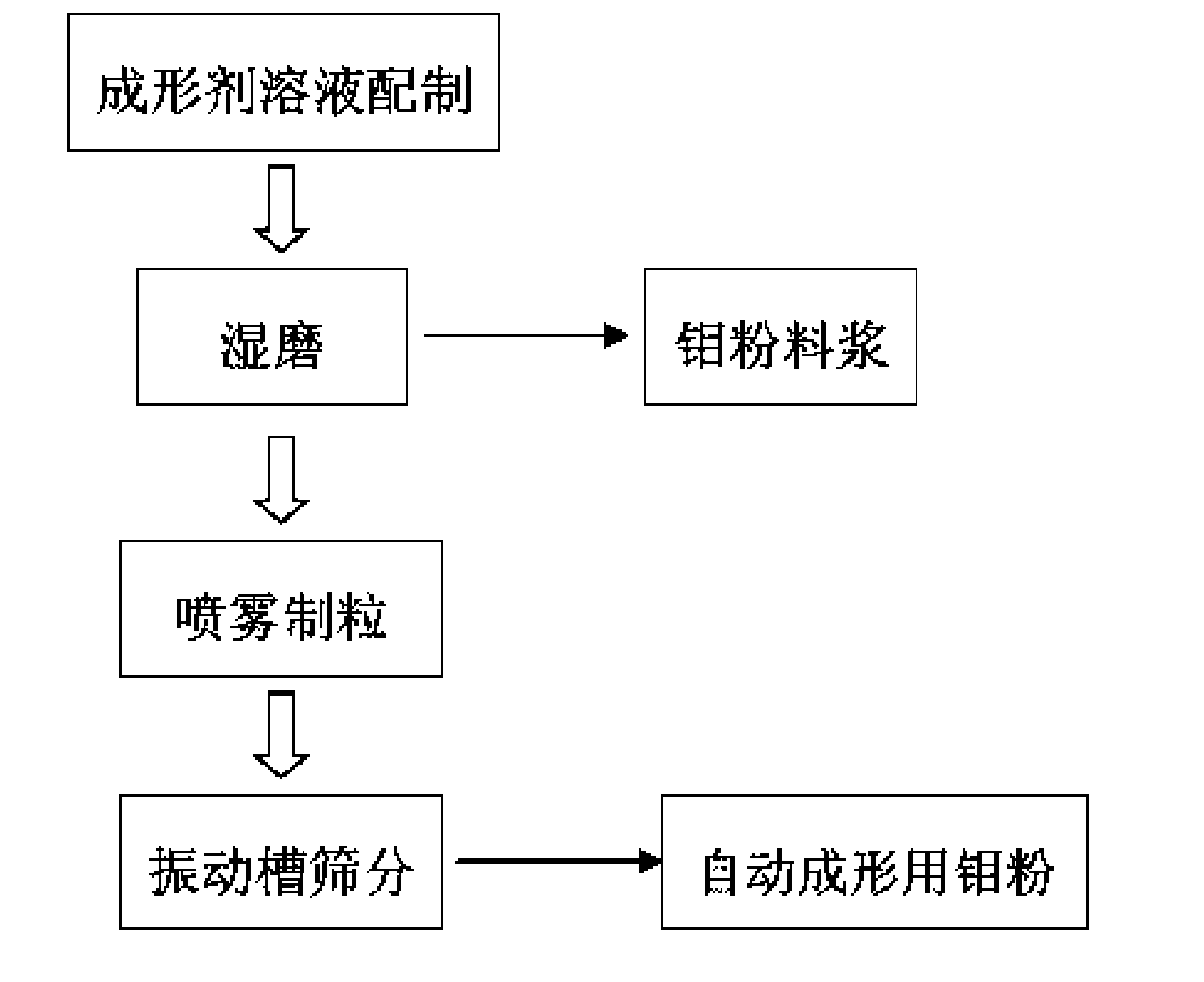
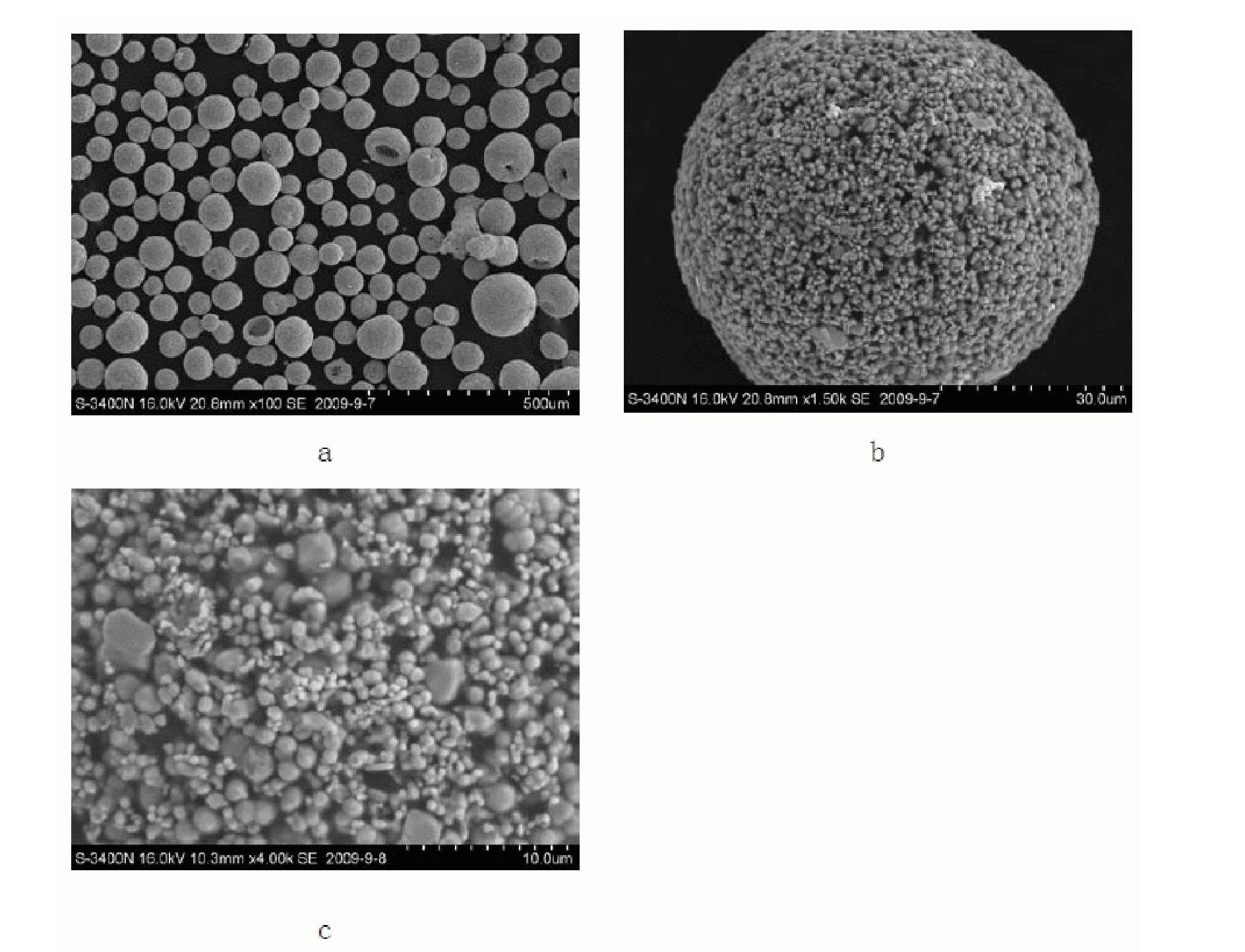
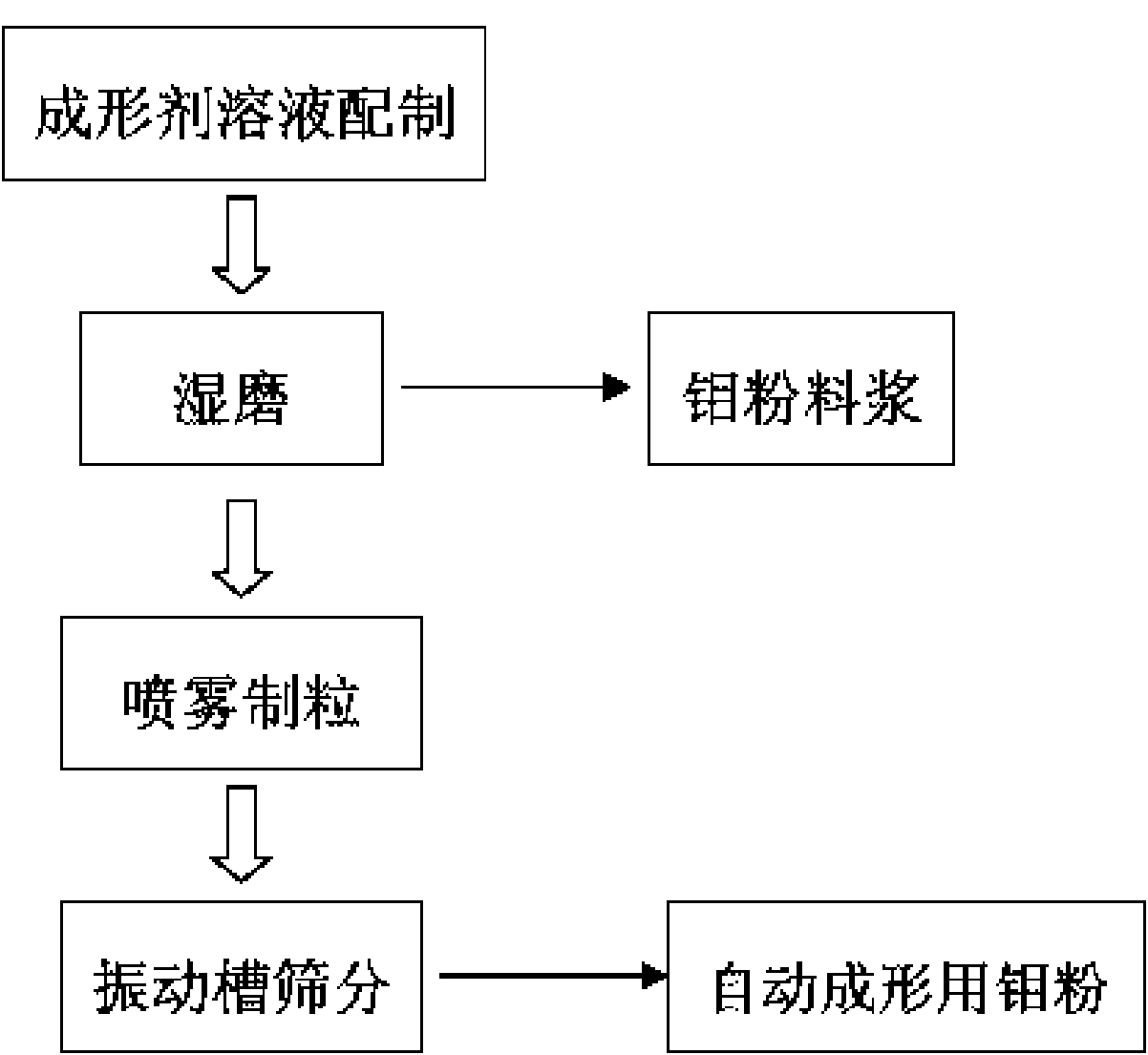
The invention discloses a special molybdenum powder which is directly used for the automatic forming of precision devices of the machinery industry and the electronic industry. The invention is characterized in that the molybdenum powder comprises the following materials according to the parts by mass: 96.6-99.5 parts of primary molybdenum powder, 0.5-2.4 parts of polyvinyl alcohol, 0-0.4 part of polyethylene glycol, 0-0.5 part of metallic stearate and 0-0.15 part of ammonium polyacrylate. The molybdenum powder has good flowability, high apparent density and appropriate particle size distribution and has the self-lubricating action in the process of the automatic forming. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the special molybdenum powder, which comprises the processes: (1) forming agent solution is prepared by the polyvinyl alcohol, the polyethylene glycol, water and other additives; (2) wet grinding is carried out on the primary molybdenum powder, metallic balls and the forming agent solution by proportion in a ball milling tank to prepare molybdenum powder slurry; (3) spray drying is carried out on the prepared molybdenum powder slurry for granulation; (4) the prepared molybdenum powder is collected by a vibrating screen arranged at the discharge hole of a spray drying tower. The preparation method has the greatest advantages of the special molybdenum powder used for the automatic forming can be prepared by one step, the efficiency is high, the cost is low, and the industrialization and no pollution can be realized.
Owner:XIAMEN HONGLU TUNGSTEN MOLYBDENUM IND CO LTD
Powder metallurgy methods and compositions
InactiveUS20070077164A1High densityLow energy costTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusOrganic acidPowder metallurgy
The present invention provides metal powder compositions for pressed powder metallurgy and methods of forming metal parts using the metal powder compositions. In one embodiment, the metal powder composition according to the invention includes a blend of primary metal particles, one or more liquid phase forming materials or precursors thereof, a lubricant and an organic acid that is capable of reacting with an oxide of a metal in the primary metal particles to form an organic metal salt that decomposes when the metal powder composition is sintered under reducing or non-oxidizing conditions. During a “delubing” step, the organic acid reacts with an oxide of a metal in the primary metal particles to form an organic metal salt that decomposes into a base metal or a metal-carbide during sintering.
Owner:APEX ADVANCED TECH
Gallium oxide-zinc oxide sputtering target, method of forming transparent conductive film, and transparent conductive film
ActiveUS7686985B2Improve conductivityHigh densityConductive layers on insulating-supportsConductive materialSputteringHigh density
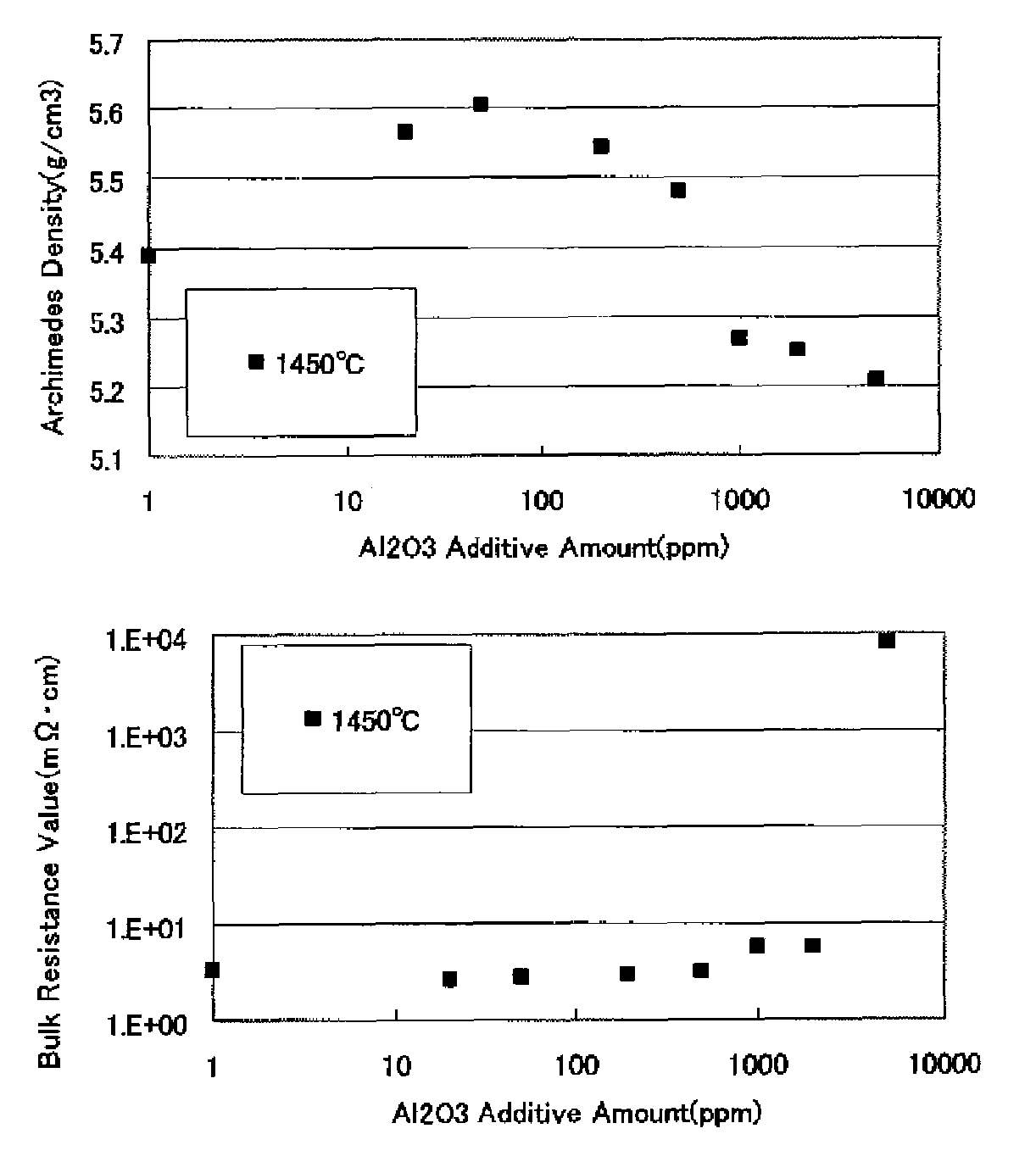
Provided is a high density gallium oxide-zinc oxide series sintered body sputtering target for forming a transparent conductive film containing 20 to 500 mass ppm of aluminum oxide. In a gallium oxide (Ga2O3)-zinc oxide (ZnO) series sputtering target (GZO series target) for forming a transparent conductive film, trace amounts of specific elements are added to obtain a target capable of improving the conductivity and the bulk density of the target; in other words, capable of improving the component composition to increase the sintered density, inhibit the formation of nodules, and prevent the generation of an abnormal electrical discharge and particles. Also provided are a method for forming a transparent conductive film using such a target, and a transparent conductive film formed thereby.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CORP
Selective metallization method of surface of ceramic, and ceramic and its application
The invention provides a selective metallization method of the surface of a ceramic. The method comprises the following steps: 1, molding and sintering a ceramic composition to obtain a ceramic substrate, wherein the ceramic composition comprises ceramic powder and functional powder dispersed in the ceramic powder, the functional powder comprises one or more selected from an oxide, a nitride, an oxynitride and a carbide of M, and an M elementary substance, and the ceramic powder comprises one or more selected from an oxide, a nitride, an oxynitride and a carbide of E; 2, irradiating a selected area of the surface of the ceramic substrate by energy beams to form a chemical plating activity center in the selected area; and 3, chemically plating the surface of the ceramic substrate subjected to step 2 to form a metal coating in the selected area. The invention also provides the ceramic. The metal coating is formed on the surface of the ceramic through the chemical plating in the invention, so the coating has a high adhesion with the ceramic substrate, and has a low cost.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Large-size high-density non-binding-phase tungsten carbide target material and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN110171975AGuaranteed purityQuality improvementVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingHigh pressureMaterials science
The invention provides a preparing method of a large-size high-density non-binding-phase tungsten carbide target material. The method includes the following steps of S1, preparing materials; S2, conducting ball-milling and screening treatment; S3, conducting sintering treatment; S4, conducting after-treatment. The raw materials include tungsten carbide powder and free carbon. The dynamic vibrationpressure is exerted in the sintering treatment process. By introducing the free carbon into the pure tungsten carbide powder, traditional medical binding phases are abandoned, the purity of the target material is ensured, and the quality of a magnetron sputtering coating can be easily improved. The dynamic vibration pressure is introduced in the sintering process, particle rearrangement is promoted in the early sintering stage of the tungsten carbide powder, the removal of residual pores is promoted in the later sintering stage, and the grain is refined when the sintering density is improved;by means of the high-pressure vibration assisted sintering, the sintering temperature is lowered by 50-200 DEG C on the basis of a traditional hot pressing process, the tungsten carbide target material with high density and fine grain is prepared, and the film coating quality is improved.
Owner:株洲万融新材科技有限公司 +1
Powder metallurgy stainless steel and preparation method thereof
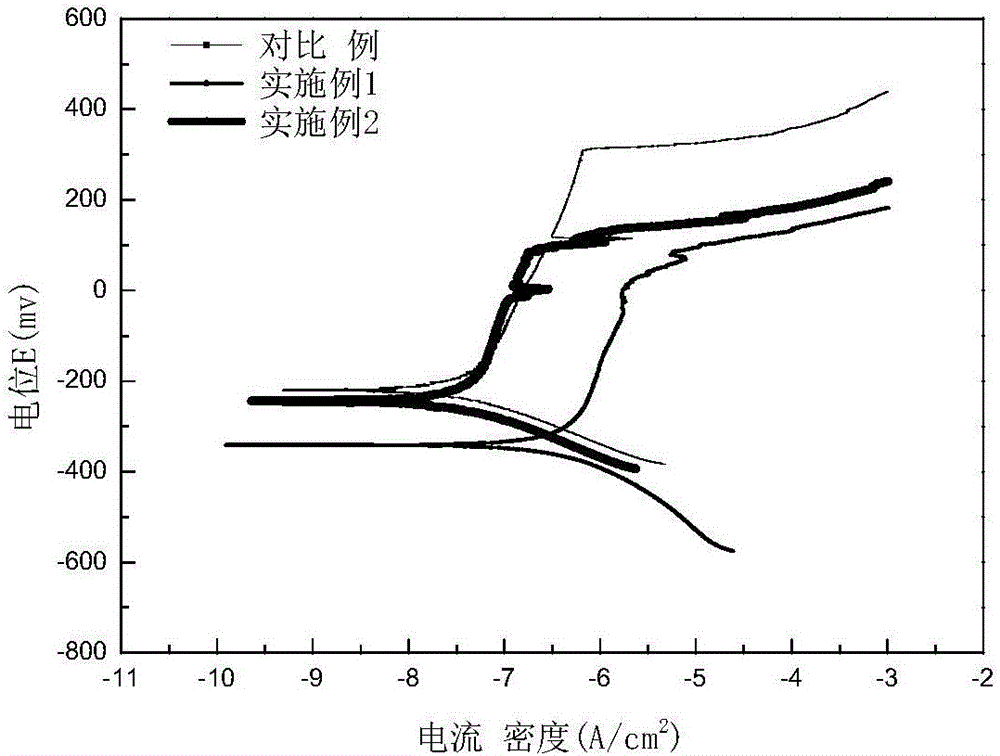
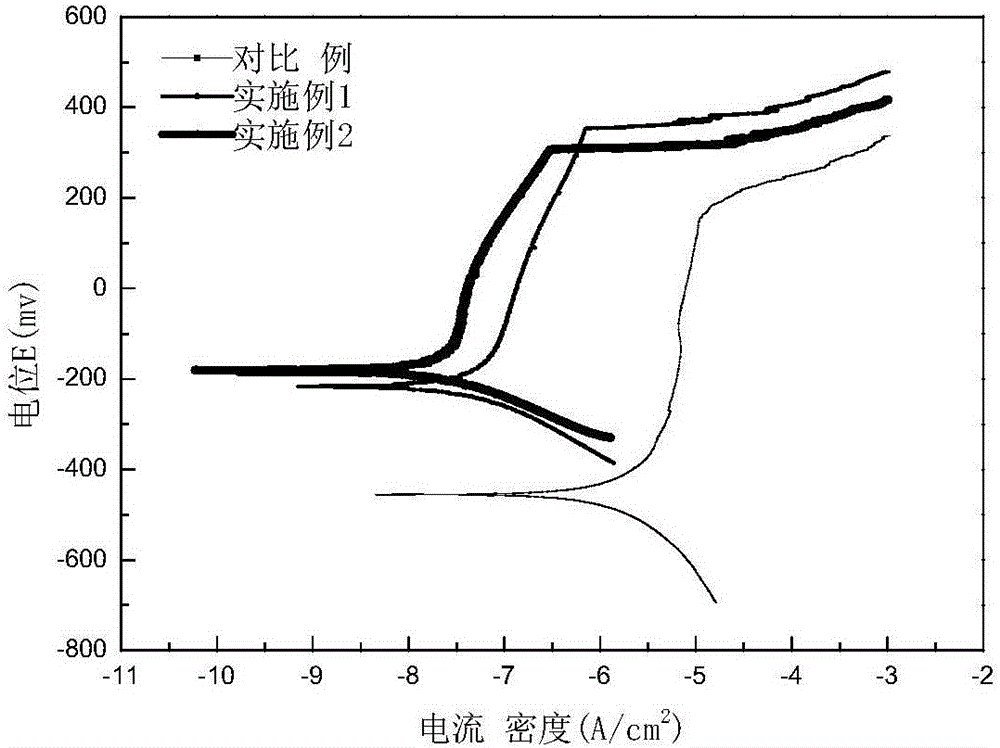
The invention provides powder metallurgy stainless steel and a preparation method thereof. The powder metallurgy stainless steel is prepared from, by weight, 95-98% of stainless steel powder, 1.5-2.5% of Cu powder and 0.5-2.5% of Sn powder. The stainless steel powder, the Cu powder, the Sn powder and a lubricating agent are mixed, pressed, pre-sintered and sintered, and then the powder metallurgy stainless steel is obtained. The porosity of the powder metallurgy stainless steel provided by the invention is lower than 5%; and compared with traditional powder metallurgy 316LN stainless steel, the tensile strength is improved by 21%, the elongation percentage is increased by 56%, the hardness is improved by 27%, and the pitting potential is improved by 60% after the powder metallurgy stainless steel is soaked in a 3.5wt% NaCl solution for 15 days. The preparation method provided by the invention is easy and convenient to operate and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +1
Silicon carbide ceramic and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106588021AImprove sintered densityImprove bending strengthDensity distributionFlexural strength
The invention provides silicon carbide ceramic and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method includes: subjecting a ceramic main raw material, a binder accounting for 2.5-3% of weight of the ceramic main raw material and a dispersant accounting for 1.5-2.5% of the weight of the ceramic main raw material to cold isostatic pressing and liquid phase sintering. Generally, dry pressing is adopted for forming a ceramic material; during dry pressing, various performances of a material are influenced by nonuniform density distribution inside a blank caused by nonuniform pressure distribution; compared with dry pressing, cold isostatic pressing is uniform in pressurizing, pressures received by the material in all directions are identical, and sintering density, bending strength and rupture strength of the material are improved.
Owner:BEIJING GUOWANG FUDA SCI & TECH DEV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com